- 1Laboratory for Zero-Carbon Energy, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Meguro, Japan
- 2Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Saitama University, Saitama, Japan
We studied the fission barrier of 236U with a microscopic mean-field model employing Skyrme-type effective interaction. It has been known that the microscopic mean-field calculation had a trend of overestimating the fission barriers derived from the fission cross section, and our results were found to be in accord with it. To reveal a major factor of the discrepancy, we investigated various components of the Skyrme energy-density functional building of the fission barrier height by a static mean-field model, including nuclear pairing correlation. We found that the spin-orbit and pairing terms affected the fine structure of the fission barrier as a function of elongation of the nucleus. Therefore, we investigated the sensitivity of the fission barrier height on the pairing strength, considering the change of level density along the calculated fission path.
1 Introduction
Nuclear fission arises as a result of large-amplitude collective motion in which a nucleus transforms into two or more nuclei, releasing a huge amount of binding energy in the form of kinetic energies of particles produced. Theoretical description of nuclear fission with microscopic models has attracted great interests not only in fundamental physics but also in nuclear applications [1, 2]. The nuclear fission has been one of the core topics in nuclear physics for more than 70 years since it has been discovered accidentally by German scientists. As a recent topic in fundamental physics such as nuclear astrophysics, nuclear fission is one of the key issues to understand nucleosynthesis in the rapid neutron-capture process (r-process) proceeding in the neutron star merger and supernova explosion [3, 4]. In nuclear engineering applications, accurate knowledge on nuclear fission is essential for safely operating nuclear reactors and predicting fission product yields in the reactor [5, 6]. For this purpose, one is tempted to employ theoretical models that should be able to treat “any” fissioning nuclei, because the yields of fission fragments from the region of superheavy elements (the endpoint of the r-process) are recycled to the start points of the r-process [7]. However, it is almost impossible to directly investigate the reaction mechanism of nuclear fission experimentally because the time scale from the ground state to scission is very short, about
There are many kinds of theoretical models to describe unique structure of finite nuclear systems [8–11]. Nuclei are self-bound systems consisting of a few hundred nucleons at most, in each of which an average potential or mean-field is formed. In the mean-field, there is a shell structure which makes the distribution of single-particle energies spaced unequally, and in which the nucleons occupy single-particle orbitals according to the Pauli principle, like electrons in an atomic system. Furthermore, there is a pairing correlation in nuclei that couples two nucleons in the time-reversed states to form a Cooper pair as described by BCS theory similar to the correlation in condensed matter physics [12]. The nuclear pairing correlation makes fractional occupation probabilities of the orbitals in the mean-field and has an essential role in forming the nuclear structure, including its shape. The mean-field and the pairing correlation are fundamental features of nuclei, and they affect strongly the fission mechanisms [13, 14]. Since the structures of nuclei depend on mass number, the theoretical model to describe fission phenomena should be able to treat nuclei comprehensively regardless of the mass number. Therefore, microscopic mean-field models with modern effective interactions and a pairing correlation have often been employed to study nuclear structure and fission. The modern effective interaction can be written with nuclear densities, and then it is also called the energy density functional (EDF). Several types of EDFs have been proposed with different contexts, such as relativistic [15–17] or non-relativistic [18–20], finite-range [21] or zero-range force [22], and so on. Although the mean-field model calculation with the EDF needs huge computational resources, we have been able to perform the theoretical studies for the nuclei without symmetry restrictions due to the recent progress in computer science.
Furthermore, a beyond mean-field model is also proposed to describe precisely the dynamical phenomena such as nuclear fission. The time-dependent generator-coordinate-method (TDGCM) is one of the methods to restore the spontaneous symmetry breaking [23]. In the TDGCM approach, the many-body wave function composes of a continuous or linear superposition of the single-Slater wave function. The stochastic mean-field model is also a skillful method for incorporating the quantum fluctuation [24]. In the stochastic methods, the statistical assumption in the microscopic treatment supplies the quantum fluctuation in the initial state of nuclear dynamics, and its effects propagate in the time evolution. The calculations with the stochastic method show a qualitative trend of fission fragment yield and the distribution of total kinetic energy [25, 26].
The many studies with the mean-field model calculation have shown the mass asymmetric distributions of fission fragments due to the shell structure of nuclei as mentioned above. They are consistent with experimental results and this fact offers a rational reason to choose the mean-field model to describe nuclear fission. Potential energy surfaces (PESs) concerning multi-dimensional deformations of the fissioning nuclei are often calculated with the mean-field model to investigate the fission path from the stable or metastable state to scission [27–29]. The studies using static PESs with the deformation constraints for quadrupole and octupole moments have been known to correspond with the fission product yields successfully [30, 31]. Even though these studies do not include dynamical and diabatic effects, they are useful for predicting fission barrier height, fission fragment yields, and other fission quantities [32, 33]. The fission barrier height is used to evaluate the fission cross sections in terms of the Hauser-Feshbach theory. Although the fission cross sections can be estimated from the fission barrier height evaluated by the available experimental data, the accuracy of the fission barriers is insufficient when there are a few experimental data that disagree with each other, which is the case for actinide nuclei [34]. This is so since the experimental fission barriers were evaluated to reproduce the fission cross sections or fission probabilities by the statistical models, which include extra parameters such as optical potential and level density which are different from analysis to analysis, then they affect the deduced barrier heights. The situation is worse, of course, for nuclei where there is no fission barrier data obtained experimentally.
The study of PES is a typical approach to predict the fission barrier height and has been able to reproduce a characteristic barrier structure with the double humps [35, 36]. Simple liquid-drop models fail to produce the double-humped structure, and then the spin-orbit coupling force is essential to reproduce the structure [37, 38]. The mean-field model calculation can reproduce the double-humped fission barrier via a complex competition among energy terms in the EDF, which simultaneously describes the ground states of nuclei for a whole nuclear chart. Although UNEDF1 [39], optimized including fission isomers observables, provides lower fission barriers, the mean-field calculations [40–42] tend to overestimate the fission barrier heights derived from the analysis of neutron-induced fission cross section [34]. The purpose of this work is to reveal the reasons for the discrepancy between theoretical and derived fission barrier heights by analyzing various components of a microscopic EDF. For this aim, we calculate the PES of 236U as a function of quadrupole and octupole deformations using the mean-field model with Skyrme EDF and pairing correlation, and focus on the energy components of the fission barrier to analyze the energy competition on the fission path. We apply the constrained Skyrme Hartree-Fock plus BCS model (CSHF + BCS) [43] to the PES calculation and investigate how the pairing strength affects the fission barrier height, using the level density near the Fermi energy on the PES.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2 we present the mean-field model to investigate the PES, and show the energy components in the Skyrme EDF and pairing correlation. The results of PES calculations using three Skyrme EDFs are shown and discussed in Section 3. We focus on the double-humped barrier shape, its heights for each EDF result, the competition among energy terms, and the effects of pairing strength. Finally, summary and conclusion are shown in Section 4.
2 Mean-field model and energy components in the model
We employ the constrained Skyrme Hartree-Fock plus BCS (CSHF + BCS) model to calculate the PES of 236U as a function of the quadrupole and octupole moments. The PES is obtained as difference of energies between states for various values of the quadrupole and octupole moments and that of the ground state. In this section, we explain briefly the CSHF + BCS model, various terms of the Skyrme EDF, and the characters of three Skyrme parameter sets (SkM* [40], SLy4 [44], SkI3 [45]) and show the specific forms of the constraints and the pairing correlation.
We can obtain wave functions |Ψ⟩ of quantum systems from the variational principle
where the
where
To calculate the PES as a function of quadrupole Q20 and octupole Q30 moments, we add constraints to the Hamiltonian as follows:
where l = 2, 3 are employed, and we take m = 0, 2 for l = 2 and m = 0, 1, 2, 3 for l = 3. The Qlm is the expectation value
We employed the Skyrme effective interactions [47] for the calculation of the EDF. The Skyrme EDF has about ten parameters tuned to reproduce the nuclear properties according to strategy of each parameter set. The total binding energy Etot is calculated as the expectation value of the Hamiltonian including the Skyrme interaction with |ΨBCS⟩, and we decomposed the Etot into seven terms:
where Ekin, Et0, Et1, t2, Et3, Els, ECoul, and Epair correspond to the kinetic, central, non-local, density-dependent, spin-orbit, Coulomb, and pairing energy terms. Et0 is deduced from only δ(r) terms, Et1, t2 corresponds to the momentum-dependent terms, and Et3 contains the density-dependent term: ρα, where the
For the pairing correlation, we employ the monopole-type pairing functional; the smoothed constant G model [48]. Although the pairing functional does not include the density dependent term such as Ref. [49], the pairing strength can be obtained self-consistently with the mean-field. The pairing energy Epair and the pairing strength Gτ are:
where fτ is a cutoff function, and τ means neutron and proton, and ɛk is the single-particle energy of k orbital. Furthermore, the constant gτ is self-consistently obtained by solving the continuously smoothed equations for the nucleon number conservation and the gap parameters simultaneously, in which the single-particle level densities are used:
where the
3 Result
We first show the PESs of 236U obtained using three EDFs, and the fission barrier heights are compared with the data evaluated experimentally. Next, we decompose the PES to the energy terms in the Skyrme EDF and search for the major components to be in phase with the double-humped barrier structure. Finally, the sensitivity to pairing strength for the barrier heights is investigated.
3.1 Fission barrier calculated by the mean-field models
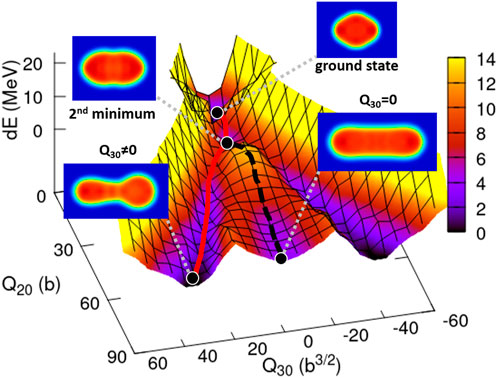
Figure 1 shows the PES of 236U as a function of Q20 and Q30 calculated with the SkM* parameter set. The dE is defined by the difference between the energies of the ground state and each configuration point in Q20 and Q30; dE(Q20, Q30) = E(Q20, Q30) − E(G.S.). The investigated ranges of Q20 and Q30 are [0 : 87] b and [0 : 65] b for all calculations. The nuclear density distributions in Figure 1 are those at the ground state, second minimum, mass symmetric (Q30 = 0), and mass asymmetric (Q30 ≠ 0) configurations. The solid line represents the lowest energies on the PES for nuclear elongation, which corresponds to the fission path in the mean-field model calculation, although the dashed line means the symmetric elongated configuration (Q30 = 0). The calculated fission path having the finite octupole momentum corresponds to the fission fragment distribution with mass asymmetry as obtained in the measurements, which indicates the significance of the static PES in the study of fission phenomena.
Figure 2 shows the energies on the PES of the symmetric deformation paths with Q30 = 0 (left panel) and that along the calculated fission paths (right panel) using three Skyrme EDFs (SkM*, SLy4, SkI3). In each result, the double-humped barrier structures appear in both of the fission and symmetric deformation paths. We can see two characteristic barriers for all EDF results: the one noted as Binner appears at slightly less than Q20 = 20 b, and the second one noted as Bouter appears over Q20 = 40 b. A similar barrier structure appears in the three EDFs calculations, although there are differences in the heights and slopes near Bouter. The effects of finite Q30 is significant for the configuration having elongation larger than the second minimum. A remarkable reduction of Bouter due to the finite octupole momentum, namely, mass asymmetry, is also confirmed. As an example, the reduction on Bouter for SLy4 is indicated by an arrow in the right panel of Figure 2. The double-humped fission barriers and the reduction effects on Bouter by the mass asymmetry are reported in the early researches by Strutinsky [35, 36] and Möller [50] using other models. The calculated E(G.S.), Binner, Bouter (Q30 = 0), and Bouter (Q30 ≠ 0) with SkM*, SLy4, and SkI3 EDFs together with the experimental and derived values are listed in Table 1. In the derived values, Binner is lower than Bouter, while all calculations fail to reproduce this relation. Both the Binner and Bouter (Q30 ≠ 0) calculated with all Skyrme EDFs overestimate the derived values, although the amplitude of the overestimation is not constant for Binner and Bouter, which might indicate the configuration dependence of the barrier.
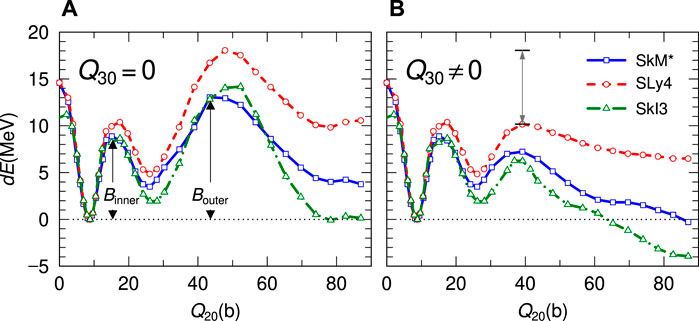
FIGURE 2. Energies of the symmetric path (A) and fission path (B) of 236U as functions of Q20 for the three EDFs (SkM*, SLy4, and SkI3). The effect of mass asymmetry for SLy4 is indicated by the arrow in right panel.
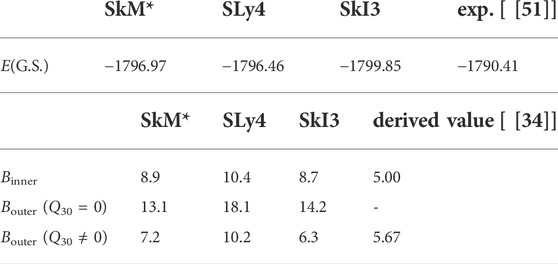
TABLE 1. Calculated ground state energies, fission barrier heights, experimental, and derived values (MeV) of236U.
3.2 Searching for energy components to form the barrier
Here, we decompose the PES along the fission path obtained in this work and investigate which energy term changes the fission barrier heights and how. The PES is decomposed into seven terms as in Eq. 4. Figure 3 shows the behaviors of the energy terms dEx in SkM* EDF concerning Q20, where dEx(Q20) = Ex(Q20) − Ex(G.S.), and x is a subscript corresponding to those of Eq. 4. Even though the amplitudes of dEt0 and dEt3 are much larger than other energy terms, they are almost canceled out due to their opposite signs. The right panel in Figure 3 shows a complicated competition among the other energy terms. It is difficult to extract the small amplitude like Binner or Bouter from the competition among large values shown in Figure 3. We focus on comparing the results with different EDFs since there might be a common mechanism to form a similar barrier structure from the energy competition in the EDF, as in Figure 2.
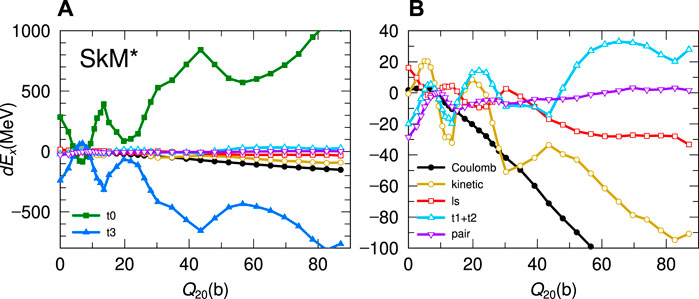
FIGURE 3. (A) Magnitude of the decomposed terms dEx of 236U along the fission path as in Eq. 4. (B) The same as the left panel but excluding the dEt0 and dEt3 terms. They are represented as functions of Q20. The symbols denote the followings: solid squares dEt0, open triangles dEt1, t2, solid triangles dEt3, open circles dEkin, solid circles dECoul, open squares dEls, and inverted open triangles dEpair.
We compare here various components dEx on the fission path calculated by the three EDFs to extract similarities and differences depending on the effective interactions. Furthermore, we wish to extract the component that forms the double-humped barrier structures specific to the fission barriers of the actinide nuclei. For this aim, we plot dEkin + dEt0 + dEt1, t2 + dEt3, dECoul, dEls, and dEpair in Figure 4. The upper left panel, exhibiting dEkin + dEt0 + dEt1, t2 + dEt3, shows that relatively small difference among the results of the three EDFs in which this combination of dEx’s increases for a large Q20, corresponding to the increase of nuclear surface. On the other hand, in the upper right panel, it is seen that the dECoul does not depend much on the choice of EDFs, and decreases commonly toward a large Q20 due to the enlarged distance between localized charge distributions. The bottom panels of Figure 4 show dEls and dEpair. They have structures corresponding to the double-humped structure in the fission barrier. The arrows in the bottom panels indicate the positions of bumps and dips of the barriers. We can see a similar phase on bumps and dips of the fission barrier in the behavior of dEls. On the other hand, dEpair has an opposite phase of the barrier structure as is known well from their dependence on the single-particle level densities. Therefore, we can conclude that dEls and dEpair have significant roles in forming the fission barrier height from their dependence on the nuclear elongation.
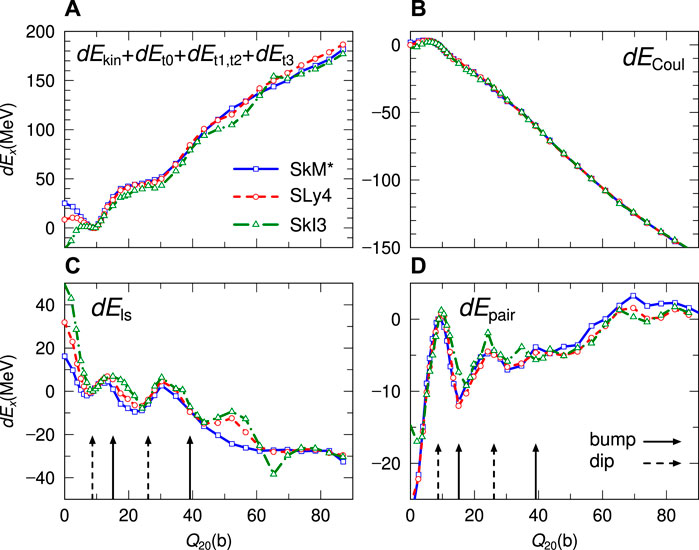
FIGURE 4. The dEx on the fission path for the three EDFs (SkM*:solid, SLy4:dashed, SkI3:dashed-dotted) as functions of Q20. (A,B) show the results of dEx for dEkin + dEt0 + dEt1, t2 + dEt3, and for dECoul, respectively. (C,D) show the results of dEx for dEls and dEpair. The solid and dashed arrows in the bottom panels indicate the positions of bumps and dips of the fission barriers.
3.3 Sensitivity of the fission barrier to the pairing strength
The comparison among the decomposed PESs for the three EDFs indicates that dEls and dEpair play an important role to form the characteristic structure of the fission barrier. We investigate the sensitivity of the fission barrier heights to the pairing correlation by changing the pairing strength G. In our model, the pairing strength G is self-consistently calculated using the level density at each configuration. This G is the original pairing strength that can consistently deduce the pairing gap parameter with the empirical one. In the investigation, we only change the value of this original G by ± 20% and the changed G is fixed in the self-consistent calculation for each configuration at (Q20, Q30). Figure 5 shows the fission paths for the three EDFs with the enhanced and reduced values of G, where dE ± 20% = E ± 20%(Q20) − E ± 20%(G.S.). For all results of EDFs, the enhanced value of G makes both of Binner and Bouter smaller, and vice versa. Magnitude of the change in the dE brought by the change of the G parameter depends on the EDF. Moreover, the change in dE depends on Q20, indicating configuration dependence of the effect of the pairing correlation. The barrier heights and E(G.S.) for each interaction are shown in Table 2. In all the cases investigated, it is concluded that enhancement of the pairing strength leads to better reproduction of the derived fission barrier heights.Furthermore, we compare the changes of pairing energy and local level densities
where Δɛ is the energy window to count the single-particle states, and
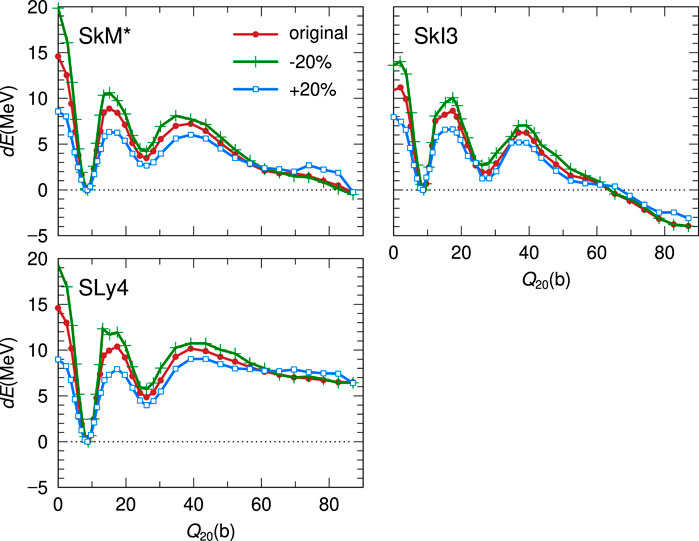
FIGURE 5. The dE on the fission paths of 236U for the three EDFs (SkM*, SLy4, SkI3) with the original strength of G (circle), − 20% G (cross), and + 20% G (square).
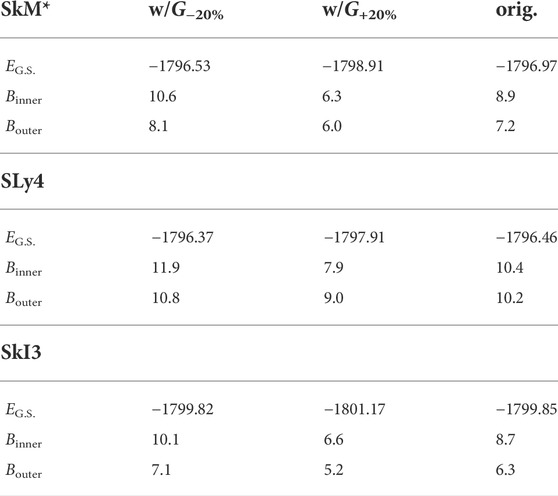
TABLE 2. EG.S., Binner, and Bouter in MeV along the fission path of236U for three EDFs and three values of pairing strength G.
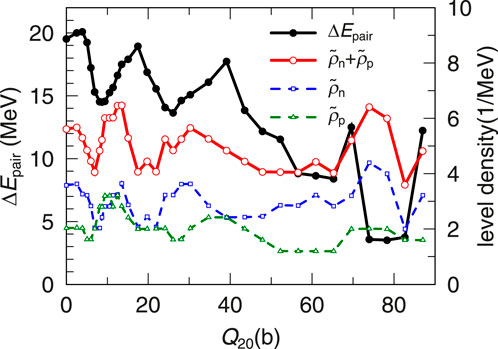
FIGURE 6. The local level densities
Finally, we investigate dependence of the decomposed energy terms obtained with SkM* on the change in the pairing strength G. The decomposed and the combination of energy terms are shown in Figure 7, where circle, cross, and open square symbols show the results obtained with G, 0.8G, and 1.2G, respectively. We can see very small changes in the combination: dEkin + dEt0 + dEt1, t2 + dEt3, and in dECoul. Effects of the change in pairing strength are the best seen for dEls and dEpair. For dEls, the effects of pairing strength appear near the arrows which correspond to fission barriers. These behaviors are consistent with the previous discussion. The peak structure in dEls is smeared out for results with 1.2G, while opposite trend is true for dEpair by out of phase. By combining these two results, it leads to reduction of the fission barrier heights. Therefore, dEls and dEpair contribute much to the barriers since they depend on the details of behaviors of single-particle states.
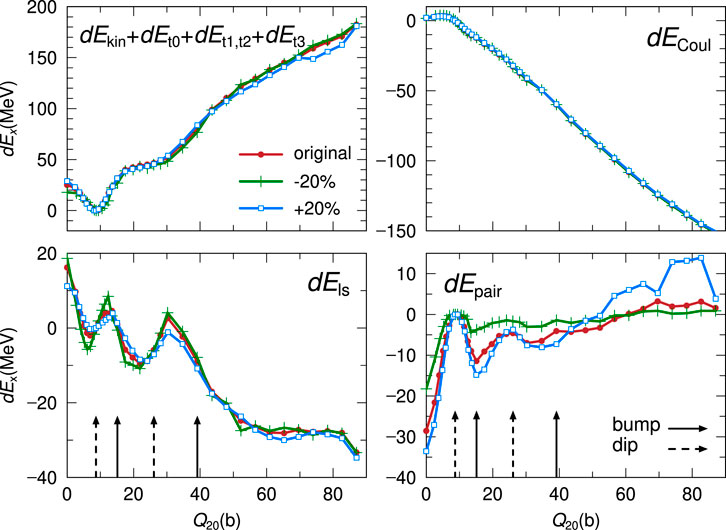
FIGURE 7. Same as Figure 4, but for SkM* with three choices of the pairing strength G.
4 Conclusion
We investigated the fission barrier structure of 236U using a constrained Skyrme HF + BCS model represented in the three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate space. The barrier structure was deduced from the potential energy surface (PES) obtained as a function of quadrupole Q20 and octupole Q30 moments. The fission path was estimated as the lowest energy path of the PES projected to Q20 axis with a finite Q30. We employed three Skyrme parameter sets (SkM*, SLy4, and SkI3) in this work to calculate the fission paths. We confirmed that the double-humped barrier structure of 236U arises, inclusion of the Q30 degree-of-freedom reduces the height of the outer fission barrier Bouter significantly, and the calculated barrier heights are overestimated compared to the value estimated experimentally in all of the employed three EDFs.
To elucidate the major components to form the structure of the barrier, we decomposed the energy on the PES along the fission paths into seven energy terms of the Skyrme EDF. We found the complicated energy competition of the barrier in which the large components, the central and density-dependent terms, almost cancel each other, and role of the kinetic, non-local, spin-orbit, Coulomb, and pairing terms have been entangled. We searched for the combination of energy terms that differ among the three EDFs. The Coulomb term and the energy combination excluding the spin-orbit and pairing terms, have a small EDF dependence and change monotonically on the fission path. The changes of spin-orbit energy term dEls on the fission path are in phase with the bumps and dips of the barrier, and the pairing term dEpair is in the opposite phase with them. Therefore, it can be expected that their competition will decide the characteristic structure of the double-humped fission barrier.
We also checked the sensitivity of the barrier structure on the pairing correlation by changing the pairing strength. It was found that fission barrier height decreases when the pairing strength is enhanced, and vice versa. Furthermore, we found that the change is not constant on the fission path. Nevertheless, enhanced pairing strength was able to realize a lower Binner than an Bouter. It indicates a possibility of theoretically reproducing the fission barrier estimated experimentally by adjusting the pairing functional. To investigate the configuration dependence of the change of the fission barrier by changing the pairing correlation, we calculated the local level density, which counts the occupation probabilities near the Fermi energy related to the pairing correlation. The changes in the pairing energy on the fission path correspond well to the local level density behavior. Therefore, we expect that the internal nuclear structure strongly affects the fission barrier height through the spin-orbit force and pairing correlation.
We will investigate the fission phenomenon using static and dynamic models in future works. Furthermore, we will extend our model to the beyond mean-field models by including the stochastic effects on the initial state caused by temperature and the quantum tunneling penetration. To realize the extension of the theory, we will need to combine models which can treat different time-scale.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
KF, SE, and SC contributed to the conception and design of the study. KF, TI, and CI designed the proceed of the study and sections of the manuscript. KF and SE wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision and read and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by Leading Initiative for Excellent Young Researchers, MEXT, Japan, and by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number JP20K03943.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bender M, Bernard R, Bertsch G, Chiba S, Dobaczewski J, Dubray N, et al. Future of nuclear fission theory. J Phys G: Nucl Part Phys (2020) 47(11):113002. doi:10.1088/1361-6471/abab4f
2. Bulgac A, Jin S, Stetcu I. Nuclear fission dynamics: Past, present, needs, and future. Front Phys (2020) 8. doi:10.3389/fphy.2020.00063
3. Holmbeck EM, Sprouse TM, Mumpower MR, Vassh N, Surman R, Beers TC, et al. Actinide production in the neutron-rich ejecta of a neutron star merger. Astrophys J (2018) 870(1):23. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aaefef
4. Horowitz CJ, Arcones A, Côté B, Dillmann I, Nazarewicz W, Roederer IU, et al. r-process nucleosynthesis: connecting rare-isotope beam facilities with the cosmos. J Phys G: Nucl Part Phys (2019) 46(8):083001. doi:10.1088/1361-6471/ab0849
5. Mumpower MR, Jaffke P, Verriere M, Randrup J. Primary fission fragment mass yields across the chart of nuclides. Phys Rev C (2020) 101:054607. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.101.054607
6. Jaffke P, Möller P, Talou P, Sierk AJ. Hauser-Feshbach fission fragment de-excitation with calculated macroscopic-microscopic mass yields. Phys Rev C (2018) 97:034608. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.034608
7. Schatz H. Trends in nuclear astrophysics. J Phys G: Nucl Part Phys (2016) 43(6):064001. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/43/6/064001
8. Myo T, Toki H, Ikeda K, Horiuchi H, Suhara T. Tensor-optimized antisymmetrized molecular dynamics as a successive variational method in nuclear many-body system. Phys Lett B (2017) 769:213–8. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2017.03.059
9. Maheshwari B, Kassim HA, Yusof N, Jain AK. Evolution of nuclear structure in and around Z=50 closed shell: Generalized seniority in Cd, Sn and Te isotopes. Nucl Phys A (2019) 992:121619. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2019.121619
10. Otsuka T, Abe T, Yoshida T, Tsunoda Y, Shimizu N, Itagaki N, et al. α-Clustering in atomic nuclei from first principles with statistical learning and the Hoyle state character. Nat Commun (2022) 13(1):2234. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29582-0
11. Mahmoud ZMM. Energy density functional for α clustering and scattering of light A = 4m nuclei. Phys Rev C (2022) 105:044609. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.105.044609
12. Bardeen J, Cooper LN, Schrieffer JR. Theory of superconductivity. Phys Rev (1957) 108:1175–204. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.108.1175
13. Sadhukhan J, Dobaczewski J, Nazarewicz W, Sheikh JA, Baran A. Pairing-induced speedup of nuclear spontaneous fission. Phys Rev C (2014) 90:061304. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.90.061304
14. Bernard R, Giuliani SA, Robledo LM. Role of dynamic pairing correlations in fission dynamics. Phys Rev C (2019) 99:064301. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.99.064301
15. Nikšić T, Vretenar D, Ring P. Relativistic nuclear energy density functionals: Adjusting parameters to binding energies. Phys Rev C (2008) 78:034318. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.78.034318
16. Zhao PW, Li ZP, Yao JM, Meng J. New parametrization for the nuclear covariant energy density functional with a point-coupling interaction. Phys Rev C (2010) 82:054319. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.82.054319
17. Agbemava SE, Afanasjev AV, Ray D, Ring P. Assessing theoretical uncertainties in fission barriers of superheavy nuclei. Phys Rev C (2017) 95:054324. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.95.054324
18. Baldo M, Robledo LM, Schuck P, Viñas X. New Kohn-Sham density functional based on microscopic nuclear and neutron matter equations of state. Phys Rev C (2013) 87:064305. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.87.064305
19. Behera B, Viñas X, Routray TR, Robledo LM, Centelles M, Pattnaik SP. Deformation properties with a finite-range simple effective interaction. J Phys G: Nucl Part Phys (2016) 43(4):045115. doi:10.1088/0954-3899/43/4/045115
20. Bulgac A, Forbes MM, Jin S, Perez RN, Schunck N. Minimal nuclear energy density functional. Phys Rev C (2018) 97:044313. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.044313
21. Bender M, Heenen PH, Reinhard PG. Self-consistent mean-field models for nuclear structure. Rev Mod Phys (2003) 75:121–80. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.75.121
22. Vautherin D, Brink DM. Hartree-Fock calculations with skyrme’s interaction. I. Spherical nuclei. Phys Rev C (1972) 5:626–47. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.5.626
23. Goutte H, Casoli P, Berger JF. Mass and kinetic energy distributions of fission fragments using the time dependent generator coordinate method. Nucl Phys A (2004) 734:217–20. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2004.01.038
24. Ayik S. A stochastic mean-field approach for nuclear dynamics. Phys Lett B (2008) 658(4):174–9. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2007.09.072
25. Regnier D, Dubray N, Schunck N. From asymmetric to symmetric fission in the fermium isotopes within the time-dependent generator-coordinate-method formalism. Phys Rev C (2019) 99:024611. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.99.024611
26. Tanimura Y, Lacroix D, Ayik S. Microscopic phase-space exploration modeling of 258Fm spontaneous fission. Phys Rev Lett (2017) 118:152501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.152501
27. Bassichis WH, Kerman AK, Svenne JP. Unrestricted Hartree-Fock treatment of finite nuclei. Phys Rev (1967) 160:746–52. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.160.746
28. Flocard H, Quentin P, Kerman AK, Vautherin D. Nuclear deformation energy curves with the constrained Hartree-Fock method. Nucl Phys A (1973) 203(3):433–72. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(73)90357-6
29. Flocard H, Quentin P, Vautherin D, Veneroni M, Kerman AK. Self-consistent calculation of the fission barrier of 240Pu. Nucl Phys A (1974) 231(1):176–88. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(74)90300-5
30. Möller P, Nilsson SG. The fission barrier and odd-multipole shape distortions. Phys Lett B (1970) 31(5):283–6. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(70)90171-1
31. Knitter HH, Hambsch FJ, Budtz-Jorgensen C, Theobald JP. Three exit channels in the fission of 235U(n, f). Z Naturforschung A (1987) 42(8):786–90. doi:10.1515/zna-1987-0802
32. Warda M, Robledo LM. Microscopic description of cluster radioactivity in actinide nuclei. Phys Rev C (2011) 84:044608. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.84.044608
33. Sadhukhan J, Nazarewicz W, Schunck N. Microscopic modeling of mass and charge distributions in the spontaneous fission of 240Pu. Phys Rev C (2016) 93:011304. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.93.011304
34. Capote R, Herman M, Oblozinsky P, Young PG, Goriely S, Belgya T, et al. RIPL - reference input parameter library for calculation of nuclear reactions and nuclear data evaluations. Nucl Data Sheets (2009) 110(12):3107–214. Special Issue on Nuclear Reaction Data. doi:10.1016/j.nds.2009.10.004
35. Strutinsky VM. Shell effects in nuclear masses and deformation energies. Nucl Phys A (1967) 95(2):420–42. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(67)90510-6
36. Strutinsky VM. “Shells” in deformed nuclei. Nucl Phys A (1968) 122(1):1–33. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(68)90699-4
37. Mayer MG. On closed shells in nuclei. II. Phys Rev (1949) 75:1969–70. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.75.1969
38. Haxel O, Jensen JHD, Suess HE. On the ”magic numbers” in nuclear structure. Phys Rev (1949) 75:1766. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.75.1766.2
39. Kortelainen M, McDonnell J, Nazarewicz W, Reinhard PG, Sarich J, Schunck N, et al. Nuclear energy density optimization: Large deformations. Phys Rev C (2012) 85:024304. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.85.024304
40. Bartel J, Quentin P, Brack M, Guet C, Hakansson HB. Towards a better parametrisation of skyrme-like effective forces: A critical study of the SkM force. Nucl Phys A (1982) 386(1):79–100. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(82)90403-1
41. Rodriguez-Guzman R, Humadi YM, Robledo LM. Microscopic description of fission in superheavy nuclei with the parametrization D1M$$^{*}$$ of the Gogny energy density functional. Eur Phys J A (2020) 56:43. doi:10.1140/epja/s10050-020-00051-w
42. Rutz K, Maruhn JA, Reinhard PG, Greiner W. Fission barriers and asymmetric ground states in the relativistic mean-field theory. Nucl Phys A (1995) 590(3):680–702. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(95)00192-4
43. Ebata S, Nakatsukasa T. Octupole deformation in the nuclear chart based on the 3D Skyrme Hartree–Fock plus BCS model. Phys Scr (2017) 92(6):064005. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/aa6c4c
44. Chabanat E, Bonche P, Haensel P, Meyer J, Schaeffer R. A Skyrme parametrization from subnuclear to neutron star densities Part II. Nuclei far from stabilities. Nucl Phys A (1998) 635(1):231–56. doi:10.1016/s0375-9474(98)00180-8
45. Reinhard PG, Flocard H. Nuclear effective forces and isotope shifts. Nucl Phys A (1995) 584(3):467–88. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(94)00770-n
47. Skyrme THR. The effective nuclear potential. Nucl Phys (1958) 9(4):615–34. doi:10.1016/0029-5582(58)90345-6
48. Tajima N, Takahara S, Onishi N. Extensive Hartree-Fock+BCS calculation with Skyrme SIII force. Nucl Phys A (1996) 603(1):23–49. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(96)00156-x
49. Dobaczewski J, Nazarewicz W, Stoitsov MV. Nuclear ground-state properties from mean-field calculations. Eur Phys J A (2002) 15(1):21–6. doi:10.1140/epja/i2001-10218-8
50. Möller P. Odd-multipole shape distortions and the fission barriers of elements in the region 84 z 120. Nucl Phys A (1972) 192(3):529–80. doi:10.1016/0375-9474(72)90090-5
Keywords: nuclear fission barrier, mean-field and DFT-based methods, spin-orbit force, nuclear pairing interaction, Uranium 236
Citation: Fujio K, Ebata S, Inakura T, Ishizuka C and Chiba S (2022) Energy competition and pairing effect for the fission path with a microscopic model. Front. Phys. 10:986488. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2022.986488
Received: 05 July 2022; Accepted: 15 August 2022;
Published: 26 September 2022.
Edited by:
Bidyut Jyoti Roy, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), IndiaReviewed by:
Jhilam Sadhukhan, Government of India, IndiaMaria Colonna, Laboratori Nazionali del Sud (INFN), Italy
Copyright © 2022 Fujio, Ebata, Inakura, Ishizuka and Chiba. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kazuki Fujio, ZnVqaW8uay5hYUBtLnRpdGVjaC5hYy5qcA==; Shuichiro Ebata, ZWJhdGFAbWFpbC5zYWl0YW1hLXUuYWMuanA=
 Kazuki Fujio
Kazuki Fujio Shuichiro Ebata
Shuichiro Ebata Tsunenori Inakura1
Tsunenori Inakura1 Chikako Ishizuka
Chikako Ishizuka