- 1College of First Clinical Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Liver Disease, The 960th Hospital of the PLA Joint Logistics Support Force, Jinan, China
- 3The third department of encephalopathy, Jinan Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital, Jinan, China
- 4Diagnosis and Treatment Center for Liver Diseases, Tai’an 88 Hospital, Taian, China
Background: The early detection and intervention of liver fibrosis (LF) in patients with chronic liver disease is critical to their management. The accuracy of serum Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) in the diagnosis of LF remains controversial. This study aimed to comprehensively assess the value of serum M2BPGi in diagnosing LF.
Methods: The PubMed, Embase, MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases were searched. The effect values were combined using a random-effects model. Meta-regression and subgroup analysis were used to explore the sources of heterogeneity. In addition, publication bias assessment and sensitivity analysis were conducted.
Results: This study includes 12 studies with 2,416 patients. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and AUROC of M2BPGi in the diagnosis of significant fibrosis (≥F2) were 0.65 (95% CI: 0.57–0.71), 0.79 (95% CI: 0.72–0.84), and 0.78 (95% CI: 0.74–0.81), respectively, while those for predicting extensive fibrosis (≥F3) were 0.76 (95% CI: 0.71–0.80), 0.75 (95% CI: 0.68–0.81), and 0.81 (95% CI: 0.77–0.84). Sensitivity analysis indicated stable results in this study. The disease type, cut-off values, study country, average age, and male proportion were the sources of heterogeneity in diagnosing significant fibrosis of M2BPGi (p < 0.05). Sample size, disease type, study country, publication year, cut-off values, average age, and male proportion were important sources of heterogeneity in diagnosing extensive fibrosis (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Serum M2BPGi has good diagnostic performance for significant fibrosis and extensive fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), chronic hepatitis C (CHC), or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and is an effective, non-invasive, and convenient marker.
Systematic Review Registration: https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2023-10-0086/.
Introduction
Liver fibrosis (LF) is a necessary stage in the progression of chronic liver disease (CLD) of various causes. If not intervened in time, it can further develop into cirrhosis, liver cancer, and eventually liver failure (Chen et al., 2022; Khanam et al., 2021). Accurate assessment of the extent of LF in patients with CLD is critical to their management. Hepatic histological examination is considered the gold standard for the diagnosis of LF, but it is an invasive operation with potential complications and low acceptance. Therefore, it is difficult to apply for dynamic monitoring of the progression of LF. Therefore, it is necessary to find effective and convenient non-invasive tests for staging and monitoring LF.
Although biomarkers such as Golgi protein 73 (GP73), ceruloplasmin, and chitinase 3-like protein 1 (CHI3L1, also known as YKL-40) have been proposed, their diagnostic accuracy remains to be confirmed (Liu et al., 2018; Kang et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2018). Mac-2 binding protein (M2BP), a secreted glycoprotein present in the extracellular matrix, is associated with cell adhesion (Lian et al., 2022). Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi), also known as serum wisteria floribunda agglutinin (WFA) positive Mac-2 binding protein (WFA+-M2BP), is a novel marker for assessing LF, which was first proposed by Kuno et al. (2013). In their study, six candidate lectins were selected for binding to M2BP, with WFA being superior to the other five for diagnosing LF (Ishii et al., 2017). Bekki et al. (2017) found that hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the source of M2BPGi in subpopulations of liver-derived cells. Another study showed that M2BPGi is a messenger sent by HSCs to Kupffer cells during LF (Shirabe et al., 2018). These findings indicated that M2BPGi plays an important role in the progression of fibrosis.
M2BPGi has been increasingly used in clinical applications for diagnosing LF in chronic hepatitis B(CHB), chronic hepatitis C (CHC), nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) risk in these diseases (Tamaki et al., 2021; Morio et al., 2017; Fujita et al., 2018; Inoue et al., 2018; Nishikawa et al., 2016a; Atsukawa et al., 2018). Furthermore, it has been reported that M2BPGi can also be used for the diagnosis of LF in autoimmune liver disease (Nishikawa et al., 2016b; Migita et al., 2018; Umemura et al., 2015; Nishikawa et al., 2016c; Umetsu et al., 2018) and biliary atresia (Ueno et al., 2018). However, systematic reviews regarding the accuracy of M2BPGi in staging LF are relatively rare and need to be further enriched. Therefore, we provide an updated meta-analysis, not limited to LF patients with one single cause, to better assess the diagnostic performance of serum M2BPGi in staging LF.
Methods
Literature search
This study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines with the registration number INPLASY2023100086 (Liberati et al., 2009). The PubMed, Embase, MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases were searched. The search period was from the start of database construction until 8 September 2023. Search terms were set as follows: (‘Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer’ OR (‘Mac 2’ AND (‘binding’/exp OR binding) AND (‘protein’/exp OR protein) AND (‘glycosylation’/exp OR glycosylation) AND (‘isomer’/exp OR isomer)) OR ‘wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein’ OR ((‘wisteria’/exp OR wisteria) AND (‘floribunda’) AND (‘agglutinin positive’) AND (‘Mac 2 binding’) AND (‘protein’/exp OR protein)) OR ‘wfa M2bp’ OR, (‘wfa’, AND ‘M2bp’), OR ‘M2bpgi’, OR ‘wfa-binding M2bp’ OR (‘wfa binding’ AND ‘M2bp’), OR ‘wfa + M2bp’)) AND (‘liver diseases’ OR ‘liver’ OR ‘hepatic’) NOT ‘animals’ NOT (‘humans’ AND ‘animals’).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria of the literature
Literature inclusion criteria: (1) Patients aged ≥18 years; (2) A precise classification of LF using pathological diagnosis as the gold standard; (3) Patients tested for M2BPGi; and (4) The number of direct or indirect true positives (TP), false positives (FP), true negatives (TN), or false negatives (FN) identified by M2BPGi in each case group.
Exclusion criteria for literature: (1) Animal experiments, cell experiments, case reports, conference abstracts, reviews, comments, or letters; (2) Patients without a clear diagnosis based on liver biopsy; (3) Sample size less than ten cases; (4) Inability to extract key data; (5) Duplication of published data; and (6) Full text of literature not found.
Data extraction
The study data were extracted by two researchers independently using the pre-defined data extraction form, and any disagreements were resolved by the third reviewer. The following data were extracted: first author, publication year, disease type, fibrosis stage, study location, study design, gold standard methodology, staging criteria of LF, cut-off value, sample size, sensitivity, specificity, TP, FP, FN, and TN.
Evaluation of quality
Two researchers independently assessed the quality of the included studies using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2) tool (Whiting et al., 2011). Disagreements were resolved through consultation. The results of the quality assessment were presented using Review Manager software (Version 5.3.5; Nordic Cochrane Centre; Copenhagen, Denmark).
Definition of LF
LF was staged according to the Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NSH) Clinical Research Network (CRN) system, Brunt’s criteria, and the Metavir scoring system (Goodman, 2007; Bedossa and Poynard, 1996; Kleiner et al., 2005). The scoring methods of the included studies were translated into uniform criteria for staging LF. Significant fibrosis and extensive fibrosis were defined as stages ≥ F2 and ≥ F3, respectively.
Statistical analysis
All data analysis and image generation were carried out using Stata software (version 14.0; Stata Corp LP; Texas, United States) and Meta-Disc 1.4. The pooled values of sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic score, diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and the summary area under the curve (sAUC) were summarized using the “MIDAS” module. Diagnostic accuracy was evaluated using the sAUC. The Meta-Disc software was used to test the threshold effect, which was assessed by the Spearman correlation coefficient. Heterogeneity between studies was assessed using Cochran’s Q statistic) in Stata. A fixed-effects method was used when I2 < 50 or the p-value was <0.10. If not, a random-effects model was suitable. Meta-regression and subgroup analysis were used to explore the sources of heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis was used to assess the influence of individual studies on heterogeneity and to observe the stability of the summary statistics. Publication bias was assessed using Deeks’ funnel plot. A two-tailed p < 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.
Results
Search results
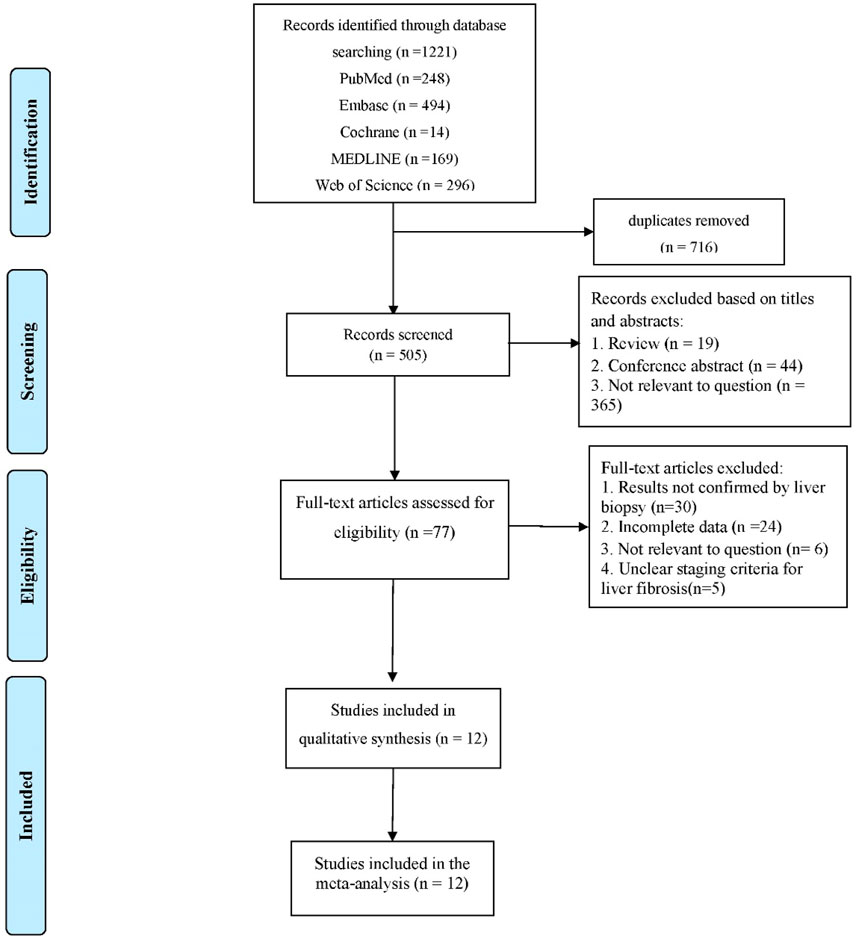
A total of 1,221 articles were retrieved after the selection process (Figure 1). After successively checking for duplicates, reading titles and abstracts, and reading the full text, 12 articles were finally included in the analysis (Nishikawa et al., 2016a; Atsukawa et al., 2018; Yeh et al., 2019; Nishikawa et al., 2016d; Abe et al., 2015; Lai et al., 2017; Huang et al., 2017; Jang et al., 2021; Tsuji et al., 2020; Numao et al., 2021; Noguchi et al., 2017; Jang et al., 2022).
Study characteristics and quality
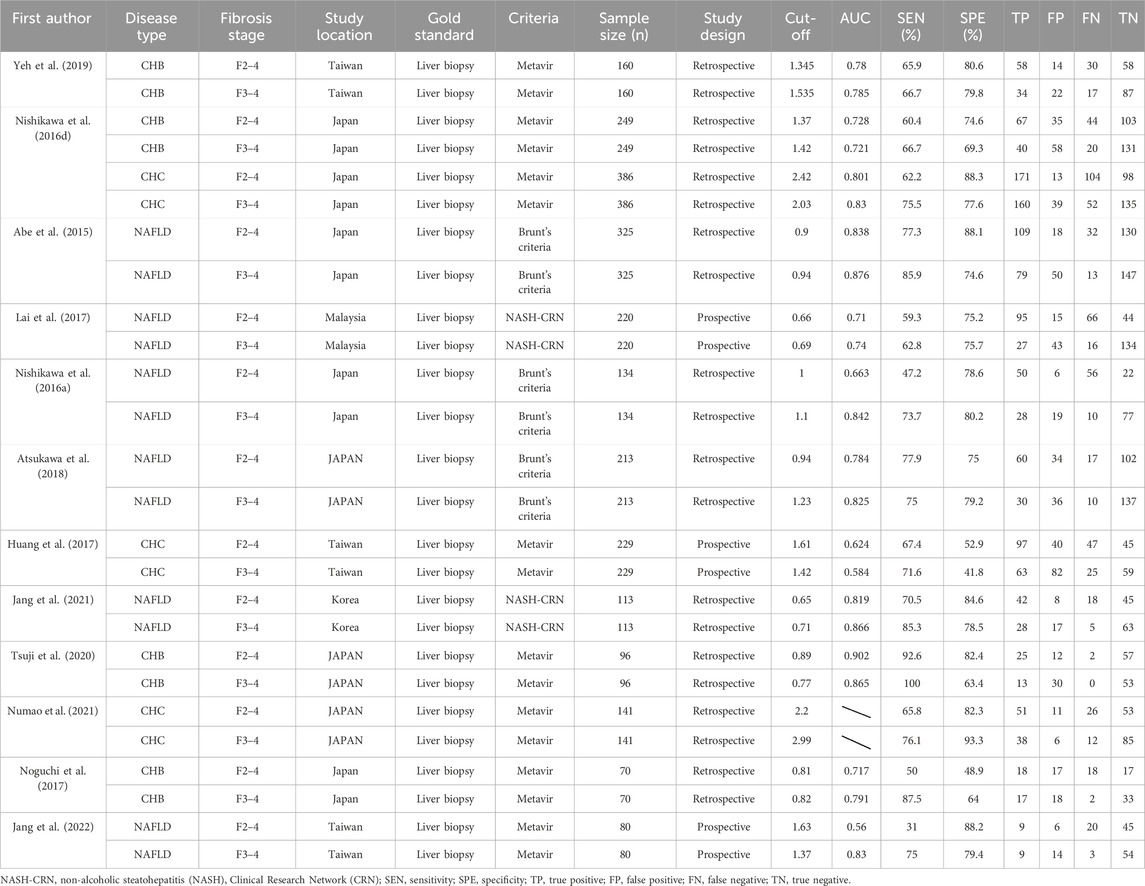
This study includes 12 studies with a total of 2,416 patients with CHB, CHC, or NAFLD. The gold standard for staging LF in all studies was liver biopsy. The cut-off value of M2BPGi for the diagnosis of each LF stage was set in various studies. Basic patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The results of the quality assessment based on the QUADAS-2 tool are shown in Figure 2.
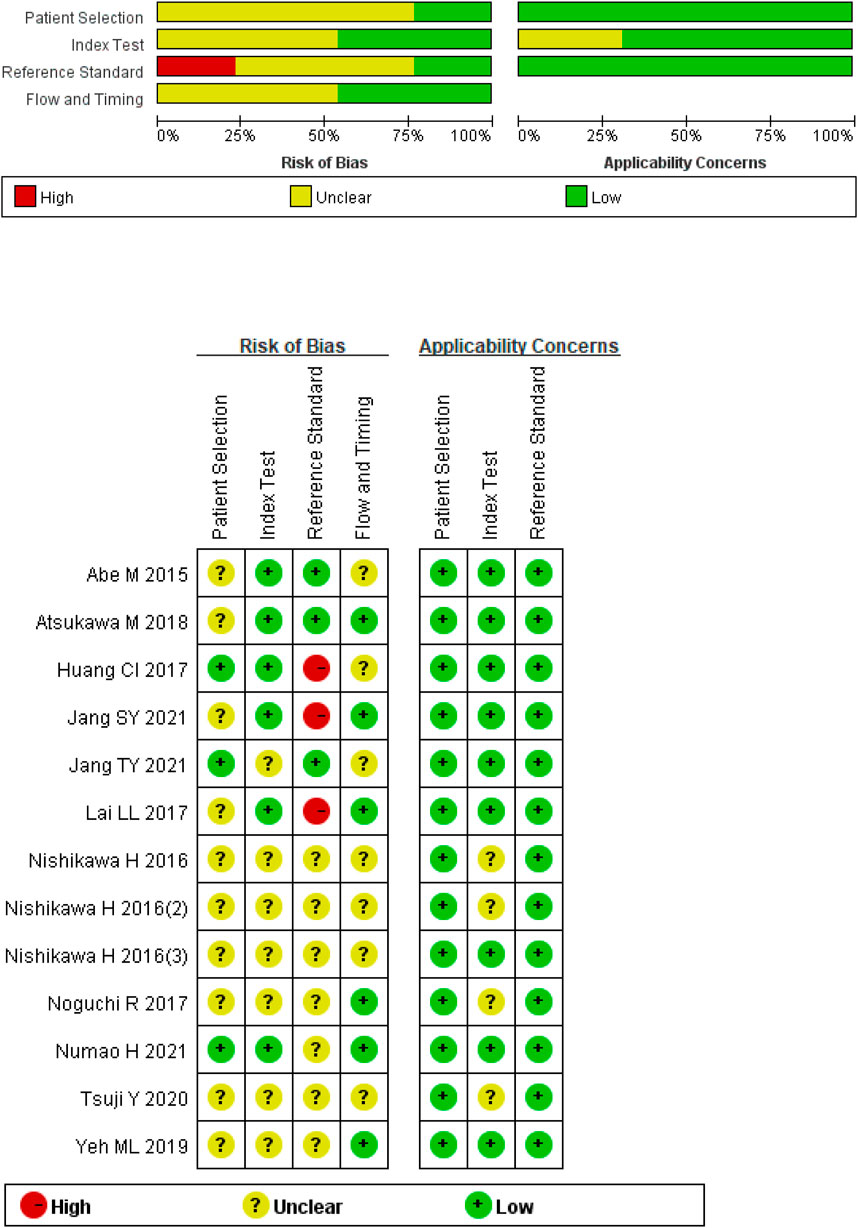
Figure 2. Quality assessment of included studies based on the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies tool criteria.
Heterogeneity
The Spearman’s correlation analysis showed that the correlation coefficient of M2BPGi was −0.132 (p = 0.668) for staging significant fibrosis (≥F2) and 0.206 (p = 0.499) for staging extensive fibrosis (≥F3), indicating no heterogeneity due to threshold effects. The I2 for sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, diagnostic score, and DOR were all >50% (p <0.001) (Figures 3A–C; Figures 4A–C), suggesting the existence of a non-threshold impact due to inter-literature heterogeneity. Therefore, the effect values were combined using the random-effects model.

Figure 3. Forest plots showing the pooled evaluation indicators of M2BPGi for staging significant fibrosis (≥F2). (A) Pooled sensitivity and specificity. (B) Pooled positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio. (C) Pooled diagnostic score and diagnostic odds ratio.

Figure 4. Forest plots showing the pooled evaluation indicators of M2BPGi for staging extensive fibrosis (≥F3). (A) Pooled sensitivity and specificity. (B) Pooled positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio. (C) Pooled diagnostic score and diagnostic odds ratio.
Diagnostic accuracy of M2BPGi for staging LF
The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and AUROC of M2BPGi in the diagnosis of significant fibrosis (≥F2) were 0.65 (95% CI: 0.57–0.71), 0.79 (95% CI: 0.72–0.84), and 0.78 (95% CI: 0.74–0.81), respectively, (Figure 3A; Figure 5A), while those for predicting extensive fibrosis (≥F3) were 0.76 (95% CI: 0.71–0.80), 0.75 (95% CI: 0.68–0.81), and 0.81 (95% CI: 0.77–0.84) (Figure 4B; Figure 5B). The PLR, NLR, diagnostic score, and DOR for diagnosing significant fibrosis (≥F2) were 3.02 (95% CI: 2.22–4.10), 0.45(95% CI: 0.36–0.57), 1.90(95% CI: 1.40–2.40), and 6.68 (95% CI: 4.06–11.00), respectively (Figures 3B, C). The values for staging extensive fibrosis (≥F3) were 3.03 (95% CI: 2.34–3.93), 0.32 (95% CI: 0.26–0.40), 2.24 (95% CI: 1.82–2.66), and 9.40 (95% CI: 6.19–14.28), respectively (Figures 4B, C).
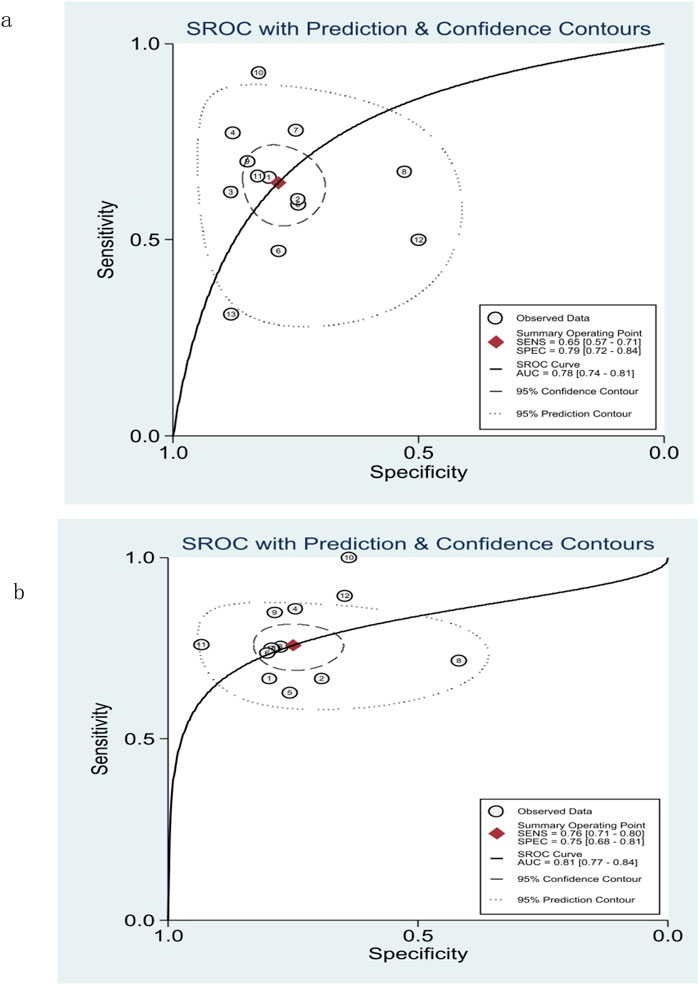
Figure 5. Summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of M2BPGi for predicting significant fibrosis (≥F2) (A) and extensive fibrosis (≥F3) (B).
Subgroup analysis and meta-regression
Sources of heterogeneity were analyzed using meta-regression and subgroup analysis. Eight covariables were included: sample size (≥100 cases or <100 cases), disease type (chronic viral hepatitis or NAFLD), study design (prospective or retrospective studies), study location (Japan or not Japan), publication year (2014–2017 or 2018–2023), cut-off value (≥1 or <1), average age (≥50 or <50), and male proportion (≥0.5 or <0.5). The results indicated that male proportion and cut-off value were the sources of sensitivity heterogeneity in diagnosing significant fibrosis (≥F2) in M2BPGi (P<0.01), while disease type, study location, cut-off value, average age, and male proportion were important sources of specificity heterogeneity (Figure 6A). Sample size, disease type, study country, publication year, cut-off value, average age, and male proportion were important sources of sensitivity heterogeneity in diagnosing extensive fibrosis (≥F3), while disease type, average, and male proportion were important sources of specificity heterogeneity (Figure 6B).
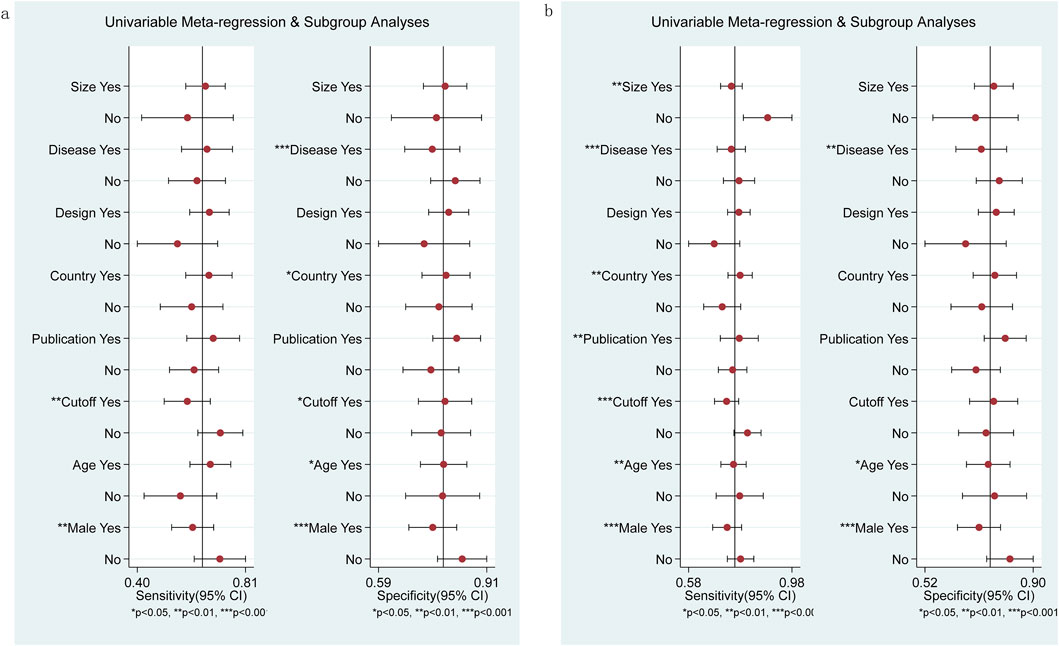
Figure 6. Subgroup and meta-regression analyses for M2BPGi in the diagnosis of significant fibrosis (≥F2) (A) and extensive fibrosis (≥F3) (B).
Publication bias
The Deeks funnel plot showed no significant publication bias in the included studies diagnosing significant fibrosis (≥F2) (p = 0.4, Figure 7A) and extensive fibrosis (≥F3) (p = 0.33, Figure 7B).
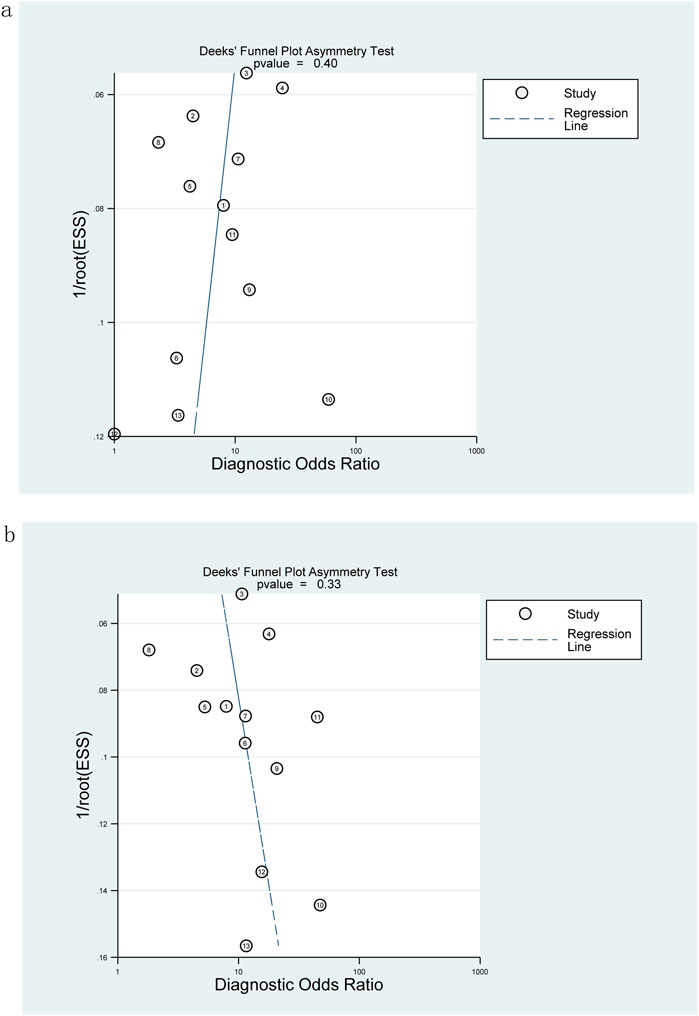
Figure 7. Deeks funnel plot for evaluating publication bias: M2BPGi was used to detect significant fibrosis (≥F2) (A) and extensive fibrosis (≥F3) (B).
Sensitivity analysis
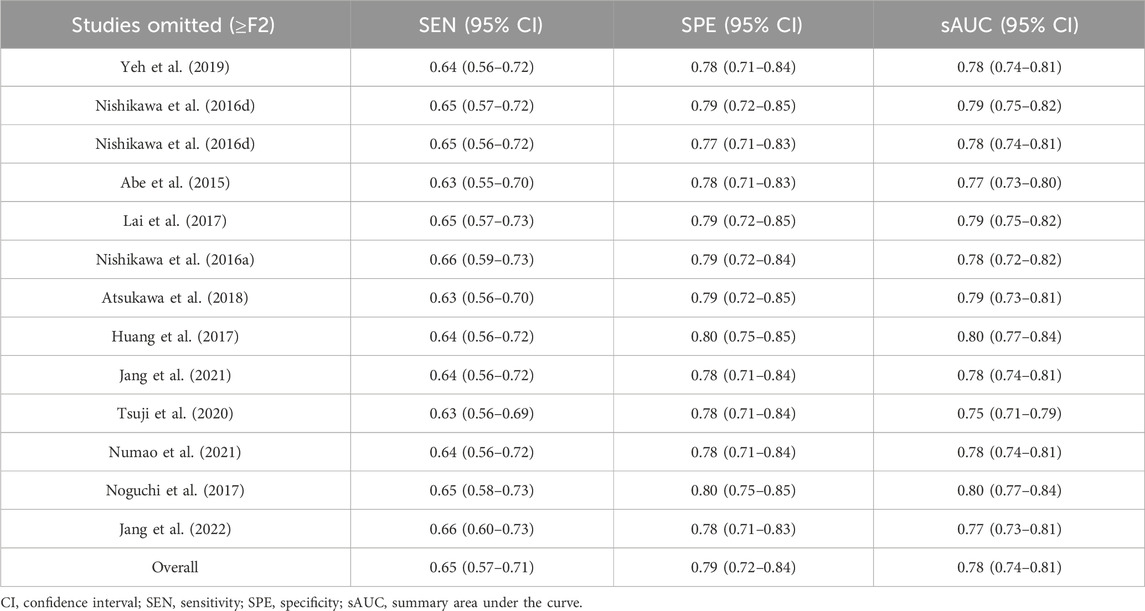
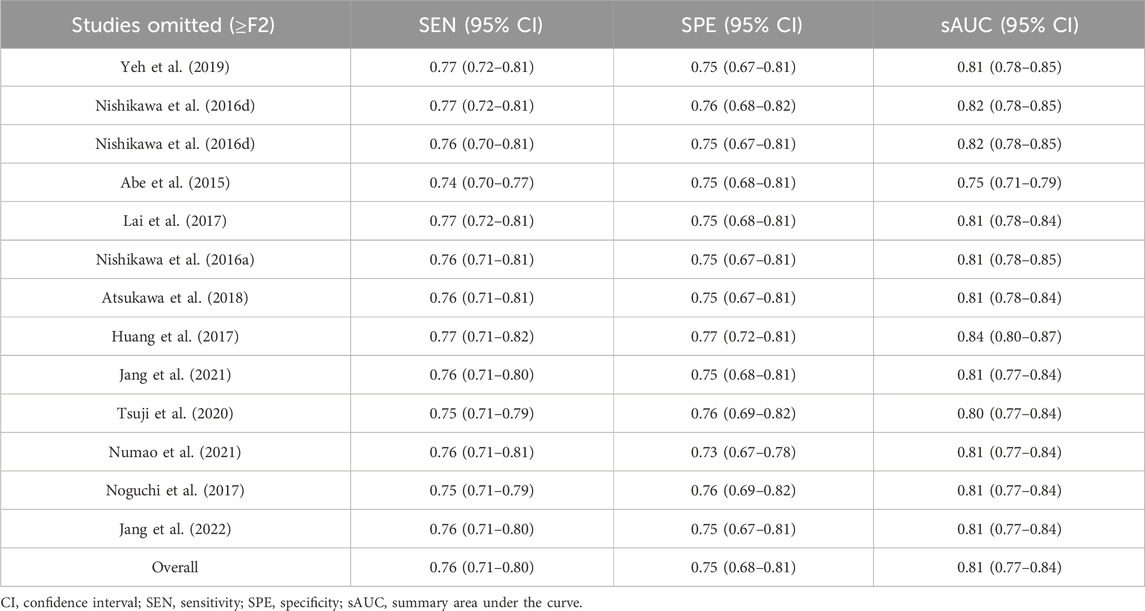
The sensitivity analyses, performed by eliminating each study individually, showed no significant changes in overall diagnostic values, sensitivity, specificity, and their 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs), which were within the 95% CIs of the total combination values, indicating stable results in this study (Tables 2, 3).
Discussion
Early detection and intervention of LF in patients with CLD can reduce the risk of fibrosis-related complications and HCC. The promotion of non-invasive, simple, and effective tests can be used with more LF patients who refuse liver biopsy. In this meta-analysis, we included 12 studies on LF with causes of CHB, CHC, or NAFLD and synthesized the accuracy of M2BPGi in staging LF. Although it has been reported that M2BPGi can also be used for the diagnosis of LF with other causes (such as autoimmune hepatitis (Nishikawa et al., 2016b; Migita et al., 2018) or primary biliary cholangitis (Umemura et al., 2015; Nishikawa et al., 2016c)), these studies were excluded for small sample size or absence of liver biopsy, the gold standard for staging LF. In this study, the AUROC values for significant fibrosis (≥F2) and extensive fibrosis (≥F3) were 0.78 and 0.81, respectively. In general, an AUROC of 0.7–0.8 is considered acceptable, and 0.8 to 0.9 is considered excellent (Mandrekar, 2010; Hosmer and Lemeshow, 2000). The results of this study showed that M2BPGi had low sensitivity and acceptable diagnostic value in diagnosing significant fibrosis, while it had excellent diagnostic value in diagnosing extensive fibrosis. By eliminating each study one by one, the sensitivity analysis showed that the study results were stable.
The results of the quality assessment indicated that many studies were at risk of bias. Due to the disproportionately high percentage of retrospective studies included and the fact that some studies did not specify the interval between blood sampling and liver biopsy, there may be selective bias in patient selection and case flow. In some included studies, the blinding methods were not mentioned, and in addition, the pathological diagnosis results were only completed by one expert, which could lead to risks of bias in the detection of indexes and gold standards. Some studies were determined to have an unclear risk of bias for flow and timing because the derivation of serum samples and performance of liver biopsy were not described. Some studies were considered to be at unclear risk of bias in terms of flow and timing because they did not specify when serum samples were obtained and liver biopsies were performed.
The sources of heterogeneity were explored among the included studies. The levels of M2BPGi vary among different disease types, which may lead to heterogeneity in meta-analysis. According to reports, the levels of M2BPGi in patients with CHC are higher than those in patients with CHB (Nishikawa et al., 2016d). Compared with patients with CHC or CHB, patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) have the lowest levels of M2BPGi (Shirabe et al., 2018). The difference in gender ratio seems to be one of the sources of heterogeneity, which needs further confirmation. In most studies, each study established an optimal threshold without using a pre-specified threshold. Therefore, there were differences in the optimal cut-off value for staging LF. In addition, this index took different cut-off values in diagnosing LF of different etiologies, which may also contribute to the high degree of heterogeneity in our review. The diagnostic performance of M2BPGi may be affected by geographical bias (7 of 12 studies included were from Japan), which may be due to the first introduction of M2BPGi as a biomarker for LF and its approval for clinical practice happened in Japan (Lian et al., 2022). In addition, we found that age was also an influential factor in the diagnostic performance of M2BPGi.
This study has the following advantages: (1) Compared to previous meta-analyses that usually included studies using liver stiffness measurement (LSM) for staging LF, this study explicitly included studies using liver biopsy as the gold standard for staging LF. (2) This study was not limited to patients with one single cause of LF. (3) The heterogeneity sources of the included studies were analyzed by subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis. (4) The sensitivity analysis was carried out to prove the stability of the research results. Limitations of this study: (1) There were differences in the design and conduct of the included studies, which may lead to confounding bias. (2) Although this study included patients with various causes of LF, it did not include all causes of LF. (3) The different scoring criteria for staging LF in the included studies were translated into a unified staging method, which was acceptable but resulted in bias. (4) Clinical applicability was limited by the fact that all included patients were from Asian countries, and it is hoped that further studies will include patients from more countries.
Conclusion
Serum M2BPGi is an effective, non-invasive, and convenient marker for staging significant fibrosis and extensive fibrosis in patients with CHB, CHC, or NAFLD. Despite its limitations, it can be a promising method of dynamic monitoring of the progression or regression of LF.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
XL: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing–original draft. WZ: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing–original draft. BM: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, and writing–original draft. CL: Project administration, Writing–review and editing. MS: conceptualization, supervision, and writing–review and editing. QS: conceptualization, supervision, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abe M., Miyake T., Kuno A., Imai Y., Sawai Y., Hino K., et al. (2015). Association between Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein and the fibrosis stage of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 50 (7), 776–784. doi:10.1007/s00535-014-1007-2
Atsukawa M., Tsubota A., Okubo T., Arai T., Nakagawa A., Itokawa N., et al. (2018). Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein more reliably distinguishes liver fibrosis stages in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than serum Mac-2 binding protein. Hepatol. Res. 48 (6), 424–432. doi:10.1111/hepr.13046
Bedossa P., Poynard T. (1996). An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 24, 289–293. doi:10.1002/hep.510240201
Bekki Y., Yoshizumi T., Shimoda S., Itoh S., Harimoto N., Ikegami T., et al. (2017). Hepatic stellate cells secreting WFA+ -M2BP: its role in biological interactions with Kupffer cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 32 (7), 1387–1393. doi:10.1111/jgh.13708
Chen L., Kong D., Xia S., Wang F., Li Z., Zhang F., et al. (2022). Crosstalk between autophagy and innate immunity: a pivotal role in hepatic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 891069. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.891069
Fujita K., Kuroda N., Morishita A., Oura K., Tadokoro T., Nomura T., et al. (2018). Fibrosis staging using direct serum biomarkers is influenced by hepatitis activity grading in hepatitis C virus infection. J. Clin. Med. 7 (9), 267. Published 2018 Sep 11. doi:10.3390/jcm7090267
Goodman Z. D. (2007). Grading and staging systems for inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 47 (4), 598–607. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2007.07.006
Hosmer D. W., Lemeshow S. (2000). Applied logistic regression. 2nd Edn. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, 160–164. Chapter 5.
Huang C. I., Huang C. F., Yeh M. L., Lin Y. H., Liang P. C., Hsieh M. H., et al. (2017). Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein expression predicts disease severity in chronic hepatitis C patients. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 33 (8), 394–399. doi:10.1016/j.kjms.2017.05.017
Inoue T., Tsuzuki Y., Iio E., Shinkai N., Matsunami K., Fujiwara K., et al. (2018). Clinical evaluation of hepatocarcinogenesis and outcome using a novel glycobiomarker wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive mac-2 binding protein (WFA+-M2BP) in chronic hepatitis C with advanced fibrosis. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 71 (3), 177–183. doi:10.7883/yoken.JJID.2017.459
Ishii A., Nishikawa H., Enomoto H., Iwata Y., Kishino K., Shimono Y., et al. (2017). Clinical implications of serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein in treatment-naïve chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Res. 47 (2), 204–215. doi:10.1111/hepr.12703
Jang S. Y., Tak W. Y., Park S. Y., Kweon Y. O., Lee Y. R., Kim G., et al. (2021). Diagnostic efficacy of serum mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer and other markers for liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. Ann. Lab. Med. 41 (3), 302–309. doi:10.3343/alm.2021.41.3.302
Jang T. Y., Huang C. F., Yeh M. L., Dai C. Y., Tsai P. C., Hsu P. Y., et al. (2022). Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein expression predicts disease severity in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 38 (3), 261–267. doi:10.1002/kjm2.12474
Kang N. L., Zhang J. M., Lin M. X., Chen X. D., Huang Z. X., Zhu Y. Y., et al. (2020). Serum ceruloplasmin can predict liver fibrosis in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 26 (27), 3952–3962. doi:10.3748/wjg.v26.i27.3952
Khanam A., Saleeb P. G., Kottilil S. (2021). Pathophysiology and treatment options for hepatic fibrosis: can it Be completely cured? Cells 10 (5), 1097. doi:10.3390/cells10051097
Kleiner D. E., Brunt E. M., Van Natta M., Behling C., Contos M. J., Cummings O. W., et al. (2005). Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41, 1313–1321. doi:10.1002/hep.20701
Kuno A., Ikehara Y., Tanaka Y., Ito K., Matsuda A., Sekiya S., et al. (2013). A serum “sweet-doughnut” protein facilitates fibrosis evaluation and therapy assessment in patients with viral hepatitis. Sci. Rep. 3, 1065. doi:10.1038/srep01065
Lai L. L., Chan W. K., Sthaneshwar P., Nik Mustapha N. R., Goh K. L., Mahadeva S. (2017). Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One 12 (4), e0174982. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174982
Lian M. J., Chen Z. Q., Wang Q. M., Zheng G. S., Hong G. L. (2022). Diagnostic accuracy of mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer for diagnosing hepatitis B-related fibrosis: a meta-analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 23 (10), 550–560. doi:10.1111/1751-2980.13140
Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A., et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339, b2700. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2700
Liu L. L., Wang J. W., Feng J. Y., Yao M., Hao C., You Y., et al. (2018). Serum Golgi protein 73 is a marker comparable to APRI for diagnosing significant fibrosis in children with liver disease. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 16730. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-34714-y
Mandrekar J. N. (2010). Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 5 (9), 1315–1316. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ec173d
Migita K., Horai Y., Kozuru H., Koga T., Abiru S., Yamasaki K., et al. (2018). Serum cytokine profiles and Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) level in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Med. Baltim. 97 (50), e13450. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000013450
Morio K., Imamura M., Daijo K., Teraoka Y., Honda F., Nakamura Y., et al. (2017). Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2-binding protein level increases in patients with acute liver injury. J. Gastroenterol. 52 (12), 1252–1257. doi:10.1007/s00535-017-1345-y
Nishikawa H., Enomoto H., Iwata Y., Hasegawa K., Nakano C., Takata R., et al. (2016b). Clinical significance of serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2-binding protein level and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentration in autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatol. Res. 46 (7), 613–621. doi:10.1111/hepr.12596
Nishikawa H., Enomoto H., Iwata Y., Hasegawa K., Nakano C., Takata R., et al. (2016c). Impact of serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2-binding protein and serum interferon-γ-inducible protein-10 in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 46 (6), 575–583. doi:10.1111/hepr.12595
Nishikawa H., Enomoto H., Iwata Y., Kishino K., Shimono Y., Hasegawa K., et al. (2016a). Clinical significance of serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2-binding protein level in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Res. 46 (12), 1194–1202. doi:10.1111/hepr.12662
Nishikawa H., Enomoto H., Iwata Y., Kishino K., Shimono Y., Hasegawa K., et al. (2016d). Serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein for patients with chronic hepatitis B and C: a comparative study. J. Viral Hepat. 23, 977–984. doi:10.1111/jvh.12575
Noguchi R., Kaji K., Namisaki T., Moriya K., Kitade M., Takeda K., et al. (2017). Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme level for evaluating significant fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 23 (36), 6705–6714. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6705
Numao H., Shimaya K., Kakuta A., Shibutani K., Igarashi S., Hasui K., et al. (2021). The utility of two-dimensional real-time shear wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 33 (11), 1400–1407. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001887
Shirabe K., Bekki Y., Gantumur D., Araki K., Ishii N., Kuno A., et al. (2018). Mac-2 binding protein glycan isomer (M2BPGi) is a new serum biomarker for assessing liver fibrosis: more than a biomarker of liver fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. 53 (7), 819–826. doi:10.1007/s00535-017-1425-z
Tamaki N., Kurosaki M., Loomba R., Izumi N. (2021). Clinical utility of mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer in chronic liver diseases. Ann. Lab. Med. 41 (1), 16–24. doi:10.3343/alm.2021.41.1.16
Tsuji Y., Namisaki T., Kaji K., Takaya H., Nakanishi K., Sato S., et al. (2020). Comparison of serum fibrosis biomarkers for diagnosing significant liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Exp. Ther. Med. 20 (2), 985–995. doi:10.3892/etm.2020.8798
Ueno T., Kodama T., Noguchi Y., Saka R., Takama Y., Tazuke Y., et al. (2018). Clinical implications of serum Mac-2-binding protein (M2BPGi) during regular follow-up of patients with biliary atresia. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 34 (10), 1065–1071. doi:10.1007/s00383-018-4317-2
Umemura T., Joshita S., Sekiguchi T., Usami Y., Shibata S., Kimura T., et al. (2015). Serum wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive mac-2-binding protein level predicts liver fibrosis and prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 110 (6), 857–864. doi:10.1038/ajg.2015.10.1038/ajg.2015.118
Umetsu S., Inui A., Sogo T., Komatsu H., Fujisawa T. (2018). Usefulness of serum Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein in children with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatol. Res. 48 (5), 355–363. doi:10.1111/hepr.13004
Whiting P. F., Rutjes A. W., Westwood M. E., Mallett S., Deeks J. J., Reitsma J. B., et al. (2011). QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern Med. 155, 529–536. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009
Yan L. L., Deng Y. Q., Zhou J. Y., Zhao H., Wang G. (2018). Serum YKL-40 as a biomarker for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal and mildly elevated ALT. Infection 46 (3), 385–393. doi:10.1007/s15010-018-1136-2
Keywords: mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer, liver fibrosis, diagnosis, meta-analysis, non-invasive diagnostic index
Citation: Liu X, Zhang W, Ma B, Lv C, Sun M and Shang Q (2024) The value of serum Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 15:1382293. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1382293
Received: 16 February 2024; Accepted: 30 September 2024;
Published: 30 October 2024.
Edited by:
Giuliano Ramadori, University of Göttingen, GermanyReviewed by:
Patryk Lipiński, Maria Sklodowska-Curie Medical Academy, PolandKessarin Thanapirom, Royal Free Hospital, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Zhang, Ma, Lv, Sun and Shang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mimi Sun, bWlteXN1bkAxNjMuY29t; Qinghua Shang, c3ExNzEzMjc3Mzk3QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xinyu Liu
Xinyu Liu Wei Zhang2†
Wei Zhang2†