- 1Space and Astrophysics Research Lab, National Centre of GIS and SpaceApplications, Department of Space Science, Institute of Space Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan
- 2University of Wah, Wah Cantonment, Punjab, Pakistan
- 3Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering, Taif University, Ta’if, Saudi Arabia
The nuclear ground state properties of 63Co and 63Ni nuclei have been investigated within the framework of the relativistic mean field (RMF) approach. The RMF model with density-dependent meson-exchange (DD-ME2) interaction is used to calculate the potential energy curves (PECs) and nuclear ground state deformation parameters
1 Introduction
The rapid neutron-capture process (
The Gamow–Teller (GT) transition is widely believed to contribute to the stellar rates [5]. GT distributions have been produced experimentally using various approaches [6, 7]. The GT strength may be measured by charge-exchange reactions for nuclei in or close to the beta stability valley under terrestrial conditions when the parent nuclei stay in their ground states [8]. Several nuclei located beyond the beta stability valley play a crucial role in various astrophysical processes, including the
Weak interactions between finite nuclei hold significance in various disciplines, including particle physics and nuclear astrophysics [9–11]. Reliable weak-interaction rates of finite nuclei in high temperatures and high-densities stellar scenarios are crucial for understanding astrophysical challenges like stellar advancement and the origins of heavy elements. There are three different sorts of implications from stellar weak-interaction processes: converting neutrons to protons, reducing the density of positrons or electrons inside the stellar environment, and neutrino emissions [12–17]. Understanding the core-collapse supernova is therefore dependent on the stellar weak rates [18], the
The GT strength and the weak-interaction rates have been studied theoretically using a variety of nuclear structure models that have been developed over the past few decades. Fuller, Fowler, and Newman (FFN) accomplished groundbreaking work for the systematic calculation of nuclear stellar weak-interaction rates [12–14]. For the analysis of GT transition and stellar weak-interaction rate, the most dependable approach in current practice is the shell model (SM), which has a full diagonalization of an effective Hamiltonian in a selected model space [23]. Additional methods are anticipated for the GT strength and stellar weak rates in applications, such as the hybrid model based on the shell model Monte Carlo approach and the random-phase approximation (RPA) [24], the quasiparticle random-phase approximation (QRPA) [25], and the most recent traditional projected shell model (PSM) [26, 27].
Massive stars have an onion-like structure prior to the supernova stage, where the Fe, Co, and Ni mass-region nuclei play crucial roles in the core. Depending on neutron excess, nuclear beta decays and electron captures compete before the core collapses [28]. However, it is anticipated that most heavy nuclei close to or inside the beta stability valley originated from the
In the present work, we employed the RMF approach with density-dependent meson-exchange interactions to examine the nuclear ground state properties, including the binding energies and
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we provide a brief explanation of the RMF and pn-QRPA models used to calculate the nuclear structure and
2 Theoretical framework
2.1 The RMF model
The RMF model is a theoretical tool used for the description of nuclear structure properties of nuclei (see [29] and related references). The preliminary model [30] struggled to describe nuclear surface features and the incompressibility of nuclear matter. To address this, a nonlinear model was developed [29]. The later versions of the model were termed covariant density functional theory and included a density-dependent meson-exchange model [31]. In the present investigation, the ground state parameters for nuclei have been determined by employing the density-dependent meson-exchange (DD-ME2) [32] version of the RMF framework. According to the RMF model, nucleons interact by exchanging various mesons and photons [30]. The first version of the RMF model ran into several issues while attempting to describe the incompressibility of nuclear matter and the surface characteristics of nuclei. This led to the introduction of the model’s nonlinear variant [29]. Subsequent versions of the RMF framework, known as covariant density functional theory, developed with elements including point coupling (PC) and meson-exchange (ME) [31, 33, 34]. We utilized the density-dependent -(ME) framework in our analysis. The density-dependent meson-exchange variant of the RMF model considers the isoscalar scalar
In Equation 1, the terms
where i is generalized for the
whereas for the
The DD-ME2 interactions ([35–38]) are often employed as covariant density functionals in the DD-ME model.
Studying even-even systems within the mean field approach is a good approximation. In this case, the configurations, neglected above the mean field ground state, are 4- or higher-quasiparticle (qp) configurations. The 2-qp configurations do not couple to the Hamiltonian
2.2 The pn-QRPA model
The pn-QRPA model is employed to analyze GT strength distributions and stellar weak rates. The Hamiltonian configuration in the pn-QRPA model may be characterized using Equation 5:
The Hamiltonian for a single particle is denoted as
where
where
Here, the summation is taken on all the p-n pairs having
Here, X(Y) represent forward (backward) amplitudes. The
Here, the
where
with
In order to calculate the
with
The
where
where
The stellar
where
The construction of low-lying excited levels and computation of nuclear matrix elements in our present analysis may be found in [46].
for
where
where
where
Here,
where
3 Result and discussion
In the initial phase of our Investigation, we are focusing on the nuclear structure properties of 63Co and 63Ni isobars by utilizing the DD-ME2 interaction parameters within the RMF framework. The odd
In Figure 1, the PECs are expressed as a function of
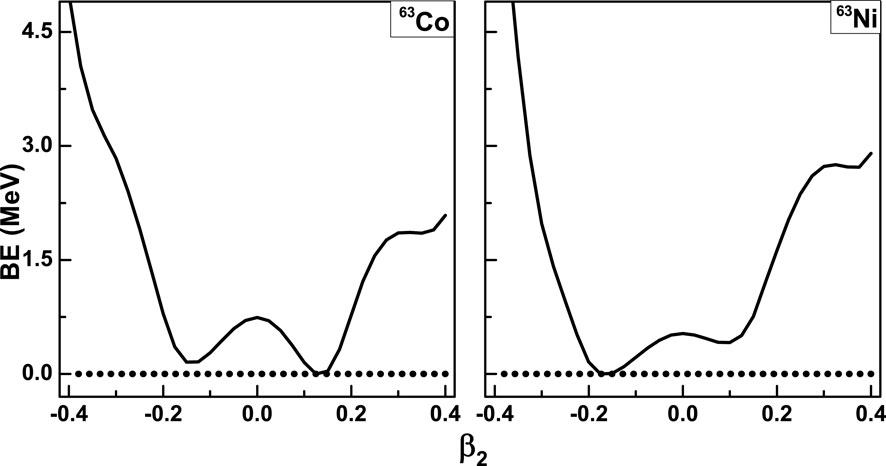
Figure 1. Binding energy against the constraint
The nuclear deformations computed via the RMF model are used as an input parameter in the pn-QRPA model to perform self-consistent calculations of the
At higher temperatures and densities, 63Co is one of the most important candidates in the core collapse of a massive star. Figure 2 depicts the present model-based computed GT strength along with the measured GT strength [54] and previously computed GT strength based on PSM [27] within the
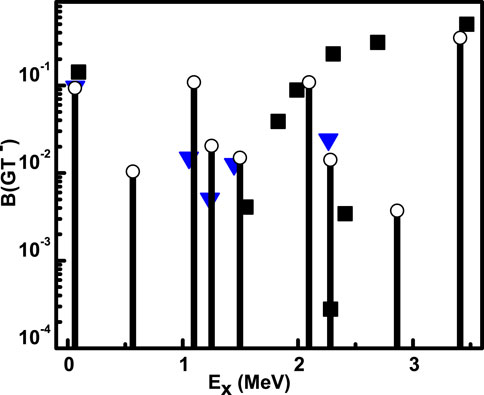
Figure 2. GT strength for 63Co via
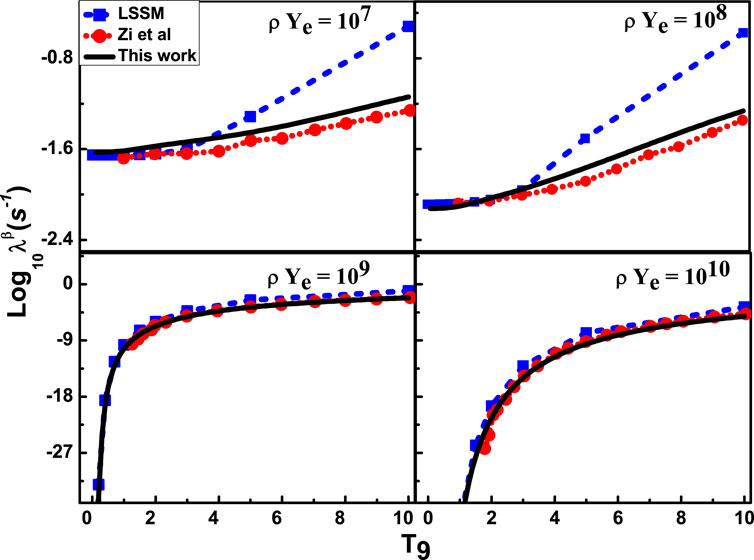
The temperature conditions in the stellar environment are so high (in order of
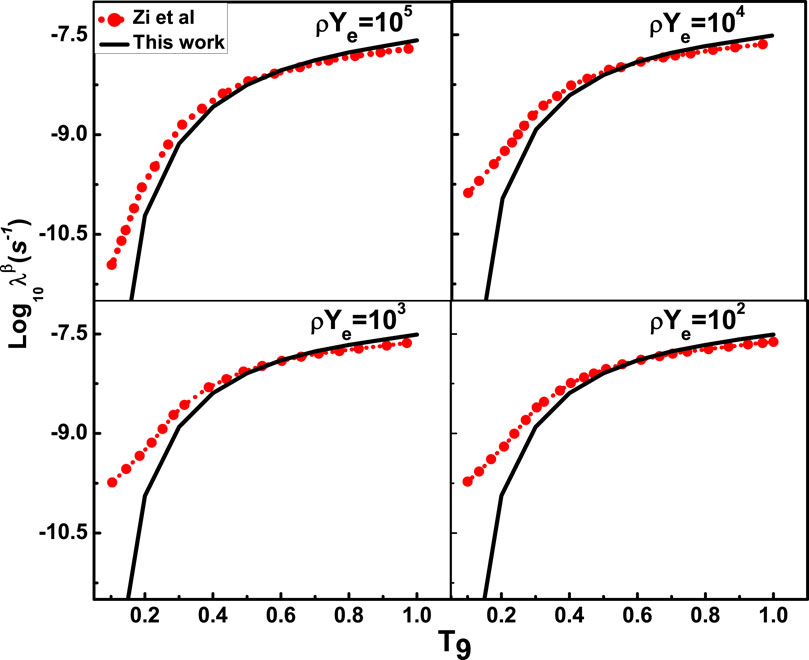
Figure 4. Computed stellar
4 Conclusion
The RMF model has been utilized to analyze the nuclear structural properties, including PECs and deformation parameters for 63Co and 63Ni. The analysis was performed using the DD-ME2 interaction under the blocking technique. The RMF-based analysis predicted an oblate shape for 63Co and a prolate shape for the 63Ni in their ground states. The
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
AK: conceptualization, investigation, software, supervision, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. J-UN: investigation and writing–original draft. HA: funding acquisition, project administration, software, and writing–review and editing. IA: data curation and writing–review and editing. N-UR: investigation and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Taif University, Saudi Arabia, Project No. TU-DSPP-2024-33.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to Taif University, Saudi Arabia, for supporting this work through project number (TU-DSPP-2024-33). Jameel-Un Nabi would like to acknowledge the support of Higher Education Commission Pakistan through the project number 20-15394/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2021.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Burbidge EM, Burbidge GR, Fowler WA, Hoyle F. Synthesis of the elements in stars. Rev Mod Phys (1957) 29:547–650. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.29.547
2. Coryell CD. The chemistry of creation of the heavy elements. J Chem (1961) 38:67. doi:10.1021/ed038p67
3. Kratz KL, Bitouzet JP, Thielemann FK, Moeller P, Pfeiffer B. Isotopic r-process abundances and nuclear structure far from stability - implications for the r-process mechanism. Astrophys J (1993) 403:216–38. doi:10.1086/172196
4. Usman S, Mushtaq A. Magnetorotational instability in dense electron-positron-ion plasmas. Sci Rep (2023) 13:15315. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-42397-3
5. Langanke K, Martínez-Pinedo G. Shell-model calculations of stellar weak interaction rates: II. Weak rates for nuclei in the mass range A = 45 − −65 in supernovae environments. Nucl Phys A (2000) 673:481–508. doi:10.1016/S0375-9474(00)00131-7
6. Fujita Y, Akimune H, Daito I, Fujimura H, Fujiwara M, Harakeh MN, et al. Mirror-symmetry structure of A = 27, T = 1/2 nuclei studied through strong, weak, and electromagnetic interactions. Phys Rev (1999) 59:90–100. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.59.90
7. Cole AL, Akimune H, Austin SM, Bazin D, Berg AV, GPA B, et al. Measurement of the Gamow-Teller strength distribution in Co-58 via the Ni-58 (t, He-3) reaction at 115-MeV/nucleon. Phys Rev C (2006) 74:034333. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.74.034333
8. Fujita Y, Rubio B, Gelletly W. Spin-isospin excitations probed by strong, weak and electro-magnetic interactions. Prog Part Nucl Phys (2011) 66:549–606. doi:10.1016/j.ppnp.2011.01.056
9. Avignone IIIFT, Elliott SR, Engel J. Double beta decay, Majorana neutrinos, and neutrino mass. Rev Mod Phys (2008) 80:481–516. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.80.481
10. Wang LJ, Engel J, Yao JM. Quenching of nuclear matrix elements for 0νββ decay by chiral two-body currents. Phys Rev C (2018) 98:031301. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.98.031301
11. Yao JM, Engel J, Wang LJ, Jiao CF, Hergert H. Generator-coordinate reference states for spectra and 0νββ decay in the in-medium similarity renormalization group. Phys Rev (2018) 98:054311. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.98.054311
12. Fuller GM, Fowler WA, Newman MJ. Stellar weak-interaction rates for sd-shell nuclei. I-Nuclear matrix element systematics with application to Al-26 and selected nuclei of importance to the supernova problem. Astrophys J Suppl Ser (1980) 42:447. doi:10.1086/190657
13. Fuller GM, Fowler WA, Newman MJ. Stellar weak interaction rates for intermediate-mass nuclei. II-A = 21 to A = 60. Astrophys J (1982) 252:715. doi:10.1086/159597
14. Fuller GM, Fowler WA, Newman MJ. Stellar weak interaction rates for intermediate mass nuclei. III-Rate tables for the free nucleons and nuclei with A = 21 to A = 60. Astrophys J Suppl Ser (1982) 48:279. doi:10.1086/190779
15. Langanke K, Martínez-Pinedo G. Nuclear weak-interaction processes in stars. Rev Mod Phy (2003) 75:819–62. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.75.819
16. Martínez-Pinedo G, Lam YH, Langanke K, Zegers RGT, Sullivan C. Astrophysical weak-interaction rates for selected A = 20 and A = 24 nuclei. Phys Rev (2014) 89:045806. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.89.045806
17. Langanke K, Martínez-Pinedo G, Zegers RGT. Electron capture in stars. Rep Prog Phys (2021) 84:066301. doi:10.1088/1361-6633/abf207
18. Janka H-T, Langanke K, Marek A, Martínez-Pinedo G, Müller B. Theory of core-collapse supernovae. Phys Rep (2007) 442:38–74. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2007.02.002
19. Käppeler F, Gallino R, Bisterzo S, Aoki W. The s process: nuclear physics, stellar models, and observations. Rev Mod Phys (2013) 83:157–93. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.83.157
20. Kabir A, Abideen ZU, Nabi J-U. Re-Investigation of neutron capture by 84Kr and 86Kr in the s-process nucleosynthesis. Braz J Phys (2024) 54:8. doi:10.1007/s13538-024-01455-5
21. Cowan JJ, Sneden C, Lawler JE, Aprahamian A, Wiescher M, Langanke K, et al. Origin of the heaviest elements: the rapid neutron-capture process. Rev Mod Phys (2021) 93:015002. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.93.015002
22. Schatz H, Aprahamian A, Görres J, Wiescher M, Rauscher T, Rembges JF, et al. rp-Process nucleosynthesis at extreme temperature and density conditions. Phys Rep (1998) 294:167–263. doi:10.1016/s0370-1573(97)00048-3
23. Cole AL, Anderson TS, Zegers RGT, Austin SM, Brown BA, Valdez L, et al. Gamow-Teller strengths and electron-capture rates for pf-shell nuclei of relevance for late stellar evolution. Phys Rev (2012) 86:015809. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.86.015809
24. Langanke K, Martínez-Pinedo G, Sampaio JM, Dean DJ, Hix WR, Messer OEB, et al. Electron capture rates on nuclei and implications for stellar core collapse. Phys Rev Lett (2003) 90:241102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.241102
25. Ejiri H, Suhonen J, Zuber K. Neutrino-nuclear responses for astro-neutrinos, single beta decays and double beta decays. Phys Rep (2019) 797:1–102. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2018.12.001
26. Sun Y, Feng DH. High spin spectroscopy with the projected shell model. Phys Rep (1996) 264:375–91. doi:10.1016/0370-1573(95)00049-6
27. Chen ZR, Wang LJ. Stellar β− decay rates for 63Co and 63Ni by the projected shell model. Symmetry (2023) 15:315. doi:10.3390/sym15020315
28. Heger A, Langanke K, Martínez-Pinedo G, Woosley SE. Presupernova collapse models with improved weak-interaction rates. Phys Rev Lett (2001) 86:1678–81. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.1678
29. Ring P. Relativistic mean field theory in finite nuclei. Prog Part Nucl Phys (1996) 37:193–263. doi:10.1016/0146-6410(96)00054-3
30. Walecka JD. A theory of highly condensed matter. Ann Phys (1974) 83:491–529. doi:10.1016/0003-4916(74)90208-5
31. Nikšić T, Vretenar D, Ring P. Relativistic nuclear energy density functionals: adjusting parameters to binding energies. Phys Rev C (2008) 78:034318. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.78.034318
32. Lalazissis GA, Nikšić T, Vretenar D, Ring P. New relativistic mean-field interaction with density-dependent meson-nucleon couplings. Phys Rev (2005) 71:024312. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.71.024312
33. Typel S, Wolter HH. Relativistic mean field calculations with density-dependent meson-nucleon coupling. Nucl Phys A (1999) 656:331–64. doi:10.1016/S0375-9474(99)00310-3
34. Meng J, Toki H, Zhou SG, Zhang SQ, Long WH, Geng LS. Relativistic continuum Hartree Bogoliubov theory for ground-state properties of exotic nuclei. Prog Part Nucl Phys (2006) 57:470–563. doi:10.1016/j.ppnp.2005.06.001
35. Nikšić T, Vretenar D, Finelli P, Ring P. Relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov model with density-dependent meson-nucleon couplings. Phys Rev (2002) 66:024306. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.66.024306
36. Nabi JU, Kabir A, Khalid W, Rida SA, Anwaar I. Investigation of nuclear structure and β-decay properties of as isotopes. Chin J Phys (2024) 92:22–32. doi:10.1016/j.cjph.2024.08.037
37. Nabi JU, Kabir A, Bayram T. Re-analysis of the Gamow-Teller distributions for N = Z nuclei, 24Mg, 28Si, and 32S. Chin J Phys (2024) 87:797–803. doi:10.1016/j.cjph.2023.12.036
38. Nabi JU, Khalid W, Kabir A, Rida SA. Study of β-decay, log ft values and nuclear structure properties of neutron-rich Ge nuclei. Arab J Sci Eng (2024) 1–13. doi:10.1007/s13369-024-09619-w
40. Stoitsov MV, Dobaczewski J, Nazarewicz W, Ring P. Axially deformed solution of the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock-Bogolyubov equations using the transformed harmonic oscillator basis. The program HFBTHO (v1.66p). Comp Phys Commu (2005) 167:43–63. doi:10.1016/j.cpc.2005.01.001
41. Nikšić T, Paar N, Vretenar D, Ring P. DIRHB-A relativistic self-consistent mean-field framework for atomic nuclei. Comp Phys Commu (2014) 185:1808–21. doi:10.1016/j.cpc.2014.02.027
42. Nilsson SG. Binding states of individual nucleons in strongly deformed nuclei. Dan Mat Fys Medd (1955) 29:1–69.
43. Ragnarsson I, Sheline RK. Systematics of nuclear deformations. Phys Scr (1984) 29:385–401. doi:10.1088/0031-8949/29/5/001
44. Kondev FG, Wang M, Huang WJ, Naimi S, Audi G. The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear physics properties. Chin Phys C (2021) 45:030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae
45. Möller P, Sierk AJ, Ichikawa T, Sagawa H. Nuclear ground-state masses and deformations: FRDM. Data Nucl Data Tables (2012) 109:1–204. doi:10.1016/j.adt.2015.10.002
46. Muto K, Bender E, Klapdor HV. Proton-neutron quasiparticle RPA and charge-changing transitions. Z Phys A Atom Nuclei (1989) 333:125–9. doi:10.1007/BF01565141
47. Homma H, Bender E, Hirsch M, Muto K, Klapdor-Kleingrothaus HV, Oda T. Systematic study of nuclear β decay. Phys Rev (1996) 54:2972–85. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.54.2972
48. Ikeda K, Fujii S, Fujita JI. The reactions and beta decays. Phys Lett (1963) 3:271–2. doi:10.1016/0031-9163(63)90255-5
49. Staudt A, Bender E, Muto K, Klapdor-Kleingrothaus HV. Second-generation microscopic predictions of beta-decay half-lives of neutron-rich nuclei. Data Nucl Data Tables (1990) 44:79–132. doi:10.1016/0092-640X(90)90020-K
50. Hirsch M, Staudt A, Klapdor-Kleingrothaus HV. Prediction of average β and γ energies and probabilities of β-delayed neutron emission in the region of fission products. Data Nucl Data Tables (1992) 51:243–71. doi:10.1016/0092-640X(92)90002-Y
51. Muto K, Bender E, Oda T, Klapdor-Kleingrothaus HV. Proton-neutron quasiparticle RPA with separable Gamow-Teller forces. Z Phys A Hadrons Nuclei (1992) 341:407–15. doi:10.1007/BF01301384
52. Gove NB, Martin MJ. Log-f tables for beta decay. Data Nucl Data Tables (1971) 10:205–19. doi:10.1016/S0092-640X(71)80026-8
53. phynu (2024). Available from: https://www-phynu.cea.fr/science_en_ligne/carte_potentiels_microscopiques/noyaux/zz28/zz28nn36all_eng.html (Accessed June 29, 2024).
54. nndc (2024). Available from: https://www.nndc.bnl.gov (Accessed June 29, 2024).
Keywords: pn-QRPA, β-decay properties, GT strength distribution, deformation parameter, RMF model, stellar rates
Citation: Kabir A, Nabi J-U, Almujibah H, Anwaar I and Raza N-UA (2025) Re-examining the impact of 63Co and 63Ni in the stellar environment. Front. Phys. 13:1484460. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1484460
Received: 21 August 2024; Accepted: 08 January 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Ignazio Bombaci, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Andres Arazi, National Atomic Energy Commission, ArgentinaShashi K. Dhiman, Himachal Pradesh University, India
Parada Tobel Paraduan Hutauruk, Pukyong National University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Kabir, Nabi, Almujibah, Anwaar and Raza. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abdul Kabir, a2FiaXJraGFuYWsxQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Abdul Kabir
Abdul Kabir Jameel-Un Nabi
Jameel-Un Nabi Hamad Almujibah3
Hamad Almujibah3