- Key Laboratory of Aquacultural Biotechnology of MOE, School of Marine Science, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
Temperature changes had a huge impact on the growth of aquaculture organisms, which mainly involved two parameters: the changing amplitude and the changing speed. Wide-adaptability and narrow-adaptability were divided by the amplitude, while fast-adaptability and slow-adaptability proposed in this article were divided based on the speed. Investigating the impact of the changing speed on artificial farming was vital. In this study, two fish species of wide-adaptability, Hippocampus kuda and Oryzias melatigma, were selected as research objects, explored the effects of temperature changing speeds on them under 2 changing amplitudes of 2°C and 4°C. The similarities and differences in their responses to temperature changes were analyzed and compared from the aspects of feeding, metabolism, physiology, immunity, and growth. The results showed that all 3 changing speeds (0.5°C/h, 1°C/h, and direct input) had no effect on the growth of O. melatigma under the 2°C amplitude, while there were significant differences in various aspects of H. kuda in the treatments with the speeds between 0.5°C/h and direct input, such as a significant difference in growth, in food intake, and in response speeds and response levels of several enzymes and related genes. Under 4°C amplitude, the impact of all 4 changing speeds (0.5°C/h, 1°C/h, 2°C/h and direct input) on both fish was more pronounced. H. kuda showed a significant difference of growth among 3 groups, and the critical safe speed was about 0.5°C/h in its heating treatments. And the growth decrease only occured the heating treatment of direct input in O. melatigma. Furthermore, some genes responded quickly and efficiently to the low-speed changes of temperature in H. kuda, but were inhibited in the treatments with high-speed changes. However, they can still express rapidly and efficiently in the high-speed treatments of O. melatigma, included several stress-related genes, lipid metabolic-related genes, and immune-related genes. Seen from these differences, the energy source used in H. kuda to resist stress was single and short-lived. So, under a long-term stress, H. kuda gradually transformed from normal physiological stress into pathological stress, leading to the outbreak of diseases. Therefore, for precise aquaculture of H. kuda, stricter and more precise control of environmental temperature is necessary to prevent rapid and big temperature changes from affecting the growth and survival of the seahorse.
1 Introduction
Throughout the whole life history of fish, water temperature is one of the crucial non-biological factors for its growth and development. Changes in water temperature can affect its physiological processes such as feeding, digestion, metabolism, and reproduction. Generally, temperature affects organisms in all aspects (Alfonso et al., 2021, p.1496), included oxidative stress, e.g., changes in activity or content of superoxide dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT), malondialdehyde (MDA) and peroxidase (POX) (Kato, 1997, p.25), digestibility and metabolism, e.g., α-Amylase (AMS), lipase (LPS) and proteinase (Hu et al., 2016, p.13; Pan et al., 2022, p.1084), non-specific immunity, e.g., alkaline phosphatase (AKP) and acid phosphatase (ACP) (Xiang and Liu, 2007, p.396; Dittmar et al., 2014, p.744; Makrinos and Bowden, 2016, p.50; Wang et al., 2021, p.e73776), and growth and development (Ye et al., 2016, p.101; Burggren et al., 2019, p.732; Lu et al., 2020, p.e73547), and so on. Therefore, investigating the effects of temperature changes is of great significance for fish farming and provides important guarantees for the success of aquaculture (Xu, 2019, p.1; Lu et al., 2023, p.e739114).
Previously, the fish was divided into widely-adapted and narrowly-adapted types based on its ability to adapt to temperature changes. This classification had a good guiding role in selecting suitable breeding species. However, it only investigated the amplitude of adaptation to temperature changes, and does not fully reflect the impact of the changing speed of temperature. Following the above division, we divided the fish into slowly-adapted and fast-adapted types based on its ability to adapt to temperature changing speeds. The slow-adaption referred to being sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and its growth and physiology was easily affected by rapid temperature changes. The fast-adaption was less sensitive. For example, Hippocampus kuda was a widely-adapted fish with an amplitude of 6°C–32°C (Mu et al., 2017, p.355). And, Oryzias melatigma, known as Indian madaka, also was a widely-adapted fish (4°C–35°C, Murata, et al., 2020, p.59). However, there was a significant difference in their performance in adapting to rapid temperature changes. Previous researches in our laboratory had found that within the temperature range of 22°C–28°C, there was a 70% probability of anorexia reaction of H. kuda occurred under the temperature change of 2°C within 2 h, and part individuals even developed into enteritis and died. While O. melatigma had no effect at the speed of 4°C/h. It can be preliminarily determined that H. kuda was a slowly-adapted fish, and O. melatigma was a fast-adapted fish. This phenomenon was also reflected in their artificial farming, where the seahorse was characterized by strict environmental requirements and difficult to successful farming (Lv et al., 2003, p.46; Wang et al., 2020, p.730; Xie et al., 2020, p.e735168). And O. melatigma was so easy to be farmed. There were also many reports of other organisms being affected by sudden changes of temperature. included the non-specific immunity of sea cucumber (Liu et al., 2013a, p.1342), the survival of Panulirus homarus (Huang et al., 2017, p.5973), the food conversion rate of sea urchins (Siikavuopio et al., 2012, p.27), the antioxidant capacity and immunity of marine medaka (Wang et al., 2019, p.378), and the feeding behavior of California moray prey (Moretto, et al., 2022, p.126030), and so on.
Therefore, it is necessary and important to pay attention to the adaptability of farmed organisms to rapid changes in environmental factors, and finds safety measures to avoid risks, in order to improve aquaculture technology. This study explored the responses of H. kuda and O. melatigma to rapid temperature changes, compared their similarities and differences in growth, behavior, physiological and biochemical aspects, and expressions of several functional genes, then analyzed the response mechanisms and self-regulation characteristics of fast-adapted and slowly-adapted, and promoted aquaculture technology of fish farming.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental fish
The seahorse of H. kuda (body length 4.96 ± 0.34 cm, weight 0.276 ± 0.031 g) was provided by Xiangshan Base of Ningbo Yonghe Biotechnology Company, and temporarily raised for 2 weeks at the pilot base of Meishan campus, Ningbo University. Individuals with clean body and good vitality were randomly selected for the experiment. O. melatigma (body length 3.12 ± 0.46 cm, weight 1.730 ± 0.243 g) was bred in our laboratory in Meishan campus, also randomly selected for the experiment. Both fishes had similar ages of about 45 days old.
The temporary breeding conditions were: water temperature of 25°C ± 0.5°C, salinity of 25, dissolved oxygen (DO) >5 mg/L, light intensity of 1000lx, and photoperiod of 14L:10D. During the periods of temporary breeding and experiment, H. kuda was fed frozen Mysis (Tianjin Fengnian Aquaculture Company, China) with a total length of 1–1.5 cm as bait, and O. melatigma was fed with artificial formula feed (Ningbo Tianbang Group, China). Fed once a day at 8:00 Am, and removed any remained bait and feces after 2 h of feeding. The seawater was exchanged approximately 50% before feeding.
2.2 Experimental design
The experiment consisted of two tests.
Test 1: The set temperature changing amplitude was ±2°C. There were 3 groups of breeding temperature in the test, included the control group (Ck) with the temperature of 25°C, the heating group (HG) with an increase of 2°C (27°C) and the cooling group (CG) with a decrease of 2°C (23°C). There were 3 ways to reach the set temperatures (from 25°C to 23 or 27°C), that was 3 types of changing speeds: direct input (Marked as 0H2±), increasing or decreasing 2°C within 2 h (2H2±), where the changing speed was 1°C/h, and changing 2°C within 4 h (4H2±, 0.5°C/h).
Test 2: The set temperature changing amplitude was ±4°C. There were 3 groups of breeding temperature (25°C, 29°C, 21°C) and 4 speed treatments of 0H4± (direct input), 2 h (2H4±, 2°C/h), 4 h (4H4±, 1°C/h), and 8 h (8H4±, 0.5°C/h).
The temperature changing process was carried out in controlled-temperature illuminated incubators (Jiangnan GXM-508A, Ningbo, China). By conducting pilot experiments, appropriate temperature changed conditions were identified to ensure that the temperature changing amplitude was achieved within the required time (not sure at a uniform rate). The air temperature inside the incubator was controlled within the variable range of ±0.5°C, and the water temperature fluctuation was less than ±0.2°C in the incubator. After the temperature changes completed, it would be maintained the target temperature for 7 days before ending the experiment. In the experiment, the salinity of each treatment remained at 25, with three replicates for each treatment.
2.3 Experimental methods
2.3.1 Analysis of related gene expression
The tissue samples were taken from H. kuda and O. melatigma at 12 h, 4 day, and 7 day after the temperature changed completeness in each treatment. During the sampling process, the fish were anesthetized, and their liver tissues from 2 individuals were taken from each replicate (a total of 6 individuals), then merged as one sample. Total RNA was extracted from each sample using the Trizol method, followed by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis (Pan et al., 2020, p.1421; Pan et al., 2022, p.1084).
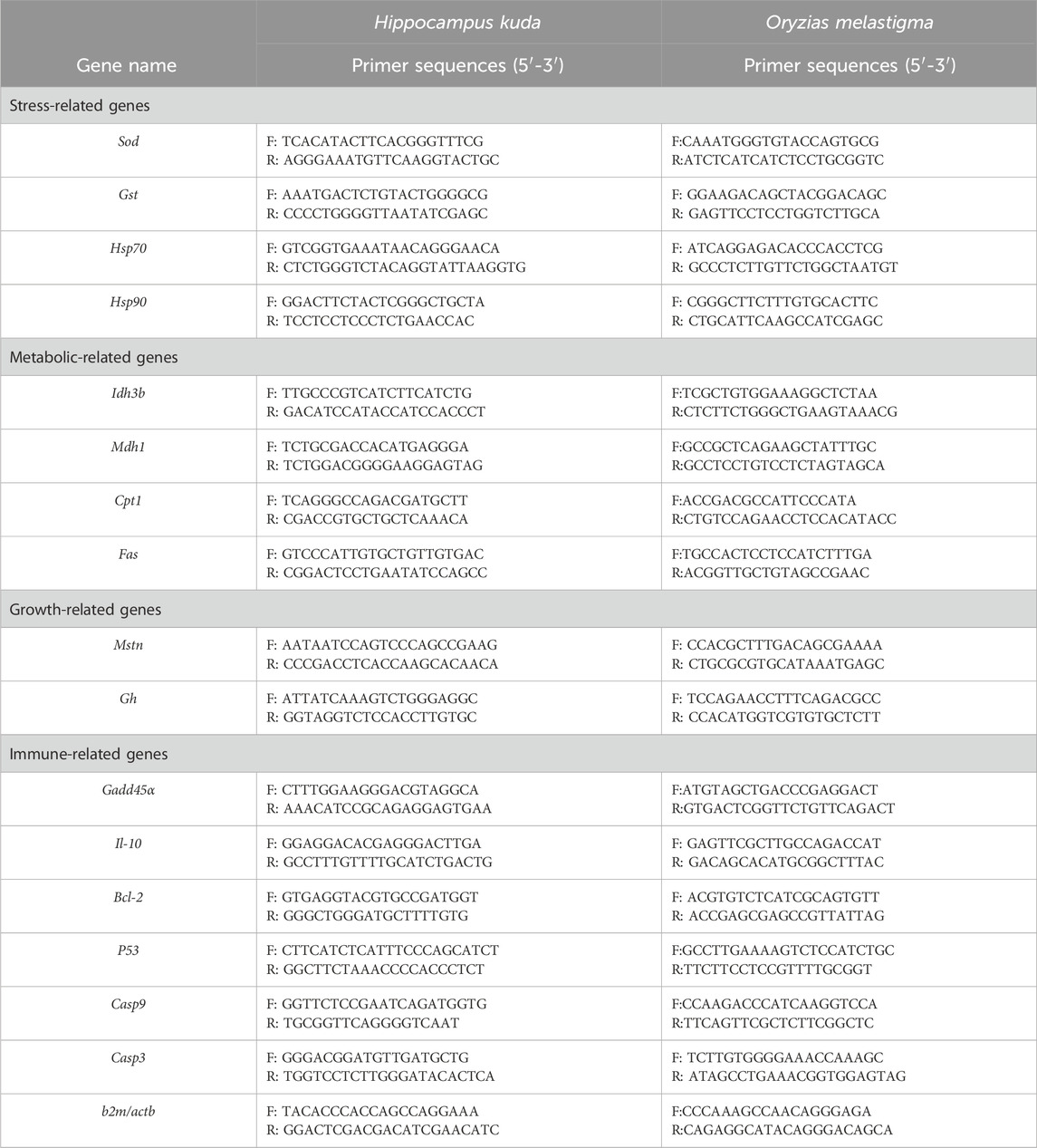
According to literature reports and our previous researches, 16 genes were selected in H. kuda, and another 16 genes were selected in O. melatigma as candidate genes for the response analysis. Their specific primers were designed with the software of Primer Premier 5, using mRNA sequences from NCBI. Alternatively, based on the reported Unigene sequences in the transcriptome library, the primer sequences of all genes were shown in Table 1. At the same time, b2m and actb were used as an internal reference gene for gene expression analysis in H. kuda and O. melatigma, respectively. The relative expression levels of each target genes were calculated using Livak analysis method, and the 2−ΔΔCT method was used to calculate the relative expression of the target gene.
2.3.2 Analysis of related enzyme activity
The visceral tissue (without liver) was used for enzyme activity analysis. Accurately weighed 1 g tissue, added 9 ML 0.1 mol/L pH 7.4 phosphate buffer, mechanically homogenized (DIRAD DR-310, Jiangsu, China) under ice bath, centrifuged at 2,500 rpm for 10 min in a high-speed centrifuge (Eppendorf 5430R, Germany), and extracted the supernatant. The supermatant would be diluted with the phosphate buffer, and for determination of the following enzymes. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) by the Hydroxylamine method, malondialdehyde (MDA) by the Thiobarbituric acid (TBA) method, α-Amylase (AMS) by the Starch-iodine colorimetric method, lipase (LPS) by the Methyl resorufin substrate method, alkaline phosphatase (AKP) and acid phosphatase (ACP) by the Disodium phenyl phosphate method. The above analysis was carried out using the corresponding reagent kits from Nanjing Jiancheng Biotechnology Institute (Nanjing, China) according to the instructions. The protein content was measure with Coomassie brilliant blue staining (Candiano et al., 2004, p.1327; Yuan et al., 2024, p.1403391).
2.3.3 Analysis of the RNA/DNA ratio
According to Buckly’s (1979) analysis method, the RNA/DNA ratio was anaylzed for showing the growth of both fish. Take respectively an appropriate amount of muscle tissue from the 4-day and 7-day samples and mix it with Tris buffer (0.05 mol/L, pH = 7.4) for homogenization. Suction 1.4 mL of the homogenization solution and mix it with 0.7 mL of 0.6 mol/L HClO4. Cool it on ice bath for 15 min, centrifuge at 4°C (12,000 r/min) for 10 min, and then remove the supernatant. Wash the precipitate in 1.12 mL of 0.3 mol/L KOH at 37°C in water bath for 1 h and then in ice bath for 30 min, and centrifuge again. Take out the supernatant and measure its absorbance value at 260 nm (Mettler UV5 nano, Germany), which was the absorbance value of RNA. At the same time, the precipitate was washed with 2.0 mL 0.2 mol/L HClO4, after centrifugation, the supernatant was removed. Then add 2.2 mL of 0.6 mol/L HClO4 to the precipitate and incubate at 85°C for 15 min, followed by an ice bath for 15 min. Centrifuge again, the precipitate was protein. Suction the supernatant and measure its absorbance value at 260 nm, which was the absorbance value of DNA. Thus, the ratio of RNA/DNA can be calculated.
2.3.4 Analysis of feeding behavior
On the 4th and 7th days, 6-8 individuals of fish were randomly selected from each treatment for observing their feeding behavior. A glass aquarium (L15 cm × W10 cm × H13 cm) was used for behavioral photography. Two Panasonic VX1 portable cameras (Panasonic Co., Japan) were placed directly above and in front of the aquarium for recording the feeding behavior, in order to subsequent repeated observation and analysis. The water temperature, salinity, light intensity and other conditions inside the aquarium were the same as the original experimental environment. The specific steps in the entire feeding process were as follows: first, let an individual adapt to the new environment in the aquarium for 60 min, and then fed live Artemia larvae with a density of 1 ind./mL. The cameras started recording 5 min before feeding and lasted for 45 min. The following 3 parameters of feeding behavior were analyzed in each treatment based on the recorded videos.
Feeding response time (second): the period time elapsed from the entry of Artemia into the water to the first larvae was swallowed by fish.
Feeding rate (ind./min): The average rate of Artemia consumed by fish during a 10-min period from the 11th minute to the 20th minute.
Food intake (individual): The total number of Artemia consumed by fish throughout the feeding.
2.4 Data processing and statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of experimental data was conducted using SPSS 22.0 (IBM Co., NY, United States). Two-way ANOVA was used to examine the effects of temperature changes in amplitude and in speed on the growth, feeding behavior, gene expression levels, and enzyme activity of both fish. T-test was used to analyze the effects of different temperature changes and compare the differences in average values within and between 2 species fish. The data were expressed as mean ± standard error, with P < 0.05 indicating significant differences. Use GraphPad Prism 8.0 to plot data and statistical results.
3 Results
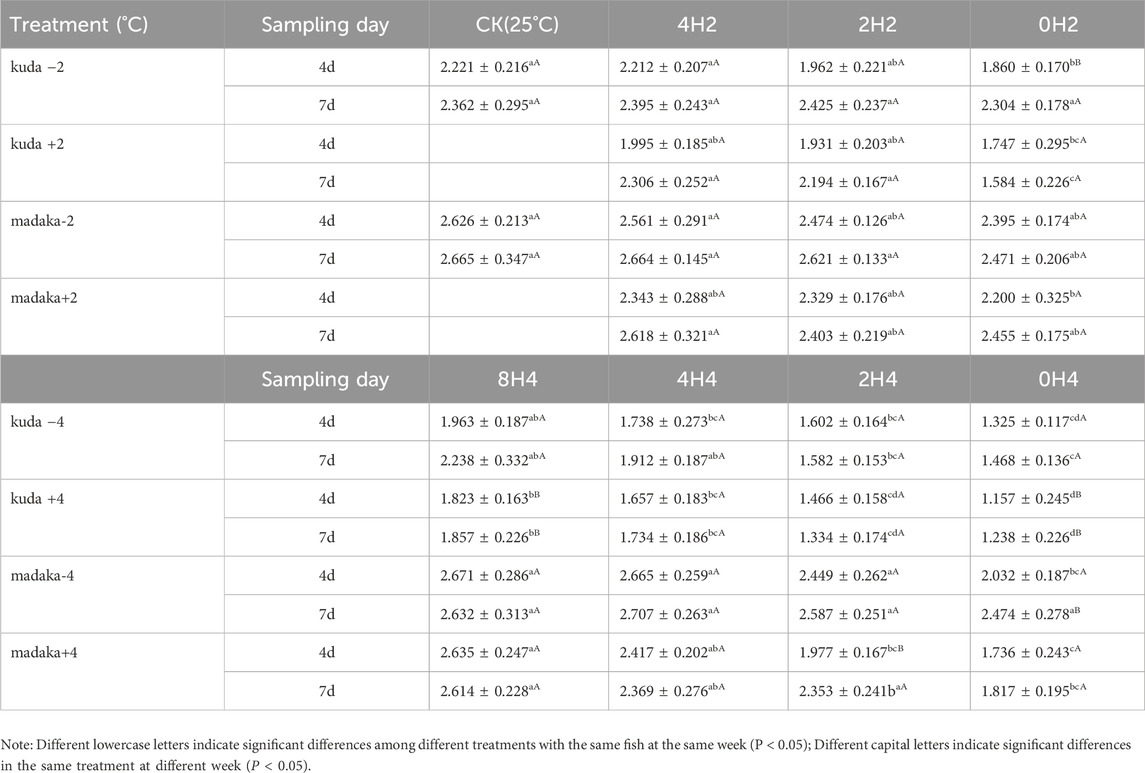
3.1 Effects on RNA/DNA ratio
The variations of RNA/DNA ratios in their muscles of H. kuda and O. melastigma under different changing amplitudes and speeds of temperature were shown in Table 2.
Under 2°C amplitude, there was a mild difference on the RNA/DNA ratios among 3 groups with different speeds in H. kuda, and no difference on O. melastigma at all, compared with their CK, respectively. The ratios of H. kuda in 3 treatments of 0H2± and 2H2+ had significantly decreased on the 4th day (P < 0.05). And 0H2- and 2H2+ had recovered on the 7th day, but 0H2+ became worse (Table 2). Under 4°C amplitude, there was a significant effect on the RNA/DNA ratios among 3 groups with different speeds in both H. kuda and O. melastigma. For O. melastigma, the 0H4- treatment on the 4th day was affected by a −4°C cooling (P < 0.05), and recovered on the 7th day. 2H4+ and 0H4+ were also affected by the heating (P < 0.05), and 2H4+ had recovered while 0H4+ was still suffered on the 7th day. For H. kuda, all treatments showed a significant decrease on the 4th day (P < 0.05). And 4H4± and 8H4± had recovered, while 2H4± and 0H4± became even worse on the 7th day. Comparing both fish, the impact of temperature changes on the growth of H. kuda was greater than that on O. melastigma. At the same time the impact of the same speed was different under different amplitudes, reflecting the synergistic effect of two factors on growth. Roughly summarized, the critical safe speed of O. melastigma was quite big, while that of H. kuda was around 1°C/h with 2°C amplitude.
3.2 Effects on feeding behavior
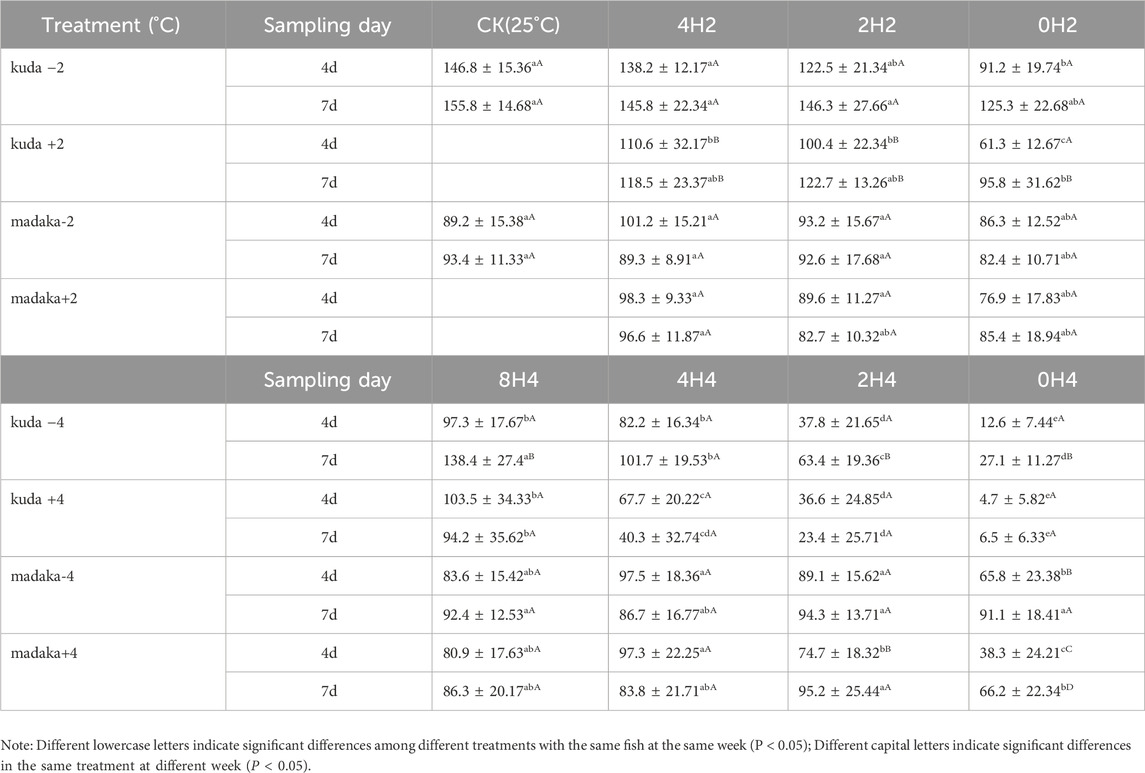
Three parameters of feeding behavior, included feeding response time, feeding rate, and food intake, were measured for both H. kuda and O. melastigma in each treatment on the 4th and 7th day. The variations of food intake were shown in Table 3.
Overall, the variations in food intake of both fish were basically consistent with their growth. Under 2°C amplitude, different speeds of temperature changes had almost no effect on O. melastigma (P> 0.05), whether in heating or in cooling groups. For H. kuda, the food intake decreased obviously in 2 treatments of 0H2± on the 4th day (P < 0.05), and only 0H2- had recovered on the 7th day (Table 3). Under 4°C amplitude, the decreases in food intake of O. melastigma only occurred in 0H4± and 2H4+ treatments (P < 0.05). And all treatments (except for 0H4+) had recovered on the 7th day. However, the food intake of all H. kuda treatments had significantly decreased on the 4th day (P < 0.05). At the end of the experiment, only 8H4± had recovered, 2H4- had improved slightly, other 3 treatments of 0H4± and 2H4+ were even worse (Table 3). Comparing the treatments of the same speed under different amplitudes, it was evident that larger amplitudes had a greater impact on H. kuda.
By analysis, the other 2 feeding parameters also showed a similar characteritic, with the feeding response time prolonging and the feeding rate decreasing in H. kuda.
3.3 Effects on enzyme activity
The activities or content of six enzymes (SOD, MDA, LPS, AMS, ACP, AKP) were analyzed in the experiment. The variations of SOD, LPS, and AKP in H. kuda and O. melastigma were shown in Figure 1.
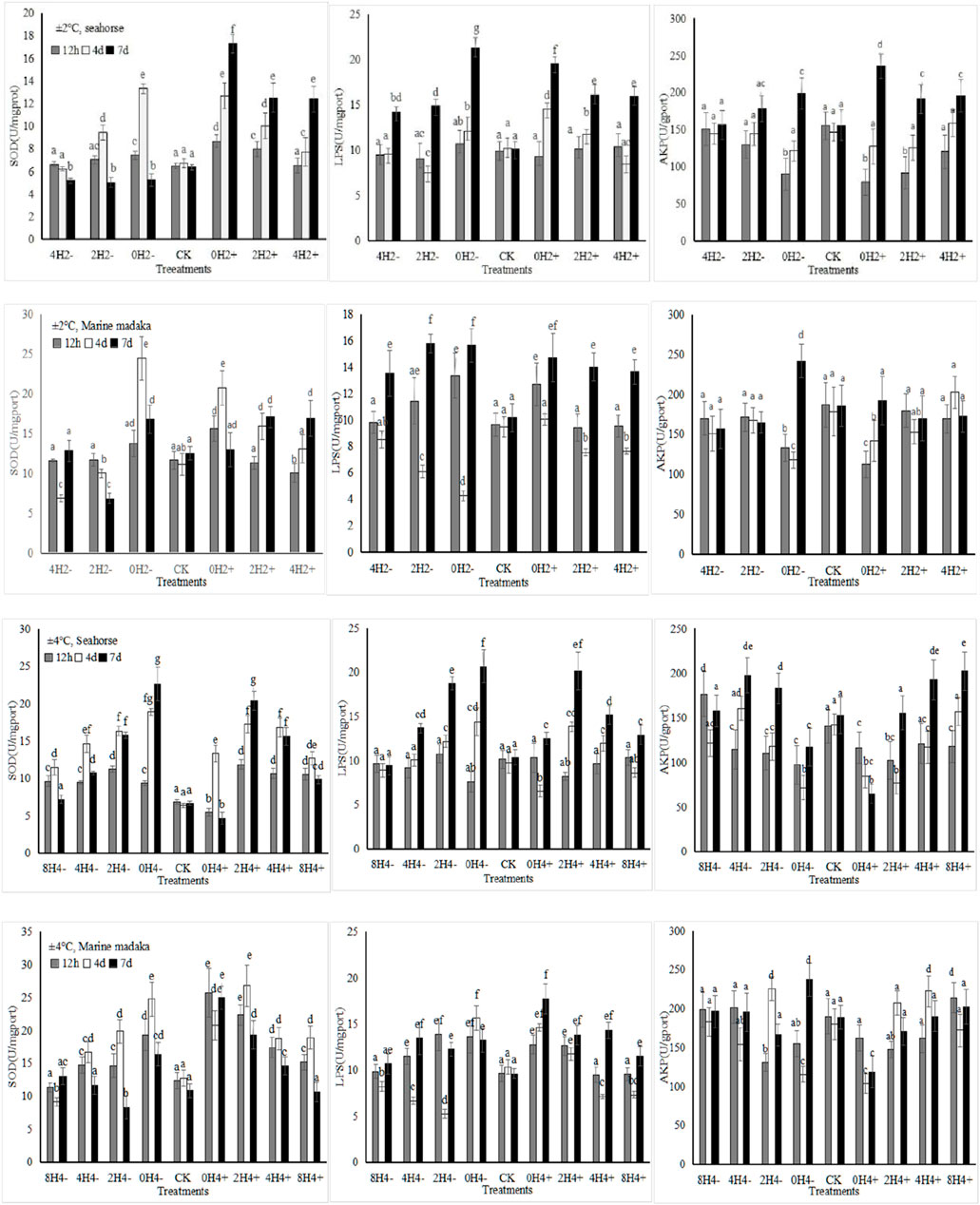
Figure 1. The effects of rapid temperature changes on SOD, LPS, and AKP activities in H. kuda and O. melastigma.
Under both amplitudes, various enzymes showed their significant fluctuations in response to the different speeds of temperature changes, and their response trends were basically similar in H. kuda and O. melastigma (Figure 1). The bigger the amplitude, the greater the enzymes’ response was. And the faster the speed, the greater the enzymes’ response also was. At the same time, all enzymes also showed similar responses to temperature increasing/heating or deseasing/cooling, the impact of increasing temperature was greater. Certainly, there was some difference between H. kuda and O. melastigma at different speed with same amplitude, the main performance was that each enzyme had a difference in response time and response magnitude (Figure 1). Under 2°C amplitude, There was not much difference between 2 fish, except in 2H2- and 4H2+, where the enzyme expressions were slightly differed between 2H2- and 4H2+ in H. kuda (P < 0.05), which did not occur in O. melastigma. Under 4°C amplitude, the difference was also reflected in the rapid response at 12 h, as well as the increasing number of treatments involved in the continuous increase in enzyme activities in H. kuda (Figure 1).
3.4 Effects on the expression of related genes
3.4.1 Stress-related genes
The relative expression levels of 4 stress-related genes (Sod, Gst, Hsp70, Hsp90) were analyzed in H. kuda and O. melastigma. Their variations of Sod and Gst genes were shown in Figure 2.
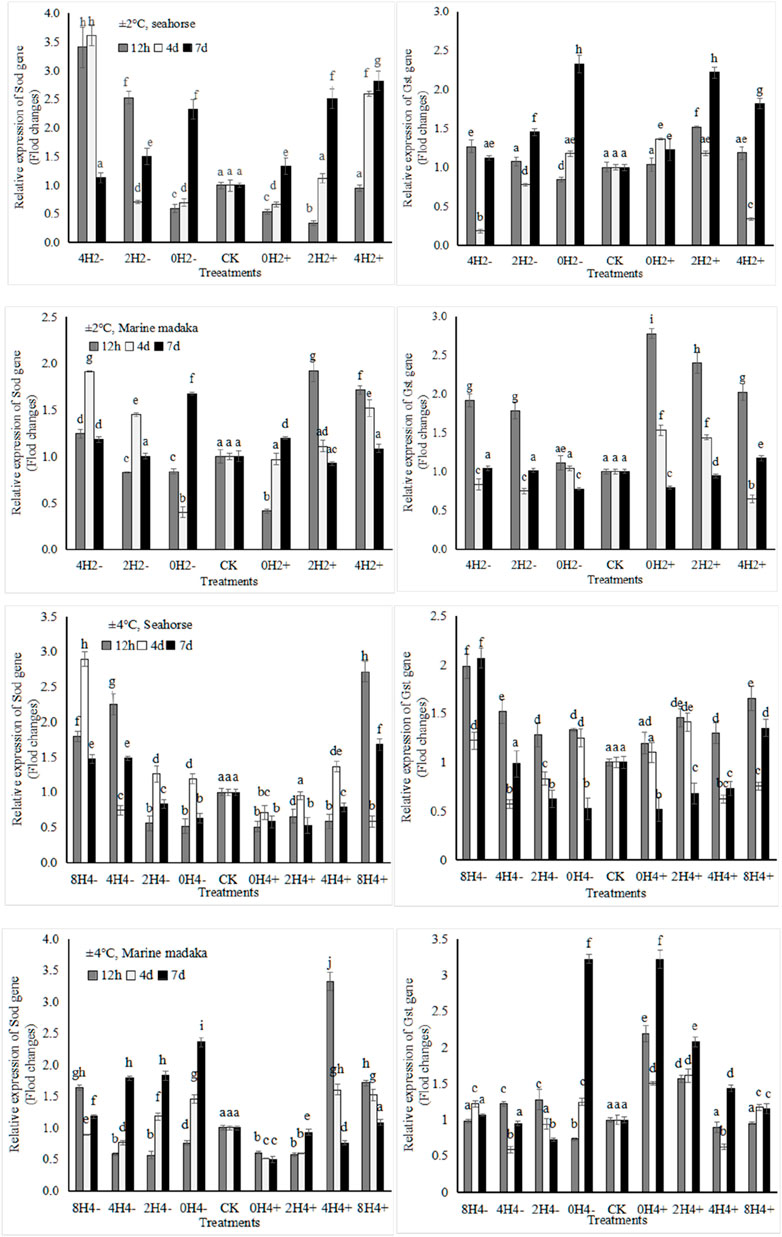
Figure 2. Variations in relative expression levels of Sod and Gst genes in H. kuda and O. melastigma.
Their variation trends in both fish were similar. They exhibited up and down oscillations at 12 h, 4 day, and 7 day after temperature changes, and gradually recovered in each treatment. The specific differences were shown as follows, under 2°C amplitude, Sod had a rapid expression of upregulation at 12 h in O. melastigma, but it had a slow response in H. kuda, even being inhibited (e.g., downregulation in 0H2± and 2H2+) or no response (4H2+) at 12h, and then upregulated at 4th and 7th days. Gst also exhibited a similar slow response in H. kuda. There was a greater difference between the 2 fish under 4°C amplitude. Sod showed its obvious different expression in the correspondent treatments between H. kuda and O. melastigma (P < 0.05), except in 0H4+, which was inhibited throughout the experiment. Gst was interesting, its response was similar to the control in all treatments of O. melastigma at 12h, except in 0H4± and 2H4+, where its expression was significant upregulated. Gst at 12 h also showed a rapid upregulation in all treatments of H. kuda, followed by up and down fluctuation in 8H4± and 4H4±, and continued to decrease in 0H4± and 2H4± on 4th and 7th day (Figure 2).
3.4.2 Metabolic-related genes
The relative expression levels of 4 metabolic-related genes (Mdh1, Idh3b, Cpt1, Fas) were also analyzed in both fish. The expressions of Mdh1, involved in sugar-metabolism and Cpt1, involved in lipid-metabolism were shown in Figure 3.
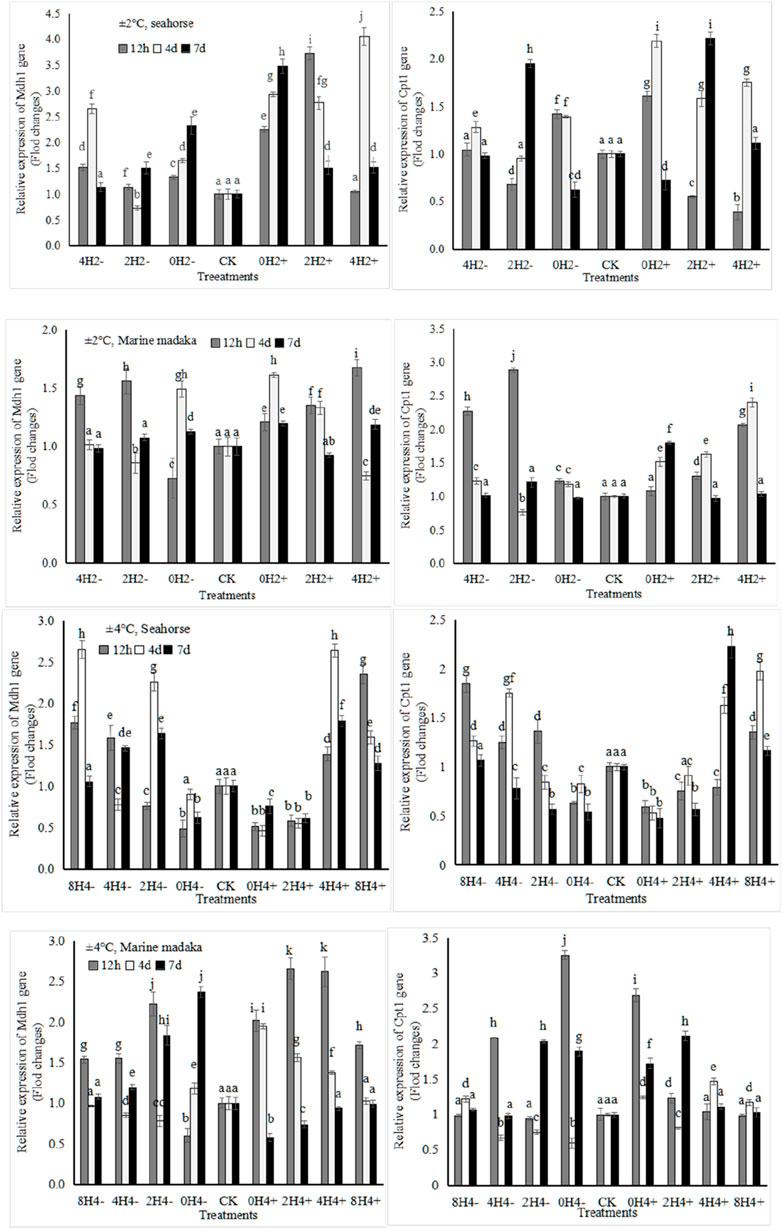
Figure 3. Variations in relative expression levels of Mdh1 and Cpt1 genes in H. kuda and O. melastigma.
Their variation trends were also similar in both fish. The specific differences were shown as follows, under 2°C amplitude, the Mdh1 expression in H. kuda was generally higher than that in O. melastigma, especially in 0H2±, whose expression was significantly higher at 12 h (P < 0.05), and continued to rise on the 4 and 7 day. And it showed up and down fluctuations in 0H2± of O. melastigma. Cpt1 showed a rapid upregulated response at 12 h in 0H2± of H. kuda, and had a similar performance in 4H2± and 2H2- of O. melastigma (Figure 3). Under 4°C amplitude, the Mdh1 expression was nevertheless slightly upregulated in almost treatments of O. melastigma, especially had a significant upregulation at 12 h. In H. kuda, the upregulated expression of Cpt1 only appeared in the slow-speed treatments (8H4± and 4H4±), while its downregulated response appeared in the high-speed treatments (0H4± and 2H4+). It can be seen that the expressions of both genes was similar in H. kuda, while their up-regulations only showed in the high-speed treatments of O. melastigma.
3.4.3 Immune-related genes
Six immune-related genes (Bcl-2, P53, Gadd45α, Il-10, Casp3, and Casp9) were analyzed in the experiment. And the variations of P53, Il-10, and Casp3 in both fish were shown in Figure 4.
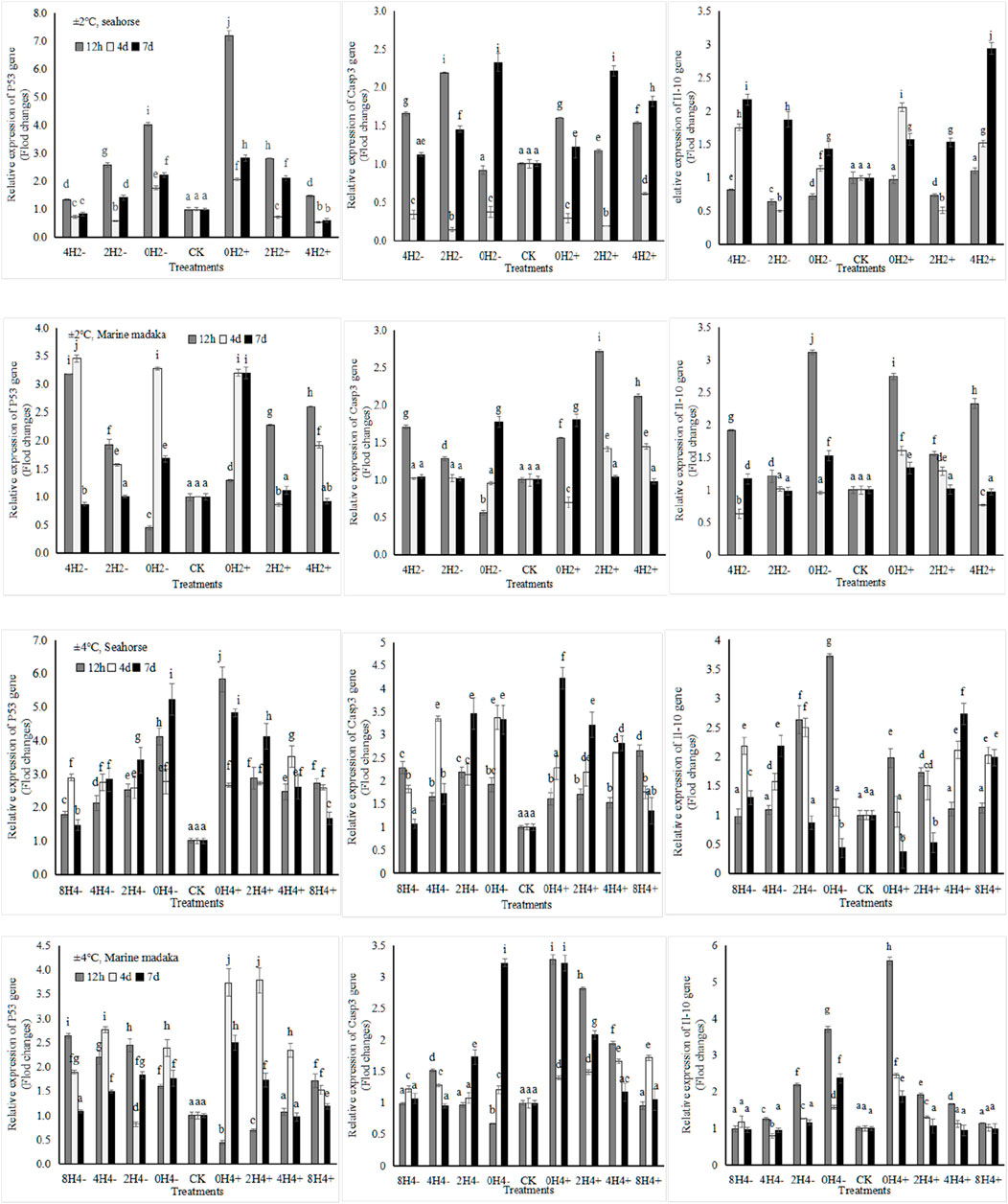
Figure 4. Variations in relative expression levels of P53, Il-10 and Casp3 in H. kuda and O. melastigma.
Their expressions were also similar between 2 fish, all showed up and down fluctuation, and gradually returned to normal with the extension of experiment in almost treatments.
The specific differences were, under 2°C amplitude, the expression level of P53 at 12 h increased with the increasing speed in H. kuda, while it was the opposite in O. melastigma. Casp3 was similar at 12 h between 2 fish. Il-10 had a rapid upregulation at 12 h in O. melastigma, but no response in H. kuda. At the end of the experiment, All genes had nearly recovered in O. melastigma, except in 0H2±. But Casp3 and Il-10 had still at a high expression in H. kuda. Under 4°C amplitude, all genes had a rapid upregulation at 12 h in H. kuda, and kept still at a high expression levels on the 7th day, except for Il-10 in 2H4± and 0H4±. In O. melastigma, P53 had also a rapid response at 12 h in almost treatments, other 2 genes only happened in 2H4± and 0H ± 4. All genes had recovered in slow-speed treatments on the 7th day, but still needed time to recover in the high-speed treatments.
3.4.4 Growth-related gene expression
Two growth-related genes (Gh and Mstn) were analyzed in the experiment. They were also similar in both fish (Figure 5). Compared to the control treatment, Gh was slightly downregulated and Mstn was slightly upregulated with temperature changes. Under 2°C amplitude, the expressions of Gh and Mstn in O. melastigma were a slight change at the beginning, and had recovered at the end of the experiment. However, their expressions in H. kuda were impacted in all treatments at the beginning, and had recovered only in 4H2± on the 7 day. Under 4°C amplitude, their expressions were comprehensively affected in H. kuda, while had an obvious impact only in the high-speed treatments of O. melastigma.
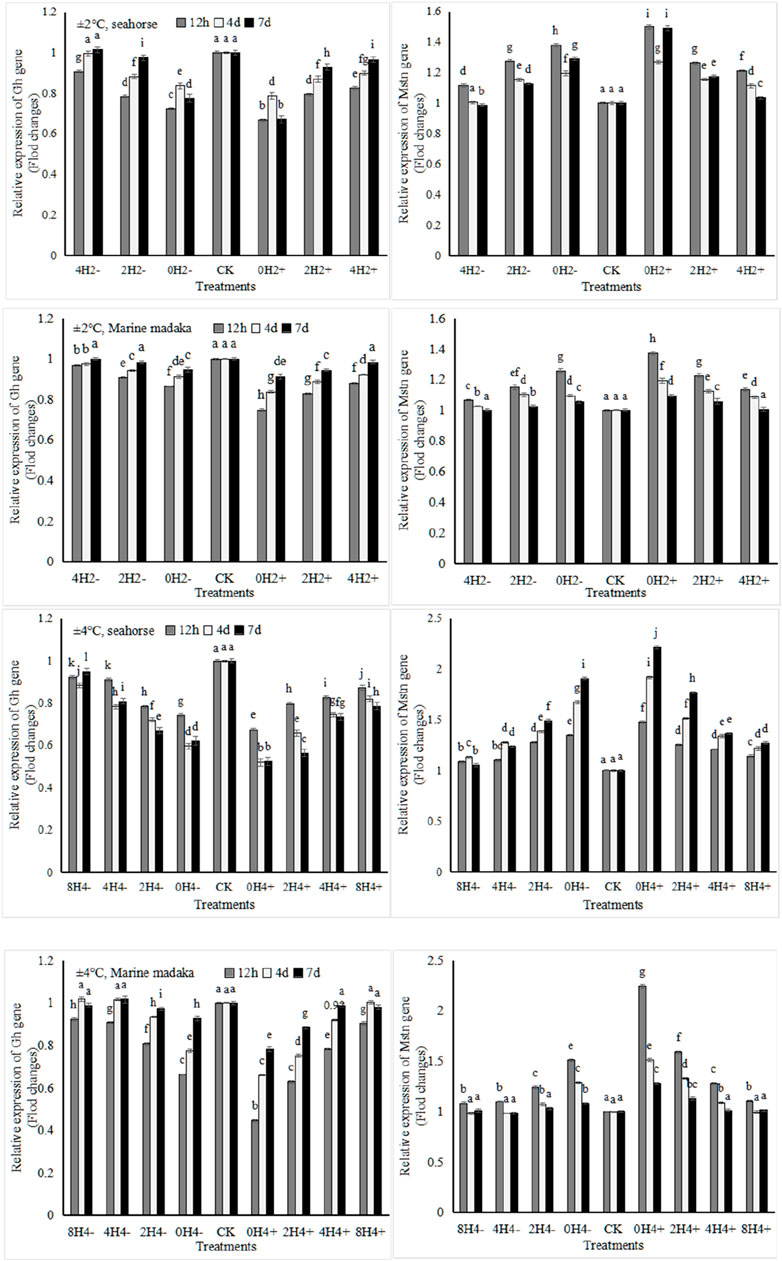
Figure 5. Variations in relative expression levels of Gh and Mstn genes in H. kuda and O. melastigma.
4 Discussion
In this study, the results revealed that the growth of farmed fish had an impact by the rapid changes of temperature in the short term. Different fish was affected differently, which reflected in their adaptabilities to changing amplitudes and changing speeds of temperature. The smaller the amplitude and slower the speed was, the less impact it had, making it easier to recover from stress. Compared to the slowly-adapted H. kuda, O. melastigma had a smaller impact and faster recovery. Here, we analyzed the differences between them.
4.1 Growth and expressions of growth genes
The growth is the process of synthesizing and accumulating proteins, thereby achieving an increase in indicators such as body weight and body length. The expression of growth-related genes can directly or indirectly reflect protein synthesis in organisms (Luo et al., 2023, p.e81858). MSTN (myostatin) is a muscle growth inhibitor produced by the expression of Mstn gene, and is an important regulatory protein that inhibits muscle growth and development (Luo et al., 2023, p.e81858). GH (growth hormone) produced by the expression of Gh gene, which can accelerate cell division, and promote protein synthesis (Luo et al., 2023, p.e81858). Both Mstn and Gh play important regulatory roles in the growth and development of fish (Pan et al., 2022, p.1084). In this study, under the stresses of rapid temperature changes, Gh was downregulated and Mstn was upregulated in both fish, which indicated the growth of both fish had been affected. There was a good correlation between both genes expressions and the speeds of temperature changes. This indicated that the fish slowed down its cell division and reduced protein synthesis as the changing speed increased (Pan et al., 2022, p.1084), diverting some energy originally used for growth to alleviate the stress, leading to a slowdown in growth (Rasmussen and McLean, 2004, p.397; Pan et al., 2022, p.1084).
Many studies had used the ratio of RNA/DNA as an indicator to evaluate the growth status of fish, such as Sardina pilchardus (Ramirez et al., 2004, p.57), Labeo rohita (Siddiqua and Khan, 2022, p.e738114), and so on. Generally, RNA is highly expressed in rapidly growing fish, and DNA is relatively stable (Siddiqua and Khan, 2022, p.e738114). A high RNA/DNA ratio indicated there was a fast growth of fish (Siddiqua and Khan, 2022, p.e738114). In addition, the ratio was also highly consistent with the relative expressions of growth-related genes (Gh and Mstn) (Pan et al., 2020, p.1421). According the ratio and the expressions of both genes, we found the growth of O. melastigma was rapid recovery in the experiment, but the growth of H. kuda was severely inhibited, and the degree was increased with increasing amplitude or speed of temperature changes. The rapid recovery/adaptation ability of O. melastigma had also been reported in other species, such as O. sinensis, whose growth was not significant difference under the stress of temperature changes (±8°C, for 15 days) (Fang, 2021). In this study, the growth inhibition of O. melastigma only appeared in 0H4+ under 4°C amplitude. However, there was a critical line of growth difference observed in H. kuda, which was 2°C amplitude +1°C/h speed with 7 day, or 4°C amplitude +1°C/h speed with 4 day. Obviously, O. melastigma was more adaptable to the stresses caused by rapid temperature changes than H. kuda.
In fact, growth was a comprehensive performance that was related to all internal and external conditions, e.g., food. Usually, low food intake inhibited Gh and promoted Mstn to slow down the growth (Jackson et al., 2020, p.113319). So that, the fish not only required more energy to resist stresses (Portz et al., 2006, p.125), their poor physiological and health state in turn affected their appetite and led to a decrease in food intake, resulting in a decrease in growth rate.
4.2 Feeding and nutrition metabolism
Many studies had delved into the impact of temperature on fish’s feeding, indicating that changes in temperature could affect its digestive tract homeostasis, thereby affecting feeding quantity and feeding behavior (Sharma et al., 2017, p.134; Folkedal et al., 2012, p.350). Therefore, the changes of feeding quantity or behavior can be used to evaluate the impact of temperature stresses in fish. For example, temperature stress had a significant impact on the feeding rate and feed conversion rate of Cyprinus carpio (Chen et al., 2022, p.737636), Seriola lalandi (Stone et al., 2022, p.738567), and Scophthalmus maximus (Aydn et al., 2021, p.736891). Our previous researches also observed an increase in feeding response time and a gradual decrease in feeding rate and frequency for H. kuda with increasing temperature changes (Pan et al., 2020, p.1084). In this study, both the amplitude and speed of temperature changes had an impact on the feeding behavior of both fish, included prolonged the feeding response time, decreased the feeding rate and the food intake. Actually, the impact was relatively limited on O. melastigma, while obviously decreased the food intake in almost treatments of H. kuda (Table 3). It indicated that rapid temperature changes had a greater impact on the feeding of H. kuda.
In fact, a decrease in food intake was an external manifestation of internal physiology, which included the enzyme activities and gene expressions related to nutrition and metabolism. Under rapid temperature changes, the homeostasis in fish was affected to a certain extent. In order to adapt to new environmental conditions, the fish had to expend high energy costs for adaptive regulation (Portz et al., 2006, p.125). Carbohydrate and lipid were the two main energy substrates in fish (Portz et al., 2006, p.125). Therefore, it was of great significance that exploring the impact of environmental changes on the activities of key enzymes mainly involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolisms and the relative expressions of genes encoded the key enzymes. This study analyzed two key enzyme genes encoding carbohydrate metabolism, Idh3b and Mdh1, and two key enzyme genes encoding lipid metabolism, Cpt1 and Fas, as well as two endogenous digestive enzymes, AMS and LPS, to compare the effects of temperature stresses on energy metabolism of O. melastigma and H. kuda.
Endogenous digestive enzymes were important indicators for studying the digestion and utilization of nutrients. The enhancement of their activities can promote the absorption and utilization of nutrients in fish (Jiang et al., 2021, p.57). It was generally believed that sugar was short-lived energy substances that underwent rapid decomposition through the action of AMS enzyme. Lipids, on the other hand, were long-lived energy substances that decomposed by LPS enzyme. In this study, the activities of AMS and LPS in different treatments had a significant change. Based on data of food intake, it was speculated that both fish may have increased their digestive enzyme activities, thereby increasing the assimilation efficiency of foodborne sugars and lipids to cope with excessive energy consumption (Tan et al., 2016, p.637). After a prolonged period of 4 or 7 days with severe stress, energy supplementation from carbohydrates became insufficient, and the consumption of lipids increased, showed by an increase in LPS activity (Figure 1). However, the LPS activity in O. melastigma and H. kuda was significantly different, which had been consistently increasing in H. kuda and showed up and down oscillations in O. melastigma. It indicated that O. melastigma may have already adapted to the temperature stress, with a relatively balanced assimilation alienation effect in the body. However, H. kuda was constantly consuming energy to resist the stress, thus fat-decomposition continued to increase. It was speculated that H. kuda will require a longer period to adapt to rapid temperature changes under the same stress.
Glucose was the primary energy substrate preferred by organisms (Portz et al., 2006, p.125). Malic acid dehydrogenase (MDH), generated by the expression of Mdh1 gene, was a key limiting-rate enzyme in glucose metabolism. Fish regulated carbohydrate metabolism by enhancing MDH activity in the liver to reduce the energy burden (Sharma et al., 2017, p.134; Chang et al., 2020, p.110744). Researches had found that the expression of Mdh1 was also easily affected in temperature-sensitive organisms. For example, Cyprinus carpio who was sensitive to low temperature was significantly lower of Mdh1 expression than that in cold-tolerant individuals (Liu et al., 2018, p.168). In this study, after 12 h stress of rapid temperature changes, the Mdh1 expression was rapidly upregulated in both fish, indicating that the fish increased their sugar metabolism levels in order to maintain a normal internal physiological state (Sharma et al., 2017, p.134). Clearly, O. melastigma had a faster response and earlier recovered at the following 4th or 7th day, while its expression was still increasing or oscillating in H. kuda at the same time (Figure 3). Similar results had also been reported in other fish (Chang et al., 2020, p.110744). Based on the results, it was speculated that there was some difference in the nutritional metabolism mechanism between O. melastigma and H. kuda in response to rapid temperature changes. Firstly, H. kuda faced a larger energy gap under the stress, secondly, aerobic carbohydrate metabolism was probablly the main energy pathway for H. kuda to resist stress (Sharma et al., 2017, p.134), so did O. melastigma, but O. melastigma was relatively stable and less affected under the same conditions. In a word, O. melastigma had a stronger adaptability and its more sources of energy than H. kuda to deal with rapid temperature changes (Chang et al., 2020, p.110744).
Lipid was also important energy storage substances in fish, and the decomposition of fatty acids can be accompanied by a large amount of energy release. Similarly, the mobilization and decomposition of stored lipids were strictly regulated by various internal and external factors (Cheng et al., 2017, p.110744; Sharma et al., 2017, p.134). The liver also was the main site of lipid metabolism in fish. Before fatty acids entered its decomposition pathway, they needed to be catalyzed by carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) to form acyl CoA, which then entered the mitochondria β-oxidation reaction. CPT1, generated by the expression of Cpt1 gene, was the main limiting-rate enzyme in this process (Sharma et al., 2017, p.134). In this study, the expression of Cpt1 in both fish was affected by temperature changes. H. kuda showed an upregulated response in all treatments under 2°C ampitude and in the low-speed treatments under 4°C ampitude, and downregualted response (expression inhibition) in the high-speed treatments. Moreover, Cpt1 in O. melastigma showed little or no response under 2°C ampitude, and quickly upregulated and recovered under 4°C ampitude (Figure 4). It can be seen that Cpt1 gene in H. kuda was obviously upregulated in the treatments with slight temperature changes, which indicated that H. kuda increased the level of lipid metabolism in the liver, providing more energy for maintaining normal physiological activities (Sharma et al., 2017, p.134). In evidence, it also exceeded its regulatory capacity with large temperature changes. In O. melastigma, carbohydrate metabolism could ensure energy supply under slight changes. The lipid metabolism was only called on under large changes of temperature. Based on the above analysis, it indicated that the fish provided more additional energy for further adaptation to stress by upregulating the level of fatty acid decomposition (Volkoff et al., 2005, p.3). It also indicated that in the response to rapid temperature changes, the utilization mechanism of fatty acids in both fish was the same, but the utilization efficiency was significant difference.
4.3 Antioxidation and immunity
Generally, environmental stresses made the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) increasing, and organisms had to consume a large amount of energy from sugar and lipid decomposition to improve their antioxidant defense system. This system included antioxidant enzymes and antioxidant active substances, which were used to clear excess intracellular ROS and maintain normal physiology (Pan et al., 2022, p.1421). As an important member, SOD participated in the catalytic decomposition reaction of ROS, and its activity was an important indicator for evaluating the antioxidant capacity and health state of organisms (Pan et al., 2022, p.1421). MDA was a product of lipid peroxidation in cells and widely used to evaluate the degree of oxidative stress in organisms (Pan et al., 2022, p.1421). In addition, oxidative stress and immunity were closely related, jointly maintaining normal physiology (Fan et al., 2019). In this study, the antioxidant and immune responses of O. melastigma and H. kuda under rapid temperature changes were analysed and compared. Obviously, rapid temperature changes had a significant impact on the SOD activities and MDA contents in the 2 fish. Many similar results had been reported (Tan et al., 2016, p.637; Shi et al., 2022, p.1), indicating that the stress of rapid temperature changes can also induce antioxidant responses in both O. melastigma and H. kuda in this study. However, the timing of inducing antioxidant responses was different. In H. kuda, there was a significant increase in SOD activity and MDA content in the treatments with >1°C/h of changing speeds of temperautre, indicating that the stresses in the high-speed treatments may cause more serious oxidative damage to H. kuda. For the same reason, the critical safe speed of temperature changes in O. melastigma was relatively much higher.
Phosphatases, included ACP and AKP, were important metabolic and immune regulatory enzymes in organisms. They can enhance non-specific immune ability in fish (Fan et al., 2019, p.58). Temperature changes can affect their activity fluctuations (Ning et al., 2016, p.117). In this study, AKP activity did not change significantly in the 2 fish under small ampitude. However, it had significantly decreased with increasing changing speeds in H. kuda under 4°C ampitude of temperature, making it difficult to recover healthy, indicating that rapid temperature changes possibly inhibited the non-specific immune function of H. kuda, also happened in the 0H4± treatments of O. melastigma. In fact, temperature changes and duration of stress had a significant impact on AKP activity in fish (Meng et al., 2020, p.122). So, the non-specific immune abilities produced by O. melastigma and H. kuda in response to different amplitudes and speeds of temperature changes were different, and their antioxidant abilities were also different, resulting in different outcomes.
The enzymes involved in antioxidation and immunity were synthesized through the expressions of related genes. There were also some differences in the expression of Sod gene between O. melastigma and H. kuda. H. kuda had a significant expression response to slight temperature changes, while showed an inhibition and downregulation to large temperature changes. On the contrary, O. melastigma had little response to slight stress, and had strong regulatory ability against large stress. The expression of Gst gene, for synthetizing glutathione thiol transferase (GST) (Hooper et al., 2014, p.26), had a similar trend to that of Sod. The rapid upregulation of Gst was observed in O. melastigma treatments with 2°C amplitude and in H. kuda treatments with 4°C amplitude. All results indicated that H. kuda was more sensitive and had limited regulatory ability to rapid temperature changes in this study. This had been confirmed in terms of food supplementation, energy metabolism, and growth performance. In this study, the expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs) and its related genes (Hsp70, Hsp90) also were analyzed and compared. HSPs can repair cell damage caused by oxidative stress (Iwama et al., 1998, p.35). When the fish felt abnormal stress signals, its heat shock response was activated, and the expression of Hsp gene was upregulated, starting to produce HSPs to repair cell damage (Iwama et al., 1998, p.35; Chu et al., 2022, p.528). Therefore, the Hsp expression level can reflect the degree of stress response in organisms (Iwama et al., 1998, p.35; Chu et al., 2022, p.528). This mechanism was widely present in aquatic organisms, such as Chlamys farreri (Liu et al., 2013b, p.462), Procambarus clarkii (Xu et al., 2017, p.9), and Pampus argenteus (Shi et al., 2022, p.1). Temperature fluctuations, caused Hsp genes expression, and their expression levels were related to the stress-regulation mechanism of organisms under temperature stress (Cui et al., 2013, p.919; Shi et al., 2022, p.1). In this study, the expression level of hsp70 in H. kuda gradually increased with the increase of speed of temperature changes, but without significant changes in O. melastigma, further indicating that rapid temperature changes caused significant oxidative damage to H. kuda.
In this study, the variations in cell apoptosis signaling pathways were also analyzed and compared in O. melastigma and H. kuda. Apoptosis was the main pathway for maintaining the stability of the internal environment in organisms, and was controlled by genes for autonomous and orderly cell death (Zhou et al., 2020, p.735681). It was one of the important forms of non-specific immune system response and regulation to environmental stress (Zhou et al., 2020, p.735681). When a fish was subjected to stress, abnormal stress signals would activate its cell apoptosis signaling factors, inducing the activation of cell apoptosis signaling pathways (Zhou et al., 2020, p.735681). Among them, P53 (tumor suppressor protein) was an important component of the cell cycle signaling process (Siikavuopio and Sather, 2006, p.351). Caspase3 (CASP3), a key enzyme, was widely involved in processes such as the P53 signaling pathway and cell apoptosis pathway (Siikavuopio and Sather, 2006, p.351). In this study, rapid temperature changes had a significant impact on the relative expression levels of P53 and Casp3 genes in the liver of H. kuda, with significantly increased expression levels and gradually upregulated with increasing amplitude and speed of temperature changes, indicating that the process of apoptosis in liver cells of H. kuda had been activated (Liu et al., 2019, p.1407; Zhou et al., 2020, p.735681). The expressions of these 2 genes were also upregulated in O. melastigma, mainly showed by up and down oscillations and quick recovery. Overall, the expression levels of P53 and Casp3 in H. kuda were higher than those in O. melastigma, indicating that the transmission of apoptotic signals in liver cells of H. kuda was more responsive to rapid temperature changes than that in O. melastigma, which was possibly related to the fact that H. kuda was more sensitive to temperature changes (Dawood et al., 2022, p.397).
Interleukin-10 (Il-10) was an important inhibitory factor, and played an important role in the inflammation and immune regulation of organisms (Hossain et al., 2022, p.101038). In this study, the Il-10 expression in O. melastigma was regular, but chaotic in H. kuda. (Pan et al., 2020, p.1421) speculated that the main reason was the disruption of immune system in H. kuda caused by rapid temperature changes and its stress. Because of thermal stimulation, the expression of Il-10 as an anti-inflammatory factor fluctuated rapidly and disorderly, which probably was an expression of transitioning from normal physiological stress into pathological stress in H. kuda, represented a weakened response to anti-inflammation and a significant decrease in non-specific immune disease resistance (Liu et al., 2013a, p.462). It was generally believed that the intestine was the central organ of biological stress response. Pathological stress induced pathological changes of intestinal tissues, mainly manifested as mucosal erosion, ulcers, bleeding, and structural damage to mesenteric lymph nodes, leading to a decrease in immune function (Liu et al., 2013b, p.462), and ultimately an increase in disease incidence. This speculation was consistent with the actual situation in production (Wang et al., 2020, p.730). Under rapid temperature changes, H. kuda was likely to experience anorexia, then developed into enteritis and death.
5 Conclusion
From the results, it can be seen that temperature changes had an impact on both O. Melastigma and H. Kuda. And H. kuda was more sensitive. Under a 2°C amplitude of temperature, H. kuda, as a slowly-adapted fish, had significant differences among different speeds of temperature changes, and existd a critical safe speed was about 1°C/h, while the fast-adapted O. Melastigma had no effect in all treaments. Under 4°C amplitude, the critical safe speed of H. kuda decreased to about 0.5°C/h, while O. Melastigma only had a slight impact in the heating treatment with direct input. The reason was comprehensive, including decreased food intake capacity, weakened immune function, increased energy consumption for stress resistance, and so on. The key reason was that H. kuda had a single energy supply pathway, which mainly relied on carbohydrate decomposition.
Based on the biological characteristics of H. kuda, its precise aquaculture technique needs a stricter and more precise control of environmental temperature to prevent rapid and big temperature changes from affecting the growth and survival.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
YX: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft, Validation, Conceptualization. PL: Writing–original draft, Validation, Supervision, Software, Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. WZ: Writing–review and editing, Software, Methodology, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Data curation. XP: Writing–review and editing, Project administration, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Data curation. JL: Writing–review and editing, Supervision, Methodology, Data curation. YB: Writing–review and editing, Resources, Methodology, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (41276123) and The Special Research Fund of the Discipline Group of “Marine Biotechnology and Ocean Engineering” of Ningbo University (No. 422004582).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alfonso S., Gesto M. S., Sadoul B. (2021). Temperature increase and its effects on fish stress physiology in the context of global warming. J. Fish Biol. 98 (6), 1496–1508. doi:10.1111/jfb.14599
Aydn I., Kucuk E., Polat H., Zturk R. A., Altinok L., Altınok İ. (2021). Growth and feed conversion ratio of diploid and triploid induced juvenile turbot reared at different water temperatures. Aquaculture 543, 736981. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736981
Buckly L. J. (1979). Relationships between RNA/DNA ratio, prey density, and growth rate in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhus) larvae. J. Fish Res. Board Can. 36, 1497–1502. doi:10.1139/f79-217
Burggren W. W., Mendez S. J., Martinez B. P., Dastings D. (2019). Developmental changes in oxygen consumption and hypoxia tolerance in the heat and hypoxia-adapted tabasco line of Oreochromis niloticus, with a survey of the metabolic literature for the genus Oreochromis. J. Fish Biol. 94 (5), 732–744. doi:10.1111/jfb.13945
Candiano G., Bruschi M., Musante L., Santucci L., Ghiggeri G. M., Carnemolla B., et al. (2004). Blue silver: a very sensitive colloidal Coomassie G-250 staining for proteome analysis. Electrophoresis 25 (9), 1327–1333. doi:10.1002/elps.200305844
Chang C. H., Zhou X. W., Wang Y. C., Lee T. H. (2020). Differential effects of hypothermal stress on lactate metabolism in fresh water- and seawater-acclimated milkfish, Chanos chanos. Comp. Biochem. Physiology Part A Mol. Integr. Physiology 248, 110744. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.110744
Chen C. Z., Li P., Wang W. B., Li Z. H. (2022). Response of growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, antioxidant capacity, and digestive enzyme activity to different feeding strategies in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) under high-temperature stress. Aquaculture 548, 737636. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737636
Cheng C. H., Ye C. X., Guo Z. X., Wang A. L. (2017). Immune and physiological responses of pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus) under cold stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 64, 137–145. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2017.03.003
Chu T. Q., Liu F., Chen H. L., Chen L. F. (2022). Response of hsp90b1 and hspb1 to temperature stress in the liver of Larimichthys polyactis. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 30 (3), 528–538. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2022.03.011
Cui S. L., Liu B., Xu P., Xie J., Zhou M. L. (2013). Effects of emodin on growth, haemotological parameters and Hsp70 mRNA expression of Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) at two temperatures. ACTA Hydrobiol. Sin. 37 (5), 919–928. doi:10.7541/2013.119
Dawood M. A. O., Alkafafy M., Sewilam H. (2022). The antioxidant responses of gills, intestines and livers and blood immunity of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to salinity and temperature stressors. Fish Physiology Biochem. 48 (2), 397–408. doi:10.1007/s10695-022-01052-w
Dittmar J., Janssen H., Kuske A. F., Kurtz J., Ardia D. (2014). Heat and immunity: an experimental heat wave alters immune functions in three-spined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). J. Animal Ecol. 83 (4), 744–757. doi:10.1111/1365-2656.12175
Fan L. S., Shao P., Jia S. Y., Gao J. W., Dou Y., Shi X. R., et al. (2019). The effect of temperature stress on antioxidant and non-specific immune indicators in Paramisgurnus dabryanus. Prog. Fish. Sci. 40 (2), 58–64. doi:10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20180306001
Fang L. X. (2021). The effect of temperature on the growth, exercise ability, and enzyme activity of Oryzias sinensis[D]. Harbin Normal University.
Folkedal O., Stien L. H., Torgersen T., Oppedal F., Plsen E. R., Fosseidengen E. J., et al. (2012). Food anticipatory behaviour as an indicator of stress response and recovery in Atlantic salmon post-smolt after exposure to acute temperature fluctuation. Physiology Behav. 105 (2), 350–356. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.08.008
Hooper C., Day R., Slocombe R., Benkendorff R., Handlinger K., Goulias J. (2014). Effects of severe heat stress on immune function, biochemistry and histopathology in farmed Australian abalone (Haliotis laevigata×H. rubra). Aquaculture 432, 26–37. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.03.032
Hossain F., Islam S. M., Islam M. S., Shahjahan M. D. (2022). Behavioral and histo-pathological indices of striped catfish (Pangasionodon hypophthalmus) exposed to different salinities. Aquac. Rep. 23, 101038. doi:10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101038
Hu L. C., Dong Z. M., Zhao S., Wang H. F., Song J. (2016). The effect of salinity on the vitality, feeding, and survival of Glyptocidaris crenularis under suitable temperature conditions. Hebei Fish. 7, 13–16.
Huang D. K., Liang H. F., Zhang Z. (2017). Effects of temperature on the survival, feeding, shedding, and growth of Panulirus homarus. Acta Ecol. Sin. 37 (18), 5973–5980.
Iwama G. K., Thomas P. T., Forsyth R. B., Vijayan M. M. (1998). Heat shock protein expression in fish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 8 (1), 35–56. doi:10.1023/a:1008812500650
Jackson S. S., Nicole L. H., Kevin T. L., Kasey L. C., Theresa V. B., Meredith L. J., et al. (2020). Effects of food deprivation on plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 (Igf1) and Igf binding protein (Igfbp) gene transcription in juvenile cabezon (Scorpaenichthys marmoratus). General Comp. Endocrinol. 286, 113319. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.113319
Jiang X. Y., Huang M., Yang X. G., Chen L. Y. (2021). The effect of acute high temperature stress on antioxidant enzyme activity in rainbow trout and hard headed trout juveniles. J. Fish. Sci. China 28 (1), 57–65.
Kato R. (1997). Drug metabolism under pathological and abnormal physiological states in animals and man. Xenobiotica 7 (1/2), 25–92. doi:10.3109/00498257709036242
Liu S. J., Tian F., Zhang C. F., He Z. Y. (2018). Transcriptome sequencing analysis of liver and pancreas in carp under low-temperature stress. Biotechnol. Bull. 34 (11), 168–178.
Liu S. K., Wang X. L., Sun F. Y., Jiang Y., Zhang Y., Liu H., et al. (2013a). RNA-Seq reveals expression signatures of genes involved in oxygen transport, protein synthesis, folding, and degradation in response to heat stress in catfish. Physiol. Genomics 45 (12), 462–476. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00026.2013
Liu W., Chang Y. Q., Ding J. (2013b). A preliminary study of effects of mild and acute drop of temperature on serum non-specific immunity in“Shuiyuan No.1”sea cucumber populations and the cultured sea cucumber populations. J. Fish. China 37 (9), 1342–1348. doi:10.3724/sp.j.1231.2013.38659
Liu X. F., Ma A. J., Huang Z. H., Liu Z., Yang S., Yang K. (2019). Expression characteristics analysis of major QTL chandidate genes in response to high temperature stress in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). J. Fish. China 43 (6), 1407–1415. doi:10.11964/jfc.20180811413
Lu J., Bo Y., Wang Y., Yuan H. Y., Xu Y. J. (2023). Effect of water quality ununiformity on production of marine medaka. Aquaculture 565, e739114. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.739114
Lu T., Peng T., Lei Y., Zhu W., Xu D. (2020). Effects of salinity on the growth, plasma ion concentrations, osmoregulation, non-specific immunity, and intestinal microbiota of the yellow drum (Nibea albiflora). Aquaculture 528, e73547. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735470
Luo Z. B., Han S., Yin X. J., Quan L. H., Kang J. D., Xuan M., et al. (2023). Fecal transplant from myostatin deletion pigs positively impacts the gut-muscle axis. Elife 12, e81858. doi:10.7554/eLife.81858
Lv J. Y., Sun Y. Y., Li B. J. (2003). Research on the application of beneficial microorganisms in healthy aquaculture of Hippocampus kuda. J. Fish. Sci. China 10 (1), 46–50.
Makrinos D. L., Bowden T. J. (2016). Natural environmental impacts on teleost immune function. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 53, 50–57. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2016.03.008
Meng Z., Zhang H. L., Liu X. F., Wang S. (2020). The effect of acute heat stress on blood biochemical indicators of Scophthatmus maximus. Mar. Sci. 44 (1), 122–131. doi:10.11759/hykx20190814001
Moretto W. I., Stahl A. K., Mehta R. S. (2022). Effects of acute temperature change on California moray prey manipulation and transport behavior. Zoology 154, 126030. doi:10.1016/j.zool.2022.126030
Mu J. T., Xie S. D., Yong P. Z., Sun J. H., Xu Y. J., Li J. (2017). Effect of temperature on feeding behavior and growth rate of the yellow seahorse, Hippocampus kuda Bleeker. J. Fish. Sci. China 24 (2), 355–361. doi:10.3724/sp.j.1118.2017.16315
Murata K., Kinoshita M., Kiyoshi N., Tanaka M., Kamer Y. (2020). Madaka: biology, management, and experimental protocols[M]. USA: Wiley Blackwell Press.
Ning J. H., Chang Y. Q., Liu W., Li W. (2016). The stress effect of sudden temperature drop on Potamocorbula laevis. Fish. Sci. 35 (2), 117–122.
Pan X., Sheng X., Zhang W. X., Xu Y. J. (2022). Effects of short-term temperature changes on the physiology, biochemistry and feeding behaviour of the juvenile yellow seahorse— Hippopotamus kuda Bleeker. Aquac. Res. 53, 1084–1097. doi:10.1111/are.15649
Pan X., Xu Y. J., Ning Y., Zhang W. X. (2020). Effects of temperature stress on genes’ transcription and expression in juvenile Hippocampus kuda Bleeker. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 34 (7), 1421–1431. doi:10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.07.1421
Portz D. E., Woodley C. M., Cech J. J. (2006). Stress-associated impacts of short-term holding on fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 16, 125–170. doi:10.1007/s11160-006-9012-z
Ramirez T., Cortes D., Garcia A., Carpena A. (2004). Seasonal variations of RNA/DNA ratios and growth rates of the Alboran Sea sardine larvae (Sardina pilchardus). Fish. Res. 68 (1), 57–65. doi:10.1016/j.fishres.2004.02.008
Rasmussen M. R., McLean E. (2004). Comparison of two different methods for evaluating the hydrodynamic performance of an industrial-scale fish-rearing unit. Aquaculture 242 (1-4), 397–416. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.08.045
Sharma J., Singh S. P., Chakrabarti R. (2017). Effect of temperature on digestive physiology, immune-modulatory parameters, and expression level of Hsp and LDH genes in Catla catla (Hamilton, 1822). Aquaculture 479, 134–141. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.05.031
Shi C. Y., Zhao C. B., Hu Y. X., Sha T. P. (2022). Effects of high temperature stress on physiology and expression of related gene in Pampus argenteus. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 41 (1), 1–7.
Siddiqua K. S., Khan M. A. (2022). Effects of dietary lipid levels on growth, feed utilization, RNA/DNA ratio, digestive tract enzyme activity, non-specific immune response and optimum inclusion in feeds for fingerlings of rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Aquaculture 554, e738114. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738114
Siikavuopio S. I., James P., Lysne H., Sather B. S., Samuelsen T. A., Mortensen A. (2012). Effects of size and temperature on growth and feed conversion of juvenile green sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis). Aquaculture 354, 27–30. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.04.036
Siikavuopio S. I., Sather B. S. (2006). Effects of chronic nitrite exposure on growth in juvenile Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. Aquaculture 255 (1-4), 351–356. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.11.058
Stone D. J., Bansemer M. S., Salini M. J. (2022). Dietary lipid and protein levels influence the growth and feed utilisation of large yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi) at summer water temperatures. Aquaculture 560, 738567. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738567
Tan E., Kinoshita S., Suzuki Y., Ineno T., Tamaki K., Kera A., et al. (2016). Different gene expression profiles between normal and thermally selected strains of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, as revealed by comprehensive transcriptome analysis. Gene 576 (2), 637–643. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2015.10.028
Volkoff H., Canosa L. F., Unniappan S., Cerda-Reverter M. J., Bernier J. N., Kelly P. S., et al. (2005). Neuropeptides and the control of food intake in fish. General Comp. Endocrinol. 142 (1-2), 3–19. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2004.11.001
Wang L., Wei C., Chang Y. Q., Ding J. (2021). Response of bacterial community in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus intestine, surrounding water and sediment subjected to high-temperature stress. Aquaculture 535, 736353. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736353
Wang R., Dai L. L., Chen Y. F., Xu Y. J. (2019). Effects of short-term temperature and salinity stress on the feeding behavior and antioxidant capacity of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Oceanol. Limnologia Sinica 50 (2), 378–387. doi:10.11693/hyhz20181000234
Wang R., Pan X., Xu Y. (2020). Altered intestinal microbiota composition associated with enteritis in yellow seahorses Hippocampus kuda (Bleeker, 1852). Curr. Microbiol. 77, 730–737. doi:10.1007/s00284-019-01859-6
Xiang J. H., Liu B. Z. (2007). Basic research on the occurrence and immune prevention of important marine animal diseases in aquaculture. Chin. Bull. Life Sci. 19 (4), 396–399.
Xie J. S., Bu L. F., Jin S., Xu Y. J., Zhao Q., Zhou S., et al. (2020). Outbreak of vibriosis caused by Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio alginolyticus in farmed seahorse Hippocampus kuda in China. Aquaculture 523, e735168. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735168
Xu J., Wei K. J., Xu B., Lu J. C. (2017). Physiological response of Procambarus clarkii to high temperature stress. Freshw. Fish. 47 (6), 9–13. doi:10.13721/j.cnki.dsyy.2017.06.002
Xu Y. J. (2019). The concept of micro-environment aquaculture and its technical implications. J. Ningbo Univ. (NSEE) 32 (4), 1–7.
Ye N. H., Zhuang Z. M., Wang Q. Y. (2016). Develpoment strategy for realizing the healthy aquaculture industry concept. Eng. Sci. China 18 (3), 101–104. doi:10.15302/J-SSCAE-2016.03.017
Yuan Q., Wu C. C., Yang H., Lv W. W., Huang W. W., Zhang Q., et al. (2024). Effects of four types of natural bait on water quality, feeding, growth, and antioxidant enzyme activity of Monopterus albus in a recirculating aquaculture system. Front. Physiology 15, e1403391. doi:10.3389/fphys.2024.1403391
Keywords: Hippocampus kuda, Oryzias melastigma, rapid temperature change, adaptability and growth, precision aquaculture
Citation: Xu Y, Lin P, Zhang W, Pan X, Lu J and Bo Y (2024) Adaptability and growth of Hippocampus kuda and Oryzias melastigma under rapid temperature changes. Front. Physiol. 15:1464123. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1464123
Received: 13 July 2024; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 19 September 2024.
Edited by:
Yafei Duan, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, ChinaReviewed by:
D. K. Meena, Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute (ICAR), IndiaWuxiao Zhang, Yancheng Institute of Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Lin, Zhang, Pan, Lu and Bo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongjian Xu, eHV5b25namlhbkBuYnUuZWR1LmNu
 Yongjian Xu
Yongjian Xu Penghong Lin
Penghong Lin Wenxin Zhang
Wenxin Zhang