
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol., 28 March 2025
Sec. Pharmacology of Infectious Diseases
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1564070
This article is part of the Research TopicADME of Drugs to Treat Infectious DiseasesView all 8 articles
Fluconazole pharmacokinetics in acute renal failure (ARF) patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) are significantly influenced by the combined effects of impaired renal function and CRRT, yet current dosing guidelines do not account for these complexities, leading to suboptimal therapy and treatment failure. This study aimed to address these limitations by developing a population pharmacokinetic model for fluconazole in ARF patients receiving CRRT, evaluating guideline-recommended dosing regimens for pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic target attainment, and then developing software to optimize fluconazole dosing in complex clinical CRRT scenarios. A total of 297 literature-sourced plasma concentration data points from 15 ARF patients and one patient with normal renal function, all receiving CRRT, were used for model construction. The treatment target was set as the 24-h area under the free drug concentration-time curve to the minimum inhibitory concentration ratio ≥100. The web application was developed using R and R packages. The final pharmacokinetic model comprised a central and CRRT compartment, with renal failure and CRRT doses influencing clearance and body weight affecting central compartment distribution volume. Simulations revealed that the guideline-recommended loading (800 mg or 12 mg/kg QD) and maintenance doses (400 mg or 6 mg/kg QD) achieved limited target attainment at low CRRT doses and failed at moderate to high CRRT doses. Consequently, dose adjustments based on body weight and CRRT parameters are recommended. A user-friendly, visual, and interactive Shiny application was developed to assist clinicians in optimizing fluconazole dosing in this challenging patient population.
Invasive fungal disease, mainly caused by opportunistic fungi, imposes a substantial global health burden, with over 150 million severe cases and three million deaths annually (Jenks et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2023). Candida spp. Remain the most common cause of mycoses worldwide, with a mortality rate of up to 50%, largely due to inadequate antifungal therapy (Concia et al., 2009).
Fluconazole, a broad-spectrum triazole antifungal agent, is widely used against Candida and Cryptococcus species (Pappas et al., 2016; Martin-Loeches et al., 2019). As one of the most commonly used antifungal agents, fluconazole exhibits good pharmacokinetic characteristics and favorable tolerability (Thaler et al., 1995; Charlier et al., 2006). However, significant pharmacokinetic variability of fluconazole has been observed in critically ill patients (Boonstra et al., 2021). Dose optimization based on therapeutic drug monitoring is considered to significantly improve fluconazole exposure in obese, pediatric, and critically ill patients with renal failure (Boonstra et al., 2021; van der Elst et al., 2014; Alobaid et al., 2016).
As a hydrophilic drug with low plasma protein binding (12%) and a molecular weight of 306.2 Da, fluconazole is predominantly excreted unchanged via the kidneys (80%) (Debruyne and Ryckelynck, 1993; Roos et al., 2008). In critically ill patients with renal failure, changes in pathological physiological states or organ function can lead to alterations in fluconazole distribution and elimination (Smith et al., 2012). Research has demonstrated that in patients with acute renal failure (ARF), the clearance of fluconazole is reduced to 50% of that in healthy volunteers, with a clearance of 10 mL/kg/h and a half-life period of 96 h, compared to 15–24 mL/kg/h and 30 h in healthy individuals (Bellmann and Smuszkiewicz, 2017; Toon et al., 1990). Moreover, the incorporation of various organ support therapies like renal replacement therapy (RRT) can alter the pharmacokinetics of drugs to varying degrees, with fluconazole being efficiently cleared through the RRT membrane due to its small molecular weight and high water solubility (Bellmann and Smuszkiewicz, 2017; Coenradie et al., 2025). Studies (Oono et al., 1992; Debruyne and Ryckelynck, 1992; Yagasaki et al., 2003; Kishino et al., 2001; Gharibian and Mueller, 2016; Sinnollareddy et al., 2015) have shown that nearly all types of renal replacement therapy clear fluconazole to varying degrees, highlighting its dependence on RRT duration and parameters. This complexity necessitates meticulous consideration of fluconazole pharmacokinetics in critically ill patients undergoing RRT.
Effective antibiotic dosing in critically ill patients is crucial for optimal bactericidal efficacy and clinical outcomes (Kollef et al., 2021), yet current guideline-recommended dosing regimens are considered inadequate for this population (Muilwijk et al., 2020; Pappas et al., 2016; Martin-Loeches et al., 2019). While previous studies have explored fluconazole dose optimization in various critically ill populations, research specific to patients with renal failure on continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) remains limited (Boonstra et al., 2021; Alobaid et al., 2016; Muilwijk et al., 2020; Sandaradura et al., 2021; Van Daele et al., 2021). Existing studies, often with small sample size (4–15 patients, 26–80 samples), have not quantitatively assessed the impact of different CRRT types or doses on fluconazole exposure (Muilwijk et al., 2020; Sandaradura et al., 2021; Patel et al., 2011; Novy et al., 2024; Han et al., 2013).
This study aimed to develop a population pharmacokinetic model for critically ill patients undergoing CRRT, quantitatively describe the impact of CRRT on fluconazole clearance, and explore optimal dosing regimens for ARF patients with varying body weights and CRRT doses. Additionally, we developed a model-based fluconazole dose optimization application, aiming to facilitate optimal fluconazole dosing in complex clinical scenarios.
A literature search was conducted using the query “((Fluconazole) AND ((((((((continuous renal replacement therapy) OR (CRRT)) OR (continuous venovenous hemofiltration)) OR (continuous venovenous haemodialysis)) OR (continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration)) OR (CVVH)) OR (CVVHD)) OR (CVVHDF))” in the PubMed, Embase and Web of Science databases up to October 2024. Five publications (Yagasaki et al., 2003; Wolter et al., 1994; Valtonen et al., 1997; Muhl et al., 2000; Lopez and Phillips, 2014) were identified based on predefined inclusion criteria, including the availability of individual plasma concentration-time data, specific dosing information, sampling schemes, and sufficient CRRT parameter details for model development. Data on plasma concentration and accumulated drug dosage in the filtrate were digitized using WebPlotDigitizer (version 4.3). The detailed patient demographics, fluconazole doses, and CRRT parameter settings were summarized in Table 1. Missing values were imputed with mean or median values. Based on CRRT mode and relevant parameters, we calculated CRRT clearance, which were detailed in the Supplementary Material (Section 1). A scatter plot of plasma concentration over time was shown in Figure 1.
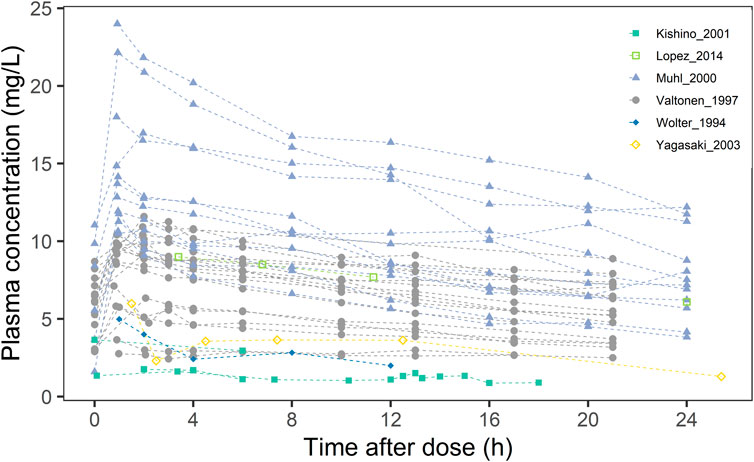
Figure 1. Scatter plot of fluconazole blood concentrations in 16 critically ill CRRT patients from different studies.
A nonlinear mixed effects modelling approach was undertaken using NONMEM® software (version 7.3, Icon Development Solutions, Ellicott City, MD, USA), with parameter estimation executed via the FOCEI algorithm. The Perl-Speaks-NONMEM program (version 4.60, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden) supported the modelling processes, while Pirana software (version 2.9.6, Pirana Software & Consulting BV) served as the interface. Analysis and visualization of the NONMEM output were accomplished using the R package (version 4.3.1; http://www.r-project.org).
Structural models, including one-compartment and two-compartment models, as well as one-compartment models with a tandem CRRT compartment, were evaluated. The selection of the structural model was based on comparisons of the objective function value and goodness of fit (GOF) plots. Different random effects models were assessed separately, with preferences given to models exhibited the smallest variance values. The final structural model was a one-compartment model incorporating a CRRT compartment in series with total clearance (CLTotal) calculated as the sum of CRRT clearance (CLcrrt) and residual body clearance (CLbody). The final model structure was shown in Figure 2.
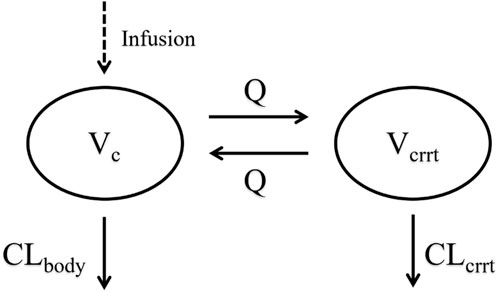
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the model structure. CLbody, central compartment clearance; CLcrrt, CRRT compartment clearance; Vc, central compartment apparent distribution volume; Q, intercompartmental clearance; Vcrrt, the apparent distribution volume of the CRRT compartment.
Covariate modelling was employed to delineate interindividual variation in pharmacokinetic parameters. Potential covariates such as age, body weight, and filter membrane area were considered continuous factors, while sex, ARF, and filter membrane type were regarded as categorical variables. Covariates were identified using a stepwise method comprising forward inclusion and backwards elimination.
The model was assessed using GOF, prediction-corrected visual predictive check (pc-VPC), and sampling importance resampling (SIR) analyses. GOF plots facilitated visual comparison between predicted and observed values, including the distribution and trend of residuals. Pc-VPC, a simulation-based diagnostic tool, utilizes 1,000 simulations to examine model prediction performance. SIR analyses employed 1,000 final proposal samples and 1,000 resamples to evaluate the uncertainty of the parameter estimates.
Monte Carlo simulations assessed the probability of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) target attainment (PTA) for various fluconazole dosing regimens in patients with different body weights and CRRT clearance intensities (n = 1,000). The PK/PD target was defined as the ratio of the plasma-free fluconazole AUC to the minimum inhibitory concentration (fAUC/MIC), with a threshold of 100 according to the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) (EUCAST, 2020b). Based on the primary MIC distribution of Candida species to fluconazole, the MICs ranging from 0.06–32 mg/L were examined, with particular attention given to the clinical susceptibility breakpoints of 2 mg/L defined by the EUCAST and 4 mg/L (susceptible dose-dependent breakpoint) defined by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (EUCAST, 2020a; Pappas et al., 2016). The simulations assumed fluconazole plasma protein binding at 12% and utilized mean sieving coefficients to calculate CRRT clearance.
To explore optimal efficacy, six fixed-dose regimens (200 mg, 400 mg, 600 mg, 800 mg, 1,000 mg, and 1,200 mg QD) and four weight-based dosing regimens (6 mg/kg, 8 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and 12 mg/kg QD) were examined across four body weight tiers (45 kg, 70 kg, 95 kg, and 120 kg) and four CRRT doses (20 mL/kg/h, 35 mL/kg/h, and 50 mL/kg/h). The PTAs were calculated for the various loading and maintenance doses on the first day and at a steady state. Any dosing regimen achieving a PTA ≥90% was considered optimal.
An interactive R-based application was developed using software packages such as Shiny and Mrgsolve, with the final model embedded. The input data included patient information, dosing regimen (loading dose, maintenance dose, frequency, and supplemental dosing), RRT-related information (start and end times, intensity of each RRT), and microbial drug sensitivity information. Supplemental dosing scenarios specify the additional dose to be administered during each RRT session or at the next dose after RRT ends.
The population pharmacokinetic analysis included 16 patients undergoing CRRT (15 ARF patients and one liver transplant patient) from five published studies. Patient characteristics were detailed in Table 1, with nine males in the cohort. The median age and weight were 72 years and 77 kg, respectively. Among the renal failure patients, seven were anuric, and seven were oliguric. The fluconazole dosages ranged from 50–1,200 mg.
A total of 297 plasma concentration points from 16 patients were utilized for population pharmacokinetic modelling. The model structure, comprising a central compartment in tandem with the CRRT compartment, best fits the plasma concentration-time data. The central compartment describes the body’s drug clearance, while the CRRT compartment describes drug elimination via CRRT. Drug transfer between these compartments is denoted by Q. The residual model employed a summed residual structure. Covariate analysis incorporated the presence of renal failure for clearance and total body weight for volume of distribution. Table 2 summarizes the final model parameters and associated uncertainties. The relative standard error and SIR results confirmed the accurate estimation of the PK parameters. The GOF plots demonstrated a good fit of the model predictions to the observed data, with a symmetrical residual distribution (Supplementary Material, Supplementary Figure S2). The pc-VPC showed good predictive performance of the final model (Figure 3).
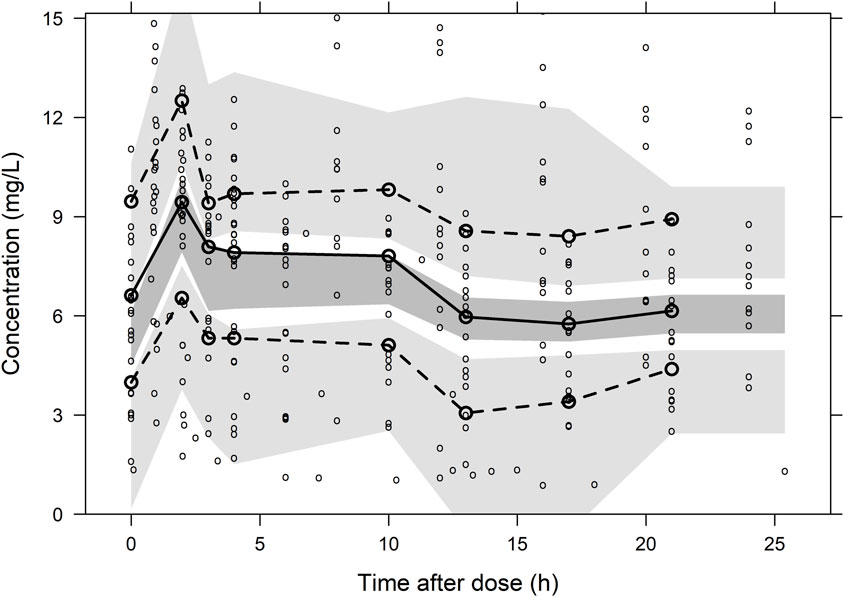
Figure 3. Prediction-corrected visual predictive check plot for the final population pharmacokinetic model of Fluconazole. The lower, middle and upper solid lines are the 5%, 50% and 95% quantile lines of the observed concentrations, and the shaded areas represent the 95% confidence intervals for the prediction lines.
The simulations indicated that loading doses of 800 mg, 1,000 mg, 12 mg/kg and 12 mg/kg were necessary to achieve 90% PTA on day 1 (Figures 4A,B) for ARF patients across four different weight groups, and were slightly lower for patients without CRRT. For fungi with an MIC of 4 mg/L, none of the tested dosing regimens met the target on day one.
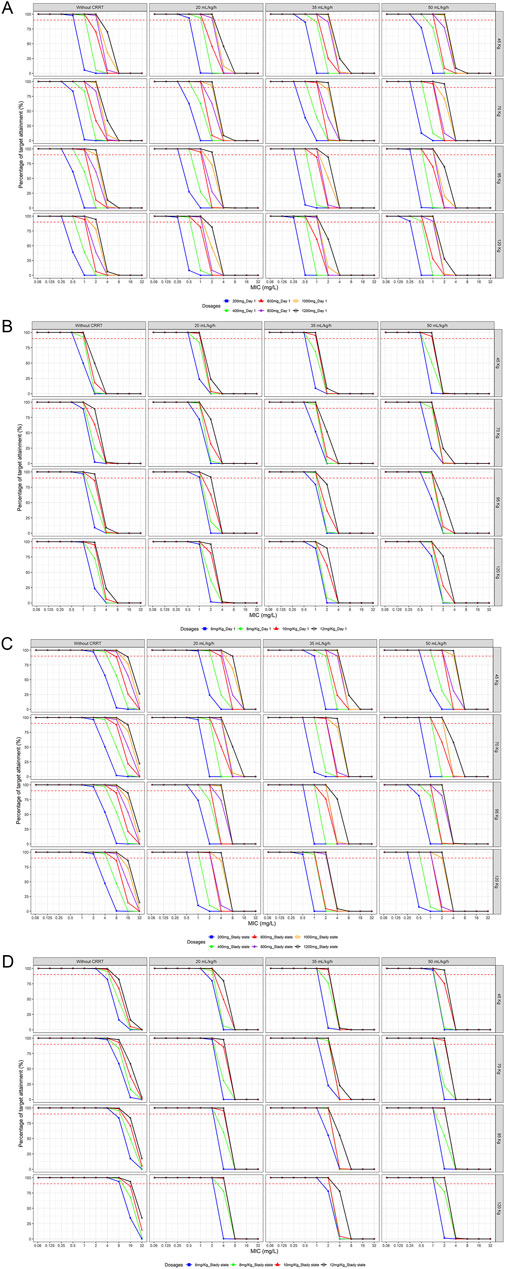
Figure 4. Probability of target attainment of various loading and maintenance dose regimens for different body weights and CRRT doses (A) Fixd-dose regimens at Day 1 (B) Weight-based dosing regimens at Day 1 (C) Fixd-dose regimens at steady state (D) Weight-based dosing regimens at steady state (PK/PD target: fAUC/MIC≥100)
Upon reaching a steady state (Figures 4C,D), a 200 mg maintenance dose was effective against fungi with MIC ≤2 mg/L in patients without CRRT. Even in patients with higher body weights (120 kg), a maintenance dose of 400 mg achieved optimal targets against fungi with an MIC of 4 mg/L. The maintenance dose required for ARF patients varied significantly across different body weights and CRRT intensities. None of the maintenance dose regimens tested at medium to high body weights or CRRT doses met the target for fungi with an MIC ≥4 mg/L.
Regarding the guideline-recommended loading doses of 800 mg and 12 mg/kg for Candida infections (Pappas et al., 2016; Martin-Loeches et al., 2019), simulations suggested their appropriateness for ARF patients without RRT or with low-flow CRRT, ensuring good PD coverage against fungi with an MIC ≤2 mg/L. When CRRT clearance rates reached 35 mL/kg/h, higher loading doses were indicated. Among the commonly used maintenance dose regimens of fluconazole in critically ill patients, a 200 mg maintenance dose was found to be effective against fungi, with an MIC of 1 mg/L primarily at lower body weights and CRRT flow rates. The 400 mg maintenance dose was effective against fungi with an MIC of 2 mg/L in lower weight scenarios (e.g., 45 kg with 35 mL/kg/h or 70 kg with 20 mL/kg/h). The weight-based 6 mg/kg maintenance dose regimen was effective only in patients with lower CRRT flow rates (70–120 kg, mL/kg/h 20 mL/kg/h) against fungi with an MIC of 2 mg/L. For fungi with an MIC of 4 mg/L, only the 400 mg maintenance dose regimen met the 90% threshold in ARF patients without RRT. The detailed minimum attainment doses were listed in Tables 3 and 4.
A user-friendly R Shiny application for fluconazole dose optimization in ARF patients receiving RRT was developed and is freely available at https://xy3yx.shinyapps.io/fluconazole-crrt-dosing/, with the interface shown in Figure 5 and a detailed user guide in the Supplementary Material (Supplementary Material, Section 4). The application integrates patient information, dosing details (including whether supplemental dosing was performed and its timing), and RRT-related information. It performs Monte Carlo simulations based on the final model, visualizing the predicted results as plasma concentration-time curves and fAUC/MIC values every 24 h during the treatment period, and updating them in real-time. It allows for the simulation of multiple intermittent RRT sessions with and without supplemental dosing, highlighting the differences in PK/PD results. Additionally, the application features a user-friendly point-and-click interface for time information input, allowing users to enter actual dosing and RRT times down to the minute. This approach enhances accuracy and flexibility, reducing the physician’s computational workload.
Fluconazole exhibits significant pharmacokinetic variability in critically ill populations (Boonstra et al., 2021; Muilwijk et al., 2020; Sandaradura et al., 2021), particularly those with renal failure, where clearance is often dependent on RRT. Previous research showed that RRT enhances fluconazole clearance in a dose-dependent manner (Bellmann and Smuszkiewicz, 2017; Valtonen et al., 1997; Muhl et al., 2000), complicating its pharmacokinetics in ARF patients on RRT. This study developed the largest population pharmacokinetic model of fluconazole in ARF patients undergoing CRRT to date, which provides valuable insights into the impact of CRRT dose on optimal fluconazole dosing in this population.
In contrast to previous fluconazole pharmacokinetic models (Muilwijk et al., 2020; Sandaradura et al., 2021; Patel et al., 2011; Novy et al., 2024; Han et al., 2013), our model structure combined a central compartment and a CRRT compartment, effectively characterizing the pharmacokinetic dataset. We posit that this model aligns more closely with the clearance patterns of fluconazole among CRRT patients. Our model showed good consistency with previous findings, estimating residual clearance in ARF patients at 0.407 L/h (Toon et al., 1990; Muilwijk et al., 2020; Sandaradura et al., 2021; Han et al., 2013), whole body clearance at 1.25 L/h in non-ARF patients (Debruyne and Ryckelynck, 1993), and central compartment distribution volume (Vc) of 37.9 L, indicating the reliability of the model (Muilwijk et al., 2020; Patel et al., 2011). For obese critically ill patients, weight-based dosing regimens were recently advocated (Alobaid et al., 2016). Previous studies (Sandaradura et al., 2021; Novy et al., 2024) have incorporated the impact of body weight on CL or Vc. In our study, the body weight-to-70 kg ratio was integrated into the Vc calculation using a power function. In this study, although we had 297 samples, they were derived from only 16 patients. The SIR method was chosen for parameter uncertainty estimation due to its robustness in small sample size scenarios compared to the bootstrap (Dosne et al., 2016).
Simulations revealed that ARF patients require different maintenance doses based on CRRT status and dose. While guideline-recommended loading doses (800 mg or 12 mg/kg QD) and maintenance dose regimens (400 mg or 6 mg/kg QD) for Candida infections were effective against fungi with an MIC ≤1 mg/L, they only partially met the current susceptibility breakpoints for Candida (4 mg/L by CLSI and 2 mg/L by EUCAST) in patients not receiving RRT or under low CRRT flow. These findings were consistent with prior research (Boonstra et al., 2021; Muilwijk et al., 2020; Sandaradura et al., 2021). Sandaradura et al. (Sandaradura et al., 2021) recommended a loading dose of 800 mg for critically ill underweight (40 kg) patients and a 12 mg/kg loading dose for patients of other body weights. Boonstra et al. (Boonstra et al., 2021) suggested that critically ill adults not undergoing CRRT require a loading dose of either 1,000 mg or 12 mg/kg for fungi with an MIC of 2 mg/L. In our study, 45 kg patients required at least an 800 mg loading dose, and patients with other body weights could be treated with either a 1,000 mg or 12 mg/kg initial dosing regimen. For fungi with an MIC of 4 mg/L, Muilwijk et al. (Muilwijk et al., 2020) advocated a maintenance dose of 400 mg for patients with impaired renal function and 800 mg for those undergoing CRRT. Our findings suggest that typical weight ARF patients (70 kg) necessitate approximately the same maintenance dose without RRT or at low CRRT flow rates, whereas a CRRT dose of 35 mL/kg/h mandates a maintenance dose of 1,200 mg or higher. Notably, most Candida species remain highly susceptible to fluconazole in vitro. The MIC90 values for C. albicans, C. parapsilosis, and C. tropicalis were 0.5, 2, and 2 mg/L, respectively, with only 3%, 8%, and 10% of the isolates having an MIC ≥4 mg/L (EUCAST, 2020b).
We developed an interactive web-based dose optimization application using R, which allows for a highly flexible input of renal replacement therapy events, enabling physicians to directly input actual or anticipated usage times and dialysis intensity. Additionally, this Shiny-based dose optimization application allows for the precise input of detailed timing (including date and time) and specific RRT information (including time, intensity, and frequency). Furthermore, we incorporated two possible supplementary dosing scenarios to enable physicians to promptly correct low drug concentrations. The real-time update of the PK/PD results output promotes the selection of the optimal dosing regimen.
Our study has several limitations, including reliance on digitized concentration data and literature-derived dosing and CRRT information, which may introduce discrepancies between the obtained data and the actual data. However, digitization methods have been demonstrated to effectively generate accurate data in previous studies (Wojtyniak et al., 2020) and have been confirmed in our application as well (Supplementary Material, Section 1). Another major limitation was the insufficient external validation due to the limited availability of data. Although 297 concentration data points were utilized, they were derived from only 16 patients, which may constrain the generalizability of the findings to a broader patient population. The model has been primarily validated in only a small number of samples from two studies (Patel et al., 2011; Sinnollareddy et al., 2015) (Supplementary Material, Section 3). Future prospective studies are required to further validate the accuracy and effectiveness of both the model and the software.
This study successfully established a population pharmacokinetic model of fluconazole in ARF patients with CRRT based on literature-sourced concentration data, revealing that guideline-recommended dosing regimens may be insufficient under moderate to high CRRT doses. Dosing adjustments based on body weight and CRRT dose are recommended to achieve optimal therapeutic targets. The developed R Shiny application provides a practical tool for clinicians to optimize fluconazole dosing in complex clinical settings.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because all data used in the study were anonymized and obtained from previously published sources. No potentially identifiable images or data are presented in this study.
PQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing-review and editing. Z-SN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing-original draft, Writing-review and editing. Z-WH: Data curation, Investigation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review and editing. W-TT: Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing-review and editing. Q-YF: Data curation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2022JJ30899) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82373966).
We would like to express our gratitude to the authors of the original studies whose data contributed significantly to the development of this pharmacokinetic model.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1564070/full#supplementary-material
Alobaid, A. S., Wallis, S. C., Jarrett, P., Starr, T., Stuart, J., Lassig-Smith, M., et al. (2016). Effect of obesity on the population pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in critically ill patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 6550–6557. doi:10.1128/aac.01088-16
Bellmann, R., and Smuszkiewicz, P. (2017). Pharmacokinetics of antifungal drugs: practical implications for optimized treatment of patients. Infection 45, 737–779. doi:10.1007/s15010-017-1042-z
Boonstra, J. M., Märtson, A. G., Sandaradura, I., Kosterink, J. G. W., van der Werf, T. S., Marriott, D. J. E., et al. (2021). Optimization of fluconazole dosing for the prevention and treatment of invasive candidiasis based on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in critically ill patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65, e1620. doi:10.1128/aac.01554-20
Charlier, C., Hart, E., Lefort, A., Ribaud, P., Dromer, F., Denning, D. W., et al. (2006). Fluconazole for the management of invasive candidiasis: where do we stand after 15 years? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 57, 384–410. doi:10.1093/jac/dki473
Coenradie, S. M., Smeets, T. J. L., Kamp, R. C., Elderman, J. H., Koch, B. C. P., Endeman, H., et al. (2025). Higher doses of fluconazole are needed to ensure target attainment in critically ill adults on continuous Veno-venous hemodialysis. J. Crit. Care 85, 154924. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2024.154924
Concia, E., Azzini, A. M., and Conti, M. (2009). Epidemiology, incidence and risk factors for invasive candidiasis in high-risk patients. Drugs 69 (Suppl. 1), 5–14. doi:10.2165/11315500-000000000-00000
Debruyne, D., and Ryckelynck, J. P. (1992). Fluconazole serum, urine, and dialysate levels in CAPD patients. Perit. Dial. Int. 12, 328–330. doi:10.1177/089686089201200314
Debruyne, D., and Ryckelynck, J. P. (1993). Clinical pharmacokinetics of fluconazole. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 24, 10–27. doi:10.2165/00003088-199324010-00002
Dosne, A. G., Bergstrand, M., Harling, K., and Karlsson, M. O. (2016). Improving the estimation of parameter uncertainty distributions in nonlinear mixed effects models using sampling importance resampling. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 43, 583–596. doi:10.1007/s10928-016-9487-8
EUCAST. (2020a). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs for antifungal agents Version 10.0. Available online at: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/AFST/Clinical_breakpoints/AFST_BP_v10.0_200204_updatd_links_200924.pdf [Accessed October 08, 2024].
EUCAST (2020b). Fluconazole: rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 3.0. Available online at: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Rationale_documents/Fluconazole_RD_v3.0_final_18_02.pdf (Accessed October 08, 2024).
Gharibian, K. N., and Mueller, B. A. (2016). Fluconazole dosing predictions in critically-ill patients receiving prolonged intermittent renal replacement therapy: a Monte Carlo simulation approach. Clin. Nephrol. 86, 43–50. doi:10.5414/cn108824
Han, S., Kim, J., Yim, H., Hur, J., Song, W., Lee, J., et al. (2013). Population pharmacokinetic analysis of fluconazole to predict therapeutic outcome in burn patients with Candida infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57, 1006–1011. doi:10.1128/aac.01372-12
Jenks, J. D., Cornely, O. A., Chen, S. C., Thompson, G. R., and Hoenigl, M. (2020). Breakthrough invasive fungal infections: who is at risk? Mycoses 63, 1021–1032. doi:10.1111/myc.13148
Kishino, S., Koshinami, Y., Hosoi, T., Suda, N., Takekuma, Y., Gandoh, S., et al. (2001). Effective fluconazole therapy for liver transplant recipients during continuous hemodiafiltration. Ther. Drug Monit. 23, 4–8. doi:10.1097/00007691-200102000-00002
Kollef, M. H., Shorr, A. F., Bassetti, M., Timsit, J. F., Micek, S. T., Michelson, A. P., et al. (2021). Timing of antibiotic therapy in the ICU. Crit. Care 25, 360. doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03787-z
Lopez, N. D., and Phillips, K. M. (2014). Fluconazole pharmacokinetics in a morbidly obese, critically ill patient receiving continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Pharmacotherapy 34, e162–e168. doi:10.1002/phar.1470
Martin-Loeches, I., Antonelli, M., Cuenca-Estrella, M., Dimopoulos, G., Einav, S., DE Waele, J. J., et al. (2019). ESICM/ESCMID task force on practical management of invasive candidiasis in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 45, 789–805. doi:10.1007/s00134-019-05599-w
Muhl, E., Martens, T., Iven, H., Rob, P., and Bruch, H. P. (2000). Influence of continuous veno-venous haemodiafiltration and continuous veno-venous haemofiltration on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 56, 671–678. doi:10.1007/s002280000216
Muilwijk, E. W., DE Lange, D. W., Schouten, J. A., Wasmann, R. E., Ter Heine, R., Burger, D. M., et al. (2020). Suboptimal dosing of fluconazole in critically ill patients: time to rethink dosing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64, e1020. doi:10.1128/aac.00984-20
Novy, E., Abdul-Aziz, M. H., Cheng, V., Burrows, F., Buscher, H., Corley, A., et al. (2024). Population pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in critically ill patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and continuous renal replacement therapy: an ASAP ECMO study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 68, e0120123. doi:10.1128/aac.01201-23
Oono, S., Tabei, K., Tetsuka, T., and Asano, Y. (1992). The pharmacokinetics of fluconazole during haemodialysis in uraemic patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 42, 667–669. doi:10.1007/bf00265934
Pappas, P. G., Kauffman, C. A., Andes, D. R., Clancy, C. J., Marr, K. A., Ostrosky-Zeichner, L., et al. (2016). Clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 62, e1–e50. doi:10.1093/cid/civ933
Patel, K., Roberts, J. A., Lipman, J., Tett, S. E., Deldot, M. E., and Kirkpatrick, C. M. (2011). Population pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in critically ill patients receiving continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration: using Monte Carlo simulations to predict doses for specified pharmacodynamic targets. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55, 5868–5873. doi:10.1128/aac.00424-11
Roos, J. F., Kirkpatrick, C. M., Tett, S. E., Mclachlan, A. J., and Duffull, S. B. (2008). Development of a sufficient design for estimation of fluconazole pharmacokinetics in people with HIV infection. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 66, 455–466. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03247.x
Sandaradura, I., Marriott, D. J. E., Day, R. O., Norris, R. L. G., Pang, E., Stocker, S. L., et al. (2021). Current fluconazole treatment regimens result in under-dosing of critically ill adults during early therapy. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 40, 1521–1528. doi:10.1007/s10096-021-04201-w
Sinnollareddy, M. G., Roberts, M. S., Lipman, J., Peake, S. L., and Roberts, J. A. (2015). Influence of sustained low-efficiency diafiltration (SLED-f) on interstitial fluid concentrations of fluconazole in a critically ill patient: Use of microdialysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 46, 121–124. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.02.017
Smith, B. S., Yogaratnam, D., Levasseur-Franklin, K. E., Forni, A., and Fong, J. (2012). Introduction to drug pharmacokinetics in the critically ill patient. Chest 141, 1327–1336. doi:10.1378/chest.11-1396
Thaler, F., Bernard, B., Tod, M., Jedynak, C. P., Petitjean, O., Derome, P., et al. (1995). Fluconazole penetration in cerebral parenchyma in humans at steady state. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39, 1154–1156. doi:10.1128/aac.39.5.1154
Toon, S., Ross, C. E., Gokal, R., and Rowland, M. (1990). An assessment of the effects of impaired renal function and haemodialysis on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 29, 221–226. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03623.x
Valtonen, M., Tiula, E., and Neuvonen, P. J. (1997). Effect of continuous venovenous haemofiltration and haemodiafiltration on the elimination of fluconazole in patients with acute renal failure. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 40, 695–700. doi:10.1093/jac/40.5.695
Van Daele, R., Wauters, J., Lagrou, K., Denooz, R., Hayette, M. P., Gijsen, M., et al. (2021). Pharmacokinetic variability and target attainment of fluconazole in critically ill patients. Microorganisms 9, 2068. doi:10.3390/microorganisms9102068
Van Der Elst, K. C., Pereboom, M., VAN Den Heuvel, E. R., Kosterink, J. G., SchöLVINCK, E. H., and Alffenaar, J. W. (2014). Insufficient fluconazole exposure in pediatric cancer patients and the need for therapeutic drug monitoring in critically ill children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 59, 1527–1533. doi:10.1093/cid/ciu657
Wojtyniak, J. G., Britz, H., Selzer, D., Schwab, M., and Lehr, T. (2020). Data digitizing: accurate and precise data extraction for quantitative systems pharmacology and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst. Pharmacol. 9, 322–331. doi:10.1002/psp4.12511
Wolter, K., Marggraf, G., Dermoumi, H., and Fritschka, E. (1994). Elimination of fluconazole during continuous veno-venous haemodialysis (CVVHD) in a single patient. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 47, 291–292. doi:10.1007/bf02570511
Yagasaki, K., Gando, S., Matsuda, N., Kameue, T., Ishitani, T., Hirano, T., et al. (2003). Pharmacokinetics and the most suitable dosing regimen of fluconazole in critically ill patients receiving continuous hemodiafiltration. Intensive Care Med. 29, 1844–1848. doi:10.1007/s00134-003-1980-z
Keywords: fluconazole, acute renal failure, continuous renal replacement therapy, population pharmacokinetics, PK/PD, shiny application
Citation: Zhang S, Zhang W, Wu T, Qin Y and Pei Q (2025) Optimizing fluconazole dosing in acute renal failure patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy: A population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1564070. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1564070
Received: 21 January 2025; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 28 March 2025.
Edited by:
Caisheng Wu, Xiamen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xi Luo, First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Wu, Qin and Pei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qi Pei, cGVpcWkxMDI4QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.