- 1CYG Insulator Co., Ltd, Dongguan, China
- 2School of Electrical Engineering and New Energy, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, China
Introduction: As a new and efficient method for obstacle removal, laser clearance has promising applications in eliminating tree obstacles in transmission lines. This paper aims to explore various aspects related to the laser ablation of tree obstacles in transmission lines through simulation and experimentation.
Methods: This paper employs simulation and experimentation to test the ignition time, burn-through time, peak temperature, and basic carbonization rate of various types of tree obstacles in transmission lines. Additionally, it analyzes the effects of tree density, laser power, clearance distance, and tree moisture content on laser ablation characteristics.
Results: The results reveal that different types of tree obstacles exhibit distinct ablation characteristics. With increasing tree density, both the ignition and burn-through times increase, while the peak temperature and basic carbonization rate decrease. Additionally, laser power and clearance distance significantly influence laser ablation behavior. Higher laser energy density results in greater heat flux density, leading to shorter ignition and burn-through times and higher peak temperatures and carbonization rates. Moreover, the tree obstacle with the highest moisture content (58.4%) had the shortest burn-through time of 46.56 s, whereas the one with the lowest moisture content (14.8%) took the longest at 58.41 s, which demonstrates that increased moisture content enhances the laser ablation rate.
Discussion: These findings provide a basis for the application of laser-based tree obstacle removal in power transmission lines. The understanding of how different factors such as tree density, laser power, clearance distance, and moisture content affect the laser ablation process can help in optimizing the laser clearance operations for more efficient removal of tree obstacles in transmission lines.
1 Introduction
In power systems, transmission lines cover the entire country, often have to cross through forests. When the space between trees and the lines is less than the safety distance, thunderstorms can make the trees conductive, causing fires, outages, and trips [1–3]. In recent years, power outages caused by tree obstacles have become increasingly common. On 14 August 2003, three transmission lines in the United States and Canada tripped due to unexpected tree growth within the transmission corridors, leading to a massive blackout [4]. In 2009, a major power outage in eastern Malaysia was caused by an explosion resulting from tree contact with power lines [5]. In 2017, Hunan Province in China experienced up to 300 tripping incidents of 110 kV and above transmission lines due to “tree-line conflicts”. Over the past 3 years, tree obstacle hazards have accounted for 46% of transmission line tripping incidents in Guangdong Province, China. Therefore, overgrown trees within transmission line corridors are considered a key cause of large-scale power outages.
To better address the “tree-line conflict” and ensure the safe and stable operation of overhead transmission lines, power departments primarily use telescopic ladders, chainsaws, and axes to remove branches and trunks that are staying too close to the lines. However, these methods are unsuitable for remote mountainous or wilderness areas and pose electric shock risks to construction workers. Additionally, methods such as clearance robots, drones, and helicopters also have drawbacks such as immature technology, complex operations, and high costs, preventing them from being used on a large scale [6–8].
In recent years, rapid advancements in laser technology, known for its excellent directionality and high energy transmission, have impacted many traditional technological fields. Using lasers to clear transmission line obstacles has also emerged as a new technical solution. Qi et al. [9] used Nd: YAG and CO2 lasers for ice removal from transmission lines, analyzing the rate of laser de-icing with different lasers. They concluded that different wavelengths of laser are absorbed differently by ice layers, and transmission line laser de-icing systems should select lasers with high output power and absorption coefficients. Nd: YAG lasers were found to be more suitable for de-icing power lines than CO2 lasers. Luo et al. [10] proposed a safe and effective laser de-icing method using high-power mid-infrared lasers to de-ice composite insulators, concluding that appropriate laser parameters can efficiently remove ice without damaging equipment. Liu et al. [11] proposed a method for remotely clearing foreign objects from overhead lines using lasers, conducting simulations, experiments, and field tests. Liu et al. [12] introduced the impact of structural changes on laser clearance of transmission line foreign objects and discussed the selection of laser parameters for rapid polyethylene cutting through simulation results. Chen [13] proposed an advanced an advanced laser-based distance measurement and cleaning method and developed laser aiming, cooling, and safety measures. These studies each from different points prove the feasibility of using laser technology to remove tree obstacles from power transmission lines.
However, the ablation characteristics of tree obstacles are particularly complex. Bryden [14] developed a combustion model for wood of different thicknesses, comparing it with experimental results to summarize the characteristics of different combustion zones. Beaumon et al. [15] studied the effects of heating rate, temperature, and moisture on wood pyrolysis. Wang et al. [16] examined the combustion characteristics of traditional building wood, identifying differences from modern wood combustion characteristics. This work provides significant guidance for studying the combustion characteristics in different types of trees. Franz Richter et al. [17] experimentally and computationally studied the effects of oxygen concentration and heat flux on wood combustion characteristics and carbonization behavior. Kathinka [18] summarized factors influencing wood combustion carbonization and analyzed the carbonization process of trees, offering important references for subsequent research.
From previous studies, it is evident that most wood combustion tests are related to fire simulation and fire resistance testing, but their combustion processes differ significantly from laser clearance of tree obstacles. Integrating laser clearance ablation characteristics into traditional test trials is questionable. Currently, research on laser clearance of tree obstacles in transmission lines is still in its infancy.
To further investigate the ablation characteristics of laser clearance of tree obstacles in transmission lines, this paper combines simulation and experimentation to test the ignition time, burn-through time, peak temperature, and carbonization rate of different types of tree obstacles. It also analyzes the effects of tree species, laser power, clearance distance, and tree moisture content on ablation characteristics, providing more accurate data support for the application of laser clearance of tree obstacles in transmission lines.
2 Simulation model
2.1 Theoretical study
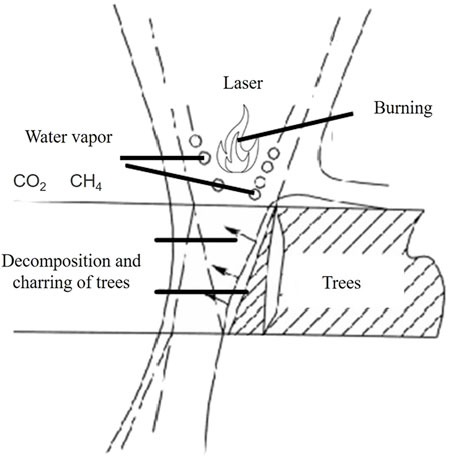
The interaction between laser and material is a complex process. When a laser irradiates the surface of a tree, the moisture within the tree evaporates under thermal action, causing the tree to decompose and produce gases such as water vapor and carbon dioxide. When the surface temperature of the tree reaches the ignition point, combustion with flames occurs. The tree continues to burn until the irradiated area is completely decomposed into ashes, causing the tree to break and fall, thereby achieving the obstacle removal effect. The schematic of the laser obstacle removal process is shown in Figure 1.
To accurately simulate the transient process of laser interaction with materials, the heat conduction equation can be used to study the temperature distribution within the tree obstacle. In the simulation calculations, the transient heat transfer equation of the tree obstacle [19] is as Equation 1:
Where Q(x,y,z,t) is the internal heat source; T is temperature; c is specific heat capacity; ρ is material density; and k is thermal conductivity.
The energy density distribution on the surface irradiated by the laser [20] is described as Equation 2:
Where ε is the absorption rate of the material to the laser; P is the laser power; and r is the laser spot radius. Considering the temperature, surface roughness, and other factors that affect the laser absorption rate of the tree obstacle [21], ε is taken as 0.8 after comprehensive consideration.
The apparent ablation reaction rate constant k(T) can be described as Equation 3:
Where A is the Arrhenius constant; E is the activation energy; T is the temperature; and R is the molar gas constant.
2.2 Model establishment
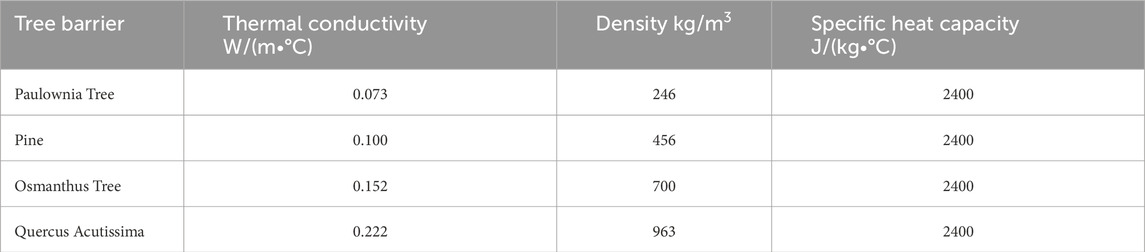
In the finite element simulation part, considering the various factors affecting the laser absorption rate, to simplify the model and reduce computation time, a three-dimensional equivalent material model is established based on the basic parameters of the tree obstacle, as shown in Table 1. The tree obstacle model has a diameter of 0.04 m and a length of 0.15 m. The ambient temperature and initial model temperature are set to room temperature, i.e., 20°C. Figure 2 displays the three-dimensional finite element model of laser ablation tree obstacles, with the laser energy following a Gaussian distribution in both time and space.
2.3 Laser temperature distribution pattern
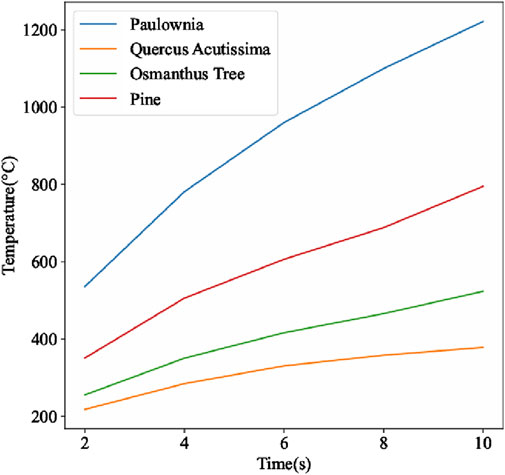
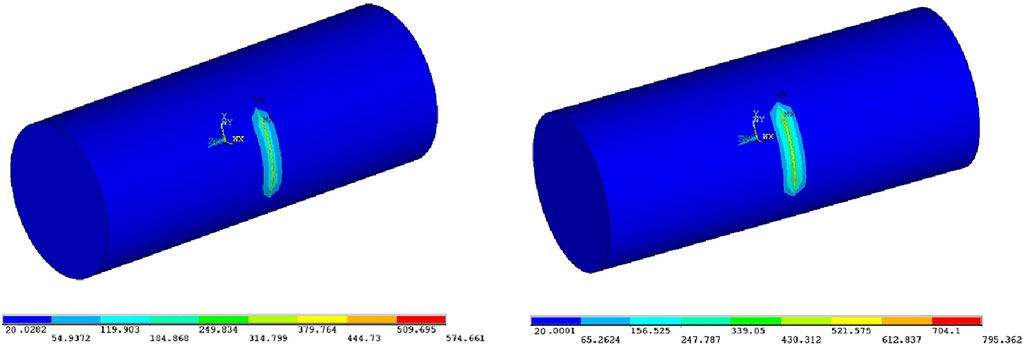
A 200W laser was employed as a narrow surface heat source applied to the surface of the wood for 10 s. The temperature variations at the center of the narrow light spot on four different types of wood during this process are illustrated in Figure 3.
For the four different types of wood, the rate of temperature increase at the center of the laser-irradiated narrow strip gradually slows down as the heating time increases. This is because the thermal conductivity of the wood decreases as the temperature rises, resulting in a reduced rate of temperature increase. At 10 s, the temperature at the center of the narrow strip of pine reached 795.362°C, and this temperature gradually decreased along the surface of the narrow strip, which are shown in Figure 4.
2.4 Temperature differences among different woods
Figure 5 displays that after 10 s of laser irradiation on the narrow surface, the center temperature of the Paulownia tree was the highest at 1238.79°C, while the corresponding temperature for the Quercus acutissima was the lowest at 378.516°C. The temperature for the Osmanthus tree in that area was 520.99°C, and for the pine, it was 795.362°C. From the thermal conductivity coefficients presented in Table 1, it can be inferred that the surface temperature of the wood is related to its thermal conductivity. At high temperatures, the magnitude of the thermal conductivity determines the surface temperature of the wood; the lower the thermal conductivity, the higher the surface temperature of the wood.
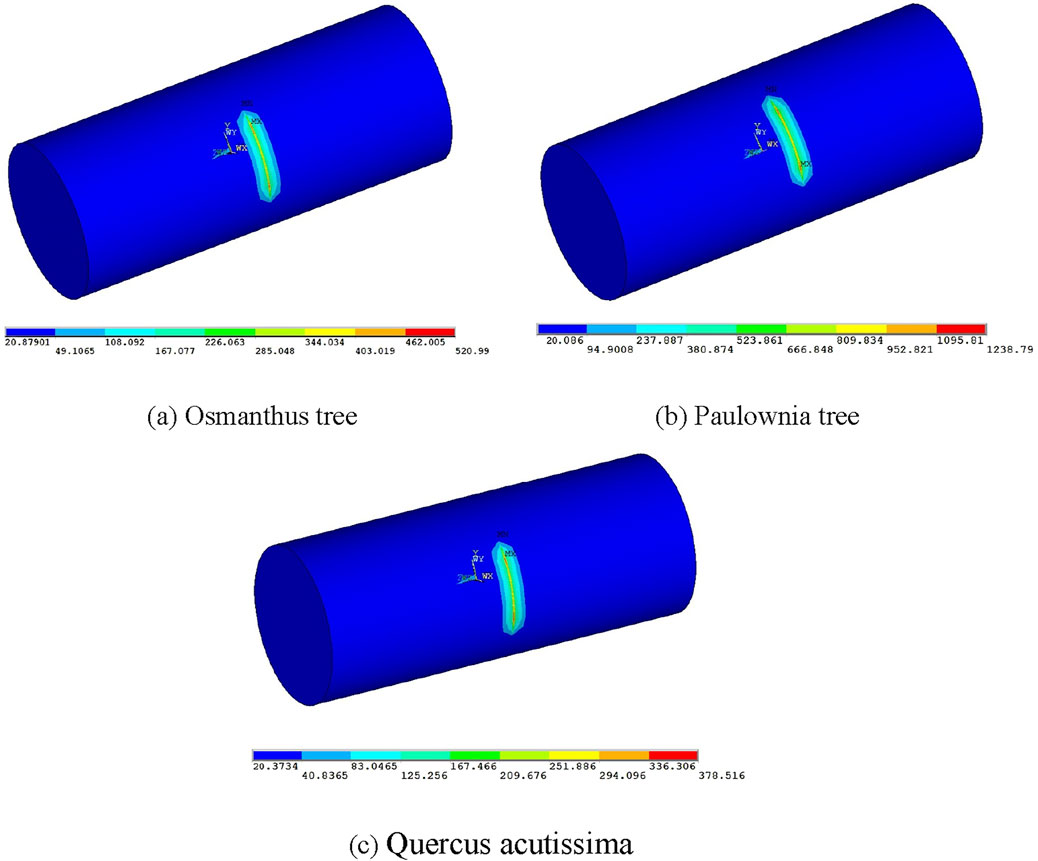
Figure 5. Surface Temperature Distribution Map of Various Woods at 10 s. (A) Osmanthus tree. (B) Paulownia tree. (C) Quercus acutissima.
2.5 Time for tree obstacle removal
As shown in Figure 3, with the progression of the laser irradiation process, the temperature of the narrow surface reached 1000°C, far exceeding the ignition point of wood, which ranges from 250°C to 300°C. Additionally, the narrow surface temperature of most trees exceeded 400°C within 4–6 s. Therefore, during the laser removal of tree obstacles, thinner branches were cleared within 5 s; branches with a diameter of 6 cm could be cleared in 15–30 s. For branches or trunks greater than 6 cm in diameter, the time required for obstacle removal would be extended based on their thickness and actual conditions.
3 Experimental study
3.1 Experimental setup and samples
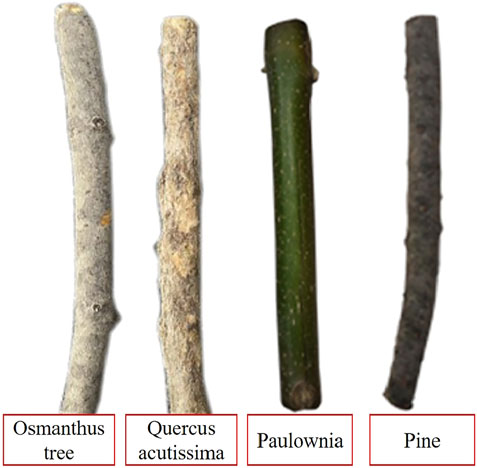
On the basis of field operation surveys, common tree obstacles such as Paulownia, pine, Osmanthus, and Quercus acutissima were selected as experimental samples, as shown in Figure 6. The thickness of the tree obstacles was all set to 40 mm. The experimental equipment mainly included an air-cooled continuous fiber laser, collimator, motorized pan-tilt tripod, stopwatch, FASTCAM Mini UX100 high-speed camera, and Ti480Pro infrared thermal imager. The schematic of the laser clearing device for transmission line tree obstacles is shown in Figure 7. The device controls the laser output position by adjusting the pan-tilt, ensuring the laser aiming point is positioned on the tree obstacle, and then starts the laser for tree obstacle clearing.
3.2 Experimental methods
To obtain the ablation characteristics of laser clearing tree obstacles, three ablation characteristic parameters were tested and evaluated in this experimental study: ignition time, burn-through time, peak temperature, and carbonization rate. To ensure the accuracy of the ablation characteristic parameters, a high-speed camera was used to capture the ignition and burn-through phenomena during the ablation process, and the time was recorded. Considering the actual flame burning situation, a frame rate of 500 fps was selected to meet the requirements.
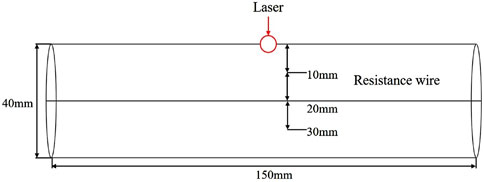
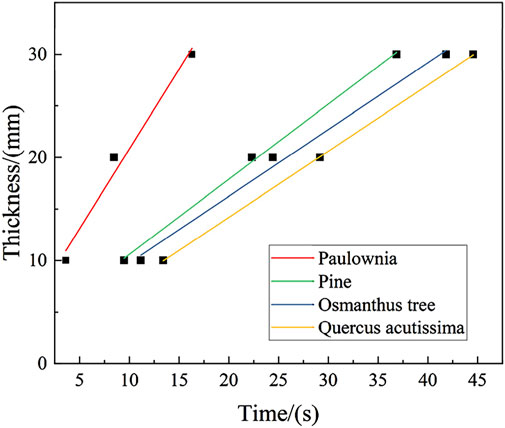
During the laser burn-through process of the tree obstacle, carbonization significantly affects the burn-through speed. Many scholars use the measurement of carbonization temperature as the standard for tree carbonization. In this experiment, 300°C was set as the carbonization limit temperature [22]. Thermocouple resistance wires were placed at 10 mm, 20 mm, and 30 mm along the thickness of the tree’s middle section to measure the time when the temperature at three points reached 300°C, as shown in Figure 8. The instantaneous carbonization rate is described as Equation 4:
Where ηi is the instantaneous carbonization rate; which is the local rate of change at different time points during combustion; xi is the position of the resistance wire; ti is the carbonization time. The slope of the linear regression between xi and ti is defined as the basic carbonization rate [16].
4 Experimental and numerical analysis
4.1 Tree species
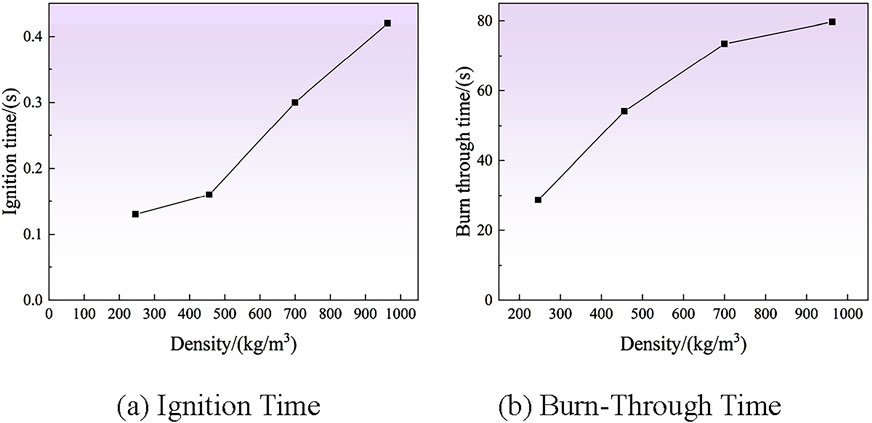
To investigate the ablation characteristics of different tree obstacles, this experiment employed a laser with a power of 100W and a spot diameter of 10 mm to irradiate the center of the trees until the obstacles were burned through. High-speed camera observations revealed the ignition and burn-through times for different tree obstacles, as illustrated in Figures 9A, B. In laser ablation experiments, due to the laser being a high-energy heat source, the tree surface reaches the ignition point within approximately 1 s. From Figures 9A, B, it can be observed that the ignition and burn-through times are closely related to tree density.
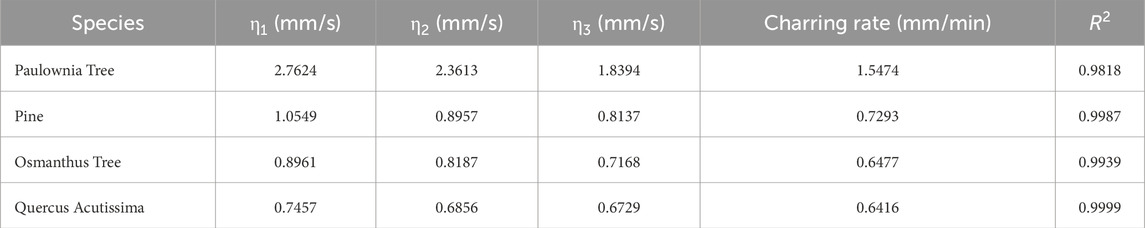
Based on the density values of the four types of tree obstacles presented in Table 1, it can be concluded that the Paulownia tree has the lowest density, with the shortest ignition and burn-through times of 0.13s and 28.69s, respectively. The Quercus acutissima has the highest density, requiring the longest ignition and burn-through times of 0.42 and 79.72 s, respectively. The Osmanthus and pine trees have moderate densities, with ignition and burn-through times of 0.31 and 73.27 s, and 0.16 and 57.31 s, respectively. Additionally, it can be observed that as density increases, the internal defects of the wood gradually decrease, while the thermal conductivity of the tree obstacles increases. Consequently, the heat in the ablation zone is quickly and uniformly distributed within the samples. Under identical conditions, tree obstacles with greater density require longer ignition and burn-through times, resulting in longer times for obstacle removal.
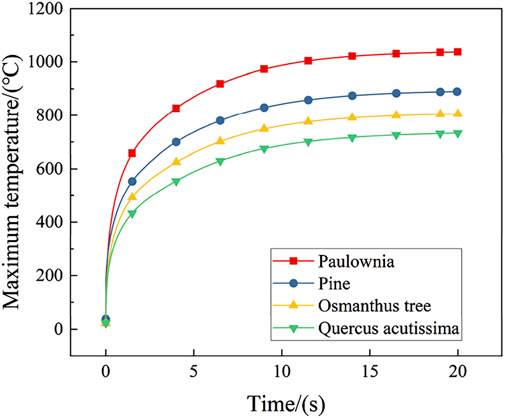
Figure 10 shows the relationship between the maximum temperature at the ablation center and ablation time for different densities of tree obstacles. Significant temperature differences were observed on the surface of the four tree obstacles. However, all their process of transformation can be divided into two stages: a rapid heating stage from 0 to 5 s, where the surface temperature rises quickly, and a stabilization stage from 5 to 20 s, where temperature changes within a certain range. Within 20 s, the highest temperatures were 1036.74°C for Paulownia and 733.34°C for Quercus acutissima. As density increases, the maximum temperature during the ablation process rises.
When the temperature of the resistance wire reaches 300°C, the times at three different positions (10mm, 20mm, and 30 mm) are recorded., as shown in Figure 11. The instantaneous and effective carbonization rates for different obstacles are shown in Table 2. As carbonization depth increases, the instantaneous carbonization rate decreases due to the increasing hindrance of the carbonized layer to laser energy. As tree density increases, internal defects decrease, exposing less tree surface to the ablation environment, reducing the effective carbonization rate.
4.2 Laser power
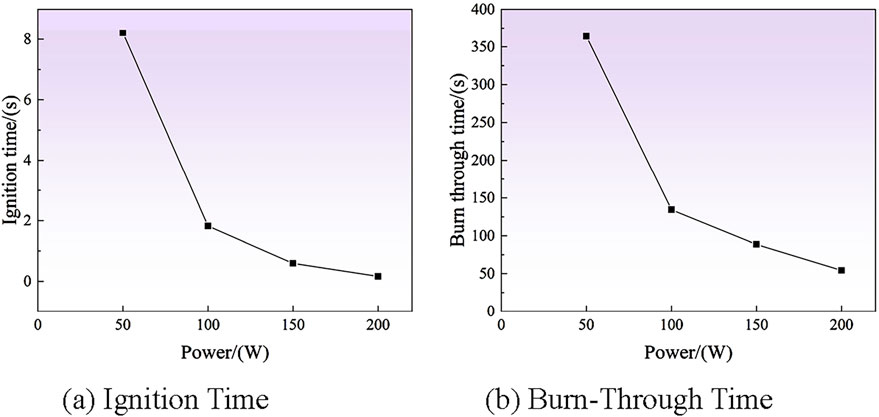
To compare the ablation capacity and efficiency of different laser powers, this experiment adopted 50W, 100W, 150W, and 200W continuous lasers to ablate pine obstacles. Figures 12A, B compare the ignition and burn-through times for pine at different laser powers. At 50W, burn-through took 363.73 s; at 100W, 134.32 s; and at 200W, only 54.16 s. Laser power is a major factor influencing ablation behavior [23]. When the laser power is 50W, the ignition time is as long as 8.21 s; when the laser power is 100W, the ignition time is only 0.16 s. This is because when laser power output energy density is less than the heat load of the obstacle, much energy is lost through reflection, refraction, and thermal conduction, resulting in slow temperature rise. High-power lasers concentrate energy, rapidly raising the surface temperature to the ignition point, causing combustion.
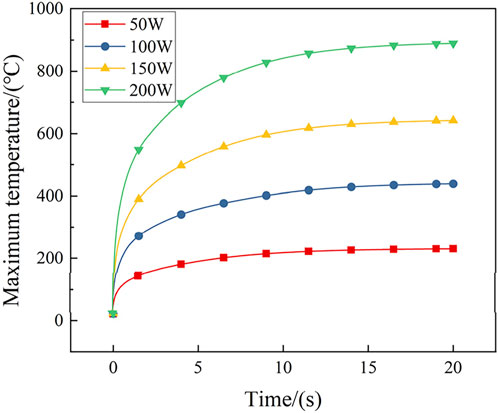
Figure 13 compares the maximum temperature changes within 20 s under different laser powers. When the laser power is 200W, the maximum temperature is 889.60°C; when the laser power is 50W, the maximum temperature is 230.19°C. The maximum temperature of the tree obstacle is not linearly related to the laser power. Higher laser power results in higher maximum temperatures, with temperature rise stabilizing after 10 s for all power levels. This indicates that under a fixed laser energy density output environment, the extension of laser ablation time has a limited impact on the maximum temperature of the tree obstacle. Therefore, compared to the duration of laser ablation, laser power is a more significant factor affecting laser ablation behavior [24].
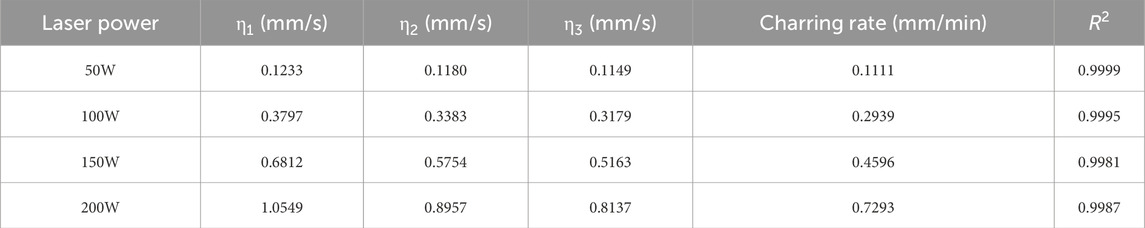
Table 3 shows the carbonization rates increasing with power. At 200W, the basic carbonization rate is 0.7293 mm/s, 6.56 times that at 50W. Factors influencing carbonization rate include density and internal structure. High-power lasers concentrate energy, rapidly increasing temperature at the laser spot, leading to carbonization.
4.3 Clearance distance
The complex terrain in field operations makes clearance distance variable, significantly affecting ablation characteristics. Clearance distance directly affects laser spot diameter, The relationship between the laser spot diameter and the clearing distance can be describled as Equation 5:
Where d is beam diameter 2.2 mm, N is beam expander multiple 5×, L is clearance distance, and θ is beam divergence angle 0.007 rad.
Using a 200W laser, distances of 1m, 2m, 5m, and 10 m were tested, with spot diameters of 12.4, 13.8, 18, and 25 mm, respectively. Ignition and burn-through times are shown in Figures 14A, B. As clearance distance increases, both times increase, with a greater increase at longer distances. Energy density is inversely proportional to the square of the spot radius and directly proportional to clearance distance, impacting ablation phenomena.
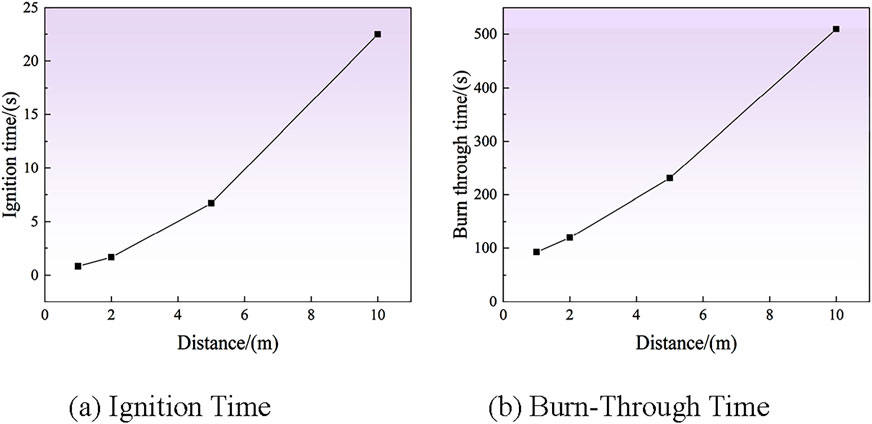
Figure 14. Ablation times at different clearance distances. (A) Ignition time. (B) Burn-through time.
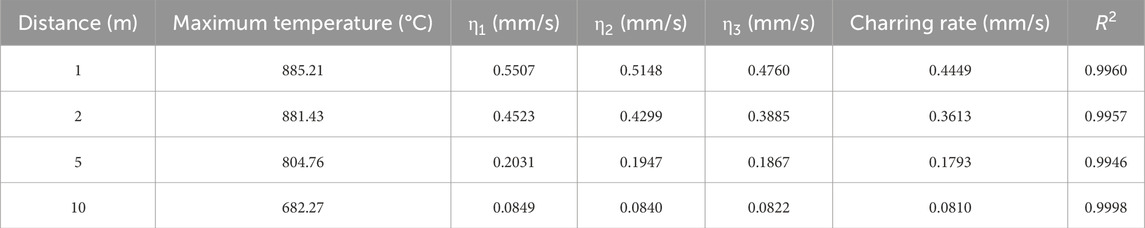
Table 4 shows the highest temperature of 885.21°C when the clearing distance is 1m and 712.27°C at 5 m. Due to the continuous action of the laser, the shorter the clearing distance, the higher the maximum temperature during the experiment. However, as the clearing distance increases, the spot area becomes larger, resulting in a larger carbonization area of the tree obstacles. Due to severe carbonization, the center of the laser irradiation is blocked by charcoal and residual powder, and a significant amount of energy is absorbed by the carbonized part. Therefore, when the clearing distance is too long, the laser ablation rate slows down, and the maximum temperature decreases compared to shorter distances.
When the clearing distance is 10 m, the spot area is 490.63 mm2, with a basic carbonization rate of 0.0810 mm/s; at 1m, the spot area is 120.70 mm2, with a carbonization rate of 0.4449 mm/s, 5.79 times that at 10 m. In actual experiments, the carbonization area at 10 m is much larger than that at 1 m, as shown in Figures 15A, B. This is because the larger the clearing distance, the more dispersed the laser energy distribution, leading to a slower longitudinal temperature rise in the ablation area. Additionally, the further the clearing distance, the more complex the environmental influence on the laser energy transmission process. When the laser energy density decreases, the heat in the ablation area quickly becomes uniform internally, and the basic carbonization rate decreases accordingly.
4.4 Moisture content
To explore ablation characteristics under different environmental conditions, four 40 mm thick pine samples were prepared: A (dry), B (soaked 5 h), C (soaked 12 h), and D (soaked 24 h), with moisture contents of 14.8%, 29.4%, 45.9%, and 58.4%, respectively, utilizing the HT632 digital probe-type wood moisture meter. Samples are shown in Figure 16.
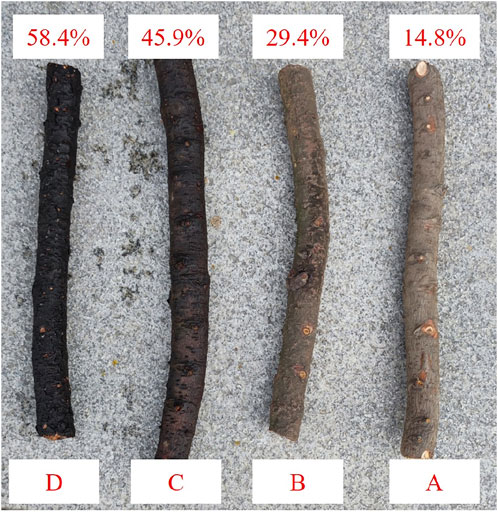

Figure 16. Tree obstacles with different moisture contents. (A) 14.8%. (B) 29.4%. (C) 45.9%. (D) 58.4%.
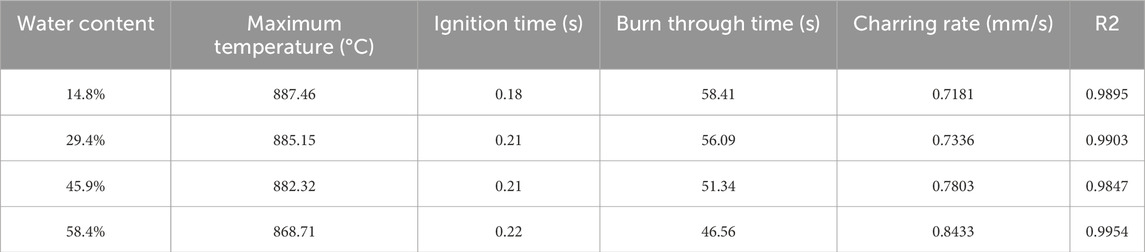
During the experiment, the samples ABCD were irradiated using a laser with 200W of power until they were burned through. The ablation characteristics parameters are shown in Table 5. From the data in the table, it can be observed that the maximum temperature of the trees and the ignition time remain almost unchanged when laser ablating trees with different moisture content. The tree obstacle with the highest moisture content of 58.4% had a burn-through time of 46.56 s, the shortest time; the tree obstacle with the lowest moisture content of 14.8% had a burn-through time of 58.41 s, the longest time. The results suggest that an appropriate moisture content makes the ablation rate of trees faster and improves the efficiency of laser removal of tree barriers obstacles.
Further cutting tests were performed on obstacles with 14.8% and 58.4% moisture content. Figure 17 displays that the 14.8% sample showed severe carbonization with white powder and clumps, which blocked the center of the laser spot, leading to an uneven cutting surface and consequently slowing down the ablation rate. This issue primarily arises from severe carbonization, where the center of the laser irradiation is obstructed by charcoal and residual powder. A significant amount of energy is absorbed by the charcoal and transferred axially, resulting in blackening and other phenomena along the axis. Consequently, not all of the laser’s energy can be effectively transmitted to the deeper layers of the wood, leading to an uneven cutting surface and affecting the efficiency of laser obstacle clearing.
In contrast, for tree obstacles with a moisture content of 58.4%, the carbonized portion is minimal, with only a 3 mm thick layer of carbonization on the cutting surface, which remains smooth. Due to the absence of unnecessary carbonization processes, most of the laser’s energy can effectively penetrate layer by layer. In this case, the cutting surface remains smooth, resulting in higher efficiency in laser obstacle removal.
5 Conclusion
This study examined the laser ablation characteristics of four common tree obstacles in transmission lines. Simulation and experimentation yielded the following results:
(1) Different tree obstacles have distinct ablation characteristics. With increasing density, ignition and burn-through times increase, while peak temperature and basic carbonization rate decrease. Paulownia had the shortest ignition and burn-through times (0.13s and 28.69s), while Quercus acutissima had the longest (0.42s and 79.72s). Higher density reduces internal defects and exposed surface area, decreasing carbonization rate.
(2) Laser power and clearance distance affect ablation behavior. Clearance distance is positively related to spot diameter and inversely related to energy density, which is positively related to laser power. Higher energy density shortens ignition and burn-through times, increasing peak temperature and carbonization rate.
(3) Different moisture contents also affect ablation. The 58.4% sample had the shortest burn-through time (46.56s), while the 14.8% sample had the longest (58.41s). Lower moisture levels cause severe carbonization, absorbing energy and slowing ablation, while higher moisture levels lead to smoother surfaces and higher efficiency.
The study of ablation characteristics holds significant value for the application of laser clearing of tree obstacles in power transmission lines. In this research, we summarized the factors influencing the ablation characteristics of laser clearing of tree obstacles and conducted simulation and experimental analyses for each factor. Also, the variations in ablation characteristics under different conditions were thoroughly discussed. We hope this research can provide relevant references for the field of obstacle removal in power transmission lines, contributing to greater economic and social benefits for power system maintenance.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WX: Writing–original draft, Conceptualization. YZ: Writing–original draft, Conceptualization. WC: Writing–original draft, Investigation. CF: Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. TH: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. BH: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. JZ: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors WX, YZ, and WC were employed by CYG Insulator Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Chen Y, Lin J, Liao X Early detection of tree encroachment in high voltage powerline corridor using growth model and UAV-borne LiDAR. Int J Appl Earth Observation Geoinformation (2022) 108:102740. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2022.102740
2. Ma J, Cheng JC, Jiang F, Gan VJ, Wang M, Zhai C. Real-time detection of wildfire risk caused by powerline vegetation faults using advanced machine learning techniques. Adv Eng Inform (2020) 44:101070. doi:10.1016/j.aei.2020.101070
3. Ahmad J, Malik AS, Xia L, Ashikin N. Vegetation encroachment monitoring for transmission lines right-of-ways: a survey. Electric Power Syst Res (2013) 95:339–52. doi:10.1016/j.epsr.2012.07.015
4. Kamel N, Glotfelty J. Interim report: causes of the august 14th blackout in the United States and Canada. 2003.
5. Commission E. Interim report on the performance of the electricity supply in Malaysia for the first half year of 2009. Putrajaya, Malaysia: Energy Commission (2009).
6. Zhu A, Tu Y, Zheng W, Shen H, Zhang X. Design and implementation of high-voltage transmission line inspection and foreign bodies removing robot. In: Proceedings of the 2018 15th international conference on ubiquitous robots (UR) (2018). p. 852–6.
7. Liang Y, Yang F. Development and application of foreign objects removal device for high voltage transmission line. In: Proceedings of the IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (2019).042023
8. Zhang Y, Li J, Li C, Tao Q, Xiong X. Development of foreign matter removal robot for overhead transmission lines. In: Proceedings of the journal of Physics: conference series (2019).012021
10. Luo J, Li B, Zhou XD, Qin ZP, Xie GQ. Laser deicing for high-voltage composite insulator by high-power mid-infrared fiber laser. Opt Eng (2022) 61:6. doi:10.1117/1.Oe.61.2.021005
11. Liu Y, Zhao H, Chen J, Tan X, Li C. Research and application of remote removal of floating foreign objects on transmission lines based on fiber laser. In: Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE conference on industrial electronics and applications (ICIEA) (2019). p. 488–92.
12. Qifeng L, Xia L, Hong L. Simulation research on laser rapid cutting of foreign objects in high voltage transmission lines. In: Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th international conference on automation, electronics and electrical engineering (AUTEEE) (2022). p. 212–6.
13. Chen M. A method for remotely removing foreign objects in overhead lines by laser at 10.64 um wavelength. In: Proceedings of the AIP conference proceedings (2019).020071
14. Bryden KM. Computational modeling of wood combustion. The University of Wisconsin-Madison (1998).
15. Beaumont O, Schwob Y. Influence of physical and chemical parameters on wood pyrolysis. Ind and Eng Chem Process Des Development (1984) 23:637–41. doi:10.1021/i200027a002
16. Wang Y, Wang W, Zhou H, Qi F. Burning characteristics of ancient wood from traditional buildings in shanxi Province, China. Forests (2022) 13:190. doi:10.3390/f13020190
17. Richter F, Jervis FX, Huang X, Rein G. Effect of oxygen on the burning rate of wood. Combustion and Flame (2021) 234:111591. doi:10.1016/j.combustflame.2021.111591
18. Friquin KL. Material properties and external factors influencing the charring rate of solid wood and glue-laminated timber. Fire Mater (2011) 35:303–27. doi:10.1002/fam.1055
19. Li X, Tian J, Ma Z, Zhou W, Qin Y. Numerical analysis and experimental study of the laser cleaning of ceramic insulator contamination. IEEE Access (2022) 10:49285–96. doi:10.1109/access.2022.3173309
20. Fang C, Hu T, Pu Z, Li P, Wu T, Jiang J, et al. Effect of laser cleaning parameters on surface filth removal of porcelain insulator. Photonics (2023) 10:269. doi:10.3390/photonics10030269
22. Schmid J, Klippel M, Just A, Frangi A. Review and analysis of fire resistance tests of timber members in bending, tension and compression with respect to the Reduced Cross-Section Method. Fire Saf J (2014) 68:81–99. doi:10.1016/j.firesaf.2014.05.006
23. Yang N, Dong Z, Wu L, Zhang L, Shen X, Chen D, et al. A comprehensive review of security-constrained unit commitment. J Mod Power Syst Clean Energy (2022) 10(No.3):562–76. doi:10.35833/mpce.2021.000255
Keywords: transmission lines, tree obstacles, laser, ablation characteristics, carbonization rate
Citation: Xu W, Zhao Y, Chen W, Fang C, Hu T, Huang B and Zhang J (2024) Study on laser ablation characteristics of tree obstacles in transmission lines. Front. Phys. 12:1486486. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1486486
Received: 01 September 2024; Accepted: 25 October 2024;
Published: 12 November 2024.
Edited by:
Venugopal Rao Soma, University of Hyderabad, IndiaReviewed by:
Shunchun Yao, South China University of Technology, ChinaSunku Sreedhar, Department of Physics Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, India
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Zhao, Chen, Fang, Hu, Huang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chunhua Fang, ZmFuZzIwMjMwMzE5QDE2My5jb20=
 Wenrong Xu1
Wenrong Xu1 Tao Hu
Tao Hu Jin Zhang
Jin Zhang