- 1Department of General Internal Medicine, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin, China
- 2Department of Hand Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin, China
Background: LRFN4 is expressed in various tumors and leukemia cell lines. This study aims to explore the effect of LRFN4 in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Methods: The data on LUAD patients were collected from the Cancer Genome Atlas and Gene Expression Omnibus database. The expression of LRFN4 in LUAD and LUAD cell lines was analyzed via differential gene analysis, qRT-PCR assay, and Western blotting assay. The correlation of LRFN4 expression with the onset of LUAD were calculated using Pearson correlation analysis. The transcription factors correlated with LRFN4 expression were screened by differential expression analysis and Pearson correlation analysis. Moreover, the effect of LRFN4 on the immune landscape of LUAD was analyzed using CIBERSORT algorithm. The GDSC and CTRP databases were used to analyze the drug sensitivity of hub gene.
Results: LRFN4 was highly expressed in LUAD patients and cells, and LRFN4 expression was correlated with metastasis, pathological stages, and age of LUAD patients. The transcription factors E2F1 and E2F3 could regulate LRFN4 expression by binding upstream of LRFN4. The 8 immune cell infiltration levels were differential between LRFN4high and LRFN4low patients. The ESTIMATEScore and ImmuneScore levels were decreased, the TumorPurity level was elevated, and 6 immune checkpoint expressions were increased in LRFN4high patients. Moreover, LRFN4high patients had inferior prognosis. The mutation rate of TP53, TTN, and MUC6 and the level of TMB were increased in LRFN4high patients. The expressions of TCF3, E2F1, E2F3, and LRFN4 were correlated with the IC50 of multiple drugs.
Conclusion: LRFN4 may serve as a novel prognostic biomarker for LUAD, shows specific overexpression in LUAD and may be a potential therapeutic target for LUAD patients.
1 Introduction
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most frequent form of primary lung cancer, accounting for more than 40% of these cases, and its prevalence is rising (Zhao et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024; Wei et al., 2024). The major symptoms of LUAD patients are shortness of breath and a persistent cough. LUAD is divided into several subtypes, including adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA), invasive adenocarcinoma, and variants of invasive adenocarcinoma (Liu et al., 2019b). However, the therapies for LUAD include many approaches, such as radiotherapy, surgical resection, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy (Hirsch et al., 2017). As LUAD often metastasizes by the time it’s diagnosed, identifying patients in the early stages has been a great challenge in clinical practice (Lin et al., 2021b). In addition, LUAD cells can rapidly develop drug resistance after initial therapy and are often untreatable with chemotherapeutic drugs (Min et al., 2022; Ascenzi et al., 2024). The 5-year overall survival rate of LUAD remains less than 20% (Lin et al., 2016). Thus, it is necessary to explore novel biomarkers to guide the prognosis of LUAD patients.
Leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain-containing proteins (LRFN), also known as synaptic adhesion-like molecules (SALM), are a family of leucinerich repeat (LRR)-containing synaptic cell adhesion molecules (Lie et al., 2018; Gu et al., 2023). This family consists of five know members: LRFN1/SALM2, LRFN2/SALM1, LRFN3/SALM4, LRFN4/SALM3, and LRFN5/SALM5 (Lie et al., 2018). It has been demonstrated that LRFN plays important roles in neurite outgrowth and synapse formation (Karki et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2023). A study that evaluated all known members of the LRFN family has discovered that only LRFN4 and LRFN5 were capable of initiating presynaptic differentiation in axons (Mah et al., 2010). Recently, LRFN4 has been found to be expressed in a variety of tumors and leukemia cell lines (Konakahara et al., 2011). This study has also reported that in the monocytic cell line THP-1 and in primary monocytes, LRFN4 expression is elevated following macrophage differentiation, and LRFN4 signaling could regulate both transendothelial migration and elongation of THP-1 cells by actin cytoskeleton reorganization (Konakahara et al., 2011). Zheng and colleagues have documented that in colorectal cancer (CRC), LRFN4 expression was tightly correlated with tumor location and TNM staging (Zheng et al., 2020). LRFN4 is upregulated in clinical gastric cancer cells and fibroblasts, and a high level of LRFN4 is found to be substantially linked with tumor invasive features and shorter survival rate of patients (Liu et al., 2019a), and LRFN4 overexpression is associated with higher risk of gastric cancer (Huang et al., 2021). In addition, LRFN4 is a risk gene for ovarian cancer (Li et al., 2021) and a prognostic biomarker for stomach adenocarcinoma (Han et al., 2021). However, to the best of our knowledge, the role of LRFN4 in LUAD has rarely been reported.
Thus, the purpose of this work is to explore the effect of LRFN4 in LUAD, and to investigate the molecular mechanism of LRFN4 in regulating the progression of LUAD. This study is the first to report the role of LRFN4 in the prognosis and immune microenvironment of LUAD patients, and is expected to provide a reference for the future development of new LUAD diagnosis and treatment strategies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data collection
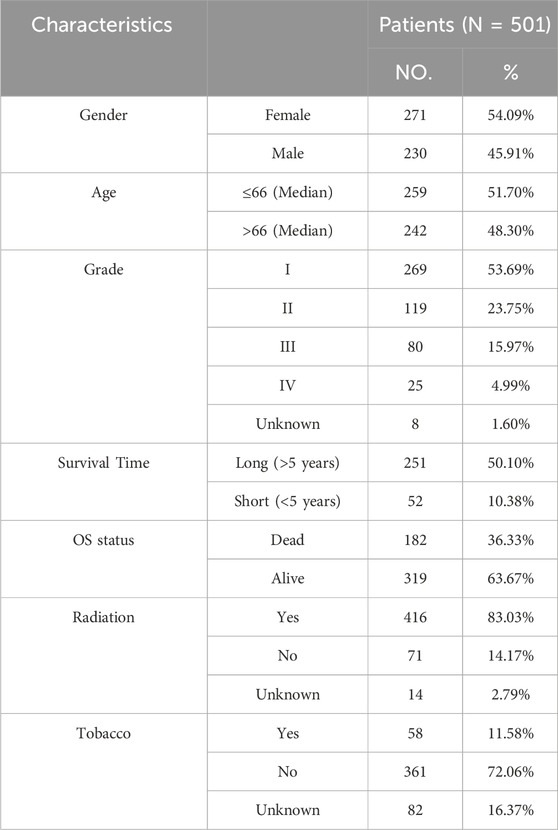
The mRNA expression profiles of 585 samples, including 525 LUAD and 60 normal samples, were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA, https://tcga-data.nci.nih.gov/tcga/) database. Among 585 samples, 501 samples contained complete survival information (Table 1). In addition, the GSE116959, GSE19188 and GSE68465 datasets were downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) database. GSE116959 included 57 LUAD samples and 11 normal samples, GSE19188 contained 91 LUAD samples and 65 normal samples, among which 82 samples had valid survival information. GSE68465 included 442 LUAD samples with complete and valid survival information. The data of three datasets (GSE116959, GSE19188 and GSE68465) were obtained using Agilent-039494 SurePrint G3 Human GE v2 8 × 60K Microarray 039,381, Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array, and Affymetrix Human Genome U133A Array platforms, respectively.
2.2 Differential gene analysis
The differential gene analysis was carried out between the two groups using the “limma” (Ritchie et al., 2015) function package in R (version 4.2.1, the same below). The |Log2FC| > 1 and P.adjust <0.05 were used to screen the differentially expressed genes (DEGs).
2.3 Cell collection and culture
The human lung epithelial cell line BEAS-2B (SCSP-5067) and human LUAD cell lines NCI-H1395 (NCI-H1395), NCI-H1975 (SCSP-597), and NCI-H441 (SCSP-5239) were obtained from the cell bank of the Type Culture Collection Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). These cell lines were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (11,875,085, GIBCO, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, A5670701, GIBCO, Carlsbad, CA) and maintained in a chamber at 37°C with 5% CO2.
2.4 qRT-PCR assay
The cells were utilized for RNA extraction with the TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). Following this, the RNA underwent conversion into cDNA utilizing the HiScript IV RT SuperMix for qPCR (+gDNA wiper) kit (Vazyme, R423-01, Nanjing, China). AceQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme, Q511-02, Nanjing, China) was employed for qRT-PCR as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. Table 2 displayed the primer sequences. GADPH served as the internal reference, with each sample undergoing triplicate runs. mRNA expression levels were determined using the 2−ΔΔCT calculation.
2.5 Western blotting assay
Total protein was extracted from cells using the RIPA buffer (Solarbio, China) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Western blotting assay was performed essentially as described previously (Wang et al., 2024). The primary antibodies used in this study included Anti-LRFN4 (Abcam, ab106369, USA) and beta Tubulin Polyclonal Antibody (Proteintech, 10068-1-AP, China). The secondary antibody was HRP-conjugated Affinipure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) (SA00001-2, Proteintech). The internal reference used in this study was Tubulin. The Western blot signal intensities were quantified using Image software.
2.6 Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)
In TCGA cohort, the patients were split into LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups according to the median value of LRFN4 expression. The DEGs between these two groups were obtained and were then subjected to GSEA using R language function package “clusterprofiler” (Yu et al., 2012). The significantly enriched pathways were screened by |NES| >1 and P < 0.05.
2.7 Survival analysis
The overall survival rate of different groups was estimated using the R language “survival” and “survminer” packages (https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival). The significance of differences in survival rate between different groups was tested using the log-rank. The multivariate Cox regression model was used to analyze whether the target gene could predict the survival of LUAD patients independently of other factors.
2.8 Immune cell infiltration
The CIBERSORT software (Newman et al., 2015) was applied to calculate the relative proportions of the 22 immune cells in the samples. CIBERSORT can describe the composition of immune infiltrating cells using the 547 preset barcode genes in deconvolution algorithm, based on the gene expression matrix. The immune score of samples was calculated using the “estimate” function package (https://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/estimate/). Moreover, the tumor immune dysfunction and ejection (TIDE, http://tide.dfei.harvard.edu/) score was used to evaluate tumor immunotherapy response.
2.9 Screening of transcription factors correlated with LRFN4 expression
In TCGA-LUAD mRNA cohort, the significantly differentially expressed transcription factors were selected using the DEGs between LUAD and normal samples according to LogFC >1 and P < 0.05. The correlation of transcription factors with LRFN4 expression were calculated using Pearson correlation, and the transcription factors significantly correlated with LRFN4 were screened according to P < 0.05 and Rho >0.5.
2.10 Prediction of transcription factor binding sites
The 1,000 bp sequence file upstream of LRFN4 gene start site was downloaded from UCSC (http://genome.ucsc.edu/). The corresponding motif file for the transcription factor was downloaded from the JASPER database (https://jaspar.genereg.net/). The online tool FIMO (https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/fimo) was then used to predict whether there is a transcription factor binding motif in the region upstream of LRFN4 promoter.
2.11 Drug sensitivity analysis
The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 265 small molecules from the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC) database in 860 cell lines, along with their corresponding mRNA levels, and those of 481 small molecules from the Cancer Therapeutics Response Portal (CTRP) database in 1,001 cell lines, along with their corresponding mRNA levels, were collected. Combined the mRNA expression and drug sensitivity data, the relationship between drug IC50 and gene mRNA expression was obtained using Pearson analysis. The P-values were adjusted by false discovery rate (FDR).
2.12 Statistical analysis
The Wilcoxon rank sum test was utilized to compare the expression differences of LRFN4 in tumor and normal samples, as well as other clinicopathological characteristics. Univariate cox regression analysis was used to analyze the correlation between LRFN4 and other reported biomarkers and prognosis. The effects of the mRNA expression of LRFN4 and clinicopathological characteristics on overall survival were determined through a multivariate Cox regression proportional hazards model. Statistical significance was considered present when the P < 0.05.
Additionally, the statistical analysis of all experimental data was performed with GraphPad Prism version 9.5.0, and the results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). For comparisons between two groups, an unpaired two-tailed t-test was employed, and a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 LRFN4 was highly expressed in LUAD patients, and LRFN4 was correlated with metastasis, pathological stages and age of LUAD
Firstly, we analyzed the expression of LRFN4 in LUAD patients in TNMplot database (The entire database contains 56,938 samples, including 33,520 samples from 3180 gene chip-based studies (453 metastatic, 29,376 tumorous and 3691 normal samples), 11,010 samples from TCGA (394 metastatic, 9886 tumorous and 730 normal), 1193 samples from TARGET (1 metastatic, 1180 tumorous and 12 normal) and 11,215 normal samples from GTEx). We found that in the TNMplot database, LRFN4 expression was significantly increased in LUAD samples compared to normal samples in both TCGA and Chip datasets (Figures 1A, B), and LRFN4 upregulated in metastatic LUAD samples in Chip datasets (Figure 1C, metastatic vs non-metastatic, p < 0.001). As expected, the expression level of LRFN4 in TCGA-LUAD and GEO cohorts were consistent with TNMplot database (Figures 1D–F). We also performed qRT-PCR and Western blotting assay verification, and the results showed that LRFN4 expression trend in LUAD cells was consistent with the transcriptome result (Figures 1G, H).
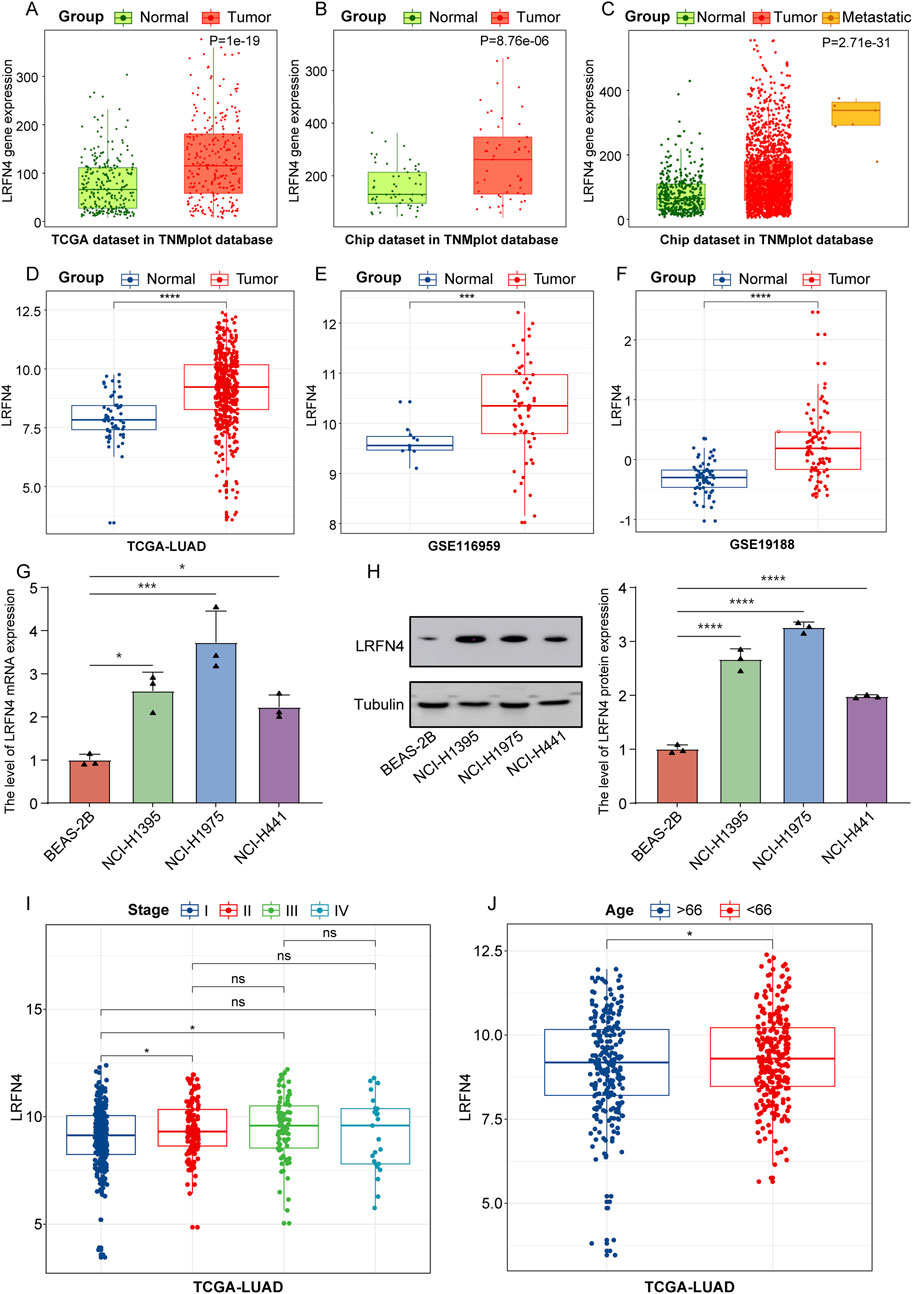
Figure 1. LRFN4 was high expressed in LUAD patients, and LRFN4 expression was correlated with metastasis, pathological stages and age of LUAD. (A, B) The expression of LRFN4 in LUAD samples in both TCGA and Chip datasets in TNMplot database. (C) The expression of LRFN4 in metastatic and non-metastatic LUAD samples in Chip datasets in TNMplot database. (D–F) The expression of LRFN4 in LUAD samples in TCGA-LUAD, GSE116959, GSE19188 datasets, respectively. (G) The expression of LRFN4 mRNA in the three LUAD cell lines was measured by qRT-PCR assay. (H) The expression of LRFN4 protein in the three LUAD cell lines was measured by Western blotting assay. (I) The expression of LRFN4 in different pathological stages (I, II, III, IV) of LUAD in TCGA-LUAD cohort. (J) The correlation of LRFN4 expression with age in TCGA-LUAD cohort *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns: no significant.
Next, we analyzed the correlation of LRFN4 expression with different pathological stages (I, II, III, IV) of LUAD in TCGA-LUAD cohort, and found that LRFN4 expression was increased in stage II and III compared to stage I (Figure 1I) and was significantly higher in patients younger than 66 years compared to those older than 66 years (Figure 1J). Nevertheless, LRFN4 expression was not remarkably differential between men and women (Supplementary Figure S1). In short, LRFN4 was highly expressed in LUAD patients, and LRFN4 probably contributed to the malignant progression of LUAD.
3.2 The pathways correlated with LRFN4 in LUAD
The GSEA results showed that a total of 19 and 86 signaling pathways were observably activated and inhibited in LRFN4high group compared to in LRFN4low group, respectively (Supplementary Table S1; Figure 2A (top 10 activated and inhibited terms)). Among which, the Ras signaling pathway, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Proteoglycans in cancer, Gastric cancer, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, mTOR signaling pathway, Hippo signaling pathway and Wnt signaling pathway were widely reported to correlate with various cancers (Figures 2B–I).
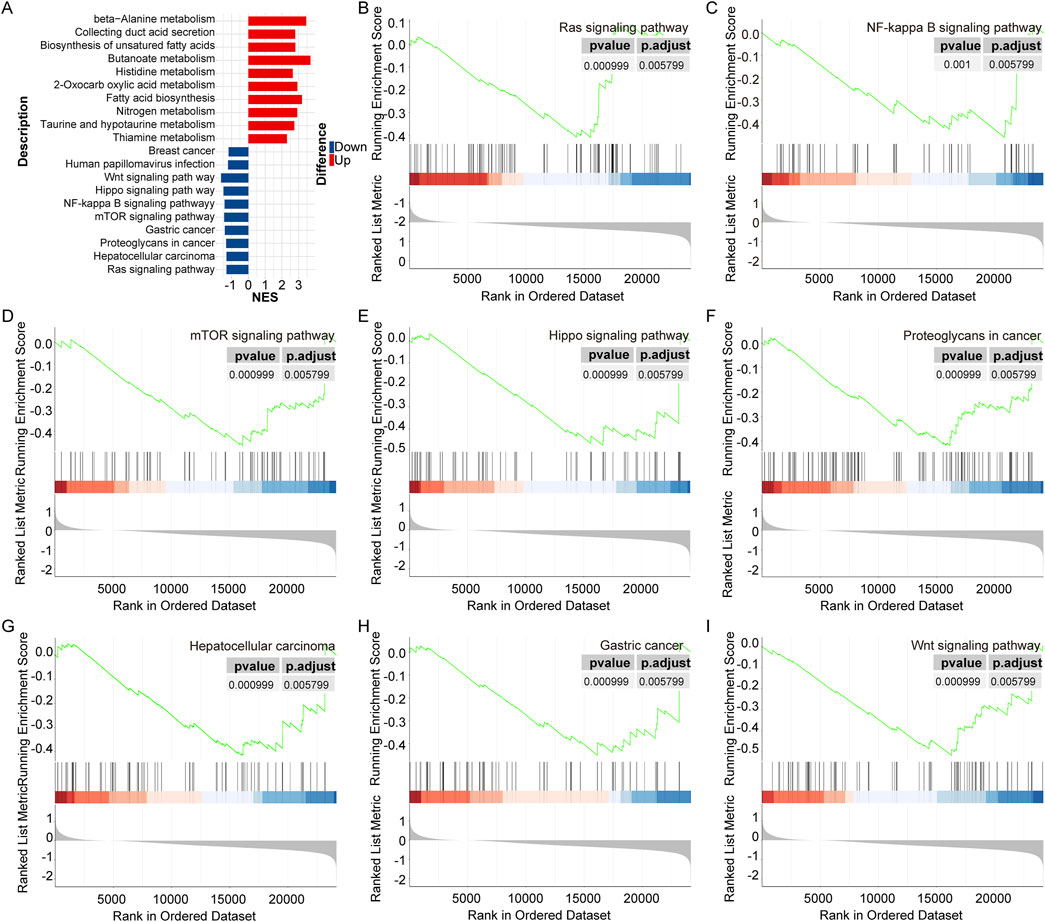
Figure 2. The pathways correlated with LRFN4 in LUAD. (A) The top 10 significantly activated and inhibited pathways. (B–I) The Ras signaling pathway, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Proteoglycans in cancer, Gastric cancer, NF-kappa B signaling pathway, mTOR signaling pathway, Hippo signaling pathway and Wnt signaling pathway were correlated with cancer.
3.3 The transcription factors E2F1 and E2F3 could regulate LRFN4 expression by binding upstream of LRFN4
We obtained 212 differentially expressed transcription factors between LUAD and normal samples. The Person correlation analysis showed that 10 transcription factors (TCF3, HMGA1, UHRF1, HDGF, OTX1. RAD51, E2F2, E2F3, FOXM1, MEN1) were dramatically positively correlated with LRFN4 expression (Figures 3A–J). We discovered that in the about 369bp, 761bp, 844bp upstream of LRFN4 promoter, there were binding sites for transcription factors TCF3 (MA0522.3.meme), E2F1 (MA0024.2.meme) and E2F3 (MA0469.1.meme), respectively (Supplementary Table S2). These results suggested that the transcription factors TCF3, E2F1 and E2F3 might regulate LRFN4 expression by binding upstream of LRFN4.

Figure 3. The transcription factors E2F1 and E2F3 could regulate LRFN4 expression by binding upstream of LRFN4. (A–J) The 10 transcription factors (TCF3, HMGA1, UHRF1, HDGF, OTX1. RAD51, E2F2, E2F3, FOXM1, MEN1) expression were dramatically positively correlated with LRFN4 expression. (K) E2F1 had a distinct binding peak upstream of the LRFN4 gene in Breast-GSM2501567 dataset. (L) E2F3 exhibited a distinct binding peak upstream of the LRFN4 gene in Colon-GSM1239452 dataset.
Furthermore, in chip-seq database (http://cistrome.org/db/#/), we found that E2F1 and E2F3 had a distinct binding peak at upstream of LRFN4 gene in Breast-GSM2501567 dataset (Gallenne et al., 2017) (Figure 3K, score = 2.693) and in Colon-GSM1239452 dataset (Yan et al., 2013) (Figure 3L, score = 1.856), respectively. Thus, transcription factors E2F1 and E2F3 could regulate LRFN4 expression by binding at upstream of LRFN4.
3.4 LRFN4 might involve in affecting the immune landscape of LUAD
In TCGA-LUAD cohort, we calculated the relative content of 22 immune cell infiltration in LUAD samples using CIBERSORT (Figure 4A). As presented in Figure 4B, the relative contents of 3 immune cells’ infiltration (activated memory CD4+T cells, T follicular helper cells (Tfh), M0 macrophages) were significantly reduced and 5 immune cells’ infiltration (resting memory CD4+T cells, monocytes, resting dendritic cells, activated dendritic cells, resting mast cells) were significantly increased in LRFN4high group compared to in LRFN4low group. Moreover, the levels of CD4+T cell subsets, such as effector memory CD4+T cells, memory CD4+T cells, T helper 1 cell (Th1), and Th2 were significantly different between LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups using xCell algorithm (Supplementary Figure S2A). MCPcounter algorithm showed that Monocyte was also higher in LRFN4high group compared to in LRFN4low group (Supplementary Figure S2B). LRFN4 expression was significantly negatively correlated with resting memory CD4+T cells and resting mast cells (Figures 4C, D), and was remarkably positively associated with M0 macrophages (Figure 4E).
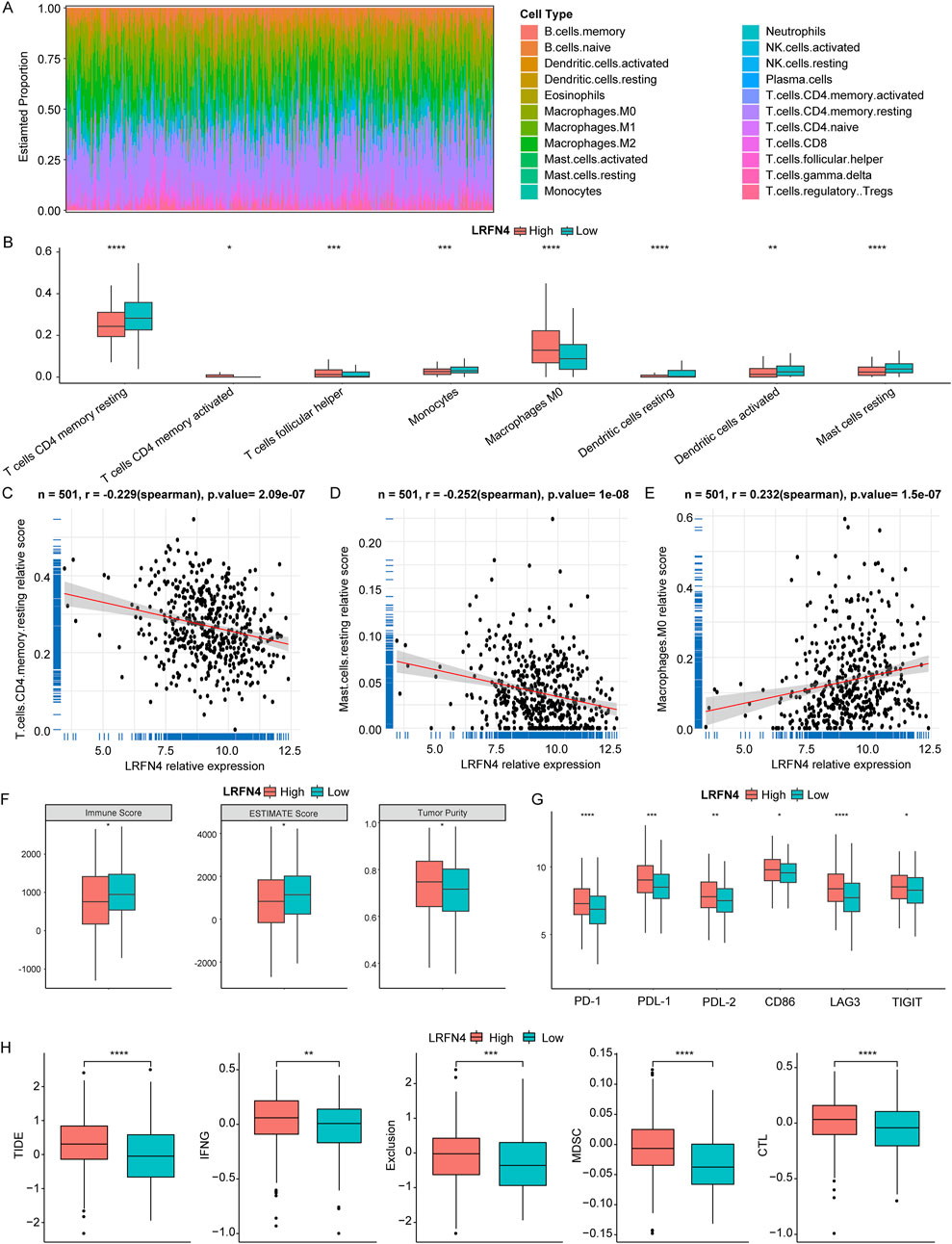
Figure 4. LRFN4 might involve in the immune landscape of LUAD. (A) The relative content of 22 immune cell infiltration in LUAD samples. (B) The relative content of 8 immune cell infiltration in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups. (C–E) The correlation of LRFN4 expression with T cells CD4 memory resting Mast cells resting and Macrophages M0. (F) The level of ESTIMATEScore, ImmuneScore and TumorPurity in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups. (G) The 6 immune checkpoints (PD-1 (PDCD1), PDL-1 (CD274), PDL-2 (PDCD1LG2), CD86, LAG3, TIGIT) expression in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups. (H) The levels of Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion (TIDE), Interferon gamma (IFNG), Exclusion, Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Moreover, we found that the ESTIMATE Score and Immune Score were observably decreased and Tumor Purity was significantly increased in LRFN4high group compared to in LRFN4low group (Figure 4F). The 6 immune checkpoints (PD-1 (PDCD1), PDL-1 (CD274), PDL-2 (PDCD1LG2), CD86, LAG3, TIGIT) expression were markedly increased in LRFN4high group compared to LRFN4low group (Figure 4G). We further analyzed the TIDE in both the LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups to evaluate the response to immunotherapy. As shown in Figure 4H, TIDE, Interferon gamma (IFNG), Exclusion, Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) were significantly elevated in the LRFN4high group (high vs low, p < 0.05). These results suggested that LUAD patients with high LRFN4 expression were less likely to benefit from immunotherapy.
3.5 LRFN4 could predict the prognosis of LUAD patients
Subsequently, we analyzed the correlation between LRFN4 expression and prognosis of LUAD patients. In TCGA-LUAD, GSE19188 and GSE68465 cohorts, the patients in LRFN4high group were correlated with inferior prognosis (Figures 5A–C). In TCGA-LUAD cohort, we preformed the multivariate Cox regression analysis to further determine the independent prognostic indicators, including age, gender, stage and LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups (eight samples without stage information were removed). The results showed that LRFN4 could independently predict the prognosis of LUAD patients (Figure 5D). Furthermore, we examined the relationship between LRFN4 and other biomarkers, specifically YKT6 (Zhang et al., 2024a), SPOCK1 (Liu et al., 2023), and MCM4 (Tan et al., 2023), in relation to the prognosis of LUAD patients. Our analysis revealed that, compared to the other biomarkers (YKT6, MCM4), LRFN4 exhibited a stronger correlation with the prognosis of LUAD patients (Supplementary Figure S3).
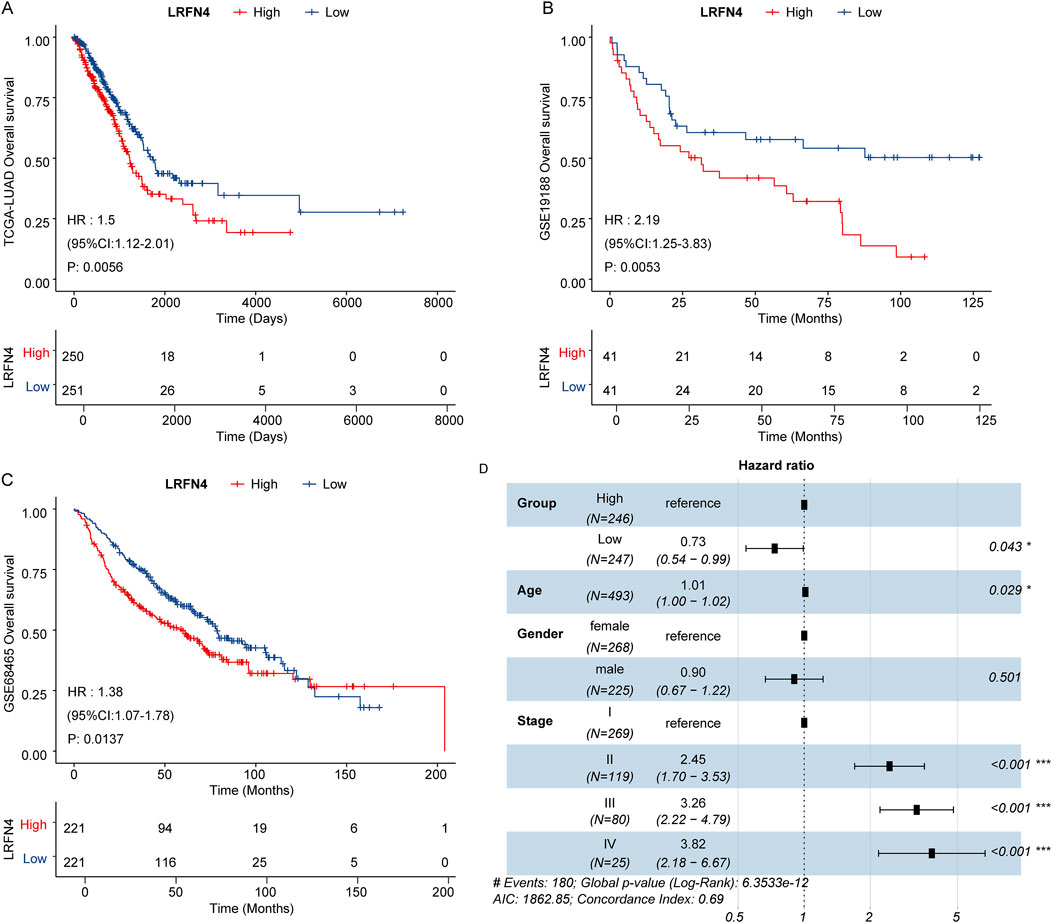
Figure 5. LRFN4 could predict the prognosis of LUAD patients. (A) The Kaplan–Meier survival curve (LRFN4high and LRFN4low LUAD patients) for overall survival in TCGA-LUAD cohort. (B) The Kaplan–Meier survival curve (LRFN4high and LRFN4low LUAD patients) for overall survival in GSE19188 dataset. (C) The Kaplan–Meier survival curve (LRFN4high and LRFN4low LUAD patients) for overall survival in GSE68465 dataset. (D) The multivariate Cox regression analysis including age, gender, stage, LRFN4high and LRFN4low group.
3.6 The copy number variation (CNV), gene mutation and tumor mutation burden (TMB) in LRFN4high and LRFN4low LUAD patients
To investigate the potential cause of upregulation of LRFN4 in LUAD, we analyzed the CNV in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups using TCGA-LUAD cohort. As showed in Figures 6A, B, the high-level copy number amplification accounted for 53% and 60% in LRFN4high group and LRFN4low group, respectively. Thus, the copy number amplification might be one of the reasons for LRFN4 upregulation in LUAD patients. Next, we analyzed the gene mutation and TMB level in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups. The mutation rate of TP53, TTN and MUC6 were increased in LRFN4high group compared to LRFN4low group (Figure 6C). The level of TMB was observably increased in LRFN4high group compared to LRFN4low group (Figure 6D).
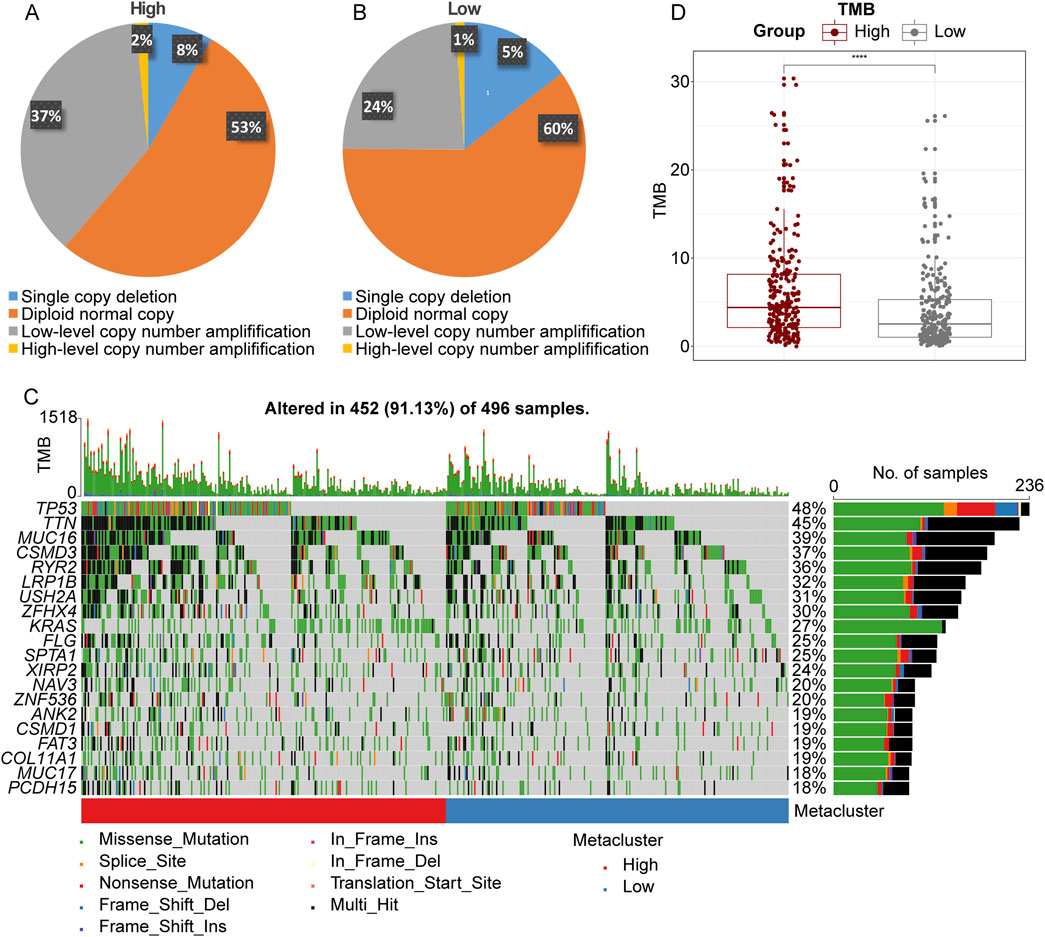
Figure 6. The copy number variation (CNV), gene mutation and tumor mutation burden (TMB) in LRFN4high and LRFN4low LUAD patients. (A, B) The CNV in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups. (C) The mutation rate of genes in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups. (D) The level of TMB in LRFN4high and LRFN4low groups.
3.7 The correlation of TCF3, E2F1, E2F3, LRFN4 expression with drug sensitivity
Finally, we analyzed the correlation of TCF3, E2F1, E2F3, LRFN4 expression with drug sensitivity. We collected a total of 265 small molecules of IC860 and 481 small molecules of IC1001 from 50 different cell lines, along with their corresponding mRNA gene expressions in the GDSC and CTRP, and combined the mRNA expression and drug sensitivity data. We found that in GDSC, LRFN4 expression was negatively correlated with IC50 of 17-AAG, the E2F1, E2F3 and TCF3 expression was positively associated with the IC50 of RDEA119, trametinib, selumetinib and 17-AAG, and was negatively correlated with the IC50 of many drugs, such as AR-40, BX-912 (Figure 7A; Supplementary Table S3). In CTRP, LRFN4 expression exhibited positive correlation with the IC50 of BRD−K34222889, NSC95397, PL-DI, PRIMA-1, necrosulfonamide, while the E2F1, E2F3 and TCF3 expression had negative association with the IC50 of these drugs (Figure 7B; Supplementary Table S4).
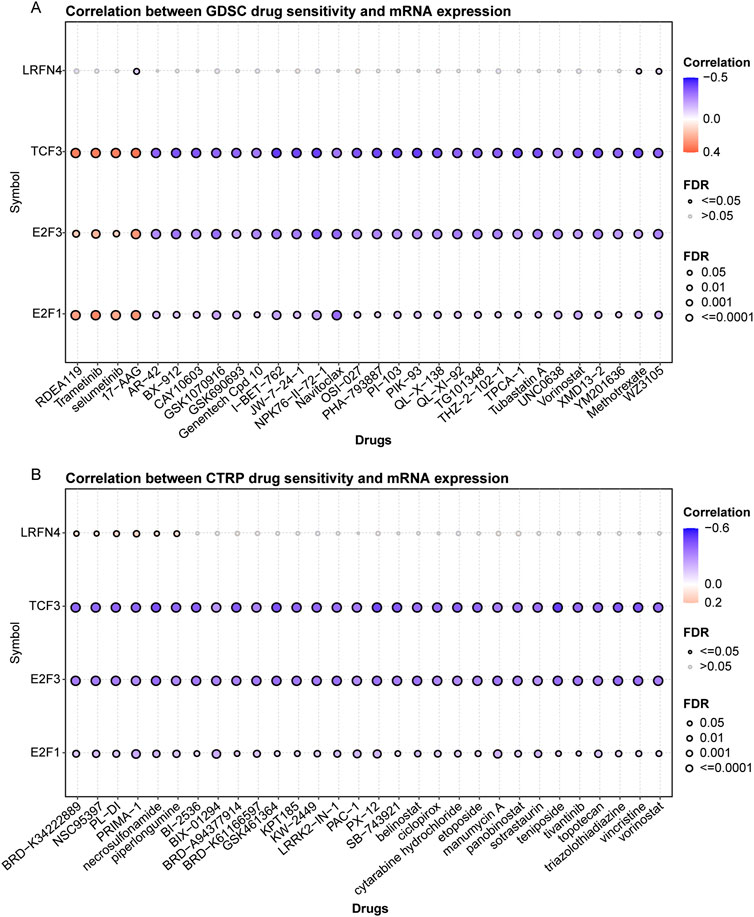
Figure 7. The correlation of TCF3, E2F1, E2F3, LRFN4 expression with drug sensitivity. (A, B) The correlation of TCF3, E2F1, E2F3, LRFN4 expression with IC50 of drugs in Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC) and Response Portal for Therapeutic Genomics (CTRP).
4 Discussion
Previous studies have reported that the LRFN proteins were essential for neuritis development and branching, as well as synapse formation and maturation (Ko et al., 2006; Lie et al., 2016). In recent years, some researchers have found that in nonneural tissues, the LRFN were also expressed and exerted vital functions. The LRFN2 protein may subvert hematopoietic differentiation to enhance erythropoiesis, and it can cause erythroblastosis in MEnTCD2.5 lymph node cells when it collaborates with Myc (Castellanos et al., 2007). Noteworthily, Konakahara and colleagues have revealed that LRFN4 protein was expressed in a wide range of human cancer and leukemia cell lines, gastric cancer MKN7 cells, T-cell leukemia Jurkat cells, breast cancer SK-BR-3 cells Burkitt’s lymphoma Ramos cells and monocytic leukemia THP-1 and U937 cells (Konakahara et al., 2011). LRFN4 is a risk gene for ovarian cancer (Li et al., 2021) and a prognostic biomarker for stomach adenocarcinoma (Han et al., 2021). Liu et al. have reported that the in clinical gastric cancer tissues, LRFN4 expression was elevated in tumor cells and fibroblasts, and the overexpress of LRFN4 was substantially linked with tumor invasive features, and the gastric cancer patients with high LRFN4 expression had poor prognosis (Liu et al., 2019a). In the present study, LRFN4 was high expressed in LUAD patients, and the patients with upregulated LRFN4 exhibited inferior prognosis. In addition, in CRC, LRFN4 expression was closely correlated with tumor location, T staging, N staging and TNM staging (Zheng et al., 2020), these findings were consistent with our results. Moreover, we also discovered that LRFN4 expression was correlated with metastasis and age of LUAD patients. Accordingly, LRFN4 was a risk gene for LUAD, and it might predict the prognosis of LUAD patients.
In addition, we discovered that the expression of LRFN4 was regulated via transcription factors E2F1 and E2F3 by binding upstream of LRFN4 in LUAD. E2F1 and E2F3 are members of E2F family, and this family genes were important in the development of tumors because they could regulate DNA replication and cell cycle progression (Chen et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2015). It has been demonstrated that the level of E2F1 and E2F3 expression were related to the clinical outcomes of multiple tumors, such as lung cancer (Ren et al., 2017), pediatric retinoblastoma (Chen et al., 2022), breast cancer (Han et al., 2020), hepatocellular carcinoma (Han et al., 2019). Sun and colleagues have indicated that the levels of E2F1 and E2F3 expression were increased in LUAD and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) tissues (Sun et al., 2018). They also found that the high transcription level of E2F1 was linked with shorter relapse-free survival (RFS), while the high E2F3 transcription level was correlated with longer RFS in lung patients (Sun et al., 2018). Wang et al. have revealed that the high expression of E2F1 was significantly related to poor patient survival in lung cancer (Wang et al., 2021). The E2F1 expression exhibited positive associate with Ki-67 proliferation index in NSCLC cells (Meng et al., 2020). Furthermore, in gastric cancer, E2F1 was a potential downstream target of CHPF, and knockdown of E2F1 reduced the CHPF-induced promotion of gastric cancer (Lin et al., 2021a). In pediatric retinoblastoma, E2F1 could increase the expression of CKS2 via binding to its promotor, thereby promoting the promotes cell proliferation and tumor formation (Chen et al., 2022). In endometrial cancer, the knocking down E2F3 could inhibit the ability of HOXB9 in promoting migration of tumor cell (Wan et al., 2018). In this work, the E2F1 and E2F3 had distinct binding peak upstream of LRFN4 gene in LUAD. These evidences indicated that E2F1 and E2F3 might regulate the expression of LRFN4 to involve in the progression of LUAD. However, this requires further verification, and it would be an interesting question for a future study.
We also discovered that LRFN4 expression was significantly negatively correlated with T cells CD4 memory resting and Mast cells resting, and was remarkably positively associated with Macrophages M0. The T cells predominated in lung cancer immune landscape, and CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells were the common prevalent T cell subtypes (Kraemer et al., 2023). The increased levels of CD3+ and CD8+T cells exhibited better prognosis of NSCLC patients (Schalper et al., 2015), and the NSCLC patients with higher CD8+ counts had longer overall survival rate. It has been reported that the inactivated mast cells and inactivated CD4 memory T cells were closely associated with good prognosis of LUAD patients (Gentles et al., 2015). Mast cells are innate immune cells that live in the tissue and play an important role in the inflammatory response and tissue homeostasis (Plum et al., 2024; Shu et al., 2025). In tumor microenvironment, mast cells could regulate cell proliferation and survival, invasiveness, metastasis, and angiogenesis (Aponte-Lopez and Munoz-Cruz, 2020). M1 macrophages limit tumor growth by secreting proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α (Zhang et al., 2024b; Hsiao et al., 2025; Murray et al., 2014). The M2 macrophages promoted the PD-1 expression, inhibiting T cell immune function and promoting tumor cell immune escape (Gordon et al., 2017). Konakahara et al. have found that in the monocytic cell line THP-1 and in primary monocytes, LRFN4 expression is elevated following macrophage differentiation (Konakahara et al., 2011). Based on this evidence, LRFN4 may promote an immunosuppressive environment in LUAD, potentially impeding T cell activity and diminishing the effectiveness of treatments such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Immune checkpoints, including PD-1, play a crucial role in regulating T cell responses (Andrews et al., 2024). In the present study, PD-1 expression was significantly increased in the LRFN4 high-expression group compared to the LRFN4 low-expression group. This indicates that LRFN4 may promote T cell exhaustion by upregulating PD-1 expression, thereby inhibiting anti-tumor immune responses.
Furthermore, the level of TMB was notably higher in the LRFN4 high-expression group compared to the LRFN4 low-expression group. TMB has been associated with improved responses to immunotherapy in various cancers (Ribas and Wolchok, 2018) and is positively correlated with the efficacy of PD-1 checkpoint inhibition (Goodman et al., 2017). However, we observed that patients with LUAD exhibiting elevated levels of LRFN4 expression had higher TIDE scores, suggesting that these patients may be less likely to benefit from immunotherapy. These results indicate that although TMB levels were elevated in the high-expression group of LRFN4, it is plausible that LRFN4 inhibits T cell activity through the upregulation of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression, which may consequently reduce the efficacy of ICIs. Moreover, drug sensitivity showed that LRFN4 and transcription factors (E2F1 and E2F3) were correlated with IC50 of multiple drugs, indicating that the expression of LRFN4 and the transcription factors that regulate its expression in LUAD may be of great significance in guiding clinical medication.
While this study elucidates the expression of LRFN4 in LUAD and its implications for prognosis, tumor microenvironment, and drug sensitivity, several limitations warrant attention. First, the study is based on retrospective data from TCGA and GEO database, the limited sample size in public databases may cause possible bias to the results, and lacks validation through independent clinical samples. Thus, prospective studies with larger sample sizes are essential for future research. Additionally, although GSEA has identified potential pathways involving LRFN4 in LUAD, further functional experiments are necessary to clarify the precise mechanisms by which LRFN4 contributes to LUAD progression. Furthermore, the predicted interactions of transcription factors with the LRFN4 promoter require validation through experimental methods. Lastly, a comprehensive understanding of the role of LRFN4 in the LUAD prognosis, immune microenvironment and its implications for immunotherapy necessitates additional clinical samples and prospective studies.
5 Conclusion
LRFN4 is significantly upregulated in LUAD samples and cells and is correlated with poor prognosis. As a new prognostic biomarker for LUAD, LRFN4 may be a potential therapeutic target for LUAD patients. LRFN4 is associated with immunological characteristics of LUAD. This study provides new insights into the prediction of disease progression and the development of targeted therapies for LUAD. However, the biological role of LRFN4 in the prognosis and immune microenvironment of LUAD patient needs to be further studied in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database at [https://tcga-data.nci.nih.gov/tcga/] and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database at [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/] (accession number: GSE116959, GSE19188 and GSE68465).
Author contributions
NW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. SC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. XT: Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. ML: Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1540636/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1 | The correlation between LRFN4 expression and gender.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S2 | The immune cell infiltration of LUAD was estimated via xCell (A) and MCPcounter (B) algorithms. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S3 | The result of univariate Cox regression analysis.
Abbreviations
LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; CNV, copy number variation; TMB, tumor mutation burden; AIS, adenocarcinoma in situ; MIA, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma; LRFN, Leucine rich repeat and fibronectin; SALM, synaptic adhesion like molecules; LRR, leucinerich repeat; CRC, colorectal cancer; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; GEO, Gene Expression Omnibus; DEGs, differentially expressed genes; GSEA, Gene set enrichment analysis; GDSC, Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer; TCF3, transcription factors; CNV, copy number variation; TMB, tumor mutation burden; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; RFS, relapse-free survival.
References
Andrews, L. P., Butler, S. C., Cui, J., Cillo, A. R., Cardello, C., Liu, C., et al. (2024). LAG-3 and PD-1 synergize on CD8(+) T cells to drive T cell exhaustion and hinder autocrine IFN-gamma-dependent anti-tumor immunity. Cell 187 (16), 4355–4372.e22. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.016
Aponte-Lopez, A., and Munoz-Cruz, S. (2020). Mast cells in the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1273, 159–173. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-49270-0_9
Ascenzi, F., Esposito, A., Bruschini, S., Salvati, V., De Vitis, C., De Arcangelis, V., et al. (2024). Identification of a set of genes potentially responsible for resistance to ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cancer stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 15 (4), 303. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06667-w
Castellanos, A., Lang, G., Frampton, J., and Weston, K. (2007). Regulation of erythropoiesis by the neuronal transmembrane protein Lrfn2. Exp. Hematol. 35 (5), 724–734. doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2007.02.004
Chen, H. Z., Tsai, S. Y., and Leone, G. (2009). Emerging roles of E2Fs in cancer: an exit from cell cycle control. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9 (11), 785–797. doi:10.1038/nrc2696
Chen, M., Zhao, Z., Wu, L., Huang, J., Yu, P., Qian, J., et al. (2022). E2F1/CKS2/PTEN signaling axis regulates malignant phenotypes in pediatric retinoblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 13 (9), 784. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05222-9
Chen, Y., Zhou, Y., Ren, R., Chen, Y., Lei, J., and Li, Y. (2024). Harnessing lipid metabolism modulation for improved immunotherapy outcomes in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 12 (7), e008811. doi:10.1136/jitc-2024-008811
Gallenne, T., Ross, K. N., Visser, N. L., Desmet, C. J., Wittner, B. S., Wessels, F. A., et al. (2017). Systematic functional perturbations uncover a prognostic genetic network driving human breast cancer. Oncotarget 8 (13), 20572–20587. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16244
Gentles, A. J., Newman, A. M., Liu, C. L., Bratman, S. V., Feng, W., Kim, D., et al. (2015). The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat. Med. 21 (8), 938–945. doi:10.1038/nm.3909
Goodman, A. M., Kato, S., Bazhenova, L., Patel, S. P., Frampton, G. M., Miller, V., et al. (2017). Tumor mutational burden as an independent predictor of response to immunotherapy in diverse cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 16 (11), 2598–2608. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0386
Gordon, S. R., Maute, R. L., Dulken, B. W., Hutter, G., George, B. M., McCracken, M. N., et al. (2017). PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity. Nature 545 (7655), 495–499. doi:10.1038/nature22396
Gu, Y. H., Wang, J., Lu, W. C., Cheng, Y., Tao, R., Zhang, S. J., et al. (2023). POU2F1/DNMT3a pathway participates in neuropathic pain by hypermethylation-mediated LRFN4 downregulation following oxaliplatin treatment. Neurochem. Res. 48 (12), 3652–3664. doi:10.1007/s11064-023-04011-w
Han, R., Chen, X., Li, Y., Zhang, S., Li, R., and Lu, L. (2019). MicroRNA-34a suppresses aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating E2F1, E2F3, and Caspase-3. Cancer Manag. Res. 11, 2963–2976. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S202664
Han, R., Zhao, J., and Lu, L. (2020). MicroRNA-34a expression affects breast cancer invasion in vitro and patient survival via downregulation of E2F1 and E2F3 expression. Oncol. Rep. 43 (6), 2062–2072. doi:10.3892/or.2020.7549
Han, S., Zhu, W., Yang, W., Guan, Q., Chen, C., He, Q., et al. (2021). A prognostic signature constructed by CTHRC1 and LRFN4 in stomach adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet. 12, 646818. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.646818
Hirsch, F. R., Scagliotti, G. V., Mulshine, J. L., Kwon, R., Curran, W. J., Wu, Y. L., et al. (2017). Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 389 (10066), 299–311. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30958-8
Hsiao, Y. J., Hsieh, M. S., Chang, G. C., Hsu, Y. C., Wang, C. Y., Chen, Y. M., et al. (2025). Tp53 determines the spatial dynamics of M1/M2 tumor-associated macrophages and M1-driven tumoricidal effects. Cell Death Dis. 16 (1), 38. doi:10.1038/s41419-025-07346-0
Huang, S., Ma, L., Lan, B., Liu, N., Nong, W., and Huang, Z. (2021). Comprehensive analysis of prognostic genes in gastric cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 13 (20), 23637–23651. doi:10.18632/aging.203638
Karki, S., Shkumatov, A. V., Bae, S., Kim, H., Ko, J., and Kajander, T. (2020). Structural basis of SALM3 dimerization and synaptic adhesion complex formation with PTPσ. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 11557. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-68502-4
Ko, J., Kim, S., Chung, H. S., Kim, K., Han, K., Kim, H., et al. (2006). SALM synaptic cell adhesion-like molecules regulate the differentiation of excitatory synapses. Neuron 50 (2), 233–245. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2006.04.005
Konakahara, S., Saitou, M., Hori, S., Nakane, T., Murai, K., Itoh, R., et al. (2011). A neuronal transmembrane protein LRFN4 induces monocyte/macrophage migration via actin cytoskeleton reorganization. FEBS Lett. 585 (14), 2377–2384. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2011.06.011
Kraemer, A. I., Chong, C., Huber, F., Pak, H., Stevenson, B. J., Muller, M., et al. (2023). The immunopeptidome landscape associated with T cell infiltration, inflammation and immune editing in lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 4 (5), 608–628. doi:10.1038/s43018-023-00548-5
Li, H., Li, M., Tang, C., and Xu, L. (2021). Screening and prognostic value of potential biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 9 (12), 1007. doi:10.21037/atm-21-2627
Lie, E., Ko, J. S., Choi, S. Y., Roh, J. D., Cho, Y. S., Noh, R., et al. (2016). SALM4 suppresses excitatory synapse development by cis-inhibiting trans-synaptic SALM3-LAR adhesion. Nat. Commun. 7, 12328. doi:10.1038/ncomms12328
Lie, E., Li, Y., Kim, R., and Kim, E. (2018). SALM/Lrfn family synaptic adhesion molecules. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 11, 105. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2018.00105
Lin, J. J., Cardarella, S., Lydon, C. A., Dahlberg, S. E., Jackman, D. M., Janne, P. A., et al. (2016). Five-year survival in EGFR-mutant metastatic lung adenocarcinoma treated with EGFR-TKIs. J. Thorac. Oncol. 11 (4), 556–565. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2015.12.103
Lin, X., Han, T., Xia, Q., Cui, J., Zhuo, M., Liang, Y., et al. (2021a). CHPF promotes gastric cancer tumorigenesis through the activation of E2F1. Cell Death Dis. 12 (10), 876. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04148-y
Lin, Y. Y., Wang, Y. C., Yeh, D. W., Hung, C. Y., Yeh, Y. C., Ho, H. L., et al. (2021b). Gene expression profile in primary tumor is associated with brain-tropism of metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (24), 13374. doi:10.3390/ijms222413374
Liu, H., Tang, X., Srivastava, A., Pecot, T., Daniel, P., Hemmelgarn, B., et al. (2015). Redeployment of Myc and E2f1-3 drives Rb-deficient cell cycles. Nat. Cell Biol. 17 (8), 1036–1048. doi:10.1038/ncb3210
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Chen, X., Yang, X., Song, Q., and Wu, H. (2019a). High SALM3 expression in tumor cells and fibroblasts is correlated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. Dis. Markers 2019, 8282414. doi:10.1155/2019/8282414
Liu, Y., Han, T., Wu, J., Zhou, J., Guo, J., Miao, R., et al. (2023). SPOCK1, as a potential prognostic and therapeutic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma, is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and immune evasion. J. Transl. Med. 21 (1), 909. doi:10.1186/s12967-023-04616-3
Liu, Y., Ye, X., Yu, Y., and Lu, S. (2019b). Prognostic significance of anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement in patients with completely resected lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis. 11 (10), 4258–4270. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.09.65
Mah, W., Ko, J., Nam, J., Han, K., Chung, W. S., and Kim, E. (2010). Selected SALM (synaptic adhesion-like molecule) family proteins regulate synapse formation. J. Neurosci. 30 (16), 5559–5568. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4839-09.2010
Meng, Q., Liu, M., and Cheng, R. (2020). LINC00461/miR-4478/E2F1 feedback loop promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and migration. Biosci. Rep. 40 (2). doi:10.1042/BSR20191345
Min, W., Sun, L., Li, B., Gao, X., Zhang, S., and Zhao, Y. (2022). lncCRLA enhanced chemoresistance in lung adenocarcinoma that underwent EpithelialMesenchymal transition. Oncol. Res. 28 (9), 857–872. doi:10.3727/096504021X16203818567367
Murray, P. J., Allen, J. E., Biswas, S. K., Fisher, E. A., Gilroy, D. W., Goerdt, S., et al. (2014). Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 41 (1), 14–20. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008
Newman, A. M., Liu, C. L., Green, M. R., Gentles, A. J., Feng, W., Xu, Y., et al. (2015). Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 12 (5), 453–457. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3337
Plum, T., Feyerabend, T. B., and Rodewald, H. R. (2024). Beyond classical immunity: mast cells as signal converters between tissues and neurons. Immunity 57 (12), 2723–2736. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.11.016
Ren, J., Ding, L., Xu, Q., Shi, G., Li, X., Li, X., et al. (2017). LF-MF inhibits iron metabolism and suppresses lung cancer through activation of P53-miR-34a-E2F1/E2F3 pathway. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 749. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00913-2
Ribas, A., and Wolchok, J. D. (2018). Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 359 (6382), 1350–1355. doi:10.1126/science.aar4060
Ritchie, M. E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C. W., Shi, W., et al. (2015). Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (7), e47. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv007
Schalper, K. A., Brown, J., Carvajal-Hausdorf, D., McLaughlin, J., Velcheti, V., Syrigos, K. N., et al. (2015). Objective measurement and clinical significance of TILs in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 107 (3), dju435. doi:10.1093/jnci/dju435
Shu, F., Yu, J., Liu, Y., Wang, F., Gou, G., Wen, M., et al. (2025). Mast cells: key players in digestive system tumors and their interactions with immune cells. Cell Death Discov. 11 (1), 8. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-02258-y
Sun, C. C., Zhou, Q., Hu, W., Li, S. J., Zhang, F., Chen, Z. L., et al. (2018). Transcriptional E2F1/2/5/8 as potential targets and transcriptional E2F3/6/7 as new biomarkers for the prognosis of human lung carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 10 (5), 973–987. doi:10.18632/aging.101441
Tan, Y., Ding, L., and Li, G. (2023). MCM4 acts as a biomarker for LUAD prognosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 27 (21), 3354–3362. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17819
Wan, J., Liu, H., Feng, Q., Liu, J., and Ming, L. (2018). HOXB9 promotes endometrial cancer progression by targeting E2F3. Cell Death Dis. 9 (5), 509. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0556-3
Wang, L., Yang, X., Song, Q., Fu, J., Wang, W., Du, K., et al. (2021). Uncovering the pharmacological mechanism of 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5 -Diene-1,4-Dione against lung cancer based on network pharmacology and experimental evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 617555. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.617555
Wang, X., Niu, R., Yang, H., Lin, Y., Hou, H., and Yang, H. (2024). Fibroblast activation protein promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating the immunity. Cell Biol. Int. 48 (5), 577–593. doi:10.1002/cbin.12154
Wei, J., Wang, X., Guo, H., Zhang, L., Shi, Y., and Wang, X. (2024). Subclassification of lung adenocarcinoma through comprehensive multi-omics data to benefit survival outcomes. Comput. Biol. Chem. 112, 108150. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2024.108150
Xu, K., Zheng, P., Zhao, S., Wang, J., Feng, J., Ren, Y., et al. (2023). LRFN5 and OLFM4 as novel potential biomarkers for major depressive disorder: a pilot study. Transl. Psychiatry 13 (1), 188. doi:10.1038/s41398-023-02490-7
Yan, J., Enge, M., Whitington, T., Dave, K., Liu, J., Sur, I., et al. (2013). Transcription factor binding in human cells occurs in dense clusters formed around cohesin anchor sites. Cell 154 (4), 801–813. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.034
Yu, G., Wang, L. G., Han, Y., and He, Q. Y. (2012). clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 16 (5), 284–287. doi:10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Zhang, L., Wang, S., and Wang, L. (2024a). Comprehensive analysis identifies YKT6 as a potential prognostic and diagnostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 24 (1), 1235. doi:10.1186/s12885-024-12975-3
Zhang, W., Wang, M., Ji, C., Liu, X., Gu, B., and Dong, T. (2024b). Macrophage polarization in the tumor microenvironment: emerging roles and therapeutic potentials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 177, 116930. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116930
Zhao, Y., Shi, W., and Tang, Q. (2023). An eleven-gene risk model associated with lymph node metastasis predicts overall survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 6852. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-27544-0
Keywords: LRFN4, lung adenocarcinoma, E2F1, E2F3, immune landscape, drug sensitivity
Citation: Wang N, Cao S, Tan X and Liu M (2025) Significance of LRFN4 in prognosis and tumor microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1540636. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1540636
Received: 06 December 2024; Accepted: 27 January 2025;
Published: 25 February 2025.
Edited by:
Bing Yang, Tianjin Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Suparata Kiartivich, Krirk University, ThailandHuiping Wang, Xuzhou Medical University, China
MM Elmg, Istanbul University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Cao, Tan and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meirong Liu, dGp5eWJlZ2lubmluZzIwMjNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Nana Wang1
Nana Wang1 Meirong Liu
Meirong Liu