- 1Department of Nephrology, Seventh People’s Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Shanghai Frontiers Science Center of TCM Chemical Biology, Institute of Interdisciplinary Integrative Medicine Research, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Nephrology, Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
Acute kidney injury (AKI) represents significant medical challenges due to its elevated rates of morbidity and mortality, with limited therapeutic options currently available. Hence, the exploration of novel medicinal treatments for AKI management remains vital. Substances of medicine food homology (SMFH), referring to substances having characteristics of both food and medicine, have been applied in China for thousands years.They could be used for daily diets and body conditioning. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), with its naturally derived components and demonstrated effectiveness, presents distinctive benefits in AKI treatment. Numerous studies have shown that SMFH and TCM phytochemicals could function satisfactorily with nephroprotective effects and have a significant effect on alleviating AKI as well as its complications. In this review, the pathogenesis of AKI was illustrated. We concentrated on SMFH and TCM phytochemicals against AKI and tried to summarize the underlying mechanisms in various kinds of AKI, highlighting the crucial phytochemical components in AKI prevention and therapy. Besides, strategies for SMFH and TCM phytochemicals globalization are analysed. This review comprehensively reveals that SMFH and TCM phytochemicals exhibit promising potential for AKI intervention by targeting various signal pathways and targets, which would contribute to AKI’s cognition, preventive treatments, as well as global promotion.
1 Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) represents a critical medical condition linked to rising morbidity and mortality rates, affecting 10%–15% of hospitalized individuals, with up to 50% of those requiring admission to intensive care units (Ronco et al., 2019; Neyra et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2024). This condition ranks among the most prevalent critical illnesses, characterized by a reduced glomerular filtration rate, accumulation of nitrogenous waste products, disturbances in water and electrolyte balance, and acid-base imbalance as its primary clinical features. Currently, no effective treatment exists for AKI; however, the primary approach involves addressing the underlying diseases, eliminating risk elements, sustaining acid-base homeostasis and water-electrolyte equilibrium, along with renal replacement therapy. Despite these interventions, the mortality rate remains considerably high (Allinson et al., 2023; Du et al., 2023). Survivors of AKI are notably predisposed to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (Tao et al., 2024). Clinically, AKI may arise from a variety of causes, encompassing sepsis, ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, and exposure to different nephrotoxin, among others (Chen and Gong, 2022; Chen et al., 2024a). The treatment of AKI primarily emphasizes supportive interventions, encompassing optimizing hemodynamic volume status and minimizing nephrotoxic exposure. Apart from conservative management, there are presently no medical or surgical alternatives available for the prevention or treatment of AKI other than renal replacement therapy (Vijayan, 2021; Shi et al., 2023). AKI is recognized as a worldwide healthcare concern, thus highlighting the urgent need to identify novel therapeutic approaches and agents for managing this condition (Song and Gong, 2023).
Substances of medicine food homology (SMFH), referring to substances having characteristics of both food and medicine, have been applied in China for thousands years (Chen, 2023). As an integral and important part of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), they could be used for daily diets and body conditioning (Qu et al., 2023; Liu H. et al., 2024). Over the past few years, TCM has experienced growing acceptance worldwide for treating AKI, attributed to its comprehensive dialectical system and remarkable clinical efficacy (Chen et al., 2022; Song et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024b). Investigations into the use of TCM and its compounds for treating AKI have gradually intensified. These treatments are characterized by their numerous ingredients, diverse targets, and distinct mechanisms, possibly providing special clinical benefits in AKI prevention and control (Zhong et al., 2023). Phytochemicals, the bioactive compounds within TCM, exhibit potential in preventing and managing AKI via multiple pathways, encompassing reducing oxidative stress (OS), modulating autophagy processes, suppressing inflammation, and alleviating damage to mitochondria (Shi et al., 2023). However, a systematic review of SMFH and TCM phytochemicals addressing various types of AKI remains lacking. This review summarizes the existing data supporting the capacity of SMFH and TCM phytochemicals to enhance AKI outcomes and provides both clinical and experimental evidence relevant to AKI management. Additionally, strategies for SMFH and TCM phytochemicals globalization are analysed for their global promotion.
2 Literature search strategies
The PubMed database was chosen due to its exceptional precision in document classification, rendering it the most suitable platform for bibliometric evaluation. A literature exploration was conducted on 12 May 2024, through PubMed to identify publications addressing the application of TCM botanical compounds in relation to AKI spanning from 12 May 2014, to 12 May 2024. The database investigation employed the following criteria (TS = (Acute Kidney Injury) OR TS = (Acute Renal Injury) OR TS = (Acute Renal Insufficiency) OR TS = (Acute Kidney Insufficiency)) AND (TS = (traditional Chinese medicine) OR TS = (Herbal Medicine) OR TS = (Chinese medicine) OR TS = (Chinese herbs) OR TS = (Substances of medicine food homology) OR TS = (Phytochemicals)). Contents include reviews, clinical trials, in vivo or in vitro experiments, etc., 140 articles were selected for discussion after filtering the search results and excluding non-relevant literature. All findings are depicted in the form of narrative reviews within this document.
3 The pathogenesis of AKI
The primary factors leading to AKI encompass sepsis, nephrotoxic agents, renal I/R injury, rhabdomyolysis (RM), post-major surgeries, etc (Bellomo et al., 2017; Tang C. et al., 2023; Yang W. et al., 2023). The pathogenesis of different types of AKI varies according to the different causes. AKI could be divided into the following categories (Figure 1).
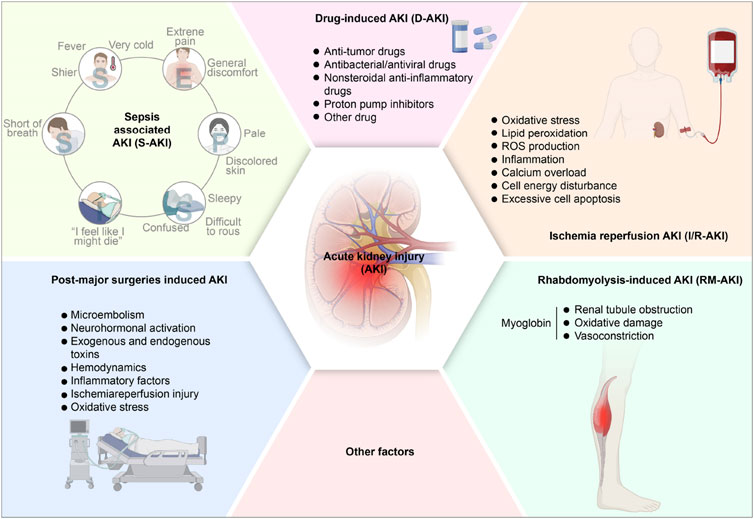
Figure 1. The pathogenesis of acute kidney injury. AKI, acute kidney injury; S-AKI, Sepsis associated acute kidney injury; D-AKI, drug-induced acute kidney injury; I/R-AKI, Ischemia-reperfusion acute kidney injury; RM-AKI, Rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury.
3.1 Sepsis-associated AKI (S-AKI)
Sepsis, characterized as a systemic inflammatory response syndrome associated with infection, frequently leads to multiple organ dysfunction, particularly impacting the kidneys and resulting in sepsis-associated AKI (S-AKI). S-AKI is regarded as the most common complication of sepsis (Peerapornratana et al., 2019). Generally, sepsis is responsible for 45%–70% of AKI occurrences in critically ill individuals (Zarbock et al., 2023), correlating with extended stays in hospitals, elevated mortality rates, an increased incidence of long-term disabilities, and a reduced quality of life (Poston and Koyner, 2019; White et al., 2023). Importantly, the pathophysiology of sepsis is intricate and distinct, rendering S-AKI unique among other AKI phenotypes (Poston and Koyner, 2019). Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are pivotal in the pathogenesis of sepsis. The underlying mechanisms contributing to S-AKI are multifaceted, encompassing alterations in microcirculation, complex inflammatory pathways, and cellular demise (Chang et al., 2022). To date, various patterns of cell death, encompassing apoptosis, necrosis, necroptosis, and autophagy, have been identified as significant in S-AKI (Wu Z. et al., 2022). The mechanisms underlying LPS-induced AKI may involve inflammation, renal I/R injury, OS, and systemic hypotension. The inflammatory and oxidative pathways present possible therapeutic interventions for addressing AKI during septic conditions (Cao et al., 2024). Consequently, addressing S-AKI through preventive measures and treatment protocols, as well as the reduction of morbidity and mortality among septic patients, represent critical public health challenges.
3.2 Drug-induced AKI (D-AKI)
Drug-induced AKI (D-AKI) represents a serious adverse event, constituting roughly 20% of AKI incidents (Hosohata, 2016; Perazella and Rosner, 2022). Frequently encountered nephrotoxic substances include anticancer medications (notably cisplatin and doxorubicin), antimicrobial and antiviral compounds (like gentamicin), Non-Steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), contrast media, and proton pump blockers. While cisplatin stands as a potent chemotherapeutic compound, its therapeutic application faces constraints owing to kidney toxicity. Cisplatin-induced AKI (Cis-induced AKI) exhibits strong connections with DNA harm, OS, and inflammation (Guo et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2023). The involvement of various regulated cell death mechanisms, encompassing ferroptosis, in Cis-induced AKI, has only recently gained recognition (Kim et al., 2022). In recent years, relevant studies (Gong et al., 2015; Gong et al., 2019; Li and Gong, 2022) have shown that contrast agents-induced AKI also account for a considerable proportion. Its mechanism of action is mainly due to the nephrotoxic effect of contrast agents on renal tubules and vascular endothelial cells, which leads to hemodynamic changes, OS, apoptosis, and inflammatory reactions in the kidney.
3.3 I/R-induced AKI (I/R-AKI)
AKI caused by renal I/R injury (I/R-AKI) emerges when blood circulation to kidneys suddenly decreases, with subsequent reperfusion generating an imbalance between oxygen and nutrient availability, harming endothelial cells and eventually progressing to kidney failure (Pan et al., 2021; Oh et al., 2023). I/R-AKI is implicated in cell death and tissue damage across various conditions, including AKI, stroke, and coronary occlusion. The I/R-AKI mechanism involves a complex series of interactions among inflammatory components, including oxidative stress, degradation of lipids through peroxidation, and reactive oxygen species generation, initiating an inflammatory sequence that results in cellular destruction and renal tissue damage (Shiva et al., 2020; Wu J. et al., 2022; Zhang B. et al., 2023). I/R-AKI frequently occurs in conditions such as septic shock, blood volume depletion, kidney transplantation, heart operations, and post-trauma stress. Recent studies (Junho et al., 2022; Wang S. et al., 2022; Yang C. et al., 2023) suggest that its pathogenesis is related to the mechanism of ROS. Inflammation, calcium overload, cell energy disturbance, and excessive cell apoptosis are closely related, and the main pathological changes are tubular epithelial necrosis and microvascular endothelial cell injury.
3.4 RM-induced AKI (RM-AKI)
Various clinical manifestations, encompassing disturbances in electrolytes, disorders of acid-base balance, abnormal coagulation, and impaired renal function, typify RM. The tissue damage in RM causes hazardous cellular components to enter the bloodstream, including myoglobin, creatine phosphokinase, and lactate dehydrogenase (Petejova and Martinek, 2014; Jiang et al., 2022; Williams et al., 2023). Among RM’s serious complications, AKI occurs in approximately 13%–50% of cases (Petejova and Martinek, 2014). The definite causing factors of RM-induced AKI remains incompletely known. The potential mechanisms might be related to myoglobin, a major renal toxin in RM and a key contributor to the disease, causing renal tubule obstruction, oxidative damage, and vasoconstriction, leading to AKI (Sun T. et al., 2022; Wang J. et al., 2022). In an acidic environment, myoglobin readily passes through glomerular filtration and accumulates in kidney tubules, and it is also easy to interact with Tamm Horsfall protein and precipitate in the renal tubules, thereby inducing lipid peroxidation and producing prostaglandins, resulting in renal arteriolar dysfunction and hypoperfusion.
3.5 Post-major surgeries induced AKI
AKI often occurs after major surgery. Mechanisms such as microembolism, neurohormonal activation, exogenous and endogenous toxins, hemodynamics, inflammatory factors, I/R injury, and OS may be involved. Those mechanisms might lead to renal changes: sustained vasoconstriction, overresponse to exogenous vasoconstrictors, and vascular endothelium, impairment of tubular cells, etc (Vives et al., 2019). During liver transplantation, blocked inferior vena cava and portal vein are prone to hypotension and intestinal congestion. Hypotension leads to renal hypoperfusion and I/R injury, and intestinal congestion promotes endotoxin production, which would result in AKI (Yuan et al., 2019). The pathogenesis of AKI after major surgery is complicated and multi-factors. The postoperative perfusion in renal tissue is reduced, and the compensatory blood volume in the kidney is increased, which dilates the entering arterioles and constricts the exiting arterioles, thereby maintaining glomerular filtration, leading to renal medullary ischemia and triggering AKI. In addition, anesthetics cause peripheral vasodilation and myocardial inhibition, impairing renal perfusion (Gameiro et al., 2018).
4 Applications of SMFH and phytochemicals of TCM against AKI
TCM (including SMFH and TCM phytochemicals) possesses distinct therapeutic benefits in AKI prevention and treatments, encompassing its holistic philosophy, pattern identification methodology, and unique properties of its diverse components and targets (Figure 2). Prior researches have demonstrated that SMFH and TCM phytochemicals exert reno-protective effects by modulation of renal autophagy, inflammatory responses, and OS, etc., (Dong et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2022; Rui et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023). To illustrate comprehensively the nephroprotective effects of SMFH and TCM phytochemicals via multiple targets and pathways, we will elaborate from the following categories (Tables 1–4).
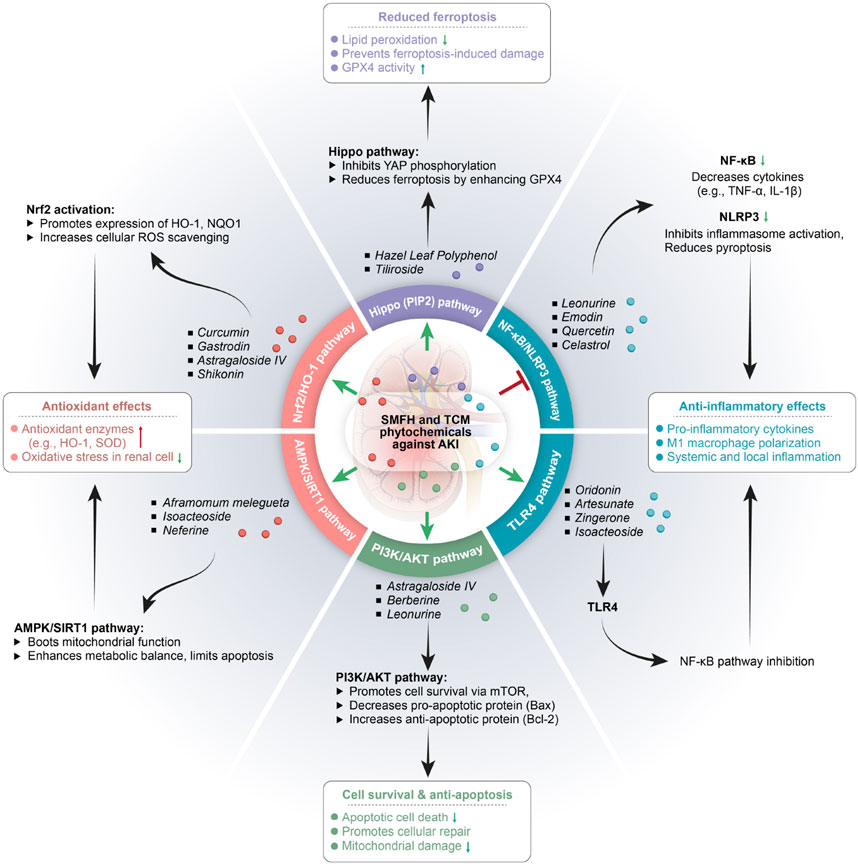
Figure 2. Substances of medicine food homology and phytochemicals of Traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of acute kidney injury. SMFH, substances of medicine food homology; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; AKI, acute kidney injury; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; HO-1, Hemeoxygenase −1; NQO1, NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3; SOD, superoxide dismutase; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-Β.
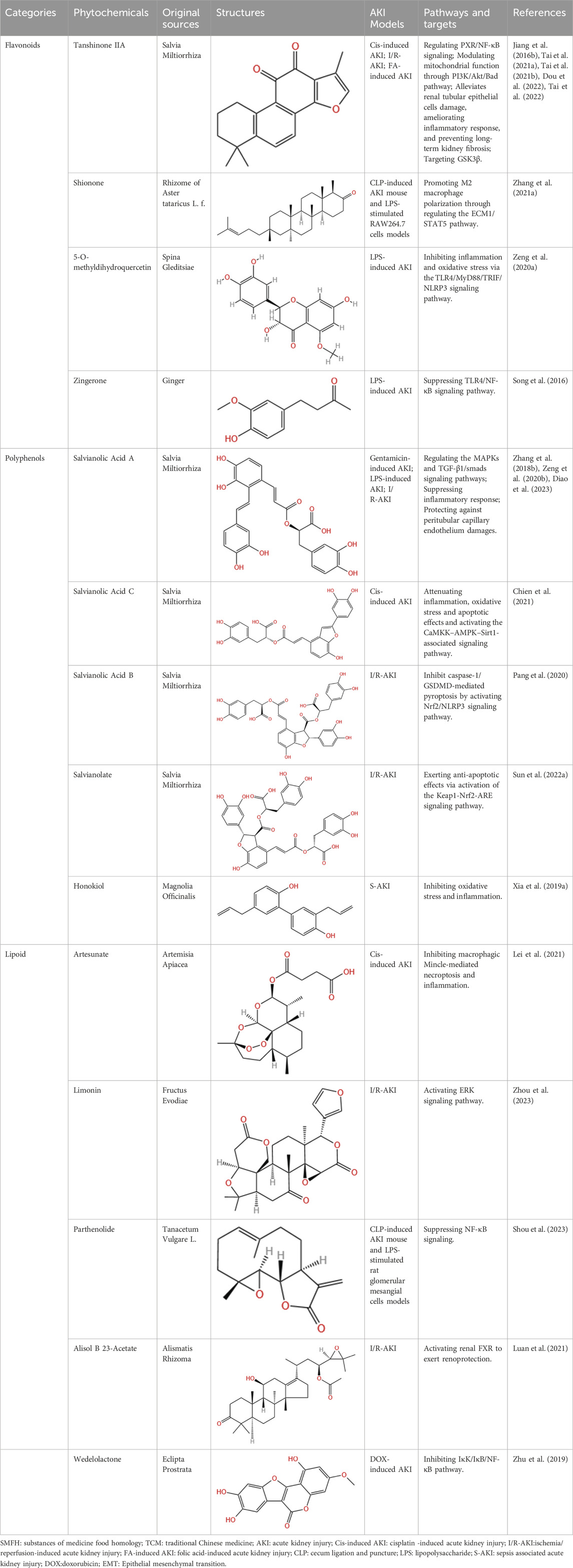
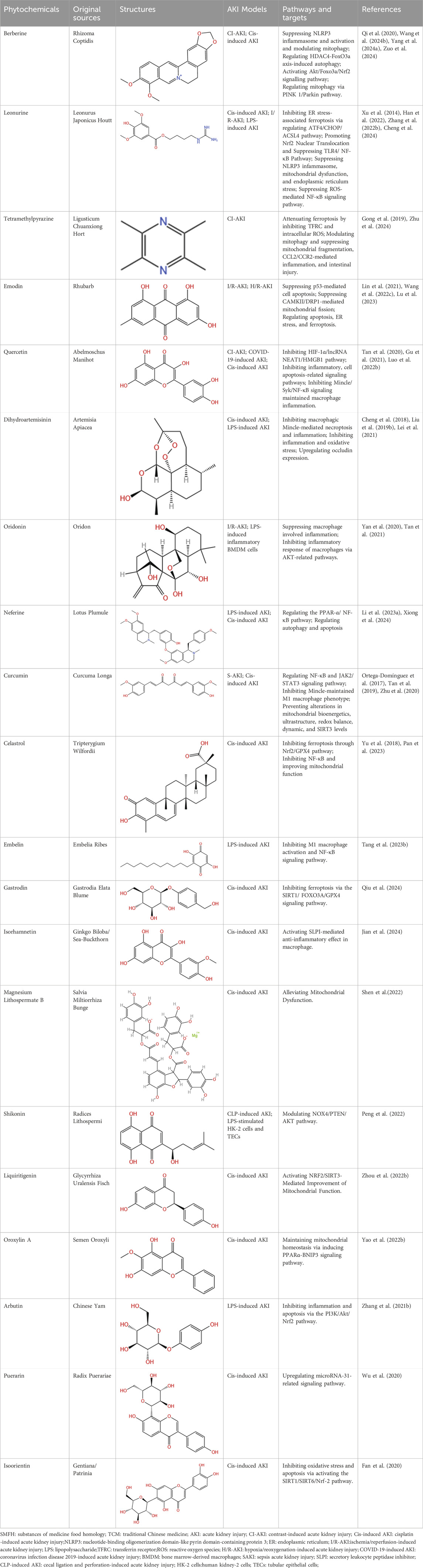
Table 3. Flavonoids, Polyphenols,and Lipoid of SMFH and TCM phytochemicals against AKI via various pathways and targets.
4.1 Alkaloids
4.1.1 Berberine
Berberine (BBR), extracted from the rhizomacoptidis, possesses multi-pharmacological effects, including antioxidative effects, reduction of mitochondrial injury, anti-inflammatory actions, autophagy regulation, and cell death (Hashemzaei and Rezaee, 2021; Rui et al., 2022). Mitophagy has been recognized as a vital mechanism for eliminating damaged mitochondria and facilitating cellular repair. Yang et al. (2024a) indicated BBR effectively mitigated contrast-induced AKI (CI-AKI) mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and promoting mitophagy. Qi et al. (2020) elucidated that the mitophagy induced by BBR was mediated through PINK1/Parkin pathway activation in mice and renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs). In the context of CI-AKI, the activation of mitophagy by BBR may counteract damaging effects via the reduction of ROS accumulation. Furthermore, BBR could diminish metabolic disturbances, inflammation, and apoptosis induced by cisplatin-mediated methylation (Shen et al., 2020). Significantly, BBR has emerged as a widespread inhibitor of HDACs and is capable of down-regulating HDAC4, thereby enhancing epigenetic modifications through increased histone acetylation (Kandasamy et al., 2023). Zuo et al. (2024) evaluates the renal protective effects of BBR and its potential mechanisms involving HDAC4. BBR exhibited marked protective outcomes against CI-AKI, preventing apoptosis by enhancing Bcl-2 protein expression while diminishing Bax levels. Their research also demonstrated that the ioversol contrast medium increased HDAC4 expression. Wang et al. (Wang W. et al., 2024) found BBR effectively counteracted ioversol-triggered apoptosis and ferroptosis. BBR’s protective mechanisms operated through regulation of Akt/Foxo3a/Nrf2 signaling cascade, resulting in CI-AKI improvement.
4.1.2 Leonurine
Leonurine (LEO) is a distinctive alkaloid that demonstrates a variety of bioactivities, encompassing antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory properties, and improve microcirculation (Liu et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2018). In a gouty arthritis model, LEO has been shown to suppress NLRP3 activation and diminish IL-1β and TNF-α generation (Liu Y. et al., 2018). Xu et al. (2014) revealed LEO exerted significant nephroprotective effects in an LPS mice model. The inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production, maintenance of redox balance, and suppression of ROS-mediated NF-κB signaling activation may mediate the nephroprotective properties of LEO. Zhang Q. et al. (2022) indicated that LEO serves a protective function in CI-AKI and could function as a viable therapeutic approach. The kidney-protective properties of LEO against cell death appear to be mediated through diminished NLRP3 and inflammatory mediators, improving mitochondrial function, and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. In renal disease treatment, LEO has been demonstrated to ameliorate AKI induced by LPS, mitigate adriamycin-related podocyte injury, and reduce the nephrotoxic effects of cisplatin (Hu et al., 2022; Zhang Q. et al., 2022). Chen P. et al. (2019) reported that LEO decreases OS in aging mice by activating Nrf2 pathway. Han et al. (2022) showed LEO pretreatment could alleviate ischemic AKI by promoting Nrf2 nuclear translocation, which counteracts OS injury and inhibits TLR4/NF-κB pathway that mediates inflammatory expression. A recent study (Wu et al., 2023) discovered LEO’s in vitro anti-ferroptotic capabilities, achieved partly via p62/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation. LEO diminishes AKI and preserves renal function by controlling ferroptosis and reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Significantly, ER stress demonstrates close connections with erastin-triggered ferroptosis. Cheng et al. (2024) unveiled fresh perspectives regarding LEO’s protective mechanisms against AKI, emphasizing its capacity to suppress ER stress-associated ferroptosis through ATF4/CHOP/ACSL4 pathway regulation.
4.1.3 Tetramethylpyrazine
Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) is identified as a bioactive constituent within Chuanxiong, exhibiting nephroprotective properties attributed to its antioxidant capabilities (Li and Gong, 2022). The potential mechanisms through which TMP acts against AKI have been reviewed by Li et al. (Li and Gong, 2022). The findings suggest that the mechanisms involved in TMP’s protective effects against AKI primarily revolve around the mitigation of OS injury, suppression of inflammation, prevention of apoptosis in intrinsic renal cells, and regulation of autophagy. It has been demonstrated TMP can reduce renal damage in a CI-AKI animal model via multiple pathways, with the modulation of tubular epithelial cell death paramount. In the CI-AKI mouse model, significant attenuation of renal tubular cell apoptosis by TMP was observed, potentially mediated by suppressing the p38 MAPK and FoxO1 pathways (Gong et al., 2013). Studies (Gong et al., 2015; Gong et al., 2016) have underscored the potential of TMP as an innovative therapeutic option in CI-AKI prevention by suppressing the p38 MAPK and FoxO1 pathways, additionally protecting renal tubular cells against arsenite-induced nephrotoxicity by averting mitochondrial dysfunction and regulating autophagy. Gong et al. (2019) demonstrated that TMP suppresses CCL2/CCR2 pathway activation in CI-AKI, alleviates renal OS and abnormal mitochondrial dynamics, and modulates mitochondrial autophagy within renal tubular cells. Zhu et al. (2024) explored involvement of ferroptosis in RTECs concerning the reno-protective effects of TMP against CI-AKI and the molecular mechanisms governing TMP’s regulation of ferroptosis. The results indicated that tubular cell injury was associated with ferroptosis, evidenced by elevated Fe2+ levels, lipid peroxidation, and reduced GPX4 levels. Furthermore, TMP markedly inhibits renal dysfunction, lowers AKI biomarkers, prevents ROS production, diminishes renal Fe2+ accumulation, and enhances GPX4 expression. Findings from siRNA silencing and plasmid amplification of transferrin receptor (TFRC) suggested TFRC is crucial for TMP’s ability to mitigate ferroptosis and decrease LDH release, Fe2+ buildup, and intracellular ROS.
4.1.4 Emodin
Emodin is recognized as an anthraquinone derivative derived from the rhizome of Rheum palmatum L, serving as the principal active monomer in Da Huang. Recent evidence (Ma et al., 2018; Xia et al., 2019b) has demonstrated that emodin has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunosuppressive, and anti-renal fibrosis effects. Lu et al. (2023) integrated network pharmacology with experimental validation to assess the preventive efficacy and underlying mechanisms of emodin in the context of AKI. These effects are likely linked to its anti-apoptotic responses and enhancement of angiogenesis through the regulation of the p53/Caspase-9/Caspase-3, p53/Bcl-2, and HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathways. Li et al. (2015) demonstrated emodin effectively protects NRK-52E cells from LPS-induced injury by downregulating expression of TLR2, NF-κB, and inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, emodin demonstrated suppressive effects on LPS-triggered TLR2 and NF-κB expression within NRK-52E cells. Upon administration of emodin, a concentration-dependent reduction was noted in both mRNA and protein expressions of NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. The investigation has revealed that emodin provides protection to RTECs via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thus reducing inflammatory processes and attenuating AKI caused by lipopolysaccharide. Lin et al. (2021) revealed chrysophanol has a protective effect against AKI, and it might alleviat H/R-induced lipid ROS accumulation and ferroptosis via regulating apoptosis, ER stress, and ferroptosis. Wang Y. et al. (2022) reported that emodin markedly improved I/R-induced renal dysfunction and reduced apoptosis in RTECs via the modulation of mitochondrial dynamics.
4.1.5 Quercetin
Within kidney disease research, studies indicate that quercetin exhibits protective capabilities against radiation-induced DNA damage and kidney cell death (Özyurt et al., 2014; Zhang N. et al., 2024), while simultaneously mitigating AKI via inflammatory suppression and enhancement of antioxidant systems and SIRT1 (Khajevand-Khazaei et al., 2018). Additionally, quercetin has demonstrated protective effects against Cis-induced AKI in vivo (Sánchez-González et al., 2017) and has been shown to safeguard human renal proximal tubular cells against the toxicity of radiocontrast media in vitro (Andreucci et al., 2018). Significantly, recent investigations (Lu et al., 2018) illustrated that quercetin diminishes kidney injury by modulating the polarization of M1/M2 macrophages, thereby providing evidence that quercetin’s improvement of kidney inflammation and injury may be linked to macrophage function regulation. Tan’s research (Tan et al., 2020) established that quercetin reduces inflammatory mediator expression and release from macrophages, consequently alleviating renal damage in AKI. This mechanism is primarily associated with inhibiting Mincle and its associated signaling components Syk and NF-κB, which regulate macrophage polarization—specifically reducing pro-inflammatory M1 phenotypes while enhancing anti-inflammatory M2 populations. A study (Luo M. et al., 2022) indicated that quercetin reduces cellular damage and death, thereby limiting inflammatory processes in CI-AKI models through HIF-1α/lncRNA NEAT2/HMGB1 pathway inhibition. Gu’s research (Gu et al., 2021) emphasizes quercetin’s protective functions in COVID-19-related AKI through network pharmacological analyses and molecular docking investigations, identifying potential pathological mechanisms in coronavirus-induced renal damage. While quercetin’s complete regulatory mechanisms in COVID-19-associated AKI require further investigation, these findings provide valuable insights supporting quercetin’s potential development as a therapeutic intervention during the pandemic.
4.1.6 Dihydroartemisinin
Recent research (Lei et al., 2021) indicated artesunate can mitigate renal damage and necroptosis, enhancing renal function and reducing inflammation. The underlying mechanism primarily inhibits macrophagic Mincle-mediated necroptosis and inflammation affecting tubular epithelial cells. In summary, artesunate acts by reducing M1 macrophage activation and suppressing the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL signaling cascade through the downregulation of Mincle expression, thereby diminishing the inflammatory response and necroptosis, which contributes to improvement of renal injury in AKI. Additionally, Liu’s investigation (Liu X. et al., 2019) illustrated that DHA may mitigate LPS-triggered AKI by suppressing NF-κB-mediated inflammation and inhibiting OS. Cheng et al. (2018) further demonstrated that DHA effectively improves S-AKI. Moreover, by preserving occludin expression, DHA prevents TNF-α induced hyperpermeability of the glomerular endothelium.
4.1.7 Oridonin
Oridonin, an essential diterpenoid compound commonly found in traditional East Asian medicine, has gained significant recognition among medical researchers for its multiple therapeutic properties, encompassing anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, hepatic fibrosis prevention, and neurological effects (Xu et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2019). In a spontaneous lupus erythematosus mouse model, oridonin has been shown to diminish proteinuria and renal damage, while in vitro investigations have indicated that this compound reduces inflammatory cytokine production and the inflammatory cascade triggered by LPS following oridonin treatment (Tan et al., 2021). Furthermore, recent studies merging selenium nanoparticles and oridonin for esophageal cancer cell targeting reveal that oridonin enhances cell death by suppressing PI3K/AKT and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling cascades (Pi et al., 2017). Tan’s research (Tan et al., 2021) illustrated that oridonin exerts a notable anti-inflammatory effect and protects the kidneys during AKI, presumably through suppressing Mincle and its subsequent NF-κB and AKT signaling mechanisms. Additionally, Yan et al. (2020) reported that oridonin could mitigate I/R-AKI, presumably by suppressing macrophage inflammatory responses by inhibiting AKT-related signaling pathways.
4.1.8 Neferine
Neferine (Nef), a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid procured from the seed embryo of N. Nucifera, demonstrates various notable therapeutic characteristics, encompassing anti-tumor, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects, as well as cardioprotective capabilities (Deng et al., 2017). It was revealed that Nef could alleviate Cis-induced AKI via autophagy stimulation (Li H. et al., 2017), suggesting that further confirmation and elucidation in animal models are warranted. Li H. et al. (2023) testified to Nef’s notable protective effects on Cis-induced AKI mice, partly attributed to autophagy activation. However, additional inquiries remain regarding the mechanisms by which Nef contributes to renal protection, particularly concerning autophagy’s function and its interactions with apoptosis, OS, and inflammation; further exploration of these mechanisms is essential for future research. Prior studies have established Nef’s renoprotective properties within kidney and vascular endothelium, potentially through the enhancement of autophagy (Li H. et al., 2017), inhibition of pyroptosis (Tang et al., 2019), or suppression of the inflammatory NF-κB pathway (Li H. et al., 2019). Xiong et al. (2024) demonstrated that Nef is capable of alleviating inflammation in by counteracting PPAR-α deficiency, thereby suppressing NF-κB pathway activation and inflammatory mediator production.
4.1.9 Curcumin
Curcumin, the primary active compound of the plant Curcuma longa, has recently garnered attention for its potential renoprotective effects against AKI, encompassing glycerol-induced, gentamicin-induced, I/I-induced, and Cis-induced AKI (Fan et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2017). Notably, a recent study demonstrated that Curcumin mitigates inflammation triggered by titanium particles through regulating macrophage polarization (Li B. et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2023). However, the exact mechanisms by which Curcumin influences AKI remain unclear, particularly whether it modulates macrophage polarization in AKI via the regulation of Mincle. One investigation (Ortega-Domínguez et al., 2017) assessed mitochondrial-related mechanisms associated with Curcumin’s protective effects in Cis-induced AKI by examining several parameters, including bioenergetics, ultrastructure, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) generation, dynamics, SIRT3 protein levels, and mitophagy. Tan’s research (Tan et al., 2019) revealed that treatment with Curcumin significantly downregulated Mincle expression in infiltrated macrophages, alleviating renal inflammation mediated by M1 macrophages through a Syk/NF-κB-dependent mechanism. Zhu et al. (2020) established Curcumin’s protective function in both cellular and mouse models of S-AKI, partially attributing its mechanism to decreased inflammatory mediator production through suppression of JAK2/STAT3 and TNF-α signaling pathways.
4.1.10 Celastrol
Celastrol, a bioactive triterpenoid derived from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. F exhibits notable biological activities, encompassing anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects (Lu et al., 2021). Celastrol has reportedly alleviated CKD by upregulating cannabinoid receptor 2 (Tang et al., 2018). Furthermore, the targeted delivery of Celastrol to glomerular endothelium and podocytes can potentially enhance renal function (Wu Q. et al., 2022). The function of Celastrol in AKI is increasingly being elucidated, with findings indicating that it can improve Cis-induced AKI by suppressing NF-κB and enhancing mitochondrial function (Yu et al., 2018). Celastrol has also been effective against mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis (Guo et al., 2017), recent studies (Chu et al., 2014) have additionally reported that Celastrol ameliorates IR-AKI, which correlates with inhibiting NF-κB activation and inflammation. However, the impact of Celastrol on Cis-induced AKI remains to be thoroughly investigated. Another investigation (Yu et al., 2018) demonstrated that Celastrol could mitigate Cis-induced AKI by antagonizing NF-κB-mediated inflammation and safeguarding mitochondrial function. These findings strongly suggest that Celastrol possesses translational potential as a natural therapeutic agent for treating Cis-induced AKI in clinical settings. Pan et al. (2023) found cisplatin-induced ferroptosis leads to tubular cell injury and renal dysfunction, characterized by lipid peroxidation. The upregulation of Nrf2 by Celastrol markedly enhances GPX4 expression, thereby preserving renal function and redox homeostasis.
4.1.11 Embelin
Embelin, a benzoquinone derivative extracted from Embelia ribes, exhibits potential antibacterial, antidiabetic, antioxidant, analgesic, antifertility, and anticancer properties (Ning et al., 2018). Research indicates that Embelin functions as an inhibitor of NF-κB signaling, thereby suppressing NF-κB-regulated anti-apoptotic and metastatic gene products. Additionally, it may serve a regulatory function in immune cells during acute liver injury and allergic asthma (Wang H. et al., 2019; Azman et al., 2021). Nonetheless, the precise mechanisms and significance of Embelin in S-AKI remain unclear. Tang Q. et al. (2023) investigated the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of Embelin in LPS- induced AKI, revealing that Embelin can mitigate AKI by inhibiting M1 macrophage activation and blocking NF-κB signaling in mice.
4.1.12 Gastrodin
Gastrodin (GAS), the primary active component derived from G. elata Blume, has been clinically employed to treat patients experiencing vertigo (Lai et al., 2022; Chen X.-Y. et al., 2023). Observations suggest that GAS can restore GPX4 expression in two models of OS (Jiang et al., 2020). Current findings (Qiu et al., 2024) demonstrate that FOXO3A regulates the transcription of GPX4. Additionally, GAS has been shown to activate SIRT1, thereby protecting Cis-induced AKI by suppressing ferroptosis through the SIRT1/FOXO3A/GPX4 signaling pathway.
4.1.13 Isorhamnetin
Isorhamnetin is a flavonoid compound derived from various plants, encompassing ginkgo biloba and sea-buckthorn, and demonstrates diverse therapeutic activities. These effects include immunomodulatory, antiviral, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and serum cholesterol reduction properties (Tian et al., 2021). Recent studies demonstrated isorhamnetin possesses significant anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages, including regulating macrophage inflammatory responses in conditions such as cord injury, atherosclerosis, and osteoarthritis, leading to M1 macrophage inhibition and M2 macrophage upregulation (Chen et al., 2021). However, the effect of isorhamnetin on AKI remains unknown, and whether isorhamnetin can suppress M1 macrophage activation and promote M2 macrophage in AKI kidneys through the regulation of SLPI needs further investigation. A study (Jian et al., 2024) clarified that isorhamnetin markedly upregulated SLPI to inhibit the Mincle/Syk/NF-κB signaling pathway, which diminished M1 macrophage differentiation while facilitating M2 macrophage differentiation to attenuate AKI-triggered renal inflammatory reactions.
4.1.14 Magnesium lithospermate B
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge exhibits a range of pharmacological activities, including promoting blood circulation, mitigating OS damage, and preventing apoptosis (Gao F. et al., 2019). Magnesium lithospermate B (Mlb), the primary water-soluble active component of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, contributes to managing cardiovascular diseases and offers protective effects against renal disorders. In renal ablation/infarction models, significant reductions in renal injury and apoptosis have been attributed to Mlb (Wang M. et al., 2019). Salvianolate, a compound derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza extracts and primarily composed of salvia magnesium acetate, has been demonstrated to mitigate contrast-induced AKI while alleviating OS associated with podocyte injury (Liang et al., 2021). Our findings (Shen et al., 2022) indicate that Mlb treatment lessens the severity of CI-AKI by suppressing ROS generation, apoptosis, and mitochondrial damage by modulating Drp1 levels.
4.1.15 Shikonin
Peng’s study (Peng et al., 2022) showed that shikonin could improve cecal ligation and perforation-induced AKI and LPS-induced dysfunction of RTECs. Besides, the mechanism of apoptosis, OS, and inflammatory response may be partially linked to modulating the NOX4/PTEN signaling pathway.
4.1.16 Liquiritigenin
Studies have demonstrated that liquiritigenin possesses diverse biochemical and pharmacological attributes, which include hepatoprotective, anti-hyperlipidemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects (Jain et al., 2022). Evidence indicates licorice could alleviate cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity through mechanisms involving anti-apoptosis, OS reduction, anti-inflammatory actions, and enhanced metabolic processes (Man et al., 2020). Furthermore, liquiritigenin was observed to amplify the suppressive impact of cisplatin on invasion and metastasis by downregulating MMP-2/9 and modulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (Shi et al., 2015). However, the effects and underlying mechanisms of liquiritigenin concerning Cis-induced AKI remain to be elucidated. Zhou’s study (Zhou M. et al., 2022) confirmed that liquiritigenin could function as a nephroprotective agent against Cis-induced AKI by enhancing mitochondrial function.
4.1.17 Oroxylin A
A study (Yao M. et al., 2022) has demonstrated the therapeutic potential of Oroxylin A (OA), a principal active constituent of Scutellaria baicalensis, in addressing AKI and its progression to CKD. Mechanistically, it was shown that OA markedly ameliorated mitochondrial injury induced by hypoxia-reoxygenation through the enhancement of the PPARα-BNIP3 signaling pathway. Consequently, therapeutic strategies that utilize OA or target the PPARα-BNIP3 axis to regulate mitochondrial homeostasis may present innovative approaches for managing the transition from AKI to CKD.
4.1.18 Arbutin
Previous studies have reported that arbutin (Ar), isolated from Chinese yam, exhibits a concentration of 0.08‰ in extracts measured through liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) (Zeng et al., 2018). Data derived from NP analysis indicated that Ar potentially mitigates AKI by demonstrating anti-inflammatory properties and modulating the Akt signaling pathway. Recent findings (Zhang et al., 2021b) indicated that Ar could confer protection against LPS-induced AKI by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through the Akt signaling pathway, thereby establishing a molecular foundation for innovative therapeutic strategies for AKI.
4.1.19 Puerarin
Puerarin, derived from Radix puerariae (R. puerariae), has garnered recent interest due to its diverse pharmacological properties for treating kidney disorders, including AKI and CKD (Ma et al., 2014; She et al., 2014). Additionally, Ma et al. reported that puerarin might alleviate CI-AKI (Ma et al., 2017). Nonetheless, the renal protective mechanisms of puerarin in CI-AKI remain poorly understood. Wu et al. (2020) demonstrated that puerarin could alleviate CI-AKI by downregulating miR-31 expression, enhancing Numb activation, and subsequently inhibiting the Notch signaling pathway.
4.1.20 Isoorientin
Previous research (Anilkumar et al., 2017) has demonstrated that Isoorientin (Iso) exhibits multiple pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Furthermore, it has been established that Iso mitigates APAP-induced hepatotoxicity by stimulating the Nrf2 antioxidative pathway and engaging AMPK/Akt/GSK3β (Fan et al., 2018). Natural products serve as primary activators of Nrf2, capable of modulating the Nrf2/ARE pathway to alleviate OS, thus garnering increasing scholarly interest in recent years. Fan’s investigation (Fan et al., 2020) offers an extensive overview of Iso’s therapeutic promise in Cis-induced AKI and its mechanistic pathways. The findings suggest that the lack of Nrf2 exacerbates Cis-induced AKI, and the pharmacological activation of Nrf2 may provide a novel therapeutic approach to avert kidney damage.
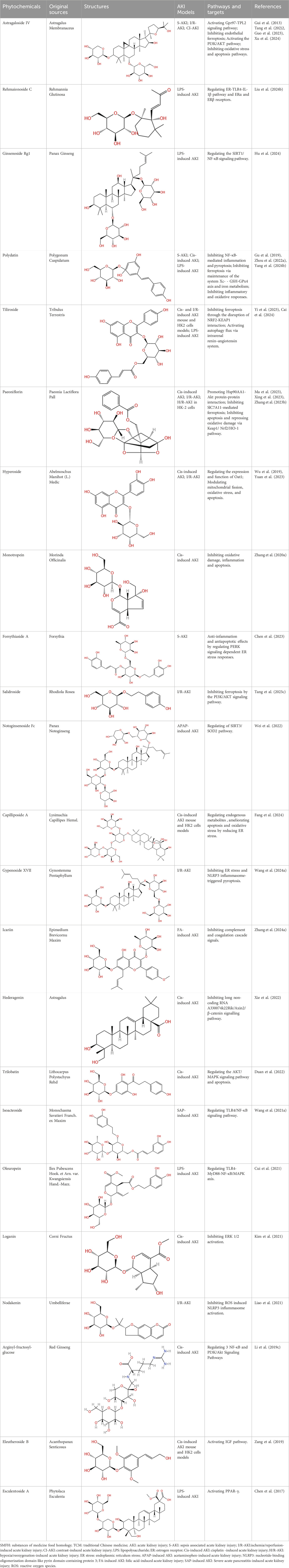
4.2 Saponins
4.2.1 Astragaloside IV
Astragaloside IV (AS-IV), a key active constituent procured from Astragalus membranaceus, is associated with a multitude of pharmacological functions (Zhang D. Q. et al., 2018; You et al., 2019) and has been evidenced to offer protective effects in diverse models of kidney disease (Feng et al., 2022). Gui et al. (2013) established that AS-IV mitigated structural and biochemical abnormalities while also inhibiting OS and apoptosis in rats suffering from AKI. Tang et al. (2022) demonstrated that AS-IV protect S-AKI in RTECs by strengthening the PI3K/AKT pathway. Recent research (Guo et al., 2023) has indicated that AS-IV mitigates ferroptosis during I/R-AKI, confirmed through NP, molecular docking, MD simulation, and experimental validation. It has been demonstrated that AS-IV reduces ROS and Fe2+ levels while promoting the expressions of GPX4 and SLC7A11 in OGD/R-injured HUVECs, thereby effectively restraining ferroptosis in I/R-AKI. Other investigations (Shi et al., 2021; Zhang M. et al., 2022) propose an alternative mechanism for AS-IV in I/R-AKI cases. Prior reports have established that AS-IV can modulate MAPK, NF-κB, and Nrf2 expression to mitigate renal injury. However, the specific impact of AS-IV on HHcy-exacerbated S-AKI remains inadequately understood. A recent study (Xu et al., 2024) revealed that TPL2 elevation in HHcy-intensified S-AKI occurs through Gpr97 pathway activation, mechanistically amplifying inflammatory responses and cellular mortality. Moreover, initial findings demonstrated AS-IV’s ability to minimize Hcy-intensified S-AKI through suppression of Gpr97-TPL2 signaling cascades. Ast potentially guards against AKI by strengthening multiple metabolic processes, encompassing amino acid pathways, glyoxylic acid, dibasic acid metabolism, glutathione processes, and UFA synthesis. These mechanisms potentially connect to inflammatory control, metabolic enhancement, and OS suppression (Song et al., 2021). Additionally, Ast has the capability to inhibit expression of NLRP3 inflammasomes and restrict proinflammatory mediator release through autophagy induction (Qu et al., 2019).
4.2.2 Frehmaglutin D and rehmaionoside C
Violetone substances Frehmaglutin D and rehmaionoside C, extracted from Rehmannia glutinosa, demonstrate estrogenic properties in combating S-AKI. Research indicates that these compounds potentially achieve their beneficial impact on S-AKI via the ER-TLR4-IL-1β signaling cascade, leading to enhanced regulation of inflammation, apoptosis, and OS (Liu M. et al., 2024). Both substances exhibit activity through ERα and ERβ receptors, showing comparable mechanistic pathways. Furthermore, studies have established that ERα and ERβ can form direct or indirect associations with TLR4, and these interactions vary based on concentration levels.
4.2.3 Ginsenoside Rg1
Ginsenoside Rg1 (Rg1) is an active compound procured from Panax ginseng, exhibiting diverse therapeutic effects, encompassing immunoregulatory, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective activities (Chen J. et al., 2019). Notably, numerous studies (Mao et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2019) revealed Rg1 alleviates podocyte damage caused by angiotensin II, experimental glomerular nephritis, and glomerular fibrosis. Evidence provided by Hu et al. (2024) supports the advantageous effects of Rg1 in S-AKI model. Specifically, Rg1 reduces renal damage and decreases cell apoptosis, oxidative damage, and inflammation in S-AKI mice by modulating SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway.
4.2.4 Polydatin
Polydatin (PD), a natural bioactive compound extracted from Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc.‘s dried roots, exhibit potential therapeutic benefits in diverse renal conditions. Studies indicate that PD operates through multiple mechanisms, encompassing oxidative stress reduction, inflammation suppression, fibrosis prevention, mitochondrial function enhancement, and autophagy modulation (Sun and Wang, 2020; Peritore et al., 2021). In vitro studies demonstrate PD effectively blocks the production of inflammatory cytokines (Lou et al., 2015). Additionally, previous investigations have established that PD provides protective effects against AKI induced by cecal ligation and puncture, as well as renal I/R injury in mice (Gao et al., 2015; Meng et al., 2016). The compound substantially shields mice from AKI by modulating Scr, BUN, and inflammatory mediator levels. This protection stems from its dual action of suppressing NF-κB pathway activity while enhancing Nrf2 signaling (Gu et al., 2019). Contemporary research (Huang et al., 2021) suggests PD’s ability to suppress ferroptosis, leading to improvements in myocardial I/R damage and cerebral trauma. Yet, PD’s specific influence on Cis-induced AKI remains to be fully elucidated. Findings from one investigation (Zhou L. et al., 2022) highlight PD’s significant renoprotective impact against ferroptosis in Cis-induced AKI models, achieved through multiple mechanisms: limiting excessive cellular iron accumulation, decreasing ROS generation, preserving GSH levels, boosting GPX4 functionality, thus minimizing lipid oxidation and ferroptotic susceptibility, ultimately decelerating AKI progression.
4.2.5 Tiliroside
Tiliroside (Tili) is a natural flavonoid frequently found in various plants and exhibits numerous biological activities, encompassing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (Grochowski et al., 2018). The renoprotective effects of Tili on LPS-induced AKI have been emphasized by Yi et al. (2023), who noted its ability to suppress inflammation, OS, and tubular cell apoptosis while promoting autophagy flux through a shift towards the intrarenal ACE2/Ang1-7 axis and away from the intrarenal ACE/Ang II axis. Additionally, Cai’s study (Cai et al., 2024) demonstrated that Tili triggered Nrf2 activation through disruption of Keap1-Nrf2 interaction, indicating that tiliroside administration significantly safeguarded mice from Cis- and I/R-induced AKI. The protective outcomes of Tili on renal tissue were achieved through ferroptosis suppression via Nrf2 pathway activation.
4.2.6 Paeoniflorin
Paeoniflorin (PF), isolated from Paeonia lactiflora Pal, is associated with diverse biological effects (Xing et al., 2023), including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, analgesic, and immunomodulatory properties. Recently, it was figured out by Wen et al. (2019) that PF mitigates the impairment of autophagy flux caused by intestinal I/R via LKB1/AMPK pathway activation. Research has indicated PF’s capacity to reduce acute necrotizing pancreatitis-linked AKI by suppressing inflammatory responses and kidney cell death (Wang et al., 2016). A study (Xing et al., 2023) demonstrated PF prevents HK-2 cells from hypoxia-reoxygenation (H/R) injuries, suggesting its protective mechanism involves Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathways. The Nrf2/HO-1 signaling cascade emerges as a crucial therapeutic target in H/R-induced OS management. PF’s cell-protective and antioxidant capabilities show promise for clinical applications in I/R-induced AKI treatment. Ma et al. (2023) indicated that PF reduced serum biochemical markers, histological damage, ferroptosis, and inflammation in I/R- AKI mice. Additionally, ferroptosis and inflammation triggered by H/R were inhibited by PF in HK-2 cells. RNA sequencing analysis suggested PF inhibits ferroptosis in HK-2 cells by enhancing SLC7A11 following H/R exposure. Consequently, these findings suggest PF prevention of ferroptosis by AKI depends on SLC7A11. Zhang M. Y. et al. (2023) utilized an integrated network pharmacological approach alongside RNA-Seq methods to investigate transcriptional alterations triggered by PF in Cis-induced AKI, revealing that PF reduces cellular death and inflammatory responses in Cis-induced AKI via enhancement of Hsp90AA1-Akt protein-protein interactions.
4.2.7 Hyperoside
Hyperoside (Hyp), a flavonol glycoside compound, has been indicated to enhance the progression of kidney diseases. Wu et al. (2019) demonstrated that Hyp protects against I/R-induced tubular cell injury through its influence on mitochondrial fission, OS, and apoptosis. Notably, Hyp targets the OMA1-OPA1 system to prevent mitochondrial fragmentation, thereby promoting tubular cell survival. Pre-treatment with Hyp has markedly reduced apoptosis and OS in cases of I/R AKI (Wu et al., 2019). Furthermore, Hyp mitigates Cis-induced AKI by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome, mediated through ROS/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway (Li Z. et al., 2023). Additionally, Hyp inhibits AMPK-ULK1-mediated autophagic activity, which attenuates D-galactose-induced renal aging and injury (Liu B. et al., 2018). Moreover, Hyp pre-treatment markedly reduces proteinuria in diabetic mice and protects the glomerular basement membrane from OS and damage (An et al., 2017). The impact of Hyp on Cis-induced AKI in rats requires further investigation. Yuan et al. (2023) found that Hyp could enhance OAT1 expression through HNF-1α and PXR regulation, thereby improving OAT1 uptake capacity, lowering indoxyl sulfate accumulation in vivo, and facilitating its urinary elimination, consequently reducing Cis-induced AKI.
4.2.8 Monotropein
Monotropein is characterized by diverse pharmacological activities, encompassing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects (Zhu et al., 2016). Zhang et al. (2020a) demonstrated that monotropein mitigates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity while decreasing Scr and BUN levels. Additionally, monotropein effectively inhibits cisplatin-induced OS by lowering MDA levels and boosting GSH, SOD, and CAT enzymatic functions. The protective effects of monotropein against cisplatin-mediated AKI operate through multiple pathways: it stimulates the Nrf2/HO-1 cascade to counter OS, blocks NF-κB signal transduction to reduce inflammatory responses, and modulates the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in this kidney damage model.
4.2.9 Forsythiaside A
Modern pharmacology demonstrates that Forsythiaside A (FTA), derived from Forsythia Fructus, exhibits various pharmacological effects, including antibacterial, antioxidant, antiviral, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties (Chen Y. et al., 2023). However, limited studies have been conducted regarding the protective effects of FTA on the kidneys and its potential to ameliorate renal damage in the context of S-AKI. Chen Y. et al. (2023) developed an LPS-induced AKI model and discovered FTA provided protection to renal tissue during sepsis initiation, thereby diminishing kidney inflammation and cell death. Additionally, FTA has emerged as a promising suppressor of ER stress-associated apoptosis, with its regulatory mechanisms operating partly through PERK pathway suppression.
4.2.10 Salidroside
Salidroside (SA), a bioactive compound of Rhodiola rosea, is celebrated for its extensive biological properties encompass anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, anti-tumorigenic, and anti-radiation effects (Rong et al., 2020). A multitude of investigations have established the protective benefits of SA against various organ damages, mainly through the mitigation of OS, the inhibition of apoptosis, the reduction of intracellular calcium overload, and the enhancement of mitochondrial function (Zhang P. et al., 2023). Tang Z. et al. (2023) demonstrated SA augmented the activity of SODs via activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, resulting in the elimination of ROS, attenuation of OS injuries and ferroptosis, thereby safeguarding renal function.
4.2.11 Notoginsenoside Fc
A recent report has indicated Notoginsenoside Fc (Fc) facilitates re-endothelialization acceleration after vascular injury in diabetic rats by promoting autophagy (Liu J. et al., 2019). It has been observed Fc mitigates injury to vascular endothelial cells through modulating PPAR-γ-mediated pathway in diabetic rats (Liu J. et al., 2018). Furthermore, another study has demonstrated (Wei et al., 2022) Fc reduces tubular injury and alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction in AKI mice, in part through the modulation of the SIRT3/SOD2 pathway.
4.2.12 Capilliposide A
Fang’s study (Fang et al., 2024) indicated that the extract of Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl, known as Capilliposide A, may be an effective therapeutic agent against Cis-induced AKI. This effect is thought to arise from a synergistic interaction with endogenous metabolites linked to amino acid metabolism and ER stress, achieved by suppressing PERK-ATF4-CHOP-mediated apoptosis and OS.
4.2.13 Gypenoside XVII
Gypenoside XVII (GP-17), a tetracyclic triterpenoid saponin extracted from Gynostemma pentaphyllum, exhibits multiple pharmacological benefits against disorders affecting cerebrovascular, cardiovascular, and skin systems. Previous studies have revealed that GP-17 offers protection from myocardial I/R injury through the suppression of ER stress-related protein expression, including GRP78 and CHOP, thus reducing ER stress (Yu et al., 2021; Su et al., 2022). Research has also established that GP-17 reduces mitochondria-linked apoptotic processes in myocardial tissue (Lee et al., 2019). Studies by Wang J. et al. (2024) established GP-17 attenuates ER stress during renal I/R while suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation, consequently inhibiting pyroptosis and delivering anti-inflammatory benefits.
4.2.14 Icariin
Icariin could alleviate Cisp-induced AKI, primarily through downregulation of TNF-α levels and inhibition of NF-κB and apoptosis-related proteins (Ma et al., 2015). Additionally, icariin has exhibited effectiveness in decreasing S-AKI-related mortality by lessening oxidative injury, regulating inflammatory responses, and disrupting proapoptotic pathways (Xie et al., 2018). Zhang D. et al. (2024) examined the pathological mechanisms of FA-induced AKI and icariin’s protective role using proteomic analysis. Their research revealed complement and coagulation cascade pathways play significant roles in AKI development and progression, and icariin attenuates AKI by suppressing these signaling cascades.
4.2.15 Hederagenin
Recent studies have indicated Hederagenin (HDG) can both attenuate cerebral I/R injury through the regulation of MLK3 signaling pathway (Yu et al., 2020) and enhance renal fibrosis by targeting muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (Yang and He, 2022). Xie’s research (Xie et al., 2022) identified lncRNA-A330074k22Rik in kidney tissues of Cis-induced AKI and highlighted its crucial role in the pathogenesis and progression of AKI, where it exerts a promoting effect. Furthermore, HDG protects against Cis-induced AKI and LPS-induced inflammatory injury in RTECs. Mechanistically, the inhibition of lncRNA A330074k22Rik by HDG markedly suppresses the Axin2/β-catenin pathway, thereby downregulating the inflammatory response associated with AKI.
4.2.16 Trilobatin
Duan et al. (2022) developed a Cis-induced AKI model in mice. Subsequently, they assessed the protective role of Trilobatin (TLB) pretreatment against renal toxicity by inhibiting oxidative damage and apoptosis. Observations indicated that the parameters in the TLB treatment group exhibited varying degrees of improvement compared to the control group, with the 100 mg/kg dosage showing superior protective effects, thus signifying a dose-dependent response to TLB administration. The current investigation demonstrated that TLB pretreatment markedly reduced apoptosis induced by cisplatin.
4.2.17 Isoacteoside
Previous research has indicated that the inflammatory response associated with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) might be diminished by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway (Wang et al., 2017). Wang B. et al. (2021) established rat models of SAP to examine anti-inflammatory properties of isoacteoside in SAP-induced AKI. Isoacteoside was found to mitigate AKI resulting from SAP by reducing inflammation. Consequently, isoacteoside could serve as a potential therapeutic agent for both SAP and SAP-induced AKI. This mechanism may involve inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB p65 signaling pathway.
4.2.18 Oleuropein
Cui et al. (2021) indicated Oleuropein (OP) exerted anti-inflammatory effects via the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway by suppressing the dimerization of TLR4. These effects of OP may contribute to its capability to ameliorate LPS-associated AKI by modulating the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB/MAPK axis.
4.2.19 Loganin
Loganin is an iridoid glycoside derived from Corni fructus, known for its use in replenishing liver and kidney functions while suppressing sweating and seminal emissions. A study (Kim et al., 2021) demonstrated that loganin displayed reno-protective properties against Cis-induced AKI by inactivating ERK 1/2. These findings suggest that loganin may be an effective adjuvant in cisplatin-based cancer therapies.
4.2.20 Nodakenin
Nodakenin, a furanocoumarin glycoside isolated from Peucedanum decursivum Maxim, has recently been shown to enhance progressive fibrosis by mediating the expression of Snail1 (Li et al., 2020). Liao’s research (Liao et al., 2021) highlighted that nodakenin markedly inhibited I/R-induced AKI in mice and hypoxia-treated primary RTECs by modulating the activation of the NF-κB and ROS-induced NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby improving inflammation in I/R-AKI.
4.2.21 Arginyl-fructosyl-glucose
Arginyl-fructosyl-glucose is one of the key non-saponins present in red ginseng, which, along with saponins, is recognized for its strong protective effects against kidney injury (Kim et al., 2014). Li R. Y. et al. (2019) found AFG mitigated the side effects of Cis-induced AKI mice, partly by restoring antioxidative activity and reducing the inflammatory response. Notably, AFG pretreatment enhanced recovery from renal injury by alleviating OS, mediating NF-κB-related inflammation, and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt apoptotic signaling pathways.
4.2.22 Eleutheroside B
Eleutheroside B has been reported to exhibit a range of pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and anti-radiation effects. Zang’s study (Zang et al., 2019) found that eleutheroside B offers protection against Cis-induced AKI in mice, mitigating the damage caused by cisplatin exposure and hypoxia-reoxygenation in HK-2 cells. It has been shown that eleutheroside B inhibits the expression of KIM-1, reduces inflammation, and prevents both apoptosis and programmed necrosis. The underlying mechanism may involve the activation of the IGF pathway and its downstream signaling by downregulating IGFBP-7 expression, thereby promoting cellular proliferation.
4.2.23 Esculentoside A
Esculentoside A (EsA), derived from the root of Phytolaca esculenta, has been noted for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Chen’s study (Chen et al., 2017) demonstrated the protective effects of EsA against LPS-induced AKI in mice. It was observed that EsA protects against LPS-induced AKI by inhibiting the inflammatory response through the activation of PPAR-γ.
4.3 Flavonoids
4.3.1 Tanshinone IIA
Tanshinone IIA represents a bioactive compound extracted from Salvia miltiorrhiza, which has been extensively utilized in treating various ailments throughout Asia. Jiang et al. (2016b) revealed that Tanshinone IIA mitigated the overactivity of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)3β, as well as the hyperactivation of its downstream mitogen-activated protein kinases, which are fundamentally involved in renal fibrogenesis and inflammatory processes. The inhibition of GSK3β is likely a pivotal mechanism through which the therapeutic efficacy of Tanshinone IIA is mediated, as sodium nitroprusside, a known GSK3β activator, markedly counteracts its renoprotective benefits. Additionally, another investigation (Jiang et al., 2016a) demonstrates that Tanshinone IIA reduces kidney damage following folic acid exposure in a murine model. This compound mitigates damage to RTECs, facilitates recovery, alleviates the inflammatory response, and obstructs the progression of long-term kidney fibrosis. Mitochondrial dysfunction can be interpreted as a direct pathophysiological link between kidney-lung interactions during the phases of AKI and ALI triggered by renal IR. Renal IR is known to provoke mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis within myocardial cells. Tanshinone IIA, in combination with cyclosporine A, is viewed as a protective agent that diminishes lung apoptosis through the modulation of mitochondrial function by activating PI3K/Akt/Bad pathway (Tai et al., 2021b; Tai et al., 2022). In the research of Tai et al. (2021a), mitochondria were isolated from rat myocardial tissues, establishing that mitochondrial dysfunction within the myocardium occurred alongside renal IR, subsequently leading to myocardial cell apoptosis, which was worsened by obesity. Dou et al. (2022) employed network pharmacological analysis to investigate target genes and regulatory networks associated with the effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza in AKI treatment. Complementary experiments using an in vivo AKI mouse model and in vitro methodologies were conducted to explore the renal protective properties of Tanshinone IIA. Tanshinone IIA may enhance renal inflammation attenuation by inhibiting PXR-mediated NF-κB activation.
4.3.2 Shionone
Shionone is a natural constituent derived from the dried rhizome of Aster tataricus L. f., exhibiting anti-inflammatory properties (Wang X. et al., 2021). Prior investigations have indicated the administration of LPS to animal models or cellular systems may elicite an inflammatory response analogous to that observed in clinical sepsis (Zhang et al., 2020b). Zhang et al. (2021a) proposed that sepsis induced AKI leads to the production of M1 macrophages, which may function in the inflammatory response associated with AKI. By inhibiting ECM1 and activating the GM-CSF/STAT5/Arg1 pathway to promote the differentiation of alternative macrophage M2, Shionone effectively diminishes the inflammatory response, thereby facilitating tissue repair and mitigating AKI.
4.3.3 5-O-methyldihydroquercetin and cilicicone B
5-O-methyldihydroquercetin (GS1) and cilicicone B (GS2) were identified as the two predominant flavonoids extracted from the plant; however, their pharmacological activities remain underexplored. Zeng M. et al. (2020) discovered that GS1 and GS2 exhibit significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, markedly alleviating renal damage. It is suggested that GS1 and GS2 may exert their effects by inhibiting TLR4/MyD88/TRIF/NLRP3 signaling pathway.
4.3.4 Zingerone
Zingerone, a phenolic alkanone extracted from ginger, has been noted for its diverse pharmacological properties. Prior investigations have indicated that zingerone demonstrates anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway (Hsiang et al., 2015). It has been reported that zingerone treatment mitigates activation of NF-κB in models of acute lung injury induced by LPS (Xie et al., 2014). Research conducted by Song et al. (2016) revealed that a dose of 10 mg/kg of zingerone could attenuate LPS-induced expression of TLR4, although this inhibition was relatively modest. Notably, zingerone markedly suppressed LPS-induced NF-κB activation. This study further established that zingerone possesses protective effects against LPS-induced AKI. The promising anti-inflammatory mechanism of zingerone is attributed to its capacity to inhibit TLR4-mediated NF-κB activation and the inflammatory response.
4.4 Polyphenols
4.4.1 Salvianolate
Salvianolate (SAL) is known for its ability to scavenge free radicals, exert anti-OS effects and inhibit thrombosis. Its efficacy in treating conditions such as coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, diabetes, and other ailments has been well-established (Yang et al., 2021). Furthermore, clinical studies have demonstrated that salvianolate exhibits both effectiveness and safety in patients with diabetic nephropathy (Qi et al., 2007). Sun D. et al. (2022) indicated that SAL facilitates Nrf2 activation and promotes the expression of its downstream target genes, which markedly contributes to reducting ROS levels within cells. Additionally, SAL impacts the thermal stability of Keap1, with modifications to the Cys151 residue of Keap1 being crucial for Nrf2-dependent transcriptional activation mediated by SAL.
As a multitarget agent, salvianolic acid A (SAA) demonstrates significant potential in treating kidney disorders (Yao L. et al., 2022). Zhang Z. et al. (2018) suggest that SAA may confer protection against I/R-AKI, possibly due to its capacity to mitigate damage to PTC endothelium and to preserve PTC integrity, thereby alleviating hypoxia in the vicinity of renal tubules and ameliorating acute tubular necrosis. Recent investigations have indicated that SAA exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-OS effects by activating the Akt/GSK-3β/Nrf2 and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in 5/6Nx rats (Zhang et al., 2019). Moreover, in LPS-induced AKI, SAA enhances renal function by inhibiting the activation of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway, subsequently reducing the release of inflammatory mediators (Zeng X. et al., 2020). Diao et al. (2023) reported that SAA improved gentamicin-induced AKI and 5/6Nx-induced CKD, likely through the inhibition of inflammatory factor release, alleviation of OS injury, and modulation of the MAPK and TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathways. Prior investigations have indicated that salvianolic acid B (SalB) mitigates injuries in various organs and maintains redox homeostasis, particularly the balance of ROS (Tang et al., 2014). SalB confers protection by enhancing the Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway in animal models (Liao et al., 2020). Pang et al. (2020) revealed that the primary mechanism by which SalB improves AKI involves inhibiting NLRP3 activation through direct stimulation of nuclear Nrf2 expression, subsequently reducing pyroptosis. Prior investigation has shown that salvianolic acid C (SalC) diminishes inflammation, OS, and caspase-mediated apoptosis by inactivating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in AKI (Uzunoglu et al., 2011; Mercantepe et al., 2018). A study (Chien et al., 2021) demonstrated that SalC regulates inflammatory responses in Cis-induced AKI animal model by suppressing renal histopathological changes, inflammatory cell infiltration, and the release of proinflammatory cytokines. SalC presents potential as a therapeutic agent, providing robust anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects against AKI, mediated by the inhibition of signaling axes involving TLR-4, NF-κB, MAPK, HO-1, and Nrf2.
4.4.2 Honokiol
Honokiol, isolated from Magnolia officinalis, exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Honokiol may inhibit OS and inflammation associated with renal I/R injury (Yu et al., 2016). The current investigation (Xia et al., 2019a) has demonstrated that honokiol decreases iNOS, NO, and MPO levels in vitro experiments. Conversely, the activities of GSH and SOD exhibit significant increases following honokiol treatment. Additionally, honokiol enhances the antioxidant capacity of HO-1 in rats subjected to CLP and ameliorates the morphological alterations in the kidneys of these rats. ZnPPIX, an inhibitor of HO-1, can diminish the antioxidant effect of honokiol. Collectively, these findings indicate that honokiol alleviates OS in sepsis-induced AKI. Moreover, protein analysis of TLR2, TLR4, TRIF, MyD88, IκBα, and p-IκBα reveals that honokiol can inhibit the aberrant activation of the TLR signaling pathway.
4.5 Lipoid
4.5.1 Artesunate
Beyond its anti-malarial properties, many investigations report artesunate exhibits considerable anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-autophagy characteristics. A recent study has indicated that the effect of artesunate in mitigating ulcerative colitis is linked to its ability to alleviate excessive ER stress-mediated intestinal barrier impairment and the inflammatory response (Yin et al., 2021). Furthermore, Lei et al. (2021) revealed that artesunate markedly diminishes renal damage and necroptosis, enhancing renal function and inflammation. The underlying mechanism is primarily associated with inhibiting macrophage Mincle-mediated necroptosis and the inflammatory response directed towards tubular epithelial cells. In summary, artesunate inhibits the activation of M1 macrophages and the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL signaling cascade by down-regulating Mincle expression, consequently reducing both the inflammatory response and necroptosis, thereby ameliorating renal injury in AKI.
4.5.2 Limonin
In various medical contexts, limonin exhibits numerous biological activities, such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiproliferative effects (Duan et al., 2021; Luo J. et al., 2022). Zhou et al. (2023) have stated that limonin acts as an ERK2 agonist, possessing the ability to confer protection against ischemic AKI. The findings clearly illustrated that limonin reduces cellular mortality and facilitates tubule repair and regeneration by activating ERK.
4.5.3 Parthenolide
A sesquiterpene lactone known as parthenolide (PTL) is derived from the perennial plant feverfew and has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties (Freund et al., 2020). According to Shou et al. (2023), PTL has the capability to modulate inflammatory factors in cases of AKI and mitigate CLP-induced sepsis through the NF-κB p65 signaling pathway.
4.5.4 Alisol B 23-acetate
Luan et al. (2021) reported that Alisol B 23-acetate (ABA) displays renal FXR agonistic activity in vitro and FXR-dependent gene modulation in vivo. Treatment with ABA effectively diminishes renal inflammation, reduces apoptosis, and alleviates OS, thereby protecting mouse kidneys from IRI.
4.5.5 Wedelolactone
Experimental data have indicated that wedelolactone (WED) can inhibit the proliferation of renal mesangial cells and safeguard renal podocytes (Shen et al., 2017). In summary, WED protects against inflammation and OS damage induced by doxorubicin in MPC-5 cells. The results (Zhu et al., 2019) demonstrated that WED alleviates doxorubicin-induced inflammation and OS damage to podocytes via the IκK/IκB/NF-κB pathway.
4.6 Other compounds
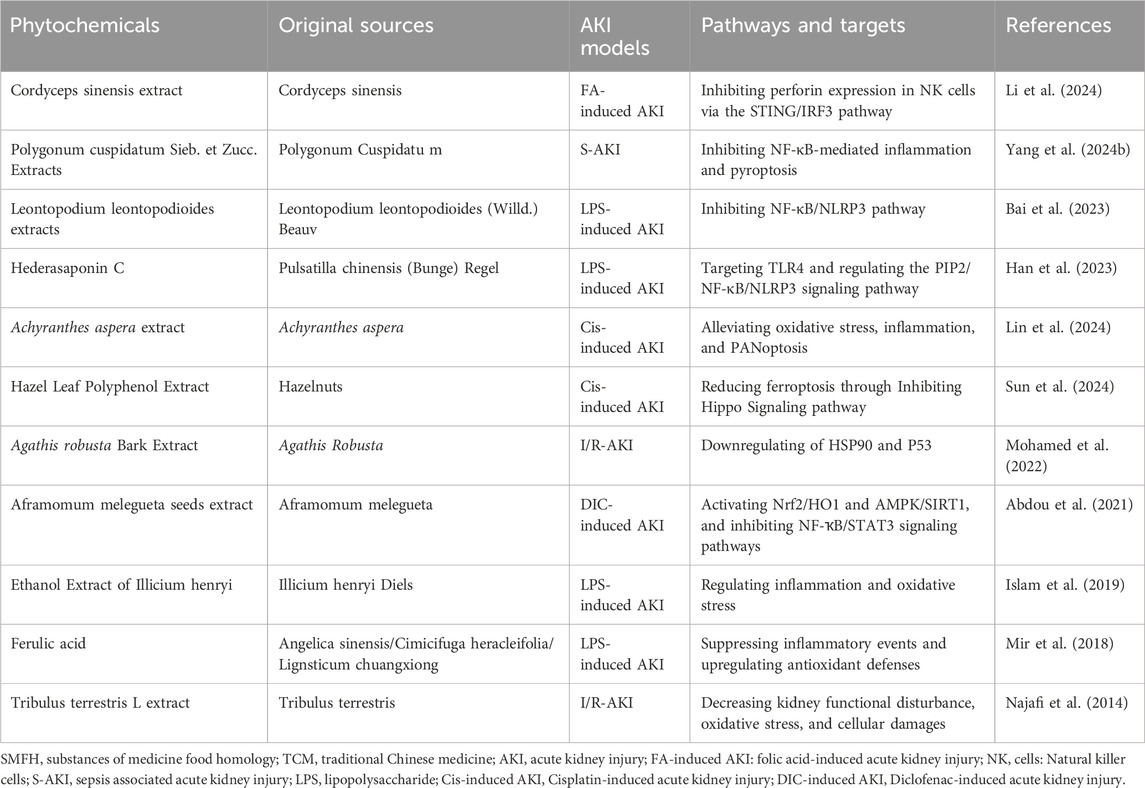
4.6.1 Cordyceps sinensis extract
Cordyceps sinensis (CS) has been shown to reduce renal vascular resistance and enhance nephrotoxicity-induced renal dysfunction through antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-autophagic mechanisms (Wu et al., 2011). A recent study (Deng et al., 2020) revealed that the extract of C. cicadae mycelium regulates inflammatory responses in Cis-induced AKI model by inhibiting renal pathological alterations, inflammatory cell infiltration, and the release of various proinflammatory cytokines. It suggests that the C. cicadae mycelium extract exhibits significant anti-inflammatory properties, which are mediated through the inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK and HO-1/Nrf2 signaling pathways. Furthermore, the alleviation of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity attributed to the C. cicadae mycelium extract can, in part, be ascribed to the regulation of autophagy, the inhibition of apoptosis, and the upregulation of OAT expressions in kidney tissues. Li et al. (2024) found that CS extract 2′-deoxyadenosine mitigated AKI by improving renal pathophysiological alterations and inhibiting the expression of perforin and IFN-γ released from NK cells through the STING/IRF3 signaling pathway, thereby reducing damage to RTECs.
4.6.2 Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc. Extracts
Polydatin (PD), a key component found in P. cuspidatum, has been shown to mitigate inflammation and OS in rats with AKI models. Additionally, emodin (Emo), another constituent of P. cuspidatum, has demonstrated the capacity to ameliorate AKI in vivo (Wang Y. et al., 2022). The domain of pharmacological research, which employs bioinformatics and network analysis, is emerging as a significant area referred to as NP. Collectively, the findings of this investigation (Yang et al., 2024b) suggest that PCE, along with its principal active constituents (Emo and PD), may confer protection against S-AKI through the attenuation of OS, inflammatory processes, and pyroptosis.
4.6.3 Leontopodium leontopodioides extracts
Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauv (LLB) is primarily utilized in the management of both acute and chronic nephritis, urinary tract infections, proteinuria, and hematuria. Recent investigations have elucidated that LLB possesses anti-inflammatory, analgesic, diuretic, nephroprotective, and antioxidant properties (Gao Y. et al., 2019). Reports have indicated that LLB effectively inhibited the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-induced AKI. Moreover, LLB was found to downregulate NF-κB, p-PI3K, and pAKT, while simultaneously upregulating IκB expression, thereby providing renal protection against mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis (MsPGN) in rat models (Zhao et al., 2019). Bai et al. (2023) noted that LLB holds promise in treating AKI via modulation of the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway.
4.6.4 Hederasaponin C
Han et al. (2023) demonstrate that Hederasaponin C (HSC) inhibits the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome through its interaction with the TLR4-regulated NF-κB and PIP2 signaling pathways. This discovery reveals previously unrecognized anti-inflammatory mechanisms of HSC, suggesting that its therapeutic strategy involving TLR4 modulation for AKI diverges from conventional clinical approaches such as dialysis and antibiotic therapies.
4.6.5 Achyranthes aspera extract
Lin’s research (Lin et al., 2024) indicates that the water-soluble extract of Achyranthes aspera mitigates nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin. This positive outcome can be partially ascribed to the activity of one of its active constituents, 20-hydroxyecdysone, which regulates various molecular signaling networks. Specifically, it downregulates genes and pathways related to DNA damage, OS, inflammation, and PANoptosis, while concurrently upregulating genes and signaling pathways associated with cell survival, including autophagy and mitophagy.
4.6.6 Hazel leaf polyphenol extract
Sun et al.’s study (Sun et al., 2024) illustrated that cisplatin-induced ferroptosis leads to damage of renal tubular cells and renal dysfunction, which is associated with increased phosphorylation of yes-associated protein. The extract of hazel leaf polyphenols effectively mitigates AKI by inhibiting OS, apoptosis, and ferroptosis within the kidney, achieved through suppressing the Hippo signaling pathway.
4.6.7 Agathis robusta Bark Extract
Recent findings (Mohamed et al., 2022) employing phytochemical analyses, in silico network modeling, docking techniques, and subsequent in vivo preclinical validation indicate that Agathis robusta Bark Extract (ARBE) may demonstrate renal protection by mitigating inflammation and apoptosis. The underlying mechanism is potentially associated with the downregulation of HSP90 and P53. Further investigations into drug discovery, alongside preclinical and clinical studies focusing on key components of ARBE, are recommended due to their predicted interactions with multiple targets, particularly the central hubs.
4.6.8 Aframomum melegueta seeds extract
A recent study (Abdou et al., 2021) has provided compelling evidence regarding the involvement of Nrf2/HO1 and AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathways in diclofenac-induced AKI. Additionally, the nephroprotective effects of AMSE against diclofenac-induced AKI have been demonstrated. These protective actions are believed to be mediated through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic properties. Specifically, this involves the activation of the Nrf2 and AMPK/SIRT1 pathways alongside inhibiting NF-κB and STAT3 signaling.
4.6.9 Ethanol extract of Illicium henryi
Recent research (Islam et al., 2019) demonstrated that the EEIH provides a favorable pharmacological intervention for preventing LPS-induced AKI, exhibiting significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Pretreatment with EEIH has been found to improve renal pathological alterations, inflammatory responses, and oxidative/nitrosative stress. The therapeutic effects of EEIH are thought to be achieved by downregulation of the TLR4 and NF-κB pathways and upregulation of Nrf2 expression.
4.6.10 Ferulic acid
Ferulic acid (FA), a widely distributed phytochemical and phenolic derivative of cinnamic acid, is predominantly found in the cell wall components of Angelica sinensis. It has been observed that FA exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by reducing production of inflammatory cytokines and release of ROS and RNS through the suppression of iNOS and COX-2, mediated by the activation of the NF-κB pathway (Lampiasi and Montana, 2016). Furthermore, FA has been shown to mitigate oxidative damage associated with sepsis by enhancing antioxidant capacity and reducing DNA damage in animal models subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (Bacanlı et al., 2014). Additionally, research has demonstrated the renal protective effects of FA against nephrotoxicity in various animal models (Bami et al., 2017). FA is a potent anti-inflammatory in acute and chronic inflammatory conditions (Sadar et al., 2016). A recent study (Mir et al., 2018) illustrated FA is a promising pharmacological intervention for preventing LPS-induced renal damage with minimal toxic effects. The protective mechanism of FA is believed to involve the downregulation of OS and inflammatory responses through the upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 proteins and the inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathways.
4.6.11 Tribulus terrestris L extract
The extract of Tribulus terrestris enhances RBF during the reperfusion phase via its vasodilatory effects, restoring the glomerular filtration rate to baseline levels (Najafi et al., 2014). This effect results in a relative improvement in plasma parameters indicative of kidney function. Furthermore, by reducing cellular damage and OS, Tribulus terrestris has the potential to inhibit the onset and progression of cellular injuries.
5 Strategies for SMFH and TCM phytochemicals globalization
The multi-targets and multi-levels regulation effects of TCM, are significant for various acute and chronic diseases. TCM is promoting the transformation of contemporary medical model from treatments of disease to the preventive treatments, from adversarial medicine to collaborative medicine, and from local medicine to holistic medicine. Researches on TCM are increasingly emphasizing the concept of translational medicine, adoption and compliance with standards and norms, which would make the researches more in-depth, quantitative and systematic.
The interaction of each component of TCM formulas are quantitatively analyzed, observed and studied by using internationally recognized methods and indexes. Finally, the mechanisms of action are illustrated scientifically, and researches’ papers are published in high-quality academic journals. It is required researchers to firmly grasp the three fundamental systems of Chinese medicine resources, C. medicine quality, and clinical efficacy to consolidate the scientific basis for the development of TCM. Modern medicine emphasizes the concept, norms and statistical analysis of evidence-based medicine. TCM should continue to explore and improve the efficacy evaluation techniques and methods that reflect its own characteristics and patterns, and strengthen the real-world research methods.
Actionable strategies advancing research, fostering global standardization, promoting interdisciplinary collaboration, and implementing robust clinical trials could be adopted. Measures such as optimizing the overall layout of TCM standard system, strengthening the supply of TCM standards in key fields, promoting the interactive development of TCM standards and scientific and technological innovation, promoting the internationalization of TCM standards, deepening the reform and innovation of TCM standardization, and consolidating the foundation for the development of TCM standardization are taken to achieve the standardization and internationalization of TCM, so as to integrate with mainstream medicine.
As mentioned previously, there are several preclinical/clinical studies demonstrating the short-term benefits of these SMFH and TCM phytochemicals. Previous research has revealed celastrol may alleviate inflammation and preclinical studies have confirmed its anticancer effects (Pan et al., 2023). Gastrodin injection has demonstrated positive treatment effects on dizziness or vertigo in clinic (Lai et al., 2022). The chemical composition of A. robusta Bark Extract (ARBE), depicted the interrelationship of the bioactive ingredients of ARBE with the I/R-AKI related molecular targets, and validated a nephroprotective effect (Mohamed et al., 2022). Ambiguous mechanisms of medical action, lacking purification procedures, relevant defective clinical ethical approval standards and low general recognitions, etc., are the barriers to translating these findings into clinical practice.
SMFH and TCM phytochemicals are promising therapeutic drugs for treating AKI. Although some TCM bioactive components have come into preclinical trials, it is essential to initiate preclinical pharmacologic and toxicologic researches to evaluate their efficacy and safety. In addition, it is widely recognized that modern medicine could relieve symptoms quickly while SMFH and TCM phytochemicals function therapeutic effects comprehensively (Li H. D. et al., 2019). In this regard, the combination of SMFH and TCM phytochemicals and modern medicine might become treatment strategies for AKI by taking advantages of both and limiting side effects.
6 Conclusion and perspectives
AKI is a clinical emergency condition. Western medicine treatment of AKI is still mainly symptomatic treatment, and with a further understanding of modern Chinese medicine for AKI, SMFH and TCM phytochemicals treatment of AKI has also achieved a certain effect. SMFH and TCM phytochemicals has gained increasing attention lately due to its plant-based sources and minimal adverse reactions, thus offering a promising avenue for addressing AKI. Early detection of the inducement of AKI, improvement of homeostasis, and avoidance of nephrotoxic drugs are helpful to the recovery of renal function. However, despite the unanimous recognition of the necessity of early recovery of AKI, studies on the treatment of AKI by SMFH and phytochemicals are still insufficient and lack uniform and objective syndrome differentiation standards. The results of this review clearly demonstrate that SMFH and TCM phytochemicals might alleviate AKI via multifunctional signal pathways and targets.
This review systematically elaborated the inducement factors of AKI and the potential mechanisms of various SMFH and TCM phytochemicals on AKI, providing evidences for the early diagnosis and preventive treatments of AKI, and offering a favorable basis for future experimental and clinical researches.
Author contributions
LC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JH: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XG: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from Pudong New Area Traditional Chinese Medicine Brand Multiplication Plan - Chronic Nephropathy (PDZY-2021-0302); Construction of He Liqun’s famous TCM studio (PDZY-2022-0703); Clinical Observation on the Efficacy of Guben Tongluo Formula in Treating Chronic Kidney Disease Phase 1-3 (PW2022D-12); Pilot Project of Inheritance, Innovation and Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Pudong New Area (YC-2023-0602); Pudong New Area’s Peak and Plateau Discipline Development in Clinical Medicine for Novel and Special Diseases (2025-PWXZ-15).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdou, R. M., El-Maadawy, W. H., Hassan, M., El-Dine, R. S., Aboushousha, T., El-Tanbouly, N. D., et al. (2021). Nephroprotective activity of Aframomum melegueta seeds extract against diclofenac-induced acute kidney injury: a mechanistic study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 273, 113939. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.113939
Allinson, C. S., Pollock, C. A., and Chen, X. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and the AKI-to-CKD transition. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 10 (1), e00014. doi:10.1097/imna-d-22-00014
An, X., Zhang, L., Yuan, Y., Wang, B., Yao, Q., Li, L., et al. (2017). Hyperoside pre-treatment prevents glomerular basement membrane damage in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting podocyte heparanase expression. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 6413. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06844-2
Andreucci, M., Faga, T., Pisani, A., Serra, R., Russo, D., De Sarro, G., et al. (2018). Quercetin protects against radiocontrast medium toxicity in human renal proximal tubular cells. J. Cell Physiol. 233 (5), 4116–4125. doi:10.1002/jcp.26213
Anilkumar, K., Reddy, G. V., Azad, R., Yarla, N. S., Dharmapuri, G., Srivastava, A., et al. (2017). Evaluation of anti-inflammatory properties of Isoorientin isolated from tubers of pueraria tuberosa. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 5498054. doi:10.1155/2017/5498054
Azman, S., Sekar, M., Wahidin, S., Gan, S. H., Vaijanathappa, J., Bonam, S. R., et al. (2021). Embelin alleviates severe airway inflammation in OVA-LPS-induced rat model of allergic asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 14, 1511–1525. doi:10.2147/jaa.S298613
Bacanlı, M., Aydın, S., Taner, G., Göktaş, H. G., Şahin, T., Başaran, A. A., et al. (2014). The protective role of ferulic acid on sepsis-induced oxidative damage in Wistar albino rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 38 (3), 774–782. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2014.08.018
Bai, X., Ma, Q., Li, Q., Yin, M., Xin, Y., Zhen, D., et al. (2023). Protective mechanisms of Leontopodium leontopodioides extracts on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury viathe NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 21 (1), 47–57. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(23)60384-x
Bami, E., Ozakpınar, O. B., Ozdemir-Kumral, Z. N., Köroglu, K., Ercan, F., Cirakli, Z., et al. (2017). Protective effect of ferulic acid on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 54, 105–111. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2017.06.026
Bellomo, R., Kellum, J. A., Ronco, C., Wald, R., Martensson, J., Maiden, M., et al. (2017). Acute kidney injury in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 43 (6), 816–828. doi:10.1007/s00134-017-4755-7
Cai, F., Li, D., Zhou, K., Zhang, W., and Yang, Y. (2024). Tiliroside attenuates acute kidney injury by inhibiting ferroptosis through the disruption of NRF2-KEAP1 interaction. Phytomedicine 126, 155407. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155407
Cao, Y., Chen, X., Zhu, Z., Luo, Z., Hao, Y., Yang, X., et al. (2024). STING contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced tubular cell inflammation and pyroptosis by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress in acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 15 (3), 217. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06600-1
Chang, Y. M., Chou, Y. T., Kan, W. C., and Shiao, C. C. (2022). Sepsis and acute kidney injury: a review focusing on the bidirectional interplay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (16), 9159. doi:10.3390/ijms23169159
Chao, Y. H., Wu, K. H., Lin, C. W., Yang, S. F., Chao, W. R., Peng, C. T., et al. (2017). PG2, a botanically derived drug extracted from Astragalus membranaceus, promotes proliferation and immunosuppression of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 207, 184–191. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.06.018
Chen, D. Z., Chen, L. Q., Lin, M. X., Gong, Y. Q., Ying, B. Y., and Wei, D. Z. (2017). Esculentoside A inhibits LPS-induced acute kidney injury by activating PPAR-γ. Microb. Pathog. 110, 208–213. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2017.06.037
Chen, F., Hu, M., Shen, Y., Zhu, W., Cao, A., Ni, B., et al. (2021). Isorhamnetin promotes functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury by abating oxidative stress and modulating M2 macrophages/microglia polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 895, 173878. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173878
Chen, J. (2023). Essential role of medicine and food homology in health and wellness. Chin. Herb. Med. 15 (3), 347–348. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2023.05.001
Chen, J., Zhang, X., Liu, X., Zhang, C., Shang, W., Xue, J., et al. (2019a). Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes cerebral angiogenesis via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in ischemic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 856, 172418. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172418
Chen, L., and Gong, X. (2022). Drug-induced acute kidney injury: epidemiology, mechanisms, risk factors, and prevention via traditional Chinese medicine. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 9 (1), 5. doi:10.4103/2773-0387.345767
Chen, L., Hu, J., Lu, J., and Gong, X. (2024a). Bibliometric and visual analysis of immunisation associated with acute kidney injury from 2003 to 2023. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1388527. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1388527
Chen, L., Wang, Q., Li, T., Li, L., Wang, C., Xu, B., et al. (2024b). Exploring therapeutic mechanisms of Chuan Huang Fang-II in the treatment of acute kidney injury on chronic kidney disease patients from the perspective of lipidomics. Ren. Fail 46 (1), 2356021. doi:10.1080/0886022x.2024.2356021
Chen, L., Ye, Z., Wang, D., Liu, J., Wang, Q., Wang, C., et al. (2022). Chuan Huang Fang combining reduced glutathione in treating acute kidney injury (grades 1-2) on chronic kidney disease (stages 2-4): a multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 969107. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.969107
Chen, P., Chen, F., and Zhou, B. H. (2019b). Leonurine ameliorates D-galactose-induced aging in mice through activation of the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 11 (18), 7339–7356. doi:10.18632/aging.101733
Chen, X.-Y., He, Y., and Chen, J.-Y. (2023a). Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of Gastrodia elata and its active ingredients in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Traditional Med. Res. 8, 52–54. doi:10.53388/TMR20230425001
Chen, Y., Wei, W., Fu, J., Zhang, T., Zhao, J., and Ma, T. (2023b). Forsythiaside A ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via anti-inflammation and antiapoptotic effects by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23 (1), 35. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-03855-7
Cheng, R., Wang, X., Huang, L., Lu, Z., Wu, A., Guo, S., et al. (2024). Novel insights into the protective effects of leonurine against acute kidney injury: inhibition of ER stress-associated ferroptosis via regulating ATF4/CHOP/ACSL4 pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 395, 111016. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111016
Cheng, Z., Qi, R., Li, L., Liu, Q., Zhang, W., Zhou, X., et al. (2018). Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates sepsis-induced hyperpermeability of glomerular endothelium via up-regulation of occludin expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 99, 313–318. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.078
Chien, L. H., Wu, C. T., Deng, J. S., Jiang, W. P., Huang, W. C., and Huang, G. J. (2021). Salvianolic acid C protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through attenuation of inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptotic effects and activation of the CaMKK-AMPK-sirt1-associated signaling pathway in mouse models. Antioxidants (Basel) 10 (10), 1620. doi:10.3390/antiox10101620
Chu, C., He, W., Kuang, Y., Ren, K., and Gou, X. (2014). Celastrol protects kidney against ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in rats. J. Surg. Res. 186 (1), 398–407. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2013.07.048
Cui, Y., Gao, H., Han, S., Yuan, R., He, J., Zhuo, Y., et al. (2021). Oleuropein attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in vitro and in vivo by regulating toll-like receptor 4 dimerization. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 617314. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.617314
Deng, G., Zeng, S., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., Qu, Y., Han, Y., et al. (2017). The anti-tumor activities of Neferine on cell invasion and oxaliplatin sensitivity regulated by EMT via Snail signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 7, 41616. doi:10.1038/srep41616
Deng, J. S., Jiang, W. P., Chen, C. C., Lee, L. Y., Li, P. Y., Huang, W. C., et al. (2020). Cordyceps cicadae mycelia ameliorate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK and activating the HO-1/Nrf2 and sirt-1/AMPK pathways in mice. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 7912763. doi:10.1155/2020/7912763
Diao, H. Y., Zhu, W., Liu, J., Yin, S., Wang, J. H., and Li, C. L. (2023). Salvianolic acid A improves rat kidney injury by regulating MAPKs and TGF-β1/smads signaling pathways. Molecules 28 (8), 3630. doi:10.3390/molecules28083630
Dong, W., Zhang, H., Zhao, C., Luo, Y., and Chen, Y. (2021). Silencing of miR-150-5p ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by targeting SIRT1/p53/AMPK pathway. Front. Physiol. 12, 624989. doi:10.3389/fphys.2021.624989
Dou, J. Y., Zhang, M., Cen, H., Chen, Y. Q., Wu, Y. F., Lu, F., et al. (2022). Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (danshen) and bioactive compound Tanshinone IIA alleviates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through regulating PXR/NF-κB signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 860383. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.860383
Duan, L., Cheng, S., Li, L., Liu, Y., Wang, D., and Liu, G. (2021). Natural anti-inflammatory compounds as drug candidates for inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 684486. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.684486
Duan, Y. Y., Mi, X. J., Su, W. Y., Tang, S., Jiang, S., Wang, Z., et al. (2022). Trilobatin, an active dihydrochalcone from lithocarpus polystachyus, prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway-mediated apoptosis in mice. ACS Omega 7 (42), 37401–37409. doi:10.1021/acsomega.2c04142
Du, Y., Li, J., Ye, M., Guo, C., Yuan, B., Li, S., et al. (2023). Hyperuricemia-induced acute kidney injury in the context of chronic kidney disease: A case report. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 10 (4), e00008. doi:10.1097/imna-d-23-00008
Fan, X., Lv, H., Wang, L., Deng, X., and Ci, X. (2018). Isoorientin ameliorates APAP-induced hepatotoxicity via activation Nrf2 antioxidative pathway: the involvement of AMPK/Akt/GSK3β. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1334. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01334
Fan, X., Wei, W., Huang, J., Liu, X., and Ci, X. (2020). Isoorientin attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through the inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis via activating the SIRT1/SIRT6/nrf-2 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 264. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00264
Fan, Y., Chen, H., Peng, H., Huang, F., Zhong, J., and Zhou, J. (2017). Molecular mechanisms of curcumin renoprotection in experimental acute renal injury. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 912. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00912
Fang, J., Wang, L., Zhang, D., Liang, Y., Li, S., Tian, J., et al. (2024). Integrative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome provide new insights into mechanisms of Capilliposide A against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 238, 115814. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115814
Feng, M., Lv, J., Zhang, C., Chen, D., Guo, H., Tu, Y., et al. (2022). Astragaloside IV protects sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 28 (34), 2825–2834. doi:10.2174/1381612828666220902123755
Freund, R. R. A., Gobrecht, P., Fischer, D., and Arndt, H. D. (2020). Advances in chemistry and bioactivity of parthenolide. Nat. Prod. Rep. 37 (4), 541–565. doi:10.1039/c9np00049f
Gameiro, J., Fonseca, J. A., Neves, M., Jorge, S., and Lopes, J. A. (2018). Acute kidney injury in major abdominal surgery: incidence, risk factors, pathogenesis and outcomes. Ann. Intensive Care 8 (1), 22. doi:10.1186/s13613-018-0369-7
Gao, F., Li, J. M., Xi, C., Li, H. H., Liu, Y. L., Wang, Y. P., et al. (2019a). Magnesium lithospermate B protects the endothelium from inflammation-induced dysfunction through activation of Nrf2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 40 (7), 867–878. doi:10.1038/s41401-018-0189-1
Gao, Y., Rao, H., Mao, L. J., and Ma, Q. L. (2019b). Chemical composition, antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of essential oil of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauverd. Nat. Prod. Res. 33 (4), 612–615. doi:10.1080/14786419.2017.1402310
Gao, Y., Zeng, Z., Li, T., Xu, S., Wang, X., Chen, Z., et al. (2015). Polydatin inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction in the renal tubular epithelial cells of a rat model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Anesth. Analg. 121 (5), 1251–1260. doi:10.1213/ane.0000000000000977
Gong, X., Duan, Y., Zheng, J., Ye, Z., and Hei, T. K. (2019). Tetramethylpyrazine prevents contrast-induced nephropathy via modulating tubular cell mitophagy and suppressing mitochondrial fragmentation, CCL2/CCR2-mediated inflammation, and intestinal injury. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 7096912. doi:10.1155/2019/7096912
Gong, X., Ivanov, V. N., Davidson, M. M., and Hei, T. K. (2015). Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) protects against sodium arsenite-induced nephrotoxicity by suppressing ROS production, mitochondrial dysfunction, pro-inflammatory signaling pathways and programed cell death. Arch. Toxicol. 89 (7), 1057–1070. doi:10.1007/s00204-014-1302-y
Gong, X., Ivanov, V. N., and Hei, T. K. (2016). 2,3,5,6-Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) down-regulated arsenic-induced heme oxygenase-1 and ARS2 expression by inhibiting Nrf2, NF-κB, AP-1 and MAPK pathways in human proximal tubular cells. Arch. Toxicol. 90 (9), 2187–2200. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1600-z
Gong, X., Wang, Q., Tang, X., Wang, Y., Fu, D., Lu, H., et al. (2013). Tetramethylpyrazine prevents contrast-induced nephropathy by inhibiting p38 MAPK and FoxO1 signaling pathways. Am. J. Nephrol. 37 (3), 199–207. doi:10.1159/000347033
Grochowski, D. M., Locatelli, M., Granica, S., Cacciagrano, F., and Tomczyk, M. (2018). A review on the dietary flavonoid tiliroside. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 17 (5), 1395–1421. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12389
Gu, L., Liu, J., Xu, D., and Lu, Y. (2019). Polydatin prevents LPS-induced acute kidney injury through inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative responses. Microb. Pathog. 137, 103688. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103688
Gu, Y. Y., Zhang, M., Cen, H., Wu, Y. F., Lu, Z., Lu, F., et al. (2021). Quercetin as a potential treatment for COVID-19-induced acute kidney injury: based on network pharmacology and molecular docking study. PLoS One 16 (1), e0245209. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245209
Gui, D., Huang, J., Liu, W., Guo, Y., Xiao, W., and Wang, N. (2013). Astragaloside IV prevents acute kidney injury in two rodent models by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis pathways. Apoptosis 18 (4), 409–422. doi:10.1007/s10495-013-0801-2
Guo, L., Luo, S., Du, Z., Zhou, M., Li, P., Fu, Y., et al. (2017). Targeted delivery of celastrol to mesangial cells is effective against mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis. Nat. Commun. 8 (1), 878. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00834-8
Guo, X., Xu, L., Velazquez, H., Chen, T. M., Williams, R. M., Heller, D. A., et al. (2022). Kidney-targeted renalase agonist prevents cisplatin-induced chronic kidney disease by inhibiting regulated necrosis and inflammation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 33 (2), 342–356. doi:10.1681/asn.2021040439
Guo, X., Zhang, J., Liu, M., and Zhao, G. C. (2019). Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on attenuating anti-GBM glomerular nephritis by activating NRF2 signalling. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47 (1), 2972–2979. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1640712
Guo, Y., Wang, J., Hua, Y., Jiang, M., Xu, W., Shi, Y., et al. (2023). Network pharmacology and in vitro experimental verification to reveal the mechanism of Astragaloside IV against kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Heliyon 9 (11), e21711. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21711
Han, L., Chen, A., Liu, L., and Wang, F. (2022). Leonurine preconditioning attenuates ischemic acute kidney injury in rats by promoting Nrf2 nuclear translocation and suppressing TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 70 (1), 66–73. doi:10.1248/cpb.c21-00740
Han, S., Li, S., Li, J., He, J., Wang, Q. Q., Gao, X., et al. (2023). Hederasaponin C inhibits LPS-induced acute kidney injury in mice by targeting TLR4 and regulating the PIP2/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. 37 (12), 5974–5990. doi:10.1002/ptr.8014
Hashemzaei, M., and Rezaee, R. (2021). A review on pain-relieving activity of berberine. Phytother. Res. 35 (6), 2846–2853. doi:10.1002/ptr.6984
Hosohata, K. (2016). Role of oxidative stress in drug-induced kidney injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17 (11), 1826. doi:10.3390/ijms17111826
Hsiang, C. Y., Cheng, H. M., Lo, H. Y., Li, C. C., Chou, P. C., Lee, Y. C., et al. (2015). Ginger and zingerone ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute systemic inflammation in mice, assessed by nuclear factor-κb bioluminescent imaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 (26), 6051–6058. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01801
Hu, J., Gu, W., Ma, N., Fan, X., and Ci, X. (2022). Leonurine alleviates ferroptosis in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by activating the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 179 (15), 3991–4009. doi:10.1111/bph.15834
Hu, Y., Xiang, C., Zhang, D., Zhou, F., and Zhang, D. (2024). Nephroprotective effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice through the SIRT1/NF-κB signaling. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 62 (1), 13–24. doi:10.5603/fhc.97140
Huang, L., He, S., Cai, Q., Li, F., Wang, S., Tao, K., et al. (2021). Polydatin alleviates traumatic brain injury: role of inhibiting ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 556, 149–155. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.108
Islam, M. S., Miao, L., Yu, H., Han, Z., and Sun, H. (2019). Ethanol extract of illicium henryi attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury in mice via regulating inflammation and oxidative stress. Nutrients 11 (6), 1412. doi:10.3390/nu11061412
Jain, R., Hussein, M. A., Pierce, S., Martens, C., Shahagadkar, P., and Munirathinam, G. (2022). Oncopreventive and oncotherapeutic potential of licorice triterpenoid compound glycyrrhizin and its derivatives: molecular insights. Pharmacol. Res. 178, 106138. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106138
Jian, J., Yu-Qing, L., Rang-Yue, H., Xia, Z., Ke-Huan, X., Ying, Y., et al. (2024). Isorhamnetin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice by activating SLPI-mediated anti-inflammatory effect in macrophage. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 46 (3), 319–329. doi:10.1080/08923973.2024.2329621
Jiang, C., Zhu, W., Shao, Q., Yan, X., Jin, B., Zhang, M., et al. (2016a). Tanshinone IIA protects against folic acid-induced acute kidney injury. Am. J. Chin. Med. 44 (4), 737–753. doi:10.1142/s0192415x16500403
Jiang, C., Zhu, W., Yan, X., Shao, Q., Xu, B., Zhang, M., et al. (2016b). Rescue therapy with Tanshinone IIA hinders transition of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease via targeting GSK3β. Sci. Rep. 6, 36698. doi:10.1038/srep36698
Jiang, S., Alisafaei, F., Huang, Y. Y., Hong, Y., Peng, X., Qu, C., et al. (2022). An ex vivo culture model of kidney podocyte injury reveals mechanosensitive, synaptopodin-templating, sarcomere-like structures. Sci. Adv. 8 (35), eabn6027. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abn6027
Jiang, T., Cheng, H., Su, J., Wang, X., Wang, Q., Chu, J., et al. (2020). Gastrodin protects against glutamate-induced ferroptosis in HT-22 cells through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Toxicol Vitro 62, 104715. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104715
Junho, C. V. C., González-Lafuente, L., Neres-Santos, R. S., Navarro-García, J. A., Rodríguez-Sánchez, E., Ruiz-Hurtado, G., et al. (2022). Klotho relieves inflammation and exerts a cardioprotective effect during renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiorenal syndrome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 153, 113515. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113515
Kandasamy, S., Selvaraj, M., Muthusamy, K., Varadaraju, N., Kannupal, S., Sekar, A. K., et al. (2023). Structural exploration of common pharmacophore based berberine derivatives as novel histone deacetylase inhibitor targeting HDACs enzymes. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 41 (5), 1690–1703. doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.2024254
Khajevand-Khazaei, M. R., Mohseni-Moghaddam, P., Hosseini, M., Gholami, L., Baluchnejadmojarad, T., and Roghani, M. (2018). Rutin, a quercetin glycoside, alleviates acute endotoxemic kidney injury in C57BL/6 mice via suppression of inflammation and up-regulation of antioxidants and SIRT1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 833, 307–313. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.06.019
Kim, D. H., Choi, H. I., Park, J. S., Kim, C. S., Bae, E. H., Ma, S. K., et al. (2022). Farnesoid X receptor protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by regulating the transcription of ferroptosis-related genes. Redox Biol. 54, 102382. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102382
Kim, D. U., Kim, D. G., Choi, J. W., Shin, J. Y., Kweon, B., Zhou, Z., et al. (2021). Loganin attenuates the severity of acute kidney injury induced by cisplatin through the inhibition of ERK activation in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (3), 1421. doi:10.3390/ijms22031421
Kim, Y. J., Lee, M. Y., Son, H. Y., Park, B. K., Ryu, S. Y., and Jung, J. Y. (2014). Red ginseng ameliorates acute cisplatin-induced nephropathy. Planta Med. 80 (8-9), 645–654. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1368571
Lai, Y., Wang, R., Li, W., Zhu, H., Fei, S., Shi, H., et al. (2022). Clinical and economic analysis of Gastrodin injection for dizziness or vertigo: a retrospective cohort study based on electronic health records in China. Chin. Med. 17 (1), 6. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00561-9
Lampiasi, N., and Montana, G. (2016). The molecular events behind ferulic acid mediated modulation of IL-6 expression in LPS-activated Raw 264.7 cells. Immunobiology 221 (3), 486–493. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2015.11.001
Lee, H. C., Yu, H. P., Liao, C. C., Chou, A. H., and Liu, F. C. (2019). Escin protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via attenuating inflammatory response and inhibiting ERK signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (8), 5170–5182.
Lei, X. Y., Tan, R. Z., Jia, J., Wu, S. L., Wen, C. L., Lin, X., et al. (2021). Artesunate relieves acute kidney injury through inhibiting macrophagic Mincle-mediated necroptosis and inflammation to tubular epithelial cell. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25 (18), 8775–8788. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16833
Li, B., Hu, Y., Zhao, Y., Cheng, M., Qin, H., Cheng, T., et al. (2017a). Curcumin attenuates titanium particle-induced inflammation by regulating macrophage polarization in vitro and in vivo. Front. Immunol. 8, 55. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.00055
Li, H., Chen, W., Chen, Y., Zhou, Q., Xiao, P., Tang, R., et al. (2019a). Neferine attenuates acute kidney injury by inhibiting NF-κB signaling and upregulating klotho expression. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 1197. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01197
Li, H., Ge, H., Song, X., Tan, X., Xiong, Q., Gong, Y., et al. (2023a). Neferine mitigates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice by regulating autophagy and apoptosis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 27 (2), 122–131. doi:10.1007/s10157-022-02292-z
Li, H., Tang, Y., Wen, L., Kong, X., Chen, X., Liu, P., et al. (2017b). Neferine reduces cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 484 (3), 694–701. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.180
Li, H. D., Meng, X. M., Huang, C., Zhang, L., Lv, X. W., and Li, J. (2019b). Application of herbal traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of acute kidney injury. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 376. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00376
Li, J., and Gong, X. (2022). Tetramethylpyrazine: an active ingredient of Chinese herbal medicine with therapeutic potential in acute kidney injury and renal fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 820071. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.820071
Li, J., Wang, L., Tan, R., Zhao, S., Zhong, X., and Wang, L. (2020). Nodakenin alleviated obstructive nephropathy through blunting Snail1 induced fibrosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24 (17), 9752–9763. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15539
Li, R. Y., Zhang, W. Z., Yan, X. T., Hou, J. G., Wang, Z., Ding, C. B., et al. (2019c). Arginyl-fructosyl-glucose, a major maillard reaction product of red ginseng, attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by regulating nuclear factor κB and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 67 (20), 5754–5763. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00540
Li, S., Pang, W., Wang, Y., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Cordyceps sinensis extract protects against acute kidney injury by inhibiting perforin expression in NK cells via the STING/IRF3 pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 16 (7), 5887–5904. doi:10.18632/aging.205676
Li, Y., Xiong, W., Yang, J., Zhong, J., Zhang, L., Zheng, J., et al. (2015). Attenuation of inflammation by emodin in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury via inhibition of toll-like receptor 2 signal pathway. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 9 (3), 202–208.
Li, Z., Liao, W., Yin, X., Liu, L., Zhao, Z., Lu, X., et al. (2023b). Hyperoside attenuates Cd-induced kidney injury via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ROS/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 172, 113601. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2023.113601
Liang, Y., Liu, H., Fang, Y., Lin, P., Lu, Z., Zhang, P., et al. (2021). Salvianolate ameliorates oxidative stress and podocyte injury through modulation of NOX4 activity in db/db mice. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25 (2), 1012–1023. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16165
Liao, D., Chen, Y., Guo, Y., Wang, C., Liu, N., Gong, Q., et al. (2020). Salvianolic acid B improves chronic mild stress-induced depressive behaviors in rats: involvement of AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. J. Inflamm. Res. 13, 195–206. doi:10.2147/jir.S249363
Liao, Y., Lin, X., Li, J., Tan, R., Zhong, X., and Wang, L. (2021). Nodakenin alleviates renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting reactive oxygen species-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nephrol. Carlt. 26 (1), 78–87. doi:10.1111/nep.13781
Lin, C. H., Tseng, H. F., Hsieh, P. C., Chiu, V., Lin, T. Y., Lan, C. C., et al. (2021). Nephroprotective role of chrysophanol in hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced renal cell damage via apoptosis, ER stress, and ferroptosis. Biomedicines 9 (9), 1283. doi:10.3390/biomedicines9091283
Lin, S. Y., Chang, C. L., Liou, K. T., Kao, Y. K., Wang, Y. H., Chang, C. C., et al. (2024). The protective role of Achyranthes aspera extract against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by alleviating oxidative stress, inflammation, and PANoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 1), 117097. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117097
Liu, B., Tu, Y., He, W., Liu, Y., Wu, W., Fang, Q., et al. (2018a). Hyperoside attenuates renal aging and injury induced by D-galactose via inhibiting AMPK-ULK1 signaling-mediated autophagy. Aging (Albany NY) 10 (12), 4197–4212. doi:10.18632/aging.101723
Liu, H., Wang, Y., Huang, J., Dong, Z., and Xiao, P. (2024a). Analysis on patents of health care products with substances of medicine food homology in China. Chin. Herb. Med. 16 (3), 412–421. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2024.03.005
Liu, J., Jiang, C., Ma, X., Feng, L., and Wang, J. (2019a). Notoginsenoside Fc accelerates reendothelialization following vascular injury in diabetic rats by promoting endothelial cell autophagy. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 9696521. doi:10.1155/2019/9696521
Liu, J., Jiang, C., Ma, X., and Wang, J. (2018b). Notoginsenoside Fc attenuates high glucose-induced vascular endothelial cell injury via upregulation of PPAR-γ in diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats. Vasc. Pharmacol. 109, 27–35. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2018.05.009
Liu, M., Guo, P., Zeng, M., Zhang, Y., Jia, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2024b). Effects and mechanisms of frehmaglutin D and rehmaionoside C improve LPS-induced acute kidney injury through the estrogen receptor-mediated TLR4 pathway in vivo and in vitro. Phytomedicine 123, 155218. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155218
Liu, X., Lu, J., Liao, Y., Liu, S., Chen, Y., He, R., et al. (2019b). Dihydroartemisinin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 117, 109070. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109070
Liu, X. H., Pan, L. L., Yang, H. B., Gong, Q. H., and Zhu, Y. Z. (2012). Leonurine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells: involvement of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 680 (1-3), 108–114. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.01.012
Liu, Y., Duan, C., Chen, H., Wang, C., Liu, X., Qiu, M., et al. (2018c). Inhibition of COX-2/mPGES-1 and 5-LOX in macrophages by leonurine ameliorates monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 351, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2018.05.010
Liu, Y., Gong, S., Li, K., Wu, G., Zheng, X., Zheng, J., et al. (2022). Coptisine protects against hyperuricemic nephropathy through alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 156, 113941. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113941
Lou, T., Jiang, W., Xu, D., Chen, T., and Fu, Y. (2015). Inhibitory effects of polydatin on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflammation 38 (3), 1213–1220. doi:10.1007/s10753-014-0087-8
Lu, H., Wu, L., Liu, L., Ruan, Q., Zhang, X., Hong, W., et al. (2018). Quercetin ameliorates kidney injury and fibrosis by modulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Biochem. Pharmacol. 154, 203–212. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2018.05.007
Lu, H., Xie, D., Qu, B., Li, M., He, Y., and Liu, W. (2023). Emodin prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via suppression of p53-mediated cell apoptosis based on network pharmacology. Heliyon 9 (5), e15682. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15682
Lu, Y., Liu, Y., Zhou, J., Li, D., and Gao, W. (2021). Biosynthesis, total synthesis, structural modifications, bioactivity, and mechanism of action of the quinone-methide triterpenoid celastrol. Med. Res. Rev. 41 (2), 1022–1060. doi:10.1002/med.21751
Luan, Z. L., Ming, W. H., Sun, X. W., Zhang, C., Zhou, Y., Zheng, F., et al. (2021). A naturally occurring FXR agonist, alisol B 23-acetate, protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 321 (5), F617–f628. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00193.2021
Luo, J., Sun, Y., Li, Q., and Kong, L. (2022a). Research progress of meliaceous limonoids from 2011 to 2021. Nat. Prod. Rep. 39 (6), 1325–1365. doi:10.1039/d2np00015f
Luo, M., Liu, Z., Hu, Z., and He, Q. (2022b). Quercetin improves contrast-induced acute kidney injury through the HIF-1α/lncRNA NEAT1/HMGB1 pathway. Pharm. Biol. 60 (1), 889–898. doi:10.1080/13880209.2022.2058558
Ma, J. Q., Ding, J., Xiao, Z. H., and Liu, C. M. (2014). Puerarin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative DNA damage and inflammation in mouse kidney through ERK/Nrf2/ARE pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 71, 264–271. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2014.06.017
Ma, L., Li, H., Zhang, S., Xiong, X., Chen, K., Jiang, P., et al. (2018). Emodin ameliorates renal fibrosis in rats via TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and function study of Smurf 2. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 50 (2), 373–382. doi:10.1007/s11255-017-1757-x
Ma, L., Liu, X., Zhang, M., Zhou, L., Jiang, L., Gao, L., et al. (2023). Paeoniflorin alleviates ischemia/reperfusion induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting Slc7a11-mediated ferroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 116, 109754. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109754
Ma, P., Zhang, S., Su, X., Qiu, G., and Wu, Z. (2015). Protective effects of icariin on cisplatin-induced acute renal injury in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 7 (10), 2105–2114.
Ma, Q., Xu, Y., Tang, L., Yang, X., Chen, Z., Wei, Y., et al. (2020). Astragalus polysaccharide attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2851349. doi:10.1155/2020/2851349
Ma, X., Yan, L., Zhu, Q., and Shao, F. (2017). Puerarin attenuates cisplatin-induced rat nephrotoxicity: the involvement of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS One 12 (2), e0171612. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171612
Man, Q., Deng, Y., Li, P., Ma, J., Yang, Z., Yang, X., et al. (2020). Licorice ameliorates cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity through antiapoptosis, antioxidative stress, anti-inflammation, and acceleration of metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 563750. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.563750
Mao, N., Tan, R. Z., Wang, S. Q., Wei, C., Shi, X. L., Fan, J. M., et al. (2016). Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits angiotensin II-induced podocyte autophagy via AMPK/mTOR/PI3K pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 40 (8), 917–925. doi:10.1002/cbin.10634
Meng, Q. H., Liu, H. B., and Wang, J. B. (2016). Polydatin ameliorates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by decreasing apoptosis and oxidative stress through activating sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 96, 215–225. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2016.07.032
Mercantepe, F., Mercantepe, T., Topcu, A., Yılmaz, A., and Tumkaya, L. (2018). Protective effects of amifostine, curcumin, and melatonin against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 391 (9), 915–931. doi:10.1007/s00210-018-1514-4
Mir, S. M., Ravuri, H. G., Pradhan, R. K., Narra, S., Kumar, J. M., Kuncha, M., et al. (2018). Ferulic acid protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing inflammatory events and upregulating antioxidant defenses in Balb/c mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 100, 304–315. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.169
Mohamed, M. E., Tawfeek, N., Elbaramawi, S. S., Elbatreek, M. H., and Fikry, E. (2022). Agathis robusta Bark extract protects from renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: phytochemical, in silico and in vivo studies. Pharm. (Basel) 15 (10), 1270. doi:10.3390/ph15101270
Najafi, H., Firouzifar, M. R., Shafaat, O., Changizi Ashtiyani, S., and Hosseini, N. (2014). Protective effects of Tribulus terrestris L extract against acute kidney injury induced by reperfusion injury in rats. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 8 (4), 292–298.
Neyra, J. A., Ortiz-Soriano, V., Liu, L. J., Smith, T. D., Li, X., Xie, D., et al. (2023). Prediction of mortality and major adverse kidney events in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 81 (1), 36–47. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.06.004
Ning, N. Z., Liu, X., Chen, F., Zhou, P., Hu, L., Huang, J., et al. (2018). Embelin restores carbapenem efficacy against NDM-1-positive pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 9, 71. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.00071
Oh, C. J., Kim, M. J., Lee, J. M., Kim, D. H., Kim, I. Y., Park, S., et al. (2023). Inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 ameliorates kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing succinate accumulation during ischemia and preserving mitochondrial function during reperfusion. Kidney Int. 104 (4), 724–739. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.06.022
Ortega-Domínguez, B., Aparicio-Trejo, O. E., García-Arroyo, F. E., León-Contreras, J. C., Tapia, E., Molina-Jijón, E., et al. (2017). Curcumin prevents cisplatin-induced renal alterations in mitochondrial bioenergetics and dynamic. Food Chem. Toxicol. 107 (Pt A), 373–385. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.07.018
Özyurt, H., Çevik, Ö., Özgen, Z., Özden, A. S., Çadırcı, S., Elmas, M. A., et al. (2014). Quercetin protects radiation-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in kidney and bladder tissues of rats. Free Radic. Res. 48 (10), 1247–1255. doi:10.3109/10715762.2014.945925
Pan, B., Sun, J., Liu, Z., Wang, L., Huo, H., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021). Longxuetongluo Capsule protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress and MAPK-mediated mechanisms. J. Adv. Res. 33, 215–225. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2021.01.016
Pan, M., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Jiang, X., Fan, Y., Gong, F., et al. (2023). Celastrol alleviated acute kidney injury by inhibition of ferroptosis through Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 166, 115333. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115333
Pang, Y., Zhang, P. C., Lu, R. R., Li, H. L., Li, J. C., Fu, H. X., et al. (2020). Andrade-oliveira salvianolic acid B modulates caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via Nrf2 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 541426. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.541426
Peerapornratana, S., Manrique-Caballero, C. L., Gómez, H., and Kellum, J. A. (2019). Acute kidney injury from sepsis: current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 96 (5), 1083–1099. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2019.05.026
Peng, Y., Li, Y., Li, H., and Yu, J. (2022). Shikonin attenuates kidney tubular epithelial cells apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response through nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4/PTEN pathway in acute kidney injury of sepsis model. Drug Dev. Res. 83 (5), 1111–1124. doi:10.1002/ddr.21936
Perazella, M. A., and Rosner, M. H. (2022). Drug-induced acute kidney injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17 (8), 1220–1233. doi:10.2215/cjn.11290821
Peritore, A. F., D'Amico, R., Cordaro, M., Siracusa, R., Fusco, R., Gugliandolo, E., et al. (2021). PEA/Polydatin: anti-inflammatory and antioxidant approach to counteract DNBS-induced colitis. Antioxidants (Basel) 10 (3), 464. doi:10.3390/antiox10030464
Petejova, N., and Martinek, A. (2014). Acute kidney injury due to rhabdomyolysis and renal replacement therapy: a critical review. Crit. Care 18 (3), 224. doi:10.1186/cc13897
Pi, J., Jiang, J., Cai, H., Yang, F., Jin, H., Yang, P., et al. (2017). GE11 peptide conjugated selenium nanoparticles for EGFR targeted oridonin delivery to achieve enhanced anticancer efficacy by inhibiting EGFR-mediated PI3K/AKT and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathways. Drug Deliv. 24 (1), 1549–1564. doi:10.1080/10717544.2017.1386729
Poston, J. T., and Koyner, J. L. (2019). Sepsis associated acute kidney injury. Bmj 364, k4891. doi:10.1136/bmj.k4891
Qi, C. X., Tan, X. H., Li, Q. G., and Wang, X. L. (2007). Clinical study of diabetic retinopathy treated by compound danshen dripping pills. Zhong Yao Cai 30 (3), 375–377. doi:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2007.03.045
Qi, J., Xue, Q., Kuang, L., Xie, L., Luo, R., and Nie, X. (2020). Berberine alleviates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by regulating mitophagy via PINK 1/Parkin pathway. Transl. Androl. Urol. 9 (4), 1712–1724. doi:10.21037/tau-20-1129
Qiu, C. W., Chen, B., Zhu, H. F., Liang, Y. L., and Mao, L. S. (2024). Gastrodin alleviates cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting ferroptosis via the SIRT1/FOXO3A/GPX4 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 3), 117282. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117282
Qu, S., Yu, S., Ma, X., and Wang, R. (2023). Medicine food homology plants promote periodontal health: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and inhibition of bone resorption. Front. Nutr. 10, 1193289. doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1193289
Qu, X., Gao, H., Tao, L., Zhang, Y., Zhai, J., Sun, J., et al. (2019). Astragaloside IV protects against cisplatin-induced liver and kidney injury via autophagy-mediated inhibition of NLRP3 in rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 44 (3), 167–175. doi:10.2131/jts.44.167
Ronco, C., Bellomo, R., and Kellum, J. A. (2019). Acute kidney injury. Lancet 394 (10212), 1949–1964. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32563-2
Rong, L., Li, Z., Leng, X., Li, H., Ma, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Salidroside induces apoptosis and protective autophagy in human gastric cancer AGS cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 122, 109726. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109726
Rui, Y., Li, S., Luan, F., Li, D., Liu, R., and Zeng, N. (2022). Several alkaloids in Chinese herbal medicine exert protection in acute kidney injury: focus on mechanism and target analysis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2427802. doi:10.1155/2022/2427802
Sadar, S. S., Vyawahare, N. S., and Bodhankar, S. L. (2016). Ferulic acid ameliorates TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis through modulation of cytokines, oxidative stress, iNOs, COX-2, and apoptosis in laboratory rats. Excli J. 15, 482–499. doi:10.17179/excli2016-393
Sánchez-González, P. D., López-Hernández, F. J., Dueñas, M., Prieto, M., Sánchez-López, E., Thomale, J., et al. (2017). Differential effect of quercetin on cisplatin-induced toxicity in kidney and tumor tissues. Food Chem. Toxicol. 107 (Pt A), 226–236. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.06.047
She, S., Liu, W., Li, T., and Hong, Y. (2014). Effects of puerarin in STZ-induced diabetic rats by oxidative stress and the TGF-β1/Smad2 pathway. Food Funct. 5 (5), 944–950. doi:10.1039/c3fo60565e
Shen, D., Guo, M., Geng, X., Yu, J., Zhang, Z., Lin, J., et al. (2022). Magnesium lithospermate B protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 16, 2293–2304. doi:10.2147/dddt.S358830
Shen, J., Wang, W., Shao, X., Wu, J., Li, S., Che, X., et al. (2020). Integrated analysis of m6A methylome in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury and berberine alleviation in mouse. Front. Genet. 11, 584460. doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.584460
Shen, P., Yang, X., Jiang, J., Wang, X., Liang, T., and He, L. (2017). Wedelolactone from Eclipta alba inhibits lipopolysaccharide-enhanced cell proliferation of human renal mesangial cells via NF-κB signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 9 (5), 2132–2142.
Shi, H., Wu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, M., Yan, S., Chen, Z., et al. (2015). Liquiritigenin potentiates the inhibitory effects of cisplatin on invasion and metastasis via downregulation MMP-2/9 and PI3 K/AKT signaling pathway in B16F10 melanoma cells and mice model. Nutr. Cancer 67 (5), 761–770. doi:10.1080/01635581.2015.1037962
Shi, H., Zhou, P., Gao, G., Liu, P. P., Wang, S. S., Song, R., et al. (2021). Astragaloside IV prevents acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Food Biochem. 45 (7), e13757. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13757
Shi, Y., Shi, X., Zhao, M., Chang, M., Ma, S., and Zhang, Y. (2023). Ferroptosis: a new mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine compounds for treating acute kidney injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 163, 114849. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114849
Shiva, N., Sharma, N., Kulkarni, Y. A., Mulay, S. R., and Gaikwad, A. B. (2020). Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: an insight on in vitro and in vivo models. Life Sci. 256, 117860. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117860
Shou, D. W., Li, Y. R., Xu, X. J., Dai, M. H., Zhang, W., Yang, X., et al. (2023). Parthenolide attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury in rats by reducing inflammation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2023, 8759766. doi:10.1155/2023/8759766
Song, J., Chen, L., Yuan, Z., and Gong, X. (2023). Elevation of serum human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) as predicting factors for the occurrence of acute kidney injury on chronic kidney disease: a single-center retrospective self-control study. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1269311. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1269311
Song, J., Fan, H. J., Li, H., Ding, H., Lv, Q., and Hou, S. K. (2016). Zingerone ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 772, 108–114. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.12.027
Song, Z., and Gong, X. (2023). Research progress on the potential mechanisms of acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease induced by proton pump inhibitors. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 10 (2), e00027. doi:10.1097/imna-d-22-00027
Song, Y., Hu, T., Gao, H., Zhai, J., Gong, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Altered metabolic profiles and biomarkers associated with astragaloside IV-mediated protection against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats: an HPLC-TOF/MS-based untargeted metabolomics study. Biochem. Pharmacol. 183, 114299. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114299
Su, S., Wang, J., Wang, J., Yu, R., Sun, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Cardioprotective effects of gypenoside XVII against ischemia/reperfusion injury: role of endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, and mitochondrial fusion fission balance. Phytother. Res. 36 (7), 2982–2998. doi:10.1002/ptr.7493
Sun, D., Cui, S., Ma, H., Zhu, P., Li, N., Zhang, X., et al. (2022a). Salvianolate ameliorates renal tubular injury through the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway in mouse kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 293, 115331. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115331
Sun, J., Wei, S., Zhang, Y., and Li, J. (2021). Protective effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Anal. Cell Pathol. (Amst) 2021, 7178253. doi:10.1155/2021/7178253
Sun, M., Chang, H., Jiang, F., Zhang, W., Yang, Q., Wang, X., et al. (2024). Hazel leaf polyphenol extract alleviated cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by reducing ferroptosis through inhibiting Hippo signaling. Molecules 29 (8), 1729. doi:10.3390/molecules29081729
Sun, T., Wu, D., Deng, Y., and Zhang, D. (2022b). EGFR mediated the renal cell apoptosis in rhabdomyolysis-induced model via upregulation of autophagy. Life Sci. 309, 121050. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121050
Sun, Z., and Wang, X. (2020). Protective effects of polydatin on multiple organ ischemia-reperfusion injury. Bioorg Chem. 94, 103485. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103485
Tai, H., Cui, X. Z., He, J., Lan, Z. M., Li, S. M., Li, L. B., et al. (2022). Renoprotective effect of Tanshinone IIA against kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in obese rats. Aging (Albany NY) 14 (20), 8302–8320. doi:10.18632/aging.204304
Tai, H., Jiang, X. L., Lan, Z. M., Li, Y., Kong, L., Yao, S. C., et al. (2021a). Tanshinone IIA combined with CsA inhibit myocardial cell apoptosis induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in obese rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 21 (1), 100. doi:10.1186/s12906-021-03270-w
Tai, H., Jiang, X. L., Song, N., Xiao, H. H., Li, Y., Cheng, M. J., et al. (2021b). Tanshinone IIA combined with cyclosporine A alleviates lung apoptosis induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion in obese rats. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 8, 617393. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.617393
Tan, R. Z., Liu, J., Zhang, Y. Y., Wang, H. L., Li, J. C., Liu, Y. H., et al. (2019). Curcumin relieved cisplatin-induced kidney inflammation through inhibiting Mincle-maintained M1 macrophage phenotype. Phytomedicine 52, 284–294. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.210
Tan, R. Z., Wang, C., Deng, C., Zhong, X., Yan, Y., Luo, Y., et al. (2020). Quercetin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting Mincle/Syk/NF-κB signaling maintained macrophage inflammation. Phytother. Res. 34 (1), 139–152. doi:10.1002/ptr.6507
Tan, R. Z., Yan, Y., Yu, Y., Diao, H., Zhong, X., Lin, X., et al. (2021). Renoprotective effect of oridonin in a mouse model of acute kidney injury via suppression of macrophage involved inflammation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 44 (5), 714–723. doi:10.1248/bpb.b21-00071
Tang, C., Livingston, M. J., Safirstein, R., and Dong, Z. (2023a). Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: new insights and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 19 (1), 53–72. doi:10.1038/s41581-022-00631-7
Tang, J. L., Xin, M., and Zhang, L. C. (2022). Protective effect of Astragalus membranaceus and Astragaloside IV in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Aging (Albany NY) 14 (14), 5855–5877. doi:10.18632/aging.204189
Tang, M., Cao, X., Zhang, K., Li, Y., Zheng, Q. Y., Li, G. Q., et al. (2018). Celastrol alleviates renal fibrosis by upregulating cannabinoid receptor 2 expression. Cell Death Dis. 9 (6), 601. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0666-y
Tang, Q., Tang, Y., Yang, Q., Chen, R., Zhang, H., Luo, H., et al. (2023b). Embelin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury through the inhibition of M1 macrophage activation and NF-κB signaling in mice. Heliyon 9 (3), e14006. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14006
Tang, Y., Jacobi, A., Vater, C., Zou, X., and Stiehler, M. (2014). Salvianolic acid B protects human endothelial progenitor cells against oxidative stress-mediated dysfunction by modulating Akt/mTOR/4EBP1, p38 MAPK/ATF2, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 90 (1), 34–49. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2014.04.008
Tang, Y. S., Zhao, Y. H., Zhong, Y., Li, X. Z., Pu, J. X., Luo, Y. C., et al. (2019). Neferine inhibits LPS-ATP-induced endothelial cell pyroptosis via regulation of ROS/NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway. Inflamm. Res. 68 (9), 727–738. doi:10.1007/s00011-019-01256-6
Tang, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., and Li, C. (2023c). Salidroside inhibits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced ferroptosis by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 26 (5), 507. doi:10.3892/etm.2023.12206
Tao, P., Huo, J., and Chen, L. (2024). Bibliometric analysis of the relationship between gut microbiota and chronic kidney disease from 2001–2022. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 11 (1), e00017. doi:10.1097/imna-d-23-00017
Tian, X., Peng, X., Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Zhan, L., Yin, J., et al. (2021). Isorhamnetin ameliorates Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis by reducing fungal load, inhibiting pattern-recognition receptors and inflammatory cytokines. Invest Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 62 (3), 38. doi:10.1167/iovs.62.3.38
Uzunoglu, S., Karagol, H., Ozpuyan, F., Cosar, R., Cicin, I., Yurutcaloglu, V., et al. (2011). Protective effect of L-carnitine versus amifostine against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Med. Oncol. 28 (Suppl. 1), S690–S696. doi:10.1007/s12032-010-9746-2
Vijayan, A. (2021). Tackling AKI: prevention, timing of dialysis and follow-up. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 17 (2), 87–88. doi:10.1038/s41581-020-00390-3
Vives, M., Hernandez, A., Parramon, F., Estanyol, N., Pardina, B., Muñoz, A., et al. (2019). Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: prevalence, impact and management challenges. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 12, 153–166. doi:10.2147/ijnrd.S167477
Wang, B., Li, X. H., Song, Z., Li, M. L., Wu, X. W., Guo, M. X., et al. (2021a). Isoacteoside attenuates acute kidney injury induced by severe acute pancreatitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 23 (4), 287. doi:10.3892/mmr.2021.11926
Wang, B., Xu, X. B., Jin, X. X., Wu, X. W., Li, M. L., Guo, M. X., et al. (2017). Effects of ω-3 fatty acids on toll-like receptor 4 and nuclear factor κB p56 in the pancreas of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 46 (10), 1267–1274. doi:10.1097/mpa.0000000000000935
Wang, H., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Yang, L., and Wang, D. (2019a). Embelin can protect mice from thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109360. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109360
Wang, J., Xu, G., Jin, H., Chai, Y., Yang, X., Liu, Z., et al. (2022a). Ulinastatin alleviates rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation 45 (5), 2052–2065. doi:10.1007/s10753-022-01675-4
Wang, J., Yu, Y., Zhang, H., Li, L., Wang, J., Su, S., et al. (2024a). Gypenoside XVII attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and NLRP3 inflammasome-triggered pyroptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 962, 176187. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176187
Wang, M., Yang, L., Yang, J., Zhou, Y., and Wang, C. (2019b). Magnesium lithospermate B attenuates renal injury in 5/6 renal ablation/infarction rats by mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109316. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109316
Wang, P., Wang, W., Shi, Q., Zhao, L., Mei, F., Li, C., et al. (2016). Paeoniflorin ameliorates acute necrotizing pancreatitis and pancreatitis-induced acute renal injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 14 (2), 1123–1131. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5351
Wang, S., Chen, Y., Han, S., Liu, Y., Gao, J., Huang, Y., et al. (2022b). Selenium nanoparticles alleviate ischemia reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury by modulating GPx-1/NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway. Theranostics 12 (8), 3882–3895. doi:10.7150/thno.70830
Wang, W., Yu, R., Wu, C., Li, Q., Chen, J., Xiao, Y., et al. (2024b). Berberine alleviates contrast-induced nephropathy by activating Akt/Foxo3a/Nrf2 signalling pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 28 (1), e18016. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18016
Wang, X., Yin, H., Fan, L., Zhou, Y., Tang, X., Fei, X., et al. (2021b). Shionone alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome mediated pyroptosis in interstitial cystitis injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 90, 107132. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107132
Wang, Y., Liu, Q., Cai, J., Wu, P., Wang, D., Shi, Y., et al. (2022c). Emodin prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via suppression of CAMKII/DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 916, 174603. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174603
Wei, M., Gao, Y., Cheng, D., Zhang, H., Zhang, W., Shen, Y., et al. (2022). Notoginsenoside Fc ameliorates renal tubular injury and mitochondrial damage in acetaminophen-induced acute kidney injury partly by regulating SIRT3/SOD2 pathway. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9, 1055252. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.1055252
Wen, J., Xu, B., Sun, Y., Lian, M., Li, Y., Lin, Y., et al. (2019). Paeoniflorin protects against intestinal ischemia/reperfusion by activating LKB1/AMPK and promoting autophagy. Pharmacol. Res. 146, 104308. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104308
White, K. C., Serpa-Neto, A., Hurford, R., Clement, P., Laupland, K. B., See, E., et al. (2023). Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: incidence, patient characteristics, timing, trajectory, treatment, and associated outcomes. A multicenter, observational study. Intensive Care Med. 49 (9), 1079–1089. doi:10.1007/s00134-023-07138-0
Williams, J. D., Kumar, R., Afolabi, J. M., Park, F., and Adebiyi, A. (2023). Rhabdomyolysis aggravates renal iron accumulation and acute kidney injury in a humanized mouse model of sickle cell disease. Free Radic. Res. 57 (6-12), 404–412. doi:10.1080/10715762.2023.2269313
Wu, A. J., Chen, N. Q., Huang, L. H., Cheng, R., Wang, X. W., Li, C., et al. (2023). Leonurine inhibits ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells by activating p62/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 48 (8), 2176–2183. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20221115.401
Wu, J., Pan, X., Fu, H., Zheng, Y., Dai, Y., Yin, Y., et al. (2017). Effect of curcumin on glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 10114. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-10693-4
Wu, J., Zhang, F., Zheng, X., Zhang, J., Cao, P., Sun, Z., et al. (2022a). Identification of renal ischemia reperfusion injury subtypes and predictive strategies for delayed graft function and graft survival based on neutrophil extracellular trap-related genes. Front. Immunol. 13, 1047367. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1047367
Wu, L., Li, Q., Liu, S., An, X., Huang, Z., Zhang, B., et al. (2019). Protective effect of hyperoside against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via modulating mitochondrial fission, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Res. 53 (7), 727–736. doi:10.1080/10715762.2019.1623883
Wu, M. F., Li, P. C., Chen, C. C., Ye, S. S., Chien, C. T., and Yu, C. C. (2011). Cordyceps sobolifera extract ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced renal dysfunction in the rat. Am. J. Chin. Med. 39 (3), 523–535. doi:10.1142/s0192415x11009007
Wu, Q., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Xiang, L., Tan, Y., Feng, J., et al. (2022b). Targeted delivery of celastrol to glomerular endothelium and podocytes for chronic kidney disease treatment. Nano Res. 15 (4), 3556–3568. doi:10.1007/s12274-021-3894-x
Wu, Z., Deng, J., Zhou, H., Tan, W., Lin, L., and Yang, J. (2022c). Programmed cell death in sepsis associated acute kidney injury. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9, 883028. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.883028
Wu, Z., Li, C., Li, Q., Li, J., and Lu, X. (2020). Puerarin alleviates cisplatin-induced acute renal damage and upregulates microRNA-31-related signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 20 (4), 3122–3129. doi:10.3892/etm.2020.9081
Xia, S., Lin, H., Liu, H., Lu, Z., Wang, H., Fan, S., et al. (2019a). Honokiol attenuates sepsis-associated acute kidney injury via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflammation 42 (3), 826–834. doi:10.1007/s10753-018-0937-x
Xia, S., Ni, Y., Zhou, Q., Liu, H., Xiang, H., Sui, H., et al. (2019b). Emodin attenuates severe acute pancreatitis via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Inflammation 42 (6), 2129–2138. doi:10.1007/s10753-019-01077-z
Xie, C., Liu, L., Wang, Z., Xie, H., Feng, Y., Suo, J., et al. (2018). Icariin improves sepsis-induced mortality and acute kidney injury. Pharmacology 102 (3-4), 196–205. doi:10.1159/000487955
Xie, K. H., Liu, X. H., Jia, J., Zhong, X., Han, R. Y., Tan, R. Z., et al. (2022). Hederagenin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via inhibiting long non-coding RNA A330074k22Rik/Axin2/β-catenin signalling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 112, 109247. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109247
Xie, X., Sun, S., Zhong, W., Soromou, L. W., Zhou, X., Wei, M., et al. (2014). Zingerone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 19 (1), 103–109. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2013.12.028
Xing, D., Ma, Y., Lu, M., Liu, W., and Zhou, H. (2023). Paeoniflorin alleviates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in HK-2 cells by inhibiting apoptosis and repressing oxidative damage via Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. BMC Nephrol. 24 (1), 314. doi:10.1186/s12882-023-03366-0
Xiong, Y., Zhong, J., Chen, W., Li, X., Liu, H., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Neferine alleviates acute kidney injury by regulating the PPAR-α/NF-κB pathway. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 28, 969–987. doi:10.1007/s10157-024-02504-8
Xu, D., Chen, M., Ren, X., Ren, X., and Wu, Y. (2014). Leonurine ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury via suppressing ROS-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Fitoterapia 97, 148–155. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2014.06.005
Xu, J., Wold, E. A., Ding, Y., Shen, Q., and Zhou, J. (2018). Therapeutic potential of oridonin and its analogs: from anticancer and antiinflammation to neuroprotection. Molecules 23 (2), 474. doi:10.3390/molecules23020474
Xu, J., Zhang, Z., Ren, D., Liu, L., Xing, H., Wang, D., et al. (2024). Astragaloside Ⅳ negatively regulates Gpr97-TPL2 signaling to protect against hyperhomocysteine-exacerbated sepsis associated acute kidney injury. Phytomedicine 125, 155346. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155346
Xu, L., Li, L., Zhang, C. Y., Schluesener, H., and Zhang, Z. Y. (2019). Natural diterpenoid oridonin ameliorates experimental autoimmune neuritis by promoting anti-inflammatory macrophages through blocking Notch pathway. Front. Neurosci. 13, 272. doi:10.3389/fnins.2019.00272
Xu, Z., Zhang, M., Wang, W., Zhou, S., Yu, M., Qiu, X., et al. (2023). Dihydromyricetin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and ferroptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 473, 116595. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2023.116595
Yan, Y., Tan, R. Z., Liu, P., Li, J. C., Zhong, X., Liao, Y., et al. (2020). Oridonin alleviates IRI-induced kidney injury by inhibiting inflammatory response of macrophages via AKT-related pathways. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, e921114. doi:10.12659/msm.921114
Yang, C., Xu, H., Yang, D., Xie, Y., Xiong, M., Fan, Y., et al. (2023a). A renal YY1-KIM1-DR5 axis regulates the progression of acute kidney injury. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 4261. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40036-z
Yang, C., Xu, Y., Zhang, W., Ma, M., Wang, S., Chai, L., et al. (2021). Salvianolate lyophilized injection regulates the autophagy-lysosomal pathway in cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 271, 113898. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.113898
Yang, W., and He, L. (2022). The protective effect of hederagenin on renal fibrosis by targeting muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Bioengineered 13 (4), 8689–8698. doi:10.1080/21655979.2022.2054596
Yang, W., Li, X., He, L., Zhu, S., Lai, S., Zhang, X., et al. (2023b). Empagliflozin improves renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing inflammation and enhancing mitochondrial fusion through AMPK-OPA1 pathway promotion. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 28 (1), 42. doi:10.1186/s11658-023-00457-6
Yang, Y., Jiang, S., Mu, Y., Liu, C., Han, Y., Jiang, J., et al. (2024a). Berberine alleviated contrast-induced acute kidney injury by mitophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation in a mice model. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 486, 116952. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2024.116952
Yang, Y., Xu, J., Tu, J., Sun, Y., Zhang, C., Qiu, Z., et al. (2024b). Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc. Extracts improve sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation and pyroptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 1), 117101. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117101
Yao, L., Zhao, R., He, S., Feng, Q., Qiao, Y., Wang, P., et al. (2022a). Effects of salvianolic acid A and salvianolic acid B in renal interstitial fibrosis via PDGF-C/PDGFR-α signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 106, 154414. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154414
Yao, M., Qin, S., Xiong, J., Xin, W., Guan, X., Gong, S., et al. (2022b). Oroxylin A ameliorates AKI-to-CKD transition through maintaining PPARα-BNIP3 signaling-mediated mitochondrial homeostasis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 935937. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.935937
Yi, X., Xu, C., Yang, J., Zhong, C., Yang, H., Tang, L., et al. (2023). Tiliroside protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury via intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (21), 15556. doi:10.3390/ijms242115556
Yin, S., Li, L., Tao, Y., Yu, J., Wei, S., Liu, M., et al. (2021). The inhibitory effect of artesunate on excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress alleviates experimental colitis in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 629798. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.629798
You, L., Fang, Z., Shen, G., Wang, Q., He, Y., Ye, S., et al. (2019). Astragaloside IV prevents high glucose-induced cell apoptosis and inflammatory reactions through inhibition of the JNK pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 19 (3), 1603–1612. doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.9812
Yu, H., Song, L., Cao, X., Li, W., Zhao, Y., Chen, J., et al. (2020). Hederagenin attenuates cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury by regulating MLK3 signalling. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 1173. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01173
Yu, X., Meng, X., Xu, M., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Ding, G., et al. (2018). Celastrol ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting NF-κB and improving mitochondrial function. EBioMedicine 36, 266–280. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.031
Yu, Y., Li, M., Su, N., Zhang, Z., Zhao, H., Yu, H., et al. (2016). Honokiol protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via the suppression of oxidative stress, iNOS, inflammation and STAT3 in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 13 (2), 1353–1360. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.4660
Yu, Y., Wang, M., Chen, R., Sun, X., Sun, G., and Sun, X. (2021). Gypenoside XVII protects against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting ER stress-induced mitochondrial injury. J. Ginseng Res. 45 (6), 642–653. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2019.09.003
Yuan, D., Li, X., Luo, C., Li, X., Cheng, N., Ji, H., et al. (2019). Inhibition of gap junction composed of Cx43 prevents against acute kidney injury following liver transplantation. Cell Death Dis. 10 (10), 767. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1998-y
Yuan, W., Kou, S., Ma, Y., Qian, Y., Li, X., Chai, Y., et al. (2023). Hyperoside ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by regulating the expression and function of Oat1. Xenobiotica 53 (8-9), 559–571. doi:10.1080/00498254.2023.2270046
Zang, H., Yang, Q., and Li, J. (2019). Eleutheroside B protects against acute kidney injury by activating IGF pathway. Molecules 24 (21), 3876. doi:10.3390/molecules24213876
Zarbock, A., Nadim, M. K., Pickkers, P., Gomez, H., Bell, S., Joannidis, M., et al. (2023). Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: consensus report of the 28th Acute Disease Quality Initiative workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 19 (6), 401–417. doi:10.1038/s41581-023-00683-3
Zeng, M., Qi, M., Wang, Y., Xu, R., Wu, Y., Li, M., et al. (2020a). 5-O-methyldihydroquercetin and cilicicone B isolated from Spina Gleditsiae ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in mice by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via the TLR4/MyD88/TRIF/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 80, 106194. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106194
Zeng, M., Zhang, L., Li, M., Zhang, B., Zhou, N., Ke, Y., et al. (2018). Estrogenic effects of the extracts from the Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposite thunb.) and its effective compounds in vitro and in vivo. Molecules 23 (2), 11. doi:10.3390/molecules23020011
Zeng, X., Chen, X., Qin, H., Han, Y., Chen, X., Han, Z., et al. (2020b). Preventive effects of a natural anti-inflammatory agent Salvianolic acid A on acute kidney injury in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 135, 110901. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.110901
Zhang, B., Chen, Z. Y., Jiang, Z., Huang, S., Liu, X. H., and Wang, L. (2023a). Nephroprotective effects of cardamonin on renal ischemia reperfusion injury/UUO-induced renal fibrosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71 (36), 13284–13303. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01880
Zhang, B., Xue, Y., Zhao, J., Jiang, H., Zhu, J., Yin, H., et al. (2021a). Shionone attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by regulating macrophage polarization via the ECM1/STAT5 pathway. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 8, 796743. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.796743
Zhang, B., Zeng, M., Li, B., Kan, Y., Wang, S., Cao, B., et al. (2021b). Arbutin attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Phytomedicine 82, 153466. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153466
Zhang, D., Liu, S., Jiang, H., Liu, S., and Kong, F. (2024a). DIA proteomics analysis reveals the mechanism of folic acid-induced acute kidney injury and the effects of icariin. Chem. Biol. Interact. 390, 110878. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2024.110878
Zhang, D. Q., Li, J. S., Zhang, Y. M., Gao, F., and Dai, R. Z. (2018a). Astragaloside IV inhibits Angiotensin II-stimulated proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells via the regulation of CDK2 activity. Life Sci. 200, 105–109. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.036
Zhang, H. F., Wang, J. H., Wang, Y. L., Gao, C., Gu, Y. T., Huang, J., et al. (2019). Salvianolic acid A protects the kidney against oxidative stress by activating the akt/GSK-3β/nrf2 signaling pathway and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2853534. doi:10.1155/2019/2853534
Zhang, M., Dong, R., Da, J., Yuan, J., Zha, Y., and Long, Y. (2022a). Hyperhomocysteinemia exacerbates acute kidney injury via increased mitochondrial damage. Front. Physiol. 13, 967104. doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.967104
Zhang, M. Y., Ma, L. J., Jiang, L., Gao, L., Wang, X., Huang, Y. B., et al. (2023b). Paeoniflorin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through targeting Hsp90AA1-Akt protein-protein interaction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 310, 116422. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116422
Zhang, N., Zhang, H.-X., Ma, X.-L., and Hong, J.-N. (2024b). Protective effects of quercetin against H2O2 induced KGN cells injury. Traditional Med. Res. 9, 7–12. doi:10.53388/TMR20230803002
Zhang, P., Xu, J., Cui, Q., Lin, G., Wang, F., Ding, X., et al. (2023c). Multi-pathway neuroprotective effects of a novel salidroside derivative SHPL-49 against acute cerebral ischemic injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 949, 175716. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175716
Zhang, Q., Sun, Q., Tong, Y., Bi, X., Chen, L., Lu, J., et al. (2022b). Leonurine attenuates cisplatin nephrotoxicity by suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 54 (9), 2275–2284. doi:10.1007/s11255-021-03093-1
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Li, B., Ding, P., Jin, D., Hou, S., et al. (2020a). The effect of monotropein on alleviating cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting oxidative damage, inflammation and apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 129, 110408. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110408
Zhang, Y., Li, X., Luo, Z., Ma, L., Zhu, S., Wang, Z., et al. (2020b). ECM1 is an essential factor for the determination of M1 macrophage polarization in IBD in response to LPS stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117 (6), 3083–3092. doi:10.1073/pnas.1912774117
Zhang, Z., Qi, D., Wang, X., Gao, Z., Li, P., Liu, W., et al. (2018b). Protective effect of Salvianolic acid A on ischaemia-reperfusion acute kidney injury in rats through protecting against peritubular capillary endothelium damages. Phytother. Res. 32 (1), 103–114. doi:10.1002/ptr.5954
Zhao, Y., Yang, W., Zhang, X., Lv, C., and Lu, J. (2023). Icariin, the main prenylflavonoid of Epimedii Folium, ameliorated chronic kidney disease by modulating energy metabolism via AMPK activation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 312, 116543. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116543
Zhao, Y., You, X. M., Jiang, H., Zou, G. X., and Wang, B. (2019). Spectrum-effect relationships between high-performance liquid chromatography fingerprints and anti-inflammatory activities of Leontopodium leontopodioides (Willd.) Beauv. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 1104, 11–17. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.11.001
Zhong, K., Zhang, H.-Q., Fang, Y.-X., Lan, Q.-M., Zhou, Z.-J., Zhao, Y.-R., et al. (2023). Acute kidney injury: microRNAs and new therapeutic opportunities for natural products. Traditional Med. Res. 8, 61–66. doi:10.53388/TMR20230616001
Zhou, L., Yu, P., Wang, T. T., Du, Y. W., Chen, Y., Li, Z., et al. (2022a). Polydatin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 9947191. doi:10.1155/2022/9947191
Zhou, M., Dai, Y., Ma, Y., Yan, Y., Hua, M., Gao, Q., et al. (2022b). Protective effects of liquiritigenin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via NRF2/SIRT3-mediated improvement of mitochondrial function. Molecules 27 (12), 3823. doi:10.3390/molecules27123823
Zhou, X., Xiang, Y., Li, D., Zhong, M., Hong, X., Gui, Y., et al. (2023). Limonin, a natural ERK2 agonist, protects against ischemic acute kidney injury. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 19 (9), 2860–2878. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82417
Zhu, F. B., Wang, J. Y., Zhang, Y. L., Hu, Y. G., Yue, Z. S., Zeng, L. R., et al. (2016). Mechanisms underlying the antiapoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of monotropein in hydrogen peroxide-treated osteoblasts. Mol. Med. Rep. 14 (6), 5377–5384. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5908
Zhu, H., Wang, X., Wang, X., Liu, B., Yuan, Y., and Zuo, X. (2020). Curcumin attenuates inflammation and cell apoptosis through regulating NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway against acute kidney injury. Cell Cycle 19 (15), 1941–1951. doi:10.1080/15384101.2020.1784599
Zhu, L.-C., Tan, P.-L., Sun, J.-Q., and Yao, Y.-M. (2023). Curcumin attenuates iron-overloaded stress to macrophages via up-regulation of SOD and Nrf2. Traditional Med. Res. 8, 48. doi:10.53388/TMR20230216006
Zhu, M. M., Wang, L., Yang, D., Li, C., Pang, S. T., Li, X. H., et al. (2019). Wedelolactone alleviates doxorubicin-induced inflammation and oxidative stress damage of podocytes by IκK/IκB/NF-κB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 117, 109088. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109088
Zhu, Y. Z., Wu, W., Zhu, Q., and Liu, X. (2018). Discovery of Leonuri and therapeutical applications: from bench to bedside. Pharmacol. Ther. 188, 26–35. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.006
Zhu, Z., Li, J., Song, Z., Li, T., Li, Z., and Gong, X. (2024). Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates renal tubular epithelial cell ferroptosis in contrast-induced nephropathy by inhibiting transferrin receptor and intracellular reactive oxygen species. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 138 (5), 235–249. doi:10.1042/cs20231184
Keywords: nephroprotective effects, substances of medicine food homology, traditional Chinese medicine, phytochemicals, acute kidney injury
Citation: Chen L, Deng Y, Hu J and Gong X (2025) Nephroprotective effects of substances of medicine food homology and traditional Chinese medicine phytochemicals against acute kidney injury. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1539886. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1539886
Received: 05 December 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 19 February 2025.
Edited by:
Abeda Jamadar, University of Kansas Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Aabid Hussain, Cleveland Clinic, United StatesVenkata Sanaboyana, Corteva Agriscience, United States
Ashish Dhayani, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Afsana Naaz, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Deng, Hu and Gong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Hu, NjI2NDU3MEBxcS5jb20=; Xuezhong Gong, c2huYW5zaGFuQHllYWgubmV0
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ling Chen
Ling Chen Yanyan Deng
Yanyan Deng Jing Hu
Jing Hu Xuezhong Gong
Xuezhong Gong