- Department of Medicine, Feinberg School of Medicine, Feinberg Cardiovascular and Renal Research Institute, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, United States
The lymphatic system is crucial for the maintenance of interstitial fluid and protein homeostasis. It has important roles in collecting excess plasma and interstitial fluid leaked from blood vessels, lipid absorption and transportation in the digestive system, and immune surveillance and response. The development of lymphatic vessels begins during fetal life as lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells first differentiate into lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) by expressing the master lymphatic vascular regulator, prospero-related homeobox 1 (PROX1). The lymphatic vasculature forms a hierarchical network that consists of blind-ended and unidirectional vessels. Although much progress has been made in the elucidation of the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the formation of the lymphatic vascular system, the causes of lymphatic vessel abnormalities and disease are poorly understood and complicated; specifically, the mechanistic basis for transcriptional dysregulation in lymphatic vessel development remains largely unclear. In this review, we discuss the recent advances in our understanding of the molecular and cellular mechanisms of lymphatic vascular development, including LEC differentiation, lymphangiogenesis, and valve formation, and the significance of mechanical forces in lymphatic vessels, with a focus on transcriptional regulation. We also summarize the current knowledge on epigenetic mechanisms of lymphatic gene expression.
Introduction
A well-organized lymphatic system including proper lymph fluid absorption and drainage is imperative for maintaining interstitial fluid and protein homeostasis. The lymphatic system is composed of a blind-ended, unidirectional network that contains absorptive vessels, primary lymphoid organs such as thymus and bone marrow, secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleen, and Peyer’s patches, and lymphoid tissues as adenoids and tonsils (Ruddle and Akirav, 2009; Choi et al., 2012). Lymphatic fluid is collected from the interstitial space into lymphatic capillaries, and these lymphatic vessels merge and gradually thicken as lymphatic collecting vessels. Lymph is eventually drained at the angulus venosus, which is the junction of the subclavian vein and internal jugular vein (Ruddle and Akirav, 2009; Choi et al., 2012; Randolph et al., 2017; Oliver et al., 2020). The lymphatic system also plays crucial roles in lipid absorption and transportation from the digestive tract to the blood circulation, as well as immune cell transport from the interstitium into the venous circulation (Alitalo et al., 2005; Tammela and Alitalo, 2010; Petrova and Koh, 2020; Landau et al., 2021). Lymphatic dysfunction causes interstitial fluid imbalance and edema, nutrient malabsorption, and inflammatory pathologies (Tammela and Alitalo, 2010; Saito et al., 2013; Abouelkheir et al., 2017). Lymphangiogenesis, the formation of new lymphatic vessels from the preexisting lymphatic vessels, relates to various diseases and pathologies such as lymphedema, tumor metastasis, and chronic inflammatory diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (Detmar and Hirakawa, 2002; Alitalo, 2011; Masood et al., 2022); however, the molecular mechanisms that regulate lymphatic endothelial cell proliferation and migration via transcriptional regulation remain largely unknown. In this review, we provide an update on the current knowledge regarding the development of the lymphatic vasculature and its mechanical force signals, especially focusing on transcriptional regulatory mechanisms.
The development of the lymphatic vascular system
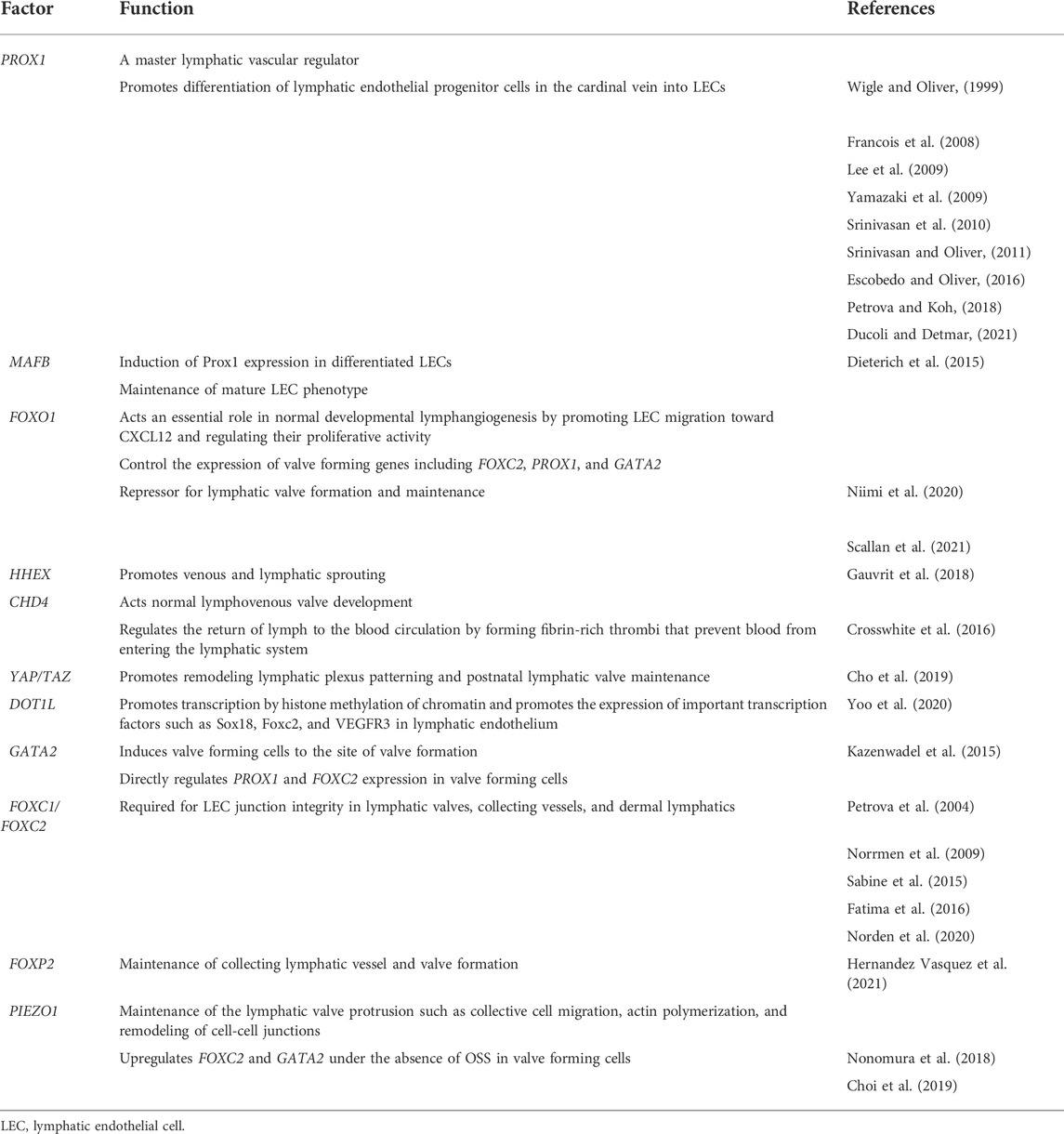
The development of the lymphatic vascular system initiates shortly after blood circulation is established in mouse embryos (Yang and Oliver, 2014). At embryonic day (E) 9.5, a subpopulation of lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells in the anterior cardinal vein start to express the Prospero-related homeobox 1 (PROX1) transcription factor, which is a master lymphatic vascular regulator (Wigle and Oliver, 1999; Francois et al., 2008; Ducoli and Detmar, 2021), and then differentiate into lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) (Lee et al., 2009; Yamazaki et al., 2009; Srinivasan et al., 2010; Srinivasan and Oliver, 2011; Escobedo and Oliver, 2016; Petrova and Koh, 2018). By around E10.0, PROX1 positive lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells expressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 3 sprout via stimulation with mesenchyme-derived VEGF-C ligand. These cells further migrate dorsolaterally from cardinal and intersomitic veins and establish primary lymph sacs and superficial lymphatic vessels identified as the jugular lymph sac by E11.5 (Wigle and Oliver, 1999; Karkkainen et al., 2004; Francois et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012; Hagerling et al., 2013; Stritt et al., 2021). Another study also suggests LEC fate is decided during transition through the paraxial mesoderm (PXM) lineage. PXM-derived ECs selectively transdifferentiate from the cardinal vein to form LEC progenitors and form the lymphatic endothelium of multiple organs and tissues (Stone and Stainier, 2019). There is accumulating evidence that mesenchyme- or non-venous derived lymphatic progenitor cells contribute to the early lymphatic vasculature and the development of the lymphatic vascular network in various organs including the skin, heart, and mesentery (Bernier-Latmani et al., 2015; Klotz et al., 2015; Martinez-Corral et al., 2015; Stanczuk et al., 2015; Kazenwadel and Harvey, 2016; Ducoli and Detmar, 2021). This network spreads throughout the mouse embryo by E14.5 and subsequently goes through remodeling and maturation from E15.5-E16.0, forming the hierarchical structure of the lymphatic vascular network in which lymphatic capillaries merge to form pre-collecting and collecting lymphatic vessels (Coso et al., 2014; Norden and Kume, 2020) (Figure 1).
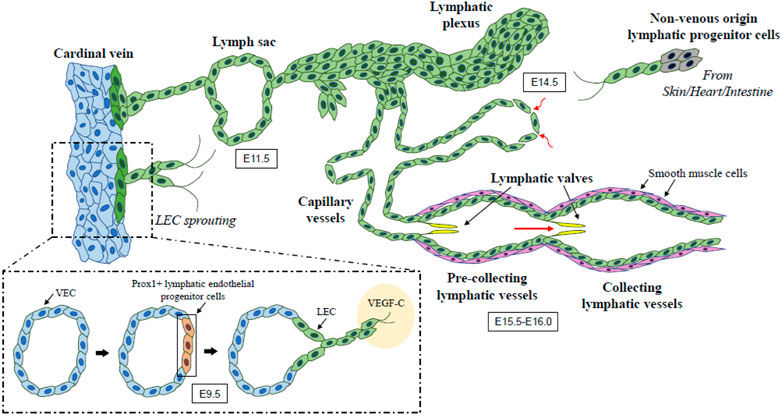
FIGURE 1. The developmental process of lymphatic vessel. Lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells in the cardinal vein begin to express PROX1 (known as a master lymphatic vascular regulator) at E9.5 and then differentiate into LECs expressing VEGFR3. VEGF-C/VEGFR3 signaling promotes the sprouting and migration of PROX1-positive LECs, which leads to the formation of lymph sacs and initial lymphatic plexus by E11.5. Extended sprouting and migration of LECs from the initial lymphatic structures give rise to the hierarchical lymphatic vessel network. Non-venous origin lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells also contribute to the early lymphatic vasculature and the development of its network. This network undergoes remodeling and maturation during E15.5-E16.0 and forms the organized lymphatic vascular network including lymphatic capillaries and pre-collecting and collecting lymphatic vessels. Arrows show the direction of lymph flow. LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; VEC, venous endothelial cell; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Lymphatic vessels are composed of lymphatic capillaries, which are also called initial lymphatics, and collecting lymphatic vessels. The basement membrane of lymphatic capillaries is discontinuous without lining of any pericytes or lymphatic smooth muscle cells (SMCs); therefore, they work for collecting excess plasma and interstitial fluid leaked from blood vessels (Norden and Kume, 2020). In contrast, collecting lymphatic vessels have lymphatic valves to prevent the backflow of lymph, and smooth muscle to transport lymph fluid by contraction (Kume, 2015). The development of the lymphatic vascular network is conducted by several critical signaling pathways including lymphangiogenic signaling such as the VEGF-C/D-VEGFR3 and Angiopoietin (Angpt)-tunica interna endothelial cell kinase (TEK, also known as Tie2) pathways (Potente and Makinen, 2017). Two transcription factors, the SRY-Box transcription factor 18 (SOX18) and the chick ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor 2 (COUP-TFII), also play an important role in lymphatic specification via the induction of PROX1 expression, whereas different pathways such as Notch, retinoic acid, and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling are involved in this process (Nicenboim et al., 2015; Ducoli and Detmar, 2021). VEGFR3 also regulates PROX1 by establishing a feedback loop necessary to maintain the identity of LEC progenitor cells, and VEGF-C-mediated activation of Vegfr3 signaling is required to maintain PROX1 expression in LEC progenitor cells (Srinivasan et al., 2014). In collecting lymphatic vessels, platelet-derived growth factor B (PDGFB) regulates lymphatic SMC recruitment, but PDGFB overexpression is insufficient to mediate recruitment to lymphatic capillaries (Wang et al., 2017).
A recent study has demonstrated the deficiency of Folliculin, a tumor suppressor, causes ectopic expression of PROX1 in venous endothelial cells (VECs), leading to the misconnection of blood and lymphatic vessels (Tai-Nagara et al., 2020). In LEC-biased VECs deficient for Folliculin, the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor E3 (TFE3) translocate into the nucleus, binds to a regulatory element of the PROX1 gene, and induces its ectopic venous expression (Tai-Nagara et al., 2020). Thus, in mice, it has been shown that the transition of lymphatic specification and differentiation from venous cell fate is tightly controlled during development. Importantly, the development of the zebrafish anal fin begins along with the formation of lymphatic vessels, but not blood vessels. Following the progressive loss of lymphatic markers during the anal fin growth, these vessels subsequently acquire a blood vessel fate leading to the connection to blood circulation. Thus, this specialized blood vessel formation occurs through LEC transdifferentiation (Das et al., 2022). Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis in this study further reveals that the loss of lymphatic fate results in the upregulation of several blood endothelial markers, such as VEGFR1, Delta-like (DLL) 4, and SRY-box (SOX) 17. Of note, mosaic overexpression of SOX17 in zebrafish ECs results in reduced lymphatic gene expression in the anal fin as well as the absence or incomplete formation of the thoracic duct (Das et al., 2022), demonstrating the importance of SOX17 function in the transition process.
Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation in lymphangiogenesis
Transcriptional regulation during lymphangiogenesis is strictly controlled, and recent evidence suggests the specific functions of several key transcription factors in lymphangiogenesis. The transcription factor V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B (MAFB), which is involved in the differentiation of various cell types, regulates the transcriptional changes invoked by VEGF-C in LECs (Dieterich et al., 2015; Dieterich et al., 2020; Rondon-Galeano et al., 2020; Arnold et al., 2022). MAFB induces the expression of PROX1, other transcription factors and markers of differentiated LECs, indicating the role of MAFB in the maintenance of the mature LEC phenotype (Dieterich et al., 2015). LEC-specific MAFB deficiency in mice causes increased lymphatic branching in the diaphragm at P7, enhanced tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis, increased perinatal lethality associated with cyanosis, and excessive smooth muscle cell coverage indicating a defect in the maturation of lymphatic networks. This suggests MAFB could be a potential target for therapeutic modulation of lymphangiogenesis (Dieterich et al., 2020; Rondon-Galeano et al., 2020). The transcription factor hematopoietically expressed homeobox (HHEX), an upstream regulator of VEGF-C/VEGFR3/PROX1 signaling during angiogenic sprouting and lymphatic formation, is required cell-autonomously in endothelial cells to promote venous and lymphatic sprouting. Mice deficient for HHEX exhibit severe vascular defects in blood and lymphatic vessel development (Gauvrit et al., 2018).
Forkhead box (Fox) O1, a member of the Fox transcription factor family, acts an essential role in developmental lymphangiogenesis by promoting LEC migration toward the chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL) 12 and regulating their proliferative activity (Niimi et al., 2020). The LEC-specific deletion of FOX O1 in mice decreases LEC migration toward CXCL12 by downregulating C-X-C chemokine receptor (CXCR) 4, induces excess LEC proliferation, and decreases LEC apoptosis, which leads to the disconnected and dilated structure of the lymphatic vessels (Niimi et al., 2020).
Brahma-related gene 1 (BRG1), a chromatin-remodeling enzyme, epigenetically regulates COUP-TFII expression, by remodeling chromatin within the COUP-TFII promoter and impacting the ability of transcriptional machinery to access the promoter (Davis et al., 2013). The EC-specific deletion of Brg1 in mice results in downregulation of COUP-TFII expression in developing veins (Davis et al., 2013).
Chromodomain helicase DNA-binding 4 (CHD4), an ATPase subunit of the nucleosome remodeling deacetylase (NuRD) chromatin-remodeling complex, regulates vascular integrity in the mid-gestation (Ingram et al., 2013). Specifically, CHD4 controls the development of lymphovenous valves, which regulates the return of lymph to the blood circulation by forming fibrin-rich thrombi that prevent blood from entering the lymphatic system (Crosswhite et al., 2016). The LEC-specific deletion of CHD4 in mice leads to increased transcription of the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), thereby facilitating activation of the fibrin-degrading protease plasmin and then degrading the fibrin near the lymphovenous valves (Crosswhite et al., 2016). In addition, CDH4 is functionally associated with the Hippo signaling pathway in lymphatic endothelial cells (Figure 2). The Hippo pathway final effectors Yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) promote remodeling of lymphatic plexus patterning and postnatal lymphatic valve maintenance by negatively regulating Prox1 expression (Cho et al., 2019). LEC-specific deletion of YAP/TAZ in mice suppresses both lymphatic plexus patterning and valve initiation via upregulation of PROX1, whereas LEC-specific YAP/TAZ overexpression downregulates PROX1, disrupts lymphatic specification, and restricts lymphatic sprouting (Cho et al., 2019).
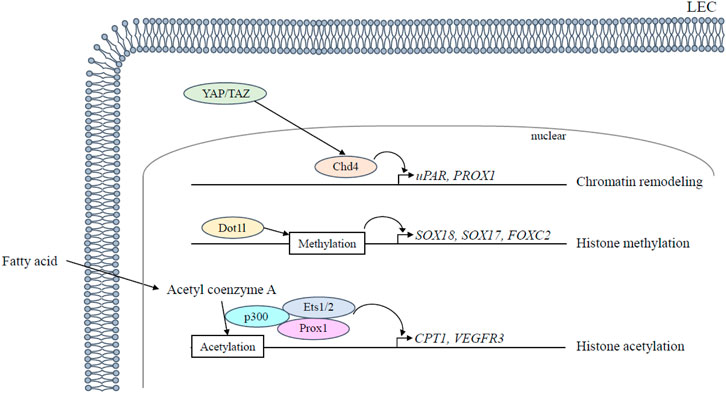
FIGURE 2. Epigenetic regulation in lymphangiogenesis. Epigenetic regulation regarding lymphatic development is mediated in LECs as follows: 1) Chd4 is functionally associated with the Hippo signaling pathway and downregulates Prox1 expression together with Hippo pathway final effectors YAP/TAZ; 2) Dot1l promotes transcription by histone methylation of chromatin; 3) Acetyl coenzyme A is used by the histone acetyltransferase p300 that interacts with Prox1 to acetylate histones. ETS 1/2 participates in VEGFR3 gene expression by recruiting the histone acetyltransferase p300 to the VEGFR3 locus and leading to histone acetylation. LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell.
Disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L), a histone H3 lysine (H3K) 79 methyltransferase, promotes transcription by histone methylation of chromatin and is a crucial factor in the homeostasis of various organs such as the heart and hematopoiesis (Jo et al., 2011; Nguyen et al., 2011). Vascular endothelial cell (VEC)-specific, but not LEC-specific, deletion of DOT1L causes fully penetrant lymphatic aplasia by altering the lymphatic transcription program and reducing H3K79me2 enrichment at lymphatic genes, including the transcription factors SOX18, SOX17, and FOXC2, which are critical for LEC differentiation and valve formation, as well as Vegfr3, which is critical for LEC proliferation and migration (Yoo et al., 2020) (Figure 2).
LECs use fatty acid β-oxidation for proliferation and epigenetic regulation of PROX1, which mediates epigenetic changes that promote lymphangiogenesis during LEC differentiation (Figure 2): 1) PROX1 upregulates carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) 1A expression, which increases fatty acid β-oxidation-dependent acetyl coenzyme A production; 2) Acetyl coenzyme A is used by the histone acetyltransferase p300 to acetylate histones at lymphangiogenic genes; 3) histone acetyltransferase p300 interacts with Prox1 to facilitate preferential histone acetylation at the loci of PROX1-targeted genes (Wong et al., 2017). LEC-specific deletion of CPT1A in mice impairs lymphatic vessel development by exhibiting severe impairment of dermal lymphatic vessel outgrowth and branching at E16.5. (Wong et al., 2017). Other transcription factors expressed in LEC, E26 avian leukemia oncogene (ETS) 1 and 2, act as downstream effectors of the Ras/MAPK pathway and participate in VEGFR3 gene expression in LECs by recruiting the histone acetyltransferase p300 to the VEGFR3 locus and leading to histone acetylation and transcriptional activation of the VEGFR3 promoter (Ichise et al., 2012). In addition, ETS2 enhances inflammatory lymphangiogenesis and endothelial migration towards VEGF-C through the induction of VEGFR3 expression by binding to the VEGFR3 promoter in concert with PROX1 (Yoshimatsu et al., 2011). Additionally, mitochondrial complex III also regulates the critical PROX1-VEGFR3 feedback loop. The functional inactivation of mitochondrial complex III impairs lymphatic vessel development by disrupting the maintenance of the PROX1-VEGFR3 feedback loop through the reduction in H3K4me3 and H3K27ac histone modifications at the VEGFR3 and PROX1 promoters (Ma et al., 2021).
Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation in lymphatic valve formation
Lymph flow is essential for the development and maturation of lymphatic valves (Kume, 2015), which play a critical role in preventing the backflow of lymph fluid. The lymphatic valves are formed from lymphatic endothelial cells, a process that is occurred by flow-dependent lymphatic vessel remodeling caused by oscillatory share stress (OSS) at branching points in the lymphatic plexus during the early stage of lymphatic development (Sabine et al., 2012; Shin and Lawson, 2021). The OSS response leads to an increase in the expression of GATA-binding protein 2 (GATA2), Prox1, and Foxc2, which induce valve forming cells to the site of valve formation (Kazenwadel et al., 2015; Sweet et al., 2015; Shin and Lawson, 2021). In valve forming cells, Gata2 directly regulates PROX1 and FOXC2 expression, whereas Foxc2 regulates valve maturation in cooperation with Prox1 to control intraluminal invagination of LECs and reorganization into valve forming leaflets by postnatal day (P)1 (Kazenwadel et al., 2015). As an upstream epigenetic factor, the histone-modifying enzyme histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) regulates lymphatic valve formation. In response to OSS, Hdac3 is recruited to the Gata2 enhancer element and physically interacts with the transcription factors T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia protein 1 (TAL1), Gata2, and Ets1/2 to promote Gata2 expression (Janardhan et al., 2017) (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3. Lymphatic valve formation. The lymphatic valves are formed through lymph flow-dependent lymphatic vessel remodeling. At the bifurcation of lymphatic vessels, the flow of lymph generates OSS (broken arrows) that leads to the upregulation of GATA2 in LECs via Hdac3 (A). Gata2 regulates PROX1 and FOXC2 expression to establish valve-forming cells (B). Following these processes, the valve formation area is determined (C), and the lymphatic valve (broken circle) has a role in keeping the lymph flow unidirectional (D). Red arrow shows the direction of lymph flow. LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; OSS, oscillatory share stress.
Human FOXC2 is a causative gene whose mutations are dominantly associated with lymphedema-distichiasis syndrome characterized by failure of lymph drainage in limbs, venous valve failure, and the growth of an extra set of eyelashes (Fang et al., 2000; Traboulsi et al., 2002; Mellor et al., 2007; Tavian et al., 2016). Foxc2 regulates connexin 37 expression and activation of calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) signaling during lymphatic collecting vessel maturation and valve formation (Petrova et al., 2004; Norrmen et al., 2009; Sabine et al., 2012). Foxc2 is also identified as a crucial factor for lymphatic valve maintenance by regulating LEC junctional integrity and cellular quiescence under reversing flow conditions via restriction of TAZ-mediated proliferation (Sabine et al., 2015). Foxc1 is a closely related member of the Fox transcription factor family, and LEC-specific deletion of FOXC1, FOXC2, or both in mice leads to increased LEC proliferation, enlarged lymphatic vessels, and abnormal lymphatic vessel morphogenesis, accompanied by increased Ras/ERK signaling during embryonic lymphangiogenesis (Fatima et al., 2016). Unlike FOXC2, LEC-specific FOXC1 mutant mice normally develop initial mesenteric lymphatic valves; however, the formation of matured lymphatic vessels (v-shaped or semilunar bi-leaflet structures) is significantly impaired (Norden et al., 2020). Importantly, the number of mesenteric lymphatic valves is remarkably reduced in the LEC-specific deletion of FOXC1 and FOXC2 compared to LEC-specific FOXC2 deletion alone, suggesting that FOXC1 and FOXC2 function cooperatively in the maturation and maintenance of lymphatic valves (Norden et al., 2020).
Foxo1 is crucial for controlling the expression of valve forming genes including FOXC2, PROX1, and GATA2 as a key downstream effector of shear stress by regulating lymphatic valve maintenance, and LEC-specific deletion of FOXO1 in mice leads to the formation of additional lymphatic valves compared to control mice (Scallan et al., 2021). Another study also reveals the role of Foxo1 as a repressor for lymphatic valve formation and maintenance via the inhibition of OSS-induced upregulation of lymphatic valve-specific genes such as PROX1 and FOXC2 (Niimi et al., 2021).
A recent study has shown that Foxp2, another Fox transcription factor previously implicated in speech development, is expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells of collecting vessels and their valve-forming cells, and that Foxp2 is induced after initiation of lymph flow and upon OSS on LECs (Hernandez Vasquez et al., 2021). LEC-specific FOXP2 mutant mice exhibit enlarged collecting vessels and defective lymphatic valves characterized by loss of NFATc1 activity (Hernandez Vasquez et al., 2021).
Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 (PIEZO1), a cation channel activated by mechanical forces such as fluid shear stress or membrane stretch, is a causative gene associated with congenital lymphedema with pleural effusion (Nonomura et al., 2018). The LEC-specific deletion of PIEZO1 in mice leads to a reduction in the number of lymphatic valves and impairments in lymphatic valve protrusion such as collective cell migration, actin polymerization, and remodeling of cell-cell junctions, whereas the expression patterns of Foxc2 and NFATc1, both of which are crucial factors for lymphatic valve development, are normally detected in these mutant mice (Nonomura et al., 2018). Another study demonstrated that PIEZO1 is the force sensor in the mechanotransduction pathway controlling lymphatic valve development and maintenance, although PIEZO1 knockdown in cultured LECs largely abrogated the OSS-induced upregulation of the lymphatic valve signature genes including FOXC2 and GATA2 (Choi et al., 2019). Moreover, overexpressing PIEZO1 in cultured LECs upregulates FOXC2 and GATA2 in the absence of OSS, demonstrating that ectopic expression of PIEZO1 can recapitulate the lymphatic valve gene profile (Choi et al., 2019). Treatment with Yoda1, a chemical agonist of PIEZO1, leads to changes in LEC morphology by inducing the remodeling of actomyosin and/or VE-cadherin+ cell–cell adhesion and activates the expression of some lymphatic valve genes such as FOXC2 and GATA2 in a PIEZO1-dependent manner (Nonomura et al., 2018; Choi et al., 2019). Together, these results suggest that the activation of mechanosensitive PIEZO1 can control, at least in part, transcriptional regulation of lymphatic valve forming cells under the absence of mechanical forces.
Concluding remarks
Many studies have been conducted on the formation, maintenance, and function of lymphatic vessels, which are essential to maintain homeostasis. This review focuses on the mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in LECs during lymphatic vessel development (Table 1), but the precise control of lymphatic gene expression in lymphangiogenesis under physiological and pathological conditions remains unexplored. Recent single-cell RNA-sequencing studies using LEC markers such as PROX1 and VEGFR3 have started to clarify LEC heterogeneity in various organs including functional multiformity. For example, single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis using the zebrafish anal fin was the key to characterizing the different endothelial cell populations and transition states involved in the LEC transdifferentiation process (Das et al., 2022). Moreover, single-cell transcriptomic analysis of normal and glaucomatous Angpt1 deficient eyes has recently identified distinct trabecular meshwork (TM) and Schlemm’s canal (SC) cell populations and revealed additional TM-SC signaling pathways (Thomson et al., 2021). Yet, additional comprehensive studies are needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms of transcriptional regulation of LECs with which the signaling pathways are associated. In particular, uncovering the transcriptional mechanisms underlying lymphangiogenesis will likely lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies for various diseases regarding lymphatic vessels.
Author contributions
NU contributed to the writing of the manuscript and making the figures. TK contributed to the concepts, editing, and final formatting of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01HL144129 and R01HL159976 to TK).
Acknowledgments
We thank Can Tan (Northwestern University) for her helpful advice.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abouelkheir G. R., Upchurch B. D., Rutkowski J. M. (2017). Lymphangiogenesis: Fuel, smoke, or extinguisher of inflammation's fire? Exp. Biol. Med. 242, 884–895. doi:10.1177/1535370217697385
Alitalo K., Tammela T., Petrova T. V. (2005). Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature 438, 946–953. doi:10.1038/nature04480
Alitalo K. (2011). The lymphatic vasculature in disease. Nat. Med. 17, 1371–1380. doi:10.1038/nm.2545
Arnold H., Panara V., Hussmann M., Filipek-Gorniok B., Skoczylas R., Ranefall P., et al. (2022). Mafba and mafbb differentially regulate lymphatic endothelial cell migration in topographically distinct manners. Cell Rep. 39, 110982. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110982
Bernier-Latmani J., Sabine A., Petrova T. V. (2015). Meet me in the middle: Dual origins of dermal lymphatic vasculature in mammals. Circ. Res. 116, 1630–1632. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306436
Cho H., Kim J., Ahn J. H., Hong Y. K., Makinen T., Lim D. S., et al. (2019). YAP and TAZ negatively regulate Prox1 during developmental and pathologic lymphangiogenesis. Circ. Res. 124, 225–242. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313707
Choi D., Park E., Jung E., Cha B., Lee S., Yu J., et al. (2019). Piezo1 incorporates mechanical force signals into the genetic program that governs lymphatic valve development and maintenance. JCI Insight 4, 125068. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.125068
Choi I., Lee S., Hong Y. K. (2012). The new era of the lymphatic system: No longer secondary to the blood vascular system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2, a006445. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a006445
Coso S., Bovay E., Petrova T. V. (2014). Pressing the right buttons: Signaling in lymphangiogenesis. Blood 123, 2614–2624. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-12-297317
Crosswhite P. L., Podsiadlowska J. J., Curtis C. D., Gao S., Xia L., Srinivasan R. S., et al. (2016). CHD4-regulated plasmin activation impacts lymphovenous hemostasis and hepatic vascular integrity. J. Clin. 126, 2254–2266. doi:10.1172/JCI84652
Das R. N., Tevet Y., Safriel S., Han Y., Moshe N., Lambiase G., et al. (2022). Generation of specialized blood vessels via lymphatic transdifferentiation. Nature 606, 570–575. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04766-2
Davis R. B., Curtis C. D., Griffin C. T. (2013). BRG1 promotes COUP-TFII expression and venous specification during embryonic vascular development. Development 140, 1272–1281. doi:10.1242/dev.087379
Detmar M., Hirakawa S. (2002). The formation of lymphatic vessels and its importance in the setting of malignancy. J. Exp. Med. 196, 713–718. doi:10.1084/jem.20021346
Dieterich L. C., Klein S., Mathelier A., Sliwa-Primorac A., Ma Q., Hong Y. K., et al. (2015). DeepCAGE transcriptomics reveal an important role of the transcription factor MAFB in the lymphatic endothelium. Cell Rep. 13, 1493–1504. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.10.002
Dieterich L. C., Tacconi C., Menzi F., Proulx S. T., Kapaklikaya K., Hamada M., et al. (2020). Lymphatic MAFB regulates vascular patterning during developmental and pathological lymphangiogenesis. Angiogenesis 23, 411–423. doi:10.1007/s10456-020-09721-1
Ducoli L., Detmar M. (2021). Beyond PROX1: Transcriptional, epigenetic, and noncoding RNA regulation of lymphatic identity and function. Dev. Cell 56, 406–426. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2021.01.018
Escobedo N., Oliver G. (2016). Lymphangiogenesis: Origin, specification, and cell fate determination. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 32, 677–691. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-111315-124944
Fang J., Dagenais S. L., Erickson R. P., Arlt M. F., Glynn M. W., Gorski J. L., et al. (2000). Mutations in FOXC2 (MFH-1), a forkhead family transcription factor, are responsible for the hereditary lymphedema-distichiasis syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67, 1382–1388. doi:10.1086/316915
Fatima A., Wang Y., Uchida Y., Norden P., Liu T., Culver A., et al. (2016). Foxc1 and Foxc2 deletion causes abnormal lymphangiogenesis and correlates with ERK hyperactivation. J. Clin. Invest. 126, 2437–2451. doi:10.1172/JCI80465
Francois M., Caprini A., Hosking B., Orsenigo F., Wilhelm D., Browne C., et al. (2008). Sox18 induces development of the lymphatic vasculature in mice. Nature 456, 643–647. doi:10.1038/nature07391
Francois M., Short K., Secker G. A., Combes A., Schwarz Q., Davidson T. L., et al. (2012). Segmental territories along the cardinal veins generate lymph sacs via a ballooning mechanism during embryonic lymphangiogenesis in mice. Dev. Biol. 364, 89–98. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.032
Gauvrit S., Villasenor A., Strilic B., Kitchen P., Collins M. M., Marin-Juez R., et al. (2018). HHEX is a transcriptional regulator of the VEGFC/FLT4/PROX1 signaling axis during vascular development. Nat. Commun. 9, 2704. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05039-1
Hagerling R., Pollmann C., Andreas M., Schmidt C., Nurmi H., Adams R. H., et al. (2013). A novel multistep mechanism for initial lymphangiogenesis in mouse embryos based on ultramicroscopy. EMBO J. 32, 629–644. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.340
Hernandez Vasquez M. N., Ulvmar M. H., Gonzalez-Loyola A., Kritikos I., Sun Y., He L., et al. (2021). Transcription factor FOXP2 is a flow-induced regulator of collecting lymphatic vessels. EMBO J. 40, e107192. doi:10.15252/embj.2020107192
Ichise T., Yoshida N., Ichise H. (2012). Ras/MAPK signaling modulates VEGFR-3 expression through Ets-mediated p300 recruitment and histone acetylation on the Vegfr3 gene in lymphatic endothelial cells. PLoS One 7, e51639. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051639
Ingram K. G., Curtis C. D., Silasi-Mansat R., Lupu F., Griffin C. T. (2013). The NuRD chromatin-remodeling enzyme CHD4 promotes embryonic vascular integrity by transcriptionally regulating extracellular matrix proteolysis. PLoS Genet. 9, e1004031. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004031
Janardhan H. P., Milstone Z. J., Shin M., Lawson N. D., Keaney J. F., Trivedi C. M. (2017). Hdac3 regulates lymphovenous and lymphatic valve formation. J. Clin. Invest. 127, 4193–4206. doi:10.1172/JCI92852
Jo S. Y., Granowicz E. M., Maillard I., Thomas D., Hess J. L. (2011). Requirement for Dot1l in murine postnatal hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis by MLL translocation. Blood 117, 4759–4768. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-12-327668
Karkkainen M. J., Haiko P., Sainio K., Partanen J., Taipale J., Petrova T. V., et al. (2004). Vascular endothelial growth factor C is required for sprouting of the first lymphatic vessels from embryonic veins. Nat. Immunol. 5, 74–80. doi:10.1038/ni1013
Kazenwadel J., Betterman K. L., Chong C. E., Stokes P. H., Lee Y. K., Secker G. A., et al. (2015). GATA2 is required for lymphatic vessel valve development and maintenance. J. Clin. 125, 2979–2994. doi:10.1172/JCI78888
Kazenwadel J., Harvey N. L. (2016). Morphogenesis of the lymphatic vasculature: A focus on new progenitors and cellular mechanisms important for constructing lymphatic vessels. Dev. Dyn. 245, 209–219. doi:10.1002/dvdy.24313
Klotz L., Norman S., Vieira J. M., Masters M., Rohling M., Dube K. N., et al. (2015). Cardiac lymphatics are heterogeneous in origin and respond to injury. Nature 522, 62–67. doi:10.1038/nature14483
Kume T. (2015). Lymphatic vessel development: Fluid flow and valve-forming cells. J. Clin. 125, 2924–2926. doi:10.1172/JCI83189
Landau S., Newman A., Edri S., Michael I., Ben-Shaul S., Shandalov Y., et al. (2021). Investigating lymphangiogenesis in vitro and in vivo using engineered human lymphatic vessel networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118, e2101931118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2101931118
Lee S., Kang J., Yoo J., Ganesan S. K., Cook S. C., Aguilar B., et al. (2009). Prox1 physically and functionally interacts with COUP-TFII to specify lymphatic endothelial cell fate. Blood 113, 1856–1859. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-03-145789
Ma W., Gil H. J., Liu X., Diebold L. P., Morgan M. A., Oxendine-Burns M. J., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial respiration controls the Prox1-Vegfr3 feedback loop during lymphatic endothelial cell fate specification and maintenance. Sci. Adv. 7, eabe7359. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abe7359
Martinez-Corral I., Ulvmar M. H., Stanczuk L., Tatin F., Kizhatil K., John S. W., et al. (2015). Nonvenous origin of dermal lymphatic vasculature. Circ. Res. 116, 1649–1654. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306170
Masood F., Bhattaram R., Rosenblatt M. I., Kazlauskas A., Chang J. H., Azar D. T. (2022). Lymphatic vessel regression and its therapeutic applications: Learning from principles of blood vessel regression. Front. Physiol. 13, 846936. doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.846936
Mellor R. H., Brice G., Stanton A. W., French J., Smith A., Jeffery S., et al. (2007). Mutations in FOXC2 are strongly associated with primary valve failure in veins of the lower limb. Circulation 115, 1912–1920. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.675348
Nguyen A. T., Xiao B., Neppl R. L., Kallin E. M., Li J., Chen T., et al. (2011). DOT1L regulates dystrophin expression and is critical for cardiac function. Genes Dev. 25, 263–274. doi:10.1101/gad.2018511
Nicenboim J., Malkinson G., Lupo T., Asaf L., Sela Y., Mayseless O., et al. (2015). Lymphatic vessels arise from specialized angioblasts within a venous niche. Nature 522, 56–61. doi:10.1038/nature14425
Niimi K., Kohara M., Sedoh E., Fukumoto M., Shibata S., Sawano T., et al. (2020). FOXO1 regulates developmental lymphangiogenesis by upregulating CXCR4 in the mouse-tail dermis. Development 147 (2), dev181545. doi:10.1242/dev.181545
Niimi K., Nakae J., Inagaki S., Furuyama T. (2021). FOXO1 represses lymphatic valve formation and maintenance via PRDM1. Cell Rep. 37, 110048. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110048
Nonomura K., Lukacs V., Sweet D. T., Goddard L. M., Kanie A., Whitwam T., et al. (2018). Mechanically activated ion channel PIEZO1 is required for lymphatic valve formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, 12817–12822. doi:10.1073/pnas.1817070115
Norden P. R., Kume T. (2020). Molecular mechanisms controlling lymphatic endothelial junction integrity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 627647. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.627647
Norden P. R., Sabine A., Wang Y., Demir C. S., Liu T., Petrova T. V., et al. (2020). Shear stimulation of FOXC1 and FOXC2 differentially regulates cytoskeletal activity during lymphatic valve maturation. Elife 9, e53814. doi:10.7554/eLife.53814
Norrmen C., Ivanov K. I., Cheng J., Zangger N., Delorenzi M., Jaquet M., et al. (2009). FOXC2 controls formation and maturation of lymphatic collecting vessels through cooperation with NFATc1. J. Cell Biol. 185, 439–457. doi:10.1083/jcb.200901104
Oliver G., Kipnis J., Randolph G. J., Harvey N. L. (2020). The lymphatic vasculature in the 21(st) century: Novel functional roles in homeostasis and disease. Cell 182, 270–296. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.039
Petrova T. V., Karpanen T., Norrmen C., Mellor R., Tamakoshi T., Finegold D., et al. (2004). Defective valves and abnormal mural cell recruitment underlie lymphatic vascular failure in lymphedema distichiasis. Nat. Med. 10, 974–981. doi:10.1038/nm1094
Petrova T. V., Koh G. Y. (2020). Biological functions of lymphatic vessels. Science 369, eaax4063. doi:10.1126/science.aax4063
Petrova T. V., Koh G. Y. (2018). Organ-specific lymphatic vasculature: From development to pathophysiology. J. Exp. Med. 215, 35–49. doi:10.1084/jem.20171868
Potente M., Makinen T. (2017). Vascular heterogeneity and specialization in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 477–494. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.36
Randolph G. J., Ivanov S., Zinselmeyer B. H., Scallan J. P. (2017). The lymphatic system: Integral roles in immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 35, 31–52. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055354
Rondon-Galeano M., Skoczylas R., Bower N. I., Simons C., Gordon E., Francois M., et al. (2020). MAFB modulates the maturation of lymphatic vascular networks in mice. Dev. Dyn. 249, 1201–1216. doi:10.1002/dvdy.209
Ruddle N. H., Akirav E. M. (2009). Secondary lymphoid organs: Responding to genetic and environmental cues in ontogeny and the immune response. J. Immunol. 183, 2205–2212. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0804324
Sabine A., Agalarov Y., Maby-El Hajjami H., Jaquet M., Hagerling R., Pollmann C., et al. (2012). Mechanotransduction, PROX1, and FOXC2 cooperate to control connexin37 and calcineurin during lymphatic-valve formation. Dev. Cell 22, 430–445. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.12.020
Sabine A., Bovay E., Demir C. S., Kimura W., Jaquet M., Agalarov Y., et al. (2015). FOXC2 and fluid shear stress stabilize postnatal lymphatic vasculature. J. Clin. 125, 3861–3877. doi:10.1172/JCI80454
Saito Y., Nakagami H., Kaneda Y., Morishita R. (2013). Lymphedema and therapeutic lymphangiogenesis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 804675. doi:10.1155/2013/804675
Scallan J. P., Knauer L. A., Hou H., Castorena-Gonzalez J. A., Davis M. J., Yang Y. (2021). Foxo1 deletion promotes the growth of new lymphatic valves. J. Clin. 131, 142341. doi:10.1172/JCI142341
Shin M., Lawson N. D. (2021). Back and forth: History of and new insights on the vertebrate lymphatic valve. Dev. Growth Differ. 63, 523–535. doi:10.1111/dgd.12757
Srinivasan R. S., Escobedo N., Yang Y., Interiano A., Dillard M. E., Finkelstein D., et al. (2014). The Prox1-Vegfr3 feedback loop maintains the identity and the number of lymphatic endothelial cell progenitors. Genes Dev. 28, 2175–2187. doi:10.1101/gad.216226.113
Srinivasan R. S., Geng X., Yang Y., Wang Y., Mukatira S., Studer M., et al. (2010). The nuclear hormone receptor Coup-TFII is required for the initiation and early maintenance of Prox1 expression in lymphatic endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 24, 696–707. doi:10.1101/gad.1859310
Srinivasan R. S., Oliver G. (2011). Prox1 dosage controls the number of lymphatic endothelial cell progenitors and the formation of the lymphovenous valves. Genes Dev. 25, 2187–2197. doi:10.1101/gad.16974811
Stanczuk L., Martinez-Corral I., Ulvmar M. H., Zhang Y., Lavina B., Fruttiger M., et al. (2015). cKit lineage hemogenic endothelium-derived cells contribute to mesenteric lymphatic vessels. Cell Rep. 10, 1708–1721. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.026
Stone O. A., Stainier D. Y. R. (2019). Paraxial mesoderm is the major source of lymphatic endothelium. Dev. Cell 50, 247–255. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.034
Stritt S., Koltowska K., Makinen T. (2021). Homeostatic maintenance of the lymphatic vasculature. Trends Mol. Med. 27, 955–970. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2021.07.003
Sweet D. T., Jimenez J. M., Chang J., Hess P. R., Mericko-Ishizuka P., Fu J., et al. (2015). Lymph flow regulates collecting lymphatic vessel maturation in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 125, 2995–3007. doi:10.1172/JCI79386
Tai-Nagara I., Hasumi Y., Kusumoto D., Hasumi H., Okabe K., Ando T., et al. (2020). Blood and lymphatic systems are segregated by the FLCN tumor suppressor. Nat. Commun. 11, 6314. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20156-6
Tammela T., Alitalo K. (2010). Lymphangiogenesis: Molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell 140, 460–476. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.045
Tavian D., Missaglia S., Maltese P. E., Michelini S., Fiorentino A., Ricci M., et al. (2016). FOXC2 disease-mutations identified in lymphedema-distichiasis patients cause both loss and gain of protein function. Oncotarget 7, 54228–54239. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.9797
Thomson B. R., Liu P., Onay T., Du J., Tompson S. W., Misener S., et al. (2021). Cellular crosstalk regulates the aqueous humor outflow pathway and provides new targets for glaucoma therapies. Nat. Commun. 12, 6072. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26346-0
Traboulsi E. I., Al-Khayer K., Matsumoto M., Kimak M. A., Crowe S., Wilson S. E., et al. (2002). Lymphedema-distichiasis syndrome and FOXC2 gene mutation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 134, 592–596. doi:10.1016/s0002-9394(02)01642-2
Wang Y., Jin Y., Mae M. A., Zhang Y., Ortsater H., Betsholtz C., et al. (2017). Smooth muscle cell recruitment to lymphatic vessels requires PDGFB and impacts vessel size but not identity. Development 144, 3590–3601. doi:10.1242/dev.147967
Wigle J. T., Oliver G. (1999). Prox1 function is required for the development of the murine lymphatic system. Cell 98, 769–778. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81511-1
Wong B. W., Wang X., Zecchin A., Thienpont B., Cornelissen I., Kalucka J., et al. (2017). The role of fatty acid beta-oxidation in lymphangiogenesis. Nature 542, 49–54. doi:10.1038/nature21028
Yamazaki T., Yoshimatsu Y., Morishita Y., Miyazono K., Watabe T. (2009). COUP-TFII regulates the functions of Prox1 in lymphatic endothelial cells through direct interaction. Genes 14, 425–434. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01279.x
Yang Y., Garcia-Verdugo J. M., Soriano-Navarro M., Srinivasan R. S., Scallan J. P., Singh M. K., et al. (2012). Lymphatic endothelial progenitors bud from the cardinal vein and intersomitic vessels in mammalian embryos. Blood 120, 2340–2348. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-05-428607
Yang Y., Oliver G. (2014). Development of the mammalian lymphatic vasculature. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 888–897. doi:10.1172/JCI71609
Yoo H., Lee Y. J., Park C., Son D., Choi D. Y., Park J. H., et al. (2020). Epigenetic priming by Dot1l in lymphatic endothelial progenitors ensures normal lymphatic development and function. Cell Death Dis. 11, 14. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-2201-1
Keywords: lymphatic system, lymphatic vascular development, lymphangiogenesis, valve formation, transcriptional regulation
Citation: Ujiie N and Kume T (2022) Mechanical forces in lymphatic vessel development: Focus on transcriptional regulation. Front. Physiol. 13:1066460. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1066460
Received: 10 October 2022; Accepted: 26 October 2022;
Published: 10 November 2022.
Edited by:
Toshio Ohhashi, Shinshu University, JapanReviewed by:
Yoshiko Kawai, Tohoku Medical and Pharmaceutical University, JapanMasanori Hirashima, Niigata University, Japan
Copyright © 2022 Ujiie and Kume. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tsutomu Kume, dC1rdW1lQG5vcnRod2VzdGVybi5lZHU=
 Naoto Ujiie
Naoto Ujiie Tsutomu Kume
Tsutomu Kume