- 1Division of Agriculture, Center of Excellence for Poultry Science, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, AR, United States
- 2Har-Ber High School, Springdale, AR, United States
Water scarcity and rising global temperatures are two of the greatest current and future threats to poultry sustainability. Therefore, selection for water efficiency (WE) and heat resilience are of vital importance. Additionally, intestinal integrity is of critical importance under challenging conditions to maintain nutrient absorption and therefore, growth and performance of broilers. Here, we examined the effect of chronic cyclic heat stress (HS) on the ileal expression profile of tight-junction, gap-junction, adherens, and desmosome genes in the fourth generation of divergently selected low (LWE)- and high water efficient (HWE)-chicken lines. LWE birds exhibited higher levels of gut permeability, regardless of temperature, as measured by fluorescein isothiocyanate–dextran (FITC-D). Among the claudins (CLDN), Cldn1 showed greater expression in the HWE as compared to LWE, regardless of temperature. Cldn5, -16, -20, and -34 genes were all greater in LWE and lower in HWE during HS. Conversely, Cldn25 was decreased in LWE but increased HWE under HS. Cldn4 was increased in the HWE line and decreased by HS. Cingulin (Cgn) gene expression was lower in HWE as compared to LWE and lower in HS as compared to thermoneutral (TN) condition. Gap junction protein α1 (Gja1) and desmoglein 4 (Dsg4) were greater in the HWE as compared to the LWE. Cadherin 1 (Cdh1) gene expression was greatest in the HWE in TN conditions and lowest in HWE under HS, whereas catenin α2 (Ctnna2) and desmocollin 1 (Dsc1) were highest in HWE during HS compared to all other groups. This differential expression of key genes associated with intestinal barrier integrity likely contributes to the water efficiency phenotype and the response of these birds to HS.
1 Introduction
Water insecurity is a significant current concern worldwide, with the threat of scarcity only projected to rise with global warming. As of 2023, approximately half of the global population faces some form of water insecurity for at least 1 month a year, and one-fourth face extremely high levels of water stress, withdrawing over 80% of their renewable annual freshwater supply (Kuzma et al., 2023). As global temperatures are predicted to rise, and rainfall patterns shift, an ever-increasing segment of the world population will experience water stress (Greve et al., 2018). Combating this rising concern will require action at every level; however, agricultural industries must balance any changes in water usage with potential impacts on productivity. To this end, our research group has generated two lines of chickens divergently selected for water efficiency (ratio of water consumed to body weight gain). Under thermoneutral conditions, these high water efficient (HWE) birds had 3- and 47-points better feed (FCR) and water conversion ratio (WCR), respectively, compared to their low water efficient (LWE) counterparts (Aloui et al., 2024). Under chronic heat stress conditions, the HWE line drank less water and also had better FCR and WCR compared to the LWE birds (1.47 vs. 1.51 for FCR and 2.65 vs. 3.12 for WCR), indicating that they are resilient to heat stress (Aloui et al., 2024).
It has been well established that modern broilers are particularly susceptible to elevated temperatures, with decreases seen in growth, productivity, and livability (Lara and Rostagno, 2013). Virtually all dietary nutrients, including water, are absorbed across the epithelium of the intestine, and the importance of gut health and integrity has become increasingly understood across all species. Heat stress has been shown to negatively impact intestinal morphology (crypt depth, mucous area, and villus height), and leads to decreases in nutrient absorption (Marchini et al., 2011). Breakdown of intestinal integrity, known as leaky gut syndrome, also allows for increased translocation of harmful substances (bacteria, toxins, etc.), which is further associated with increased incidence of disease. Intestinal barrier integrity is maintained through the stability of distinct intercellular junctional complexes known as tight junctions, adherens junctions, gap junctions, and desmosomes (Vancamelbeke and Vermeire, 2017). Altered expression or changes in the structure of these complexes result in decreased nutrient absorption, as well as increased passage of ions and water to the intestinal lumen (Barmeyer et al., 2015). However, how these factors may be impacted by selection for water efficiency in poultry has yet to be determined. Therefore, here, we examine the effects of HS on ileal barrier integrity in two lines of broilers divergently selected for high and low water efficiency.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Care and use of animals
All animal care and use were conducted in accordance with the recommendations in the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals from the National Institutes of Health. The protocol was approved by the University of Arkansas Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol # 23015). Full details of divergent selection for the LWE and HWE lines and the experimental design have been previously reported (Aloui et al., 2024). Briefly, for the genetic selection program, the base population utilized was a 2015 Modern Random Bred (MRB) population (broiler (meat-type) chickens) and the selection trait was water conversion ratio [WCR = water intake (g)/body weight gain (g)] as described previously (Aloui et al., 2024). On day of hatch, male chicks (240 chicks/line) were individually wing-banded for line identification and weighed, then placed in 12 controlled environmental chambers in the Poultry Environmental Research Laboratory at the University of Arkansas (2 floor pens/chamber, 6 chambers/line, 20 birds/pen). Each pen was covered with clean pine wood shavings and equipped with separate hanging feeders and a nipple water line attached to a low-flow water monitoring system (Hiltz et al., 2021). Water and standard diets were provided ad libitum, with industry standard rearing temperatures and light cycles. On d29, birds were exposed to thermoneutral (25°C) or chronic cyclic heat stress (36°C for 9 h/day from 9:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m.) conditions (3 chambers-6 pens-120 birds/line/environment). On d49, birds (n = 12/group) were humanely euthanized by cervical dislocation and approximately 3–4 cm ileum section (∼3 cm anterior to the ileocecal junction) was dissected, snap frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C for further analysis.
2.2 Determination of serum fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran (FITC-D) levels
Serum FITC-D concentrations were determined as previously described (Ruff et al., 2020; Tabler et al., 2020). Briefly, 12 birds from each group were orally gavaged with FITC-D (8.32 mg/kg, MW 3–5 kDa, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). One hour post gavage, blood was collected from the brachial wing vein, serum separated, and fluorescence was measured (Ex 428 nm/Em 528 nm) using the Synergy HTX multi-mode micro plate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT).
2.3 RNA isolation, reverse transcription, and quantitative real-time PCR
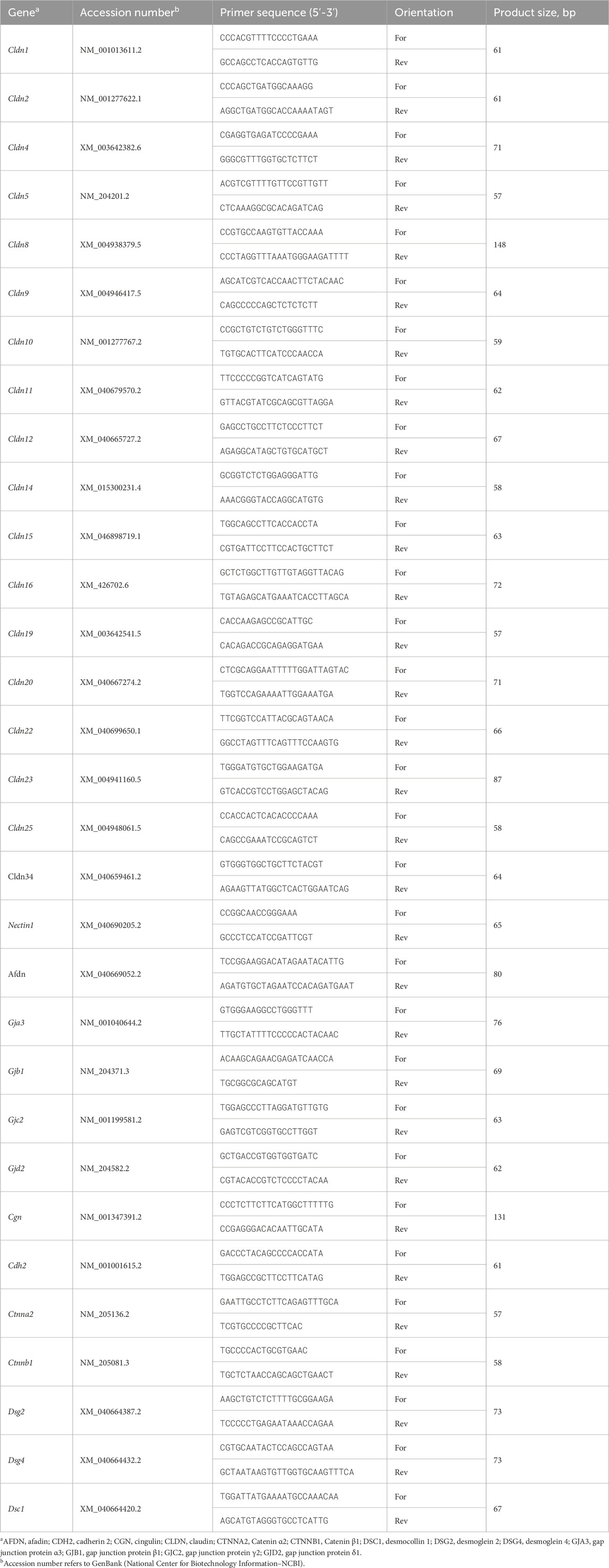
Total RNA extraction and RT-qPCR conditions were previously described (Aloui et al., 2024; Tabler et al., 2020; Greene et al., 2024; Dridi et al., 2022). Briefly, total RNA was extracted from the ileum using Trizol reagent (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) according to manufacturer’s protocol. RNA concentration was determined using the Take 3 micro volume plate and Synergy HTX multi-mode microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT). RNAs (1 µg) were reverse transcribed via qScript cDNA SuperMix (Quanta Biosciences, Gaithersburg, MD) in a 20-µL total reaction. Real-time quantitative PCR (Applied Biosystems 7,500 Real-Time PCR system) was performed using 5 µL of 10×-diluted cDNA, 0.5 µM of each forward and reverse specific primers for each gene, and SYBR Green Master Mix (ThermoFisher Scientific, Rockford, IL) in a total 20-µL reaction. Oligonucleotide primers specific for chicken were used as previously reported (Tabler et al., 2020), or as provided in Table 1. Relative expression of target genes were determined by the 2−ΔΔCT method (Schmittgen and Livak, 2008), with LWE under TN conditions used as calibrator.
2.4 Western blot
Western blot was performed as previously described (Lassiter et al., 2015). Briefly, ileal tissue was homogenized in lysis buffer containing protease- and phosphatase-inhibitors. Protein concentrations were determined via Bradford assay (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) and the Synergy HTX multimode microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT). Proteins were separated on 4%–12% Bis-Tris gels (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA), and transferred to PVDF membranes. Membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat milk in TBS-T for 1 h at room temperature, then incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. Primary antibodies used were rabbit anti-claudin 4 (CLDN4, 1:1,000, bs-2790R, Bioss, Woburn, MA), rabbit anti-CLDN5 (1:1,000, sc-28670, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX), and anti-rabbit zona occluding-2 (ZO-2, 1:1,000, 38–9,100, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Rabbit anti-Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH, 1:1,000, NB300-327, Novus Biologicals, Centennial, CO) was used as a loading control. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody (goat anti-rabbit IgG #7074, Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA) was used at 1:5,000 dilution for 1 h at room temperature. The signal was visualized by chemiluminescence (SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and captured by FluorChem M MultiFluor System (ProteinSimple, Santa Clara, CA). Image acquisition and analysis were performed with AlphaView software (version 3.4.0.0, ProteinSimple, Santa Clara, CA).
2.5 Statistics
Gene and protein expression data (n = 12/line/environment) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. When ANOVA revealed significant interaction effects, the means were compared by Tukey’s HSD multiple comparison test. If the line by environment interaction was not significant, the main effect (Line, L or Environment, E) was analyzed separately by Student’s t-test test using Graph Pad Prism version 9.00 for Windows (Graph Pad Software, La Jolla California, USA). Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean and the statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Intestinal permeability is decreased in HWE as compared to LWE broilers
As measured by FITC-D in serum, intestinal permeability was lower in the HWE as compared to the LWE birds (P = 0.0009, Figures 1A, B). There was no overall effect of HS (Figure 1A).
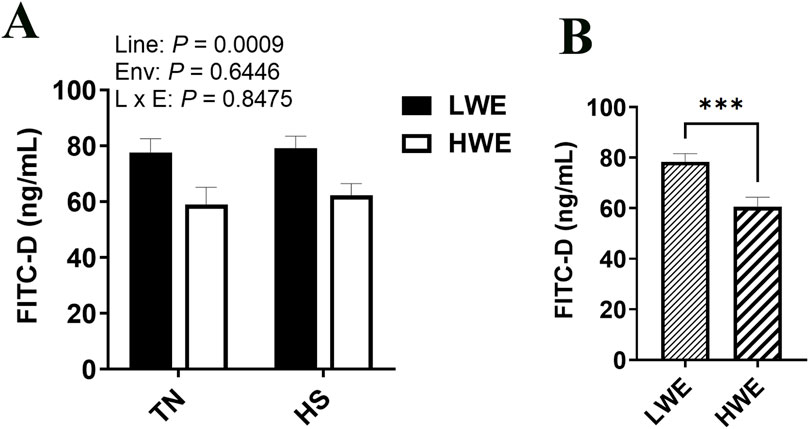
Figure 1. Effect of heat stress on serum FITC-D levels in LWE and HWE chickens. (A, B) Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 12 birds/group). When the line by environment interaction was not significant, the main effect was analyzed separately by Student’s t-test. *** indicates significant difference at P < 0.001. E and Env, environment; HS, heat stress; HWE, high water efficient; L, line; LWE, low water efficient; TN, thermoneutral.
3.2 Differential expression of tight junction proteins in heat-stressed LWE and HWE broilers
For the barrier-forming claudins, CLDN5 protein levels were significantly decreased by HS compared to TN conditions (Figures 2A–C). The expression of Cldn5 gene, however, was upregulated in LWE, and downregulated in HWE under HS conditions, which resulted in a significant line by environment interaction (Figure 2D). The expression of Cldn1 gene was significantly upregulated in the ileum of HWE birds compared to their LWE counterparts (Figures 2E, F). Cldn20 mRNA abundances were induced by HS only in LWE but not in HWE birds, resulting in a significant line by environment interaction (Figure 2G). Heat stress downregulated Cldn25 gene expression in LWE and Cldn34 in HWE birds, causing a significant line by environment interactions (P = 0.0367 and P = 0.0475 for Cldn25 and Cldn34, respectively, Figures 2H, I). There was no significant effect of line or of HS on the ileal expression of Cldn8, Cldn9, and Cldn22 (Table 2).
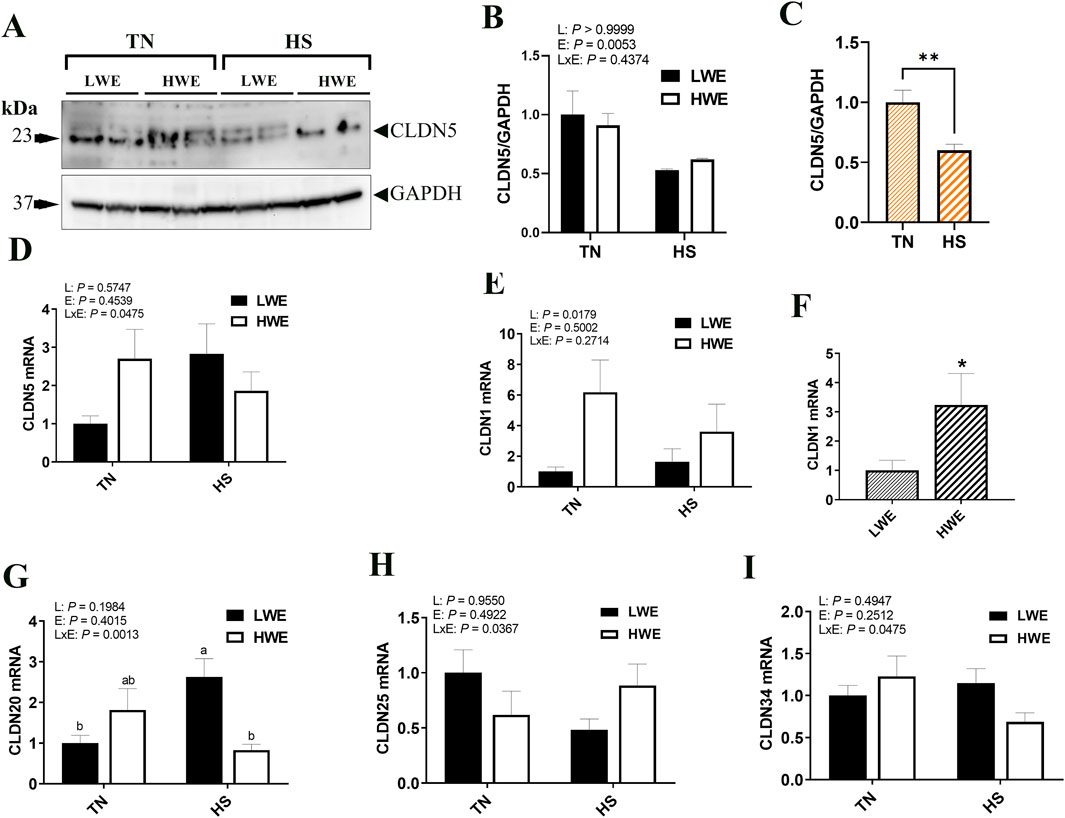
Figure 2. Effect of heat stress on the expression of barrier-forming claudins in LWE and HWE chickens. Protein expression of CLDN5 was determined by Western blot. (A–C) Gene expression of CLDN5 (D), CLDN1 (E, F), CLDN20 (G), CLDN25 (H), and CLDN34 (I) were measured by qPCR. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 12 birds/group). When the line by environment interaction was not significant, the main effect was analyzed separately by Student’s t-test. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. * and ** indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively. CLDN, claudin; HS, heat stress; HWE, high water efficient; LWE, low water efficient; TN, thermoneutral.
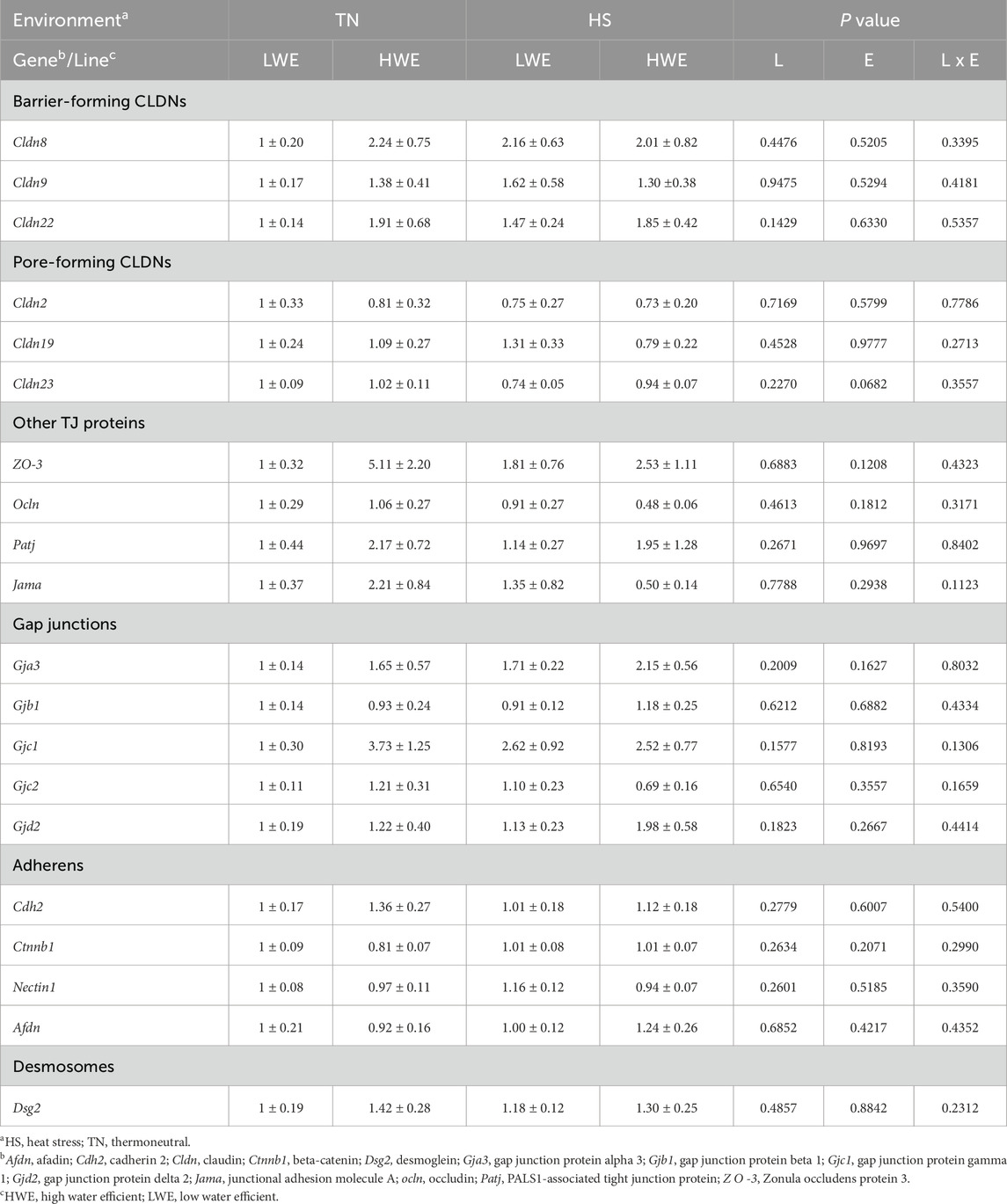
Table 2. Relative expression of ileal integrity-associated genes in heat-stressed LWE and HWE broilers.
Among the pore-forming claudins, Cldn4, Cldn15, and Cldn16 were differentially regulated. Cldn4 gene expression was affected by both line and environment, where mRNA abundances were increased in the HWE line (P = 0.0330) and decreased in HS condition (P = 0.0138, Figures 3D–F). CLDN4 protein levels were significantly reduced by HS (Figures 3A–C), although the overall effect of line was not statistically and significantly discerned (P = 0.3548). The expression of Cldn15 gene was higher in the HWE line under TN conditions, and significantly downregulated by HS in the same line, but not in the LWE counterparts (P = 0.0043, Figure 3G), resulting in a significant line by environment interaction (P = 0.0105). The expression of Cldn16 gene was upregulated by HS in the LWE and downregulated in the HWE, with a significant line by environment interaction (P = 0.0384, Figure 3H). There were no significant effects of line nor environment on Cldn2, Cldn19, or Cldn23 (Table 2).
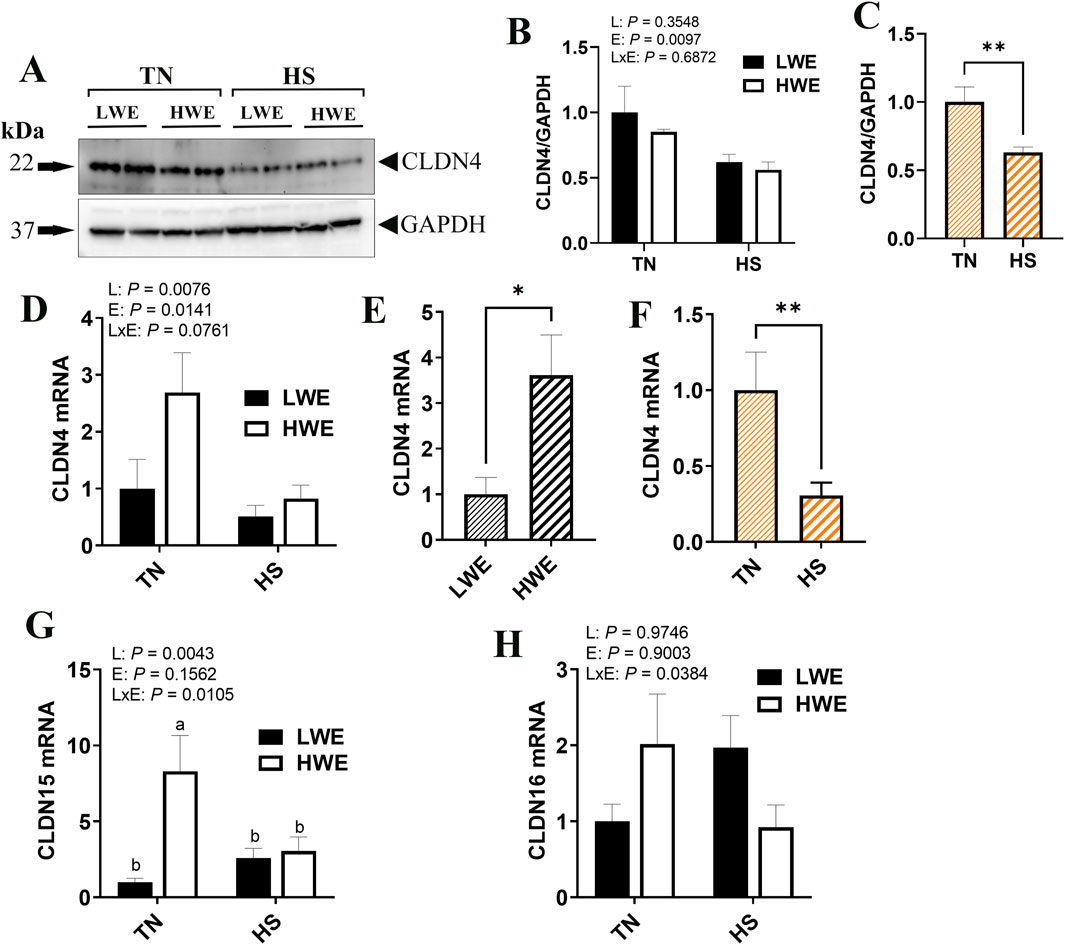
Figure 3. Effect of heat stress on the expression pore-forming claudin expression in LWE and HWE chickens. Protein expression of CLDN4 was determined by Western blot. (A–C) Gene expression of CLDN4 (D–F) CLDN15 (G), and CLDN16 (H) were measured by qPCR. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 12 birds/group). When the line by environment interaction was not significant, the main effect was analyzed separately by Student’s t-test. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. * and ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively. CLDN, claudin; HS, heat stress; HWE, high water efficient; LWE, low water efficient; TN, thermoneutral.
Protein levels of ZO-2 were significantly decreased by HS only in HWE but not in LWE birds, which resulted in a significant line by environment interaction (Figures 4A, B). The gene expression of Zo-2 remained unchanged (Figure 4C). Cingulin (Cgn) gene expression was affected by both line and environment (Figures 4D–F), where it was lower in HWE as compared to LWE (P = 0.0006) and lower in HS as compared to TN (P = 0.0018). The expressions of Occludin (Ocln), zona occludin-3 (Zo-3), PALS1-associated tight junction protein (Patj), and junctional adhesion molecule A (Jam-A) genes were all unaffected by line or environmental conditions (Table 2).
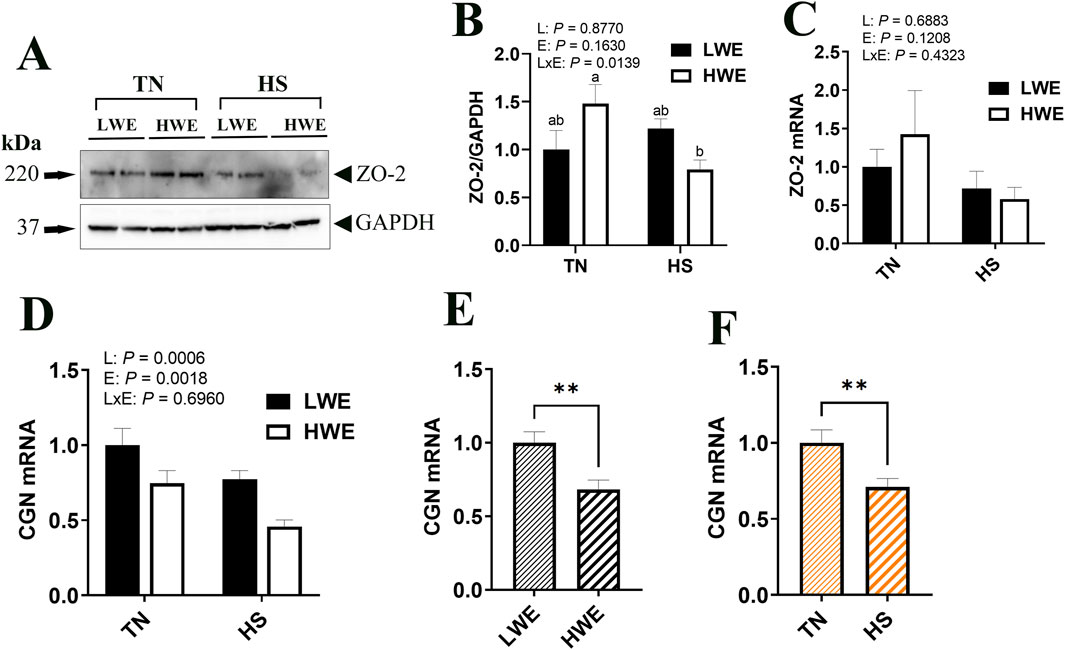
Figure 4. Effect of heat stress on tight-junction gene expression in LWE and HWE chickens. Protein expression of Zo-2 was determined by Western blot (A, B). Gene expression of ZO-2 (C) and CGN (D–F) was measured by qPCR. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 12 birds/group). When the line by environment interaction was not significant, the main effect was analyzed separately by Student’s t-test. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.01. CGN, cingulin; HS, heat stress; HWE, high water efficient; JAM-A, junctional adhesion molecule A; LWE, low water efficient; OCDN, occludin; PATJ, protein associated to tight junctions; TN, thermoneutral; ZO, zona occludin.
3.3 Differential expression of gap junction gene expression in LWE and HWE broilers during HS
Abundances of the gap junction protein α1 (Gja1) mRNA were affected by line, with a significant increase in the HWE as compared to the LWE birds under both environmental conditions (P = 0.0258, Figures 5A, B). There were no effects of line nor environment on gene expression of gap junction protein α3 (Gja3), gap junction protein β1 (Gjb1), gap junction protein γ1 (Gjc1), gap junction protein γ2 (Gjc2), or gap junction protein δ1 (Gjd2) (Table 2).
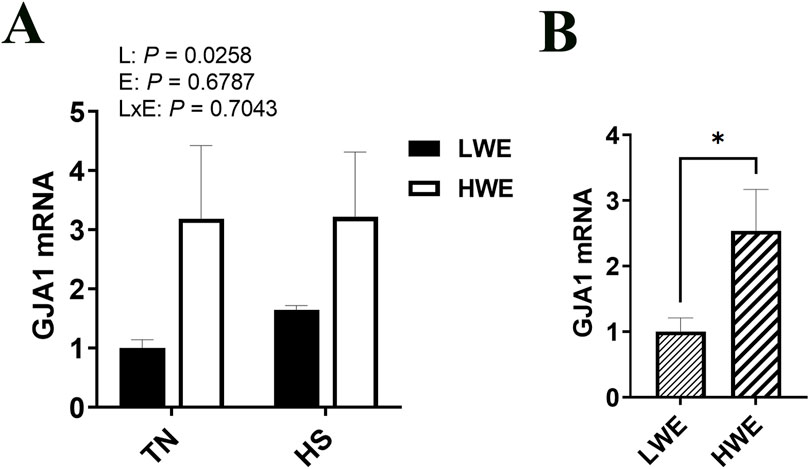
Figure 5. Effect of heat stress on GJA1 gene expression in LWE and HWE chickens. Gene expression of GJA1 (A, B) was measured by qPCR. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 12 birds/group). When the line by environment interaction was not significant, the main effect was analyzed separately by Student’s t-test. * indicates significant difference at P < 0.05. GJA, gap junction protein α; HS, heat stress; HWE, high water efficient; LWE, low water efficient; TN, thermoneutral.
3.4 Differential expression of adherens junction gene expression in LWE and HWE broilers during HS
There was a significant line by environment interaction effect on cadherin 1 (Cdh1, P = 0.0394, Figure 6A) and Catenin α2 (Ctnna2, P = 0.0243, Figure 6B) gene expression. Cadherin one expression was higher in HWE birds under TN condition and was downregulated by HS exposure (Figure 6A). Catenin α2 expression was induced by HS only in the ileum of HWE birds (Figure 6B). There were no significant effects of HS nor line on cadherin 2 (Cdh2), Catenin β1 (Ctnnb1), Nectin1, or afadin (Afdn) (Table 2).
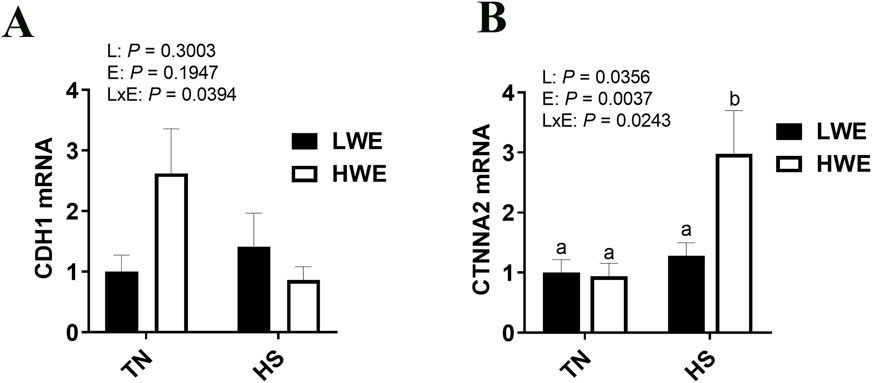
Figure 6. Effect of heat stress on CDH1and CTNNA2 gene expression in LWE and HWE chickens. Gene expression of CDH1 (A) and CTNNA2 (B) was determined by qPCR. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 12 birds/group). CDH, cadherin; CTNNA2, catenin α2; HS, heat stress; HWE, high water efficient; LWE, low water efficient; TN, thermoneutral.
3.5 Differential expression of desmosome gene expression in LWE and HWE broilers during HS
Gene expression of desmoglein 4 (Dsg4) was increased in the HWE line as compared to the LWE (P = 0.0497, Figures 7A, B). There was an interactive effect of line and environment on desmocolin 1 (Dsc1), where gene expression was increased by HS only in the HWE line (P = 0.0382, Figure 7C). There was no significant effect of HS nor line on desmoglein 2 (Dsg2) gene expression (Table 2).
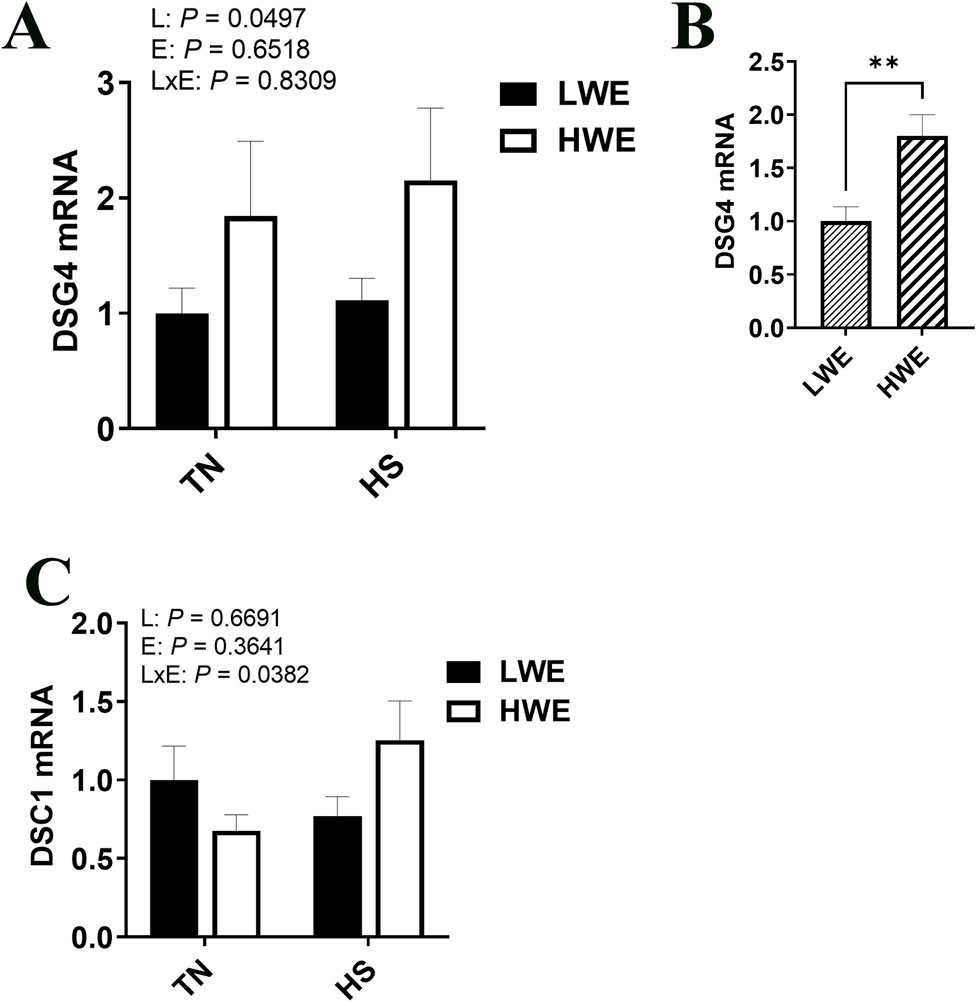
Figure 7. Effect of heat stress on desmosome gene expression in LWE and HWE chickens. Gene expression of DSG4 (A, B) and DSC1 (C) was measured by qPCR. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 12 birds/group). When the line by environment interaction was not significant, the main effect was analyzed separately by Student’s t-test. ** indicates significant difference at P < 0.01. DSC1, desmocollin 1; DSG, desmoglein; HS, heat stress; HWE, high water efficient; LWE, low water efficient; TN, thermoneutral.
4 Discussion
Maintenance of intestinal barrier integrity is critical to organismal health and allows selective permeability of transport of ions, nutrients, and water while restricting pathogens (Rescigno, 2011). Over 80 proteins have been identified as contributing to this barrier, with distinct as well as coordinated functions (Tsukita et al., 2001). A key point, however, is that none of these tight junctions, adherens junction, gap junctions, and desmosome proteins work in isolation. The complex constantly adapts to changes in the biological state through constant remodeling and intracellular trafficking, where proteins are inserted and internalized from the membrane (Shen et al., 2008). Together, they form a well-organized matrix to provide a barrier that is both functional and efficient. Here, regardless of temperature, the HWE birds displayed lower intestinal permeability, as measured by serum FITC-D, compared to the LWE line. As the intestinal barrier integrity is controlled by a complex network of tight junction, gap junction, and desmosomes, here we sought to further assess the expression of barrier integrity-related genes in these two lines of birds under HS conditions.
Claudins are tight junction proteins that can be broadly classified into two categories: barrier-forming and channel- or pore-forming. The barrier-forming claudins restrict the passage of small molecules and electrolytes, whereas the pore-forming claudins allow the passage of ions and water through paracellular channels (Krause et al., 2008). One of the first claudins isolated (Furuse et al., 1998), CLDN1 is highly expressed across the entire intestinal tract, and downregulation of CLDN1 has been shown to be associated with increased intestinal permeability via the NFκB pathway (Zhou et al., 2015). Here, the Cldn1 gene was increased in the ileum of the HWE birds as compared to their LWE counterparts, which likely contributes to the improvements seen in intestinal permeability in this line. Additionally, chronic stress has been associated with decreased intestinal CLDN1 (Zheng et al., 2017). CLDN1 was not significantly affected by HS in the current study, which might indicate an adaptation to the chronic (20 days) HSs. Cldn5 and Cldn20 genes showed similar patterns of expression in the two studied lines, with increased expression in the LWE line and decreased expression in the HWE during HS. As barrier-forming claudins, increased expression of these genes tends to decrease membrane permeability (Rahner et al., 2001; Martin et al., 2013), which is supported by the downregulation of Cldn5 in HS conditions. However, little is known about their function in the avian intestine. CLDN5 is tightly regulated at the blood-brain-barrier and is compromised in several neurological diseases (Hashimoto et al., 2023), while in breast-cancer models, overexpression of CLDN20 increases trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) (Martin et al., 2013), both tissue-specific roles highlighting the complex nature of claudins. Similarly, the function of CLDN25 has yet to be fully understood. A paralog of CLDN22, CLDN25 does not seem to be either directly barrier- or pore-forming; however, its role in barrier regulation seems to depend on the composition of other claudins within the tight junction (Hashimoto et al., 2024). This is supported by evidence of differential effects in different cell types in vitro. In mouse brain endothelial cells (bEnd.3), CLDN25 knockout lowered solute permeability, while it increased in Madin-Darby canine kidney strain II (MDCKII) cells. However, TEER was increased in both cell types. Future functional studies are necessary to delineate the function of CLDN25 in the chicken intestine. Likewise, CLDN34 is understudied in both mammalian and avian species. Based on studies in fish, enhanced intestinal expression is related to enhanced immune function, whether in response to a bacterial challenge (Cao et al., 2023) or a dietary immunomodulator (Zhang et al., 2024). Taken together, these data suggest that differential expressions of the barrier-forming claudins are integral components of the differences seen in water efficiency selected broilers; however, further research is necessary to delineate the functions of individual claudins, as well as their interaction in poultry intestine.
Multiple pore-forming claudins are also differentially regulated between the two lines. CLDN2, 10b, 15, 16 and 21 have been shown to form cation-selective paracellular channels, whereas CLDN10a and 17 are understood to form anion-selective channels (Günzel and Yu, 2013). Of particular interest to this work, CLDN2 and 15 are known to move water as well as other solutes such as sodium and potassium (Rosenthal et al., 2020; Samanta et al., 2018). Interestingly, Cldn2 gene was unaffected in this study; however, its protein expression and localization within the gut are known to be negatively regulated by Cgn (Guillemot et al., 2012), a gene that was lower in the HWE line. Cldn15 showed a greater mRNA expression in the HWE line, particularly under the TN environment. Together, these may be significant contributing factors to the improved water efficiency in this line, as water uptake at the small intestine may be more easily facilitated. Interestingly, CLDN15 also indirectly enhances glucose uptake via Na+ flux into the lumen of the intestine and subsequently enhances the activity of Na+-driven glucose transporter SGLT1 (Tamura et al., 2011), an additional role that may be impacting the BWG and FCR improvements seen in the HWE line (Aloui et al., 2024). CLDN16 is recognized for its role in calcium transport, as mutated CLDN16 may be responsible for defective absorption of Ca2+ along the intestine (Weber et al., 2001). Although calcium metabolism has yet to be explored in these lines of birds, it is plausible, based on the differential expression of Cldn16 due to line × environment interaction, observed here, that these lines had different Ca2+ transport, absorption, and/or metabolism. Additionally, in chickens, CLDN16 has been localized to goblet cells, suggesting a further role in mucus secretion (Ozden et al., 2010) and thereby homeostasis of intestinal flora. CLDN4 has a unique function, as it is considered pore-forming regulating, as it can interfere with and regulate CLDN2, 7, 15, and 19, and increase the complexity of tight junctions (Van Itallie et al., 2001; Shashikanth et al., 2022a; Shashikanth et al., 2022b), a role which may be indicated in the increased expression in the HWE line. Downregulation of CLDN4 has been seen in areas of intestinal inflammation (Prasad et al., 2005), which is likely reflected here in the lower expression seen in HS, regardless of line. Although the role and regulation of avian ZO-2 are not well known, its ileal downregulation by HS exposure, at least in HWE line here opposed that in the duodenum of broilers from the 1990s (Tabler et al., 2020), which suggests a tissue- or strain-specific regulation (Santos et al., 2021). Based on previous studies showing that rye diet alters gut integrity and induces leaky gut syndrome in broilers (Baxter et al., 2019), and this was accompanied by an upregulation of ileal ZO-2, it is logical to postulate that ZO-2 downregulation in our study supports a better gut integrity in HWE line.
Gap junctions are important in cell structure as well as for cell-to-cell communication via the transfer of ions and small molecules between adjacent cells (Wong et al., 2019). Gap junction genes encode connexins, which are differentially and widely expressed throughout the body. Here, among the gap junction genes, only Gja1 (encoding connexin 43) was differentially expressed, and was higher in the HWE line. GJA1 plays multiple roles in intestinal epithelial health that may be influencing the physiology of the HWE line. First, GJA1 likely impacts intestinal motility via interaction with intestinal nerve transmission (Daniel et al., 2001; Daniel and Wang, 1999), as well as its function as a necessary component for motile cilia (Jang et al., 2022). In these broilers, it may be altering motility or gastrointestinal transit time in such a manner that could be influencing increases in water and nutrient absorption and contributing to the water efficiency, BWG, and FCR improvements seen in the HWE line (Aloui et al., 2024). However, digestibility studies have yet to be conducted in these birds, so this remains speculative. Second, connexin 43 is redistributed within intestinal epithelial cells to the basolateral surface during inflammation (as seen in inflammatory bowel disease) (Al-Ghadban et al., 2016), and it has been shown to be associated with inflammasome (de)activation (Roger et al., 2023). The higher expression of Gja1 here and the downregulation of Nlrc3 in HWE blood (Greene et al., 2024), suggest that GJA1 might improve the gut inflammatory status of HWE line, resulting in better barrier integrity and better growth performance. In addition, connexins have a short half-life of only a few hours (Segretain and Falk, 2004), so investigating the spatio-temporal nature of their responses to HS in poultry gut is warranted.
Adherens junctions organize and stabilize the condensed actin filaments of the cytoskeleton with the plasma membrane and are assembled from classical cadherins, armadillo proteins, and cytoskeletal adaptor proteins (Harris and Tepass, 2010). E-cadherin (encoded by Cdh1) is the most crucial cadherin present on the epithelial surface responsible for adherens junction formation via trans adhesive homodimers with other cadherins (Gumbiner, 2005; Brasch et al., 2012). Among the cadherins studied, we saw differential regulation of Cdh1, which was greater in the HWE in TN conditions, but lower under HS. Others have reported increases in CDH1 in poultry intestine in response to HS; however, the response is likely region-specific, with increases seen in the jejunum, but not in the ileum (Varasteh et al., 2015). Cadherins bind to catenins as part of the stabilization structure, and in particular, α-catenin binds to the E-cadherin/β-catenin complex (Drees et al., 2005). The dimerization of CTNNA2 influences binding to other proteins; monomeric α-catenin binds β-catenin, but not actin, while homodimeric α-catenin binds actin but not β-catenin (Yamada et al., 2005). In this way, it helps regulate microtubule dynamics and has been shown to play a central role in cytoskeletal rearrangement in response to extracellular events (Perez-Moreno and Fuchs, 2006; Arbore et al., 2022). In a fish model, increased methylation on Ctnna2 was associated with increased intestinal integrity and decreased inflammation (Dhanasiri et al., 2020). Interestingly, Ctnnna2 expression is also associated with climate adaptation in mediterranean cattle (Flori et al., 2019). As this gene was upregulated only during HS in the HWE line, it may serve a role in helping stabilize the adherens junction, as other components (particularly the cadherins) are unchanged or downregulated as compared to TN conditions.
Desmosomes are the least well studied of the epithelial barrier regulating proteins, but have been shown to create strong intercellular adhesion, particularly in tissues subject to mechanical stress. Intercellular adhesion is normally initiated by adherens junctions, then stabilized by desmosomes via connecting intermediate filaments to the plasma membrane (Vasioukhin et al., 2000). Desmogleins form heterodimers with desmocollins (Getsios et al., 2004), and one of the strongest binding has been found between DSC1 and DSG4 (Harrison et al., 2016), both of which show greater expression in the HWE during HS, which is likely contributing to increased intestinal integrity and lower leaky gut. Desmosomes also can exist in two adhesive states, a weaker, Ca2+ dependent state, and a stronger, Ca2+ independent state termed “hyperadhesion”. This hyperadhesion is critically important in the ability of cells to resist shear forces that would separate cells and disrupt tissues (Garrod and Tabernero, 2014; Beggs et al., 2022). Protein Kinase C (PKC) pathways, which have been shown to be induced by HS (Yang et al., 2007), negatively regulate hyperadhesion (Garrod et al., 2008), a further mechanism by which HS can impact intestinal barrier integrity.
It is interesting to note that both serum FITC-D and many of the measured genes are minimally affected by HS in either line. As these birds were subject to cyclic HS for 20 days, it is plausible that some of the responses are reflective of adaptation to the environmental challenge. It is also plausible that birds were recovered during the cool phase. As the HWE, overall, responded more favorably to HS (in terms of decreased intestinal permeability, and increased growth, water and feed efficiency), it may be that the genes associated with intestinal integrity in the LWE are upregulated to try to fix or improve the disrupted barrier, while the HWE were overall more resilient. It is also possible that although gene and/or protein levels of the tight junctions are unaffected, post-translational modifications (Shigetomi and Ikenouchi, 2017) or distribution/localization within the cell, and therefore function, may be affected by genetics or HS. Indeed, this has been seen in other models, including Llc-Pk1 kidney cells (Ikari et al., 2005), Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells (Han et al., 2003), and isolated T cells (Voges et al., 2024), and warrants further investigation in these lines.
Overall, these results provide further evidence for the positive potential of water efficiency selection in poultry, as there were improvements in intestinal integrity over the LWE line, with no additional impairments due to HS. In addition, differential gene expression of intestinal barrier proteins may help delineate some of the underlying mechanisms of improved water efficiency and identify potential markers for further selection.
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the University of Arkansas Animal Care and Use Committee. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
EG: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. BR: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. MC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. SO: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. SD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by a grant from USDA NIFA Sustainable Agriculture Systems (#2019 69012-29905) to S.D.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the University of Arkansas Poultry Research farm and the University of Arkansas feed mill for their assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Ghadban S., Kaissi S., Homaidan F. R., Naim H. Y., El-Sabban M. E. (2016). Cross-talk between intestinal epithelial cells and immune cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Rep. 6, 29783. doi:10.1038/srep29783
Aloui L., Greene E. S., Tabler T., Lassiter K., Thompson K., Bottje W. G., et al. (2024). Effect of heat stress on the hypothalamic expression profile of water homeostasis-associated genes in low- and high-water efficient chicken lines. Physiol. Rep. 12, e15972. doi:10.14814/phy2.15972
Arbore C., Sergides M., Gardini L., Bianchi G., Kashchuk A. V., Pertici I., et al. (2022). Α-catenin switches between a slip and an asymmetric catch bond with F-actin to cooperatively regulate cell junction fluidity. Nat. Commun. 13, 1146. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28779-7
C. Barmeyer, J. D. Schulzke, and M. Fromm (2015). “Claudin-related intestinal diseases,” Seminars in cell and developmental biology (Elsevier).
Baxter M. F. A., Dridi S., Koltes D. A., Latorre J. D., Bottje W. G., Greene E. S., et al. (2019). Evaluation of intestinal permeability and liver bacterial translocation in two modern broilers and their jungle fowl ancestor. Front. Genet. 10, 480. doi:10.3389/fgene.2019.00480
Beggs R. R., Rao T. C., Dean W. F., Kowalczyk A. P., Mattheyses A. L. (2022). Desmosomes undergo dynamic architectural changes during assembly and maturation. Tissue Barriers 10, 2017225. doi:10.1080/21688370.2021.2017225
Brasch J., Harrison O. J., Honig B., Shapiro L. (2012). Thinking outside the cell: how cadherins drive adhesion. Trends Cell Biol. 22, 299–310. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2012.03.004
Cao M., Xue T., Huo H., Zhang X., Wang N. N., Yan X., et al. (2023). Spatial transcriptomes and microbiota reveal immune mechanism that respond to pathogen infection in the posterior intestine of Sebastes schlegelii. Open Biol. 13, 220302. doi:10.1098/rsob.220302
Daniel E., Thomas J., Ramnarain M., Bowes T., Jury J. (2001). Do gap junctions couple interstitial cells of cajal pacing and neurotransmission to gastrointestinal smooth muscle? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 13, 297–307. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2982.2001.00269.x
Daniel E. E., Wang Y. F. (1999). Gap junctions in intestinal smooth muscle and interstitial cells of cajal. Microsc. Res. Tech. 47, 309–320. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19991201)47:5<309::AID-JEMT2>3.0.CO;2-K
Dhanasiri A., Chen X., Dahle D., Siriyappagouder P., Fæste C. K., Fernandes J. M. O. (2020). Dietary inclusion of plant ingredients induces epigenetic changes in the intestine of zebrafish. Epigenetics 15, 1035–1051. doi:10.1080/15592294.2020.1747777
Drees F., Pokutta S., Yamada S., Nelson W. J., Weis W. I. (2005). Alpha-catenin is a molecular switch that binds E-cadherin-beta-catenin and regulates actin-filament assembly. Cell 123, 903–915. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.021
Dridi J. S., Greene E. S., Maynard C. W., Brugaletta G., Ramser A., Christopher C. J., et al. (2022). Duodenal metabolic profile changes in heat-stressed broilers. Anim. (Basel) 12, 1337. doi:10.3390/ani12111337
Flori L., Moazami-Goudarzi K., Alary V., Araba A., Boujenane I., Boushaba N., et al. (2019). A genomic map of climate adaptation in mediterranean cattle breeds. Mol. Ecol. 28, 1009–1029. doi:10.1111/mec.15004
Furuse M., Fujita K., Hiiragi T., Fujimoto K., Tsukita S. (1998). Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J. Cell Biol. 141, 1539–1550. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.7.1539
Garrod D., Tabernero L. (2014). Hyper-adhesion: a unique property of desmosomes. Cell Commun. Adhes. 21, 249–256. doi:10.3109/15419061.2014.930133
Garrod D. R., Fisher C., Smith A., Nie Z. (2008). Pervanadate stabilizes desmosomes. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2, 161–166. doi:10.4161/cam.2.3.6549
Getsios S., Amargo E. V., Dusek R. L., Ishii K., Sheu L., Godsel L. M., et al. (2004). Coordinated expression of desmoglein 1 and desmocollin 1 regulates intercellular adhesion. Differentiation 72, 419–433. doi:10.1111/j.1432-0436.2004.07208008.x
Greene E. S., Tabler T., Bottje W. G., Orlowski S., Dridi S. (2024). Effect of heat stress on the expression of circulating cyto(chemo)kine and inflammatory markers in broiler chickens selected for high- or low-water efficiency. FBL 29, 10359. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2910359
Greve P., Kahil T., Mochizuki J., Schinko T., Satoh Y., Burek P., et al. (2018). Global assessment of water challenges under uncertainty in water scarcity projections. Nat. Sustain. 1, 486–494. doi:10.1038/s41893-018-0134-9
Guillemot L., Schneider Y., Brun P., Castagliuolo I., Pizzuti D., Martines D., et al. (2012). Cingulin is dispensable for epithelial barrier function and tight junction structure, and plays a role in the control of claudin-2 expression and response to duodenal mucosa injury. J. Cell Sci. 125, 5005–5014. doi:10.1242/jcs.101261
Gumbiner B. M. (2005). Regulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion in morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 622–634. doi:10.1038/nrm1699
Günzel D., Yu A. S. L. (2013). Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol. Rev. 93, 525–569. doi:10.1152/physrev.00019.2012
Han X., Fink M. P., Delude R. L. (2003). Proinflammatory cytokines cause No·-dependent and -independent changes in expression and localization of tight junction proteins in intestinal epithelial cells. Shock 19, 229–237. doi:10.1097/00024382-200303000-00006
Harris T. J. C., Tepass U. (2010). Adherens junctions: from molecules to morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 502–514. doi:10.1038/nrm2927
Harrison O. J., Brasch J., Lasso G., Katsamba P. S., Ahlsen G., Honig B., et al. (2016). Structural basis of adhesive binding by desmocollins and desmogleins. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 113, 7160–7165. doi:10.1073/pnas.1606272113
Hashimoto Y., Besmond C., Boddaert N., Munnich A., Campbell M. (2024). A loss of function mutation in Cldn25 causing Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-Like Leukodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 33 (12), 1055–1063. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddae038
Hashimoto Y., Greene C., Munnich A., Campbell M. (2023). The Cldn5 gene at the blood-brain barrier in health and disease. Fluids Barriers CNS 20, 22. doi:10.1186/s12987-023-00424-5
Hiltz J., Orlowski S., Harrington L., Maynard C., Tabler T., Anthony N. (2021). Applied research note: development of a novel low flow water monitoring system in poultry/agriculture systems. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 30, 100151. doi:10.1016/j.japr.2021.100151
Ikari A., Nakano M., Suketa Y., Harada H., Takagi K. (2005). Reorganization of Zo-1 by sodium-dependent glucose transporter activation after heat stress in Llc-Pk1 Cells. J. Cell Physiol. 203, 471–478. doi:10.1002/jcp.20234
Jang D. G., Kwon K. Y., Kweon Y. C., Kim B.-g., Myung K., Lee H.-S., et al. (2022). Gja1 depletion causes ciliary defects by affecting Rab11 trafficking to the ciliary base. eLife 11, e81016. doi:10.7554/eLife.81016
Krause G., Winkler L., Mueller S. L., Haseloff R. F., Piontek J., Blasig I. E. (2008). Structure and function of claudins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1778, 631–645. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.10.018
Kuzma S., Saccoccia L., Chertock M. (2023). 25 countries, housing one-quarter of the population, face extremely high water stress. Washington: World Resources Institute. Available online at: https://www.wri.org/insights/highest-water-stressed-countries.
Lara L. J., Rostagno M. H. (2013). Impact of heat stress on poultry production. Anim. (Basel) 3, 356–369. doi:10.3390/ani3020356
Lassiter K., Greene E., Piekarski A., Faulkner O. B., Hargis B. M., Bottje W., et al. (2015). Orexin system is expressed in avian muscle cells and regulates mitochondrial dynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 308, R173–R187. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00394.2014
Marchini C. F. P., Silva P. L., Nascimento M., Beletti M. E., Silva N. M., Guimarães E. C. (2011). Body weight, intestinal morphometry and cell proliferation of broiler chickens submitted to cyclic heat stress. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 10, 455–460. doi:10.3923/ijps.2011.455.460
Martin T. A., Lane J., Ozupek H., Jiang W. G. (2013). Claudin-20 promotes an aggressive phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Tissue Barriers 1, e26518. doi:10.4161/tisb.26518
Ozden O., Black B. L., Ashwell C. M., Tipsmark C. K., Borski R. J., Grubb B. J. (2010). Developmental profile of claudin-3, -5, and -16 proteins in the epithelium of chick intestine. Anat. Rec. 293, 1175–1183. doi:10.1002/ar.21163
Perez-Moreno M., Fuchs E. (2006). Catenins: keeping cells from getting their signals crossed. Dev. Cell 11, 601–612. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2006.10.010
Prasad S., Mingrino R., Kaukinen K., Hayes K. L., Powell R. M., MacDonald T. T., et al. (2005). Inflammatory processes have differential effects on claudins 2, 3 and 4 in colonic epithelial cells. Lab. Invest 85, 1139–1162. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700316
Rahner C., Mitic L. L., Anderson J. M. (2001). Heterogeneity in expression and subcellular localization of claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the rat liver, pancreas, and gut. Gastroenterology 120, 411–422. doi:10.1053/gast.2001.21736
Rescigno M. (2011). The intestinal epithelial barrier in the control of homeostasis and immunity. Trends Immunol. 32 (6), 256–264. doi:10.1016/j.it.2011.04.003
Roger E., Chadjichristos C. E., Kavvadas P., Price G. W., Cliff C. L., Hadjadj S., et al. (2023). Connexin-43 hemichannels orchestrate Nod-like receptor protein-3 (Nlrp3) inflammasome activation and sterile inflammation in tubular injury. Cell Commun. Signal 21, 263. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01245-7
Rosenthal R., Günzel D., Piontek J., Krug S. M., Ayala-Torres C., Hempel C., et al. (2020). Claudin-15 forms a water channel through the tight junction with distinct function compared to claudin-2. Acta Physiol. 228, e13334. doi:10.1111/apha.13334
Ruff J., Barros T. L., Tellez G., Blankenship J., Lester H., Graham B. D., et al. (2020). Research note: evaluation of a heat stress model to induce gastrointestinal leakage in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 99, 1687–1692. doi:10.1016/j.psj.2019.10.075
Samanta P., Wang Y., Fuladi S., Zou J., Li Y., Shen L., et al. (2018). Molecular determination of claudin-15 organization and channel selectivity. J. Gen. Physiol. 150, 949–968. doi:10.1085/jgp.201711868
Santos R. R., Ooosterveer-van der Doelen M. A. M., Tersteeg-Zijderveld M. H. G., Molist F., Gehring R. (2021). Induction of gut leakage in young broiler chickens fed a diet with low rye inclusion. Heliyon 7, e08547. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08547
Schmittgen T. D., Livak K. J. (2008). Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative Ct method. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1101–1108. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Segretain D., Falk M. M. (2004). Regulation of connexin biosynthesis, assembly, gap junction formation, and removal. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomemb 1662, 3–21. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.01.007
Shashikanth N., France M. M., Xiao R., Haest X., Rizzo H. E., Yeste J., et al. (2022b). Tight junction channel regulation by interclaudin interference. Nat. Commun. 13, 3780. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-31587-8
Shashikanth N., Liu Y., Xing T., Turner J. (2022a). Novel contributions of claudin-4 to epithelial barrier regulation and colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 28, S51–S52. doi:10.1093/ibd/izac015.081
Shen L., Weber C. R., Turner J. R. (2008). The tight junction protein complex undergoes rapid and continuous molecular remodeling at steady state. J. Cell Biol. 181 (4), 683–695. doi:10.1083/jcb.200711165
Shigetomi K., Ikenouchi J. (2017). Regulation of the epithelial barrier by post-translational modifications of tight junction membrane proteins. J. Biochem. 163, 265–272. doi:10.1093/jb/mvx077
Tabler T. W., Greene E. S., Orlowski S. K., Hiltz J. Z., Anthony N. B., Dridi S. (2020). Intestinal barrier integrity in heat-stressed modern broilers and their ancestor wild jungle fowl. Front. Vet. Sci. 7, 249. doi:10.3389/fvets.2020.00249
Tamura A., Hayashi H., Imasato M., Yamazaki Y., Hagiwara A., Wada M., et al. (2011). Loss of claudin-15, but not claudin-2, causes Na+ deficiency and glucose malabsorption in mouse small intestine. Gastroenterol 140, 913–923. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.08.006
Tsukita S., Furuse M., Itoh M. (2001). Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 285–293. doi:10.1038/35067088
Vancamelbeke M., Vermeire S. (2017). The intestinal barrier: a fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11, 821–834. doi:10.1080/17474124.2017.1343143
Van Itallie C., Rahner C., Anderson J. M. (2001). Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J. Clin. Invest 107, 1319–1327. doi:10.1172/jci12464
Varasteh S., Braber S., Akbari P., Garssen J., Fink-Gremmels J. (2015). Differences in susceptibility to heat stress along the chicken intestine and the protective effects of galacto-oligosaccharides. PLoS One 10, e0138975. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138975
Vasioukhin V., Bauer C., Yin M., Fuchs E. (2000). Directed actin polymerization is the driving force for epithelial cell–cell adhesion. Cell 100, 209–219. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81559-7
Voges L., Weiß F., Branco A.-T., Fromm M., Krug S. M. (2024). Expression and localization profiles of tight junction proteins in immune cells depend on their activation status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 4861. doi:10.3390/ijms25094861
Weber S., Schneider L., Peters M., Misselwitz J., Rönnefarth G., Böswald M., et al. (2001). Novel paracellin-1 mutations in 25 families with familial hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 12, 1872–1881. doi:10.1681/asn.V1291872
Wong J., Chopra J., Chiang L. L. W., Liu T., Ho J., Wu W. K. K., et al. (2019). The role of connexins in gastrointestinal diseases. J. Mol. Biol. 431, 643–652. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.007
Yamada S., Pokutta S., Drees F., Weis W. I., Nelson W. J. (2005). Deconstructing the cadherin-catenin-actin complex. Cell 123, 889–901. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.020
Yang P.-C., He S.-H., Zheng P.-Y. (2007). Investigation into the signal transduction pathway via which heat stress impairs intestinal epithelial barrier function. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22, 1823–1831. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04710.x
Zhang H., Zhao L., Zhang P., Xie Y., Yao X., Pan X., et al. (2024). Effects of selenoprotein extracts from Cardamine hupingshanensis on growth, selenium metabolism, antioxidant capacity, immunity and intestinal health in largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Front. Immunol. 15, 1342210. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1342210
Zheng G., Victor Fon G., Meixner W., Creekmore A., Zong Y., Dame, M K., et al. (2017). Chronic stress and intestinal barrier dysfunction: glucocorticoid receptor and transcription repressor Hes1 regulate tight junction protein claudin-1 promoter. Sci. Rep. 7, 4502. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-04755-w
Keywords: broiler, heat stress, water efficiency, gut integrity, gene expression
Citation: Greene ES, Roach B, Cuadrado MF, Orlowski S and Dridi S (2025) Effect of heat stress on ileal epithelial barrier integrity in broilers divergently selected for high- and low-water efficiency. Front. Physiol. 16:1558201. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1558201
Received: 09 January 2025; Accepted: 18 March 2025;
Published: 07 April 2025.
Edited by:
Oyegunle Emmanuel Oke, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, NigeriaReviewed by:
Nikola Čobanović, University of Belgrade, SerbiaBirendra Mishra, University of Hawaii at Manoa, United States
Chenxi Deng, Jiangxi Biotech Vocational College, China
Sadid Al Amaz, University of Hawaii at Manoa, United States
Copyright © 2025 Greene, Roach, Cuadrado, Orlowski and Dridi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sami Dridi, ZHJpZGlAdWFyay5lZHU=
 Elizabeth S. Greene
Elizabeth S. Greene Brooklee Roach2
Brooklee Roach2 Sara Orlowski
Sara Orlowski Sami Dridi
Sami Dridi