- 1Department of Physics and Origin of Matter and Evolution of Galaxies Institute, Soongsil University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2School of Liberal Arts and Sciences, Korea Aerospace University, Goyang, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Faculty of Science and Technology, Tokyo University of Science, Noda, Japan
The accurate measurement of neutron skin thickness of 208Pb by the PREX Collaboration suggests a large value of the nuclear symmetry energy slope parameter,
1 Introduction
The astrophysical phenomena concerning compact stars as well as the characteristics of finite nuclei and nuclear matter are determined by the nuclear equation of state (EoS), characterized by the relation between the energy density and pressure of the system [1, 2]. Many nuclear EoSs have been contemplated so far through realistic nuclear models in a non-relativistic or relativistic framework [3, 4]. Relativistic mean-field (RMF) calculations, based on the one-boson exchange potential for nuclear interactions [5, 6], have achieved great success in understanding of the properties of nuclear matter and finite nuclei [7]. To reproduce a reasonable nuclear incompressibility and properties of unstable nuclei, the RMF models have been developed by introducing the non-linear self-couplings of isoscalar, Lorentz-scalar
The nuclear symmetry energy,
Owing to the precise observations of neutron stars, such as the Shapiro delay measurement of a binary millisecond pulsar J1614
The accurate measurement of neutron skin thickness of 208Pb,
To explain the PREX-2 result, Reed et al. [48] have proposed the large
In this article, we review the recently updated RMF models with non-linear couplings by introducing the isoscalar- and isovector-meson mixing,
(1) The EoSs for symmetric nuclear matter and pure neutron matter satisfy the particle flow data in heavy-ion collisions (HICs) [60–63],
(2) The EoS for neutron stars attains to the observed mass of PSR J0740
(3) The EoS for neutron stars explains the dimensionless tidal deformability from the binary merger event, GW170817
Under these constraints, we examine the effects of the
This paper is organized as follows. A summary and analytical calculations concerning the RMF model with non-linear couplings are described in Section 2. Numerical results and detailed discussions are presented in Section 3. Finally, we give a summary in Section 4.
2 Theoretical framework
2.1 Lagrangian density
In quantum hydrodynamics [7], we employ the recently updated effective Lagrangian density including the isoscalar (
where
The first and second terms in Equation 2 are introduced to obtain a quantitative description of ground-state properties for symmetric nuclear matter [8, 67]. The quartic self-interactions of
2.2 Field equations for finite nuclei in mean-field approximation
In mean-field approximation, the meson and photon fields are replaced by the mean-field values:
where
with
and
where
The total energy of the system is thus written as
where the sum
2.3 Infinite nuclear matter
To study the bulk properties of nuclear and neutron star matter, it is necessary to compute the nuclear equation of state (EoS)—a relation between the energy density,
where
and
2.4 Nuclear bulk properties
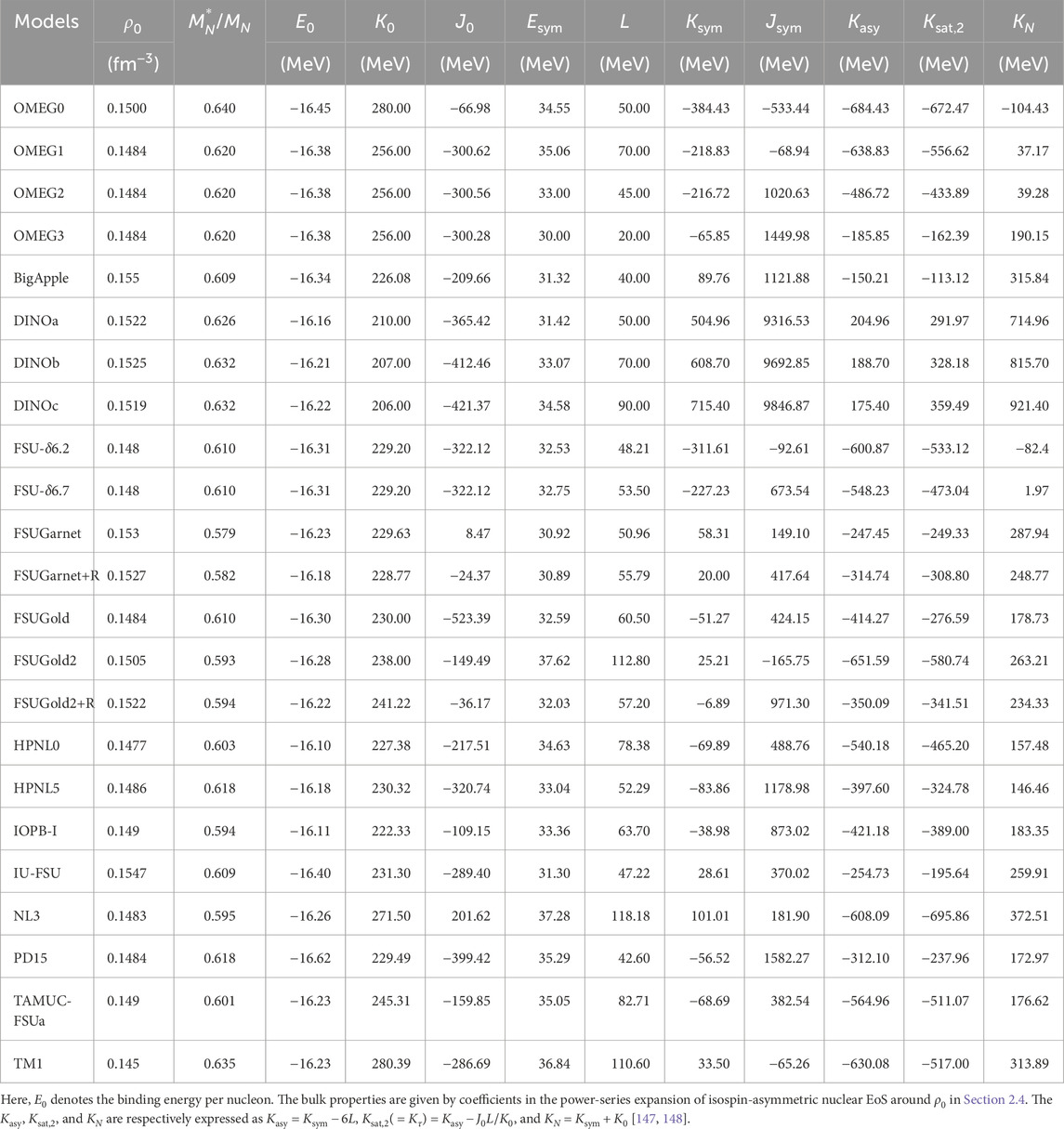
In general, the bulk properties of infinite nuclear matter are identified by the expansion of isospin-asymmetric nuclear EoS with a power series in the isospin asymmetry,
where
Besides,
with
Taking into account the thermodynamic condition, the pressure of infinite nuclear matter,
with the binding energy per nucleon in Equation 14. The nuclear incompressibility,
Hence, the incompressibility coefficient of SNM,
where the density derivatives of meson fields are calculated through the relation
with
and
We here use the following quantities:
and
with
where the effective meson masses,
According to the Hugenholtz-Van Hove theorem in nuclear matter,
where
The effective mass, (four) momentum, and energy for
with
Based on the Lorentz-covariant decomposition of NSE [82],
with the scalar
where the effective quantities at the Fermi surface in Equations 22–25 are then given by
Using Equations 20, 21,
Note that
The
where the kinetic, scalar, and time components are respectively given by
with
2.5 Stability of nuclear and neutron star matter
In order to move on the calculations of neutron stars in which the charge neutrality and
where
When we consider the stability of matter in cold neutron stars, the first principle of thermodynamics should be considered:
with
with
The total internal energy per baryon,
with
where the isospin symmetry breaking (ISB) energy of infinite nuclear matter is given by
Considering the differentiation of
where
Note that we explicitly keep
As for the pressure stability, the differentiation of
with the baryon and lepton contributions. Similar to Equation 27, the baryon contribution is given by
Using the thermodynamic definitions of pressure and incompressibility of infinite nuclear matter in Equations 18, 19, this equation can be simplified as
where the slope of ISB energy,
The lepton contribution is also given by the simple form under the
Therefore, the stability of neutron star matter under the charge neutrality and
The thermodynamic stability is used in several calculations of nuclear and neutron star matter, for instance, the compressibility of
3 Results and discussions
3.1 Nuclear models
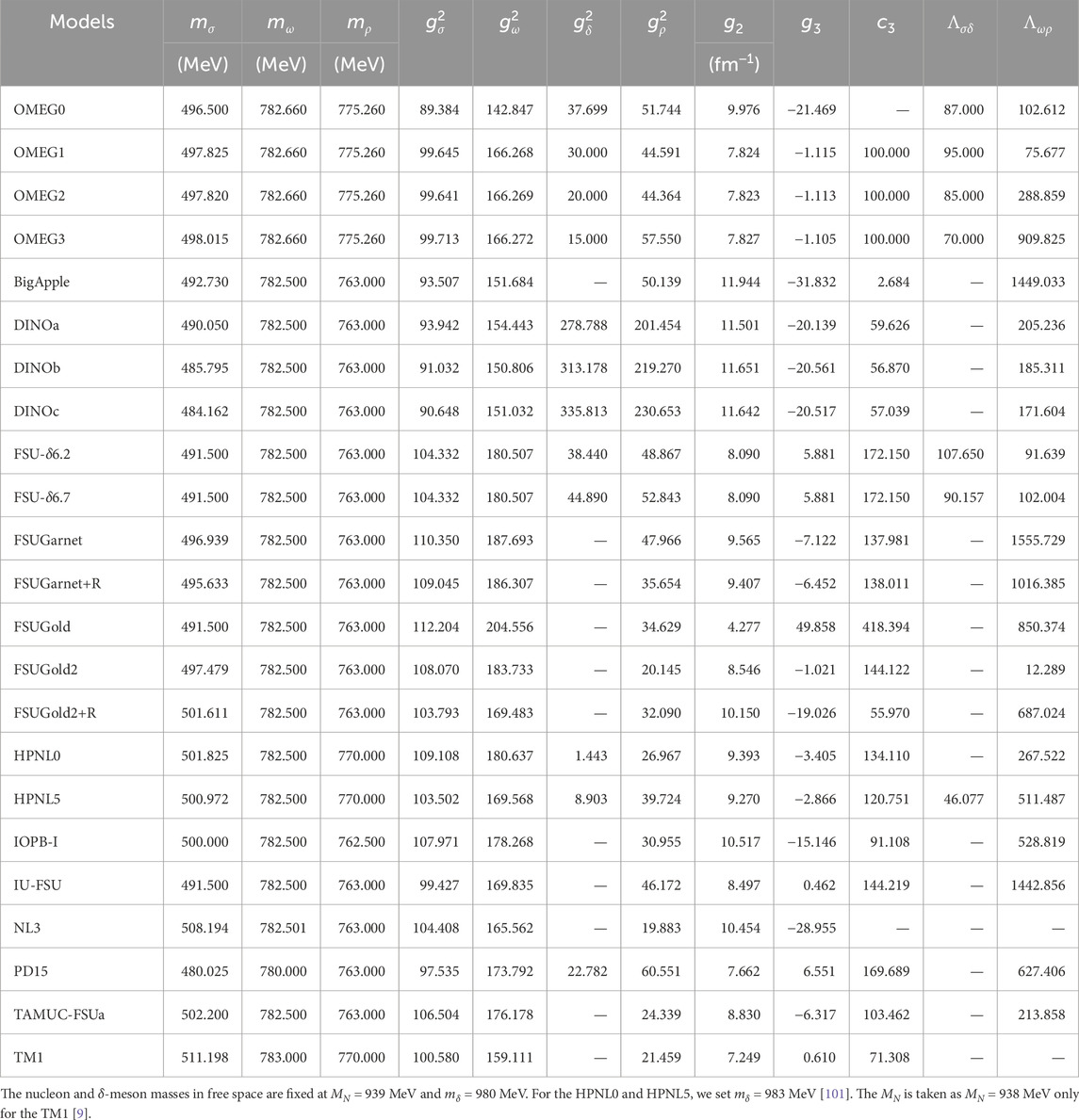
We adopt the recently developed effective interactions labeled as the OMEG family, which are constructed to reproduce the characteristics of finite nuclei, nuclear matter, and neutron stars [58, 92]. In particular, the
In addition, we present the extended interactions based on the FSUGarnet, TAMUC-FSUa, and FSUGold2 models, in which the
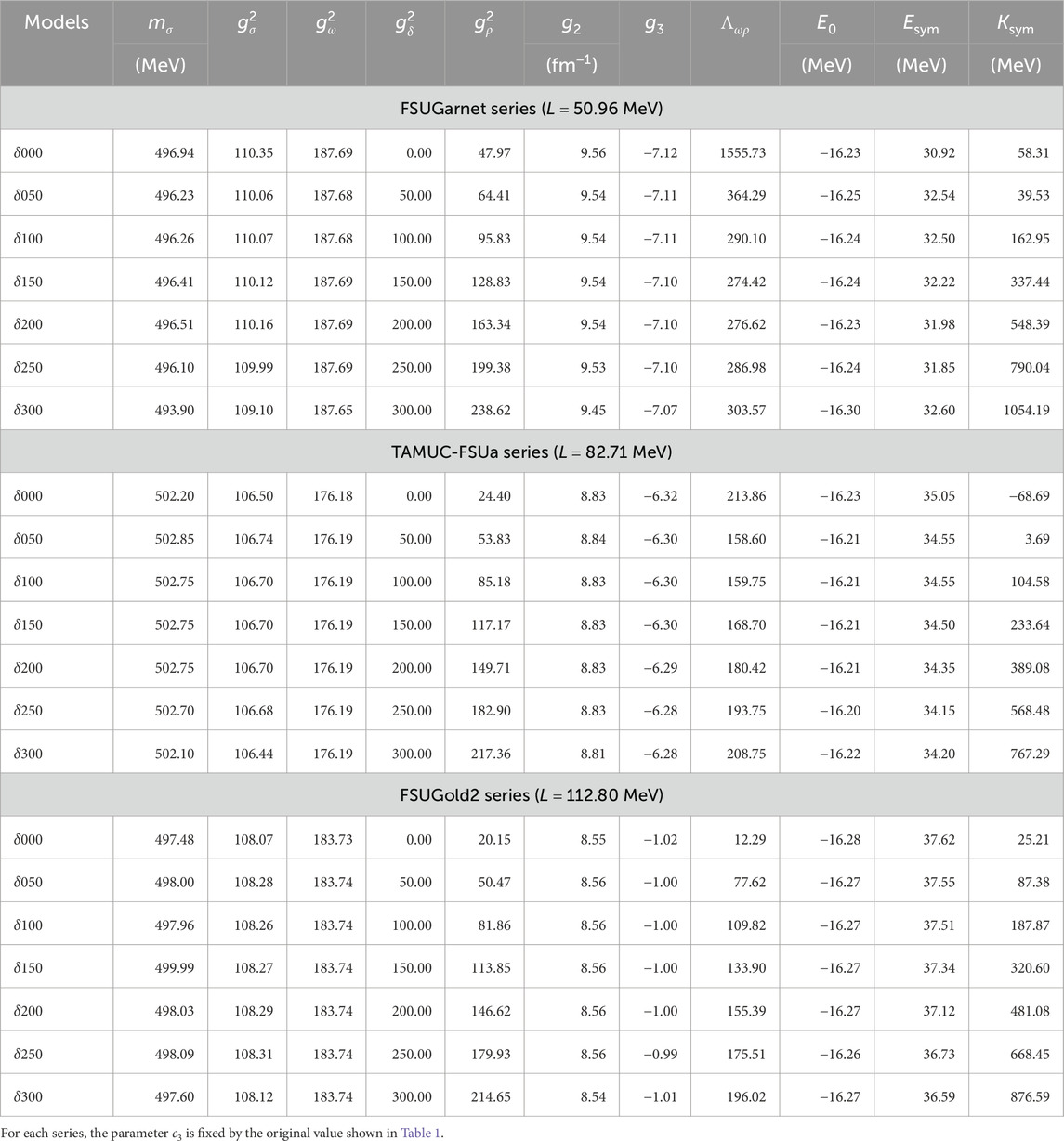
Table 3. Model parameters and nuclear properties for the extended version of the FSUGarnet, TAMUC-FSUa, and FSUGold2 models.
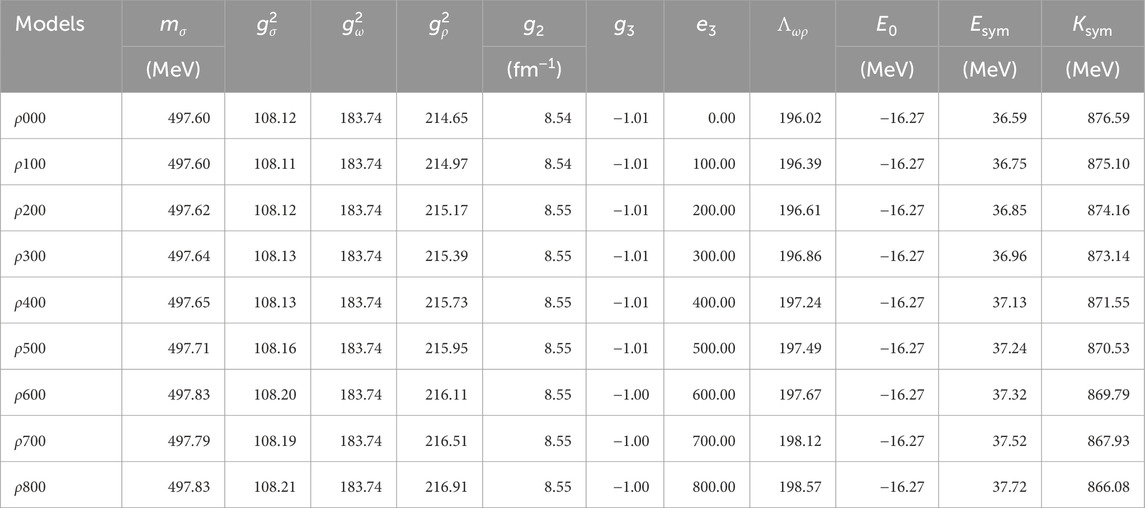
Table 4. Model parameters and several properties for the FSUGold2 with the
3.2 Finite nuclei
The theoretical predictions for the neutron skin thickness of 40Ca and 208Pb,
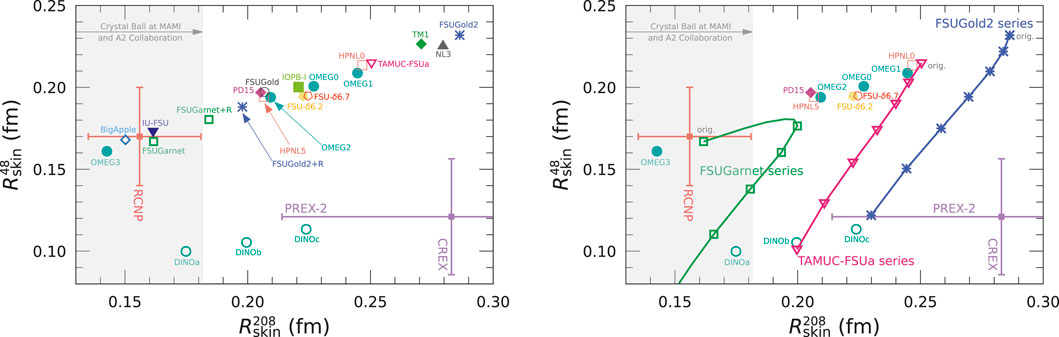
Figure 1. Neutron skin thickness of 40Ca and 208Pb,
As for the OMEG family, the OMEG0 and OMEG1 give the large values,
with
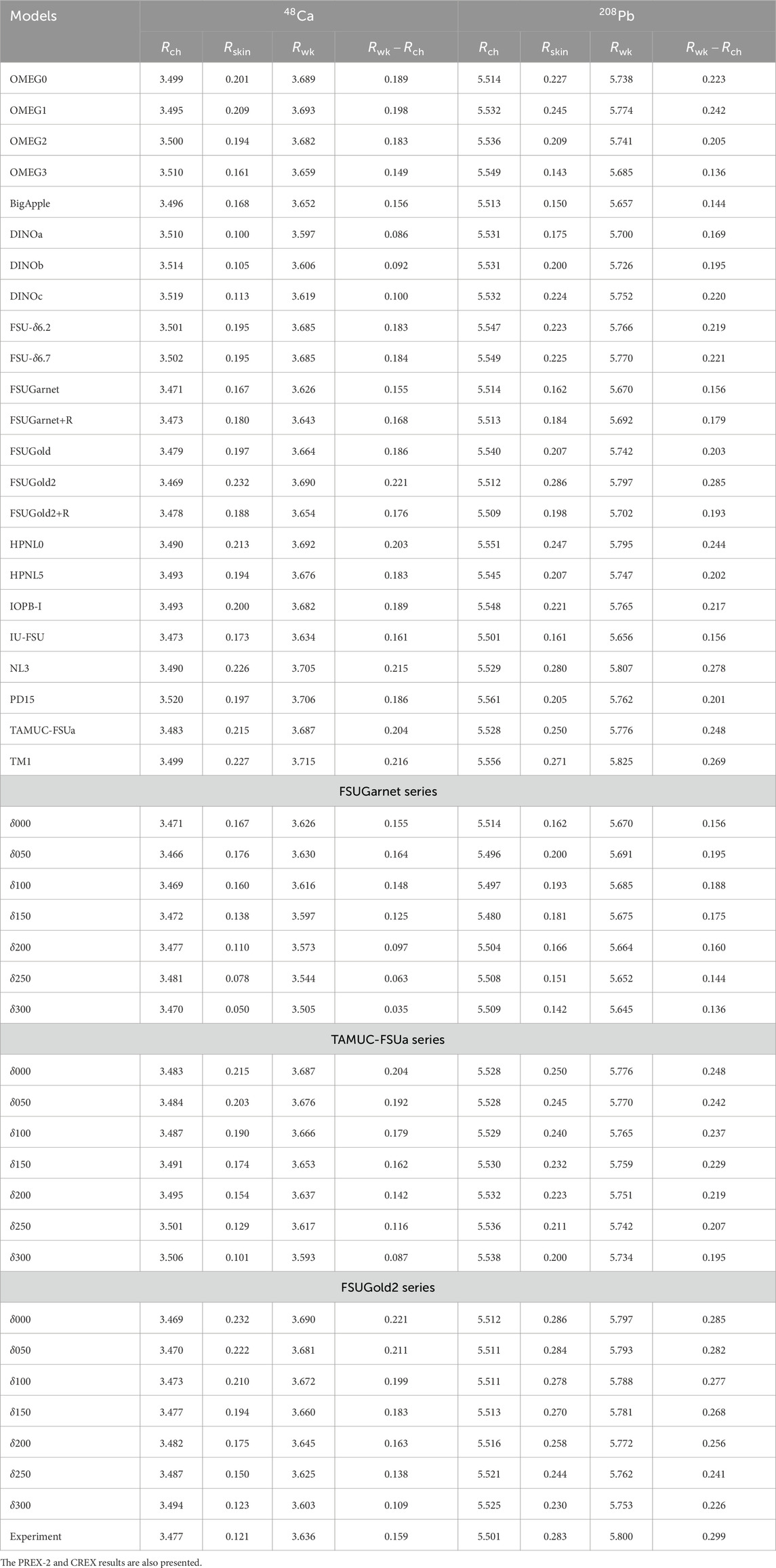
Table 5. Predictions for the charge radius,
We see the linear correlation between
To clarify the effect of
The density profiles in 208Pb are displayed in Figure 2. We here present the baryon, charge, and weak charge densities,
with
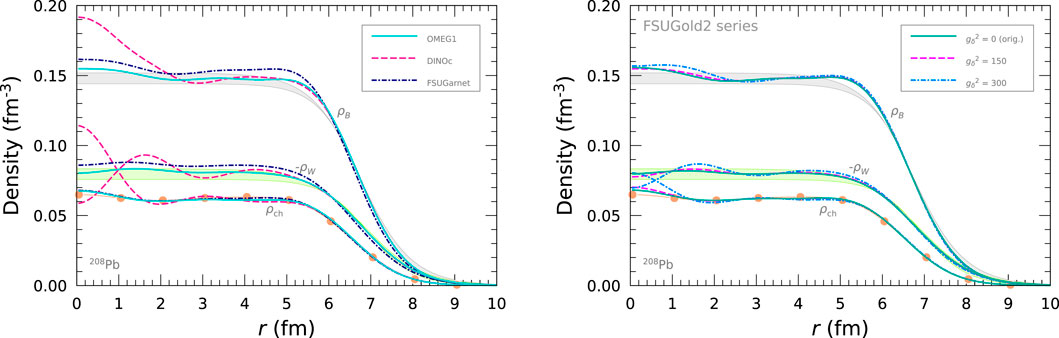
Figure 2. Baryon, charge, and weak change densities,
In the left panel of Figure 2, we present the density profiles for the OMEG1, DINOc, FSUGarnet. The OMEG1 and FSUGarnet adequately satisfy the density distributions of
The effect of
3.3 Infinite nuclear matter
The
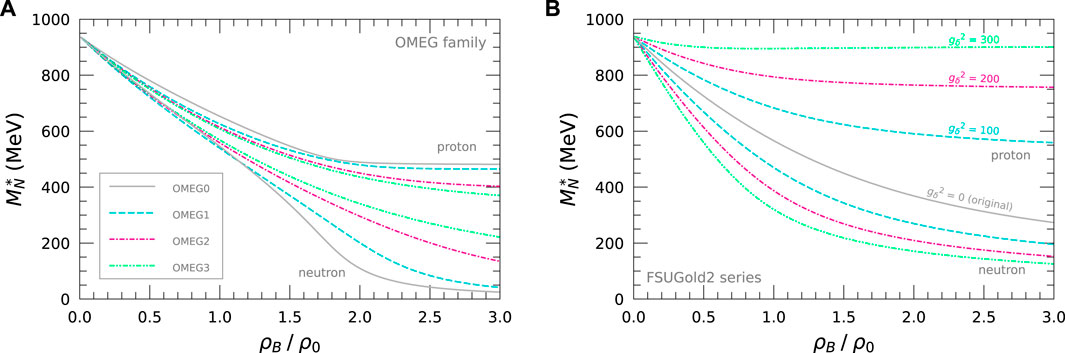
Figure 3. Effective nucleon mass,
The density dependence of nuclear symmetry energy,
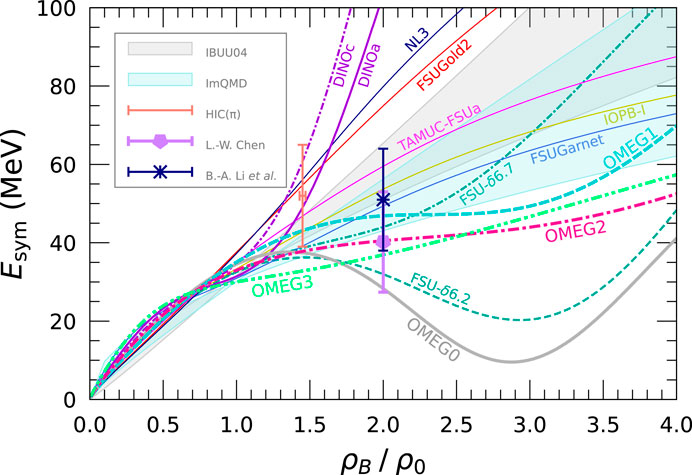
Figure 4. Density dependence of nuclear symmetry energy,
Based on the Lorentz decomposition of nucleon self-energy in Section 2.4,
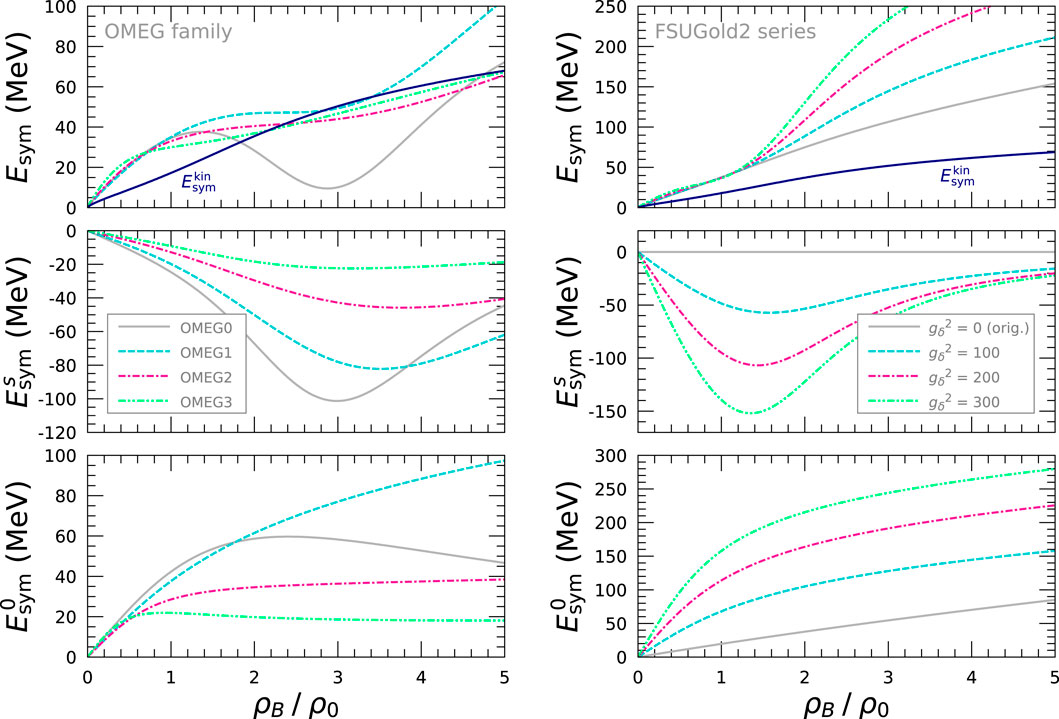
Figure 5. Lorentz decomposition of nuclear symmetry energy,
The EoSs for symmetric nuclear matter and pure neutron matter are displayed in Figure 6 with the constraints on the nuclear EoS extracted from the analyses of particle flow data in HICs [60–62]. In both panels, we show the various EoSs calculated by the OMEG, DINO, and FSU-
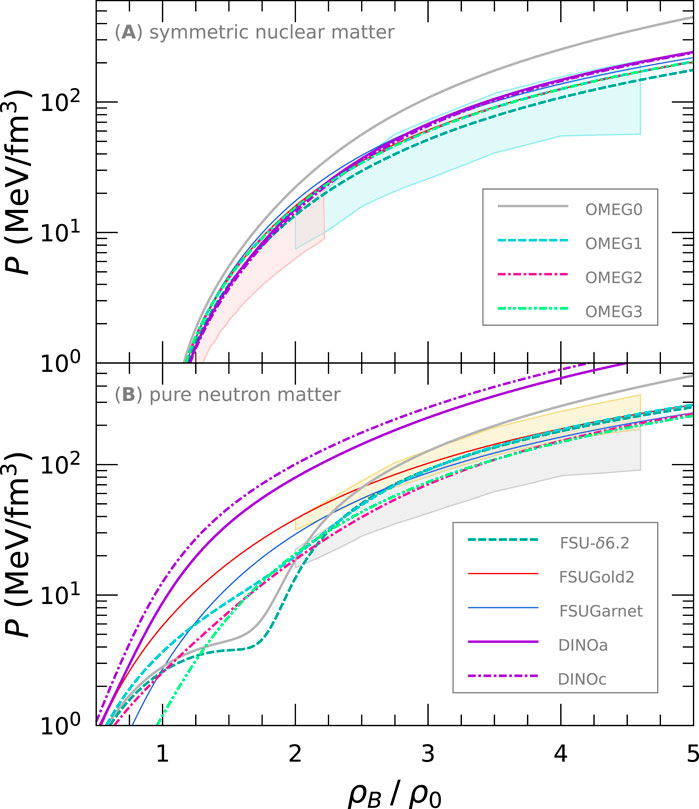
Figure 6. EoS—pressure,
We present the EoS for pure neutron matter for the FSUGold2 series in Figure 7. In the left panel, the EoS becomes hard with increasing the
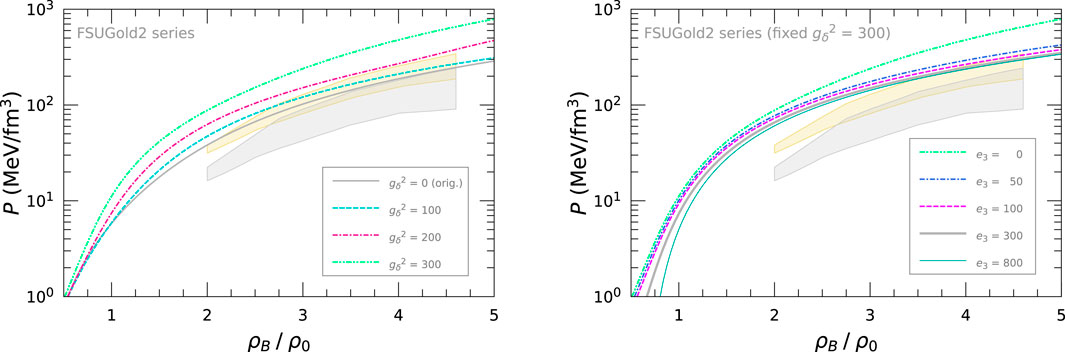
Figure 7. EoS for pure neutron matter for the FSUGold2 series. The left panel shows the dependence of
3.4 Neutron star physics
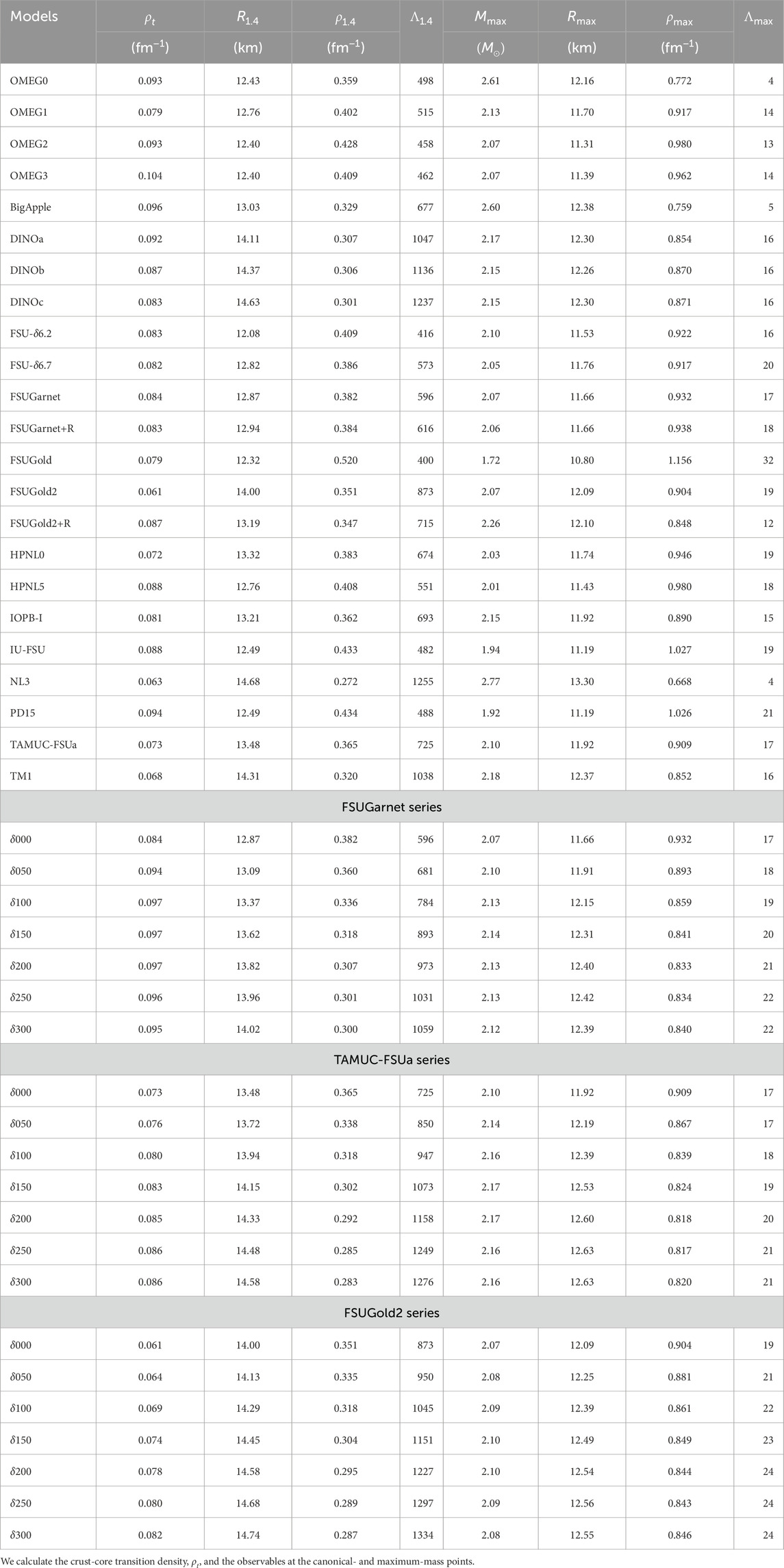
In studying neutron star physics, the EoS for non-uniform matter is additionally required as well as that for uniform nuclear matter since the radius of a neutron star is remarkably sensitive to the nuclear EoS at very low densities [120]. In the present study, to cover the crust region, we adopt the MYN13 EoS, in which nuclei are taken into consideration using the Thomas-Fermi calculation in non-uniform matter and the EoS for infinite nuclear matter is constructed with the relativistic Hartree-Fock calculation [80, 81, 121, 122]. We list in Table 6 the predicted stellar properties, which are calculated by solving the Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff (TOV) equation [123, 124].
There are three methods used widely to determine the crust-core transition density,
We summarize the results of
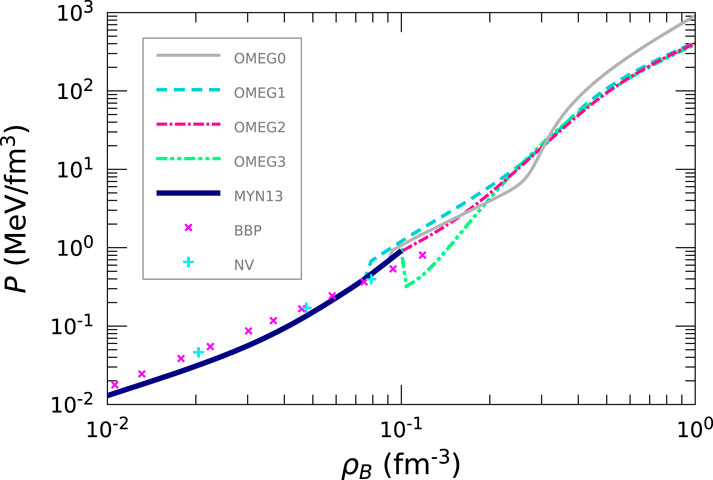
Figure 8. EoS for neutron star matter for the OMEG family. The inner-crust region is described by the EoSs of MYN13 [121], BBP [1], and NV [146].
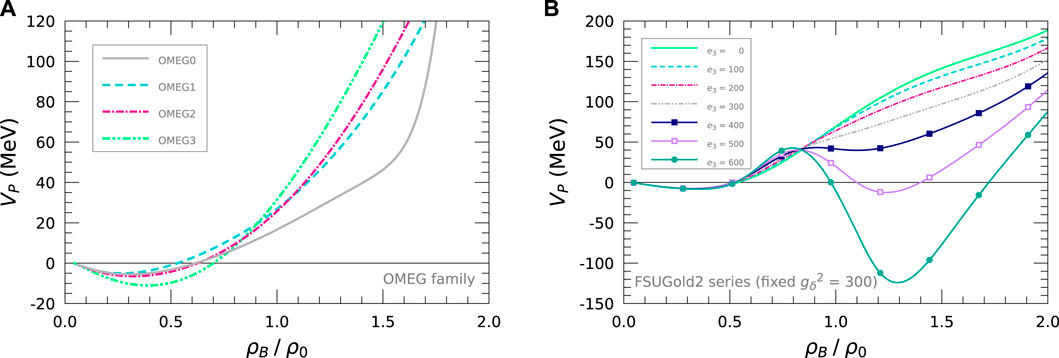
Figure 9. Thermodynamic stability of pressure,
Since the large
We illustrate in Figure 10 the proton fraction,
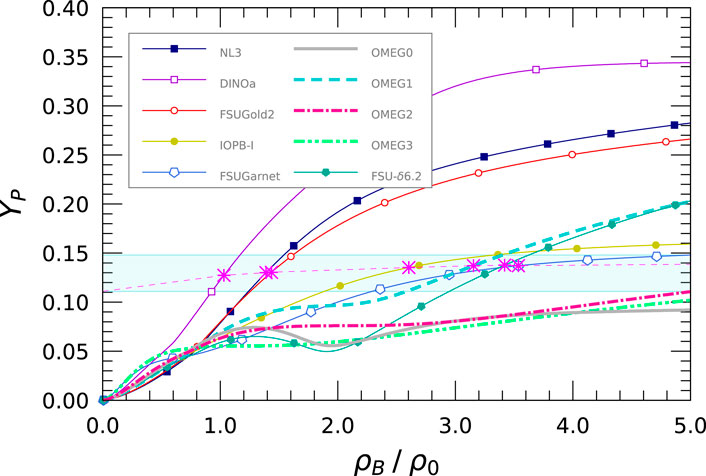
Figure 10. Proton fraction,
The mass
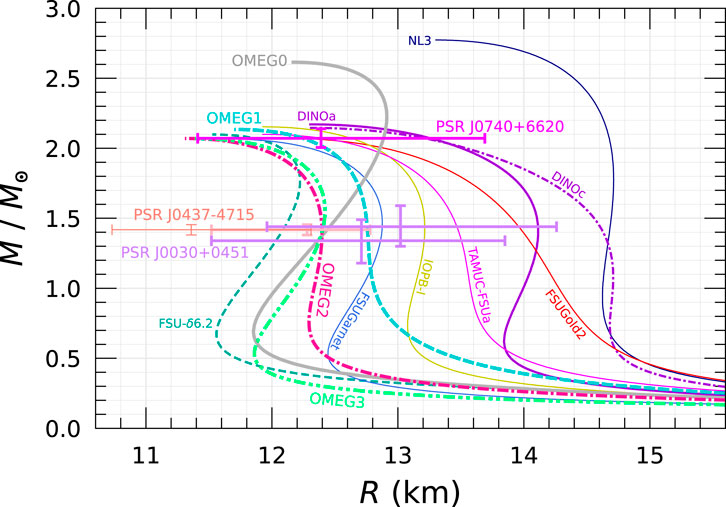
Figure 11. Mass–radius relations of neutron stars. The NICER observation data are supplemented by the constraints from PSR J0030
The dimensionless tidal deformability,
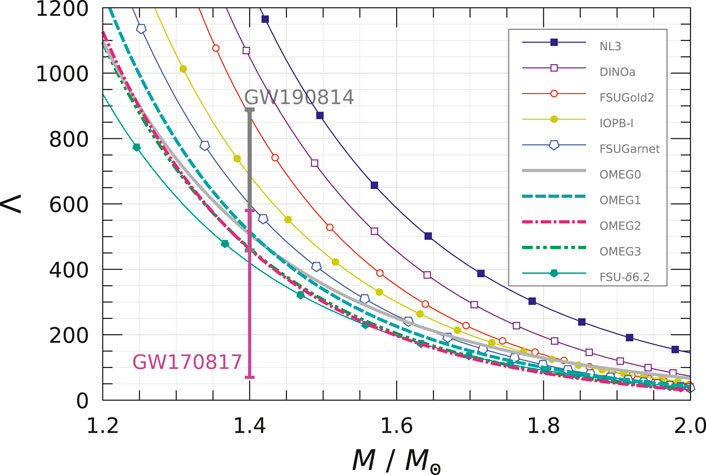
Figure 12. Dimensionless tidal deformability,
4 Summary and conclusion
We have developed a new family of nuclear EoSs, referred to as the OMEG family, using the RMF model with non-linear couplings between the isoscalar and isovector mesons. In addition to the
It has been found that the
In a future work, we plan to extend the present study to global calculations of finite nuclei properties covered the periodic table, aiming to achieve well-calibrated parameter sets for the RMF models. Finally, we comment that the further theoretical studies are necessary to reconcile the
Author contributions
TM: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. M-KC: Writing–review and editing. KK: Writing–review and editing. KS: Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant Nos. RS-2023-00242196, NRF-2021R1A6A1A03043957, NRF-2020R1A2C3006177, and NRF-2018R1A5A1025563).
Acknowledgments
TM would like to thank H. Sagawa and G. Colò for informative discussions of the neutron skin thickness of heavy nuclei.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Baym G, Bethe HA, Pethick C. Neutron star matter. Nucl Phys A (1971) 175:225–71. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(71)90281-8
2. Bethe HA, Brown GE, Applegate J, Lattimer JM. Equation of state in the gravitational collapse of stars. Nucl Phys A (1979) 324:487–533. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(79)90596-7
3. Lattimer JM, Swesty FD. A Generalized equation of state for hot, dense matter. Nucl Phys A (1991) 535:331–76. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(91)90452-C
4. Glendenning NK, Moszkowski SA. Reconciliation of neutron star masses and binding of the lambda in hypernuclei. Phys Rev Lett (1991) 67:2414–7. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.2414
5. Machleidt R, Holinde K, Elster C. The bonn meson exchange model for the nucleon nucleon interaction. Phys Rept (1987) 149:1–89. doi:10.1016/S0370-1573(87)80002-9
6. Machleidt R. The Meson theory of nuclear forces and nuclear structure. Adv Nucl Phys (1989) 19:189–376. doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-9907-0_2
8. Boguta J, Bodmer AR. Relativistic calculation of nuclear matter and the nuclear surface. Nucl Phys A (1977) 292:413–28. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(77)90626-1
9. Sugahara Y, Toki H. Relativistic mean field theory for unstable nuclei with nonlinear sigma and omega terms. Nucl Phys A (1994) 579:557–72. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(94)90923-7
10. Mueller H, Serot BD. Relativistic mean field theory and the high density nuclear equation of state. Nucl Phys A (1996) 606:508–37. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(96)00187-X
11. Horowitz CJ, Piekarewicz J. The Neutron radii of Pb-208 and neutron stars. Phys Rev C (2001) 64:062802. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.64.062802
12. Oertel M, Hempel M, Klähn T, Typel S. Equations of state for supernovae and compact stars. Rev Mod Phys (2017) 89:015007. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.89.015007
13. Alford MG, Brodie L, Haber A, Tews I. Relativistic mean-field theories for neutron-star physics based on chiral effective field theory. Phys Rev C (2022) 106:055804. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.106.055804
14. Patra NK, Venneti A, Imam SMA, Mukherjee A, Agrawal BK. Systematic analysis of the impacts of symmetry energy parameters on neutron star properties. Phys Rev C (2023) 107:055804. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.107.055804
15. Stone JR. Nuclear physics and astrophysics constraints on the high density matter equation of state. Universe (2021) 7:257. doi:10.3390/universe7080257
16. Stone JR. Nuclear symmetry energy in strongly interacting matter: past, present and future. Symmetry (2024) 16:1038. doi:10.3390/sym16081038
17. Zhou J, Xu J, Papakonstantinou P. Bayesian inference of neutron-star observables based on effective nuclear interactions. Phys Rev C (2023) 107:055803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.107.055803
18. Sun B, Bhattiprolu S, Lattimer JM. Compiled properties of nucleonic matter and nuclear and neutron star models from nonrelativistic and relativistic interactions. Phys Rev C (2024) 109:055801. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.109.055801
19. Li B-A, Chen L-W, Ko CM. Recent progress and new challenges in isospin physics with heavy-ion reactions. Phys Rept (2008) 464:113–281. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2008.04.005
20. Lattimer JM. Symmetry energy in nuclei and neutron stars. Nucl Phys A (2014) 928:276–95. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2014.04.008
21. Typel S, Brown BA. Neutron radii and the neutron equation of state in relativistic models. Phys Rev C (2001) 64:027302. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.64.027302
22. Tsang MB, Zhang Y, Danielewicz P, Famiano M, Li Z, Lynch WG, et al. Constraints on the density dependence of the symmetry energy. Phys Rev Lett (2009) 102:122701. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.122701
23. Tsang MB, Stone JR, Camera F, Danielewicz P, Gandolfi S, Hebeler K, et al. Constraints on the symmetry energy and neutron skins from experiments and theory. Phys Rev C (2012) 86:015803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.86.015803
24. Zhang N-B, Li B-A. Impact of NICER’s radius measurement of PSR J0740+6620 on nuclear symmetry energy at suprasaturation densities. Astrophys J (2021) 921:111. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac1e8c
25. Richter J, Li B-A. Empirical radius formulas for canonical neutron stars from bidirectionally selecting features of equations of state in extended Bayesian analyses of observational data. Phys Rev C (2023) 108:055803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.108.055803
26. Xie W-J, Li B-A, Zhang N-B. Impact of the newly revised gravitational redshift of x-ray burster GS 1826-24 on the equation of state of supradense neutron-rich matter. Phys Rev D (2024) 110:043025. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.110.043025
27. Demorest P, Pennucci T, Ransom S, Roberts M, Hessels J. Shapiro delay measurement of A two solar mass neutron star. Nature (2010) 467:1081–3. doi:10.1038/nature09466
28. Arzoumanian Z, Brazier A, Burke-Spolaor S, Chamberlin S, Chatterjee S, Christy B, et al. The NANOGrav 11-year data set: high-precision timing of 45 millisecond pulsars. Astrophys J Suppl (2018) 235:37. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/aab5b0
29. Miller MC, Lamb FK, Dittmann AJ, Bogdanov S, Arzoumanian Z, Gendreau KC, et al. PSR J0030+0451 mass and radius from NICER data and implications for the properties of neutron star matter. Astrophys J Lett (2019) 887:L24. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab50c5
30. Miller MC, Lamb FK, Dittmann AJ, Bogdanov S, Arzoumanian Z, Gendreau KC, et al. The radius of PSR J0740+6620 from NICER and XMM-Newton data. Astrophys J Lett (2021) 918:L28. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac089b
31. Riley TE, Watts AL, Bogdanov S, Ray PS, Ludlam RM, Guillot S, et al. A NICER view of PSR J0030+0451: millisecond pulsar parameter estimation. Astrophys J Lett (2019) 887:L21. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab481c
32. Riley TE, Watts AL, Ray PS, Bogdanov S, Guillot S, Morsink SM, et al. A NICER view of the massive pulsar PSR J0740+6620 informed by radio timing and XMM-Newton spectroscopy. Astrophys J Lett (2021) 918:L27. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac0a81
33. Abbott BP, Abbott R, Abbott TD, Acernese F, Ackley K, Adams C, et al. GW170817: observation of gravitational waves from a binary neutron star inspiral. Phys Rev Lett (2017) 119:161101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.161101
34. Abbott BP, Abbott R, Abbott TD, Acernese F, Ackley K, Adams C, et al. GW170817: measurements of neutron star radii and equation of state. Phys Rev Lett (2018) 121:161101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.161101
35. Abbott BP, Abbott R, Abbott TD, Acernese F, Ackley K, Adams C, et al. Properties of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys Rev X (2019) 9:011001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevX.9.011001
36. Hinderer T. Tidal Love numbers of neutron stars. Astrophys J (2008) 677:1216–20. Erratum: Astrophys.J. 697, 964 (2009) doi:10.1086/533487
37. Hinderer T, Lackey BD, Lang RN, Read JS. Tidal deformability of neutron stars with realistic equations of state and their gravitational wave signatures in binary inspiral. Phys Rev D (2010) 81:123016. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.81.123016
38. Annala E, Gorda T, Kurkela A, Vuorinen A. Gravitational-wave constraints on the neutron-star-matter equation of state. Phys Rev Lett (2018) 120:172703. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.172703
39. Lim Y, Holt JW. Neutron star tidal deformabilities constrained by nuclear theory and experiment. Phys Rev Lett (2018) 121:062701. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.062701
40. Most ER, Weih LR, Rezzolla L, Schaffner-Bielich J. New constraints on radii and tidal deformabilities of neutron stars from GW170817. Phys Rev Lett (2018) 120:261103. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.261103
41. Raithel C, Özel F, Psaltis D. Tidal deformability from GW170817 as a direct probe of the neutron star radius. Astrophys J Lett (2018) 857:L23. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aabcbf
42. Alam N, Agrawal BK, Fortin M, Pais H, Providência C, Raduta AR, et al. Strong correlations of neutron star radii with the slopes of nuclear matter incompressibility and symmetry energy at saturation. Phys Rev C (2016) 94:052801. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.94.052801
43. Hu J, Bao S, Zhang Y, Nakazato K, Sumiyoshi K, Shen H. Effects of symmetry energy on the radius and tidal deformability of neutron stars in the relativistic mean-field model. PTEP (2020) 2020:043D01. doi:10.1093/ptep/ptaa016
44. Li B-A, Magno M. Curvature-slope correlation of nuclear symmetry energy and its imprints on the crust-core transition, radius and tidal deformability of canonical neutron stars. Phys Rev C (2020) 102:045807. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.102.045807
45. Lopes LL. Role of the symmetry energy slope in neutron stars: exploring the model dependency. Phys Rev C (2024) 110:015805. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.110.015805
46. Lim Y, Schwenk A. Symmetry energy and neutron star properties constrained by chiral effective field theory calculations. Phys Rev C (2024) 109:035801. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.109.035801
47. Adhikari D, Albataineh H, Androic D, Aniol K, Armstrong D, Averett T, et al. Accurate determination of the neutron skin thickness of 208Pb through parity-violation in electron scattering. Phys Rev Lett (2021) 126:172502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.172502
48. Reed BT, Fattoyev FJ, Horowitz CJ, Piekarewicz J. Implications of PREX-2 on the equation of state of neutron-rich matter. Phys Rev Lett (2021) 126:172503. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.172503
49. Reinhard P-G, Roca-Maza X, Nazarewicz W. Information content of the parity-violating asymmetry in Pb208. Phys Rev Lett (2021) 127:232501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.232501
50. Adhikari D, Albataineh H, Androic D, Aniol K, Armstrong D, Averett T, et al. Precision determination of the neutral weak form factor of 48Ca. Phys Rev Lett (2022) 129:042501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.042501
51. Zenihiro J, Sakaguchi H, Murakami T, Yosoi M, Yasuda Y, Terashima S, et al. Neutron density distributions of Pb-204, Pb-206, Pb-208 deduced via proton elastic scattering at Ep=295 MeV. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:044611. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.82.044611
52. Tamii A, Poltoratska I, von Neumann-Cosel P, Fujita Y, Adachi T, Bertulani CA, et al. Complete electric dipole response and the neutron skin in 208Pb. Phys Rev Lett (2011) 107:062502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.062502
53. Centelles M, Roca-Maza X, Vinas X, Warda M. Nuclear symmetry energy probed by neutron skin thickness of nuclei. Phys Rev Lett (2009) 102:122502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.122502
54. Dutra M, Lourenço O, Avancini SS, Carlson BV, Delfino A, Menezes DP, et al. Relativistic mean-field hadronic models under nuclear matter constraints. Phys Rev C (2014) 90:055203. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.90.055203
55. Trzcinska A, Jastrzebski J, Lubinski P, Hartmann FJ, Schmidt R, von Egidy T, et al. Neutron density distributions deduced from anti-protonic atoms. Phys Rev Lett (2001) 87:082501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.082501
56. Zabari N, Kubis S, Wójcik W. Influence of the interactions of scalar mesons on the behavior of the symmetry energy. Phys Rev C (2019) 99:035209. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.99.035209
57. Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K, Saito K. Asymmetric nuclear matter in relativistic mean-field models with isoscalar- and isovector-meson mixing. Astrophys J (2022) 929:82. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac5f40
58. Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K, Kim K, Saito K. Can the PREX-2 and CREX results be understood by relativistic mean-field models with the astrophysical constraints? Phys Lett B (2023) 843:138013. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2023.138013
59. Li F, Cai B-J, Zhou Y, Jiang W-Z, Chen L-W. Effects of isoscalar- and isovector-scalar meson mixing on neutron star structure. Astrophys J (2022) 929:183. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac5e2a
60. Danielewicz P, Lacey R, Lynch WG. Determination of the equation of state of dense matter. Science (2002) 298:1592–6. doi:10.1126/science.1078070
61. Fuchs C. Kaon production in heavy ion reactions at intermediate energies. Prog Part Nucl Phys (2006) 56:1–103. doi:10.1016/j.ppnp.2005.07.004
62. Lynch WG, Tsang MB, Zhang Y, Danielewicz P, Famiano M, Li Z, et al. Probing the symmetry energy with heavy ions. Prog Part Nucl Phys (2009) 62:427–32. doi:10.1016/j.ppnp.2009.01.001
63. Oliinychenko D, Sorensen A, Koch V, McLerran L. Sensitivity of Au+Au collisions to the symmetric nuclear matter equation of state at 2–5 nuclear saturation densities. Phys Rev C (2023) 108:034908. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.108.034908
64. Cromartie HT, Fonseca E, Ransom SM, Demorest PB, Arzoumanian Z, Blumer H, et al. Relativistic Shapiro delay measurements of an extremely massive millisecond pulsar. Nat Astron (2019) 4:72–6. doi:10.1038/s41550-019-0880-2
65. Fonseca E, Cromartie HT, Pennucci TT, Ray PS, Kirichenko AY, Ransom SM, et al. Refined mass and geometric measurements of the high-mass PSR J0740+6620. Astrophys J Lett (2021) 915:L12. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac03b8
66. Ring P. Relativistic mean field theory in finite nuclei. Prog Part Nucl Phys (1996) 37:193–263. doi:10.1016/0146-6410(96)00054-3
67. Lalazissis GA, Konig J, Ring P. A New parametrization for the Lagrangian density of relativistic mean field theory. Phys Rev C (1997) 55:540–3. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.55.540
68. Pradhan BK, Chatterjee D, Gandhi R, Schaffner-Bielich J. Role of vector self-interaction in neutron star properties. Nucl Phys A (2023) 1030:122578. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2022.122578
69. Malik T, Dexheimer V, Providência C. Astrophysics and nuclear physics informed interactions in dense matter: inclusion of PSR J0437-4715. Phys Rev D (2024) 110:043042. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.110.043042
70. Todd-Rutel BG, Piekarewicz J. Neutron-Rich nuclei and neutron stars: a new accurately calibrated interaction for the study of neutron-rich matter. Phys Rev Lett (2005) 95:122501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.122501
71. Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K, Saito K. Equation of state for neutron stars in SU(3) flavor symmetry. Phys Rev C (2013) 88:015802. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.88.015802
72. Horowitz CJ, Piekarewicz J. Neutron star structure and the neutron radius of Pb-208. Phys Rev Lett (2001) 86:5647–50. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.5647
73. Haidari MM, Sharma MM. Sigma-omega meson coupling and properties of nuclei and nuclear matter. Nucl Phys A (2008) 803:159–72. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2008.02.296
74. Sharma MM. Scalar-vector Lagrangian without nonlinear self-interactions of bosonic fields in the relativistic mean-field theory. Phys Lett B (2008) 666:140–4. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2008.07.005
75. Kubis S, Wójcik W, Castillo DA, Zabari N. Relativistic mean-field model for the ultracompact low-mass neutron star HESS J1731-347. Phys Rev C (2023) 108:045803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.108.045803
76. Chen L-W, Ko CM, Li B-A. Isospin-dependent properties of asymmetric nuclear matter in relativistic mean-field models. Phys Rev C (2007) 76:054316. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.76.054316
77. Chen L-W, Cai B-J, Ko CM, Li B-A, Shen C, Xu J. Higher-order effects on the incompressibility of isospin asymmetric nuclear matter. Phys Rev C (2009) 80:014322. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.80.014322
78. Czerski P, De Pace A, Molinari A. Revisiting the Hugenholtz-Van Hove theorem in nuclear matter. Phys Rev C (2002) 65:044317. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.65.044317
79. Cai B-J, Chen L-W. Lorentz covariant nucleon self-energy decomposition of the nuclear symmetry energy. Phys Lett B (2012) 711:104–8. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2012.03.058
80. Miyatsu T, Katayama T, Saito K. Effects of Fock term, tensor coupling and baryon structure variation on a neutron star. Phys Lett B (2012) 709:242–6. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2012.02.009
81. Katayama T, Miyatsu T, Saito K. EoS for massive neutron stars. Astrophys J Suppl (2012) 203:22. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/203/2/22
82. Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K, Ishizuka C, Kim KS, Maruyama T, Saito K. Decomposition of nuclear symmetry energy based on Lorentz-covariant nucleon self-energies in relativistic Hartree-Fock approximation. Phys Lett B (2020) 803:135282. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2020.135282
83. Kubis S. Nuclear symmetry energy and stability of matter in neutron stars. Phys Rev C (2007) 76:025801. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.76.025801
84. Lattimer JM, Prakash M. Neutron star observations: prognosis for equation of state constraints. Phys Rept (2007) 442:109–65. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2007.02.003
85. Xu J, Chen L-W, Li B-A, Ma H-R. Nuclear constraints on properties of neutron star crusts. Astrophys J (2009) 697:1549–68. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/697/2/1549
86. Moustakidis CC, Niksic T, Lalazissis GA, Vretenar D, Ring P. Constraints on the inner edge of neutron star crusts from relativistic nuclear energy density functionals. Phys Rev C (2010) 81:065803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.81.065803
87. Psonis VP, Moustakidis CC, Massen SE. Nuclear symmetry energy effects on neutron stars properties. Mod Phys Lett A (2007) 22:1233–53. doi:10.1142/S0217732307023572
88. Kubis S, Wójcik W, Zabari N. Multilayer neutron stars with scalar mesons crossing term. Phys Rev C (2020) 102:065803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.102.065803
89. Routray TR, Viñas X, Basu DN, Pattnaik SP, Centelles M, Robledo L, et al. Exact versus Taylor-expanded energy density in the study of the neutron star crust–core transition. J Phys G (2016) 43:105101. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/43/10/105101
90. Zhang N-B, Li B-A, Xu J. Combined constraints on the equation of state of dense neutron-rich matter from terrestrial nuclear experiments and observations of neutron stars. Astrophys J (2018) 859:90. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aac027
91. Xie W-J, Li B-A. Bayesian inference of high-density nuclear symmetry energy from radii of canonical neutron stars. Astrophys J (2019) 883:174. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab3f37
92. Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K, Kim K, Saito K. Massive neutron stars with small radii in relativistic mean-field models optimized to nuclear ground states. Preprint arXiv:2209.02861 (2022) [nucl–th]. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2209.02861
93. Abbott R, Abbott TD, Abraham S, Acernese F, Ackley K, Adams C, et al. GW190814: gravitational waves from the coalescence of a 23 solar mass black hole with a 2.6 solar mass compact object. Astrophys J Lett (2020) 896:L44. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab960f
94. Fattoyev FJ, Horowitz CJ, Piekarewicz J, Reed B. GW190814: impact of a 2.6 solar mass neutron star on the nucleonic equations of state. Phys Rev C (2020) 102:065805. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.102.065805
95. Reed BT, Fattoyev FJ, Horowitz CJ, Piekarewicz J. Density dependence of the symmetry energy in the post–PREX-CREX era. Phys Rev C (2024) 109:035803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.109.035803
96. Chen W-C, Piekarewicz J. Searching for isovector signatures in the neutron-rich oxygen and calcium isotopes. Phys Lett B (2015) 748:284–8. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2015.07.020
97. Fattoyev FJ, Piekarewicz J. Sensitivity of the moment of inertia of neutron stars to the equation of state of neutron-rich matter. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:025810. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.82.025810
98. Chen W-C, Piekarewicz J. Building relativistic mean field models for finite nuclei and neutron stars. Phys Rev C (2014) 90:044305. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.90.044305
99. Salinas M, Piekarewicz J. Bayesian refinement of covariant energy density functionals. Phys Rev C (2023) 107:045802. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.107.045802
100. Salinas M, Piekarewicz J. Building an equation of state density ladder. Symmetry (2023) 15:994. doi:10.3390/sym15050994
101. Kumar S, Kumar M, Kumar R, Dhiman SK. Implications of isoscalar and isovector scalar meson mixed interaction on nuclear and neutron star properties. Phys Rev C (2023) 108:055802. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.108.055802
102. Kumar B, Agrawal BK, Patra SK. New relativistic effective interaction for finite nuclei, infinite nuclear matter and neutron stars. Phys Rev C (2018) 97:045806. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.045806
103. Fattoyev FJ, Horowitz CJ, Piekarewicz J, Shen G. Relativistic effective interaction for nuclei, giant resonances, and neutron stars. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:055803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.82.055803
104. Liliani N, Diningrum JP, Sulaksono A. Tensor and Coulomb-exchange terms in the relativistic mean-field model with δ-meson and isoscalar-isovector coupling. Phys Rev C (2021) 104:015804. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.104.015804
105. Fattoyev FJ, Piekarewicz J. Has a thick neutron skin in 208Pb been ruled out? Phys Rev Lett (2013) 111:162501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.162501
106. Piekarewicz J. Symmetry energy constraints from giant resonances: a theoretical overview. Eur Phys J (2014) A 50:25. doi:10.1140/epja/i2014-14025-x
107. Birkhan J, Miorelli M, Bacca S, Bassauer S, Bertulani C, Hagen G, et al. Electric dipole polarizability of 48Ca and implications for the neutron skin. Phys Rev Lett (2017) 118:252501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.252501
108. Tarbert CM, Watts D, Glazier D, Aguar P, Ahrens J, Annand J, et al. Neutron skin of 208Pb from coherent pion photoproduction. Phys Rev Lett (2014) 112:242502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.242502
109. Reinhard PG, Rufa M, Maruhn J, Greiner W, Friedrich J. Nuclear ground state properties in a relativistic meson field theory. Z Phys A (1986) 323:13–25. doi:10.1007/bf01294551
110. Liliani N, Nugraha AM, Diningrum JP, Sulaksono A. Tensor and isovector–isoscalar terms of relativistic mean field model: impacts on neutron-skin thickness, charge radius, and nuclear matter. Nucl Phys A (2024) 1042:122812. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2023.122812
111. De Vries H, De Jager CW, De Vries C. Nuclear charge-density-distribution parameters from elastic electron scattering. Atom Data Nucl Data Tabl (1987) 36:495–536. doi:10.1016/0092-640X(87)90013-1
112. Horowitz CJ, Pollock SJ, Souder PA, Michaels R. Parity violating measurements of neutron densities. Phys Rev C (2001) 63:025501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.63.025501
113. Horowitz CJ, Ahmed Z, Jen CM, Rakhman A, Souder PA, Dalton MM, et al. Weak charge form factor and radius of 208Pb through parity violation in electron scattering. Phys Rev C (2012) 85:032501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.85.032501
114. Niksic T, Vretenar D, Finelli P, Ring P. Relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov model with density-dependent meson-nucleon couplings. Phys Rev C (2002) 66:024306. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.66.024306
115. Ma Y-L, Rho M. Topology change, emergent symmetries and compact star matter. AAPPS Bull (2021) 31:16. doi:10.1007/s43673-021-00016-1
116. Lee HK, Ma Y-L, Paeng W-G, Rho M. Cusp in the symmetry energy, speed of sound in neutron stars and emergent pseudo-conformal symmetry. Mod Phys Lett A (2022) 37:2230003. doi:10.1142/S0217732322300038
117. Chen L-W, Ko CM, Li B-A. Nuclear matter symmetry energy and the neutron skin thickness of heavy nuclei. Phys Rev C (2005) 72:064309. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.72.064309
118. Maruyama T, Chiba S. Equation of state of neutron star matter and the isovector nucleon optical model potential. J Phys G (1999) 25:2361–9. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/25/12/306
119. Maruyama T, Balantekin AB, Cheoun M-K, Kajino T, Kusakabe M, Mathews GJ. A relativistic quantum approach to neutrino and antineutrino emission via the direct Urca process in strongly magnetized neutron-star matter. Phys Lett B (2022) 824:136813. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2021.136813
121. Miyatsu T, Yamamuro S, Nakazato K. A new equation of state for neutron star matter with nuclei in the crust and hyperons in the core. Astrophys J (2013) 777:4. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/777/1/4
122. Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K, Saito K. Equation of state for neutron stars with hyperons and quarks in the relativistic Hartree–Fock approximation. Astrophys J (2015) 813:135. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/813/2/135
123. Tolman RC. Static solutions of Einstein’s field equations for spheres of fluid. Phys Rev (1939) 55:364–73. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.55.364
124. Oppenheimer JR, Volkoff GM. On massive neutron cores. Phys Rev (1939) 55:374–81. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.55.374
125. Sulaksono A, Alam N, Agrawal BK. Core–crust transition properties of neutron stars within systematically varied extended relativistic mean-field model. Int J Mod Phys E (2014) 23:1450072. doi:10.1142/S0218301314500724
126. Providência C, Avancini SS, Cavagnoli R, Chiacchiera S, Ducoin C, Grill F, et al. Imprint of the symmetry energy on the inner crust and strangeness content of neutron stars. Eur Phys J (2014) A 50:44. doi:10.1140/epja/i2014-14044-7
127. Li B-A, Krastev PG, Wen D-H, Zhang N-B. Towards understanding astrophysical effects of nuclear symmetry energy. Eur Phys J (2019) A 55:117. doi:10.1140/epja/i2019-12780-8
128. Horowitz CJ, Piekarewicz J. Constraining URCA cooling of neutron stars from the neutron radius of Pb-208. Phys Rev C (2002) 66:055803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.66.055803
129. Page D, Geppert U, Weber F. The Cooling of compact stars. Nucl Phys A (2006) 777:497–530. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2005.09.019
130. Lattimer JM, Prakash M, Pethick CJ, Haensel P. Direct URCA process in neutron stars. Phys Rev Lett (1991) 66:2701–4. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.66.2701
131. Rutherford N, Mendes M, Svensson I, Schwenk A, Watts AL, Hebeler K, et al. Constraining the dense matter equation of state with new NICER mass–radius measurements and new chiral effective field theory inputs. Astrophys J Lett (2024) 971:L19. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ad5f02
132. Choudhury D, Salmi T, Vinciguerra S, Riley TE, Kini Y, Watts AL, et al. A NICER view of the nearest and brightest millisecond pulsar: PSR J0437–4715. Astrophys J Lett (2024) 971:L20. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ad5a6f
133. Guichon PAM. A possible quark mechanism for the saturation of nuclear matter. Phys Lett B (1988) 200:235–40. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(88)90762-9
134. Saito K, Thomas AW. A Quark - meson coupling model for nuclear and neutron matter. Phys Lett B (1994) 327:9–16. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(94)91520-2
135. Saito K, Thomas AW. The Nolen-Schiffer anomaly and isospin symmetry breaking in nuclear matter. Phys Lett B (1994) 335:17–23. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(94)91551-2
136. Saito K, Tsushima K, Thomas AW. Nucleon and hadron structure changes in the nuclear medium and the impact on observables. Prog Part Nucl Phys (2007) 58:1–167. doi:10.1016/j.ppnp.2005.07.003
137. Saito K, Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K. Effect of isoscalar and isovector scalar fields on baryon semileptonic decays in nuclear matter. Phys Rev D (2024) 110:113001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.110.113001
138. Nagai S, Miyatsu T, Saito K, Tsushima K. Quark-meson coupling model with the cloudy bag. Phys Lett B (2008) 666:239–44. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2008.07.065
139. Chen L-W, Ko CM, Li B-A. Determination of the stiffness of the nuclear symmetry energy from isospin diffusion. Phys Rev Lett (2005) 94:032701. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.032701
140. Li B-A, Chen L-W. Nucleon-nucleon cross sections in neutron-rich matter and isospin transport in heavy-ion reactions at intermediate energies. Phys Rev C (2005) 72:064611. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.72.064611
141. Estee J, Lynch W, Tsang C, Barney J, Jhang G, Tsang M, et al. Probing the symmetry energy with the spectral pion ratio. Phys Rev Lett (2021) 126:162701. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.162701
142. Lynch WG, Tsang MB. Decoding the density dependence of the nuclear symmetry energy. Phys Lett B (2022) 830:137098. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2022.137098
143. Tsang CY, Tsang MB, Lynch WG, Kumar R, Horowitz CJ. Determination of the equation of state from nuclear experiments and neutron star observations. Nat Astron (2024) 8:328–36. doi:10.1038/s41550-023-02161-z
144. Chen L-W. Symmetry energy systematics and its high density behavior. EPJ Web Conf (2015) 88:00017. doi:10.1051/epjconf/20158800017
145. Li B-A, Cai B-J, Xie W-J, Zhang N-B. Progress in constraining nuclear symmetry energy using neutron star observables since GW170817. Universe (2021) 7:182. doi:10.3390/universe7060182
146. Negele JW, Vautherin D. Neutron star matter at subnuclear densities. Nucl Phys A (1973) 207:298–320. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(73)90349-7
147. Sotani H, Ota S. Neutron star mass formula with nuclear saturation parameters for asymmetric nuclear matter. Phys Rev D (2022) 106:103005. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.106.103005
Keywords: isospin-asymmetric nuclear matter, neutron skin thickness, neutron stars, NICER, nuclear equation of state, nuclear symmetry energy, PREX-2, relativistic mean-field models
Citation: Miyatsu T, Cheoun M-K, Kim K and Saito K (2025) Novel features of asymmetric nuclear matter from terrestrial experiments and astrophysical observations of neutron stars. Front. Phys. 12:1531475. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1531475
Received: 20 November 2024; Accepted: 11 December 2024;
Published: 06 February 2025.
Edited by:
Masayuki Matsuzaki, Fukuoka University of Education, JapanReviewed by:
Tomoyuki Maruyama, Nihon University, JapanAnto Sulaksono, University of Indonesia, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Miyatsu, Cheoun, Kim and Saito. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tsuyoshi Miyatsu, dHN1eW9zaGkubWl5YXRzdUBzc3UuYWMua3I=
†ORCID: Tsuyoshi Miyatsu, orcid.org/0000-0001-9186-8793; Myung-Ki Cheoun, orcid.org/0000-0001-7810-5134; Koichi Saito, orcid.org/0000-0002-8563-9262
 Tsuyoshi Miyatsu
Tsuyoshi Miyatsu Myung-Ki Cheoun
Myung-Ki Cheoun Kyungsik Kim
Kyungsik Kim Koichi Saito3†
Koichi Saito3†