
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol. , 02 April 2025
Sec. Experimental Pharmacology and Drug Discovery
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1537022
 Rania T. Ibrahim1
Rania T. Ibrahim1 Yasser M. Moustafa2,3
Yasser M. Moustafa2,3 Maha Abdullah Alwaili4
Maha Abdullah Alwaili4 Amjad N. Alrebdi4
Amjad N. Alrebdi4 Afaf Alharthi5
Afaf Alharthi5 Noha R. Noufal6,7
Noha R. Noufal6,7 Dina M. Khodeer3*
Dina M. Khodeer3*The development of asthma is impacted by fat. Asthma is more common in obese persons. The purpose of the experimental study is to determine how chromium, formoterol, and their combination can improve the quality of life for obese people with lung anomalies. Thirty-six male Wistar rats were divided into six groups: control (C), obesity (CO), obese-asthma (COA), and obese-asthma groups treated with formoterol (OAF), chromium (OACR), or both (OACRF). Except for group C, all groups received a high-fat diet for 4 weeks. Subsequently, ovalbumin (OVA) was administered subcutaneously (s.c.) to all groups except C and CO to induce sensitization. Asthma was triggered via 1% OVA aerosol challenges on days 26–28. Over 5 days, OAF and OACRF received daily formoterol inhalations (50 μg/kg), while OACR and OACRF were given chromium (400 μg/kg). Treatments were timed to align with asthma induction protocols. Lipid profile and inflammatory indicators were examined at the end of the trial—Immunohistochemical analysis of lung tissue, Histopathological and lung tissue stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin. The combination therapy (OACRF) significantly reduced body weight (p < 0.05), lowered LDL and triglycerides, increased HDL, and normalized lung tissue architecture compared to controls. Immunohistochemistry revealed reduced IL-1β and IL-17α expression. The (OACRF) group demonstrated superior asthma control by reducing body weight, improving inflammatory indicators, and restoring lung tissue to its normal state by administering chromium and formoterol therapy. The most effective strategy for treating both obesity and asthma is to address their two connected conditions. These findings demonstrate that combined chromium and formoterol therapy effectively addresses metabolic and inflammatory components of obesity-induced asthma, offering a promising dual-target therapeutic strategy.
In the contemporary medical literature, obesity is the accumulation of excessive adipose tissue in the abdominal region as visceral fat, a condition associated with many health risks (Magdy et al., 2020; Mohamed et al., 2021; Piché et al., 2020). This pathological state is implicated in the etiology of various chronic diseases, including but not limited to cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and a spectrum of malignancies. Furthermore, obesity and metabolic syndrome are known to predispose individuals to several pulmonary disorders, with asthma being a notable example (Abo-Al-Ela et al., 2014; Badawy et al., 2021a; Petrie et al., 2018). Globally, the prevalence of overweight individuals is estimated at approximately 13%, while the incidence of obesity among children and adolescents was reported at 17% for the period between 2011 and 2014 (AlEnazi et al., 2023; Shaban et al., 2023).
Moreover, the epidemiological trends indicate a concerning rise in global obesity prevalence, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive strategies targeting its prevention and management (Hegab et al., 2018; Koliaki et al., 2023). The multifaceted etiology of obesity encompasses genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors, contributing to its complexity and the challenges inherent in its mitigation (Elmetwalli et al., 2023; Tiwari and Balasundaram, 2024). The socioeconomic implications of obesity are profound, encompassing increased healthcare costs, lost productivity, and diminished quality of life. Addressing this public health crisis necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, integrating individual, community, and policy interventions (Anekwe et al., 2020; Badawy et al., 2021b). Research efforts continue to explore innovative therapeutic and preventive measures, aiming to curb the rising prevalence of obesity and its associated comorbidities. As the understanding of obesity’s pathophysiology evolves, so does the potential for developing targeted interventions that address the underlying causes and risk factors, offering hope for more effective management and prevention strategies (El-Demerdash et al., 2021; Lin and Li, 2021; Smith et al., 2020).
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition, manifests through a constellation of common symptoms such as wheezing, airway constriction, chest tightness, persistent coughing, and difficulties in breathing (Ukena et al., 2008; Zedan et al., 2021). These symptoms indicate the inflammatory processes occurring within the pulmonary airways, which can be precipitated by various triggers, including physical exertion, exposure to airborne irritants, meteorological variations, and viral respiratory pathogens (Attia et al., 2020; D’Amato et al., 2018). In the context of obesity, the pathophysiological landscape of asthma undergoes notable alterations; obese individuals exhibit an increased production of pro-inflammatory markers and a disrupted lipid metabolism within the pulmonary system (Elkelish, 2024; Khodeer, 2024; Shailesh and Janahi, 2022). This alteration in the inflammatory and metabolic milieu complicates asthma management, particularly given the diminished efficacy of corticosteroids in targeting the underlying metabolic and immunological dysfunctions characteristic of obesity-induced asthma (Forno et al., 2011; Peters et al., 2018). Consequently, the management of asthma in the context of obesity demands a tailored approach, focusing on both the respiratory and metabolic aspects of the condition. Current therapies for obesity-induced asthma, such as corticosteroids, show reduced efficacy in obese populations due to altered immune-metabolic interactions. Despite evidence linking adipokines and inflammation to asthma severity, no studies have explored the combined use of chromium (metabolic modulator) and formoterol (bronchodilator) to address this dual pathology.
Emerging evidence suggests that the interplay between obesity and asthma exacerbates the severity and control of asthma symptoms, necessitating alternative therapeutic strategies that address the unique pathophysiological features of asthma in obese patients (Garg et al., 2024). These strategies may include weight management programs, targeted pharmacotherapy that considers the altered response to conventional asthma medications, and interventions to modulate the inflammatory profile specific to obese individuals (Tchang et al., 2000). Understanding the intricate relationship between obesity and asthma is crucial for developing effective treatment plans that improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Further research into the mechanisms linking obesity with asthma is essential for identifying potential therapeutic targets and optimizing care for this subset of patients (Marko and Pawliczak, 2018a).
One endocrine organ that becomes bigger when overweight is adipose tissue. It produces inflammatory cytokines known as adipocytokinases (Hui et al., 2018). Examples of adipocytokinases are leptin and interleukin-6 (IL-6). There is some evidence that these adipocytokinases contribute to developing lung abnormalities and may cause subtle inflammation (Palma et al., 2022a). For example, a rise in leptin levels may modulate lung damage and repairs, leading to weight gain associated with asthma. In addition, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) affected the progression of lung diseases (Wang and Hu, 2022a). Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) contribute to obesity (DPP-4). One of the transcription factors that regulate lipid synthesis is SREBPS. Two categories, (SREPs1) and (SREPs2), were established for it. One subunit of SREBPs1, SREBPs1a, is responsible for developing and synthesizing lipids globally (Lee et al., 2017). The regulation of energy and fatty acid storage is overseen by (SREBPs1c). Many cell types, including immune cells, express (DPP-4). It is involved in immune response and inflammatory pathogenesis and is classified into many chemokines and peptide hormones (Huang et al., 2022).
To enhance the quality of life for patients experiencing obesity-induced asthma, they must receive specialized therapeutic interventions. Chromium picolinate, a dietary supplement, is pivotal in regulating carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, influencing the body’s lipid profile. Its significance extends to the modulation of lipid metabolism, which contributes to a reduction in total cholesterol levels and aids in reducing body fat accumulation (Ngala et al., 2018). This dual action of chromium picolinate could potentially offer therapeutic benefits in the management of obesity-induced asthma by addressing the metabolic dysfunctions that exacerbate asthma symptoms in obese individuals. Consequently, incorporating chromium picolinate into the treatment regimen for patients with obesity-induced asthma may represent a novel approach to mitigate the impact of metabolic factors on respiratory health, thus promoting an improvement in both metabolic and respiratory outcomes (Yuan et al., 2018a). Further research into the efficacy and safety of chromium picolinate supplementation in this patient population is warranted to elucidate its therapeutic potential fully.
Formoterol, a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), is increasingly recognized for its efficacy in asthma management, offering a significant therapeutic option for patients requiring maintenance treatment (Rajesh et al., 2020). As a bronchodilator, formoterol operates by stimulating beta-2 adrenergic receptors in the airway smooth muscle, leading to relaxation and subsequent relief of bronchoconstriction. This mechanism of action provides a rapid onset of relief from asthma symptoms and sustained improvement in airway function over time (Reddel et al., 2023). Formoterol is distinct in its ability to commence action within minutes, and its effects can last for approximately 12 h, making it an effective agent for both the prevention of asthma symptoms and the control of exacerbations (Tashkin, 2020).
Incorporating formoterol into asthma management plans is predicated on its capacity to enhance lung function, reduce the frequency of asthma attacks, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with asthma. It is often prescribed with inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), which address the underlying inflammation associated with asthma, offering a comprehensive approach to asthma management (Rupani et al., 2021). This synergistic combination has been shown to provide superior control of asthma symptoms and reduce the risk of exacerbations compared to the use of either medication alone.
This study’s primary aim is to investigate chromium supplementation’s efficacy in conjunction with formoterol therapy as a novel approach to managing asthma symptoms in overweight patients. Specifically, the study seeks to determine whether this combined intervention can serve as an effective strategy for obesity prevention, thereby improving the quality of life for patients with asthma exacerbated by overweight conditions. This research hypothesizes that the metabolic benefits of chromium, including its potential to modulate lipid metabolism and reduce body fat accumulation, when used alongside the bronchodilatory effects of formoterol, a beta 2 agonist, may synergistically alleviate asthma symptoms. The investigation aims to provide empirical evidence to support or refute the hypothesis that this combined therapeutic approach can significantly improve respiratory function, asthma symptom control, and overall patient wellbeing.
The National Center of Research in Cairo, Egypt, provided the 36 male Wister rats utilized in this investigation; their weight ranged from 180 to 200 g. The rats were kept at about 22°C in stainless steel cages with a regular light-dark cycle. A high-fat diet (HFD) it was prepared by 6% fat, 8% water, 18% protein, and 5% fiber (Pala et al., 2020; Yuan et al., 2018), given to thirty rats. Every week, the body weights of the rats were noted. Approval was obtained from the Animal Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Suez Canal University, Egypt (IACUC License No. 202011MA1). At the end of the study, 0% mortality was observed in the normal and obese-asthma groups.
The following reagents were obtained: ovalbumin (OVA), phosphate-buffered saline, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were sourced from Sigma (St. Louis, United States). Sodium chloride was procured from ADWIC CO., located in Egypt. Formoterol was purchased from NOVARTIS PHARMA SAE in Cairo. Additionally, chromium was acquired from MEPACO-MEDIFOOD, an Egyptian company specializing in pharmaceuticals and medicinal plants.
All experimental groups, except for groups 1 and 2, were administered subcutaneous (S.C) injections of ovalbumin (OVA). To induce asthma in the animal model, additional treatments with 1% (OVA) aerosol were administered on days 26, 27, and 28 following the sensitization phase (Conrad et al., 2009).
The 36 rats were randomly divided into six groups, six rats per each.
Group (control (C)): Rats fed with Basal diet; Group 2 (control obese (CO)): Rats fed with HFD for 4 weeks (Pala et al., 2020; Yuan et al., 2018). Group 3 (control obese and asthma (COA)): Rats fed with HFD for 4 weeks. OVA for 28 days (Conrad et al., 2009). Group 4 (Obese and asthma with chromium picolinate (OACR)): Rats fed with HFD for 4 weeks. OVA for 28 days. Then, it was switched to a basal diet and treated with chromium picolinate 400 µg/kg of diet, which was dissolved in water and taken orally for 6 weeks. Group 5 (Obese and asthma with formoterol (OAF)): Rats fed with HFD for 4 weeks. OVA for 28 days. Then, switch to a basal diet. Then, treated with 50 µg/kg by inhalation of formoterol for 15 min once/day For 5 days, and the final dosage should be administered five to 6 hours (Showalter et al., 2018). Group 6 (Obese and asthma with chromium picolinate and formoterol (OACRF)): Rats fed with HFD for 4 weeks. OVA for 28 days. Then, switch to a basal diet. Then, treated with chromium picolinate elemental 400 µg/kg of diet was dissolved in water, after that 50 µg/kg by inhalation for 15 min once/day for formoterol (Supplementary Figure S1).
After 6 weeks of treatment and the end of the experiment, rats were sacrificed by cervical decapitation (Clarkson et al., 2022) under ketamine anesthesia. Blood samples were collected and centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 15 min; serum was aliquoted and stored at −80°C for kits measurements. The lungs were rapidly dissected, weighted, and stored in 4% phosphate-buffered formalin for histological examination. The weight of the rats was measured and recorded each week during the experimental period.
Lipid profile including serum total cholesterol, total triglyceride, LDL and HDL was measured by Elisa kit (XPRESSBIO PRODUCTS).
Quantitative detection of rat Adiponectin in cell culture supernatants using a sandwich ELISA kit (PicoKine®, United States). Leptin was measured by rat leptin ELISA kit (RayBio®, United States) using an automated ELISA reader. Absorbance (OD) was measured at 450 nm using a BioTek Synergy H1 reader.
For the in vitro quantitative evaluation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) in rat tissue homogenates, a sandwich enzyme immunoassay was used (My BioSource, United States). TNFα was measured by quantitative detection of TNFα in rat cell culture supernatants ELISA kit (MY BioSource, United States). The quantitative assessment of TLR4 in cell culture supernates was performed in vitro using a sandwich enzyme immunoassay (My BioSource, United States).
Tissue Fixation: Lung tissues were immediately fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin for 24–48 h to preserve cellular architecture. Embedding and Sectioning: Fixed tissues were dehydrated, cleared, and embedded in paraffin. Serial sections (2-μm thickness) were cut using a microtome for downstream analysis. Staining Protocol: Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) using standardized protocols (Bancroft and Cook, 1994) to visualize general histology, including inflammatory infiltrates and structural alterations.
Histopathological Analysis: Fibrosis Assessment: Collagen deposition and fibrotic changes were evaluated using established diagnostic criteria (Cheng et al., 2021). Inflammatory Infiltration: Bronchial and alveolar immune cell infiltration (e.g., neutrophils, lymphocytes) was quantified to assess chronic inflammation (Zainal et al., 2019). Microscopic Evaluation: Five random fields per section were analyzed under light microscopy (10×–4×0 magnification) (Garlisi et al., 1997). Blinded scoring was performed by two independent investigators to ensure reproducibility.
Generally, tissue samples fixed in paraffin were regularly dewaxed, rehydrated, and rinsed in 3% hydrogen peroxide to inhibit endogenous peroxidase. Immunostaining was performed on 4-mm thick, deparaffinized slices and heated for 15 min in a 0.01 M citrate buffer solution (PH = 7) to extract antigen. Mice monoclonal antibodies against interleukin-17 alpha (IL-17α) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) were then applied to the sections for an entire overnight (BIO SB, Santa Felicia, USA, Cat. # CA93117). Sections were incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:500, Abcam #ab6789) for 1 h. Color was developed with DAB (Vector Labs #SK-4100). Staining intensity was quantified using ImageJ (v1.53).
The expression for each result is the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Benferroni’s post hoc is performed after one-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) has evaluated the data. The statistical package for social science, version 26, was used to analyze the data (SPSS software, SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA). A statistically significant difference in means has been defined as P < 0.05.
Monitoring the body weight change during the experiment time, the data demonstrated a statistically significant difference in % body weight change across the four groups at P < 0.05 (Figure 1). The data representing a decrease in body weight percentage in the treated groups (OACR) and (OACRF) with chromium picolinate at a dose (400 μg/kg) compared to the (C) group. On the other hand, other groups (OAF), (CO), and (COA), which were not treated with chromium piclonate, did not show the noticed change in body weight percentage.
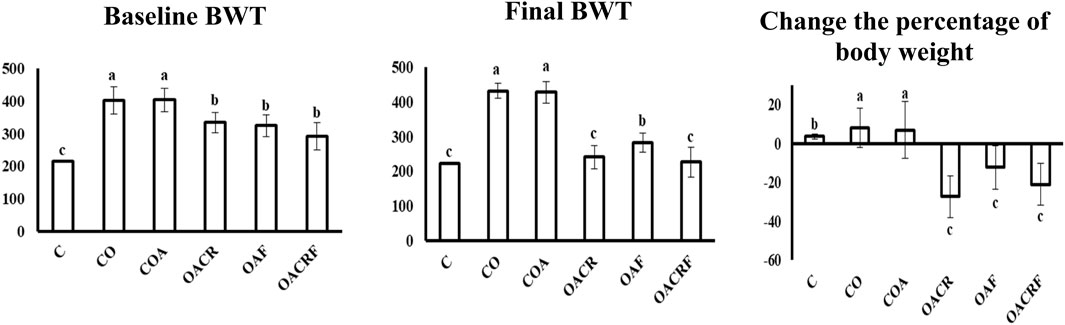
Figure 1. Effect of chromium picolinate on the percentage of body weight in different treated groups. Results are expressed as mean ± S. D and analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. C, control; CO, control obese; COA, control obese-asthmatic; OACR, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate; OAF, obese-asthmatic treated with formoterol; OACRF, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate & and formoterol. The different letters (a, b, and c) are above the bars mean a statistically significant difference between groups at p < 0.05, n = 6 3. The effect of chromium and/or formoterol on the level of Cholesterol, Triglyceride, HDL, and LDL in obese asthmatic rats.
It was observed that there is a statistically significant difference between the four groups for Cholesterol, Triglycerides, and LDL at P < 0.05. It was revealed that there was a statistically significant difference between each group (Table 1). The data represents a decrease in the level of cholesterol in the group (OACR) and (OACRF), as well as a reduction in body weight percentage compared to (C) (Table 1). On the other hand, the other group (CO), (COA), and (OAF) recorded the highest value of the level of cholesterol according to its % of body weight (Figure 1; Table 1).
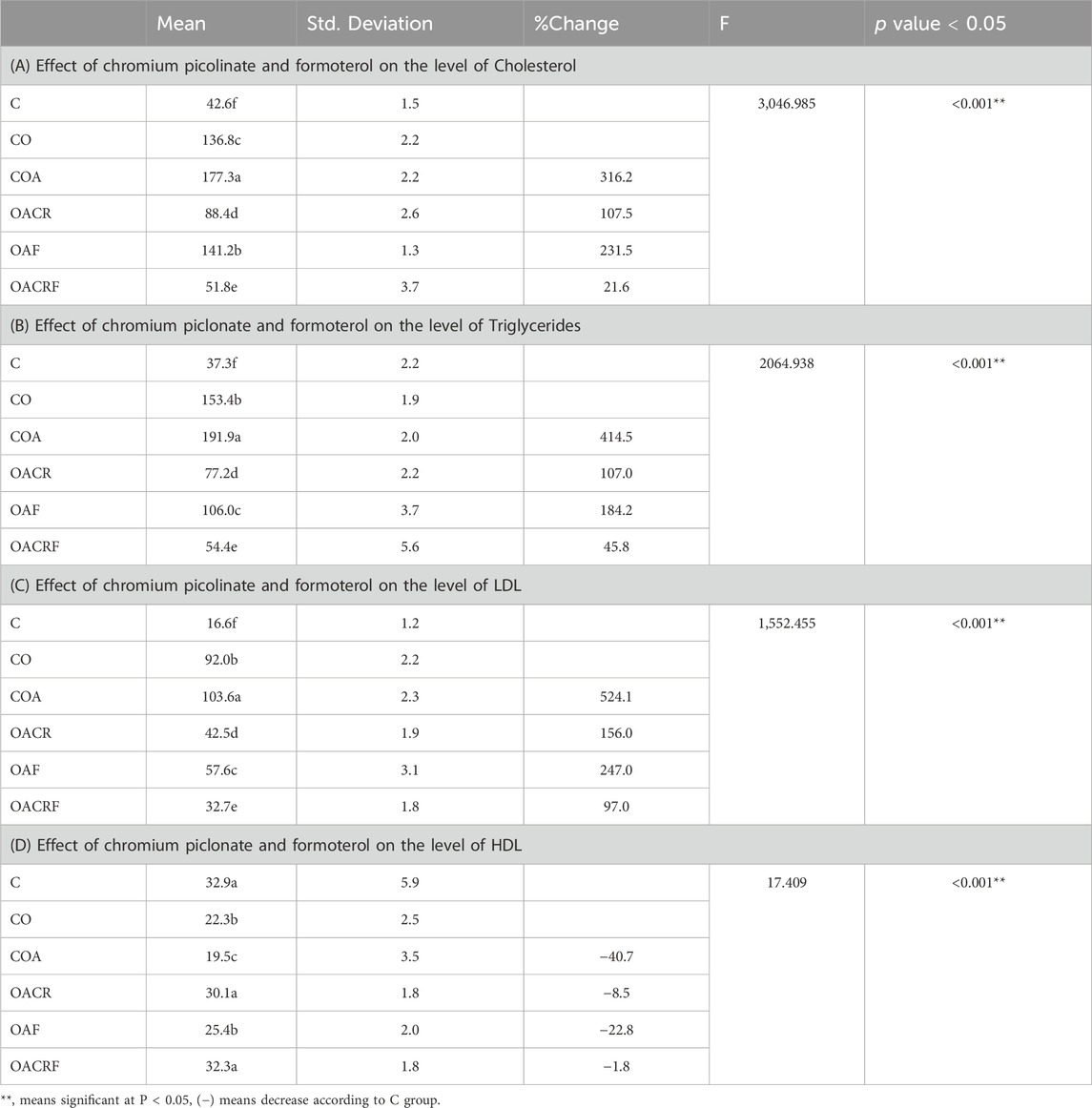
Table 1. Effect of chromium picolinate and formoterol on the level of lipid profile in serum including (A) total cholesterol, (B) total triglycerides, (C) LDL and (D) HDL. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E and analyzed using one way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. C, control; CO, control obese; COA, control obese-asthmatic; OACR, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate; OAF, obese-asthmatic treated with formoterol; OACRF, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate & and formoterol. The different letters (a, b, c, d, e, and f) are above the bars, meaning statistically significant difference between groups at P < 0.05, n = 6.
According to the data (Tab ID), there is a statistically significant difference between the four groups for HDL at P < 0.05. It was revealed that there was a statistically significant difference between each group. The data showed increasing in the level of HDL in the group (OACRF) and (OACR), which decreased in % of body weight compared to (C) (Figure 1). The other groups (CO), (COA) and (OAF) showed the lowest value of the level of HDL according to its % of body weight (Table 1).
The data showed in (Figure 2A) a statistically significant difference between the four groups for ADP at P < 0.05. The data showed increasing in the serum level of ADP in the group (OACRF), (OACR), and (OAF), which decreased in % of body weight compared to (C) (Figure 1). The other group (CO) and (COA) showed the lowest value of the serum level of (ADP) according to its % of body weight (Figure 3A).
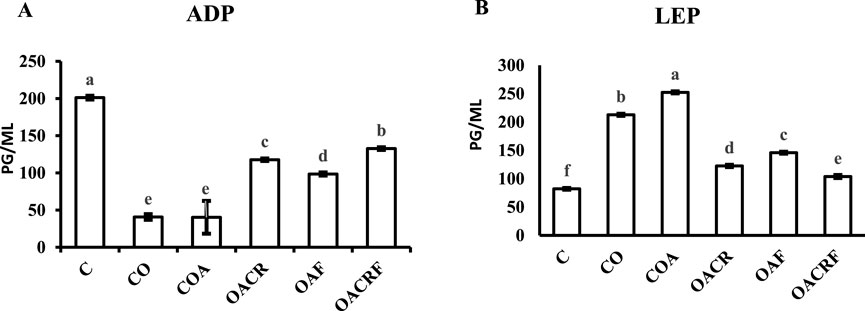
Figure 2. Effect of chromium picolinate and formoterol on lung tissue levels of (A) adiponectin (ADP), (B) leptin (LEP). Results are expressed as mean ± S.E and analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. C, control; CO, control obese; COA, control obese-asthmatic; OACR, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate; OAF, obese-asthmatic treated with formoterol; OACRF, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate & and formoterol. The different letters (a, b, c, d, e, and f) are above the bars, mean statistically significant difference groups at P < 0.05, n = 6.
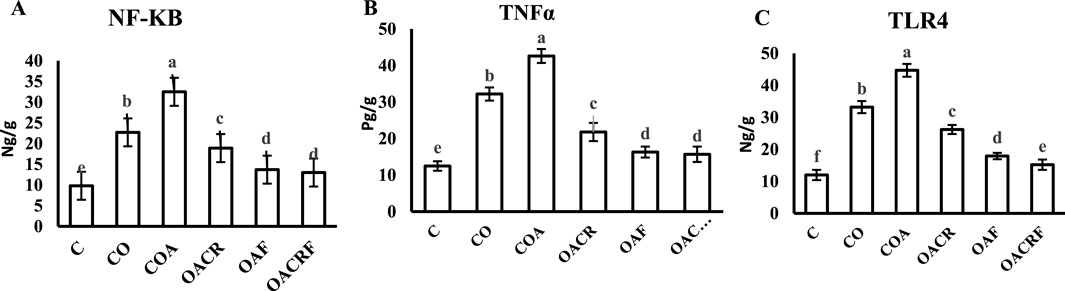
Figure 3. Effect of chromium picolinate and formoterol on lung tissue level of (A) NF-KB (B) TNF-α (C) TLR4. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E and analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. C, control; CO, control obese; COA, control obese-asthmatic; OACR, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate; OAF, obese-asthmatic treated with formoterol; OACRF, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate and and formoterol. The different letters (a, b, c, d, e, and f) are above the bars, mean significant difference between groups at P < 0.05, n = 6.
Regarding the data observed in (Figure 2B), there was a statistically significant difference between the four groups for LEP at P < 0.05. It was observed that there was a significant decrease in LEP serum level in treated groups (OACRF), (OACR), and (OAF) compared to (C) at P < 0.05. On the other hand, it showed the highest values in the percentage of body weight for the groups (CO) and (COA) (Figure 1).
Using of chromium picolinate at dose (400 μg/kg) and inhalation of formoterol at (50 µg/kg) for 15 min once/day in groups (OACRF) and (OAF) showed a significant decrease in (NF-kB), (TNFα) and (TLR4) compared to (C) at P < 0.05 (Figures 4A–C). On the other hand, the groups (CO), (COA), and (OACR), which were not treated with formoterol, showed the highest value of (NF-kB), (TNFα), and (TLR4) (Figures 3A–C).
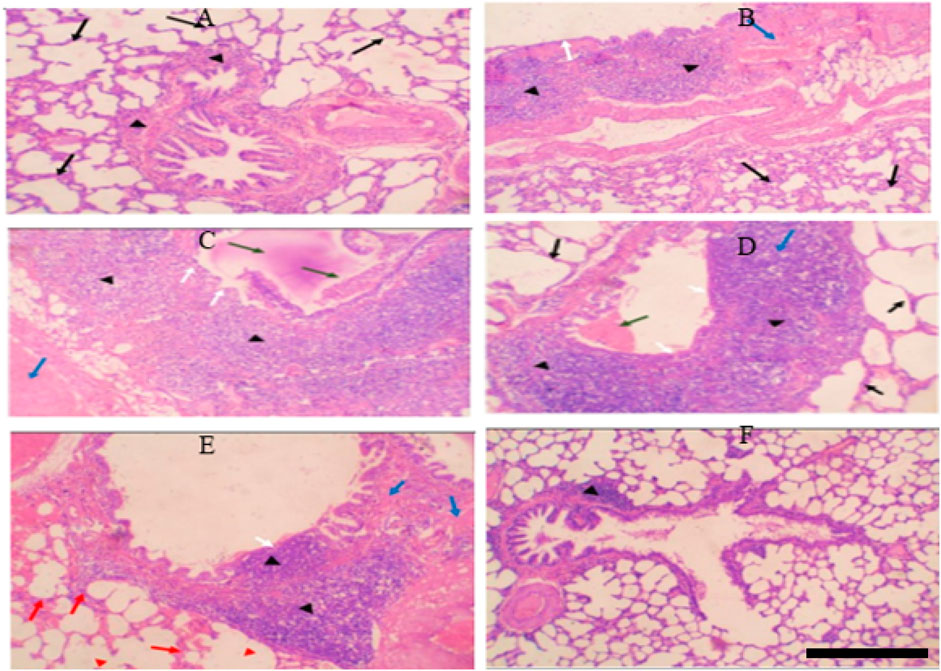
Figure 4. (A) Control group: Normal alveolar walls (black arrows) and bronchioles (black arrowheads). (B) Control-obese group: Fibrosis (blue arrow), chronic inflammation in bronchial walls (black arrowheads), thickened alveolar walls (black arrows), intact bronchiolar lining (white arrows). (C) Control-obese asthma group: Chronic inflammation (black arrowheads), fibrosis (blue arrow), mucus plug and obstructing cells (green arrows), bronchiolar epithelium ulceration (white arrows). (D) Chromium picolinate-treated group: Mild inflammation (black arrowheads), no fibrosis, small mucus plug (green arrow), intact bronchiolar lining (white arrow), normal alveolar walls (black arrows). (E) Formoterol-treated group: Reduced inflammation (black arrowheads), focal fibrosis (blue arrows), intact bronchiolar lining with focal ulceration (white arrow), alveolar hemorrhage (red arrows), emphysematous areas (red arrowheads). (F) Combined treatment: Restored lung tissue, minor lymphoid aggregate in bronchiolar walls (black arrowheads), no inflammation, fibrosis, or hemorrhage.
Before being embedded in paraffin, the samples were fixed with 10% formalin. Sections of 3 µm in thickness were taken from each block, put on a glass slide, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), and then analyzed (Fig V). The transverse section (T.S) of the control group’s lung tissue revealed homogeneous bronchioles and alveolar walls (H&E, 10x) (Figure 4A).
T.S. revealed considerable fibrosis and infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells involving the bronchial walls in the lung tissue from the control obesity group. Is the lining of the bronchi intact? Chronic inflammatory cells invade and thicken the alveolar walls (H&E, 10x). Alveolar infiltration of proliferating, persistent inflammatory cells is substantial. There are spots with emphysema (Figure 4B).
T.S in lung tissue from the control obesity-asthma group showed significant chronic inflammatory cell infiltration involving bronchiolar walls and significant fibrosis. There is a thick mucus plug and spelled inflammatory cells obstructing the bronchiolar lumen. There is sloughing and ulceration of bronchiolar epithelium (H&E, 10x). Most chronic inflammatory cells infiltrate composed of eosinophils. There are emphysematous areas, and chronic inflammatory cells infiltrate involving alveolar walls (Figure 4C).
T.S. in lung tissue from the control obesity-asthma group treated with chromium showed a mild reduction in the severity of chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate involving bronchiolar walls. No fibrosis could be seen. A small mucous plug is seen in the bronchiolar lumen. The bronchiolar lining is intact. The alveolar walls show no evidence of thickening or inflammatory cell infiltration (H&E, 10x) (Figure 4D).
T.S. in lung tissue from the control obesity-asthma group treated with formoterol showed a significant reduction in the severity of chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate involving bronchiolar walls. Small fibrosis could be seen. No mucous plug or spelled inflammatory cells are seen in the bronchiolar lumen. The bronchiolar lining is intact except for focal ulceration above inflammatory cell infiltrates. The alveolar walls show evidence of hemorrhage with few chronic inflammatory cells. There are emphysematous areas (H&E, 10x) (Figure 4E).
T.S. in lung tissue from the control obesity-asthma group treated with formoterol and chromium showed almost complete restoration of lung tissue to its normal state, except for a small lymphoid aggregate within bronchiolar walls. No evidence of diffuse chronic inflammation, fibrosis, ulceration, or hemorrhage (H&E, 10 x). The focal lymphoid aggregates within the bronchiolar wall (Figure 4F).
Tumor tissue was assessed. Positive cells were those that expressed IL-1β and IL-17α in the cytoplasm. Guidelines for a semi-quantitative grading system (Ilić et al., 2019). The staining intensity of the reaction (0–3) and the proportion of positive cells (0–5) were added to determine the final grades. The transverse section (T.S) of lung tissue from the control group revealed weak expression of IL-1β in a small number of bronchiolar epithelial cells (IHC, 40x) (Figure 5A). Furthermore, T.S. in lung tissue from the control-obese group revealed weak expression of IL-1β in bronchiolar epithelial cells with moderate expression of IL-1beta in chronic inflammatory cells (IHC, 40x) (Figure 5B). However, strong expressions of IL-1β were observed in chronic inflammatory cells (IHC, 40x) and lung tissue from the control obese-asthmatic group (Figure 5C). Further, there was a weak expression of IL-1β in bronchiolar epithelial cells and chronic inflammatory cells (IHC, 40x) (Figure 5D) observed in lung tissue from the obese-asthmatic group treated with chromium picolinate. Similarly, there was a significant decrease in IL-1β expression was seen in T.S. lung tissue from the formoterol-treated obese-asthmatic group in the epithelial cells of the bronchi (IHC, 40x) along with weak localized expression of IL-1β (Figure 5E). When both formoterol and chromium picolinate were given to the obese-asthmatic group, T.S. in their lung tissue revealed weak expression of IL-1β in a small number of chronic inflammatory cells (IHC, 40x) (Figure 5F).

Figure 5. (A) Weak IL-1β expression in bronchiolar epithelial cells (black arrows) in control lung tissue (IHC, 40x). (B) Weak IL-1β expression in bronchiolar epithelial cells (black arrows) and moderate expression in chronic inflammatory cells (black arrows) in control obese lung tissue (IHC, 40x). (C) Strong IL-1β expression in chronic inflammatory cells (arrowheads) in control obese-asthmatic lung tissue (IHC, 40x). (D) Weak IL-1β expression in bronchiolar epithelial cells (black arrows) and chronic inflammatory cells (arrowheads) in asthmatic lungs treated with chromium picolinate (IHC, 40x). (E) Significant reduction in IL-1β expression with no bronchiolar epithelial cell expression (black arrows) and weak focal expression in chronic inflammatory cells (arrowheads) in obese-asthmatic lungs treated with formoterol (IHC, 40x). (F) Weak IL-1β expression in a few chronic inflammatory cells (arrowheads) in obese-asthmatic lungs treated with chromium picolinate and formoterol (IHC, 40x). (G) Optical density% of IL-1β expression in different groups expressed as mean ± S.E. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test, P < 0.05, n = 6. Groups: C, control; CO, control obese; COA, control obese-asthmatic; OACR, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate; OAF, obese-asthmatic treated with formoterol; OACRF, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate and formoterol. Different letters indicate significant differences between groups.
On the other hand, The transverse section (T.S) of lung tissue from the control group revealed weak expression of IL-17α in a small number of bronchiolar epithelial cells (IHC, 40x) (Figure 6A). While T.S. in lung tissue from the control obese group revealed moderate focal expression of IL-17α in both bronchiolar epithelial cells and chronic inflammatory cells (IHC, 40x) (Figure 6B). Strong expressions of IL-17α were observed in chronic inflammatory cells (IHC, 40x) and lung tissue from the control obese-asthmatic group (Figure 6C). Further, moderate expression of IL-17α in bronchiolar epithelial cells and chronic inflammatory cells was observed in lung tissue from the obese-asthmatic group treated with chromium picolinate (IHC, 40x) (Figure 6D). Further, weak expression of IL-17α in bronchiolar epithelial cells and chronic inflammatory cells was observed in lung tissue from the obese-asthmatic group treated with formoterol (IHC, 40x) (Figure 6E). When both formoterol and chromium picolinate were given to the obese-asthmatic control group, T.S in their lung tissue revealed Prominent expression of IL-17α in bronchiolar epithelial cells and chronic inflammatory cells (IHC, 40x) (Figures 6F, G).
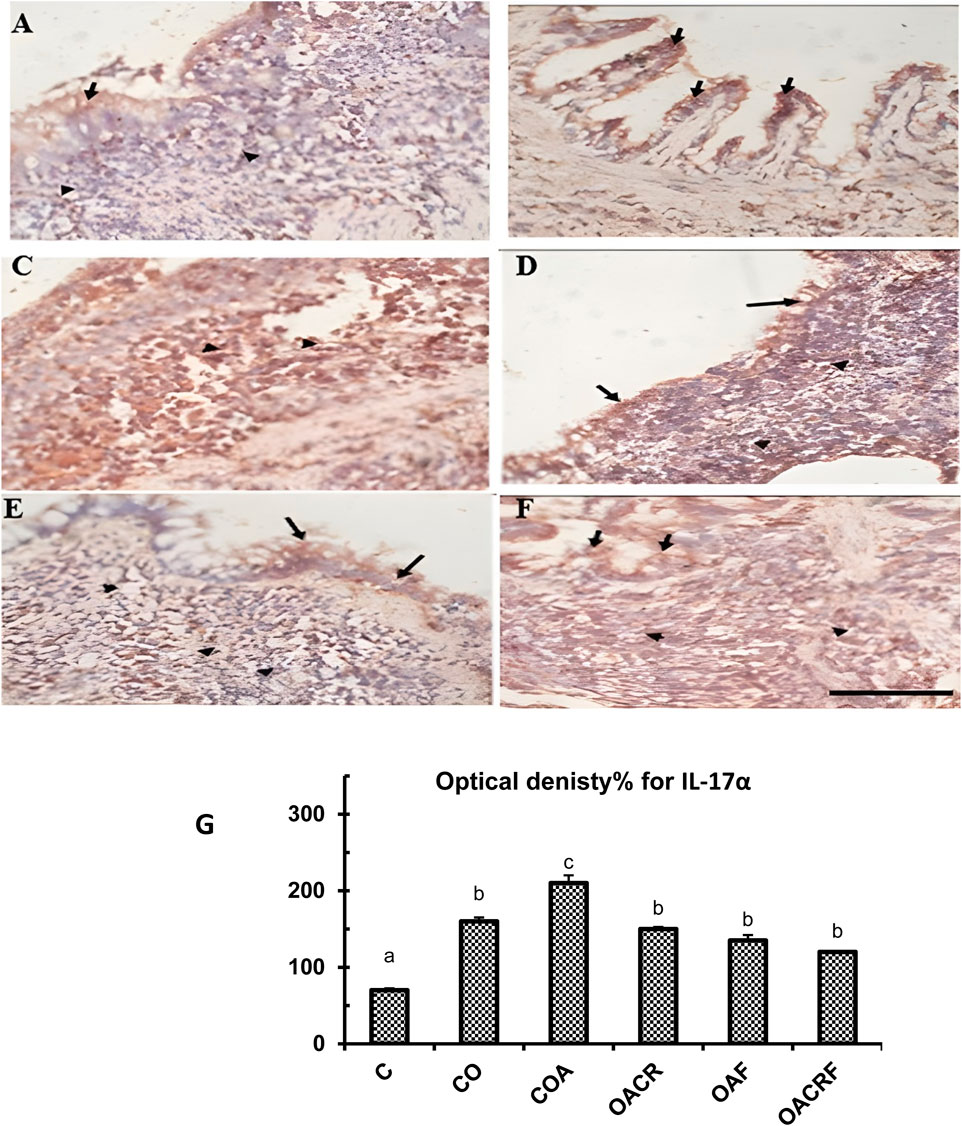
Figure 6. (A) T.S in lung tissue from the control group of IL-17α showed weak focal expression of IL-17α in a few bronchiolar epithelial cells (Black arrows) (IHC, 40x). (B) T.S. in lung tissue from the control obese group of IL-17 α showed moderate expression of IL-17α in bronchiolar epithelial cells (Black arrows) and in chronic inflammatory cells (Black arrows) (IHC, 40x). (C) T.S. in lung tissue from the control obese-asthmatic group of IL-17α showed Strong expression of IL-17α in chronic inflammatory cells (Arrow heads) (IHC, 40x). (D) T.S in lung tissue from obese-asthmatic group treated with chromium picolinate of IL-17α showed Moderate expression of IL-17α in bronchiolar epithelial cells (Black arrows) and in chronic inflammatory cells (Arrowheads) (IHC, 40x). (E) T.S in lung tissue from obese-asthmatic group treated with formoterol of IL-17 α showed Weak expression of IL-17α in bronchiolar epithelial cells (Black arrows) and in chronic inflammatory cells (Arrowheads) (IHC, 40x). (F) T.S in lung tissue from obese-asthmatic group treated with both formoterol and chromium picolinate of IL-17α showed Moderate expression of IL-17α in bronchiolar epithelial cells (Black arrows) and in chronic inflammatory cells (Arrowheads) (IHC, 40x). (G) Optical density% of expression for IL-17α in different groups. Results were expressed as mean ± S.E and analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons. C, control; CO, control obese; COA, control obese-asthmatic; OACR, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate; OAF, obese-asthmatic treated with formoterol; OACRF, obese-asthmatic treated with chromium picolinate & and formoterol. The different letters (a, b, c, d, e, and f) are above the bars, mean significant difference between different groups at P < 0.05, n = 6.
This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of chromium and formoterol on experimentally induced asthma in obese rats. An asthmatic obese rat model was created by feeding rats a high-fat diet along with subcutaneous injections and inhalation of ovalbumin (OVA) to exacerbate asthma. The pilot trial successfully induced asthma in the rats. The primary objective was to evaluate the impact of chromium and formoterol on the asthma condition in these obese rats, with their weights recorded weekly. Studies on obesity and its metabolic consequences are crucial due to the close link between the immune system and metabolic pathways. Therefore, Signaling pathways that respond to diet and pathogens are highly integrated and evolutionarily conserved. Innate recognition receptors detect obesity-related foods, triggering pro-inflammatory and stress responses when consumed in excess (Rogero and Calder, 2018). Saturated fatty acids activate nuclear factor-kabba (NF-kB) and upregulate the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha via Toll-like receptors (TLR4) and (TLR2). This triggers the innate immune response (Salas-Venegas et al., 2022; Scott et al., 2011).
Likewise, In obesity, adipocytes secrete inflammatory mediators due to an adipokine imbalance. These mediators activate the inflammatory microsome, including NLRP3 and M1 macrophages. The release of IL-1β and IL-17α secreted by M1 macrophages in the lungs and adipose tissue is enhanced when NLRP3 is activated, alleviating asthmatic episodes in patients. Among the factors leading to asthma development include pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNFα (Bantulà et al., 2021).
The study found that obesity and obese-asthma groups had significant weight changes, lower HDL, and higher total cholesterol, TG, and LDL compared to the normal group. This increased TNF-alpha and activation of inflammatory pathways (TLRs, IKKs, NF-KB). Additionally, These groups showed higher leptin and lower adiponectin levels. Obesity, characterized by excess fat storage, has been linked to health issues like asthma (Bonetti et al., 2022; Michelini et al., 2020). Body mass index (BMI) is the gold standard for determining excess body weight by indicating that being overweight is positively related to low HDL levels and high TG, LDL, and cholesterol levels (Ding et al., 2022). Previous study indicates that there is a negative correlation between body fat percentage and body mass index (BMI) and brown adipose tissue. Additionally, the adipose tissue of lean people primarily secretes anti-inflammatory indicators, whereas the adipose tissue of obese people secretes more pro-inflammatory markers (Akhter et al., 2021; Khanna et al., 2022). Furthermore, Immune cells called macrophages sense and respond to various stimuli in metabolic organs, such as adipose tissue, leading to persistent inflammatory reactions (Cai et al., 2018; Tabas and Lichtman, 2017). Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, have important roles in inflammation initiation and resolution and are played by pattern recognition receptors, also known as toll-like receptors (Ben et al., 2019). NF-KB, a transcription factor involved in immune-mediated and inflammatory disorders, is activated by TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) (Yamamoto et al., 2021), activating IKKs (Kawai and Akira, 2010; Liang et al., 2022). Additionally, it is well-documented that circulating levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines grow in obese individuals due to excess adipose tissue (Palma et al., 2022; Scott et al., 2011). Adipocytes transmit information about the status of peripheral tissues' energy reserves to the brain via the hormone leptin. Leptin controls metabolism and food intake by sending signals to the brain’s control centers. Regarding metabolic diseases and obesity in humans, the leptin system’s network is crucial (Stover et al., 2023).
Furthermore, one component of the negative feedback loop that regulates body weight is the production and release of leptin by adipose tissue in fat. It enters the hypothalamus via the circulatory system and acts by binding to leptin receptors. The quantity of adipose tissue in your body is closely correlated with the level of leptin in your blood. Stated differently, a lower body fat percentage corresponds to a higher leptin level, and vice versa (Obradovic et al., 2021). Moreover, when plasma leptin levels drop, which activates orexigenic responses and represses anorexigenic responses, energy expenditure is suppressed, and food intake is raised until fat mass is recovered. As fat mass grows, the hypothalamic neural circuits work together to make people eat less and burn more calories. This increases plasma leptin levels (M.-D. Li, 2011; Martelli and Brooks, 2023).
Regarding the change in body weight percentage, the body secretes the hormone leptin, which aids in long-term weight maintenance (Izquierdo et al., 2019; Landecho et al., 2019). The hormone leptin controls hunger, weight, reproductive health, fetal development, and immunological responses that promote inflammation (Obradovic et al., 2021). Following caloric restriction, the concentration of circulating leptin falls, but it rises during refeeding (Hernández et al., 2000; Obradovic et al., 2021).
Additionally, adipose tissue is responsible for producing and secreting adiponectin. Unlike other adipokines, adiponectin levels are inversely related to total fat mass (Clemente-Suárez et al., 2023; Silha et al., 2003). This is especially true in the case of the adiponectin-leptin interaction. These two adipokines are controlled in opposing ways under nearly physiological circumstances. When leptin levels are high, it indicates that adiponectin is low, and vice versa when leptin levels are low. Furthermore, adiponectin secretion is regulated by adipose tissue quality, not quantity (Zhao et al., 2021).
On the other hand, asthma is only one of several allergy diseases linked to mast cells, which are innate immune cells (Shou et al., 2019). The stimulation of mast cells also initiates signaling pathways, including those involving NF-kB. These pathways produce inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (Lertnimitphun et al., 2021). OVA may bring on inflammation of the airways and asthma. Furthermore, increased TLR4 signaling might be involved (Wu et al., 2022).
Moreover, previous research has shown that obesity is one of the major pathogenic variables associated with asthma. The body mass index (BMI) measures a patient’s illness severity (Mohammed et al., 2023). There may be a connection between the pathophysiology of asthma and the adipocytes, adiponectin, and leptin produced by the body (Ma et al., 2019).
Our study found that chromium picolinate therapy significantly reduced body weight in obese-asthmatic subjects compared to controls. This weight loss improved lipid profiles by decreasing TG and LDL levels and increasing HDL levels. Chromium also reduced inflammatory cytokines and inhibited NF-kB pathways, lowering BMI. Asthma symptoms improved due to reduced fat cells, lower leptin, and higher adiponectin levels. Histopathological analysis showed reduced chronic inflammatory cell infiltration and no fibrosis in the chromium-treated group, while the control group had significant fibrosis and chronic inflammation. Immunohistochemically, the chromium-treated group had minimal IL-1β and moderate IL-17α expression compared to strong expressions in controls. Chromium therapy alleviated lung inflammation, reduced fibrosis, and improved respiratory health in obese-asthmatic subjects. Previous studies showed that chromium picolinate has been shown in earlier research to have the potential to prevent obesity (Pala et al., 2020). In lipid metabolism, chromium is an important player. Chromium is believed to influence several pathways that regulate hunger, energy balance, and caloric intake (Aksoy et al., 2021). Research has shown that chromium may help people lose weight while maintaining muscle mass. So, it is best used for slimming down (Derosa et al., 2019). It has been found that lowering body weight improves lipid profiles in overweight people. This included reducing triglycerides, raising HDL, decreasing LDL concentration, and reducing pro-inflammatory characteristics (Zhou et al., 2022). A healthier lipid profile (lower LDL-C, TG, and total cholesterol (TC) and higher HDL-C) was related to a significant reduction in body weight (Georgoulis et al., 2022). Regarding body weight, the previous research found that the risk of developing late-onset asthma was much higher when the body weight percentage rose. There is a correlation between obesity and an increased risk of developing asthma in people of all ages and genders (Nystad et al., 2004; Sikorska-Szaflik et al., 2022). Because of impaired lung function, obesity makes asthma management more challenging. Exacerbations are more common in obese asthmatics compared to those who are not overweight (Barros et al., 2017; Reyes Noriega et al., 2023). Furthermore, there is some overlap between the inflammatory processes that cause asthma and fat. This discovery suggests that the two inflammatory processes may contribute to the problem. Adipose tissue in obese asthmatics produces more pro-inflammatory cytokines, which may affect their lung function and clinical symptoms (Bantulà et al., 2021). Moreover, it is found that leptin mediated an indirect connection between obesity and chronic asthma (Z. Li et al., 2019). According to the research, asthma was also linked to elevated leptin levels. According to Bantulà et al., (2021), the leptin pathway might also explain the obesity-asthma connection. Elevated levels of interleukins, and TNF-α, are also linked to the obesity-related asthma phenotype (Leiria, Martins, and Saad, 2015; Wang and Hu, 2022). Asthmatic patients showed an increase in TNF-α expression proportional to their BMI (Tenório et al., 2021). Likewise, reducing body fat improves lung function tests, quality of life, and asthma control and exacerbations (Dias-Júnior et al., 2014; Eslick et al., 2020). By lowering the expression of target genes, such as those involved in inflammation (e.g., adiponectin, (TNF-α), leptin, and TLR 4), obesity treatment leads to the prevention of NF-kB activation (Kasprzak-Drozd et al., 2022). This research found that chromium may help lower body weight, which in turn helps regulate asthma by reducing inflammation (Fotschki et al., 2023).
Our study showed better improvement in lipid profile of OAF group than untreated group specifically in serum cholesterol, TG and LDL. Formoterol (50 μg/kg) inhaled for 15 minutes daily over 6 days alleviated asthma symptoms. The weight of the formoterol-treated obese-asthmatic group (OAF) was lower than the control groups (CO and COA) but higher than the chromium-treated groups (OACR and OACRF). OAF had better serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL levels than CO and COA, but these levels were still higher than OACR and OACRF. HDL levels in OAF were similar to CO but differed from OACR and OACRF, indicating chromium’s superior impact on the lipid profile. TNF-α was significantly reduced in OAF compared to CO, COA, and OACR, with no significant difference between OAF and OACRF in TNF-α and NF-κB levels. Formoterol improved adiponectin and leptin levels, enhancing asthma conditions compared to control groups, with significant body mass index differences between OAF and chromium-treated groups. Chromium treatment also improved lung inflammation in the obese-asthma group compared to controls, which had substantial fibrosis, bronchiolar wall infiltration, chronic inflammatory cells, thick mucus plugs, and epithelial sloughing and ulceration. Additionally, prior research found that formoterol treatment reduced generated inflammatory mediators by enhancing the inflammatory marker, a consequence of the drug’s anti-inflammatory effects (Zhang et al., 2022).
Formoterol significantly reduced chronic inflammatory cell infiltration and mucus plugs in the bronchiolar walls of the OAF group. The CO group had severe fibrosis and inflammation, while the COA group showed extensive fibrosis, inflammation, and epithelial damage. Immunohistochemistry showed decreased IL-1β and IL-17α expression in the OAF group compared to the COA group. Moreover, With a short half-life (1–3 min) and a lengthy half-life (12 h), formoterol is unlike any other selective long-acting β2-agonist (Burkes and Panos, 2020; Rodrigo et al., 2010). Asthma management has been improved by using formoterol as maintenance medication or as required in mild, moderate, and severe chronic cases (Cusack et al., 2020; Pauwels et al., 2003). Reasons to use formoterol include its long half-life and the possibility that it might lessen the frequency of bronchodilator dosing. Formoterol, an inhaled long-acting beta2-agonist, is useful in managing chronic asthma because it improves lung function and decreases the frequency of asthma attacks (Reddel et al., 2022; Rodrigo et al., 2010). Treatment with formoterol decreases induced NF-kB activation and TNF production and has an anti-inflammatory effect (Martín et al., 2018). The pro-inflammatory adipokine adiponectin suppresses the cytokines nuclear factor-B and tumor necrosis factor-contributing to inflammation. Obese people have lower amounts of adiponectin, even though it is mostly produced by visceral adipose tissue. A possible explanation for this mystery might be the finding that macrophages produce TNF-alpha in adipose tissue, which could directly restrict the production of adiponectin (Kim et al., 2014; Zorena et al., 2020). The reason formoterol lowered TNF-alpha production, adiponectin levels rose, and leptin levels fell was explained. If leptin levels are low, adiponectin levels are high, and vice versa (Zhao et al., 2021).
The study found that combining formoterol and chromium picolinate effectively manages asthma and improves health in obese rats. Formoterol, administered at 50 μg/kg daily for 6 days, reduced inflammation by lowering TNF-α and deactivating NF-kB pathways. Chromium picolinate, taken orally at 400 μg/kg for 6 weeks, significantly aided weight loss and lipid profile improvement. The OACRF group, receiving both treatments, showed the best results in reducing body weight, improving lipid profiles, and lowering inflammatory mediators, outperforming other groups. Thus, this combination therapy is the most effective for managing asthma and enhancing overall health in obese rats. In addition, prior research has shown that formoterol enhances the inflammatory mediator, reducing inflammation; chromium’s weight-loss effects and its impact on lipid profiles are also noteworthy (Zhang et al., 2022). Dietary changes and rising rates of overweight and obesity have been linked in earlier research to an increase in asthma cases. There is a correlation between obesity and asthma that is associated with worse asthma control, more severe asthma episodes, and an increased risk of asthma exacerbation (Marko and Pawliczak, 2018). Among the subgroups of people with moderate to severe asthma, several recent studies have focused on those who are overweight. When compared to the non-obese asthma population, these people have higher exacerbations, more treatments, reduced lung function, and more difficult-to-control asthma. Treatment to manage both body mass index and asthma was shown to be the most effective method for controlling asthma in the obese-asthmatic group in the present investigation (Bantulà et al., 2021). This study used male rats only; future work should include females. The treatment duration (6 weeks) may not reflect long-term effects. Mechanistic insights into chromium-formoterol synergy remain to be explored.
The study investigated the potential protective effects of chromium and formoterol in mitigating asthma symptoms in obese rats. The combination of these therapies demonstrated significant improvements in metabolic and respiratory parameters, highlighting a promising strategy for managing obesity-induced asthma. The dual treatment with chromium and formoterol effectively reduced body weight, improved lipid profiles, and decreased inflammatory markers, restoring lung tissue to its normal state. This synergistic approach addresses both the metabolic dysfunctions and respiratory challenges associated with obesity-induced asthma, offering a comprehensive therapeutic strategy. Further research is warranted to explore this combined therapy’s clinical applications in humans and elucidate the underlying mechanisms contributing to its efficacy.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The animal study was approved by Institutional animal usage committee’s rules number 202011MA1. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
RI: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YM: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. MA: Data analysis, Visualization, Funding, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AmA: Data analysis, Visualization, Funding, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AfA: Data analysis, Visualization, Funding, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. NN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. DK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This paper are funded and suppourted by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2025R227), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Also the authors extend their appreciation to Taif University, Saudi Arabia, for supporting this work through project number (TU-DSPP-2024-119).
We want to thanks Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2025R227), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Also the authors extend their appreciation to Taif University, Saudi Arabia, for supporting this work through project number (TU-DSPP-2024-119).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1537022/full#supplementary-material
Abo-Al-Ela, H. G., El-Magd, M. A., El-Nahas, A. F., and Mansour, A. A. (2014). Association of a novel SNP in exon 10 of the IGF2 gene with growth traits in Egyptian water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Trop. Animal Health Prod. 46 (6), 947–952. doi:10.1007/s11250-014-0588-3
Akhter, N., Wilson, A., Thomas, R., Al-Rashed, F., Kochumon, S., Al-Roub, A., et al. (2021). ROS/TNF-α crosstalk triggers the expression of IL-8 and MCP-1 in human monocytic THP-1 cells via the NF-κB and ERK1/2 mediated signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (19), 10519. doi:10.3390/ijms221910519
Aksoy, H., Karadag, A. S., and Wollina, U. (2021). Cause and management of lipedema-associated pain. Dermatol. Ther. 34 (1), e14364. doi:10.1111/dth.14364
AlEnazi, S., AlAjlan, R., AlKhalaf, H., Abolfotouh, M., Alharbi, O., Alfawaz, R., et al. (2023). Prevalence of obesity among children and adolescents in Saudi Arabia: a multicenter population-based study. Saudi J. Med. and Med. Sci. 11 (1), 19–25. doi:10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_417_22
Anekwe, C. V., Jarrell, A. R., Townsend, M. J., Gaudier, G. I., Hiserodt, J. M., and Cody Stanford, F. (2020). Socioeconomics of obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 9 (3), 272–279. doi:10.1007/s13679-020-00398-7
Attia, A. M., Khodair, A. I., Gendy, E. A., El-Magd, M. A., and Elshaier, Y. A. M. M. (2020). New 2-oxopyridine/2-thiopyridine derivatives tethered to a benzotriazole with cytotoxicity on MCF7 cell lines and with antiviral activities. Lett. Drug Des. and Discov. 17 (2), 124–137. doi:10.2174/1570180816666190220123547
Badawy, A., Hassanean, H., Ibrahim, A. K., Habib, E. S., El-Magd, M. A., and Ahmed, S. A. (2021a). Isolates from thymelaea hirsuta inhibit progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Prod. Res. 35 (11), 1799–1807. doi:10.1080/14786419.2019.1643859
Badawy, A. A., Othman, R. Q. A., and El-Magd, M. A. (2021b). Effect of combined therapy with camel milk-derived exosomes, tamoxifen, and hesperidin on breast cancer. Mol. and Cell. Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s13273-021-00163-4
Bancroft, J. D., and Cook, H. C. (1994). Manual of histological techniques and their diagnostic application. Churchill Livingstone.
Bantulà, M., Roca-Ferrer, J., Arismendi, E., and Picado, C. (2021). Asthma and obesity: two diseases on the rise and bridged by inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 10 (2), 169. doi:10.3390/jcm10020169
Barros, R., Moreira, P., Padrão, P., Teixeira, V. H., Carvalho, P., Delgado, L., et al. (2017). Obesity increases the prevalence and the incidence of asthma and worsens asthma severity. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 36 (4), 1068–1074. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2016.06.023
Ben, J., Jiang, B., Wang, D., Liu, Q., Zhang, Y., Qi, Y., et al. (2019). Major vault protein suppresses obesity and atherosclerosis through inhibiting IKK-NF-κB signaling mediated inflammation. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 1801. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09588-x
Bonetti, G., Herbst, K. L., Dhuli, K., Kiani, A. K., Michelini, S., Michelini, S., et al. (2022). Dietary supplements for lipidemia. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 63 (2 Suppl. 3), E169–E173. doi:10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2022.63.2S3.2758
Burkes, R. M., and Panos, R. J. (2020). Ultra long-acting β-agonists in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 12, 589–602. doi:10.2147/JEP.S259328
Cai, Y., Li, H., Liu, M., Pei, Y., Zheng, J., Zhou, J., et al. (2018). Disruption of adenosine 2A receptor exacerbates NAFLD through increasing inflammatory responses and SREBP1c activity. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 68 (1), 48–61. doi:10.1002/hep.29777
Cheng, W.-H., Chen, C.-L., Chen, J.-Y., Lin, C.-H., and Chen, B.-C. (2021). Hypoxia-induced preadipocyte factor 1 expression in human lung fibroblasts through ERK/PEA3/c-Jun pathway. Mol. Med. Camb. Mass. 27 (1), 69. doi:10.1186/s10020-021-00336-w
Clarkson, J. M., Martin, J. E., and McKeegan, D. E. F. (2022). A review of methods used to kill laboratory rodents: issues and opportunities. Lab. Anim. 56 (5), 419–436. doi:10.1177/00236772221097472
Clemente-Suárez, V. J., Redondo-Flórez, L., Beltrán-Velasco, A. I., Martín-Rodríguez, A., Martínez-Guardado, I., Navarro-Jiménez, E., et al. (2023). The role of adipokines in health and disease. Biomedicines 11 (5), 1290. Article 5. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11051290
Conrad, M. L., Yildirim, A. Ö., Sonar, S. S., Kılıç, A., Sudowe, S., Lunow, M., et al. (2009). Comparison of adjuvant and adjuvant-free murine experimental asthma models. Clin. Exp. Allergy 39 (8), 1246–1254. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2009.03260.x
Cusack, R. P., Satia, I., and O’Byrne, P. M. (2020). Asthma maintenance and reliever therapy. Ann. Allergy, Asthma and Immunol. 125 (2), 150–155. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2020.04.009
D’Amato, M., Molino, A., Calabrese, G., Cecchi, L., Annesi-Maesano, I., and D’Amato, G. (2018). The impact of cold on the respiratory tract and its consequences to respiratory health. Clin. Transl. Allergy 8 (1), 20. doi:10.1186/s13601-018-0208-9
Derosa, G., Pascuzzo, M. D., D’Angelo, A., and Maffioli, P. (2019). Ascophyllum Nodosum, Fucus Vesiculosus and chromium picolinate nutraceutical composition can help to treat type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome Obes. Targets Ther. 12, 1861–1865. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S212429
Dias-Júnior, S. A., Reis, M., de Carvalho-Pinto, R. M., Stelmach, R., Halpern, A., and Cukier, A. (2014). Effects of weight loss on asthma control in obese patients with severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 43 (5), 1368–1377. doi:10.1183/09031936.00053413
Ding, X., Chang, X., Wang, J., Bian, N., An, Y., Wang, G., et al. (2022). Serum Metrnl levels are decreased in subjects with overweight or obesity and are independently associated with adverse lipid profile. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 938341. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.938341
El-Demerdash, F. M., El-Magd, M. A., and El-Sayed, R. A. (2021). Panax ginseng modulates oxidative stress, DNA damage, apoptosis, and inflammations induced by silicon dioxide nanoparticles in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 36 (7), 1362–1374. doi:10.1002/tox.23132
Elkelish, A. (2024). New plant extracts toward multidrug resistance: the convergence of nanotechnology and nanoscience. Spectr. Sci. J. 1 (1), 1–14. doi:10.21608/sasj.2024.396119
Elmetwalli, A., Hashish, S. M., Hassan, M. G., El-Magd, M. A., El-Naggar, S. A., Tolba, A. M., et al. (2023). Modulation of the oxidative damage, inflammation, and apoptosis-related genes by dicinnamoyl-L-tartaric acid in liver cancer. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives Pharmacol. 396 (11), 3087–3099. doi:10.1007/s00210-023-02511-8
Eslick, S., Jensen, M. E., Collins, C. E., Gibson, P. G., Hilton, J., and Wood, L. G. (2020). Characterising a weight loss intervention in obese asthmatic children. Nutrients 12 (2), 507. doi:10.3390/nu12020507
Forno, E., Lescher, R., Strunk, R., Weiss, S., Fuhlbrigge, A., Celedón, J. C., et al. (2011). Decreased response to inhaled steroids in overweight and obese asthmatic children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 127 (3), 741–749. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2010.12.010
Fotschki, B., Ognik, K., Fotschki, J., Napiórkowska, D., Cholewińska, E., Krauze, M., et al. (2023). Chromium nanoparticles together with a switch away from high-fat/low-fiber dietary habits enhances the pro-healthy regulation of liver lipid metabolism and inflammation in obese rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (3), 2940. doi:10.3390/ijms24032940
Garg, D., Que, L. G., and Ingram, J. L. (2024). Effects of biological therapies on patients with Type-2 high asthma and comorbid obesity. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1315540. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023
Garlisi, C. G., Falcone, A., Hey, J. A., Paster, T. M., Fernandez, X., Rizzo, C. A., et al. (1997). Airway eosinophils, T cells, Th2-type cytokine mRNA, and hyperreactivity in response to aerosol challenge of allergic mice with previously established pulmonary inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 17 (5), 642–651. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.17.5.2866
Georgoulis, M., Chrysohoou, C., Georgousopoulou, E., Damigou, E., Skoumas, I., Pitsavos, C., et al. (2022). Long-term prognostic value of LDL-C, HDL-C, lp(a) and TG levels on cardiovascular disease incidence, by body weight status, dietary habits and lipid-lowering treatment: the ATTICA epidemiological cohort study (2002–2012). Lipids Health Dis. 21, 141. doi:10.1186/s12944-022-01747-2
Hegab, M. H., Abd-Allah, S. H., Badawey, M. S., Saleh, A. A., Metwally, A. S., Fathy, G. M., et al. (2018). Therapeutic potential effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on chronic liver disease in murine Schistosomiasis Mansoni. J. Parasit. Dis. 42 (2), 277–286. doi:10.1007/s12639-018-0997-8
Hernández, C., Simó, R., Chacón, P., Sabin, P., Baena, J. A., Castellanos, J. M., et al. (2000). Influence of surgical stress and parenteral nutrition on serum leptin concentration. Clin. Nutr. 19 (1), 61–64. doi:10.1054/clnu.1999.0075
Huang, J., Liu, X., Wei, Y., Li, X., Gao, S., Dong, L., et al. (2022). Emerging role of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in autoimmune disease. Front. Immunol. 13, 830863. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.830863
Hui, H. X., Feng, T., Hui, H. X., and Feng, T. (2018). “Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ,” in Adipose tissue London, United Kingdom (IntechOpen). doi:10.5772/intechopen.76220
Ilić, I. R., Stojanović, N. M., Radulović, N. S., Živković, V. V., Randjelović, P. J., Petrović, A. S., et al. (2019). The quantitative ER immunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer: detecting the 3 + 0, 4 + 0, and 5 + 0 allred score cases. Medicina 55 (8), 461. Article 8. doi:10.3390/medicina55080461
Izquierdo, A. G., Crujeiras, A. B., Casanueva, F. F., and Carreira, M. C. (2019). Leptin, obesity, and leptin resistance: where are we 25 Years later? Nutrients 11 (11), 2704. doi:10.3390/nu11112704
Kasprzak-Drozd, K., Oniszczuk, T., Gancarz, M., Kondracka, A., Rusinek, R., and Oniszczuk, A. (2022). Curcumin and weight loss: does it work? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (2), 639. doi:10.3390/ijms23020639
Kawai, T., and Akira, S. (2010). The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11 (5), 373–384. doi:10.1038/ni.1863
Khanna, D., Khanna, S., Khanna, P., Kahar, P., and Patel, B. M. (2022). Obesity: a chronic low-grade inflammation and its markers. Cureus 14 (2), e22711. doi:10.7759/cureus.22711
Khodeer, D. M. (2024). Beyond glycemic control: cardiovascular, renal, and hepatic benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Spectr. Sci. J. 1 (1), 15–26. doi:10.21608/sasj.2024.396448
Kim, S.-H., Sutherland, E. R., and Gelfand, E. W. (2014). Is there a link between obesity and asthma? Allergy, Asthma and Immunol. Res. 6 (3), 189–195. doi:10.4168/aair.2014.6.3.189
Koliaki, C., Dalamaga, M., and Liatis, S. (2023). Update on the obesity epidemic: after the sudden rise, is the upward trajectory beginning to flatten? Curr. Obes. Rep. 12 (4), 514–527. doi:10.1007/s13679-023-00527-y
Landecho, M. F., Tuero, C., Valentí, V., Bilbao, I., De La Higuera, M., and Frühbeck, G. (2019). Relevance of leptin and other adipokines in obesity-associated cardiovascular risk. Nutrients 11 (11), 2664. doi:10.3390/nu11112664
Lee, J. Y., Jang, B. K., Song, M. K., Kim, H. S., and Kim, M.-K. (2017). Association between serum dipeptidyl peptidase-4 concentration and obesity-related factors in health screen examinees. J. Obes. and Metabolic Syndrome 26 (3), 188–196. doi:10.7570/jomes.2017.26.3.188
Leiria, L. O. S., Martins, M. A., and Saad, M. J. A. (2015). Obesity and asthma: beyond T(H)2 inflammation. Metabolism Clin. Exp. 64 (2), 172–181. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2014.10.002
Lertnimitphun, P., Zhang, W., Fu, W., Yang, B., Zheng, C., Yuan, M., et al. (2021). Safranal alleviated OVA-induced asthma model and inhibits mast cell activation. Front. Immunol. 12, 585595. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.585595
Li, M.-D. (2011). Leptin and beyond: an odyssey to the central control of body weight. Yale J. Biol. Med. 84 (1), 1–7.
Li, Z., Leynaert, B., Dumas, O., Diaz Gil, O., Garcia-Aymerich, J., Fito Colomer, M., et al. (2019). Role of leptin in the association between body adiposity and persistent asthma: a longitudinal study. Obes. (Silver Spring, Md) 27 (6), 894–898. doi:10.1002/oby.22466
Liang, W., Qi, Y., Yi, H., Mao, C., Meng, Q., Wang, H., et al. (2022). The roles of adipose tissue macrophages in human disease. Front. Immunol. 13, 908749. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.908749
Lin, X., and Li, H. (2021). Obesity: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 706978. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021
Ma, C., Wang, Y., and Xue, M. (2019). Correlations of severity of asthma in children with body mass index, adiponectin and leptin. J. Clin. Laboratory Analysis 33 (6), e22915. doi:10.1002/jcla.22915
Magdy, A., Sadaka, E., Hanafy, N., El-Magd, M. A., Allahloubi, N., and El Kemary, M. (2020). Green tea ameliorates the side effects of the silver nanoparticles treatment of Ehrlich ascites tumor in mice. Mol. and Cell. Toxicol. 16 (3), 271–282. doi:10.1007/s13273-020-00078-6
Marko, M., and Pawliczak, R. (2018a). Obesity and asthma: risk, control and treatment. Adv. Dermatology Allergology/Postȩpy Dermatologii i Alergologii 35 (6), 563–571. doi:10.5114/ada.2018.77607
Marko, M., and Pawliczak, R. (2018b). Obesity and asthma: risk, control and treatment. Adv. Dermatology Allergology/Postȩpy Dermatologii i Alergologii 35 (6), 563–571. doi:10.5114/ada.2018.77607
Martelli, D., and Brooks, V. L. (2023). Leptin increases: physiological roles in the control of sympathetic nerve activity, energy balance, and the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (3), 2684. doi:10.3390/ijms24032684
Martín, A. I., Gómez-SanMiguel, A. B., Priego, T., and López-Calderón, A. (2018). Formoterol treatment prevents the effects of endotoxin on muscle TNF/NF-kB, Akt/mTOR, and proteolytic pathways in a rat model. Role of IGF-I and miRNA 29b. Am. J. Physiology. Endocrinol. Metabolism 315 (4), E705–E714. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00043.2018
Michelini, S., Chiurazzi, P., Marino, V., Dell’Orco, D., Manara, E., Baglivo, M., et al. (2020). Aldo-keto reductase 1C1 (AKR1C1) as the first mutated gene in a family with nonsyndromic primary lipedema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (17), 6264. doi:10.3390/ijms21176264
Mohamed, A. E., El-Magd, M. A., El-Said, K. S., El-Sharnouby, M., Tousson, E. M., and Salama, A. F. (2021). Potential therapeutic effect of thymoquinone and/or bee pollen on fluvastatin-induced hepatitis in rats. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 15688. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-95342-7
Mohammed, H. A. E.-M., Hassan, M. H., Abdalla, H., Mahmoud, M. A., Maher, A., Malak, M., et al. (2023). Body mass index as a major prognostic contributing factor in COVID-19: a multicentral Egyptian study. Infect. Drug Resist. 16, 5985–6004. doi:10.2147/IDR.S426440
Ngala, R. A., Awe, M. A., and Nsiah, P. (2018). The effects of plasma chromium on lipid profile, glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus. A case—control study. PLoS ONE 13 (7), e0197977. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0197977
Nystad, W., Meyer, H. E., Nafstad, P., Tverdal, A., and Engeland, A. (2004). Body mass index in relation to adult asthma among 135,000 Norwegian men and women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 160 (10), 969–976. doi:10.1093/aje/kwh303
Obradovic, M., Sudar-Milovanovic, E., Soskic, S., Essack, M., Arya, S., Stewart, A. J., et al. (2021). Leptin and obesity: role and clinical implication. Front. Endocrinol. 12, 585887. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.585887
Pala, R., Sari, M. A., Erten, F., Er, B., Tuzcu, M., Orhan, C., et al. (2020). The effects of chromium picolinate on glucose and lipid metabolism in running rats. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 58, 126434. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.126434
Palma, G., Sorice, G. P., Genchi, V. A., Giordano, F., Caccioppoli, C., D’Oria, R., et al. (2022a). Adipose tissue inflammation and pulmonary dysfunction in obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (13), 7349. doi:10.3390/ijms23137349
Palma, G., Sorice, G. P., Genchi, V. A., Giordano, F., Caccioppoli, C., D’Oria, R., et al. (2022b). Adipose tissue inflammation and pulmonary dysfunction in obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (13), 7349. doi:10.3390/ijms23137349
Pauwels, R. A., Sears, M. R., Campbell, M., Villasante, C., Huang, S., Lindh, A., et al. (2003). Formoterol as relief medication in asthma: a worldwide safety and effectiveness trial. Eur. Respir. J. 22 (5), 787–794. doi:10.1183/09031936.03.00055803
Peters, U., Dixon, A. E., and Forno, E. (2018). Obesity and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 141 (4), 1169–1179. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.004
Petrie, J. R., Guzik, T. J., and Touyz, R. M. (2018). Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: clinical insights and vascular mechanisms. Can. J. Cardiol. 34 (5), 575–584. doi:10.1016/j.cjca.2017.12.005
Piché, M.-E., Tchernof, A., and Després, J.-P. (2020). Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circulation Res. 126 (11), 1477–1500. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316101
Rajesh, V., Augustine, J., Divya, R., and Cleetus, M. (2020). Inhaled formoterol-fluticasone single inhaler therapy in asthma: real-world efficacy, budget impact, and potential to improve adherence. Can. Respir. J. 2020, 8631316. doi:10.1155/2020/8631316
Reddel, H. K., Bacharier, L. B., Bateman, E. D., Brightling, C. E., Brusselle, G. G., Buhl, R., et al. (2022). Global initiative for asthma strategy 2021. Executive summary and rationale for key changes. Arch. Bronconeumología 58 (1), 35–51. doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2021.10.003
Reddel, H. K., Brusselle, G., Lamarca, R., Gustafson, P., Anderson, G. P., and Jorup, C. (2023). Safety and effectiveness of as-needed formoterol in asthma patients taking inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)-Formoterol or ICS-salmeterol maintenance therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 11 (7), 2104–2114.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2023.03.046
Reyes Noriega, N., Del-Río-Navarro, B. E., Berber, A., de Jesús Romero Tapia, S., and Molina Díaz, D. J. M. (2023). Effect of obesity on lung function in the pediatric and adult populations with asthma: a review. J. Clin. Med. 12 (16), 5385. doi:10.3390/jcm12165385
Rodrigo, G. J., Neffen, H., Colodenco, F. D., and Castro-Rodriguez, J. A. (2010). Formoterol for acute asthma in the emergency department: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann. Allergy, Asthma and Immunol. Official Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy, Asthma, and Immunol. 104 (3), 247–252. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2009.11.064
Rogero, M. M., and Calder, P. C. (2018). Obesity, inflammation, toll-like receptor 4 and fatty acids. Nutrients 10 (4), 432. doi:10.3390/nu10040432
Rupani, H., Fong, W. C. G., Kyyaly, A., and Kurukulaaratchy, R. J. (2021). Recent insights into the management of inflammation in asthma. J. Inflamm. Res. 14, 4371–4397. doi:10.2147/JIR.S295038
Salas-Venegas, V., Flores-Torres, R. P., Rodríguez-Cortés, Y. M., Rodríguez-Retana, D., Ramírez-Carreto, R. J., Concepción-Carrillo, L. E., et al. (2022). The obese brain: mechanisms of systemic and local inflammation, and interventions to reverse the cognitive deficit. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 16, 798995. doi:10.3389/fnint.2022.798995
Scott, H. A., Gibson, P. G., Garg, M. L., and Wood, L. G. (2011). Airway inflammation is augmented by obesity and fatty acids in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 38 (3), 594–602. doi:10.1183/09031936.00139810
Shaban, A. M., Raslan, M., Sharawi, Z. W., Abdelhameed, M. S., Hammouda, O., El-Masry, H. M., et al. (2023). Antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer effects of camel milk exosomes: an in vitro study. Veterinary Sci. 10 (2), 124. doi:10.3390/vetsci10020124
Shailesh, H., and Janahi, I. A. (2022). Role of obesity in inflammation and remodeling of asthmatic airway. Life 12 (7), 948. Article 7. doi:10.3390/life12070948
Shou, Q., Lang, J., Jin, L., Fang, M., Cao, B., Cai, Y., et al. (2019). Total glucosides of peony improve ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma by inhibiting mast cell degranulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 244, 112136. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.112136
Showalter, M. R., Nonnecke, E. B., Linderholm, A. L., Cajka, T., Sa, M. R., Lönnerdal, B., et al. (2018). Obesogenic diets alter metabolism in mice. PLOS ONE 13 (1), e0190632. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0190632
Sikorska-Szaflik, H., Połomska, J., and Sozańska, B. (2022). The impact of dietary intervention in obese children on asthma prevention and control. Nutrients 14 (20), 4322. doi:10.3390/nu14204322
Silha, J. V., Krsek, M., Skrha, J. V., Sucharda, P., Nyomba, B. L. G., and Murphy, L. J. (2003). Plasma resistin, adiponectin and leptin levels in lean and obese subjects: correlations with insulin resistance. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 149 (4), 331–335. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1490331
Smith, J. D., Fu, E., and Kobayashi, M. (2020). Prevention and management of childhood obesity and its psychological and health comorbidities. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 16, 351–378. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-100219-060201
Stover, P. J., Field, M. S., Andermann, M. L., Bailey, R. L., Batterham, R. L., Cauffman, E., et al. (2023). Neurobiology of eating behavior, nutrition, and health. J. Intern. Med. 294 (5), 582–604. doi:10.1111/joim.13699
Tabas, I., and Lichtman, A. H. (2017). Monocyte-Macrophages and T Cells in atherosclerosis. Immunity 47 (4), 621–634. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.09.008
Tashkin, D. P. (2020). Formoterol for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 15, 3105–3122. doi:10.2147/COPD.S273497
Tchang, B. G., Aras, M., Kumar, R. B., and Aronne, L. J. (2000). “Pharmacologic treatment of overweight and obesity in adults,” in Endotext. MDText. Editors K. R. Feingold, B. Anawalt, M. R. Blackman, A. Boyce, G. Chrousos, E. Corpaset al. (South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279038/
Tenório, L. H. S., Vieira, F. C., de Souza, H. C. M., de Andrade, A. de F. D., de Lorena, V. M. B., Medeiros, D., et al. (2021). Respiratory burden in obese and young asthmatics: a study of diaphragmatic kinetics. J. Bras. Pneumol. 47 (5), e20210166. doi:10.36416/1806-3756/e20210166
Tiwari, A., and Balasundaram, P. (2024). “Public health considerations regarding obesity,” in StatPearls (Treasure Island (FL) StatPearls Publishing). Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572122/.
Ukena, D., Fishman, L., and Niebling, W.-B. (2008). Bronchial asthma: diagnosis and long-term treatment in adults. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 105 (21), 385–394. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2008.0385
Wang, Y., and Hu, C. (2022a). Leptin and asthma: what are the interactive correlations? Biomolecules 12 (12), 1780. doi:10.3390/biom12121780
Wang, Y., and Hu, C. (2022b). Leptin and asthma: what are the interactive correlations? Biomolecules 12 (12), 1780. doi:10.3390/biom12121780
Wu, Z., Mehrabi Nasab, E., Arora, P., and Athari, S. S. (2022). Study effect of probiotics and prebiotics on treatment of OVA-LPS-induced of allergic asthma inflammation and pneumonia by regulating the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. J. Transl. Med. 20 (1), 130. doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03337-3
Yamamoto, M., Gohda, J., Akiyama, T., and Inoue, J. (2021). TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) plays crucial roles in multiple biological systems through polyubiquitination-mediated NF-κB activation. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 97 (4), 145–160. doi:10.2183/pjab.97.009
Yamano, S., Takeda, T., Goto, Y., Hirai, S., Furukawa, Y., Kikuchi, Y., et al. (2023). Mechanisms of pulmonary disease in F344 rats after workplace-relevant inhalation exposure to cross-linked water-soluble acrylic acid polymers. Respir. Res. 24, 47. doi:10.1186/s12931-023-02355-z
Yuan, Y., Ran, N., Xiong, L., Wang, G., Guan, X., Wang, Z., et al. (2018a). Obesity-related asthma: immune regulation and potential targeted therapies. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 1943497. doi:10.1155/2018/1943497
Yuan, Y., Ran, N., Xiong, L., Wang, G., Guan, X., Wang, Z., et al. (2018b). Obesity-related asthma: immune regulation and potential targeted therapies. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 1943497–1943513. doi:10.1155/2018/1943497
Zainal, Z., Abdul Rahim, A., Khaza’ai, H., and Chang, S. K. (2019). Effects of palm oil tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF) and carotenes in ovalbumin (OVA)-Challenged asthmatic Brown Norway rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (7), 1764. doi:10.3390/ijms20071764
Zedan, A. M., Sakran, M. I., Bahattab, O., Hawsawi, Y. M., Al-Amer, O., Oyouni, A. A., et al. (2021). Oriental Hornet (Vespa orientalis) larval extracts induce antiproliferative, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-migratory effects on MCF7 Cells. Molecules 26 (11), 3303. doi:10.3390/molecules26113303
Zhang, X., Che, L., Shan, J., Wang, Y., Jia, Y., and Wu, H. (2022). The effects of Formoterol in preventing adipogenesis and obesity are mediated by PPARγ/C/EBPα axis and AMPK/PGC-1α pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., zbac103. doi:10.1093/bbb/zbac103
Zhao, S., Kusminski, C. M., and Scherer, P. E. (2021). Adiponectin, leptin and cardiovascular disorders. Circulation Res. 128 (1), 136–149. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.314458
Zhou, C., Wang, M., Liang, J., He, G., and Chen, N. (2022). Ketogenic diet benefits to weight loss, glycemic control, and lipid profiles in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (16), 10429. doi:10.3390/ijerph191610429
Keywords: chromium, formoterol, asthma, obesity, inflammatory markers, lipid profile
Citation: Ibrahim RT, Moustafa YM, Alwaili MA, Alrebdi AN, Alharthi A, Noufal NR and Khodeer DM (2025) Chromium and formoterol therapy for obesity-induced asthma in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1537022. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1537022
Received: 29 November 2024; Accepted: 06 February 2025;
Published: 02 April 2025.
Edited by:
Mohamed Abdo Rizk, Mansoura University, EgyptReviewed by:
Mohammed Abu El-Magd, Kafrelsheikh University, EgyptCopyright © 2025 Ibrahim, Moustafa, Alwaili, Alrebdi, Alharthi, Noufal and Khodeer. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dina M. Khodeer, ZGluYV9raG91ZGFlckBwaGFybS5zdWV6LmVkdS5lZw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.