
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol. , 11 February 2025
Sec. Drugs Outcomes Research and Policies
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1528459
Background: STING is a core signaling hub molecule in the innate immune system, involved in various diseases, including infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, tumors, aging, organ fibrosis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Its activation has shown great potential in anti-tumor and anti-infective therapies, with STING agonists emerging as a promising approach in cancer immunotherapy in recent years. This study identifies research trends and potential directions in the field by collecting and analyzing relevant literature.
Methods: A total of 527 publications regarding STING agonists and 107 about inhibitors were retrieved from the WOS Core Collection database. Bibliometric information was extracted with CiteSpace and VOSviewer software for visualization.
Results: It shows that research on both STING agonists and inhibitors is burgeoning rapidly. The United States and China are leading contributors in this field. Application of STING agonists primarily focuses on cancer immunotherapy, while STING inhibitors target inflammation, particularly neuroinflammation and acute lung injury.
Conclusion: Current research emphasizes optimizing STING agonists for permeability, efficacy, and safety, with nanotechnology and lipid nanoparticles being prominent delivery techniques. Future research is expected to focus on drug development and clinical applications. This comprehensive bibliometric analysis provides clinical insights and a guide for further investigation to STING agonist/inhibitor.
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) was identified as a core adaptor protein in DNA sensing during 2008–2009 by four independent groups: Glen Barber, Hongbing Shu, Zhengfa Jiang, and John Cambier (Ishikawa and Barber, 2008; Jin et al., 2008; Zhong et al., 2008; Wenxiang et al., 2009). As a signaling hub in innate immunity, STING is a danger signal sensor in orchestrating the body’s response to pathogenic, tumor, or self-DNA in human diseases. In the classical STING signaling pathway, pathogen DNA, Cyclic Dinucleotides (CDNs) substances, tumor dsDNA, or aberrant cytosolic mtDNA are recognized by cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) (Decout et al., 2021), which then catalyzes the formation of cGAMP from GTP and ATP. cGAMP mobilizes STING conformational change and initiates the translocation of STING from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. During the translocation process, STING recruits TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), which then translocate into the nucleus, inducing the expression of type I IFN (IFN-I) response, NF-kB activation, and other inflammatory cytokines, unleashing innate immune responses and establishing a ubiquitous and effective surveillance system against tissue damage and pathogen invasion (Chen and Xu, 2023). Activation of STING can induce a potent immune response against pathogen infections and cancer, while imbalances of this pathway may lead to a variety of human diseases, including infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, tumors, organ fibrosis, and neurodegenerative diseases (Hopfner and Hornung, 2020; Dvorkin et al., 2024).
Over the past decade, the field of STING-related research has experienced rapid development, attracting widespread attention from numerous scholars. With the gradual elucidation of the cellular and pathophysiological mechanisms of cGAS-STING, the role of STING in many diseases has been clarified. Subsequently, new immunotherapeutic methods targeted to the regulation of STING have been developed, such as the use of STING agonists and inhibitors. STING agonists have been an emerging strategy for cancer immunotherapy (Minlin et al., 2020; Cai et al., 2023; Chen Y. et al., 2024; Wang J. et al., 2024). Through targeting antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages, STING agonists not only activate innate immune response but also sensitized and enhanced T-cell immunity, thus showing efficacious immune activation and antitumor effects in a spectrum of clinical and preclinical studies. In addition to antitumor treatment, STING agonists have also been applied in anti-infective treatment and vaccine development (Skouboe et al., 2018a; Humphries et al., 2021a; Zhang Y. et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024). Mounting evidence has indicated that the abnormal activation of the cGAS-STING pathway is closely associated with the development of autoimmune diseases (AID) (Liu and Pu, 2023), nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic inflammation, Parkinson’s disease, and cardiovascular diseases (Oduro et al., 2022). STING inhibitors also hold potential therapeutic value for these diseases (Shen et al., 2022; Liu and Pu, 2023).
Bibliometric analysis applies statistical methods and mathematical models to analyze bibliographic data, including publications, citations, and other scholarly communications. It is used to assess the productivity of researchers, institutions, and countries in a specific field (Anton et al., 2022). Additionally, it offers valuable insights for developing guidelines, making decisions, and treating diseases (Wilson et al., 2021). It is helpful to analyze the publication trends, disciplinary frontiers, hot contents, collaborative relationships, and influential factors of scholarly works (Romanelli et al., 2021). Bibliometric research can reveal the temporal dynamics of academic focus in a particular field, capture the hallmarks of emerging research areas, identify frontier issues in scholarly research, adjust the direction of scientific funding, and, more importantly, provide significant reference resources for literature reviews.
Therefore, conducting a bibliometric analysis of STING agonists/inhibitors is necessary to assess the current state of this emerging therapeutic and pharmaceutical strategy, explore the research scope and content within the field, and reasonably assume the future development direction. In this study, we performed a bibliometric analysis of STING agonists and antagonists, including publications from 2013 to 2024, to identify publication trends and highlight hotspot research areas.
To achieve an exhaustive and accurate literature search, the Web of Science core collection database, which contains data from SCIE and SSCI, was queried using the following search terms on 11 August 2024: TS= (“sting agonist”) OR TS= (“sting activator”) for literature related to STING agonists; TS= (“sting inhibitor”) OR TS= (“sting antagonist”) for literature on STING inhibitors. The inclusion criteria for this study were as follows: English language only; document types limited to articles or review articles. Ultimately, 527 articles regarding STING agonists and 107 about STING inhibitors met the inclusion criteria and were retrieved from the WOS Core Collection database, as shown in Figure 1.
In this study, VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) and CiteSpace (version 5.8. R1.7z) were developed based on the JAVA programming language and have a robust visualization function. They were used to extract bibliometric information for co-cited references, countries, institutions, journals, co-authorship networks, keyword co-occurrence networks, and burstiness analyses and then generate bibliometric map visualization, calculation and analysis of co-occurrence network terms, national collaboration axis, co-citation, and bibliographic coupling of inter-author network relationships extracted from publication titles and abstracts. For descriptive analysis, the maximum, minimum, average, trend, and median were provided. To offer a more in-depth perspective on the translational potential of STING agonists and inhibitors, we incorporated a statistical analysis of the global drug development database for STING agonists and inhibitors extracted from the “Pharnextcloud” platform (https://data.pharnexcloud.com/).
All citation information was exported from the ISI WoS database in.txt format and subsequently imported into VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Two reviewers (QW and YG) independently reviewed these data searches to exclude irrelevant content and then reached a final agreement. In case of disagreement between the two researchers, a third researcher intervened to resolve the dispute.
Publication numbers extracted from the WOS Core Collection database are classified by year. The evolution of STING agonist research is depicted in Figure 2A, while the research on STING inhibitors is presented in Figure 2B. Research on STING agonists has emerged as a focus over the past decade and has gained significant attention in recent years. In contrast, research on STING antagonists started later but has also shown a strong growth momentum in recent years. There are still many questions to be addressed and a great deal of space to explore regarding the regulation of STING and the application of its agonists/ antagonists. As the theoretical framework in this field continues to deepen and improve, the pace of publication will continue to grow rapidly in the next 5 years.
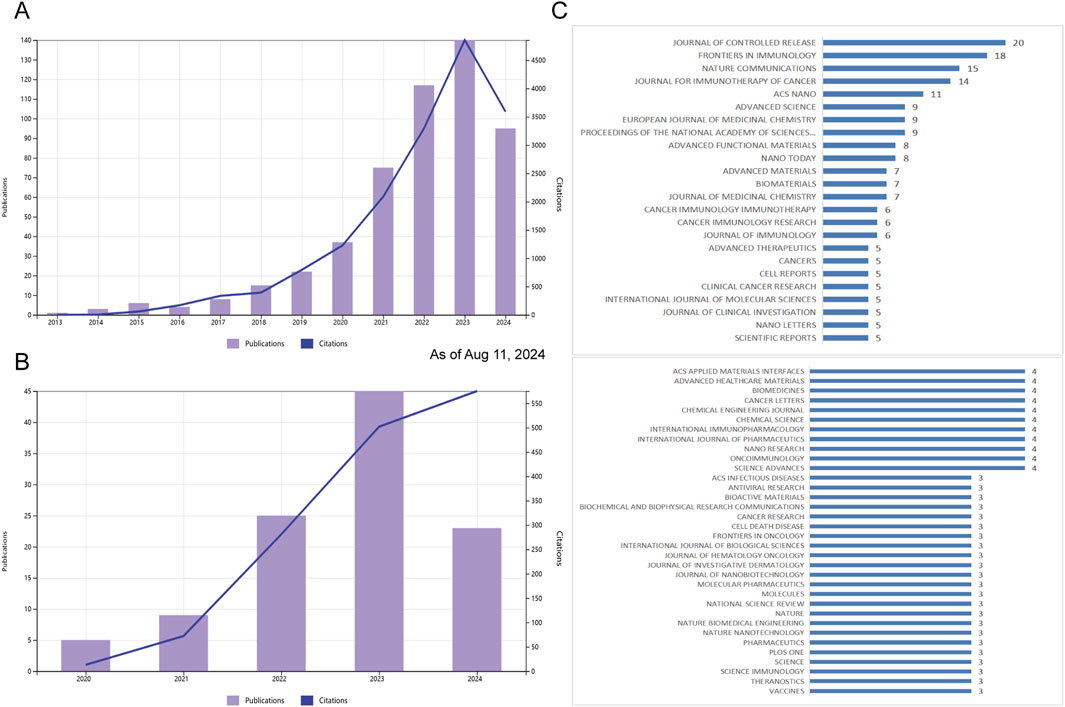
Figure 2. Publication and citation trends and journal distribution for STING agonist and inhibitor research (as of 11 Aug 2024). (A) Annual publication count and citation trends for STING agonist research from 2013 to 2024. (B) Annual publication count and citation trends for STING inhibitor research from 2013 to 2024. (C) Top journals publishing studies related to STING agonists and inhibitors, with counts indicating the number of relevant articles.
A total of 200 journals published the literature, as shown in Figure 2C. The top 10 journals [ranked by the number of publications (NPs)] are presented in Table 1 along with additional journal information, including the NPs, number of citations (NCs), journal impact factor (IF), average citations per item [also known as citations per article (CA)], and H-index. The JOURNAL OF CONTROLLED RELEASE published the highest number of relevant articles. CA serves as an indicator of contribution impact in a specific domain. A higher CA figure means a greater contribution. Although every journal did not publish similar articles, they played a significant role in shaping this sphere. In particular, NATURE COMMUNICATIONS (n = 15, CA = 49.6), JOURNAL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF CANCER (n = 14, CA = 46.64), and the PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE United States (n = 9, CA = 33.56) showed a substantial impact. These findings indirectly highlight the significance of STING regulation and the potential application of STING agonists/antagonists.
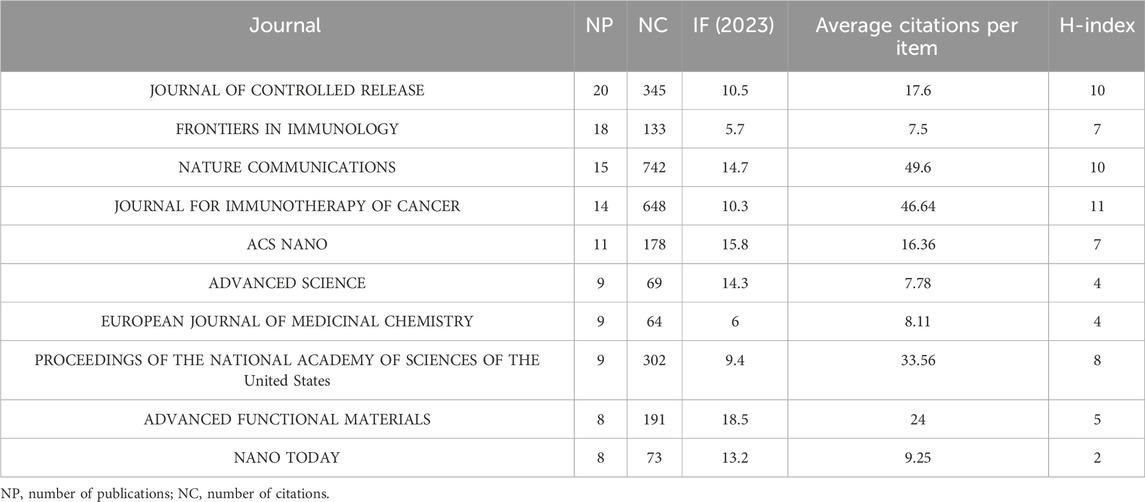
Table 1. Quantitative measurement of top 10 journals publishing articles about STING agonists and/or inhibitors.
The top 10 article categories related to STING agonists are presented in Figure 3A. Over half of the publications were classified as “Oncology” (n = 184, 34.92%), followed by “Immunology” (n = 126, 23.91%), “Chemistry Multidisciplinary” (n = 104, 19.73%), “Nanotechnology” (n = 81, 15.37%), and “Pharmacology Pharmacy” (n = 74, 14.04%). As shown in Figure 3B, the top five article categories related to STING inhibitors are “Pharmacology Pharmacy,” “Immunology,” “Cell biology,” “Neuroscience,” and “Multidisciplinary science.” According to the categorization result, STING agonists are more advanced in clinical application, particularly in oncology. In contrast, STING inhibitors are in the early stages of research and development, with a broader therapeutic potential under exploration. For further understanding, we referred to the global drug development database for STING agonists and inhibitors from the “Pharnextcloud” platform (https://data.pharnexcloud.com/). The analysis, as depicted in Figure 3C, reveals that most STING agonists are in the preclinical and Phase I clinical trial stages. Some are in Phase II clinical trials, while there are very few STING inhibitors under development. Additional details, including company information, indications, and target molecules, are compiled in Supplementary Table S1. Additionally, we conducted a keyword timeline and clustering analysis of the publications from the top five categories, as well as counterparts in the field of pathogenology, as shown in Supplementary Figures S1–S6.
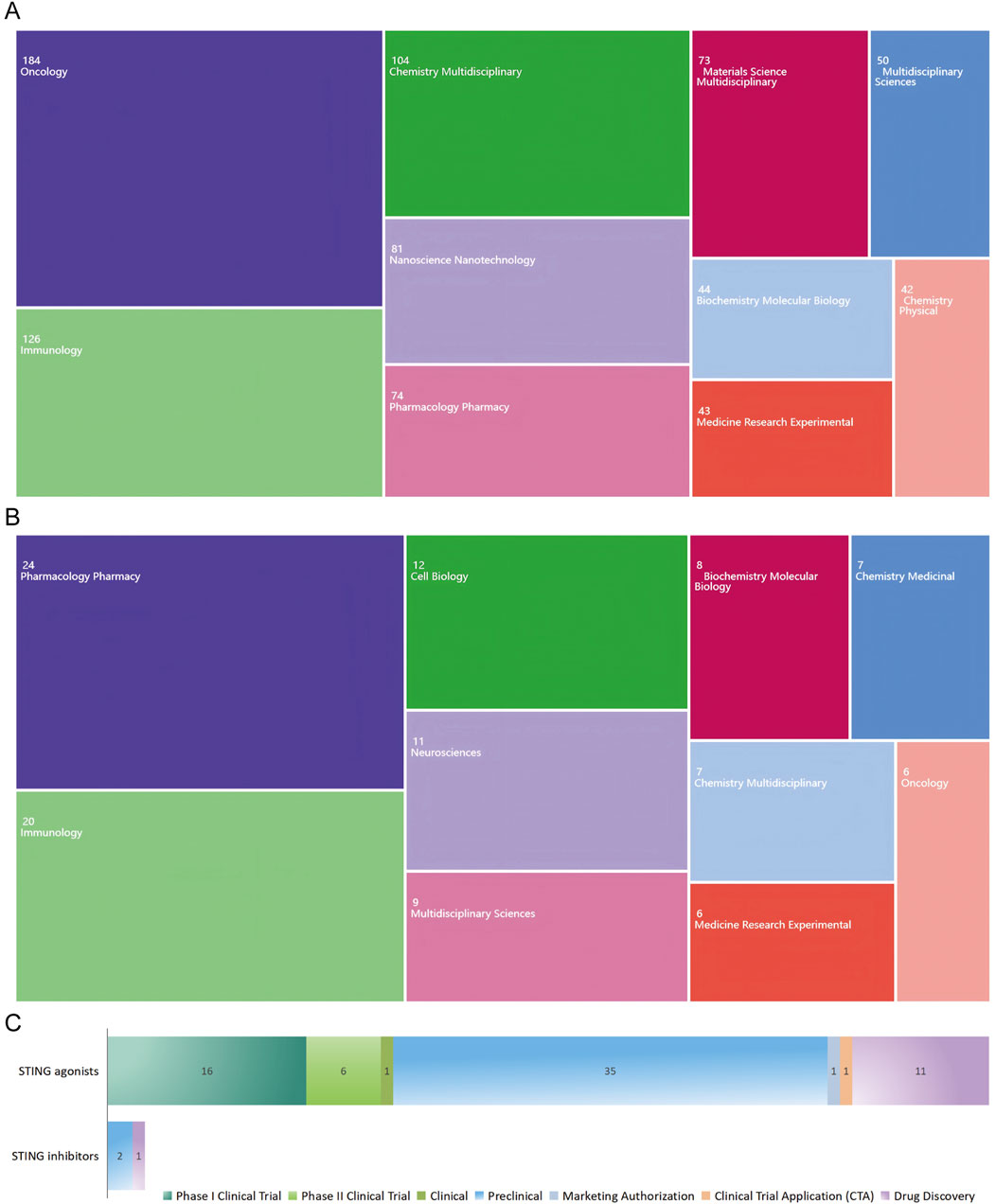
Figure 3. Publication distribution across WOS categories and drug development overview. (A) Publication categories related to STING agonists. (B) Publication categories related to STING inhibitors. (C) STING agonist and inhibitor development stage overview.
These articles were published across 42 countries. As shown in Figure 4A, the top 10 most productive countries are China (n = 335, 63.57%), the United States (n = 244, 46.30%), South Korea (n = 26, 4.93%), Japan (n = 26, 4.93%), and Germany (n = 24, 4.55%), followed by England (n = 15, 2.85%), Canada (n = 14, 2.65%), Netherlands (n = 9, 1.71%), Switzerland (n = 9, 1.71%), and Belgium (n = 6, 1.14%). The collaboration network was visualized by VOSviewer, as depicted in Figure 4B, which reflects international collaborations, with a higher number of lines indicating greater activity and the thickness of the line between two countries indicating the strength of the collaborative relationship. China has the most publications, while the United States has the highest collaborative strength. The United States and China had the most robust links.
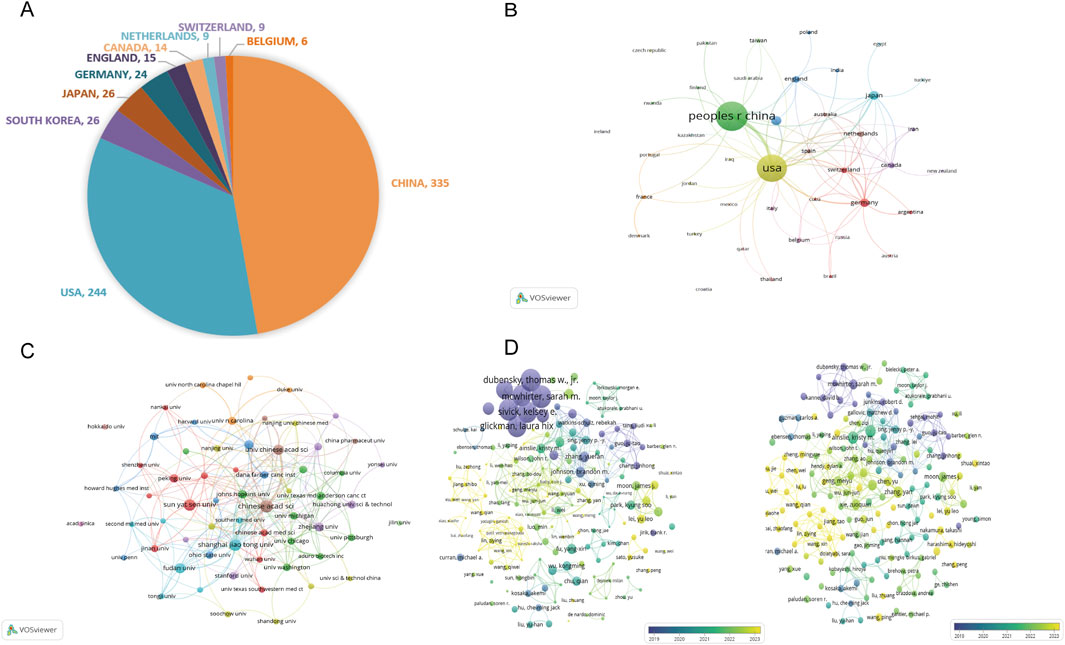
Figure 4. Global distribution and collaborative networks in STING agonist/inhibitor research. (A) The top 10 most productive countries according to the number of articles. (B) Visualization of international collaborative relationships. (C) Visualization of the institutional network. (D) Visualization of co-authorship network.
The top 10 most prolific institutions are presented in Table 2, mirroring the county contribution ranking. They are all from China and the United States, and the CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES has published the most articles (n = 38, NC = 681, China, CA = 18.45, H = 15), while the UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS SYSTEM gained the highest number of citations (n = 27, NC = 1482, the United States, CA = 55.52, H = 17). The partnership visualization of each institution is presented in Figure 4C. Chinese universities have strong and close collaborative ties with one another, which may drive their high productivity.
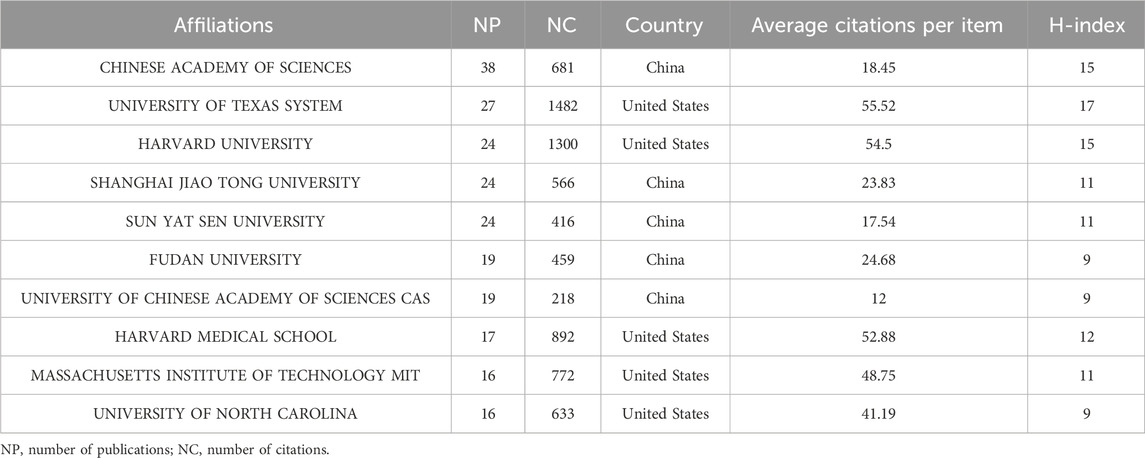
Table 2. Quantitative measurement of top 10 institutions conducting STING agonist/inhibitor research.
The co-authorship analysis of researchers is visualized in Figure 4D. Based on the volume of citations (as shown on the left), the collaborative team of Sarah M. McWhirter, Laura Hix Glickman, David B. Kanne, Thomas W. Dubensky, Jr., and Kelsey E. Sivick has published the most highly cited articles. In terms of the volume of documents (as shown on the right), Kristy Ainslie and Eric M. Bachelder have the highest NPs. Chinese scholars have published relatively newer literature, indicating their rapid exploration and application of new research directions. This highlights a solid scientific research foundation of the United States and China’s strength in applied innovation in this field. In general, the United States and China have made significantly far greater contributions to this field than other countries, and their responses to new research directions are more timely and rapid.
Keywords were extracted from the titles and abstracts and then analyzed using VOSviewer and Citespace. Keyword analysis is helpful in monitoring scientific questions and highlighting emerging hotspots. In Figure 5, the significance of each term is highlighted by the size of the circle, with a larger circle indicating greater importance. Lines connecting the terms represent the association, and the thickness of the lines indicates the strength of the association between the two terms. By pointing to a specific keyword, one can obtain research directions and hotspots related to that keyword. Keywords co-occurrence analysis related to STING agonists is shown in Figure 5A, while STING antagonists are shown in Figure 5B. The research on STING agonists mainly centered around “cancer immunotherapy.” In addition, “adjuvant,” “innate immunity,” “nanoparticles,” “inflammation,” “apoptosis,” “immune checkpoint blockade,” and other aspects are also active research topics related to STING agonists in recent years. Inflammation is the main direction of exploration for STING antagonists, among which neuroinflammation and acute lung injury are important application directions.
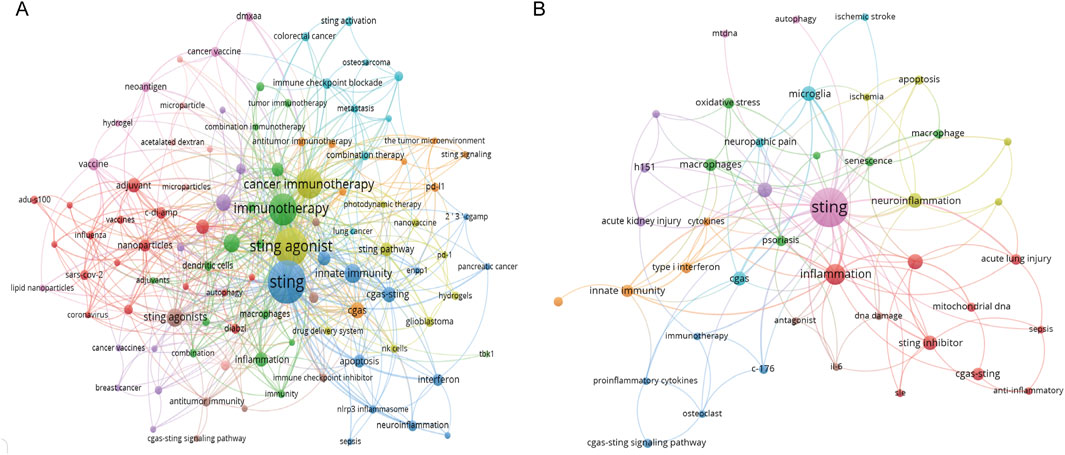
Figure 5. Analysis of the co-occurrence network of keywords. (A) Co-occurrence network of keywords related to STING agonists. (B) Co-occurrence network of keywords related to STING inhibitors.
A detailed display of keywords associated with the top four nodes is presented in Supplementary Figure S7. Among these hot words (minimum number of occurrences of a keyword is more than five; 45 words meet the threshold) that co-occur with STING agonist include: STING, cancer immunotherapy, immunotherapy, tumor microenvironment, innate immunity, colorectal cancer, macrophages, type I interferon, diABZI, photothermal therapy, immunogenic cell death, cGAS-STING pathway, combination therapy, SARS-CoV-2, adjuvant, c-di-AMP, cGAS, cyclic dinucleotides, cGAMP, nanoparticles, melanoma, glioblastoma, DMXAA, cancer, antitumor immunity, vaccine, neoantigen, and drug delivery. For the specific STING agonists and inhibitors, Table 3 summarizes the keywords co-occurring with specific STING agonist drugs, such as c-di-AMP, 2′3′-cGAMP, DMXAA, ADU-S100, 2′3′-c-di-AM(PS)2 (Rp,Rp), and diABZI, MSA-2, and with specific STING inhibitor drugs, such as C176, H151, ISD-017, as well as their usage and main producers.
Through analysis with CiteSpace, it is able to identify research hotspots, reveal research trends, and predict future research directions. Keyword burst refers to a sudden and significant increase in citation frequency within a certain period of time. The citation burst of these keywords usually indicates research hotspots in the field. The red mark on the keyword timelines in Figure 6A indicates the importance of and attention to keywords in the research field: the longer the length, the longer the duration of keywords, and the stronger the research frontier. The top 10 keywords with the strongest citation bursts include innate immunity, influenza vaccine, cytotoxic T cells, checkpoint blockade, 3 dioxygenase (IDO), bispecific antibody, antitumor immunity, immune checkpoint blockade, and cell death, sorted by time. The timeline distribution and clustering of these keywords are shown in Figure 6B. A time slice is located at the top of the figure. The center color of the circle represents the time when a keyword first appeared, and the dark red of the circle indicates that the keyword continues to be a research hotspot to the present day. The larger the circle, the longer the research. Keywords with the same color font belong to the same cluster. Cancer immunotherapy and nanoparticle formulation are long-term research focuses. Drug delivery and immunology research are hot topics in recent years and may be future research directions.
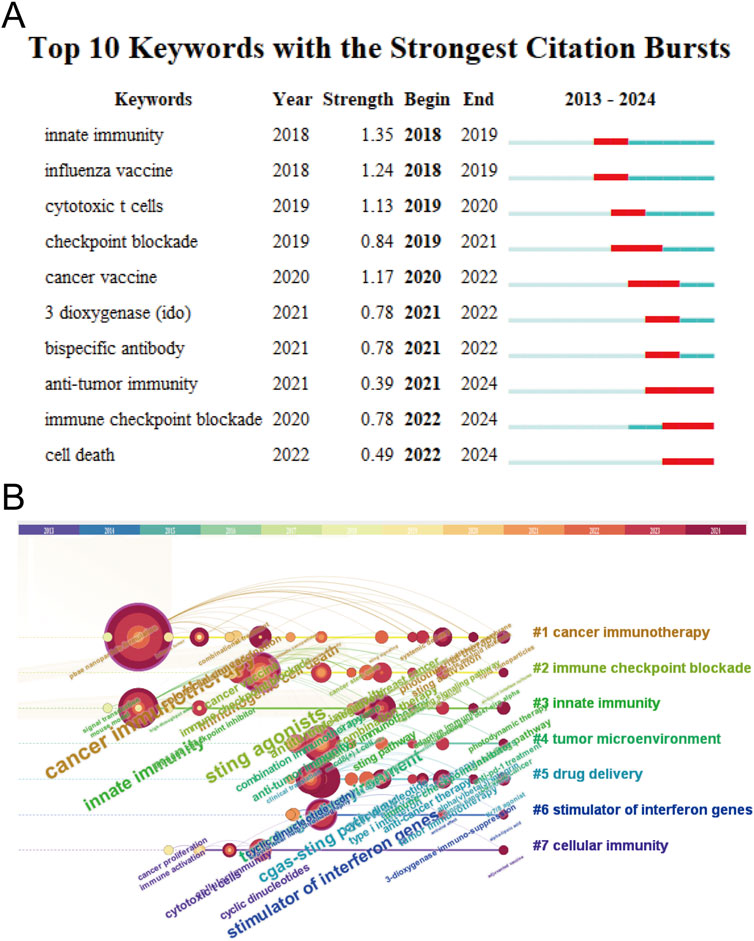
Figure 6. Citation bursts and conceptual networks from keyword analysis. (A) Top 10 keywords with the strongest citation bursts from 2013 to 2024. (B) Timeline view of research clusters based on keyword co-occurrence.
The top 10 most-cited papers about STING agonists are shown in Table 4. These publications were all published in prestigious journals between 2015 and 2021. All of them received a high number of citations per year. The top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts are shown in Figure 7A. Conceptual clusters were created when a set of publications were cited repeatedly together. A timeline view of the top five clusters divided by CiteSpace, nanoparticles, apoptosis, dendritic cells, hepatitis B virus, lipid nanoparticles, and cGAMP adjuvants is presented in Figure 7B. Publications about nanoparticles had the most citation bursts. Dendritic cells are the most extensively studied immune cells.
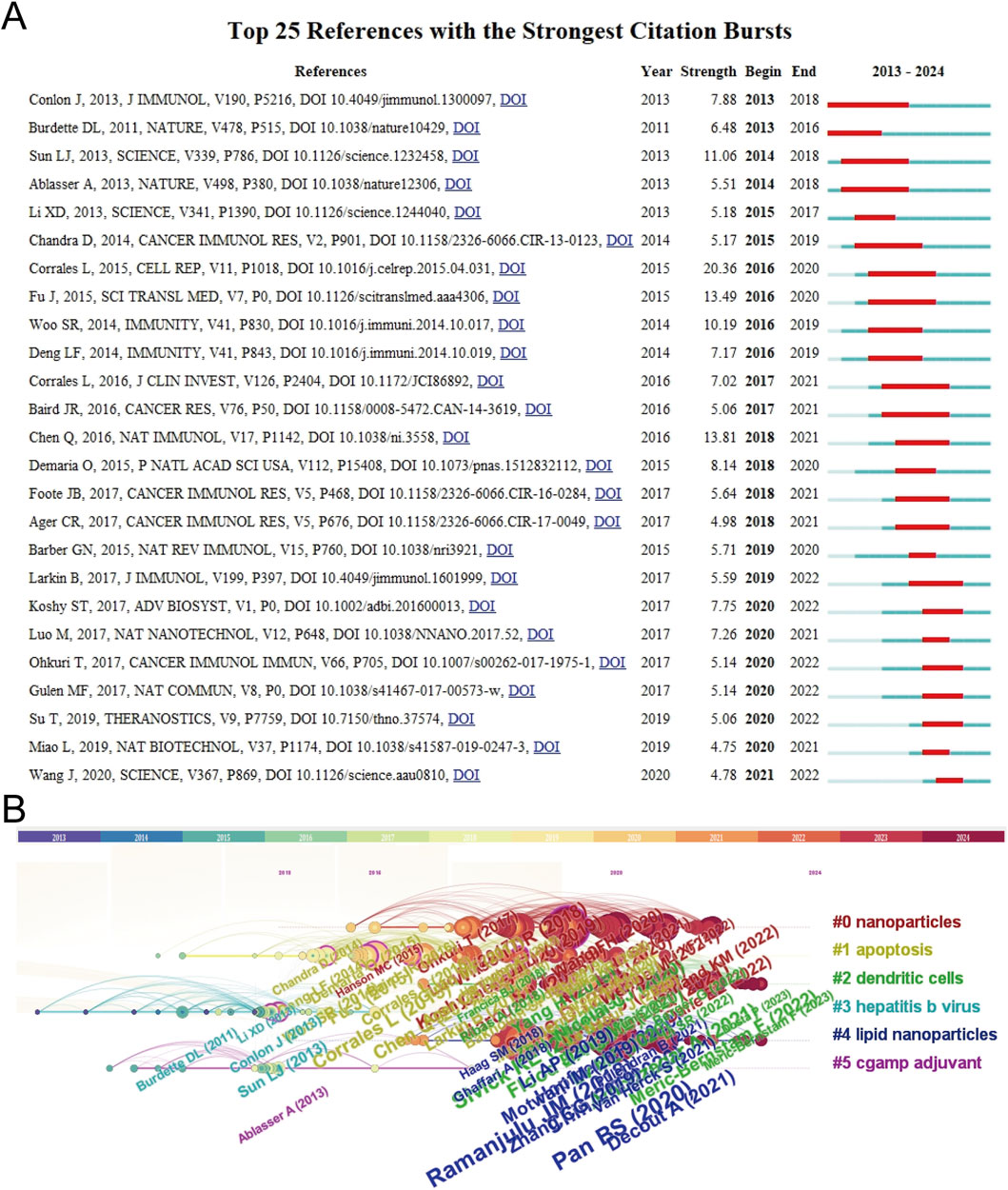
Figure 7. Citation bursts and conceptual networks from reference analysis. (A) Top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts. (B) Timeline view of thematic research topics based on references.
Here, we clarified the current pattern of development trends and research hotspots in the field of STING agonist/antagonist literature. We have included all articles related to STING agonists and antagonists for journal analysis and analysis of collaborative networks across countries, institutions, and authors. Because STING is an emerging therapeutic target, research and development (R&D) efforts on both agonists and antagonists have shown soaring growth over the past decade, as indicated by rising annual publication figures and citation counts. Moreover, the top 10 journals by publication count and co-cited journals are all categorized as Q1, indicating their high quality and impact on the STING research field.
China and the United States are the leading contributors in the field. Both countries dominated the top 10 most productive institutions. Chinese institutions have established a strong collaborative network. The Chinese Academy of Sciences, the University of Texas System, Harvard University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Sun Yat Sen University are the prominent contributors. This leadership can be attributed to a solid scientific research foundation of the United States and China’s strength in applied innovation in this field, as well as substantial investments. China also shows the most achievements in the study of the STING signaling pathway, establishing a perfect theoretical knowledge system.
Kristy Ainslie and Eric M. Bachelder (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill), Zuoquan Xie (Chinese Academy of Sciences), Jenny P. Ting (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill), and James J. Moon (University of Michigan) are the top five most prolific authors. The research collaboration team of Kristy Ainslie and Eric M. Bachelder focuses on the development of new vaccines and immunotherapies, including nanoparticle delivery systems for STING agonists and the application of STING agonists in seasonal influenza vaccines and autoimmune diseases. Their latest research showed that the encapsulation of cGAMP in acetylated dextran (Ace-DEX) microparticles (MPs) with multi-COBRA hemagglutinin enhances its intracellular delivery, eliciting protective immune responses against human seasonal and pre-pandemic strains (Hendy et al., 2024b; Zhang et al., 2024).
Xie primarily specializes in antitumor immunity, and his latest research reported a new compound 202 (C202) that made a structure modification to MSA-2 by replacing the carbonyl group with a difluoromethylene, exhibiting better oral bioavailability and plasma exposure than MSA-2. Encouragingly, it induced complete tumor regression in many tumor models of mice and stimulated powerful immune memory effects, contributing to long-term immune response against cancer (Wang et al., 2023; Ding et al., 2023). Furthermore, his team designed a new diABZI-based STING agonist, HB3089, currently undergoing preclinical development as a promising drug candidate that triggers substantial antitumor immunity and exhibits robust antitumor activity (Xie et al., 2022). Jenny P. Ting also specializes in developing a STING agonist delivery platform, new STING agonist compounds, and influenza vaccines (Watkins-Schulz et al., 2019; Gallovic et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2022). She recently reported a universal STING mimic (uniSTING) based on a polymeric architecture. It can selectively stimulate tumor control IRF3/IFN-I pathways but not tumor progression NF-κB pathways. Intratumoral or systemic injection of uniSTING-mRNA via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) results in potent antitumor efficacy across triple-negative breast cancer, lung cancer, melanoma, and orthotopic/metastatic liver malignancies (Wang Y. et al., 2024).
James J. Moon has expertise in nanotechnology, immunotherapies, and combination treatments for cancer (Sun et al., 2020). He recently demonstrated a prototype of cancer metalloimmunotherapy by using manganese (Mn2+) that has been proven to effectively activate the cGAS-STING signaling pathway (Lv et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021). By focusing on the research contents of these outstanding scholars, we can keep abreast of the cutting-edge achievements in this field.
We conducted individual keyword analysis and category analysis for STING agonists and antagonists. The application of STING agonists mainly focuses on cancer immunotherapy and vaccine adjuvants, as well as inflammation-associated diseases. Unlike agonists, STING inhibitors are being developed to mitigate unwanted STING activation, which is associated with chronic inflammatory diseases like lupus, Aicardi–Goutières syndrome, myocardial infarction, and other interferonopathies (Zhang et al., 2022). By inhibiting the pathway, researchers aim to reduce inappropriate immune responses triggered by self-DNA or chronic cytoplasmic DNA presence, which could otherwise lead to tissue damage and persistent inflammation. Neuroinflammation and AID treatment may be an important paradigm for the application of STING inhibitors.
According to the keyword co-occurrence and burst analysis, research in this domain primarily focuses on the following aspects:
(1) Development of new STING delivery vehicles: Scientists are employing a variety of novel technologies to modify STING agonists, aiming to synthesize ones with more targeted effects. STING agonists administered systemically often suffer from issues such as insufficient tumor accumulation, rapid clearance, and short duration of action, leading to limited therapeutic effectiveness (Van Herck et al., 2021; Li et al., 2023). To address these limitations, researchers are developing efficient agonist delivery platforms, including nanoparticle systems (Chen et al., 2023), lipid microparticles (Lu et al., 2020; Hao et al., 2023; Hendy et al., 2024a), ultrasound-activated vehicles (Jiang et al., 2023), and various polymers and bio-degradable materials that can encapsulate STING agonists (Huang et al., 2023). Thus, research in this area is multidisciplinary.
(2) Combined therapeutic strategies: To enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy, researchers are combining nano-engineered STING agonists with other treatment modalities, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (Su et al., 2019; Zhang P. et al., 2023), mild-temperature photothermal therapy (Ma et al., 2023), synergy with chemotherapy, combination with CAR-T therapy (Xu et al., 2021), and sono-activatable immunotherapy (Jiang et al., 2023). The primary strategy is to target and influence the tumor microenvironment (TME) to increase STING agonist accumulation within tumor tissues and amplify immune cell activation. The preliminary data showed that some combination therapies had encouraging antitumor activity with a tolerable safety profile (Yi et al., 2022).
(3) Exploring therapeutic effects across various diseases: The therapeutic impact of STING activation is complex. Although it has shown significant results in antitumor and antiviral applications, potential side effects such as cytokine storms and autoimmune diseases remain limiting factors. In striking contrast to their tumor suppressive roles, cGAS and STING have also been implicated in promoting tumor burden and worse disease outcomes in models of cancer (Decout et al., 2021). Additionally, studies on STING agonists in bacterial or fungal infections are limited. There is growing interest in using STING agonists for bacterial infections and chronic inflammatory diseases. The effects of STING agonists are being explored in various diseases, including melanoma, colorectal cancer, anti-vascular therapies, metastasis, pancreatic cancer, influenza, aging, breast cancer, cervical cancer, SARS-CoV-2, HIV, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections.
(4) Application as vaccine adjuvants (Tian et al., 2024): STING agonists can be applied in the development of cancer vaccines, including those for melanoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer, by activating the STING pathway to promote tumor antigen recognition and presentation, thus enhancing T cell-specific immune responses against cancer cells. Research on COVID-19 vaccines has further driven interest in STING agonists as vaccine adjuvants as they can enhance immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 and provide broad and durable protective effects (Humphries et al., 2021a; Zhang Y. et al., 2023). STING agonists also show potential in influenza (Luo et al., 2019), BCG (Erik et al., 2018), and HIV vaccines (Chattopadhyay and Hu, 2020) by promoting dendritic cell (DC) activation, increasing antibody production, and enhancing T-cell responses. As adjuvants in cancer and viral vaccines, STING agonists exhibit significant potential, with future research aiming to optimize their safety, efficacy, and delivery methods.
In summary, for STING agonists, the most urgent challenges include the development of drug delivery and release systems and understanding their working patterns in vivo, devising effective combination therapy strategies, and the development of biomarkers. When considering the developmental stages of cancer, the regulation of STING becomes complex. Some reports have also confirmed that chronic stimulation of STING can mediate tumor formation and metastasis through inflammation (Nambiar et al., 2023); thus, understanding their working patterns in vivo is important.
Combination therapy strategies address the resistance and inefficacy associated with the monotherapeutic use of STING agonists (Li et al., 2022). Biomarkers for monitoring the safety and efficacy of STING agonists/inhibitors therapy must be studied. Additionally, it is crucial for researchers across various fields to delve into the mechanisms by which STING operates in diseases, especially in inflammatory pathology during the course of disease. More clinical data need to be carefully analyzed and evaluated. STING inhibitors show promising prospects in the treatment of autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. However, as small-molecule drugs, they also face the tricky issue of drug delivery system development. Their development is relatively recent and currently still in the preclinical or drug discovery stages. Understanding the dual role of STING signaling in different disease states may promote the development of STING inhibitors.
This analysis reveals the development trends in the research of both STING agonists and inhibitors, providing a detailed overview of this field. STING agonists show great potential in cancer immunotherapy, with a focus on enhancing their stability, cell permeability, and target concentration through advanced drug delivery systems like nanotechnology and lipid nanoparticles. Future research directions for STING agonists include developing high specificity and potency STING agonists, devising effective combination therapy strategies, and developing biomarkers. In contrast, STING inhibitors are emerging as promising candidates for the treatment of autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases, facing the same challenges of drug delivery and specificity. Additionally, there is a growing interest in understanding the role of the cGAS-STING pathway in non-neoplastic diseases, which may reveal new opportunities for the application of both STING agonists and inhibitors.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
XW: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, visualization, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. QW: data curation, validation, and writing–review and editing. YG: data curation, validation, and writing–review and editing. LJ: data curation, validation, and writing–review and editing. LT: conceptualization, project administration, supervision, and writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1528459/full#supplementary-material
Alee, I., Chantawichitwong, P., Leelahavanichkul, A., Paludan, S. R., Pisitkun, T., and Pisitkun, P. (2024). The STING inhibitor (ISD-017) reduces glomerulonephritis in 129.B6.Fcgr2b-deficient mice. Sci. Rep. 14, 11020. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61597-z
Anton, N., Jason, F., and Lauren, M. (2022). Bibliometrics: methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect. Med. Educ. 11, 173–176. doi:10.1007/s40037-021-00695-4
Cai, L., Wang, Y., Chen, Y., Chen, H., Yang, T., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Manganese(ii) complexes stimulate antitumor immunity via aggravating DNA damage and activating the cGAS-STING pathway. Chem. Sci. 14, 4375–4389. doi:10.1039/d2sc06036a
Chattopadhyay, S., and Hu, C.-M. J. (2020). Nanomedicinal delivery of stimulator of interferon genes agonists: recent advances in virus vaccination. Nanomedicine (Lond) 15, 2883–2894. doi:10.2217/nnm-2020-0269
Chen, C.Xu (2023). Cellular functions of cGAS-STING signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 33, 630–648. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2022.11.001
Chen, X., Meng, F., Xu, Y., Li, T., Chen, X., and Wang, H. (2023). Chemically programmed STING-activating nano-liposomal vesicles improve anticancer immunity. Nat. Commun. 14, 4584. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40312-y
Chen, X., Xu, Z., Li, T., Thakur, A., Wen, Y., Zhang, K., et al. (2024a). Nanomaterial-encapsulated STING agonists for immune modulation in cancer therapy. Biomark. Res. 12, 2. doi:10.1186/s40364-023-00551-z
Chen, Y., Li, R., Duan, Q., Wu, L., Li, X., Luo, A., et al. (2024b). A DNA-modularized STING agonist with macrophage-selectivity and programmability for enhanced anti-tumor immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11, e2400149. doi:10.1002/advs.202400149
Decout, A., Katz, J. D., Venkatraman, S., and Ablasser, A. (2021). The cGAS-STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 21, 548–569. doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00524-z
Ding, C., Du, M., Xiong, Z., Wang, X., Li, H., He, E., et al. (2023). Photochemically controlled activation of STING by CAIX-targeting photocaged agonists to suppress tumor cell growth. Chem. Sci. 14, 5956–5964. doi:10.1039/d3sc01896b
Ding, C., Song, Z., Shen, A., Chen, T., and Zhang, A. (2020). Small molecules targeting the innate immune cGAS‒STING‒TBK1 signaling pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 10, 2272–2298. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2020.03.001
Donnelly, C. R., Jiang, C., Andriessen, A. S., Wang, K., Wang, Z., Ding, H., et al. (2021). STING controls nociception via type I interferon signalling in sensory neurons. Nature 591, 275–280. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-03151-1
Dvorkin, S., Cambier, S., Volkman, H. E., and Stetson, D. B. (2024). New frontiers in the cGAS-STING intracellular DNA-sensing pathway. Immunity 57, 718–730. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.02.019
Erik, V. D., Kimberly, S., Chris, R., Kelsey, S., Natalie, S., Meredith, L., et al. (2018). STING-activating adjuvants elicit a Th17 immune response and protect against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Cell Rep. 23, 1435–1447. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.003
Gallovic, M. D., Junkins, R. D., Sandor, A. M., Pena, E. S., Sample, C. J., Mason, A. K., et al. (2022). STING agonist-containing microparticles improve seasonal influenza vaccine efficacy and durability in ferrets over standard adjuvant. J. Control Release 347, 356–368. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.017
Hao, Y., Ji, Z., Zhou, H., Wu, D., Gu, Z., Wang, D., et al. (2023). Lipid-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy. MedComm 4, e339. doi:10.1002/mco2.339
Hendy, D. A., Ma, Y., Dixon, T. A., Murphy, C. T., Pena, E. S., Carlock, M. A., et al. (2024a). Polymeric cGAMP microparticles affect the immunogenicity of a broadly active influenza mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine. J. Control Release 372, 168–175. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.06.007
Hendy, D. A., Pena, E. S., Batty, C. J., Ontiveros-Padilla, L., Iii, J. A. R., Dixon, T. A., et al. (2024b). Cobra hemagglutinin and cGAMP loaded ace-dex microparticles provide a broadly active and shelf-stable influenza vaccine platform. Adv. Ther. 7, 2300273. doi:10.1002/adtp.202300273
Hopfner, K.-P., and Hornung, V. (2020). Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS–STING signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 501–521. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-0244-x
Huang, C., Shao, N., Huang, Y., Chen, J., Wang, D., Hu, G., et al. (2023). Overcoming challenges in the delivery of STING agonists for cancer immunotherapy: a comprehensive review of strategies and future perspectives. Mater Today Bio 23, 100839. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100839
Humphries, F., Shmuel-Galia, L., Jiang, Z., Wilson, R., Landis, P., Ng, S.-L., et al. (2021a). A diamidobenzimidazole STING agonist protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Immunol. 6, eabi9002. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abi9002
Humphries, F., Shmuel-Galia, L., Jiang, Z., Wilson, R., Landis, P., Ng, S.-L., et al. (2021b). A diamidobenzimidazole STING agonist protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Immunol. 6, eabi9002. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abi9002
Ishikawa, H., and Barber, G. N. (2008). STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 455, 674–678. doi:10.1038/nature07317
Jiang, J., Zhang, M., Lyu, T., Chen, L., Wu, M., Li, R., et al. (2023). Sono-driven STING activation using semiconducting polymeric nanoagonists for precision sono-immunotherapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Adv. Mater. 35, 2300854. doi:10.1002/adma.202300854
Jin, L., Waterman, P., Jonscher, K., Short, C., Reisdorph, N., and Cambier, J. (2008). MPYS, a novel membrane tetraspanner, is associated with major histocompatibility complex class II and mediates transduction of apoptotic signals □. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 5014–5026. doi:10.1128/MCB.00640-08
Joshi, R., G Scott, P., Jingsong, Y., Nestor, C., Robert, S., Shu-yan, Z., et al. (2018). Design of amidobenzimidazole STING receptor agonists with systemic activity. Nature 564, 439–443. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0705-y
Leekha, A., Saeedi, A., Kumar, M., Sefat, K. M. S. R., Martinez-Paniagua, M., Meng, H., et al. (2024). An intranasal nanoparticle STING agonist protects against respiratory viruses in animal models. Nat. Commun. 15, 6053. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-50234-y
Li, S., Mirlekar, B., Johnson, B. M., Brickey, W. J., Wrobel, J. A., Yang, N., et al. (2022). STING-induced regulatory B cells compromise NK function in cancer immunity. Nature 610, 373–380. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05254-3
Li, X., Wang, H., Chen, Y., Li, Z., Liu, S., Guan, W., et al. (2023). Novel emerging nano-assisted anti-cancer strategies based on the STING pathway. Acta Mater. Medica 2, 323–341. doi:10.15212/AMM-2023-0023
Liu, Y., and Pu, F. (2023). Updated roles of cGAS-STING signaling in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 14, 1254915. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1254915
Liu, Z., Zhou, J., Wang, W., Zhang, G., Xing, L., Zhang, K., et al. (2024). Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 and JN.1 by CF501 adjuvant-enhanced immune responses targeting the conserved epitopes in ancestral RBD. Cell Rep. Med. 5, 101445. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101445
Lu, T., Hu, F., Yue, H., Yang, T., and Ma, G. (2020). The incorporation of cationic property and immunopotentiator in poly (lactic acid) microparticles promoted the immune response against chronic hepatitis B. J. Control Release 321, 576–588. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.039
Luo, J., Liu, X.-P., Xiong, F.-F., Gao, F.-X., Yi, Y.-L., Zhang, M., et al. (2019). Enhancing immune response and heterosubtypic protection ability of inactivated H7N9 vaccine by using STING agonist as a mucosal adjuvant. Front. Immunol. 10, 2274. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02274
Lv, M., Chen, M., Zhang, R., Zhang, W., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Manganese is critical for antitumor immune responses via cGAS-STING and improves the efficacy of clinical immunotherapy. Cell Res. 30, 966–979. doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00395-4
Ma, W., Sun, R., Tang, L., Li, Z., Lin, L., Mai, Z., et al. (2023). Bioactivable STING nanoagonists to synergize NIR-II mild photothermal therapy primed robust and long-term anticancer immunity. Adv. Mater. 35, 2303149. doi:10.1002/adma.202303149
Messaoud-Nacer, Y., Culerier, E., Rose, S., Maillet, I., Rouxel, N., Briault, S., et al. (2022). STING agonist diABZI induces PANoptosis and DNA mediated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Cell Death Dis. 13, 269. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04664-5
Minlin, J., Peixin, C., Lei, W., Wei, L., Bin, C., Yu, L., et al. (2020). cGAS-STING, an important pathway in cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. and Oncol. 13, 81. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-00916-z
Nambiar, D. K., Viswanathan, V., Cao, H., Zhang, W., Guan, L., Chamoli, M., et al. (2023). Galectin-1 mediates chronic STING activation in tumors to promote metastasis through MDSC recruitment. Cancer Res. 83, 3205–3219. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0046
Oduro, P. K., Zheng, X., Wei, J., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). The cGAS-STING signaling in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: future novel target option for pharmacotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 12, 50–75. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.011
Pan, B.-S., Perera, S. A., Piesvaux, J. A., Presland, J. P., Schroeder, G. K., Cumming, J. N., et al. (2020). An orally available non-nucleotide STING agonist with antitumor activity. Science 369, eaba6098. doi:10.1126/science.aba6098
Romanelli, J. P., Gonçalves, M. C. P., de Abreu Pestana, L. F., Soares, J. A. H., Boschi, R. S., and Andrade, D. F. (2021). Four challenges when conducting bibliometric reviews and how to deal with them. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 28, 60448–60458. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-16420-x
Shamseddine, A., Patel, S. H., Chavez, V., Moore, Z. R., Adnan, M., Di Bona, M., et al. (2023). Innate immune signaling drives late cardiac toxicity following DNA-damaging cancer therapies. J. Exp. Med. 220, e20220809. doi:10.1084/jem.20220809
Shao, J., Meng, Y., Yuan, K., Wu, Q., Zhu, S., Li, Y., et al. (2023). RU.521 mitigates subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced brain injury via regulating microglial polarization and neuroinflammation mediated by the cGAS/STING/NF-κB pathway. Cell Commun. Signal 21, 264. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01274-2
Shen, A., Chen, M., Chen, Q., Liu, Z., and Zhang, A. (2022). Recent advances in the development of STING inhibitors: an updated patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 32, 1131–1143. doi:10.1080/13543776.2022.2144220
Sibal, P. A., Matsumura, S., Ichinose, T., Bustos-Villalobos, I., Morimoto, D., Eissa, I. R., et al. (2024). STING activator 2’3’-cGAMP enhanced HSV-1-based oncolytic viral therapy. Mol. Oncol. 18, 1259–1277. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.13603
Skouboe, M. K., Knudsen, A., Reinert, L. S., Boularan, C., Lioux, T., Perouzel, E., et al. (2018a). STING agonists enable antiviral cross-talk between human cells and confer protection against genital herpes in mice. PLoS Pathog. 14, e1006976. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006976
Skouboe, M. K., Knudsen, A., Reinert, L. S., Boularan, C., Lioux, T., Perouzel, E., et al. (2018b). STING agonists enable antiviral cross-talk between human cells and confer protection against genital herpes in mice. PLoS Pathog. 14, e1006976. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006976
Su, T., Zhang, Y., Valerie, K., Wang, X.-Y., Lin, S., and Zhu, G. (2019). STING activation in cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics 9, 7759–7771. doi:10.7150/thno.37574
Sun, Q., Bai, X., Sofias, A. M., van der Meel, R., Ruiz-Hernandez, E., Storm, G., et al. (2020). Cancer nanomedicine meets immunotherapy: opportunities and challenges. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 41, 954–958. doi:10.1038/s41401-020-0448-9
Sun, X., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Park, K. S., Han, K., Zhou, X., et al. (2021). Amplifying STING activation by cyclic dinucleotide-manganese particles for local and systemic cancer metalloimmunotherapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1260–1270. doi:10.1038/s41565-021-00962-9
Tian, X., Ai, J., Tian, X., and Wei, X. (2024). cGAS-STING pathway agonists are promising vaccine adjuvants. Med. Res. Rev. 44, 1768–1799. doi:10.1002/med.22016
Van Herck, S., Feng, B., and Tang, L. (2021). Delivery of STING agonists for adjuvanting subunit vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 179, 114020. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2021.114020
Wang, J., Li, S., Wang, M., Wang, X., Chen, S., Sun, Z., et al. (2024a). STING licensing of type I dendritic cells potentiates antitumor immunity. Sci. Immunol. 9, eadj3945. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.adj3945
Wang, X., Shen, A., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Ding, J., Zhang, A., et al. (2023). A novel STING agonist with systemic and durable anti-tumour activity. Clin. Transl. Discov. 3, e231. doi:10.1002/ctd2.231
Wang, Y., Li, S., Hu, M., Yang, Y., McCabe, E., Zhang, L., et al. (2024b). Universal STING mimic boosts antitumour immunity via preferential activation of tumour control signalling pathways. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 856–866. doi:10.1038/s41565-024-01624-2
Watkins-Schulz, R., Tiet, P., Gallovic, M. D., Junkins, R. D., Batty, C., Bachelder, E. M., et al. (2019). A microparticle platform for STING-targeted immunotherapy enhances natural killer cell- and CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity. Biomaterials 205, 94–105. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.03.011
Wenxiang, S., Yang, L., Lu, C., Huihui, C., Fuping, Y., Xiang, Z., et al. (2009). ERIS, an endoplasmic reticulum IFN stimulator, activates innate immune signaling through dimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 8653–8658. doi:10.1073/pnas.0900850106
Wilson, M., Sampson, M., Barrowman, N., and Doja, A. (2021). Bibliometric analysis of neurology articles published in general medicine journals. JAMA Netw. Open 4, e215840. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5840
Xie, Z., Wang, Z., Fan, F., Zhou, J., Hu, Z., Wang, Q., et al. (2022). Structural insights into a shared mechanism of human STING activation by a potent agonist and an autoimmune disease-associated mutation. Cell Discov. 8, 133–217. doi:10.1038/s41421-022-00481-4
Xu, N., Palmer, D. C., Robeson, A. C., Shou, P., Bommiasamy, H., Laurie, S. J., et al. (2021). STING agonist promotes CAR T cell trafficking and persistence in breast cancer. J. Exp. Med. 218, e20200844. doi:10.1084/jem.20200844
Yang, J., Luo, Z., Ma, J., Wang, Y., and Cheng, N. (2024). A next-generation STING agonist MSA-2: from mechanism to application. J. Control. Release 371, 273–287. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.05.042
Yang, K., Han, W., Jiang, X., Piffko, A., Bugno, J., Han, C., et al. (2022). Zinc cyclic di-AMP nanoparticles target and suppress tumours via endothelial STING activation and tumour-associated macrophage reinvigoration. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 1322–1331. doi:10.1038/s41565-022-01225-x
Yi, M., Zheng, X., Niu, M., Zhu, S., Ge, H., and Wu, K. (2022). Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: current advances and future directions. Mol. Cancer 21, 28. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01489-2
Zhang, P., Rashidi, A., Zhao, J., Silvers, C., Wang, H., Castro, B., et al. (2023a). STING agonist-loaded, CD47/PD-L1-targeting nanoparticles potentiate antitumor immunity and radiotherapy for glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 14, 1610. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-37328-9
Zhang, X., Shi, H., Hendy, D., Bachelder, E., Ainslie, K., and Ross, T. (2024). Multi-COBRA hemagglutinin formulated with cGAMP microparticles elicits protective immune responses against influenza viruses. mSphere 9, e0016024. doi:10.1128/msphere.00160-24
Zhang, Y., Yan, J., Hou, X., Wang, C., Kang, D. D., Xue, Y., et al. (2023b). STING agonist-derived LNP-mRNA vaccine enhances protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2. Nano Lett. 23, 2593–2600. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c04883
Zhang, Z., Zhou, H., Ouyang, X., Dong, Y., Sarapultsev, A., Luo, S., et al. (2022). Multifaceted functions of STING in human health and disease: from molecular mechanism to targeted strategy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7, 394. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01252-z
Zhao, Z., Ma, Z., Wang, B., Guan, Y., Su, X.-D., and Jiang, Z. (2020). Mn2+ directly activates cGAS and structural analysis suggests Mn2+ induces a noncanonical catalytic synthesis of 2’3’-cGAMP. Cell Rep. 32, 108053. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108053
Keywords: STING agonist, STING inhibitor, bibliometric analysis, cancer immunotherapy, innate immune
Citation: Wang X, Wang Q, Gao Y, Jiang L and Tang L (2025) Profile of STING agonist and inhibitor research: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1528459. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1528459
Received: 14 November 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 11 February 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaoqi Sun, University of Michigan, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Gao, Jiang and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lingli Tang, bGluZ2xpdGFuZ0Bjc3UuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.