
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Phys. , 14 March 2025
Sec. Social Physics
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2025.1538742
With the iteration of information technology and the enhancement of the arithmetic power of huge amounts of data, the economic model of digital platforms driven by data has become an important carrier of digital trade and digital economic development. By the reason of the dynamism, cross-border and complexity characteristics compared with traditional physical platforms, the development of digital platforms is no longer limited to the level of specific commodity goods or services, and the traditional regulatory system cannot match and adapt to the new attributes of digital platforms them. Therefore, the construction of a flexible, diversified and pluralistic co-management hybrid regulatory model is imminent. This article constructs small-world model to study government regulation of digital platforms. The small world model can effectively describe the connectivity between nodes (users, platforms, regulators, etc.) in the ecosystem of digital platforms, which helps researchers to understand the complexity of the network structure and the propagation pattern of information in the network and design more effective regulatory strategies. In addition, small-world models can be used to assess the robustness of regulatory measures in different scenarios, and to study the stability and information flow capability of the network in the face of node failure or attacks, reflecting the interaction between users and platforms. The research results and relevant discussion are as follows: First, the simulation results of government regulatory intensity indicate the government’s regulatory strength for the algorithmic black-box problem needs to be kept at an appropriate standard. Second, the simulation results government punishment intensity show that we can not only rely on a single regulatory means, but also need to take the composite strategy as far as possible, encouraging multiple bodies to participate in the regulation and collaborative governance to construct a fair and efficient digital transaction environment. Finally, the dynamic simulation results of sample size variation suggest that the government needs to adopt a variety of means to cooperate in forming an efficient and reasonable regulatory system to regulate digital platforms in accordance with the law, avoiding one-size-fits-all regulatory strategies.
The digital economy is a more advanced economic form following the agricultural and industrial economies, and its development not only improves resource allocation, penetration and integration, but also enhances total factor productivity, becoming an important factor in promoting the strategic adjustment of the industrial structure and fostering national competitiveness [1]. As the most typical innovative business model of the digital age, the digital platform has the exponential growth in scale, increasing architectural complexity and spreading to many different industries [2].
Digital platforms are business organizations that use digital technologies for their production and services, as well as those that provide digitally related services. Digital platforms combine digital information with other factors of production, and utilize digital technology and digital interfaces to facilitate bilateral or multi-stakeholder interactions to achieve value creation [3]. In the era of digital economy, digital platforms, as a new type of organization with data as the main factor of production, are bursting with strong development momentum. Through the accumulation of online and offline industrial elements, it breaks the boundaries between virtual and real, subverts the traditional consumption and production modes [4] in the industrial era, and effectively integrates industrial resources and market resources [5]. Currently, most digital platform enterprises use algorithmic decision-making based on big data, which not only improves the operational efficiency of enterprises, but also enhances the experience and satisfaction of platform users.
However, the complexity of the algorithmic decision-making process leads to the inability of users or users of algorithms to understand and explain some of the phases of the operations [6, 7], and consequently, opacity in decision-making [8, 9]. This phenomenon is often described as black boxes, their complexity and technical opacity hiding and obfuscating their inner workings [10]. Some scholars point out that algorithm black box occurs because the confidentiality, the complexity of the algorithm itself and the norms of algorithm use. That is, the algorithm black box is not only a technical problem, but also may be caused by human factors [11]. There are two main negative impacts generated by the algorithmic black box of digital platforms: the crisis of data loss of control and the crisis of discrimination in decision-making results, which is manifested in the illegal surveillance and access to personal data [12], price discrimination, racial discrimination, etc., and can even jeopardize personal safety as well as public safety [13, 14]. It can be found that, on the one hand, digital platforms rely on capital expansion and technological barriers, gather massive user resources, quickly open up the upstream and downstream of the industry, build an autonomous order of digital platforms, and to a certain extent play the public service function as a digital infrastructure, realizing the unique value creation of the digital economy. At the same time, some digital platforms have abused their power of autonomy, formed monopoly in the market, harmed the order of benign competition in the market, and pursued “private interests” to commit acts detrimental to the public interest, jeopardizing the social and public interests and national security.
In this context, we suggest that the government should strengthen the regulation of digital platforms, promote market fairness, and prevent digital platforms from expanding beyond reasonable boundaries in an uncontrolled manner, so as to ensure the healthy and smooth operation of the market economy [15]. On the one hand, the government should stimulate the innovation and vitality of digital platforms [16], encourage platforms to put industry self-regulation into effect [17] which may help respect individual agency and rational consumer choice [18, 19]. On the other hand, the government should continue to improve the vacant part of the scope of regulation, and regulate the illegal behaviors of digital platforms in an appropriate and timely manner, so as to establish a scientific and sustainable governance system for digital platforms and ensure a fair and stable competitive order in the market [20].
There are precedents of regulation in the international community, such as the European Union‘s major breakthrough in the regulation of digital platforms is the establishment of the “digital gatekeeper” [21] as the regulatory model. By setting up quantitative criteria for judging gatekeepers (relating to indicators such as market shares, the number of users affected by the operation of the platform, the time users remain on the platform site and the annual economic revenues of the platform) [22], the European Union aims to ensure contestable and fair markets in the digital sector and define a series of specific obligations that gatekeepers will need to respect, including prohibiting them from engaging in certain behaviors in a list of do’s and don’ts. The European Union wants to reduce malicious competition at the source and curbing the infringement of the rights and interests of digital platform users.
In this article, we choose the perspective of complex networks theory to study based on the following reasons: First of all, complex network theory focuses on systems consisting of a large number of nodes and edges that represent entities (e.g., individuals, organizations, technologies, etc.) and edges that represent relationships or interactions between them. Through complex networks, it is possible to analyze the structure of the regulation system, its dynamic evolution, and the impact of different strategies, and helps understand the complexity of algorithms, helps governments make sense of how they work and their impact on user behavior and information dissemination, and lays the groundwork for effective regulatory policy.
Second, In the study of complex networks, the statistical properties are of great significance for the study and derivation of networks, and analyzing the statistical properties of complex networks helps to deeply understand the structure, function and its dynamic behavior. These statistical properties mainly include the following points: the degree, which is the number of edges connected to a node, usually shows a power-law distribution, resulting in most nodes having a small degree and a few nodes (“hubs”) having a large degree; clustering coefficient, which is divided into local and global clustering coefficients and is used to measure the degree of connectivity between node neighbors; path length, especially the average path length, which shows the efficiency of information propagation in the network; network diameter, which refers to the longest and shortest path length between any two nodes, the smaller the diameter, the greater the potential for information dissemination; small-world property, which indicates that the short average path length and high clustering coefficient of any two nodes promote the rapid dissemination of information.
Meanwhile, the statistical properties of the network can be understood more deeply through several generative models such as small-world networks. The computation and analysis of these properties form a basic framework for studying various networks, which can help us predict the behavior of networks in dynamic processes such as propagation, flow and cooperation, and are of great significance in the fields of social network analysis, propagation model design and network optimization.
In complex networks, the selection of the small world model (WS model) is very helpful in studying government regulation of digital platforms, and its necessity is mainly reflected in the following aspects: firstly, the small world model can effectively describe the connectivity between nodes (users, platforms, regulators, etc.) in the ecosystem of digital platforms, which helps researchers to understand the complexity of the network structure, in particular, the network agglomeration and short-path characteristics. Second, by analyzing the small-world model, we can better understand the propagation pattern of information in the network and design more effective regulatory strategies. In addition, small-world models can be used to assess the robustness of regulatory measures in different scenarios, and to study the stability and information flow capability of the network in the face of node failure or attacks [23]. Meanwhile, small-world models can reflect the interaction between users and platforms, which is crucial to understand the importance of user feedback in algorithmic transparency and fairness. By constructing small-world models, the impact of different regulatory strategies on network structure and functionality can be simulated, providing a basis for policy assessment and formulation. Small-world models are also able to adapt to dynamic changes in the digital platform environment, helping researchers understand the evolution of network structure and adjust regulatory strategies in a timely manner [24].
In contrast to alternative models, the small-world model is more congruent with the investigative domain of governmental regulation pertaining to algorithmic opacity within digital platforms, given its distinctive attributes. Primarily, concerning connectivity and clustering tendencies, the small-world paradigm integrates elevated clustering coefficients with succinct mean path lengths. Within the ecological framework of digital platforms, interconnections between users and platforms frequently manifest heightened clustering, wherein users’ propensity to coalesce into compact communities or groupings. Despite the existence of these densely knit communities, the overarching network characterizes a comparatively brief mean path length, thereby facilitating expeditious information dissemination. This particularity is adeptly encapsulated by the small-world model, whereas random networks typically exhibit diminished clustering coefficients, and scale-free networks, whilst potentially embodying short paths, may not evince clustering attributes as prominently as the small-world construct.
Moreover, in regard to information dissemination patterns intrinsic to small-world models, user interactions and information propagation within digital platforms often entail both localized intracommunal diffusion and expansive intercommunal transmission. The small-world model effectively simulates this hybrid propagation modality, whereas random networks may inadequately capture local clustering phenomena, and scale-free networks might overaccentuate the roles of a select few highly connected nodes.
Additionally, the small-world model demonstrates a degree of resilience to stochastic node removals but may exhibit vulnerability to targeted assaults on particular nodes. In the context of overseeing algorithmic opaqueness in digital platforms, appraising network performance under diverse attack scenarios is crucial for formulating efficacious regulatory strategies. The small-world model empowers researchers to evaluate the stability of regulatory interventions in networks subjected to various perturbations.
Lastly, considering the dynamic nature of digital platform environments, with user-platform connections perpetually evolving, the small-world model, in comparison to scale-free or random networks, is better equipped to accommodate this fluidity. It thereby assists researchers in comprehending the evolution of network architectures and calibrating regulatory approaches accordingly.
To build the WS small-world network involved in this research, we first construct a nearest forest coupling network containing n nodes, and give all nodes in the network are connected to each other in an unoriented and unweighted way, and denote the set of all the nodes in this network by n = {n1, n2, n3, … , nn}, and in this set of nodes, there exist two nodes, ni and nj, which are connected to each other by an edge, then these two nodes can be defined as neighbor nodes. In this node set there are two nodes ni and nj connected by an edge, then these two nodes can be defined as neighboring nodes, in the starting state of this network each node is connected only to the surrounding neighboring nodes, and another node is randomly selected from the entire network to reconnect with a probability of p. The average number of connections of all nodes in the network is K and there are nK/2 edges in the entire network. The whole network G = (n, p, K) and all digital platform firms will play a game with their neighbors in the network G.
As a special case of complex networks, the small-world model inherently exhibits two topological characteristics related to complex networks: average path length and clustering coefficient.
The average path length [25] refers to the mean value of the shortest path lengths between all pairs of nodes within a network. It quantifies the average distance between nodes and serves as a crucial metric for assessing the global efficiency and connectivity of the network. Specifically, the average path length measures the average distance between any two nodes i and j in the network, representing the average number of intermediate nodes that information must traverse during propagation. In a small-world network, this distance is relatively short, facilitating efficient information dissemination. The formal definition of average shortest path length is provided below.
where N is the total number of nodes for this visibility graph, dij is the shortest path between the time nodes i and j.
The clustering coefficient is a fundamental metric in graph theory and network science, employed to quantify the propensity of nodes in a network to form densely interconnected clusters. It measures the extent of mutual connectivity among the neighbors of a given node, thereby reflecting the degree of local cohesiveness within the network. Empirical evidence demonstrates that, in many real-world networks, particularly social networks, nodes exhibit a tendency to form relatively tightly knit groups, with this likelihood typically exceeding the average probability of forming a connection between any two nodes selected at random. This phenomenon is well-documented, as demonstrated by Newman’s research, which provides the following formal definition of the clustering coefficient [26].
where Ei is the edges between the neighbors of node i, and the total number of edges is
The formula for the average clustering coefficient can be derived as follows when N denotes the number of all nodes.
Concerning the detailed rules for the experimental process, the design is carried out according to the following logic: Each digital platform enterprise has two pure strategies to follow the regulatory requirements of “optimizing the transparency of the algorithmic black box” or “keeping the algorithmic black box unchanged”. In the process of the experiment, assuming that each digital platform enterprise has a perfectly competitive relationship and sells homogeneous products or services, which may result in the total demand in the market remains unchanged. When a digital platform firm chooses to optimize its algorithmic black-box transparency strategy, it bears some research costs for the optimization and disclosure risks as the extent of the algorithmic black-box decreases, but it also receives some reputational benefits from consumers for the regulatory compliance optimization. On the other hand, the government will penalize and publicize digital platforms that do not comply with regulatory behavior, which will result in market share loss and reputational loss for firms that choose to maintain an algorithmic black box strategy. Consumers, as assisting regulators, will provide the government with targets for regulation and punishment through complaints, further increasing the likelihood that platform firms choosing to maintain their strategies will be penalized and suffer reputational losses from the government, and ultimately influencing platform firms’ strategic choices in response to government regulation.
To make the design of the selection iteration rules of digital platform experiment as close as possible to the reality, the Fermi evolution rule [27] is adopted for the iteration of the process to encapsulate the irrational behavior of individuals in the network. Furthermore, individuals in the network can only adjust their own game strategies, but cannot change their own game relationships, and the gain relationships do not change over time [28]. Platforms can only learn strategy updating by constantly participating in the experiment, and comparing the gains with their neighbors, and eventually evolve into stable strategy choices. Lastly, after the end of a game, each digital platform enterprise updates its strategy, and the probability of the platform imitating its neighbors’ strategies with probability.
In this context, Ui and Uj represent the earnings obtained by platform enterprise ni and its neighbor nj in this round of the game, respectively. Furthermore, according to previous research, a noise effect occurs when ω ≥ 0, so ω is set to 0.1.
As shown in Figure 1 below, we add the factor about the impact of government decisions on processes. Specifically, the government’s decision is divided into two dimensions: supervision and punishment. The changes of these two dimensions will have an impact on the strategies adopted by the digital platform enterprises in the network to cope with the algorithmic black box, while the fundamental reason for the impact is that the changes of these two dimensions will ultimately affect the revenues of the digital platform enterprises, which will lead the digital platform enterprises to make the corresponding decisions.
Every digital platform company has two strategic choices: “optimize” and “keep”. When a platform company chooses the “optimization” strategy, it needs to pay for research costs and losses due to disclosure. However, when a platform company chooses the “optimization” strategy, it gains consumer reputation. On the other hand, when a platform chooses the “keep” strategy, it may lose market share due to the reputation problem caused by the black box algorithm. At the same time, governmental algorithmic review with certain regulatory efforts may penalize platform companies that choose the “keep” strategy.
At the initial stage, each digital platform enterprise considers choosing between “optimization” or “keep” strategies. When choosing a strategy, each enterprise determines the strategy based on its own costs, benefits, and the choices of its neighbors. Digital platform companies will evaluate the results by calculating the final return based on the level of government regulation, the level of consumer regulation, and the company’s market performance, and will again make strategy choices until the strategy choices have stabilized.
The lower portion of Figure 1 outlines the game’s progression, broken into five stages within the research framework: decision phase for digital platform ni, decision-making by adjacent platforms nj, governmental intervention, consumer choice, and strategy stabilization.
In the initial stage, digital platform ni chooses between “optimize” or “keep” strategies based on costs, benefits, and market predictions. Optimization incurs R&D costs and increased transparency risks but enhances consumer reputation. Maintaining current practices can lead to market share erosion due to reputational damage from algorithmic opacity.
In the next stage, ni factors in the strategies of adjacent platforms nj, recognizing the interdependence of their environments and the influence of peers’ strategies on its own trajectory.
Following this, the government imposes regulations and penalties, reviewing platforms’ algorithms and sanctioning those with maintain strategies, affecting enterprise revenue and influencing strategic reevaluations.
Simultaneously, consumer behavior, driven by platform reputation, impacts enterprises. Optimization strategies foster higher consumer trust, while maintaining strategies risk consumer alienation due to transparency concerns.
Ultimately, enterprises engage in iterative strategy revisions, reassessing returns in response to regulatory pressures, market reactions, and performance metrics, until a stable equilibrium is reached, leading to a steady market configuration.
According to the game process illustrated in the Figure 1, we make the assumptions for various game parameters as presented in the Table 1 below:
Building upon the findings of Wang et al. regarding the construction process of evolutionary games in complex networks [29], we proceed with our investigation.
When both the digital platform enterprise and its neighbors choose the strategy of optimizing the algorithm’s black box, their payoff equations can be derived as follows Equation 1.
If the digital platform enterprise chooses the strategy of optimizing the algorithm’s black box issue, while its neighbors choose to maintain their strategy, the payoff equations for the two will differ. The payoff equation for the digital platform enterprise that opts for the optimization strategy is consistent with the formula mentioned above, while the payoff equation for the digital platform enterprise that chooses to maintain its strategy is as follows:
On the other hand, when both the digital platform enterprise and its neighbors choose to maintain the strategy of keeping the algorithm as a black box, their payoff equations are the same as Equation 2 In summary, the payoff matrix for each scenario in the game process can be derived as shown in the Table 2 below.
According to the statistics of “China E-commerce Report 2022”, in Figure 2, the number of Chinese netizens is 1.067 billion, so it is assumed that the total market demand is 1.067 billion units, and then deduced that the average demand of each digital platform is 5.41 million units of demand, and at the same time, China’s annual e-commerce individual transaction volume is 1.379 billion yuan, so each unit of netizens’ consumption is 0.13 million yuan, that is to say, the digital platform through the marginal profit that can be obtained by the market demand is 0.13 million yuan [30].
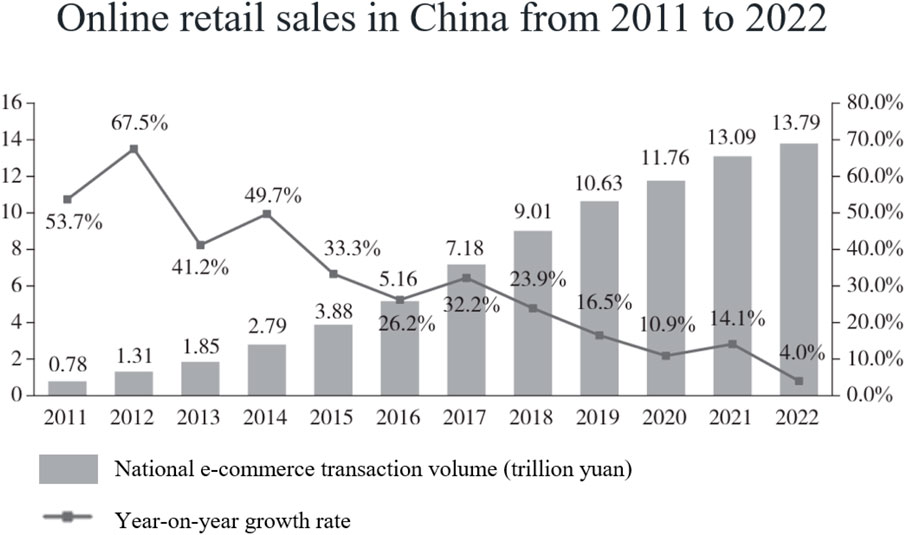
Figure 2. Online retail sales in China from 2011 to 2022. Reprinted with permission from [31].
According to the “2020 Data Leakage Cost Report” jointly released by IBM Security Ponemon Institute, in Figure 3, the average cost generated by data leakage in 2020 is 3.86 million dollars [31], so the cost of information leakage is set at 25.96 million yuan according to the exchange rate in 2022 after combining this information in this simulation.
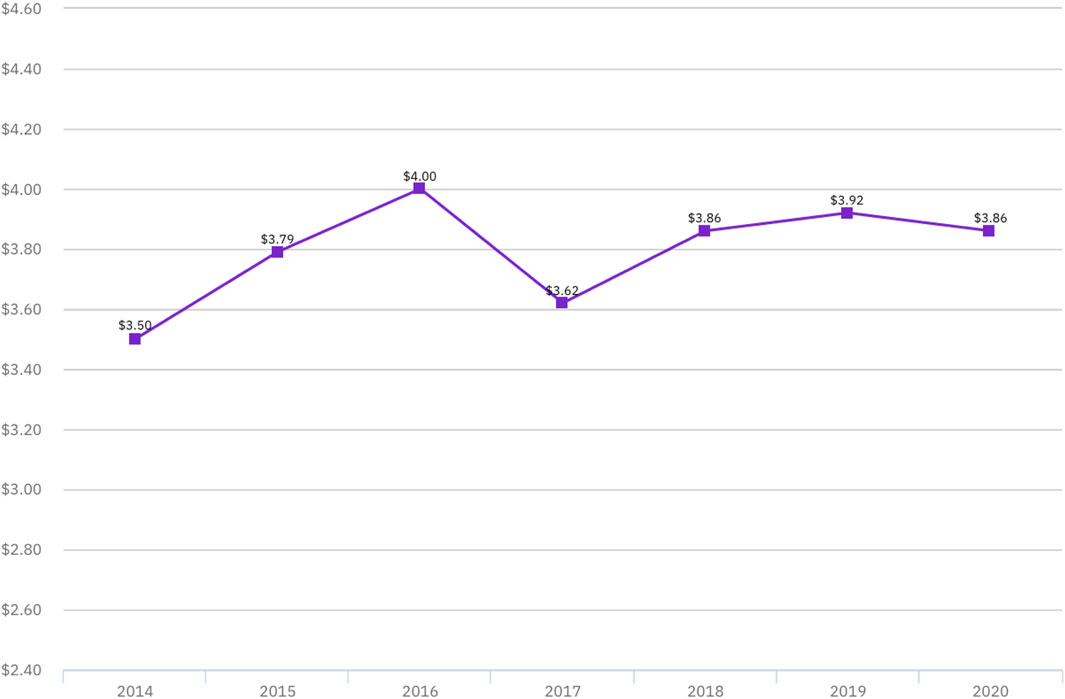
Figure 3. Average total cost of data breaches in millions of dollars. Reprinted with permission from [30].
According to the market share decline of DDT after being punished by the government for the algorithm black box problem in 2021, the market share impact after being punished by the government is assumed to be 0.211, because after being informed by the Office of the Internet Information Office [32], DDT’s order volume in the following month dropped by 21.1%.
According to the “Regulations on the Administration of Algorithmic Recommendation of Internet Information Services”, if the algorithmic problems are serious, it is ordered to suspend the information updating and impose a fine of more than 10,000 yuan and less than 100,000 yuan, so the range of the penalty strength is set to be between 1 and 10 in this simulation experiment [33].
This article focuses on Chinese digital platform companies with a market capitalization of over 1 billion USD. According to publicly available data, as of the end of 2020, there were 197 digital platform enterprises in China that exceeded this scale [34], so the number of nodes in this network is initialized to 196, i.e., n = 196. Furthermore, existing research indicates that changes in the value of K within the network have a minimal impact on the simulation evolution of the model. Therefore, based on prior studies, the average connection number K is set to 4, i.e., K = 4. On the other hand, through previous literature, when the random reconnection probability p = 0.3, the system’s coordination in the network reaches its optimal level [35–37]. Hence, the random reconnection probability in this model network is set to 0.3. Based on the above parameters, the network is constructed as shown in Figure 4 below.
Based on all the above data this study relies on Python 3.12 in Win11 system for simulation.
As can be seen from Figure 5, under the established network size (n = 196) and the light penalty (the penalty is set to 1), when the regulatory strength is 0, in a completely free competition and profit-driven environment, 86.2% of the digital platform enterprises chose the strategy of algorithmic optimization for the algorithmic black-box problem, whereas when the regulatory strength is increased, the digital platform enterprises that chose optimization did not show a linear increase with the increase of the regulatory strength. Strength continues to increase and show a linear increase in the drive, especially when the regulatory strength reaches 0.8, the proportion of those who chose to optimize is only 80.1%, on the other hand even when the regulatory strength reaches the maximum value of 1, the proportion of digital platforms that chose to optimize the strategy is 82.1%, although higher relative to the regulatory strength of 0.8, but still lower than that of the proportion of the regulatory strength of 0. However, under this scale and penalty strength Under this condition, the highest peak of 89.3% of the proportion of choosing optimization is reached when the regulatory strength is 0.4. This trend illustrates that, in the complex digital platform environment, the government’s regulatory strength for the algorithmic black-box problem needs to be kept at an appropriate standard, rather than just adopting the strategy of strict regulation, or else it may not be able to achieve the desired effect under the combined influence of the benefits.
Figure 6 shows the trend of the proportion of digital platform enterprises choosing the optimization strategy when the regulatory strength is 0.4 and 1 respectively under the established network size (n = 196), adjusting the penalty strength from weak to strong, and it is obvious that the dynamic simulation results also do not show a linear positive correlation because of the increase of the penalty strength, but rather the proportion of the relative highest value occurs at a certain suitable point, and moreover, from the simulation results of the two In addition, from the simulation results of the two, the simulation results of the regulatory strength of 0.4 are not always higher than the simulation results of the regulatory strength of 1. Therefore, in the face of the algorithmic black box problem, if you want to prompt the digital platform enterprises to follow the regulation, and ultimately achieve a better regulatory effect, you can not only rely on a single regulatory means but also need to take the composite strategy as far as possible, multi-faceted and multi-dimensional common scientific supervision.
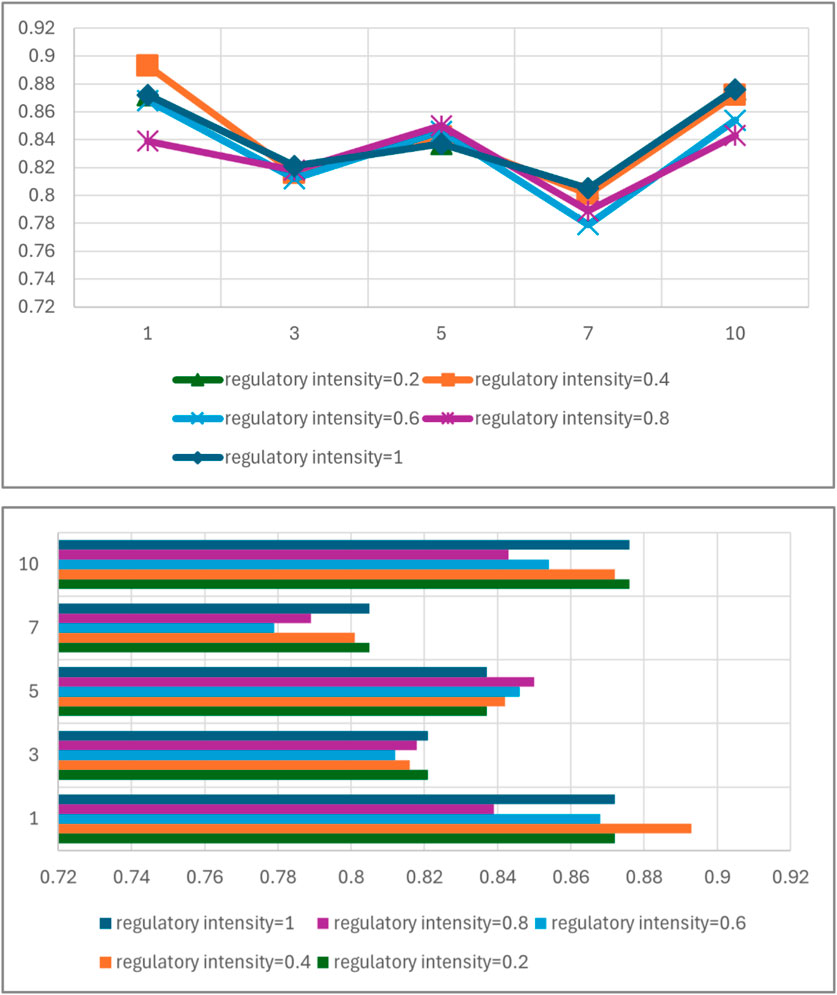
Figure 6. The trend of changes in regulatory enforcement on the diffusion rate of regulatory policies.
The results in Figure 7 from present the trend of the dynamic simulation results of different regulatory strengths in network environments with different sample sizes, and the number of digital platforms with a volume greater than $1 billion in 2020 was chosen for the initial setting of this network. In pace with the number of digital platforms compounding this target will inevitably increase year by year as the realistic time passes, therefore, in order to derive the environment of digital platforms after 2020, the number of samples in the dynamic simulation will be increased to greater than 196 of 300 for the same regulatory strength dimension of the simulation. From the simulation results, it can be clearly seen that when the number of samples is increased to 300, the regulatory strength of the proportion of digital platform enterprises that can obtain the highest selection of optimization strategies is 0.8, indicating that in this sample network environment, due to the great increase in the number of the government’s difficulty in regulating the industry as a whole has risen, and that it is necessary to further increase the regulatory strength in order to deal with the problem of the algorithmic black box more effectively through regulatory means. At the same time, the change of this trend also proves that, when dealing with the algorithmic black box problem, the government needs to reasonably adopt strategies and means, and needs to carry out reasonable and efficient regulation, avoiding one-size-fits-all and other single and direct regulatory strategies.
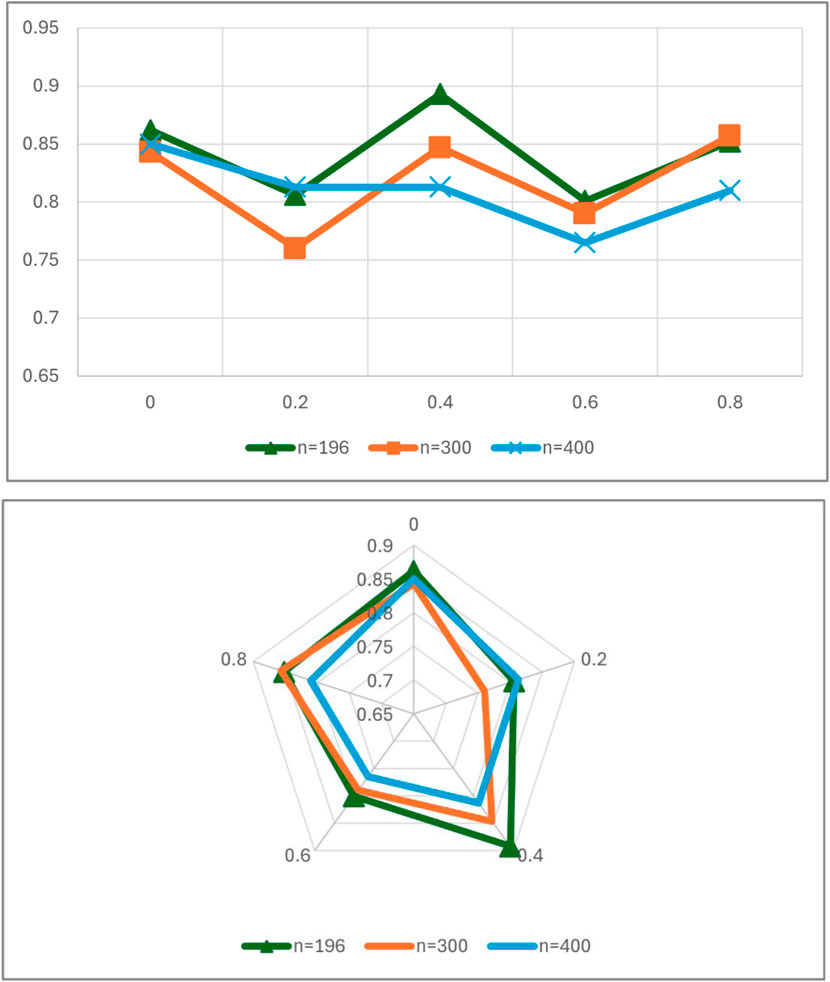
Figure 7. The impact of sample size n on the diffusion rate of regulatory policies under varying levels of regulatory enforcement.
Based on the current development of digital platforms, this study clarifies the characteristics and trends of digital platforms, and explores the important role of government regulation in optimizing the development system of digital platforms after sorting out the possible negative impacts of the algorithmic black box. The main conclusions are as follows:
First of all, as digital platforms flourish and new types of problems such as centralized monopoly, technological barriers and algorithmic discrimination continue to emerge, the government not only needs to pay attention to the role of regulation, but also needs to limit regulation to a reasonable scope, avoiding overly strict regulation that stifles the enthusiasm of digital platforms. According to the research of government regulatory intensity, the simulation results indicate the government’s regulatory strength for the algorithmic black-box problem needs to be kept at an appropriate standard. Over-regulation may make negative impact on the digital platforms, undermine the process of digital platform development, and harm economic efficiency, innovation and consumer welfare. Therefore, the government should fully respect the free space of digital platforms within legitimate boundaries, prudently intervene in the governance of digital platforms, and avoid excessive interference of public power in the autonomy mechanism of digital platforms. The government should fully interact with digital platform enterprises, provide timely and matching institutional resources for digital platform autonomy, safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of digital platforms, motivate digital platforms to optimize the transparency of their algorithms, and follow the principle of due process when regulating digital platforms, rather than enforcing the law arbitrarily or selectively.
Secondly, in order to strictly correct the unfair competition behavior of digital platforms and prevent the occurrence of incidents infringing on the rights and interests of users, we should encourage multiple bodies to participate in the regulation and collaborative governance to construct a fair and efficient digital transaction environment. On the basis of government punishment intensity, the simulation results show that we can not only rely on a single regulatory means, but also need to take the composite strategy as far as possible. In practice, governments face serious regulatory challenges, such as how to define the relevant market for digital platforms precisely. Relevant market refers to the range of goods and geographical scope in which operators compete over a certain period of time for specific goods or services. In antitrust case, it can help identify competitors and potential competitors, determine an operator’s market share and market concentration, and determine whether an operator’s behavior is illegal and the legal liability to be borne in case of violation. In the regulation of digital platforms, the products and services of digital platforms are updated extremely fast, and the whole market is extremely dynamic, so it is difficult to rely on solely the government to analyze its services from the traditional dimensions of function, price, quality, etc. Therefore, we should appropriately provide ways for other regulatory bodies, such as consumers and industry associations, to participate in regulation, which is not only conducive to share regulatory tasks, but also strengthens social supervision and more efficiently safeguards the fairness and impartiality of the market environment.
Finally, the government needs to adopt a variety of means to cooperate in forming an efficient and reasonable regulatory system to regulate digital platforms in accordance with the law. In the light of sample size variation, the dynamic simulation results indicate that the government needs to reasonably adopt strategies and means, avoiding one-size-fits-all and other single and direct regulatory strategies. In concrete terms, the government can provide the necessary prior prompts for compliance management of digital platforms and learn from the advanced regulatory experience to enhance regulatory efficiency. For instance, In the context of existing practice, the EU has established gatekeeper rules in the regulation of digital platforms through the Digital Markets Act. A small number of large undertakings providing core platform services have emerged with considerable economic power that could qualify them to be designated as gatekeepers. We could build legal rules similar to gatekeeper systems to contribute to the proper functioning of the internal market by laying down rules to ensure contestability and fairness for the markets in the digital sector in general, and for business users and end users of core platform services provided by gatekeepers in particular.
In addition, the characteristics of digital platforms make it difficult for external regulators to investigate and supervise each transaction on digital platforms. Digital platforms naturally have the advantage of constructing an autonomous order. The government can mobilize the intrinsic motivation of digital platforms to self-regulate through compliance incentive mechanisms, promote digital platform enterprises to continuously improve compliance systems and processes, strengthen compliance risk management. For example, regular compliance effectiveness evaluation and inspection should be implemented to urge digital platforms to fulfill their main responsibilities and promote the healthy and standardized development of digital platform enterprises. It should be added that the government can also draw on the experience of the European Union in the governance of digital platforms. According to different platforms’ positioning, main functions, the scale of users and the types of business, the platforms will be categorized into different levels, so as to enhance the flexibility and effectiveness of regulation through categorization.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
GZ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, conceptualization, formal analysis, project administration, investigation, validation. MT: Writing–review and editing, data curation, conceptualization, formal analysis, validation. XJ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, methodology, conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization, investigation, validation. TM: Writing–review and editing, supervision, formal analysis, validation, project administration.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by the Law School, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Dahlman C, Mealy S. Wermelinger. Harnessing the digital economy for developing countries. OECD Develop Centre Working Pap (2016) 2–67. doi:10.1787/4adffb24-en
2. Bukht R, Heeks R. Defining, conceptualising and measuring the digital economy. Development Inform Working Paper (2017) 68:1–24. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3431732
3. Sasikumar SK, Sersia K. Digital platform economy: overview, emerging trends and policy perspectives. Productivity (2020) 61(3):336–47. doi:10.32381/prod.2020.61.03.8
4. Cheney-Lippold J. A new algorithmic identity: soft biopolitics and the modulation of control. Theor Cult &Society (2011) 28(6):164–81. doi:10.1177/0263276411424420
5. Dijck Jv Datafication, dataism and dataveillance: big data between scientific paradigm and ideology. Surveill Soc (2014) 12(2):197–208. doi:10.24908/ss.v12i2.4776
6. Mager A. Algorithmic ideology. Inf Commun and Soc (2012) 15(5):769–87. doi:10.1080/1369118X.2012.676056
7. Draper N. Group power: discourses of consumer power and surveillance in group buying websites. Surveill and Soc (2012) 9(4):394–407. doi:10.24908/ss.v9i4.4343
8. van Dijck J, Poell T, de Waal M. The platform society: public values in a connective world. Oxford, Oxford University Press (2018). doi:10.1093/oso/9780190889760.001.0001
9. Diakopoulos N. Algorithmic accountability reporting: on the investigation of black boxes. Tow Cent Digital Journalism, Columbia Journalism Sch (2013) 1–30. doi:10.7916/D8ZK5TW2
10. Burrell J. How the machine ‘thinks’: understanding opacity in machine learning algorithms. Big Data and Soc (2016) 3(1). doi:10.1177/2053951715622512
11. Lyon D. The culture of surveillance: watching as a way of life. Soc and Cult Geogr (2018). doi:10.1080/14649365.2018.1525837
12. Cohen JE. Law for the platform economy. U.C Davis L Rev (2017) 51:133–204. Available from: https://scholarship.law.georgetown.edu/facpub/2015.
13. Couldry N, Mejias UA. The costs of connection: how data is colonizing human life and appropriating it for capitalism. Stanford Univ Press (2019) 50(3):223–4. doi:10.1177/00943061211006085g
14. Bart C, Robin M. Digital platform policy and regulation: toward a radical democratic turn. Int J Commun (2020) 135–54. Available from: https://ijoc.org/index.php/ijoc/article/view/11182/2901.
15. Kosinski M, Stillwell D, Graepel T. Private traits and attributes are predictable from digital records of human behavior. PNAS (2013) 110:5802–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.1218772110
16. Price ME, Verhulst SG. Self-regulation and the Internet. Kluwer L Int (2005) 2005:5–68. ISBN: 9789041123060.
17. Schmidt E, Cohen J. The New Digital Age: reshaping the future of people, nations and business. New York: Knopf (2013). doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0413-84b
18. Tambini D, Leonardi D, Marsden C. Codifying cyberspace: communications self-regulation in the age of Internet convergence. London: Routledge (2007). doi:10.4324/9780203947067
19. Bietti E. A genealogy of digital platform regulation. Geo L Tech Rev (2023) 7:1. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3859487
21. Hučková R, Semanová M. The position and regulation of gatekeepers in the context of the new European legislation. EU Comp L Issues challenges Ser (2022) 6:509–26. doi:10.25234/eclic/22441
22. Li Y, Jiao Y, Tang Y. An evolutionary analysis on the effect of government policies on electric vehicle diffusion in complex network. Energy Policy (2019) 129:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.01.070
23. Li H, Cao H, Feng Y, Li X, Pei J. Optimization of graph clustering inspired by dynamic belief systems. IEEE Trans Knowledge Data Eng (2024) 36(11):6773–85. doi:10.1109/TKDE.2023.3274547
24. Li H, Feng Y, Xia C, Cao J. Overlapping graph clustering in attributed networks via generalized cluster potential game. ACM Trans Knowledge Discov Data (2024) 18(1):1–26. doi:10.1145/3597436
25. Fronczak A, Fronczak P, Holyst JA. Average path length in random networks. Phys Rev E (2004) 70(5):056110. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.70.056110
26. Newman ME. Properties of highly clustered networks. Phys Rev E (2003) 68(2):026121. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.68.026121
27. Liu X, He M, Kang Y, Pan Q. Fixation of strategies with the Moran and Fermi processes in evolutionary games. Physica A: Stat Mech its Appl (2017) 484:336–44. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2017.04.154
29. Wang L, Zheng J. Research on low-carbon diffusion considering the game among enterprises in the complex network context. J Clean Prod (2019) 210:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.297
30. Ibm. Data leakage cost Report (2020). Available from: https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/BK0BB0V1?mhsrc=ibmsearch_a&mhq=%26%23x6cc4%3B%26%23x9732%3B2022.
31. Dzsws. China E-commerce Report (2022). Available from: http://dzsws.mofcom.gov.cn/zthd/ndbg/art/2023/art_21d89f715e43476eae4c420a9d787d41.html.
32. Weixin. The ride-hailing regulatory information exchange platform released the basic operational status of the ride-hailing industry for August (2021). Available from: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI3MDQwMDQ5NQ==&mid=2247551799&idx=1&sn=e430c5ad954e3f939f7fa2b1604c6d4f&scene=0.
33. Cac. Internet information service algorithm recommendation management regulations (2024). Available from: https://www.cac.gov.cn/2022-01/04/c_1642894606364259.htm.
34. Bai Y, Liu L. The ‘double disorder’ of platform economy development and the financial governance choices oriented towards common prosperity. J Hebei Univ (2022) 47(1):10–23. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-6378.2022.01.002
35. Albert R, Barabási AL. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys (2002) 74:47–97. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.74.47
36. Albert R, Jeong H, Barabási AL. Diameter of the world-wide web. Nature (1999) 401:130–1. doi:10.1038/43601
Keywords: digital platform, complex network, algorithm black box, government regulation, digital economy
Citation: Zhu G, Tang M, Jian X and Mu T (2025) A study of government regulation’s strategy for solving the algorithmic black-box puzzle of digital platforms: a complex network-based perspective. Front. Phys. 13:1538742. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1538742
Received: 03 December 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 14 March 2025.
Edited by:
Hui-Jia Li, Nankai University, ChinaReviewed by:
Jinlong Ma, Hebei University of Science and Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhu, Tang, Jian and Mu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiao Jian, amFueHRpYW40QDE2My5jb20=; Tong Mu, MTM3MTc5MzM3OTZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.