
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol., 21 March 2025
Sec. Cardiovascular and Smooth Muscle Pharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1524584
 Muneer Ahmed Khoso1,2,3
Muneer Ahmed Khoso1,2,3 Heng Liu1,2,3
Heng Liu1,2,3 Tong Zhao1,2,3
Tong Zhao1,2,3 Wenjie Zhao1,2,3
Wenjie Zhao1,2,3 Qiang Huang1,2,3
Qiang Huang1,2,3 Zeqi Sun1,2,3
Zeqi Sun1,2,3 Khuzin Dinislam1,2,3
Khuzin Dinislam1,2,3 Chen Chen1,2,3
Chen Chen1,2,3 Lingyi Kong1,2,3
Lingyi Kong1,2,3 Yong Zhang1,2,3*
Yong Zhang1,2,3* Xin Liu1,2,3*
Xin Liu1,2,3*Heart aging involves a complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences, leading to a gradual deterioration of cardiovascular integrity and function. Age-related physiological changes, including ventricular hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, myocardial fibrosis, increased arterial stiffness, and endothelial dysfunction, are influenced by key mechanisms like autophagy, inflammation, and oxidative stress. This review aims to explore the therapeutic potential of plant-derived bioactive antioxidants in mitigating heart aging. These compounds, often rich in polyphenols, flavonoids, and other phytochemicals, exhibit notable antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective properties. These substances have intricate cardioprotective properties, including the ability to scavenge ROS, enhance endogenous antioxidant defenses, regulate signaling pathways, and impede fibrosis and inflammation-promoting processes. By focusing on key molecular mechanisms linked to cardiac aging, antioxidants produced from plants provide significant promise to reduce age-related cardiovascular decline and improve general heart health. Through a comprehensive analysis of preclinical and clinical studies, this work highlights the mechanisms associated with heart aging and the promising effects of plant-derived antioxidants. The findings may helpful for researchers in identifying specific molecules with therapeutic and preventive potential for aging heart.
There is a growing interest in the field of medicine and aging research regarding the effects of plant-derived antioxidants on heart aging. The aging global population underscores the need of to understand the mechanism of heart aging mechanisms and exploring novel treatment techniques. Recent studies have focused on the potential of plant-based antioxidants to enhance cardiovascular health and mitigate the effects of heart aging (Phu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2022). The risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, coronary heart disease, and stroke, is well recognized to increase with age (Flora and Nayak, 2019). Heart aging leads to alterations in heart structure and function, lowering the threshold for CVDs. With the projected increase in the aged population, nearly 50% of adult Americans are expected to have CVDs by 2030, resluting in greater burden of CVDs (Benjamin et al., 2017). The foremost cause of mortality in United States CVDs, are considerably increased by the aging process. A substantial proportion of CVDs, related fatalities and cases approximately 485·6 million are attributed to adults aged 75 years and above on a global scale (Zhou et al., 2016; Fan et al., 2023). Over 40% of all fatalities in China are attributed to CVD, making it the principal cause of mortality. Additionally, China has largest elderly population (aged 65 and above) in the world (Madhavan et al., 2018; Zhou et al., 2019). The exponential and steady growth of this demographic has presented significant challenges in the prevention and management of CVD (Slivnick and Lampert, 2019; Healthcare Engineering, 2022). In the past, efforts to reduce the risk of CVDs primarily focused on controlling known risk factors, which include hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and elevated circulating triglycerides.
Novel approaches to addressingCVDs, have been developed in recent preclinical studies. Research has shown that restricting calories reliably increase longevity in experimental animal models (Sciarretta et al., 2021). Calories restriction mimetic and other pharmaceutical interventions have been developed to delay the onset of age-related diseases, which are leading causes of mortality and morbidity due to their impact on the heart and blood circulation (Ma et al., 2020). Notable advancements in the field of aging studies have enhanced our understanding of the fundamental processes involved in aging, demonstrated that biological aging is adaptive (Saenjum et al., 2023). Age is a key risk factor for many persistent diseases that cause functional decline and loss of independence, such as dementia, type 2 diabetes, CVDs, and cancer, age is a key risk factor (Figure 1). With the substantial increase in the older adult population, projected to reach 12.6% in North America and 12% globally by 2030, it is expected that this percentage will continue to increase (Sinclair et al., 2020; Olayem et al., 2024).
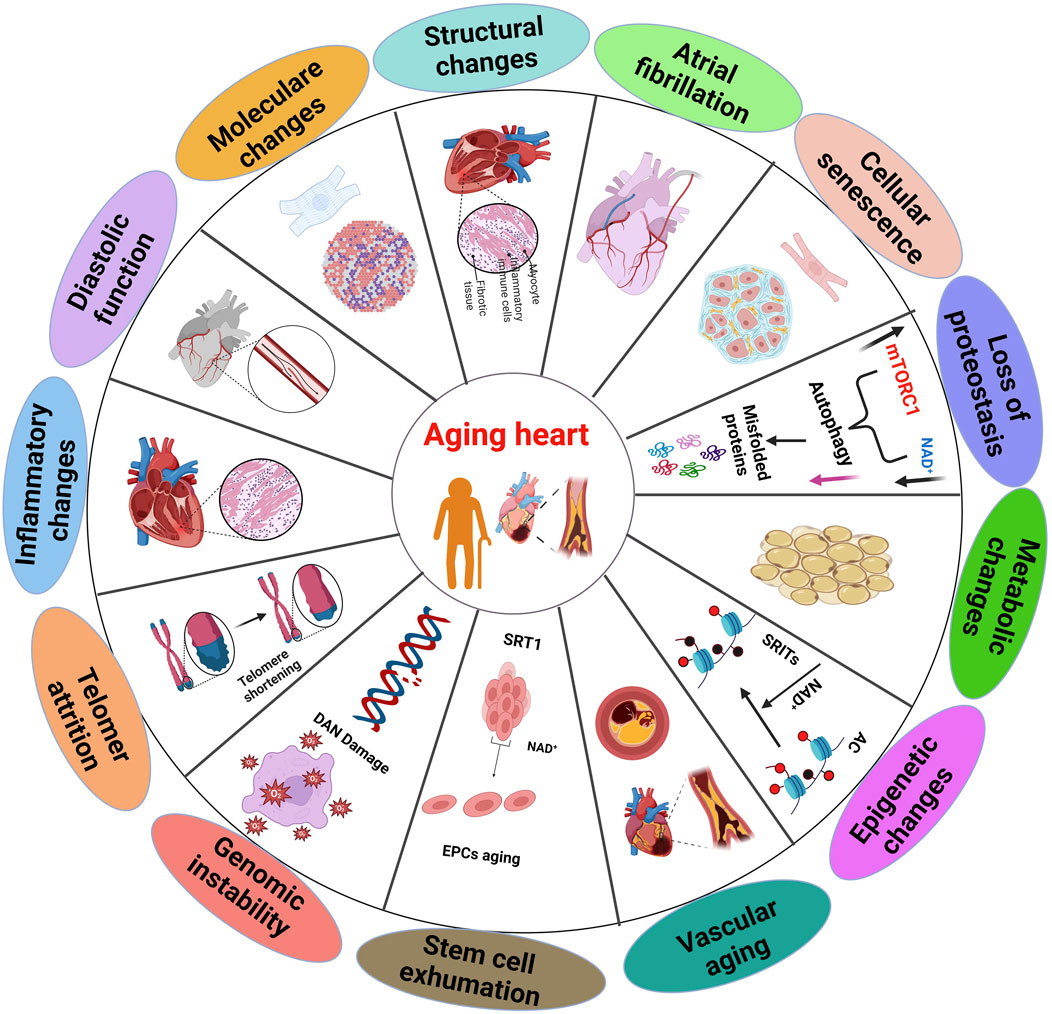
Figure 1. Multiple aspects of the aging heart, which displaying distinct sections and summary of the biochemical and physiological alterations that occur in the heart aging (Haddad et al., 2008).
The aging process involves alterations in the intricate regulatory interactions between cells, organs, and systems (Guo et al., 2022). Cardiac and smooth muscle cells are involved in the involuntary regulation of heart and vascular activities (Chen et al., 2023). The cardiovascular regulation depends on the integrity, excitability, conductivity, contractility, and flexibility of these cells. Cellular aging associated with gradual decline in the physiological activity of cardiomyocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells (Huang and Lei, 2023). Aging causes structural changes in the cardiovascular system, that can impair the function and flexibility of the heart and blood vessels (Ribeiro et al., 2023).
In humans, heart aging is associated with an enlargement of left ventricle, development of fibrosis, and impaired ability of the heart to relax during diastole. This leads to reduced filling of the heart and decreased ejection fraction (Ribeiro et al., 2023; Hamo et al., 2024). While the precise mechanisms remain poorly understood, studies suggest that demise of cardiac myocytes is a crucial factor, (cardiomyocyte apoptosis) and increased stiffness of blood vessels are associated with the structural and functional changes that occur with aging (Anwar et al., 2024;Totoń-Żurańska et al., 2024). Aging significantly increases the susceptibility to numerous diseases. As a result, aging, the heart becomes predisposed to numerous detrimental structural and functional alterations as a result of aging (Figure 2), making age primary risk factor for CVDs. Generally, heart failure is most prevalent in the elderly population, particularly those over 65 years of age (Saheera and Krishnamurthy, 2020).
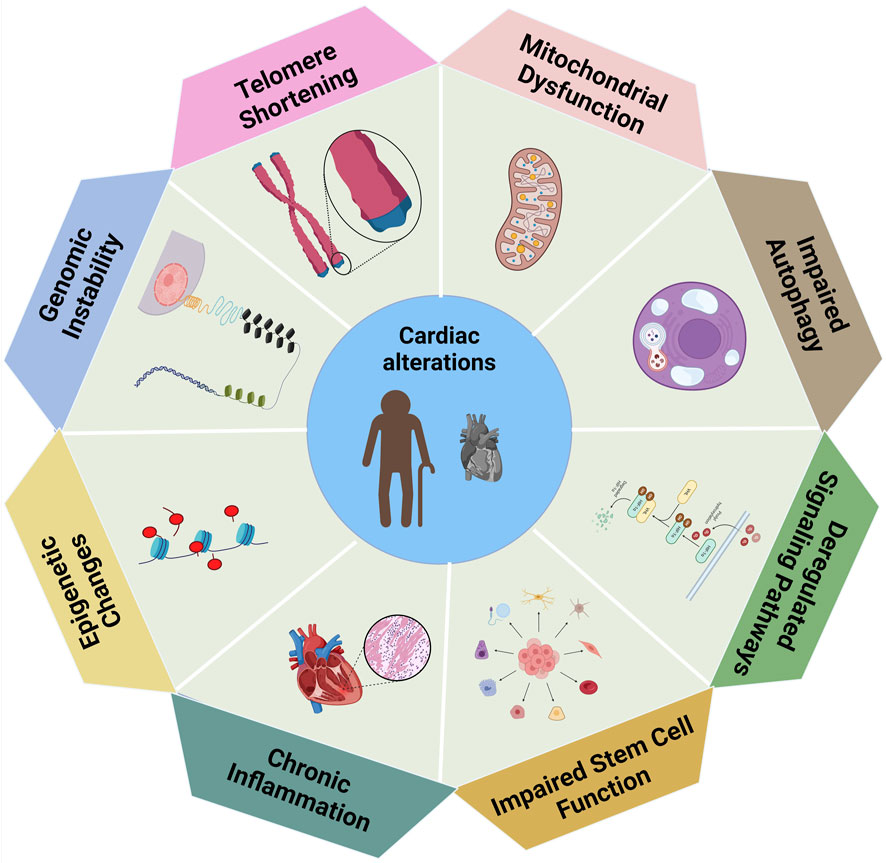
Figure 2. The biological variables associated with cardiac modifications, in which each element indicating a distinct contributor to changes in heart function (Handy et al., 2011).
The functional anomalies of the aged myocardium arise from both structural modifications and cellular and molecular changes. Heart aging is influenced by various molecular processes such as cardiac hypertrophy being a characteristic feature of this aging process in the heart (Hastings et al., 2024). As the heart ages, it undergoes hypertrophy, leading to changes in nutrient and growth signaling (Oldfield et al., 2020). The mechanistic target Rapamycin (mTOR) (Dai et al., 2023), and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) are two significant signaling pathways that have an involvement in heart hypertrophy and aging (Abdellatif et al., 2023). The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), governs cellular development and has been shown to be a significant regulator of the aging process and age related diseases (Liu and Sabatini, 2020). Enhanced mTOR signaling hinders resilience to heart aging, whereas diminished mTOR signaling improves it in mice models (Mannick and Lamming, 2023).
In animal models, the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway is essential for controlling longevity. Deficiency in this signaling pathway in mice leads to a decrease in age-related dysfunction of cardiomyocytes (Lee and Kim, 2018). The decline in IGF-1 levels associated with aging increases the heart failure risk in individuals (Khan et al., 2002). The functional damage caused by dysfunctional mitochondria can shorten life expectancy by impairing cellular and organ function (Amorim et al., 2022). Age-related diseases increase mitochondrial ROS production result in enlarged, bloated, and damaged mitochondria (Liu et al., 2020; Schneider et al., 2020). In the heart, mitochondrial function is regulated by PGC-1α, also known as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator (Qian et al., 2024).
Cardiac dysfunction results from the repression of its expression in failing hearts (He et al., 2022). Mitochondrial malfunction and aberrant ROS generation accelerate the aging process, by directly harming cellular macromolecules and interfering with normal regular signaling and energetics (Proshkina et al., 2020). The ECM, a conglomeration of proteins located outside cells, offers structural and metabolic support to neighboring cells (Karamanos et al., 2021). Cardiac fibroblasts are the main producers of ECM proteins, such as collagen, elastin, fibronectin, laminin, and fibrinogen (Halper, 2021). Heart stiffness increases when there is an abundance of ECM deposited on the heart contributed to diastolic dysfunction (Lunde et al., 2024). MMPs, TIMPs, and other proteases regulate the production and breakdown of ECM proteins (Shan et al., 2023). Aging hearts exhibit myocardial fibrosis and dysregulation of ECM protein production and breakdown. Profibrotic factors, such as transforming growth factor-β, stimulate the production of ECM proteins and hinder the breakdown of the matrix by MMPs (Antar et al., 2023; Lunde et al., 2024). The regulation of MMPs and TIMPs varies with on aging; however, their precise roles in heart aging remain inadequately understood (Rodrigues et al., 2024).
The process of heart aging causes microscopic alterations, such as an increase in the thickness of inner layer of blood vessels (intima) and the buildup of collagen. Symptoms includeelevated systolic blood pressure and pulse wave velocity, along with increase in pulse pressure (Xu et al., 2017; Liu W. et al., 2023). Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) may occur as a consequence of increased afterload and wall stress brought on by arterial stiffness. The volume of the myocardium remains constant with age in the heart (Đorđević et al., 2024). Research indicated that within the age range of 30–70 years, approximately 35% of the total myocytes in the ventricle are lost (Oknińska et al., 2022).
Tocounteract the loss of cells, the surviving myocytes undergo hypertrophy, accompanied by an increase in the nonmyocyte compartment. While the exact cause of cell death remains uncertain, aging is associated with a decrease in capillary density, which leads to ischemic injury, (Bradley et al., 2021). Mouse models are commonly used to study heart aging because they accurately replicate the characteristics of human heart aging (Lindsey et al., 2021). Another advantage of using mouse models to research the molecular underpinnings of heart aging is their relatively short lifespan and the availability of genetically engineered animals (García-García et al., 2021). Laboratory mice do not exhibit elevated blood pressure or adverse cholesterol and blood glucose levels, allowing researchers to study the natural heart aging process without additional cardiac complications (Badmus et al., 2023). The echocardiogram conducted on a mouse model revealed phenotypic alterations such as elevated left ventricular mass, impaired diastolic function, and deteriorated myocardial performance index (MPI), resembling the aging process of the human heart (Lazzeroni et al., 2022).
OS significantly contributes to aging and the development of degenerative and chronic diseases by binding to transition metal ions. This includes a range of conditions such as autoimmune disorders, inflammation, cancer, arthritis, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular issues (Leyane et al., 2022). It causes various health problems by triggering abnormalities (Lobo et al., 2010). It occurs when the ability of antioxidants to counteract pro-oxidant compounds is exceeded, OS occurs, leading to disruptions in biological signaling and pathological events, particularly in older adults (Martemucci et al., 2023). Antioxidants are vital for the body’s defense against oxidation, as they help prevent the formation of free radicals and minimize cellular damage (Bratovcic, 2020; Jomova et al., 2024). Non-enzymatic substances found in blood plasma, such as transferrin, ferritin, ceruloplasmin, and albumin, act as preventive antioxidants through attaching itself to ions of transition metals, thereby inhibiting the formation of new reactive species (Skoryk and Horila, 2023). These non-enzymatic antioxidants provide an intermediate defense, neutralizing oxidants and radicals (Rudenko et al., 2023).
Additionally the third line of defense focuses on repairing damage and removing harmful substances, facilitating the regeneration of bio-molecules affected by OS (Umber et al., 2023). When ROS and the body antioxidant defenses are out of balance, which leads to oxidative stress, resulting from both external and internal sources. Exogenous sources of pollution include environmental pollution, tobacco smoke, ionizing radiation, household chemicals, and agricultural chemicals like herbicides as well as insecticides (Jomova et al., 2023). Within the body, ROS are generated by mitochondria, cytochrome P450 enzymes linked to the endoplasmic reticulum, membrane-bound NADPH oxidases (NOX 1-5), and peroxisomes (Alwadei, 2023). ROS, including both free and non-free radicals, are mostly produced in regions of elevated oxygen consumption such as mitochondria, peroxisomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum (Figure 3.) (Bouyahya et al., 2024; Santos et al., 2024). This imbalance linked to a number of diseases, such as heart conditions, since OS may harm DNA, lipids, and proteins (Chen S. et al., 2024).
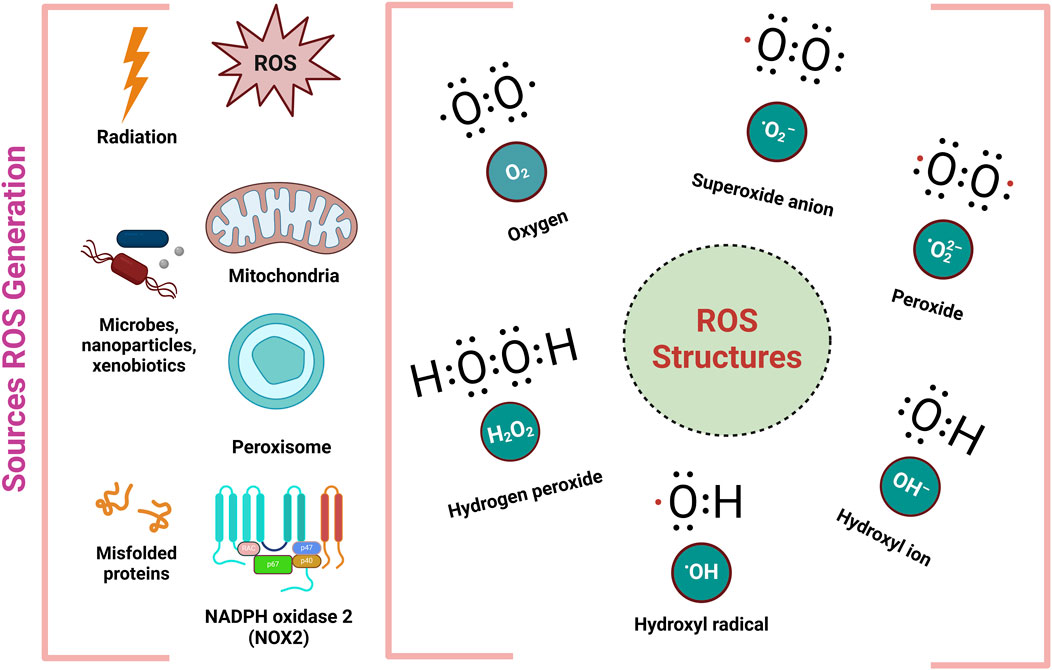
Figure 3. Different sources and structures of ROS (Ahmad et al., 2017).
Cardiovascular disorders such as functional hypoxia, metabolic disturbances, uncoupling of mitochondrial electron transport, and inflammation induce oxidative stress in hypertrophied failing hearts. Oxidative stress, induced by these pathogenic stressors, activates metallo-matrix proteases and destroys extracellular matrix proteins, resulting in cardiac remodeling and heart failure. It also causes subcellular remodeling, problems in Ca2+ handling, and loss of cardiomyocytes owing to apoptosis, necrosis, and fibrosis. Transient low levels of oxyradical production may stimulate redox-sensitive pathways linked to cardiac hypertrophy, whereas sustained high levels can lead to oxidative stress, calcium handling abnormalities, and protease activation, significantly contributing to detrimental cardiac remodeling, cardiac dysfunction, and the progression of heart failure (Shah et al., 2021).
The mechanism for producing ROS is oxidative phosphorylation, which entails the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH via four mitochondrial enzymes, culminating in the synthesis of ATP from ADP (Berthiaume et al., 2019). Electrons lost during this process generate superoxide radicals, resulting in functional degradation of tissues and damage to macromolecules. Superoxide and nitric oxide may react to form peroxynitrite, a strong oxidant that penetrates membranes and nitrates numerous enzymes. It may also be converted into hydrogen peroxide via superoxide dismutase, generating a highly reactive radical known as hydroxyl radical (Juan et al., 2021;Möller and Denicola, 2024). ROS derived from mitochondria contribute significantly to vascular dysfunction by downregulating Nrf2, decreasing NO bioavailability, and increasing the production of vasoconstrictor molecules (Pang et al., 2024). This sequence of events disrupts the mitochondrial membrane, leading to the release pro-apoptotic factors, which results in the apoptosis of plaque cells and inflammation (Chang et al., 2023).
Furthermore, ROS generated by NADPH oxidases during inflammatory reactions are essential for the endogenous production of free radicals (Banerjee et al., 2020). Individuals with a genetic deficit in NOX2 suffer chronic granulomatous disease, makingthem vulnerable to common infections (Garay et al., 2022). A baseline level of ROS is necessary for maintaining cellular homeostasis; however, excessive ROS can damage cellular macromolecules and are linked to aging and CVDs (Gianazza et al., 2021). Improved endothelial vasodilation following the inhibition of NADPH oxidase with apocynin suggests that endothelial dysfunction is mediated by NADPH oxidation (Leal et al., 2020).
Proteins including albumin, ferritin, ceruloplasmin, and transferrin regulate iron homeostasis, reduce oxidative stress, and preserve endothelial function, all of which are important in heart ageing. These proteins are mostly present in humans and animals. These do not come directly from plants, but they do include substances like iron-binding molecules, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that may affect how these proteins work. Transferrin (Tf), a monomeric glycoprotein that binds iron, is mostly synthesized in the liver. Two moles of iron in two homologous iron-binding domains may bind to 1 mole of transferrin (Talukder, 2021). It is the crucial transport protein that facilitates the movement of iron throughout the bloodstream for most vital processes (Vogt et al., 2021). Tf is internalized by cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis, whereupon it binds to the Tf receptor, functioning as a transporter to maintain intracellular iron homeostasis. Although essential for basic biological processes, iron becomes toxic in excess. Therefore, iron movement into and out of cells is prudently controlled (Leon-Sicairos et al., 2015). A system involving transferrin receptor 1, divalent metal-ion transporter 1, and other proteins carries most of the iron to cells attached to plasma transferrin (Li and Qian, 2002). Transferrin facilitates the controlled distribution of iron to cells by binding and transferring it in the bloodstream. Both an excess and a deficiency of iron may adversely affect cardiac function, making the maintenance of iron equilibrium crucial (Anderson and Vulpe, 2009). Through the Fenton reaction, unbound iron can accelerate the generation of ROS, leading to oxidative damage. Transferrin reduces the availability of free iron for the generation of ROS by sequestering it. The cornerstone of an iron-based mechanism of ischemic preconditioning that protects heart cells from iron-mediated oxidative damage associated with ischemia-reperfusion injury is the synthesis of ferritin, which is prevalent in the H subunit and sequesters redox-active iron (Talukder, 2021). A recent experiment in a mouse cardiomyocyte cell line shown that L-type channels are the principal mediators of iron absorption (Rose et al., 2011).
The importation of ferrous iron via L-type channels, leading to elevated ROS production, may hinder calcium influx, hence affecting cardiac excitation-contraction coupling, which is very sensitive to changes in cellular redox state (Cheng and Lian, 2013). This may therefore lead to suboptimal systolic and diastolic function, symptomatic of iron-overload cardiomyopathy. Recent research shown that iron accumulation mediated by the iron-binding protein Lipocalin-2 leads to cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac remodeling (Xu et al., 2012). Ferritin, play key role in maintaining iron homeostasis and defending cells from iron induced oxidative stress, it is actually a primary iron storage protein (Imam et al., 2017). Ferritin plays key functions in heart aging this includes, iron regulation, cellular senescence, oxidative stress and inflammation (Rosenblum, 2023). Iron deficiency is related to reduced or impaired cardiac function, even deprived of anemia, this leads to reduced exercise capacity, as well as worse consequences in heart failure patients (Jankowska et al., 2010). While iron accumulation such as hemochromatosis, this promotes oxidative stress, fibrosis and cardiomyocyte damage (Mancardi et al., 2021). Iron deficiency is related to reduced or impaired cardiac function, even deprived of anemia, this leads to reduced exercise capacity, as well as worse consequences in heart failure patients (Kremastinos and Farmakis, 2011). While iron accumulation such as hemochromatosis, this promotes oxidative stress, fibrosis and cardiomyocyte damage (Kremastinos and Farmakis, 2011). Through impounding free iron, ferritin supports to mitigate oxidative damage, thus reducing ROS production. Though, when ferritin levels are insufficient or excess, this leads oxidative stress can accelerate heart aging (Alfei et al., 2020).
Ceruloplasmin, plays a key function in heart aging via controlling iron homeostasis and oxidative stress, it is a copper containing ferroxidase (Orzheshkovskyi and Trishchynska, 2019). In heart aging ceruloplasmin helps to mitigate ROS via oxidation of ferrous iron to ferric iron. Therefore, reducing the availability of ferric iron for Fenton reactions, which generate very toxic hydroxy radicals and thus mechanism is key to avoid iron mediated oxidative damage to cardiac tissues (Tian et al., 2022). Additionally, its antioxidant abilities contribute to the upkeep of endothelial function and the decrease of inflammation, both of which are vital for cardiac ageing (Arenas de Larriva et al., 2020). However, dysregulation of ceruloplasmin levels or role may donate to iron overload and heightened oxidative stress, henceforth deteriorating age-related heart dysfunction (Rosenblum, 2023). Numerous studies have shown that the lack of ceruloplasmin is associated with increased cardiovascular risk, underscoring its significance in preserving heart health with ageing (Fox et al., 2000; Vassiliev et al., 2005).
Albumin, plays key roles in heart aging via upholds osmatic pressure, transporting hormones and fatty acids. It is most abundant plasma protein, exerting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (Shastri et al., 2024). Albumin binds and neutralizes free radicals, minimizing oxidative damage to cardiac tissues and lowering oxidative stress and inflammation in the ageing heart (Shastri et al., 2024). The ability of albumin to bind nitric oxide and promote endothelial function is essential for maintaining vascular health and treating age-related conditions including heart failure and atherosclerosis. Albumin, plays key roles in heart aging via upholds osmatic pressure, transporting hormones and fatty acids. It is most abundant plasma protein, exerting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Albumin binds and neutralizes free radicals, minimizing oxidative damage to cardiac tissues and lowering oxidative stress and inflammation in the ageing heart. The ability of albumin to bind nitric oxide and promote endothelial function is essential for maintaining vascular health and treating age-related conditions including heart failure and atherosclerosis (Belinskaia et al., 2021). Furthermore, its function in balancing and controlling fluid to minimize edema is a crucial factor in cardiac ageing, which is affected (Hankins, 2006). The decreased levels of albumin, often seen in elderly adults, have been linked with an elevated risk for cardiovascular disease, underscoring its protective role in cardiac ageing (Riviati et al., 2024).
Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles that contain a circular genome known as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) (Ferreira and Rodriguez, 2024). Among the many important tasks they perform is the synthesis of ATP, regulation of nutrient metabolism, calcium homeostasis, and programmed cell death (Perrone et al., 2023). Mitochondria, located in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, function as dynamic networks that perpetually engage in synthesis, fusion, fission, and destruction (mitophagy). Their proper functioning is vital in high energy tissues like the heart, where cardiomyocytes depend on ATP for their activity (Grel et al., 2023). In mature cardiomyocytes, mitochondria produce 95% of the ATP the heart needs and make up over one-third of the intracellular volume (Chang et al., 2023).
Dysfunctional cardiac mitochondria have been identified as a major factor inCVDs, leading to decreased ATP production, increased production of ROS, increased cell apoptosis, and disrupted mitochondrial dynamics (Chistiakov et al., 2018). An essential part of the whole cellular ROS generation process is the activity of mitochondria, originating from the reduction of oxygen (Napolitano et al., 2021; Palma et al., 2024). These ROS can subsequently be converted into H2O2, which influences the redox state of proteins (Okoye et al., 2023). The generation of mtROS is specific to certain sites and varies depending on the stimuli (Sadiq, 2023). Electrons derived from substrates can reduce O2 to O2⋅− at eight distinct mitochondrial sites, with complex I (CI) and complex III (CIII) being the most significant (Skulachev et al., 2023). Rotenone, an inhibitor of CI, increases O2⋅− production at CI, potentially increasing in mitochondria with lower energy production, elevated ΔpH, higher CoQ ratio, or high NADH-to-NAD+ ratio, causing O2⋅− to leak into the mitochondrial matrix (Jiménez-Gómez et al., 2023;Ježek et al., 2024).
Mitochondria possess a complex network of ROS scavenging systems that help regulate OS resulting from mitochondrial ROS (Surai, 2016). These systems include SODs, which convert superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide, which is then detoxified by catalase, GSH-PX, and the peroxiredoxin/thoredoxin (PRX/Trx) system (Wang et al., 2018; Peoples et al., 2019). SODs serve as the primary defense against mitochondrial ROS, with three isoforms (SOD1, SOD2, and SOD3) managing ROS levels in specific compartments (Eleutherio et al., 2021). Whereas SOD2 is found in the mitochondrial matrix, SOD1 is mostly present in the cytosol and has also been identified in the mitochondrial intermembrane gap (Kim et al., 2017). Proper regulation of the localization and activity of SOD1 and SOD2 is essential for effective mitochondrial ROS scavenging (Mailloux, 2020).
Mitochondrial ROS are essential for cardiac tissue, comprising 45% of the heart’s cellular volume (Kaludercic and Di Lisa, 2020). ROS can activate TFs for instance NF-kB as well as AP-1, hence facilitating an inflammatory process in tissues (Li A.-L. et al., 2023; Sobhon et al., 2023). Pinpointing the underlying cause of this dysfunction is challenging because of the interconnected nature of various processes (Addo and Khan, 2024). Aging-related mitochondrial dysfunction impacts cells through several simultaneous factors, including elevated mitochondrial ROS production, irregular assembly and recycling of mitochondria, alterations in the quality and quantity of mitochondrial DNA, and changes in the substrates related to mitochondrial respiration (Rai and Fessler, 2024). These molecular indicators are particularly evident in aged cardiovascular cells.
The heart aging process is defined by key features such as progressive hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes, cardiac fibrosis, and inflammation (Hastings et al., 2024). Hypertrophied cardiomyocytes contribute to a hypoxic environment, which produces an abundance of free radicals that may damage cellular constituents (Pena et al., 2020). In response to this stress, cardiomyocytes release pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, initiating an immunological response and augmenting the population of macrophages in the left ventricle (Ciutac and Dawson, 2021; Moskalik et al., 2022). Due to the poor rate of proliferation of mature cardiomyocytes, damaged areas are replaced with fibrotic scar tissue, ultimately leading to organ failure (Bishop et al., 2022). The production of ROS increases with age due to various factors, including physical, chemical, and biological agents, resulting in endothelial dysfunction and cellular damage (Scioli et al., 2020; Pacinella et al., 2022).
Furthermore, when free radicals are produced excessively or uncontrollably, they can trigger an inflammatory response, this is integral to the aging process (Sadiq, 2023). Atherosclerosis, heart problems, diabetes, and other age-related diseases are linked to persistent low-grade inflammation (Candore et al., 2010; Shen et al., 2024). The causes of this syndrome include stress and continuous antigen exposure, leading to a diminished ability to manage stressors and a gradual rise in pro-inflammatory activity (Bennett et al., 2018). The term “inflammaging” refers to the increased inflammatory response that accompanies aging, resulting in a persistent low-grade systemic pro-inflammatory condition (Giunta et al., 2022).
Aging is marked by alterations in the immune, hormonal, and adipose systems, which result in a chronic inflammatory state (Oishi and Manabe, 2016). This chronic inflammatory can lead to issues such as frailty, cognitive decline, and various cardiovascular, neurological, and vascular events (Ijaz et al., 2024). Despite its negative associations, inflammation is crucial for sustaining life and maintaining individual integrity (Ahuja et al., 2023; Baechle et al., 2023). An inflammatory state arises when pro-inflammatory compounds exceed anti-inflammatory controls (Bhol et al., 2024). The origins of this low-grade inflammatory process are still under discussion; however, one theory posits that ongoing stimulation of the immune system drives a pro-inflammatory shift (Gusev and Sarapultsev, 2024). Typically, aging leads toa gradual dysregulation of the immune response, particularly affecting cellular and adaptive immunity, with a notably impact on T cell function (Tobin et al., 2020). The persistent inflammatory condition experienced by elderly individuals is largely caused by this imbalance (Conte et al., 2022). The causes are likely multifactorial, involving chronic stimulation from viruses, bacteria, and endogenous cellular factors, along with ongoing activation of the immune system’s defenses (Endres et al., 2022).
Oral quercetin, administered at 50 mg/kg, significantly mitigates isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury by reducing pro-inflammatory mediators and enhancing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mediators (Kumar et al., 2017). Quercetin treatment may improve heat stroke outcomes in rats by mitigating hyperthermia and cardiac damage via its anti-lipid peroxidation, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects (Lin et al., 2017). The rat vena cava exhibited comparable outcomes with a reduced dosage but extended treatment duration (20 mg/kg/42 days) via the suppression of reactive oxygen species, the PI3/AKT pathway, and the release of inflammatory cytokines, possibly averting myocardial infarction and ischaemic heart disease. EGCG (40 mg/kg) mitigates myocardial damage in animals by blocking the AKT/mTOR and Hippo pathways (Ma et al., 2019), while enhancing the NQO1 antioxidant pathway (Cui et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2022; Li Y. et al., 2022).
The potential therapeutic benefits of plant-derived antioxidants on aging heart and other areas of health have received increasing attention in recent years. This interest arises from the extensive pharmacological properties of several plant compounds, which have been investigated for their ability to slow down aging and its impact on the cardiovascular system. Naturally occurring plant-based products are essential for treating and preventing diseases linked to heart aging (Sreedevi and Mavilavalappil, 2024). For many years, natural plant-based products have been used as active ingredients in conventional medicine (Najmi et al., 2022). Various natural compounds obtained from plants provide a diverse array of biological and pharmacological attributes that are crucial in modern pharmacotherapy (Chaachouay and Zidane, 2024). Among these products are the anticancer medication paclitaxel, which is derived from Taxus brevifolia (YADAV et al., 2023); the anticancer drugs vincristine and vinblastine, which are derived from catharanthus roseus (Qu et al., 2019); the anticancer drug camptothecin, which is de-rived from camptotheca acuminata (Fan et al., 2022); and the anticancer drug quercetin, a polyphenol present in a variety of vegetables and fruits (Rauf et al., 2018).
Plants are believed to require certain nutrients, such as phytochemicals or secondary plant components like polyphenols (Hosoda et al., 2023). These compondsbelong to a large family found in plants and algae, and their primary function is to protect the organism from UV rays, diseases, and herbivore consumption (Del Mondo et al., 2021). Polyphenols possess a variety of structural forms, ranging from simple monomers to intricate polymerized structures (Nagarajan et al., 2020). Seaweed polyphenols have been shown to reduce chronic inflammation (Murray et al., 2021), OS (Begum et al., 2021), hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, metabolic abnormalities associated with CVDs, and the aftereffects of diabetes (Gabbia and De Martin, 2020).
Recent research on marine macroalgae has demonstrated that plant-derived polyphenols can improve health outcomes, including reducing the risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease (Pereira and Cotas, 2023). Polyphenols are significant secondary metabolites derivedfrom plants that have notable benefits against cancer, CVDs, diabetes, and neurological disorders (Shahrajabian and Sun, 2023). Various plant species, such as dipteryx odorata, hierochloe odorata, galium odoratum, dichanthelium clandestinum, verbascum spp., and anthoxanthum odoratum, comprise a range of substances, including as tannins, lignins, coumarins, flavonoids, and phenicic acid (Iqbal et al., 2023). Resveratrol, known for its antioxidant properties, has been shown to improve inflammation, cancer, aging, obesity, diabetes, and provide cardio-protective and neurological benefits (Carrizzo et al., 2013; Mohammadi S. et al., 2024). The benefits of antioxidative therapy are increasingly acknowledged as a means of lowering ROS in the vascular and, consequently, decreasing their deleterious consequences (Senoner and Dichtl, 2019).
In addition to their antihypertensive effects, ACE inhibitors decrease circulation Ang II also have detoxifying properties (Dandona et al., 2007). Similarly, statins, or cholesterol-lowering medications, target to control HMG CoA reductase in addition to their cholesterol-lowering effects (Crismaru et al., 2020). To mitigate oxidative damage, vitamins E and C are often used as dietary supplements in addition to other medications (Higgins et al., 2020). Conversely, polyphenols are gaining interest as potential therapeutic agents to lower OS and protect individuals from heart disease (Muscolo et al., 2024). Polyphenols are the most common antioxidant in the diet, consumed ten times more frequently than water-soluble vitamin C and one hundred times more frequently than lipid-soluble vitamin E and carotenoids (Gulcin, 2020). This review study highlights the most extensively studied plant-based antioxidants that have been identified.
It has been shown that the naturally occurring polyphenol molecule resveratrol, which is present in a variety of plants, may help to maintain cardiovascular health and delay the aging process (Figure 4). A wide variety of plant species, including groundnuts and grapes, contain resveratrol, a naturally occurring stilbene (Kaur et al., 2022). Future studies suggest that resveratrol could serve as a potential chemo-preventive drug due to its ability to inhibit polyphenolic cyclooxygenase. It can be isolated from red wine, grape skins and seeds, and Polygonum cuspidatum roots (Kaur et al., 2022). The cardioprotective effects caused by resveratrol are associated with a notable augmentation in antioxidant activity and mitochondrial transmembrane potential, with a decrease in oxidative damage (Yang et al., 2023a).
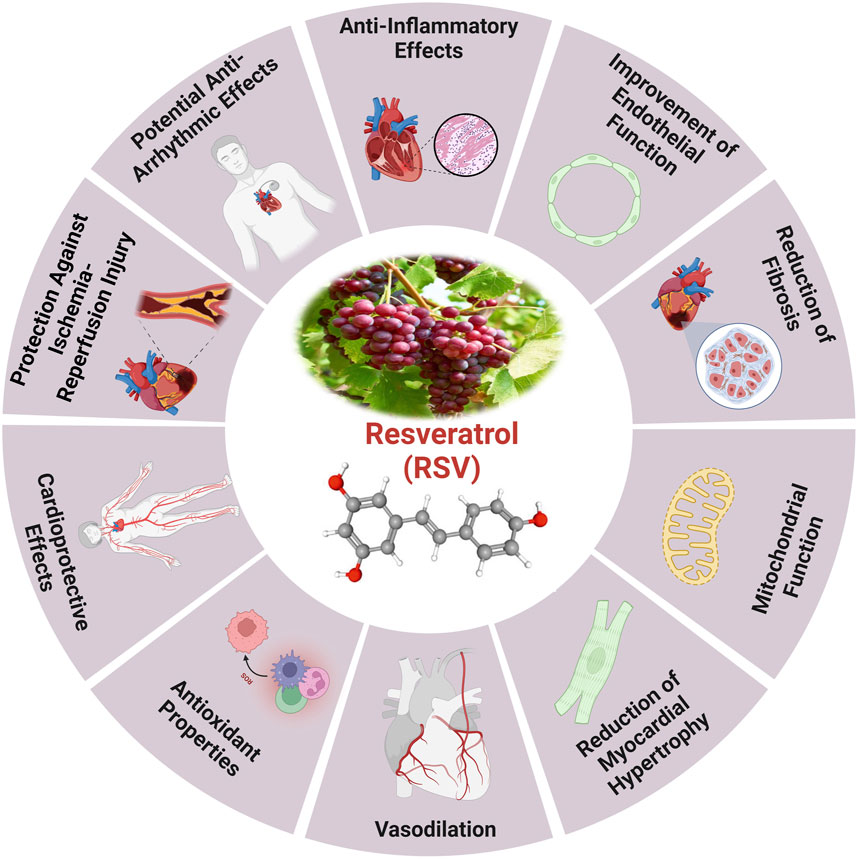
Figure 4. The health benefits of resveratrol and the cardioprotective effects induced by RV (Zhang et al., 2021).
Mechanistically, resveratrol primarily inhibits NADPH oxidase, decreases the production of ROS, and preserves activity of crucial antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, CAT, as well as glutathione peroxidase (Li M. et al., 2024). The modifications induced by resveratrol decrease lipid peroxidation, enhance cardiomyocyte viability, and decrease cardiac hypertrophy (Aires and Delmas, 2015). Resveratrol significantly mitigates cardiac metabolic diseases by the process involves reestablishing glucose homeostasis, regulating free fatty acid oxidation (FFAO), and increasing glucose consumption (Sulaiman et al., 2010). These processes enhance the metabolism of cardiac energy, especially in cardiomyocytes when glucose levels are elevated (Kolwicz Jr and Tian, 2011).
Currently, numerous studies suggest that resveratrol protects mitochondrial oxidation in endothelial cells, supports endothelial function, and it improves blood circulation and cardiac function by promoting vasodilation and vascular angiogenesis (Schmitt et al., 2010). Administration mitigated increased ROS production, MDA levels, the percentage of apoptotic cells, and Bax expression, while also enhancing SOD activity in rat CMEC. The substance also demonstrated antioxidative and anti-apoptotic properties by activating AMPK/Sirt1 (Li J. et al., 2023). The antioxidant properties of resveratrol through SIRT1 are illustrated by its activation of AMPK (Ungurianu et al., 2023). This activation inhibits NADPH oxidase an enzyme that generates ROS and increases SOD levels, leading to reduced OS (Ilkun and Boudina, 2013). The resveratrol action is attributed to an increase in antioxidant enzyme activity, which varies with age, particularly through modulating crucial pathways (Zhang et al., 2021). Analysis of SIRT1 revealed that the pathway is silenced in leukocytes treated with resveratrol during aging (Xia et al., 2020). SIRT1 affects the acetylation of FOXO family TFs, which are crucial for lipid and glucose metabolism and cellular response to OS (Nayakanti, 2022). The interaction between SIRT1 and AMPK enhances FOXO3 transcriptional activity, thereby increasing MnSOD production in cells with higher FOXO3 levels (Ho et al., 2022).
Additionally, resveratrol activated SIRT3/FOXO3a-dependent antioxidant enzymes, leading to a reduction in oxidative and DNA damage. Through the activation of the SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway, obese mice that were given extended resveratrol demonstrated a decrease in the damage caused by myocardial ischemia (Zhu et al., 2024). By inhibiting NADPH oxidase, ROS production is diminished, thus decreasing OS (Kitamoto et al., 2018). Furthermore, the complex, including SIRT1 (Hsu et al., 2008), FOXO3 (Tseng et al., 2013), and PGC-1α (Feng et al., 2019), activates Nrf2 (Kasai et al., 2020), a transcriptional regulator, enhancing antioxidant response gene expression and promoting MnSOD production to protect mitochondria from oxidative damage (Zhang et al., 2021). Additionally, resveratrol may effectively inhibit oxidation and inflammation associated with ageing, notably via the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory Nrf2 pathway (Franco et al., 2025). In aged mice resveratrol reduced the expression of TLR4, NF-κB, p65, and Notch 1 proteins, leading to lowering pro-inflammatory cytokine levels. This suggesting heart protection depends on suppressing the Notch/NF-κB pathway (Sahu et al., 2024). Middle-aged individuals exhibited an improved anti-inflammatory profile in response to resveratrol compared to elderly individuals, particularly in the middle group. This response resulted in a reduction of key biomarkers associated with oxidation and inflammation (Santos et al., 2023).
Furthermore, resveratrol decreased the pH levels in the feces of these mice and increased short-chain fatty acids in the intestinal contents. The production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, specifically IL-1β and TNF-κ, was suppressed by injection of resveratrol (Lu et al., 2024). Additionally, resveratrol, melatonin, and their combined use may reverse the reduced antioxidant activity and enhance the expression of GLUT4, SIRT1, and PGC-1α genes in the heart tissue of elderly female diabetic rats. Supplementation with resveratrol and melatonin may help preserve cardiac function in this model of aging female diabetes (Akgun-Unal et al., 2023).
Resveratrol has demonstrated the ability to mitigate age-related ventricular dysfunction by suppressing OS and inflammation in heart tissue via the Notch/NF-κB pathway (Sahu et al., 2024). It has been investigated that resveratrol activates the NAD+- dependent protein deacetylase SIRT1, reduces the hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes and age-related sarcopenia in mice (Hosoda et al., 2023). Resveratrol therapy resulted in the restoration of autophagic activity in the TA muscle and a reduction in acetylated protein levels (Sin et al., 2016). It may also impede autophagy in the context of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion damage via DJ-1 regulation of the MEKK1/JNK pathway (Liu S. et al., 2023). In addition resveratrol significantly mitigated the loss of SLC7A11, inhibited ferroptosis, and improved cardiac function via activating the Sirt1/p53 pathway in heart failure (Zhang W. et al., 2023).
Furthermore, Resveratrol has been shown to improve lifespan and physical activity in mice with LV pressure, overload-induced hypertension. The investigation elucidates the physiological and molecular processes behind this impact. By decreasing cardiac fibrosis, increasing heart remodeling, and boosting diastolic, vascular, and energy metabolic processes, resveratrol therapy reduces the severity of heart failure in mice (Sung et al., 2015). In addition to maintaining endothelium-dependent coronary artery function and resveratrol improves myocardial perfusion and angiogenesis indicators associated with the VEGF signaling pathway, while also reduces anomalies in wall motion (Robich et al., 2010). In the context of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion damage, the investigation evaluated the impact of resveratrol on STIM1-mediated intracellular Ca2+ buildup and cell death. Resveratrol dramatically enhanced heart function, lowered infarct size, and decreased apoptosis in mice. Resveratrol reduced intracellular Ca2+ buildup and downregulated STIM1 expression in rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. In vitro, STIM1 over-expression enhanced the effects of resveratrol on STIM1-mediated intracellular Ca2+ buildup, while the SOCE inhibitor SKF96365 partially eliminated these effects (Xu et al., 2019).
In another study it has investigated that resveratrol play a key role in modulating ferroptosis and cardiac damage in MI. Resveratrol reduced myocardial damage and fibrosis associated with MI in rats, inhibited IL-6, IL-1β levels, decreased GPX4 and SLC7A11 expression. It alleviated cardiomyocyte damage generated by oxygen-glucose deprivation and inhibited ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes under OGD conditions in vitro. Resveratrol mitigated myocardial damage by suppressing ferroptosis via the activation of KAT5/GPX4 in MI, offering additional evidence for its potential therapeutic efficacy (Liu J. et al., 2022). Furthermore, the administration of resveratrol protected cells from LPS-induced apoptotic cell death by reducing proinflammatory cytokine generation, increasing Nrf2 activation in human heart cells, and mitigating LPS-induced heart damage in rats (Kosuru et al., 2018a).
Extended resveratrol consumption may protect obese mice from myocardial ischemia damage by restoring intracellular redox equilibrium through the activation of the SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway (Zhu et al., 2024). Resveratrol cardioprotective effects in older mice include increased antioxidant activity, mitochondrial transmembrane potential, and decreased oxidative damage. It inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines and suppresses the Notch/NF-κB pathway, enhancing its cardioprotective properties (Bohara et al., 2022; Peng et al., 2023).
It has been established that resveratrol activates Sirt1, which in turn mediates the deacetylation of Smad3 and suppresses the fibrotic response generated by TGF-β1 (Chen et al., 2015). The level of acetylation of Smad3 (Ac-Smad3) was elevated in rats with cardiac fibrosis, and renal fibrosis but it was reduced in the normal myocardium and nephridial tissue of rats. The Ac-Smad3 has the ability to control the DNA binding activity and transcriptional activity of certain profibrotic genes. Elevating the level of Ac-Smad3 through the action of TGF-β1 facilitates the progression and advancement of tissue fibrosis (Chen et al., 2015; Chen Q. et al., 2022). Resveratrol has demonstrated not only its ability to slow down the aging process, but also its ability to provide protection against CVD by eliminating ROS and improving the functioning of several antioxidant enzymes.
Curcumin, a naturally occurring substance obtained from the desiccated rhizomes of Curcuma longa L., commonly known as turmeric, is extensively used in medical practice to address an extensive range of ailments (Figure 5). Several studies have demonstrated that curcumin has positive effects on cardiac conditions and endothelial system dysfunction (Cox et al., 2022; Ghorbanzadeh et al., 2022). Research on a rat model of hypertension and ischemia have shown that curcumin may improve cardiac hemodynamic function and attenuate heart failure (Aziz et al., 2022). Additionally, by reducing OS and inflammation, it increases myocardial infarction size and boosts cardiac function after ischemia events (Hori and Nishida, 2009).
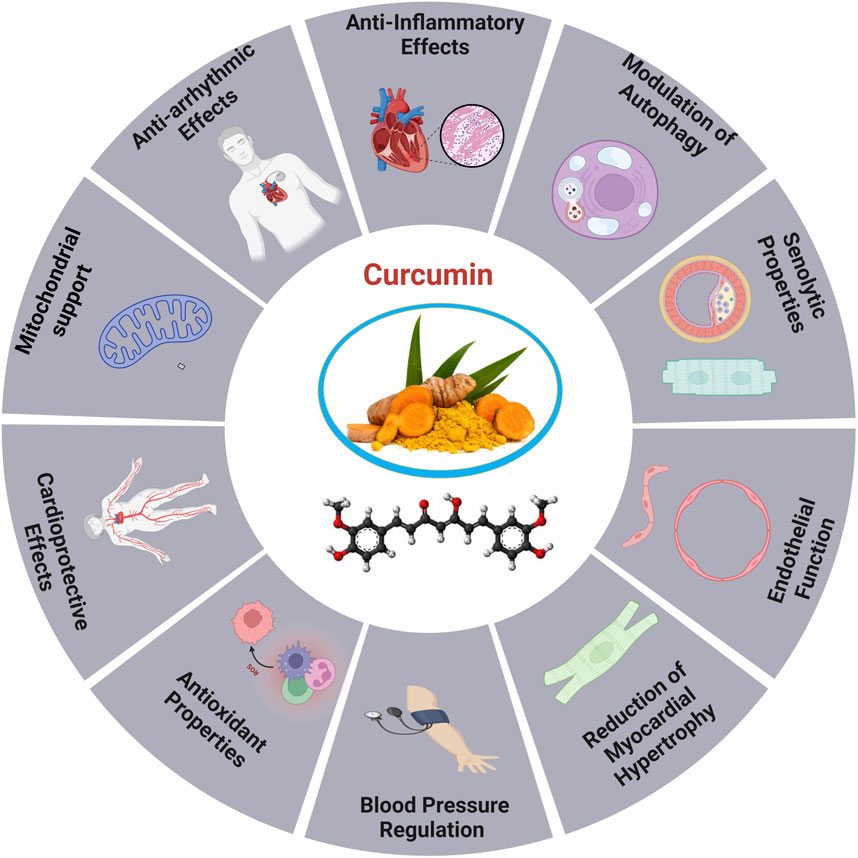
Figure 5. Cardioprotective roles of curcumin (Srivastava and Mehta, 2009).
Curcumin has garnered interest in the realm of CVDs for its ability to provide variety of beneficial effects on the heart. Due to its antioxidant properties, curcumin has been proposed to mitigate heart disease risk factors, such as cardiac angiogenesis, and delay the development of age-related disorders (Rysz et al., 2021; Aziz et al., 2022). Curcumin, administered at 100 mg/kg, increased O-GlcNAcylation and the production of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase in HaCaT cells, therefore improving the stability of apolipoprotein C3, a substrate of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase (Sun et al., 2025). For instance, curcumin contributes to heart aging by promoting autophagy and restoring it through the SIRT1/AMPK/mTOR pathway. The antioxidant capacity of SIRT1 was reduced by siRNA-mediated knockdown, highlighting its anti-aging, and autophagy-enhancing effects, indicating its potential as an effective treatment for cardiac aging (Yang et al., 2022). The study explores the involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in DCM by employing curcumin and shRNA-Nrf2 as activators. A Type 2 diabetes animal model induced by streptozotocin and a high-fat diet was used to assess the impact of curcumin on H9C2 cells. The results indicated that excessive production of ROS impaired Nrf2-related signaling, leading to reduced cellular energy metabolism and increased apoptosis. In contrast, activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway improved cardiomyocyte viability, decreased ROS generation, and inhibited apoptosis (Wu et al., 2022).
Moreover, Curcumin enhances mitochondrial integrity, mitigates oxidative stress, and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1α. It also prevents the translocation of DRP1 in sepsis models, indicating potential therapeutic advantages for sepsis-related cardiac muscle (SCM). The SIRT1-DRP1/PGC-1α pathway involved in regulating mitochondrial mass may constitute a prospective target for the advancement of organ-protective pharmacotherapies in critical care environments (Hou et al., 2024).
Additionally, curcumin, a natural remedy, has been shown to increase the longevity of postmitotic cells even in the absence of mitochondria, although it does not exhibit hormetic effects. Its mechanism includes the inhibition of TORC1 activity, elevated ATP levels and the onset of oxidative damage, indicating potential therapeutic uses in age-related diseases (Naaz et al., 2024). Curcumin supplementation can reduce vascular OS and restore arterial function in aging, positioning it as a promising antioxidant therapy for addressing age-related arterial dysfunction (Fleenor et al., 2013). The treatment of curcumin increased VEGF-A, TSP-1, and NF-κB levels and boosted age-related decreases in angiogenesis. By upregulating the production of VEGF and NF-κB proteins and downregulating TSP-1 protein levels, it mitigates heart tissue damage and supports cardiac angiogenesis in diabetic rats. Curcumin also induced molecular changes lead to a reduced apoptosis index in cardiac tissue (Ghorbanzadeh et al., 2022). The study revealed a substantial drop in autophagy and SIRT-1 levels, while the levels of MDA, NOX4, p-NF-κb, and P62 were considerably elevated in the heart of the old group compared to the young group (Aziz et al., 2022; Lv et al., 2022).
Additionally, it was found that the hearts of older rats exhibited notably elevated levels of apoptosis and fibrosis in comparison to younger rats. However, the administration of exercise and curcumin shown a positive effect in ameliorating these negative alterations. The combined treatment of curcumin and exercise in elderly rats had a more pronounced impact on molecular mediators and histological alterations in the heart than the use of curcumin alone (Dong et al., 2020).
Through its capacity to activate and repair autophagy curcumin influences heart aging through the SIRT1/AMPK/mTOR mechanism. In aged cardiomyocytes subjected to D-galactose treatment, there was a significant increase in the number of cells that tested positive for intracellular ROS, P53, P16, and senescence-associated β-galactosidase. Curcumin-induced autophagy elevated SIRT1 and AMPK levels, while reducing mTOR. SIRT1-siRNA stimulated the SIRT1/AMPK/mTOR pathway, limiting the antioxidative, antiaging, and autophagy-enhancing effects of curcumin in a dose-dependent manner (Yang et al., 2022). Thymoquinone and curcumin synergistically reduced D-gal induced necrosis in the brain and heart, leading to a reduction in caspase-3, calbindin, IBA1, cardiac caspase-3, and BCL2 levels. The combination reduced mRNA expression of TP53, p21, Bax, and CASP-3 in the brain and heart, while enhancing BCL2 expression relative to the D-gal group. This indicates that TQ and curcumin provide a viable approach for mitigating aging (Dong et al., 2020).
One of the most well-known dietary antioxidants is quercetin, a phenolic member of the flavonoid family that is crucial to the process of heart aging (Figure 6). It is found in vegetables, fruits, tea, wine, and many other healthy goods (Carrillo-Martinez et al., 2024). The antioxidant effects of quercetin include scavenging free radicals such superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, peroxyl, and hydroxyl (Cizmarova et al., 2023).
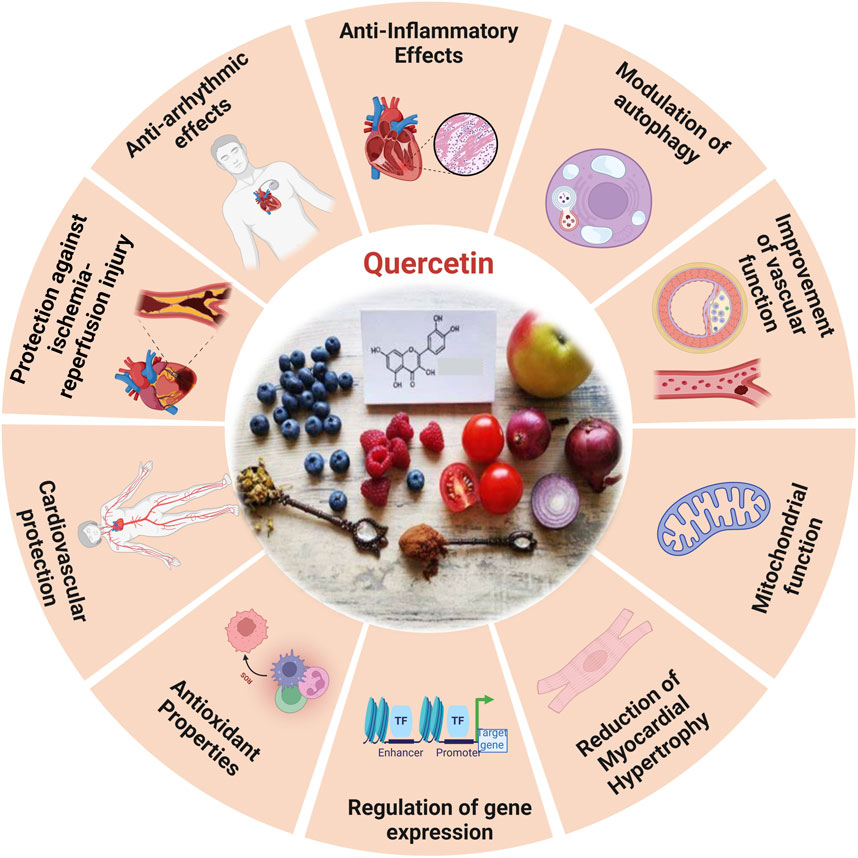
Figure 6. The diverse functional role of quercetin and the cardioprotective effects induced by quercetin (Ferenczyova et al., 2020).
Quercetin, a non-toxic flavonoid with antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory characteristics, is essential in the treatment of aging-related disorders within a safe dosage range. Quercetin improves mice left ventricle function (Ulasova et al., 2013), myofibrillar tissue, and mitochondrial structure by lowering OS brought on by aging, restoring myocardial microcirculation, and decreasing the size of infarcts (Gao et al., 2014). The study reveals that in rats with myocardial infarction, quercetin increases the activity of enzymes related to the respiratory chain and the tricarboxylic acid cycle (Cui et al., 2022). The inhibitory impact of quercetin on cellular senescence is associated with the preservation of MERCs and enhanced mitochondrial activity, which may mitigate cardiac failure (Jiménez et al., 2025). The production of biomarkers linked to OS generated by myocardial infarction in rats has been observed to decrease (Albadrani et al., 2021).
Moreover, quercetin has been shown to defend AC16 cells against OS caused by hyperlipidemia in elevating p-SIRT1 levels, enhancing endothelial NOS, and diminishing iNOS (Cui et al., 2022). This defensive action is facilitated by the signaling pathway PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 (Srivastava et al., 2023), by obstructing the HMGB1-TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway, quercetin efficiently reduces inflammatory responses (Wang et al., 2021).
Studies indicated that quercetin markedly moderates cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats, this material preserves mitochondrial integrity, lowers levels of mitochondrial superoxide, and enhances heart performance.
In addition, in vitro studies demonstrated quercetin alleviated hypertrophic response in rats by maintaining mitochondrial function, while partially weakened mitochondrial protection and PARP-1 inhibition after SIRT3 knockdown. Quercetin reduces cardiac hypertrophy by increasing mitochondrial activity by regulating the SIRT3/PARP-1 pathway, according to study (Chen et al., 2021). Prolonged treatment with quercetin in older spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) markedly inhibited MYC expression, reduced CYP2E1 levels, and decreased lipid peroxidation. Quercetin amplifies antioxidant activity, improving the equilibrium between prooxidants and antioxidants in the heart, which may result in reduced blood pressure and relative heart weight in older spontaneously hypertensive rats administered quercetin (Maksymchuk et al., 2023). Quercetin decreased MMP activity, TGF-β levels, and OS in the coronary arteries and left ventricles of 2K1C rats. However, it had no effect on hypertrophic remodeling or functioning in the coronary arteries damaged by hypertension (Da Rocha et al., 2023). Quercetin pretreatment activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, alleviates CDDP-induced oxidative stress, protects mitochondrial function, and lowers mitochondrial apoptosis in PCs. In vitro BLB models show quercetin diminishes CDDP-induced apoptosis and improves endothelial barrier permeability (Huang et al., 2024).
Quercetin reduces apoptosis in vivo by phosphorylating JNK and p38, upregulating Bcl-2 expression, and inhibits the activation of Bax and caspase-3 (Jubaidi et al., 2021), and via SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling, quercetin inhibits MI/R-induced apoptosis (Cui et al., 2022). Atherosclerosis is primarily caused by endothelial dysfunction, which occurs during the solute exchange between blood and nerve tissues. The peripheral nerve substructures are defended by the blood-nerve barrier (BNB), which is made up of endothelium. Atherosclerosis is exacerbated by oxidative injury to endothelial cells induced by oxidized low-density lipo-protein. Consequently, oxLDL promotes the development of foam cells derived from RAW264.7 macrophages, which worsen cellular lipid accumulation and increase ROS levels that result in the oxidation of LDL particles into ox-LDL. Quercetin could inhibit the production of foam cells generated by ox-LDL and prevent cellular senescence (Cao et al., 2019). In contrast, quercetin hinders the apoptosis of macrophages induced by cholesterol accumulation, thus resulting in a reduction in atherosclerosis. Quercetin additionally enhances the antioxidant function of cells via the Nrf2 pathway (Lu et al., 2017).
Moreover, chronic atherosclerosis throughout aging stimulates the formation and buildup of ROS, leading to mitochondrial damage caused by damage to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) (Shemiakova et al., 2020). OxLDL molecules are connected to NF-κB, TLR, and scavenger receptors, among other pattern recognition receptors, and have the capacity to activate the immune system (Bhaskar et al., 2016). Quercetin, on the other hand, effectively prevents the ox-LDL-containing macrophages from activating NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles leading to a reduction in cell lipoatrophy and the secretion of IL-1β (Cui et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2024). It markedly decreased VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression in HUVECs, downregulated MCP-1 mRNA levels, and mitigated nuclear translocation of the NF-κB, p65 subunit in oxLDL-stimulated HUVECs. Additionally, quercetin reduced TLR2 and TLR4 expression, diminished inflammatory mediators, and mitigated the inflammatory process in atherosclerotic rats subjected to a hypercholesterolemic diet. Quercetin functions as an anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic compound (Bhaskar et al., 2016). The primary mechanism by which quercetin inhibits the development of atherosclerotic plaque is by controlling caspase-3 and NF-κB activation through the PI3K/AKT pathway (Lu et al., 2017).
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the predominant and physiologically active polyphenol found in green tea (Eng et al., 2018). As a strong redox agent, EGCG has a strong antioxidant effect and plays a significant role in heart aging (Figure 7). Its structural phenolic hydroxyl group oxidizes to produce a relatively stable molecule and serves as a hydrogen source for redox reactions. This procedure successfully rids the body of a significant amount of harmful free radicals (Singh et al., 2011).
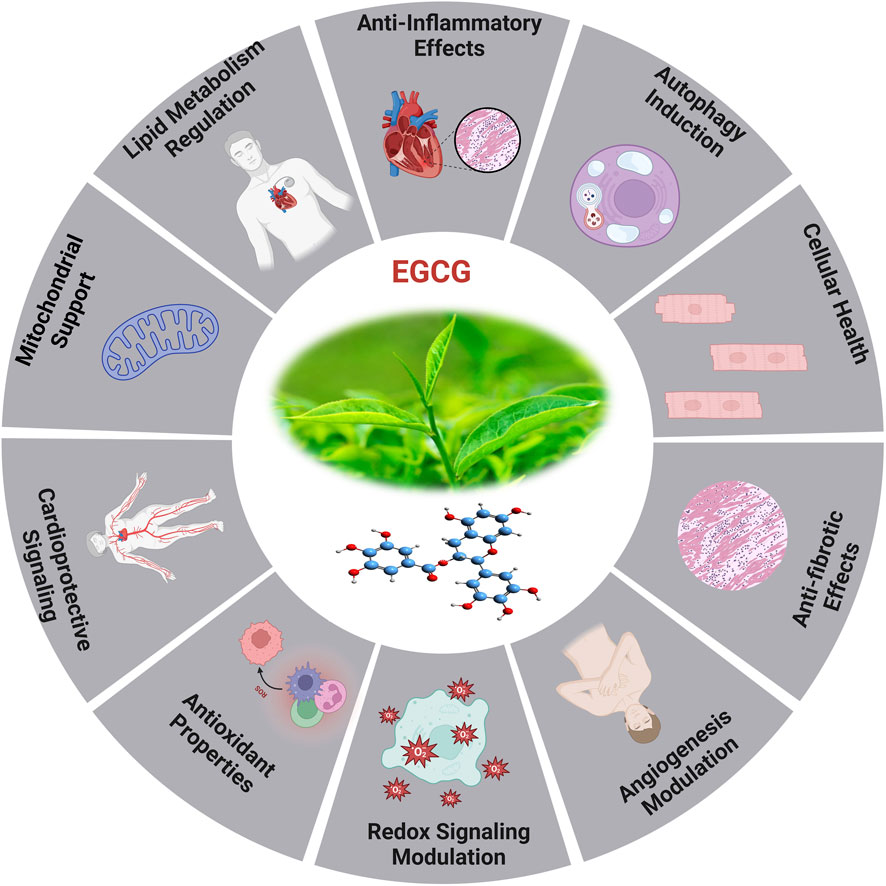
Figure 7. The diverse efficient roles of EGCG and the cardioprotective effects induced by EGCG (Zheng et al., 2011).
Mechanistic investigations through its modification of MAPK, PKC, and PI3K activity, EGCG protects cells against oxidative damage, according to mechanistic studies (Zhao et al., 2018). EGCG possesses anti-oxidant properties and can mitigate the inflammatory response through its impact on inflammation-related pathways, resulting in suppression of inflammatory factor expression (Mokra et al., 2022). The research indicates that EGCG could reduce vascular calcification via influencing the MAPK-JunB pathway, with the downregulation of JunB being essential. Ingesting green tea or EGCG medicine may elevate EGCG concentrations, perhaps addressing JunB for the prevention and therapy of vascular calcification (Li et al., 2025). In vitro studies show that EGCG decreases inflammatory factors caused by LPS via phosphorylating signaling molecules associated to the NF-κB/p65, MAPK/p38, Akt, and ERK pathways, as well as by reducing the production of iNOS and COX-2 (Zhong et al., 2012; Kim et al., 2022). Furthermore, EGCG has the potential to decelerate the aging process through its modulation of the AMPK pathway, mitochondrial function restoration, and induction of autophagy (Xu et al., 2023).
Oxidative stress caused by pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy shortens telomeres in the hypertrophic myocardium and depletes TRF2. EGCG, a powerful antioxidant, may impede cardiac myocyte death by averting telomere shortening and the loss of TRF2 (Eng et al., 2018; Brandt et al., 2022). An investigation has revealed that aged rodents treated for 8 weeks with EGCG exhibited enhanced cardiac diastolic function (Oyama et al., 2017). In the aged myocardium, EGCG therapy restored the reduced expression of cTnI, and lowered HDAC1 and HDAC3 expression and HDAC1 binding in the proximal promoter of cTnI. Additionally, higher concentrations of AcH3K9 were found in the cTnI promoter, following EGCG treatment. In response to EGCG, transcription factors GATA4 and Mef2c bound to the cTnI promoter at higher amounts (Pan et al., 2017). The cTnI gene plays a crucial role in regulating heart function, particularly in relation to diastolic function (Pan et al., 2016), and deficiencies and mutations in cTnI have been associated with diastolic dysfunction and HEpEF (Heinzel et al., 2020). The examination of limited samples of human heart tissues reveals a reduction in cTnI concentration in left ventricular myocardial cells in elderly adults, irrespective of cardiac disease status (Myhre et al., 2019). It has revealed that a decrease in cTnI in aging hearts may be a contributing factor to the diastolic dysfunction observed in elderly mice.
The EGCG not only affects the sensitivity of myofilament Ca2+, but it also controls gene ex-pression through epigenetic alterations. The study demonstrated that the administration of EGCG reversed the decrease in cTnI expression, which is linked to age-related cardiac diastolic dysfunction. This was achieved by increasing the expression of acetylated lysine-9 on histone H3 in aging hearts. The additional it has suggested that the administration of EGCG may have the potential to prevent heart failure through the modulation of histone acetylation (Quan et al., 2024). EGCG exhibits antioxidant activity in HepG2 cells and offers protection against oxidative stress caused by ABAP. In a dose-dependent way, the procedure was accomplished by lowering ROS and increasing the activity of cellular antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px. Theoretical foundations for the creation of functional food components can be derived from the antioxidant effects exhibited by combinations of EGCG (Zhang Q. et al., 2023). The therapeutic impacts of EGCG on CVD are associated with its capability to reduce LDL cholesterol, NF-κB, plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin levels, myeloperoxidase activity, inflammatory indicators, and ROS formation. For example, the combination of EGCG consumption and regular exercise in postmenopausal women who are over-weight or obese resulted in a decrease in their resting heart rate (Eng et al., 2018). A study involving randomized controlled trials found that green tea consumption or low polyphenol dosage significantly reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure in humans by 1.98 and 1.92 mmHg, respectively. The findings of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over study demonstrated that the administration of a single dose of 300 mg EGCG resulted in the amelioration of endothelial function and enhancement of arterial-mediated dilation in individuals diagnosed with coronary arterial diseases. However, the administration of 150 mg of EGCG twice daily for a duration of 2 weeks did not yield any statistically significant effects (Mahdavi-Roshan et al., 2020).
Recently investigated study on the impact of HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of NRF1 on cardiac hypertrophy and mitochondrial stability. An HDAC1 inhibitor called EGCG was reported to enhance LysoTracker + cardiomyocytes in hypertrophic circumstances, decrease heart-to-body weight ratios, and improve cardiac function. In hypertrophic H9C2 cells treated with PE, EGCG decreases cell hypertrophy and increases the presence of LC3B II + MitoTracker + puncta. It also inhibits HDAC1-mediated histone deacetylation, which aids in maintaining NRF1 levels (Li G. et al., 2024). Eight weeks of EGCG treatment significantly reduced systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressure while increasing the liasodilator-hypertensive ratio. This suggests a shift towards sympathetic nervous system dominance or reduced parasympathetic nervous system activity. The results may be attributed to EGCG acting as a sympathetic potentiator or compensatory response. SBP was linked to obesity and insulin resistance, while DBP showed a positive association with HF nu and a negative correlation with LF ms2, this highlighted EGCG’s potential protective effects against hypertension (Wilasrusmee et al., 2024).
In addition, study on adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC) pretreated with EGCG enhanced cell functions in diabetic cardiomyopathy while inhibiting the effects of small interfering C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (siCXCR4) administration. These results were validated in a diabetic animal model, indicating that EGCG-pretreated ADSC may have promising clinical applications to diabetic patients suffering from cardiomyopathy (Chen T.-S. et al., 2024). EGCG is crucial for epigenetic regulation and can reduce DNA hypomethylation in genes like Sod2, Gpx1, Cat, and TrxR. The antioxidant properties and epigenetic modifications in CpG methylation can aid in the administration of antioxidant substances and DNA methylation-modifying medicines for chronic disease prevention and treatment (Banzubaze et al., 2024).
The impact of plant-derived antioxidants on heart aging has garnered significant attention in scientific research. This interest is driven by mounting evidence showing the potential benefits of several plant-based components, including flavonoids, polyphenols, and other phytochemicals, in relation to the changes in the heart caused by aging. These substances exhibit a variety of mechanisms that are essential for maintaining cardiovascular function. For instance, many plant-derived compounds demonstrate antioxidant properties that can effectively counteract oxidative stress, a critical factor in the senescence of the cardiovascular system (Corrêa et al., 2018; Akbari et al., 2022).
Anthocyanins, found in vibrant fruits and vegetables, have recently been the subject of studies exploring their potential, and mechanisms in human vascular endothelial cells and rat thoracic aortas subjected to aging models (Wallace, 2011). These studies examined the ability of specific anthocyanins, such as cyanidin-3-rutinoside (C-3-R) and cyanidin-3-glucoside (C-3-G), to inhibit senescence induced by d-galactose in human endothelial cells (Lee et al., 2020). The findings demonstrated a reduction in the activity of certain markers of cellular senescence, as well as a suppression of ROS production and NADPH oxidase activity in the presence of D-galactose (Hafez et al., 2024). Anthocyanins were shown to counteract the inhibition of endothelial eNOS activity, leading to the recovery of NO levels in endothelial cells (Edirisinghe et al., 2011). It was observed that anthocyanins induced eNOS deacetylation via SIRT1, resulting in increased eNOS activity. In an in vivo study involving aged rats, administration of anthocyanin-rich mulberry extract over 8 weeks led to a reduction in oxidative stress and endothelial senescence in the aorta, as well as an increase in serum NO levels, eNOS phosphorylation, SIRT1 expression, alongside a decrease in nitro-tyrosine levels in the aorta (Lee et al., 2020).
Additionally consuming anthocyanins has been shown to enhance antioxidant defense enzymes, total antioxidant capacity, and the antioxidant properties of HDL in both preclinical and clinical populations (Garcia and Blesso, 2021). Anthocyanins exhibit direct antioxidant capabilities and indirectly stimulate Nrf2 and antioxidant gene expression, mitigating oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling in atherosclerotic plaque cells, such as macrophages and endothelial cells. This may potentially protecting against atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (Mohammadi N. et al., 2024).
Scientifically known as s-allyl-2-ene-1-thiosulfite, allicin is a physiologically active compound derived garlic. It demonstrates a broad spectrum of pharmacological characteristics, such as immunoregulatory, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, renal, nerve, and cardiac protective, as well as anti-tumor effects. It has been shown that allicin and its derivatives operate biologically by modifying gene expression and interacting with a variety of signaling pathways (El-Saber Batiha et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2024). Allicin, a medication for myocardial infarction, reduces infarction area and fibrosis, increases SHP2 protein levels, and inhibits ROS in infarction tissue. However, specific knockdown of SHP2 negates ROS changes. Allicin also modulates p-PERK activation, mitigate oxidative stress in rodents (Gao et al., 2024). The study revealed that allicin exerted effects on cardiac function, myocardial fibrosis, and the modulation of NF-κB signaling pathways in the myocardial tissue of rats afflicted with diabetic cardiomyopathy. The study provided evidence that allicin exhibited positive effects on cardiac dysfunction and reduced myocardial fibrosis in the rats, possibly via facilitating the deactivation of the NF-κB signaling cascade (Ma et al., 2017).
The longevity of G. biloba L. has led to its widespread recognition as a living fossil tree. Throughout its lifespan, G. biloba L. is presumed to have acquired or evolved resistance to many diseases as a mechanism of adjusting to its surroundings. Many different phytochemicals, such as flavonoids, terpenoids, alkylphenols, and carboxylic acids, are present in the leaves of G. biloba (van Beek and Montoro, 2009; Liu X.-G. et al., 2022). Only G. biloba trees contain ginkgolides A, B, C, and J. Ginkgo contains mono-, di-, and tri-glycosides as its main flavonoids (Medicine et al., 2021). Ginkgo leaf contains several chemical compounds that have different functions, such as removing oxygen free radicals and decreasing oxidation, regulating superoxide dismutase and catalases, and removing NO. Engaging in these activities has the potential to enhance protection against heart injury and potentially reduce the likelihood of MI (Kadhim et al., 2020).
Moreover, G. biloba has the ability to stimulate the AKT signaling pathway, the activation of AKT initiates cell-specific processes, such as GSK3β phosphorylation, which protect cells from acute AMI damage and reduces the AKT signaling pathway due to cardiac ischemia-reperfusion damage (Cho et al., 2009; Lejri et al., 2019). The GBE50 is an orally given GBE formulation that corresponds to the German product, EGb761, which has been used in the treatment of AMI (Liu et al., 2013). While GBE80 activates the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway, successfully preventing myocardial damage from AMI and H2O2-generated cardiomyocyte cytotoxicity (Zheng et al., 2021).
Additionally, the effects of GBE administration on autophagy and cardiac hypertrophy may be mitigated by the SIRT1 inhibitor EX-527, which also lowers Ang II oxidative stress and the production of SIRT1 and FoxO1. This implies that GBE may be useful as a medication to treat pathological heart hypertrophy (Jiang et al., 2021). GBE has demonstrated cardioprotective properties in individuals with diabetes, namely, in the context of DCM. Investigation demonstrates that giving diabetic rats GBE treatment successfully lowers metabolic irregularities, enhances cardiac function, and lessens degenerative changes to the heart. GBE treatment, however, may be able to address defective autophagy and dysregulation of the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. GBE demonstrated a reduction in apoptosis produced by HG in H9C2 cells in vitro (Yang et al., 2023b). The study establishes a correlation between heightened cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and histo-morphological alterations in cardiotoxicity generated by Cs-A.
Furthermore, GBE administration has been shown to reduce the cardiotoxic effects of Cs-A by activating the mTOR/ERK1/2 signaling pathways. The aforementioned pathways are linked to the suppression of oxidative stress and inflammatory mechanisms, thereby serving as a preventive measure against heart injury. Immunohistochemistry and bio-chemical assays were employed in the study to demonstrate that the supplementation of GBE leads to a reduction in cardiotoxicity through the enhancement of the mTOR/ERK1/2 signaling pathways (Asiwe et al., 2024). The extract of GBE shown significant efficacy in mitigating myocardial infarction through the enhancement of the body’s inherent antioxidant defense mechanism and the reduction of inflammatory cytokine release and heart injury marker enzymes. The leaves of GBE, specifically EGb761, are commonly used to treat cerebrovascular diseases due to their neuroprotective proper-ties. Studies have demonstrated the protective effect of EGb761 on rats’ cognitive performance, involves preventing apoptosis and autophagy in models of VD, as well as improving cognitive performance in rats with VD through the activation of AMPK-mTOR signaling (Yin et al., 2024).
Berberine (BBR), a fundamental constituent of the Chinese herb Rhizoma coptidis, is an iso-quinoline alkaloid derived from Berberidaceae (Phogat et al., 2024). Recent research has shown that BBR possess strong anti-dysenteric qualities in addition to a variety of cardiovascular pharmacological actions, such as controlling dyslipidemia, preventing arrhythmias, inhibiting heart failure, myocardial remodeling, and lowering blood pressure. BBR prevents cardiac senescence by boosting cardiac myocytes production of KL mRNA and protein and controlling the KL/SIRT1 signaling pathway, thereby enhancing its protective effects (Li C. et al., 2022). BBR has the ability to improve diabetic cardiomyopathy by increasing the expression of myocardial methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA) and simultaneously inhibiting cardiac CaMKII oxidation (Sun et al., 2023). It has been investigated by Wang et al., 2023, that BBR and its derivative tetrahydroberberrubine (THBru) improve cardiac remodeling and reduce heart aging. Compared to BBR, THBru has a greater anti-heart aging effect because it prevents heart aging via PHB2-mediated mitophagy (Wang L. et al., 2023).
Moreover, researchers are progressively focused on investigating the impact of plant-derived antioxidant on heart aging. This has led to an exploration of various chemical compounds produced from plants, with the aim of promoting cardiovascular health and mitigating the adverse effects of aging on the heart. An excellent proof is seen in several naturally occurring compounds present in plants. These drugs have garnered considerable interest owing to their potential advantages for cardiovascular health, such as enhancing endothelial function, reducing inflammation, and demonstrating antioxidant qualities (Table 1). The effects outlined above are particularly relevant to the phenomenon of heart aging, as they have the potential to mitigate the oxidative stress and inflammation associated with the aging of the cardiovascular system. The research findings indicate that these antioxidants may aid in preserving optimal heart function and vascular health, perhaps decelerating the heart aging process.
The rising prevalence of age-related heart aging underscores the urgent need for effective treatment strategies. In this context, investigating plant-derived antioxidants shows considerable potential in addressing this challenge. The results presented in this review confirm that some plant-based antioxidants such as polyphenols, terpenoids and alkaloids might reduce heart aging effects and moderate expression of genes involved in the same process. Plant-derived antioxidants provide protection to the heart by acting on several molecular pathways and signaling cascades. It will need further study to fully comprehend the complex interplay between antioxidant chemicals produced from plants and the aging process in the cardiovascular system, with a particular emphasis on the examination of pathways and signaling cascades. To enhance the effectiveness of antioxidant treatments, it is crucial to evaluate gene expression patterns, epigenetic modifications, and cellular signaling networks. With the use of innovative techniques and formulations, such as targeted-tissue delivery and controlled-release formulations, it is possible to overcome obstacles like poor stability and enhance the absorption and distribution of these antioxidants. The increasing prevalence of aging-related cardiovascular disorders necessitates the development of effective treatment approaches.
This review highlights the potential of plant-derived antioxidants, including polyphenols, terpenoids, and alkaloids, to mitigate the negative effects of heart aging and alter gene expression. These compounds offer cardioprotective benefits through various molecular pathways and signaling cascades, highlighting the need for efficient treatment approaches in this rapidly aging-related issue. The development of innovative delivery methods and formulations can significantly improve the therapeutic effectiveness of plant-based antioxidants. These methods can overcome challenges like poor solubility, low stability, and restricted tissue targeting associated with some plant-based agents, such as transdermal patches, controlled release formulation, and nanoparticle-based drug delivery. Effective collaboration among researchers in the fields of plant biochemistry, pharmacology, molecular biology, and cardiovascular medicine is essential for converting promising preclinical research findings into viable therapeutic interventions. For plant-base antioxidants to be used in comprehensive heart aging care management, rigorous clinical trials assessing their safety, effectiveness, and long-term effects on heart aging and related biomarkers are necessary to determine their therapeutic potential.
In conclusion, plant antioxidants, found in fruits, vegetables, and other plants, have been found to have significant cardioprotective properties. These compounds, including carotenoids, phenolic acids, and flavonoids, work by neutralizing ROS, enhancing antioxidant capacity, and modulating cellular signaling pathways. Plant antioxidants not only prevent cardiovascular damage but also promote tissue repair and functional recovery. They may be effective adjuncts in treating CVDs, either in the diet or as supplements. However, further research is needed to optimize doses, conduct clinical trials, evaluate bioavailability, metabolism, and specific effects of each antioxidant, analyze interactions with other drugs or treatments, identify potential side effects from high doses, and identify potential side effects of their use in treating CVDs. Researchers may discover novel approaches to prevent and manage heart aging by using the wide range of plant-based antioxidants and their complex mechanisms of action. This might eventually result in improved quality of life and health outcomes for the aging population.
MK: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. TZ: Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. WZ: Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. QH: Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. ZS: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. KD: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. CC: Writing–review and editing. LK: Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82273919, 82270396 and U24A20813) and the Science Foundation for the Excellent Youth Scholars of Heilongjiang Province (YQ2023H005).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The manuscript has been presented in “pre-print” at https://www.preprints.org/
Abdellatif, M., Madeo, F., Sedej, S., and Kroemer, G. (2023). Antagonistic pleiotropy: the example of cardiac insulin-like growth factor signaling, which is essential in youth but detrimental in age. Expert Opin. Ther. targets 27, 87–90. doi:10.1080/14728222.2023.2178420
Addo, K. M., and Khan, H. (2024). Factors affecting healthy aging and its interconnected pathways. 1, 9-24. Turkish Journal of Healthy Aging Medicine.
Ahmad, G., Almasry, M., Dhillon, A. S., Abuayyash, M. M., Kothandaraman, N., and Cakar, Z. (2017). “Overview and sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the reproductive system,” in Oxidative stress in human reproduction: shedding light on a complicated phenomenon, 1–16.
Ahuja, S. K., Manoharan, M. S., Lee, G. C., Mckinnon, L. R., Meunier, J. A., Steri, M., et al. (2023). Immune resilience despite inflammatory stress promotes longevity and favorable health outcomes including resistance to infection. Nat. Commun. 14, 3286. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-38238-6
Aires, V., and Delmas, D. (2015). Common pathways in health benefit properties of RSV in cardiovascular diseases, cancers and degenerative pathologies. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 16, 219–244. doi:10.2174/1389201016666150118132457
Akbari, B., Baghaei-Yazdi, N., Bahmaie, M., and Mahdavi Abhari, F. (2022). The role of plant-derived natural antioxidants in reduction of oxidative stress. BioFactors 48, 611–633. doi:10.1002/biof.1831
Akgun-Unal, N., Ozyildirim, S., Unal, O., Gulbahce-Mutlu, E., Mogulkoc, R., and Baltaci, A. K. (2023). The effects of resveratrol and melatonin on biochemical and molecular parameters in diabetic old female rat hearts. Exp. Gerontol. 172, 112043. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2022.112043
Albadrani, G. M., Binmowyna, M. N., Bin-Jumah, M. N., El–Akabawy, G., Aldera, H., and Al-Farga, A. M. (2021). Quercetin prevents myocardial infarction adverse remodeling in rats by attenuating TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling: different mechanisms of action. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 28, 2772–2782. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.02.007
Alfei, S., Marengo, B., and Zuccari, G. (2020). Oxidative stress, antioxidant capabilities, and bioavailability: ellagic acid or urolithins? Antioxidants 9, 707. doi:10.3390/antiox9080707
Alwadei, N. S. (2023). The role of cytochrome P450 2E1 in hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species formation. Chapman University.
Amorim, J. A., Coppotelli, G., Rolo, A. P., Palmeira, C. M., Ross, J. M., and Sinclair, D. A. (2022). Mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 18, 243–258. doi:10.1038/s41574-021-00626-7
Anderson, G. J., and Vulpe, C. D. (2009). Mammalian iron transport. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 3241–3261. doi:10.1007/s00018-009-0051-1
Antar, S. A., Ashour, N. A., Marawan, M. E., and Al-Karmalawy, A. A. (2023). Fibrosis: types, effects, markers, mechanisms for disease progression, and its relation with oxidative stress, immunity, and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 4004. doi:10.3390/ijms24044004
Anwar, I., Wang, X., Pratt, R. E., Dzau, V. J., and Hodgkinson, C. P. (2024). The impact of aging on cardiac repair and regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 300, 107682. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107682
Arenas De Larriva, A. P., Limia-Pérez, L., Alcalá-Díaz, J. F., Alonso, A., López-Miranda, J., and Delgado-Lista, J. (2020). Ceruloplasmin and coronary heart disease—a systematic review. Nutrients 12, 3219. doi:10.3390/nu12103219
Asiwe, J. N., Ben-Azu, B., Yovwin, G. D., Igben, V.-J. O., Oritsemuelebi, B., Efejene, I. O., et al. (2024). Ginkgo biloba supplement modulates mTOR/ERK1/2 activities to mediate cardio-protection in cyclosporin-A-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats. Clin. Traditional Med. Pharmacol. 5, 200134. doi:10.1016/j.ctmp.2024.200134
Aziz, S.G.-G., Pourheydar, B., Chodari, L., and Hamidifar, F. (2022). Effect of exercise and curcumin on cardiomyocyte molecular mediators associated with oxidative stress and autophagy in aged male rats. Microvasc. Res. 143, 104380. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2022.104380
Badmus, O. O., Kipp, Z. A., Bates, E. A., Da Silva, A. A., Taylor, L. C., Martinez, G. J., et al. (2023). Loss of hepatic PPARα in mice causes hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Physiology-Regulatory, Integr. Comp. Physiology 325, R81–R95. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00057.2023
Baechle, J. J., Chen, N., Makhijani, P., Winer, S., Furman, D., and Winer, D. A. (2023). Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging. Mol. Metab. 74, 101755. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101755
Banerjee, S., Ghosh, S., Mandal, A., Ghosh, N., and Sil, P. C. (2020). ROS-associated immune response and metabolism: a mechanistic approach with implication of various diseases. Archives Toxicol. 94, 2293–2317. doi:10.1007/s00204-020-02801-7
Banzubaze, E., Ondari, E., Aja, P., Shinkafi, T., and Mulindwa, J. (2024). Epigenetic regulation by Epi-gallocatechin-3-Galatte on antioxidant gene expression in mice that are at high risk for heart disease. J. Anesth. Pain Med. 9, 01–12.
Begum, R., Howlader, S., Mamun-or-Rashid, A., Rafiquzzaman, S., Ashraf, G. M., Albadrani, G. M., et al. (2021). Antioxidant and signal-modulating effects of Brown seaweed-derived compounds against oxidative stress-associated pathology. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 9974890. doi:10.1155/2021/9974890
Belinskaia, D. A., Voronina, P. A., Shmurak, V. I., Jenkins, R. O., and Goncharov, N. V. (2021). Serum albumin in health and disease: esterase, antioxidant, transporting and signaling properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 10318. doi:10.3390/ijms221910318
Benjamin, E. J., Blaha, M. J., Chiuve, S. E., Cushman, M., Das, S. R., Deo, R., et al. (2017). Heart disease and stroke statistics—2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. circulation 135, e146–e603. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000000485
Bennett, J. M., Reeves, G., Billman, G. E., and Sturmberg, J. P. (2018). Inflammation–nature's way to efficiently respond to all types of challenges: implications for understanding and managing “the epidemic” of chronic diseases. Front. Med. 5, 316. doi:10.3389/fmed.2018.00316
Berthiaume, J. M., Kurdys, J. G., Muntean, D. M., and Rosca, M. G. (2019). Mitochondrial NAD+/NADH redox state and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Antioxidants and Redox Signal. 30, 375–398. doi:10.1089/ars.2017.7415
Bhaskar, S., Sudhakaran, P., and Helen, A. (2016). Quercetin attenuates atherosclerotic inflammation and adhesion molecule expression by modulating TLR-NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell. Immunol. 310, 131–140. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2016.08.011
Bhol, N. K., Bhanjadeo, M. M., Singh, A. K., Dash, U. C., Ojha, R. R., Majhi, S., et al. (2024). The interplay between cytokines, inflammation, and antioxidants: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials of various antioxidants and anti-cytokine compounds. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 178, 117177. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117177
Bishop, S. P., Zhang, J., and Ye, L. (2022). Cardiomyocyte proliferation from fetal-to adult-and from normal-to hypertrophy and failing hearts. Biology 11, 880. doi:10.3390/biology11060880
Bohara, R. A., Tabassum, N., Singh, M. P., Gigli, G., Ragusa, A., and Leporatti, S. (2022). Recent overview of resveratrol’s beneficial effects and its nano-delivery systems. Molecules 27, 5154. doi:10.3390/molecules27165154
Bouyahya, A., Bakrim, S., Aboulaghras, S., El Kadri, K., Aanniz, T., Khalid, A., et al. (2024). Bioactive compounds from nature: antioxidants targeting cellular transformation in response to epigenetic perturbations induced by oxidative stress. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 174, 116432. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116432
Bradley, L. A., Young, A., Li, H., Billcheck, H. O., and Wolf, M. J. (2021). Loss of endogenously cycling adult cardiomyocytes worsens myocardial function. Circulation Res. 128, 155–168. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318277
Brandt, M., Dörschmann, H., Khraisat, S. A., Knopp, T., Ringen, J., Kalinovic, S., et al. (2022). Telomere shortening in hypertensive heart disease depends on oxidative DNA damage and predicts impaired recovery of cardiac function in heart failure. Hypertension 79, 2173–2184. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18935
Bratovcic, A. (2020). Antioxidant enzymes and their role in preventing cell damage. Acta Sci. Nutr. Health 4, 01–07. doi:10.31080/asnh.2020.04.0659
Candore, G., Caruso, C., Jirillo, E., Magrone, T., and Vasto, S. (2010). Low grade inflammation as a common pathogenetic denominator in age-related diseases: novel drug targets for anti-ageing strategies and successful ageing achievement. Curr. Pharm. Des. 16, 584–596. doi:10.2174/138161210790883868
Cao, H., Jia, Q., Yan, L., Chen, C., Xing, S., and Shen, D. (2019). Quercetin suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis by regulating MST1-mediated autophagy in ox-LDL-induced RAW264. 7 macrophage foam cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 6093. doi:10.3390/ijms20236093
Carrillo-Martinez, E. J., Flores-Hernández, F. Y., Salazar-Montes, A. M., Nario-Chaidez, H. F., and Hernández-Ortega, L. D. (2024). Quercetin, a flavonoid with great pharmacological capacity. Molecules 29, 1000. doi:10.3390/molecules29051000
Carrizzo, A., Forte, M., Damato, A., Trimarco, V., Salzano, F., Bartolo, M., et al. (2013). Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in cardiovascular, cerebral and metabolic diseases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 61, 215–226. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.021
Chaachouay, N., and Zidane, L. (2024). Plant-derived natural products: a source for drug discovery and development. Drugs Drug Candidates 3, 184–207. doi:10.3390/ddc3010011
Chang, X., Liu, R., Li, R., Peng, Y., Zhu, P., and Zhou, H. (2023). Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial quality control in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 19, 426–448. doi:10.7150/ijbs.76223
Chen, C.-H., Hsia, C.-C., Hu, P.-A., Yeh, C.-H., Chen, C.-T., Peng, C.-L., et al. (2022a). Bromelain ameliorates atherosclerosis by activating the TFEB-mediated autophagy and antioxidant pathways. Antioxidants 12, 72. doi:10.3390/antiox12010072
Chen, Q., Zeng, Y., Yang, X., Wu, Y., Zhang, S., Huang, S., et al. (2022b). Resveratrol ameliorates myocardial fibrosis by regulating Sirt1/Smad3 deacetylation pathway in rat model with dilated cardiomyopathy. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 22, 17. doi:10.1186/s12872-021-02401-y
Chen, R., Mcvey, D. G., Shen, D., Huang, X., and Ye, S. (2023). Phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 12, e031121. doi:10.1161/JAHA.123.031121
Chen, S., Li, Q., Shi, H., Li, F., Duan, Y., and Guo, Q. (2024a). New insights into the role of mitochondrial dynamics in oxidative stress-induced diseases. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 178, 117084. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117084
Chen, T., Li, J., Liu, J., Li, N., Wang, S., Liu, H., et al. (2015). Activation of SIRT3 by resveratrol ameliorates cardiac fibrosis and improves cardiac function via the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. Am. J. Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiology 308, H424–H434. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00454.2014
Chen, T.-S., Kuo, W.-W., and Huang, C.-Y. (2024b). Autologous transplantation of green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate pretreated adipose-derived stem cells increases cardiac regenerative capability through CXC motif chemokine receptor 4 expression in the treatment of rats with diabetic cardiomyopathy. Exp. Anim. 73, 246–258. doi:10.1538/expanim.23-0109
Chen, W.-J., Cheng, Y., Li, W., Dong, X.-K., Wei, J.-L., Yang, C.-H., et al. (2021). Quercetin attenuates cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction through SIRT3/PARP-1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 739615. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.739615
Cheng, C.-F., and Lian, W.-S. (2013). Prooxidant mechanisms in iron overload cardiomyopathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 740573. doi:10.1155/2013/740573
Cheng, Y., Yan, M., He, S., Xie, Y., Wei, L., Xuan, B., et al. (2024). Baicalin alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy and modulates the AMPK/mTOR pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 28, e18321. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18321
Chistiakov, D. A., Shkurat, T. P., Melnichenko, A. A., Grechko, A. V., and Orekhov, A. N. (2018). The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease: a brief review. Ann. Med. 50, 121–127. doi:10.1080/07853890.2017.1417631
Cho, J.-H., Sung, J.-H., Cho, E.-H., Won, C.-K., Lee, H.-J., Kim, M.-O., et al. (2009). Gingko biloba Extract (EGb 761) prevents ischemic brain injury by activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 37, 547–555. doi:10.1142/S0192415X09007041
Cicek, B., Hacimuftuoglu, A., Yeni, Y., Danisman, B., Ozkaraca, M., Mokhtare, B., et al. (2023). Chlorogenic acid attenuates doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and markers of apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via Nrf2/HO-1 and dityrosine signaling. J. Personalized Med. 13, 649. doi:10.3390/jpm13040649
Ciutac, A. M., and Dawson, D. (2021). The role of inflammation in stress cardiomyopathy. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 31, 225–230. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2020.03.005
Cizmarova, B., Hubkova, B., and Birkova, A. (2023). Quercetin as an effective antioxidant against superoxide radical. Funct. Food Science-Online ISSN 2767-3146 3, 15–25. doi:10.31989/ffs.v3i3.1076
Conte, M., Petraglia, L., Poggio, P., Valerio, V., Cabaro, S., Campana, P., et al. (2022). Inflammation and cardiovascular diseases in the elderly: the role of epicardial adipose tissue. Front. Med. 9, 844266. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.844266
Corrêa, R. C., Peralta, R. M., Haminiuk, C. W., Maciel, G. M., Bracht, A., and Ferreira, I. C. (2018). New phytochemicals as potential human anti-aging compounds: reality, promise, and challenges. Crit. Rev. food Sci. Nutr. 58, 942–957. doi:10.1080/10408398.2016.1233860
Cox, F. F., Misiou, A., Vierkant, A., Ale-Agha, N., Grandoch, M., Haendeler, J., et al. (2022). Protective effects of curcumin in cardiovascular diseases—impact on oxidative stress and mitochondria. Cells 11, 342. doi:10.3390/cells11030342
Crismaru, I., Pantea Stoian, A., Bratu, O. G., Gaman, M.-A., Stanescu, A. M. A., Bacalbasa, N., et al. (2020). Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering treatment: the current approach. Lipids health Dis. 19, 85–10. doi:10.1186/s12944-020-01275-x
Cui, Y., Wang, Y., and Liu, G. (2021). Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) attenuates myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis induced by transverse aortic constriction via inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway. Pharm. Biol. 59, 1305–1313. doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1972124
Cui, Z., Zhao, X., Amevor, F. K., Du, X., Wang, Y., Li, D., et al. (2022). Therapeutic application of quercetin in aging-related diseases: SIRT1 as a potential mechanism. Front. Immunol. 13, 943321. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.943321
Dai, D.-F., Kang, P., and Bai, H. (2023). The mTOR signaling pathway in cardiac aging. J. Cardiovasc. aging 3, 24. doi:10.20517/jca.2023.10
Dandona, P., Dhindsa, S., Ghanim, H., and Chaudhuri, A. (2007). Angiotensin II and inflammation: the effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockade. J. Hum. Hypertens. 21, 20–27. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1002101
Da Rocha, E. V., Falchetti, F., Pernomian, L., De Mello, M. M. B., Parente, J. M., Nogueira, R. C., et al. (2023). Quercetin decreases cardiac hypertrophic mediators and maladaptive coronary arterial remodeling in renovascular hypertensive rats without improving cardiac function. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives Pharmacol. 396, 939–949. doi:10.1007/s00210-022-02349-6
Del Mondo, A., Smerilli, A., Ambrosino, L., Albini, A., Noonan, D. M., Sansone, C., et al. (2021). Insights into phenolic compounds from microalgae: structural variety and complex beneficial activities from health to nutraceutics. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 41, 155–171. doi:10.1080/07388551.2021.1874284
Dong, M., Yang, Z., Fang, H., Xiang, J., Xu, C., Zhou, Y., et al. (2020). Aging attenuates cardiac contractility and affects therapeutic consequences for myocardial infarction. Aging Dis. 11, 365–376. doi:10.14336/AD.2019.0522
Đorđević, D. B., Koračević, G. P., Đorđević, A. D., and Lović, D. B. (2024). Hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. J. Hypertens. 10, 1097. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000003774
Edirisinghe, I., Banaszewski, K., Cappozzo, J., Mccarthy, D., and Burton-Freeman, B. M. (2011). Effect of black currant anthocyanins on the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in vitro in human endothelial cells. J. Agric. food Chem. 59, 8616–8624. doi:10.1021/jf201116y
Eleutherio, E. C. A., Magalhães, R. S. S., De Araújo Brasil, A., Neto, J. R. M., and De Holanda Paranhos, L. (2021). SOD1, more than just an antioxidant. Archives Biochem. Biophysics 697, 108701. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2020.108701
El-Saber Batiha, G., Magdy Beshbishy, A., Wasef, L. G., Elewa, Y. H. A., Al-Sagan, A. A., Abd El-Hack, M. E., et al. (2020). Chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of garlic (Allium sativum L.): a review. Nutrients 12, 872, doi:10.3390/nu12030872
Elseweidy, M. M., Ali, S. I., Shaheen, M. A., Abdelghafour, A. M., and Hammad, S. K. (2023). Vanillin and pentoxifylline ameliorate isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats via the Akt/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway. Food and Funct. 14, 3067–3082. doi:10.1039/d2fo03570g
Endres, M., Moro, M. A., Nolte, C. H., Dames, C., Buckwalter, M. S., and Meisel, A. (2022). Immune pathways in etiology, acute phase, and chronic sequelae of ischemic stroke. Circulation Res. 130, 1167–1186. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319994
Eng, Q. Y., Thanikachalam, P. V., and Ramamurthy, S. (2018). Molecular understanding of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 210, 296–310. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.035
Fan, L., Wu, Y., Wei, J., Xia, F., Cai, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2023). Global, regional, and national time trends in incidence for migraine, from 1990 to 2019: an age-period-cohort analysis for the GBD 2019. J. Headache Pain 24, 79. doi:10.1186/s10194-023-01619-9
Fan, X., Lin, X., Ruan, Q., Wang, J., Yang, Y., Sheng, M., et al. (2022). Research progress on the biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of the anti-cancer drug camptothecin in Camptotheca acuminate. Industrial Crops Prod. 186, 115270. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115270
Feng, H., Wang, J.-Y., Yu, B., Cong, X., Zhang, W.-G., Li, L., et al. (2019). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α inhibits vascular calcification through sirtuin 3-mediated reduction of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Antioxidants and redox Signal. 31, 75–91. doi:10.1089/ars.2018.7620
Ferenczyova, K., Kalocayova, B., and Bartekova, M. (2020). Potential implications of quercetin and its derivatives in cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1585. doi:10.3390/ijms21051585
Ferreira, T., and Rodriguez, S. (2024). Mitochondrial DNA: inherent complexities relevant to genetic analyses. Genes. 15, 617. doi:10.3390/genes15050617
Fleenor, B. S., Sindler, A. L., Marvi, N. K., Howell, K. L., Zigler, M. L., Yoshizawa, M., et al. (2013). Curcumin ameliorates arterial dysfunction and oxidative stress with aging. Exp. Gerontol. 48, 269–276. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2012.10.008
Flora, G. D., and Nayak, M. K. (2019). A brief review of cardiovascular diseases, associated risk factors and current treatment regimes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 25, 4063–4084. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190925163827
Fox, P. L., Mazumder, B., Ehrenwald, E., and Mukhopadhyay, C. K. (2000). Ceruloplasmin and cardiovascular disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 28, 1735–1744. doi:10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00231-8
Franco, F. N., Peixoto, B. E., De Araújo, G. R., and Chaves, M. M. (2025). Silencing of the Nrf2 pathway in aging promotes a decrease in the anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol. Archives Gerontology Geriatrics 129, 105694. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2024.105694
Gabbia, D., and De Martin, S. (2020). Brown seaweeds for the management of metabolic syndrome and associated diseases. Molecules 25, 4182. doi:10.3390/molecules25184182
Gan, M., Zheng, T., Shen, L., Tan, Y., Fan, Y., Shuai, S., et al. (2019). Genistein reverses isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy by regulating miR-451/TIMP2. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 112, 108618. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108618
Gao, C., Chen, X., Li, J., Li, Y., Tang, Y., Liu, L., et al. (2014). Myocardial mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunction in intense exercise: regulatory effects of quercetin. Eur. J. Appl. physiology 114, 695–705. doi:10.1007/s00421-013-2802-9
Gao, H.-L., Yu, X.-J., Hu, H.-B., Yang, Q.-W., Liu, K.-L., Chen, Y.-M., et al. (2021). Apigenin improves hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy through modulating NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation and cytokines in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 21, 721–736. doi:10.1007/s12012-021-09662-1
Gao, T., Liu, M., Fu, D., Xue, Y., Liao, J., Yang, P., et al. (2024). Allicin treats myocardial infarction in I/R through the promotion of the SHP2 axis to inhibit p-PERK-mediated oxidative stress. Aging (Albany NY) 16, 5207–5223. doi:10.18632/aging.205640
Garay, J. A., Silva, J. E., Di Genaro, M. S., and Davicino, R. C. (2022). The multiple faces of nitric oxide in chronic granulomatous disease: a comprehensive update. Biomedicines 10, 2570. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10102570
Garcia, C., and Blesso, C. N. (2021). Antioxidant properties of anthocyanins and their mechanism of action in atherosclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 172, 152–166. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.05.040
García-García, V. A., Alameda, J. P., Page, A., and Casanova, M. L. (2021). Role of NF-κB in ageing and age-related diseases: lessons from genetically modified mouse models. Cells 10, 1906. doi:10.3390/cells10081906
Ghorbanzadeh, V., Pourheydar, B., Dariushnejad, H., Ghalibafsabbaghi, A., and Chodari, L. (2022). Curcumin improves angiogenesis in the heart of aged rats: involvement of TSP1/NF-κB/VEGF-A signaling. Microvasc. Res. 139, 104258. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104258
Gianazza, E., Brioschi, M., Martinez Fernandez, A., Casalnuovo, F., Altomare, A., Aldini, G., et al. (2021). Lipid peroxidation in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants and redox Signal. 34, 49–98. doi:10.1089/ars.2019.7955
Giunta, S., Wei, Y., Xu, K., and Xia, S. (2022). Cold-inflammaging: when a state of homeostatic-imbalance associated with aging precedes the low-grade pro-inflammatory-state (inflammaging): meaning, evolution, inflammaging phenotypes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiology 49, 925–934. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13686
Gomaa, A. M., Abdelhafez, A. T., and Aamer, H. A. (2018). Garlic (Allium sativum) exhibits a cardioprotective effect in experimental chronic renal failure rat model by reducing oxidative stress and controlling cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase activity and Ca 2+ levels. Cell. Stress Chaperones 23, 913–920. doi:10.1007/s12192-018-0898-x
González-Hedström, D., García-Villalón, Á. L., Amor, S., De La Fuente-Fernández, M., Almodóvar, P., Prodanov, M., et al. (2021). Olive leaf extract supplementation improves the vascular and metabolic alterations associated with aging in Wistar rats. Sci. Rep. 11, 8188. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-87628-7
Grel, H., Woznica, D., Ratajczak, K., Kalwarczyk, E., Anchimowicz, J., Switlik, W., et al. (2023). Mitochondrial dynamics in neurodegenerative diseases: unraveling the role of fusion and fission processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 13033. doi:10.3390/ijms241713033
Gulcin, İ. (2020). Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: an updated overview. Archives Toxicol. 94, 651–715. doi:10.1007/s00204-020-02689-3
Guo, J., Huang, X., Dou, L., Yan, M., Shen, T., Tang, W., et al. (2022). Aging and aging-related diseases: from molecular mechanisms to interventions and treatments. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 391. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01251-0
Guo, W., Huang, D., and Li, S. (2023). Lycopene alleviates oxidative stress-induced cell injury in human vascular endothelial cells by encouraging the SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 45, 2205051. doi:10.1080/10641963.2023.2205051
Gusev, E., and Sarapultsev, A. (2024). Exploring the pathophysiology of long COVID: the central role of low-grade inflammation and multisystem involvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 6389. doi:10.3390/ijms25126389
Hada, Y., Uchida, H. A., Otaka, N., Onishi, Y., Okamoto, S., Nishiwaki, M., et al. (2020). The protective effect of chlorogenic acid on vascular senescence via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 4527. doi:10.3390/ijms21124527
Haddad, F., Hunt, S. A., Rosenthal, D. N., and Murphy, D. J. (2008). Right ventricular function in cardiovascular disease, part I: anatomy, physiology, aging, and functional assessment of the right ventricle. Circulation 117, 1436–1448. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.653576
Hafez, A. M., Gaafar, N. K., Mohamed, L., Dawood, M. M. M., and Wagih, A. a.E.-F. (2024). The beneficial effects of anthocyanin on D-galactose induced cardiac muscle aging in rats. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 8, 498–506. doi:10.33545/26174693.2024.v8.i6f.1356
Halper, J. (2021). “Basic components of connective tissues and extracellular matrix: fibronectin, fibrinogen, laminin, elastin, fibrillins, fibulins, matrilins, tenascins and thrombospondins,” in Progress in heritable soft connective tissue diseases, 105–126.
Hamo, C. E., Dejong, C., Hartshorne-Evans, N., Lund, L. H., Shah, S. J., Solomon, S., et al. (2024). Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 10, 55. doi:10.1038/s41572-024-00540-y
Handy, D. E., Castro, R., and Loscalzo, J. (2011). Epigenetic modifications: basic mechanisms and role in cardiovascular disease. Circulation 123, 2145–2156. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.956839
Hankins, J. (2006). The role of albumin in fluid and electrolyte balance. J. Infusion Nurs. 29, 260–265. doi:10.1097/00129804-200609000-00004
Hastings, M. H., Zhou, Q., Wu, C., Shabani, P., Huang, S., Yu, X., et al. (2024). Cardiac aging: from hallmarks to therapeutic opportunities. Cardiovasc. Res., cvae124. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvae124
He, X., Du, T., Long, T., Liao, X., Dong, Y., and Huang, Z.-P. (2022). Signaling cascades in the failing heart and emerging therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 134. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00972-6
Healthcare Engineering, J. O. (2022). Retracted: changes of multisectoral collaboration and service delivery in hypertension prevention and control before and after the 2009 new Healthcare reform in China: an interrupted time-series study. Wiley Online Library.
Heinzel, F. R., Hegemann, N., Hohendanner, F., Primessnig, U., Grune, J., Blaschke, F., et al. (2020). Left ventricular dysfunction in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction—molecular mechanisms and impact on right ventricular function. Cardiovasc. diagnosis Ther. 10, 1541–1560. doi:10.21037/cdt-20-477
Higgins, M. R., Izadi, A., and Kaviani, M. (2020). Antioxidants and exercise performance: with a focus on vitamin E and C supplementation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17, 8452. doi:10.3390/ijerph17228452
Ho, J.-H., Baskaran, R., Wang, M.-F., Yang, H.-S., Lo, Y.-H., Mohammedsaleh, Z. M., et al. (2022). Bioactive peptides and exercise modulate the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α/FOXO3 pathway as a therapeutic approach for hypertensive rats. Pharmaceuticals 15, 819. doi:10.3390/ph15070819
Hori, M., and Nishida, K. (2009). Oxidative stress and left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 81, 457–464. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvn335
Hosoda, R., Nakashima, R., Yano, M., Iwahara, N., Asakura, S., Nojima, I., et al. (2023). Resveratrol, a SIRT1 activator, attenuates aging-associated alterations in skeletal muscle and heart in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 152, 112–122. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2023.04.001
Hou, D., Liao, H., Hao, S., Liu, R., Huang, H., and Duan, C. (2024). Curcumin simultaneously improves mitochondrial dynamics and myocardial cell bioenergy after sepsis via the SIRT1-DRP1/PGC-1α pathway. Heliyon 10, e28501. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28501
Hsu, C.-P., Odewale, I., Alcendor, R. R., and Sadoshima, J. (2008). Sirt1 protects the heart from aging and stress. Biol. Chem. 389, 221–231. doi:10.1515/BC.2008.032
Huang, C.L.-H., and Lei, M. (2023). Cardiomyocyte electrophysiology and its modulation: current views and future prospects. Philosophical Trans. R. Soc. B 378, 20220160. doi:10.1098/rstb.2022.0160
Huang, H., Wang, T., Wang, L., Huang, Y., Li, W., Hu, Y., et al. (2023). Saponins of Panax japonicus ameliorates cardiac aging phenotype in aging rats by enhancing basal autophagy through AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 182, 112305. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2023.112305
Huang, T.-L., Jiang, W.-J., Zhou, Z., Shi, T.-F., Yu, M., Yu, M., et al. (2024). Quercetin attenuates cisplatin-induced mitochondrial apoptosis via PI3K/Akt mediated inhibition of oxidative stress in pericytes and improves the blood labyrinth barrier permeability. Chemico-Biological Interact. 393, 110939. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2024.110939
Huang, X., Chu, Y., Ren, H., and Pang, X. (2022). Antioxidation function of EGCG by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mice with coronary heart disease. Contrast media and Mol. imaging 2022, 8639139. doi:10.1155/2022/8639139
Ijaz, N., Jamil, Y., Brown Iv, C. H., Krishnaswami, A., Orkaby, A., Stimmel, M. B., et al. (2024). Role of cognitive frailty in older adults with cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 13, e033594. doi:10.1161/JAHA.123.033594
Ilkun, O., and Boudina, S. (2013). Cardiac dysfunction and oxidative stress in the metabolic syndrome: an update on antioxidant therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 19, 4806–4817. doi:10.2174/1381612811319270003
Imam, M. U., Zhang, S., Ma, J., Wang, H., and Wang, F. (2017). Antioxidants mediate both iron homeostasis and oxidative stress. Nutrients 9, 671. doi:10.3390/nu9070671
Iqbal, I., Wilairatana, P., Saqib, F., Nasir, B., Wahid, M., Latif, M. F., et al. (2023). Plant polyphenols and their potential benefits on cardiovascular health: a review. Molecules 28, 6403. doi:10.3390/molecules28176403
Jankowska, E. A., Rozentryt, P., Witkowska, A., Nowak, J., Hartmann, O., Ponikowska, B., et al. (2010). Iron deficiency: an ominous sign in patients with systolic chronic heart failure. Eur. heart J. 31, 1872–1880. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehq158
Ježek, P., Dlasková, A., Engstová, H., Špačková, J., Tauber, J., Průchová, P., et al. (2024). Mitochondrial physiology of cellular redox regulations. Physiological Res. 73, S217–S242. doi:10.33549/physiolres.935269
Jiang, Q., Lu, M., Li, J., and Zhu, Z. (2021). Ginkgolide B protects cardiomyocytes from angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy via regulation of autophagy through SIRT1-FoxO1. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2021, 5554569. doi:10.1155/2021/5554569
Jiménez, R., Zúñiga-Muñoz, A., Álvarez-León, E., García-Niño, W. R., Navarrete-Anastasio, G., Soria-Castro, E., et al. (2025). Quercetin preserves mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum contact sites improving mitochondrial dynamics in aged myocardial cells. Biogerontology 26, 29. doi:10.1007/s10522-024-10174-y
Jiménez-Gómez, B., Ortega-Sáenz, P., Gao, L., González-Rodríguez, P., García-Flores, P., Chandel, N., et al. (2023). Transgenic NADH dehydrogenase restores oxygen regulation of breathing in mitochondrial complex I-deficient mice. Nat. Commun. 14, 1172. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36894-2
Jomova, K., Alomar, S. Y., Alwasel, S. H., Nepovimova, E., Kuca, K., and Valko, M. (2024). Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Archives Toxicol. 98, 1323–1367. doi:10.1007/s00204-024-03696-4
Jomova, K., Raptova, R., Alomar, S. Y., Alwasel, S. H., Nepovimova, E., Kuca, K., et al. (2023). Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Archives Toxicol. 97, 2499–2574. doi:10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9
Juan, C. A., Pérez De La Lastra, J. M., Plou, F. J., and Pérez-Lebeña, E. (2021). The chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ROS) revisited: outlining their role in biological macromolecules (DNA, lipids and proteins) and induced pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4642. doi:10.3390/ijms22094642
Jubaidi, F. F., Zainalabidin, S., Taib, I. S., Hamid, Z. A., and Budin, S. B. (2021). The potential role of flavonoids in ameliorating diabetic cardiomyopathy via alleviation of cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 5094. doi:10.3390/ijms22105094
Kadhim, S. M., Mohammed, M. T., and Abbood, S. M. (2020). Biochemical studies of Ginkgo biloba extract on oxidative stress-induced myocardial injuries. Drug Invent. Today 14, 817–820.
Kaludercic, N., and Di Lisa, F. (2020). Mitochondrial ROS formation in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 7, 12. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2020.00012
Karamanos, N. K., Theocharis, A. D., Piperigkou, Z., Manou, D., Passi, A., Skandalis, S. S., et al. (2021). A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix. FEBS J. 288, 6850–6912. doi:10.1111/febs.15776
Kasai, S., Shimizu, S., Tatara, Y., Mimura, J., and Itoh, K. (2020). Regulation of Nrf2 by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in physiology and pathology. Biomolecules 10, 320. doi:10.3390/biom10020320
Kaur, A., Tiwari, R., Tiwari, G., and Ramachandran, V. (2022). Resveratrol: a vital therapeutic agent with multiple health benefits. Drug Res. 72, 5–17. doi:10.1055/a-1555-2919
Khan, A. S., Sane, D. C., Wannenburg, T., and Sonntag, W. E. (2002). Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-1 and the aging cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Res. 54, 25–35. doi:10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00533-8
Kim, H., Lee, Y. D., Kim, H. J., Lee, Z. H., and Kim, H. H. (2017). SOD2 and Sirt3 control osteoclastogenesis by regulating mitochondrial ROS. J. Bone Mineral Res. 32, 397–406. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2974
Kim, S.-R., Seong, K.-J., Kim, W.-J., and Jung, J.-Y. (2022). Epigallocatechin gallate protects against hypoxia-induced inflammation in microglia via NF-κB suppression and Nrf-2/HO-1 activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 4004. doi:10.3390/ijms23074004
Kitamoto, K., Miura, Y., Karnan, S., Ota, A., Konishi, H., Hosokawa, Y., et al. (2018). Inhibition of NADPH oxidase 2 induces apoptosis in osteosarcoma: the role of reactive oxygen species in cell proliferation. Oncol. Lett. 15, 7955–7962. doi:10.3892/ol.2018.8291
Kolwicz Jr, S. C., and Tian, R. (2011). Glucose metabolism and cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc. Res. 90, 194–201. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr071
Kosuru, R., Cai, Y., Kandula, V., Yan, D., Wang, C., Zheng, H., et al. (2018a). AMPK contributes to cardioprotective effects of pterostilbene against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by suppressing cardiac oxidative stress and apoptosis. Cell. Physiology Biochem. 46, 1381–1397. doi:10.1159/000489154
Kosuru, R., Kandula, V., Rai, U., Prakash, S., Xia, Z., and Singh, S. (2018b). Pterostilbene decreases cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation via activation of AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in fructose-fed diabetic rats. Cardiovasc. drugs Ther. 32, 147–163. doi:10.1007/s10557-018-6780-3
Kremastinos, D. T., and Farmakis, D. (2011). Iron overload cardiomyopathy in clinical practice. Circulation 124, 2253–2263. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.050773
Kumar, M., Kasala, E. R., Bodduluru, L. N., Kumar, V., and Lahkar, M. (2017). Molecular and biochemical evidence on the protective effects of quercetin in isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial injury in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 31, 1–8. doi:10.1002/jbt.21832
Lazzeroni, D., Villatore, A., Souryal, G., Pili, G., and Peretto, G. (2022). The aging heart: a molecular and clinical challenge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 16033. doi:10.3390/ijms232416033
Leal, M. A., Aires, R., Pandolfi, T., Marques, V. B., Campagnaro, B. P., Pereira, T. M., et al. (2020). Sildenafil reduces aortic endothelial dysfunction and structural damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats: role of NO, NADPH and COX-1 pathways. Vasc. Pharmacol. 124, 106601. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2019.106601
Lee, G. H., Hoang, T. H., Jung, E. S., Jung, S. J., Han, S. K., Chung, M. J., et al. (2020). Anthocyanins attenuate endothelial dysfunction through regulation of uncoupling of nitric oxide synthase in aged rats. Aging Cell. 19, e13279. doi:10.1111/acel.13279
Lee, S.-Y., Kuo, Y.-H., Du, C.-X., Huang, C.-W., and Ku, H.-C. (2023). A novel caffeic acid derivative prevents angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 162, 114709. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114709
Lee, W.-S., and Kim, J. (2018). Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling in cardiac aging. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis Dis. 1864, 1931–1938. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.08.029
Lejri, I., Grimm, A., and Eckert, A. (2019). Ginkgo biloba extract increases neurite outgrowth and activates the Akt/mTOR pathway. PloS one 14, e0225761. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0225761
Leon-Sicairos, N., Reyes-Cortes, R., Guadrón-Llanos, A. M., Madueña-Molina, J., Leon-Sicairos, C., and Canizalez-Román, A. (2015). Strategies of intracellular pathogens for obtaining iron from the environment. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 476534. doi:10.1155/2015/476534
Leyane, T. S., Jere, S. W., and Houreld, N. N. (2022). Oxidative stress in ageing and chronic degenerative pathologies: molecular mechanisms involved in counteracting oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7273. doi:10.3390/ijms23137273
Li, A.-L., Lian, L., Chen, X.-N., Cai, W.-H., Fan, X.-B., Fan, Y.-J., et al. (2023a). The role of mitochondria in myocardial damage caused by energy metabolism disorders: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 208, 236–251. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.08.009
Li, C., Jiang, S., Wang, H., Wang, Y., Han, Y., and Jiang, J. (2022a). Berberine exerts protective effects on cardiac senescence by regulating the Klotho/SIRT1 signaling pathway. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 151, 113097. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113097
Li, D., Liu, X., Pi, W., Zhang, Y., Yu, L., Xu, C., et al. (2022b). Fisetin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting ferroptosis through SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway activation. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 808480. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.808480
Li, D., Wang, X., Huang, Q., Li, S., Zhou, Y., and Li, Z. (2018). Cardioprotection of CAPE-oNO2 against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion induced ROS generation via regulating the SIRT1/eNOS/NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Redox Biol. 15, 62–73. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.023
Li, G., Pan, B., Liu, L., Xu, X., Zhao, W., Mou, Q., et al. (2024a). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate restores mitochondrial homeostasis impairment by inhibiting HDAC1-mediated NRF1 histone deacetylation in cardiac hypertrophy. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 479, 963–973. doi:10.1007/s11010-023-04768-2
Li, H., and Qian, Z. M. (2002). Transferrin/transferrin receptor-mediated drug delivery. Med. Res. Rev. 22, 225–250. doi:10.1002/med.10008
Li, J., Feng, Z., Lu, B., Fang, X., Huang, D., and Wang, B. (2023b). Resveratrol alleviates high glucose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cell through AMPK/Sirt1 activation. Biochem. Biophysics Rep. 34, 101444. doi:10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101444
Li, M., Luo, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, F., Xia, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2024b). Resveratrol inhibits restenosis through suppressing proliferation, migration and trans-differentiation of vascular adventitia fibroblasts via activating SIRT1. Curr. Med. Chem. 31, 242–256. doi:10.2174/0929867330666230505161041
Li, T., Fang, F., Yin, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Wang, E., et al. (2025). EGCG alleviates vascular calcification via the MAPK/JunB signaling pathway. Genes. and Dis. 12, 101237. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101237
Li, Y., Ge, J., and Kong, J. (2022c). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate exerts protective effect on epithelial function via PI3K/AKT signaling in thrombosis. Microvasc. Res. 144, 104408. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2022.104408
Lin, L., Xu, H., Yao, Z., Zeng, X., Kang, L., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Jin-Xin-Kang alleviates heart failure by mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction through the Calcineurin/Dynamin-Related Protein 1 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 335, 118685. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118685
Lin, X., Lin, C.-H., Zhao, T., Zuo, D., Ye, Z., Liu, L., et al. (2017). Quercetin protects against heat stroke-induced myocardial injury in male rats: antioxidative and antiinflammatory mechanisms. Chemico-biological Interact. 265, 47–54. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2017.01.006
Lindsey, M. L., Brunt, K. R., Kirk, J. A., Kleinbongard, P., Calvert, J. W., De Castro Brás, L. E., et al. (2021). Guidelines for in vivo mouse models of myocardial infarction. Am. J. Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiology 321, H1056–H1073. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00459.2021
Liu, A.-H., Bao, Y.-M., Wang, X.-Y., and Zhang, Z.-X. (2013). Cardio-protection by Ginkgo biloba extract 50 in rats with acute myocardial infarction is related to Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Am. J. Chin. Med. 41, 789–800. doi:10.1142/S0192415X13500535
Liu, G. Y., and Sabatini, D. M. (2020). mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 183–203. doi:10.1038/s41580-019-0199-y
Liu, J., Zhang, M., Qin, C., Wang, Z., Chen, J., Wang, R., et al. (2022a). Resveratrol attenuate myocardial injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via inducing KAT5/GPX4 in myocardial infarction. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 906073. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.906073
Liu, L., Liao, X., Wu, H., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., and Chen, Q. (2020). Mitophagy and its contribution to metabolic and aging-associated disorders. Antioxidants and Redox Signal. 32, 906–927. doi:10.1089/ars.2019.8013
Liu, P., Li, J., Liu, M., Zhang, M., Xue, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Hesperetin modulates the Sirt1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in counteracting myocardial ischemia through suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 139, 111552. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111552
Liu, S., Ren, J., Liu, S., Zhao, X., Liu, H., Zhou, T., et al. (2023a). Resveratrol inhibits autophagy against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through the DJ-1/MEKK1/JNK pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 951, 175748. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175748
Liu, W., Huang, J., He, S., Du, R., Shi, W., Wang, Y., et al. (2023b). Senescent endothelial cells’ response to the degradation of bioresorbable scaffold induces intimal dysfunction accelerating in-stent restenosis. Acta Biomater. 166, 266–277. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2023.05.028
Liu, X.-G., Lu, X., Gao, W., Li, P., and Yang, H. (2022b). Structure, synthesis, biosynthesis, and activity of the characteristic compounds from Ginkgo biloba L. Nat. Product. Rep. 39, 474–511. doi:10.1039/d1np00026h
Lobo, V., Patil, A., Phatak, A., and Chandra, N. (2010). Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 4, 118–126. doi:10.4103/0973-7847.70902
Lu, X.-L., Zhao, C.-H., Yao, X.-L., and Zhang, H. (2017). Quercetin attenuates high fructose feeding-induced atherosclerosis by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis via ROS-regulated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 85, 658–671. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.077
Lu, Y. N., Lu, J. M., Jin, G. N., Shen, X. Y., Wang, J. H., Ma, J. W., et al. (2024). A novel mechanism of resveratrol alleviates Toxoplasma gondii infection-induced pulmonary inflammation via inhibiting inflammasome activation. Phytomedicine 131, 155765. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155765
Luan, F., Lei, Z., Peng, X., Chen, L., Peng, L., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Cardioprotective effect of cinnamaldehyde pretreatment on ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and gasdermin D mediated cardiomyocyte pyroptosis. Chemico-Biological Interact. 368, 110245. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110245
Lunde, I. G., Rypdal, K. B., Van Linthout, S., Diez, J., and González, A. (2024). Myocardial fibrosis from the perspective of the extracellular matrix: mechanisms to clinical impact. Matrix Biol. 134, 1–22. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2024.08.008
Lv, X.-F., Wen, R.-Q., Liu, K., Zhao, X.-K., Pan, C.-L., Gao, X., et al. (2022). Role and molecular mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in preventing cardiotoxicity associated with chemoradiotherapy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9, 1047700. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.1047700
Ma, L.-N., Li, L.-D., Li, S.-C., Hao, X.-M., Zhang, J.-Y., He, P., et al. (2017). Allicin improves cardiac function by protecting against apoptosis in rat model of myocardial infarction. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 589–597. doi:10.1007/s11655-016-2523-0
Ma, L.-Y., Chen, W.-W., Gao, R.-L., Liu, L.-S., Zhu, M.-L., Wang, Y.-J., et al. (2020). China cardiovascular diseases report 2018: an updated summary. J. geriatric Cardiol. JGC 17, 1–8. doi:10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2020.01.001
Ma, Y., Hu, Y., Wu, J., Wen, J., Li, S., Zhang, L., et al. (2019). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via regulating Hippo signaling pathway in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes. Acta Biochimica Biophysica Sinica 51, 422–430. doi:10.1093/abbs/gmz018
Madhavan, M. V., Gersh, B. J., Alexander, K. P., Granger, C. B., and Stone, G. W. (2018). Coronary artery disease in patients≥ 80 years of age. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 71, 2015–2040. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.12.068
Mahdavi-Roshan, M., Salari, A., Ghorbani, Z., and Ashouri, A. (2020). The effects of regular consumption of green or black tea beverage on blood pressure in those with elevated blood pressure or hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Ther. Med. 51, 102430. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102430
Mailloux, R. J. (2020). An update on mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. Antioxidants 9, 472. doi:10.3390/antiox9060472
Maksymchuk, O., Shysh, A., and Kotliarova, A. (2023). Quercetin inhibits the expression of MYC and CYP2E1 and reduces oxidative stress in the myocardium of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Biochim. Pol. 70, 199–204. doi:10.18388/abp.2020_6517
Mancardi, D., Mezzanotte, M., Arrigo, E., Barinotti, A., and Roetto, A. (2021). Iron overload, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis in the failing heart and liver. Antioxidants 10, 1864. doi:10.3390/antiox10121864
Mannick, J. B., and Lamming, D. W. (2023). Targeting the biology of aging with mTOR inhibitors. Nat. Aging 3, 642–660. doi:10.1038/s43587-023-00416-y
Martemucci, G., Portincasa, P., Centonze, V., Mariano, M., Khalil, M., and D'alessandro, A. G. (2023). Prevention of oxidative stress and diseases by antioxidant supplementation. Med. Chem. 19, 509–537. doi:10.2174/1573406419666221130162512
Medicine, C. a.O. I., Association, C. M. D., Cardiology, N. C. R. C. F. C. M., Group, C. D. W., Group, E. D. W., Medicine, C. C. F. E.-B. C., et al. (2021). Chinese expert consensus on clinical application of oral Ginkgo biloba preparations (2020). Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27, 163–169. doi:10.1007/s11655-021-3289-6
Miao, X., Rong, L., Fu, B., Cui, S., Gu, Z., Hu, F., et al. (2024). Astragalus polysaccharides attenuate rat aortic endothelial senescence via regulation of the SIRT-1/p53 signaling pathway. BMC Complementary Med. Ther. 24, 80. doi:10.1186/s12906-024-04387-4
Mohammadi, N., Farrell, M., O’sullivan, L., Langan, A., Franchin, M., Azevedo, L., et al. (2024a). Effectiveness of anthocyanin-containing foods and nutraceuticals in mitigating oxidative stress, inflammation, and cardiovascular health-related biomarkers: a systematic review of animal and human interventions. Food and Funct. 15, 3274–3299. doi:10.1039/d3fo04579j
Mohammadi, S., Moghadam, M. D., Nasiriasl, M., Akhzari, M., and Barazesh, M. (2024b). Insights into the therapeutic and pharmacological properties of resveratrol as a nutraceutical antioxidant polyphenol in health promotion and disease prevention. Curr. Rev. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Former. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 19, 327–354. doi:10.2174/0127724328268507231218051058
Mokra, D., Joskova, M., and Mokry, J. (2022). Therapeutic effects of green tea polyphenol (‒)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in relation to molecular pathways controlling inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 340. doi:10.3390/ijms24010340
Möller, M. N., and Denicola, A. (2024). Diffusion of peroxynitrite, its precursors, and derived reactive species, and the effect of cell membranes. Redox Biochem. Chem. 9, 100033. doi:10.1016/j.rbc.2024.100033
Moskalik, A., Niderla-Bielińska, J., and Ratajska, A. (2022). Multiple roles of cardiac macrophages in heart homeostasis and failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 27, 1413–1430. doi:10.1007/s10741-021-10156-z
Murray, M., Dordevic, A. L., Cox, K., Scholey, A., Ryan, L., and Bonham, M. P. (2021). Twelve weeks’ treatment with a polyphenol-rich seaweed extract increased HDL cholesterol with no change in other biomarkers of chronic disease risk in overweight adults: a placebo-controlled randomized trial. J. Nutr. Biochem. 96, 108777. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108777
Muscolo, A., Mariateresa, O., Giulio, T., and Mariateresa, R. (2024). Oxidative stress: the role of antioxidant phytochemicals in the prevention and treatment of diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 3264. doi:10.3390/ijms25063264
Myhre, P. L., Claggett, B., Ballantyne, C. M., Selvin, E., Røsjø, H., Omland, T., et al. (2019). Association between circulating troponin concentrations, left ventricular systolic and diastolic functions, and incident heart failure in older adults. JAMA Cardiol. 4, 997–1006. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2019.3113
Naaz, A., Zhang, Y., Faidzinn, N. A., Yogasundaram, S., Dorajoo, R., and Alfatah, M. (2024). Curcumin inhibits TORC1 and prolongs the lifespan of cells with mitochondrial dysfunction. Cells 13, 1470. doi:10.3390/cells13171470
Nagarajan, S., Nagarajan, R., Kumar, J., Salemme, A., Togna, A. R., Saso, L., et al. (2020). Antioxidant activity of synthetic polymers of phenolic compounds. Polymers 12, 1646. doi:10.3390/polym12081646
Najmi, A., Javed, S. A., Al Bratty, M., and Alhazmi, H. A. (2022). Modern approaches in the discovery and development of plant-based natural products and their analogues as potential therapeutic agents. Molecules 27, 349. doi:10.3390/molecules27020349
Napolitano, G., Fasciolo, G., and Venditti, P. (2021). Mitochondrial management of reactive oxygen species. Antioxidants 10, 1824. doi:10.3390/antiox10111824
Nayakanti, S. R. (2022). Role of FoxO3 transcription factor in right ventricular remodeling and failure.
Oishi, Y., and Manabe, I. (2016). Macrophages in age-related chronic inflammatory diseases. NPJ aging Mech. Dis. 2, 16018–8. doi:10.1038/npjamd.2016.18
Oknińska, M., Mączewski, M., and Mackiewicz, U. (2022). Ventricular arrhythmias in acute myocardial ischaemia—focus on the ageing and sex. Ageing Res. Rev. 81, 101722. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2022.101722
Okoye, C. N., Koren, S. A., and Wojtovich, A. P. (2023). Mitochondrial complex I ROS production and redox signaling in hypoxia. Redox Biol. 67, 102926. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102926
Olayem, B. S., Olaitan, O. B., and Akinola, A. B. (2024). “Immunomodulatory plant based foods, it’s chemical, biochemical and pharmacological approaches,” in Medicinal plants-chemical, biochemical, and pharmacological approaches.
Oldfield, C. J., Duhamel, T. A., and Dhalla, N. S. (2020). Mechanisms for the transition from physiological to pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Can. J. physiology Pharmacol. 98, 74–84. doi:10.1139/cjpp-2019-0566
Orzheshkovskyi, V., and Trishchynska, M. (2019). Ceruloplasmin: its role in the physiological and pathological processes. Neurophysiology 51, 141–149. doi:10.1007/s11062-019-09805-9
Oskuye, Z. Z., Mehri, K., Mokhtari, B., Bafadam, S., Nemati, S., and Badalzadeh, R. (2024). Cardioprotective effect of antioxidant combination therapy: a highlight on MitoQ plus alpha-lipoic acid beneficial impact on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in aged rats. Heliyon 10, e28158. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28158
Oyama, J.-I., Shiraki, A., Nishikido, T., Maeda, T., Komoda, H., Shimizu, T., et al. (2017). EGCG, a green tea catechin, attenuates the progression of heart failure induced by the heart/muscle-specific deletion of MnSOD in mice. J. Cardiol. 69, 417–427. doi:10.1016/j.jjcc.2016.05.019
Pacinella, G., Ciaccio, A. M., and Tuttolomondo, A. (2022). Endothelial dysfunction and chronic inflammation: the cornerstones of vascular alterations in age-related diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 15722. doi:10.3390/ijms232415722
Palma, F. R., Gantner, B. N., Sakiyama, M. J., Kayzuka, C., Shukla, S., Lacchini, R., et al. (2024). ROS production by mitochondria: function or dysfunction? Oncogene 43, 295–303. doi:10.1038/s41388-023-02907-z
Pan, B., Quan, J., Liu, L., Xu, Z., Zhu, J., Huang, X., et al. (2017). Epigallocatechin gallate reverses cTnI-low expression-induced age-related heart diastolic dysfunction through histone acetylation modification. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 21, 2481–2490. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13169
Pan, B., Xu, Z., Xu, Y., Liu, L., Zhu, J., Wang, X., et al. (2016). Diastolic dysfunction and cardiac troponin I decrease in aging hearts. Archives Biochem. biophysics 603, 20–28. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2016.05.008
Pang, B., Dong, G., Pang, T., Sun, X., Liu, X., Nie, Y., et al. (2024). Emerging insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for vascular endothelial injury-associated diseases: focus on mitochondrial dysfunction. Angiogenesis 27, 623–639. doi:10.1007/s10456-024-09938-4
Pena, E., Brito, J., El Alam, S., and Siques, P. (2020). Oxidative stress, kinase activity and inflammatory implications in right ventricular hypertrophy and heart failure under hypobaric hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 6421. doi:10.3390/ijms21176421
Peng, X., Wang, S., Chen, H., and Chen, M. (2023). Role of the Notch1 signaling pathway in ischemic heart disease. Int. J. Mol. Med. 51, 1–13. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2023.5230
Peoples, J. N., Saraf, A., Ghazal, N., Pham, T. T., and Kwong, J. Q. (2019). Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in heart disease. Exp. and Mol. Med. 51, 1–13. doi:10.1038/s12276-019-0355-7
Pereira, L., and Cotas, J. (2023). Therapeutic potential of polyphenols and other micronutrients of marine origin. Mar. drugs 21, 323. doi:10.3390/md21060323
Perrone, M., Patergnani, S., Di Mambro, T., Palumbo, L., Wieckowski, M. R., Giorgi, C., et al. (2023). Calcium homeostasis in the control of mitophagy. Antioxidants and Redox Signal. 38, 581–598. doi:10.1089/ars.2022.0122
Phogat, A., Singh, J., and Malik, V. (2024). Pharmacological effects of Berberine-A Chinese medicine, against xenobiotics toxicity. Pharmacol. Res. - Mod. Chin. Med. 100507. doi:10.1016/j.prmcm.2024.100507
Phu, H. T., Thuan, D. T., Nguyen, T. H., Posadino, A. M., Eid, A. H., and Pintus, G. (2020). Herbal medicine for slowing aging and aging-associated conditions: efficacy, mechanisms and safety. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 18, 369–393. doi:10.2174/1570161117666190715121939
Ping, P., Yang, T., Ning, C., Zhao, Q., Zhao, Y., Yang, T., et al. (2024). Chlorogenic acid attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via up-regulating Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor1 to inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress. ESC Heart Fail. 11, 1580–1593. doi:10.1002/ehf2.14707
Proshkina, E., Solovev, I., Shaposhnikov, M., and Moskalev, A. (2020). Key molecular mechanisms of aging, biomarkers, and potential interventions. Mol. Biol. 54, 883–921. doi:10.31857/S0026898420060099
Qian, L., Zhu, Y., Deng, C., Liang, Z., Chen, J., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 (PGC-1) family in physiological and pathophysiological process and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9, 50. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01756-w
Qu, Y., Safonova, O., and De Luca, V. (2019). Completion of the canonical pathway for assembly of anticancer drugs vincristine/vinblastine in Catharanthus roseus. Plant J. 97, 257–266. doi:10.1111/tpj.14111
Quan, J., Jia, Z., Liu, L., and Tian, J. (2024). The effect of long-term administration of green tea catechins on aging-related cardiac diastolic dysfunction and decline of troponin I. Genes. and Dis. 12, 101284. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101284
Rai, P., and Fessler, M. B. (2024). Mechanisms and effects of activation of innate immunity by mitochondrial nucleic acids. Int. Immunol., dxae052. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxae052
Rauf, A., Imran, M., Khan, I. A., Ur-Rehman, M., Gilani, S. A., Mehmood, Z., et al. (2018). Anticancer potential of quercetin: a comprehensive review. Phytotherapy Res. 32, 2109–2130. doi:10.1002/ptr.6155
Ribeiro, A. S. F., Zerolo, B. E., López-Espuela, F., Sánchez, R., and Fernandes, V. S. (2023). Cardiac system during the aging process. Aging Dis. 14, 1105–1122. doi:10.14336/AD.2023.0115
Riviati, N., Legiran, , Indrajaya, T., Saleh, I., Ali, Z., Irfannuddin, P., et al. (2024). Serum albumin as prognostic marker for older adults in hospital and community settings. Gerontology Geriatric Med. 10, 23337214241249914. doi:10.1177/23337214241249914
Robich, M. P., Osipov, R. M., Nezafat, R., Feng, J., Clements, R. T., Bianchi, C., et al. (2010). Resveratrol improves myocardial perfusion in a swine model of hypercholesterolemia and chronic myocardial ischemia. Circulation 122, S142–S149. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.920132
Rodrigues, K. E., Pontes, M. H. B., Cantão, M. B. S., and Prado, A. F. (2024). The role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in cardiac remodeling and dysfunction and as a possible blood biomarker in heart failure. Pharmacol. Res. 206, 107285. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107285
Rose, R. A., Sellan, M., Simpson, J. A., Izaddoustdar, F., Cifelli, C., Panama, B. K., et al. (2011). Iron overload decreases CaV1. 3-dependent L-type Ca2+ currents leading to bradycardia, altered electrical conduction, and atrial fibrillation. Circulation Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 4, 733–742. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.110.960401
Rosenblum, S. L. (2023). Inflammation, dysregulated iron metabolism, and cardiovascular disease. Front. Aging 4, 1124178. doi:10.3389/fragi.2023.1124178
Rudenko, N. N., Vetoshkina, D. V., Marenkova, T. V., and Borisova-Mubarakshina, M. M. (2023). Antioxidants of Non-Enzymatic Nature: their function in higher plant cells and the ways of boosting their Biosynthesis. Antioxidants 12, 2014. doi:10.3390/antiox12112014
Rysz, J., Franczyk, B., Rysz-Górzyńska, M., and Gluba-Brzózka, A. (2021). Ageing, age-related cardiovascular risk and the beneficial role of natural components intake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 183. doi:10.3390/ijms23010183
Sadiq, I. Z. (2023). Free radicals and oxidative stress: signaling mechanisms, redox basis for human diseases, and cell cycle regulation. Curr. Mol. Med. 23, 13–35. doi:10.2174/1566524022666211222161637
Saenjum, C., Pattananandecha, T., and Apichai, S. (2023). “Plant bioactives, aging research, and drug industry: procedures and challenges,” in Plant bioactives as natural panacea against age-induced diseases (Elsevier), 447–468.
Saheera, S., and Krishnamurthy, P. (2020). Cardiovascular changes associated with hypertensive heart disease and aging. Cell. Transplant. 29, 0963689720920830. doi:10.1177/0963689720920830
Sahu, Y., Jamadade, P., Maharana, K. C., and Singh, S. (2024). Role of mitochondrial homeostasis in D-galactose-induced cardiovascular ageing from bench to bedside. Mitochondrion 78, 101923. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2024.101923
Santos, D. F., Simão, S., Nóbrega, C., Bragança, J., Castelo-Branco, P., Araújo, I. M., et al. (2024). Oxidative stress and aging: synergies for age related diseases. FEBS Lett. 598, 2074–2091. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.14995
Santos, M. A., Franco, F. N., Caldeira, C. A., De Araújo, G. R., Vieira, A., and Chaves, M. M. (2023). Resveratrol has its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory protective mechanisms decreased in aging. Archives Gerontology Geriatrics 107, 104895. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2022.104895
Schmitt, C. A., Heiss, E. H., and Dirsch, V. M. (2010). Effect of resveratrol on endothelial cell function: molecular mechanisms. Biofactors 36, 342–349. doi:10.1002/biof.109
Schneider, A. M., Özsoy, M., Zimmermann, F. A., Feichtinger, R. G., Mayr, J. A., Kofler, B., et al. (2020). Age-related deterioration of mitochondrial function in the intestine. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 4898217. doi:10.1155/2020/4898217
Sciarretta, S., Forte, M., Castoldi, F., Frati, G., Versaci, F., Sadoshima, J., et al. (2021). Caloric restriction mimetics for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 117, 1434–1449. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvaa297
Scioli, M. G., Storti, G., D’amico, F., Rodríguez Guzmán, R., Centofanti, F., Doldo, E., et al. (2020). Oxidative stress and new pathogenetic mechanisms in endothelial dysfunction: potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Clin. Med. 9, 1995. doi:10.3390/jcm9061995
Senoner, T., and Dichtl, W. (2019). Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases: still a therapeutic target? Nutrients 11, 2090. doi:10.3390/nu11092090
Shah, A. K., Bhullar, S. K., Elimban, V., and Dhalla, N. S. (2021). Oxidative stress as a mechanism for functional alterations in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Antioxidants 10, 931. doi:10.3390/antiox10060931
Shahrajabian, M. H., and Sun, W. (2023). Medicinal plants, economical and natural agents with antioxidant activity. Curr. Nutr. and Food Sci. 19, 763–784. doi:10.2174/1573401318666221003110058
Shan, L., Wang, F., Zhai, D., Meng, X., Liu, J., and Lv, X. (2023). Matrix metalloproteinases induce extracellular matrix degradation through various pathways to alleviate hepatic fibrosis. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 161, 114472. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114472
Shastri, D., Raj, V., and Lee, S. (2024). Revolutionizing Alzheimer's treatment: harnessing human serum albumin for targeted drug delivery and therapy advancements. Ageing Res. Rev. 99, 102379. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2024.102379
Shemiakova, T., Ivanova, E., Grechko, A. V., Gerasimova, E. V., Sobenin, I. A., and Orekhov, A. N. (2020). Mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage in the context of pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Biomedicines 8, 166. doi:10.3390/biomedicines8060166
Shen, C.-Y., Lu, C.-H., Cheng, C.-F., Li, K.-J., Kuo, Y.-M., Wu, C.-H., et al. (2024). Advanced glycation end-products acting as immunomodulators for chronic inflammation, inflammaging and carcinogenesis in patients with diabetes and immune-related diseases. Biomedicines 12, 1699. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12081699
Sin, T. K., Tam, B. T., Yu, A. P., Yip, S. P., Yung, B. Y., Chan, L. W., et al. (2016). Acute treatment of resveratrol alleviates doxorubicin-induced myotoxicity in aged skeletal muscle through SIRT1-dependent mechanisms. Journals Gerontology Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 71, 730–739. doi:10.1093/gerona/glv175
Sinclair, A., Saeedi, P., Kaundal, A., Karuranga, S., Malanda, B., and Williams, R. (2020). Diabetes and global ageing among 65-99-year-old adults: findings from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 162, 108078. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108078
Singh, B. N., Shankar, S., and Srivastava, R. K. (2011). Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 82, 1807–1821. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.07.093
Skoryk, O., and Horila, M. (2023). Oxidative stress and disruption of the antioxidant defense system as triggers of diseases. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 14, 665–672. doi:10.15421/022395
Skulachev, V. P., Vyssokikh, M. Y., Chernyak, B. V., Mulkidjanian, A. Y., Skulachev, M. V., Shilovsky, G. A., et al. (2023). Six functions of respiration: isn’t it time to take control over ROS production in mitochondria, and aging along with it? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 12540. doi:10.3390/ijms241612540
Slivnick, J., and Lampert, B. C. (2019). Hypertension and heart failure. Heart Fail. Clin. 15, 531–541. doi:10.1016/j.hfc.2019.06.007
Sobhon, P., Savedvanich, G., and Weerakiet, S. (2023). Oxidative stress and inflammation: the root causes of aging. Explor. Med. 4, 127–156. doi:10.37349/emed.2023.00129
Sreedevi, K., and Mavilavalappil, S. P. (2024). “Cardiovascular therapeutics from natural sources,” in Drugs from nature: targets, assay systems and leads (Springer), 475–504.
Srivastava, A., Kumari, A., Jagdale, P., Ayanur, A., Pant, A. B., and Khanna, V. K. (2023). Potential of quercetin to protect cadmium induced cognitive deficits in rats by modulating NMDA-R mediated downstream signaling and PI3K/AKT—Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways in hippocampus. NeuroMolecular Med. 25, 426–440. doi:10.1007/s12017-023-08747-0
Srivastava, G., and Mehta, J. L. (2009). Currying the heart: curcumin and cardioprotection. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 14, 22–27. doi:10.1177/1074248408329608
Sulaiman, M., Matta, M. J., Sunderesan, N., Gupta, M. P., Periasamy, M., and Gupta, M. (2010). Resveratrol, an activator of SIRT1, upregulates sarcoplasmic calcium ATPase and improves cardiac function in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiology 298, H833–H843. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00418.2009
Sun, G., Xu, Y., Liang, X., Wang, L., and Liu, Y. (2025). Curcumin inhibits the progression of hyperlipidemia via OGT mediated O-GlcNAcylation modulation of APOC3. Int. Immunopharmacol. 144, 113647. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113647
Sun, S., Ruan, Y., Yan, M., Xu, K., Yang, Y., Shen, T., et al. (2021). Ferulic acid alleviates oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte injury by the regulation of miR-499-5p/p21 signal cascade. Evidence Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2021, 1921457. doi:10.1155/2021/1921457
Sun, X., Li, Z., Wang, L., Wang, Y., and Lu, C. (2023). Berberine ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice by decreasing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress. Cardiovasc. Innovations Appl. 8, 20230064. doi:10.15212/cvia.2023.0064
Sung, M. M., Das, S. K., Levasseur, J., Byrne, N. J., Fung, D., Kim, T. T., et al. (2015). Resveratrol treatment of mice with pressure-overload–induced heart failure improves diastolic function and cardiac energy metabolism. Circ. Heart Fail. 8, 128–137. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.001677
Surai, P. F. (2016). Antioxidant systems in poultry biology: superoxide dismutase. J. Animal Res. Nutr. 1, 8.
Talukder, J. (2021). “Role of transferrin: an iron-binding protein in health and diseases,” in Nutraceuticals (Elsevier), 1011–1025.
Testai, L., Piragine, E., Piano, I., Flori, L., Da Pozzo, E., Miragliotta, V., et al. (2020). The citrus flavonoid Naringenin protects the myocardium from ageing-dependent dysfunction: potential role of SIRT1. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 4650207. doi:10.1155/2020/4650207
Tian, Y., Tian, Y., Yuan, Z., Zeng, Y., Wang, S., Fan, X., et al. (2022). Iron metabolism in aging and age-related diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 3612. doi:10.3390/ijms23073612
Tobin, S. W., Alibhai, F. J., Weisel, R. D., and Li, R.-K. (2020). Considering cause and effect of immune cell aging on cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Cells 9, 1894. doi:10.3390/cells9081894
Totoń-Żurańska, J., Mikolajczyk, T. P., Saju, B., and Guzik, T. J. (2024). Vascular remodelling in cardiovascular diseases: hypertension, oxidation, and inflammation. Clin. Sci. 138, 817–850. doi:10.1042/CS20220797
Tseng, A. H., Shieh, S.-S., and Wang, D. L. (2013). SIRT3 deacetylates FOXO3 to protect mitochondria against oxidative damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 63, 222–234. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.002
Ulasova, E., Perez, J., Hill, B. G., Bradley, W. E., Garber, D. W., Landar, A., et al. (2013). Quercetin prevents left ventricular hypertrophy in the Apo E knockout mouse. Redox Biol. 1, 381–386. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2013.07.001
Umber, J., Qasim, M., Ashraf, S., Ashfaq, U. A., Iram, A., Bhatti, R., et al. (2023). Antioxidants mitigate oxidative stress: a general overview. Role Nat. Antioxidants Brain Disord., 149–169. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-41188-5_7
Ungurianu, A., Zanfirescu, A., and Margină, D. (2023). Sirtuins, resveratrol and the intertwining cellular pathways connecting them. Ageing Res. Rev. 88, 101936. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2023.101936
Van Beek, T. A., and Montoro, P. (2009). Chemical analysis and quality control of Ginkgo biloba leaves, extracts, and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. A 1216, 2002–2032. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2009.01.013
Vassiliev, V., Harris, Z. L., and Zatta, P. (2005). Ceruloplasmin in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Rev. 49, 633–640. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2005.03.003
Vogt, A.-C. S., Arsiwala, T., Mohsen, M., Vogel, M., Manolova, V., and Bachmann, M. F. (2021). On iron metabolism and its regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4591. doi:10.3390/ijms22094591
Wallace, T. C. (2011). Anthocyanins in cardiovascular disease. Adv. Nutr. 2, 1–7. doi:10.3945/an.110.000042
Wang, L., Tang, X.-Q., Shi, Y., Li, H.-M., Meng, Z.-Y., Chen, H., et al. (2023a). Tetrahydroberberrubine retards heart aging in mice by promoting PHB2-mediated mitophagy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 44, 332–344. doi:10.1038/s41401-022-00956-w
Wang, Y., Branicky, R., Noë, A., and Hekimi, S. (2018). Superoxide dismutases: dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell. Biol. 217, 1915–1928. doi:10.1083/jcb.201708007
Wang, Y., Cai, Z., Zhan, G., Li, X., Li, S., Wang, X., et al. (2023b). Caffeic acid phenethyl ester suppresses oxidative stress and regulates M1/M2 microglia polarization via Sirt6/Nrf2 pathway to mitigate cognitive impairment in aged mice following anesthesia and surgery. Antioxidants 12, 714. doi:10.3390/antiox12030714
Wang, Z., Chen, W., Li, Y., Zhang, S., Lou, H., Lu, X., et al. (2021). Reduning injection and its effective constituent luteoloside protect against sepsis partly via inhibition of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 270, 113783. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.113783
Wilasrusmee, K. T., Sitticharoon, C., Keadkraichaiwat, I., Maikaew, P., Pongwattanapakin, K., Chatree, S., et al. (2024). Epigallocatechin gallate enhances sympathetic heart rate variability and decreases blood pressure in obese subjects: a randomized control trial. Sci. Rep. 14, 21628. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-72269-3
Wu, X., Zhou, X., Lai, S., Liu, J., and Qi, J. (2022). Curcumin activates Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to relieve diabetic cardiomyopathy injury by reducing ROS in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J. 36, e22505. doi:10.1096/fj.202200543RRR
Xia, K., Zhang, Y., and Sun, D. (2020). miR-217 and miR-543 downregulation mitigates inflammatory response and myocardial injury in children with viral myocarditis by regulating the SIRT1/AMPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 45, 634–646. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4442
Xie, W.-J., Liu, M., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y.-G., Jian, Z.-H., and Xiong, X.-X. (2024). Astaxanthin suppresses LPS-induced myocardial apoptosis by regulating PTP1B/JNK pathway in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 127, 111395. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111395
Xu, G., Ahn, J., Chang, S., Eguchi, M., Ogier, A., Han, S., et al. (2012). Lipocalin-2 induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis by increasing intracellular iron accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 4808–4817. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.275719
Xu, H., Cheng, J., Wang, X., Liu, H., Wang, S., Wu, J., et al. (2019). Resveratrol pretreatment alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting STIM1-mediated intracellular calcium accumulation. J. Physiology Biochem. 75, 607–618. doi:10.1007/s13105-019-00704-5
Xu, L., Yang, Q., and Zhou, J. (2024). Mechanisms of abnormal lipid metabolism in the pathogenesis of disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 8465. doi:10.3390/ijms25158465
Xu, W., Luo, Y., Yin, J., Huang, M., and Luo, F. (2023). Targeting AMPK signaling by polyphenols: a novel strategy for tackling aging. Food and Funct. 14, 56–73. doi:10.1039/d2fo02688k
Xu, X., Wang, B., Ren, C., Hu, J., Greenberg, D. A., Chen, T., et al. (2017). Age-related impairment of vascular structure and functions. Aging Dis. 8, 590–610. doi:10.14336/AD.2017.0430
Xue, Y., Zhang, M., Liu, M., Liu, Y., Li, L., Han, X., et al. (2021). 8-Gingerol ameliorates myocardial fibrosis by attenuating reactive oxygen species, apoptosis, and autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 711701. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.711701
Yadav, R., Pandita, A., Pandita, D., and Murthy, K. S. (2023). “Taxus brevifolia (Nutt.) Pilger. Potent anticancer medicinal plants: secondary metabolite profiling,” in Active ingredients, and pharmacological outcomes, 10.
Yang, L., Shi, J., Wang, X., and Zhang, R. (2022). Curcumin alleviates D-galactose-induced cardiomyocyte senescence by promoting autophagy via the SIRT1/AMPK/mTOR pathway. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2022, 2990843. doi:10.1155/2022/2990843
Yang, X., Liu, X., Nie, Y., Zhan, F., and Zhu, B. (2023a). Oxidative stress and ROS-mediated cellular events in RSV infection: potential protective roles of antioxidants. Virology J. 20, 224. doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02194-w
Yang, X., Zhao, X., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, L., An, Z., et al. (2023b). Ginkgo biloba extract protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy by restoring autophagy via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of the rapamycin pathway modulation. Phytotherapy Res. 37, 1377–1390. doi:10.1002/ptr.7746
Yin, Y., Yan, C., Zhang, R., Wang, Y., Song, Y., Hu, S., et al. (2024). Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761) inhibits autophagy and apoptosis in a rat model of vascular dementia via the AMPK-mTOR signalling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 116, 106168. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2024.106168
Yuvaraj, S., Ramprasath, T., Saravanan, B., Vasudevan, V., Sasikumar, S., and Selvam, G. S. (2021). Chrysin attenuates high-fat-diet-induced myocardial oxidative stress via upregulating eNOS and Nrf2 target genes in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 476, 2719–2727. doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04105-5
Zhang, J., Wang, Q.-Z., Zhao, S.-H., Ji, X., Qiu, J., Wang, J., et al. (2017). Astaxanthin attenuated pressure overload-induced cardiac dysfunction and myocardial fibrosis: partially by activating SIRT1. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subj. 1861, 1715–1728. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.03.007
Zhang, L.-X., Li, C.-X., Kakar, M. U., Khan, M. S., Wu, P.-F., Amir, R. M., et al. (2021). Resveratrol (RV): a pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 143, 112164. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112164
Zhang, Q., Pan, J., Liu, H., and Jiao, Z. (2023a). Characterization of the synergistic antioxidant activity of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and kaempferol. Molecules 28, 5265. doi:10.3390/molecules28135265
Zhang, W., Qian, S., Tang, B., Kang, P., Zhang, H., and Shi, C. (2023b). Resveratrol inhibits ferroptosis and decelerates heart failure progression via Sirt1/p53 pathway activation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 27, 3075–3089. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17874
Zhang, Z., Li, X., Sang, S., Mcclements, D. J., Chen, L., Long, J., et al. (2022). Polyphenols as plant-based nutraceuticals: health effects, encapsulation, nano-delivery, and application. Foods 11, 2189. doi:10.3390/foods11152189
Zhao, G., Zhang, X., Wang, H., and Chen, Z. (2020). Beta carotene protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from advanced glycation end product-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, and autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 8, 647. doi:10.21037/atm-20-3768
Zhao, X., Li, R., Jin, H., Jin, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, W., et al. (2018). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate confers protection against corticosterone-induced neuron injuries via restoring extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathways. Plos One 13, e0192083. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0192083
Zheng, J., Lee, H. C. M., Bin Sattar, M. M., Huang, Y., and Bian, J.-S. (2011). Cardioprotective effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 652, 82–88. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.10.082
Zheng, X., Gao, Q., Liang, S., Zhu, G., Wang, D., and Feng, Y. (2021). Cardioprotective properties of ginkgo biloba extract 80 via the activation of AKT/GSK3β/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8, 771208. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.771208
Zhong, Y., Chiou, Y.-S., Pan, M.-H., and Shahidi, F. (2012). Anti-inflammatory activity of lipophilic epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) derivatives in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages. Food Chem. 134, 742–748. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.172
Zhou, M., Wang, H., Zeng, X., Yin, P., Zhu, J., Chen, W., et al. (2019). Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 394, 1145–1158. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1
Zhou, M., Wang, H., Zhu, J., Chen, W., Wang, L., Liu, S., et al. (2016). Cause-specific mortality for 240 causes in China during 1990–2013: a systematic subnational analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 387, 251–272. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00551-6
Zhu, X., Ma, E., Ge, Y., Yuan, M., Guo, X., Peng, J., et al. (2024). Resveratrol protects against myocardial ischemic injury in obese mice via activating SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway and restoring redox homeostasis. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 174, 116476. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116476
Keywords: heart aging, cardiac alterations, antioxidants, mechanism, reactive oxygen species
Citation: Khoso MA, Liu H, Zhao T, Zhao W, Huang Q, Sun Z, Dinislam K, Chen C, Kong L, Zhang Y and Liu X (2025) Impact of plant-derived antioxidants on heart aging: a mechanistic outlook. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1524584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1524584
Received: 07 November 2024; Accepted: 07 March 2025;
Published: 21 March 2025.
Edited by:
Yan Sanders, Eastern Virginia Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Tao Ban, Harbin Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Khoso, Liu, Zhao, Zhao, Huang, Sun, Dinislam, Chen, Kong, Zhang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong Zhang, aG11emhhbmd5b25nQGhvdG1haWwuY29t; Xin Liu, ZnJleWFsaXV4aW5AMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.