- Department of Physiology and Cell Biology, College of Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, United States
A Corrigendum on
Muscle Twitch Kinetics Are Dependent on Muscle Group, Disease State, and Age in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mouse Models
by Peczkowski, K. K., Rastogi, N., Lowe, J., Floyd, K. T., Schultz, E. J., Karaze, T., et al. (2020) Front. Physiol. 11:568909. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.568909
Error in Figure/Table
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 3 as published. In Figure 3, the C57 EDL RT50% data (Figure 3A, dataset 8) was erroneously duplicated from the C57 DIA RT50% data (Figure 3A, dataset 4). This mistake happened when we re-made our figures for the final submission. The data in the text, as well as statistics, all outcomes, and all conclusions, are all based on the correct data. The corrected Figure 3 appears below.
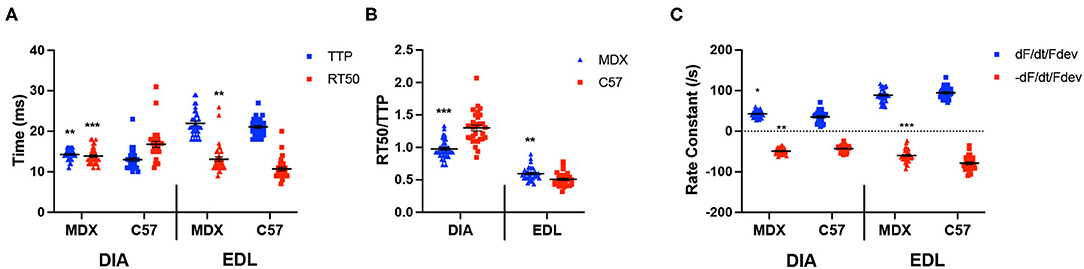
Figure 3. (A) Time to peak and 50% relaxation of 52 week old dystrophic and wildtype muscle types. Kinetic analysis was conducted in diaphragm and EDL muscles from the same mice. Mouse models include dystrophic MDX and wildtype C57BL/10. Statistical analysis was conducted using a two-sided t-test. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared to C57BL/10 mice. The line represents the group mean; error bars are standard error of mean. (B) 50% relaxation of 52 week old dystrophic and wildtype muscle types. Mouse models include dystrophic MDX and wildtype C57BL/10. Statistical analysis was conducted using a two-sided t-test. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared to C57BL/10 mice. The line represents the group mean; error bars are standard error of mean. (C) Rate constants of individual diaphragm and EDL twitches. Mouse models include dystrophic MDX and wildtype C57BL/10. Statistical analysis was conducted using a two-sided t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared to C57BL/10 mice. The line represents the group mean; error bars are standard error of mean.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: skeletal muscle, muscular dystrophies, contraction, relaxation, age
Citation: Peczkowski KK, Rastogi N, Lowe J, Floyd KT, Schultz EJ, Karaze T, Davis JP, Rafael-Fortney JA and Janssen PML (2022) Corrigendum: Muscle Twitch Kinetics Are Dependent on Muscle Group, Disease State, and Age in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mouse Models. Front. Physiol. 12:820245. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.820245
Received: 22 November 2021; Accepted: 10 December 2021;
Published: 05 January 2022.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2022 Peczkowski, Rastogi, Lowe, Floyd, Schultz, Karaze, Davis, Rafael-Fortney and Janssen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Paul M. L. Janssen, amFuc3Nlbi4xMEBvc3UuZWR1
 Kyra K. Peczkowski
Kyra K. Peczkowski Neha Rastogi
Neha Rastogi Jonathan P. Davis
Jonathan P. Davis Paul M. L. Janssen
Paul M. L. Janssen