
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Plant Sci., 12 February 2020
Sec. Plant Pathogen Interactions
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01692
This article is a correction to:
Characterization of the Spatial and Temporal Expression of Two Soybean miRNAs Identifies SCL6 as a Novel Regulator of Soybean Nodulation
A Corrigendum on
Characterization of the Spatial and Temporal Expression of Two Soybean miRNAs Identifies SCL6 as a Novel Regulator of Soybean Nodulation.
By Hossain MdS, Hoang NT, Yan Z, Tóth K, Meyers BC and Stacey G (2019). Front. Plant Sci. 10:475. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00475
It was brought to our attention that, in the original article, inappropriate manipulation of Figures 1 and 5 took place, specifically, Figures 1B, 1C, 1D, 1E, 1F, 1G and 5B, 5C, 5D, 5E, 5F, 5G. Upon review, we have agreed that these figures be removed from the article. The manipulation of the figures involved an effort to increase the contrast of the images to make them more presentable.
Although this did not change the interpretation of the data, the manipulation was clearly against our lab policy and the policies of the journal. Given that other data in the paper (e.g., qPCR and other experiments) confirm the data presented in these figures, we feel that the conclusions of the paper remain valid even with the figures removed.
To avoid any additional questions or concerns, we have also corrected Figures 2D, 2E and 2F, as well as Figures 4D, 4E, 4F, and 4G, and replaced these figures with original images. The corrected figures appear below. Due to the changes mentioned above, a correction has been made to the Results, subsection Gma-miR171o and Gma-miR171q Exhibit Distinct Expression Patterns in Response to Bacterial Infection:
“To understand the symbiotic role of gma-miR171o and gma-miR171q in soybean, we measured the relative expression level of these two miRNAs in nodules 3 weeks post-inoculation with B. japonicum, as compared to uninfected root tissues (Figure 1A). Interestingly, these two miRNAs showed opposite expression patterns in response to B. japonicum infection (Figure 1A); gma-miR171o expression was suppressed upon bacterial infection, while gma-miR171q was induced.”
A correction has also been made to the Results, subsection Gene Expression and Promoter Localization of GmSCL6-1 and GmNSP2.1 Are Inversely Correlated With Gma-miR171o and Gma-miR171q. Paragraph two has been removed entirely.
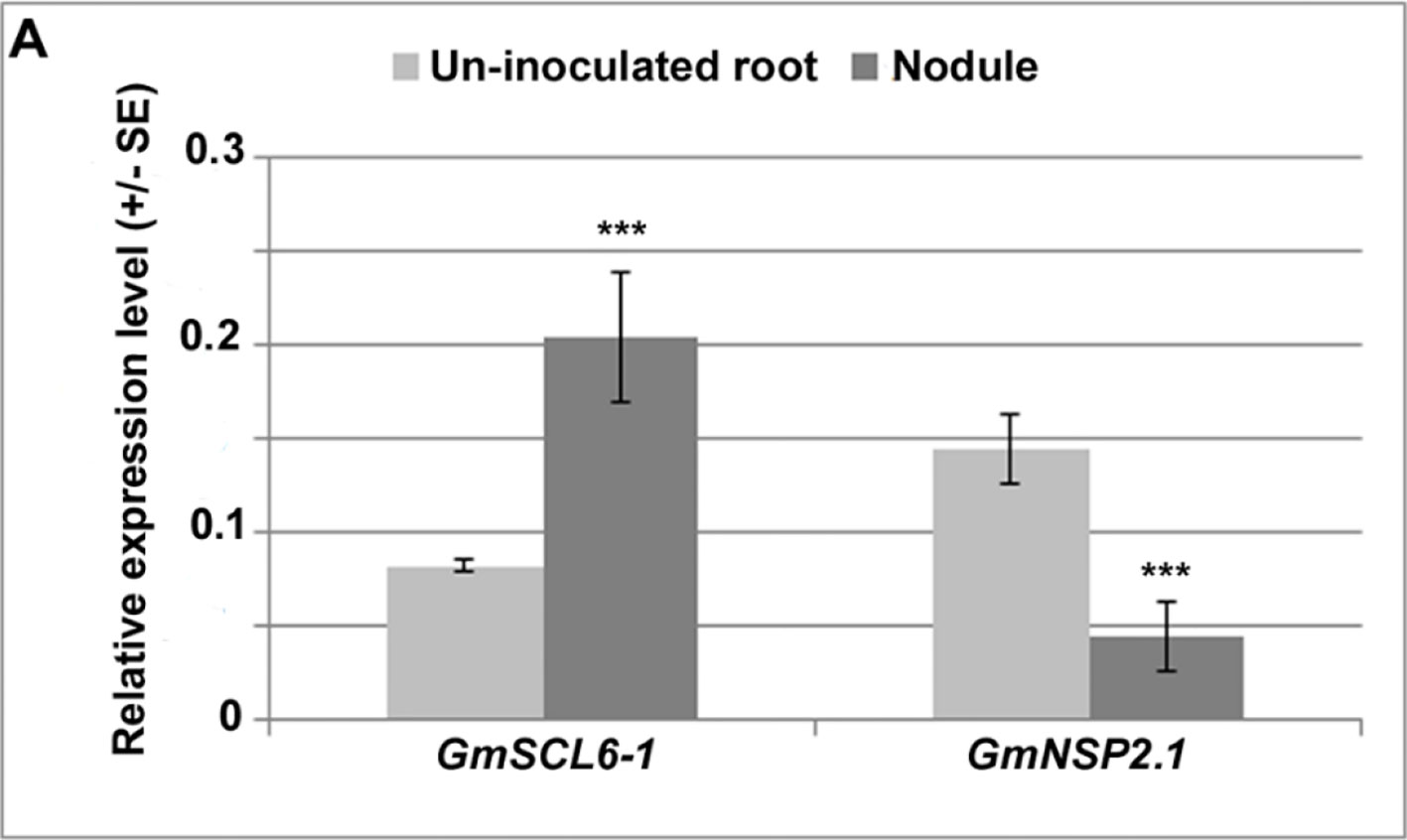
Figure 5 Expression analysis of target genes, GmSCL6-1 and GmNSP2.1 in soybean hairy root transgenic tissues.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: miRNA, miR171, GRAS TF, Scarecrow like-6, NSP2, nodulation, symbiosis, soybean
Citation: Hossain MS, Hoang NT, Yan Z, Tóth K, Meyers BC and Stacey G (2020) Corrigendum: Characterization of the Spatial and Temporal Expression of Two Soybean miRNAs Identifies SCL6 as a Novel Regulator of Soybean Nodulation. Front. Plant Sci. 10:1692. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01692
Received: 24 October 2019; Accepted: 29 November 2019;
Published: 12 February 2020.
Edited and reviewed by: Aardra Kachroo, University of Kentucky, United States
Copyright © 2020 Hossain, Hoang, Yan, Tóth, Meyers and Stacey. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gary Stacey, c3RhY2V5Z0BtaXNzb3VyaS5lZHU=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.