- 1Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China
- 2Electric Power Research Institute, CSG, Guangzhou, China
Dissolved gas analysis (DGA) of transformer oil can deeply understand the operation status of oil-immersed transformers, and detect early transformer failures as early as possible, thus achieving the purpose of preventing further damage to the transformer. It is a highly reliable method for identifying early-stage faults in transformers. This paper reviews the commonly used sensing technologies for analyzing dissolved gases in transformer oil, including Raman spectroscopy (RS), fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) and photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS). The progress of research on these four gas sensing technologies is reviewed, with a detailed analysis of their respective principles and characteristics. This work provides guidance for the selection of appropriate online gas preliminary sensing technology, which is essential for the assessment of transformer operating conditions to ensure the stable operation of power systems.
1 Introduction
Power transformer is a significance part of the power system, its operational reliability affects the safety and stability of the system. Failure of power transformers during operation not only leads to transformer damage or even complete failure, but also may cause extensive interruptions that may paralyze the entire power grid and cause huge economic losses [1]. Thus, monitoring the health of power transformers is a crucial step in ensuring the stable operation of power grids [2]. At the same time, this can often improve the operational efficiency of the transformer and extend its life, to a certain extent, but also to avoid the occurrence of catastrophic accidents, from the protection of human life and property safety [3].
During prolonged operation or abnormal conditions, transformers are affected by heat and electricity, which may result in the decomposition of the paper and oil in them to produce gases, thus affecting the performance of the transformer or even causing damage [4, 5]. The gases produced from the decomposition of oil include hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), acetylene (C2H2), ethylene (C2H4), and ethane (C2H6), while the decomposition of paper leads to the production of carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) [6–9]. The concentration of the gases produced due to the faults allows an assessment of the transformer faults as well as their severity. DGA is a very common and effective method for assessing the condition of transformers. By analyzing the rule of change of different types of dissolved gases and combining advanced optical sensing technology, it serves as a foundation for the operation and maintenance of equipment. It contributes to prolonging the lifespan of the equipment and mitigating the risks associated with its operation, which is highly significant for the advancement of the power industry.
In recent years, a variety of gas sensing technologies for detecting dissolved gases have been widely researched and applied. These technologies can be broadly categorized into non-spectroscopic and spectroscopic technologies. Among the non-spectroscopic technologies, gas chromatography (GC) is now widely used in the analysis of dissolved gases [10]. This technology is highly sensitive and has a wide detection range, but it requires the consumption of carrier gas and a long analysis time, which makes it unsuitable for online monitoring. However, spectroscopic technologies are non-contact gas sensing technologies that do not require carrier gas, offer high detection sensitivity, fast analysis speeds, and are particularly well-suited for online monitoring. As a result, they have become a focal point of research in recent years [11, 12]. Commonly used spectroscopic technologies for the analysis of dissolved gases include RS, FTIR, TDLAS, and PAS. This paper reviews and discusses the research progress of these four technologies in the analysis of dissolved gases in transformer oil. It introduces the sensing principles of each technology, explains their advantages and disadvantages, and provides a comparative analysis.
2 Transformer fault types and gas concentration
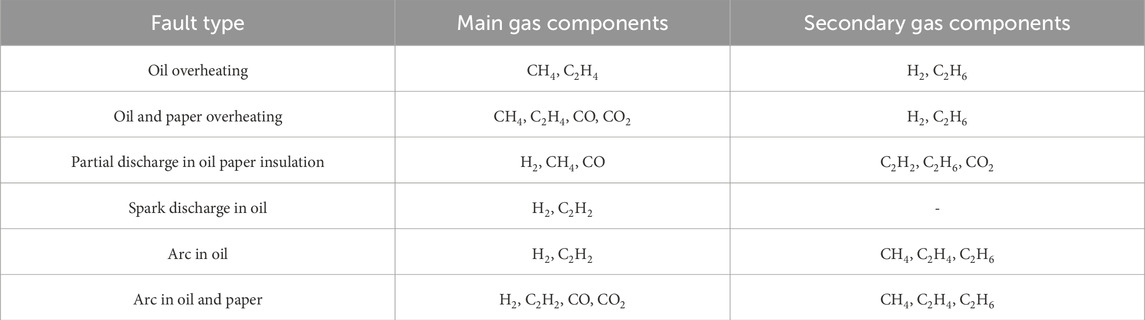
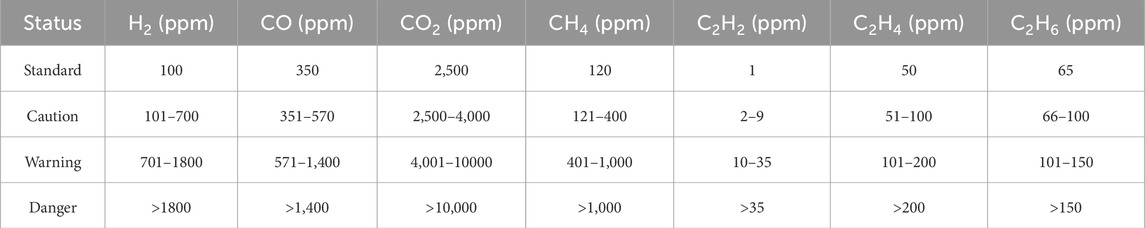
The structure of the transformer is very complex, the internal failure types are diverse, mainly can be divided into electrical, thermal, mechanical three types of failure, which, mechanical failure is usually in the form of electrical failure or thermal failure, so the transformer failure is mainly in the form of faults and thermal faults two kinds of faults as the main form of expression [13]. The characteristic gas components corresponding to different types of faults in transformers are shown in Table 1 [14], and the concentrations of dissolved gases in different states are shown in Table 2 [15]. By monitoring the type and content of characteristic gases dissolved in transformer oil, the fault type and severity of the transformer can be diagnosed, and early latent faults inside the transformer can be predicted.
3 Infrared gas molecular absorption spectroscopy
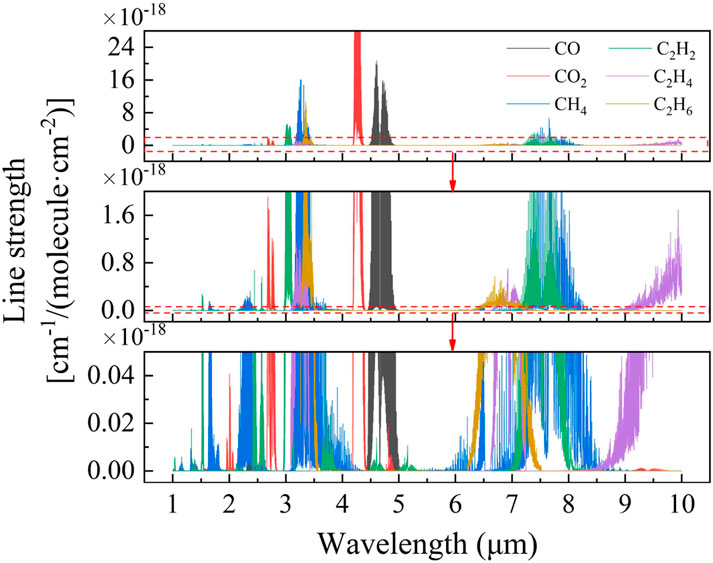
FTIR, TDLAS and PAS are all technologies based on infrared absorption spectroscopy, where gases selectively absorb infrared light. Moreover, the same gas can absorb infrared light at different wavelengths to different extents. As a result, different gas molecules have unique absorption spectra, often referred to as their “fingerprint” spectra. The absorption spectra of various fault gases, as simulated from the database, are shown in Figure 1 [16]. In selecting spectral lines, key considerations include the intensity of the spectral lines and the avoidance of mutual interference between them. The infrared spectroscopy process relies on the Lambert-Beer law: As a laser beam of a specific wavelength passes through some specific gas molecules, it is absorbed, causing the intensity of the light to decay. By measuring the strength of the transmitted laser light, information about the concentration of the gas molecules can be obtained.
4 RS
RS is based on the Raman scattering effect, a technology that analyzes the structure and properties of a substance by measuring the Raman-scattered light produced when a laser illuminates it. RS offers several advantages, including non-destructive testing, rapid analysis, and simplicity. As a result, it is extensively used in fields such as chemical analysis and biomedicine [17–20]. Over the past few years, with the continuous progress of Raman enhancement technology, RS has been increasingly used in the analysis of dissolved gases.
4.1 Principles of RS
In 1923, Smekal predicted Raman scattering [21], and in 1928, Raman experimentally discovered it [22]. The principle of RS as shown schematically in Figure 2A. Electrons in gas molecules absorb photons with energy
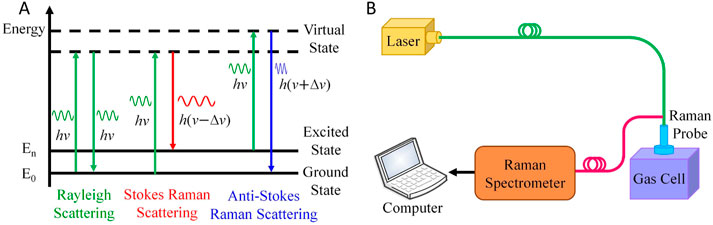
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of RS. (A) Principle of Raman scattering. (B) A typical RS gas sensing technology device.
4.2 Survey on RS-based on DGA in transformer oil
In 1997, Liu et al. introduced a method for online monitoring of dissolved CH4 and C2H2 concentrations using RS [24]. Over the nearly 10 years that followed, there were relatively few reports on the use of RS for sensing dissolved gases in transformer oil. One reason for this may be the high cost of early RS sensing systems, which were primarily used in laboratory settings and seldom applied in industrial environments. Another challenge is the low concentration of dissolved gases, which makes it difficult to detect trace gases using RS alone. This issue requires the integration of RS enhancement technologies to achieve accurate detection. However, with advancements in laser and fiber optic technologies in recent years, the application scope of RS has significantly expanded.
In 2008, Li et al. designed a multi-trace gas Raman sensing system for the detection of dissolved gases, and the experimental setup is shown in Figure 3A [25]. This system employed a near-confocal cavity to enhance the sensitivity for detecting trace gases, and the experimental results are shown in Figure 3B. The minimum detection limits (MDLs) of the system for C2H2, C2H2, CO2, CH4, and H2 were 42, 63, 126, 21, and 96.6 ppm, respectively. These MDLs achieve the requirements for monitoring dissolved gases and are capable of on-line monitoring.
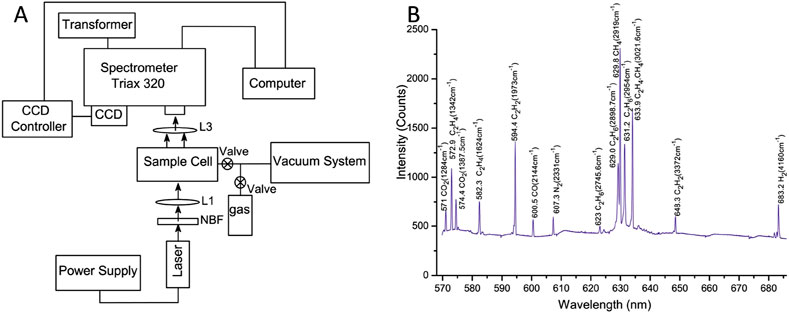
Figure 3. Schematic diagram and experimental results. (A) Whole experimental setup. (B) Raman spectra of eight gases. Reprinted with permission from Li et al. [25], Copyright © 2008, Springer-Verlag.
In 2013, Somekawa et al. proposed an RS-based method for in-situ sensing of dissolved gases in oil [26]. The method avoids the tedious step of separating oil and gas and allows direct analysis using RS to detect the composition of dissolved gases. In 2014 Chen et al. analyzed Raman spectra of multiple critical fault gases in transformer oil [27]. In order to promote the utilization of incident light and the collection of scattered light, a quartz glass tube with a silver-plated inner wall was employed as the gas cell, thereby improving the sensitivity of gas Raman sensing. This system achieved a MDL of 5 ppm for C2H2. While this approach increases the detection sensitivity to some extent, the silver layer on the inside of the quartz glass tube may oxidize under certain environmental conditions, which could affect the stability of the system.
In 2015, Qi et al. developed a confocal micro RS-based system for detecting dissolved gases [28]. To enhance detection sensitivity, they incorporated a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrate, which achieved Raman signal enhancement through the coupling effect of localized surface plasmon resonance. In 2016, Wan et al. designed a frequency-locked cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (FLCERS) system for the detection of faulty gases. This system, based on the principle of frequency locking of Raman scattering and cavity length modulation, enabled the simultaneous detection of seven different fault gases [29]. The MDLs of the system for CH4, C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, CO, CO2, and H2 were 25, 45, 73, 41, 170, 126, and 106 ppm, respectively. The frequency-locked enhanced cavity technology significantly improved the system’s performance, increasing its sensitivity by approximately 68 times. In 2018, Wang et al. developed an experimental system based on fiber-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (FERS) [30]. By utilizing a hollow-core photonic crystal fiber as gas cell, they increased the light length, thus increasing the photon collection rate. The system is capable of detecting Raman spectra of many different gas mixtures together.
In 2020, Wang et al. designed a V-shaped cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (CERS) system to identify key fault gases associated with transformer failures. The experimental setup is shown in Figure 4A [31]. The system utilized optical feedback frequency-locked technology to couple the laser into a high-precision optical resonant cavity, leading to a significant increase in intracavity laser power, approximately 2,100 times greater than the incident laser power. Using CERS, the fault gases characteristic of transformer failures were detected qualitatively, and the Raman spectra for each gas were captured, as illustrated in Figure 4B. The system did not require a high-power laser source, had a gas MDL in the ppm range at 1 atm cell pressure, and provided highly sensitive detection of a wide range of fault gases.
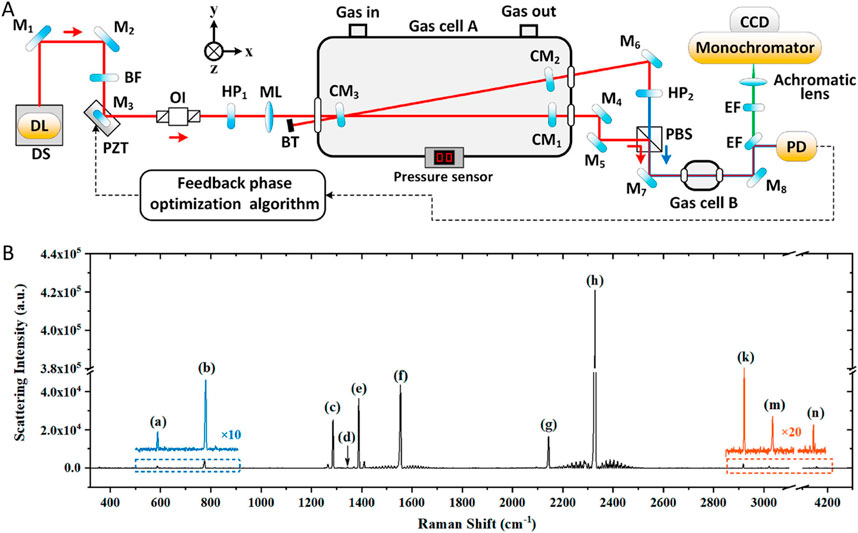
Figure 4. Schematic diagram and experimental results. (A) Whole experimental setup. (B) Raman spectra of each gas. Reprinted with permission from Wang et al. [31], Copyright © 2020, American Chemical Society.
In 2022, Wang et al. employed hollow-core anti-resonant optical fiber to develop a fiber-enhanced RS system for detecting dissolved gases. The system is responsible for detecting a wide range of gases in the ambient air of the laboratory [32]. It achieved a stable laser-fiber coupling efficiency of approximately 85%. The MDLs for H2, CO, CO2, CH4, C2H6, C2H4, and C2H2 gases were 8, 22, 5, 2, 6, 3, and 3 ppm, respectively.
RS offers several advantages over traditional gas sensing methods, such as overcoming cross-interference between different gas components, improving detection stability, and enabling the detection of all gases. However, the Raman scattering intensity for trace gases is weak owing to the small Raman scattering cross-section of the gas itself, leading to relatively low sensitivity of RS-based gas sensing. To address this limitation, technologies like SERS, FERS, and CERS are often employed to enhance detection sensitivity.
SERS can improve the sensitivity of gas RS to some extent, but the use of metal nanoparticles introduces challenges such as susceptibility to oxidation. Even slight changes in the SERS substrate can cause significant fluctuations in the sensing results. As a result, SERS tends to suffer from poor stability and low repeatability. In contrast, FERS typically employs hollow-core photonic crystal fibers as the gas cell. This significantly increases the effective laser path length and enhances the efficiency of Raman scattering light collection, thus improving detection sensitivity. FERS also requires only a small amount of gas, making it highly suitable for gas sensing. However, the small core diameter of the fiber may slow down gas entry, and fiber bending losses can affect the intensity of the Raman scattering, which limits its performance to some extent. CERS is known for its high sensitivity and offers good long-term stability and repeatability, thanks to its cavity-enhancement technology. However, CERS requires high technical precision, including accurate cavity length, mirror reflectivity, and proper alignment of cavity mirrors. Furthermore, it demands high optical stability and has strict requirements regarding the type of gas being measured.
5 FTIR
FTIR is a broadband spectroscopic measurement technology known for its high sensitivity, fast response time, and ability to simultaneously measure multiple gas components. Over the past few years, FTIR has been extensively applied in the fields of fire scene analysis, coal mine safety, atmospheric monitoring [33–35]. With advancements in FTIR technology, it has also become commonly used for the analysis of dissolved gases.
5.1 Principles of FTIR
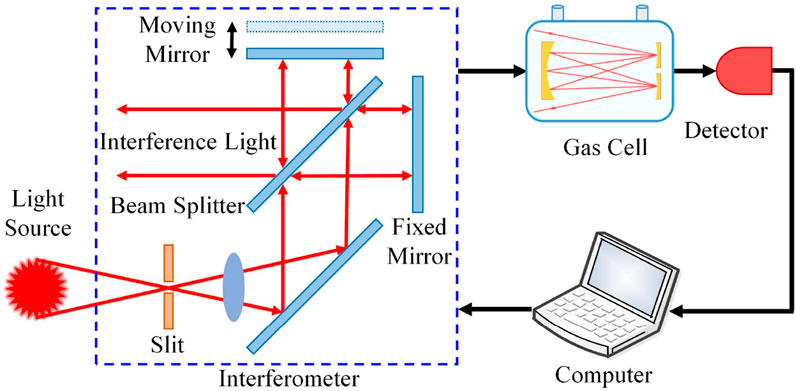
The schematic of a typical FTIR spectrometer is shown in Figure 5. The infrared light is split into two beams as it passes through the interferometer. These beams then travel toward the moving mirror and the fixed mirror, respectively. As the moving mirror shifts at a constant speed, the infrared light passing through it and the light passing through the fixed mirror accumulate a specific optical path difference. The two beams, now with this optical path difference, reconvene at the beam splitter, where they combine to produce interference light. This interference light is then processed by the interferometer and interacts with the gas sample as it passes through the gas chamber. Finally, the light is detected by a detector [36].
5.2 Survey on FTIR-based DGA in transformer oil
In 2002, Liu et al. utilized a closed gas cell with an optical length of 2.4 m (physical length of 11.5 cm) to analyze dissolved gases in transformer oil [37]. Their results demonstrated that all diagnostic gases, except H2, could be accurately detected using FTIR. The MDLs for CO, CO2, CH4, C2H2, C2H4, and C2H6 were 2.8, 0.9, 0.6, 0.3, 1.9, and 17 ppm, respectively. FTIR showed great potential for enabling real-time, simultaneous measurement of dissolved gases, significantly contributing to the development of online monitoring and fault diagnosis for power transformers. The following year, they further improved the technology, achieving MDLs of 0.43, 0.03, 0.09, 0.02, 0.12, and 0.36 ppm for CO, CO2, CH4, C2H2, C2H4, and C2H6, respectively [38].
In 2005, Li et al. employed FTIR to collect absorption spectra of C2H2, a key gas for diagnosing transformer faults. They fitted curves to the output characteristics and investigated how the concentration range and the selection of quantitative features influenced the accuracy of the quantification [39]. For C2H2, the MDLs were below 0.3 ppm using a 2.4-meter gas cell and below 3 ppm using a 10 cm gas cell. In 2014, Zhao et al. simulated transformer operating conditions and developed a comprehensive experimental system based on FTIR in the laboratory [40]. They applied the spectral baseline correction by piecewise dividing (SBCPD) algorithm and the Tikhonov regularization algorithm, which improved the accuracy of the computed results.
For conventional FTIR spectrometers, a large amount of gas is needed to fill the tubular gas cell. In 2018, Tang et al. introduced a novel two-cone shaped gas cell to reduce the required gas volume, as illustrated in Figure 6A. A standard mixture of gases extracted from transformer oil was analyzed, and a physical diagram of the on-site FTIR inspection is shown in Figure 6B [41]. The experimental results showed that the MDLs for all gases were below 0.1 ppm, which met the detection requirements.
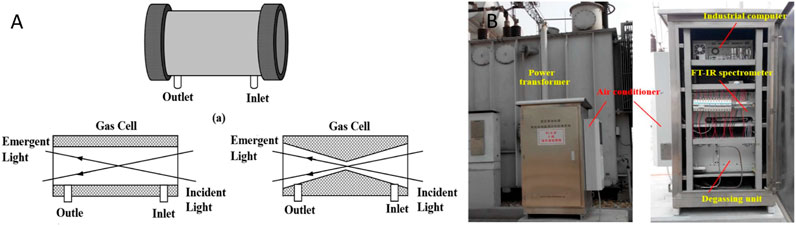
Figure 6. Experimental setup. (A) Two-cone shape gas cell. (B) Physical diagram. Reprinted with permission from Tang et al. [41], licensed under CC BY 4.0.
In 2019, Jiang et al. introduced an FTIR-based method that eliminates the need for oil-gas separation, aiming to enable real-time and accurate measurement of dissolved gases [42]. The results showed that the method could be used at a 4 cm optical length with an MDL of 194.5 ppm for C2H2. This work provides a foundation for developing a new DGA technology that does not require the oil-gas separation process. In 2024, Darwish et al. designed two test cells, illustrated in Figures 7A, B, to investigate both electrical and thermal faults in the laboratory [43]. FTIR was used to analyze gas samples and assess the condition of the oil under various fault scenarios. The results, shown in Figures 8A–C, demonstrated that the FTIR spectral data outperformed traditional diagnostic methods, highlighting its superior ability to detect early-stage transformer faults.
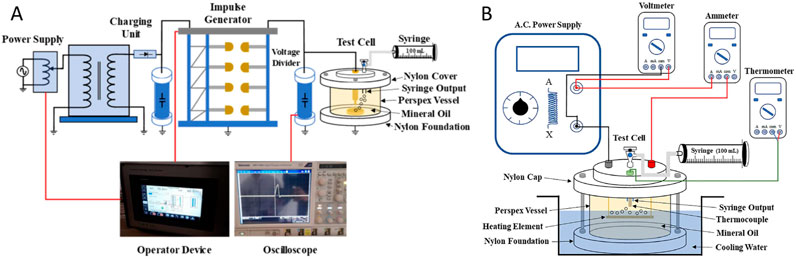
Figure 7. Schematic of the two test cells. (A) Electrical fault. (B) Thermal fault. Reprinted with permission from Darwish et al. [43], licensed under CC BY.
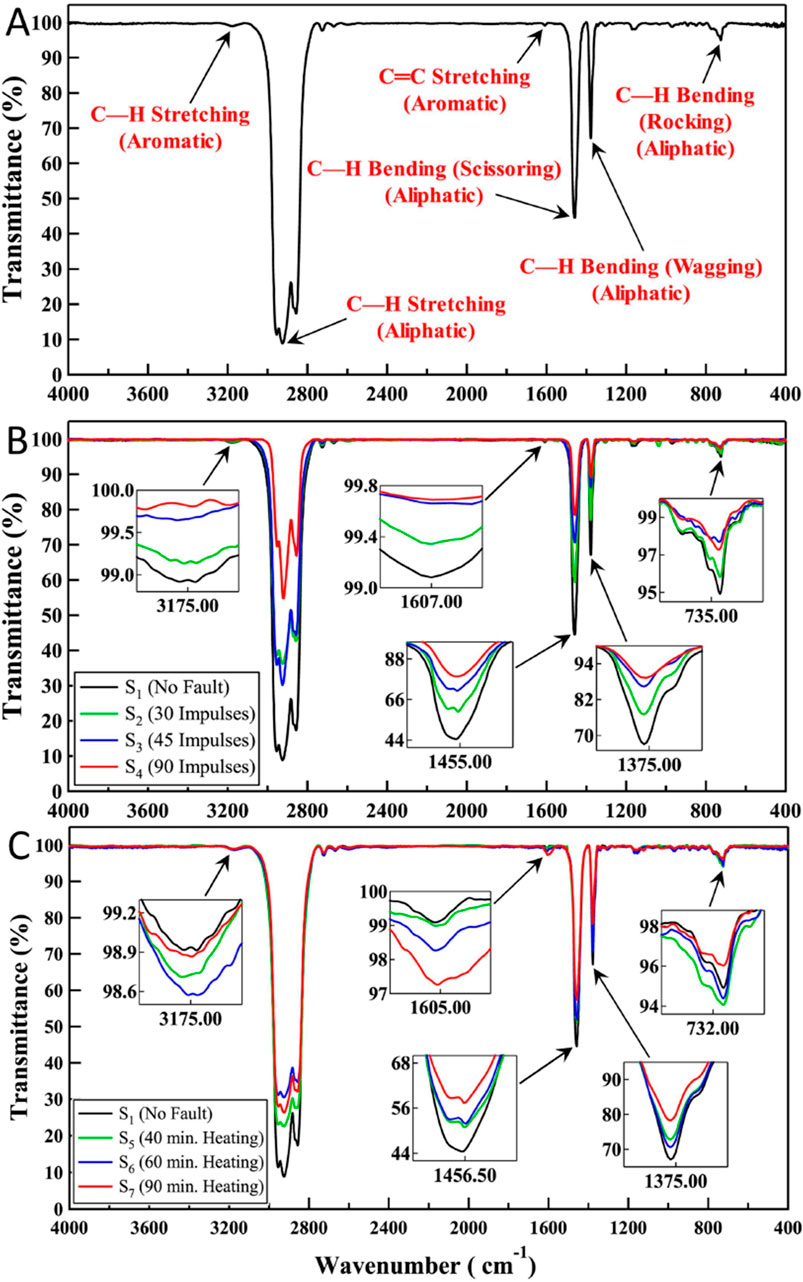
Figure 8. FTIR spectral. (A) No-fault. (B) Electrical fault. (C) Thermal fault. Reprinted with permission from Darwish et al. [43], licensed under CC BY.
Compared to RS, FTIR has higher sensitivity and faster response times, making it ideal for a variety of analytical applications. However, FTIR is more susceptible to environmental factors such as humidity, which can lead to inaccurate results and limit its use in certain conditions. In addition, FTIR instruments are larger, more complex and more expensive to maintain, requiring regular calibration and care to avoid contamination. Despite these drawbacks, FTIR remains a well-suited technology for dissolved gas sensing in oil when used in a controlled environment.
6 TDLAS
TDLAS has seen rapid development in recent years owing its high sensitivity and selectivity, making it widely used in environmental monitoring, industrial production, and biomedical fields [44–49]. However, the application of TDLAS to the analysis of dissolved gases lagged behind that of RS and FTIR. With the growing expansion of TDLAS in research applications, it has gradually evolved into a commercial technology for high-precision multi-component gas concentration sensing [50, 51], and is now increasingly applied to gas analysis in transformer oil.
6.1 Principles of TDLAS
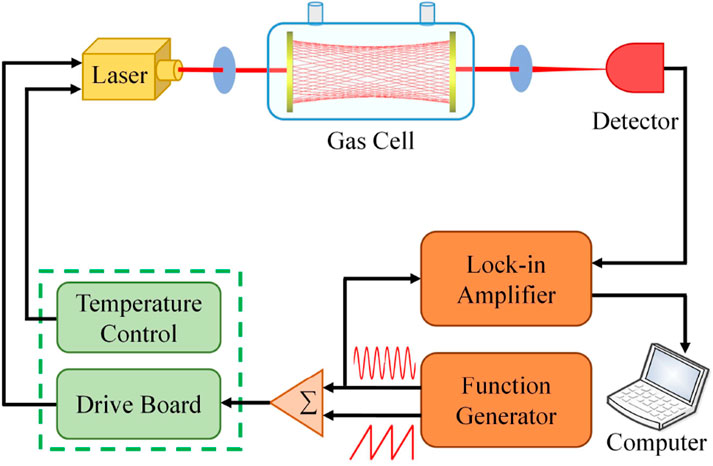
TDLAS utilizes the infrared absorption properties of gases. According to Lambert-Beer law, it analyzes the reduction of laser energy due to the selective absorption by gas molecules, thereby determining the composition and concentration of the gas. TDLAS may be classified into two main categories: direct absorption spectroscopy and modulated absorption spectroscopy [52, 53]. A typical TDLAS experimental setup is shown in Figure 9.
6.2 Survey on TDLAS-based on DGA in transformer oil
In 2016, Jiang et al. introduced a promising new method for the detection of dissolved CH4 using TDLAS and performed methane sensing experiments in the laboratory [54]. The system achieved a detection cycle of under 5 min, with a MDL of 0.28 ppm at the SNR of 3:1. The system offers several advantages, including rapid response to concentration changes, no cross-interference, and the absence of a carrier gas, making it a promising, maintenance-free technology that could potentially replace traditional DGA equipment. In 2017, Ma et al. developed an optical gas sensing system based on TDLAS for detecting dissolved C2H2 [55]. The experimental setup is shown in Figure 10A. The detection process was completed in just 8 min, with an MDL of 0.49 ppm for C2H2 at the SNR of 3:1. Furthermore, as illustrated in Figure 10B, the system showed no interference from other fault gases in the detection of C2H2.
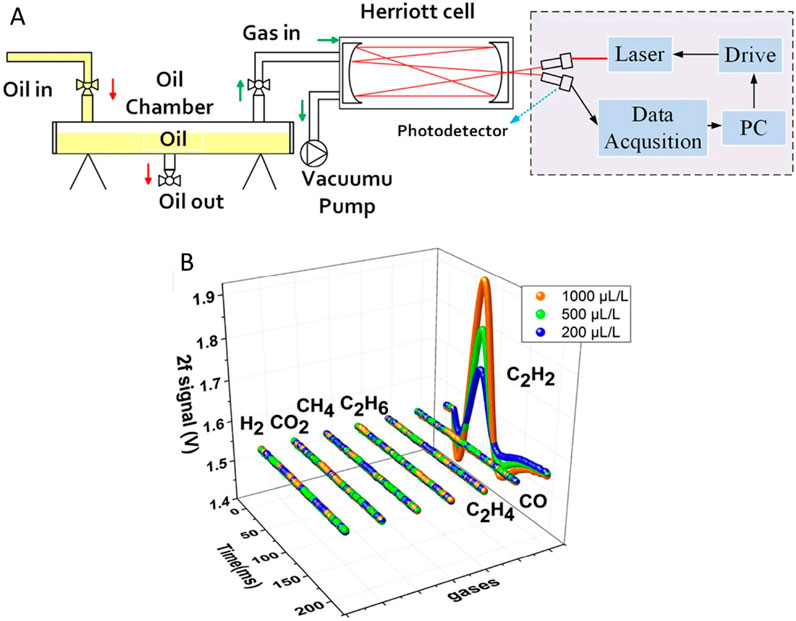
Figure 10. Schematic diagram and experimental results. (A) The experimental setup. (B) 2f signal of seven gases. Reprinted with permission from Ma et al. [55], licensed under CC BY.
In 2018, Jiang et al. developed a vibration-resistant integrated Herriott cell to address the practical challenges of field trials [56]. The photodetector, collimator, and Herriott cell were combined into a single unit to minimize the impact of vibrations. The following year, they introduced a TDLAS system for multi-gas sensing [57]. This system utilized a gas cell with an extended optical length of 10.13 m to further mitigate the effects of field vibrations. The TDLAS-based online testing equipment was deployed for monitoring of a 220 kV main transformer. The results indicated that the system’s error levels met the standards of the relevant criteria. They proved the effectiveness of TDLAS for transformer condition testing through field trials.
In 2021, Chen et al. developed an online sensing system to measure the concentration of dissolved multi-component gases using TDLAS [58]. The system employed three lasers to detect gases: a 1,684 nm laser for CH4, C2H4, and C2H6; a 1,579 nm laser for CO and CO2; and a 1,532 nm laser for C2H2. The experimental setup are presented in Figures 11A, B. To enhance the structural robustness of the optical system, a common optical path was created using a time-division multiplexing technology. Experimental results showed that the error for C2H2 detection reached the ppb level, while errors for the other gases were in the ppm range. The results of the TDLAS system for various gases are shown in Figure 11C. The results of the experiments complied with the test criteria and the condition of the transformer was evaluated on the basis of the detected gas concentrations.
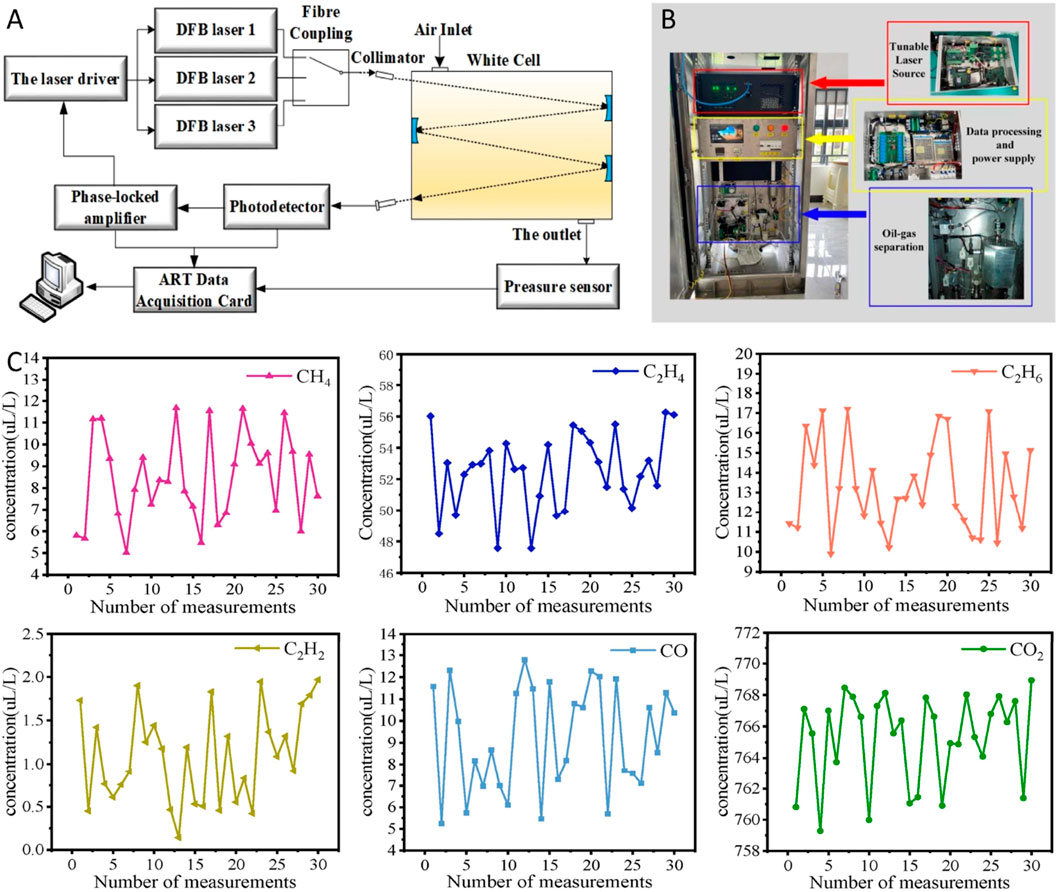
Figure 11. Experimental setup and results. (A) Schematic diagram. (B) Physical diagram. (C) Measurement results of the TDLAS system for various gases. Reprinted with permission from Chen et al. [58], licensed under CC BY 4.0.
TDLAS offers exceptional sensitivity and selectivity, making it highly effective for detecting trace gases with precision. However, in multi-gas sensing applications, TDLAS typically requires multiple lasers to target the distinct absorption features of each gas, which can complicate system design and increase operational costs. The stability and reliability of TDLAS systems are key issues, as fluctuations in laser performance, detector sensitivity, and environmental conditions can reduce measurement accuracy. Therefore, the current focus is on improving the stability, miniaturization, and cost-effectiveness of TDLAS based multi gas sensing systems to meet the growing demand for continuous, real-time, and high-precision gas analysis.
7 PAS
PAS differs to other direct absorption technologies in that it is not a direct measurement of light intensity. Instead, it relies on the indirect detection of acoustic signals, offering a measurement approach with zero background noise. PAS has a wide range of applications in a variety of fields such as environmental monitoring, industrial production and biomedical research [59–72].
7.1 Principles of PAS
PAS is based on the photoacoustic effect, and its sensing principle is illustrated in Figure 12A. When a modulated or pulsed laser irradiates gas molecules, the molecules absorb the incident light, causing a transition from the ground state to an excited state. Subsequently, the molecules undergo a non-radiative transition through a collisional relaxation process, where the energy released is converted into the internal energy of the molecules, leading to a localized temperature increase. This periodic temperature fluctuation induces corresponding expansion and contraction of the gas volume, generating acoustic waves that are detected by sensors such as microphones [73]. A typical PAS experimental setup is shown in Figure 12B.
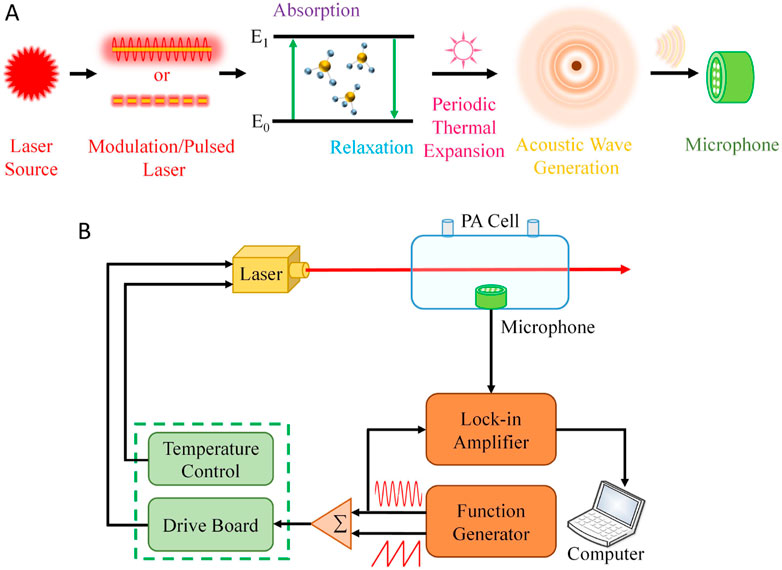
Figure 12. Schematic diagram of PAS. (A) Principle of photoacoustic effect. (B) A typical experimental setup for PAS.
7.2 Survey on PAS-based on DGA in transformer oil
In 2008, Yun et al. employed electric pulse infrared light combined with filters to detect fault gases in transformer oil [74]. The results obtained from PAS were compared with those from conventional GC, demonstrating that PAS is an accurate method for detecting dissolved gases. In 2011, Li et al. utilized a small-volume non-resonant photoacoustic cell and a microphone to detect CO and CO2, achieving MDLs of 3 ppm for CO and 10 ppm for CO2 [75]. In 2015, Mao et al. designed a PAS system to detect dissolved gases, as shown in Figures 13A, B [76]. The MDLs of this system were 4 ppb for C2H2, 39 ppm for CO, and 34 ppm for CO2. Furthermore, they investigated the relationship between high-voltage discharge and the generation of C2H2 gas using a discharge simulation device.
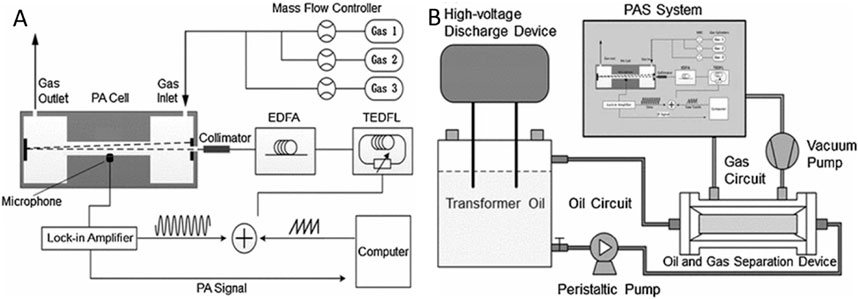
Figure 13. Experimental setup. (A) Schematic of the PAS. (B) Diagram of the experimental setup. Reprinted with permission from Mao et al. [76], Copyright © 2014, Springer Science Business Media New York.
In 2018, Li et al. introduced a PAS system incorporating an active gas cell structure. The system featured an integrated design that combined the active gas cell, resonance tube, microphone, and photodetector [77]. The experimental results demonstrated that the MDLs for C2H2, CH4, and CO were 0.5, 0.5, and 1 ppm, respectively. This design effectively addressed the limitations associated with the large size of traditional photoacoustic cells and the complexities of calibrating the light source. By miniaturizing the PAS system, the authors were able to enhance both measurement accuracy and operational stability. In 2019, Zhou et al. designed an immersion PAS (iPAS) system specifically to detect arc faults [78]. This iPAS system could be directly submerged in an oil bath to detect dissolved C2H2, with an MDL of 47 ppb for C2H2. Notably, the system eliminates the need for oil-gas separation, offering a simple structure, ease of operation, and adaptability for detecting other gases associated with transformer faults.
In 2020, Yang et al. incorporated fiber laser power amplification technology to enhance the laser power from 20 mW to 200 mW [79]. They developed a cantilever beam Fabry-Pérot (F-P) fiber acoustic sensor probe, specifically designed for matching the resonance frequency of the photoacoustic cell. This configuration enabled dual resonance enhancement for both the cantilever beam and the photoacoustic cell. As a result, the system achieved a MDL of 15 ppb for C2H2. In 2021, Chen et al. introduced a portable PAS system that utilized an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) to further enhance detection sensitivity [80]. The system achieved an MDL of 3.4 ppb for C2H2. This portable, integrated design simplifies operation and maintenance, allowing for wider application in various scenarios.
In 2022, Chen et al. designed a PAS gas sensing system with ultra-high sensitivity [81]. To enhance the laser power, they utilized an EDFA, which significantly increased the intensity of the signal. The enhanced signal was then detected using a cantilevered fiber-optic acoustic sensor, achieving a MDL of 50 ppb for C2H2. In the same year, Li et al. proposed a multi-pass absorption-enhanced photoacoustic spectrometer (MPAEPAS) for analyzing dissolved based on a combined light source [82]. Absorption enhancement was achieved through multiple reflections, as illustrated in the experimental setup shown in Figure 14A. The system utilized mid-infrared broad-spectrum light to detect dissolved C2H6, C2H4, CO, and CO2, and a DFB laser to detect C2H2 and CH4, respectively. As shown in Figure 14B, revealed that the MDLs for dissolved CO, CO2, CH4, C2H2, C2H4, and C2H6 were 30, 100, 3, 0.5, 3, and 3 ppm, respectively. The instrument demonstrates high accuracy and provides a technical solution for monitoring of dissolved multi-component gases.
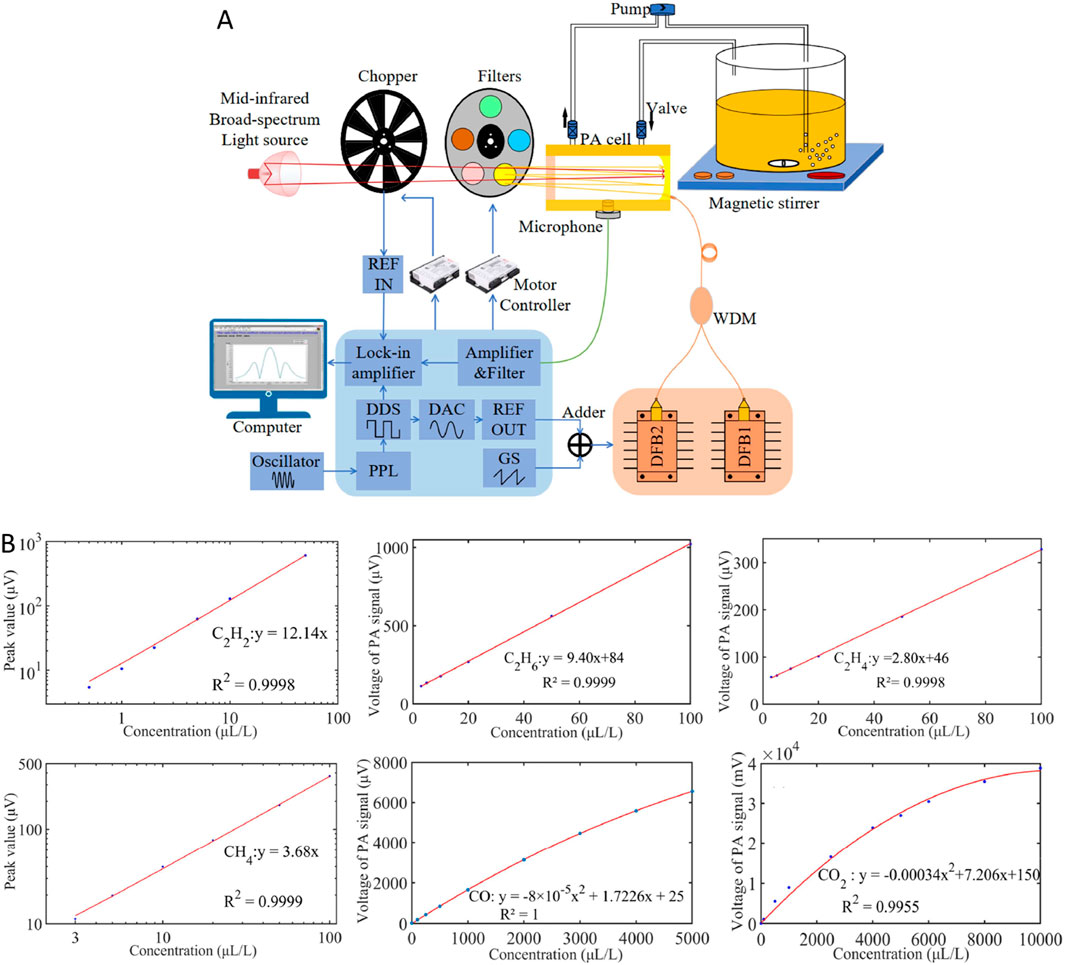
Figure 14. MPAEPAS experimental setup and results. (A) Experimental setup for MPAEPAS (B) The MPAEPAS for various gases. Reprinted with permission from Li et al. [82], © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
PAS, like TDLAS, has the advantages of fast response speed and high sensitivity. Moreover, PAS is not limited by wavelength and has a wide measurement range. These features make PAS highly suitable for detecting low concentrations of gases in real-time. However, similar to TDLAS, multi-gas sensing in PAS typically requires the use of multiple lasers, each targeting specific absorption features of different gases, which can lead to increased system complexity, cost, and maintenance requirements. Despite these challenges, PAS remains a promising technique for high-precision, multi-component gas sensing in both laboratory and field applications.
8 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages
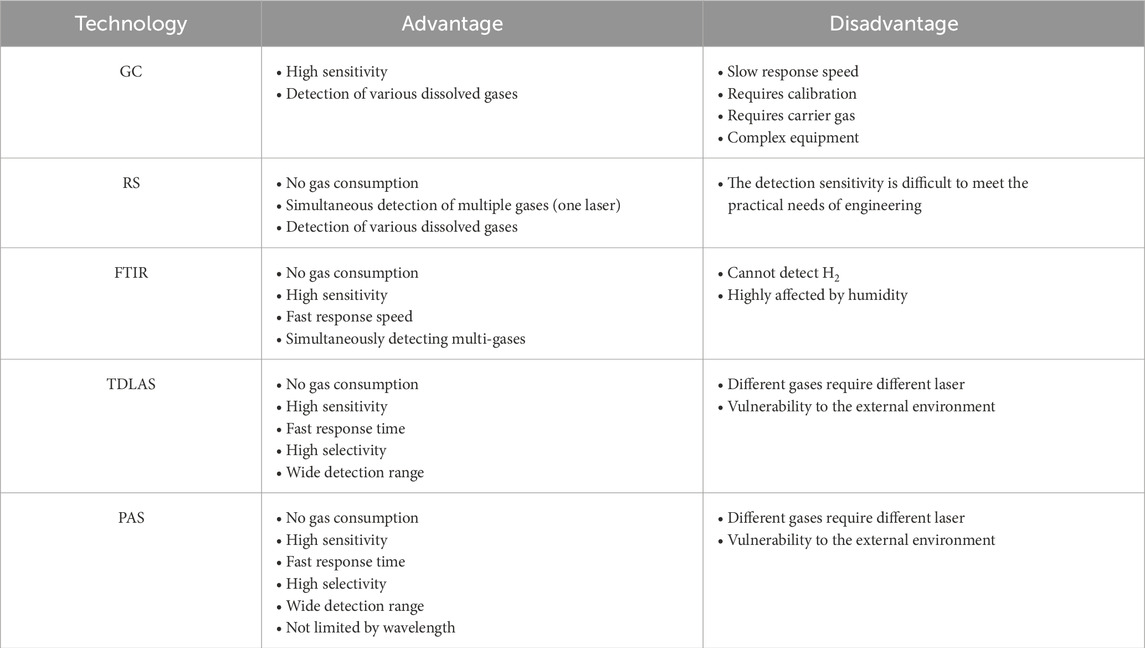
Table 3 summarizes the performance and characteristics of commonly used technologies for DGA in transformer oil. Non-optical gas sensing technologies have several inherent drawbacks: 1) This sensing method typically requires gas sample consumption, leading to poor repeatability. 2) Sensors tend to suffer from aging, necessitating periodic calibration or replacement, which makes them unsuitable for long-term, continuous monitoring. 3) These technologies are often prone to interference from electromagnetic fields and environmental factors, affecting operational reliability. On the other hand, optical gas sensing technologies offer several distinct advantages: 1) Non-contact measurement, which eliminates the need for gas sample consumption and ensures good repeatability. 2) Devices typically exhibit stable performance and, in many cases, operate without the need for frequent calibration, making them more suitable for long-term deployment. 3) High sensitivity and rapid response times, facilitating quick and accurate monitoring. However, when applied to the sensing of dissolved gases, optical sensing technologies still face certain challenges: 1) It remain susceptible to electromagnetic interference and environmental damage, which can affect the accuracy of measurements. 2) Cross-sensitivity between different gases may occur, leading to potential measurement inaccuracies. 3) These technologies are often more reliant on effective oil-gas separation technologies, which can complicate the overall system setup.
9 Conclusion and outlook
Transformers are one of the most important components of the power grid, and accurate diagnosis of their faults is critical to improving the safety of the grid. The primary objective of on-line monitoring of dissolved gases is to rapidly, accurately, and continuously detect the concentration of gases in order to assess the transformer’s operational status. To date, optical gas sensing technologies have been widely reported and continuously improved for dissolved gas analysis. This paper presents a review of the research progress in RS, FTIR, TDLAS and PAS. The principles, experimental results, and key characteristics of each technology have been discussed comprehensively, offering valuable insights for researchers in the field. However, it remains challenging to identify a single technology that meets all requirements, as each method has its strengths and limitations. Nevertheless, combining different technologies could lead to more effective strategies tailored to specific monitoring needs. Oil gas separation is a key step in the analysis of dissolved gases in transformer oil, and the efficiency of oil gas separation directly affects the detection performance. Therefore, optimizing oil and gas separation technology is also a way to improve detection performance.
In addition to the technologies mentioned in this review, new developments such as quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (QEPAS) and light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy (LITES) hold significant potential. QEPAS, an advanced form of PAS, uses a quartz tuning fork instead of the microphone to improve the detection of weak signals, while maintaining the advantages of PAS, such as zero background noise, broad wavelength applicability, and low cost. LITES, a new advancement of TDLAS, employs a quartz tuning fork to replace the photodetector and measures light intensity directly, offering high sensitivity, no wavelength selectivity, and cost-effectiveness. In recent years, both QEPAS [83–94] and LITES [95–98] have received growing interest in the field of gas sensing and are expected to be used for analysis of dissolved gases in transformer oil. These innovative technologies could significantly contribute to enhancing the performance of online DGA systems, providing more efficient and reliable solutions for transformer monitoring in the future.
Author contributions
JD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. BL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. WH: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. RC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JW: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HZ: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. WX: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZZ: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LD: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Engineering Research Center of UHV Technology and New Electrical Equipment Basis (Grant No. NERCUHE-2024-KF-12).
Conflict of interest
Authors BL, HZ, WX and ZZ were employed by Electric Power Research Institute, CSG. Authors JD, BL, XS, WH, RC, JW, HZ, WX, ZZ, LD and HW are collaborating on a research project at Electric Power Research Institute, CSG.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Wong SY, Ye XF, Guo FK, Goh HH. Computational intelligence for preventive maintenance of power transformers. Appl Soft Comput (2022) 114:108129. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108129
2. Shahidehpour M, Tinney F, Fu Y. Impact of security on power systems operation. Proc IEEE (2005) 93(11):2013–25. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2005.857490
3. Zhang JQ, Huang YB, Qiu XJ, Zhu TY. A review on fire research of electric power grids of China: state-of-the-art and new insights. Fire Technol (2024) 60:1027–76. doi:10.1007/s10694-022-01343-x
4. Bakar NA, Abu-Siada A, Islam S. A review of dissolved gas analysis measurement and interpretation techniques. IEEE Electr Insul Mag (2014) 30(3):39–49. doi:10.1109/MEI.2014.6804740
5. Sun HC, Huang YC, Huang CM. A review of dissolved gas analysis in power transformers. Energ Proced (2012) 14:1220–5. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2011.12.1079
6. Wei ZJ, Xu LN, Peng SD, Zhou Q. Application of WO3 hierarchical structures for the detection of dissolved gases in transformer oil: a mini review. Front Chem (2020) 8:188. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00188
7. Sun CH, Ohodnicki PR, Stewart EM. Chemical sensing strategies for real-time monitoring of transformer oil: a review. IEEE Sens J (2017) 17(18):5786–806. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2017.2735193
8. Abu-Siada A, Islam S. A new approach to identify power transformer criticality and asset management decision based on dissolved gas-in-oil analysis. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul (2017) 19(3):1007–12. doi:10.1109/TDEI.2012.6215106
9. Rangel Bessa A, Farias Fardin J, Marques Ciarelli P, Frizera Encarnação L. Conventional dissolved gases analysis in power transformers: review. Energies (2023) 16(21):7219. doi:10.3390/en16217219
10. N’cho JS, Fofana I, Hadjadj Y, Beroual A. Review of physicochemical-based diagnostic techniques for assessing insulation condition in aged transformers. Energies (2016) 9(5):367. doi:10.3390/en9050367
11. Bustamante S, Manana M, Arroyo A, Castro P, Laso A, Martinez R. Dissolved gas analysis equipment for online monitoring of transformer oil: a review. Sensors (2019) 19(19):4057. doi:10.3390/s19194057
12. Gong WH, Hu J, Wang ZW, Wei YB, Li YF, Zhang TT, et al. Recent advances in laser gas sensors for applications to safety monitoring in intelligent coal mines. Front Phys (2022) 10:1058475. doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.1058475
13. IEEE Std C57. IEEE Guide for the interpretation of gases generated in mineral oil-immersed transformers. IEEE Std C57.104-2019 (Revision of IEEE Std C57.104-2008) (2019) 1–98. doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.2019.8890040
14. GB/T 7252-2001. Guide to the analysis and the diagnosis of gases dissolved in transformer oil. China: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (2001).
15. Jiang J, Ma GM. Dissolved gases detection with optical methods. Opt Sensing Power Transformers (2021) 65–135. doi:10.1002/9781119765325.ch4
16. Gordon IE, Rothman LS, Hargreaves RJ, Hashemi R, Karlovets EV, Skinner FM, et al. The HITRAN2020 molecular spectroscopic database. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transfer (2022) 277:107949. doi:10.1016/j.jqsrt.2021.107949
17. Qian GC, Wan F, Zhou F, Wang JX, Kong WP, Chen WG. Fiber-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for trace-gas sensing in the high-concentration gas background with an anti-resonant hollow core fiber. Front Phys (2022) 10:917688. doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.917688
18. Yang DW, Li WH, Guo L, Ji YH, Gong YZ, Chu JW, et al. Rapid and real-time analysis of multi-component dissolved gas in seawater by Raman spectroscopy combined with continuous gas−liquid separator. Chin J Chem Eng (2024) 73:146–53. doi:10.1016/j.cjche.2024.04.020
19. Yang DW, Li WH, Tian HY, Chen ZG, Ji YH, Dong H, et al. High-sensitivity and in situ multi-component detection of gases based on multiple-reflection-cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sensors (2024) 24(17):5825. doi:10.3390/s24175825
20. Zheng YH, Zou XE, He SL. Gas detection using cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with a bidirectional multi-pass cell and polarization beam-splitting optical path. Appl Phys B (2024) 130:144. doi:10.1007/s00340-024-08285-y
21. Smekal A. Zur quantentheorie der dispersion. Naturwissenschaften (1923) 11:873–5. doi:10.1007/BF01576902
22. Raman CV, Krishnan KS. A new type of secondary radiation. Nature (1928) 121:501–2. doi:10.1038/121501c0
23. Wang PY, Chen WG, Wan F, Wang JX, Hu J. A review of cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy as a gas sensing method. Appl Spectrosc Rev (2019) 55(5):393–417. doi:10.1080/05704928.2019.1661850
24. Liu Y, Huang SL, Li XM. Measuring the gases dissolved in transformer oil by Raman spectra. J Test Meas Technology (1997) 11(2):1–3.
25. Li XY, Xia YX, Huang JM, Zhan L. A Raman system for multi-gas-species analysis in power transformer. Appl Phys B (2008) 93(93):665–9. doi:10.1007/s00340-008-3170-8
26. Somekawa T, Kasaoka M, Kawachi F, Nagano Y, Fujita M, Izawa Y. Analysis of dissolved C2H2 in transformer oils using laser Raman spectroscopy. Opt Lett (2013) 38(7):1086–8. doi:10.1364/OL.38.001086
27. Chen WG, Zhao LZ, Peng SY, Liu J, Zhou JJ. Analysis of dissolved gas in transformer oil based on laser Raman spectroscopy. Proc CSEE (2014) 34(15):2485–92. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.15.020
28. Qi W, Chen WG, Xiong YH. The research on simultaneous detection of dissolved gases in transformer oil using Raman spectroscopy. In: 2015 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC); 7-10 June 2015; Seattle, WA, USA (2015). p. 154–7. doi:10.1109/ICACACT.2014.7223606
29. Wan F, Yang ML, He P, Wang JX, Wang PY, Chen WG. Raman spectroscopy detection and signal processing method for the gases in transformer oil. Chin J Scientific Instrument (2016) 37(11):2482–8. doi:10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2016.11.010
30. Wang JX, Chen WG, Wan F, Wang PY, Wang JX, Shi HY, et al. Fiber-enhanced Raman spectroscopic monitoring of fault characteristic gases dissolved in transformer oil by hollow-core photonic crystal fiber. In: IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application; 25-29 Sept. 2022; Athens, Greece. ICHVE (2018). p. 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICHVE.2018.8641989
31. Wang PY, Chen WG, Wang JX, Tang J, Shi YL, Wan F. Multi gas analysis by cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for power transformer diagnosis. Anal Chem (2020) 92(8):5969–77. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00179
32. Wang JX, Chen WG, Wang PY, Zhang ZX, Chao W, Wan F, et al. Analysis of fault characteristic gases dissolved in transformer oil based on hollow-core anti-resonant fiber-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Proc CSEE (2022) 42(16):6136–44. doi:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.211472
33. Liu WQ, Xing CZ. Needs and challenges of optical atmospheric monitoring on the background of carbon neutrality in China. Front Environ Sci Eng (2024) 18:73. doi:10.1007/s11783-024-1833-2
34. Wang JX, Zhou MQ, Langerock B, Nan WD, Wang T, Wang PC. Optimizing the atmospheric CO2 retrieval based on the NDACC-type FTIR mid-infrared spectra at Xianghe, China. Remote Sens (2024) 16(5):900. doi:10.3390/rs16050900
35. Ju W, Lu CH, Liu C, Jiang WW, Zhang WJ, Hong F. Rapid identification of atmospheric gaseous pollutants using fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy combined with independent component analysis. J Spectrosc (2020) 2020:1–14. doi:10.1155/2020/8920732
36. Fathy A, Sabry WM, Hunter IW, Khalil D, Bourouina T. Direct absorption and photoacoustic spectroscopy for gas sensing and analysis: a critical review. Laser Photon Rev. (2022) 16:2100556. doi:10.1002/lpor.202100556
37. Liu XY, Zhou FJ, Huang FL. Research on on-line DGA using FTIR [power transformer insulation testing]. In: Proceedings. International Conference on Power System Technology; 13-17 Oct. 2002; Kunming, China, 3 (2002). p. 1875–80. doi:10.1109/ICPST.2002.1067858
38. Liu XY, Liu YL, Yue L. On-line monitoring of dissolved gas-in-oil with FTIR spectra. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing (2003) 10(4):65–8.
39. Li HL, Zhou FJ, Tan KX, Gao WS. Quantitative analysis of FTIR used in transformer on-line monitoring. Automation Electric Power Syst (2005) 29(18):62–5.
40. Zhao AX, Tang XJ, Liu JH, Zhang ZH. The on-site DGA detecting and analysis system based on the Fourier transform infrared instrument. In: 2014 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC) Proceedings; 12-15 May 2014; Montevideo, Uruguay (2014). p. 1036–40. doi:10.1109/I2MTC.2014.6860900
41. Tang XJ, Wang WJ, Zhang XL, Wang EZ, Li XJN. On-line analysis of oil-dissolved gas in power transformers using fourier transform infrared spectrometry. Energies (2018) 11(11):3192. doi:10.3390/en11113192
42. Jiang J, Wang ZW, Ma GM, Song HT, Zhang CH. Direct detection of acetylene dissolved in transformer oil using spectral absorption. Optik (2019) 176:214–20. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.09.053
43. Darwish MMF, Hassan MHA, Abdel-Gawad NMK, Lehtonen M, Mansour DA. A new technique for fault diagnosis in transformer insulating oil based on infrared spectroscopy measurements. High Voltage (2024) 9(2):319–35. doi:10.1049/hve2.12405
44. Gong WH, Hu J, Wang ZW, Wei YB, Li YF, Zhang TT, et al. Recent advances in laser gas sensors for applications to safety monitoring in intelligent coal mines. Front Phys (2022) 10:1058475. doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.1058475
45. Lin S, Chang J, Sun JC, Xu P. Improvement of the detection sensitivity for tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy: a review. Front Phys (2022) 10:853966. doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.853966
46. Wei W, Peng WY, Wang Y, Choudhary R, Wang SK, Shao JK, et al. Demonstration of non-absorbing interference rejection using wavelength modulation spectroscopy in high-pressure shock tubes. Appl Phys B (2019) 125:9. doi:10.1007/s00340-018-7118-3
47. Liu C, Wang G, Zhang C, Patimisco P, Cui RY, Feng CF, et al. End-to-end methane gas detection algorithm based on transformer and multi-layer perceptron. Opt Express (2024) 32(1):987–1002. doi:10.1364/OE.511813
48. Li GL, Dong ET, Ji WH. A near-infrared trace CO2 detection system based on an 1,580 nm tunable diode laser using a cascaded integrator comb (CIC) filter-assisted wavelength modulation technique and a digital lock-in amplifier. Front Phys (2019) 7:199. doi:10.3389/fphy.2019.00199
49. Liu K, Wang L, Tan T, Wang GS, Zhang WJ, Chen WD, et al. Highly sensitive detection of methane by near-infrared laser absorption spectroscopy using a compact dense-pattern multipass cell. Sens Actuators, B (2015) 220:1000–5. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.136
50. Gu MS, Chen JJ, Mei JX, Tan T, Wang GS, Liu K, et al. Open-path anti-pollution multi-pass cell-based TDLAS sensor for the online measurement of atmospheric H2O and CO2 fluxes. Opt Express (2022) 30(24):43961–72. doi:10.1364/OE.474070
51. Sun JC, Chang J, Wang C, Shao JK. Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy for detection of multi-component gas: a review. Appl Spectrosc Rev (2024) 59(8):1086–107. doi:10.1080/05704928.2024.2302608
52. Zhu CG, Wang PP, Chu TW, Peng F, Sun YJ. Second harmonic phase angle method based on WMS for background-free gas detection. IEEE Photon J (2021) 13(5):1–6. doi:10.1109/JPHOT.2021.3113503
53. Zhu CG, Chu TW, Liu YY, Wang PP. Modeling of scanned wavelength modulation spectroscopy considering nonlinear behavior of intensity response. IEEE Sens J (2022) 22(3):2301–8. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2021.3134413
54. Jiang J, Ma GM, Song HT, Zhou HY, Li CR, Wang HB, et al. Tracing methane dissolved in transformer oil by tunable diode laser absorption spectrum. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul (2016) 23(6):3435–42. doi:10.1109/TDEI.2016.005810
55. Ma GM, Zhao SJ, Jiang J, Song HT, Li CR, Luo YT, et al. Tracing acetylene dissolved in transformer oil by tunable diode laser absorption spectrum. Sci Rep (2017) 7:14961. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-13823-0
56. Jiang J, Zhao MX, Ma GM, Song HT, Li CR, Han X, et al. TDLAS-based detection of dissolved methane in power transformer oil and field application. IEEE Sens J (2018) 18(6):2318–25. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2017.2788871
57. Jiang J, Wang ZW, Han X, Zhang CH, Ma GM, Li CR, et al. Multi-gas detection in power transformer oil based on tunable diode laser absorption spectrum. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul (2019) 26(1):153–61. doi:10.1109/TDEI.2018.007535
58. Chen Y, Wang ZT, Li Z, Zheng HQ, Dai JM. Development of an online detection setup for dissolved gas in transformer insulating oil. Appl Sci (2021) 11(24):12149. doi:10.3390/app112412149
59. Liu K, Mei JX, Zhang WJ, Chen WD, Gao XM. Multi-resonator photoacoustic spectroscopy. Sens Actuators, B (2017) 251:632–6. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.114
60. Sun JL, Liu B, Liu LX, Huan HT, Zhang L, Zhang XS, et al. Multicomponent gas sensors based on photoacoustic spectroscopy technology: a review. Microw Opt Technol Lett (2024) 66:e34039. doi:10.1002/mop.34039
61. Wang Z, Wang Q, Zhang H, Borri S, Galli I, Sampaolo A, et al. Doubly resonant sub-ppt photoacoustic gas detection with eight decades dynamic range. Photoacoustics (2022) 27:100387. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2022.100387
62. Wang Z, Wang Q, Zhang WP, Wei HY, Li Y, Ren W. Ultrasensitive photoacoustic detection in a high-finesse cavity with Pound-Drever-Hall locking. Opt Lett (2019) 44(8):1924–7. doi:10.1364/OL.44.001924
63. Wang Q, Wang Z, Ren W. Theoretical and experimental investigation of fiber-ring laser intracavity photoacoustic spectroscopy (FLI-PAS) for acetylene detection. J Lightwave Technol (2017) 35(20):4519–25. doi:10.1109/JLT.2017.2748137
64. Wang FP, Fu LY, Zhang JG, Han Z, Pang S, Xue QS, et al. TT-type resonator-based differential photoacoustic spectroscopy for trace gas detection. Opt Lett (2024) 49(8):2173–6. doi:10.1364/OL.520154
65. Feng CF, Li B, Jing YJ, Wang JP, Patimisco PSV, et al. Enrichment-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy based on vertical graphene. Sens Actuators B: Chem (2024) 147:136204. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2024.136204
66. Yin XK, Dong L, Wu HP, Zheng HD, Ma WG, Zhang L, et al. Sub-ppb nitrogen dioxide detection with a large linear dynamic range by use of a differential photoacoustic cell and a 3.5W blue multimode diode laser. Sens Actuators, B (2017) 247:329–35. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.058
67. Yin XK, Gao M, Miao RQ, Zhang L, Zhang XS, Liu LX, et al. Near-infrared laser photoacoustic gas sensor for simultaneous detection of CO and H2S. Opt Express (2021) 29(21):34258–68. doi:10.1364/OE.441698
68. Wu GJ, Zhang YJ, Gong ZF, Fan YM, Xing JW, Wu X A mini-resonant photoacoustic sensor based on a sphere-cylinder coupled acoustic resonator for high-sensitivity trace gas sensing. Photoacoustics (2024) 37:100595. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2024.100595
69. Wu GJ, Xing JW, Gong ZF, Ma JS, Fan YM, Wu X, et al. Single fiber-type double cavity enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy sensor for trace methane sensing. J Lightwave Technology (2024) 42(9):3393–8. doi:10.1109/JLT.2024.3353200
70. Wu GJ, Wu X, Gong ZF, Xing JW, Fan YM, Ma JS, et al. Highly sensitive trace gas detection based on a miniaturized 3D-printed Y-type resonant photoacoustic cell. Opt Express (2023) 31(21):34213–23. doi:10.1364/OE.502733
71. Wu RM, Ni WJ, Yang CY, He BZ, Lu P, Ran SX, et al. Multiple optical path length reflections enhancement based on balloon-type photoacoustic cell for trace gas sensing. Photoacoustics (2025) 41:100681. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2024.100681
72. Zhao ZK, Ni WJ, Yang CY, Ran SX, He BZ, Wu RM, et al. Highly sensitive and miniaturized microcone-curved resonant photoacoustic cavity for trace gas detection. Photoacoustics (2024) 40:100650. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2024.100650
73. Wang FP, Cheng YC, Xue QS, Wang Q, Liang R, Wu JH, et al. Techniques to enhance the photoacoustic signal for trace gas sensing: a review. Sens Actuators, A (2022) 345:113807. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2022.113807
74. Yun YX, Chen WG, Wang YY, Pan C. Photoacoustic detection of dissolved gases in transformer oil. Euro Trans Electr Power (2008) 18:562–76. doi:10.1002/etep.191
75. Li YL, Zhao XZ. Monitoring system for dissolved gases in transformer oil based on photoacoustic spectroscopy. Transducer Microsystem Tech (2011) 30(6):103–5. doi:10.13873/j.1000-97872011.06.012
76. Mao XF, Zhou XL, Zhai L, Yu QX. Dissolved gas-in-oil analysis in transformers based on near-infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy. Int J Thermophys (2015) 36:940–6. doi:10.1007/s10765-014-1713-2
77. Li ZJ, Chen WG, Deng S, Cao LY, Wang F, Zhang JX. Photoacoustic spectroscopy technology based on active photoacoustic cell. High Voltage Eng (2018) 44(5):1605–11. doi:10.13336/j.10036520.hve.20180211003
78. Zhou S, Iannuzzi D. Immersion photoacoustic spectrometer (iPAS) for arcing fault detection in power transformers. Opt Lett (2019) 44(15):3741–4. doi:10.1364/OL.44.003741
79. Yang TK, Chen WG, Li ZJ. Detection of trace ethyne by photoacoustic spectroscopy based on Fiber-optic cantilever acoustic sensor. High Voltage Eng (2020) 46(6):1922–8. doi:10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20200615009
80. Chen TN, Ma FX, Zhao Y, Zhao YK, Wan LJ, Li K, et al. Portable ppb-level acetylene photoacoustic sensor for transformer on-field measurement. Optik. (2021) 243:167440. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167440
81. Chen K, An R, Li CX, Kang Y, Ma FX, Zhao XY, et al. Detection of ultra-low concentration acetylene gas dissolved in oil based on fiber-optic photoacoustic sensing. Opt Laser Technol (2022) 154:108299. doi:10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108299
82. Li CX, Qi HC, Zhao XY, Guo M, An R, Chen K. Multi-pass absorption enhanced photoacoustic spectrometer based on combined light sources for dissolved gas analysis in oil. Opt Laser Eng (2022) 159:107221. doi:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2022.107221
83. Wu HP, Sampaolo A, Dong L, Patimisco P, Liu XL, Zheng HD, et al. Quartz enhanced photoacoustic H2S gas sensor based on a fiber-amplifier source and a custom tuning fork with large prong spacing. Appl Phys Lett (2015) 107(11):111104. doi:10.1063/1.4930995
84. Wu HP, Dong L, Zheng HD, Yu YJ, Ma WG, Zhang L, et al. Beat frequency quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and calibration-free continuous trace-gas monitoring. Nat Commun (2017) 8:15331. doi:10.1038/ncomms15331
85. Sampaolo A, Patimisco P, Giglio M, Zifarelli A, Wu HP, Dong L, et al. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for multi-gas detection: a review. Anal Chim Acta (2022) 1202:338894. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2021.338894
86. Hu LE, Zheng CT, Zhang MH, Yao D, Zheng J, Zhang Y, et al. Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopic methane sensor system using a quartz tuning fork-embedded, double-pass and off-beam configuration. Photoacoustics (2020) 18:100174. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100174
87. Hu LE, Zheng CT, Zheng J, Wang YD, Tittel FK. Quartz tuning fork embedded off-beam quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Opt Lett (2019) 44(10):2562–5. doi:10.1364/OL.44.002562
88. Wang LH, Lv HH, Zhao YH, Wang CL, Luo HJ, Lin HY, et al. Sub-ppb level HCN photoacoustic sensor employing dual-tube resonator enhanced clamp-type tuning fork and U-net neural network noise filter. Photoacoustics (2024) 38:100629. doi:10.1016/j.pacs.2024.100629
89. Wu Q, Lv HH, Lin LQ, Wu HP, Giglio M, Zhu WG, et al. Clamp-type quartz tuning fork enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Opt Lett (2022) 47(17):4556–9. doi:10.1364/OL.464334
90. Wang JP, Wu HP, Sampaolo A, Patimisco P, Spagnolo V, Jia ST, et al. Quartz-enhanced multiheterodyne resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy. Light Sci Appl (2024) 13:77. doi:10.1038/s41377-024-01425-1
91. Ma YF, Hong YH, Qiao SD, Lang ZT, Liu XN. H-shaped acoustic micro-resonator-based quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Opt Lett (2022) 47(3):601–4. doi:10.1364/OL.449822
92. Qiao SD, He Y, Sun HY, Patimisco P, Sampaolo A, Spagnolo V, et al. Ultra-highly sensitive dual gases detection based on photoacoustic spectroscopy by exploiting a long-wave, high-power, wide-tunable, single-longitudinal-mode solid-state laser. Light Sci Appl (2024) 13:100. doi:10.1038/s41377-024-01459-5
93. Kinjalk K, Paciolla F, Sun B, Zifarelli A, Menduni G, Giglio M, et al. Highly selective and sensitive detection of volatile organic compounds using long wavelength InAs-based quantum cascade lasers through quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Appl Phys Rev (2024) 11:021427. doi:10.1063/5.0189501
94. Wu HP, Dong L, Zheng HD, Liu XL, Yin XK, Ma WG, et al. Enhanced near-infrared QEPAS sensor for sub-ppm level H2S detection by means of a fiber amplified 1582 nm DFB laser. Sens Actuators B Chem (2015) 221:666–72. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.049
95. Ma YF, He Y, Tong Y, Yu X, Tittel FK. Quartz-tuning-fork enhanced photothermal spectroscopy for ultra-high sensitive trace gas detection. Opt Express (2018) 26(24):32103–10. doi:10.1364/OE.26.032103
96. He Y, Ma YF, Tong Y, Yu X, Tittel FK. Ultra-high sensitive light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy sensor with a high Q-factor quartz tuning fork and a multipass cell. Opt Lett (2019) 44(8):1904–7. doi:10.1364/OL.44.001904
97. Dai JL, Wang CY, Liu PH, Huang L, Li YF, Lou CG, et al. Sensitive light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy-based oxygen sensor with a perovskite-modified quartz tuning fork. IEEE Sens J (2023) 23(19):22380–8. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2023.3304654
Keywords: DGA, transformer oil, RS, FTIR, TDLAS, PAS, gas sensing
Citation: Dai J, Luo B, Shen X, Han W, Cui R, Wu J, Zhang H, Xiao W, Zhong Z, Dong L and Wu H (2025) A review of optical gas sensing technology for dissolved gas analysis in transformer oil. Front. Phys. 13:1547563. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1547563
Received: 18 December 2024; Accepted: 07 January 2025;
Published: 05 February 2025.
Edited by:
Kaijie Xu, University of Alberta, CanadaReviewed by:
Wenjun Ni, South-Central University for Nationalities, ChinaFang Song, Jilin University, China
Gong Zhenfeng, Dalian University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Dai, Luo, Shen, Han, Cui, Wu, Zhang, Xiao, Zhong, Dong and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Dong, ZG9uZ2xlaUBzeHUuZWR1LmNu; Hongpeng Wu, d3VocEBzeHUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jialiang Dai1,2†
Jialiang Dai1,2† Lei Dong
Lei Dong Hongpeng Wu
Hongpeng Wu