
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
EDITORIAL article
Front. Pharmacol., 19 March 2025
Sec. Experimental Pharmacology and Drug Discovery
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1580686
This article is part of the Research TopicTargeting Cellular Signalling Pathways for Disease Therapy: The Potential of Cellular Reprogramming and Protein Kinase InhibitorsView all 7 articles
Editorial on the Research Topic
Targeting cellular signalling pathways for disease therapy: the potential of cellular reprogramming and protein kinase inhibitors
Cellular reprogramming is particularly active during development, regeneration and cancer, when dynamic signaling pathways orchestrate cellular changes in response to input signals (Huyghe et al., 2024). It facilitates adaptation to exogenous pressure enabling tumor cells to adapt and survive in response to adverse microenvironments (Anderson and Simon, 2020; Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011). Understanding the mechanism these adaptations happen has fueled significant advances in medical science, particularly in regenerative medicine and targeted cancer therapies (He et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2024). Spatial-temporal integration of cellular signaling is fundamental to effective reprogramming. Dysregulation of protein kinases is key to the pathogenesis of various pathologies, particularly cancer, dictating disease progression and inhibitors targeting this family represent pivotal tools in modern therapeutics (Cohen, 2002). Transduction via MAPK and PI3K pathway has been extensively studied and is stablished as mediator of cancer signals (Corrales et al., 2022). Molecules targeting key signaling pathways like MAPK and PI3K providing tailored therapies have already been approved for clinical applications (Bahar et al., 2023; Dos Santos et al., 2022). Despite advances, cross-communication between these pathways occurs and further understanding is needed to uncover the mechanism signaling rewiring develops (Corrales et al., 2022). This Research Topic focuses on the rewiring signaling cascades as result of cellular reprograming and their target as therapeutic strategy consolidates recent advancements in understanding how cellular signaling pathways are modulated for therapeutic purposes. The studies included in this here provide a comprehensive overview of some aspects and developments in this field and are summarized in Figure 1.
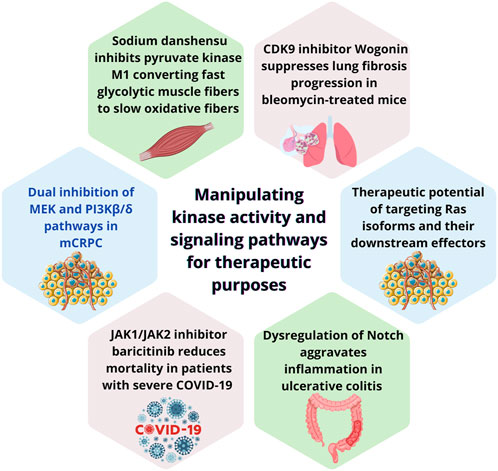
Figure 1. Summary of key findings from each study featured in this editorial, highlighting diverse therapeutic strategies targeting kinase activity and signaling pathways. (a) dual inhibition of MEK and PI3Kβ/δ pathways to overcome docetaxel resistance in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC); (b) Sodium danshensu‘s promotion of muscle fiber transformation by inhibiting pyruvate kinase M1, enhancing endurance and metabolic efficiency; (c) Wogonin‘s antifibrotic effects through CDK9 inhibition, reducing cellular senescence and fibrosis; (d) the therapeutic potential of targeting Ras isoforms and their downstream effectors, including advances in KRAS inhibitors; (e) the role of JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor baricitinib in reducing mortality among severe COVID-19 patients; and (f) dysregulation of the Notch signaling pathway in ulcerative colitis, revealing opportunities for pathway-specific interventions. Collectively, these studies highlight the transformative potential of manipulating kinase signaling in diverse disease contexts.
Ruiz de Porras et al. and Healy et al. explored the therapeutic potential of kinase inhibitor, offering valuable insights into their applications and mechanisms of action. Ruiz de Porras et al. show that MAPK and PI3K pathways are overactive in docetaxel-resistant cell lines. Dual inhibition of MEK1/2 (selumetinib) and PI3Kβ/δ (AZD8186) was sufficient to overcame resistance to docetaxel in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). The combination reduced tumor growth and induced apoptosis in both in vitro and DU145-DR-derived xenograft mouse model expressing phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) wild-type. This study shows the therapeutic potential of targeting MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT crosstalk, which often drives resistance to monotherapies. The Ras family is a key regulator of cellular proliferation, survival, and differentiation known to mediate crosstalk between signaling cascades (Catozzi et al., 2022). Healy et al. provides a comprehensive review on Ras-mediated signaling activation in cancer and highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting Ras isoforms and their downstream effectors, particularly the MAPK and PI3K pathways. Ras mutations, particularly in KRAS, are prevalent in various cancers. A Gly to Cys mutation (KRAS-G12C) made mutated Ras a druggable target, revolutionizing the field. Nevertheless, challenges remain in addressing wild type Ras, other Ras mutations and associated drug resistance. By integrating biochemical, genomic, and proteomic information, current studies progress towards effective treatment and better outcomes for Rasopathies. Mao et al. work on a retrospective study investigate the use of kinase inhibitors in critical care settings. Baricitinib is a JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, which use was shown to be associated with reduction of 28-day mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Intriguingly, patients in the baricitinib group were associated to increased hypertension and more likely to receive the antiviral drug nirmatrelvir and ritonavir.
In Zhang et al., the versatility of natural products as modulators of cellular signaling pathways was demonstrated by the effects of sodium danshensu (SDSS), a stable derivative of danshensu, on skeletal muscle fiber transformation. SDSS promoted the conversion of fast glycolytic muscle fibers to slow oxidative fibers by inhibiting pyruvate kinase M1 (PKM1), a kinase responsible for the generation of pyruvate and ATP during glycolysis. This shift enhances muscle endurance and metabolic efficiency in mice, providing new insights into the role of kinase modulation in muscle physiology. Both, SDSS-treated C2C12 myoblasts and mice exhibited increased oxidative capacity, improved glucose tolerance, and reduced markers of muscle atrophy. Wang et al. has also explored a compound of natural source. Wogonin, extracted from Scutellaria baicalensis, is a cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) inhibitor and was shown to have an effective antifibrotic property in mice with bleomycin (BLM)-induced lung fibrosis, thereby mitigating its progression.
Notch signaling participates in various cellular processes, including the regulation of intestinal homeostasis. Ning et al. reviewed the role of notch pathway in ulcerative colitis, emphasizing how its dysregulation disrupts the balance of gut cell lineages, weakens the mucosal barrier, and aggravates inflammation. The complex architecture of this pathway creates a complex web of signaling transduction, including shifts in signaling as result of Notch cleavage by γ-secretase and the synergetic activity the doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) in crypt epithelial cells or microorganism-specific signaling. Future therapeutic strategies could involve selective inhibition or activation of Notch components to achieve disease-specific outcomes, including the use of cleavage by γ-secretase inhibitors.
Despite the current progress, challenges remain in translating the current knowledge into clinical practice. The insights provided here pave the way for new studies, exploring alternative therapeutic strategies and the adaptability of cellular signaling pathways. They emphasize the potential of kinase inhibitors and pathway modulators in addressing a range of medical challenges, from cancer and fibrosis to metabolic diseases and inflammation.
VM: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. PO: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AZ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. AZ acknowledges the support of the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq-Brazil) through a research productivity fellowship (PQ2, Grant No. 313311/2021-8) and a postdoctoral fellowship abroad (Grant No. 402973/2022-4).
We acknowledge the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq-Brazil); Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES), CAPES-PrInt, LAQVREQUIMTE. We are grateful to the contributing authors who chose this Research Topic and to the reviewers for their extremely helpful work. We thank Dr. Gurnit Kaur (University of Toronto) for proofreading the article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Anderson, N. M., and Simon, M. C. (2020). The tumor microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 30 (16), R921-R925–r5. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2020.06.081
Bahar, M. E., Kim, H. J., and Kim, D. R. (2023). Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway for cancer therapy: from mechanism to clinical studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8 (1), 455. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01705-z
Catozzi, S., Ternet, C., Gourrege, A., Wynne, K., Oliviero, G., and Kiel, C. (2022). Reconstruction and analysis of a large-scale binary Ras-effector signaling network. Cell Commun. Signal. 20 (1), 24. doi:10.1186/s12964-022-00823-5
Cohen, P. (2002). Protein kinases—the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 1 (4), 309–315. doi:10.1038/nrd773
Corrales, E., Levit-Zerdoun, E., Metzger, P., Mertes, R., Lehmann, A., Münch, J., et al. (2022). PI3K/AKT signaling allows for MAPK/ERK pathway independency mediating dedifferentiation-driven treatment resistance in melanoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 20 (1), 187. doi:10.1186/s12964-022-00989-y
Dos Santos, D. C., Rafique, J., Saba, S., Grinevicius, V., Filho, D. W., Zamoner, A., et al. (2022). IP-Se-06, a selenylated imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, modulates intracellular redox state and causes akt/mTOR/HIF-1α and MAPK signaling inhibition, promoting Antiproliferative effect and apoptosis in Glioblastoma cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 3710449. doi:10.1155/2022/3710449
Hanahan, D., and Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144 (5), 646–674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
He, Y., Sun, M. M., Zhang, G. G., Yang, J., Chen, K. S., Xu, W. W., et al. (2021). Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6 (1), 425. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5
Huyghe, A., Trajkova, A., and Lavial, F. (2024). Cellular plasticity in reprogramming, rejuvenation and tumorigenesis: a pioneer TF perspective. Trends Cell Biol. 34 (3), 255–267. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2023.07.013
Keywords: cancer, cell signal inhibitors, cellular reprograming, kinase, inflammation
Citation: Marensi V, Oliveira PF and Zamoner A (2025) Editorial: Targeting cellular signalling pathways for disease therapy: the potential of cellular reprogramming and protein kinase inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1580686. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1580686
Received: 20 February 2025; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 19 March 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Heike Wulff, University of California, Davis, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Marensi, Oliveira and Zamoner. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ariane Zamoner, YXJpYW5lLnphbW9uZXJAdWZzYy5icg==, YXJpYW5lenBzQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.