- 1Department of Computer Science, University of Aizu, Aizu-Wakamatsu, Japan
- 2Department of Anatomy and Histology, Fukushima Medical University, Fukushima, Japan
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is one of the most common types of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. The activity of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is known to influence episodes of AVNRT, yet the precise mechanisms underlying this effect remain incompletely understood. In this study, we update our compact multifunctional model of the rabbit atrioventricular (AV) node with ANS control to simulate AVNRT. The refractoriness of the model cells is adjusted by a specific ANS coefficient, which impacts the effective refractory periods, conduction delays, and intrinsic frequency of pacemaker cells. Using this model, we investigate the onset, sustainability, and spontaneous termination of typical slow-fast and atypical fast-slow forms of AVNRT under ANS modulation. The conditions for the onset and sustainability of AVNRT can exist independently in various combinations. Differences in the effective refractory periods of the slow and fast pathways of the AV node during anterograde and retrograde conduction determine the specific form of AVNRT. For the first time, a computer model reveals the potential to identify hidden processes within the AV node, thereby bringing us closer to understanding the role of ANS control in AVNRT. The results obtained are consistent with clinical and experimental data and represent a novel tool for studying the electrophysiological mechanisms behind this type of arrhythmia.
1 Introduction
The atrioventricular (AV) node consists of dual pathways: a fast pathway (FP) with a relatively longer effective refractory period (ERP) and a slow pathway (SP) with a shorter ERP. These pathways can create a reentrant circuit, a substrate for AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), the most common type among regular supraventricular arrhythmias (Straus and Schocken, 2021).
AVNRT manifests as sudden episodes of a few cycles of abnormally fast heartbeats (reciprocal or echo beats) or as sustained or persistent tachycardia. AVNRT is electrophysiologically classified as typical (slow-fast) and atypical (fast-slow and slow-slow) forms corresponding to anterograde-retrograde conduction sequence through the dual AV nodal pathways (Katritsis and Josephson, 2013).
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) plays a crucial role in the initiation and termination of supraventricular tachycardias within the AV node (Nigro et al., 2010). Sympathetic stimulation typically facilitates the induction of AVNRT, while enhancing vagal (parasympathetic) tone via pharmacological means or Valsalva maneuvers is commonly employed to terminate the tachycardia (Appelboam et al., 2015; Xiao et al., 2024). The effect of ANS control on dual pathways interaction in the initiation, sustainability, and spontaneous termination of AVNRT is still poorly understood despite some attempts to explain its exact underlying physiological mechanism.
Several functional computer models of the AV node have been developed (Inada et al., 2009; Climent et al., 2011; Plappert et al., 2022). However, to our knowledge, only one incorporates ANS control (Plappert et al., 2022). In the latter model, the authors modulate vagal tone by modifying parameters of AV node refractoriness and conduction velocity separately. Recently, we have developed a compact, multi-functional rabbit AV node model based on the simplified two-variable cardiac cell model (Ryzhii and Ryzhii, 2023a). The one-dimensional model is fitted to existing experimental data and includes dual pathway physiology, a primary pacemaker in the sinus node (SN), and a secondary pacemaker in the SP. Visualization of interactions between intact and post-ablated SP and FP in the form of Lewis ladder diagrams facilitates the study of AVNRT.
Experimental observations show that FP has a significantly longer effective refractory period (ERP) in the case of anterograde conduction (
To overcome this drawback, we updated the functionality of our AV node model incorporating the ANS control. The control by both sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the ANS was achieved by introducing a single coefficient to scale parameters related to the refractoriness of the model cells. This coefficient also influences other key properties of the cardiac conduction system, including the intrinsic rates of pacemakers and conduction times.
In the current work, we used the modified model to study the onset, susceptibility, and spontaneous termination of typical slow-fast and atypical fast-slow forms of AVNRT. We consider the induction of AVNRT not only by premature atrial and His bundle stimulation, referred to in clinical practice as premature atrial (PAC) and ventricular (PVC) complexes but also by electrical impulses originating within the AVjunction (premature junctional complex, PJC) (Straus and Schocken, 2021).
2 Model and methods
The scheme of the compact AV node model used in this study is shown in Figure 1A. Each model cell is described by Aliev-Panfilov cardiac cell model (Aliev and Panfilov, 1996) given by a couple of reaction-diffusion type ordinary differential equations
where
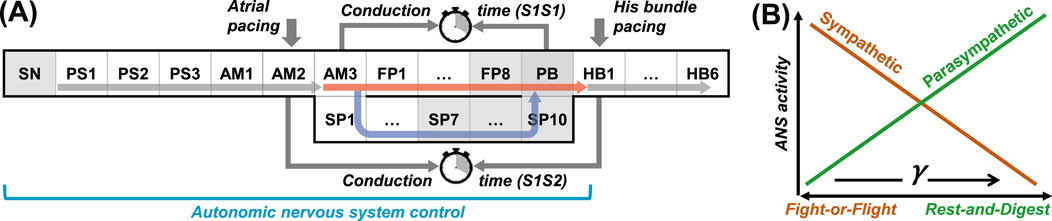
Figure 1. (A) Schematic representation of the rabbit atrioventricular node model. SN - sinus node, PS - peripheral sinus node cells, AM - atrial muscle cells, FP - fast pathway cells, SP - slow pathway cells, PB - penetrating bundle cell, HB - His bundle cells. Thick vertical arrows denote places of stimuli application for atrial and His bundle pacing. The arrows within the structure correspond to normal conduction. The gray shading indicates pacemaker cells. (B) Relation between ANS activity and the coefficient
in the one-dimensional system account for the coupling asymmetry, where
Standard S1S2 stimulation consisted of nine pulses with constant basic S1–S1 interval equal to spontaneous sinus rhythm interval determined by the current ANS state, and S2 premature test stimulus with S1–S2 interval introduced with a decrement of 1 ms until conduction through AV node is blocked. The S1S2 conduction time was measured betweenatrial muscle cell AM2 and His bundle cell HB1. S1S1 stimulation was performed by applying ten pulses with 1 ms interval decrement starting from the interval of spontaneous sinus rhythm in the current state of the ANS. For this stimulation type, we measured atria-His and His-atria conduction delays within the AV node ringbetween atrial muscle cell AM3 and penetrating bundle cell PB. Atrial and His bundle stimulation pulses were 1 ms and 2 ms long, respectively, and 1.3 times above the threshold.
We implemented the effect of the ANS in our rabbit cardiac conduction system model by introducing a control coefficient
The rationale for this method of ANS control was discussed in detail in our recent report (Ryzhii and Ryzhii, 2024).The value of the coefficient
Since only isolated rabbit heart preparations were used in the experiments (Reid et al., 2003; Climent et al., 2011; Billette and Tadros, 2019), any influence of the ANS was absent, leaving the hearts in a state representing a static invariable situation regarding the cardiac conduction system. At such conditions, the onset of AVNRT was observed in the S1S2 protocol stimulation at short atrial test pulses with a normal sinus rhythm of about 166 bpm (360 ms beating interval) (Reid et al., 2003). However, it is known that enhancing sympathetic tone may provoke AVNRT onset (Hartikainen et al., 1997). At the same time, Valsalva maneuver or adenosine administration (Appelboam et al., 2015; Xiao et al., 2024) causes the vagal tone enhancement, resulting in reduced heart rate and consequent termination of AVNRT. Considering the above facts, we set
The three AV node model variants considered had similar anterograde conduction characteristics (
– The first model variant had
– The second model variant had slightly reduced diffusion coefficient
– The third model variant had the coupling asymmetry coefficient
For each model variant, we considered three scenarios of premature cardiac complexes classified by their origin - atrial (premature atrial complex, PAC), ventricular or His bundle (premature ventricular complex, PVC), and AV intranodal or junctional (premature junctional complex, PJC).Since our model does not include ventricles, we assume that PVCs originate in the His bundle region, which is observed in clinical practice [see, for example, work by Yamada et al. (2008)]. The cases of PAC and PVC required proper selection of intervals of premature extrastimuli within the AVNRT induction window. For PJC, a short burst of sympathetic activity with high sinus tachycardia was applied to stimulate the conduction block within the AV node.
The ANS coefficient
The simulations were performed using MATLAB (R2023a, Mathworks Inc., Natick, MA, United States). The ordinary differential Equations 1, 2 were solved using ode23 solver which utilizes second and third order Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg formulas with automatic step-size. Other parameter values were similar to that in (Ryzhii and Ryzhii, 2023a) and are based on rabbit experimental data (Reid et al., 2003; Billette and Tadros, 2019). Additional details of the basic rabbit AV node model and its properties can be also found in (Ryzhii and Ryzhii, 2023a).
3 Results
In what follows, we refer to AVNRT as sustained oscillations within the AV ring and echo beats (reciprocating pulses) as decaying oscillations with with no more than a few cycles.
3.1 The first model variant
Figure 2 demonstrates simulation results of AVNRT onset and spontaneous termination for the first model variant with varying ANS tone
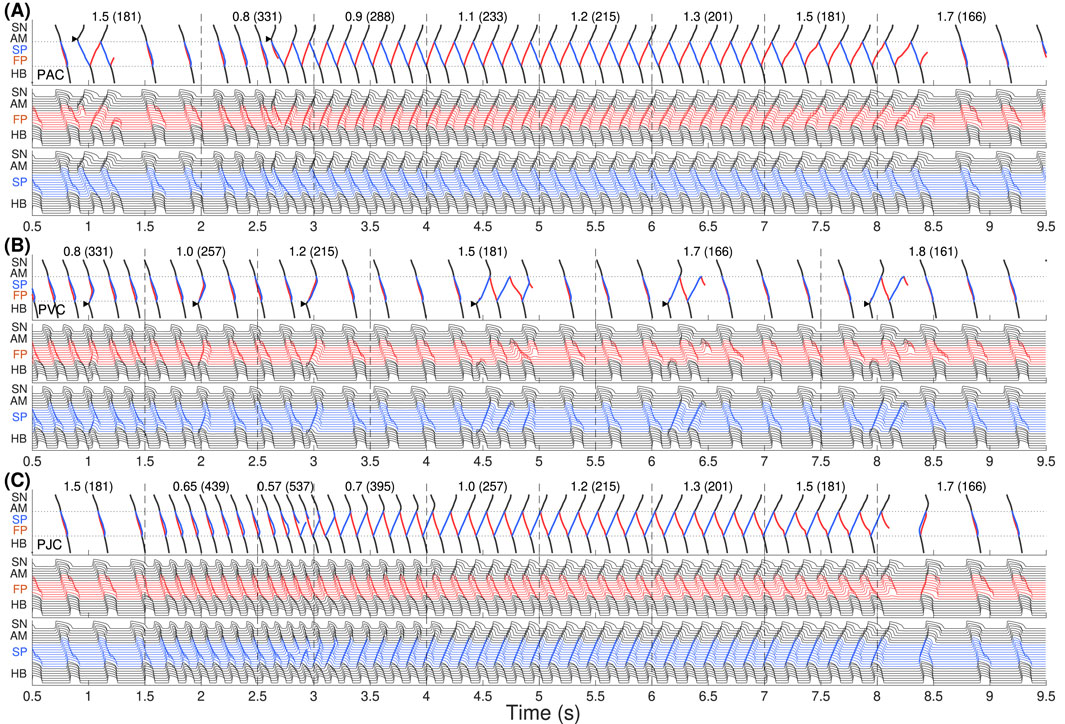
Figure 2. The first model variant with
In Figure 2A, we started with an increased sympathetic tone at
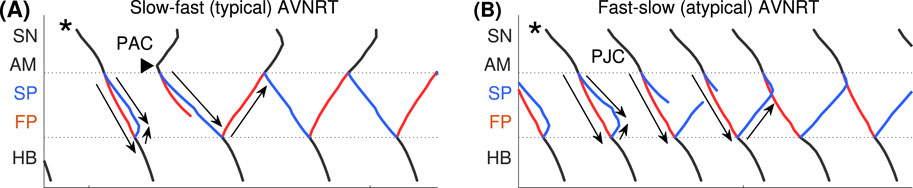
Figure 3. Schemes of AVNRT onset in the first model variant. (A) Slow-fast (typical) AVNRT form at the premature atrial complex (PAC) (from Figure 2A), and (B) fast-slow (atypical) form at the premature junctional complex (PJC) (from Figure 2C). Arrows show the direction of conduction via pathways. Arrowhead denotes the place and moment of premature stimulation. Asterisk indicates normal conduction.
With His bundle premature stimulation (PVC), trying to provoke AVNRT at different
AVNRT with PJC originates from within the AV node, so it does not require an external premature stimulus. A brief episode with a sudden decrease of
To investigate the underlying physiological background of the results in Figure 2, we performed simulations using S1S2 and S1S1 stimulation protocols. Figure 4 presents various related conduction curves for the first model variant calculated for different ANS states represented by the coefficient
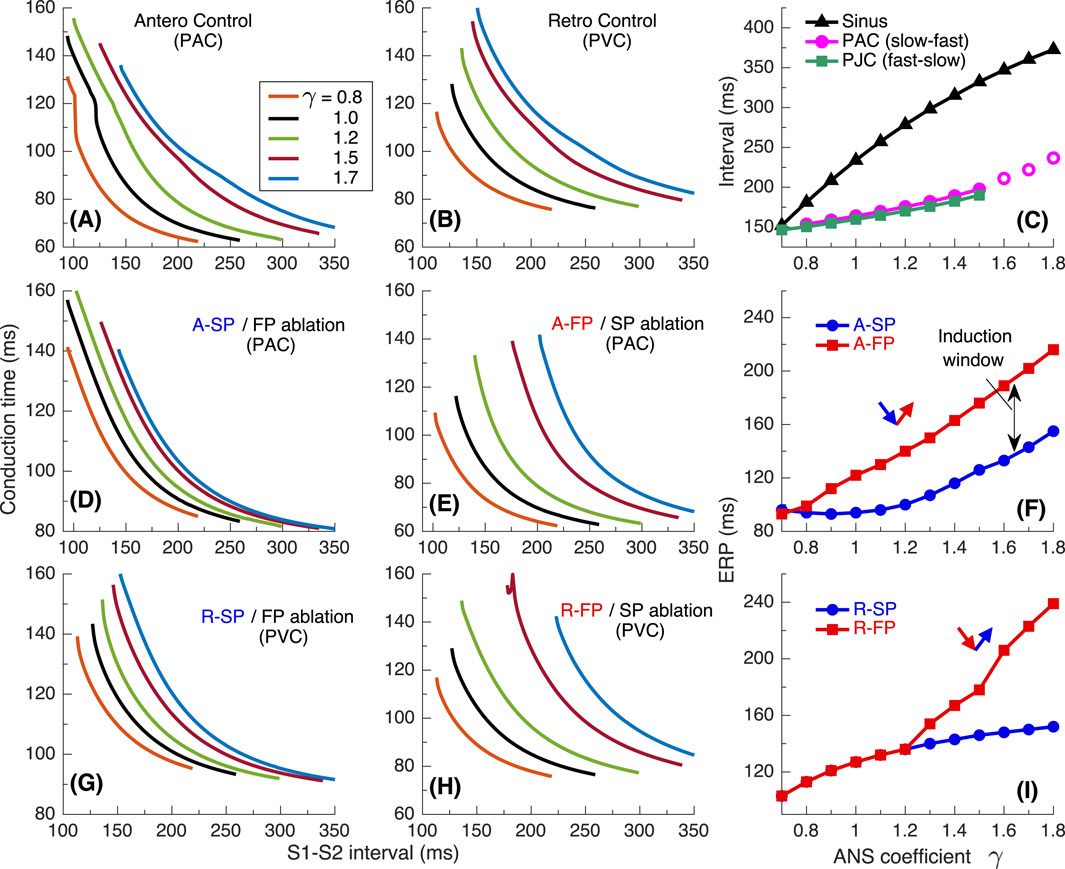
Figure 4. Conduction characteristics using S1S2 stimulation protocol for the first model variant. (A) Control case with atrial pacing (PAC). (B) Control case with His bundle pacing (PVC). (C) Dependence of sinus rhythm and AVNRT intervals of PAC and AV intranodal (PJC) origin on the coefficient
Maximal S1-S2 interval values for the conduction curves are limited by spontaneous sinus rhythm interval, which decreases with smaller
The S1S2 conduction curves obtained for individual SP and FP pathways (post-ablation cases) and the dependence of their ERPs on
Figures 5A–C show the conduction time calculated using S1S1 pacing protocol for anterograde SP, retrograde FP and their sum for slow-fast AVNRT form, and Figures 5D–F - anterograde FP and retrograde SP and their sum for fast-slow form.
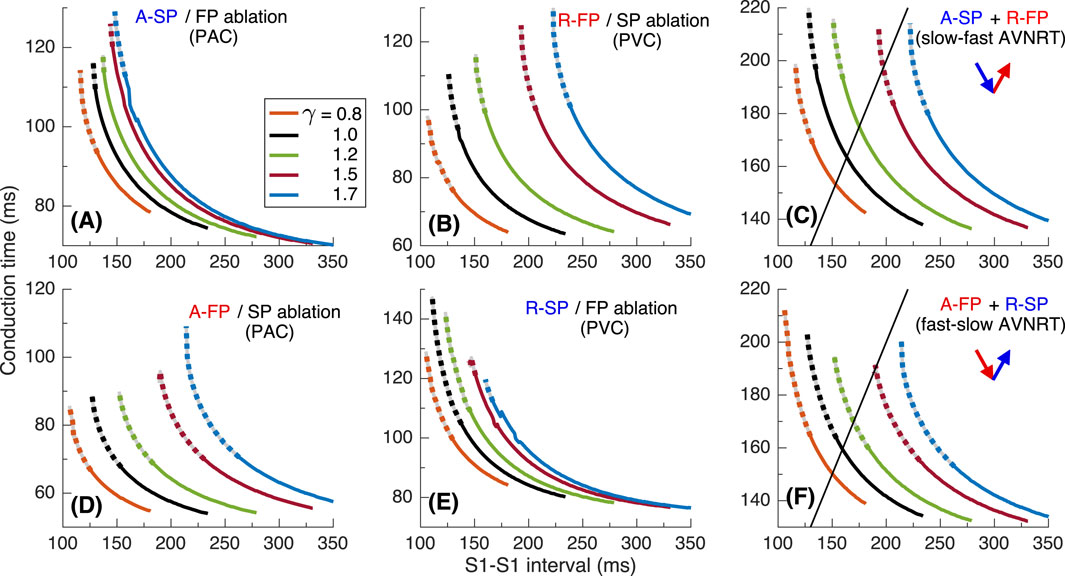
Figure 5. Conduction characteristics using S1S1 stimulation protocol for the first model variant. (A, B) - anterograde SP and retrograde FP conduction times and their sum (C) versus pacing interval. (D, E) - anterograde FP and retrograde SP conduction times and their sum (F) versus pacing interval. Unstable conduction is indicated by thick dotted parts on the conduction curves. Black straight lines in panels (C, F) represent the AVNRT sustainability lines on which the stimulation interval equals the sum of the SP and FP conduction times.
In our simulations, the initial time delay preceding the first S1 stimulus of the S1S1 protocol affected the stability of conduction in the pathways. The variation of the initial delay resulted in the unstable conduction of last S1 test stimulus at short S1-S1 intervals [left ends of the conduction curves in Figures 5A,B,D,E. The instability is also reflected in the summation curves in Figures 5C,F. The unstable regions are marked by thick dotted lines of the same color. The earliest (leftmost) point on each summation curve and the width of its unstable region are determined by the largest first unstable point and the largest last unstable point of corresponding conduction curves of either pathway.
AVNRT is a self-sustained oscillation with a cycle length equal to the stimulation period. The AVNRT cycle length equals the sum of the anterograde SP (A-SP) and retrograde FP (R-FP) conduction times for slow-fast AVNRT form and the sum of the anterograde FP (A-FP) and retrograde SP (R-SP) conduction times for fast-slow form (Figures 5C,F). At the same time, the pathway conduction time is cycle-length dependent. The existence of stable periodic oscillations in the AV ring can be determined by the presence of the intersection point of the summation curve with the identity line
As seen from Figures 5C,F, at
3.2 The second model variant
Figures 6–9 present results with a similar simulation setup but for the second model variant with
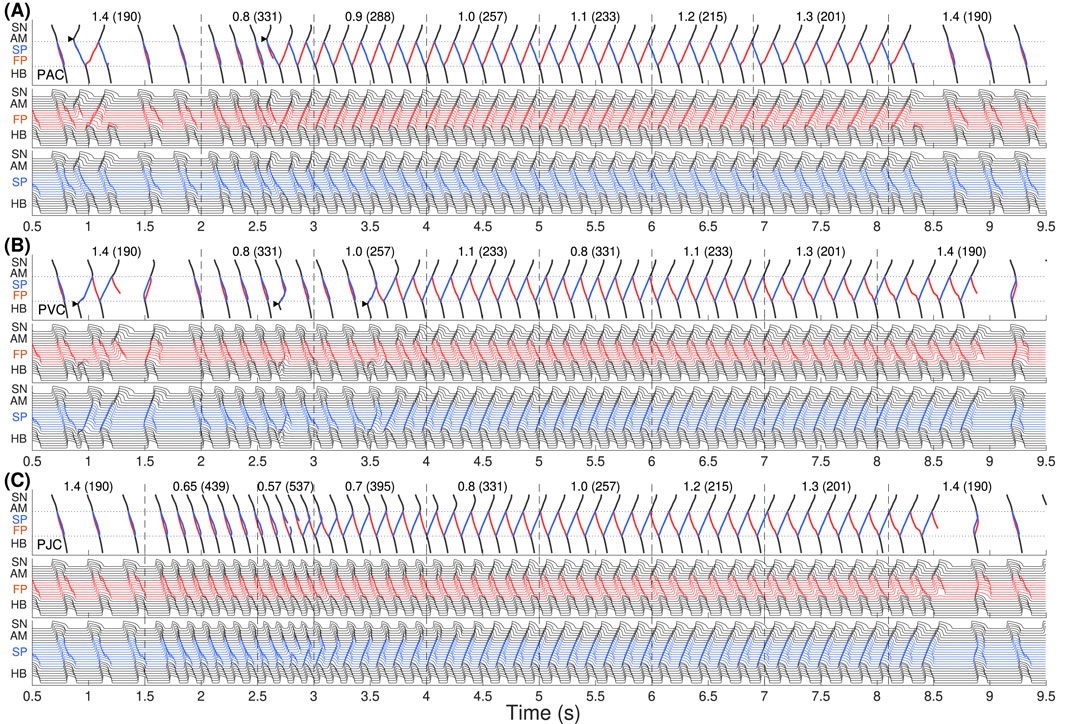
Figure 6. The same as in Figure 2 but for the second model variant with

Figure 7. Scheme of the fast-slow AVNRT onset with PVC in the second model variant (from Figure 6B). Arrows show the direction of conduction via pathways. Arrowhead denotes the place and moment of premature stimulation. Asterisk indicates normal conduction.
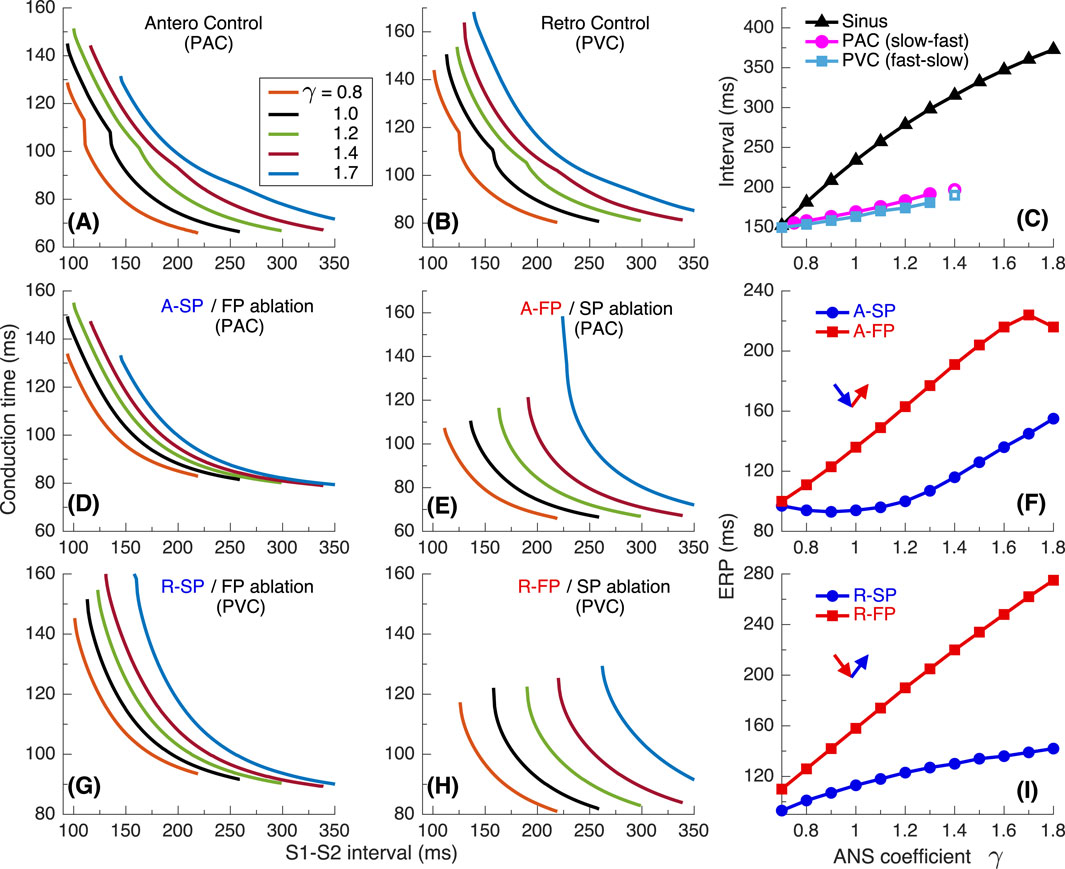
Figure 8. Conduction characteristics using S1S2 stimulation protocol for the second model variant. (A) Control case with atrial pacing (PAC). (B) Control case with His bundle pacing (PVC). (C) Dependence of sinus rhythm and AVNRT intervals of PAC and AV intranodal (PJC) origin on the coefficient γ. Empty markers correspond to echo beats. (D, E) - anterograde (A-) conduction times for SP (FP ablation) and FP (SP ablation), and their ERPs (F); (G, H) - retrograde (R-) conduction times for SP and FP, and their ERPs (I).
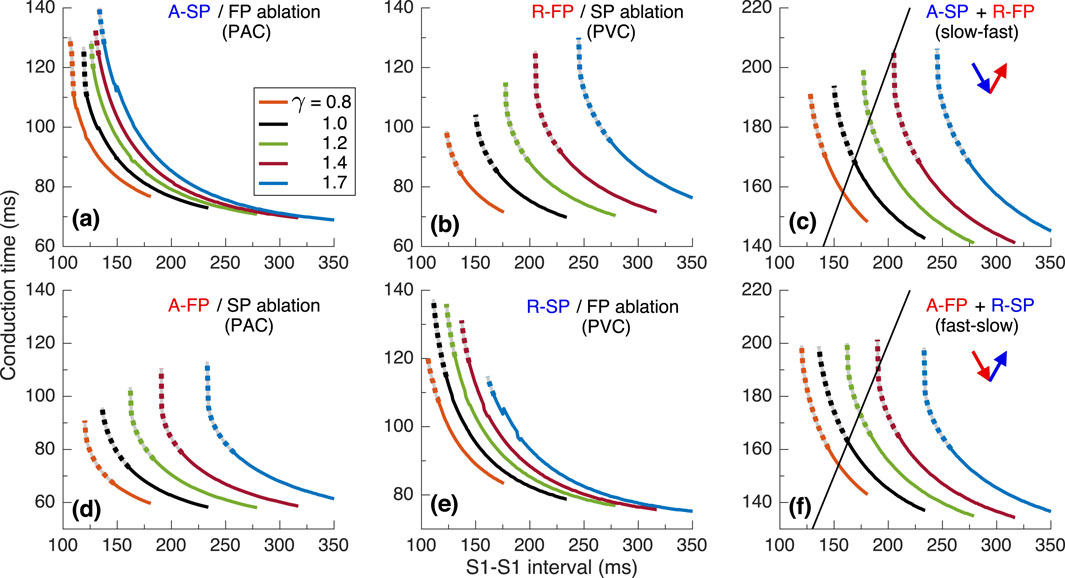
Figure 9. Conduction characteristics using S1S1 stimulation protocol for the second model variant. (A, B) - anterograde SP and retrograde FP conduction times and their sum (C) versus pacing interval. (D, E) - anterograde FP and retrograde SP conduction times and their sum (F) versus pacing interval. Unstable conduction is indicated by thick dotted parts on the conduction curves. Black straight lines in panels (C, F) Represent the AVNRT sustainability lines on which the stimulation interval equals the sum of the SP and FP conduction times.
In Figure 6A with atrial pacing we observed a similar situation as in Figure 2A, but spontaneous termination of slow-fast AVNRT occurred earlier at lower
Figure 7 demonstrates on the ladder diagram the details of the onset of fast-slow AVNRT with His bundle pacing (PVC). The beginning of the oscillations was facilitated by a subsequent sinus impulse, similar to the situation with PJC-originated fast-slow AVNRT shown in Figure 3B.
The anterograde S1S2 conduction curves in Figures 8A,D,E and the relationship of anterograde ERPs between SP and FP (Figure 8F) remained similar to those of the first model variant (Figures 4A,D,E,F). However, in contrast to Figure 4B, noticeable transitions of the conduction from FP to SP appeared on the retrograde control curves (Figure 8B). They became sharper with decreasing
Figure 9 shows the conduction characteristics using S1S1 stimulation protocol similar to that shown in Figure 5. As seen from Figures 6A, 9C, the sustainability of slow-fast AVNRT persisted only at
3.3 The third model variant
Figures 10–13 present simulation results obtained with the third model variant in which we set the relationship
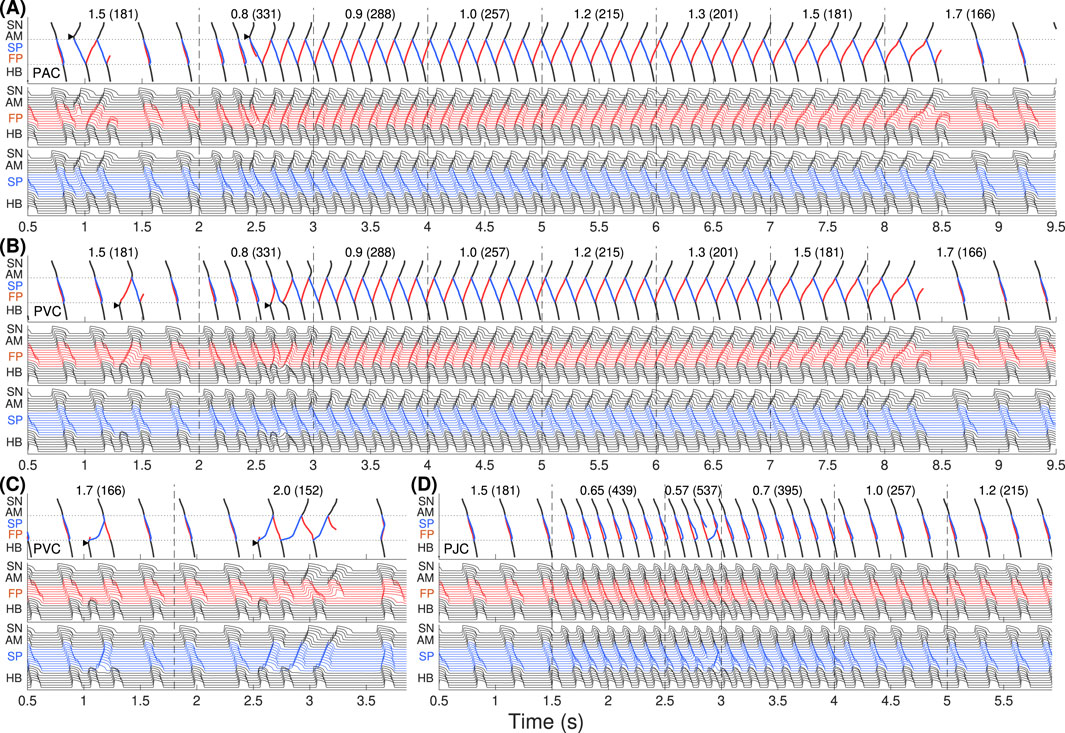
Figure 10. The same as in Figure 2 but for the third model variant. Onset of slow-fast AVNRT with PAC (A) and with PVC (B) at enhanced sympathetic tone, and spontaneous termination of the oscillations at increasing vagal tone at
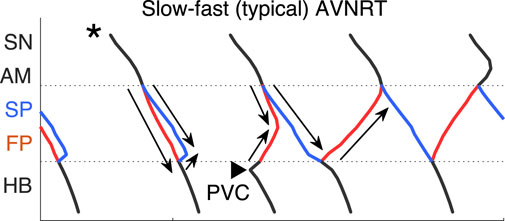
Figure 11. Scheme of slow-fast AVNRT onset with PVC in the third model variant (from Figure 10B). Arrows show the direction of conduction via pathways. Arrowhead denotes the place and moment of premature stimulation. Asterisk indicates normal conduction.
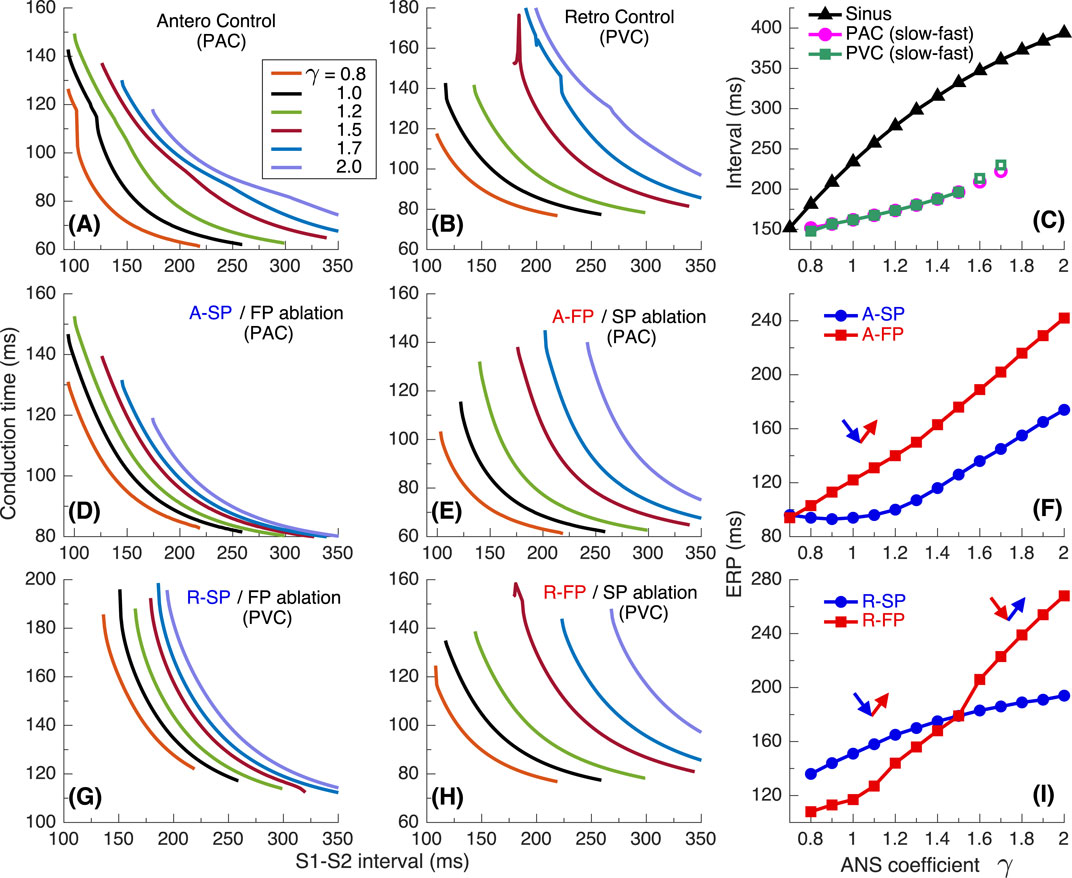
Figure 12. Conduction characteristics using S1S2 stimulation protocol for the third model variant. (A) Control case with atrial pacing (PAC). (B) Control case with His bundle pacing (PVC). (C) Dependence of sinus rhythm and AVNRT intervals of PAC and AV intranodal (PJC) origin on the coefficient γ. Empty markers correspond to echo beats. (D, E) - anterograde (A-) conduction times for SP (FP ablation) and FP (SP ablation), and their ERPs (F); (G, H) - retrograde (R-) conduction times for SP and FP, and their ERPs (I).
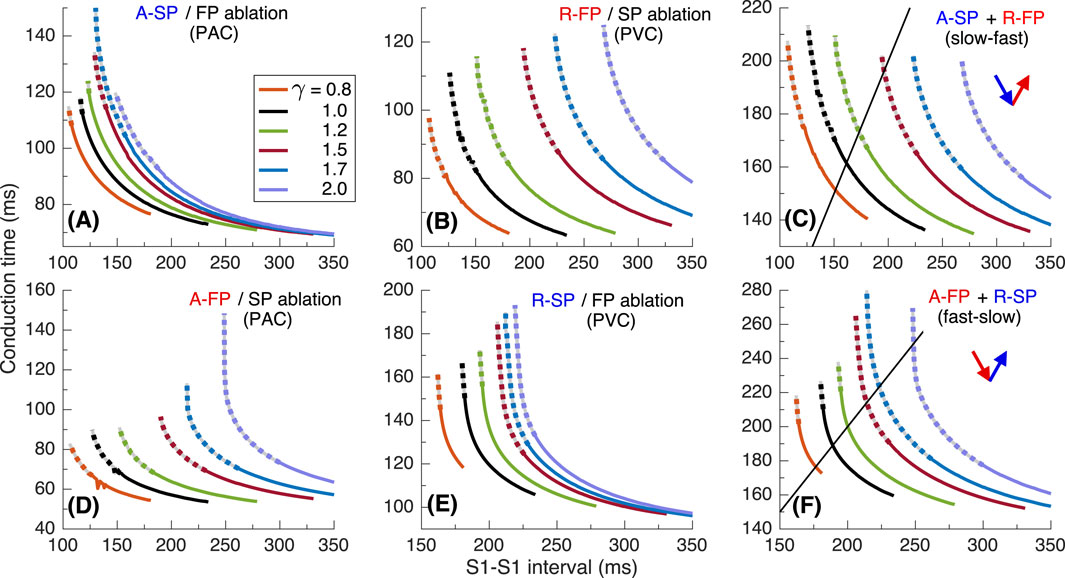
Figure 13. Conduction characteristics using S1S1 stimulation protocol for the third model variant. (A, B) - anterograde SP and retrograde FP conduction times and their sum (C) versus pacing interval. (D, E) - anterograde FP and retrograde SP conduction times and their sum (F) versus pacing interval. Unstable conduction is indicated by thick dotted parts on the conduction curves. Black straight lines in panels (C, F) represent the AVNRT sustainability lines on which the stimulation interval equals the sum of the SP and FP conduction times.
The situation with slow-fast AVNRT induction (Figure 10A) looks the same as in Figures 2A, 6A due to the similarity of anterograde conduction and refractory curves in panels (D)–(F) of Figures 4, 8, 12. However, with His bundle pacing (PVC, Figure 10B) we obtained the same typical slow-fast AVNRT form as with atrial pacing (PAC, Figure 10A). At
In contrast to the first and second model variants, in the third variant, no AVNRT was induced with brief bursts of very strong sympathetic tone (Figure 10D). In Figure 11 the details of the onset of slow-fast AVNRT with His bundle pacing (PVC) are shown on ladder diagrams.
According to the setup of the third model variant, the retrograde FP and SP ERP curves shown in Figure 12I intersect at
Results using S1S1 stimulation are demonstrated in Figure 13. Sustained slow-fast AVNRT can exist in the range
4 Discussion
Using our compact multifunctional model of rabbit AV node, we simulated the effect of ANS on the behavior of AVNRT. Incorporating a single ANS coefficient
The validity of our approach to the incorporation of ANS control into our rabbit AV node model and obtained results are supported by the following clinical and experimental observations.
Clinical studies suggest that sustained typical slow-fast AVNRT episodes are preceded by an increase in sympathetic tone (Nigro et al., 2010). Accordingly, for the induction of AVNRT in most cases, we set
The atypical fast-slow AVNRT form appeared in our simulation in rare cases: in the case with PJC (Figures 2C, 6C), occurring primarily in children and postoperative patients (Chen et al., 2015), in the case with PVC (Figure 6B) with
According to Katritsis et al. (2015a), under certain conditions, the difference in retrograde ERPs between SP and FP can become inverted with variation of the ANS state (Figure 12I), resulting in both slow-fast and fast-slow AVNRT forms can occur in the same subject. In Figure 10A, typical slow-fast AVNRT appeared during predominance of sympathetic tone in
While the onset of AVNRT is mainly observed during enhanced sympathetic activity, a possibility exists for tachycardia or reciprocating beats induction with increased vagal tone due to the widening of the induction window (Chiou et al., 2003; Sinkovec et al., 2011). With increasing parameter
The onset of AVNRT requires four factors: (A) the presence of at least two functional pathways in the AV node, (B) a specific ANS state that ensures the appropriate refractoriness of the pathways and conduction delays in them, (C) a difference in ERPs between the slow and fast pathways, and (D) the presence of a premature atrial or His bundle (ventricular) stimulus delivered at the proper time. The latter condition is not required when AVNRT originated within the AV node (PJC). Induction of AVNRT in response to a brief burst of enhanced sympathetic tone accompanied by fast sinus rhythm or atrial pacing was reported in patients (Chiou et al., 2003). This phenomenon was also observed in our simulations (Figures 2C, 6C).
The sustainability of AVNRT is determined by the coincidence of the total duration of anterograde and retrograde conduction in slow and fast pathways with the AVNRT cycle length dependent on the state of the ANS (panels (C) and (F) in Figures 5, 9, 13). If the AVNRT sustainability condition is not satisfied but the conditions for its onset mentioned in the previous paragraph are met, a few echo beats may occur (Figures 6B, 8I).
As seen in Figures 2A, 6B, 10A,B, at the same coefficient
The shapes of anterograde control conduction curves, obtained using the S1S2 protocol with varying coefficient
In most cases of anterograde and retrograde conduction, vagal modulation affected the ERPs of the FP more strongly than the ERPs of the SP (see panels (F) and (I) in Figures 4, 8, 12), as quantitatively demonstrated by Chiou et al. (2003).
Applying S1S1 stimulation protocols, we observed some cases of nodal conduction alternans with variation of conduction time from beat to beat (Sun et al., 1995; Garfinkel, 2007), which are reflected in some bumps on conduction curves in Figures 5A,E, 9A,E, 13B,D.
The spontaneous termination of AVNRT occurs due to increased refractoriness and nodal conduction delays (Plappert et al., 2022), resulting from enhanced vagal tone, which is utilized in Valsalva maneuvers and pharmaceutical treatments (Appelboam et al., 2015; Xiao et al., 2024). When the combined delays of anterograde and retrograde conduction in the SP and FP become unequal to the pacing interval, the condition for persistent AVNRT is no longer met (panels (C) and (F) in Figures 5, 9, 13). In the vast majority of cases, spontaneous termination of AVNRT occurred when the conduction was blocked through FP regardless of the AVNRT form (Figures 2A,C, 6, 10A–C). This aligns with clinical observations regarding spontaneous AVNRT termination (Chiale et al., 2015).
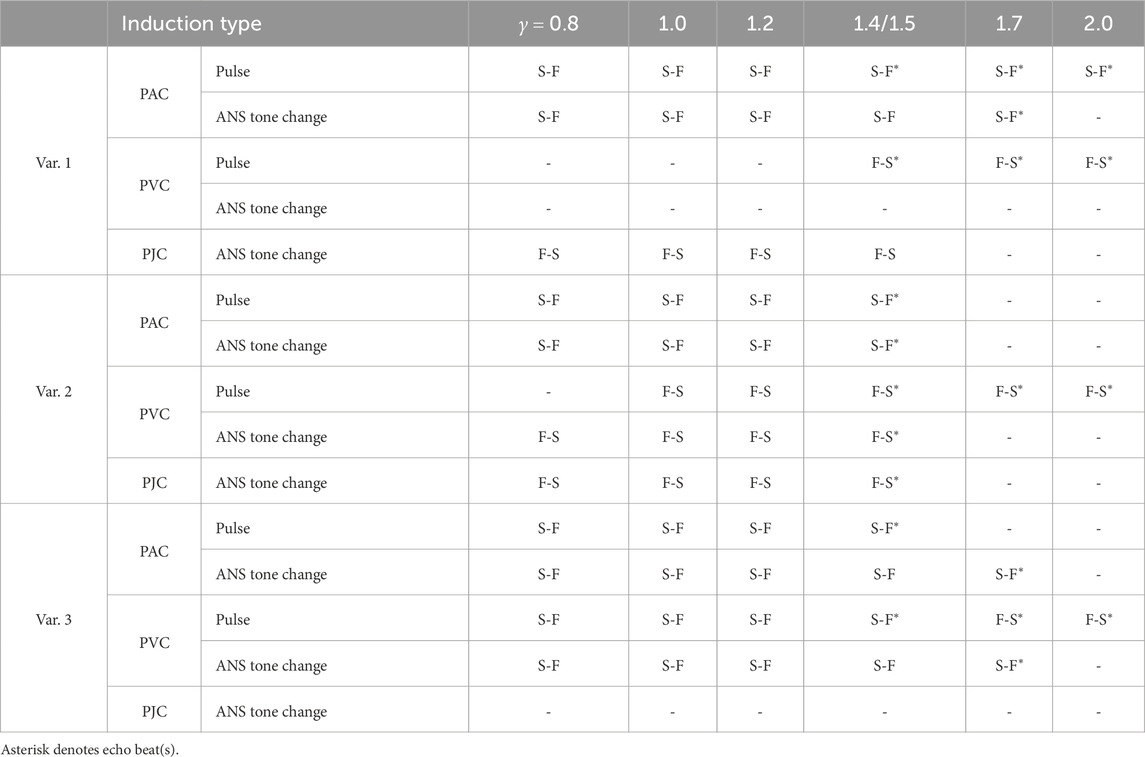
The summary of different types of AVNRT and echo beats obtained in our simulations is given in Table 1, where S-F and F-S mean slow-fast and fast slow types, and asterisk denotes echo beats. In the table, “Pulse” type corresponds to the onset of AVNRT induced by either PAC or PVC, and “ANS tone change” type is related to the sustainability of the oscillations. As seen from Table 1, at enhanced parasympathetic tone
While there are differences in the detailed electrophysiology of the atrioventricular (AV) nodes between rabbits and humans, particularly regarding the origin of AV nodal pacemaking (Mazgalev et al., 2001), the general behavior is similar across mammals. Therefore, experiments and simulations conducted on animals remain important (Bartolucci et al., 2024). We believe that the assumptions underlying the proposed model, the simulation results obtained, and the conclusions drawn correspond qualitatively, if not in perfect detail, to the actual processes occurring in the human heart.
5 Limitations
While a simplified approach views the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) as having opposite effects, a contemporary perspective recognizes that the sympathetic branch is responsible for quick mobilization responses, whereas the parasympathetic branch serves as a gradually activated damping system. Our phenomenological model adopts this simplified view to provide a general macroscopic description of the ANS control over the cardiac conduction system. Though a uniform coefficient makes the ANS control implementation simple, it complicates studying the effects of medications on the sympathetic and parasympathetic limbs of the ANS separately.
The second limitation of the current version of the rabbit conduction system model is the absence of heart rate variability (HRV). HRV is also governed by the balance between parasympathetic and sympathetic tones of the ANS (Guzzetti et al., 2005; Rovere et al., 2020), and impacts the cardiac conduction system, particularly the sinus pacemaker, over the relatively long term (24 h). However, our study specifically focuses on the effects of the ANS over a shorter time scale. The slow variation in the sinus rate has minimal impact on AVNRT since the rate in the latter is consistently higher, and sinus rhythm is effectively overdriven [panels (C) in Figures 4, 8, 12]. Consequently, we can disregard the influence of HRV in our analysis.
The third limitation is that we applied the ANS control coefficient
Finally, the current structure of the AV node model includes only one slow pathway. The atypical slow-slow form of AVNRT was left out of our model. This form of AVNRT is observed in a small percentage of cases in both humans (Katritsis et al., 2015b) and rabbits (Patterson and Scherlag, 2003). However, due to the limited data available on rabbits, incorporating a second slow pathway into the AV node model presents challenges. This remains a topic for future development of the AV node model.
6 Conclusion
In this work, we extended the functionality of our previously developed model of the rabbit cardiac conduction system based on the Aliev-Panfilov cardiac cell model by incorporating control from the autonomic nervous system. The control is accomplished by altering cell refractoriness using a single coefficient, which changes the conduction delays in the AV nodal pathways and intrinsic frequency of pacemaker cells. The influence of the autonomic nervous system extends to the model cells from the sinus node to the penetrating bundle.
Using the modified model, we studied conditions for the onset, sustainability, and spontaneous termination of typical slow-fast and atypical fast-slow AVNRT forms. The conditions for the onset and sustainability of AVNRT can occur independently in various combinations. The difference in effective refractory periods between slow and fast pathways and the state of the autonomic nervous system determine the type of AVNRT and its sustainability with both atrial pacing and His bundle pacing.The updated computationally lightweight but detailed model of rabbit cardiac conduction system with dual AV nodal pathways is suitable for studying physiological mechanisms of various forms of AVNRT. Inclusion of autonomic nervous system control into the model provides more lifelike functionality and allows realization of various situations that are nearly impossible to reproduce in animal or human experiments. Our model could also serve as an educational tool to help students and practitioners visualize and understand the dynamic and complex interactions leading to AVNRT.
Data availability statement
The MATLAB code used in this study can be found in the GitHub repository https://github.com/mryzhii/rabbit-AVNRT and Zenodo repository https://zenodo.org/records/14604033.
Author contributions
MR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ER: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Grant No. 20K12046, JSPS KAKENHI.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aliev R. R., Panfilov A. V. (1996). A simple two-variable model of cardiac excitation. Chaos Solit. Fractals 7, 293–301. doi:10.1016/0960-0779(95)00089-5
Appelboam A., Reuben A., Mann C., Gagg J., Ewings P., Barton A., et al. (2015). Postural modification to the standard Valsalva manoeuvre for emergency treatment of supraventricular tachycardias (revert): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 386, 1747–1753. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61485-4
Bartolucci C., Mesirca P., Ricci E., Sales-Bellés C., Torre E., Louradour J., et al. (2024). Computational modelling of mouse atrio ventricular node action potential and automaticity. J. Physiol. 602, 4821–4847. doi:10.1113/JP285950
Billette J., Tadros R. (2019). An integrated overview of AV node physiology. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 42, 805–820. doi:10.1111/pace.13734
Chen H., Shehata M., Cingolani E., Chugh S. S., Chen M., Wang X. (2015). Differentiating atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia from junctional tachycardia: conflicting responses? Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 8, 232–235. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.114.002169
Chiale P. A., Baranchuk A., González M. D., Sã¡nchez R. A., Garro H. A., Fernández P. A., et al. (2015). The mechanisms of spontaneous termination of reentrant supraventricular tachycardias. Int. J. Cardiol. 191, 151–158. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.04.239
Chiou C.-W., Chen S.-A., Kung M.-H., Chang M.-S., Prystowsky E. N. (2003). Effects of continuous enhanced vagal tone on dual atrioventricular node and accessory pathways. Circulation 107, 2583–2588. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000068339.04731.4D
Climent A. M., Guillem M. S., Zhang Y., Millet J., Mazgalev T. N. (2011). Functional mathematical model of dual pathway AV nodal conduction. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 300, H1393–H1401. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01175.2010
Cossú S. F., Rothman S. A., Chmielewski I. L., Hsia H. H., Vogel R. L., Miller J. M., et al. (1997). The effects of isoproterenol on the cardiac conduction system: site-specific dose dependence. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 8, 847–853. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8167.1997.tb00845.x
Fedorov V. V., Ambrosi C. M., Kostecki G., Hucker W. J., Glukhov A. V., Wuskell J. P., et al. (2011). Anatomic localization and autonomic modulation of atrioventricular junctional rhythm in failing human hearts. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 4, 515–525. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.111.962258
Garfinkel A. (2007). Eight (or more) kinds of alternans. J. Electrocardiol. 40, S70–S74. doi:10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2007.06.011
Guzzetti S., Borroni E., Garbelli P. E., Ceriani E., Della Bella P., Montano N., et al. (2005). Symbolic dynamics of heart rate variability: a probe to investigate cardiac autonomic modulation. Circulation 112, 465–470. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.518449
Hartikainen J. E., Kautzner J., Malik M., Camm A. J. (1997). Sympathetic predominance of cardiac autonomic regulation in patients with left free wall accessory pathway and orthodromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia. Eur. Heart J. 18, 1966–1972. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a015207
Inada S., Hancox J. C., Zhang H., Boyett M. R. (2009). One-dimensional mathematical model of the atrioventricular node including atrio-nodal, nodal, and nodal-His cells. Biophys. J. 97, 2117–2127. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2009.06.056
Izhikevich E. M. (2006). Dynamical systems in neuroscience: the geometry of excitability and bursting. The MIT Press. doi:10.7551/mitpress/2526.001.0001
Katritsis D. G., Josephson M. E. (2013). Classification of electrophysiological types of atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia: a reappraisal. EP Eur. 15, 1231–1240. doi:10.1093/europace/eut100
Katritsis D. G., Marine J. E., Latchamsetty R., Zografos T., Tanawuttiwat T., Sheldon S. H., et al. (2015a). Coexistent types of atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia implications for the tachycardia circuit. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 8, 1189–1193. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.115.002971
Katritsis D. G., Sepahpour A., Marine J. E., Katritsis G. D., Tanawuttiwat T., Calkins H., et al. (2015b). Atypical atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia: prevalence, electrophysiologic characteristics, and tachycardia circuit. Europace 17, 1099–1106. doi:10.1093/europace/euu387
Martin P. (1977). The influence of the parasympathetic nervous system on atrioventricular conduction. Circ. Res. 41, 593–599. doi:10.1161/01.res.41.5.593
Mazgalev T. N., Ho S. Y., Anderson R. H. (2001). Anatomic-electrophysiological correlations concerning the pathways for atrioventricular conduction. Circulation 103, 2660–2667. doi:10.1161/01.cir.103.22.2660
Morady F., Nelson S. D., Kou W. H., Pratley R., Schmaltz S., Buitleir M. D., et al. (1988). Electrophysiologic effects of epinephrine in humans. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 11, 1235–1244. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(88)90287-2
Nigro G., Russo V., de Chiara A., A A. R., Cioppa N. D., Chianese R., et al. (2010). Autonomic nervous system modulation before the onset of sustained atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 15, 49–55. doi:10.1111/j.1542-474X.2009.00339.x
Patterson E., Scherlag B. J. (2003). Slow:fast and slow:slow av nodal reentry in the rabbit resulting from longitudinal dissociation within the posterior av nodal input. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 8, 93–102. doi:10.1023/a:1023600615459
Plappert F., Wallman M., Abdollahpur M., Platonov P. G., Östenson S., Sandberg F. (2022). An atrioventricular node model incorporating autonomic tone. Front. Physiol. 13, 976468. doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.976468
Reid M. C., Billette J., Khalife K., Tadros R. (2003). Role of compact node and posterior extension in direction-dependent changes in atrioventricular nodal function in rabbit. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 14, 1342–1350. doi:10.1046/j.1540-8167.2003.03382.x
Rovere M. T. L., Porta A., Schwartz P. J. (2020). Autonomic control of the heart and its clinical impact. a personal perspective. Front. Physiol. 11, 582. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.00582
Ryzhii M., Ryzhii E. (2022). Pacemaking function of two simplified cell models. PLoS ONE 17, e0257935. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0257935
Ryzhii M., Ryzhii E. (2023a). A compact multi-functional model of the rabbit atrioventricular node with dual pathways. Front. Physiol. 14, 1126648. doi:10.3389/fphys.2023.1126648
Ryzhii M., Ryzhii E. (2023b). “Revealing the origin of typical and atypical forms of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia with a compact computer model of rabbit AV node,” in Computing in cardiology CinC2023 (IEEE), 1–4. doi:10.22489/CinC.2023.080
Ryzhii M., Ryzhii E. (2024). “Compact computer model of rabbit atrioventricular node with autonomic nervous system control,” in Computing in cardiology CinC2024 (IEEE), 1–4. doi:10.22489/CinC.2024.162
Sinkovec M., Pernat A., Rajković Z., Jan M., Antolic B., Rakovec P. (2011). Electrophysiology of anterograde right-atrial and left-atrial inputs to the atrioventricular node in patients with atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia. Europace 13, 869–875. doi:10.1093/europace/euq459
Straus D. G., Schocken D. D. (2021). Marriott’s practical electrocardiography. 13th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health.
Sun J., Amellal F., Glass L., Billette J. (1995). Alternans and period-doubling bifurcations in atrioventricular nodal conduction. J. Theor. Biol. 173, 79–91. doi:10.1006/jtbi.1995.0045
Sung R. J., Styperek J. L., Myerburg R. J., Castellanos A. (1978). Initiation of two distinct forms of atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia during programmed ventricular stimulation in man. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 42, 404–415. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(78)90935-9
Tamura S., Nakajima T., Iizuka T., Hasegawa H., Kobari T., Kurabayashi M., et al. (2020). Unique electrophysiological properties of fast-slow atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia characterized by a shortening of retrograde conduction time via a slow pathway manifested during atrial induction. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 31, 1420–1429. doi:10.1111/jce.14501
Wu D., ad F., Amat-Y-Leon P. D., Wyndham C. R., Dhingra R., Rosen K. M. (1977). An unusual variety of atrioventricular nodal re-entry due to retrograde dual atrioventricular nodal pathways. Circulation 56, 50–59. doi:10.1161/01.cir.56.1.50
Xiao L., Ou X., Liu W., Lin X., Lin P., Qiu S., et al. (2024). Combined modified Valsalva maneuver with adenosine supraventricular tachycardia: a comparative study. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 78, 157–162. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2024.01.035
Yamada T., McElderry H. T., Doppalapudi H., Kay G. N. (2008). Catheter ablation of ventricular arrhythmias originating in the vicinity of the his bundle: significance of mapping the aortic sinus cusp. Heart rhythm. 5, 37–42. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.08.032
Keywords: atrioventricular node, rabbit heart model, Aliev-Panfilov model, dual pathway, autonomic nervous system, AVNRT, effective refractory period, computer simulation
Citation: Ryzhii M and Ryzhii E (2025) Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia onset, sustainability, and spontaneous termination in rabbit atrioventricular node model with autonomic nervous system control. Front. Physiol. 15:1529426. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1529426
Received: 16 November 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 17 January 2025.
Edited by:
Richard Gary Trohman, Rush University, United StatesReviewed by:
Richard Ang, University College London, United KingdomSridharan Rajamani, Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, United States
Copyright © 2025 Ryzhii and Ryzhii. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maxim Ryzhii, bS1yeXpoaWlAdS1haXp1LmFjLmpw
 Maxim Ryzhii
Maxim Ryzhii Elena Ryzhii
Elena Ryzhii