
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Phys. , 10 September 2024
Sec. Fusion Plasma Physics
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2024.1424755
This article is part of the Research Topic Proton Boron Nuclear Fusion: From Energy Production to Medical Applications View all 8 articles
Improving the energy efficiency in generating high-energy proton or boron ions is crucial for advancing the feasibility of neutronless laser-based proton–boron (p-B11) fusion reactions. The primary objective of this work is to optimize the fusion energy efficiency of a proposed advanced p-B11 fusion scheme. In the proposed scheme, an ultrashort laser pulse is guided by a plasma channel filled with carbon–hydrogen (CH2) clusters. The MeV protons are generated by the Coulomb explosion (CE) of the cluster, which, therefore, interact with surrounding boron to produce alpha particles. To evaluate the fusion energy efficiency under various conditions, 2D particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations are used, supplemented with analytical calculations and estimations. The Bayesian optimization (BO) algorithm is utilized to optimize the key interaction parameters. The BO approach allows us to identify optimal cluster and laser parameters that would have higher fusion energy efficiency.
The proton–boron (p-B11) fusion reaction is highly desired due to its aneutronic nature, which results in a cleaner energy output than that in D-T fusion. One of the promising directions of the research in this field is the possibility of initiating p-B11 fusion reactions with laser-driven accelerated ions around the cross-section peak with the center of mass energy of ions at approximately 650 keV [1, 2]. The development of ultrafast laser technologies has shown that it is possible to efficiently accelerate ions in plasma to MeV energies [3], paving the way for applications in p-B11 fusion.
As a result, there has been a growing interest in laser-based p-B11 fusion in recent years [4–19]. Two mainstream proton–boron fusion schemes that recently demonstrated high alpha-particle yields are pitcher–catcher and in-target configurations. For example, Guiffrida et al. utilized in-target configuration [20] and demonstrated ∼3∙1010/sr α-particles with a 0.6 kJ, 0.3 ns laser pulse. The pitcher–catcher configurations [5, 21] have also shown a high yield ∼109/sr with a laser energy of 1.4 kJ. In these experiments, the main target did not utilize the energy efficiency enhancement that has been shown in laser-driven ion-acceleration experiments with various advanced target designs [22–24]. However, several recent works addressed this problem and proposed advanced fusion schemes and advanced target designs for higher energy efficiency. For example, H. Ruhl and G. Korn numerically investigated boron nanorod (BN) interactions with ultra-intense laser pulses [25]. [4] used a 600 nm hydrocarbon plasma polymer film on top of the BN target in order to increase the proton concentration. Several advanced schemes that utilize a strong magnetic field or hybrid fusion scheme with ps and ns lasers have been proposed to increase energy efficiency [10, 26]. V. Krainov proposed a theory of fusion in BH microdroplets [27]. However, compared to the field of laser-driven proton acceleration, advancements in target nanoengineering are still emerging. Improved control over target design, including both shape optimization and the ion composition control on μm and nm scales, has led to increased ion flux, higher ion energies, and better control over the ion energy spectrum [22, 23]. These developments are pivotal for improving the fusion energy efficiency of the p-B11 reaction and can be adapted to the actively developing laser-driven p-B11 fusion.
In the current paper, we propose and analyze the fusion energy efficiency during the interaction of high-intensity laser with nanocluster suspensions in a long plasma channel. The proposed scheme features a high-intensity short-pulse laser propagating in a relatively low-density plasma channel generated by capillary discharge [28, 29]. Structured CH2 targets (clusters) concurrently flow in the plasma channel produced in a BN capillary. The laser can interact with the targets to produce the accelerated protons. When the energy of the accelerated protons is high enough (of the order of 1 MeV), they, in turn, can collide with background low-density boron ions or solid boron walls of the capillary and interact to produce the alpha particles. As the process of laser interaction is carried out in a plasma channel, the laser pulse is confined, and the interaction can be extended to a significant length (defined by laser depletion), which, in turn, increases the process efficiency.
The described scheme will depend on various parameters, such as the laser intensity, cluster radius and density, and pulse duration. The parameter space of the proposed scheme is wide; hence, a thorough theoretical search is required in order to find the optimal conditions for the proposed fusion scheme. Improvements in the computing hardware allow us to collect data for many possible configurations in computationally intense particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations within a reasonable amount of time. At such rates, the amounts of data that can be extracted are sufficient to apply advanced numerical techniques such as optimization algorithms and machine learning methods to deal more efficiently with multidimensional problems. Recent works applied Bayesian optimization to both PIC simulations to find the optimal simulation parameters and experiments for the real-time optimization of the experiment setup [30–32]. The ability of a deep neural network to model complex physical phenomena in laser–plasma physics was also assessed for the typical laser-driven ion acceleration scheme [33]. The comprehensive overview of the data-driven techniques applied to laser–plasma physics by [34] emphasizes the huge potential of advanced numerical techniques in the enhancement of experimental and simulation approaches. Thus, to optimize the fusion energy efficiency for the proposed scheme, we use the Bayesian optimization (BO) method due to the computationally intense nature of PIC simulations.
In this paper, we describe a method that uses Gaussian process regression [35] within BO to examine the variables involved in the laser-driven Coulomb explosion (CE) of CH2 clusters inside the plasma channel. We aim to improve the laser ion conversion efficiency, which will result in better fusion energy efficiency by adjusting various influencing parameters. By applying Bayesian optimization, we seek to better understand and adjust the relationships between these parameters, thereby enhancing the output of fusion energy in our proposed model.
The proposed fusion scheme that has been investigated is shown in Figure 1. In the initial stage, the boron-containing gas is mixed with sub-micron CH2 clusters as they are injected into the boron-coated capillary. Shortly after the injection, an electrical discharge is used to ionize the gas. The hydrodynamic expansion and cooling of the plasma form a plasma channel that will guide the laser [29, 36]. As the high-intensity pulse propagates through the capillary with the formed channel, it interacts with the clusters, expelling electrons and causing the remaining positively charged cores to undergo a Coulomb explosion. The protons resulting from this explosion are accelerated, and as they propagate, they can interact with the low-density boron plasma and the boron capillary walls. This laser–cluster interaction is crucial for the fusion process as it leads to the production of high-energy protons necessary for p-B11 reactions.
According to the proposed fusion scheme, we can calculate the energy of the laser EL according to Equation 1, which depends on the area of the beam Abeam, laser intensity I0, and full pulse width at half-maximum
The total energy released by the fusion reactions Etot from the single-cluster CE is given by Equation 2. It is proportional to the reactivity
Thus, the fusion energy efficiency G is proportional to the number of protons NH multiplied by the reactivity
Expanding the reactivity term in (3), we can introduce the single-cluster fusion parameter η0 Equation 4 that will depend on the ion energy spectrum f(E), the cross-section of the reaction
The goal of the optimization is to evaluate theoretically and through numerical simulations various cluster densities n0, cluster radius r, pulse intensity I0, and pulse duration τ to determine the parameters that will correspond to the higher fusion energy efficiency. The laser propagating through the plasma channel will interact with many clusters, of which many are located in the shadow of other clusters (e.g., cluster 2 is located in the shadow of cluster 1, as shown in Figure 1). Their position along the laser propagation direction is different (z-axis), while their position in the x–y plane is the same, and we have to extend the single-cluster fusion parameter η0 from Equation 4 to account for all the clusters that would interact with the laser.
In the subsequent paragraph, we analyze the methods used to scale up the calculations of the single-cluster fusion parameter η0 to encompass the entire volume of the plasma channel with many CH2 clusters. To analyze the interaction of a laser with a single CH2 cluster, PIC simulations are employed utilizing numerical code Epoch [37]. The single pre-ionized cluster is positioned in the center of the square
Assuming that the low-density plasma channel does not have a significant effect on the single-cluster interaction, we will not explicitly model the plasma channel in PIC simulations and assume ideal guiding, which is validated by comparative PIC simulations with and without a low-density background plasma channel. To extend the single-cluster results to the volume of the plasma channel, we evaluate the total number of clusters in the cross-section of the plasma channel Ncross, as well as ηi,– which is the single-cluster fusion parameters for clusters that face laser intensity Ii affected by the interaction with i−1 clusters. Thus, the net fusion parameter ηnet that considers all clusters in the volume of the plasma channel can be calculated using Ncross and ηi as follows:
To extend the single-cluster PIC simulation results to the entire area of the plasma channel, we must calculate the number of clusters in the plasma channel that will interact with the unperturbed intensity. Each cluster, which is characterized by its radius r and density n0, can be represented by the effective area, which, in turn, is the area of the laser field that was affected by the interaction with the cluster. This effect is shown in Figures 2A, B, which show slices of the 2D intensity profile on a log scale from PIC simulations before and after interaction with
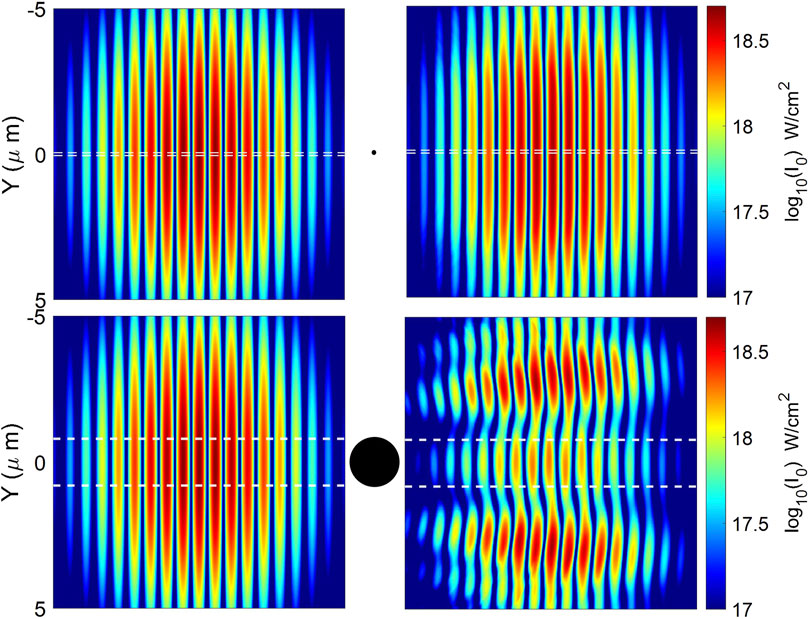
Figure 2. Intensity map from 2D PIC simulation before (left) and after (right) the interaction with the clusters with r = 50 nm (top) and r = 800 nm (bottom). The black circles illustrate the position of the cluster. Horizontal dashed lines indicate the radius of the cluster.
To avoid extensive PIC simulations, it is necessary to find a suitable model that will describe the area of the laser beam that will be affected by the cluster depending on its size. In this work, the cluster radii are assumed to be in the range
The number of clusters Ncross that will interact with unattenuated intensity I0 can be calculated by dividing the plasma channel area Abeam by the effective area of a single cluster Seff.
Next, we need to calculate the effect of ηi from Equation 5 for
The PIC simulations with a fixed target (r=50 nm and n0=100∙ncrit) and various intensities showed that proton energy cutoff
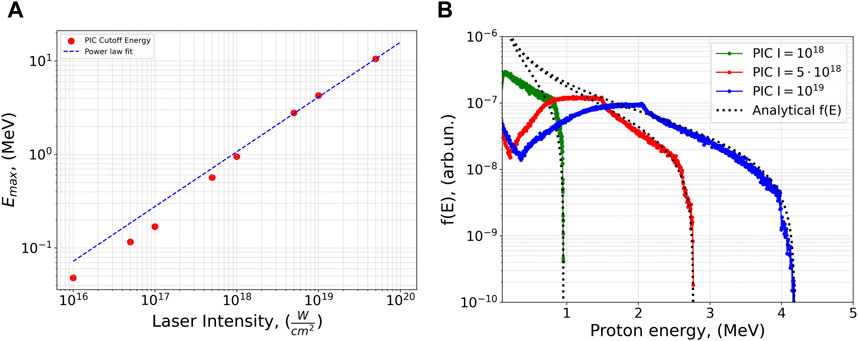
Figure 4. (A) PIC cutoff energies and power law fit for a cluster with r = 50 nm and n0 = 100 ncrit. (B) Normalized PIC proton energy spectrum for various laser intensities I and analytical probability density function (PDF) based on equations derived by [39].
Reconstructed energy spectrums f(E), in turn, are used to calculate the single-cluster fusion parameter η0 introduced in Equation 4 with the cross-section data for protons with energies in a broad range
Here,
Bayesian optimization is a method well suited for optimization problems that are characterized by computationally intensive calculations, such as PIC simulations [41]. It is used to optimize the black-box objective function, such as the net fusion parameter ηnet described in Equation 7. Thus, ηnet was chosen as the objective function (a function that is minimized in the optimization process). The BO method uses a surrogate model to estimate the objective function. This model plays a dual role: it attempts to predict the objective function’s output and quantifies the uncertainty associated with those predictions, thus allowing us to assess the parameter space and sample the next points from it. For the given parameter space, a Gaussian process regression model is used as a standard surrogate model best suited for low-dimensional (n=4) optimization problems [42]. The expected improvement (EI) acquisition function is chosen due to its good balance between exploration and exploitation [43], ensuring a systematic optimization approach.
The parameter space that needs to be optimized includes the cluster radius r, density n0, laser intensity I0, and pulse duration τ and is shown in Table 1. The laser intensity I0 range was chosen based on the reasonable range of proton energies that can contribute to the p-B11 fusion reaction. The cross-section rapidly decreases for protons with energies above 9 MeV and below 150 keV. The pulse duration was added to control the total laser energy while keeping the intensity I0 the same and maintaining the ultrafast character of the interaction, which has a major impact on the CE process.
The optimization process is orchestrated by a master script, which serves as the primary controlling entity coordinating the entire optimization workflow. The master script connects to the high-performance computing (HPC) cluster and selects initial parameters for the optimization. It generates the necessary input files and submits the simulations to the HPC workload manager, monitoring their progress until completion. Post-processing scripts, initiated by the master script, process the output data from the PIC simulations. As a result, the net fusion parameter ηnet is used to update the surrogate model. The EI acquisition function determines the next point to sample from the search space. The process iterates, with the updated surrogated model generating new points to evaluate until convergence criteria are met.
The optimization results show that an increase in the single-cluster number density n0 leads to an enhancement of the net fusion parameter ηnet. This is clear from Equation 7, where an increase in the cluster number density will result in an increase in the proton cutoff energy through enhanced Coulomb explosion and will not affect the laser energy attenuation. If other parameters are fixed, the cluster with higher density would produce more energetic protons and, therefore, will have higher ηnet due to the CE energy spectrum that is proportional to the square root of energy
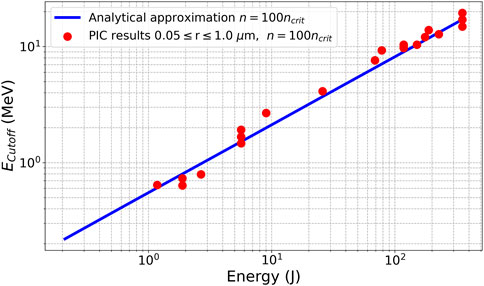
Figure 5. Various proton energy cutoffs from PIC simulations and analytical approximation cutoff energy dependency on the laser energy.
Figures 6A, B show the evolution of various net fusion parameters ηnet and intensity attenuation during propagation inside the plasma channel under different initial conditions. The x-axis shows a dimensionless distance into the plasma channel normalized to the average inter-cluster distance. As we propagate deeper into the plasma channel, we consider interactions with more clusters, and the net fusion parameter increases, while the laser energy decreases due to the interaction with the clusters. The saturation plateau in the fusion parameter is reached in all cases and indicates that a significant part of the laser energy has been lost, and the remaining energy is not sufficient to produce a strong CE of the clusters. In the case of a large radius, the plateau is reached within few iterations, while a small cluster requires several tens of iterations depending on the radius until reaching a plateau. The moderate intensities in the range 5⋅1017–1018 W/cm2 (red and black lines in Figure 6), regardless of cluster parameters, have higher ηnet than the high laser intensities (blue and green lines).
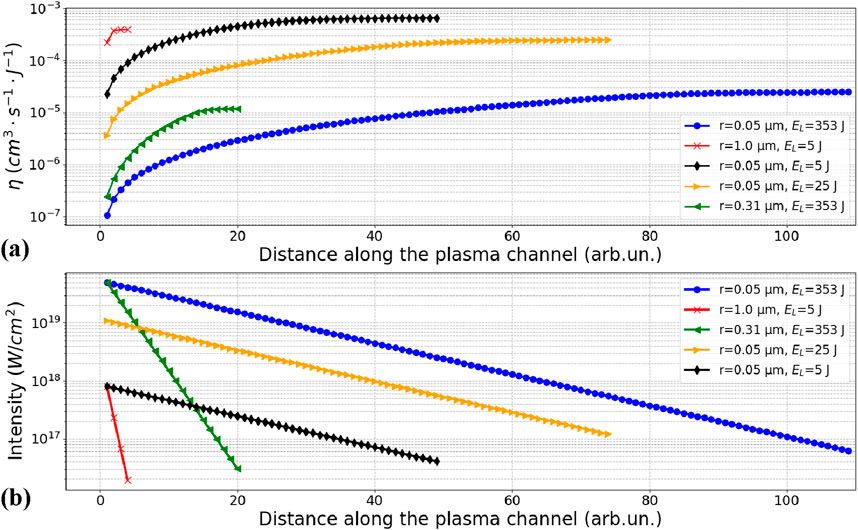
Figure 6. (A) Evolution of the net fusion parameter after the interaction with the Nth “row” of clusters according to Equation 5. (B) Decay of laser intensity attenuated by the interaction with N clusters.
This result confirms the existence of optimal energy for a given radius, where ηnet might be several orders of magnitude larger than in the high-laser energy case. Therefore, for given cluster parameters, ηnet is expected to exhibit a maximum at a certain moderate laser energy. This will be the optimal laser energy for a given cluster.
To verify the existence of an optimum laser energy for a given cluster and efficiently visualize the 4D parameter space, we consider the laser energy as a single parameter representing the laser intensity and pulse duration, while cluster parameters are categorized into four separate groups depending on the density and radius, as shown in Table 2, which will allow us to identify the edge points for the cluster parameter space:
Splitting the various cluster parameters into different types will allow us to visualize the effect of all parameters on the net fusion parameter ηnet, which is shown in Figure 7. The small and large high-density clusters ηnet lie well above all other results and show an efficiency peak at a laser energy close to 2–6 J, while the clusters with low density, regardless of their radius, typically have the lowest fusion parameter ηnet, as expected from (7), while most of the cases that fall in between the cluster types given in Table 2 lie within the dashed lines connecting the highest and lowest ηnet. Each of the types indicates the existence of a subtle peak within the laser energy range
Thus, the highest energy efficiency requires a high-density cluster interacting with moderate laser energies. This provides the general direction for the parameter space to reach high energy efficiency. These results were obtained by analyzing all BO outputs. In addition to that, the BO algorithm identified the optimal combination of radius and laser energy within the given parameter space that will lead to the highest energy efficiency.
The following parameters provided the best results: radius r = 50 nm, density n = 100 ncrit cm-3, I0 =
The convergence plot that illustrates the average and best ηnet evolution as a function of BO iteration is shown in Figure 8. Each Bayesian optimization iteration consists of four independent PIC simulations with different laser and plasma parameters. The net fusion parameter ηnet was calculated based on the results of PIC simulations, and the results were used to update the surrogate model. The EI acquisition function samples the next four points from the parameter space to evaluate ηnet, based on accumulated knowledge. The boundary values for each parameter can vary by few orders of magnitude. This variability provides a broad operational range for parameters such as intensity and radius to identify the optimum. Therefore, even after identifying promising values, the EI continues to explore untested parameters before returning to the best conditions that result in a gradual increase in the average ηnet.
The smallest radius from the BO parameter space (Table 1)
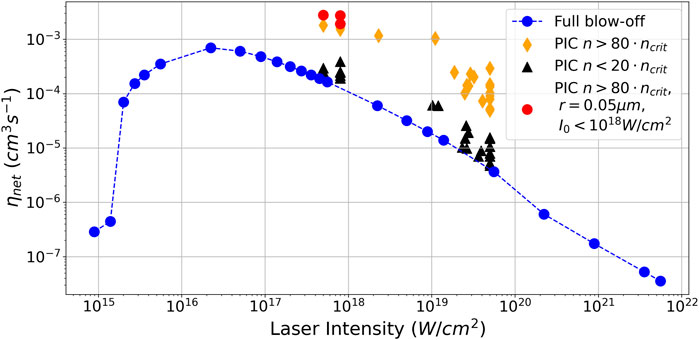
Figure 9. BO optimization ηnet for dense clusters and theoretically calculated η based on the equations derived by [45].
We introduced a method for optimizing p-B11 fusion during the interaction of high-intensity lasers confined inside the plasma channel with clusters. The interaction is optimized so that cluster CE results in a generation of MeV protons and presents several key advantages. Based on our previous experimental works, which demonstrated laser guiding through the plasma channel over long distances, we can effectively increase the interaction length in the proposed scheme. Other advantages demonstrated in this paper include the use of a nanocluster CE approach that leads to the efficient conversion of laser energy to high-energy protons. In addition to that, the CE-based scheme yields a more favorable energy spectrum than the conventional thin-foil targets [46].
Through 2D PIC simulations guided by the BO algorithm, we optimized key interaction parameters such as laser energy and cluster radius and density. The optimization not only aids in identifying optimal conditions for high fusion energy efficiency but also allows us to explore the parameter space and draw conclusions on each of the parameters that can affect the result. Our findings show that high-density clusters, given in Table 2, have higher energy efficiency than low-density clusters due to the increase in the expelled electrons without adversely affecting the laser energy. The cluster radius has an optimum value, which lies between r = 2 nm and r = 50 nm. Additionally, for any given cluster radius and number density within the parameter space, maintaining a moderate laser intensity
BO is particularly suited for complex, computationally demanding problems such as laser–plasma PIC simulations. The probabilistic approach of BO allows it to systematically sample the parameter space, reducing the risk of becoming trapped in a local minimum of the black-box function. The method is well adaptable to unknown, non-linear relationships between input parameters and the output, which are typical for complex laser–plasma interaction problems. This adaptability is crucial for accurately identifying the optimal conditions. The model in BO is continuously updated with each new data point, refining predictions. This feature is particularly beneficial for future experiments with the proposed fusion scheme, where results are received after each laser pulse.
In the future, there will be a need to develop more complex optimization models to account for realistic experiment factors, such as the real spatial profile of the beam, finite precision of the focal-spot position, local density perturbations in the plasma channel, and cluster size distribution. Another limitation of the 2D PIC simulations is the overestimation of the proton energies in cluster Coulomb explosions due to the logarithmic divergence of the accelerating potential in 2D. Therefore, it would be beneficial to perform a series of 3D PIC simulations to obtain a more accurate representation of the energy spectrum and cutoff energies. Despite that, current results serve as a solid starting point for future experiments with the proposed scheme. Additionally, the results presented demonstrate the pivotal role of advanced computational techniques, such as BO, in investigating and optimizing the p-B11 fusion energy efficiency. Increasing the fusion energy gain remains an essential problem for advancing fusion as a sustainable energy source. Many p-B11 schemes that are currently investigated can benefit from these numerical optimization methods. It is well known that such methods tend to excel with large amounts of data. Thus, it is necessary to develop and integrate such tools into conventional PIC simulations and experiments. This will help accumulate data and accelerate research in the field of laser-based p-B11 fusion.
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
AK: writing–original draft, conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, and visualization. MB: writing–review and editing, conceptualization, methodology, project administration, supervision, and validation. AZ: writing–review and editing, conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, and validation.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
This work was partially supported by the Israel Ministry of Energy and the Center for Fusion Studies. The authors sincerely appreciate their support.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Tosca M, Molloy D, McNamee A, Pleskunov P, Protsak M, Biliak K, et al. Plasma polymers as targets for laser-driven proton-boron fusion. Front Phys (2023) 11. doi:10.3389/fphy.2023.1227140
2. Last I, Ron S, Jortner J. Aneutronic H+B11 nuclear fusion driven by Coulomb explosion of hydrogen nanodroplets. Phys Rev A (2011) 83:043202. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.83.043202
3. Daido H, Nishiuchi M, Pirozhkov AS. Review of laser-driven ion sources and their applications. Rep Prog Phys (2012) 75:056401. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/75/5/056401
4. Istokskaia V, Tosca M, Giuffrida L, Psikal J, Grepl F, Kantarelou V, et al. A multi-MeV alpha particle source via proton-boron fusion driven by a 10-GW tabletop laser. Commun Phys (2023) 6(6):27–8. doi:10.1038/s42005-023-01135-x
5. Bonvalet J, Nicolaï P, Raffestin D, D’Humieres E, Batani D, Tikhonchuk V, et al. Energetic α -particle sources produced through proton-boron reactions by high-energy high-intensity laser beams. Phys Rev E (2021) 103:053202. doi:10.1103/PHYSREVE.103.053202
6. Liu AD, Liu ZY, Li K, Yao YL, Zhou CT, Zhu SP, et al. Enhancement of proton-boron nuclear reactions by utilizing a meshed catcher target. Phys Rev Appl (2023) 20:034053. doi:10.1103/PHYSREVAPPLIED.20.034053
7. Daido H, Nishiuchi M, Pirozhkov - AS, Jang S, Kwon R-Y, Linker JA, et al. Perspectives on research on laser driven proton-boron fusion and applications. J Instrumentation (2023) 18:C09012. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/18/09/C09012
8. Turcu ICE, Margarone D, Giuffrida L, Picciotto A, Spindloe C, Robinson APL, et al. Borane (B m H n), Hydrogen rich, Proton Boron fusion fuel materials for high yield laser-driven Alpha sources. J Instrumentation (2024) 19:C03065. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/19/03/C03065
9. Gruenwald J, Teodorescu C. Novel target design for a laser-driven aneutronic fusion reactor. Fusion Eng Des (2020) 151:111397. doi:10.1016/J.FUSENGDES.2019.111397
10. McKenzie W, Batani D, Mehlhorn TA, Margarone D, Belloni F, Campbell EM, et al. HB11—understanding hydrogen-boron fusion as a new clean energy source. J Fusion Energy (2023) 42:17–0. doi:10.1007/s10894-023-00349-9
11. Kong D, Xu S, Shou Y, Gao Y, Mei Z, Pan Z, et al. Alpha-particle generation from H-11B fusion initiated by laser-accelerated boron ions. Laser Part Beams (2022) 2022:e7. doi:10.1155/2022/5733475
12. Ribeyre X, Capdessus R, Wheeler J, d’Humières E, Mourou G. Multiscale study of high energy attosecond pulse interaction with matter and application to proton–Boron fusion. Scientific Rep (2022) 12:4665–14. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-08433-4
13. Azizi N, Hora H, Miley GH, Malekynia B, Ghoranneviss M, He X. Threshold for laser driven block ignition for fusion energy from hydrogen boron-11. Laser Part Beams (2009) 27:201–6. doi:10.1017/S0263034609000263
14. Ochs IE, Fisch NJ. Lowering the reactor breakeven requirements for proton-boron 11 fusion. Phys Plasmas (2024) 31:12503. doi:10.1063/5.0184945
15. Scholz M, Król K, Kulińska A, Karpiński L, Wójcik-Gargula A, Fitta M. On the possibility of initiating the proton–boron nuclear fusion reaction in the plasma-focus device. J Fusion Energy (2019) 38:522–30. doi:10.1007/s10894-019-00225-5
16. Baccou C, Depierreux S, Yahia V, Neuville C, Goyon C, De Angelis R, et al. New scheme to produce aneutronic fusion reactions by laser-accelerated ions. Laser Part Beams (2015) 33:117–22. doi:10.1017/S0263034615000178
17. Labaune C, Baccou C, Yahia V, Neuville C, Rafelski J. Laser-initiated primary and secondary nuclear reactions in Boron-Nitride. Scientific Rep (2016) 6:21202–8. doi:10.1038/srep21202
18. Gruenwald J. Proposal for a novel type of small scale aneutronic fusion reactor. Plasma Phys Control Fusion (2016) 59:025011. doi:10.1088/1361-6587/59/2/025011
19. Volosov VI. Aneutronic fusion on the base of asymmetrical centrifugal trap. Nucl Fusion (2006) 46:820–8. doi:10.1088/0029-5515/46/8/007
20. Giuffrida L, Belloni F, Margarone D, Petringa G, Milluzzo G, Scuderi V, et al. High-current stream of energetic α particles from laser-driven proton-boron fusion. Phys Rev E (2020) 101:013204. doi:10.1103/physreve.101.013204
21. Margarone D, Morace A, Bonvalet J, Abe Y, Kantarelou V, Raffestin D, et al. Generation of α-particle beams with a multi-kJ, peta-watt class laser system. Front Phys (2020) 8:561410. doi:10.3389/fphy.2020.00343
22. Schwoerer H, Pfotenhauer S, Jäckel O, Amthor KU, Liesfeld B, Ziegler W, et al. Laser-plasma acceleration of quasi-monoenergetic protons from microstructured targets. Nature (2006) 439:445–8. doi:10.1038/nature04492
23. Lübcke A, Andreev AA, Höhm S, Grunwald R, Ehrentraut L, Schnürer M. Prospects of target nanostructuring for laser proton acceleration. Scientific Rep (2017) 7:44030–8. doi:10.1038/srep44030
24. Zigler A, Palchan T, Bruner N, Schleifer E, Eisenmann S, Botton M, et al. 5.5-7.5A MeV proton generation by a moderate-intensity ultrashort-pulse laser interaction with H2O nanowire targets. Phys Rev Lett (2011) 106:134801. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.134801
26. Mehlhorn TA, Labun L, Hegelich BM, Margarone D, Gu MF, Batani D, et al. Path to increasing p-B11 reactivity via ps and ns lasers. Laser Part Beams (2022) 2022:e1. doi:10.1155/2022/2355629
27. Krainov VP. Theory of laser induced fusion in compound boron-hydrogen microdroplets. Contrib Plasma Phys (2005) 45:198–203. doi:10.1002/CTPP.200510021
28. Kaganovich D, Ting A, Moore CI, Zigler A, Burris HR, Ehrlich Y, et al. High efficiency guiding of terawatt subpicosecond laser pulses in a capillary discharge plasma channel. Phys Rev E (1999) 59:R4769–72. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.59.R4769
29. Ehrlich Y, Cohen C, Zigler A, Krall J, Sprangle P, Esarey E. Guiding of high intensity laser pulses in straight and curved plasma channel experiments. Phys Rev Lett (1996) 77:4186–9. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.4186
30. Shalloo RJ, Dann SJD, Gruse JN, Underwood CID, Antoine AF, Arran C, et al. Automation and control of laser wakefield accelerators using Bayesian optimization. Nat Commun (2020) 11:6355–8. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20245-6
31. Jalas S, Kirchen M, Messner P, Winkler P, Hübner L, Dirkwinkel J, et al. Bayesian optimization of a laser-plasma accelerator. Phys Rev Lett (2021) 126:104801. doi:10.1103/PHYSREVLETT.126.104801
32. Irshad F, Karsch S, Döpp A. Multi-objective and multi-fidelity Bayesian optimization of laser-plasma acceleration. Phys Rev Res (2023) 5:013063. doi:10.1103/physrevresearch.5.013063
33. Djordjević BZ, Kemp AJ, Kim J, Simpson RA, Wilks SC, Ma T, et al. Modeling laser-driven ion acceleration with deep learning. Phys Plasmas (2021) 28:43105. doi:10.1063/5.0045449
34. Döpp A, Eberle C, Howard S, Irshad F, Lin J, Streeter M. Data-driven science and machine learning methods in laser–plasma physics. High Power Laser Sci Eng (2023) 11:e55. doi:10.1017/hpl.2023.47
35. Schulz E, Speekenbrink M, Krause A. A tutorial on Gaussian process regression: modelling, exploring, and exploiting functions. J Math Psychol (2018) 85:1–16. doi:10.1016/J.JMP.2018.03.001
36. Krushelnick K, Ting A, Moore CI, Burris HR, Esarey E, Sprangle P, et al. Plasma Channel formation and guiding during high intensity short pulse laser plasma experiments. Phys Rev Lett (1997) 78:4047–50. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.4047
37. Arber TD, Bennett K, Brady CS, Lawrence-Douglas A, Ramsay MG, Sircombe NJ, et al. Contemporary particle-in-cell approach to laser-plasma modelling. Plasma Phys Control Fusion (2015) 57:113001. doi:10.1088/0741-3335/57/11/113001
38. Wriedt T. Mie theory: a review. Springer Ser Opt Sci (2012) 169:53–71. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-28738-1_2
39. Islam MR, Saalmann U, Rost JM. Kinetic energy of ions after Coulomb explosion of clusters induced by an intense laser pulse. Phys Rev A (2006) 73:041201. doi:10.1103/PHYSREVA.73.041201
40. Tentori A, Belloni F. Revisiting p-11B fusion cross section and reactivity, and their analytic approximations. Nucl Fusion (2023) 63:086001. doi:10.1088/1741-4326/ACDA4B
41. Jones DR, Schonlau M, Welch WJ. Efficient global optimization of expensive black-box functions. J Glob Optimization (1998) 13:455–92. doi:10.1023/A:1008306431147
42. Rasmussen CE, Williams CKI. Gaussian processes for machine learning. Gaussian Process Machine Learn (2005). doi:10.7551/MITPRESS/3206.001.0001
44. Last I, Jortner J. Nuclear fusion induced by Coulomb explosion of heteronuclear clusters. Phys Rev Lett (2001) 87:033401–4. doi:10.1103/PHYSREVLETT.87.033401
45. Nishihara K, Amitani H, Murakami M, Bulanov S, Esirkepov T High energy ions generated by laser driven Coulomb explosion of cluster, 464 (2001).
46. Mora P. Plasma expansion into a vacuum. Phys Rev Lett (2003) 90:185002. doi:10.1103/PHYSREVLETT.90.185002
47. Margarone D, Velyhan A, Dostal J, Ullschmied J, Perin JP, Chatain D, et al. Proton acceleration driven by a nanosecond laser from a cryogenic thin solid-hydrogen ribbon. Phys Rev X (2016) 6:041030. doi:10.1103/physrevx.6.041030
48. Macchi A, Borghesi M, Passoni M. Ion acceleration by superintense laser-plasma interaction. Rev Mod Phys (2013) 85:751–93. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.85.751
Keywords: proton–boron fusion, high-intensity laser, laser–plasma acceleration, Coulomb explosion, Bayesian optimization
Citation: Kim A, Botton M and Zigler A (2024) Bayesian optimization of proton generation in terawatt laser–CH2 cluster interactions within a plasma channel. Front. Phys. 12:1424755. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1424755
Received: 28 April 2024; Accepted: 26 August 2024;
Published: 10 September 2024.
Edited by:
Noaz Nissim, Soreq Nuclear Research Center, IsraelReviewed by:
Emmanuel D’Humières, Université de Bordeaux, FranceCopyright © 2024 Kim, Botton and Zigler. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Artem Kim, a2ltdGVtMUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.