
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol., 17 March 2025
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1528919
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by memory decline, cognitive impairment, and behavioral abnormalities. Pathologically, AD is marked by neurofibrillary tangles caused by excessive phosphorylation of Tau protein and abnormal deposition of β-amyloid (Aβ) in the brain. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the development, survival, and metabolic regulation of the central nervous system, particularly in neuronal growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. However, this pathway is often inhibited in AD patients.In recent years, studies have shown that herbal formulations and extracts derived from Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) can regulate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby improving AD pathological models. This study reviews fundamental research on both active metabolites and compound formulations from TCM for the treatment of AD, targeting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Keywords include “Alzheimer’s disease” “AD” “dementia” “PI3K” “AKT” “Traditional Chinese Medicine” “Chinese herbology” “Chinese medicine” and “TCM”.The study is based on relevant literature published over the past 15 years, primarily sourced from electronic databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP databases.The findings indicate that herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM can mitigate AD pathology by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, reducing Tau protein phosphorylation and Aβ deposition, inhibiting inflammatory responses and oxidative stress, and alleviating neuronal apoptosis. This study enhances our understanding of the anti-AD mechanisms of TCM through the PI3K/AKT pathway and offers new insights for the future.
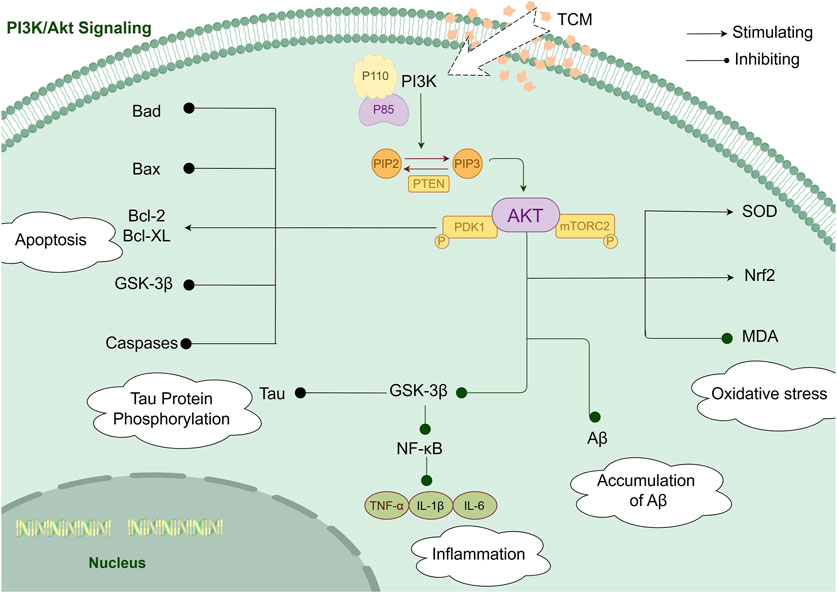
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT | The diagram illustrates how herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM exert potential effects on AD through modulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Various bioactive compounds present in these formulations and extracts have been reported to influence multiple pathological mechanisms associated with AD, including cell apoptosis, Tau protein phosphorylation, oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and Aβ deposition.While these findings suggest a mechanistic basis for the potential effects of TCM-derived formulations and extracts in AD, further well-designed pharmacological and clinical studies are required to confirm their efficacy and elucidate their precise molecular targets.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by an insidious onset and progressive cognitive impairment. With the aging population in China, even in the world, the incidence of AD continues to rise. Currently, there are 15.07 million dementia patients aged 60 and above in China, of which 9.83 million suffer from AD (R et al., 2022). AD has become a major medical and social issue. The neuropathological hallmarks of AD include extracellular deposits of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) composed of aggregated and hyperphosphorylated Tau protein (AuthorAnonymous, 2023). The pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease is shown in Figure 1. Various signaling pathways are involved in the pathological processes of AD, with the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathway playing a critical role in the central nervous system, including functions such as cell survival, autophagy, neurogenesis, neuronal proliferation and differentiation, and synaptic plasticity. It is especially closely related to AD pathological processes like Tau protein phosphorylation and apoptosis, making it a key pathway in AD treatment (Manish Kumar and Bansal, 2022). Multiple studies have shown that activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway has a positive effect on AD treatment.
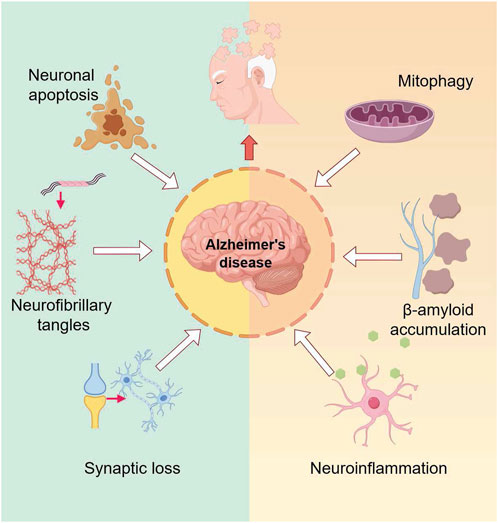
Figure 1. The pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. The diagram illustrates the multifactorial pathogenic mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease, including neuronal apoptosis, neurofibrillary tangle formation due to excessive tau protein phosphorylation, Aβ deposition, synaptic loss, neuroinflammation, and mitophagy.
The activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway begins with the binding of insulin to the insulin receptor (IR). Its numerous downstream targets, including AKT, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and Bad, play roles in promoting cell survival, proliferation, growth, and metabolic pathway changes. This pathway serves as a critical drug target for various AD-related pathogenic factors, including aging, abnormal glucose metabolism, Aβ deposition, synaptic dysfunction, and neuronal apoptosis (Seidler and Barrow, 2022; Zhang et al., 2021). Activation of this pathway can help alleviate oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, reduce Aβ aggregation and NFT formation, and block the pathogenesis of AD. A growing number of natural products, as well as synthetic and semi-synthetic molecules, have been found to mitigate AD pathology by modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway (Kumar and Bansal, 2022; Huang et al., 2018).
In recent years, an increasing number of studies have suggested that certain herbal formulations and extracts derived from Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) may influence the pathological processes of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by modulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. These studies have reported that some bioactive compounds exhibit potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, inhibit apoptosis, and alleviate oxidative stress. However, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying these effects require further investigation.A deeper exploration of how TCM-derived active compounds or extracts regulate AD-related pathological changes through the PI3K/AKT pathway could contribute to a better understanding of their potential mechanisms and provide new research directions for AD treatment. This review encompasses experimental research on TCM-related formulations and extracts in regulating AD via the PI3K/AKT pathway. It explores the proposed mechanisms, assesses available evidence on their efficacy, and discusses future research directions.”
This review used the Web of Science, PubMed, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP databases as data sources. The keywords included “Alzheimer’s disease” “AD” “dementia” “PI3K” “AKT” “Traditional Chinese Medicine” “Chinese herbology” “Chinese medicine” and “TCM” The search period was from January 2010 to January 2025.
Apoptosis is a cell death mechanism that regulates neuronal development, characterized by DNA fragmentation and the loss of mitochondrial membrane integrity (Gupta et al., 2023; Fleisher, 1997). It has been reported that neuronal loss in AD exhibits characteristics of apoptosis, pyroptosis (programmed necrosis), or necroptosis. Extensive neuronal loss, attributed to apoptosis, is closely related to the progression of AD (Sharma et al., 2021). The degree of neuronal loss worsens with the severity and duration of the disease. The extrinsic and intrinsic pathways are the main executors of apoptosis in mammalian cells, with caspases being the primary enzymes involved. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulates apoptosis by modulating caspase-3 activity (VK et al., 2021). Activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway can counteract neuronal apoptosis (Khezri et al., 2023). Activated AKT promotes the phosphorylation of Bad at the serine 136 site. When Bad is poorly phosphorylated, it translocates to the mitochondrial outer membrane, inactivating anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins like Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL, thereby triggering mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2021; Cheng et al., 2020). Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) is also involved in activating caspase-2 and caspase-8, which can induce the cleavage of Bid (Bcl-2 homology three interacting domain death agonist) and the release of cytochrome C, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis (Lin et al., 2016; Kumari et al., 2023). Furthermore, GSK-3β can promote the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by increasing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, contributing to neurodegenerative diseases (Toral-Rios et al., 2020).
Studies have reported that Shenqi Pill may help mitigate learning and memory impairments, pathological damage, and cell apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) rat models. This effects are associated with increased expression of Bcl-2, PI3K, PDK1, P-AKT, and GSK-3β, along with decreased phosphorylation levels of Bax and Caspase-3 (Huang JHJ. et al., 2022). Similarly, Dabu Yuanjian has been observed to enhance cognitive function in AD rat models, potentially by upregulating Bcl-2, P-AKT, and P-GSK-3β, while decreasing Caspase-3 expression. Transmission electron microscopy findings suggest treatment with Dabu Yuanjian may alleviate myelin-like changes and mitochondrial swelling in the hippocampus of AD rat models (Xi et al., 2022). Modulated Shuyu Pill-containing serum has been found to a reduction in the levels of the phosphorylated α-subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (p-eIF2α/eIF2α) in the apoptosis-related pathway in primary neurons of APP/PS1 mice, effectively increased the expression of P-AKT/AKT and Nrf2, and mitigating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal apoptosis (Jing et al., 2019). Metabolites Danshen, composed of Danshen, Panax notoginseng, and Borneol, has been reported to inhibit Bad expression and increase P-AKT expression, providing protective effects for hippocampal neurons in AD mouse models (Liang et al., 2018).Polygala saponins, active metabolites of Polygala, have also been investigated. Junping Wang and colleagues found that Polygala saponins combined with β-asarone enhanced cell viability in AD cell model, increased AKT expression, inhibited GSK-3β activation, and reduced apoptosis rates (Junping et al., 2018). Forsythoside A, a phenylethanoid glycoside isolated from the dried fruit of Forsythia (Qu et al., 2012), was shown by Chunyue Wang and colleagues to improve cell viability in AD models, reduce apoptosis rates, and downregulate caspase-3, -8, and -9 levels (Wang H. C. et al., 2020).Aconitine, a key active component of Aconitum, has pharmacological effects such as cardiotonic, analgesic, antitumor, and immune-modulatory properties (Xiu et al., 2019). Weizhi Quan and colleagues observed that aconitine could reduce apoptosis rates and GSK-3β expression in AD cell models (Zhi-quan et al., 2021). Hydroxy-α-sanshool, the main active component of Sichuan pepper, is the most abundant amide metabolite in the plant and has been shown to improve learning and memory (Khoshsirat et al., 2019). Ruolan Li and colleagues found that hydroxy-α-sanshool increased the expression of P-AKT, P-PI3K, AKT, and Bcl-2 in AD cell models, while reducing the expression of caspase-3 and Bax, thus alleviating apoptosis (Lan, 2021).Lastly, crocetin has been observed to significantly increase the expression levels of PI3K, Akt, and Bcl-2 proteins and mRNA in hippocampal neuron models of AD induced by Aβ25-35, while decreasing the expression of Bax protein and mRNA, thereby inhibiting apoptosis and protecting hippocampal neurons (Yan Y. et al., 2020).
Tau protein is a microtubule-associated protein widely expressed in the nervous system. Under pathological conditions, abnormal post-translational modifications of Tau, primarily hyperphosphorylation, reduce its ability to bind to microtubules. This leads to a conformational change in Tau from its natural unfolded state to paired helical filaments and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) (Ossenkoppele et al., 2022; Chu et al., 2024). NFTs are a hallmark and definitive evidence of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology, and their presence is positively correlated with cognitive impairment (Ashton et al., 2021; Naseri et al., 2019). Dysregulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is a major factor in Tau hyperphosphorylation. Overexpression of AKT can significantly reverse Aβ-induced Tau phosphorylation, while excessive activation of GSK-3β is also closely related to Tau hyperphosphorylation (Shi et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2013). Dysregulation of PI3K/AKT signaling leads to increased GSK-3β activity and decreased PP2A activity, which contributes to tau hyperphosphorylation and the formation of NFTs (Yang et al., 2014).GSK-3β can phosphorylate Tau at multiple residue sites. Studies have shown that after transfecting GSK-3β into rat brains, increased GSK-3β expression and abnormal Tau phosphorylation were detected, with Tau hyperphosphorylation co-localizing with GSK-3β, suggesting that GSK-3β-induced Tau hyperphosphorylation is involved in the mechanism of neurodegenerative diseases (Wang et al., 2013). Autopsies of AD patients revealed reduced PI3K/AKT signaling activity in the frontal cortex, along with elevated levels of phosphorylated GSK-3β and abnormally hyperphosphorylated Tau (Ochiai et al., 2021).
Studies have demonstrated that the TCM formula Jinsiwei(GAPT) exhibited the ability to improve learning and memory abilities in APP/PS1 Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mouse models by reducing the expression of phosphorylated Tau (P-Tau) and increasing the expression of P-AKT and P-AKT/AKT (Li, 2017; Zhuo, 2022). Yuanzhi Powder has been shown to decrease the expression of P-Tau (Ser199)/Tau5 and P-Tau (Thr231)/Tau5 in the hippocampus of AD rat models, while increasing the expression of P-AKT/AKT and P-GSK-3β/GSK-3β (Peijun et al., 2020). Xiaoyao Powder decreases GSK-3β expression in AD mouse models, thereby inhibiting Tau hyperphosphorylation (Wei-Xian et al., 2014).Litchi seed polyphenols, derived from litchi seeds, have been reported by Rui Xiong et al. to inhibit the expression of P-IRS-1 (Ser612) in AD cell models, restore the expression of P-PI3K (Tyr199/Tyr458), P-AKT (Thr308), and P-GSK-3β (Ser9), and ultimately suppress Tau hyperphosphorylation (Xiong et al., 2020). Curcuma aromatica volatile oil, an active component from the dried roots of Curcuma aromatica, significantly reduces the phosphorylation levels of Tau protein (Thr231, Ser404) in AD mouse models, while increasing the expression of P-PI3K/PI3K and P-AKT/AKT, as shown by Qi Yue et al. (Yue et al., 2017).Paeoniflorin, the main bioactive component of Paeonia and a monoterpene glycoside, has beneficial effects on neurodegenerative diseases (Chao-fang et al., 2023). Research by Xiao-Hui Ma showed that paeoniflorin improves morphological changes in AD cell models, such as reducing cell swelling and synaptic shrinkage, this is achieved by lowering Tau phosphorylation levels, increasing AKT and GSK-3β phosphorylation levels, and stabilizing microtubule structures (Ma et al., 2018). In APP/PS1 AD mouse models, Forsythoside A has been reported to enhance memory and cognitive abilities, reduces Aβ plaque deposition in the brain, and inhibits Tau protein phosphorylation (Wang C. et al., 2020).Osthole, a coumarin metabolites extracted from Cnidium monnieri, was found by Ni Yingnan and colleagues to reduce the expression of P-Tau (Ser202), effectively enhances PI3K, P-AKT/AKT, and P-GSK-3β/GSK-3β expression, and alleviate cognitive dysfunction in AD mouse models (Ying-nan et al., 2019).
Neuroinflammation refers to the complex immune response of the central nervous system (CNS) to various endogenous or exogenous stimuli, such as misfolded proteins, toxins, and pathogens. This process leads to the infiltration of inflammatory cells, gliosis, and neuronal loss in brain tissue (Stephenson et al., 2018). Aging-induced neuroinflammatory responses play a crucial role in the onset and progression of AD (Calsolaro and Edison, 2016; Leclerc et al., 2023). Persistent neuroinflammation in the CNS causes chronic microglial activation, which releases inflammatory mediators and initiates an inflammatory response. This chronic inflammation eventually results in neuronal death and cognitive dysfunction (Wang Y. et al., 2024). Microglial activation and the inflammatory cascade mediated by pro-inflammatory factors are fundamental mechanisms in AD pathogenesis (Wang et al., 2022a). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), play a central role in AD. Studies have shown that the levels of TNF-α are significantly elevated in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of AD patients (Decourt et al., 2016).In animal models of brain diseases, including AD, upregulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway can inhibit downstream targets such as nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) (Yang et al., 2020), which leads to a reduction in the gene expression and activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α (Bathina et al., 2020). Conversely, the crosstalk between GSK-3β and NF-κB can increase the expression of pro-inflammatory chemokines and apoptotic factors, ultimately causing severe neurodegeneration. This interplay between inflammatory pathways and PI3K/AKT signaling highlights the critical role of neuroinflammation in AD pathology and provides a therapeutic target for modulating inflammation in AD treatment (Shih et al., 2015).
Schisandrin and nootkatone, active metabolites of Schisandra chinensis and Alpinia oxyphylla, respectively, have been shown to significantly increase the expression of P-PI3K/PI3K, P-AKT/AKT, and P-GSK-3β/GSK-3β in Aβ1-42-induced AD cell models. These metabolites also reduce the expression of inflammation-related proteins, such as NF-κB, inhibitor of kappa B kinase (IKK), IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α (Qi et al., 2020). Tanshinone, a primary active metabolite in Salvia miltiorrhiza (derived from Danshen), has been found to lower the levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and P-NF-κB/NF-κB in the brain tissue of AD mouse model, while increasing the expression of BDNF, P-PI3K/PI3K, and P-AKT/AKT, thereby improving cognitive function (Yi et al., 2021). Gardenia has been shown to effectively lower the expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-1β in the 3×Tg-AD mouse model (Meng, 2018). Additionally, the modified formula San Jia San is capable of alleviating neuroinflammation in AD cell models by downregulating PI3K, P-AKT, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, while upregulating anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 (Miao, 2018).
Oxidative stress is the result of an imbalance between pro-oxidants and antioxidants in the body, leading to mitochondrial damage and dysfunction. Mitochondrial dysfunction, in turn, causes the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and exacerbates oxidative stress, ultimately resulting in age-related neurodegenerative diseases (Bai et al., 2022). The oxidants and oxidative products generated under oxidative stress can increase the expression of amyloid precursor protein (APP), leading to the aggregation of Aβ (Tamagno et al., 2012). Aβ itself can promote the increase of ROS and induce the occurrence of oxidative stress (Ill-Raga et al., 2010). The inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway can trigger insulin resistance, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and the subsequent surge of various types of free radicals. Conversely, the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway can inhibit oxidative stress by enhancing the expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Jiang et al., 2015). Research has shown that the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway enhances the antioxidant pathway of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) (Zhang et al., 2019), which is the main regulatory factor for antioxidants (Bahn and DG, 2019). Due to the impairment of the PI3K/AKT pathway, the unregulated activity of GSK-3β accelerates the biosynthesis of free radicals (Kanninen et al., 2011). The activity of GSK-3β enhances oxidative stress (Koundouros and Poulogiannis, 2018). By upregulating the expression and activity of eNOS in the PI3K/AKT pathway in the brains of rats, levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) decreased, while reduced glutathione (GSH) levels and SOD activity increased, significantly improving the memory of the rats (Xu et al., 2015).
Research conducted by Ma Tao and colleagues found that administering a decoction of Rehmannia to APPsw/PS1ΔE9 AD mouse models, the latency to enter a dark room was prolonged, the number of errors decreased, and the expression levels of SOD, GSH-PX, P-AKT, and P-GSK-3β effectively increased (Tao et al., 2014). Research by Qiu Jing and colleagues reported that the intervention of Jiajian Shuyu Pills improved the learning and memory abilities of APP/PS1 AD mouse models improved significantly, with a notable increase in the expression levels of Nrf2 in the hippocampus (Jing et al., 2019). Deer antler peptides, one of the main active metabolites of deer antlers, are composed of various amino acids and have a significant role in promoting neuronal regeneration. Studies have shown that deer antler peptides have the potential to enhance the expression levels of SOD, GSH-PX, PI3K, and AKT in AD cell models while reducing the expression levels of MDA (Xin, 2021). The Bushen Jianpi Kai Xin Decoction has also been demonstrated to significantly increase the expression of SOD in D-galactose + Aβ1-42 induced AD rat models, reduce the expression of NOS, and improve oxidative stress levels (Rong, 2018). These processes are inherently connected to the PI3K/AKT signaling cascade.
Accumulation of Aβ is a key early pathophysiological event in AD, leading to neurodegeneration and cognitive impairment by inducing abnormal accumulation of tau protein (Walsh and DJ, 2007; Selkoe and J, 2016). Excessive accumulation of Aβ in the brain can trigger various pathological changes, including neuronal degeneration and apoptosis caused by the inactivation of AKT (Zeng et al., 2016). Aggregated Aβ induces tau hyperphosphorylation by enhancing the activity of GSK-3β and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK-5) (Terwel et al., 2008). Multiple studies have shown that Aβ plaques downregulate several neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), negatively regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway, resulting in significant cognitive impairment (Chen et al., 2009; Garabadu and J, 2019). The activation of the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway can trigger protective factors against Aβ neurotoxicity (Yin et al., 2011). The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is involved in autophagy induced by Aβ25-35 and is highly correlated with Aβ clearance mediated by autophagy. Activation of PI3K/AKT can offset the neuronal effects induced by Aβ by influencing Aβ production/clearance and cell death (Sofola et al., 2012; Sánchez-Alegría et al., 2018; Sotolongo et al., 2020). GSK-3β plays an important role in the mechanism of amyloidosis in AD. GSK-3 alters Aβ levels by regulating APP processing (Phiel et al., 2003; Rockenstein et al., 2007). In the familial AD (FAD) 5 × FAD mouse model, increased expression of GSK-3 (α/β) isoforms hinders Aβ clearance in the brain, leading to increased Aβ plaque deposition and memory deficits (Avrahami et al., 2013).
Research has indicated that the Yifei Wenyang Huazhuo Decoction tends to reduce Aβ levels in the neurons of AD rat models, lowering the expression levels of PI3K and AKT (Jinping et al., 2019). Puerarin, a bioactive isoflavone glycoside extracted from Pueraria, has been observed to exert neuroprotective effects in AD through various mechanisms (Haixia et al., 2023). Mei Zhengrong and colleagues found that puerarin exhibits the ability to improve learning and memory deficits in APP/PS1 AD mouse models by reducing Aβ production and increasing P-GSK-3β expression (Zheng-rong et al., 2016). Cui-Zhu Yang and colleagues found that Astragaloside enhances cognitive function in APP/PS1 AD mouse models by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, reducing hippocampal neuronal damage, and alleviating Aβ pathology (Yang et al., 2023). Curcumin, a lipophilic phenolic pigment extracted from the rhizome of turmeric, is the main active component of turmeric (Wei-wei et al., 2024). Wang Chen’s research found that curcumin treatment improved cognitive dysfunction in AD mouse models, reducing the number of Aβ-positive cells in the hippocampus as well as the expression of PI3K, AKT, and mTOR (Chen, 2013). The essential oil of Acorus tatarinowii, obtained from the dried rhizome of the plant, combined with total ginsenosides from ginseng, has been demonstrated to increase the expression of P-AKT in AD mouse models while decreasing the expression of Aβ1-42 (Zhen, 2016). Ginsenosides are one of the main active metabolites of ginseng and have protective effects on the central nervous system (Jing et al., 2023). Ginsenoside CK has shown potential in reducing the extracellular Aβ levels in AD cell models while increasing the expression of PI3K, AKT, and P-AKT (Jia-nan et al., 2021). Research findings have shown that upregulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway eliminates Aβ plaque formation in transgenic Drosophila models of AD (Zhang et al., 2016).
TCM has a long-standing history in China, known for its therapeutic efficacy and minimal adverse reactions. In contrast to single-component drugs, herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM offers the advantage of multi-component, multi-pathway, and multi-target approaches, which makes it a promising candidate for treating complex chronic diseases such as AD. Studies have identified the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a key regulator of neuronal cell growth and survival. Several traditional Chinese herbal formulations, including Kaixin San, Dihuang Yinzi, and Liuwei Dihuang Wan (Table 1), as well as potent TCM metabolites like Cnidii Monnieri, ginsenosides, and paeoniflorin (Table 2), have demonstrated beneficial effects in AD models. Table 3 shown the classifications, botanical drug and family of anti-AD active ingredients of Chinese botanical drug. These findings suggest that herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM can potentially alleviate Aβ accumulation, inhibit tau hyperphosphorylation, reduce neuronal apoptosis, counteract neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, and enhance synaptic function by regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway, thus improving memory and cognitive function in AD. These results provide strong evidence supporting the effectiveness of herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM in AD treatment and emphasize the importance of targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway. Although significant progress has been made in the basic research on TCM for the treatment of AD, the complexity of its components and the unknown, intricate changes that occur in the body make the current research results speculative. Further in-depth investigation is needed to clarify the specific components and molecular mechanisms through which TCM intervenes in AD, in order to better understand its therapeutic effects and guide clinical applications. The following are some limitations in the research design of TCM for the treatment of AD, existing issues, and future research needs.
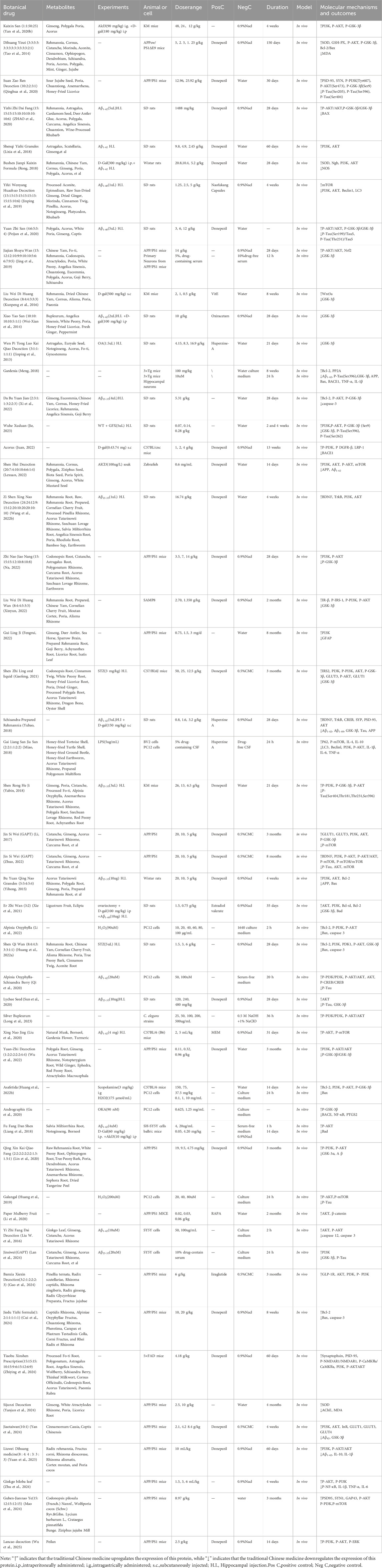
Table 1. Traditional Chinese botanical drugs for Treating Alzheimer’s Disease by Intervening in the PI3K/AKT Pathway.
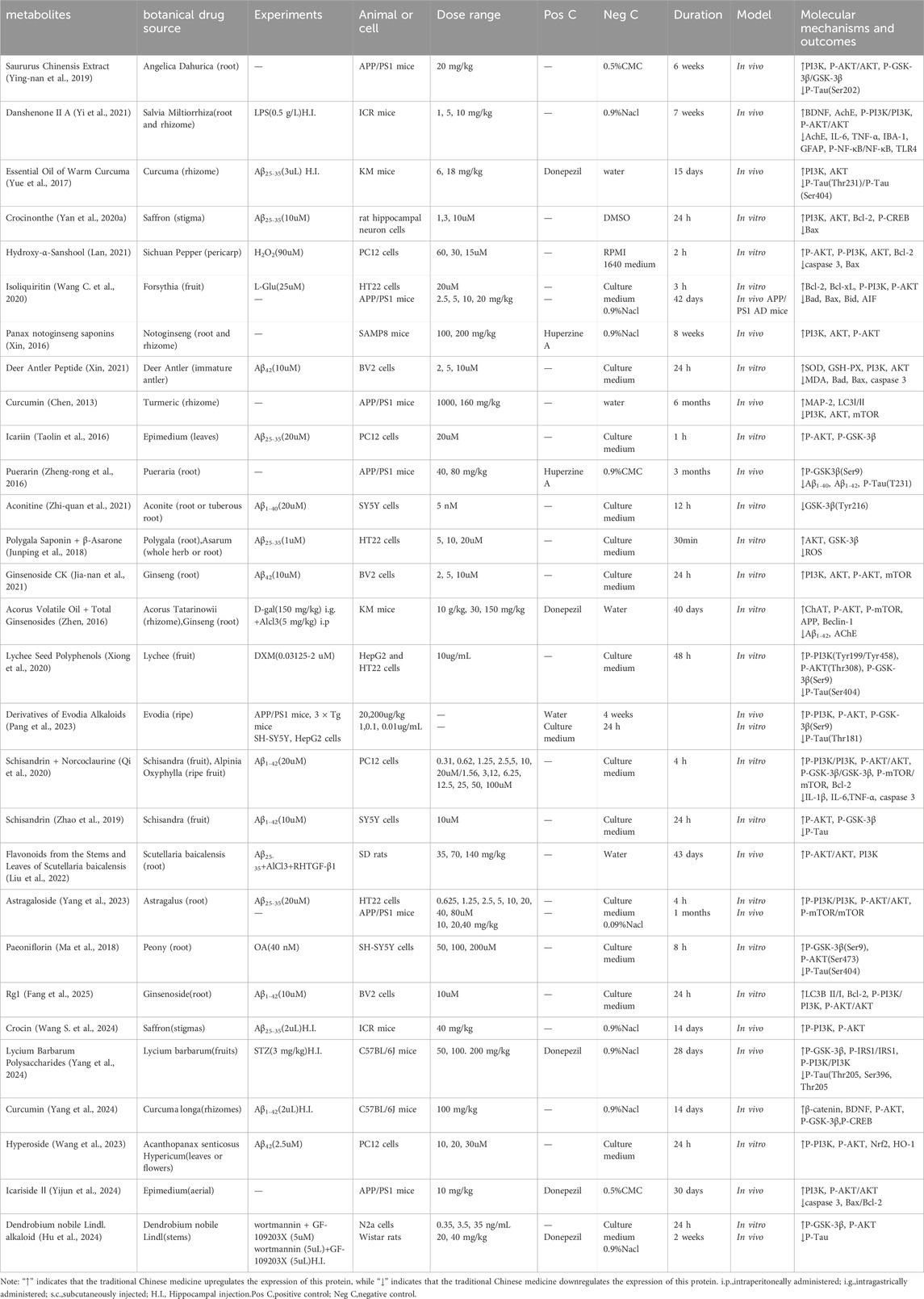
Table 2. Active metabolites of traditional Chinese medicine that intervene in the PI3K/AKT pathway for the treatment of AD.
Although herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM have demonstrated great potential in regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway for treating AD, corresponding clinical studies are still lacking, particularly those on individual Chinese herbal compounds. Additionally, in related experimental studies, some lack positive control drugs, some have undefined compositions or ratios of herbal formulas (with their components not yet disclosed), and others rely solely on in vitro experiments. More comprehensive in vivo studies are needed to simulate the complex environment within organisms, explore their mechanisms of action, and assess the efficacy and safety of long-term use of TCM components. The study of herbal formulas faces numerous challenges, such as the complexity of TCM components making it difficult to elucidate their mechanisms, as well as variability in sourcing, species, processing methods, and formulations that can affect reproducibility. In the future, standardization of formula preparation and use will need further development. Employing analytical approaches such as metabolomics and network pharmacology could facilitate higher-quality, more in-depth research.
Specific components of TCM regulate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway through multiple levels and targets, either directly or indirectly. This regulation involves activating upstream receptors, modulating key enzymes, and influencing downstream effector proteins (Kumar and Bansal, 2022). For example, icariin can enhance the expression of IGF and BDNF, thereby activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, inhibiting Aβ production and tau protein phosphorylation, and alleviating symptoms in AD animal models (Wang et al., 2012). Curcumin improves adult neurogenesis in AD mice by increasing BDNF expression and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway (Lou et al., 2024). The herbal formula Jin Siwei(GAPT) boosts glucose uptake in specific brain regions of AD mice, increases glucose transport, and repairs damaged PI3K/AKT signaling pathways (Li, 2017). Ginsenoside CK upregulates PI3K, AKT, and phosphorylated AKT in AD model cells (Jia-nan et al., 2021). Herbal formulation Erzhi Pill enhances the expression of Akt and PI3K, participating in the regulation of key enzymes within the PI3K/AKT pathway (Xie et al., 2021). Herbal formulation Xingnaojing lowers GSK-3β expression and raises mTOR expression, exerting regulatory effects through downstream effector proteins of the PI3K/AKT pathway (Liu et al., 2020). Although existing studies have uncovered how certain TCM components influence the PI3K/AKT pathway, the direct targets and specific regulatory mechanisms of some components remain unclear. Further investigation is warranted in future research.
In addition to the PI3K/AKT pathway, research has shown that herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM can improve AD pathology through multiple targets by modulating pathways such as NF-κB, Nrf2, JAK/STAT, ubiquitin-proteasome, PPARα, AMPK/mTOR, and SIRT1 (Ding et al., 2022). For instance, Naoxintong capsule has been found to improve cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice by downregulating the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, NF-κB, Aβ, and phosphorylated Tau (p-Tau) (Wang et al., 2021). Qin et al. demonstrated that astragalus polysaccharide increases nuclear Nrf2 expression as well as SOD and GSH-Px activity, reduces MDA accumulation, alleviates oxidative stress damage, and enhances spatial learning and memory in APP/PS1 mice (Qin et al., 2020). Long et al. reported that Suanzaoren decoction alleviated cognitive deficits in an AD mouse model, reduced Aβ plaque deposition and neuronal loss, downregulated the expression of p-JAK2-Tyr1007 and p-STAT3-Tyr705 proteins, and modulated the JAK2/STAT3 pathway (Long et al., 2021). Another study found that protopine, a component of Corydalis, exhibited neuroprotective effects in P301S Tau and 3xTg-AD mouse models by inhibiting histone deacetylase 6 activity while enhancing the expression of molecular chaperones such as HSP70, HSP90, HSC70, and acetylated HSP90, thereby influencing the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in AD (Sreenivasmurthy et al., 2022).
At present, most basic studies on the intervention of AD with TCM are conducted using animal or cell models. Animal models can realistically simulate the pathological features of AD in living organisms, while cell models allow researchers to investigate the disease mechanisms at a microscopic level. However, existing AD models have certain limitations. Different cell models can only represent certain aspects of AD pathogenesis and fail to replicate its full complexity. The criteria for establishing cell models are not yet standardized; using changes in cell viability or the expression of certain factors as evaluation metrics cannot fully reflect the pathological features of AD. Moreover, the effects of various metabolic intermediates, ions, serum components, and substrates on cell growth and differentiation during cell culture require further exploration (Ting et al., 2020). Similarly, animal models can only partially mimic the pathological characteristics and clinical symptoms of AD and cannot comprehensively represent all the pathological, biochemical, and neurobehavioral changes. Therefore, screening drugs with one or two AD cell or animal models, or using a combined modeling approach, may be more convincing than relying on a single model (Lei and Xiaoli, 2020).
Currently, drugs directly targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway in AD treatment remain in the research stage. Exploring herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM modulates the PI3K/AKT pathway in treating AD could provide valuable insights for developing synthetic drugs targeting this pathway. TCM contains numerous active compounds that can exert synergistic effects, intervening at multiple targets and regulating both upstream and downstream molecules of the PI3K/AKT pathway. In the future, the development of multi-target drugs may be necessary to address the complex pathological mechanisms of AD.
Many herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM extracts have demonstrated promising therapeutic effects against AD. It is worth considering whether derivatives based on these extracts could be designed to offer greater potency, stability, and selectivity as PI3K/AKT-targeting agents. For example, curcumin is quickly eliminated in the body due to its hydrophobicity and low bioavailability (Mirzael et al., 2017). Structural modifications of curcumin, synthesis of a series of derivatives, or the use of nanoemulsions to improve oral bioavailability might address these issues (Ghasemi et al., 2020; Liu L. et al., 2016). As our understanding of the role of herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM in modulating this pathway and its involvement in AD pathogenesis deepens, new therapeutic strategies may emerge.
Currently, treatment for AD primarily includes cholinesterase inhibitors, NMDA receptor antagonists, and monoclonal antibody-based drugs. These therapies mainly target short-term cognitive improvements and slow disease progression, but they are associated with varying degrees of adverse effects and have limited efficacy for moderate to severe AD patients. In contrast, numerous herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM have shown promising therapeutic effects in basic experimental studies. Some TCM formulations have also been tested in clinical research with encouraging results. A multicenter, randomized, observer-blind controlled trial confirmed that modified Guipi Decoction significantly improved BPSD in AD patients (Nogami et al., 2023). Wang HC et al. found that Jiannao Yizhi Formula was as effective and safe as donepezil for treating mild to moderate AD (Wang H. C. et al., 2020). Shenmai or Shenfu Injection and Huannao Yicong Formula have been demonstrated to be effective and safe for treating mild to moderate AD (Chen et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015). Liu P et al. reported that treatment with Reinforcing Kidney Essence improved cognitive function and daily living in AD patients (Liu et al., 2013). Yu L et al. discovered that syndrome-differentiation-based TCM treatment effectively enhanced cognitive function in mild to moderate AD patients and improved brain connectivity between the posterior cingulate cortex and specific brain regions (Yu et al., 2012).
Clinical studies suggest that herbal formulations and extracts derived from TCM offer substantial potential for treating AD, with advantages such as fewer side effects, convenient administration, and lower treatment costs. However, clinical evaluations of TCM efficacy often rely on subjective symptom improvement rather than objective biomarker validation. Furthermore, TCM treatments lack standardized dosing and protocols, and some medications may have potential toxicity with long-term use. Therefore, high-quality, large-scale, multicenter clinical trials are still needed to verify the safety and efficacy of TCM in AD treatment.
LM: Data curation, Writing–original draft. JW: Visualization, Writing–original draft. RZ: Writing–review and editing. MC: Writing–review and editing. ZH: Writing–review and editing. SL: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The work was supported by the Department of Science and Education, Wenzhou TCM Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ashton, N. J., Pascoal, T. A., Karikari, T. K., Benedet, A. L., Lantero-Rodriguez, J., Brinkmalm, G., et al. (2021). Plasma p-tau231: a new biomarker for incipient Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 141, 709–724. doi:10.1007/s00401-021-02275-6
AuthorAnonymous, (2023). Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 19(4):1598–1695. doi:10.1002/alz.13016
Avrahami, L., Farfara, D., Shaham-Kol, M., Vassar, R., Frenkel, D., and Eldar-Finkelman, H. (2013). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 ameliorates β-amyloid pathology and restores lysosomal acidification and mammalian target of rapamycin activity in the Alzheimer disease mouse model: in vivo and in vitro studies. J. Biol. Chem. 288 (2), 1295–1306. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.409250
Bahn, G., and DG, J. (2019). Approaches to Alzheimer’s disease through modulation of NRF2. Neuromol med 21. Neuromol Med. 21, 1–11. doi:10.1007/s12017-018-08523-5
Bai, R., Guo, J., Ye, X.-Y., Xie, Y., and Xie, T. (2022). Oxidative stress: the core pathogenesis and mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 77 (77), 101619. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2022.101619
Bathina, S., Nkv, G. P. R., Rhenghachar, P., Polavarapu, S., Hari, A. D., Sadananda, M., et al. (2020). Resolvin D1 ameliorates nicotinamide-streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus by its anti-inflammatory action and modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in the brain. Arch. Med. Res. 51 (6), 492–503. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.05.002
Calsolaro, V., and Edison, P. (2016). Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: current evidence and future directions. J. Alzheimer's Assoc. 12 (6), 719–732. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2016.02.010
Chao-fang, L., Zhi-gang, C., and Yue-yun, L. (2023). Research progress on pharmacological effects of paeoniflorin in the treatment of nervous system diseases. Chin. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 38 (04), 1697–1701.
Chen, T. J., Wang, D. C., and Ss, C. (2009). Amyloid-beta interrupts the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway that could be involved in brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced Arc expression in rat cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 87 (10), 2297–2307. doi:10.1002/jnr.22057
Chen, S., X, Y., Y, L., Mei, W., Liu, X., and Zhang, C. (2015). Alzheimer's disease treated with combined therapy based on nourishing marrow and reinforcing Qi. Tradit. Chin. Med. 35 (3), 255–259. doi:10.1016/s0254-6272(15)30094-7
Chen, W. (2013). The molecular mechanism of curcumin onneuroprotective effect via Inducingautophagy in appswe/ps1 double transgenicmice. Chongqing: Chongqing Medical University.
Cheng, M., Tang, Z., and Liang, D. (2020). The effects of Porphyromonas gingivalis on the apoptosis of hippocampal cells in Sprague-Dawley rats and its underlying mechanisms. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 13 (1), 300–309.
Chu, D., Yang, X., Wang, J., Zhou, Y., Gu, J. H., Miao, J., et al. (2024). Tau truncation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: a narrative review. Neural Regen. Res. 19 (6), 1221–1232. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.385853
Cui, T., P, Y., X, F., Song, Q., Yang, D., Li, M., et al. (2024). Elucidation of the inhibitory effects of Jiedu Yizhi formula on neuronal apoptosis in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease based on network pharmacology and in vivo experiments. Metab. Brain Dis. 40 (1), 38. doi:10.1007/s11011-024-01444-2
Decourt, B., Lahiri, D. K., and Mn, S. (2017). Targeting tumor necrosis factor alpha for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 14 (4), 412–425. doi:10.2174/1567205013666160930110551
Ding, M-R., Qu, Y-J., Hu, B., and Hong, M. (2022). Signal pathways in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease with traditional Chinese medicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 152, 113208. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113208
Fang, H., Tian, H., Liu, J., Peng, T., and Wang, D. (2025). Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates Aβ1-42-induced microglial cell apoptosis and inflammation in Alzheimer's disease via the GATA4/PDE4A/PI3K/AKT axis. Neuroscience 565, 377–385. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.12.011
Fengrui, H. (2022). Study on the effect of Guiling Ji on learning and memory dysfunction in APP/PS1 mice. Xi’an: Shanxi University of Science and Technology.
Fleisher, T. A. (1997). Apoptosis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 78 (3), 245–9. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)63176-6
Gao, C. Y., Gf, Q., Mc, Z., Tian, M. J., He, Y. N., and Wang, P. W. (2024). Banxia Xiexin decoction alleviated cerebral glucose metabolism disorder by regulating Intestinal Microbiota in APP/PS1 mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 30 (8), 701–712. doi:10.1007/s11655-023-3606-3
Gaofeng, Q. (2021). Study on the mechanism of the regulation of cerebral glucose metabolism by Shenzhiling oral liquid on AD neuroprotection. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine.
Garabadu, D., and J, V. (2019). Exendin-4 attenuates brain mitochondrial toxicity through PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway in amyloid beta (1–42)-induced cognitive defcit rats. Neurochem. Int. 128, 39–49. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2019.04.006
Ghasemi, F., Barreto, G. E., Rafiee, R., Sathyapalan, T., and Sahebkar, A. (2020). Effects of curcumin on mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases. Biofactors 46 (1), 5–20. doi:10.1002/biof.1566
Gu, L. G. L., Lu, J. L. J., and Li, Q. L. Q. (2020). A network-based analysis of key pharmacological pathways of Andrographis paniculata acting on Alzheimer's disease and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol., 251.
Gupta, R., Kumari, S., Tripathi, R., Ambasta, R. K., and Kumar, P. (2023). Unwinding the modalities of necrosome activation and necroptosis machinery in neurological diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 86, 101855. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2023.101855
Haixia, X., Qiang, L., and Yumin, W. (2023). Research progress of puerarin in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Chin. ARCHIVES TRADITIONAL Chin. Med. 41 (05), 29–33. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2023.05.007
Huang, X., G, L., J, G., and Su, Z. (2018). The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 14 (11), 1483–1496. doi:10.7150/ijbs.27173
Huang, L. H. L., Lin, M. L. M., Zhong, X. Z. X., Yang, H., and Deng, M. (2019). Galangin decreases p‑tau, Aβ42 and β‑secretase levels, and suppresses autophagy in okadaic acid‑induced PC12 cells via an Akt/GSK3β/mTOR signaling‑dependent mechanism. Mol. Med. Rep. 19 (3), 1767–1774. doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.9824
Huang, J. H. J., Xu, Z., Chen, H. C. H., Lin, Y., Wei, J., Wang, S., et al. (2022a). Shen Qi wan ameliorates learning and memory impairment induced by STZ in AD rats through PI3K/AKT pathway. BRAIN Sci. 12 (6), 758. doi:10.3390/brainsci12060758
Huang, Q., Zhang, C., Dong, S., Han, J., Qu, S., Xie, T., et al. (2022b). Asafoetida exerts neuroprotective effect on oxidative stress induced apoptosis through PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Chin. Med. 17 (1), 83. doi:10.1186/s13020-022-00630-7
Huang, J., Huang, N., Qiu, Y., and Shi, J. (2024). Dendrobium nobile Lindl. alkaloid decreases Tau hyperphosphorylation via regulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 322, 117592. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117592
Ill-Raga, G., Ramos-Fernández, E., Guix, F. X., Tajes, M., Bosch-Morató, M., Palomer, E., et al. (2010). Amyloid-β peptide fibrils induce nitro-oxidative stress in neuronal cells. Alzheimers Dis. 2 (22), 641–652. doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-100474
Jia-nan, L., Mo, K., and Xiao-ran, L. (2021). Effects mechanism of ginsenoside CK inhibiting Aβ-induced microglia activation andinflammatory response based on PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. China J. Traditional Chin. Med. 36 (08), 4652–4657.
Jiang, J., Wang, Z. H., Qu, M., Gao, D., Liu, X. P., Zhu, L. Q., et al. (2015). Stimulation of EphB2 attenuates tau phosphorylation through PI3K/Akt-mediated inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Sci. Rep. 5, 11765. doi:10.1038/srep11765
Jie, Z. (2023). Mechanism of Wuhe Xuduanon improving cognitive dysfunctionin rats with AD by regulatingPI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Enshi: Hubei Minzu Un.
Jing, Q., Zi-hu, T., and Qiong, Y. (2019). Modified Shuyuwan ameliorate neuronal apoptosis ofAPP/PS1 mice via akt/GSK3β/Nrf2 pathway. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 25 (21), 38–44. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20192140
Jing, H. W., Hui, H. L., and Le, W. (2023). The research progress on ginseng active ingredients in improving age-related memory decline and alzheimer's disease. Chin. J. Gerontology 43 (11), 2811–2815.
Jinping, Y., Ling, W., and Wei, C. (2013). The influence and Possible mechanism of Wenpi Tongluo Kaiqiao decoction on the activity of GSK-3β and PP2A in hippocampus of rats with alzheimer's. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-Cerebrovascular Dis. 11 (05), 581–583.
Jinping, W., Lin, W., and Lian, G. (2019). Mechanism research of Yifei Wenyang Huazhuo decoction regulating PI3K/Akt-mTOR signal pathway in protecting nerve cells of AD rat. Intern. Med. 14 (04), 381–386.
Juan, Y. (2022). Effects and mechanisms of Acorus tatarinowii on CognitiveImpairment in AD model mice induced by D-galactose. Tianjin: Tianjing University of Chinese Medicine.
Junping, W., Qingyang, B., and Jian, G. (2018). Effects of Tenuigenin and β - asarone on AD cells model in akt/GSK - 3β s signaling pathway. Chin. ARCHIVES TRADITIONAL Chin. Med. 36 (04), 838–842.
Kanninen, K., White, A. R., Koistinaho, J., and Malm, T. (2011). Targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3β for therapeutic Benefit against oxidative stress in alzheimer's disease: involvement of the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Int. J. Alzheimers 2011, 985085. doi:10.4061/2011/985085
Khezri, M. R., Ghasemnejad-Berenji, M., and Moloodsouri, D. (2023). The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and caspase-3 in alzheimer's disease: which one is the Beginner? Alzheimers Dis. 92 (2), 391–393. doi:10.3233/jad-221157
Khoshsirat, S., Ha, A., and Ms, K. (2019). Protective effect of photobiomodulation therapy and bone marrow stromal stem cells conditioned media on pheochromocytoma cell line against oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Lasers Med. Sci. 10 (3), 163–170. doi:10.15171/jlms.2019.26
Koundouros, N. G. P., and Poulogiannis, G. (2018). Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt signaling and redox metabolism in cancer. Front. Oncol. 8, 160. doi:10.3389/fonc.2018.00160
Kumar, M., and Bansal, N. (2022). Implications of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-akt (PI3K-akt) pathway in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 59 (1), 354–385. doi:10.1007/s12035-021-02611-7
Kumari, S., R, D., and Dh, R. (2023). Apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease: insight into the signaling pathways and therapeutic avenues. Apoptosis. 28 (7-8), 943–957. doi:10.1007/s10495-023-01848-y
Kunpeng, W., Jian, Y., and Qianyuan, P. (2016). Effects of Liuwei Dihuang decoction on Recognition and the expression ofWnt3a and GSK-3β in Senescence accelerated mice. J. Hunan Univ. CM 36 (03), 9–13.
Lan, M., Jing, S., and Ting, L. (2024). Effects of traditional Chinese medicine compound GAPT serum on regulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway through Ptau in AD cell models. Chin. J. Front. Med. 5, 1–9. doi:10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2024.12.001
Lan, L. R. (2021). Research on the mechanism of hydroxy-α-sanshool against Alzheimer's disease and nasal liposome preparation. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Leclerc, M., Bourassa, P., Tremblay, C., Caron, V., Sugère, C., Emond, V., et al. (2023). Cerebrovascular insulin receptors are defective in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 146, 75–90. doi:10.1093/brain/awac309
Lei, Y., and Xiaoli, H. (2020). Preliminary evaluation of commonly used experimental animal models for Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 36 (01), 1–5.
Lexuan, X. (2022). Effects of Anshen Yizhi method on behavior and Aβ expression in AD zebrafish. Wuhan: Hubei University of Chinese Medicine.
Li, Y. L. Y., Jin, Y. J. Y., Wang, X. W. X., Chen, X. L., Chen, H. B., Xu, J., et al. (2020). Neuroprotective effect of fructus broussonetiae on APP/PS1 mice via upregulation of AKT/β-Catenin signaling. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27 (2), 115–124. doi:10.1007/s11655-019-3178-4
Li, R. L. R., Wang, L. W. L., Zhang, Q. Z. Q., Duan, H., Qian, D., Yang, F., et al. (2022). Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus possesses neuroprotective effects on H2O2 stimulated PC12 cells via regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 966348. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.966348
Li, F. H. (2017). Study on the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine compound GAPT effect on early brain glucose metabolism in AD mice. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine.
Liang, C. L. C., Li, J. L. J., Zhang, Z. Z. Z., Liu, S. Q., and Yang, J. (2018). Suppression of MIF-induced neuronal apoptosis may underlie the therapeutic effects of effective components of Fufang Danshen in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. ACTA Pharmacol. SIN. 39 (9), 1421–1438. doi:10.1038/aps.2017.210
Lin, C. F., Tsai, C. C., and Huang, W. C. (2016). Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and caspase-2 mediate Ceramide- and Etoposide-induced apoptosis by regulating the LysosomalMitochondrial Axis. PLoS One 11, e145460. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145460
Lin, S. L. S., Wang, T. W. T., Xu, L. X. L., Lai, X. X., Shen, Y., Lin, J. W., et al. (2020). Qingxin Kaiqiao Recipe improves cognitive performance, inhibits apoptosis, and reduces pathological deposits in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice via the PI3K/akt pathway. EVIDENCE-BASED COMPLEMENTARY Altern. Med. 2020, 2020. doi:10.1155/2020/3019674
Liu, P., Kong, M., Liu, S., Chen, G., and Wang, P. (2013). Effect of reinforcing kidney-essence, removing phlegm, and promoting mental therapy on treating Alzheimer's disease. Tradit. Chin. Med. 33 (4), 449–454. doi:10.1016/s0254-6272(13)60147-8
Liu, Y. L. Y., Xu, S. X. S., Bian, H. B. H., Qian, Y., Li, H., Shu, S., et al. (2020). Xingnaojing ameliorates synaptic plasticity and memory deficits in an Aβ1-42 induced mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 143 (4), 245–254. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2020.05.002
Liu, Q. L. Q., Ding, S. D. S., Zhang, H. Z. H., and Shang, Y. Z. (2022). The molecular mechanism of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi Stems and Leaves Flavonoids in promoting neurogenesis and improving memory impairment by the PI3K-AKT-CREB signaling pathway in rats. Comb. Chem. & HIGH THROUGHPUT Screen. 25 (5), 919–933. doi:10.2174/1386207324666210506152320
Liu, L., Wan, W. W. W., Chen, W. C. W., Chan, Y., Shen, Q., and Li, Y. (2016). Yi-zhi-fang-dai formula protects against Aβ1-42 Oligomer induced cell damage via increasing Hsp70 and Grp78 expression in SH-SY5Y cells. EVIDENCE-BASED COMPLEMENTARY Altern. Med. 2016, 8591656. doi:10.1155/2016/8591656
Liu, W., Zhai, Y., Heng, X., Che, F. Y., Chen, W., Sun, D., et al. (2016). Oral bioavailability of curcumin: problems and advancements. Drug Target 24 (8), 694–702.
Lixia, Q., Qian, W., and Peng, X. (2018). Effect of Shenqi Yizhi Granules on PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats with Alzheimer's disease injected with Aβ1-42 bilateral hippocampus. Mod. Traditional Chin. Med. Materia Medica-World Sci. Technol. 20 (12), 2161–2166.
Long, Q. H., Wu, Y. G., He, L. L., Ding, L., Tan, A. H., Shi, H. Y., et al. (2021). Suan-Zao- Ren decoction ameliorates synaptic plasticity through inhibition of the Aβ deposition and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in AD model of APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Chin. Med. 16, 14. doi:10.1186/s13020-021-00425-2
Long, T. L. T., Chen, X. C. X., Zhang, Y. Z. Y., Zhou, Y. J., He, Y. N., Zhu, Y. F., et al. (2023). Protective effects of Radix Stellariae extract against Alzheimer's disease via autophagy activation in Caenorhabditis elegans and cellular models. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 165, 115261. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115261
Lou, S., D, G., M, Y., Qiu, Q., Luo, J., and Chen, T. (2024). Curcumin improves neurogenesis in alzheimer's disease mice via the upregulation of Wnt/β-Catenin and BDNF. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (10), 5123. doi:10.3390/ijms25105123
Ma, X. M. X., Duan, W. D. W., Mo, Y. M. Y., Chen, J. L., Li, S., Zhao, W., et al. (2018). Neuroprotective effect of paeoniflorin on okadaic acid-induced tau hyperphosphorylation via calpain/Akt/GSK-3β pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. BRAIN Res. 1690, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2018.03.022
Manish Kumar, N. B., and Bansal, N. (2022). Implications of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-akt (PI3K-akt) pathway in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 59, 354–385. doi:10.1007/s12035-021-02611-7
Mao, J. Q., L, C., Yd, Z., Xie, G. J., and Wang, P. (2024). Chinese formula Guben-Jiannao Ye alleviates the dysfunction of circadian and sleep rhythms in APP/PS1 mice implicated in activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 335, 118696. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118696
Meng, D. L. (2018). Pharmacological investigation of components from gardeniain APP/PS1/Tau Transgenic mice of Alzheimer’s disease. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical University.
Miao, X. (2018). A study on the mechanism of modified SanJiaSan in the treatment of Senile dementia by regulating the relationship betweent neuroinflammation and autophagy and apoptosis. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine.
Mirzael, H, S, A., R, B., Jalili, A., Banikazemi, Z., and Sahebkar, A. (2017). Phytosomal curcumin: a review of pharmacokinetic, experimental and clinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 85, 102–112. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.098
Na, C. (2022). Symptomatic study OF patients WITHALZHEIMER disease and the effect OF ZHINAOCAPSULE ON PI3K/akt/GSK3β IN APP/PS1 MICEINFLUENCE OF SIGNAL pathway. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine.
Naseri, N. N., Wang, H., Guo, J., Sharma, M., and Luo, W. (2019). The complexity of tau in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 705, 183–194. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2019.04.022
Nogami, T., K, I., H, K., Higashi, T., Arai, M., Butler, J. P., et al. (2023). Traditional Chinese medicine Jia Wei Gui Pi Tang improves behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia and favourable positive emotions in patients. Psychogeriatrics 23 (3), 503–511. doi:10.1111/psyg.12962
Ochiai, T., Sano, T., Nagayama, T., Kubota, N., Kadowaki, T., Wakabayashi, T., et al. (2021). Differential involvement of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2 in brain insulin signaling is associated with the effects on amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J. Pathol. 159, 105510. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105510
Ossenkoppele, R., van der Kant, R., and Hansson, O. (2022). Tau biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: towards implementation in clinical practice and trials. Lancet. Neurol. 21 (8), 726–734. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00168-5
Pang, S. P. S., Li, S. L. S., Cheng, H. C. H., Luo, Z., Qi, X., Guan, F., et al. (2023). Discovery of an evodiamine derivative for PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway activation and AD pathology improvement in mouse models. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 15. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2022.1025066
Peijun, X., Yanwei, H., and Jing, G. (2020). Yuanzhi Powder regulates phosphorylation of tau protein through PI3K/AKT/GSK-3βnPathway in alzheimer's disease model rats. Chin. ARCHIVES TRADITIONAL Chin. Med. 38 (11), 167–170. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2020.11.041
Phiel, C. J., Wilson, C. A., Lee, V. M., and Klein, P. S. (2003). GSK-3alpha regulates production of Alzheimer's disease amyloid-beta peptides. Nature 423 (6938), 435–439. doi:10.1038/nature01640
Qi, Y. Q. Y., Cheng, X. C. X., Gong, G. G. G., Yan, T., Du, Y., Wu, B., et al. (2020). Synergistic neuroprotective effect of schisandrin and nootkatone on regulating inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy via the PI3K/AKT pathway. FOOD & Funct. 11 (3), 2427–2438. doi:10.1039/c9fo02927c
Qin, X., Hua, J., Lin, S., Zheng, H. T., Wang, J. J., Li, W., et al. (2020). Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates cognitive impairment and β-amyloid accumulation in APP/PS1 mice via Nrf2 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 531, 431–437. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.122
Qinghua, L., Binbin, Z., and Li, D. (2020). Discussion on the effect of Suanzaoren Decoction on hippocampal neurons and synapticdamage in APP/PS1 double transgenic dementia mice based onPI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway. China J. Traditional Chin. Med. 35 (05), 2546–2551.
Qu, H, Zhang, Y, Chai, X, and Sun, W (2012). Isoforsythiaside, an antioxidant and antibacterial phenylethanoid glycoside isolated from Forsythia suspensa. Bioorg. Chem. 40, 87–91. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2011.09.005
R, R., J, Q., S, L., Liu, X., Yin, P., Wang, Z., et al. (2022). The China alzheimer Report 2022. Gen. Psychiatr. 35 (1), e100751. doi:10.1136/gpsych-2022-100751
Rockenstein, E., Torrance, M., Adame, A., Mante, M., Bar-on, P., Rose, J. B., et al. (2007). Neuroprotective effects of regulators of the glycogen synthase kinase-3beta signaling pathway in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease are associated with reduced amyloid precursor protein phosphorylation. J. Neurosci. 27 (8), 1981–1991. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4321-06.2007
Rong, Y. F. (2018). “Study on the mechanism of dementia and the effect of Bushen Jianpi Gaoxing Recipe on PI3K/AKT pathway in alzheimer's disease rats based on drug Guideline,” in Compendium of Materia Medica”. (Wuhan: Hubei University of Chinese Medicine).
Sánchez-Alegría, K., Flores-León, M., Avila-Muñoz, E., Rodríguez-Corona, N., and Arias, C. (2018). PI3K signaling in neurons: a central node for the control of multiple functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (12), 3725. doi:10.3390/ijms19123725
Seidler, K. B. M., and Barrow, M. (2022). Intermittent fasting and cognitive performance-Targeting BDNF as potential strategy to optimise brain health. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 65, 100971. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2021.100971
Selkoe, D. J., and J, H. (2016). The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 8 (6), 595–608. doi:10.15252/emmm.201606210
Sharma, V. K., Singh, T. G., Singh, S., Garg, N., and Dhiman, S. (2021). Apoptotic pathways and alzheimer's disease: Probing therapeutic potential. Neurochem. Res. 46 (12), 3103–3122. doi:10.1007/s11064-021-03418-7
Shi, X., Wang, J., Lei, Y., Cong, C., Tan, D., and Zhou, X. (2019). Research progress on the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in gynecological cancer (review). Mol. Med. Rep. 19 (6), 4529–4535. doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.10121
Shih, R. H., Cy, W., and Cm, Y. (2015). NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 8, 77. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2015.00077
Sofola, O., Kerr, F., Rogers, I., Killick, R., Augustin, H., Gandy, C., et al. (2012). Correction: inhibition of GSK-3 ameliorates Aβ pathology in an adult-onset Drosophila model of alzheimer's disease. PLOS Genet. 6 (9), e1001087. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001087
Sotolongo, K., Rostagno, G. J., and Rostagno, A. (2020). Nrf2 activation through the PI3K/GSK-3 axis protects neuronal cells from Aβ-mediated oxidative and metabolic damage. Alz Res. Ther. 12, 13. doi:10.1186/s13195-019-0578-9
Sreenivasmurthy, S. G., Iyaswamy, A., Krishnamoorthi, S., Senapati, S., Malampati, S., Zhu, Z., et al. (2022). Protopine promotes the proteasomal degradation of pathological tau in Alzheimer’s disease models via HDAC6 inhibition. Phytomedicine 96, 153887. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153887
Stephenson, J., Nutma, E., van der Valk, P., and Amor, S. (2018). Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 154 (2), 204–219. doi:10.1111/imm.12922
Sun, Y. S. Y., Wu, A. W. A., Li, X. L. X., Qin, D., Jin, B., Liu, J., et al. (2020). The seed of Litchi chinensis fraction ameliorates hippocampal neuronal injury in an Aβ25-35-induced Alzheimer's disease rat model via the AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Pharm. Biol. 58 (1), 35–43. doi:10.1080/13880209.2019.1697298
Tamagno, E., Guglielmotto, M., Monteleone, D., and Tabaton, M. (2012). Amyloid-β production: major link between oxidative stress and BACE1. Neurotox. Res. 22 (3), 208–219. doi:10.1007/s12640-011-9283-6
Tao, M., Yan, Y., and Yun-ling, Z. (2014). Effects of kidney-tonifying,essence-replenishing method on PI3K/Akt activation and oxidative stress inAlzheimer mice. Beijing J. Traditional Chin. Med. 33 (07), 492–495.
Taolin, Z., Zhe, W., and Chao, L. (2016). Effect and mechanism of icariin on glycogen synthase kinase-3β expression in Alzheimer's disease cell model. Chin. J. Gerontology 36 (04), 800–803.
Terwel, D., Muyllaert, D., Dewachter, I., Borghgraef, P., Croes, S., Devijver, H., et al. (2008). Amyloid activates GSK-3beta to aggravate neuronal tauopathy in bigenic mice. Am. J. pathology 172 (3), 786–798. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.070904
Ting, D., Zhijie, Y., and Ying, X. (2020). Research progress on the establishment and evaluation methods of AD cell models. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 36 (04), 470–475.
Toral-Rios, D., Ps, P., Alonso-Vanegas, M., and Campos-Peña, V. (2020). GSK3β and tau protein in Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy. Front. Cell Neurosci. 14, 1–9. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.00019
Vk, S., TG, S., Singh, S., Garg, N., and Dhiman, S. (2021). Apoptotic pathways and alzheimer's disease: Probing therapeutic potential. Neurochem. Res. 46 (12), 3103–3122. doi:10.1007/s11064-021-03418-7
Walsh, D. M., and Dj, S. (2007). A beta oligomers - a decade of discovery. J. Neurochem. 101, 1172–1184. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04426.x
Wang, C, C., Hao, J., Liu, X., Li, C., Yuan, X., Lee, R. J., et al. (2020). Isoforsythiaside attenuates alzheimer's disease via regulating mitochondrial function through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (16), 5687. doi:10.3390/ijms21165687
Wang, B., C, Y., and H, J. (2012). Icariin improves cognitive deficits and activates quiescent neural stem cells in aging rats. Ethnopharmacology 142 (3), 746–753. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2012.05.056
Wang, Y., Liu, W., He, X., and Zhou, F. (2013). Parkinson's disease-associated DJ-1 mutations increase abnormal phosphorylation of tau protein through Akt/GSK-3β pathways. J. Mol. Neurosci. 51, 911–918. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-0099-0
Wang, X., Yin, Z., Cao, P., Zheng, S., Chen, Y., Yu, M., et al. (2021). NaoXinTong Capsule ameliorates memory deficit in APP/PS1 mice by regulating inflammatory cytokines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 133, 110964. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110964
Wang, S., Sudan, R., and Peng, V. (2022a). TREM2 drives microglia response to amyloid-β via SYKdependent and -independent pathways. Cell 4153–4169 (185), e4119. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.033
Wang, S., Guoheng, H., and Peiliang, C. (2022b). Effects of Zishen Xingnao decoction on learning and memory ability of alzheimer DiseaseRats based on BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/akt signaling pathway. Chin. J. Inf. Traditional Chin. Med. 29 (03), 53–58.
Wang, K., Zhang, X., Zhang, M., Li, X., Xie, J., Liu, S., et al. (2023). Hyperoside Prevents Aβ42-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells and Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Neurobiol. 60 (12), 7136–7150. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03521-6
Wang, H. C., Ny, L., Zhang, S., Yang, Y., Wang, Z. Y., Wei, Y., et al. (2020). Clinical experience in treatment of alzheimer’s disease with Jiannao Yizhi formula and routine western medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26 (3), 212–218. doi:10.1007/s11655-019-2718-2
Wang, S., Y, W., S, S., and Ye, X. (2024). Crocin ameliorates neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in mice with Alzheimer's disease by activating PI3K/AKT pathway. Brain Behav. 14 (5), e3503. doi:10.1002/brb3.3503
Wang, Y., Gong, Q., Pan, H., Wang, X., and Yan, C. (2024). Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis extract attenuates memory impairment in rats with Alzheimer’s disease by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome. Brain Res. 1824 (1824), 148687. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148687
Wei-wei, T., Bi-hua, T., and Li, L. (2024). Research progress on curcumin improving chronic low-gradeinflammation and related diseases. China J. Chin. Materia Medica, 1–13.
Wei-Xian, Z., Gao-Shen, L., and Bao-Wei, W. (2014). Effect of Xiaoyao Powder on Alzheimer's disease in hippocampal CA3 region of rats PP-2A,GSK-3β expression. Chin. J. Immunol. 30 (05), 623–626.
Wu, Q. W. Q., Li, X. L. X., Jiang, X. J. X., Yao, D., Zhou, L. J., Xu, Z. H., et al. (2022). Yuan-Zhi decoction in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: an integrated approach based on chemical profiling, network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 893244. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.893244
Wu, L., Sun, Y., Yin, Y., Wu, Z., Liu, R., Liu, Y., et al. (2025). Lancao decoction in the treatment of alzheimer's disease via activating PI3K/AKT signaling to promote ERK involving in enhancing neuronal activities in the hippocampus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1 (338), 119017.
Xi, J., Ao, S., and Jie, Z. Y. (2022). Da Buyuanjian combined with Exercise improves learning memory of AD rats by Da Buyuanjian combined with Exercise improves learning memory of AD rats byModulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. China J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 28 (20), 1–7. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20221501
Xie, Y. X. Y., Yan, B. Y. B., Hou, M. H. M., Zhou, M., Liu, C., Sun, M., et al. (2021). Erzhi pills ameliorate cognitive dysfunction and alter proteomic hippocampus profiles induced by d-galactose and Aβ1- 40 injection in ovariectomized Alzheimer's disease model rats. Pharm. Biol. 59 (1), 1400–1412. doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1990353
Xin, T. (2016). Effect of Panax notoginseng saponins on oxidative stress PI3K/Akt and PLCγ1/PKC signaling pathways in Alzheimer's disease. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.
Xin, L. Y. (2021). Studu on mechanism of Velvet antler Polypeptide improving mild cognitive Impariment via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Changchun: Changchun University of Chinese Medicine.
Xinyun, L. (2022). Study on the mechanism of the regulation of IRS/PI3K/AKT pathway in the intervention of hippocampal insulin resistance in Alzheimer's mice with renal deficiency. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine.
Xiong, R. X. R., Wang, X. W. X., and Wu, J. W. J. (2020). Polyphenols isolated from lychee seed inhibit Alzheimer's disease-associated Tau through improving insulin resistance via the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol., 251.
Xiu, Y., Yh, L., and Ej, P. (2019). Screening of antitumor active components and key targets of Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata-Pinelliae Rhizoma based on PI3K/Akt pathway. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 25, 170–179.
Xu, L., Zhu, J., Yin, W., and Ding, X. (2015). Astaxanthin improves cognitive deficits from oxidative stress, nitric oxide synthase and inflammation through upregulation of PI3K/Akt in diabetes rat. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8 (6), 6083–6094.
Yabin, W. (2018). Study on tau protein phosphorylation and related mechanism of anti-Aβ_(25-35)-induced Alzheimer's disease in a mouse model of ginseng Rong mixture. Liaoning Univ. Chin. Med.
Yan, Y., Ming, Y. A., and Jun, S. (2020a). Effects of Crocinonthe on the apoptosis of hippocampal neurons and P-CREB in Alzheimer’s disease cell model through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Integr. Traditional West. Med. 18 (23), 3954–3958.
Yan, L., Yue, S., and Wei, L. (2020b). Kaixin Powder regulates the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway to promote neural regeneration in the brains of AD model mice. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Materia Medica 36 (05), 73–78.
Yan, W., Yuqing, R., and Can, C. (2024). Jiaotai Pill improves glucose metabolism in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease model mice by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. South. Med. Univ. 44 (05), 894–903.
Yang, K., A, N., and Y, O. (2014). Dietary regulation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. 6 (3), 1–7.
Yang, L. D. X. Z. W., Dong, X., and Zhang, W. (2020). Astragaloside IV alleviates the brain damage induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 735, 135227. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135227
Yang, C. Y. C., Wang, S. W. S., Zhang, R. Z. R., Lin, J. H., Tian, Y. H., Yang, Y. Q., et al. (2023). Neuroprotective effect of astragalin via activating PI3K/Akt-mTOR-mediated autophagy on APP/PS1 mice. CELL DEATH Discov. 15 (9), 15–13. doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01324-1
Yang, H., Y, W., X, L., Qi, Y., Qu, Z., and Hu, Y. (2024). Lycium Barbarum polysaccharides improves cognitive functions in ICV-STZ-Induced alzheimer's disease mice model by improving the synaptic structural plasticity and regulating IRS1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Neuromolecular Med. 26 (1), 15. doi:10.1007/s12017-024-08784-3
Yanjun, W., Qing, Z., and Hui, M. (2024). Mechanism of Si Jun Zi Tang in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. J. Binzhou Med. Univ. 47 (02), 142–146. doi:10.19739/j.cnki.issn1001-9510.2024.02.013
Yi, F., Guangjie, S., and Li, C. (2021). Neuroprotective effect of tanshinone IIA and its effects on the PI3K/AKT pathway in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. ACTA LAB. ANIM. Sci. SIN. 29 (04), 499–505.
Yihong, P. (2015). The research of TCM Vitality Consolidation treatment theory and It's effects to alzheimer's disease. Hubei Univ. Chin. Med.
Yijun, S., Cui, W., and Caiming, W. (2024). Effects of Icariside II on learning and memory abilities in Alzheimer’s disease mice via regulation of the PI3K/akt signaling pathway. Mod. Chin. Med. 26 (07), 1164–1172. doi:10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20240222002
Yin, G., Li, L. Y., Qu, M., Luo, H. B., Wang, J. Z., and Zhou, X. W. (2011). Upregulation of AKT attenuates amyloid-β-induced cell apoptosis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 25 (2), 337–345. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-110104
Ying-nan, N., Ya-meng, W., and Liang, K. (2019). Effect of osthole on tau hyperphosphorylation and PI3K/Akt/Gsk3βsignaling pathway in the brain of AD mice. Chin. J. New Drugs 28 (23), 2865–2871.
Yu, L., Sm, L., Rq, Z., Tang, W., Huang, P., Dong, Y., et al. (2012). Chinese herbal medicine for patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease based on syndrome differentiation: a randomized controlled trial. J. Integr. Med. 10 (7), 766–776. doi:10.3736/jcim20120707
Yuan, Y., Y, L., L, H., Ma, J., Shao, S., Yu, Z., et al. (2023). The neuroprotective effects of Liuwei Dihuang medicine in the APP/PS1 mouse model are dependent on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1188893. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1188893
Yubao, C. (2018). Study on the mechanism of Schisandra chinensis-Rehmannia rehmannia compatibility in improving learning and memory in AD model rats. Chongqing: Southwestern University.
Yue, Q., Wen-yan, Q., and Kai, K. (2017). Effects of Wenyujin essential oil on tau protein phosphorylation in mice with Aβ-induced alzheimer disease through PI3k/akt pathway. Chin. J. Inf. Traditional Chin. Med. 24 (01), 45–48.
Zeng, Z., Wang, H., Shang, F., Zhou, L., Little, P. J., Quirion, R., et al. (2016). Lithium ions attenuate serum-deprivation-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells through regulation of the Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathways. Psychopharmacol. Berl. 233, 785–794. doi:10.1007/s00213-015-4168-7
Zhang, Y., C, L., L, Z., Cui, Y., Gu, Y., Guo, J., et al. (2015). Cognitive improvement during treatment for mild alzheimer's disease with a Chinese herbal formula: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 10 (6), e0130353. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130353
Zhang, B., Y, W., H, L., Xiong, R., Zhao, Z., Chu, X., et al. (2016). Neuroprotective effects of salidroside through PI3K/Akt pathway activation in Alzheimer’s disease models. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 10, 1335–1343. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S99958
Zhang, H. B., Tu, X. K., Chen, Q., and Shi, S. S. (2019). Propofol reduces inflammatory brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage: involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. 28 (12), 104375. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104375
Zhang, L., Qian, Y., Li, J., Zhou, X., Xu, H., Yan, J., et al. (2021). BAD-mediated neuronal apoptosis and neuroinflammation contribute to Alzheimer's disease pathology. iScience 24 (9), 102942. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.102942
Zhao, Z. Z. Z., Zhang, Y. Z. Y., Zhang, Y. Z. Y., Wei, X. Z., Wang, H., Zhang, M., et al. (2019). The protective underlying mechanisms of Schisandrin on SH-SY5Y cell model of Alzheimer's disease. J. Toxicol. Environ. HEALTH-PART A-CURRENT ISSUES 82 (19), 1019–1026. doi:10.1080/15287394.2019.1684007
Zhao, C.-xia, Jiang, Yu, and Sheng, G.-li (2020). Explore the effect of Yizhi Zhidai Recipe (益智治呆方) on the learning and memory ability of AD model rats and its mechanism based on PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Guid. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 26 (13), 18–22. doi:10.13862/j.cnki.cn43-1446/r.2020.13.005
Zhen, D. M. (2016). The effect and mechanism of volatile oil of Acorus tatarinowii Schott and total ginsenoside co-administration on APP/PS1 double transgenic mice. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine.
Zheng-rong, M., Xiang-ping, T., Shao-zhi, L., and Huang, H. H. (2016). Puerarin alleviates cognitive impairment and tau hyperphosphorylation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. China J. Chin. Materia Medica 41 (17), 3285–3289. doi:10.4268/cjcmm20161727
Zhi-quan, W., Chuan-hong, B., and Yi-xin, C. (2021). Aconitine attenuates neuronal damage induced by β-amyloid via inhibition of GSK-3β. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 33 (05), 831–836. doi:10.16333/j.1001-6880.2021.5.015
Zhiying, L., Minglong, Y., and Guanyi, Z. (2024). Regulation and Tonification of the Heart and kidney formula promotes the synthesis of synaptic plasticity-related proteins in 5xFAD transgenic mice with alzheimer's disease via activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Chin. J. New Drugs Clin. Remedies 35 (08), 1191–1196. doi:10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2024.08.010
Zhu, C., J, L., J, L., Xu, J., and Yu, E. (2024). Investigating the effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (9), e14914. doi:10.1111/cns.14914
Zhuo, Z. (2022). Study on the correlation between plasma BDNF and cognitive function and the regulatory effect of JinSiwei based on the PI3K/AKT-mTOR pathway. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine.
AD Alzheimer's disease
mTOR Mammalian target of rapamycin
APP Amyloid precursor protein
mTORC2 Mammalian target rapamycin complex 2
AKT Protein kinase B
MDA Malondialdehyde
Aβ Amyloid-β
Nrf2 Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
Bcl-XL B cell lymphoma-extra large
NFT Neurofibrillary tangles
Bcl-2 B-cell lymphoma-2
NF-κB Nuclear factor kappa-b
Bax Bcl-2-associated x protein
NS-PTEN KO Neuron subgroup-specific pten knockout
BDNF Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
PIP3 Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-bisphosphate
caspases Cysteine-aspartate proteases
PIP2 Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate
CDK-5 Cyclin-dependent kinases
PI3K Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
CNS Central nervous system
PI3K/AKT Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase b
eNOS Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
P-AKT Phosphorylated akt
GSH Glutathione
PH Pleckstrin homology
GSK-3β Glycogen synthase kinase-3β
PDK1 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1
IR Insulin receptor
ROS Reactive oxygen species
IL-6 Interleukin-6
SOD Superoxide dismutase
IRS Insulin receptor substrates
TCM Traditional chinese medicine
IKK Inhibitor of kappa b kinase
TNF-α Tumor necrosis factor-α
IL-1β Interleukin-1β
ULK1 Unc-51-like kinase 1
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, PI3K/Akt signal pathway, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), amyloid-β, Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)
Citation: Ma L, Wang J, Zhou R, Chen M, Huang Z and Lin S (2025) Traditional Chinese Medicine-derived formulations and extracts modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1528919. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1528919
Received: 15 November 2024; Accepted: 20 February 2025;
Published: 17 March 2025.
Edited by:
Karl Tsim, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
João M. L. Dias-Ferreira, São João University Hospital Center, PortugalCopyright © 2025 Ma, Wang, Zhou, Chen, Huang and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rong Zhou, MTkwNDQ0NzM3QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.