- School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan, Shanxi, China
To improve the assembly accuracy of intelligent assembly process, a 3D surface reconstruction system based on laser scanning for assembly targets and assembly positions was designed. The light source uses a line laser to provide structured light, enabling rapid scanning of the assembly target surface on a single line. Calculate the spatial relationship between the assembly target and the assembly position through the calibration board. A position inversion optimization algorithm has been proposed. By completing the transformation of feature points from local coordinates to global coordinates. The energy distribution in the central area of the CCD image plane was simulated and analyzed under different baseline lengths, and the optimal baseline position of 35 mm was determined. The experiment is divided into two parts, and the reconstruction of the three-dimensional surface of the free-form surface target based on laser scanning was completed in the laboratory. The optimized target 3D point cloud data is evenly distributed, with almost no scattered points on the main two local surfaces, which well reflects the surface structure of the target. In the actual outdoor assembly experiment, the system cooperated with the assembly vehicle to achieve the correct assembly of the assembly. The reconstruction accuracy deviation of most test points is very small, with over 85% of test points having an error of less than 0.54 mm. The average deviation of these points before and after optimization is 0.67 mm. This system has higher application value in the field of large-scale intelligent assembly.
1 Introduction
With the continuous updating of industrialization, traditional automated assembly technology can no longer meet the application requirements of complex structural assembly. The emergence of intelligent assembly technology can greatly improve the accuracy and stability of intelligent assembly of complex structures, and intelligent sensing units based on laser scanning are the core technology of intelligent assembly systems. It is of great significance to study the application of three-dimensional surface recognition technology for intelligent assembly processes. To quickly obtain the three-dimensional surface shape of the object being assembled, traditional contact scanning methods cannot be achieved, and non-contact optical testing methods can only be used [1–3]. The non-contact optical testing methods are mainly divided into laser scanning method and image recognition method. The image scanning method uses multi angle photography to calculate the assembly target feature position [4, 5]. This method is fast and cost-effective, but its accuracy is low and it has certain requirements for the morphology of the tested object. Compared to other methods, laser scanning has high accuracy and no special requirements for the morphology of the assembly object.
Simon et al. [6] developed a desktop 3D laser scanning system, which can be applied to collect the 3D surface shape of targets on experimental platforms. However, it is easily affected by light, so it is only suitable for dark environments, which limits its application. The handheld 3D laser scanning plane detector developed by Lavelle P et al. [7] from NASA can quickly obtain the surface shape features of the test surface, reconstruct its 3D point cloud, reconstruct geometric models such as cracks and depressions, and achieve a detection accuracy of 0.30 mm. Zhongxu Hu from the University of Newcastle in the UK [8] studied a 3D measurement method based on line laser. A vision system was installed on the arm of a robot, and combined with a line laser projector, fast 3D reconstruction of objects such as shoes was achieved, achieving good results. Tang et al. [9] achieved non-contact measurement of surface roughness by using the principle of displacement change generated by combining laser spot with area array CCD camera. Peng et al. [10] designed a three-dimensional detection device using both a translation platform and a rotation platform. In order to reduce measurement blind spots, the system uses two cameras and a line laser projector. Under the action of the rotation platform, the laser can scan the entire test surface of the object. After scanning for a week, the detection system will move in a vertical direction, scan the object up and down, and obtain the overall morphology of the object. Morozov et al. [11] performed laser scanning on aircraft skin and interpolated the test area using a feedback correction algorithm, achieving a testing accuracy of 5.0 mm. Connolly et al. [12] proposed a laser scanning module installed on a robotic arm, with a 3D scanning accuracy better than 0.5 mm. In addition, some companies also have similar laser scanning products. The Fast CAN Cobra handheld laser scanner developed by Polhemus Company can obtain 15,000 point coordinates per second, with a measurement accuracy of 1 mm within a measurement range of 200 mm, efficiently completing the three-dimensional model reconstruction of the target surface [13]. LDI GKS has developed the OM-3R scanner, which can be combined with a rotating platform to measure the external contours of teeth, crowns, and other materials, and reverse synthesize 3D models. It is widely used in the medical field, with a depth of field of up to 100 mm and a scanning accuracy of up to 40 um [14]. The 3DCaMegaDS series human body scanning system does not require marking points and utilizes texture features to complete automatic stitching. In a scanning area of 2,200 * 1,200 * 1200 mm, the accuracy can reach 0.5 mm [15]. In summary, although there are many literature based on laser scanning, the vast majority of them are fixed target scanning with a fixed laser position, which limits the positional relationship of the assembly process. This article uses the laser scanning system fixed on a 6-degree-of-freedom assembly claw and studies the calculation method of its coordinate system one. This method contributes to the matching of laser scanning and dynamic assembly.
The use of laser scanning can effectively capture the three-dimensional surface features of the captured object. During the assembly process, laser 3D scanning can accurately obtain the surface structure of the assembly area, thereby achieving precise assembly. This article proposes a fast 3D surface acquisition system based on line laser scanning, and designs a position inversion optimization algorithm based on it.
2 System design
The system is controlled by a computer, and the carrier uses an automatic tracking method to find the assembly target placement position. When the loading vehicle reaches the designated position, the camera takes a photo to obtain the precise position relationship between the loading vehicle and the assembly area. Then, the laser scans the test location to obtain three-dimensional spatial information of the area to be placed, and then feeds it back to the computer. The computer uses 3D processing software to calculate the point cloud for assembly targets and placing positions. The system is shown in Figure 1.
The system is equipped with a 6 degree of freedom robotic arm on the cargo vehicle, which assembles the approximate position of the assembly target area through camera photography. Then, a laser is used to scan the surface shape of the area and reconstruct the 3D point cloud of the assembly position. By using 3D point cloud information, precise recognition of the face shape is achieved, providing a placement path for the robotic arm. The system realizes unmanned automated loading and unloading. In order to improve its assembly accuracy, feature extraction is performed on the surface shape of the loading and unloading assemble target, thereby improving system stability. Target disk is used to provide the calibration image required for the location information of the cargo vehicle, so as to determine that the cargo vehicle will automatically travel to the designated position. The laser adopts a line scanning laser to form structured light, which can scan data on one line at a time. The laser is fixed on a six degree of freedom robotic arm, so they have a unified coordinate system. Through computer inversion calculation, a mapping relationship can be established between the spatial offset of the placement position and the spatial position of the assembly target.
3 Principle of laser scanning 3D reconstruction
3.1 Laser triangulation
The system uses a line laser as the light source to scan the surface of the assembly target. Using the principle of triangulation, convert the three-dimensional depth information of the surface of the object to be grasped into a two-dimensional laser stripe image. Establish a laser scanning measurement system model based on the relative position relationship between the laser plane and the camera. The camera obtains the three-dimensional spatial coordinates of each measurement point on the stripe, and then controls the stepper motor to automatically grasp and place the object.
The acquisition of three-dimensional laser point clouds is achieved by lasers, so the position of the laser is crucial for the construction of the point cloud. The position of the laser can be known in advance, so we use the plane constructed by the laser and the CCD photosensitive surface as the reference plane, extending towards the target direction to form a three-dimensional space. Therefore, the coordinate system of the two-dimensional CCD is positively located on the plane of z = 0 in the point cloud coordinate system.
Set the center of the camera lens as the coordinate origin and establish the camera coordinate system [16]. According to the triangular relationship in the measurement model, the coordinates of the spatial measurement points are (x, y, z), the distance from the laser to the camera center is the baseline length l, the angle between the laser optical axis and the system baseline is θ, the focal length of the lens is f, and the coordinates of the measurement points and the conjugate points on the CCD image plane are (x′, y′). The following relationship can be derived:
Calibration of the parameters in Formula 1 can accurately obtain comprehensive feature points of the target. So as to improve the testing accuracy of the system. In order to achieve measurement of the entire surface of the object to be grabbed, the measurement system needs to be mounted on a displacement platform for translational motion, where the displacement platform’s motion speed is v and the motion time is t. At this point, in the relationship between spatial coordinates (x, y, z) and (x′, y′), the coordinates on the x-axis become:
Among them, the coordinate relationship between the y-axis and the z-axis remains unchanged. When the laser is not perpendicular to the reference plane to be measured, the incident direction of the structured light is not perpendicular to the reference plane. At a certain angle with the reference plane, the object being measured is reflected, and the partially reflected light is received by the CCD and imaged on the CCD sensor. The angle between the incident light and the normal of the reference plane is θ1. The reflected light forms an angle θ2 with the normal of the reference plane [17]. According to the principle of trigonometry, it can be obtained that:
In the above equation, α is the angle between the laser optical axis and the normal direction of the image, L1 is the distance from the imaging lens to the target.,L2 is the focal length of the receiving lens, so L2 = f. According to Formulas 2, 3, the positional relationship can be obtained, we can obtain the height to be measured as:
3.2 Testing error analysis
After obtaining the height to be measured by Formula 4, analyze the measurement error of the system structure. The spatial position coordinates of the measured point in the camera coordinate system directly affect the detection accuracy of the measurement system. In order to study the influence of the structure of the laser scanning system on measurement accuracy, the errors in locating the center of the laser stripes in the x and y directions are δ1 and δ2, respectively. The errors in the measurement results in the three directions can be expressed as:
When (f cot θ - x) is 0, the system error reaches its maximum value. So x = f cot θ is the peak point of the above error formula, at which point the system error reaches its maximum value. Under the premise of considering the influence of system distortion, the center of the stripes should be as close as possible to the camera’s main point position, so the intersection position of the light plane and the optical axis determines the measurement range of the system by Formula 5. Z is the distance from the intersection point of the laser plane and the camera axis to the lens optical center. This system will be positioned at 150 mm, and it can be seen that the measurement range of the system is determined by l and θ together. Therefore, the relationship between its testing function is obtained as follows:
According to Formula 6, it can be inferred that the measurement error has a linear relationship with the baseline length l and a nonlinear relationship with θ.
4 Algorithm design and simulation analysis
4.1 Optimization algorithm for position inversion
To obtain the surface shape of the assembly target, it needs extract the center point of the laser scanning image, in order to accurately calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of the target. This article proposes a multi feature point structural parameter calibration algorithm. The traditional wire drawing method has a simple principle, but the calibration process is complex, requiring the use of a measuring arm to measure the coordinates of the intersection point between the iron wire and the light plane, resulting in low accuracy. The structural cursor calibration method based on constant alternating ratio utilizes a special stereo calibration assembly target to solve the accuracy problem of planar targets. However, the production of calibration targets is difficult, and assemble accuracy has a significant impact on test results. So, we propose a detection algorithm for multiple feature points on the light plane using a planar target.
(1) Find the local world coordinates of feature points on the light plane. Extract the fitting line between the center point of the disk and the laser stripe. Obtain sub-pixel level intersection coordinates through line fitting, and each row of the circular array calibration board intersects with the laser stripes. Obtain the three-dimensional point cloud (x, y, z) and the two-dimensional coordinates (x, y) of the CCD;
(2) After obtaining the three-dimensional point cloud coordinate system and the two-dimensional CCD plane coordinate system, the two-dimensional CCD image plane position is mapped into the three-dimensional point cloud based on their actual physical positional relationship, thus achieving the unification of the coordinate system. Parameter calculation is also carried out at this time. Import platform v and angle θ, correct the true position of the assembly target;
(3) Maintain consistent proportions in each straight line. Calculate the pixel coordinates corresponding to these feature points in the image coordinate system. Calculate L1, L2, and α to achieve optimal image quality;
(4) Complete the transformation from local coordinates of feature points to global coordinates. Fit the test point data on the corresponding circular array calibration board and unify all feature points in the global coordinate system;
(5) Using the least squares method to fit the spatial parameter equation of the plane, calculate the shortest distance between laser planes and use it as the optimization objective function. Calculate X and provide feedback to the control module to correct the assembly position and pose;
(6) Use this objective function to calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of multiple feature points.
4.2 Simulation analysis
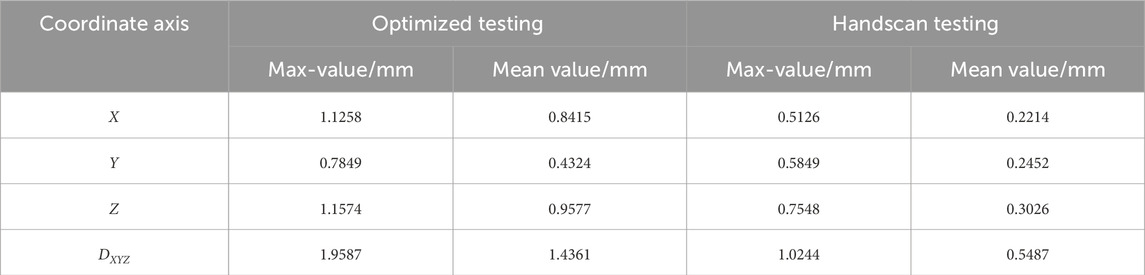
In order to obtain the optimal laser reflection intensity for CCD during dynamic assembly, it is necessary to analyze and obtain the optimal baseline position. The optimal position is determined by the energy intensity that can be obtained on the image plane under the same conditions. For different combinations of structural parameters l and θ, there are significant differences in measurement errors in the X, Y, and Z directions of the measurement results. Near the error peak point, the peak values differ by more than 10 times, and the measurement error decreases sharply with the change of x. In order to analyze measurement errors more intuitively, we take the part near the main point of the image center that is far away from the error peak. Comparing Figures 2A, B, it can be seen that when determining the measurement range of the system, the baseline length is different, and the measurement accuracy is also different. As the baseline length increases, the angle between the laser plane and the baseline length becomes smaller, and the measurement error becomes smaller. When the CCD is near the main point (−1 mm, +1 mm) and the baseline length is 30 mm, the measurement error is less than 0.5 mm, as shown in Figure 2A. The maximum measurement error for a baseline length of 35 mm is less than 0.2 mm, as shown in Figure 2B. Near x = 0, the larger the baseline length, the smaller the measurement error.
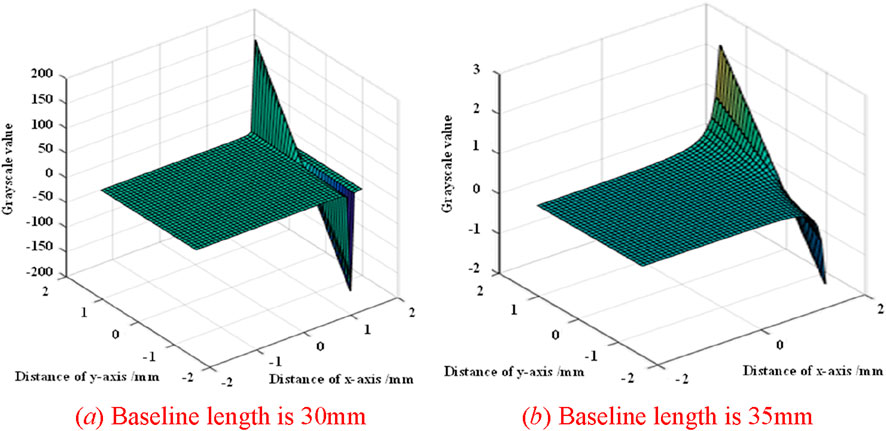
Figure 2. Measurement errors under different baseline lengths. (A) Baseline length is 30 mm (B) Baseline length is 35 mm.
As shown in Figure 2, in the central sensitive area of CCD, the intensity distribution of energy will undergo significant changes due to the baseline length. In order to achieve better imaging quality, it is necessary to optimize the selection of baseline length. When the measurement distance is fixed, as the baseline of the system increases, the measurement error of the system will become smaller. However, as the baseline length increases, the angle between the laser plane and the camera optical axis becomes smaller, resulting in an increase in the volume of the measurement system and a decrease in the measurement range. The error peak points are closer to the main point direction, which reduces the utilization rate of the CCD. Therefore, the baseline length should not be too large. After the above analysis, the baseline length of the system, the angle between the laser plane and the baseline, will have a significant impact on measurement accuracy. Although the measurement accuracy of the system will improve with the increase of baseline length, if the baseline length is too long, it will increase the external dimensions of the system, and the CCD utilization rate of the system will decrease, reducing the measurement range of the system. Finally, the baseline length of the system is selected as 35 mm, and the tangent value of the angle between the laser plane and the baseline is set to 3.5, so the error caused by the system structure is within ±0.1 mm.
5 Experiments
5.1 Laser scanning 3D reconstruction
In the experiment, the system consists of BNS 250 ZG line laser, G3-GM10 area array CCD sensor, HGTA01 mechanical guide rail, and NBB20-K power module. The scanning target is a free-form surface object in the shape of a flower pot, made of PVC material. A black velvet cloth was used to semi enclose the optical platform area to avoid stray light interference. Then place the assembly target with both curved and edge structures on the optical platform. The position relationship between the laser and CCD is determined by the baseline position in simulation analysis, and its optimal position can improve the imaging effect of CCD. And place it within the irradiation range of the laser. The laser scanning system and its scanning assembly target are shown in Figure 3A. Collect point cloud data of the surface to be tested. According to the mapping relationship of the optical system in Section 1, its three-dimensional coordinates are reconstructed in Cloud Compare software, and a three-dimensional model of the measured surface is generated to reconstruct the three-dimensional shape of the measured surface, as shown in Figure 3B.
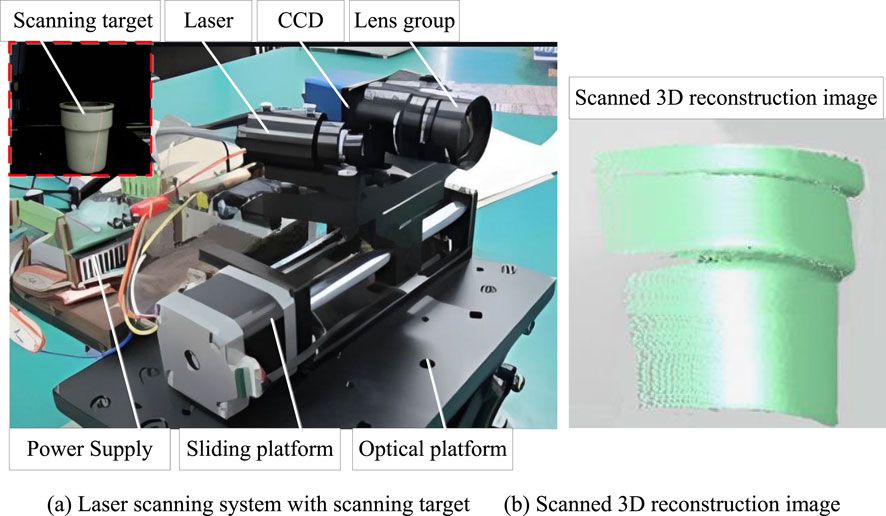
Figure 3. Laser scanning system with scanning assembly target and its 3D reconstruction. (A) Laser scanning system with scanning target (B) Scanned 3D reconstruction image.
After obtaining the energy distribution of the line laser, curve fitting of the center position can obtain the fitting equation of the structural laser scanning line; Then, based on the image positions of the standard plates in two CCDs, calculate the baseline length and the angle between the assembly target and the testing platform; Finally, each measurement section point cloud is replicated in three-dimensional space to form the assembly target three-dimensional point cloud set. Sample and fit the energy at the position of the beam irradiation. On the basis of comparing extreme value sampling and Gaussian sampling, Gaussian sampling was selected to obtain sub-pixel level standard position coordinate points. Combined with the coordinates of the circular dots on the Halcon calibration board, the two-dimensional information of the section can be converted into a three-dimensional point cloud. From Figure 3B, it can be seen that the optimized and filtered three-dimensional point cloud data of the assembly target is evenly distributed, with almost no scattered points on the main two local surfaces, which can well reflect the surface structure of the assembly target and provide good visual effects.
5.2 Assembly position accuracy test
The loading and unloading assembly system consists of a computer, a load truck, a robotic arm, a laser scanning and image acquisition module. The system assembles a fixed accessory and transports it to the placement position, and calculates the error between the placement trajectory and the assembly path by scanning the feature points on the placement area with laser. After correcting the error, place the assembly target in the corresponding position. The physical system is shown in Figure 4A. Two test targets with different curvatures were selected for the experiment, and point cloud data was collected by scanning them. The Handscan scanner was compared with the laser scanning method for testing the accuracy of assembly position, and the results are shown in Figure 4B. The Handscan scanner is commonly used for surface scanning, with high scanning accuracy but a smaller scanning range.
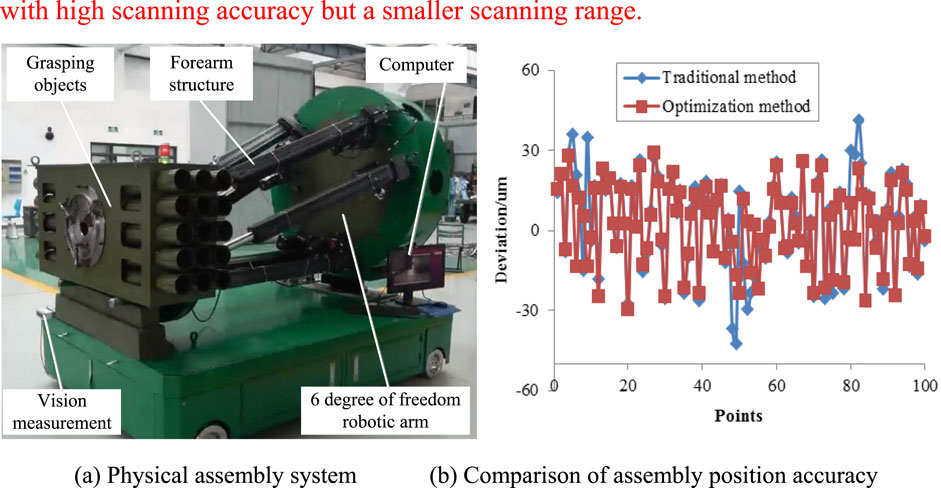
Figure 4. Analysis of assembly system and assembly position accuracy based on laser scanning. (A) Physical assembly system (B) Comparison of assembly position accuracy.
As shown in Figure 4B, when selecting 100 feature points for reconstructing the 3D point cloud, the position testing accuracy of this system is similar to the accuracy error of traditional methods, indicating that this system can also ensure good position accuracy in dynamic scanning 3D reconstruction. 1,000 coordinate points were selected for layering on the surface of the test target, with the majority distributed on two local surfaces of the target. The test results show that the reconstruction accuracy deviation of most test points is very small, with over 85% of test points having an error of less than 0.54 mm. The average deviation of these points before and after optimization is 0.67 mm. However, there are three obvious deviation positions in the unoptimized test points, with a maximum deviation of 0.85 mm, indicating that they are no longer on the same surface and are judged as scattered point noise. It can be seen that using this algorithm has a good recognition effect on abnormal points in the point cloud.
5.3 Precision analysis
The point cloud set reconstructed by this system was compared with the test data scanned using Handscan scanner, and the test results are shown in Table 1. Compare the three directions (X, Y, Z) and their spatial absolute deviation distances (DXYZ = sqrt [X2+Y2+Z2], where sqrt represents the square root) in the same coordinate system. Select 5 segmented points from the path trajectory for a total of 45 test data points.
As shown in Table 1, the scanning accuracy of The Handscan scanner is still better than that of our system. However, due to the small testing range of The Handscan scanner, for large-sized docking, this scanning time may take several minutes or even tens of minutes. It is too inefficient for intelligent assembly, so adopting this system has more obvious advantages. Our system is fast and has the ability to scan quickly over a large area.
6 Conclusion
The paper presents a surface recognition and reconstruction system for grasping objects based on line laser scanning, and proposes a position inversion optimization algorithm. The innovation of this article is to unify the three-dimensional point cloud and two-dimensional image in the same coordinate system, enabling the scanning system to achieve assembly target surface recognition on a dynamic robotic arm. The feasibility of obtaining assembly target feature points based on laser scanning was derived through simulation analysis, and the accuracy of position accuracy inversion during dynamic assemble process was verified through experimental testing. This proves that the system has the ability to obtain the surface shape of the assembly target in real-time. The average deviation of the positions in the three testing directions is less than 1.0 mm, which meets the design requirements of the online loading and unloading system. The 3D surface reconstruction provided by this system can also be applied in fields such as automatic pose adjustment in intelligent assembly. It has a certain contribution to online intelligent grasping and precise placement, and can be applied to precise control of unmanned loading and unloading systems.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YaL: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft. ZZ: Data curation, Writing–original draft. GC: Methodology, Writing–original draft. HR: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. YuL: Software, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by “Research on Automatic Supply Technology” (No. 20 - 163); Shanxi Province Applied Basic Research Program Project (20230302121119).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Hui Z, Yong-Jian Z, Lei Z, Xiao-Xue J, Li-Ying L. Fast color point cloud registration based on virtual viewpoint image. Front Phys (2022) 10:1026517. doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.1026517
2. Chen H, Cui Y, Li X, Zhang B, Cai Y, Ding J, et al. High-power dual-wavelength intracavity diamond Raman laser. Funct Diamond (2023) 3(1):2282527. doi:10.1080/26941112.2023.2282527
3. Ding W, Li M, Liang F, Gao Y, Qin W, Zhang H. Research on on-line assembly and calibration system based on laser scanning and optical fiber sensor. Front Phys (2023) 11:1185068. doi:10.3389/fphy.2023.1185068
4. Liu Z, Shao T, Zhang X. BCG signal analysis based on improved VMD algorithm. Measurement (2024) 231(114631):114631–10. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2024.114631
5. Sufeng Z, Dawei T, Xu Z, Qinzhou Y. Research on corresponding point matching and 3D reconstruction of underwater binocular stereo vision. Chin J Scientific Instrument (2022) 43(5):147–54. doi:10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2209215
6. Simon W, Sven M. Low-cost laser range scanner and fast surface registration approach. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer (2006). p. 718–28.
7. Lavelle JP, Schuet SR, Derouen M, Handheld A. Wireless 3D laser scanner for shuttle tile inspection. IV Conferencia Panamericana de END Buenos Aires (2007) 1–6. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242165734_A_Handheld_Wireless_3D_Laser_Scanner_for_Shuttle_Tile_Inspection
8. Hu Z, Marshall C, Bicker R, Taylor P. Automatic surface roughing with 3D machine vision and cooperative robot control. Robotics Autonomous Syst (2007) 55(55):552–60. doi:10.1016/j.robot.2007.01.005
9. Tang W, Tan Q. Wu Li. Research on non-contact measurement of surface parameters. J Wuhan Univ Technology (2009) 9(2):34–9. doi:10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2009.09.024
10. Peng W, Maohui Z, Sun C. Etc research on aircraft skin image scanning and positioning system. J Sensing Technology (2023) 36(11):1706–13. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2023.11.006
11. Morozov M, Pierce SG, Macleod CN, Mineo C, Summan R. Off-line scan path planning for robotic NDT. Measurement (2018) 12(2):284–90. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2018.02.020
12. Connolly T, Christine B. Technology and applications of ABB robot studio, industrial robot. An Int J (2009) 36(6):540–5. doi:10.1108/01439910910994605
13. Yang S, Sebastian S. CubeSLAM: monocular 3-d object SLAM. IEEE Trans Robotics (2019) 35(4):925–38. doi:10.1109/TRO.2019.2909168
14. Pourazar H, Samadzadegan F, Dadrass Javan F. A deep 2D/3D Feature-Level fusion for classification of UAV multispectral imagery in urban areas. Geocarto Int (2022) 37(23):6695–712. doi:10.1080/10106049.2021.1959655
15. Stroppa L, Cristalli C. Stereo vision system for accurate 3D measurements of connector pins. Exp Tech (2016) 41(1):1–10. doi:10.1007/s40799-016-0157-y
16. Mi X, Sun H, Liu Z, Han J. Research on far-field spot search and centre location algorithms. Front Phys (2023) 11:1230203. doi:10.3389/fphy.2023.1230203
Keywords: laser scanning, intelligent assembly, linear laser, optimization algorithm for position inversion, 3D surface reconstruction
Citation: Liu Y, Zhang Z, Chen G, Rong H and Li Y (2024) Based on laser scanning surface 3D reconstruction intelligent assembly system. Front. Phys. 12:1505062. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1505062
Received: 02 October 2024; Accepted: 28 October 2024;
Published: 05 December 2024.
Edited by:
Shuo Liu, Hebei University of Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Xiao Liang, Minzu University of China, ChinaHua Li, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China
Xuetao Huang, Shandong Jiaotong University, China
Mengmeng Wang, Beijing Institute of Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Zhang, Chen, Rong and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanchen Liu, bHljMzcyNDIyMTlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Yanchen Liu
Yanchen Liu Zhouqi Zhang
Zhouqi Zhang