- 1Country School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 2Sichuan Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences, Institute of Pharmacology & Toxicology of Chinese Materia Medica, Translational Chinese Medicine Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Engineering Technology Research Center of Genuine Regional Drug, Engineering Research Center for Formation Principle and Quality Evaluation of Genuine Medicinal Materials in Sichuan Province, Chengdu, China
- 3Sichuan Institute for Translational Chinese Medicine, Translational Chinese Medicine Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu, China
- 4Changsha Medical University, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of the Research and Development of Novel Pharmaceutical Preparations, The “Double-First Class” Application Characteristic Discipline of Hunan Province (Pharmaceutical Science), Changsha, China
- 5Sichuan Acupuncture and Moxibustion School, Chengdu, China
Uncontrolled hyperuricemia contributes to chronic kidney disease, characterized by renal inflammatory cell infiltration and tubulointerstitial fibrosis, eventually leading to renal failure. In addition to liver and kidney, the intestine tract plays a vital role in the development and progression of hyperuricemia and hyperuricemic nephropathy (HN) through various mechanisms. The conventional therapeutic strategy for HN is uric acid-lowering therapy (ULT) and renal protection; however, unsatisfactory results are often obtained in clinical practice. Growing evidence has demonstrated that traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) achieve an anti-HN effect by modulating multiple targets and approaches with fewer side effects. Therefore, this paper reviews the pathogenesis of HN, including the role of soluble and insoluble urates in kidney and intestine, and the role of intestinal tract in the progression of HN. Meanwhile, the recent advancements in TCMs for the treatment of HN are summarized and analyzed, with a focus on their modulation of intestinal flora and metabolites, urate-related transporters, immuno-inflammation and barrier function in the intestines. Notably, for the first time, we propose the perspective that TCMs treat HN through a dual-regulatory effect on the intestines and kidneys. Additionally, the problems existing in current research and the feasible research strategies combined with emerging technologies such as fermentation and nanotechnology are discussed, thus providing novel ideas for HN management.
1 Introduction
Hyperuricemia (HUA) is one of the most common metabolic diseases, resulting from the metabolic disorder of purine and uric acid. Currently, the prevalence of hyperuricemia is steadily rising, ranging from 2.6%–36% across the globe (Jiang J. et al., 2023), and is especially higher in the countries with high-purine and high-fructose consumption. It was estimated that the prevalence of hyperuricemia among Chinese population was 14.0% in 2018–2019, with the younger population suffering more, as deduced from two nationally representative cross-sectional investigations (Zhang M. et al., 2022). Chronic hyperuricemia might contribute to renal dysfunction, which can further develop to hyperuricemia nephropathy (or gouty nephropathy) and increases the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). It has been proposed that hyperuricemia nephropathy is a secondary inflammatory nephropathy induced by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in the distal collecting duct and the medullary interstitium (Kang, 2014). Autopsy examinations have confirmed that 75%–99% of gouty subjects exhibit prominent alterations in renal histopathology, including MSU deposits, arteriolosclerosis, glomerulosclerosis, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis (Linnane et al., 1981). Moreover, a large amount of literature has documented that asymptomatic hyperuricemia also increases the progression of CKD, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome (Aktas et al., 2022; Gaubert et al., 2020). Previous studies have demonstrated that chronic hyperuricemia induces glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis via sustained inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress amplification, and dysregulated renin-angiotensin system (RAS) activation, ultimately culminating in progressive renal dysfunction (Du et al., 2024). The deposition of excess urate in the renal tubules or extrarenal tissues triggers multiple intracellular signaling pathways, such as MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and NF-κB, which promote oxidative stress and inflammatory responses (Li K. et al., 2023). Additionally, MSU act as injury-associated molecular patterns, initiating cellular pyroptosis via the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. This results in the massive release of active IL-1β, which further amplifies the renal inflammatory cascade and accelerates the progression of renal fibrosis (Hu et al., 2022).
Although it is debatable whether elevated uric acid or MSU deposits are the main cause of hyperuricemia nephropathy, uric acid-lowering therapy is recommended to slow the progression of CKD and other complications (Fang et al., 2023). Given that hyperuricemia is a prerequisite for the occurrence of uric acid nephropathy, understanding why hyperuricemia occurs is essential for recognizing the pathogenesis and developing treatments for hyperuricemia nephropathy. Uric acid, the final product of purine nucleotide metabolism, can contribute to hyperuricemia when there is excessive production or abnormal excretion. A high-purine diet or other dietary factors [such as alcohol (Choi et al., 2004)] and high-fructose beverage consumption (Huang Y. et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2020) increase serum uric acid levels and the incidence of gout flares. However, the uric acid from dietary sources only accounts for 20% of the total uric acid pool in the human body. Approximately 80% of serum uric acid is derived from the metabolism and transport of endogenous uric acid. The liver, as the primary organ responsible for purine metabolism, orchestrates the catabolism of nucleic acids and the de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides from amino acids and other precursors, accounting for approximately 70% of endogenous uric acid production (Sharaf El Din et al., 2017). Notably, abnormalities in glycolipid metabolism significantly activate xanthine oxidase, which accelerates uric acid biosynthesis and promotes the development of hyperuricaemia (Johnson et al., 2011). It has been well-documented that about two-thirds of uric acid is excreted by the kidneys, while the remaining third is excreted by the intestines. It is worth noting that the intestinal tract plays a vital role in purine and uric acid metabolism, influenced by the urate transporters, diversity of microbiome and its sensitive mechanisms for dealing with harmful insults. Recent evidence suggested that the imbalance of the intestinal flora accelerated the progression of kidney diseases, including hyperuricemia nephropathy, diabetic nephropathy and septic nephropathy. Moreover, supplement of prebiotics and probiotics have been confirmed to ameliorate the renal dysfunction, further delaying the occurrence of CKD (Cao J. et al., 2022; García-Arroyo et al., 2018). However, the specific interplay between renal and intestinal factors and the underlying mechanisms of hyperuricemia nephropathy remain poorly understood.
Whether hypouricemic medication targeting the proteins that govern the metabolism of purines and uric acid have renoprotective potential for individuals suffering from hyperuricemia and gout depends. Due to the potential for renal impairment, the clinical application of allopurinol is cautious (Badve et al., 2020), while probenecid is contraindicated when CrCL is <60 mL/min (Kang, 2014). Unlike allopurinol, dosing adjustments are not needed for patients with renal impairment when using febuxostat, a nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, as the hypouricemic agent (Becker et al., 2005). Compared to febuxostat, benzbromarone (25 mg daily) has been confirmed to be more potent in hyperuricemia patients with eGFR ≥ 70 mL/min/1.73 m2 (Liu et al., 2022). Additionally, one of the common complications of probenecid and benzbromarone is the deposition of urates or uric acid stones in the kidney and urinary system, while increasing urine volume, alkalized urine and reducing the dosage are beneficial for managing this severe complication (FitzGerald et al., 2020; Hui et al., 2017; Yu K. H. et al., 2018). Recently, novel urate transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitors with higher selectivity, including SHR4640 (Lin et al., 2021), verinurad (Tan et al., 2017), dotinurad (Taniguchi et al., 2019), which have garnered significant attention in the development of anti- hyperuricemia therapy. However, safety concerns have hindered the further development of URAT1 inhibitors, as symbolized by the forced withdrawal of lesinurad.
A large number of literatures have documented that traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and its active ingredients are potential and potent candidates for the treatment of hyperuricemic nephropathy. Previous studies have found that TCMs effectively attenuate the progression of HN mainly by inhibiting hepatic XOD activity, modulating urate transporters, suppressing inflammatory responses, and ameliorating oxidative stress and renal fibrosis (Yang et al., 2022). With long-term clinical application in humans, the hypouricemia and renoprotective potencies of TCM and TCM formulas have been verified in preclinical and clinical trials, such as Si Miao Pills (Zhang Y. et al., 2023), Cichorium intybus L. (Jin et al., 2018), and fisetin (Ren et al., 2021), etc. Considering the potential role of the interaction between the intestine and kidneys in the pathogenesis and treatment of HN, we propose the hypothesis that soluble uric acid and urate crystals could disrupt the physiological function and structure of renal and intestinal systems by regulating multiple intracellular signals, thereby promoting renal fibrosis and furthering the progression of HN. Meanwhile, this paper summarizes and analyzes TCM formulas and single herbs with dual-regulatory effects of the intestine and kidneys in HN treatment in, providing a new perspective and research direction for TCMs.
2 The pathogenesis of HN
Growing evidence suggests that both soluble uric acid and MSU crystals can insult renal function and structure through various mechanisms (Mei et al., 2022; Ponticelli et al., 2020; Weaver, 2019). Additionally, the intestine plays a role in the pathogenesis of HN by regulating the metabolism and transport processes of soluble uric acid and MSU crystals (Grelska et al., 2023; Tseng et al., 2020).
2.1 The metabolism and transport of purine and uric acid
Uric acid (UA) is the end product of purine metabolism, catalyzed by xanthine oxidase (XOD), which is mainly expressed in the liver. In addition to XOD, blood uric acid levels are dynamically regulated by various transporters in the kidney and gut, as well as by some oxidants or nitric oxide (Gersch et al., 2008; Imaram et al., 2010). In human beings, a physiological level of uric acid (3–5 mg/dL) exists in the bloodstream in the form of soluble urates, while high concentrations of urates that exceed its solubility in the blood (serum uric acid >6.8 mg/dL) contribute to MSU crystalline deposits. Approximately two-thirds of uric acid excretion occurs through glomerular filtration and tubular reabsorption, which relies on urate transporter proteins in the kidneys, including URAT1 (encoded by the SLC22A12 gene), glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9, encoded by the SLC2A9 gene), and organic anion transporter 4 (OAT4, encoded by the SLC22A11 gene). Generally, serum uric acid (sUA) levels are modulated dynamically by two categories of transporters: urate reabsorption-promoting transporters (URAT1, GLUT9, sodium-dependent phosphate transporter protein 1 (NPT1), and NPT4 (Maiuolo et al., 2016), OAT4, OAT10, etc.) and urate excretion-promoting transporters (ABCG2, OAT1, OAT3, etc.). Benzbromarone and probenecid achieve uric acid-lowering function by inhibiting URAT1 and GLUT9, thereby increasing UA excretion (Figure 1). However, some clinical trials reported that 10% hyperuricemic patients treated with benzbromarone could not achieve satisfactory clinical outcomes with a standard therapeutic dose and duration, which might be attributed to its inhibition of OAT1 and ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2). URAT1 facilitates the reabsorption of uric acid from the renal tubules to the tubular epithelial cells and then to the renal interstitium, thus elevating serum uric acid. Conversely, as urate reabsorption-promoting transporters, inhibition of OAT1 and ABCG2 might partially counteract urate-lowering effect of benzbromarone. Therefore, drug discovery targeting urate transporters with high selectivity has attracted significant attention in the pharmaceutical industry, and has been extensively reviewed in elsewhere (Hou et al., 2023; Shi et al., 2022).
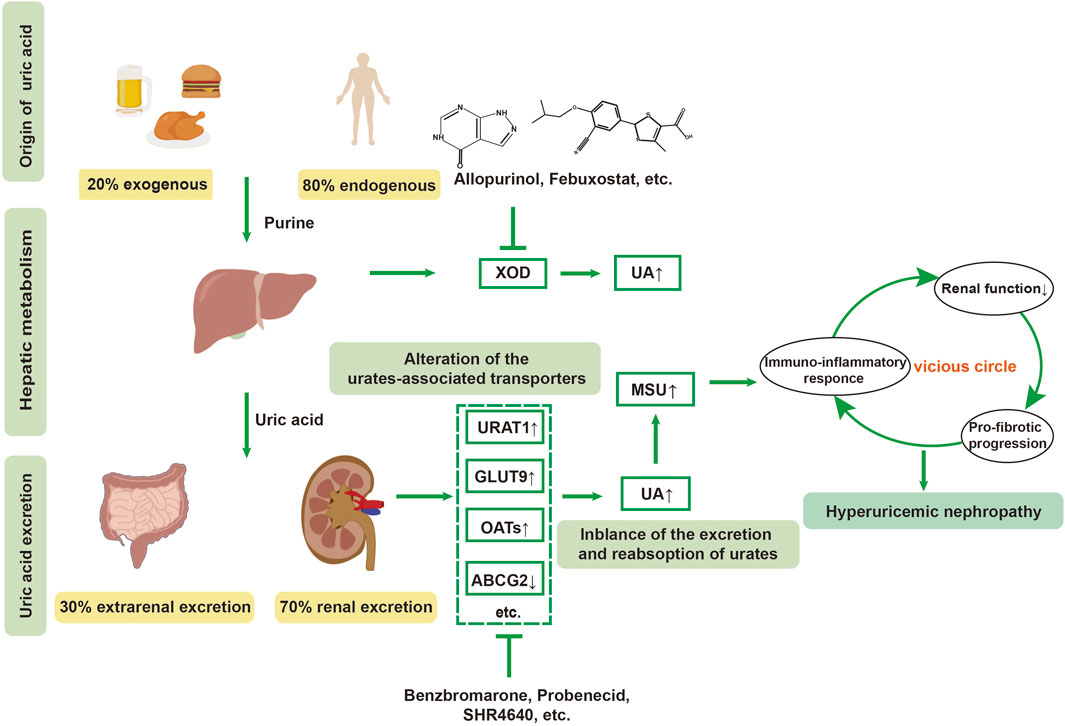
Figure 1. Pathogenesis of hyperuricemic nephropathy (HN). HN is a renal dysfunction secondary to uncontrolled long-term hyperuricemia. Dysfunction of urate-related transporters, such as urate transporter 1(URAT1), glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9), ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2), and organic anion transporters (OATs), lead to the abnormal metabolism of urates in the kidney. The chronic elevation of uric acid (UA) and monosodium urate (MSU) crystals exacerbate the vicious cycle within the kidney through promoting oxidative stress, immune-inflammatory response, renal dysfunction and pro-fibrotic progression, eventually leading to HN.
Uric acid possesses both antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties (So and Thorens, 2010). It exists in the body in soluble form, as well as crystalline form. An imbalance in uric acid metabolism can result in severe kidney diseases. Research has shown that uric acid metabolism is closely linked to the development of renal disease. Notably, the role of the intestinal tract in the metabolism of purines and uric acid has been confirmed, as about one-third of uric acid is discharged by gut (Eckenstaler and Benndorf, 2021). This is achieved through three main approaches: one involves a serial of urate transporters in the gut, the second one is the direct involvement of the intestinal flora in the metabolic breakdown of purines and uric acid (Table 1), and the third involves metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (e.g., acetate, butyrate) produced by intestinal bacteria provide energy to intestinal epithelial cells, supporting the excretion of uric acid. Currently, it is well-acknowledged that the uric acid transporters in the intestine include ABCG2, MRP2, MRP4, GLUT9, MCT9, NPT4, its homologs, OAT10, and YgfU (Xu et al., 2016). As a potent anti-hyperuricemic agent, most attention has been concentrated on the development of URAT1 inhibitors, such as dotinurad, epaminurad (URC-102) and XNW3009. In addition, ABP-671 (developed by New Elemental Pharmaceuticals) has emerged as a promising therapeutic candidate due to its concurrent inhibition of URAT1 and GLUT9, demonstrating synergistic dual-target inhibition of urate reabsorption. clinical trials have demonstrated a 30% improvement in urate-lowering efficacy compared to single-target agents, particularly in treatment-refractory populations (Dong et al., 2019). Recently, Granados et al. discovered a transport route from gut microbes to the liver, and then to kidney-mediated OAT1 transport for the gut-derived metabolites (e.g., indolyl sulfate, p-cresol sulfate, deoxycholate, etc.), indicating a central role for kidney urate transporters in modulating gut flora-dependent metabolism (Granados et al., 2023). Mechanistically, OAT1 plays a role in transporting uremic solutes or uremic toxins in the circulation by directly interacting with multiple gut-derived metabolites (Granados et al., 2023). Nevertheless, the specific role of urate transporters in modulating the intestinal microbiome and its metabolites needs further investigation to discover novel therapeutic strategies for delaying the progression of HN.
Escherichia coli and Aspergillus spp., which secrete XOD have been verified to catalyze purines into uric acid in the intestinal tract, thus reducing intestinal absorption of dietary purines (Crane et al., 2013). Yamada et al. (2016) discovered that Lactobacillus spp. regulate serum uric acid levels by uptaking and utilizing purines. The PICRUST analysis indicated that hyperuricaemia was associated with prominent alterations in gut microbiota involved in nucleotide and lipid metabolism. Allopurinol and benzbromarone exhibited uric acid-lowering potency by modulating microbial genera in hyperuricaemic rats, characterized by an increase of Bifidobacterium and a decrease of Adlercreutzia Anaerostipes (Yu Y. et al., 2018). Surprisingly, these two microbial genera have been confirmed to be closely related with the reduction of UA. Moreover, Spearman analysis showed a strong correlation between the increased in the genus Adlercreutzia and the trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) levels in CKD patients with low glomerular filtration rates (GFRs, GFR < 7 mL/min/1.73 m2) (Xu et al., 2017), which could further exaggerate hyperuricaemia. Therefore, it can be speculated that intestinal flora-derived metabolites with nephrotoxic properties, such as TMAO, raise blood UA by injuring renal function (Yu Y. et al., 2018). However, beneficial intestinal flora indirectly moderate serum UA levels by producing small molecule metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), including butyrate, and propionate (Chu et al., 2021), etc. SCFAs have been proved to play a direct and indirect role in regulating metabolism, inflammation, immune response, and maintenance of mucosal barrier function (Mann et al., 2024). Growing evidence has demonstrated that gut-derived SCFAs, mainly produced by anaerobic bacilli, bifidobacteria, fungi, streptococci, and Lactobacillus, regulate host health through energy regulation, intestinal mucosal barrier, and immune regulation, which are involved in water-electrolyte homeostasis, oxidative stress and immuno-inflammatory responses in the gut. Previous studies have found that SCFAs could significantly reduce the serum uric acid levels in HUA mice induced by potassium oxonate and hypoxanthine. Moreover, SCFAs supplementation has a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on renal transporters, URAT1 and GLUT9, with the inhibitory effect of SCFAs on GLUT9 being reversible. Activating G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs, such as GPR41 and GPR43) (Li Y. et al., 2022) and inhibiting the activity of histone deacetylase (HDACs) (Thomas and Denu, 2021), intestinal SCFAs might attenuate the immuno-inflammatory response of gut and other organs induced by hyperuricemia through activating GPCRs and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling (Zhao et al., 2018) pathways and weakening HDACs activity. However, the specific mechanism needs further investigation.
2.2 The mechanistic role of soluble uric acid (SUA) in the renal dysfunction
SUA has various effects on the kidney, including pathological and physiological processes such as renal arteriopathy, glomerulosclerosis, tubular injury, interstitial fibrosis, and tubular hypertrophy (Jing et al., 2020). Studies have reported that SUA can act as an antioxidant, scavenging unpaired oxygen, oxygen radicals, and peroxynitrite, as well as chelating transition metals. Its antioxidant capacity accounts for half of the total antioxidant capacity of human plasma (Kumar et al., 2015). As demonstrated, physiological concentrations of SUA inhibit the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β-induced inflammatory factors in primary porcine chondrocytes and exert a protective effect on cartilage in collagen-induced arthritis in mice (Lai et al., 2017). Interestingly, SUA exhibits pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory properties in several studies (So and Thorens, 2010). SUA induces vascular endothelial injury, which is closely related to micro-inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism disorders. Notably, the modeling concentration of uric acid used in vitro experiments reached 20 mg/dL (namely, 1,200 μmol/L) (Yin et al., 2019), which is much higher than the common pathological levels in hyperuricemic individuals. Therefore, it is suggested that the modeling conditions for hyperuricemia and HN should be consistent with the actual pathological situations.
Once inside the cells, SUA acts as a pro-oxidant molecule, activating fibrotic signaling pathways, including AMPK, ERK1/2, PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT, NF-κB, and the NLRP3 inflammasome, which trigger oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in the kidney (Li K. et al., 2023). In addition to stimulating an increase in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase activity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (Sautin et al., 2007), low concentrations of supraphysiologic SUA act as a pro-oxidant, playing a role in renal pathophysiology. Studies have demonstrated that mild hyperuricemia in mice that underwent 5/6 nephrectomy, exhibited significant renal injury and inflammatory responses (Omizo et al., 2020). In contrast, febuxostat protected the kidneys from hyperuricemia, suggesting the protective role of a uric acid-lowering strategy targeting XOD in the kidneys. Given that hyperuricemic nephropathy is a progressive condition, the pro-oxidant and pro-inflammatory roles of SUA need to be clarified more specifically at different stages of CKD progression.
2.3 The mechanistic role of monosodium urate (MSU) crystal in the renal dysfunction
In clinical observations, MSU deposits can be detected by ultrasonography and dual-energy CT examination in the renal tissues and joints that have been affected. As a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP), MSU deposition activates a local immuno-inflammatory response, leading to the activation of the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, which produces and releases active IL-1β and IL-18. This alteration initiates the amplification of the inflammatory cascade and profibrotic degeneration in the kidney, ultimately causing glomerular and tubular pathology (Mei et al., 2022). Notably, it has been found that MSU affects the binding of the uric acid transporter URAT1 to Numb, a protein that controls the endocytosis process (Wu et al., 2015), as well as OAT1 membrane endocytosis (Wu et al., 2016). This leads to elevated URAT1 expression and reduced OAT1 expression, which exacerbate the imbalance in urate metabolism, thereby deteriorating renal function. In addition, MSU promotes the apoptosis of kidney cells by inducing the production of reactive oxygen species, increasing nitric oxide synthase activity and mitochondrial caspase enzymes activity, as well as the activation of apoptosis-dependent signaling pathways (Choe et al., 2015), thus exacerbating kidney injury. It cannot be ignored that MSU accumulates in the urinary system, transforming from urate crystals into urate stones, which increases the risk of obstructive nephropathy, urinary tract infections, and kidney damage (Jiang C. et al., 2023). Therefore, it is generally believed that local immuno-inflammatory responses, renal fibrosis, apoptosis, and renal obstruction are responsible for the renal injury caused by MSU crystals.
2.4 The imbalance of intestinal immune barrier promotes HN progression
Currently, the pathophysiological role of gut microbiota has been confirmed in various chronic kidney diseases. It has been discovered that patients with gout and hyperuricemia exhibit an imbalance in intestinal ecology, along with increased levels of harmful metabolites in the serum and intestines (Guo et al., 2016). The intrinsic barrier of the intestinal mucosa consists of intestinal epithelial cells, associated connective structures, and robust immunity. Intestinal epithelial cells protect the intestinal barrier by forming physical and biochemical barriers against pathogenic microorganisms, thus participating in the regulation of the mucosal immune system (Yang et al., 2023). When the intestinal barrier function is impaired, endotoxins released by pathogenic microorganisms enter the bloodstream from the intestinal tract, which tends to trigger a series of immune-inflammatory responses (Peterson and Artis, 2014) (Figure 2). Guo et al. (2019) discovered that hyperuricemic mice, in which the uric acid oxidase gene was knock out, showed intestinal barrier dysfunction, subsequent elevated intestinal permeability, and exacerbated renal dysfunction, presumably associated with uric acid-induced inflammatory responses. This suggests a close relationship between hyperuricemic-induced kidney insult and the disruption of intestinal immune barrier. Meanwhile, SUA upregulates the expression of urate transporters PDZK1 (PDZ domain-containing protein 1) and ABCG2 in HT-29 (human colon cancer cells) and Caco-2 cells (human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells) by activating the TLR4-NLRP3 inflammasome and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, thereby promoting the excretion of uric acid in intestinal cells (Chen et al., 2018). Conversely, previous studies have considered the protective role of SUA in NSAID-induced enteropathy due to the antioxidant effect of uric acid. Yasutake et al. (Yasutake et al., 2017) demonstrated that the oral administration of uric acid and intraperitoneal injection of inosinic acid and potassium oxonate ameliorated NSAID-induced enteropathy in mice by decreasing oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and cytotoxicity induced by indomethacin. This implies the potential therapeutic role of SUA in inflammatory enteritis.
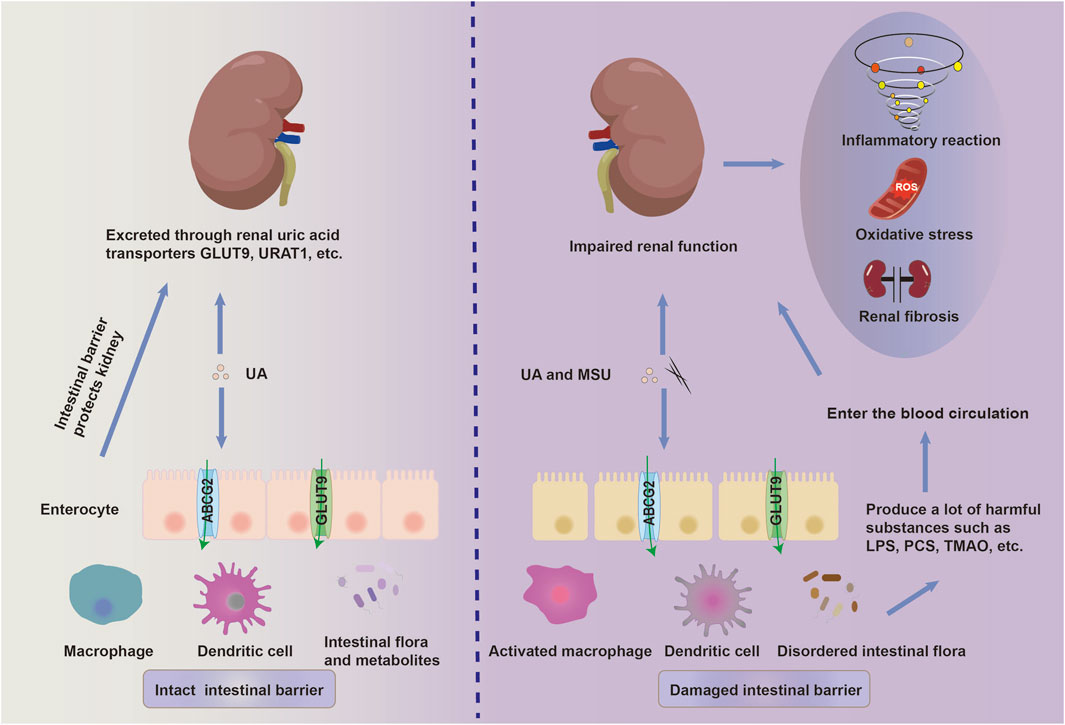
Figure 2. The disruption of the intestinal mucosal immune system promotes the progression of HN. A high-fructose and high-purine diet, along with a poor lifestyle, destroys the intestinal ecology. This disruption promotes the release of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), p-cresyl sulfate (PCS), trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), and other toxic substances. Accompanied by chronic hyperuricemia, intestinal pathogenic microorganisms and their toxic substances synergistically contribute to the breakdown of the intestinal immune barrier through the activation of intestinal innate immunity and injury to the intestinal epithelial cells. These gut-derived harmful metabolites and pro-inflammatory mediators enter the kidney via the bloodstream and further aggravate the renal dysfunction by activating inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis.
In addition to maintaining urate homeostasis by modulating urate transport-related proteins in the intestine, the gut macrobiotic communities and their metabolites affect hyperuricemia and HN progression by regulating “chronic low-grade inflammation” and activating pro-fibrotic signaling. In addition to its pro-inflammatory role in the progression of renal fibrosis, serum urate, together with pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators, aggravates renal fibrosis via multiple signaling pathways, including PI3K/AKT/mTOR, MAPK/NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammasome, IL-6/JAK2/STAT3, TGF-β/SMAD3, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. More recently, the roles of pyroptosis, neutrophil extracellular traps formation (Wu et al., 2024), and ferroptosis (Li et al., 2024) in HN have been emphasized, suggesting novel potential approaches for treating progressive HN.
Hyperuricemic animals induced by high-fat and high-fructose diets and alcohol abuse exhibit a disordered gut microbiome, which parallels that seen in hyperuricemic and gouty patients (Zhang C. et al., 2022). The concept of the “gut-kidney axis” was introduced by Meijers et al., in 2011 (Meijers and Evenepoel, 2011), highlights the bidirectional relationship between the gut microbiota and kidney function. Moreover, insoluble fiber from diets and probiotic supplements attenuate renal injury and fibrosis induced by hyperuricemia by restoring the gut microbiota and SCFAs (Li Y. et al., 2022). Furthermore, a growing body of literature has demonstrated that strategies targeting the gut microbiota and inflammation can alleviate renal fibrosis in hyperuricemia (Lv et al., 2020; Pan et al., 2020). However, well-designed experiments are needed to distinguish whether alterations in the gut microbiota are a primary cause or secondary to hyperuricemia. Notably, the role of gut therapy in HN appears to change dynamically with disease progression and the individual differences of the patients. In patients with early-stage HN or those exhibiting compensatory enhancement of intestinal uric acid excretion, therapies targeting the gut microbiota (e.g., probiotics, fecal microbiota transplants) may serve as a core therapeutic strategy. These interventions aim to restore microbial imbalance and alleviate uric acid accumulation. Conversely, in cases of advanced renal impairment, a combined approach integrating renoprotective therapies with gut-targeted interventions may be required to optimize patient management. In summary, the relationship between the gut and the kidney influences the disease process by regulating urate metabolism and transport processes. Therefore, this paper summarizes single herb and TCM formulas that have dual-regulatory effects on both the gut and the kidney. This summary aims to develop new perspectives and research ideas for the clinical treatment of hyperuricemic nephropathy and the development of TCMs drugs.
3 The dual-regulatory effect of intestine and kidneys of TCMs for HN treatment
3.1 TCM formulas
3.1.1 Regulating intestinal flora and metabolites
Ermiao San, a traditional Chinese medicinal compound, reduces uric acid levels, attenuates glomerular atrophy, and diminishes vacuolar degeneration of renal tubular epithelial cells by inhibiting XOD activity. It has been shown to have preventive and therapeutic effects on hyperuricemia and relate conditions (Shan et al., 2021; Wei et al., 2018). Bining Decoction is a Chinese medicinal preparation derived from Ermiao San, has the efficacy of clearing heat, inducing dampness and eliminating edema. Studies have found that Bining Decoction improves disease-related imbalances in vivo, inhibits XOD activity and JAK2 expression within the JAK/STAT pathway, regulates the intestinal flora, and enhances the intestinal barrier. All of these actions play crucial roles in modulating inflammatory factors and apoptotic pathways (Huang et al., 2022).
When administered via enema, the Rhubarb Compound Preparation treats chronic kidney disease by regulating autophagy, apoptosis, intestinal flora and barrier function (Zou et al., 2012; Xiang et al., 2020; Zhang F. et al., 2023). More recently, a systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that rhubarb (Rhei Radix et Rhizoma) has a positive therapeutic effect on chronic renal failure (Huang W. et al., 2023). However, as a hospital-prepared formulation, the efficacy and safety of rhubarb-based TCMs therapy needs to be evaluated by high-quality clinical trials.
Compound Tu-Fuling Oral-Liquid (CoTOL), a clinically used Chinese herbal formula for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout, works by affecting XOD activity and regulating the intestinal flora to reduce uric acid production (Gao et al., 2020). The results of a randomized double-blind controlled trial showed that CoTOL was effective in reducing sUA levels and in preventing acute arthritic flares in gouty patients (Xie et al., 2017). However, a short observation period and the absence of a positive control affect the reliability and validity of this trial. As the main ingredient, Poria cocos can significantly improve renal function, glomerular atrophy, and tubular dilation in hyperuricemic rats. Furthermore, its nephroprotective effect is achieved by increasing the abundance of Bacteroidetes, Alistipes and Parabacteroides in the intestinal tract, and decreasing the relative abundance of Firmicutes, thereby regulating the intestinal flora (Wang K. et al., 2022).
As a Tibetan medicine, Shiwuwei Rupeng Pills downregulate the expression levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), STAT3, and ALB mRNA, while upregulating the expression levels of PPARG mRNA in the renal tissues of rats with HN. These actions inhibit renal inflammatory factors and improve renal injury. Furthermore, the pills play a therapeutic role in treating HN by regulating the structure of the intestinal flora and the expression of signaling pathways and related targets, such as AGE-RAGE, interleukin-17 (IL-17), TNF, and others (Omizo et al., 2020; Xie et al., 2022). Clinical trials shows that after 3–6 courses of treatment, arthritis redness, swelling, and pain can be effectively alleviated, and the therapeutic efficiency can reach 93% (La and Tai, 2018), however, the specific mechanism requires further research.
3.1.2 Regulating intestinal urate-related transporters
Dendrobium officinalis Six Nostrum, which adds Dendrobium ironpierre to the basis of Si-Miao Pill, effectively regulates the expression levels of urate transporter proteins URAT1, ABCG2 and PDZK1 in the kidneys, as well as intestinal GLUT9, ABCG2, and CNT2 proteins, thereby reducing the level of uric acid. It also inhibits the LPS/TLR4/NF-κB signaling to reduce the secretion of renal inflammatory factors (Chen et al., 2020). Additionally, Dendrobium officinalis Six Nostrum significantly downregulates CNT2 protein expression, which reduces purine transport from the intestine back to the blood and inhibits XOD activity, leading to a decrease in uric acid production. Furthermore, it restores the protein expression of tight junctions, such as ZO-1 and claudin-1, thereby protecting the intestinal barrier function (Ge et al., 2023).
The combination of Polyonum Cuspidatum and Ramulus Cinnamomi reduces uric acid reabsorption by inhibiting the overexpression of the renal transporter protein URAT1 at both mRNA and protein levels. It also increases uric acid secretion by promoting the expression of the renal transporter protein OAT3 at the mRNA and protein levels, as well as the small intestinal ABCG2 (Shi et al., 2016; Zhu, 2018).
Miao medicine Tongfengting reduces uric acid levels through several actions: it downregulates the intestinal ABCG2 gene, and downregulates the URAT1 gene (Cao et al., 2021). Furthermore, it decreases the protein expression associated with renal injury, such as KIM-1, NGAL, TIMP-1, and MCP-1, thereby playing a role in protecting renal function (Cao Y. P. et al., 2022).
3.1.3 Inhibiting intestinal immuno-inflammation
Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang Powder, derived from Zhang Zhongjing’s The Essentials of the Golden Chamber, has anti-diarrhea activity. Modern pharmacological studies have found that Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang Powder repairs intestinal mucosal damage, regulates immune balance and intestinal flora, and reduces inflammation and oxidative stress damage (Wang S. N. et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2023). Clinical research has showed that Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang Powder significantly reduces uric acid levels in patients with hyperuricemia in CKD stages 1–3. However, further exploration of the mechanisms affecting renal function is still needed (Zhao, 2023).
3.1.4 Modulation in multiple pathways, aspects and organs
Quzhuo Tongbi Recipe is effective in strengthening the spleen and kidney, and possesses anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. It was found that Quzhuo Tongbi Recipe regulates the expression of the urate transporter protein ABCG2, regulates the intestinal microbiota and regulates cell differentiation through PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. It also downregulates the levels of amino acids dependent on the fermentation of intestinal flora, increases the abundance of intestinal butyrate-producing bacteria and the expression of their metabolites SCFAs, inhibits the production of intestinal inflammatory factors, and restores the function of the intestinal barrier (Song et al., 2023; Wen et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2019).
As a classic formula, Si Miao San is mainly composed of Atractylodes Lance (Thunb.) DC, Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex, Achyranthes bidentata, Coix lacryma-jobi var. It has the efficacy of clearing heat and dispelling dampness. The treatment of HN with Si Miao San is mainly reflected in its ability to inhibit uric acid production and promote uric acid excretion. This is achieved by regulating the transduction of JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, increasing the expression of the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10, and decreasing the expression of pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Additionally, it regulates the uric acid transporter proteins URAT1, GLUT9, and OAT1 (Cao L. et al., 2022; Zhang Y. et al., 2023). Further studies have found that Si Miao San inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome to reduce intestinal inflammation and alters the composition and function of the intestinal flora (Lin et al., 2020; Zhang, et al., 2022e). Clinically, a derivative of Si Miao San is mainly applied, with Tu Fu Ling and Lonicera japonica added to improve renal function (Zhang G. J. et al., 2022). Systematic evaluations and meta-analysis have shown that Modified Si Miao Decoction exerts therapeutic effects on gout through its anti-inflammatory and uric acid-lowering effects (Liu et al., 2017). However, due to poor quality of research methodology adopted in the included clinical trials, there is a strong need for multi-center randomized trial designs with sufficient samples to further validate its efficacy and safety.
The Bi Xie Fen Qing Yin improved renal inflammation, fibrosis and water-fluid metabolism disorders in mice by inhibiting the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and pro-fibrotic signaling. It also had a certain modulating effect on intestinal flora disorders, metabolite abnormalities, intestinal inflammation, intestinal barrier damage, and uric acid excretion in mice (Lin, 2022). In clinical practice, the combination of Bi Xie Fen Qing Yin with febuxostat was found to have more significant efficacy in improving renal function in patients with HN after drug interventions were administered (Li X. Q. et al., 2022), However, the trail conducted in a small sample size limits the clinical application.
The Cichorium intybus L. Formula inhibited the expression of STAT3, vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and SIRT1. It also regulated the diversity and community structure of intestinal flora and improved the symptoms of HN (Amatjan et al., 2023). In addition, chicory was found to regulate the expression of the intestinal ABCG2 protein to promote uric acid excretion (Wang et al., 2017).
Sishen Pill reduced the level of TMAO in serum, kidney and small bowel by regulating Firmicutes, Succinum hispidum and Clostridium butyricum. It also prevented the transmission of inflammatory factors, such as NLRP3 and IL-1β, through the “gut-kidney axis,” thereby improving intestinal barrier injury and renal fibrosis (Xie et al., 2024). (Table 2)
3.2 Single herbals
3.2.1 Regulating intestinal flora and metabolites
Poria cocos, the dried mycelium of P. cocos (Schw.) Wolf from the family Polyporaceae, is known for its dual role as both a medicine and a food. Studies have shown that it improves renal function in hyperuricemic rats by upregulating the expression of the ABCG2 protein (Liang et al., 2021). Additionally, P. cocos regulates the beneficial intestinal flora, alleviates renal tubular dilation, glomerular atrophy, and cellular vacuolization in the kidney (Wang K. et al., 2022). The polysaccharide found in P. cocos enhances the intestinal barrier in mice and maintains the balance of intestinal flora, contributing to its therapeutic effects (Duan et al., 2023).
Coicis Semen is the dried mature seed kernel of C. lacryma-jobi L.var.ma-yuen (Roman.) Stapf, from the family Gramineae. The oil derived from Coicis Semen reduces the imbalance of intestinal flora and inhibits the expression of factors that cause intestinal inflammation. This was achieved by decreasing the levels of enterococci and Enterobacteriaceae, and increasing the relative abundance of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus in mice (Wang T. et al., 2020). Additionally, an extract from C. lacryma has been shown to inhibit XOD activity, thereby reducing uric acid levels and ameliorating renal damage in cases of HN (Sui et al., 2023).
Turmeric, the dried rhizome of Curcuma Longa L. from the family Zingiberaceae, contains the active ingredient curcumin. Curcumin regulates the structure of the intestinal flora, thereby enhancing the intestinal barrier. It also inhibits XOD activity, alleviates renal tubular interstitial fibrosis, and reduces the production of inflammatory factors and the secretion of PO-1. Additionally, curcumin prevents the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. These actions contribute to curcumin’s therapeutic role in treating HN and reducing inflammation (Chen et al., 2019; Shen et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2021).
Astragalus membranaceus, the dried root of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao or A. membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge., belongs to the legume family. It possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory functions (Auyeung et al., 2016). Studies have shown that A. membranaceus reduces uric acid levels by regulating intestinal flora and metabolites (Zhao et al., 2022). Furthermore, when fermented with Bacillus subtilis, A. membranaceus downregulates the expression of uric acid transporter proteins, URAT1 and GLUT9, and inhibits XOD activity, thereby reducing uric acid levels (Wang R. et al., 2023).
Mountain waxberry, the leaf of Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. in the genus Waxberry and family Waxaceae, restores intestinal homeostasis by regulating the abundance of beneficial intestinal bacteria and the expression of proteins related to the intestinal barrier. Additionally, mountain waxberry regulates XOD activity, influences genes and proteins involved in the reabsorption and secretion of uric acid, inhibits uric acid production, and promotes its excretion, thereby reducing the UA-mediated kidney damage (Meng et al., 2023).
Andrographis paniculata is the dried aerial part of A. paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees, family Dioscoreaceae. The total saponins of A. paniculata reduce uric acid and exert anti-inflammatory effects by regulating intestinal flora and metabolites (Yu et al., 2023). They also inhibit the activities of XOD and adenosine deaminase (ADA), subsequently downregulating the expression of the OAT1, which helps in the urate metabolism.
3.2.2 Regulating intestinal urate transporters
Stevia, a member of the Asteraceae family, is rich in flavonoids and chlorogenic acid compounds. It possesses antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic effects. Studies have shown that stevia residue extract improves kidney function in hyperuricemic mice by upregulating the expression of the ABCG2 protein and downregulating the expression of the GLUT9 protein (Mehmood et al., 2019). This was achieved through the MMP-7 and MMP-9/β-catenin signaling pathways, which helped to reduce fibrosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Additionally, stevia inhibited the activation of the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway via the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway and modulated the JAK2-STAT3 and Nrf2 signaling pathways, which contributed to the reduction of renal inflammation (Mehmood et al., 2022).
3.2.3 Modulation in multiple pathways, aspects and organs
A water-soluble polysaccharide in L. japonica was able to attenuate oxidative stress in vivo, reduce kidney injury caused by excess reactive oxygen species and regulate intestinal flora, and downregulate IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α,COX-2-related inflammatory factors (Sun et al., 2023). It also reduced uric acid levels (Yang et al., 2019). Chlorogenic acid in L. japonica extract reduced serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels and downregulated the mRNA expression of IL-18, TNF-α, NLRP3, and Caspase-1. Additionally, it inhibited the activation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in the kidneys, thereby alleviating renal inflammation in hyperuricemic mice. Furthermore, it regulated the intestinal flora, metabolites, and inflammation factors gene expression to ameliorate the inflammatory response (Zhou et al., 2021).
Saffron, the dried stigma of Crocus sativus L. from the family Iridaceae, contains the main constituent crocin, a type of flavonoid. Crocin inhibited and reduced the activity of XOD, regulated the expression of renal and intestinal URAT1, GLUT9, and ABCG2 genes and proteins, lowered uric acid levels, and modulated intestinal flora. These actions effectively alleviated the symptoms of HN (Chen et al., 2022).
Poria cocos is the dried sclerotium of a fungus, not a plant, and it contains quercetin, which interacts with XOD to reduce uric acid levels (Li X. et al., 2022). It also contains flavonoids that inhibit the expression of oxidative stress and inflammatory-related factors in the kidney, and regulate the expression of genes ABCG2, OAT1, organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2), and organic cation transporters novel 2 (OCTN2) to reduce uric acid levels (Wang et al., 2019). Additionally, P. cocos regulates the content of intestinal SCFAs, thereby affecting the intestinal barrier function (Zhao et al., 2021). The contained Astilbin can increase the content of SCFAs and regulate the intestinal flora and the expression of intestinal uric acid transporter proteins, thereby modulating kidney injury and uric acid excretion (Guo, 2020).
Chicory, a traditional Uyghur medicine, comes from the dried above-ground parts or roots of two species: Cichorium glandulosum Boiss. et Huet and Cichorium intybus L., both belonging to the Asteraceae family. It is used to inhibit uric acid production by regulating OAT2 expression and inhibiting XOD activity. Additionally, it regulates the expression of intestinal flora and intestinal ABCG2, further inhibiting uric acid production and promoting its excretion (Wang et al., 2017). Further studies have found that chicory extract has a comprehensive regulatory effect on the intestinal barrier (Wang et al., 2018). It inhibits the oxidative stress-mediated tissue injury by suppressing the expression of intestinal inflammatory factors. It also reduces the serum levels of D-lactic acid and beta-microglobulin, thereby improving oxidative stress-induced tissue inflammation (Wang et al., 2020b; Wang et al., 2020c).
Rhubarb consists of the dried roots and rhizomes of several species, including Polygonum palmatum, Rheum palmatum L., Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf., and medicinal rhubarb Rheum officinale Baill. The active ingredient, rhodopsin, indirectly reduces uric acid levels by regulating intestinal Lactobacillus (Wu et al., 2020). Rhein directly reduces uric acid levels by downregulating the expression of intestinal GLUT9 (Zhou, 2017). Additionally, it inhibits XOD activity and decreases the expression of inflammatory factors such as IL-1β, TNF-α, PGE2, and TGF-β, which exerts uric acid-lowering and anti-inflammatory effects (Meng et al., 2015). Stewed Rhubarb, as a processed product of rhubarb, has been shown to exert anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of renal NLRP3 and decreasing the mRNA levels of Il-1β, TNF-α, Col1a1, and Fibronectin in adenine-induced chronic renal failure (CRF) mice. On the other hand, Stewed Rhubarb increased the abundance of Bacteroidales but reducing the contents of Rikenellaceae and Erysipelotrichaceae in CRF mice, exerting a role in restore microbial balance and intestinal barrier integrity (Wang R. et al., 2022).
Phellodendron chinense Schneid. exerted anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting renal PI3K/AKT, TNF, MAPK, TLR and NLRP3 pathway signaling pathways (Xu et al., 2022). Palmatine alkaloids inhibited XOD activity, downregulated GLUT9 and URAT1 protein expression, and upregulated OAT1 and ABCG2 expression to reduce serum uric acid levels. It also alleviated renal inflammation and oxidative stress caused by hyperuricemia, which contribute to targeting the Keap1-Nrf2/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway (Ai et al., 2023). Furthermore, recent research discovered that phellodendrine, the characteristic component of P. chinense Schneid., regulates the composition of intestinal flora and the AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy pathway to restore the intestinal mucosa injury induced by intestinal inflammation (Su et al., 2021).
In conclusion, TCM preparations and single herbals alleviate HN symptoms by regulating the urate-related transporters, intestinal flora and metabolites, and immune-inflammatory responses. The involved signaling pathways include MAPK, AMPK/SIRT1, JAK2/STAT3, PPAR/NF-κB, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, MMP9/β-catenin and NLRP3 inflammasome, etc. Besides promoting uric acid excretion by regulating urate transporters, the restorative effects of TCMs on the intestinal and renal dysfunction are attributed to the modulation of multiple targets, pathways and aspects, which are responsible for the anti-HN potential of TCMs (Table 3).
4 Challenges and perspectives
In recent years, research on the potential role of altered intestine function in hyperuricemia and HN has surged. Thus, this paper systematically reviews the pathogenesis of HN, the effects of SUA and MSU on renal dysfunction, and the role of the intestinal tract in the progression of HN. This article primarily focuses on the advancements in traditional Chinese medicine and single-flavored Chinese medicine for HN management, summarizing and analyzing 13 types of TCM and 13 single herbs. In general, we propose the perspective that traditional Chinese medicines delay HN progression through a dual-regulatory effect on the intestines and kidneys, particularly by the modulation of intestinal flora and metabolites, uric acid transporters and the immune-inflammatory response (Figure 3).
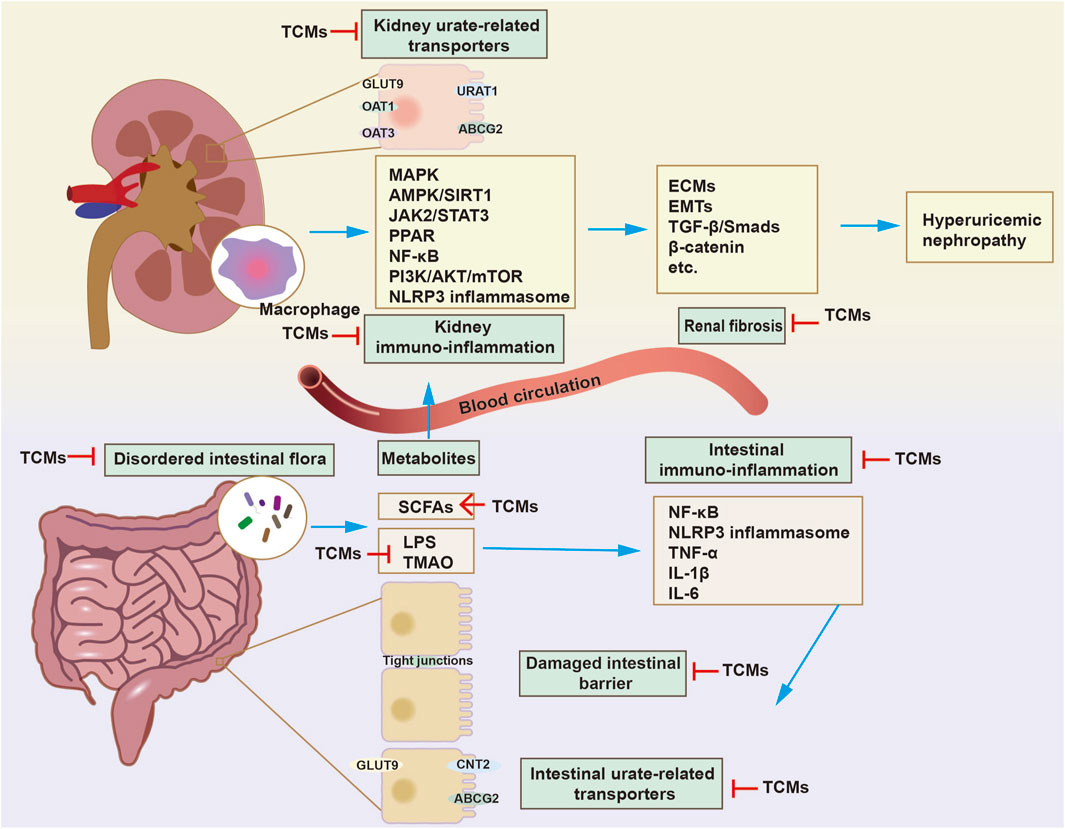
Figure 3. The mechanism of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) in delaying HN progression through dual regulation of the gut and kidneys. The treatment of HN with TCMs is mainly achieved by modulating urate-related transporters, oxidative stress, immune-inflammatory reactions, and pro-fibrosis signaling in kidneys. The modulatory effects of TCMs on disordered intestinal flora and metabolites have been discovered. Besides regulating intestinal urate-related transporters, such as concentrative nucleoside transporter 2 (CNT2), ABCG2, GLUT9, TCMs exert a uric acid-lowering effect by increasing the abundance of specific microorganisms that break down purines and uric acid. On the other hand, TCMs restore intestinal immune barrier function by inhibiting the immune-inflammatory response and increasing the expression of tight junctions, thereby inhibiting the entry of enterogenous harmful substances into the kidneys. In general, TCMs delay HN progression through a dual-regulatory effect on the intestines and kidneys.
4.1 Is intestinal therapy a core mechanism or an adjunctive therapy?
The gut (about 30%) and the kidney (about 70%) are the main pathways for uric acid excretion. When renal function is impaired, intestinal excretion may be compensatorily increased and become a key pathway for lowering serum uric acid. On the one hand, the accumulation of toxins in the circulation induced by the renal dysfunction, leads to an imbalance in the intestinal flora. On the other hand, the alteration of intestinal flora leads to the release of a large number of toxic metabolites and endotoxin, activating the immune-inflammatory response and destroying the intestinal mucosal barrier. This, in turn, aggravates to the renal dysfunction in the hyperuricemia. Therefore, the multiple modulatory effects of TCMs on intestinal excretory capacity (e.g., inhibition of the intestinal urate transporter), the abundance of specific bacteria associated with purine and uric acid metabolism, and the disturbed intestinal flora composition may become an alternative therapeutic strategy for HN.
TCMs play a key role in increasing the beneficial intestinal flora, such as E. faecalis spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. etc., which aid in digestion and absorption, and stimulate the body’s immune function to protect health. It also regulates the neutral flora, such as L. spp., E. coli, Streptococcus spp. etc., which, if imbalanced, can lead to an increase in harmful substances and toxins, promoting aging. Additionally, it helps decrease harmful flora, such as A. spp. and Bacteriodesmus spp. etc., which can reduce intestinal infections (Li X. et al., 2021). Therefore, an imbalance in the intestinal flora may lead to abnormal purine metabolism and increased uric acid production, while microbial metabolites (such as SCFAs) may affect renal inflammation and fibrosis through the “gut-kidney axis.” Intervention of intestinal flora may reduce the source of uric acid and alleviate renal injury. Notably, for patients with significant gut microbiota dysbiosis (e.g., those with chronic inflammatory bowel disease or metabolic syndrome), the gut-kidney axis could be discussed as a central mechanism. In cases of advanced renal impairment, a combined approach integrating renoprotective therapies with gut-targeted interventions may be required to optimize patient management. Growing evidence has revealed that TCMs exhibit anti-HN potential via multi-target, multi-pathway, and multi-approach. Some animal experiments have shown that TCMs (e.g., Bining Decoction, Poria, Astragalus, etc.) can both inhibit uric acid production and restore the balance of intestinal flora, suggesting the centrality of intestinal therapy. However, the causal relationship between intestinal flora and HN is still unknown. Thus, it is suggested that the causative role of gut microorganism in the development and progression of HN should be investigated through the depletion of intestinal flora. Previously, Emal et al. (2017) depleted the intestinal microflora by applying antibiotics, treated with oral administration of faecal suspensions from healthy mice for 3 days, and subsequently established a mouse model of renal ischemia-reperfusion, and found that the intestinal flora exacerbated renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating macrophage maturation and chemotaxis, while faecal transplantation attenuated the renal injury, suggesting that intestinal flora plays a central role in the progression of renal diseases. This provides a basis for targeting microorganisms in the treatment of renal diseases. However, the specific mechanism requires further exploration, especially to clarify the causal effect of specific gut flora (e.g., urease-producing bacteria) on the progression of HN, and to develop precise therapeutic strategies targeting to gut flora. Indeed, medicines targeting to the uric acid transporters in intestines and kidneys, as the crucial research hotspot of urate-lowering therapy, has also been widely studied. It has been confirmed that TCMs with regulatory activity on urate transporters in the intestine and kidney, such as Dendrobium officinalis Six Nostrum, Combination of Polyonum Cuspidatum and Ramulus Cinnamomi and Tongfengting, mainly achieve this potential by inhibiting URAT1 and upregulating ABCG2.
In general, the role of intestinal therapy in HN may show dynamic changes with the disease course and the individual differences of the patients. In the early stage, or in patients with compensatory enhancement of intestinal excretion, intestinal modulation may be regarded as a core tool for HN management. However, in cases of severely impaired renal function, the combination of renal-targeted therapy and intestinal-targeted therapy is required. What cannot be ignored is that the multi-targeting properties of TCMs (especially dual gut-kidney regulation) provide a theoretical basis for treating HN as a potential alternative intervention.
4.2 The dilemma of TCMs from basic research to clinical application
In fact, the treatment of HN with TCMs faces many dilemmas in transitioning from basic research to clinical application, such as the complexity of Chinese medicines’ components, insufficient bioavailability, and challenges in quality control. In the future, the application of emerging technologies in the research of TCMs will provide a new technical direction for the treatment of HN with TCMs. Especially in the current fermentation processes, both single-strain and multi-strain collaborative fermentation are utilized. These methods can promote the release of effective components from TCMs and the decomposition and transformation of toxic substances, and are gradually being applied to TCM fermentation (Li Q. Y. et al., 2021; Qu et al., 2023). For example, Wang et al. used Bacillus subtilis to ferment Astragalus membranaceus, thereby increasing the bioavailability of Astragalus polysaccharides. Mechanically, fermented Astragalus membranaceus significantly decreases serum UA levels and increases the abundance of butyrate-producing enzymes in HUA mice (Wang R. et al., 2023). In addition to single-flavored Chinese medicine, fermentation technology can also be applied to TCM formulas (Selvaraj and Gurumurthy, 2023). Luo et al. fermented Simiao Pill with compound bacterium agent consisting of Mucor enzymes, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and lactic acid bacteria, and selected frankincense-associated bacteria as the strain for fermenting Simiao Pill, which was then used to treat HN mice. Oral treatment with fermented Simiao Pill exhibited superior anti-hyperuricemic activity, possibly due to the release of more active substances (Luo, 2024). However, the technology of fermenting Chinese herbal medicine also has limitations, such as unclear mechanisms, a low degree of industrialization, and unstable safety, necessitating further research.
In recent years, with the development of nanotechnology, the “nanotization” of TCMs has brought new ideas for the innovative research of TCMs, improving the oral bioavailability and tissue targeting of active ingredients, thus promoting the transformation of TCMs from basic research to bedside application. For instance, exosomes or exosome-like nanovesicles derived from herbal medicines, as natural nano-preparations (Dad et al., 2021), have been confirmed to exhibit potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immune-regulatory activities (Chen et al., 2021), as well as anti-inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) effects (Li D. et al., 2023). Besides, due to their small size, strong penetration and resistance to acid, alkali, and high temperature, plant-derived exosomes or exosome-like nanovesicles are ideal carriers for drug delivery (Kim et al., 2022). To address the low aqueous solubility and non-selective toxicity of Shikonin, Matias Cardoso et al. designed a self-assembled hyaluronic acid-zein nanogel loaded with Shikonin, which selectively inhibited LPS- and nigericin-induced activation of the macrophage NLPR3 inflammasome. In short, the application of nanoagents in the field of TCMs opens up new avenues for the treatment of HN. By improving the physical and chemical properties, biological activity, and targetability of TCMs, nanotechnology significantly promotes the clinical transformation of novel TCMs drugs in the future. Nevertheless, there is insufficient evidence on the safety of nanomaterials applied to humans, as well as regulatory policies, which should be given more attention.
At present, the research on the treatment of HN through the intestinal tract is still in the initial stage. Therefore, it is necessary to further strengthen the research to determine the optimal treatment strategy, including the regulation of intestinal flora, dosage, and duration of treatment, and other related issues, and to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of HN treatments through large-sample, multi-center studies, further clarifying the mechanisms by which intestinal therapy plays a role in the treatment of uric acid nephropathy. By combining genomics, metabolomics and spatial transcriptomics, we can systematically analyze the composition of intestinal flora, the targets of active ingredient, and the specific effect on multiple renal cell types modulated by TCMs. This approach helps to clarify the regulatory mechanisms of TCMs against HN. For instance, single-cell sequencing technology enables in-depth analysis of the effects of herbal medicines on specific cellular subpopulations, as well as the modulatory effect of TCMs on the multiple signaling pathways in the HN kidney. Particular attention is given to the origin of myofibroblasts and fibroblasts, such as EMT, macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition (MMT), etc. In the future, artificial intelligence will be applied to clinical data analysis to integrate multi-omics data (genomics, metabolomics, and microbiomics) with electronic health records. This integration aims to develop personalized TCMs treatment plans that optimize therapeutic efficacy and minimize adverse effects (Medicine, 2024).
Overall, TCM formulas and single herb that have a dual-regulatory effect on the intestine and kidneys in HN treatment, as a novel therapeutic approach, hold good prospects for preventing or alleviating the progression of kidney disease secondary to hyperuricemia. With the integration of multiple disciplines and the application of emerging technologies, further advancements will be achieved in the research of anti-HN TCMs in the future.
Author contributions
TW: Writing – original draft. LLi: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. LLu: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. RT: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. QW: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. XZ: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. HH: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. YD: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. HL: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JM: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JZ: Writing – review and editing. ZY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, China (2023NSFSC0669), the open project of the Antibiotics Research and Re-evaluation Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, China (ARRLKF23-07). Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2022C009, 2024MS194) Talent Program of Sichuan Academy of Chinese Medicine Sciences (QNCJ-YZJ-01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ai, G., Huang, R., Xie, J., Zhong, L., Wu, X., Qin, Z., et al. (2023). Hypouricemic and nephroprotective effects of palmatine from Cortex Phellodendri Amurensis: a uric acid modulator targeting Keap1-Nrf2/NLRP3 axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 301, 115775. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115775
Aktas, G., Khalid, A., Kurtkulagi, O., Duman, T. T., Bilgin, S., Kahveci, G., et al. (2022). Poorly controlled hypertension is associated with elevated serum uric acid to HDL-cholesterol ratio: a cross-sectional cohort study. Postgrad. Med. 134, 297–302. doi:10.1080/00325481.2022.2039007
Amatjan, M., Li, N., He, P., Zhang, B., Mai, X., Jiang, Q., et al. (2023). A novel approach based on gut microbiota analysis and network pharmacology to explain the mechanisms of action of Cichorium intybus L. formula in the improvement of hyperuricemic nephropathy in rats. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 17, 107–128. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S389811
Auyeung, K. K., Han, Q. B., and Ko, J. K. (2016). Astragalus membranaceus: a review of its protection against inflammation and gastrointestinal cancers. Am. J. Chin. Med. 44, 1–22. doi:10.1142/S0192415X16500014
Badve, S. V., Pascoe, E. M., Tiku, A., Boudville, N., Brown, F. G., Cass, A., et al. (2020). Effects of Allopurinol on the progression of chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 2504–2513. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915833
Becker, M. A., Schumacher, H. R., Wortmann, R. L., MacDonald, P. A., Palo, W. A., Eustace, D., et al. (2005). Febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: a twenty-eight-day, multicenter, phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response clinical trial examining safety and efficacy in patients with gout. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 916–923. doi:10.1002/art.20935
Cao, J., Liu, Q., Hao, H., Bu, Y., Tian, X., Wang, T., et al. (2022a). Lactobacillus paracasei X11 ameliorates hyperuricemia and modulates gut microbiota in mice. Front. Immunol. 13, 940228. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.940228
Cao, L., Zhao, T., Xue, Y., Xue, L., Chen, Y., Quan, F., et al. (2022b). The anti-inflammatory and uric acid lowering effects of Si-Miao-San on gout. Front. Immunol. 12, 777522. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.777522
Cao, Y. P., Feng, Z. L., Yang, Y. T., Ma, W. K., Liu, Z. Q., An, Y., et al. (2022c). Exploring the protective effect of miao medicine Tongfengting on uric acid nephropathy based on the KIM-1 and other kidney injury factors. World Sci. Technol. - Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 24, 3708–3717. doi:10.11842/wst.20210929012
Cao, Y. P., Ma, W. K., Liu, Z. Q., An, Y., Zhang, X. F., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Study on the mechanism of miao medicine Tongfengting Decoction on decreasing uric acid in hyperuricemia rats. World Chin. Med. 16, 2240–2244. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2021.15.005
Chen, M., Lu, X., Lu, C., Shen, N., Jiang, Y., Chen, M., et al. (2018). Soluble uric acid increases PDZK1 and ABCG2 expression in human intestinal cell lines via the TLR4-NLRP3 inflammasome and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Arthritis Res. Ther. 20, 20. doi:10.1186/s13075-018-1512-4
Chen, N., Wang, R., Li, H., Wang, W., Wang, L., Yin, X., et al. (2022). Flavonoid extract of saffron by-product alleviates hyperuricemia via inhibiting xanthine oxidase and modulating gut microbiota. Phytother. Res. 36, 4604–4619. doi:10.1002/ptr.7579
Chen, X., Ge, H. Z., Lei, S. S., Jiang, Z. T., Su, J., He, X., et al. (2020). Dendrobium officinalis six nostrum ameliorates urate under-excretion and protects renal dysfunction in lipid emulsion-induced hyperuricemic rats. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 132, 110765. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110765
Chen, X., Liu, B., Li, X., An, T. T., Zhou, Y., Li, G., et al. (2021). Identification of anti-inflammatory vesicle-like nanoparticles in honey. J Extracell. Vesicle 10, e12069. doi:10.1002/jev2.12069
Chen, Y., Li, C., Duan, S., Yuan, X., Liang, J., and Hou, S. (2019). Curcumin attenuates potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation in mice. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 118, 109195. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109195
Chien, S. C., Yang, C. W., Tseng, Y. H., Tsay, H. S., Kuo, Y. H., and Wang, S. Y. (2009). Lonicera hypoglauca inhibits xanthine oxidase and reduces serum uric acid in mice. Planta Med. 75, 302–306. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1185300
Choe, J. Y., Park, K. Y., and Kim, S. K. (2015). Oxidative stress by monosodium urate crystals promotes renal cell apoptosis through mitochondrial caspase-dependent pathway in human embryonic kidney 293 cells: mechanism for urate-induced nephropathy. Apoptosis 20, 38–49. doi:10.1007/s10495-014-1057-1
Choi, H. K., Atkinson, K., Karlson, E. W., Willett, W., and Curhan, G. (2004). Alcohol intake and risk of incident gout in men: a prospective study. Lancet (London, England) 363, 1277–1281. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16000-5
Chu, Y., Sun, S., Huang, Y., Gao, Q., Xie, X., Wang, P., et al. (2021). Metagenomic analysis revealed the potential role of gut microbiome in gout. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 7, 66. doi:10.1038/s41522-021-00235-2
Crane, J. K., Naeher, T. M., Broome, J. E., and Boedeker, E. C. (2013). Role of host xanthine oxidase in infection due to enteropathogenic and shiga-toxigenic escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 81, 1129–1139. doi:10.1128/IAI.01124-12
Dad, H. A., Gu, T. W., Zhu, A. Q., Huang, L. Q., and Peng, L. H. (2021). Plant exosome-like nanovesicles: emerging therapeutics and drug delivery nanoplatforms. Mol. Ther. 29, 13–31. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.11.030
Dong, Y., Zhao, T., Ai, W., Zalloum, W. A., Kang, D., Wu, T., et al. (2019). Novel urate transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitors: a review of recent patent literature (2016–2019). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 29, 871–879. doi:10.1080/13543776.2019.1676727
Du, L., Zong, Y., Li, H. R., Wang, Q. Y., Xie, L., Yang, B., et al. (2024). Hyperuricemia and its related diseases: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9, 212. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01916-y
Duan, Y., Huang, J., Sun, M., Jiang, Y., Wang, S., Wang, L., et al. (2023). Poria cocos polysaccharide improves intestinal barrier function and maintains intestinal homeostasis in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 249, 125953. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125953
Eckenstaler, R., and Benndorf, R. A. (2021). The role of ABCG2 in the pathogenesis of primary hyperuricemia and gout-an update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 6678. doi:10.3390/ijms22136678
Emal, D., Rampanelli, E., Stroo, I., Butter, L. M., Teske, G. J., Claessen, N., et al. (2017). Depletion of gut microbiota protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 1450–1461. doi:10.1681/ASN.2016030255
Fang, N. Y., Lv, L. W., Lv, X. X., Xiang, Y., Li, B., Li, C. F., et al. (2023). China multi-disciplinary expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of hyperuricemia and related diseases (2023 Edition). Chin. J. Pract. Intern. Med. 43, 461–480. doi:10.19538/j.nk2023060106
Feng, Z. L., Liu, Z. Q., Cao, Y. P., Zhong, Q., Zhu, L., Zhu, D., et al. (2021). Effects of the Miao medicine gout stop soup on the expression of intestinal ABCG2 gene in hyperuricemic rats. J. Guizhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 43, 16–20. doi:10.16588/j.cnki.issn2096-8426.2021.06.004
FitzGerald, J. D., Dalbeth, N., Mikuls, T., Brignardello-Petersen, R., Guyatt, G., Abeles, A. M., et al. (2020). 2020 American college of rheumatology guideline for the management of gout. Arthrit. Care Res. 72, 744–760. doi:10.1002/acr.24180
Gao, Y., Sun, J., Zhang, Y., Shao, T., Li, H., Wang, M., et al. (2020). Effect of a traditional Chinese medicine formula (CoTOL) on serum uric acid and intestinal flora in obese hyperuricemic mice inoculated with intestinal bacteria. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 8831937. doi:10.1155/2020/8831937
García-Arroyo, F. E., Gonzaga, G., Muñoz-Jiménez, I., Blas-Marron, M. G., Silverio, O., Tapia, E., et al. (2018). Probiotic supplements prevented oxonic acid-induced hyperuricemia and renal damage. PLoS One 13, e0202901. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0202901
Gaubert, M., Bardin, T., Cohen-Solal, A., Diévart, F., Fauvel, J.-P., Guieu, R., et al. (2020). Hyperuricemia and hypertension, coronary artery disease, kidney disease: from concept to practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 4066. doi:10.3390/ijms21114066
Ge, H., Jiang, Z., Li, B., Xu, P., Wu, H., He, X., et al. (2023). Dendrobium officinalis Six Nostrum promotes intestinal urate underexcretion via regulations of urate transporter proteins in hyperuricemic rats. Comb. Chem. High. Throughput Screen 26, 848–861. doi:10.2174/1386207325666220830141531
Gersch, C., Palii, S. P., Kim, K. M., Angerhofer, A., Johnson, R. J., and Henderson, G. N. (2008). Inactivation of nitric oxide by uric acid. Nucleos. Nucleot. Nucl. Acids 27, 967–978. doi:10.1080/15257770802257952
Granados, J. C., Ermakov, V., Maity, K., Vera, D. R., Chang, G., and Nigam, S. K. (2023). The kidney drug transporter OAT1 regulates gut microbiome-dependent host metabolism. JCI Insight 8, e160437. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.160437
Grelska, A., Sharan, D., and Light, S. H. (2023). Purine-ifying uric acid by gut microbes. Cell. Chem. Biol. 30, 706–708. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.06.022
Guo, L. (2020). Study on the promoting effect and mechanism of Lonicera glycoside on uric acid excretion in kidney-damaged mice based on gut microbiota. Master’s thesis. Hangzhou, China: Zhejiang Chinese Medical University.
Guo, Y., Li, H., Liu, Z., Li, C., Chen, Y., Jiang, C., et al. (2019). Impaired intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of hyperuricemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 20, 3292–3300. doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.10586
Guo, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Ang, K. Y., Huang, S., Hou, Q., et al. (2016). Intestinal microbiota distinguish gout patients from healthy humans. Sci. Rep. 6, 20602. doi:10.1038/srep20602
Hou, Z., Ma, A., Mao, J., Song, D., and Zhao, X. (2023). Overview of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of URAT1 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Expert Opin. Drug Metabol. & Toxicol. 19, 895–909. doi:10.1080/17425255.2023.2287477
Hu, Y., Shi, Y., Chen, H., Tao, M., Zhou, X., Li, J., et al. (2022). Blockade of autophagy prevents the progression of hyperuricemic nephropathy through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome mediated pyroptosis. Front. Immunol. 13, 858494. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.858494
Huang, H., Tong, Y., Fu, T., Lin, D., Li, H., Xu, L., et al. (2022). Effect of Bining decoction on gouty nephropathy: a network pharmacology analysis and preliminary validation of gut microbiota in a mouse model. Ann. Transl. Med. 10, 1271. doi:10.21037/atm-22-5523
Huang, W., Rao, Y., Li, L., Li, C., and An, Y. (2023). Clinical effect of rhubarb on the treatment of chronic renal failure: a meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1108861. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1108861
Huang, Y., Chen, Z., Chen, B., Li, J., Yuan, X., Li, J., et al. (2023). Dietary sugar consumption and health: umbrella review. BMJ 381, e071609. doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071609
Hui, M., Carr, A., Cameron, S., Davenport, G., Doherty, M., Forrester, H., et al. (2017). The British society for rheumatology guideline for the management of gout. Rheumatol. (Oxford, England) 56, e1–e20. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kex156
Imaram, W., Gersch, C., Kim, K. M., Johnson, R. J., Henderson, G. N., and Angerhofer, A. (2010). Radicals in the reaction between peroxynitrite and uric acid identified by electron spin resonance spectroscopy and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 49, 275–281. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.04.010
Ji, C., Lu, F., Wu, Y., Lu, Z., Mo, Y., Han, L., et al. (2022). Rhubarb enema increasing short-chain fatty acids that improves the intestinal barrier disruption in CKD may be related to the regulation of gut dysbiosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 1896781–1896815. doi:10.1155/2022/1896781
Jiang, C., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Xu, R., Yang, H., and Peng, J. (2023a). Therapeutic effects of Chinese herbal medicines for treatment of urolithiasis: a review. Chin. Herb. Med. 15, 526–532. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2023.09.001
Jiang, J., Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Chang, Q., Zhao, Y., Guo, C., et al. (2023b). Prevalence of diabetes in patients with hyperuricemia and gout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Diab. Rep. 23, 103–117. doi:10.1007/s11892-023-01506-2
Jin, Y. N., Lin, Z. J., Zhang, B., and Bai, Y. F. (2018). Effects of chicory on serum uric acid, renal function, and GLUT9 expression in hyperuricaemic rats with renal injury and in vitro verification with cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 1764212. doi:10.1155/2018/1764212
Jing, P., Shi, M., Ma, L., and Fu, P. (2020). Mechanistic insights of soluble uric acid-related kidney disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 27, 5056–5066. doi:10.2174/0929867326666181211094421
Johnson, R. J., Lanaspa, M. A., and Gaucher, E. A. (2011). Uric acid: a danger signal from the RNA world that may have a role in the epidemic of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiorenal disease: evolutionary considerations. Semin. Nephrol. 31, 394–399. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2011.08.002
Kang, D. H. (2014). “Uric acid and the kidney,” in Core concepts in parenchymal kidney disease. Editors F. C. Fervenza, J. Lin, S. Sethi, and A. K. Singh (New York, NY: Springer New York), 375–388. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8166-9_26
Kim, J., Li, S., Zhang, S., and Wang, J. (2022). Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 17, 53–69. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2021.05.006
Kumar, A. N., Aruna, P., Naidu, J. N., Kumar, R., and Srivastava, A. K. (2015). Ürik Asidin Antioksidan ve Pro-Oksidan Özellikleri ile İlgili Kavram ve Tartışmalarının Derlemesi. Arşiv Kaynak Tarama Dergisi 24, 19. doi:10.17827/aktd.53469
La, M. X., and Tai, B. (2018). Clinical efficacy analysis of Tibetan medicine 15-flavour Yunpeng pill on arthritis. CJEM 24, 11. doi:10.16041/j.cnki.cn15-1175.2018.02.009
Lai, J. H., Luo, S. F., Hung, L. F., Huang, C. Y., Lien, S. B., Lin, L. C., et al. (2017). Physiological concentrations of soluble uric acid are chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory. Sci. Rep. 7, 2359. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-02640-0
Li, D., Tang, Q., Yang, M., Xu, H., Zhu, M., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023a). Plant-derived exosomal nanoparticles: potential therapeutic for inflammatory bowel disease. Nanoscale Adv. 5, 3575–3588. doi:10.1039/D3NA00093A
Li, K., Ma, Y., Xia, X., Huang, H., Li, J., Wang, X., et al. (2023b). Possible correlated signaling pathways with chronic urate nephropathy: a review. Med. (Baltimore) 102, e34540. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000034540
Li, Q. Y., Lin, L. B., Yang, X. J., Tan, C. Y., and Deng, X. Y. (2021). Current status of microbial fermentation of traditional Chinese medicine herbs. Microbiol. China 48, 2232–2244. doi:10.13344/j.microbiol.china.201133
Li, X., Jin, W., Zhang, W., and Zheng, G. (2022a). The inhibitory kinetics and mechanism of quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside and chlorogenic acid derived from Smilax China L. EtOAc fraction on xanthine oxidase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 213, 447–455. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.05.188
Li, X., Wu, D., Niu, J., Sun, Y., Wang, Q., Yang, B., et al. (2021b). Intestinal flora: a pivotal role in investigation of traditional Chinese medicine. Am. J. Chin. Med. 49, 237–268. doi:10.1142/S0192415X21500130
Li, X. Q., Gu, Y. Q., Jiang, D., Qiu, Y., Ji, W., and Shi, Y. Q. (2022b). Clinical observation on the treatment of uric acid nephropathy with Cheng's Bixiefenqing decoction. J. Yunnan Univ. Chin. Med. 45, 8–11. doi:10.19288/j.cnki.issn.1000-2723.2022.02.003
Li, Y., Li, L., Tian, J., Zheng, F., Liao, H., Zhao, Z., et al. (2022c). Insoluble fiber in barley leaf attenuates hyperuricemic nephropathy by modulating gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids. Foods 11, 3482. doi:10.3390/foods11213482
Li, Y., Zheng, F., Zhong, S., Zhao, K., Liao, H., Liang, J., et al. (2024). Protecting against ferroptosis in hyperuricemic nephropathy: the potential of ferrostatin-1 and its inhibitory effect on URAT1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 971, 176528. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176528
Liang, D., Yong, T., Diao, X., Chen, S., Chen, D., Xiao, C., et al. (2021). Hypouricaemic and nephroprotective effects of Poria cocos in hyperuricemic mice by up-regulating ATP-binding cassette super-family G member 2. Pharm. Biol. 59, 275–286. doi:10.1080/13880209.2021.1885450
Lin, X., Shao, T., Huang, L., Wen, X., Wang, M., Wen, C., et al. (2020). Simiao decoction alleviates gouty arthritis by modulating proinflammatory cytokines and the gut ecosystem. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 955. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00955
Lin, X. H. (2022). Study on the mechanism of intervention of kidney yang deficiency type hyperuricemia by Bi Xie Fen Qing drink based on gut flora. Ph.D. thesis. Wuhan (China): Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. doi:10.27134/d.cnki.ghbzc.2022.000027
Lin, Y., Chen, X., Ding, H., Ye, P., Gu, J., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Efficacy and safety of a selective URAT1 inhibitor SHR4640 in Chinese subjects with hyperuricaemia: a randomized controlled phase II study. Rheumatology 60, 5089–5097. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab198
Linnane, J. W., Burry, A. F., and Emmerson, B. T. (1981). Urate deposits in the renal medulla. Prevalence and associations. Nephron 29, 216–222. doi:10.1159/000182373
Liu, D., Zhou, B., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., Dai, X., Ji, Z., et al. (2022). Effectiveness of benzbromarone versus febuxostat in gouty patients: a retrospective study. Clin. Rheumatol. 41, 2121–2128. doi:10.1007/s10067-022-06110-5
Liu, Q. P., Yu, Y. R., Li, H. C., Wen, C. P., and He, Z. X. (2019). Regulation of Quzhuo Tongbi Preseription on gut microbiota of model rats with abnormal uric acid metabolism. China J. Tradition. Chin. Med. Pharm. 34, 1722–1726.
Liu, Y. F., Huang, Y., Wen, C. Y. Z., Zhang, J. J., Xing, G. L., Tu, S. H., et al. (2017). The effects of modified Simiao decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 6037037. doi:10.1155/2017/6037037
Luo, G. Y. (2024). Study on the efficacy of Si Miao Wan probiotic fermentation products and their improvement of urate nephropathy. Master’s thesis. Chengdu (China): Chengdu University. doi:10.27917/d.cnki.gcxdy.2024.000516
Lv, Q., Xu, D., Zhang, X., Yang, X., Zhao, P., Cui, X., et al. (2020). Association of hyperuricemia with immune disorders and intestinal barrier dysfunction. Front. Physiol. 11, 524236. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.524236
Maiuolo, J., Oppedisano, F., Gratteri, S., Muscoli, C., and Mollace, V. (2016). Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int. J. Cardiol. 213, 8–14. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.08.109
Mann, E. R., Lam, Y. K., and Uhlig, H. H. (2024). Short-chain fatty acids: linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 24, 577–595. doi:10.1038/s41577-024-01014-8
Medicine, C. A. of C. (2024). Top 10 research achievements of traditional Chinese medicine in 2023. Sci. Traditional Chin. Med. 2, 255–259. doi:10.1097/st9.0000000000000052
Mehmood, A., Althobaiti, F., Zhao, L., Usman, M., Chen, X., Alharthi, F., et al. (2022). Anti-inflammatory potential of stevia residue extract against uric acid-associated renal injury in mice. J. Food Biochem. 46, e14286. doi:10.1111/jfbc.14286
Mehmood, A., Zhao, L., Wang, C., Hossen, I., Raka, R. N., and Zhang, H. (2019). Stevia residue extract increases intestinal uric acid excretion via interactions with intestinal urate transporters in hyperuricemic mice. Food Funct. 10, 7900–7912. doi:10.1039/C9FO02032B
Mehmood, A., Zhao, L., Wang, C., Hossen, I., Raka, R. N., and Zhang, H. (2020). Correction: stevia residue extract increases intestinal uric acid excretion via interactions with intestinal urate transporters in hyperuricemic mice. Food Funct. 11, 2764. doi:10.1039/D0FO90011G
Mei, Y., Dong, B., Geng, Z., and Xu, L. (2022). Excess uric acid induces gouty nephropathy through crystal formation: a review of recent insights. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 911968. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.911968
Meijers, B. K. I., and Evenepoel, P. (2011). The gut-kidney axis: indoxyl sulfate, p-cresyl sulfate and CKD progression. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 26, 759–761. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfq818
Meng, W., Chen, L., Ouyang, K., Lin, S., Zhang, Y., He, J., et al. (2023). Chimonanthus nitens Oliv. leaves flavonoids alleviate hyperuricemia by regulating uric acid metabolism and intestinal homeostasis in mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 12, 2440–2450. doi:10.1016/j.fshw.2023.03.011
Meng, Z., Yan, Y., Tang, Z., Guo, C., Li, N., Huang, W., et al. (2015). Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of rhein in hyperuricemic mice. Planta Med. 81, 279–285. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1396241
Omizo, H., Tamura, Y., Morimoto, C., Ueno, M., Hayama, Y., Kuribayashi-Okuma, E., et al. (2020). Cardio-renal protective effect of the xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat in the 5/6 nephrectomy model with hyperuricemia. Sci. Rep. 10, 9326. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-65706-6
Pan, L., Han, P., Ma, S., Peng, R., Wang, C., Kong, W., et al. (2020). Abnormal metabolism of gut microbiota reveals the possible molecular mechanism of nephropathy induced by hyperuricemia. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 10, 249–261. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2019.10.007
Peterson, L. W., and Artis, D. (2014). Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 14, 141–153. doi:10.1038/nri3608
Ponticelli, C., Podestà, M. A., and Moroni, G. (2020). Hyperuricemia as a trigger of immune response in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 98, 1149–1159. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.056
Qu, Q. S., Li, Z. X., Zhou, Q., Yang, C. T., Shi, X. Y., and Qiao, Y. J. (2023). Research progress on fermented traditional Chinese medicine and exploration of the ‘fermentation compatibility’ theory. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 54, 2262–2273. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2023.07.027
Ren, Q., Cheng, L., Guo, F., Tao, S., Zhang, C., Ma, L., et al. (2021). Fisetin improves hyperuricemia-induced chronic kidney disease via regulating gut microbiota-mediated tryptophan metabolism and aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 10932–10942. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03449
Sautin, Y. Y., Nakagawa, T., Zharikov, S., and Johnson, R. J. (2007). Adverse effects of the classic antioxidant uric acid in adipocytes: NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidative/nitrosative stress. Am. J. Physio.Cell. Physio. 293, C584–C596. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00600.2006
Selvaraj, S., and Gurumurthy, K. (2023). An overview of probiotic health booster-kombucha tea. Chin. Herb. Med. 15, 27–32. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2022.06.010
Shan, B., Chen, T., Huang, B., Liu, Y., and Chen, J. (2021). Untargeted metabolomics reveal the therapeutic effects of Ermiao wan categorized formulas on rats with hyperuricemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 281, 114545. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114545
Sharaf El Din, U. A. A., Salem, M. M., and Abdulazim, D. O. (2017). Uric acid in the pathogenesis of metabolic, renal, and cardiovascular diseases: a review. J. Adv. Res. 8, 537–548. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2016.11.004
Shen, L., Liu, L., and Ji, H. F. (2017). Regulative effects of curcumin spice administration on gut microbiota and its pharmacological implications. Food & Nutr. Res. 61, 1361780. doi:10.1080/16546628.2017.1361780
Shi, W., Li, Z., Gu, Z. L., Huang, H. Z., Hu, X. G., Han, B., et al. (2016). Effects of the pairing of Rhizoma Pinelliae and Rhizoma Cinnamomum Cassiae on chronic hyperuricaemia and expression of renal and intestinal uric acid transporters in rats. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulas 22, 107–112. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2016020107
Shi, X., Zhao, T., Da Silva-Júnior, E. F., Zhang, J., Xu, S., Gao, S., et al. (2022). Novel urate transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitors: a review of recent patent literature (2020-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 32, 1175–1184. doi:10.1080/13543776.2022.2165911
So, A., and Thorens, B. (2010). Uric acid transport and disease. J. Clin. Invest. 120, 1791–1799. doi:10.1172/JCI42344
Song, S., Fan, M., Wen, X., Shi, X., Lou, Y., He, Z., et al. (2023). Integrated network pharmacology and gut microbiome analysis to reveal the mechanism of Qu-Zhuo-Tong-Bi decoction against hyperuricemia and gout. J. Ethnopharmacol. 316, 116736. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116736
Su, S., Wang, X., Xi, X., Zhu, L., Chen, Q., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Phellodendrine promotes autophagy by regulating the AMPK/mTOR pathway and treats ulcerative colitis. J. Cell. Mol. Medi 25, 5707–5720. doi:10.1111/jcmm.16587
Sui, Y., Xu, D., and Sun, X. (2023). Identification of anti-hyperuricemic components from Coix seed. Food Biosci. 52, 102461. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102461
Sun, W., Zhu, J., Qin, G., Huang, Y., Cheng, S., Chen, Z., et al. (2023). Lonicera japonica polysaccharides alleviate D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and restore gut microbiota in ICR mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 245, 125517. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125517
Tan, P. K., Liu, S., Gunic, E., and Miner, J. N. (2017). Discovery and characterization of verinurad, a potent and specific inhibitor of URAT1 for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Sci. Rep. 7, 665. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00706-7
Taniguchi, T., Ashizawa, N., Matsumoto, K., Saito, R., Motoki, K., Sakai, M., et al. (2019). Pharmacological evaluation of dotinurad, a selective urate reabsorption inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 371, 162–170. doi:10.1124/jpet.119.259341
Thomas, S. P., and Denu, J. M. (2021). Short-chain fatty acids activate acetyltransferase p300. Elife 10, e72171. doi:10.7554/eLife.72171
Tseng, Y. S., Wu, W. B., Chen, Y., Lo Yang, F., and Ma, M. C. (2020). Small intestine resection increases oxalate and citrate transporter expression and calcium oxalate crystal formation in rat hyperoxaluric kidneys. Clin. Sci. 134, 2565–2580. doi:10.1042/CS20200973
Wang, K., Wu, S. S., Li, P., Xiao, N., and Du, B. (2022a). Effects of Poria cocos on renal injury and intestinal flora in hyperuricemia rats. Food Sci. 43, 171–179. doi:10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211218-213
Wang, R., Hu, B., Ye, C., Zhang, Z., Yin, M., Cao, Q., et al. (2022b). Stewed Rhubarb Decoction ameliorates adenine-induced chronic renal failure in mice by regulating gut microbiota dysbiosis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 842720. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.842720
Wang, R., Lin, F., Ye, C., Aihemaitijiang, S., Halimulati, M., Huang, X., et al. (2023a). Multi-omics analysis reveals therapeutic effects of Bacillus subtilis-fermented Astragalus membranaceus in hyperuricemia via modulation of gut microbiota. Food Chem. 399, 133993. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133993
Wang, S., Fang, Y., Yu, X., Guo, L., Zhang, X., and Xia, D. (2019). The flavonoid-rich fraction from rhizomes of Smilax glabra Roxb. ameliorates renal oxidative stress and inflammation in uric acid nephropathy rats through promoting uric acid excretion. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 111, 162–168. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.050
Wang, S. N., Qiao, M., and Zhang, S. X. (2023b). Effects of Yi Yi Fu Zi Bai Jiang San on pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors and gut microbiota in patients with chronic ulcerative colitis. Hubei J. Traditional Chin. Med. 45, 7–11.
Wang, T., Fei, J. D., Nie, S. F., and Li, L. (2020a). The effect of Coix seed oil on gut microbiota and inflammatory factors in mice. China Med. Her. 17, 31–35. doi:10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2020.36.009
Wang, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, B., Nie, A., and Bian, M. (2017). Cichorium intybus L. promotes intestinal uric acid excretion by modulating ABCG2 in experimental hyperuricemia. Nutr. Metab. (Lond) 14, 38. doi:10.1186/s12986-017-0190-6
Wang, Y., Lin, Z. J., Bian, M., and Zhang, B. (2018). The impact of Vi medicine Cichorium extract on intestinal barrier in the state of hyperuricemia. China J. Tradition. Chin. Med. 33, 1718–1723.
Wang, Y., Lin, Z. J., Qu, C. C., Zou, L. N., and Zhang, B. (2020c). Study on the “gut-kidney” uric acid excretion mediated by oxidative stress in hyperuricemic rats. J. Beijing Univ. Chin. Med. 43, 310–316. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2157.2020.04.008
Wang, Y., Lin, Z. J., and Zhang, B. (2020b). Study on the improvement of 'gut-kidney' uric acid excretion mediated by Chinese herbal medicine Cichorium intybus under oxidative stress and inflammatory conditions. China J. Traditional Chin. Med. 35, 2552–2557.
Weaver, D. J. (2019). Uric acid and progression of chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. (Berlin, Germany) 34, 801–809. doi:10.1007/s00467-018-3979-2
Wei, L. Y., Hao, D. W., Hou, X. T., Wei, L. Z., Qin, Z., Yang, X., et al. (2023). Progress in clinical application and pharmacological research of Yi Yi Fu Zi Bai Jiang San. China J. Chin. Materia Medica 48, 4893–4901. doi:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230601.503
Wei, Z., Xu, C., Liu, S., Song, F., Liu, Z., and Qu, X. (2018). Metabonomics study of the effects of traditional Chinese medicine formula Ermiaowan on hyperuricemic rats. J Sep. Sci. 41, 560–570. doi:10.1002/jssc.201700985
Wen, X., Lou, Y., Song, S., He, Z., Chen, J., Xie, Z., et al. (2021). Qu-Zhuo-Tong-Bi decoction alleviates gouty arthritis by regulating butyrate-producing bacteria in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 610556. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.610556
Wu, F., Chen, C., Lin, G., Wu, C., Xie, J., Lin, K., et al. (2024). Caspase-11/GSDMD contributes to the progression of hyperuricemic nephropathy by promoting NETs formation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 81, 114. doi:10.1007/s00018-024-05136-z
Wu, J., Wei, Z., Cheng, P., Qian, C., Xu, F., Yang, Y., et al. (2020). Rhein modulates host purine metabolism in intestine through gut microbiota and ameliorates experimental colitis. Theranostics 10, 10665–10679. doi:10.7150/thno.43528
Wu, X., Liu, J., Zhang, J., Liu, H., Yan, M., Liang, B., et al. (2016). Folic acid reverses uric acid crystal-induced surface OAT1 internalization by inhibiting RhoA activity in uric acid nephropathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 13, 2385–2392. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.4837
Wu, X., Zhang, J., Liu, T., Yan, M., Liu, H., Xie, H., et al. (2015). Uric acid crystal could inhibit Numb-induced URAT1 lysosome degradation in uric acid nephropathy. J. Physiol. Biochem. 71, 217–226. doi:10.1007/s13105-015-0399-7
Xiang, H., Zuo, J., Guo, F., and Dong, D. (2020). What we already know about rhubarb: a comprehensive review. Chin. Med. 15, 88. doi:10.1186/s13020-020-00370-6
Xie, H.C., Zhang, B.H., Ai, M.J., Li, N., He, P.K., Yan, H.X., et al. (2022). Exploring the mechanism of action of Tibetan medicine Shi Wu Wei Ru Peng pills against hyperuricemia nephropathy based on gut microbiota and systematic pharmacology. Chin. Tradition. Herb. Drugs 53, 6068–6082. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.19.013
Xie, S., Fang, L., Deng, N., Shen, J., Tan, Z., and Peng, X. (2024). Targeting the gut-kidney axis in diarrhea with kidney-yang deficiency syndrome: the role of Sishen pills in regulating TMAO-mediated inflammatory response. Med. Sci. Monit. 30, e944185. doi:10.12659/MSM.944185
Xie, Z. J., Wu, H. X., Jing, X. Q., Li, X. Y., Li, Y. S., Han, Y. M., et al. (2017). Hypouricemic and arthritis relapse-reducing effects of compound tufuling oral-liquid in intercritical and chronic gout: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter randomized trial. Med. (Baltimore) 96, e6315. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000006315
Xu, K. Y., Xia, G. H., Lu, J. Q., Chen, M. X., Zhen, X., Wang, S., et al. (2017). Impaired renal function and dysbiosis of gut microbiota contribute to increased trimethylamine-N-oxide in chronic kidney disease patients. Sci. Rep. 7, 1445. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-01387-y
Xu, L., Cheng, J., Lu, J., Lin, G., Yu, Q., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation to clarify the anti-hyperuricemia mechanism of cortex phellodendri in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 964593. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.964593
Xu, X., Li, C., Zhou, P., and Jiang, T. (2016). Uric acid transporters hiding in the intestine. Pharm. Biol. 54, 3151–3155. doi:10.1080/13880209.2016.1195847
Xu, X., Wang, H., Guo, D., Man, X., Liu, J., Li, J., et al. (2021). Curcumin modulates gut microbiota and improves renal function in rats with uric acid nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 43, 1063–1075. doi:10.1080/0886022X.2021.1944875
Yamada, N., Iwamoto, C., Kano, H., Yamaoka, N., Fukuuchi, T., Kaneko, K., et al. (2016). Evaluation of purine utilization by Lactobacillus gasseri strains with potential to decrease the absorption of food-derived purines in the human intestine. Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids 35, 670–676. doi:10.1080/15257770.2015.1125000
Yang, H. T., Xiu, W. J., Liu, J. K., Yang, Y., Hou, X. G., Zheng, Y. Y., et al. (2021). Gut microbiota characterization in patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia: probiotics increased. Bioengineered 12, 7263–7275. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1976897
Yang, L., Wang, B., Ma, L., and Fu, P. (2022). Traditional Chinese herbs and natural products in hyperuricemia-induced chronic kidney disease. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 971032. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.971032
Yang, Q., Wang, Q., Deng, W., Sun, C., Wei, Q., Adu-Frimpong, M., et al. (2019). Anti-hyperuricemic and anti-gouty arthritis activities of polysaccharide purified from Lonicera japonica in model rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 123, 801–809. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.077
Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., Wang, F., Li, M., Wang, Q., et al. (2023). Chinese herbal medicines for treating ulcerative colitis via regulating gut microbiota-intestinal immunity axis. Chin. Herb. Med. 15, 181–200. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2023.03.003
Yasutake, Y., Tomita, K., Higashiyama, M., Furuhashi, H., Shirakabe, K., Takajo, T., et al. (2017). Uric acid ameliorates indomethacin-induced enteropathy in mice through its antioxidant activity. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 32, 1839–1845. doi:10.1111/jgh.13785
Yin, W., Zhou, Q. L., OuYang, S. X., Chen, Y., Gong, Y. T., and Liang, Y. M. (2019). Uric acid regulates NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway and further induces vascular endothelial cells injury in early CKD through ROS activation and K+ efflux. BMC Nephrol. 20, 319. doi:10.1186/s12882-019-1506-8
Yu, D. H., Wang, X. F., Wang, Y., Yuan, J., and Liu, S. M. (2023). Effects of total saponins from tripterygium wilfordii on intestinal microbiota and short-chain fatty acid metabolism in hyperuricemic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 51, 27–33. doi:10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392.230144
Yu, K. H., Chen, D. Y., Chen, J. H., Chen, S. Y., Chen, S. M., Cheng, T. T., et al. (2018a). Management of gout and hyperuricemia: multidisciplinary consensus in Taiwan. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 21, 772–787. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.13266
Yu, Y., Liu, Q., Li, H., Wen, C., and He, Z. (2018b). Alterations of the gut microbiome associated with the treatment of hyperuricaemia in male rats. Front. Microbiol. 9, 2233. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.02233
Zhang, C., Li, L., Zhang, Y., and Zeng, C. (2020). Recent advances in fructose intake and risk of hyperuricemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 131, 110795. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110795
Zhang, C., Song, Y., Chen, L., Chen, P., Yuan, M., Meng, Y., et al. (2022a). Urolithin A attenuates hyperuricemic nephropathy in fructose-fed mice by impairing STING-NLRP3 axis-mediated inflammatory response via restoration of parkin-dependent mitophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 907209. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.907209
Zhang, F., Wu, R., Liu, Y., Dai, S., Xue, X., Li, Y., et al. (2023a). Nephroprotective and nephrotoxic effects of Rhubarb and their molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 160, 114297. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114297
Zhang, G. J., Liu, J. H., and Shen, Y. (2022b). Effect of Simiao derived formula on the gut microbiota of hyperuricemic rats. China Pharm. 31, 45–49. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2022.20.012
Zhang, M., Zhu, X., Wu, J., Huang, Z., Zhao, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2022c). Prevalence of hyperuricemia among Chinese adults: findings from two nationally representative cross-sectional surveys in 2015-16 and 2018-19. Front. Immunol. 12, 791983. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.791983
Zhang, W., Cui, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, S., Yang, A., Li, X., et al. (2022d). Astragalus membranaceus ultrafine powder alleviates hyperuricemia by regulating the gut microbiome and reversing bile acid and adrenal hormone biosynthesis dysregulation. Arabian J. Chem. 15, 103970. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103970
Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Dai, X., Liu, T., Liu, Y., Shi, H., et al. (2023b). Simiao San alleviates hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and JAK2/STAT3 signaling in hyperuricemia mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 312, 116530. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116530
Zhang, Y. Q., Chen, J. W., Ye, B. W., Hao, Z. H., and Dai, H. (2022e). Si Miao Wan upregulates the expression of ABCG2 in the small intestine to promote intestinal uric acid excretion in hyperuricemic rats. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 28, 33–39. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20221601
Zhao, F. F. (2023). Clinical efficacy study of Yi Yi Fu Zi Bai Jiang San on hyperuricemia patients in stages CKD1-3. Master’s thesis. Xuhui (China): Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. doi:10.27320/d.cnki.gszyu.2020.000951
Zhao, L., Qi, Z., Yi, L., Li, J., Cui, Y., Ur Rehman, F., et al. (2021). The interaction between gut microbiota and flavonoid extract from Smilax glabra Roxb. and its potent alleviation of fatty liver. Food Funct. 12, 7836–7850. doi:10.1039/d1fo00727k
Zhao, Y., Chen, F., Wu, W., Sun, M., Bilotta, A. J., Yao, S., et al. (2018). GPR43 mediates microbiota metabolite SCFA regulation of antimicrobial peptide expression in intestinal epithelial cells via activation of mTOR and STAT3. Mucosal Immunol. 11, 752–762. doi:10.1038/mi.2017.118
Zhao, Z. X., Tang, X. H., Jiang, S. L., Pang, J. Q., Xu, Y. B., Yuan, D. D., et al. (2022). Astragaloside IV improves the pharmacokinetics of febuxostat in rats with hyperuricemic nephropathy by regulating urea metabolism in gut microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1031509. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1031509
Zhou, P. (2017). Molecular mechanism of emodin intervention in uric acid metabolism based on intestinal transporters. Master’s thesis. Quanzhou (China): Huaqiao University.
Zhou, X., Zhang, B., Zhao, X., Lin, Y., Wang, J., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Chlorogenic acid supplementation ameliorates hyperuricemia, relieves renal inflammation, and modulates intestinal homeostasis. Food Funct. 12, 5637–5649. doi:10.1039/D0FO03199B
Zhu, C. X. (2018). Study on the mechanism of the effective component compatibility of Polygonum cuspidatum and Cinnamomum cassia on hyperuricemia and its renal protection. Master’s thesis. Guangzhou (China): Guangdong Pharmaceutical University.
Zou, C., Wu, Y. C., Luo, L., Luo, Q., Lu, Z. Y., and Liu, X. S. (2012). Clinical study on the impact of traditional Chinese medicine rhubarb enema on the gut microbiome and intestinal barrier function in stage 5 chronic kidney disease (non-dialysis). Liaoning J. Traditional Chin. Med. 39, 1309–1311. doi:10.13192/j.ljtcm.2012.07.116.zouch.004
Keywords: hyperuricemic nephropathy, gut microbiota, urate transporters, immuno-inflammatory response, traditional Chinese medicine
Citation: Wang T, Li L, Liu L, Tan R, Wu Q, Zhu X, Hua H, Dai Y, Li H, Mao J, Zhao J and Yin Z (2025) Overview of pharmacodynamical research of traditional Chinese medicine on hyperuricemic nephropathy: from the perspective of dual-regulatory effect on the intestines and kidneys. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1517047. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1517047
Received: 25 October 2024; Accepted: 28 March 2025;
Published: 08 April 2025.
Edited by:
Duuamene Nyimanu, University of Kansas Medical Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Aabid Hussain, Cleveland Clinic, United StatesLi Li, Southern Medical University, China
Afsana Naaz, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Li, Liu, Tan, Wu, Zhu, Hua, Dai, Li, Mao, Zhao and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junning Zhao, emFybXlAMTg5LmNu; Zhujun Yin, NTA2NTkxNjI5QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Ting Wang
Ting Wang Li Li2
Li Li2 Li Liu
Li Liu Ruirong Tan
Ruirong Tan Xin Zhu
Xin Zhu Junning Zhao
Junning Zhao Zhujun Yin
Zhujun Yin