- 1AI and ML Department, Symbiosis Institute of Technology (Pune Campus), Symbiosis International Deemed University, Pune, India
- 2Symbiosis Centre for Applied Artificial Intelligence, Symbiosis Institute of Technology (Pune Campus), Symbiosis International Deemed University, Pune, India
- 3Centre for Advanced Modelling and Geospatial Information Systems (CAMGIS), School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and IT, University of Technology Sydney, Ultimo, NSW, Australia
- 4Department of Science Education, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea
This article presents a thorough examination of the progress and limitations in the application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML), particularly Deep Learning (DL), in the healthcare industry. This paper examines the progress and limitations in the utilisation of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) in the healthcare field, specifically in relation to Electronic Medical Records (EMRs). The review also examines the incorporation of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) in medical imaging as a supplementary field, emphasising the transformative impact of these technologies on the analysis of healthcare data and patient care. This review attempts to analyse both fields in order to offer insights into the current state of research and suggest potential chances for future advancements. The focus is on the use of these technologies in Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and medical imaging. The review methodically detects, chooses, and assesses literature published between 2015 and 2023, utilizing keywords pertaining to natural language processing (NLP) and healthcare in databases such as SCOPUS. After applying precise inclusion criteria, 100 papers were thoroughly examined. The paper emphasizes notable progress in utilizing NLP and ML methodologies to improve healthcare decision-making, extract information from unorganized data, and evaluate medical pictures. The key findings highlight the successful combination of natural language processing (NLP) and image processing to enhance the accuracy of diagnoses and improve patient care. The study also demonstrates the effectiveness of deep learning-based NLP pipelines in extracting valuable information from electronic medical records (EMRs). Additionally, the research suggests that NLP has the potential to optimize the allocation of medical imaging resources. The identified gaps encompass the necessity for scalable and practical implementations, improved interdisciplinary collaboration, the consideration of ethical factors, the analysis of longitudinal patient data, and the customization of approaches for specific medical situations. Subsequent investigations should focus on these deficiencies in order to fully exploit the capabilities of natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) in the healthcare sector, consequently enhancing patient outcomes and the delivery of healthcare services.
1 Introduction
1.1 Background
Text and image analysis play a vital role in the healthcare and medical sector. Medical data is essential for both diagnosing and treating individual patients, as well as extracting valuable insights from a vast collection of patient medical information [1]. The transition of imaging reports to electronic medical record systems has significant potential to advance radiology research and practice by utilizing the vast amount of data that is constantly being updated, integrated, and shared [2]. Electronic Health Record (EHR) data, originally designed to enhance clinical care by better documentation, has the potential to make significant contributions to research and clinical procedures [3]. Electronic Medical Records (EMR), or EHRs, are a central database that stores comprehensive information about a patient’s medical history, including diagnoses, medications, treatment plans, immunization dates, allergies, radiological pictures, laboratory and test results, and other pertinent data [4]. The majority of data in EHR or EMR systems is unstructured, consisting mostly of clinical notes and reports. Structured data, which includes patient demographics and vital signs, makes up a lesser fraction [5]. A standard EMR consists of several elements, including problem/diagnosis and progress charting, medication orders and administration details, past medication history, lifestyle information (such as cigarette and alcohol use), physical checkup records (such as vital signs and blood pressure measurements), laboratory test orders and results (such as lipid levels and ejection fraction), and medical records for the family [6].
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has lately been employed to extract information from Electronic Medical Record (EMR) text fields. Natural Language Processing (NLP) emerged in the 1950s as a fusion of artificial intelligence and linguistics, aiming to enable computers to comprehend the semantic aspects of human language [7]. This technique [8] can greatly improve the utilization of organized EMR data. According to a recent poll, 55% of physicians in the United States have adopted Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) in their clinics [9]. In addition, 11.9% of hospitals in the United States have adopted rudimentary Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems [10, 11]. Nevertheless, the adoption of EMRs in the United States is somewhat lower compared to other European countries [12]. However, there has been a growing worldwide acceptance of EMRs, with projected growth rates ranging from 6.6% to 9.7% in major markets such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany, the Nordic nations, Spain, Australia, Canada, and Japan from 2010 to 2013 [13]. The projected growth rate for the US EMR market is 9.7%, while Europe, Africa, and Latin America are expected to experience a growth rate of 6.6%. Moreover, it is projected that the utilization of EMR in the Asia-Pacific area will have a growth of 7.6% [13].
1.2 Relevance
Contemporary electronic health publications, such as electronic health records (EHRs) or academic articles, frequently integrate text and visual media in a complex manner and require multimodal processing [14]. Although research on autonomous text analysis and image processing has been conducted independently, there is an increasing demand for collaborative endeavors to merge these approaches. The integration of NLP and image processing in the medical field can synergistically increase healthcare decision-making, optimize data extraction, and facilitate advanced analysis of medical pictures. The healthcare sector has greatly benefited from recent breakthroughs in NLP and ML, specifically in deep learning, which have dramatically enhanced the extraction and interpretation of unstructured data from EMRs [15]. These technological innovations allow healthcare providers to extract valuable information from extensive medical data, leading to improved patient care and more efficient clinical processes. Although there have been significant breakthroughs, there are still some areas that need to be addressed. These include the requirement for scalable real-world applications, improved interdisciplinary collaboration, ethical considerations, and the integration of multimodal data to provide a comprehensive perspective of the patient. This review article seeks to offer a thorough examination of the advancements and limitations in the application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML), particularly Deep Learning (DL), in the healthcare industry. The article specifically focuses on the use of these technologies in Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and medical imaging. The review examines research on the synergistic role of natural language processing (NLP) and image processing in improving diagnostic accuracy and patient care. It investigates the effects of deep learning-based NLP pipelines on extracting information from electronic medical records (EMRs) and analyzes the potential of NLP in optimizing the allocation of medical imaging resources.
2 Methodology
2.1 Bibliometric survey
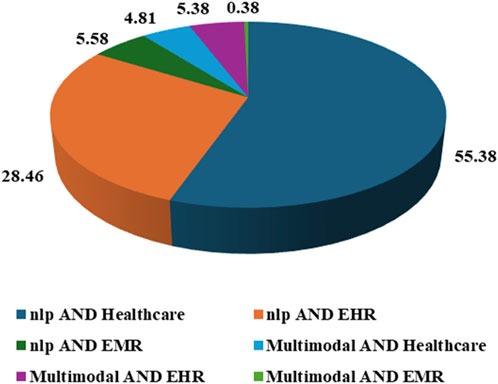
Searches were conducted between 2015 and 2023 on SCOPUS, using multiple search terms such as, “nlp AND healthcare,” “nlp AND ehr,” “nlp AND emr,” “multimodal AND her,” “multimodal AND healthcare.” The subject area constraint for the keywords were computer science and engineering and the articles were chosen from English language only. A total number of articles found for each keyword has been listed along with the articles published in India and top 5 leading research countries as shown in Table 1 and the same can be visualize from Figure 1. The PRISMA chart gives more idea about the eligibility criteria chosen for the article selection. For the present review article, following criteria were chosen for the published articles.
• The article must be published in English language only.
• The article must have been published in between 2015 and 2023 to ensure latest research inclusion.
• The article must contain implementation of ML techniques (NLP/multimodal etc.) in Electronic Health Records.

Table 1. Bibliometric survey for global distribution of research articles on NLP applications in healthcare records.
The published articles which were not compatible to the above guidelines were excluded from the review. A total of 790 articles were found in the initial SCOPUS search history, out of which 786 articles were available in English language. Further, A total of 255 articles were chosen for the subsequent studies on the basis of eligibility criteria described above, and ultimately 100 articles were reviewed in the present article. The findings of the bibliometric survey on the uses of NLP in healthcare records indicate a diverse and significant level of global research interest in this particular domain. The survey classifies publications into six distinct domains, facilitating the identification of varying research priorities and geographical contributions. Significantly, NLP has received considerable attention within the healthcare domain, as evidenced by the publication of 288 publications. Notably, India has contributed one-third of these articles, while the United States, United Kingdom, Italy, and Canada have made substantial contributions. In contrast, fields that are more specialized, such as the integration of Natural Language Processing (NLP) with Health Electronic Records (HER) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR), exhibit a comparatively smaller but significant body of literature. Notably, the United States and China have emerged as prominent contributors in this field.
Research interest in the multimodal approach to EHR and healthcare is evident, with a particular focus on the United States, China, the United Kingdom, Canada, and South Korea. This research underscores a growing trend in healthcare informatics towards the integration of different data modalities. Nevertheless, the utilization of the multimodal approach in the context of EMR has received little attention, as indicated by only two papers, indicating that this is a developing field of study. This survey underscores the geographical variation in NLP research within the healthcare sector and draws attention to specific domains that are currently the focus of academic investigation, as well as those that represent emerging frontiers in this rapidly evolving field.
2.2 PRISMA chart
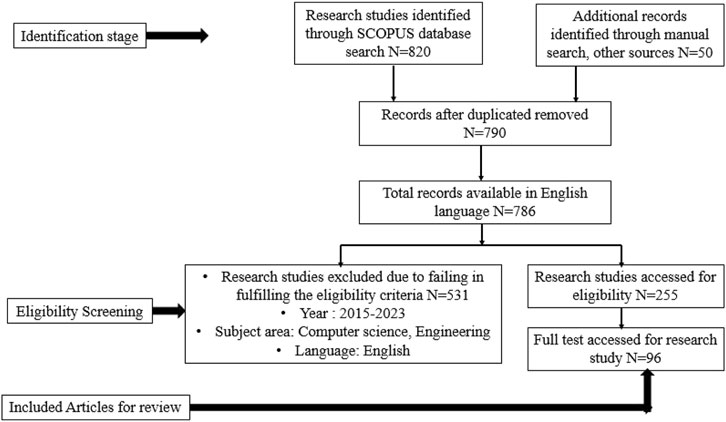
The flow diagram seen in Figure 2 illustrates the systematic procedure of study selection for a literature review, as outlined by the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. The initial step in PRISMA involves the identification of records through the utilization of database searches and supplementary sources, subsequently followed by the elimination of duplicate entries. Subsequently, the obtained records undergo a screening process that involves evaluating their titles and abstracts, resulting in the elimination of studies that fail to satisfy the predetermined eligibility criteria. In the subsequent stage, a comprehensive examination of the possibly suitable studies is conducted, followed by additional exclusions based on specific criteria such as lack of relevance to the research issue, methodological deficiencies, or inadequate data. The ultimate count of papers incorporated in the review is a condensed compilation of literature relevant to the research subject, which has undergone meticulous evaluation to ensure its pertinence and excellence. The utilization of this methodical strategy guarantees the preservation of the literature review’s integrity and comprehensiveness, thereby enabling a dependable amalgamation of preexisting research.
Medical text and image processing are becoming highly popular among researchers because of the availability of a wider range and vast volume of data and applications [15–17]. However, the unstructured, free-text nature of medical reports poses a significant challenge in converting them into a computer-manageable format. NLP applies computer-based techniques to analyze speech or text. In radiology, as in other medical settings, NLP tools have been used for information retrieval, classification, text extraction, text summarization, question answering, and text generation [18]. NLP and Image Processing are revolutionizing the domain of EMRs. NLP techniques efficiently extract and interpret unstructured data from EMRs, facilitating better healthcare decision-making and enhancing clinical workflows. For instance, NLP algorithms can identify specific medical conditions from textual data, aiding in quicker and more accurate diagnoses [19]. On the other hand, Image Processing in EMRs involves the analysis and interpretation of medical images using advanced algorithms. This integration aids in precise disease detection and monitoring, complementing the textual data analysis done by NLP. The synergy of NLP and image processing thus offers a comprehensive understanding of patient records, leading to improved patient care and outcomes. The recent advancements in deep learning have further propelled the capabilities of NLP and image processing, enabling more sophisticated data analysis and extraction from EMRs [20]. Figure 3 shows the generalized flow diagram that can be implemented in NLP/ML implementation in electronic health record analysis.
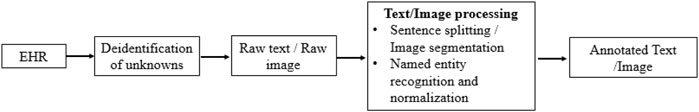
Figure 3. Generalized flow diagram to be used in implementation of NLP/ML in an electronic health records.
The objective of this review article is to critically examine recent advancements and applications of NLP and image-processing techniques in the realm of EMRs and healthcare. By analyzing relevant research, this review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how NLP and Image Processing contribute to efficient data extraction, interpretation, and decision-making support in healthcare settings. Specifically, the review will explore the synergistic role of Image Processing alongside NLP for enhancing diagnostic accuracy and patient care, investigate the impact of deep learning-based NLP pipelines on information extraction from EMRs, analyze the potential of NLP in optimizing medical imaging resource allocation, and discuss how NLP can improve hospital care efficiency and decision-making processes. Through this examination, the review seeks to identify key trends, challenges, and future directions in leveraging NLP and image processing technologies to enhance healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
2.3 Scope of work
The review proposes to analyze recent progress and uses of natural language processing (NLP) and image-processing methods in the field of electronic medical records (EMRs) and healthcare. The objective is to evaluate these improvements in a critical manner. This review offers a thorough comprehension of the ways in which NLP and Image Processing contribute to the effective extraction, interpretation, and decision-making support of data in healthcare settings, based on an analysis of pertinent research. The review specifically examines how Image Processing and NLP work together to improve diagnostic accuracy and patient care. It also investigates the effects of deep learning-based NLP pipelines on extracting information from EMRs, analyzes the potential of NLP in optimizing medical imaging resource allocation, and discusses how NLP can enhance hospital care efficiency and decision-making processes. This research aims to uncover significant trends, difficulties, and future directions in utilizing natural language processing (NLP) and image processing technology to improve healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
3 Applications of NLP and image processing in EMR
Over the past decade, significant advancements have been observed in several approaches to NLP, exhibiting a noteworthy inclination towards the integration of deep learning (DL) procedures [21–23]. In the realm of clinical applications, conventional methodologies frequently depend on engineered characteristics that are informed by biomedical dictionaries, clinical ontologies, or specialized knowledge in the field of biomedicine. On the other hand, deep learning models possess the capability to autonomously derive significant abstractions from unprocessed data, hence enabling categorization without the explicit requirement of predetermined characteristics [24]. A multitude of recent scholarly articles have emphasized the efficacy of advanced DL methodologies in several medical fields, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [25], radiology [26], cardiology [27], and neurology [1].
3.1 Studies related to unstructured text coding and classification in EMR application
RQ 1: What effects do real-world healthcare environments have on the scalability and performance of sophisticated NLP and ML algorithms when it comes to coding and classifying unstructured text in different clinical scenarios within electronic medical records (EMRs)?
RQ 2: When employing NLP and ML for unstructured text analysis in EMRs, what collaboration possibilities and obstacles occur between medical practitioners, data scientists, and AI experts?
Hossain et al. [28], examine how NLP techniques are used to derive clinical insights from EHRs, focusing on the problems and potential in the field. The results highlight the common occurrence of disorganized electronic health record data and the extensive utilization of ML and DL techniques for forecasting and categorization purposes. Sezgina and Hussain [29] intend to evaluate the practicality of using a NLP pipeline to extract medication and symptom details from real-world patient and caregiver data. The assessment of the pipeline on 87 patient notes showed effective performance in identifying drug instances and symptoms. The precision, recall, and F1 scores suggest the promising application of NLP methods for extracting information from unstructured patient-generated health data (PGHD). Falter et al. [30], explored techniques for autonomously categorizing diseases in unstructured medical documents through NLP and evaluates them against traditional ICD-10 classification. Several NLP algorithms, such as rule-based search, logistic regression, TF-IDF, XGBoost, and BioBERT, were assessed using the MIMIC-III dataset and measured in terms of precision, recall, and accuracy. The most effective algorithm was subsequently implemented on the dataset from Belgium. NLP algorithms show great accuracy in diagnostic categorization and may detect problems in ICD coding, indicating their potential to enhance the coding process in hospitals. The generalized methodology for creating clinically defined cohorts using structured and unstructured data in production EMR system [31] is shown in Figure 4.
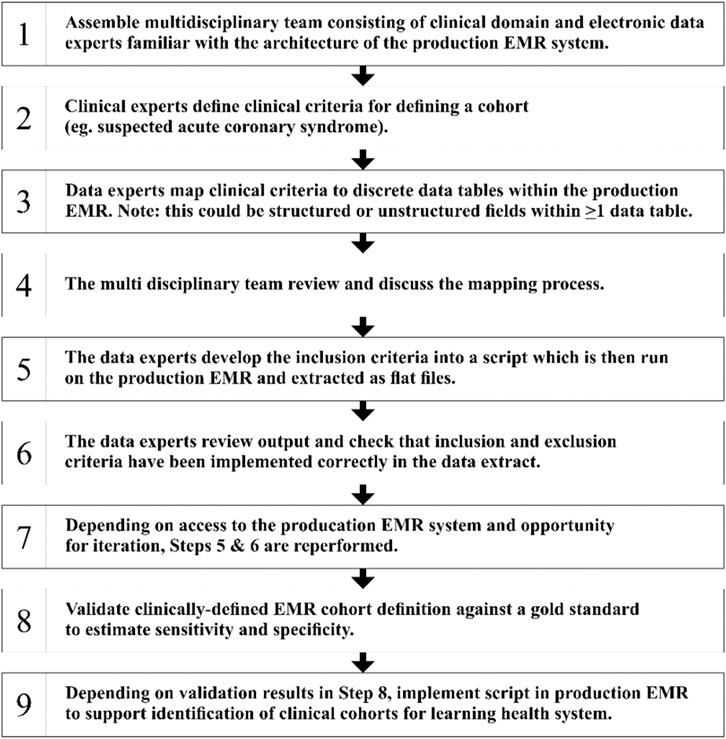
Figure 4. General methodology for creating clinically-defined cohorts using structured and unstructured data in production EMR system.
Belhaouari and Islam [32] examine the extensive impact of deep learning in the field of healthcare. The authors explored the application of advanced algorithms to different forms of medical data, resulting in enhanced diagnosis, patient care, and treatment options. Kaul et al. [33], examined the structure and functionality of deep neural networks, with a specific emphasis on their utilization in the identification and management of different ailments such as cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease. Priya et al. [34] emphasized the capacity of deep learning to analyze and offer recommendations for medical analysis utilizing EHRs. The text highlights the significance of effectively using the substantial volume of data produced by healthcare industries and the necessity of a well-trained model to extract valuable insights from EHRs. The research explores the utilization of deep learning, a type of artificial intelligence, in hierarchical learning and layered algorithmic architecture for rapid data processing. The author demonstrates effective empirical findings and highlights the diverse array of uses for deep learning in the healthcare field, suggesting its capacity to tackle obstacles in the healthcare industry.
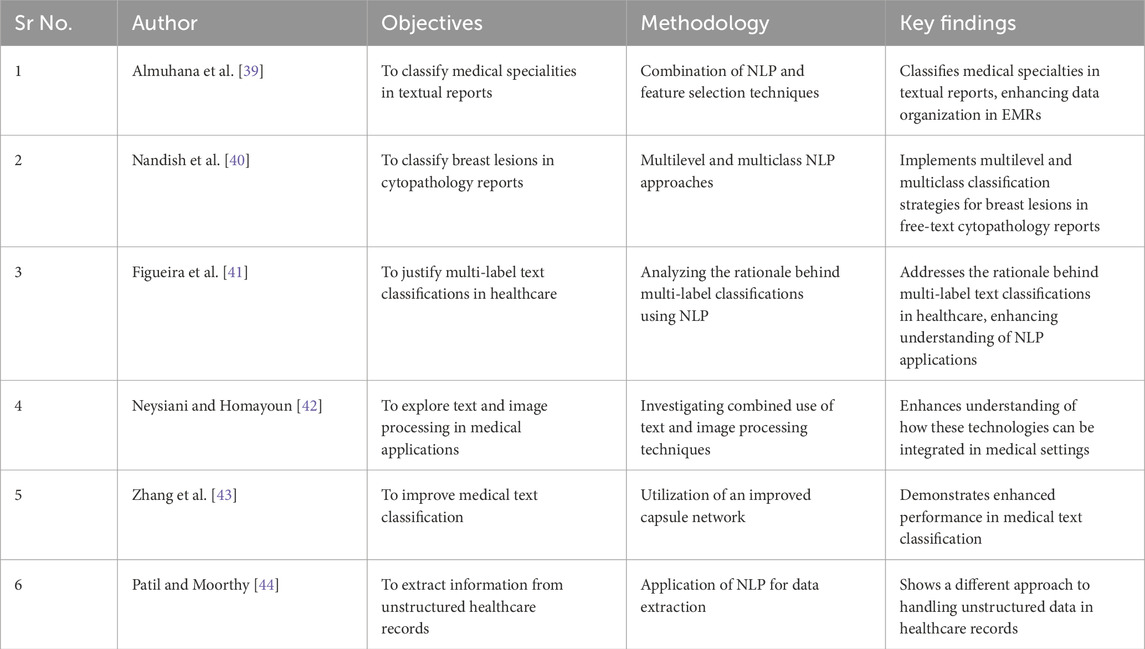
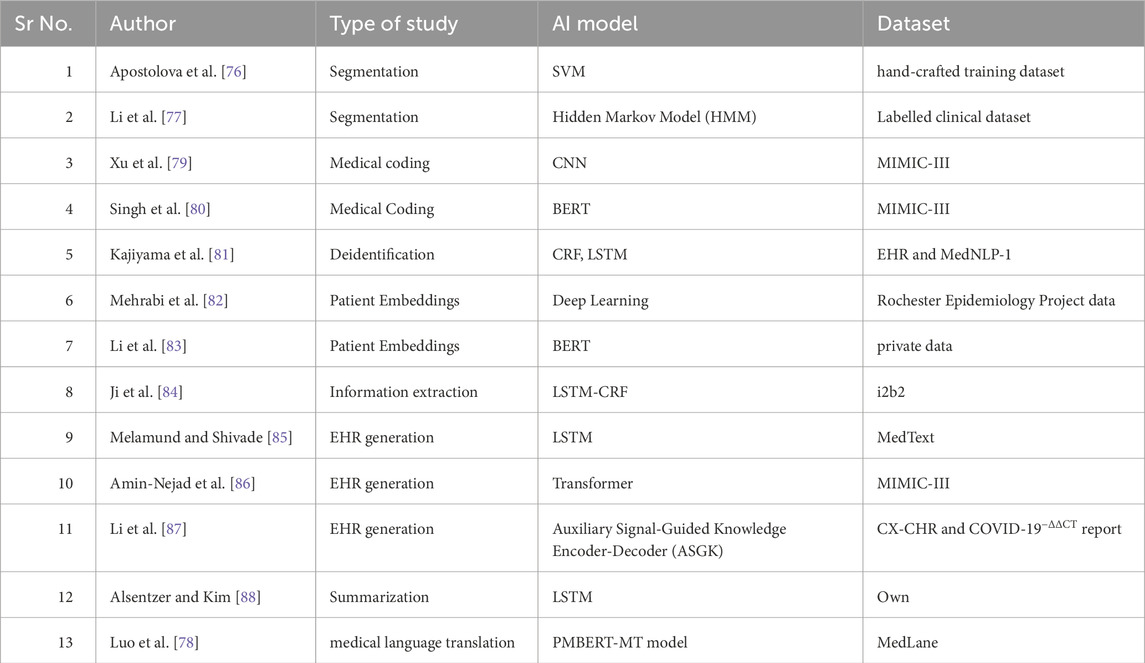
The study performed by Hu [35] examined and illustrated the application of deep learning techniques in the field of healthcare. The article first presented the possibility of applying deep learning in the medical domain. It further examined the potential advantages and difficulties of utilizing deep learning in healthcare, considering various viewpoints. Subsequently, he presented the present-day executions and uses of deep learning in the medical healthcare system. Esteva et al. [36] introduced advanced deep-learning techniques applied in the healthcare field, specifically emphasizing deep learning in computer vision, natural language processing, reinforcement learning, and generalized methodologies. The authors discuss the impact of computational techniques on different important aspects of medicine and explore the process of constructing whole systems. Huang et al. [37] investigated the shift from explainable to interpretable deep learning techniques for natural language processing (NLP) in the healthcare field. They specifically highlighted the disparity between the existing capability of these techniques and their actual use in real-world clinical environments. The problems in establishing real interpretability were identified, emphasizing the necessity for healthcare practitioners to have access to transparent models that they can trust and comprehend. This paper highlights the significance of creating techniques that may elucidate the rationale behind model predictions, which is essential for incorporating AI into regular clinical procedures. Gao et al. [38] performed a comprehensive examination of publicly accessible language tasks in clinical NLP, offering a thorough summary of the present state of NLP tasks and datasets. Their research suggests an increasing variety of activities and applications, ranging from information extraction to healthcare decision assistance. In addition, they emphasized the necessity for more standardization and public availability of datasets to assist study and advancement in this field. This paper offers a fundamental overview of the diverse range of clinical natural language processing (NLP) applications and the persistent difficulties in developing resilient and adaptable models. Some of the miscellaneous studies based on implementation of NLP in unstructured text coding has been tabulated in the Table 2. Specifically, the discussion on computer vision generally centered around its application in medical imaging, whereas the utilization of natural language processing extends to domains such as electronic health record data. In addition, the authors analyze the application of reinforcement learning in the field of robotic-assisted surgery and evaluate the use of generalized deep-learning techniques in genomics.
3.2 Studies related to use of NLP and machine learning in medical image analysis
RQ3: What are the primary benefits and challenges of interdisciplinary collaboration in the application of NLP and ML for medical image analysis between medical professionals and AI experts? RQ4: How may medical imaging data be used to improve the interpretability of deep learning models, especially when clinical decision-making is involved?
Gao et al. [38] presented a novel Enhanced Feature Extraction Network (EFEN) specifically developed for the purpose of medical picture segmentation. The network was specifically built to overcome the difficulties associated with complex backgrounds and unclear boundaries in medical images. Although EFEN primarily emphasizes picture segmentation, NLP techniques can be utilized to automatically produce textual descriptions of the segmented images, facilitating improved documentation and retrieval of medical records. After the segmentation process is finished, NLP algorithms can be employed to condense the results and establish connections with the patient’s medical history recorded in EMRs. Altarawneh [45] introduced a machine learning system that aims to automatically segment and label brain MRI data in order to identify malignant tumors. Within this particular framework, Natural Language Processing (NLP) can aid by scrutinizing radiology reports and establishing connections between the written observations and picture data. This integration facilitates the verification of the segmentation outcomes and offers a comprehensive perspective of the patient’s state by merging visual and textual data.
Zhang and Niu [46] introduced LcmUNet, a compact network designed for the rapid segmentation of medical images. Natural Language Processing (NLP) can improve the effectiveness of these networks by extracting pertinent clinical data from radiology reports and combining it with segmentation findings to offer a thorough analysis. For instance, NLP can be employed to identify disease-specific keywords from radiology reports and compare them with the segmented regions in the images, so enhancing the precision and comprehensibility of the diagnosis. Jidney et al. [47] utilized an automated machine learning technique that included neural architecture search with transfer learning to analyze medical imaging. Natural Language Processing (NLP) plays a crucial role in this context by analyzing clinical notes and reports to detect patterns and irregularities that can be linked to imaging findings. This integrated method improves the diagnosis process by offering a multi-modal viewpoint. Liu [48] conducted a comprehensive investigation of the use of machine learning in analyzing medical images, with a particular focus on how natural language processing (NLP) might improve the capacity to understand and use the results. Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods can be employed to derive valuable information from written annotations and establish connections with visual data, so enabling a more knowledgeable decision-making process. For instance, NLP can assist in finding crucial diagnostic phrases in radiology reports and associating them with specific regions of interest in medical imaging. Puttagunta and Ravi [49] discussed the progress made in artificial neural networks for medical imaging, emphasizing the possibilities that arise from integrating natural language processing (NLP) with image analysis. Natural Language Processing (NLP) employed to automate the production of radiology reports by analyzing medical pictures. This approach helps to streamline the process and alleviate the workload of radiologists.
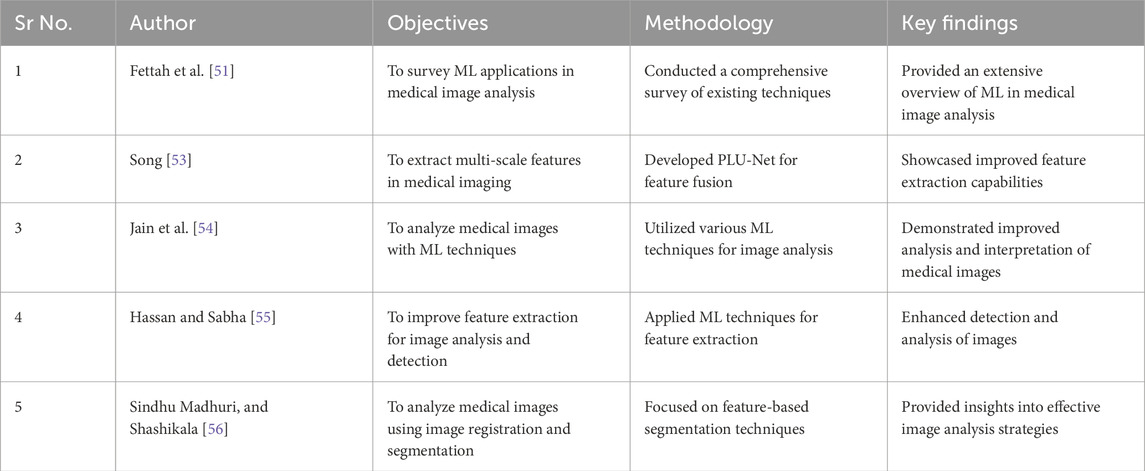
Zhang et al. [50] examined the utilization of optimization techniques and machine learning algorithms in the field of medical image processing. They specifically highlighted the significance of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in improving the integration and analysis of data. Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms have the ability to extract important clinical information from text data. This information can subsequently be utilized to enhance image processing algorithms and enhance the precision of medical diagnosis. In their study, Fettah et al. [51] did a survey focusing on the utilization of machine learning in medical image analysis. They emphasized the significance of using Natural Language Processing (NLP) to improve the interpretation of data. For example, NLP can be employed to examine patient data and detect pertinent medical conditions that must be taken into account during picture analysis. Papanastasiou et al. [52] conducted a comprehensive analysis of the involvement of attention mechanisms in medical image processing. They examined the extent to which attention is capable of managing the intricate nature of medical imaging activities. Their research indicates that although attention mechanisms have made tremendous progress in the field, there are still constraints, especially in comprehending the clinical context and incorporating multimodal data. This review advocates for the implementation of more complete methodologies that integrate attention with other techniques in order to improve the precision and comprehensibility of medical picture analysis.
Some more articles related to use of NLP technique in image analysis with their objectives, methodology and key findings are shown in the Table 3.
3.3 Case studies showcasing effectiveness of NLP and machine learning for improvements in EMR
RQ5: Given the sensitivity of electronic health record (EHR) data, what privacy-preserving techniques and ethical issues are critical for the effective application of NLP and ML in enhancing EMR analysis?
RQ6: How might individualized insights and tailored treatment plans be enabled by the optimal integration of NLP and ML with longitudinal patient data analysis within EMR systems?
Donnelly et al. [57] explored the use of NLP to evaluate radiological records. The researchers highlighted the potential of NLP in understanding radiological data through a detailed examination of NLP applications and technological breakthroughs in the field. Using NLP approaches significantly improves the accuracy and efficiency of analyzing EMR, as shown by their research findings. Jayasudha et al. [58] developed a CNN algorithm specifically designed to segment words and recognize medical phrases in EMRs. The study utilized a technology based on a CNN-based Hidden Markov Model to improve EMR analysis skills. Their inquiry resulted in the creation of a novel method that demonstrated enhanced data processing abilities in EMR analysis.
Malden et al. [59], improved the understanding of COVID-19 symptoms by using NLP approaches in their research. The researchers utilized NLP approaches to conduct an observational study with 350,000 patients in a healthcare system. Their research highlighted the effectiveness of NLP in precisely describing COVID-19 symptoms in EMRs. The study conducted by Rajpurkar et al. [60] examined the efficacy of a deep learning system in identifying diseases in chest radiographs, in comparison to the performance of radiologists in the field. Liao et al. [61] proposed a 3-D deep neural network to evaluate the whole-lung/pulmonary malignancy. Sari and Gunduz-Demir [62] presented an unsupervised feature extractor for effective representation and classification of histopathological tissue images. McDermott and Wasan [63] introduced and assesses an approach for categorizing pharmaceutical names as either opioids or non-opioids using ML and NLP methodologies. Their automated method demonstrated outstanding performance in distinguishing between opioids and non-opioids, with a 99.6% accuracy, 97.8% sensitivity, and 94.6% positive predictive value. In addition, it obtained an F1 score of 0.96 and a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.998.
Hossain et al. [64] presented a comprehensive analysis of 127 articles that examine different types of NLP applications in EHRs. These applications include medical note classification, clinical entity recognition, text summarization, deep learning architectures, information extraction, medical language translation, and other NLP applications. The study explores the utilization of ML and DL techniques, primarily for the purposes of prediction or classification, which are the most prevalent applications. The review by Nickson et al. [65], endorsed the possible application of machine learning methods with EHRs to forecast depression. All of the chosen studies utilized clinically derived, if occasionally expansive, definitions of depression as their criterion for classification. The performance reported in the studies was equivalent to or superior to that observed in primary care. There are worries regarding the applicability and comprehensibility. Shah-Mohammadi et al. [66], utilized ML in conjunction with NLP of emergency room (ER) notes to streamline the process of distinguishing between different diagnoses in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are brought to the ER. The study constructs and evaluates 4 ML models utilizing unstructured patient data gathered from the initial hospital admission records. Several more case studies showcasing effectiveness of NLP and Machine Learning for improvements in EMR are tabulated in the Table 4.
3.4 Some miscellaneous studies in use of NLP and ML in EMR analysis
RQ7: In what ways do various strategies for improving the interpretability of deep learning models benefit clinical texts in electronic medical records, and how do they improve transparency for healthcare providers?
RQ8: What are the main obstacles to and chances for advancing sophisticated NLP and ML approaches for practical use in EMR analysis?
Hu and Chi [70] investigated progress in medical image processing using computer-aided techniques. They conducted a thorough evaluation of recent technology advancements in medical image analysis as part of their technique. They found important results showing improved precision and effectiveness in detecting and treating medical disorders by using modern imaging techniques. Suzuki [71] conducted a study on the use of deep learning in medical imaging to examine its extensive applicability and effects. The study aimed to clarify important discoveries on the effectiveness and consequences of various deep learning models used in medical imaging. The analysis showed notable progress, demonstrating enhanced diagnostic precision and predictive ability in medical imaging. Kim et al. [72], evaluated deep learning methods in the field of biomedical imaging. The methodology includes a thorough examination of recent progress and uses of deep learning in several imaging techniques in the biomedical industry. The study attempts to identify important facts on the effectiveness and influence of deep learning methods in biomedical imaging. Advanced imaging methods utilizing deep learning have improved disease diagnosis and analysis, representing a notable progression in the field.
Sivakami et al. [73], explored the diverse uses of deep learning in assessing healthcare-related photos. The study intends to reveal important insights on the usefulness and impact of deep learning approaches in biological image processing by combining information from existing literature and research. The investigation shows that incorporating deep learning techniques has resulted in substantial enhancements in medical picture processing, ultimately leading to improved healthcare results. Hassouna et al. [74] evaluated the utilization of deep learning in the field of medical imaging. The methodology includes presenting an overview of different deep learning models used in medical imaging applications. The study aimed to clarify important conclusions about the impact of these models on medical imaging practices through a thorough assessment. The investigation showed that incorporating deep learning techniques has increased diagnosis accuracy and operational efficiency in medical imaging. Liu et al. [75], investigated the application of NLP methods in the field of medical picture analysis. The methodology includes a thorough examination of NLP techniques as they relate to different facets of medical imaging. The work intends to reveal important insights on how NLP improves the interpretability and usability of medical imaging data through a methodical analysis. NLP approaches are essential for extracting, interpreting, and using information from medical pictures, enhancing the effectiveness and usefulness of medical imaging systems. The results emphasize the capability of NLP to transform medical picture analysis and aid in progress in healthcare diagnosis and treatments.
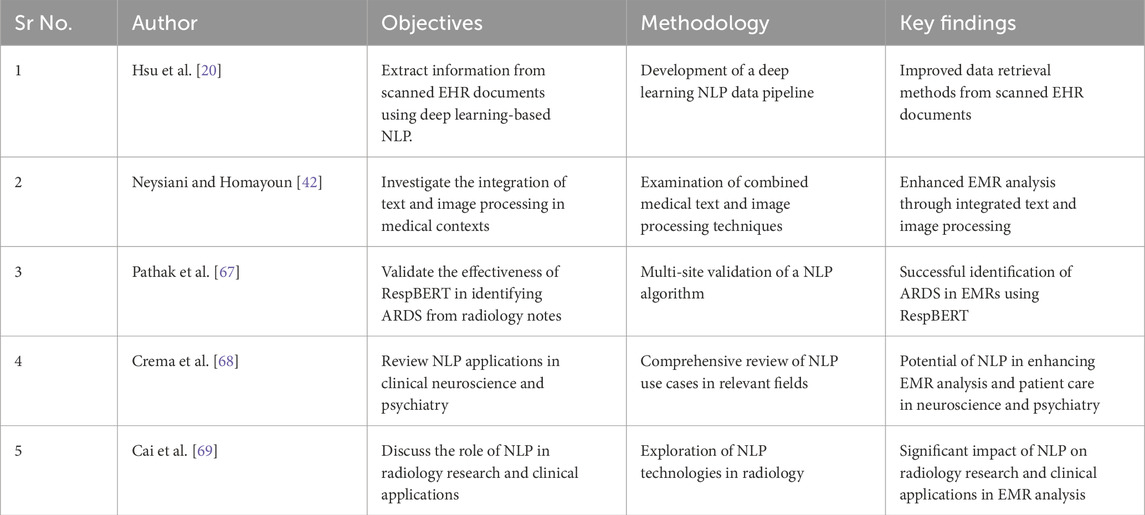
Table 5 presents a comprehensive overview of multiple studies conducted in the domain of NLP pertaining to unstructured data inside EHRs. In their study, Apostolova et al. [76] utilized Support Vector Machines (SVMs) to do text segmentation on a manually designed training dataset. Similarly, Li et al. [77] employed a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) to accomplish a comparable segmentation task on a clinical dataset that had been labeled. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and BERT, which are deep learning models, are utilized for medical coding and patient embeddings on datasets like MIMIC-III. Additional research has been conducted on LSTM for deidentification tasks, LSTM-CRF for information extraction, and Transformers for electronic health record (EHR) creation. The models address a wide range of tasks, including medical coding, patient deidentification, EHR summarization, and medical language translation. This showcases the extensive range of applications for NLP in the administration of healthcare data. The utilization of the PMBERT-MT model by Luo et al. [78] on the MedLane dataset for the purpose of medical language translation underscores the promising prospects of cross-linguistic data processing within the pharmaceutical domain. In summary, Table 5 demonstrates a growing inclination towards employing advanced machine learning models to improve the usefulness and availability of EHR data for various clinical and administrative objectives.
4 Literature summary, challenges and future direction
4.1 Literature summary
Recent research has demonstrated notable progress in use of NLP and ML, specifically DL, methods to enhance Electronic Medical Records (EMRs). The main goal of these improvements is to enhance healthcare decision-making processes by extracting important information from unstructured data in EMRs and optimizing clinical workflows. The potential of NLP in improving the utilization of structured EMR data has been demonstrated [89]. Within the domain of clinical outcomes research that leverages huge datasets, NLP facilitates the management of diverse and intricate jobs. Scientists can utilize NLP methods to extract clinical information from text notes in order to supplement structured data, verify the accuracy of structured data, and detect diseases or extract crucial diagnostic information from complex laboratory reports presented in unstructured format [90, 91]. Within the field of medical imaging, DL has emerged as a powerful tool that offers greater diagnostic accuracy, prediction capacities, and better interpretation of complex imaging data. CNNs have shown impressive effectiveness in analyzing images, emphasizing the revolutionary power of DL in changing medical imaging methods. Analyzing EMR data to provide a comprehensive understanding of patient diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment rationale can be challenging due to the need for patient and illness expertise, critical thinking, and the lack of consistent documentation in EMRs. Therefore, the extraction of complex ideas from vast volumes of EMR data using typical data searches is not a straightforward task [92]. Although modern data mining techniques like NLP can assist in identifying intricate ideas, the presence of missing and erroneous data in EMRs additionally complicates these endeavors [93–96]. Research in clinical NLP has highlighted the crucial importance of deep learning in analyzing clinical language, leading to improved comprehension and interpretation of clinical narratives and symptoms, eventually benefiting patient care.
4.2 Advancement in NLP and ML in healthcare
Notable progress has been achieved in the utilization of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) in the healthcare industry. Precise NLP algorithms, such as deep learning-based NLP pipelines, have shown exceptional accuracy in extracting clinical concepts from unorganized Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and transforming them into organized representations. This has improved the use of data and the process of making decisions in medical settings. Furthermore, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been essential in enhancing medical imaging through the enhancement of image segmentation and classification. When used in conjunction with NLP, these models facilitate the automatic creation of thorough diagnostic reports that incorporate both written and visual information, resulting in more precise and comprehensive patient diagnoses. These developments have significantly influenced patient outcomes by allowing for more accurate and prompt diagnosis, hence facilitating the creation of tailored treatment strategies. By implementing a customized approach to healthcare, the occurrence of trial-and-error in treatment tactics is minimized, resulting in faster recovery periods and enhanced patient contentment.
The incorporation of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) in healthcare has enhanced the efficiency of clinical operations by automating laborious tasks like extracting data and generating reports. This enables healthcare workers to prioritise patient care over administrative responsibilities. Furthermore, the predictive powers of these technologies have enhanced the allocation of resources, guaranteeing that urgent cases are promptly addressed, thus decreasing waiting times and enhancing the overall delivery of healthcare. The above instances and their effects highlight the influential function of NLP and ML in improving patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency, indicating notable advancements in the field.
4.3 Gap in research
While significant advancements have been made in applying NLP and ML in healthcare, challenges remain, particularly in customizing these solutions for specific medical conditions. One area where current NLP and ML solutions fall short is in the diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases. The rarity of these conditions means there is often a lack of sufficient training data, which limits the ability of machine learning models to accurately predict and diagnose these conditions. The heterogeneity of symptoms and the scarcity of annotated datasets further exacerbate this issue, making it difficult for NLP algorithms to extract relevant clinical information and for ML models to generate reliable predictions. Another challenge lies in the integration of multi-modal data, such as combining textual data from clinical notes with imaging data. While some progress has been made in this area, current solutions often struggle with effectively correlating disparate data types. This is particularly problematic in complex conditions, such as certain cancers, where understanding the interplay between genetic, imaging, and clinical data is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment. The limitations in current NLP and ML technologies, including difficulties in processing and integrating high-dimensional data, lead to suboptimal performance in these scenarios.
Moreover, the generalization of NLP and ML models across different patient populations remains a significant hurdle. Models trained on data from one population may not perform well on another due to variations in clinical practices, terminology, and patient demographics. This lack of robustness hinders the deployment of NLP and ML tools in diverse healthcare settings, reducing their overall effectiveness and reliability. These examples highlight the areas where customization for specific medical conditions is currently inadequate, underscoring the need for further research and development to address these challenges.
4.3.1 Rare disease
Due to their low occurrence, rare diseases generally lack extensive datasets, which poses challenges in training effective machine learning models. Adapting NLP and ML techniques for these settings necessitates inventive strategies to address the scarcity of data, such as employing transfer learning or data augmentation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) has the potential to enhance the diagnosis and treatment of uncommon diseases by extracting comprehensive patient histories and detecting subtle patterns in clinical notes. This is particularly important as early and precise diagnosis plays a crucial role in managing such conditions.
4.3.2 Mental health
The intricacy and diversity of symptoms in mental health illnesses pose distinct problems for Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques. These disorders frequently necessitate the examination of several data sources, such as patient self-reports, physician notes, and even social media data. Customisation in this context refers to the process of creating models that are capable of understanding subtle language nuances and identifying patterns that are symptomatic of mental health problems. Nevertheless, the subjective character of mental health data and the heterogeneity in language employed by diverse patients add complexity to the customisation process.
4.3.3 Chronic illness
Chronic diseases, such as diabetes and cardiovascular conditions, are very compatible with natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) applications because of the abundance of extensive datasets and the requirement for ongoing monitoring. The process of customising approaches for various disorders entails the creation of predictive models capable of analysing longitudinal data and identifying initial indications of disease advancement. The difficulty is in the integration of multi-modal data, including laboratory results, imaging data, and patient-reported outcomes, in order to develop comprehensive and individualised treatment programs.
4.3.4 Challenges in customization
Adapting NLP and ML approaches to suit specific medical situations is a difficult task due to various considerations. These challenges encompass the limited availability of well-documented, superior data for specific disorders, the requirement for models that can apply to various patient groups, and the incorporation of interdisciplinary expertise from doctors, data scientists, and domain experts. Moreover, the customisation process is further complicated by the ethical concerns around patient data protection and the comprehensibility of AI-generated conclusions.
4.3.5 Barriers to real-world application of NLP and ML in healthcare
Despite the significant potential of NLP and ML technologies to revolutionize healthcare, there are various obstacles that impede their practical application. The absence of standardized rules presents regulatory obstacles that hinder the approval of AI models for therapeutic use. Incorporating these technologies into existing electronic health record (EHR) systems necessitates substantial alterations and standardization endeavours, which are frequently intricate and demand large resources. Data privacy and security problems provide substantial obstacles due to the necessity of providing NLP and ML models with extensive datasets, hence increasing the likelihood of data breaches. Adhering strictly to rules such as HIPAA is essential in order to safeguard patient information. In addition, healthcare workers’ reluctance to embrace AI tools can impede the implementation process due to worries around accuracy, bias, and the potential effects on clinical workflows. To fully exploit the promise of NLP and ML in enhancing patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency, it is crucial to overcome these obstacles.
4.4 Discussions and future directions
4.4.1 Discussion and future directions
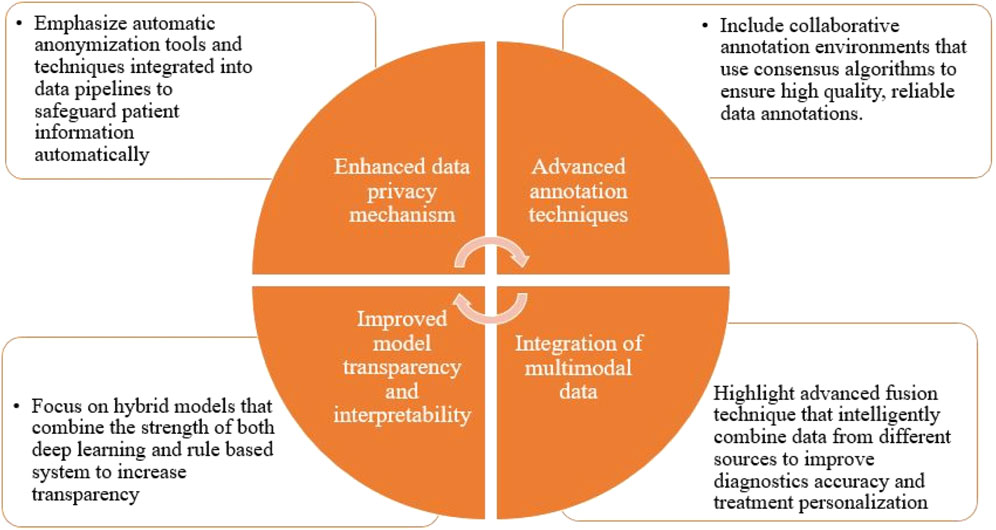
The review study specifically examines neural methodologies for assessing clinical texts in electronic health records (EHRs). Although these data possess a wealth of valuable information in the field of healthcare, they also provide notable problems and difficulties, which is shown in Figure 5.
• Confidentiality: The preservation of privacy inside analytic pipelines is of utmost importance due to the very sensitive nature of the information included in EHRs and the presence of regulatory restrictions. Hence, it is frequently necessary to undertake supplementary measures to safeguard privacy prior to executing any further operations or disseminating any data to external parties. The process of eliminating identifying information from a vast collection of electronic health records (EHRs) is costly. Automating it is challenging and necessitates annotators with specialized knowledge in the field.
• The absence of annotations: A significant portion of current machine learning and deep learning models are supervised in nature, necessitating the use of labeled data throughout the training process. The act of annotating EHR data presents challenges due to the cognitive complexity involved and the inherent unpredictability in data quality. Neural networks necessitate substantial quantities of textual data for training, and regrettably, valuable EHR data is frequently scarce. Only competent annotators can be enlisted to carry out annotations for certain jobs. Ensuring the quality of annotations can be challenging, even in cases where annotators are present. Disagreements among the annotators can complicate and generate controversy in the judgments.
• Comprehensibility: Deep neural networks have demonstrated the capability to attain greater outcomes in comparison to alternative methodologies. Nevertheless, in numerous domains, they are frequently regarded as opaque entities. In general, a neural network model is characterized by a substantial quantity of trainable parameters, hence posing significant challenges in terms of model interpretability. Furthermore, in contrast to linear models, which often exhibit greater simplicity and comprehensibility, neural networks are comprised of non-linear layers and intricate structures, hence augmenting the challenges associated with interpretation.
4.4.2 Guidelines for enhancing interdisciplinary collaboration
In order to enhance multidisciplinary collaboration among medical practitioners, data scientists, and AI experts, the following measures can be implemented:
• Establish Cross-Disciplinary Teams: Healthcare institutions need to develop specialised interdisciplinary teams including of physicians, data scientists, engineers, and ethicists. It is essential for these teams to collaborate right from the beginning of a project to guarantee that all viewpoints are taken into account in the creation of NLP and ML applications.
• Develop Shared Language and Training Programs: A major roadblock to successful collaboration is the absence of a common vocabulary across different fields. Creating training programs that offer fundamental understanding of medical language for data scientists and essential data science principles for physicians might effectively bridge this gap.
• Implement Regular Collaborative Workshops: Regular workshops and seminars that prioritise interdisciplinary collaboration have the potential to cultivate a culture of ongoing learning and creativity. The workshops should prioritise real-world issues and utilise case studies to promote practical, interactive cooperation.
• Create Collaborative Research Initiatives: Funding agencies and academic institutions should provide priority and allocate funds to research programs that necessitate multidisciplinary collaboration. These initiatives should provide explicit rules regarding the duties and responsibilities of each team member to guarantee a synchronised approach.
4.4.3 Guidelines for resolving ethical concerns
In order to mitigate ethical issues associated with the utilisation of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) in the healthcare sector, the following measures can be adopted:
• Establish Clear Ethical Guidelines: Establish and implement explicit ethical principles for the utilisation of artificial intelligence in the healthcare sector. These rules should specifically cover concerns related to data privacy, obtaining informed consent, and ensuring fair and just utilisation of AI technologies.
• Implement Privacy-Preserving Technologies: Allocate resources towards the adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies like differential privacy and federated learning. These technologies enable the examination of sensitive health data while ensuring the protection of patient confidentiality. It is imperative to incorporate these technologies into the process of creating and implementing NLP and ML models.
• Involve Ethicists in AI Development: It is essential to engage ethicists in the initial stages of AI research. Their responsibility should encompass assessing the ethical ramifications of AI applications, guaranteeing their adherence to established ethical norms, and rectifying any potential biases in the data or models.
• Enhance Transparency and Accountability: AI systems should be developed with a focus on openness and responsibility. This involves ensuring that clinicians and patients can understand how AI models make decisions, and creating systems of responsibility in situations where AI-driven judgements result in negative consequences.
• Promote Patient and Public Involvement: Facilitate active participation of patients and the general public in deliberations concerning the ethical ramifications of artificial intelligence in the healthcare sector. Public forums, surveys, and consultations can be utilised to ensure that the perspectives of individuals impacted by AI technology are acknowledged and taken into account during the development phase.
5 Conclusion and future scope
This review focusses on notable progress in the utilisation of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) in the healthcare field, namely, in the areas of Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) and medical imaging. The results highlight the significant impact that these technologies can have on improving the accuracy of diagnoses, promoting patient outcomes, and optimising the efficiency of healthcare.
5.1 Implications for practitioners
Healthcare practitioners can utilise the breakthroughs in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to optimise clinical operations and improve decision-making. These technologies can be used by professionals to obtain valuable information from unorganised data, which allows for more precise diagnoses and personalised treatment programs. Integrating natural language processing (NLP) with medical imaging can effectively decrease diagnostic errors and enhance the uniformity of patient care. It is important for practitioners to stay updated on new technologies and receive training in order to successfully integrate them into their clinical practice.
5.2 Implications for researchers
Researchers are urged to expand upon the observed progress and tackle the deficiencies emphasised in this assessment. Additional investigation into the utilisation of natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) in the context of uncommon diseases is necessary, as well as the incorporation of multi-modal data. In addition, research should prioritise enhancing the ability of models to apply to a wide range of patient populations and healthcare environments. Effective collaboration among doctors, data scientists, and engineers will be crucial in surmounting these hurdles and propelling the field forward.
5.3 Implications for policymakers
Policymakers are essential in promoting the implementation of NLP and ML technologies in the healthcare sector. In order to facilitate this integration, policies should prioritise the protection of data privacy and security, encourage interdisciplinary collaboration, and allocate financing for research and development in this field. Policymakers should additionally contemplate formulating rules and guidelines for the ethical utilisation of artificial intelligence (AI) in the healthcare sector, guaranteeing that these technologies are implemented in a way that is advantageous to all parties involved, particularly patients.
5.4 Closing remark
It is crucial to address the limitations that have been found in this research in order to make progress in the healthcare applications of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML). By surmounting these obstacles by ongoing investigation, interdisciplinary cooperation, and favorable regulations, the complete capabilities of these revolutionary technologies can be achieved, resulting in substantial enhancements in patient care, healthcare provision, and overall health results.
Author contributions
PK: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. SG: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing, Software. BP: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition. C-WL: Funding acquisition, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Centre for Advanced Modelling and Geospatial Information Systems (CAMGIS), Faculty of Engineering and IT, University of Technology Sydney. Moreover, supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Science and ICT) (RS-2022-00165154, “Development of Application Support System for Satellite Information Big Data”).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rasmussen LV, Peissig PL, McCarty CA, Starren J. Development of an optical character recognition pipeline for handwritten form fields from an electronic health record. J Am Med Inform Assoc (2012) 19(e1):e90–5. doi:10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000182
2. Haux R. Health information systems: past, present, and future. Int J Med Inform (2006) 75:268–81. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.08.002
3. Jensen PB, Jensen LJ, Brunak S. Mining electronic health records: towards better research applications and clinical care. Nat Rev Genet (2012) 13(6):395–405. doi:10.1038/nrg3208
4. Cullen E, Ranji U, Salganicoff A. Health information technology – background brief (2011). Available from: https://www.kaiseredu.org/Issue-Modules/Health-Information-Technology/Background-Brief.aspx.
5. Lowe HJ, Antipov I, Hersh W, Smith CA. Towards knowledge-based retrieval of medical images: the role of semantic indexing, image content representation, and knowledge-based retrieval. In: Proceedings of the American medical informatics association (AMIA) symposium (1998). p. 882–6.
6. Zhang D, Yin C, Zeng J, Yuan X, Zhang P. Combining structured and unstructured data for predictive models: a deep learning approach. BMC Med Inform Decis Making (2020) 20:280–11. doi:10.1186/s12911-020-01297-6
7. Jamoom E, Beatty P, Bercovitz A, Woodwell D, Palso K, Rechtsteiner E (2012). Physician adoption of electronic health record systems: United States, 2011, NCHS Data Brief, Physician adoption of electronic health record systems: United States, 2011. 98, 1–8.
8. Jha AK, DesRoches CM, Campbell EG, Donelan K, Rao SR, Ferris TG, et al. Use of electronic health records in US hospitals. New Engl J Med (2009) 360(16):1628–38. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa0900592
9. Jha AK, DesRoches CM, Kralovec PD, Joshi MS. A progress report on electronic health records in US hospitals. Health Aff (2010) 29(10):1951–7. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2010.0502
10. Pipersburgh J. The push to increase the use of EHR technology by hospitals and physicians in the United States through the HITECH Act and the Medicare incentive program. J Health Care Finance (2011) 38(2):54–78.
11. Overview of international EMR/EHR markets – results from a survey of leading health care companies. (2010). Available from: https://www.accenture.com/SiteCollectionDocuments/PDF/Accenture_EMR_Markets_Whitepaper_vfinal.pdf.
12. Hayrinen K, Saranto K, Nykanen P. Definition, structure, content, use and impacts of electronic health records: a review of the research literature. Int J Med Inform (2008) 77(5):291–304. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2007.09.001
13. Hope CJ, Garvin JH, Sauer BC (2012). Information extraction from narrative data. Am J Health-System Pharm, 69(6), 455, 455–61. doi:10.2146/ajhp110135
14. Li L, Chase HS, Patel CO, Friedman C, Weng C. Comparing ICD9-encoded diagnoses and NLP-processed discharge summaries for clinical trials pre-screening: a case study. In: AMIA annual symposium proceedings (2008). p. 404–8.
15. Esteva A, Robicquet A, Ramsundar B, Kuleshov V, DePristo M, Chou K, et al. A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nat Med (2019) 25(1):24–9. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0316-z
16. Ching T, Himmelstein DS, Beaulieu-Jones BK, Kalinin AA, Do BT, Ferrero E, et al. Opportunities and obstacles for deep learning in biology and medicine. J R Soc Interf (2018) 15(141):20170387. doi:10.1098/rsif.2017.0387
17. Ravi D, Wong C, Deligianni F, Berthelot M, Andreu-Perez J, Lo B, et al. Deep learning for health informatics. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform (2017) 21(1):4–21. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2016.2636665
18. Luo JW, Chong JJR. Review of natural language processing in radiology. Neuroimaging Clin North America (2020) 30(4):447–58. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2020.08.001
19. Bali V, Weaver J, Turzhitsky V, Schelfhout J, Paudel ML, Hulbert E, et al. Development of a natural language processing algorithm to detect chronic cough in electronic health records. BMC Pulm Med (2022) 22(1):256. doi:10.1186/s12890-022-02035-6
20. Hsu E, Malagaris I, Kuo YF, Sultana R, Roberts K. Deep learning-based NLP data pipeline for EHR scanned document information extraction. JAMIA Open (2021) 4(4):ooac045. doi:10.1093/jamiaopen/ooac045
21. Wang S, Ren P, Chen Z, Ren Z, Nie JY, Ma J, et al. Coding electronic health records with adversarial reinforcement path generation. In: Proceedings of the 43rd international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval (2020). p. 801–10.
22. Goodfellow IB, Yoshua , Courville A. Deep Learning. MIT Press. Available at: https://www.deeplearningbook.org (Accessed on 2024, March 12).
23. Gehrmann S, Dernoncourt F, Li Y, Carlson ET, Wu JT, Welt J, et al. Comparing deep learning and concept extraction based methods for patient phenotyping from clinical narratives. PLOS ONE (2018) 13(2):e0192360. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0192360
24. Bauer S, Wiest R, Nolte LP, Reyes M. A survey of MRI-based medical image analysis for brain tumor studies. Phys Med Biol (2013) 58(13):R97–R129. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/58/13/R97
25. Mazurowski MA, Buda M, Saha A, Bashir MR. Deep learning in radiology: an overview of the concepts and a survey of the state of the art with a focus on MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging (2019) 49(4):939–54. doi:10.1002/jmri.26534
26. Bizopoulos P, Koutsouris D. Deep learning in cardiology. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng (2019) 12(c):168–93. doi:10.1109/rbme.2018.2885714
27. Valliani AAA, Ranti D, Oermann EK. Deep learning and neurology: a systematic review. Neurol Ther (2019) 8(2):351–65. doi:10.1007/s40120-019-00153-8
28. Hossain E, Rana R, Higgins N, Soar J, Barua PD, Pisani AR, et al. Natural language processing in electronic health records in relation to healthcare decision-making: a systematic review. Comput Biol Med (2023) 155:106649. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106649
29. Sezgin E, Hussain SA, Rust S, Huang Y. Extracting medical information from free-text and unstructured patient-generated health data using natural language processing methods: feasibility study with real-world data. JMIR Formative Res (2023) 7:e43014. doi:10.2196/43014
30. Falter M, Godderis D, Scherrenberg M, Kizilkilic SE, Xu L, Tukanov E, et al. Identification of ICD-code misclassifications in cardiac disease using natural language processing. Eur J Prev Cardiol (2023) 30(Suppl. ment_1):zwad125–049. doi:10.1093/eurjpc/zwad125.049
31. Tam CS, Gullick J, Saavedra A, Vernon ST, Figtree GA, Chow CK, et al. Combining structured and unstructured data in EMRs to create clinically-defined EMR-derived cohorts. BMC Med Inform Decis making (2021) 21:91–10. doi:10.1186/s12911-021-01441-w
32. Samir B, Belhaouari A (2021) Deep learning in healthcare (pp. 155–68). doi:10.1007/978-3-030-67303-1_13
33. Kaul D, Raju H, Tripathy BK (2022) Deep learning in healthcare (pp. , 97–115). doi:10.1007/978-3-030-75855-4_6
34. Priya L, Sathya A, ThangaRevathi S (2021) Deep learning in healthcare (pp. , 121–33). doi:10.1007/978-3-030-60265-9_8
35. Hu S. Deep learning in healthcare. 2023 Int Conf Artif Intelligence, Database Machine Learn (AIDML 2023) (2023) 57:1–10.
36. Esteva A, Robicquet A, Ramsundar B, Kuleshov V, DePristo MA, Chou K, et al. A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nat Med (2019) 25(1):24–9. doi:10.1038/S41591-018-0316-Z
37. Huang G, Li Y, Jameel S, Long Y, Papanastasiou G. From explainable to interpretable deep learning for natural language processing in healthcare: how far from reality? Comput Struct Biotechnol J (2024) 24:362–73. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2024.05.004
38. Gao Y, Che X, Xu H, Bie M. An enhanced feature extraction network for medical image segmentation. Appl Sci (2023) 13(12):6977. doi:10.3390/app13126977
39. Almuhana HAJH, Abbas HH. Classification of specialities in textual medical reports based on natural language processing and feature selection. Indonesian J Electr Eng Computer Sci (2022) 27(1):163–70. doi:10.11591/ijeecs.v27.i1.pp163-170
40. Nandish S, Rj P, Nm N. Natural Language processing approaches for automated multilevel and multiclass classification of breast lesions on free-text cytopathology reports. JCO Clin Cancer Inform (2022) 6:e2200036. doi:10.1200/CCI.22.00036
41. Figueira J, Correia GM, Strzyz M, Mendes A. Justifying multi-label text classifications for healthcare applications. In: European conference on information retrieval. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland (2023). p. 406–13.
42. Neysiani BS, Homayoun H. Medical text and image processing: applications, methods, issues, and challenges. In: Machine learning and deep learning in medical data analytics and healthcare applications. Switzerland: Springer Nature (2022). p. 65–90.
43. Zhang Q, Yuan Q, Lv P, Zhang M, Lv L. Research on medical text classification based on improved capsule network. Electronics (2022) 11(14):2229. doi:10.3390/electronics11142229
44. Patil SS, Moorthy V. Extraction of unstructured electronic healthcare records using Natural Language Processing. In: 2023 international conference on networking and communications (ICNWC). IEEE (2023). p. 1–6.
45. Altarawneh K. Medical image categorization combining image segmentation and machine learning. J Namibian Stud Hist Polit Cult (2023) 33:361–75. doi:10.59670/jns.v33i.728
46. Zhang S, Niu Y. LcmUNet: a lightweight network combining CNN and mlp for real-time medical image segmentation. Bioengineering (2023) 10(6):712. doi:10.3390/bioengineering10060712
47. Jidney TT, Biswas A, Abdullah Al NM, Hossain I, Alam MJ, Talukder S, et al. Automl systems for medical imaging. In: Data driven approaches on medical imaging. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland (2023). p. 91–106.
49. Puttagunta M, Ravi S. Medical image analysis based on deep learning approach. Multimedia tools Appl (2021) 80(16):24365–98. doi:10.1007/s11042-021-10707-4
50. Zhang Y, Gorriz JM, Nayak DR. Optimization algorithms and machine learning techniques in medical image analysis. Math Biosci Eng (2023) 20(3):5917–20. doi:10.3934/mbe.2023255
51. Fettah A, Menassel R, Gattal A. Machine learning for medical image analysis: a survey. In: International conference on advanced intelligent systems for sustainable development. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland (2022). p. 148–64.
52. Papanastasiou G, de Herrera AGS, Wang C, Zhang H, Yang G, Wang G. Focus on machine learning models in medical imaging. Phys Med Biol (2023) 68:010301. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/aca069
53. Song W, Yu H, Wu J. PLU-Net: extraction of multi-scale feature fusion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11806 (2023) 51:2733–40. doi:10.1002/mp.16840
54. Jain N, Joshi MK, Jain V, Dubey M. Analysis of medical images using machine learning techniques. Graph Learn Netw Sci Nat Lang Process (2022) 231:231–54. doi:10.1201/9781003272649-14
55. Hassan A, Sabha M. Feature extraction for image analysis and detection using machine learning techniques. Int J Adv Networking Appl (2023) 14(4):5499–508. doi:10.35444/ijana.2023.14401
56. Madhuri GS, Shashikala HK. Analysis of medical images using image registration feature-based segmentation techniques. In: 2nd international conference on technological advancements in computational sciences (ICTACS), 10 (2022). p. 485–90. doi:10.1109/ictacs56270.2022.9987895
57. Donnelly LF, Grzeszczuk R, Guimaraes CV. Use of natural language processing (NLP) in evaluation of radiology reports: an update on applications and technology advances. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI (2022) 43(2):176–81. doi:10.1053/j.sult.2022.02.007
58. Jayasudha V, Deepa N, Devi T. CNN based hidden markov model algorithm to segment words and identify the medical term to match EMRs. In: 2023 7th international conference on intelligent computing and control systems (ICICCS). IEEE (2023). p. 580–5.
59. Malden DE, Tartof SY, Ackerson BK, Hong V, Skarbinski J, Yau V, et al. Natural Language processing for improved characterization of COVID-19 symptoms: observational study of 350,000 patients in a large integrated health care system. JMIR Public Health Surveill (2022) 8(12):e41529. doi:10.2196/41529
60. Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Ball RL, Zhu K, Yang B, Mehta H, et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: a retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. Plos Med (2018) 15(11):e1002686. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002686
61. Liao F, Liang M, Li Z, Hu X, Song S. Evaluate the malignancy of pulmonary nodules using the 3-D deep leaky Noisy-OR network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst (2019) 30(11):3484–95. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2019.2892409
62. Sari CT, Gunduz-Demir C. Unsupervised feature extraction via deep learning for Histopathological classification of Colon tissue images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging (2019) 38(5):1139–49. doi:10.1109/tmi.2018.2879369
63. McDermott SP, Wasan AD. Using Natural Language Processing and machine learning to identify opioids in electronic health record data. J Pain Res (2023) Vol. 16:2133–40. doi:10.2147/jpr.s389160
64. Hossain E, Rana R, Higgins N, Soar J, Barua PD, Pisani AR, et al. Natural language processing in electronic health records in relation to healthcare decision-making: a systematic review. Comput Biol Med (2023) 155:106649. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106649
65. Nickson D, Meyer C, Walasek L, Toro CT. Predicting depression using electronic health records: a systematic review. BMC Med Inform Decis Making (2023) 1472–90.
66. Shah-Mohammadi F, Finkelstein J. Combining NLP and machine learning for differential diagnosis of COPD exacerbation using emergency room data. Stud Health Technol Inform (2023) 305:525–8. doi:10.3233/SHTI230549
67. Pathak A, Kamaleswaran R, Marshall C, Davis C, Yang P. RespBERT: a multi-site validation of a Natural Language Processing algorithm, of radiology notes to identify acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards). Authorea Preprints (2023). doi:10.3233/SHTI230130
68. Crema C, Attardi G, Sartiano D, Redolfi A. Natural language processing in clinical neuroscience and psychiatry: a review. Front Psychiatry (2022) 13:946387. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2022.946387
69. Cai T, Giannopoulos AA, Yu S, Kelil T, Ripley B, Kumamaru KK, et al. Natural language processing technologies in radiology research and clinical applications. Radiographics (2016) 36(1):176–91. doi:10.1148/rg.2016150080
70. Cui H, Hu L, Chi L. Advances in computer-aided medical image processing. Appl Sci (2023) 13(12):7079. doi:10.3390/app13127079
71. Suzuki K. Overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Radiological Phys Technol (2017) 10(3):257–73. doi:10.1007/s12194-017-0406-5
72. Kim M, Yan C, Yang D, Wang Q, Ma J, Wu G. Deep learning in biomedical image analysis. In: Biomedical information technology. Academic Press (2020). p. 239–63.
73. Sivakami A, Balamurugan KS, Shanmugam B, Pitchaimuthu S. Deep learning techniques for biomedical image analysis in healthcare. In: Deep neural networks for multimodal imaging and biomedical applications. Japan: Springer (2020). p. 31–46.
74. Hassouna M, Al-Antary M, Saleh M, Al Barghuthi NB. Applications of deep learning in medical imaging: a brief review. In: 2023 advances in science and engineering technology international conferences (ASET). IEEE (2023). p. 1–4.
75. Liu Z, He M, Jiang Z, Wu Z, Dai H, Zhang L, et al. Survey on natural language processing in medical image analysis. J Cent South Univ Med Sci (2022) 47(8):981–93. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.220376
76. Apostolova E, Channin DS, Demner-Fushman D, Furst J, Lytinen S, Raicu D. Automatic segmentation of clinical texts. In: 2009 annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE (2009). p. 5905–8.
77. Li Y, Lipsky Gorman S, Elhadad N. Section classification in clinical notes using supervised hidden Markov model. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM international health informatics symposium (2010). p. 744–50.
78. Luo J, Zheng Z, Ye H, Ye M, Wang Y, You Q, et al. Benchmarking automated clinical language simplification: dataset, algorithm, and evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.02420 (2020). doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5334831
79. Xu K, Lam M, Pang J, Gao X, Band C, Mathur P, et al. Multimodal machine learning for automated ICD coding. In: Machine learning for healthcare conference (2019). p. 197–215.
80. Bhavani Singh K, Guntu M, Reddy Bhimi reddy A, Gichoya JW, Purkayastha S. (2020). Multi-label natural language processing to identify diagnosis and procedure codes from MIMIC-III inpatient notes.
81. Kajiyama K, Horiguchi H, Okumura T, Morita M, Kano Y. De-identifying free text of Japanese dummy electronic health records. In: Proceedings of the ninth international workshop on health text mining and information analysis. Brussels, Belgium: Association for Computational Linguistics (2018). p. 65–70.
82. Mehrabi S, Sohn S, Li D, Pankratz JJ, Therneau T, St. Sauver JL, et al. Temporal pattern and association discovery of diagnosis codes using deep learning. In: 2015 international conference on healthcare informatics (2015). p. 408–16.
83. Li F, Jin Y, Liu W, Rawat BPS, Cai P, Yu H. Fine-tuning bidirectional encoder representations from Transformers (BERT)–Based models on large-scale electronic health record notes: an empirical study. JMIR Med Inform (2019) 7(3):e14830. doi:10.2196/14830
84. Ji J, Chen B, Jiang H (2020). Fully-connected LSTM-CRF on medical concept extraction. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11(9), 1971–9. doi:10.1007/s13042-020-01087-6
85. Melamud O, Shivade C. Towards automatic generation of shareable synthetic clinical notes using neural language models. In: Proceedings of the 2nd clinical Natural Language Processing workshop. Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics (2019). p. 35–45.
86. Amin-Nejad A, Ive J, Velupillai S. Exploring transformer text generation for medical dataset augmentation. In: Proceedings of the 12th language resources and evaluation conference. Marseille, France: European Language Resources Association (2020). p. 4699–708.
87. Li M, Liu R, Wang F, Chang X, Liang X. Auxiliary signal-guided knowledge encoder-decoder for medical report generation. World Wide Web (2023) 26(1):253–70. doi:10.1007/s11280-022-01013-6
88. Alsentzer E, Kim A. Extractive summarization of ehr discharge notes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.12085 (2018).
89. Li L, Chase HS, Patel CO, Friedman C, Weng C. Comparing ICD9-encoded diagnoses and NLP-processed discharge summaries for clinical trials pre-screening: a case study. In: AMIA annu. Symp. Proc. (2008). p. 404–8.
90. Murff HJ, FitzHenry F, Matheny ME, Gentry N, Kotter KL, Crimin K, et al. Automated identification of postoperative complications within an electronic medical record using natural language processing. JAMA (2011) 306(8):848–55. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.1204
91. Perlis RH, Iosifescu DV, Castro VM, Murphy SN, Gainer VS, Minnier J, et al. Using electronic medical records to enable large-scale studies in psychiatry: treatment resistant depression as a model. Psychol Med (2012) 42(1):41–50. doi:10.1017/S0033291711000997
92. Hripcsak G, Albers DJ. Next-generation phenotyping of electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc (2013) 20(1):117–21. doi:10.1136/amiajnl-2012-001145
93. Danforth KN, Early MI, Ngan S, Kosco AE, Zheng C, Gould MK. Automated identification of patients with pulmonary nodules in an integrated health system using administrative health plan data, radiology reports, and natural language processing. J Thorac Oncol (2012) 7(8):1257–62. doi:10.1097/jto.0b013e31825bd9f5
94. Deutsch JC. Colonoscopy quality, quality measures, and a natural language processing tool for electronic health records. Gastrointest Endosc (2012) 75(6):1240–2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.02.031
95. Jones JB, Snyder CF, Wu AW. Issues in the design of Internet-based systems for collecting patient-reported outcomes. Qual Life Res (2007) 16(8):1407–17. doi:10.1007/s11136-007-9235-z
Keywords: natural language processing, clinical decision support, healthcare, electronic medical records, interdisciplinary collaboration
Citation: Khalate P, Gite S, Pradhan B and Lee C-W (2024) Advancements and gaps in natural language processing and machine learning applications in healthcare: a comprehensive review of electronic medical records and medical imaging. Front. Phys. 12:1445204. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1445204
Received: 06 June 2024; Accepted: 06 November 2024;
Published: 02 December 2024.
Edited by:
Federico Giove, Centro Fermi - Museo storico della fisica e Centro studi e ricerche Enrico Fermi, ItalyReviewed by:
Yunfei Long, University of Essex, United KingdomMayuri Mehta, Sarvajanik College of Engineering and Technology, India
Dweepna Garg, Charotar University of Science and Technology, India
Amit Ganatra, Parul University, India
Copyright © 2024 Khalate, Gite, Pradhan and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shilpa Gite, c2hpbHBhLmdpdGVAc2l0cHVuZS5lZHUuaW4=; Biswajeet Pradhan, Qmlzd2FqZWV0LlByYWRoYW5AdXRzLmVkdS5hdQ==; Chang-Wook Lee, Y3dsZWVAa2FuZ3dvbi5hYy5rcg==
 Priyanka Khalate
Priyanka Khalate Shilpa Gite1,2*
Shilpa Gite1,2* Biswajeet Pradhan
Biswajeet Pradhan Chang-Wook Lee
Chang-Wook Lee