- Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, Keio University, Yokohama, Japan
In 1952, Alan Turing accomplished a pioneering theoretical study to show that the coupling of nonlinear chemical reactions and diffusion leads to the instability of spatially homogeneous states. The activator and inhibitor are synthesized as intermediates of the reaction system in the Turing model. Turing found that spatially periodic stationary concentration patterns are spontaneously generated when the diffusion coefficient of the activator is lower than that of the inhibitor. The first experimental realization of the Turing pattern was achieved in 1990 in a chlorite–iodide–malonic acid (CIMA) reaction system. Iodide and chlorite anions act as the activator and inhibitor of this reaction system, respectively. Although there is no significant difference in the diffusion coefficient of iodide and chlorite anions, the Turing pattern was generated because starch was added to the gel reactor to enhance the color tone. This formed a complex with iodide to inhibit its diffusion to satisfy the condition for the Turing instability. Several examples were found after this finding. We focused on the high affinity of quaternary alkyl ammonium cations to iodide. The CIMA reaction was performed in an open gel reactor by adding a quaternary alkyl ammonium cationic surfactant. In addition, the polymer gel consists of the quaternary alkyl ammonium group as the side chain was utilized for the open gel reactor. The micelles of the surfactants and the polymer gels trapped iodide in their vicinity as a counter anion to lower the effective diffusivity to satisfy the condition for the Turing instability.
1 Introduction
Spatially periodic stationary patterns are ubiquitous in nature, and their representative examples include the body surfaces of animals such as the angelfish, zebra, and tiger. Pigments form spatially periodic concentration patterns spontaneously on the body surface of those animals. Alan Turing developed a theoretical model to explain that even artificial chemical systems can generate spatially periodic stationary concentration patterns by the coupling of nonlinear chemical reactions and diffusion [1].
However, the real chemical reaction system generating spatially periodic stationary concentration patterns had not been found for nearly four decades. The first experimental realization of the Turing pattern was achieved in 1990 in a chlorite–iodide–malonic acid (CIMA) reaction system by the Bordeaux’s group [2]. After this finding, several examples of Turing patterns were observed in CIMA reaction systems.
In this mini-review, the fundamental concept of the Turing pattern formation is explained, and its relevance to the concept of the dissipative structure, i.e., self-organization in far-from-equilibrium systems [3–7], is discussed. In addition, the Turing pattern formation in the CIMA reaction system in the presence of quaternary alkyl ammonium cations [8] is precisely introduced.
2 Concept of Turing pattern formation
The concept of dissipative structures, i.e., self-organization in far-from-equilibrium systems, proposed by Ilya Prigogine in 1955 explains how chemical systems have become unstable to fluctuations to let them grow by irreversible entropy-producing dissipative processes, such as heat conduction, diffusion, and reaction, to spontaneously generate temporal, spatial, and spatiotemporal patterns [3–7]. However, in 1952, 3 years before the proposition of the concept of dissipative structures, Alan Turing developed a theoretical model to show that the coupling of nonlinear chemical reactions and diffusion makes the spatial homogeneity of the chemical system unstable to generate spatially periodic stationary concentration patterns [1].
Turing reported the reaction–diffusion systems consist of chemical substances that are regarded as morphogens, i.e., the substance accounting for the main phenomenon of morphogenesis. The theoretical model was the coupling of ordinary chemical reactions and ordinary diffusion. However, chemical reactions are not simple but form a complex chemical reaction network (Figure 1) similar to the metabolic pathway. In this system, chemical substances X and Y were regarded as morphogens, and A and B were regarded as fresh reactants taken from outside the chemical system and a waste product discarded to the outer environment of the chemical system, respectively. Turing determined that instability to the spatially inhomogeneous fluctuation arises when the intermediate chemical species X and Y act as the activator and inhibitor, respectively, and the diffusion coefficient of the inhibitor is larger than that of the activator. The time evolution of the concentration of X and Y is presented as follows:
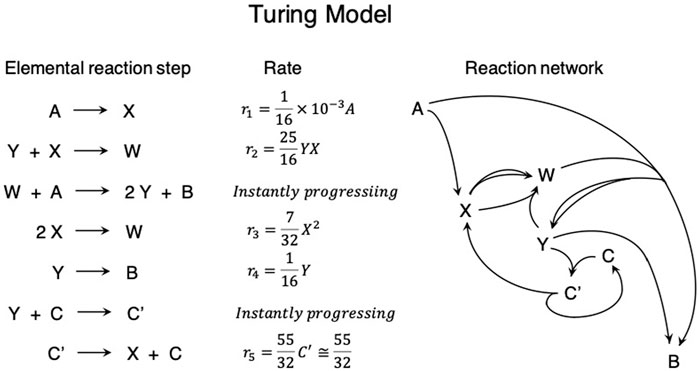
Figure 1. Schematic illustration for explaining Alan Turing’s idea for the chemical system generating a spatially periodic stationary concentration pattern as the result of the instability of the spatially homogeneous state.
The concentration of A does not appear in this equation because it is not a variable, but it is a constant by making the rate of supplying A into the chemical system equal to its rate of consumption by the chemical reactions. Because all reactions with W or C as the reactants instantly progress, their concentrations also do not appear in this equation. In addition, the concentration of C’ is also regarded as a constant because its production uses the instantly progressing process. The steady-state solutions for the concentrations of X and Y,
X and Y are regarded as the inhibitor and activator, respectively [6, 9, 10].
To evaluate the stability of this steady state to the spatially inhomogeneous fluctuation, the property of the reaction–diffusion equation,
should be analyzed. Here,
3 Forty years of journey to the experimental realization of Turing pattern formation in the CIMA reaction system
In spite of active and extensive research for the generation of the Turing pattern in a real chemical reaction system after Alan Turing’s historic theoretical study, its experimental realization had not been achieved for nearly four decades. In 1977, an example of a spatially periodic stationary pattern was found to be generated in chemical systems [11]. It was once believed that it was the first experimental realization of the Turing pattern. However, these structures were later shown to be generated by convection. The greatest challenge in the experimental realization of the Turing pattern was determining the condition under which the inhibitor diffuses more rapidly than the activator.
The first experimental realization of the Turing pattern was successful in 1990 using the CIMA reaction system by the Bordeaux’s group [2]. However, the initial purpose of this research was not the generation of the Turing pattern but the generation of the sustained chemical oscillation in the open gel reactor. They used a polyacrylamide hydrogel plate as the reaction medium to prevent convection. The hydrogel plate was then attached with circulating reservoir solutions containing reactants of the CIMA reactions. The reactants were then diffused from the circulating reservoir solutions into the hydrogel plate, and the waste products were discharged to the circulating reservoir solutions to make the polyacrylamide hydrogel plate the open chemical system. The CIMA reaction was known to generate chemical oscillation [12, 13]. Because the behavior of the CIMA reaction after the initial induction period resembles that of the chlorine dioxide–iodine–malonic acid (CDIMA) reaction, the mechanism of the CIMA reaction after the initial induction period can be regarded as that of the CDIMA reaction in which the activator, I−, and inhibitor, ClO2−, were generated as the intermediates [14, 15]. To enhance the visibility of chemical oscillation, starch was added to the acrylamide monomer solution as the color indicator before polymerization to prepare the hydrogel plate. Starch forms a complex with the triiodide anion and shows a blue–violet color. Thus, it is not only a color indicator but also traps the activator, I−, that forms the triiodide anion with an iodine molecule contained in excess in this chemical reaction system to lower the effective diffusivity. Although there is no significant difference in the diffusion coefficient of iodide and chlorite anions, the Turing pattern was found to be generated in this chemical reaction system in the open gel reactor. The condition under which Turing instability is realized was accidentally achieved in this way.
After this finding, extensive studies were conducted to determine the chemical system, in which Turing pattern formation could be experimentally realized. It was found that the CDIMA reaction also causes Turing instability in the open gel reactor containing starch [16]. In addition, the condition was found for the isolated CDIMA reaction solution containing starch to generate a transient Turing pattern [17]. Lowering the effective diffusivity of I− was achieved not only by starch but also polyvinyl alcohol contained in the open gel reactor to generate the Turing instability [18]. The CDIMA reaction in the polyacrylamide hydrogel plate that was prepared using a high concentration of a cross-linking agent also led to Turing pattern formation [19].
Not only CIMA and CDIMA reactions but also other nonlinear chemical reaction systems were found to give rise to Turing instability. Turing pattern formation was observed in a ferrocyanide–iodate–sulfite reaction system in an open one-side-fed reactor [20–22]. The Belousov–Zhabotinsky (BZ) reaction in a water-in-oil aerosol OT (AOT) micro-emulsion system was also found to realize Turing instability [23]. In this case, the higher solubility of Br2 in the continuous oil phase makes the effective diffusivity of the inhibitor, Br−, considerably larger than that of the activator, HBrO2, to satisfy the conditions of the Turing pattern formation. Quantitative analyses were conducted by utilizing the model proposed on the basis of the behavior of this chemical system, and five out of the six structures predicted by Turing were observed [24]. In addition, recent tomography analysis revealed the generation of three-dimensional Turing patterns [25]. Stationary pH patterns were found to be generated in a thiourea–iodate–sulfite reaction system in a gel one-side-fed unstirred tank reactor [26]. Turing pattern formation was reported in the system based on the autocatalytic oxidation by hydrogen peroxide [27], iodate–sulfite–thiosulfate reaction [28], and bromate–sulfite–ferrocyanide reaction systems [29]. In addition to the studies of Turing pattern formation in pure chemical systems, attempts were made to generate Turing patterns in in vitro systems, and stationary patterns were found to be generated in a two-protein reaction–diffusion system [30].
4 Turing pattern formation by the CIMA reaction in the presence of quaternary alkyl ammonium cations
Quaternary alkyl ammonium cations are known to show high affinity to I−. It was reported that N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyl-N,N’-dioctadecylethylene-1,2-diamine acts as a ligand of the ion-selective electrode for iodide anion [31]. In addition, a high counter-ion selectivity of the dodecyltrimethylammonium cation toward I− was observed for ion flotation [32, 33]. These properties of the quaternary alkyl ammonium cations motivated us to utilize them to lower the diffusivity of I− generated in the CIMA reaction system and satisfy the condition for the Turing pattern formation. Two types of attempts were made for the CIMA reaction in the open gel reactor. One was the addition of the quaternary alkyl ammonium amphiphile to the solution to form micelles to trap I− in their vicinity by selecting it as the counter anion. The other was utilizing a hydrophilic polymer with a quaternary alkyl ammonium cationic side chain as the hydrogel plate for an open gel reactor. In this case, I− was expected to be incorporated into the hydrophilic polymer as the counter anion.
Two types of hydrogel plates, PAM gel plate and P(DMAPAA-Q-AM) gel plate, were used as the open gel reactors. The PAM gel plate was prepared by the polymerization of acrylamide (AM) with a cross-liking reagent, N,N′-methylene bis-acrylamide (BAM). This gel plate was used for experiments where a quaternary alkyl ammonium amphiphile, n-dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB), was added to the reaction system. The P(DMAPAA-Q-AM) gel plate was prepared by the copolymerization of N,N-dimethylaminoethylacrylate methyl chloride quaternary salt (DMAEA-Q) and AM with BAM. Because the polymer itself possesses a quaternary alkyl ammonium cationic group, this gel plate was used for experiments in the absence of DTAB. The CIMA reaction was performed by flowing two reservoir solutions through the boxes to make the chemical reagents diffuse into the open gel reactor (Figure 2A) [8]. The gel plate along with a spacer was tucked between a pair of plastic boards with a circular hole with a diameter of 1.5 cm. This apparatus was then tucked between a pair of spacers and plastic boards with no holes. The entire system was clipped together, and the reservoir solutions were flowed continuously into the reservoir solution box, i.e., the space between the plastic board with a circular hole and the one without, to diffuse the chemical reagents into the open gel reactor. Reservoir A contained malonic acid (MA), KI, and H2SO4, whereas reservoir B contained KI, NaClO2, and DTAB. The flow rates of both reservoir solutions were 5.0 mL min−1, and they were flooded from the top of the spacer to keep the concentrations of all chemical reagents in the reservoir solutions constant. The temperature of the entire system was maintained at 25°C.
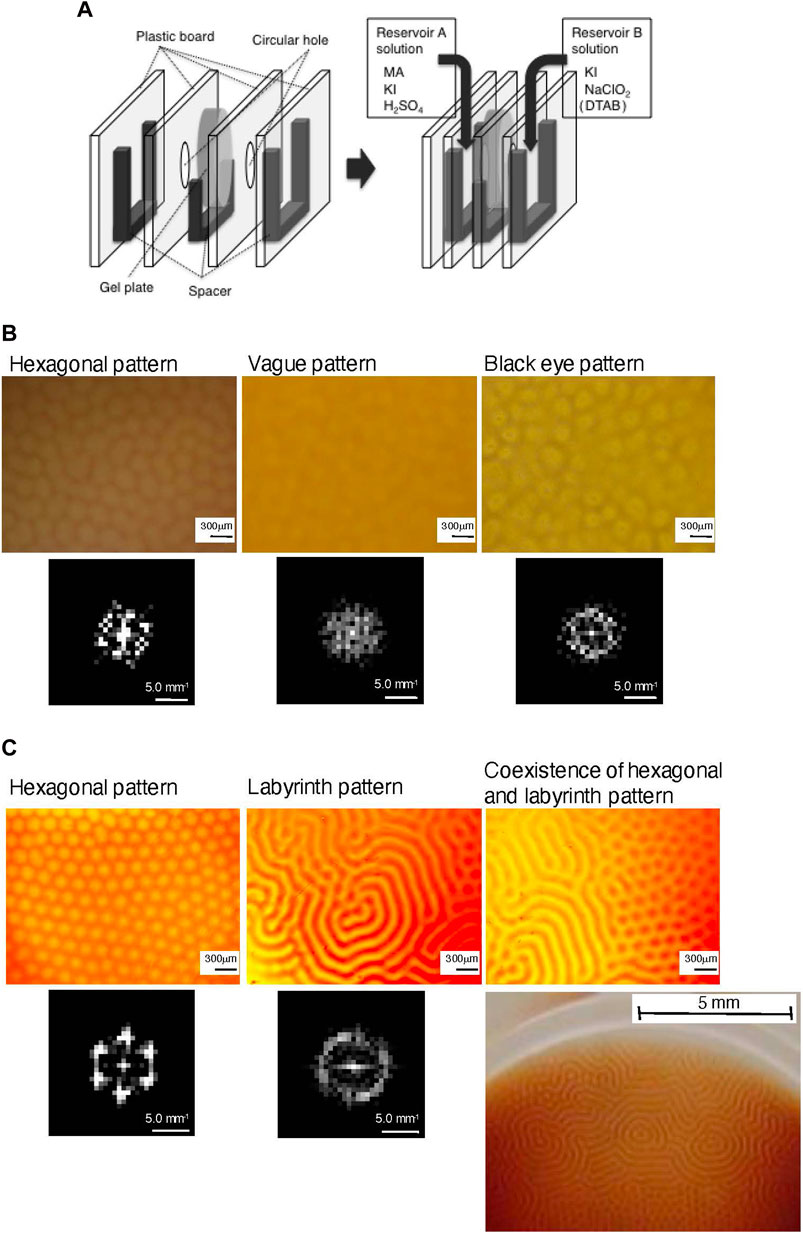
Figure 2. (A) Experimental setup for the open gel reactor. (B) Hexagonal, vague, and black eye patterns observed in the open PAM gel reactor by the CIMA reaction in the presence of DTAB. Two-dimensional spatial Fourier transform image of each pattern is shown below each pattern. (C) Hexagonal, labyrinth, and coexisting hexagonal and labyrinth patterns observed in the open P(DMAPAA-Q−AM) gel reactor by the CIMA reaction in the absence of DTAB. Two-dimensional spatial Fourier transform of hexagonal and labyrinth patterns is shown below each pattern. A picture of the coexistence of hexagonal and labyrinth patterns taken using a regular digital camera is also shown. (Reprinted with permission from ref 8. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society)
Three types of Turing patterns, hexagonal, vague, and black eye, were observed in the open PAM gel reactor when DTAB was added to the reservoir solution for the CIMA reaction (Figure 2B) [8]. All experiments were carried out by fixing the concentrations of the amphiphile at [DTAB] = 4.0 × 10−2 M in the reservoir B solution. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of DTAB and its corresponding iodide salt, DTAI, is 1.4–1.6 × 10−2 M [34] and 7.1 × 10−3 M [35], respectively, and the concentration of DTAB in the solution of reservoir B was higher than their CMC. Micelles of the n-dodecyltrimethylammonium anion are thus expected to be formed in at least two-thirds of the open gel reactor based on the exposed surface attached to the solution of reservoir B. The Turing pattern was observed in relatively large concentration regions for [KI] and [NaClO2] in the reservoir B solution by fixing the concentrations of KI, MA, and H2SO4 in the reservoir A solution at [KI] = 2.0 × 10−3 M, [MA] = 3.9 × 10−3 M, and [H2SO4] = 3.0 × 10−2 M. The Turing pattern was not generated in the control experiments where DTAB was not added to the reaction system. The spatial periodicity of these patterns was analyzed by two-dimensional spatial Fourier transform to obtain the power spectra (Figure 2B) [8].
In the case of the CIMA reaction in the P(DMAEA-Q-AM) gel reactor in the absence of DTAB, patterns with a significantly clear color contrast were generated, and a clear picture of the pattern using a regular digital camera was obtained in some cases (Figure 2C) [8]. By fixing the concentrations in the reservoir A solution at [MA] = 4.0 × 10−3 M, [KI] = 1.3 × 10−3 M, and [H2SO4] = 3.0 × 10−2 M, the Turing pattern was observed in relatively large concentration regions for [KI] and [NaClO2] in the reservoir B solution. They were hexagonal, and labyrinth patterns and coexisting hexagonal and labyrinth patterns were observed in some cases. The spatial periodicity of these patterns was analyzed by a two-dimensional spatial Fourier transform. Because the hexagonal pattern generated in the open P(DMAPAA-Q-AM) gel plate was significantly clearer than that generated in the open PAM gel reactor in the presence of DTAB, the power spectrum of the hexagonal pattern in this case also exhibited a clear hexagonal character (Figure 2B) [8].
5 Conclusion
Alan Turing studied the reaction–diffusion chemical system to show that well-known physical laws are sufficient to account for the main phenomenon of morphogenesis. Although the concept of the Turing pattern invented was categorized in the concept of dissipative structures, i.e., self-organization in far-from-equilibrium systems, its invention was 3 years before the proposition of the concept of dissipative structures by Ilya Prigogine. The Turing model showed that the coupling of nonlinear chemical reactions and diffusion leads to the instability of the spatially homogeneous state to form spatially periodic stationary concentration patterns. Two chemical species, the activator and inhibitor, were synthesized as intermediates of the nonlinear chemical reaction, and the diffusivity of the inhibitor should be higher than that of the activator for the Turing instability. The first example of the Turing pattern was realized in a CIMA system in an open gel reactor consisting of starch as the color-enhancing agent. In this case, iodide and chlorite anions were the activator and inhibitor, respectively, and the starch formed a complex with the iodide anion, the activator of this chemical system, to lower the diffusivity. The condition for the Turing instability was thus satisfied. After this finding, several experimental realizations of Turing patterns were reported. Among these examples, we successfully generated Turing patterns in a CIMA reaction system in an open gel reactor using micelles of a quaternary alkyl ammonium amphiphile and a polymer with a quaternary alkyl ammonium group as the side chain to inhibit the diffusivity of the iodide anion. In the latter case, significantly clear color tone patterns were observed.
Proposition of the concept of the Turing pattern formation [1], followed by its first experimental realization in the artificial chemical system [2], is regarded as the historic event in science. It led to extensive research on the relation between Turing pattern formation and biological pattern formation [36–39].
Author contributions
AA: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. KA: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Turing AM. The chemical basis of morphogenesis. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B (1952) 237:37–72. doi:10.1098/rstb.1952.0012
2. Castets V, Dulos E, Boissonade J, De Kepper P. Experimental evidence of a sustained standing Turing-type nonequilibrium chemical pattern. Phys Rev Lett (1990) 379:2953. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.2953
4. Nicolis G, Prigogine I. Self-organization in non-equilibrium systems. New York: John Wiley & Sons (1977).
5. Kondepudi DK, Prigogine I. Modern thermodynamics –From heat engines to dissipative structure. New York: John Wiley & Sons (1998).
6. Epstein IR, Pojman JA. An introduction to nonlinear chemical dynamics –Oscillations, waves, patterns, and chaos. New York: Oxford University Press (1998).
7. Epstein IR, Pojman JA, Steinbock O. Introduction: self-organization in nonequilibrium chemical systems. Chaos (2006) 16:037101. doi:10.1063/1.2354477
8. Asakura K, Konishi R, Nakatani T, Nakano T, Kamata M. Turing pattern formation by the CIMA reaction in a chemical system consisting of quaternary alkyl ammonium cationic groups. J Phys Chem (2011) 115:3959–3963. doi:10.1021/jp111584u
9. Lengyel I, Epstein IR. Modeling of Turing structures in the chlorite-iodide-malonic acid-starch reaction system. Science (1991) 251:650. doi:10.1126/science.251.4994.650
10. Lengyel I, Epstein IR. A chemical approach to designing Turing patterns in reaction-diffusion systems. Proc Nati Acad Sci (1992) 89:3977. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.9.3977
11. Möckel P. Photochemisch induzierte dissipative strukturen. Naturwissenschaften (1977) 64:224. doi:10.1007/BF00449978
12. De Kepper P, Epstein IR, Kustin K. A systematically designed homogeneous oscillating reaction: the arsenite-iodate-chlorite system. J Am Chem Soc (1981) 103:2133. doi:10.1021/ja00398a061
13. Orbán M, De Kepper P, Epstein IR, Kustin K. New family of homogeneous chemical oscillators: chlorite-iodate-substrate. Nature (1981) 292:816. doi:10.1038/292816a0
14. Lengyel I, Rabai G, Epstein IR. Systematic design of chemical oscillators. Part 65. Batch oscillation in the reaction of chlorine dioxide with iodine and malonic acid. J Am Chem Soc (1990) 112:4606. doi:10.1021/ja00167a103
15. Lengyel I, Rabai G, Epstein IR. Experimental and modeling study of oscillations in the chlorine dioxide-iodine-malonic acid reaction. J Am Chem Soc (1990) 112:9104–9110. doi:10.1021/ja00181a011
16. Lengyel I, Kadar S, Epstein IR. Quasi-two-dimensional Turing patterns in an imposed gradient. Phys Rev Lett (1992) 69:2729–2732. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.2729
17. Lengyel I, Kadar S, Epstein IR. Transient Turing structures in a gradient-free closed system. Science (1993) 259:493. doi:10.1126/science.259.5094.493
18. Noszticzius Z, Quyang Q, McCormick WD, Swinney HL. Effect of Turing pattern indicators on CIMA oscillators. J Phys Chem (1992) 96:6302. doi:10.1021/j100194a038
19. Lee KJ, McCormick WD, Swinney HL, Noszticzius Z. Turing patterns visualized by index of refraction variations. J Chem Phys (1992) 95:4048. doi:10.1063/1.461860
20. Lee KJ, McCormick WD, Ouyang Q, Swinney HL. Pattern formation by interacting chemical fronts. Science (1993) 261:192. doi:10.1126/science.261.5118.192
21. Lee KJ, Mccormick WD, Pearson JE, Swinney HL. Experimental-observation of self-replicating spots in a reaction-diffusion system. Nature (1994) 369:215. doi:10.1038/369215a0
22. Li G, Qi OY, Swinney HL. Transitions in two-dimensional patterns in a ferrocyanide-iodate-sulfite reaction. J Chem Phys (1996) 105:10830. doi:10.1063/1.472891
23. Vanag VK, Epstein IR. Pattern formation in a tunable medium: the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction in an Aerosol OT microemulsion. Phys Rev Lett (2001) 87:228301. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.228301
24. Tompkinsa N, Li N, Girabawe C, Heymann M, Ermentrout GB, Epstein IR, et al. Testing Turing’s theory of morphogenesis in chemical cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2014) 111:4397–402. doi:10.1073/pnas.1322005111
25. Bánsági TJ, Vanag VK, Epstein IR. Tomography of reaction-diffusion microemulsions reveals three-dimensional Turing patterns. Science (2011) 331:1309–1312. doi:10.1126/science.1200815
26. Horváth J, Szalai I, De Kepper P. An experimental design method leading to chemical Turing patterns. Science (2009) 324:772. doi:10.1126/science.1169973
27. Szalai I, Horváth J, Takács N, De Kepper P. Sustained self-organizing pH patterns in hydrogen peroxide driven aqueous redox systems. Phys Chem Chem Phys (2011) 13:20228–20234. doi:10.1039/C1CP22449B
28. Liu H, Pojman JA, Zhao Y, Pan C, Zheng J, Yuan L, et al. Pattern formation in the iodate–sulfite–thiosulfate reaction–diffusion system. Phys Chem Chem Phys (2012) 14:131. doi:10.1039/C1CP22281C
29. Molnár I, Szalai I. Pattern Formation in the bromate–sulfite–ferrocyanide reaction. J Phys Chem A (2015) 119:9954–9961. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.5b06545
30. Glock P, Ramm B, Heermann T, Kretschmer S, Schweizer J, Mucksch J, et al. Stationary patterns in a two-protein reaction-diffusion system. ACS Synth Biol (2019) 8:148–157. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.8b00415
31. Wotring VJ, Johnson DM, Bachas LG. Polymeric membrane anion-selective electrodes based on diquaternary ammonium salts. Annal Chem (1990) 62:1506–1510. doi:10.1021/ac00213a030
32. Kellaway L, Warr GG. The effect of head-group on selective counterion binding to cationic surfactants. J Colloid Interf Sci (1997) 193:312. doi:10.1006/jcis.1997.5050
33. Warr GG. Ion binding and the apparent selectivity coefficient for ion flotation. Langmuir (1997) 13:1451. doi:10.1021/la960634c
34. Mukerjee P, Mysels KJ. Critical micelle concentrations of aqueous surfactant systems. Washington, DC: US National Bureau of Standards (1971).
35. Mata J, Patel J, Jain N, Ghosh G, Bahadur P. Interaction of cationic surfactants with carboxymethylcellulose in aqueous media. J Colloid Interf Sci (2006) 297:797–804. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2005.11.022
36. Kondo S, Watanabe M, Miyazawa S, Turing AM. Studies of Turing pattern formation in zebrafish skin. Phil Trans R Soc A (2021) 379:20200274. doi:10.1098/rsta.2020.0274
37. Painter KJ, Ptashnyk M, Headon DJ. Systems for intricate patterning of the vertebrate anatomy. Phil Trans R Soc A (2021) 379:20200270. doi:10.1098/rsta.2020.0270
38. Murray DJ. Vignettes from the field of mathematical biology: the application of mathematics to biology and medicine. Interf Focus (2012) 2:397–406. doi:10.1098/rsfs.2011.0102
Keywords: Turing pattern formation, reaction–diffusion system, growth of spatiotemporal fluctuation, activator and inhibitor, chlorite–iodide–malonic acid reaction system, materials lowering the diffusivity of activators, quaternary alkyl ammonium group
Citation: Aizawa A and Asakura K (2024) Theory of Turing pattern formation and its experimental realization in the CIMA reaction system in the presence of materials lowering the diffusivity of activators. Front. Phys. 12:1358766. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2024.1358766
Received: 20 December 2023; Accepted: 05 July 2024;
Published: 31 July 2024.
Edited by:
Pawan Kumar, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, IndiaReviewed by:
Shinpei Tanaka, Hiroshima University, JapanSatoshi Nakata, Hiroshima University, Japan
Federico Rossi, University of Siena, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Aizawa and Asakura. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kouichi Asakura, YXNha3VyYUBhcHBsYy5rZWlvLmFjLmpw
 Amiko Aizawa
Amiko Aizawa Kouichi Asakura
Kouichi Asakura