
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Phys., 03 March 2025
Sec. Fluid Dynamics
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2025.1449056
The interphase interaction between water flow and sediment and particle collision in sediment laden flow will modulate the flow turbulence. Due to the complexity of suspended sediment movement, the mechanism of water-sediment interaction has always been a difficult point in the study, especially the modulation law of water-sediment interaction on flow turbulence has not reached a consistent conclusion. It is of great significance for the study of sediment laden flow to optimize the construction of the numerical model of water and sediment. In this study, a Euler solid–liquid two-phase flow model was used to investigate the effects of drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions generated by natural sand and plastic sand on flow characteristics under the condition of different sediment concentrations for the case of equilibrium suspended-load transport, so as to determine the degree of influence of various factors in the numerical simulation process on the turbulent flow properties. Results showed that the presence of sediment particles changes the flow velocity, sediment concentration distribution, and turbulent energy distribution, and that such effects strengthen with increase in sediment concentration. The effects of drag force and particle collisions on the resistance coefficient and on flow velocity are dominant. The drag force tends to reduce the resistance coefficient and increase flow velocity, whereas particle collisions produce the opposite effect. The density gradient and particle collisions are the dominant factors affecting the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load and the vertical distribution of the sediment concentration. However, they produce opposite effects that partially cancel each other. With increase in sediment concentration, the effect of sediment particles on the turbulence of sediment-laden flow increases; the drag force and density gradient inhibit turbulence, and particle collisions promote turbulence.
In rivers, a large amount of sediment is transported in the form of suspended load, such as the sediment in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China [1]. Sediment particles, which move under the driving force of flow, have an opposing action on the flow during their movement. Riverbeds are shaped specifically by the interaction of these two effects. Interaction mechanism of water and sediment is the basis for solving problems related to sediment entrainment, transport, suspension, settlement, resistance characteristics and the sediment-laden force of the sediment-laden flow [2]. It is also of great practical importance in numerical modeling in relation to water and sediment movement, channel construction, and river treatment and maintenance.
Balachandar & Eaton [3] pointed out that in a dilute suspension, there are several mechanisms that contribute to turbulence modulation:(a) the presence of particles will enhance dissipation, (b) turbulence kinetic energy will be transferred from particles to fluid, and (c) the formation of wake and vortex shedding behind particles, which is called turbulence modulation. Owing to the presence of sediment particles, the intensity of turbulence in sediment-laden flow is modified in comparison with that of clear flow [4]. The complex mechanisms of phase interactions in solid–liquid two-phase flow, such as the interactions between particles and turbulent flow masses, particle collisions, and friction, make the turbulence of sediment-laden flow much more complex than that of single-phase flow [5–7]. Because of the randomness of the motion of water and sediment, the study of the mechanism of turbulence modulation of sediment-laden flow remains a challenge in the field of fluid mechanics.
Many studies have conducted numerical and experimental research on the effect of turbulence modulation on equilibrium suspended-load transport. Experiments by Elata and Ippen [8] revealed that the suspended particles play a role in promoting the intensity of flow turbulence under high sediment concentration, and Muller [9] drew the same conclusion after performing experiments with large particle sizes. Following experiments conducted in a water tank, Zhang et al. [10] proposed that sediment has a “turbulence inhibition effect” and suggested that a near-bottom suspended load with high sediment concentration would inhibit turbulence. Wang and Qian [11] found that both natural sand and neutral suspended particles substantially inhibited the intensity of flow turbulence, and that the degree of inhibition increased markedly with increase in sediment concentration. Ingen (1981) and Lyn [12] both found through experiment that the presence of fine particles in suspension has little impact on the intensity of flow turbulence. Experimental studies have shown that sediment particles might promote, inhibit, or leave unchanged the turbulence of sediment-laden flow, but the conclusions are inconsistent.
Many early numerical studies directly adopted the Reynolds equation of single-phase flow as the basic governing equation and used the single-phase turbulence model to close the turbulence variables in the controlgoverning formula [13, 14]. However, such an approach ignores the effect of sediment–flow interaction and the impact of sediment particles on the turbulence characteristics of the flow.With development of numerical calculation methods, many studies have regarded muddy water mixed with water and sand as a mixture theory flow. Unlike single-phase flow theory, the Reynolds equation of the mixture theory flow model and the turbulence model consider the effect of the density gradient [15–17], recognizing that the density gradient could have a damping effect on the movement of the turbulent flow, which is an important influencing factor of the turbulence of sediment-laden flow [15, 16, 18–20]. However, following experiments using neutral sand with density of 1.2 g/cm3 and particle size of 0.25 mm, Noguchi and Nezu [21] found that even under the condition of a small density gradient, suspended particles inhibited the intensity of turbulence of sediment-laden flow. Thus, it can be seen that the impact of suspended particles on the turbulence of sediment-laden flow is not affected only by the density gradient. Fu and Wang [22] highlighted that sediment and flow can be macroscopically regarded as a mixed entity, and with increase in sediment concentration, the phase interactions between particles and flow and the collisions between particles will also have nonnegligible effect on the turbulence characteristics of sediment-laden flow. However, the above studies regarded the water–sediment mixture as a mixture theory flow, the effects of solid–liquid interactions and particle collisions are not included in the basic governing equation of the mixture theory flow, thereby ignoring the effect of these two factors on the turbulence of sediment-laden flow [23].
In recognition of the above problems in the theory of sediment-laden flow and the corresponding turbulence model, many studies have used the two-phase flow equation in the field of multiphase flow to study sediment-laden flow. For example, Drew [24] used the global averaging method to derive the Reynolds mean mass and momentum conservation equations for solid–liquid two-phase flow. Several other studies applied two-phase flow theory to investigate sediment movements and achieved remarkable results [23, 25–31], arguing that the two-phase flow theory has obvious advantages over the traditional sediment-carrying flow theory for the analysis of water and sediment movement [30, 32–34]. In two-phase flow theory, the solid and liquid phases have their own mass conservation and momentum conservation equations. The momentum coupling between the solid governing equation and the liquid governing equation is achieved by phase interaction terms. The velocity and concentration of each phase can be obtained accurately by calculating the basic governing equation of the two-phase flow [35]. Recently, Kim et al. [36] proposed the Euler two-phase flow model, which considers the free-surface water and sediment transport, and they used it to solve the problem of water and sediment transport under the effect of waves. In this model, the turbulence characteristics of sediment-laden flow, such as exchange of phase-to-phase turbulence, change in turbulent energy caused by the drag force, effect of particle collisions, and impact of density stratification on liquid phase turbulence, are all considered.
The two-phase flow model reflects the effects of turbulence modulation on flow velocity, sediment concentration, and turbulent energy distribution during the transfer of sediment-laden flow. However, further investigation is required into the mechanism via which various mechanical elements (e.g., solid–liquid phase interaction, particle collisions, and density gradient) affect flow velocity, sediment concentration distribution, and turbulence.
At present, in practical engineering applications, the traditional water-sediment model is often used to solve practical engineering problems. Compared with the traditional water-sediment model, the two-phase flow model has higher calculation accuracy, but it also makes the calculation amount larger and time-consuming. Therefore, it is necessary to simplify the two-phase flow equation to improve the calculation efficiency. According to the analysis and treatment of sediment particles, there are Euler-Lagrange and Euler-Euler numerical models for two-phase transport. In engineering problems, the Euler-Lagrange method is not practical for tracking a large number of particles through a flow field. Euler-Euler derived the governing equations for two phases (momentum and sediment concentration) based on continuous approximations, which are more suitable for engineering applications [37], Moreover, the Euler-Euler two-phase method is generally effective at both high and low sediment concentrations [30].
Therefore, using data acquired from the water tank experiments of Wang and Qian [11], this study undertook numerical simulation sensitivity analyses using the Euler-Euler OpenFOAM solid–liquid two-phase flow model. The objective was to study the effects of the drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions of sediment particles on the movement characteristics of flow under the condition of different sediment concentrations, and to reveal the mechanism via which turbulence modulation of sediment-laden flow affects the flow resistance, vertical diffusion coefficient of sediment concentration, and turbulence kinetic energy under equilibrium suspended-load transport conditions, which provides the basis for the specific influence of the interaction terms of water and sediment under different working conditions.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. The basic governing equation of the two-phase flow and the mechanical elements of sediment are introduced in Section 2. Section 3 introduces the construction of a two-dimensional water tank and calibration verification of the model using the water tank data from Wang and Qian [11]. In Section 4, the sensitivity analysis is described, the effects of various mechanical elements (i.e., drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions) caused by sediment particles on the flow velocity, vertical distribution of sediment concentration, and turbulent energy are analyzed, and the mechanism via which turbulence modulation affects equilibrium suspended-load transport is revealed. Finally, the main findings of the study are summarized in Section 5.
Under the OpenFOAM framework, the Euler two-phase flow model can simulate the water–sediment transport process under the free surface. The specific equation for which is described in the following.
The solid–liquid two-phase flow model uses the Reynolds averaging method, and the Reynolds mean mass equation for the liquid and solid phases can be written as follows [24, 38]:
where t is time and xi (i = 1, 2, 3) represents the three directions of Cartesian coordinate space, i.e., the components of flow, spreading, and the vertical direction, and they follow the summation convention. The variable
Where
The Reynolds average momentum equations for liquid and solid phases are as follows [36]:
where ρf and ρs represent the density of the liquid phase and of the solid phase, respectively, pf represents fluid pressure, and g is gravitational acceleration (−9.8 m/s2). The third term on the right-hand side of Equation 1 represents surface tension, where σt is the surface tension coefficient (σt = 0.074 kg/s2 at the air–water interface at 20°C), γ is the surface curvature, and τijf is fluid stress, including the fluid Reynolds stress and viscous stress, which can be obtained from the turbulent closure calculation using a modified k-ε model [39, 40]. The Tf on the right-hand side of Equation 1 represents momentum transfer caused by the drag force between the solid phase and the liquid phase, which is the result of the action of the drag force caused by the average relative velocity between the liquid phase and the solid phase, where β is the resistance coefficient. In this study, the equation proposed by Ding and Gidaspw [41] was used for the calculation. The Df on the right-hand side of Equation 1 represents the density gradient used to characterize the momentum redistribution caused by the sediment concentration distribution, where vft is the eddy viscosity, and σc is the Schmidt number (see Table 1). On the right-hand side of Equation 2, P stands for the particle positive stress term, where ps refers to the positive particle stress, and J denotes the particle shear stress term, where τs is the shear stress; both P and J are simulated through kinetic theory [41, 42] to reflect particle collisions. The methods for solving the coefficients in Equations 1 and 2 are detailed in the relevant Ref. [39, 43, 44].
The liquid phase stress τijf in Equation 1 includes the Reynolds stress Rijf and the viscous stress rijf, and the total solid stress can be calculated as follows:
where vf is the molecular viscosity coefficient of the liquid phase, and vft is eddy viscosity, which can be calculated according to vft = Cμ(kf)2/εf, where Cμ is the empirical coefficient (Table 1). The liquid phase turbulence energy kf and the liquid phase turbulence dissipation rate εf can be solved using the liquid phase k-ε equation. Parameter sijf is the tensor of the liquid-phase strain rate. For the liquid phase turbulence closure, an improved k-ε model was used in this study, which can be expressed as follows:
where σk = 1 is the Schmidt number of the liquid phase turbulence kinetic energy, and parameter
where the set values of empirical coefficients C1ε, C2ε, C3ε, C4ε, and σε are listed in Table 1. Similar to Equation 3, Te in Equation 4 shows the effect due to the drag force, and De represents the buoyancy effect due to the density gradient.
The model is subject to solid-phase turbulence closure based on particle flow dynamics theory, while considering the effects of solid–liquid interaction and particle collision [41]. Further details regarding the model construction and numerical implementation can be found in Jacobsen et al. [43], Klostermann et al. [44], and Cheng et al. [39].
Particle stress in interparticle interactions is caused by intermittent collisions between particles and persistent contact/friction [47]. Therefore, the particle pressure ps and shear stress τijs are expressed as the collision component (superscript “sc”) and the frictional contact component (superscript “sf”).
The collision component of particle pressure and particle shear stress is expressed using the concept of particle temperature Θ [41, 42].
Where e is the recovery coefficient and gs0 is the radial distribution function [48], Particle temperature Θ is calculated by its equilibrium equation, which considers advection, diffusion, shear generation, inelastic collision dissipation and particle-induced fluctuations [39, 41]. Particle shear viscosity μsc and volumetric viscosity λ are functions of particle temperature and are calculated by kinetic theory [49]. The partial Sijs is the deviation of sediment velocity.
When sediment concentrations are high, the likelihood of intermittent collisions decreases. The particle pressure and shear stress are primarily influenced by the frictional contact component. The particle pressure psf resulting from permanent contact and the particle shear stress τsf resulting from frictional contact can be defined as [39, 50, 52, 53]:
Where F = 0.05, a = 3, b = 5 are empirical coefficients, and thresholds of
Based on water tank experiment data from Wang and Qian [11], the numerical model was verified, and the natural sand (SQ) and plastic sand (SF) in the experiment were selected as representative. The density of SF and SQ was 1,050 and 2,640 kg/m3, respectively. The experimental tank was 20 m long, 0.3 m wide, and 0.4 m high, with slope of 1%. The sediment was added at the inlet. The water depth h, shear flow velocity u*, particle size d, and other experimental parameters under the simulated experimental working conditions are listed in Table 2.
Using the OpenFOAM model, a two-dimensional numerical water tank of size equivalent to that used in the physical experiments was constructed, which neglected spanwise flow. As shown in Figure 1, the x direction represents the flow direction, and the tank inlet is defined as x = 0. In the vertical (y) direction, upward is defined as positive, and the water surface at the inlet is defined as y = 0. The grid scale in the x direction is 0.01 m. In the y direction, the part with y > 0 is defined as the air part of the grid (set as 0.005 m) and the part with y ≤ 0 is defined as the water body part of the grid (set as 0.0016 m). The total number of grids is 250,000. The left and right ends of the numerical flume are the inlet and outlet condition respectively. The bottom is designated as the wall boundary, the flux of all scalar and wall normal velocity components is zero, the velocity component parallel to the wall adopts the no-slip boundary condition, the top is set as the free surface, and the vertical flux of sediment at the water-sand interface is zero. In the simulations, the time step was set as 0.001 s. The inlet flow velocity and the boundary conditions of the sediment transport volume were also consistent with the experimental data (Table 2).
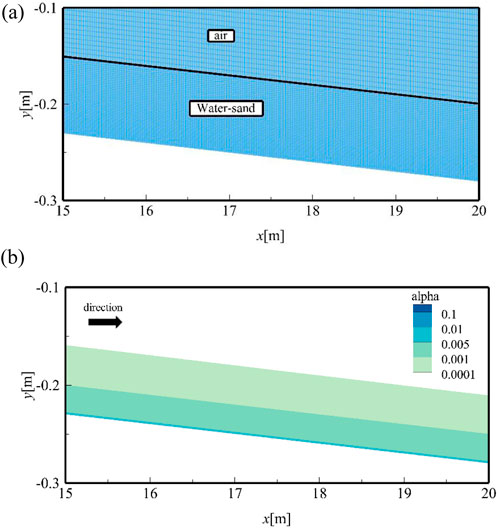
Figure 1. (A) In the grid form of the numerical flume, the grid scale of the air part is larger than that of the water-sand mixing part, so the grid of the water-sand mixing part is more dense, and the slope is 1%. (B) The water and sediment movement reaches equilibrium at t = 120 s,and the volume fraction of water and sediment does not change.
After the model was confirmed balanced and stable via calculation, the flow velocity, sediment concentration, and turbulence energy data at section x = 12.3 m were extracted for analysis. Figure 2 compares the calculated liquid phase flow velocity and vertical distribution of sediment concentration with the experimental results of Wang and Qian [11]. The solid lines represent the model calculation results, and the circles represent the experiment data. The y-axis is expressed by y+ = yu*/vf, and the x-axis is expressed by Umx0 = uf/u*, reflecting the flow velocity where u* stands for the friction flow velocity. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the calculated values of the velocity distribution and the vertical distribution of sediment concentration for both SQ and SF are in good agreement with the measured values. In the case of high sediment concentration, the results of the two-phase flow model are more reasonable than those of the traditional Rouse formula.
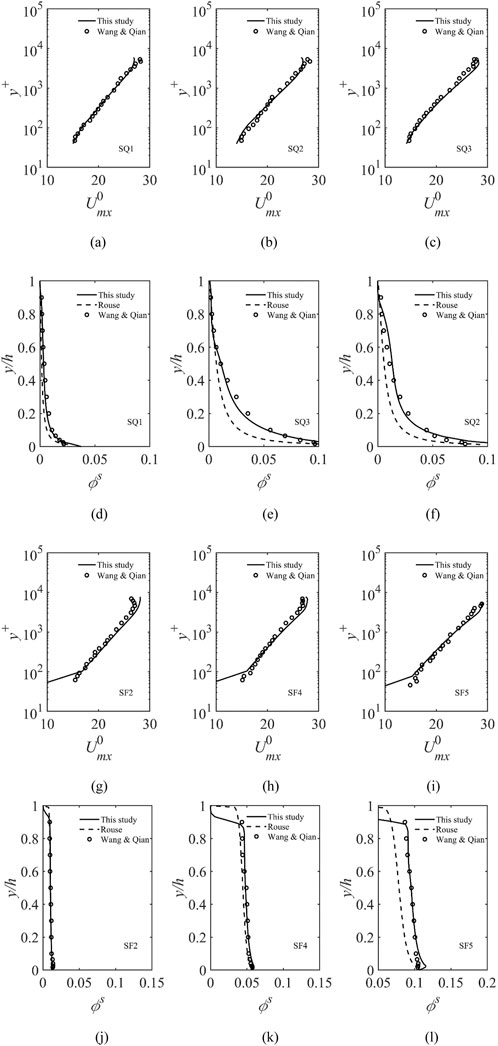
Figure 2. Flow velocity distribution and vertical distribution of sediment concentration for SQ and SF compared with the experimental results of Wang and Qian [11].
Figure 3 compares the calculated and measured values of the vertical distribution of the flow turbulence kinetic energy. The ordinate is y/δ, where δ is the boundary layer thickness, and the abscissa is the flow turbulence kinetic energy u'/u* normalized by the friction flow velocity. It can be seen that under the condition of different sediment concentrations, the calculated turbulence kinetic energy for both SQ and SF is in good agreement with the experimental results. With increase in sediment concentration, the inhibition of liquid phase turbulence for SQ and SF increases, consistent with the experimental findings of Wang and Qian [11].
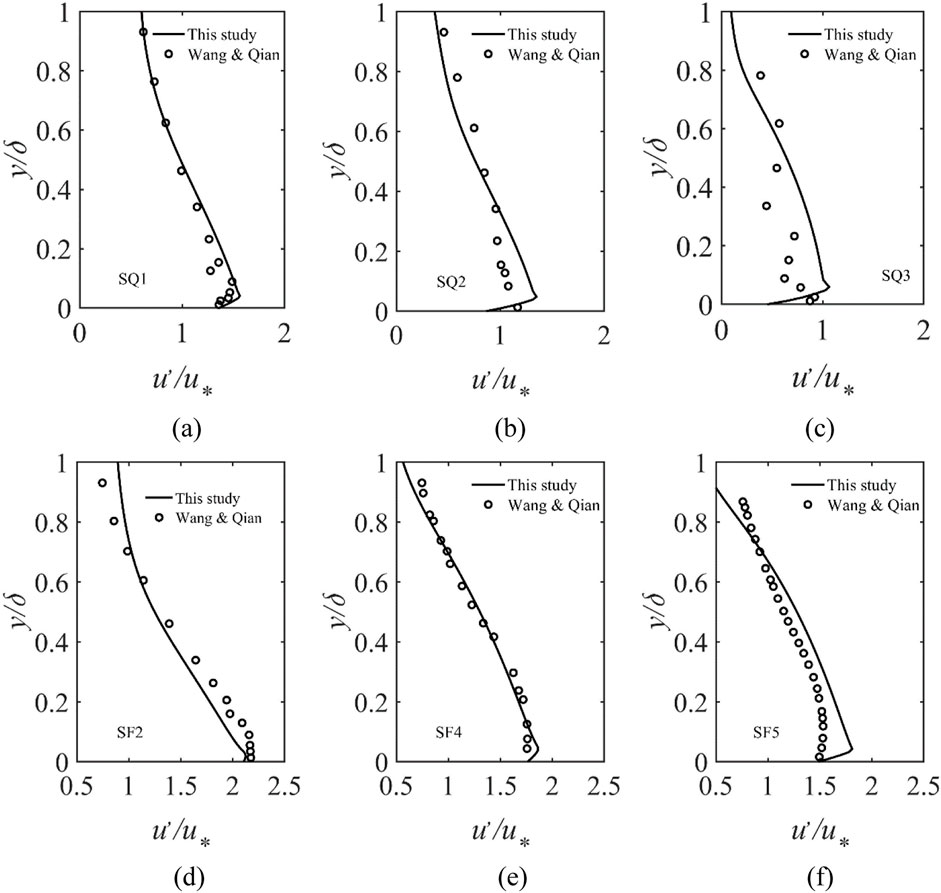
Figure 3. Flow turbulence kinetic energy for SQ and SF compared with the experimental results of Wang and Qian [11].
In comparison with single-phase flow, the turbulence characteristics of sediment-laden flow are more complex owing to the physical mechanisms of interaction of the water–sand motion, e.g., the interactions between particles and turbulent water masses, and the collisions between particles (Figure 4). Therefore, the governing equation of this model used in this study included the drag force term, density gradient term, and particle collision term. Based on the governing variable method, sensitivity analysis was performed to quantify the effect of turbulence modulation of sediment-laden flow on the motion characteristics of the water and sediment. Thus, the variations of the contributions of various mechanical elements (i.e., drag force, density gradient, and particle collision) to the turbulence modulation of sediment-laden flow under the condition of different sediment concentrations were analyzed.
In this study, four cases were developed (see Table 3), and each was implemented by adjusting the momentum equation and the related terms in the k-ε equation. Here, the Tf, Tk, and Te terms are collectively referred to as T (total drag force term), the Df, Dk, and De terms are collectively referred to as D (total density gradient term), P is the particle normal stress term, and J is the particle shear stress term. CaseN does not consider the T, D, P, and J terms. Thus, the two-phase flow equation is degenerated into the traditional basic water–sand governing equation, without considering the effects of drag force, density gradient, and particle collision. CaseT includes the T term characterizing the drag force on the basis of CaseN, without considering the P and J terms. CaseTD considers only the T and D terms, excluding the P and J terms. CaseTDP is a standard two-phase flow model case that considers the T, D, P, and J terms. By comparing and analyzing the results of CaseN with those of CaseT, CaseTD, and CaseT, CaseTDP, and CaseTD, the effects of the drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions on water and sand movement were studied, respectively.
Flow velocity distribution is an important indicator of the characteristics of turbulence, and the resistance coefficient is an important parameter with which to characterize the motion resistance of water flow, which directly affects the magnitude of flow velocity. By studying the effect of the drag force term, density gradient term, and particle collision term on the resistance coefficient, the effect of different turbulence modulation factors on the flow velocity distribution can be revealed. According to the Darcy–Weisbach formula, the resistance coefficient for each of the four cases for SQ and the SF can be calculated as follows:
where n is the comprehensive resistance coefficient, and
Figures 5, 6 show the resistance coefficient and the flow velocity distribution of different cases, respectively. For SQ and SF, drag force and particle collisions have important but opposing impact on the resistance coefficient; drag force tends to reduce the resistance coefficient, and particle collisions act to the contrary. Owing to its inhibitory effect on the resistance coefficient, drag force plays the role of increasing flow velocity, and with increase in sediment concentration, the effect becomes greater. Owing to the associated promotion of the resistance coefficient, particle collisions play the role of reducing flow velocity, and with increase in sediment concentration, the reduction effect becomes greater.

Figure 5. Flow drag coefficients of SQ and SF affected by the drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions.
As shown in Figure 2, the vertical distribution of sediment particles in the sediment-laden flow is uneven. Figure 5 shows that the presence of a density gradient has an inhibitory effect on the resistance coefficient, which is manifested as reduction in flow velocity near the bottom and increase in flow velocity near the water surface. With increase in sediment concentration from top to bottom in the vertical direction of the flow, the presence of a density gradient has strongest inhibitory effect on the bottom flow velocity and weakest inhibitory effect on the flow velocity near the water surface. For SF, because its particle density is similar to that of water, the density gradient is small, the vertical distribution of the sediment concentration is relatively uniform, and the effect of the density gradient on both the resistance coefficient and the flow velocity under the condition of different sediment concentrations may be ignored. Overall, the effect of the density gradient on the resistance coefficient and the flow velocity is less than that of the drag force and particle collisions.
The vertical sediment concentration distribution of a suspended load is an important aspect of the moving process of the suspended load, and it is a macroscopic manifestation of the comprehensive effects of sediment particle settlement, turbulent diffusion, and particle collisions. In the process of water and sediment energy exchange, the vertical distribution of sediment concentration is affected by many factors, such as the drag force, particle collisions, and density gradient. The vertical turbulent diffusion coefficient of a suspended load plays an important role in determining the vertical distribution of the sediment concentration, which can reflect the effect of the turbulent diffusion of the sediment-laden flow on sediment suspension. Therefore, it is of great importance to study the effect of various factors on the diffusion coefficient of the vertical turbulence of the suspended load. To study such effects on the vertical turbulent diffusion coefficient and on the sediment concentration distribution of a suspended load, the mass conservation equation of the suspended load under constant, uniform, and equilibrium conditions of sediment-laden flow can be expressed as follows:
where ω is the sedimentation velocity,
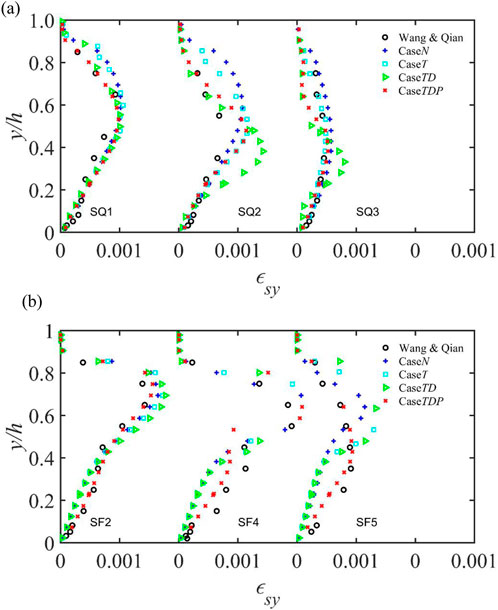
Figure 7. Suspended-load turbulent diffusion coefficient distribution in the four studied cases for SQ and SF.
As shown in Figures 7, 8 for SQ, the results of CaseN and CaseT indicate that the drag force tends to reduce the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load and slightly inhibit the suspension of sediment particles; consequently, the suspended sediment particles are reduced. The exchange of water masses in each layer of the sediment-laden flow will cause exchange of sediment between the water layers, resulting in a density gradient of the suspended load in the sediment-laden flow, and the amount of sediment carried by the upward-moving water mass will be greater than the amount of sediment carried by the downward moving water mass, which is manifested as upward movement of the suspended load. By comparing the results of CaseT and CaseTD, it can be seen that the presence of a density gradient will substantially change the vertical distribution pattern of the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load and, as a result, the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load near the bottom and the water surface is reduced, while that at intermediate depths is increased. The corresponding perpendicular distribution of sediment concentration shows a trend of increase near the bottom and decrease at approximately y/h = 0.2, and the effect is greater with increase in sediment concentration. By comparing CaseTD and CaseTDP, the effects of particle collisions and the density gradient on the turbulent diffusion coefficient are found to be the opposite. Particle collisions increase the turbulent diffusion coefficient of sediment concentration near the bottom and the surface, and reduce the diffusion coefficient at intermediate depths, canceling some of the effect of the density gradient. The vertical distribution pattern of sediment concentration is close to that of CaseT, and the bottom concentration of CaseTDP is slightly higher than that of CaseT owing to the high sediment concentration at the bottom, which is affected by particle collisions. From the perspective of contributions to the effect on the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load and the vertical distribution of sediment concentration, the density gradient and particle collisions are the dominant factors, the effect of the drag force is small, and the density gradient and particle collisions induce opposite effects that partially cancel each other.
For SF, the effects of the drag force and the density gradient on the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load are small, with little variation with increase in sediment concentration. However, the effect of particle collisions is more notable, and the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load increases at intermediate and lower depths; the greater the water depth, the smaller the impact, and the effect can be ignored when y/h > 0.5. Additionally, for SF, it can be seen from Figure 8 that the vertical distribution curve of the sediment concentration in CaseTDP, which considers particle collision, is more consistent with the measured values.
The turbulence of sediment-laden flow is the driving force of momentum exchange between flow and sediment, and the diffusion of sediment turbulence. Therefore, it is of great scientific research and application value to study the mechanism via which turbulence modulation affects sediment-laden flow. Turbulence kinetic energy is a characteristic value reflecting the degree of pulsation intensity in flow velocity, and it is the most important dynamic characteristic variable of turbulence. The turbulence modulation mechanism of sediment-laden flow can be analyzed through the vertical distribution pattern of turbulence kinetic energy. The normalized vertical distribution of turbulence kinetic energy in the flow direction under each studied case is plotted in Figure 9, and the effects of the drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions on flow turbulence are illustrated by the box plots shown in Figure 10. It can be seen that the inhibitory effect of sediment particles on the turbulence of sediment-laden flow increases with increase in sediment concentration, and the effect of each factor is analyzed quantitatively in the following.
Under the effect of the drag force, turbulence kinetic energy weakens for SQ. Specifically, the average turbulence kinetic energy in the flow direction for SQ1 decreases from 1.29 to 1.08, that for SQ2 decreases from 1.26 to 0.82, and that for SQ3 decreases from 1.30 to 0.78. The drag force inhibits flow turbulence, and with increase in sediment concentration, the inhibitory effect increases. For SF, the drag force also inhibits turbulence kinetic energy, and the inhibitory effect increases with increase in sediment concentration.
Under the effect of the density gradient, the turbulence kinetic energy decreases for SQ. The average turbulence kinetic energy in the flow direction decreases from 1.09 to 1.00, from 0.82 to 0.50, and from 0.78 to 0.41 for SQ1, SQ2, and SQ3, respectively. The density gradient inhibits flow turbulence, and with increase in sediment concentration, the inhibitory effect increases. For SF, the density is close to that of water, and the vertical distribution of sediment concentration is uniform; thus, the density gradient has little impact on the turbulence kinetic energy.
Sediment particle collisions play a role in promoting turbulence kinetic energy. For SQ, the average turbulence kinetic energy in the flow direction increases from 1.0 to 1.05, from 0.50 to 0.76, and from 0.41 to 0.77 for SQ1, SQ2, and SQ3, respectively. Particle collisions promote flow turbulence, which increases with increase in sediment concentration. The sediment concentration of SQ is higher near the bottom and the number of particle collisions is greater than that near the water surface; consequently, particle collisions near the bottom have greater effect in promoting turbulence. For SF, the sediment concentration is distributed evenly, and the turbulence-promoting effect of particle collisions is also distributed evenly in the vertical direction.
Turbulence modulation factors (i.e., drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions) have important impact on turbulence properties, and their specific laws of influence are summarized in Table 4. Generally, drag force has greater impact on flow velocity and turbulence for SQ and SF, but small effect on sediment concentration. The drag force suppresses turbulence, reduces the energy loss of the flow, and increases flow velocity. The effect of the density gradient on flow velocity and turbulence is less than that of the drag force. For SQ, the density gradient has important impact on the distribution of sediment concentration, which changes the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the sediment concentration and modifies the vertical distribution of sediment concentration. Particle collisions exhibit the effect opposite to that of both the drag force and the density gradient. For SQ and SF, particle collisions make important contributions to all three factors, promoting flow turbulence, increasing flow energy consumption, and reducing flow velocity, but they have the reverse effect to density gradient in terms of sediment concentration distribution.
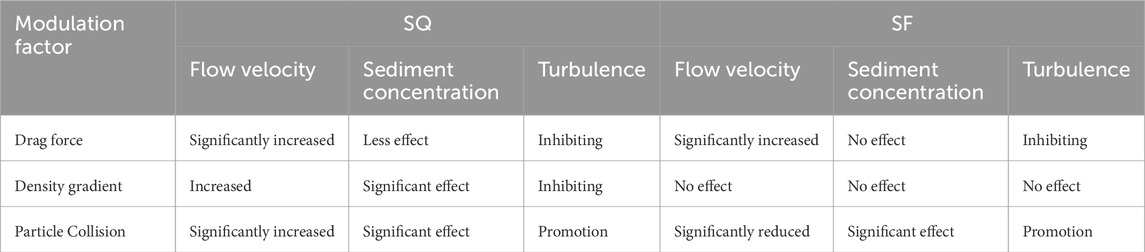
Table 4. Summary of the laws of contribution of the drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions.
In this study, the Euler solid–liquid two-phase flow model was used for numerical simulation based on the OpenFOAM platform, and the model was verified using water tank experiment data from Wang and Qian [11]. Under the condition of equilibrium suspended-load transport, the effects of the drag force, density gradient, and particle collisions caused by sediment particles on the motion characteristics of the flow under the condition of different sediment concentrations were studied quantitatively. Furthermore, sensitivity analysis was undertaken to reveal the mechanism via which turbulence modulation of sediment-laden flow affects the flow resistance, vertical diffusion coefficient of sediment concentration, and turbulence kinetic energy under equilibrium suspended-load transport conditions, so as to optimize the construction of water-sediment model. The main conclusions reached can be summarized as follows.
(1) Owing to the presence of suspended sediment particles, the vertical distribution of flow velocity and sediment concentration, and turbulence kinetic energy distribution of the sediment-laden flow are changed, and the modulation effect becomes greater with increase in sediment concentration.
(2) For both SQ and SF suspension, the drag force has more obvious inhibitory effect on flow turbulence, and reduces the energy consumption and resistance coefficient of the water mass, thereby increasing the flow velocity. The drag force has no notable impact on either the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load or the vertical distribution of sediment concentration.
(3) The density gradient formed by SQ in water is large, which substantially inhibits flow turbulence, slightly reduces the resistance coefficient, changes the vertical distribution of flow velocity, reduces flow velocity near the bottom of the bed, and increases flow velocity near the water surface. The presence of a density gradient also changes the vertical distribution of the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load, resulting in reduction in the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load at the bottom and near the water surface and increase at intermediate water depths, which promotes enhancement of the effect near the bottom surface of the sediment concentration and reduction of the effect near y/h = 0.2. For SF, the vertical distribution of sediment concentration is relatively uniform, and the density gradient effect on the movement characteristics of the sediment-laden flow is almost negligible.
(4) For SQ and SF suspension, the effect of sediment particle collisions substantially promotes flow turbulence, increases the resistance coefficient, and reduces the flow velocity. For SQ suspension, particle collisions have the opposite effect on the turbulent diffusion coefficient to that of the density gradient, and particle collisions increase the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load toward the bottom and near the water surface, while reducing it at intermediate depths, which partially cancels the effect of the density gradient. For SF suspension, particle collisions represent a key factor affecting the turbulent diffusion coefficient of the suspended load and the vertical distribution of the sediment concentration. With consideration of particle collisions, the calculation of the vertical distribution of the sediment concentration is markedly improved, and is most consistent with the measured values.
In the future, on the basis of the results presented in this paper, the effect of turbulence modulation of sediment-laden flow on the distribution of sediment concentration in the flow direction and the restoration saturation coefficient under the condition of disequilibrium sand transport will be explored further. Moreover, based on the results of the sensitivity analysis conducted in this study, the negligible terms in the basic governing equation of solid–liquid two-phase flow could be simplified to improve the calculation efficiency, thereby making it applicable to simulation of sediment-laden flow in actual rivers.
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.22258771.v1.
HX: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HC: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. HW: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. DF: Project administration, Writing–review and editing. NX: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. DX: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, Grant No. 2023J01406.
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to the reviewers and the editor for their valuable comments and constructive suggestions.
Author HC was employed by Fuzhou Research Institute of Sustainable Development in Cities Ltd. Authors DF and NX were employed by Fuzhou Planning & Design Research Institute Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Qian N, Zhou W. Evolution of riverbed in the lower reaches of the Yellow River. Beijing: Science Press (1965).
2. Hui YJ, Li YT, Hu CH, Han WL, Chen L, Ji ZW. The turbulent structure and mechanics of non-uniform sediment transport of high-concentration sediment-laden flows. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Hydraulic and Electrical Engineering Press (2000).
3. Balachandar S, Eaton JK. Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow. Annu Rev Fluid Mech (2010) 42:111–33. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.010908.165243
4. Qian N, Wan Z. Preliminary study on the effect of near-bottom high sediment concentration flow layer on flow and sediment movement. J Hydraulic Eng (1965) 4:1–19.
5. Sad Chemloul N, Benrabah O. Measurement of velocities in two-phase flow by laser velocimetry: interaction between solid particles’ motion and turbulence. J Fluids Eng (2008) 130(7). doi:10.1115/1.2948358
6. Huang H, Zhang H, Zhong D, Zhang YJ. Turbulent mechanisms in open channel sediment-laden flows. Int J Sediment Res (2019) 34(6):550–63. doi:10.1016/j.ijsrc.2019.06.002
7. Righetti M, Romano GP. Particle–fluid interactions in a plane near-wall turbulent flow. J Fluid Mech. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press (2004) 505:93–121. doi:10.1017/S0022112004008304
8. Elata C, Ippen AT (1961). The dynamics of open channel flow with suspensions of neutrally buoyant particles. In: Hydrodynamics laboratory, department of civil and sanitary engineering. Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
9. Muller A. Turbulence measurements over a movable bed with sediment transport by laser anemometry. In Proc., 15th Congress. Int Assoc Hydraulic Res. Delft, Netherlands: International Association of Hydraulic Research (1973) 1:A7–1.
10. Zhang R, Xie J, Wang M, Huang J. Dynamics of sediment in rivers. Water Resources and Electric Power Press (1989).
11. Wang X, Qian N. Turbulence Characteristics Sediment-laden Flow J Hydraulic Eng (1989) 115(6):781e800. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1989)115:6(781)
12. Lyn DA. Turbulence characteristics of sediment-laden flows in open channels. J Hydraulic Eng (1992) 118(7):971–88. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1992)118:7(971)
13. Van Beek FA, Wind HG. Numerical modelling of erosion and sedimentation around offshore pipelines. Coastal Eng (1990) 14(2):107–28. doi:10.1016/0378-3839(90)90013-M
14. Brørs B. Numerical modeling of flow and scour at pipelines. J Hydraulic Eng (1999) 125(5):511–23. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1999)125:5(511)
15. Jha SK, Bombardelli FA. Toward two-phase flow modeling of nondilute sediment transport in open channels. J Geophys Res Earth Surf (2010) 115(F3). doi:10.1029/2009JF001347
16. Jha SK, Bombardelli FA. Theoretical/numerical model for the transport of non-uniform suspended sediment in open channels. Adv Water Resour (2011) 34(5):577–91. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.02.001
17. Zhang Y, Baptista AM. SELFE: a semi-implicit Eulerian–Lagrangian finite-element model for cross-scale ocean circulation. Ocean Model (2008) 21(3-4):71–96. doi:10.1016/j.ocemod.2007.11.005
18. Chien N, Wan Z. Mechanics of sediment transport. Am Soc Civil Eng (1999). doi:10.1061/9780784404003
19. Huang R, Zhang Q, Zhang W, Li Z. Experimental research on the effect of suspended sediment stratification on turbulence characteristics. Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Sci (2022) 278:108128. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2022.108128
20. Bolla Pittaluga M. Stratification effects on flow and bed topography in straight and curved erodible streams. J Geophys Res Earth Surf (2011) 116(F3):F03026. doi:10.1029/2011JF001979
21. Noguchi K, Nezu I. Particle–turbulence interaction and local particle concentration in sediment-laden open-channel flows. J Hydro-environment Res (2009) 3(2):54–68. doi:10.1016/j.jher.2009.07.001
22. Fu X, Wang G. Error analysis of traditional sediment diffusion equation. J Sediment Res (2004)(4) 33–8.
23. Toorman EA. Vertical mixing in the fully developed turbulent layer of sediment-laden open-channel flow. J Hydraulic Eng (2008) 134(9):1225–35. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134:9(1225)
24. Drew DA. Mathematical modeling of two-phase flow. Annu Rev Fluid Mech (1983) 15(1):261–91. doi:10.1146/annurev.fl.15.010183.001401
25. Amoudry L, Hsu TJ, Liu PF. Two-phase model for sand transport in sheet flow regime. J Geophys Res Oceans (2008) 113(C3). doi:10.1029/2007JC004179
26. Chauchat J, Guillou S. On turbulence closures for two-phase sediment-laden flow models. J Geophys Res Oceans (2008) 113(C11). doi:10.1029/2007JC004708
27. Chen X, Li Y, Niu X, Li M, Chen D, Yu X. A general two-phase turbulent flow model applied to the study of sediment transport in open channels. Int J Multiphase Flow (2011) 37(9):1099–108. doi:10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2011.05.013
28. Greimann BP, Muste M, Holly Jr FM. Two-phase formulation of suspended sediment transport. J Hydraulic Res (1999) 37(4):479–500. doi:10.1080/00221686.1999.9628264
29. Greimann BP, Holly Jr FM. Two-phase flow analysis of concentration profiles. J Hydraulic Eng (2001) 127(9):753–62. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2001)127:9(753)
30. Hsu TJ, Jenkins JT, Liu PLF. On two-phase sediment transport: dilute flow. J Geophys Res Oceans (2003) 108(C3). doi:10.1029/2001JC001276
31. Peirano E, Leckner B. Fundamentals of turbulent gas-solid flows applied to circulating fluidized bed combustion. Prog Energ combustion Sci (1998) 24(4):259–96. doi:10.1016/S0360-1285(98)00002-1
32. Bakhtyar R, Barry DA, Li L, Jeng DS, Yeganeh-Bakhtiary A. Modeling sediment transport in the swash zone: a review. Ocean Eng (2009) 36(9-10):767–83. doi:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2009.03.003
33. Chauchat J, Cheng Z, Nagel T, Bonamy C, Hsu TJ. SedFoam-2.0: a 3-D two-phase flow numerical model for sediment transport. Geoscientific Model Development (2017) 10(12):4367–92. doi:10.5194/gmd-10-4367-2017
34. Enwald H, Peirano E, Almstedt AE. Eulerian two-phase flow theory applied to fluidization. Int J Multiphase Flow (1996) 22:21–66. doi:10.1016/S0301-9322(96)90004-X
35. Nguyen KD, Guillou S, Chauchat J, Barbry N. A two-phase numerical model for suspended-sediment transport in estuaries. Adv Water Resour (2009) 32(8):1187–96. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.04.001
36. Kim Y, Cheng Z, Hsu TJ, Chauchat J. A numerical study of sheet flow under monochromatic nonbreaking waves using a free surface resolving Eulerian two-phase flow model. J Geophys Res Oceans (2018) 123(7):4693–719. doi:10.1029/2018JC013930
37. Dallali M, Armenio V. Large eddy simulation of two-way coupling sediment transport. Adv Water Resour (2015) 81:33–44. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2014.12.004
38. Berberović E, van Hinsberg NP, Jakirlić S, Roisman IV, Tropea C. Drop impact onto a liquid layer of finite thickness: dynamics of the cavity evolution. Phys Rev E (2009) 79(3):036306. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.79.036306
39. Cheng Z, Hsu TJ, Calantoni J. SedFoam: a multi-dimensional Eulerian two-phase model for sediment transport and its application to momentary bed failure. Coastal Eng (2017) 119:32–50. doi:10.1016/j.coastaleng.2016.08.007
40. Yu X, Hsu TJ, Hanes DM. Sediment transport under wave groups: relative importance between nonlinear waveshape and nonlinear boundary layer streaming. J Geophys Res Oceans (2010) 115(C2). doi:10.1029/2009JC005348
41. Ding J, Gidaspow D. A bubbling fluidization model using kinetic theory of granular flow. AICHE J (1990) 36(4):523–38. doi:10.1002/aic.690360404
42. Jenkins JT, Savage SB. A theory for the rapid flow of identical, smooth, nearly elastic, spherical particles. J Fluid Mech (1983) 130(1):187–202. doi:10.1017/S0022112083001044
43. Jacobsen NG, Fuhrman DR, Fredsøe J. A wave generation toolbox for the open-source CFD library: OpenFoam®. Int J Numer Methods Fluids (2012) 70(9):1073–88. doi:10.1002/fld.2726
44. Klostermann J, Schaake K, Schwarze R. Numerical simulation of a single rising bubble by VOF with surface compression. Int J Numer Methods Fluids (2013) 71(8):960–82. doi:10.1002/fld.3692
45. Chen CP, Wood PE. A turbulence closure model for dilute gas-particle flows. Can J Chem Eng (1985) 63(3):349–60. doi:10.1002/cjce.5450630301
46. Danon H, Wolfshtein M, Hetsroni G. Numerical calculations of two-phase turbulent round jet. Int J Multiphase Flow (1977) 3(3):223–34. doi:10.1016/0301-9322(77)90002-7
47. Hsu T-J, Jenkins JT, Liu PL-F. On two-phase sediment transport: sheet flow of massive particles. Proc R Soc A: Math Phys Eng Sci (2004) 460(2048):2223–50. doi:10.1098/rspa.2003.1273
48. Carnahan NF, Starling KE. Equation of state for nonattracting rigid spheres. J Chem Phys (1969) 51(2):635–6. doi:10.1063/1.1672048
49. Gidaspow D. Multiphase flow and fluidization: continuum and kinetic theory descriptions. Academic Press (1994).
50. Johnson PC, Jackson R. Frictional–collisional constitutive relations for granular materials, with application to plane shearing. J Fluid Mech (1987) 176:67–93. doi:10.1017/S0022112087000570
51. Ding J, Gidaspow D. A bubbling fluidization model using kinetic theory of granular flow. AIChE J (1990) 36(4):523–38. doi:10.1002/aic.690360404
52. Schaeffer DG. Instability in the evolution equations describing incompressible granular flow. J differential equations (1987) 66(1):19–50. doi:10.1016/0022-0396(87)90038-6
Keywords: solid-liquid two-phase flow, turbulence modulation, drag force, density gradient, particle collisions
Citation: Xie H, Cai H, Wang H, Fu D, Xu N and Xu D (2025) Mechanism of turbulence modulation of sediment-laden flow for the case of equilibrium suspended-load transport. Front. Phys. 13:1449056. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1449056
Received: 18 June 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 03 March 2025.
Edited by:
Stefano Leonardi, The University of Texas at Dallas, United StatesReviewed by:
Daniel Cruz, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilCopyright © 2025 Xie, Cai, Wang, Fu, Xu and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao Wang, d2FuZ2hhb18wNTEyQDE2My5jb20=; Huiyi Cai, ZnprY3hfY2h5QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.