
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Physiol., 22 July 2022
Sec. Vascular Physiology
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.881750
This article is a correction to:
circAFF1 Aggravates Vascular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction Mediated by miR-516b/SAV1/YAP1 Axis
 Hong-guang Wang1,2,3,4*†
Hong-guang Wang1,2,3,4*† Hua Yan2,3†
Hua Yan2,3† Chen Wang3,5†
Chen Wang3,5† Mi-mi Li4†
Mi-mi Li4† Xin-ze Lv6†
Xin-ze Lv6† Hai-dong Wu4
Hai-dong Wu4 Zhan-hai Fang7
Zhan-hai Fang7 Dong-li Mo3,5
Dong-li Mo3,5 Zhi-yuan Zhang4
Zhi-yuan Zhang4 Bin Liang4
Bin Liang4 Ke-guan Lai6
Ke-guan Lai6 Jing-yu Bao6
Jing-yu Bao6 Xue-jia Yang6
Xue-jia Yang6 Hong-juan Zhao8
Hong-juan Zhao8 Shuang Chen5*
Shuang Chen5* Yi-mu Fan2,3,5*
Yi-mu Fan2,3,5* Xiao-guang Tong2,3,5*
Xiao-guang Tong2,3,5*A Corrigendum on
circAFF1 Aggravates Vascular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction Mediated by miR-516b/SAV1/YAP1 Axis
by Wang, H., Yan, H., Wang, C., Li, M., Lv, X., Wu, H., Fang, Z., Mo, D., Zhang, Z., Liang, B., Lai, K., Bao, J., Yang, X., Zhao, H., Chen, S., Fan, Y., and Tong, X. (2020). Front. Physiol. 11:899. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00899
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 7C as published. In the tube formation results in Figure 7C, the CoCl2 group of HUVEC-C cells and the CoCl2/si-circAFF1/aso-miR-516b group of HBEC-5i misused the same picture. This is due to the similar naming of the two images. The correct Figure 7 appears below.
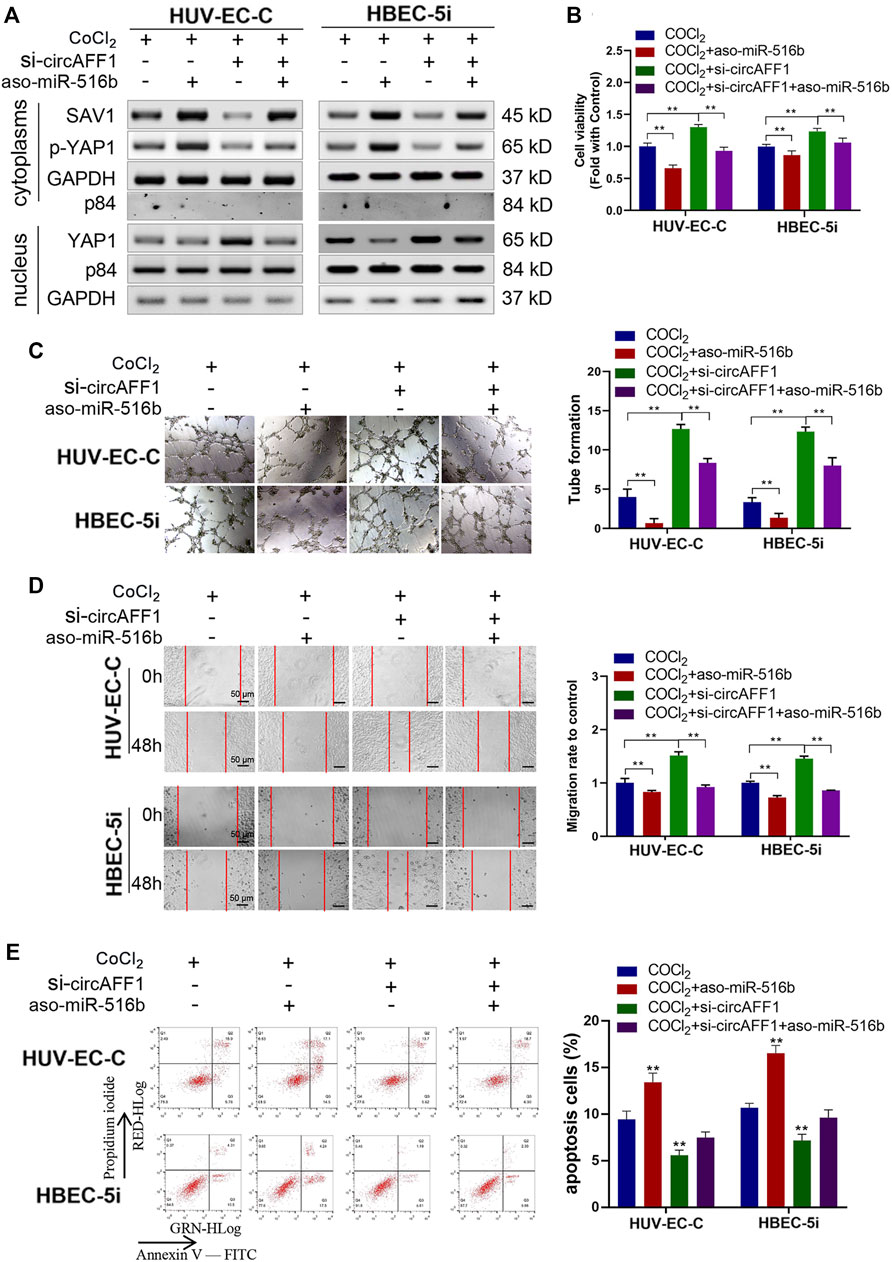
FIGURE 7. miR-516b reversed the effect of circAFF1 on endothelial cells. (A) Western blot analysis demonstrated that circAFF1 can counteract the influence of miR-516b mimics on SAV1, YAP1, and p-YAP1 expression in HUV-EC-C and HBEC-5i cells. (B) CCK-8 assay indicated that the proliferation ability of HUV-EC-C and HBEC-5i cells transfected with aso-miR-516b was reversed when co-transfected with si-circAFF1. (C) Tube formation ability of HUV-EC-C and HBEC-5i cells transfected with aso-miR-516b was reversed when co-transfected with si-circAFF1. (D) Wound healing assays indicated that the migration capability of HUV-EC-C and HBEC-5i cells transfected with aso-miR-516b was reversed when co-transfected with si-circAFF1. (E) Apoptosis assay indicated that the apoptosis ability of HUV-EC-C and HBEC-5i cells transfected with aso-miR-516b was reversed when co-transfected with si-circAFF1. Data are presented as means of three experiments, and error bars represent SD (**p < 0.01).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: vascular endothelial cell, subarachnoid hemorrhage, hypoxic, circAFF1, YAP1
Citation: Wang H-g, Yan H, Wang C, Li M-m, Lv X-z, Wu H-d, Fang Z-h, Mo D-l, Zhang Z-y, Liang B, Lai K-g, Bao J-y, Yang X-j, Zhao H-j, Chen S, Fan Y-m and Tong X-g (2022) Corrigendum: CircAFF1 aggravates vascular endothelial cell dysfunction mediated by miR-516b/SAV1/YAP1 axis. Front. Physiol. 13:881750. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.881750
Received: 23 February 2022; Accepted: 28 June 2022;
Published: 22 July 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Daniel Bia, Universidad de la República, UruguayCopyright © 2022 Wang, Yan, Wang, Li, Lv, Wu, Fang, Mo, Zhang, Liang, Lai, Bao, Yang, Zhao, Chen, Fan and Tong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong-guang Wang, bHVja3l3aGdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Shuang Chen, c2h1YW5nNzMzMkAxNjMuY29t; Yi-mu Fan, ZmFueWltdUBzaW5hLmNvbQ==, ZmFueWltdTExQHNpbmEuY29t; Xiao-guang Tong, eGlhb2d1YW5ndG9uZ0AxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.