
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol. , 24 February 2025
Sec. Neuropharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1516601
This article is part of the Research Topic Neuropharmacological Intervention for Severe Mental Illness and Suicide Prevention View all 10 articles
Atherosclerosis (AS)-related cardiovascular disease and depression are often comorbid, with patients with cardiovascular disease facing an increased risk of depression, which worsens AS. Both diseases are characterized by oxidative stress and lipid metabolism disorders. Ferroptosis, a form of cell death characterized by iron overload and harmful lipid peroxide accumulation, is found in various diseases, including AS and depression. Consistent with the iron deposition and lipid peroxidation (LPO) that characterize the ferroptosis mechanism, disturbances in iron and lipid metabolism are also crucial pathogenic mechanisms in AS and depression. The comorbid mechanisms are complex, posing challenges for clinical treatment. Chinese herbs hold significant potential owing to their multi-target pharmacological effects. Therefore, this review aims to investigate iron overload, LPO, and ferroptosis across various cell types, the shared pathogenesis of AS and depression with ferroptosis, and research on Chinese herbal medicine targeting ferroptosis in the treatment of anti-AS co-depression. This provides a comprehensive understanding of AS co-depression disease from the perspective of ferroptosis.
Atherosclerosis (AS), the pathological basis of cardiovascular disease, is a threat to human life and health. According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular disease accounts for up to 17.9 million deaths annually, representing approximately 30% of global mortality (Herrington et al., 2016; Tsao et al., 2023). AS is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by endothelial cell damage, lipid accumulation within arterial walls, smooth muscle cell growth, and foam cell formation. Depression, a mood disorder characterized primarily by persistent feelings of sadness and anhedonia, arises from diverse causes. It has become a significant public health concern, with a global prevalence rate of 4.4% (Monroe and Harkness, 2022; WHO, 2017). Extensive research has established a strong relationship between depression and cardiovascular disease (Hare et al., 2014; Kawada, 2017; Li C. et al., 2020). Meta-analyses highlight the profound detrimental effect of depression on the development and outcomes of cardiovascular disease (Krittanawong et al., 2023). Similarly, with a co-prevalence of 17%–47%, depression is highly prevalent among individuals with cardiovascular disease (Mavrides and Nemeroff, 2013). Data from a recent U.S. health survey reveals a significant positive connection between adult depression and plasma AS index (Ye et al., 2024). Furthermore, evidence from multi-omics studies (Huang et al., 2023), Mendelian randomization analyses (Lei et al., 2023; Shakt et al., 2024), and the vascular depression hypothesis (Alexopoulos et al., 1997) underscores the close relationship between AS and depression. Despite growing evidence that they occur simultaneously and affect each other, the mechanisms linking AS and depression are still poorly understood, which complicates effective treatment strategies.
The interaction mechanism between AS and depression is highly complex, involving multiple potential mechanisms, including inflammation (Chrysohoou et al., 2018; Halaris, 2017), hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction (Gu et al., 2012), endothelial dysfunction (Chrysohoou et al., 2018; Paranthaman et al., 2012), immune responses (Mousa et al., 2022), autonomic nervous system dysfunction (Pizzi et al., 2010), and intestinal flora and metabolite dysfunction (Liao et al., 2023). Lipid metabolism disorders play a crucial role, with numerous studies confirming alterations in lipid composition in the plasma and brain of patients with AS and depression. High-fat diets disrupt brain lipid metabolism and promote neuroinflammation, increasing depression risk (Wang A. et al., 2023). Mendelian randomization analysis reveals a causal connection between altered triglyceride, cholesterol levels, and depressive phenotypes (So et al., 2021). Elevated oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL) levels contribute to the development of major depression by inducing neuroinflammation (Almulla et al., 2023).
Additionally, a mouse model of AS-related depression was developed using APOE−/− mice to investigate the underlying pathogenesis. Differential phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of the model mice are closely linked to ferroptosis (Hu et al., 2022). PE, the second most abundant phospholipid in living organisms, plays a crucial role in depression. Disruptions in PE metabolism can impair mitochondrial activity in the brain, contributing to depressive symptoms (Modica-Napolitano and Renshaw, 2004). Furthermore, individuals with seasonal depression exhibit altered plasma PE levels (Otoki et al., 2017). The role of ferroptosis in AS has also been extensively demonstrated (Fang et al., 2023). Stockwell further highlights its significance in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases (Stockwell, 2022). Therefore, the study of AS co-depression diseases from the perspective of ferroptosis has a sufficient theoretical and experimental basis.
This review aims to summarize the mechanism of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic comorbid depression and to highlight the research progress on the use of Chinese medicine in treating this condition by targeting ferroptosis. Keywords included the following: “ferroptosis,” “iron death,” “atherosclerosis,” “depression,” “cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease,” “major depressive disorder,” and “Traditional Chinese medicine.” Searches were conducted using multiple online databases, including Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect, for English-language journal reports and articles published up to October 2024. References were manually screened from the extracted articles.
Cell death is fundamental to organismal growth, development, senescence, and death, involving mechanisms such as apoptosis, necrotic apoptosis, autophagy, cellular pyroptosis, and necrosis, each with distinct characteristics (Moujalled et al., 2021). Ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death distinct from apoptosis, was introduced by Dixon in 2012 (Dixon et al., 2012) and defined by the Cell Death Commission in 2018 (Galluzzi et al., 2018). The condition is characterized by redox imbalance and iron overload, with affected cells exhibiting smaller mitochondria, increased membrane density, and reduced cristae, while the nucleus shows minimal changes (Li J. et al., 2020). Cellular alterations include increased lipid peroxides, elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS), and reduced Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPX4) levels (Chen et al., 2021b). Ferroptosis affects tumor development and various disorders, including neurological, ischemic, and cardiovascular conditions (Fang et al., 2023) and depression (Chen et al., 2023). Furthermore, ferroptosis is regulated by various processes and small molecules, including iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation (LPO), the XC-GSH-GPX4 axis, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1), coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)-NAD(P)H pathway, guanosine triphosphate cycloheximide hydrolase 1, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)-dihydrofolate reductase pathway, autophagy, mitochondrial function, among others (Chen et al., 2021a; Song Y. H. et al., 2023).
Ferroptosis primarily arises from the excessive accumulation of ROS on the cell membrane owing to metabolic dysfunction. Lipid peroxides and their metabolites, such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynonenal, damage proteins, membrane integrity, and DNA structure, leading to cell membrane hyperpermeability and ferroptosis (Lei et al., 2022). Lipid peroxide accumulation results from enzymatic and non-enzymatic processes (Rochette et al., 2022). Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are converted into reactive lipid peroxides by fatty acid enzymes and through the Fenton reaction, which is driven by iron accumulation from disrupted iron metabolism.
Among the three families of lipid oxidases, lipoxygenase is crucial to the enzymatic processes driving ferroptosis. The other two families are cyclooxygenase and cytochrome P450. Lipoxygenase converts free PUFA into lipid oxides, which significantly affects iron redox reactions (Yang et al., 2016). PUFA oxidation-specific nonheme iron-containing enzymes are known as LOXs (Maheshwari, 2023). PE, derived from adrenoic acid (AdA) and arachidonic acid (AA), are key substrates for LPO. Metabolic abnormalities in PE directly influence lipid metabolic pathways involved in ferroptosis (Kagan et al., 2017).
The principal cause of ferroptosis is linked to the peroxidation of PUFAs (Gan, 2022) and PE (Amoscato et al., 2023), while monounsaturated fatty acids inhibit ferroptosis. Ferroptosis is caused by PE-AA/AdA-OOH, not by other phospholipid (PL)-OOH forms (Lei et al., 2019). The oxidation process of PE requires the involvement of ACSL4 (He et al., 2022) and LPCAT3 (Miura et al., 2021). PUFAs, particularly AA and adrenergic acid, are susceptible to oxidation owing to the weak C-H bonds in their diallyl group (Kagan et al., 2017). The LPO process proceeds as follows: Free AA/ADA is catalyzed by ACSL4 to form AA/AdA-CoA derivatives (Zhang H. L. et al., 2022). These AA/AdA-CoA derivatives are then synthesized with PE in the cell membrane by LPCAT3, producing AA/AdA-PE (Doll and Conrad, 2017). Finally, AA/AdA-PE undergoes oxidation through enzymatic and non-enzymatic pathways. The enzymatic pathway involves LOXs, while the non-enzymatic pathway is driven by hydroxyl radicals generated through the Fenton reaction. This ultimately leads to harmful lipid peroxide formation (Wang et al., 2021c).
The LPO process highlights ACSL4, LPCAT3, and LOXs as important targets for regulating ferroptosis. For instance, berberine inhibits endothelial ferroptosis and AS by suppressing ACSL4 expression (Hong et al., 2024). Xiaoyao San mitigates lipid metabolism disorder and depression in mice by inhibiting ACSL4 (Jiao et al., 2021). Myeloid LPCAT3 deficiency disrupts AA homeostasis in the liver, leading to metabolic imbalances and triglyceride accumulation (Bourgeois et al., 2021). Additionally, LOX inhibition reduces neuroinflammation and LPO by inhibiting inflammasome activation (Cakir-Aktas et al., 2023).
Ferroptosis is mainly induced by inhibiting glutathione production, with the System Xc -/GSH/GPX4 pathway playing a key role in preventing LPO. The Xc-system facilitates intracellular cysteine (Cys) absorption, which is converted into glutathione. While the Xc-system is considered the primary source of Cys, its inhibition can also lead to Cys production through the sulfur transfer pathway. Both pathways help maintain intracellular Cys levels. However, Xc-system inhibition results in glutathione and Cys deficiencies, triggering ferroptosis (Li F. J. et al., 2022). This underscores the pivotal role of the Xc-system in preserving intracellular redox balance.
GPX4, also known as phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase, consists of approximately 170 amino acids and has a molecular weight of about 19 kDa. Numerous GPX family members, including GPX1–GPX8, are found in mammals (Nishida Xavier da Silva et al., 2022). However, only GPX4 scavenges membrane lipid hydroperoxides. This feature is attributed to its distinct amino acid composition and spatial arrangement. GPX4 utilizes reduced GSH as a critical substrate and oxidizes it to GSSH while converting PLOOH to fatty alcohol to suppress the LPO process (Liu Y. et al., 2023). Targeted metabolomics reveals that GPX4 overexpression and knockdown influenced the lethality of 12 ferroptosis inducers, highlighting the role of Gpx4 in ferroptosis regulation (Lou et al., 2024). RAS-selective lethal 3 (RSL3) inhibits GPX4 by covalently binding to it, leading to lipid peroxide accumulation and ferroptosis induction. Glutathione deprivation converts GPX4-catalyzed peroxides to alcohols, leading to Cys deficiency, further inactivating GPX4 and promoting ferroptosis (Ursini and Maiorino, 2020). Targeting GPX4 can improve AS (Yang et al., 2024b) and depression (Qian et al., 2023).
The FSP1-CoQ10-NAD(P)H pathway is crucial in ferroptosis prevention, alongside the GPX4 pathway, the main defense mechanism. Apoptosis-inducing factor mitochondria-associated 2 (AIFM2), formerly FSP1, mitigates ferroptosis owing to GPX4 deletion. Ubiquinone (CoQ10) mediates this inhibition. FSP1 uses NAD(P)H, while the reduced form of ubiquinone captures lipid peroxyl radicals that cause LPO. Pharmacologically targeting FSP1 induces ferroptosis in various cancers, synergizing effectively with GPX4 inhibitors (Koppula et al., 2022). The FSP1-CoQ10-NAD(P)H pathway, alongside glutathione and GPX4, functions as an independent parallel mechanism to mitigate ferroptosis and PL peroxidation. In the absence of GPX4, FSP1 effectively inhibits PL peroxidation and ferroptosis by using NAD(P)H to convert oxidized ubiquinone into ubiquinol (Doll et al., 2019).
In this pathway, CoQ10 is crucial, and the inhibition of its synthesis leads to increased LPO (Arslanbaeva et al., 2022). CoQ10 is primarily synthesized in the mitochondria, though its exact origin remains unclear. In the absence of GPX4 activity, dihydroacetate dehydrogenase inhibits ferroptosis in mitochondria by enhancing CoQH2 production (Mao et al., 2021). Moreover, BH4 prevents ferroptosis by producing CoQH2, inhibiting LPO, and scavenging free radicals (Zhang G. et al., 2023). Targeting FSP1 can improve AS (Xie et al., 2022) and depression (Wu X. et al., 2024).
The MVA pathway is a key mechanism for inhibiting ferroptosis through interactions with the GSH-GPX4 and FSP1-CoQ10-NADPH pathways. It generates isoprenoid chemicals from acetyl coenzyme A. Acetyl coenzyme A condenses to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA), which is then converted to MVA by HMG-CoA reductase. MVA is further metabolized into isoprenoid compounds such as gibberellin A, cholesterol, and isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) (Lasunción et al., 2022). IPP is an intermediary molecule involved in ferroptosis regulation. Farnesyl phosphate synthetase converts IPP to farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), which is then converted into squalene by squalene synthase (SQS) and cyclized by squalene cyclase to produce cholesterol (Liang et al., 2023). IPP is crucial for synthesizing various biomolecules and, along with FPP, produces non-cholesterol compounds such as CoQ10 through the GGPS enzyme, which SQS inhibits (Chen et al., 2020). FIN56 induces ferroptosis by stimulating SQS and decreasing COQ10 production (Shimada et al., 2016).
Additionally, the MVA pathway is vital for GPX4 synthesis. Selenocysteine (Sec) must be incorporated into its catalytic center to enable its antioxidant function. This process requires IPP to activate isoprenyltransferase, which catalyzes the mutation of the Sec transporter RNA, facilitating GPX4 activity and maintenance (Jia et al., 2024). Consequently, FIN56 inhibits Sec integration into the catalytic subunit of GPX4, reducing its antioxidant capacity (Costa et al., 2023).
Iron is crucial for living organisms, and its deficiency can cause health issues. Intracellular iron is stored in two major forms—an unstable intracellular free ferrous iron pool and an inert form bound to ferritin (Fuhrmann and Brüne, 2022). Ferrous and ferric iron are forms of free iron, and excess Fe2⁺ can trigger the Fenton reaction, producing ROS (Bogdan et al., 2016) that induce ferroptosis and LPO. The importance of iron homeostasis is evident as the iron chelator deferoxamine effectively suppresses ferroptosis induced by intracellular iron overload (Costa et al., 2023). Additionally, iron is a cofactor for enzymes such as cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase and lipoxygenase, which synthesize lipid peroxides. Iron absorption, efflux, and cellular availability are crucial for ferroptosis.
Transferrin-bound trivalent iron binds to the transferrin receptor (TFR1), allowing direct cellular entry through endocytosis and converts it to ferrous iron through STEAP3. Ferrous iron is released by divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) and recycled into the cell membrane through TFR1 within the cellular labile iron pool. TFR1 expression is regulated by five iron-regulatory elements (IREs) in its 3′untranslated region. Under iron deficiency, iron-regulatory proteins (IRPs) bind to IREs to enhance TFR1 expression (Wang S. et al., 2024). Redox-active iron complexes within the unstable iron pool are stored in cells bound to ferritin, composed of light and heavy chain components. Ferritin stores free unstable iron. Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) enhances free iron levels by binding to ferritin-heavy chains and aiding its transport through the lysosome. Moreover, iron is exported through PROM2-mediated exocytosis or the FPN1/SLC40A1 efflux pump, forming multivesicular aggregates.
Ferroptosis can be inhibited by reducing iron uptake and using iron chelators. Conversely, transferrin removal inhibits ferroptosis, TFR1 upregulation increases susceptibility, and IRP2 inhibition confers cellular resistance (Jiang et al., 2021). Hepcidin, a liver-derived antimicrobial peptide, negatively regulates FPN1, leading to tissue iron overload and promoting ferroptosis, underscoring its crucial role in iron metabolism regulation. Typically, transferrin-bound iron predominates, but non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) can emerge in plasma during iron overload (Galy et al., 2024). NTBI comprises low molecular weight iron forms that can be absorbed and damage organs, unlike transferrin-bound iron. In summary, LPO pathways depend on intracellular iron metabolism, with disruptions leading to ferroptosis. The pathways and regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis are outlined. (Figure 1). Specific types of cell ferroptosis play a crucial role in AS co-depression diseases.
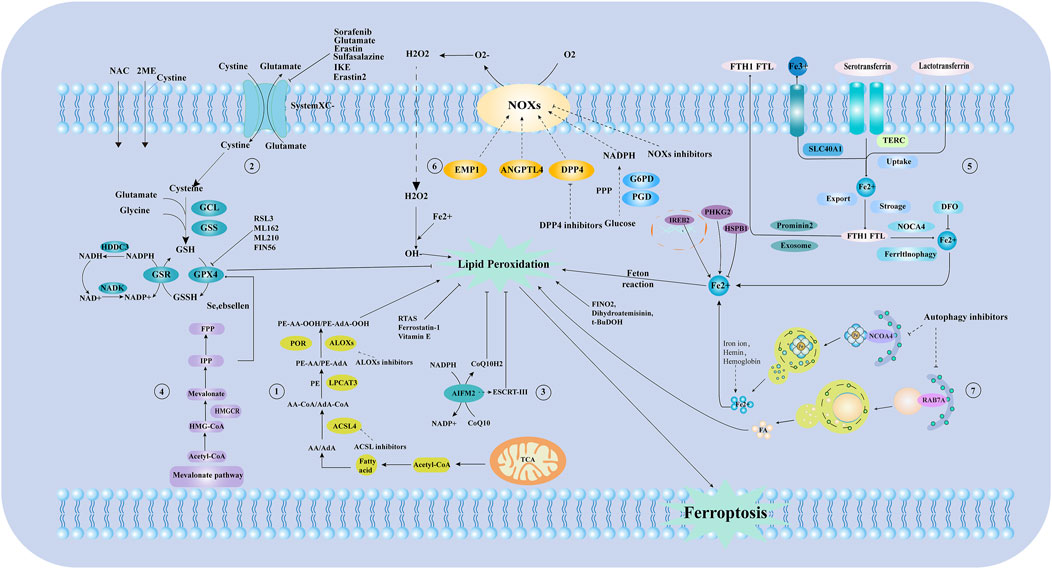
Figure 1. The mechanism of ferroptosis and iron metabolism. ① Lipid metabolic pathways. ② Xc-glutathione/glutathione peroxidase pathway. ③ Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1(FSP1) -Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)-NADPH pathway. ④ Mevalonate (MVA) pathway. ⑤ Process of iron metabolism. ⑥ Reactive oxygen species, free radical generation process. ⑦ The process of ferritin autophagy. NAC:N-Acetyl-L-cysteine; GCL: Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase; GSS: Glutathione Synthetase; GSH: Glutathione; GPX4: Glutathione Peroxidase 4; NADP: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NAD: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; IPP: Isopentenyl pyrophosphate; FPP: Farnesyl pyrophosphate; HMG-COA:3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase; Acetl-CoA: Acetoacetyl-CoA; AA/AdA: Arachidonic acid/Adrenic acid; ACSL4:long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; PE: Phosphatidyl ethanolamine; ALOXS: Arachidonate lipoxygenase; TCA: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle; AIFM2/FSP1:Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; EMP1: EPO mimetic peptide-1; ANGPTL4: Angiopoietin-Like Protein 4; DPP4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; G6PD: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; PGD: Phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase; FTH1 FTL: Ferritin Heavy Chain 1, Ferritin Light Chain; TERC: Telomerase RNA Component; NOCA4: Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 4; DFO: Deferoxamine; RSL3: GSH peroxidase 4 inhibitors; HDDC3: HD Domain Containing 3; NADK: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) kinase; HMGCR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coA reductase; GSR: glutathione-disulfide reductase; 2 ME: 2-Methoxyestradiol; T-BuDOH: t-Butyl hydroperoxide; RAB7A:ras-related protein Rab-7a; ESCRT-III: Endosomal sorting complex required for transport III; CoQ10H2: Reduced coenzyme Q10; NOXs: NADPH Oxidases; SLC40A1: Solute carrier family 40 member 1; IREB2: Iron-Responsive Element Binding Protein 2; PHKG2: Phosphorylase Kinase Catalytic Subunit Gamma 2; HSPB1:Heat shock protein beta-1; PPP: pentose phosphate pathway; POR: cytochrome p450 oxidoreductase; CoQ10: Coenzyme Q10; System Xc -: Cystine/glutamate antiporter system; NCOA4:Nuclear receptor coactivator 4.
AS begins with vascular endothelial dysfunction, characterized by increased permeability, leukocyte adhesion, heightened inflammation, and accelerated plaque and thrombus formation. The negative effects of ferroptosis in endothelial cells during AS are well established. Bai et al. demonstrated that Ox-LDL, a potent pro-atherosclerotic factor, induces ferroptosis in mouse aortic endothelial cells by increasing iron deposition, lipid peroxides, and ROS while decreasing GPX4 levels. High-fat-fed ApoE−/− mice exhibit larger atherosclerotic plaques, severe ferroptosis, increased NOX production, and reduced GSH and xCT expression in the thoracic aorta compared to wild-type mice (Bai et al., 2020). Li et al. showed that injecting endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing miR-199a-3p into high-fat fed APOE mice reduced iron accumulation and LPO, increased xCT, GSH, and GPX4 levels in the aorta, and resulted in smaller atherosclerotic plaques (Li et al., 2021). Peng et al. identified a positive correlation between endothelial cell function and N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) from glucose metabolism. Neu5Ac facilitates SLC3A2 binding to ubiquitin, initiating P62-mediated degradation, which leads to LPO and ferroptosis in high-fat-fed ApoE−/− mice. This process is inhibited by Fer-1 (Xiang et al., 2023).
Iron accumulation from various sources significantly contributes to AS and vascular endothelial cell (VEC) ferroptosis. A key PL oxidation product present in atherosclerotic lesions is 1-palmitoyl-2-glutaryl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (PGPC). Chen et al. show that PGPC treatment of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) increases fatty acid binding protein-3 (FABP3), ROS, LPO, and ferrous iron levels. It disrupts mitochondrial membrane potential and reduces glutathione and GPX4 expression. Ferroportin-1, a ferroptosis inhibitor, countered these effects. PGPC triggers ferroptosis through the CD36 receptor, impairing endothelial function (Chen et al., 2024). Iron accumulation from ferritin autophagy worsens AS, damaging endothelial cells. HUVEC exposed to high doses of ionizing radiation exhibits increased ferritin autophagy through the p38/NCOA4 pathway, leading to elevated iron levels, increased lipid peroxidation, and decreased antioxidant protein expression (GPX4, Nrf2, xCT, and SLC3A2). This cascade in significant VECs injury and ferroptosis (Wu Z. et al., 2023).
Additionally, enhancing VEC antioxidant activity is crucial for preventing ferroptosis and improving AS. Tumor necrosis factor-related protein 13 (CTRP13) is crucial for antioxidant defense and endothelial function. Du et al. developed a model of Ox-LDL-induced ferroptosis in HUVECs, showing that CTRP13 intervention increased antioxidant enzyme expression, preventing AS and protecting endothelial cells from ferroptosis (Du J. et al., 2024). Gualou-Xiebai (GLXB) inhibits ferroptosis in high-fat-fed ApoE−/− mice by reducing mitochondrial damage, boosting glutathione and superoxide dismutase levels, and decreasing LPO and MDA levels. In vitro, GLXB mitigated erastin-induced ferroptosis, alleviating Ox-LDL-induced damage in HUVEC (Zhu L. et al., 2024). Qixian granule (QXG) is used to treat postmenopausal AS in women. Zhang et al. demonstrate that QXG inhibits GPX4 and FTH1-mediated ferroptosis by activating TRPML1 directly or through the GPER pathway, slowing AS progression. In vitro, QXG-treated serum prevents human aortic endothelial cells from proliferating, migrating, and inducing ROS and mitochondrial damage from Ox-LDL (Zhang et al., 2024).
Macrophage death exhibits a dual role in atherogenesis. During the early stages of AS, moderate macrophage death reduces inflammation and metalloproteinase secretion. Conversely, in advanced stages, uncontrolled macrophage death exacerbates inflammation, promotes the formation of lipid-rich necrotic cores, and destabilizes plaques (Susser and Rayner, 2022; Wang L. et al., 2023). Numerous studies show the role of macrophage ferroptosis in promoting AS. Interleukin-23p19 (IL-23p19) is associated with cardiovascular conditions, including AS. Lu et al. created a mouse model of cardiac remodeling using transverse aortic constriction (TAC) and observed increased IL-23p19 expression levels in the heart after surgery, probably from cardiac macrophages. Silencing IL-23p19 reduces ferroptosis and M1 macrophage polarization in mice with TAC, improving cardiac remodeling and function recovery (Lu et al., 2024). Furthermore, Luo et al. report that activating Nrf2 and enhancing its nuclear translocation can inhibit Ox-LDL-induced ferroptosis in macrophages and resist ferroptosis in ApoE−/− animals on a high-fat diet (Luo et al., 2024).
Erythrocyte phagocytosis and macrophage ferroptosis are essential triggers of AS. Advanced atherosclerotic plaques exhibit intra-plaque (IP) angiogenesis. The fragile and leaky nature of IP arteries releases erythrocytes, which are subsequently phagocytosed by macrophages. This process leads to increased intracellular iron levels, LPO, and apoptosis. In vitro studies show that erythrophagocytosis by macrophages induces atypical ferroptosis, potentially causing plaque instability. Elevated heme oxygenase 1 and ferritin levels observed during this process were reduced by the ferroptosis inhibitor UAMC-3203. Research by Pauline Prall and colleagues using ApoE−/− mice reveals a significant decrease in carotid plaque thickness after 20 weeks, especially in plaques with hemorrhage or IP angiogenesis. This was accompanied by reduced expression levels of ferritin and IP heme oxygenase 1. Therefore, erythrophagocytosis-induced ferroptosis contributes to the formation of larger atherosclerotic plaques, but this effect can be reversed by UAMC-3203 (Puylaert et al., 2023). Liu et al. developed a red-line Jak2VF-expressing hyperlipidemic erythropoietin receptor Cre mice. They observed that these mice exhibit elevated iron and 4-HNE levels, increased erythrocyte phagocytosis by plaque macrophages, and enhanced macrophage ferroptosis, leading to greater necrosis in atherosclerotic plaques. These effects were amplified by selective erythropoiesis activation and inhibited by the ferroptosis inhibitor liproxstatin-1, indicating that Jak2VF signaling accelerates AS by promoting macrophage ferroptosis and erythrocyte phagocytosis (Liu W. et al., 2022).
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are essential in the early and advanced stages of AS. They infiltrate lesions, enlarge them and form a fibrous cap over the necrotic core. VSMC death causes vascular inflammation, loss of extracellular matrix (ECM) and collagen, weakening of the fibrous cap, and ultimately plaque rupture (Grootaert and Bennett, 2021; Xu X. D. et al., 2022). Ferroptosis of VSMCs is also a significant part of AS. Xie et al. observed that Fer-1 affects TFR1, FTH, and FTL expression in VSMC, reducing iron accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions in vivo and in vitro. Evidence suggests that VSMC ferroptosis may help enhance atherosclerotic lesions. Fer-1 fails to enhance the p53/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway but improves the Nrf2/ferroptosis inhibitory protein 1 pathway, boosting resistance to LPO (You et al., 2023). Zhang et al. discovered that echinacea upregulates glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic (GCLC) and modifier (GCLM) subunits in VSMC, maintaining the GSH balance essential for preventing AS. This regulation also reduces ferroptosis and matrix remodeling, both contributors to AS, by regulating GSH production (Zhang et al., 2023c). Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1—a human cysteoaspartase paraprotein—induces ferroptosis in VSMCs through protein hydrolysis. A ferroptosis inhibitor reduces carotid artery neointimal plaques and AS in C57BL/6J and ApoE−/− mice, indicating that suppressing ferroptosis in VSMCs may alleviate proliferative vascular disease (Yan et al., 2023).
Foam cells are essential in developing atherosclerotic lesions, from initial stages to advanced plaques. Macrophages—the primary source of foam cells—proliferate in the arterial intima after pro-inflammatory activation by endothelial cells, allowing them to migrate across the endothelial barrier. A small portion of VSMC and endothelial cells can differentiate into macrophages, which may then become foam cells by engulfing lipids. VSMC can also develop into foam cells (Chistiakov et al., 2017; Maguire et al., 2019). During plaque formation, foam cell death—primarily from ferroptosis and autophagy—accelerates atherosclerotic plaque development. Insufficient autophagy inhibits Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defenses, promoting iron deposition and LPO, leading to ferroptosis (Peng et al., 2022). Li et al. used bioinformatics to explore the roles of ferroptosis and isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) in foam cell formation. They observed that ferritin-1 can reverse the increase in macrophage ferroptosis and IDH1 levels caused by Ox-LDL. Inhibiting IDH1 reduces damage and apoptosis in Ox-LDL-treated macrophages while increasing Nrf2 levels, thereby decreasing foam cell formation (Li B. et al., 2022). Su et al. treated THP-1 macrophages with ferric ammonium citrate (FAC) and Ox-LDL, using SRT1 to activate SIRT1720 and rapamycin along with chloroquine to modulate autophagy. They observed that FAC exposure increases lipid ROS levels, decreases GPX4 and SIRT1 expression, and elevates IL-1β and IL-18 levels while reducing foam cell activity compared to that of macrophage activity. These findings indicate that inhibiting ferroptosis in foam cells is essential for treating AS (Su et al., 2021).
In summary, ferroptosis in VECs, macrophages, VSMC, and foam cells contributes to AS. Treatment reduces ferroptosis levels in these cells and improves the condition, highlighting the importance of anti-ferroptosis strategies in the disease.
Brain cells are mainly involved in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes. Factors such as neuronal damage in the brain, inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, cell death, and altered neuroplasticity can influence depression (Malhi and Mann, 2018). Neurons are the fundamental structural and functional units of the nervous system. Studies show that iron-sag markers can be traced in cellular and animal models of neurodegenerative diseases (Cozzi et al., 2019). Fer-1 mitigates abnormal tsRNA expression profiles in the hippocampus tissues of the chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) mouse model. Additionally, in an in vitro assay, ferroptosis is associated with reduced expression of SLC7A11 and GPX4 proteins, as well as ROS accumulation in corticosterone-constructed hippocampal progenitor neurons (Li E. et al., 2023). Xu et al. observed that alcohol consumption causes neuronal injury in the hippocampal and prefrontal cortex of mice. The alcohol-treated group shows reduced levels of synapse-associated proteins. Alcohol increases the number of iron-positively stained cells and the expression of the TFR1 protein. Following iron staining, GPX4 expression is minimized in the alcohol group. Conversely, the ferroptosis inhibitor ferritin-1 significantly prevents alcohol-induced damage to neurons in vitro and reverses the expression of the proteins mentioned above (Xu C. et al., 2022). In CUMS animals, decreased ferritin light chain 1 and Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels are observed in the proteomics of hippocampal neurons, which are associated with hippocampal neuronal survival. Additionally, ferroptosis-associated proteins are differently expressed in these animals (Cao et al., 2021). Li et al. further demonstrated that enhancing hippocampal neuronal BDNF levels could prevent hippocampus neuronal ferroptosis and potentially enhance the antidepressant effects of electroconvulsive therapy (Li X. et al., 2023). The studies mentioned above highlight the significant roles that neuronal loss and ferroptosis play in depression.
Microglia make up approximately 0.5%–16.6% of the cells in the human central nervous system and are the sole remaining mononuclear phagocytes within the brain parenchyma (Askew et al., 2017). Microglia plays various roles in brain development, synaptic plasticity, neuronal synchronization, and neuroimmune homeostasis from embryo development to adulthood. They also interact with neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes via chemical signals or direct contact throughout the life cycle of an organism. Neuroinflammation progresses because of the combined effects of inflammation and microglial iron buildup, which can be inhibited to stop the progression of neuroinflammation (Liu S. et al., 2022). Depression is frequently accompanied by inflammation, and microglia are essential starting materials and controllers of the cynaroside (CNS) inflammatory cascade responses (Wang H. et al., 2022). Neuroinflammation is another significant mechanism in many neurodegenerative diseases and is often associated with persistent activation of microglia. Microglial energy metabolism is gaining prominence in neurodegenerative disorders, as numerous brain diseases are associated with changes in brain energy metabolism and constant inflammation. Moreover, energy metabolism strongly influences the inflammatory response of microglia (Aldana, 2019).
Inhibiting microglia ferroptosis to ameliorate CNS inflammation is a promising therapeutic tool for depression. Wang et al. utilized shRNA silencing of the microglial GPX4 gene to assess the anti-inflammatory effects of saikosaponin B2 (SSB2) in LPS-induced primary microglia and CUMS-induced mouse models of depression. Consequently, SSB2 exhibits anti-ferroptosis and anti-neuroinflammatory effects, attenuating the activation of the LPS-induced primary microglial TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in a GPX4-dependent manner (Wang et al., 2023c). Jiao et al. suggest that the antidepressant mechanism of Prowessan may involve the enhancement of the iron-death-associated PEBP1-GPX4 pathway. This pathway can control the expression of PEBP1, ERK1/2, GPX4, FTH1, ACSL4, and COX2, thereby enhancing the function of hippocampal astrocytes and microglial cells in CUMS model mice (Jiao et al., 2021). Yang et al. investigated the role of gallic acid in preventing ferroptosis in spinal microglial cells in rats with chronic pain and depression. They discovered that the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of gallic acid decrease tissue iron concentration, improve mitochondrial damage, inhibit the P2X7-ROS signaling pathway, and reverse behavioral changes in these rats (Yang et al., 2023) (Table 1).
Astrocytes—the most abundant and largest class of glial cells in the mammalian brain—maintain and divide neuronal cells, aid in creating the blood-brain barrier, and regulate the onset of several disease processes (Khakh and Sofroniew, 2015). In culture, astrocytes are observed to shield neurons from oxidants and excitotoxins. This neuroprotective effect is thought to result from their ability to absorb glutamate and recycle free radicals. Astrocytes are involved in numerous neurodegenerative disorders and can significantly influence depression. In Orai1 knockout mice, the LPS-induced depression-like behavior, including the helplessness and pleasure deficit, is improved in astrocytes (Novakovic et al., 2023). Mice subjected to 6 weeks of prolonged stress followed by 6 weeks of social isolation exhibit symptoms of depression, accompanied by elevated levels of astrocyte activation in the dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus regions of the hippocampus (Du Preez et al., 2021). Prenatal exposure to air pollution in rodents causes astrocyte degeneration, microglia activation, and disruption of the blood-brain barrier, leading to depressive tendencies in rats. These rats also show a twofold increase in hippocampus iron accumulation (Woodward et al., 2018).
Inhibition of astrocyte activation and ferroptosis ameliorates depression. CUMS depression model mice treated with the compound Chinese medicine XiaoYao San for 2 weeks showed a decrease in hippocampal body weight, total iron, and ferrous iron content. Changes were made in the concentrations of proteins associated with ferroptosis, including GPX4, FTH1, ACSL4, and COX2. The expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein—a marker of activated astrocytes—decreases, enhancing astrocyte glial cell activity (Jiao et al., 2021). Diffuse depression in neurons may be caused by a discrepancy in the antioxidant system, where the energy metabolic state of astrocytes plays a crucial role. ATP depletion in astrocytes leads to reduced glutathione levels and increased ferrous ions, reducing their antioxidant capacity. The iron chelating agent deferoxamine reduces astrocyte damage, suggesting that improvements in astrocyte functionality are partly attributed to the inhibition of their ferroptosis (Lian and Stringer, 2004).
As mentioned above, microglia, neurons, and astrocytes are involved in the pathological depression process. Changes in indicators of cellular ferroptosis are observed in all three types of cells, and effective improvements can be made using drugs or other intervening behaviors. This suggests that modulating ferroptosis in these 3 cell types plays an important role in depression (Figure 2).
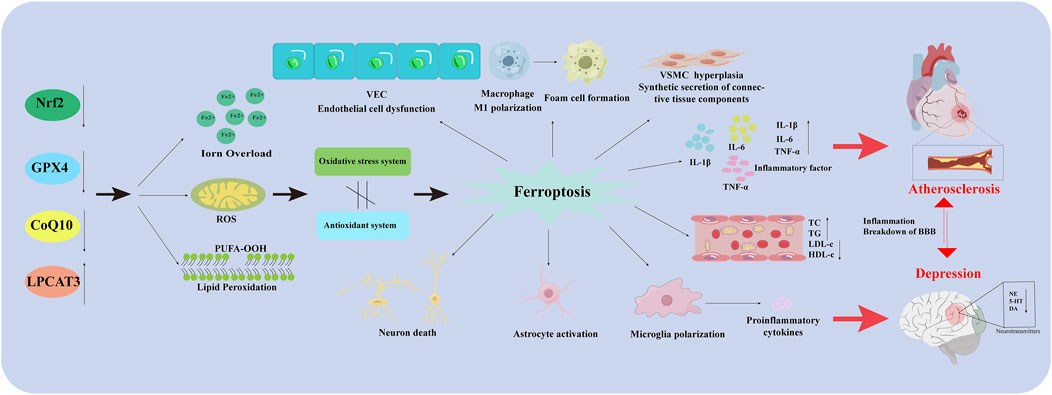
Figure 2. Ferroptosis in different types of cells in AS co-depression disease. Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; GPX4: Glutathione peroxidase 4; CoQ10H2: Reduced coenzyme Q10; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; PUFA-OOH: Polyunsaturated fatty acid-OOH; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; VSMC: Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell; IL-1β: Interleukin-1 beta; IL-6: Interleukin- 6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; TC: Total Cholesterol; TG: Triglyceride; LDL-C: Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol; HDL-C: High density lipoprotein cholesterol; BBB: Blood Brain Barrier; NE: Norepinephrine; 5-HT: 5-hydroxy tryptamine; DA: Dopamine.
We have previously discussed the separate roles of iron death in AS and depression. Ferroptosis also plays a significant role in comorbidity. After a closed head injury, ApoE−/− mice exhibit elevated levels of iron in their brains, suggesting that ApoE−/− deficiency may increase the risk of oxidative damage to hippocampal tissue (Guaraldi and Shea, 2018). A randomized controlled clinical study of 26 patients with myocardial infarction, anxiety, and depression, compared to that of 26 healthy individuals, revealed that ferroptosis is involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases associated with depression. In vitro studies show that upregulating sestrin2 decreases type I/II collagen and KEAP1 mRNA expression while increasing GPX4 and Nrf2 mRNA levels. Similar findings were observed with sestrin2 downregulation (Qian et al., 2023). Ferritin improves cognition by decreasing ROS and glutathione depletion in the MCAO model and downregulating elevated ferroptosis factors P11 and SLC53A7 (Ko et al., 2023).
We have summarized the key mechanisms of cellular ferroptosis in AS and depression. However, disease development is often complex, involving multiple mechanisms and their interactions. Ferroptosis is also closely associated with inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and the gut microbiota, which also play important roles in AS and depression.
AS—a chronic inflammatory vascular disease—is closely associated with inflammation in its development (Kong et al., 2022). Macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses significantly contribute to AS progression, with various macrophage types observed in plaques. Excessive lipid uptake primarily drives polarization into M1-type macrophages. M2-type macrophages contain less intracytoplasmic iron and metabolize it more quickly than that of M1-type macrophages, which accumulate iron owing to their high ferritin content. Iron levels influence macrophage polarization: low levels inhibit anti-inflammatory responses, while high levels promote them (Cornelissen et al., 2019). Elevated iron levels increase macrophage secretion of matrix metalloproteinases, degrading the ECM and inducing AS plaque rupture. Iron overload also hinders lipoxygenase binding to the nuclear membrane, exacerbating inflammation and promoting AS formation (Ma et al., 2022). Ferroptosis—along with iron overload and imbalanced redox reactions—is closely associated with AS, contributing to macrophage foam cell formation. It increases ROS expression by promoting P53 acetylation, driving macrophage differentiation into the M1 phenotype (Zhou et al., 2018). Additionally, M2-type macrophages can be converted into M1-type macrophages when induced by iron nanoparticles (Laskar et al., 2013). Therefore, ferroptosis enhances M1-type macrophage polarization, worsens peripheral inflammation, and accelerates AS progression (Ma et al., 2022).
Neuroinflammation is primarily initiated by astrocytes and microglia in response to factors such as injury, infection, exposure to toxins, or autoimmune reactions. Microglia—the resident immune cells of the CNS—are characterized by elevated levels of iron (Liu S. et al., 2022). This is closely associated with iron overload-mediated depression and abnormal glial cell activation (Zeng et al., 2023). Research shows that synaptic plasticity theory is a widely accepted mechanism significant to the pathophysiology of depression, with BDNF signaling being one of these. BDNF downregulation, driven by various factors, causes neurotoxic effects and is crucial for synaptic plasticity in depression (Li Y. et al., 2024; Lomeli et al., 2024). Li et al. observed that iron overload through the ferricyanide/BDNF pathway may damage hippocampal neurons by reducing BDNF levels (Li J. et al., 2024). They also suggest that etomidate may have antidepressant effects by increasing BDNF, thereby protecting hippocampal neurons from ferroptosis (Li X. et al., 2023). Additionally, lactoferrin—an iron-binding glycoprotein—reduces NF-κB (p65) and TNF-α levels, lessening inflammation and depressive behaviors in rats subjected to chronic restraint stress. This is supported by findings in CUMS model mice, where iron buildup in hippocampal microglia influences neuronal degeneration and death (Ahmed et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2019). Microglia activation, increased pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, and ferroptosis in the hippocampus of CUMS mice are reversible with further erastin therapy (Ma et al., 2024). Zhang et al. observed that deferoxamine reverses neuropathological changes caused by inflammatory factor upregulation in a CUMS mouse model (Zhang W. et al., 2022). These findings indicate a clear link between depression onset and neurotoxicity from excess iron.
Iron is essential for lipid metabolism, protein synthesis, cellular respiration, and DNA synthesis, with mitochondria playing a key role in iron metabolism. Iron also contributes to adaptive mechanisms in cardiac control (Ravingerová et al., 2020), but its regulatory role in iron metabolism is often overlooked. The heart derives energy from iron-sulfur clusters (ISCs), produced by mitochondria, the only sites of hemoglobin production. These ISCs contain hemoglobin and catalyze electron transfer through the bidirectional oxidation states of iron. Excessive iron accumulation in mitochondria causes oxidative stress, generating harmful free radicals that damage DNA, proteins, and lipids, ultimately impairing cardiac function (Kumfu et al., 2012). Altered mitochondrial morphology distinguishes ferroptosis from other cell death types. This alteration can lead to excessive ROS production, damaging VECs and causing mitochondrial dysfunction. Aortic endothelial cells (MAECs) from high-fat-fed ApoE−/− mice exhibited increased expression of mitoferrin 2 (Mfrn2), an iron transporter in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Silencing the Mfrn2 gene prevents mitochondrial iron overload in MAECs (Wang D. et al., 2021). Research on the role of ferroptosis in mitochondrial function and its effects on AS is limited. However, the studies mentioned above highlight its significance in AS and offer new insights for investigating the pathological mechanisms of AS through ferroptosis.
Mitochondria are essential for cellular energy metabolism and play a key role in inducing ferroptosis through various metabolic processes. Intracellular ROS are primarily produced by mitochondrial metabolism. Superoxide is produced when electrons leak from, ETC., complexes I and III and they are converted into hydrogen peroxide by superoxide dismutase. This hydrogen peroxide reacts with ferrous ions to form hydroxyl radicals, which then transform the bis-allyl hydrogens in PUFAs into PUFA radicals. In the presence of oxygen, these unstable free radicals quickly form PUFA peroxyl radicals, which ultimately convert into PUFA hydroperoxides. This process promotes LPO, leading to ferroptosis owing to ROS produced by mitochondria. Elevated ferrous ions and iron homeostasis imbalances can further increase ROS through the Fenton reaction, also contributing to ferroptosis. Numerous researches show that oxidative stress and disruption of the electron transport chain in mitochondria are closely related to depression (Jiang et al., 2024; Khan et al., 2023; Scaini et al., 2022). Among them, mitochondria-mediated production is positively associated with depression incidence. Excess iron ions disrupt the electron transport chain and reduce ATP synthesis in the mitochondria. Research indicates that individuals with severe depression exhibit lower ATP and glucose metabolism in brain regions associated with mood regulation, including the bilateral insula, nucleus accumbens, and cingulate gyrus (Su et al., 2014). ATP levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of CUMS depression model mice were reduced, but injecting ATP into the lateral ventricle may significantly enhance their depressive behavior (Cao et al., 2013; Shen et al., 2020). Furthermore, issues with mitochondrial iron metabolism problems may lead to depression by disrupting mitochondrial structure and function, which are key sources of cellular ROS. This disruption may also relate to depression management via the ferroptosis signaling pathway (Song Y. et al., 2023).
Gut microbes also play a key role in AS. Studies show significant changes in the gut microbiota of individuals with ASCVD. In a metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiome of 218 patients with ASCVD and 187 healthy patients, Jie et al. identified a strong association between gut microbiota and ASCVD (Jie et al., 2017). Animal models indicate that gut microbiota may contribute to ASCVD through mechanisms such as direct host invasion, immune system activation through lipopolysaccharide, altered metabolism, and the release of metabolites into the bloodstream. Trimethylamine N-oxide is the most established link to ASCVD, supported by human and animal studies (Barrington and Lusis, 2017). Recent studies show that iron storage in mice correlates positively with Clostridium spp. iron utilization, which is enhanced by dietary iron, intravenous iron, and chronic blood transfusions (La Carpia et al., 2019). An increase in Clostridium species has been observed in AS (Konturek et al., 2015). Additionally, a randomized controlled trial reveal that Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule can modify gut flora, reduce AS, and prevent ferroptosis by modulating the GPX4/xCT pathway, thereby stabilizing AS plaques (Zhang et al., 2023b). These findings highlight the significant function of ferroptosis in AS and suggest that gut microbiota are a major contributor.
The brain-gut axis is a bidirectional communication network that connects cognitive and emotional functions of the brain to gut activity through neural pathways, neuroendocrine and neuroimmune systems, and gut microbiota (Mayer et al., 2022). Disturbances in gut microbiota and its metabolites have been observed in individuals with depression and animal models, suggesting a link between depression and disrupted gut microbiota, as well as impaired neural communication (Liu L. et al., 2023; Wang Y. et al., 2024). Imbalances in serum iron homeostasis can trigger inflammation and gut microbial diseases, leading to brain stress responses. Increased IL-1β levels elevate iron regulatory protein 1 and TFR1 in oligodendrocytes, while reduced iron transporter protein 1 expression leads to intracellular iron accumulation, contributing to neurodegenerative diseases (Yang J. et al., 2024). Studies indicate a strong connection between depression onset and IL-1β-mediated signaling pathways (García-García et al., 2022; Ng et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2018), with IL-6 playing a similar role (Zhang G. et al., 2023). Individuals with depression exhibit reduced BDNF levels, highlighting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker (Rana et al., 2021). Ferroptosis is linked to depression by suppressing BDNF expression, while gut microorganisms influence BDNF and modulate depression through the brain-gut axis (Matin and Dadkhah, 2024). Depression may be associated with gut flora dysbiosis, and probiotics could help alleviate its symptoms. Iron metabolism and ferroptosis may induce neurological damage through interactions with the central nervous system, gut microbiota, and brain-gut axis, positioning them as potential therapeutic targets for depression (Figure 3).
Ferroptosis influences the onset of AS and depression through inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and gut microbiota, respectively. It also plays an important role in the comorbidity of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and depression. In patients with chronic stable angina pectoris complicated by depression and anxiety, Melissa officinalis supplements have shown significant improvement in symptoms. Melissa officinalis exhibits strong antioxidant properties, regulates lipid metabolism (Petrisor et al., 2022), and can also inhibit ferroptosis (El Hajj et al., 2023). In patients with AS and depression, elevated levels of the inflammatory factors IL-6 and IL-10 are observed (Mousa et al., 2022), while ferroptosis exerts a significant pro-inflammatory effect. In ApoE−/− mice subjected to chronic mild stress, lipid metabolism disorders, increased adipocyte hypertrophy, and reduced PPARG gene expression promote AS, while PPARG exhibits an anti-ferroptosis effect (Mao et al., 2023). Therefore, the role of ferroptosis in AS and depression is bidirectional, involving interactions through various disease mechanisms.
In summary, the significant role of ferroptosis in AS and depression has been highlighted. Ferroptosis contributes to the onset and progression of AS co-depression directly or by influencing other mechanisms. Targeted regulation of ferroptosis through drugs could represent a novel approach for treating AS-depression comorbidities. However, commonly used ferroptosis modulators are often associated with significant side effects, including pulmonary toxicity (Parry et al., 2002), liver damage, and neurotoxic effects (Zaafar et al., 2024). Currently, Chinese medicine offers promise for treating AS and depression. Its compounds exhibit anti-ferroptosis effects with minimal side effects, enhancing patient acceptability. Therefore, we will review the anti-ferroptosis effects of Chinese medicine compounds and monomers in AS and depression.
Paeonia lactiflora, a medicinal herb native to China, is the source of Paeonol (Pae), a bioactive compound with potent antioxidant and lipid-lowering properties (Shi et al., 2020). Studies indicate that Pae reduces lipid accumulation and foam cell growth, thereby lowering atherosclerotic plaque formation (Shi et al., 2022). Additionally, studies reveal that Pae enhances Nrf2 protein expression, potentially preventing lipid accumulation in foam cells by reducing ferroptosis. Gao et al. reveal that Pae effectively reduced fat growth and aortic ferroptosis in ApoE−/− mice, outperforming ferritin-1 and simvastatin. In vitro, Pae inhibited lipid accumulation from Ox-LDL in foam cells undergoing ferroptosis. The SIRT1/Nrf2/GPX4 pathway was identified as a protective mechanism, with SIRT1 knockdown reversing this effect. Therefore, Pae may inhibit lipid accumulation and alleviate AS by targeting this pathway (Gao et al., 2024).
Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA), a monochalcone glycoside derived from the Asteraceae family, is used to manage and prevent ischemic cerebrovascular diseases. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-angiogenic properties help alleviate AS (Feng et al., 2023; Xue et al., 2021). HSYA reduces oxidative damage to HUVECs caused by H2O2 and inhibits ferroptosis during reperfusion, suggesting a protective role in heart tissues. Rong et al. administered HSYA to ApoE−/− mice and applied it in an Ox-LDL-induced hyperlipidemic model in HUVEC. HSYA suppressed ferroptosis in HUVEC, increased GSH, SLC7A11, and GPX4 levels, and significantly reduced atherosclerotic plaque formation. It also downregulated miR-429, which regulated SLC7A11 expression. After SLC7A11 siRNA transfection or miR-429 mimicry, the antioxidative stress and anti-ferroptosis effects of HSYA were reduced. Therefore, HSYA holds promise as a therapeutic agent for AS (Rong et al., 2023).
Echinatin, a chalcone isolated from the Chinese herb licorice, possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Zhang established a mechanical property-based screening approach to identify compounds that alleviate arterial wall stiffness by affecting the interactions between VSMCs and the ECM. The study reveals that echinatin reduced ECM stiffness surrounding cultured VSMCs and upregulated glutamate cysteine ligases (GCLs) expression, including the catalytic (GCLC) and regulatory (GCLM) subunits. Further studies show that the upregulation of GCLC/GCLM in VSMC by echinatin helps maintain the homeostasis of GSH metabolism. Adequate glutathione is essential for counteracting AS (Zhang et al., 2023c). Icariin, the main active ingredient of epimedium, improves endothelial cell dysfunction. Wang et al. investigated the protective effect of icariin on Ox-LDL-treated VECs and ApoE−/− mice fed a high-fat diet. The findings reveal that icariin reduces the atherosclerotic plaque area and collagen fibers in aortic sinus tissue while enhancing mitochondrial activity and membrane potential. The levels of ROS in VECs were decreased. In vivo experiments, icariin reduced ferroptosis alleviated atherosclerotic lesions, and increased TFEB nucleation rate. These findings suggest that icariin could be a potential candidate for preventing VEC ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease treatment (Wang et al., 2023d). Tanshinone IIA (TSA) protects endothelial tissue from injury. We investigated its effect on ferroptosis in human coronary endothelial cells treated with TSA. TSA significantly reduces the excessive accumulation of total cell ROS and lipid ROS induced by ferroptosis inducers, restores glutathione content, and promotes nuclear translocation of Nrf2 (He et al., 2021).
TCM compounds are widely used in AS treatment due to their multi-target effects, including the anti-ferroptosis mechanism. MaiJiTong Granules (MJT), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulation, contains Mucuna pruriens, Astragalus, Cinnamon, Danshen, Poria, and Paeonia lactiflora, which effectively treat cardiovascular diseases. Key ingredients, such as Astragalus saponin IV and ferulic acid, inhibit ferroptosis (Peng et al., 2021). Jia et al. developed a mouse model of AS through high-fat feeding to assess the efficacy of MJT in preventing and treating ferroptosis and AS. The study reveals that MJT exerts anti-inflammatory effects, lowers LDL levels, inhibits foam cell formation, and reduces plaque area and instability, thereby slowing AS progression. Additionally, MJT promotes ferroptosis and alleviates iron dysregulation and LPO during atherogenesis, reducing DMT1 and SOCS1/p53 expression through STAT1 phosphorylation (Shi et al., 2024).
DiDang decoction (DDD) is a TCM formula comprising rhubarb, peach kernel, leech, and gadfly, known for its ability to break up silt. Documented in the Typhoid Fever and Golden Chamber, it is used in China to treat AS and hyperlipidemia. DDD mitigates AS by preventing vascular fibrosis, preserving endothelial function, and reducing plaque rupture (Ren et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2020). Wu et al. investigated the anti-ferroptosis effects of DDD through network pharmacology and in vitro experiments. They found that DDD therapeutically targets AS by enhancing mitochondrial function through the HIF-1 signaling pathway, reducing ROS levels, and modulating GPX4, Bcl2, and Bax protein levels, thereby benefiting AS and hyperlipidemia (Wu et al., 2023a).
The Qingxin Jieyu Granule (QXJYG), created by academician Chen Keji, is a key formula for ASCVD based on the “blood stasis and toxin” theory. It features ingredients such as Astragalus, Dangshen, and Huo Xiang. Previous studies show that QXJYG granules reduce inflammatory factors, modify intestinal flora to alleviate AS, and regulate iron metabolism in macrophages, stabilizing atherosclerotic plaques in individuals with stable coronary artery disease. Zhang et al. used RSL3 to induce macrophage ferroptosis in vitro and investigated the effects of Qing Xin Xie Du Granule on ferroptosis in ApoE−/− mice. QXJYG reduced inflammatory factors associated with ferroptosis, lowered lipid peroxides such as MDA, enhanced antioxidant capacity, and inhibited AS progression and plaque vulnerability. Additionally, QXJYG decreased total iron content compared to that of the model group and significantly increased GPX4/xCT expression in aortic tissues, reversing RSL3-induced ferroptosis in macrophages (Zhang et al., 2023b) (Table 2).
Quercetin, a flavonoid found in many fruits and vegetables, exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antidepressant effects. It also exerts various pharmacological effects, including modulation of the intestinal microbiota (Li B. et al., 2024), anti-apoptosis (Ge et al., 2024), inhibition of inflammatory vesicle activation (Du L. et al., 2024), and modulation of glutamate receptors (Wang M. et al., 2024). Quercetin regulates micronutrients by chelating iron, scavenging ROS, and reducing ferroptosis induced by various pathological factors (Zoidis et al., 2021). Wang et al. used a rat model of perimenopausal depression (OVX-CUMS) to examine the effects of quercetin on serum elemental changes. The findings reveal that OVX-CUMS rats exhibit increased iron levels in the blood and prefrontal cortex, accompanied by reduced expression of ferroptosis-associated proteins SLC7A11 and GPX4, which improve following quercetin treatment (Wang D. et al., 2024). Furthermore, Zhu et al. investigated the effects of quercetin on the lipid metabolism gene PTGS2 in breast cancer-related depression. They found that quercetin improves lipid metabolism and intestinal flora while reducing ferroptosis markers (total iron, Fe2+, MDA, and ROS). These findings confirm the potential of quercetin to inhibit neuronal ferroptosis and enhance the immune response, offering relief from depression-associated breast cancer (Zhu Q. et al., 2024).
Gastrodin, the main active compound in the Aspalathus rhizome, exhibits significant neurobiological effects. It reduces β-amyloid deposition, inhibits glutamate production, prevents ferroptosis, and restores synaptic plasticity. Furthermore, it increases BDNF levels, promotes neurogenesis, inhibits microglial activation, and regulates dopamine concentrations. Clinical studies show the effectiveness of gastrodin in managing post-stroke depression (Berezutsky et al., 2022). Catalpol, derived from dihuang, a cyclic enol ether terpene in TCM, exhibits hypoglycemic, depressive, and neuroprotective effects (Wang Y. L. et al., 2021). Wu et al. used a network pharmacology approach to predict that Catalpol could inhibit ferroptosis and mitigate fluoxetine-induced liver injury. Subsequent molecular docking reveals that ATF3/FSP1-mediated ferroptosis plays a major role in fluoxetine-induced hepatic injury. Additionally, Catalpol can reverse and enhance the antidepressant effects of fluoxetine (Wu X. et al., 2024). CNS, an antioxidant flavonoid from Chinese honeysuckle, has recently garnered attention for its potential antidepressant benefits (Yang et al., 2021). Zhou et al. conducted transcriptome analysis and validation, showing that CNS inhibits LPO, ferroptosis, and inflammatory polarization through the IRF1/SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway. Furthermore, in vivo experiments showed that CNS exhibited therapeutic effects comparable to those of fluoxetine, effectively ameliorating symptoms of anxiety, despair, and anhedonia while also inhibiting microglial activation in the hippocampus of mice subjected to CUMS. CNS was found to mitigate inflammation, lower ferroptosis levels, prevent microglial polarization to the M1 phenotype and promote overall mental health (Zhou et al., 2024). Additionally, herbal extracts such as silybin (Liu P. et al., 2023) and Lycium barbarum glycopeptide (Dai et al., 2023) have been shown to target ferroptosis with antidepressant effects.
Chinese herbal compounds are increasingly used to target ferroptosis in depression treatment. The antidepressant properties of Pure Essence, documented in the prescription compendium of the Taiping Welfare Pharmacy Bureau during the Song Dynasty, have been thoroughly validated through TCM theory, clinical applications, and pharmacological research. Furthermore, it is considered one of the classical formulas for antidepressant treatment (Ran et al., 2024). Animal studies show that it ameliorates depressive-like behavior in CUMS rats, enhances neurotransmitter transmission, and modulates gene expression in astrocytes (Wu Y. et al., 2024). Recent studies have increasingly focused on the role of ferroptosis in the pathophysiology of depression. Jiao et al. showed that free-powder administration could alleviate depressive behaviors in CUMS mice by modulating PEBP1-GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in the hippocampus. This effect was evidenced by alterations in total and ferrous iron levels in the hippocampus and an increase in the expression of PEBP1, ERK1/2, and key ferroptosis-related proteins, including GPX4, FTH1, ACSL4, and COX2 (Jiao et al., 2021). Similarly, Di Huang Yin Zi, another Chinese herbal compound, has shown potential antidepressant effects in the brains of post-stroke depressed rats. These effects are associated with increased ROS and MDA levels, as well as modifications in ferroptosis-related markers, such as Fe2+, SLC7A11, and GPX4 (Yang et al., 2024c). In addition, a recent study suggests that Suanzaoren decoction modulates the DJ-1/Nrf2 signaling pathway, alleviating neuronal loss, synaptic damage, and ferroptosis associated with Alzheimer’s disease. This modulation is evidenced by the upregulation of FPN1, DJ-1, Nrf2, GPX4, and SLC7A11 proteins in the hippocampus, coupled with the downregulation of TfR1, FTH1, FTL, and ACSL4 proteins (Long et al., 2024). Suanzaoren Decoction also exhibits multi-pathway and multi-targeted antidepressant effects, including anti-inflammatory actions and gut flora regulation (Du et al., 2023; Du Y. et al., 2024). While studies on antidepressants have not specifically focused on ferroptosis, it is likely that the actions of Suanzaoren Decoction contribute to the modulation of ferroptosis in depression (Table 3).
The preceding discussion highlights various monomers and compounds that target ferroptosis for treating AS and depression. Certain pharmacological agents, despite their differences, may share common mechanisms in targeting ferroptosis. For example, PAE not only protects against AS but also exerts neuroprotective effects by inhibiting neuronal ferroptosis in cerebral hemorrhage (Jin et al., 2021) and serves as an antidepressant (Wei et al., 2023). HSYA, known for its excellent blood-brain barrier permeability, improves depressive behavior by inhibiting hippocampal inflammation and oxidative stress (Liu Z. et al., 2022). Similarly, Icariin has shown promising antidepressant effects (Zeng et al., 2022). Quercetin also exhibits the potential to inhibit atherosclerotic ferroptosis while serving as an antidepressant by targeting ferroptosis-related mechanisms (Li H. et al., 2024). CNS inhibits the abnormal proliferation of aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (Kim et al., 2006). In summary, TCM effectively treats AS-related depression by targeting ferroptosis, which is also an important therapeutic target.
In conclusion, studying the mechanisms of comorbidity through the perspective of ferroptosis is essential, with GPX4 and Nrf2 being highlighted as critical targets. Cellular focus includes macrophages, endothelial cells, microglia, and neurons. Regarding treatment, Chinese medicine, known for its multi-target effects, holds significant potential. Ferroptosis not only directly contributes to AS but also interacts with inflammatory responses, energy metabolism, and the gut, accelerating disease progression. Targeting ferroptosis offers a promising therapeutic approach for AS and depression, providing a new strategy for addressing comorbidity. We highlighted the role of ferroptosis in comorbidities and emphasized its relevance in cardio-cerebrovascular diseases associated with AS and psychiatric disorders, such as depression. This underscores the broader significance of the ferroptosis mechanism across various diseases and provides insights into its involvement in other conditions.
Despite significant progress in understanding ferroptosis in AS and depression, its role in comorbid conditions remains unclear. In the clinical treatment of patients with atherosclerotic co-depressive disorders, combining lipid-lowering drugs and antidepressants often causes side effects such as nausea, dizziness, and vomiting, resulting in treatment failure. Therefore, identifying shared pathogenesis is crucial, and targeting ferroptosis represents a promising strategy. For example, deferoxamine, an iron-chelating agent, is an approved treatment for iron overload. It improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with coronary heart disease (Duffy et al., 2001), protects neurons from ferroptosis, and exhibits antidepressant effects (Trachtenberg et al., 2011). However, deferoxamine can cause growth delay, allergic reactions and bone abnormalities, and at high doses, it can cause nervous system damage (Entezari et al., 2022). Despite challenges such as poor solubility and instability, many active ingredients in Chinese medicine offer multi-target effects and lower toxicity, making them a preferable option.
TCM plays a significant role in treating atherosclerotic co-depression diseases through its anti-ferroptosis effects, but the specific molecular targets remain unclear. TCM consists of numerous components; however, only a few are absorbable, which complicates the understanding of their mechanisms and limits the scientific credibility of TCM. Anti-AS co-depression drugs targeting ferroptosis also have side effects. For example, thiazolidinediones, which inhibit ACSL4, can cause cardiac toxicity with prolonged use (Al Sultan et al., 2024), while zileuton, a lipoxygenase inhibitor, may lead to indigestion, nausea, and other issues. Although ferroptosis has been implicated in these diseases, its exact role in the occurrence and progression of comorbidities during specific pathogenesis remains unclear. The mechanism of ferroptosis in comorbidities is not fully understood. These limitations highlight the direction of our efforts in studying comorbidity.
YZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. PR: Conceptualization, Software, Writing–review and editing. QL: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. XL: Software, Writing–review and editing. XC: Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. YW: Validation, Writing–review and editing. XW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. National Natural Science Foundation of China (82360861), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20232BAB206173), Science and Technology Research Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (GJJ2201430), The Talent Starting Fund Project of Gannan Medical University (Grant number QD202012), The Talent Starting Fund Project of Gannan Medical University (Grant number QD202208), and Open Project of the Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education for the Prevention of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Gannan Medical University (XN202015).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ahmed, H. H., Essam, R. M., El-Yamany, M. F., Ahmed, K. A., and El-Sahar, A. E. (2023). Unleashing lactoferrin's antidepressant potential through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in chronic restraint stress rats. Food Funct. 14 (20), 9265–9278. doi:10.1039/d3fo02222f
Aldana, B. I. (2019). Microglia-specific metabolic changes in neurodegeneration. J. Mol. Biol. 431 (9), 1830–1842. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2019.03.006
Alexopoulos, G. S., Meyers, B. S., Young, R. C., Campbell, S., Silbersweig, D., and Charlson, M. (1997). Vascular depression' hypothesis. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 54 (10), 915–922. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830220033006
Almulla, A. F., Thipakorn, Y., Algon, A. A. A., Tunvirachaisakul, C., Al-Hakeim, H. K., and Maes, M. (2023). Reverse cholesterol transport and lipid peroxidation biomarkers in major depression and bipolar disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 113, 374–388. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2023.08.007
Al Sultan, A., Rattray, Z., and Rattray, N. J. W. (2024). Integrative analysis of toxicometabolomics and toxicoproteomics data: new molecular insights into thiazolidinedione-induced cardiotoxicity. Metabolomics 21 (1), 1. doi:10.1007/s11306-024-02201-3
Amoscato, A. A., Anthonymuthu, T., Kapralov, O., Sparvero, L. J., Shrivastava, I. H., Mikulska-Ruminska, K., et al. (2023). Formation of protein adducts with Hydroperoxy-PE electrophilic cleavage products during ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 63, 102758. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102758
Arslanbaeva, L., Tosi, G., Ravazzolo, M., Simonato, M., Tucci, F. A., Pece, S., et al. (2022). UBIAD1 and CoQ10 protect melanoma cells from lipid peroxidation-mediated cell death. Redox Biol. 51, 102272. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102272
Askew, K., Li, K., Olmos-Alonso, A., Garcia-Moreno, F., Liang, Y., Richardson, P., et al. (2017). Coupled proliferation and apoptosis maintain the rapid turnover of microglia in the adult brain. Cell Rep. 18 (2), 391–405. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.041
Bai, T., Li, M., Liu, Y., Qiao, Z., and Wang, Z. (2020). Inhibition of ferroptosis alleviates atherosclerosis through attenuating lipid peroxidation and endothelial dysfunction in mouse aortic endothelial cell. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 160, 92–102. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.026
Barrington, W. T., and Lusis, A. J. (2017). Atherosclerosis: association between the gut microbiome and atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 14 (12), 699–700. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2017.169
Berezutsky, M. A., Durnova, N. A., and Romanteeva, Y. V. (2022). Neurobiological effects of gastrodin and its possible use in neurology and psychiatry. Zh Nevrol. Psikhiatr Im. S S Korsakova 122 (8), 27–34. doi:10.17116/jnevro202212208127
Bogdan, A. R., Miyazawa, M., Hashimoto, K., and Tsuji, Y. (2016). Regulators of iron homeostasis: new players in metabolism, cell death, and disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41 (3), 274–286. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2015.11.012
Bourgeois, T., Jalil, A., Thomas, C., Magnani, C., Le Guern, N., Gautier, T., et al. (2021). Deletion of lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 in myeloid cells worsens hepatic steatosis after a high-fat diet. J. Lipid Res. 62, 100013. doi:10.1194/jlr.RA120000737
Cakir-Aktas, C., Bodur, E., Yemisci, M., van Leyen, K., and Karatas, H. (2023). 12/15-lipoxygenase inhibition attenuates neuroinflammation by suppressing inflammasomes. Front. Cell Neurosci. 17, 1277268. doi:10.3389/fncel.2023.1277268
Cao, H., Zuo, C., Huang, Y., Zhu, L., Zhao, J., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). Hippocampal proteomic analysis reveals activation of necroptosis and ferroptosis in a mouse model of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression. Behav. Brain Res. 407, 113261. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113261
Cao, X., Li, L. P., Wang, Q., Wu, Q., Hu, H. H., Zhang, M., et al. (2013). Astrocyte-derived ATP modulates depressive-like behaviors. Nat. Med. 19 (6), 773–777. doi:10.1038/nm.3162
Chen, J., Jiang, X., Gao, X., Wu, W., Gu, Z., Yin, G., et al. (2023). Ferroptosis-related genes as diagnostic markers for major depressive disorder and their correlations with immune infiltration. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 10, 1215180. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1215180
Chen, S., Gao, J. J., Liu, Y. J., Mo, Z. W., Wu, F. Y., Hu, Z. J., et al. (2024). The oxidized phospholipid PGPC impairs endothelial function by promoting endothelial cell ferroptosis via FABP3. J. Lipid Res. 65 (2), 100499. doi:10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100499
Chen, X., Li, J., Kang, R., Klionsky, D. J., and Tang, D. (2021a). Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy 17 (9), 2054–2081. doi:10.1080/15548627.2020.1810918
Chen, X., Yu, C., Kang, R., Kroemer, G., and Tang, D. (2021b). Cellular degradation systems in ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 28 (4), 1135–1148. doi:10.1038/s41418-020-00728-1
Chen, Y., Liu, S., Li, J., Li, Z., Quan, J., Liu, X., et al. (2020). The latest view on the mechanism of ferroptosis and its research progress in spinal cord injury. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 6375938. doi:10.1155/2020/6375938
Chistiakov, D. A., Melnichenko, A. A., Myasoedova, V. A., Grechko, A. V., and Orekhov, A. N. (2017). Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J. Mol. Med. Berl. 95 (11), 1153–1165. doi:10.1007/s00109-017-1575-8
Chrysohoou, C., Kollia, N., and Tousoulis, D. (2018). The link between depression and atherosclerosis through the pathways of inflammation and endothelium dysfunction. Maturitas 109, 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.12.001
Cornelissen, A., Guo, L., Sakamoto, A., Virmani, R., and Finn, A. V. (2019). New insights into the role of iron in inflammation and atherosclerosis. EBioMedicine 47, 598–606. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.014
Costa, I., Barbosa, D. J., Benfeito, S., Silva, V., Chavarria, D., Borges, F., et al. (2023). Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and their involvement in brain diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 244, 108373. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108373
Cozzi, A., Orellana, D. I., Santambrogio, P., Rubio, A., Cancellieri, C., Giannelli, S., et al. (2019). Stem cell modeling of neuroferritinopathy reveals iron as a determinant of senescence and ferroptosis during neuronal aging. Stem Cell Rep. 13 (5), 832–846. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.09.002
Dai, Y., Guo, J., Zhang, B., Chen, J., Ou, H., He, R. R., et al. (2023). Lycium barbarum (Wolfberry) glycopeptide prevents stress-induced anxiety disorders by regulating oxidative stress and ferroptosis in the medial prefrontal cortex. Phytomedicine 116, 154864. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154864
Dixon, S. J., Lemberg, K. M., Lamprecht, M. R., Skouta, R., Zaitsev, E. M., Gleason, C. E., et al. (2012). Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149 (5), 1060–1072. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Doll, S., and Conrad, M. (2017). Iron and ferroptosis: a still ill-defined liaison. IUBMB Life 69 (6), 423–434. doi:10.1002/iub.1616
Doll, S., Freitas, F. P., Shah, R., Aldrovandi, M., da Silva, M. C., Ingold, I., et al. (2019). FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 575 (7784), 693–698. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1707-0
Du, J., Wu, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, Q., Luo, X., Huang, X., et al. (2024a). CTRP13 mitigates endothelial cell ferroptosis via the AMPK/KLF4 pathway: implications for atherosclerosis protection. Med. Sci. Monit. 30, e942733. doi:10.12659/msm.942733
Du, L., Fan, X., Yang, Y., Wu, S., and Liu, Y. (2024b). Quercetin ameliorates cognitive impairment in depression by targeting HSP90 to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol. Neurobiol. 61, 6628–6641. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-03926-x
Du, Y., He, B., Wu, B., Yan, T., and Jia, Y. (2023). Suanzaoren decoction improves depressive-like behaviors by regulating the microbiota-gut-brain axis via inhibiting TLR4/NFκB/NLRP3 inflammation signal pathway. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 134, 102349. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2023.102349
Du, Y., Yan, T., Wu, B., He, B., and Jia, Y. (2024c). Research on the mechanism of antidepressive effect of Suanzaoren Decoction through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 1), 117190. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117190
Duffy, S. J., Biegelsen, E. S., Holbrook, M., Russell, J. D., Gokce, N., Keaney, J. F., et al. (2001). Iron chelation improves endothelial function in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 103 (23), 2799–2804. doi:10.1161/01.cir.103.23.2799
Du Preez, A., Onorato, D., Eiben, I., Musaelyan, K., Egeland, M., Zunszain, P. A., et al. (2021). Chronic stress followed by social isolation promotes depressive-like behaviour, alters microglial and astrocyte biology and reduces hippocampal neurogenesis in male mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 91, 24–47. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.07.015
El Hajj, S., Canabady-Rochelle, L., and Gaucher, C. (2023). Nature-inspired bioactive compounds: a promising approach for ferroptosis-linked human diseases? Molecules 28 (6), 2636. doi:10.3390/molecules28062636
Entezari, S., Haghi, S. M., Norouzkhani, N., Sahebnazar, B., Vosoughian, F., Akbarzadeh, D., et al. (2022). Iron chelators in treatment of iron overload. J. Toxicol. 2022, 4911205. doi:10.1155/2022/4911205
Fang, X., Ardehali, H., Min, J., and Wang, F. (2023). The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 20 (1), 7–23. doi:10.1038/s41569-022-00735-4
Feng, X., Du, M., Li, S., Zhang, Y., Ding, J., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Hydroxysafflor yellow A regulates lymphangiogenesis and inflammation via the inhibition of PI3K on regulating AKT/mTOR and NF-κB pathway in macrophages to reduce atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Phytomedicine 112, 154684. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154684
Fuhrmann, D. C., and Brüne, B. (2022). A graphical journey through iron metabolism, microRNAs, and hypoxia in ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 54, 102365. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102365
Galluzzi, L., Vitale, I., Aaronson, S. A., Abrams, J. M., Adam, D., Agostinis, P., et al. (2018). Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 25 (3), 486–541. doi:10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
Galy, B., Conrad, M., and Muckenthaler, M. (2024). Mechanisms controlling cellular and systemic iron homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 25 (2), 133–155. doi:10.1038/s41580-023-00648-1
Gan, B. (2022). ACSL4, PUFA, and ferroptosis: new arsenal in anti-tumor immunity. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 128. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01004-z
Gao, M., Dong, L., Yang, Y., Yan, J., Liang, Y., Ma, X., et al. (2024). The anti-atherosclerotic effect of Paeonol against the lipid accumulation in macrophage-derived foam cells by inhibiting ferroptosis via the SIRT1/NRF2/GPX4 signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 708, 149788. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149788
Gao, W., Wang, W., Liu, G., Zhang, J., Yang, J., and Deng, Z. (2019). Allicin attenuated chronic social defeat stress induced depressive-like behaviors through suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome. Metab. Brain Dis. 34 (1), 319–329. doi:10.1007/s11011-018-0342-z
García-García, M. L., Tovilla-Zárate, C. A., Villar-Soto, M., Juárez-Rojop, I. E., González-Castro, T. B., Genis-Mendoza, A. D., et al. (2022). Fluoxetine modulates the pro-inflammatory process of IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α levels in individuals with depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 307, 114317. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114317
Ge, C., Wang, S., Wu, X., and Lei, L. (2024). Quercetin attenuates brain apoptosis in mice with chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression. Behav. Brain Res. 465, 114934. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2024.114934
Grootaert, M. O. J., and Bennett, M. R. (2021). Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis: time for a re-assessment. Cardiovasc Res. 117 (11), 2326–2339. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvab046
Gu, H. F., Tang, C. K., and Yang, Y. Z. (2012). Psychological stress, immune response, and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 223 (1), 69–77. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.01.021
Guaraldi, M., and Shea, T. B. (2018). A high-fat and high-cholesterol diet potentiates oxidative damage in Hippocampus of mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Open Neurol. J. 12, 12–18. doi:10.2174/1874205x01812010012
Halaris, A. (2017). Inflammation-associated Co-morbidity between depression and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 31, 45–70. doi:10.1007/7854_2016_28
Hare, D. L., Toukhsati, S. R., Johansson, P., and Jaarsma, T. (2014). Depression and cardiovascular disease: a clinical review. Eur. Heart J. 35 (21), 1365–1372. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/eht462
He, L., Liu, Y. Y., Wang, K., Li, C., Zhang, W., Li, Z. Z., et al. (2021). Tanshinone IIA protects human coronary artery endothelial cells from ferroptosis by activating the NRF2 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 575, 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.08.067
He, S., Li, R., Peng, Y., Wang, Z., Huang, J., Meng, H., et al. (2022). ACSL4 contributes to ferroptosis-mediated rhabdomyolysis in exertional heat stroke. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13 (3), 1717–1730. doi:10.1002/jcsm.12953
Herrington, W., Lacey, B., Sherliker, P., Armitage, J., and Lewington, S. (2016). Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ. Res. 118 (4), 535–546. doi:10.1161/circresaha.115.307611
Hong, Y., Feng, J., Dou, Z., Sun, X., Hu, Y., Chen, Z., et al. (2024). Berberine as a novel ACSL4 inhibitor to suppress endothelial ferroptosis and atherosclerosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 177, 117081. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117081
Hu, K., Liao, X. X., Wu, X. Y., Wang, R., Hu, Z. W., Liu, S. Y., et al. (2022). Effects of the lipid metabolites and the gut microbiota in ApoE(-/-) mice on atherosclerosis Co-depression from the microbiota-gut-brain Axis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9, 786492. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2022.786492
Huang, P., Yan, L., Li, Z., Zhao, S., Feng, Y., Zeng, J., et al. (2023). Potential shared gene signatures and molecular mechanisms between atherosclerosis and depression: evidence from transcriptome data. Comput. Biol. Med. 152, 106450. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106450
Jia, C., Xiang, Z., Zhang, P., Liu, L., Zhu, X., Yu, R., et al. (2024). Selenium-SelK-GPX4 axis protects nucleus pulposus cells against mechanical overloading-induced ferroptosis and attenuates senescence of intervertebral disc. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 81 (1), 49. doi:10.1007/s00018-023-05067-1
Jiang, M., Wang, L., and Sheng, H. (2024). Mitochondria in depression: the dysfunction of mitochondrial energy metabolism and quality control systems. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (2), e14576. doi:10.1111/cns.14576
Jiang, X., Stockwell, B. R., and Conrad, M. (2021). Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22 (4), 266–282. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
Jiao, H., Yang, H., Yan, Z., Chen, J., Xu, M., Jiang, Y., et al. (2021). Traditional Chinese formula xiaoyaosan alleviates depressive-like behavior in CUMS mice by regulating PEBP1-GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in the Hippocampus. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 17, 1001–1019. doi:10.2147/ndt.S302443
Jie, Z., Xia, H., Zhong, S. L., Feng, Q., Li, S., Liang, S., et al. (2017). The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 8 (1), 845. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00900-1
Jin, Z. L., Gao, W. Y., Liao, S. J., Yu, T., Shi, Q., Yu, S. Z., et al. (2021). Paeonol inhibits the progression of intracerebral haemorrhage by mediating the HOTAIR/UPF1/ACSL4 axis. ASN Neuro 13, 17590914211010647. doi:10.1177/17590914211010647
Kagan, V. E., Mao, G., Qu, F., Angeli, J. P., Doll, S., Croix, C. S., et al. (2017). Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 13 (1), 81–90. doi:10.1038/nchembio.2238
Kawada, T. (2017). Association of depression and cardiovascular disease. JAMA Cardiol. 2 (6), 702–703. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2016.5987
Khakh, B. S., and Sofroniew, M. V. (2015). Diversity of astrocyte functions and phenotypes in neural circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 18 (7), 942–952. doi:10.1038/nn.4043
Khan, M., Baussan, Y., and Hebert-Chatelain, E. (2023). Connecting dots between mitochondrial dysfunction and depression. Biomolecules 13 (4), 695. doi:10.3390/biom13040695
Kim, T. J., Kim, J. H., Jin, Y. R., and Yun, Y. P. (2006). The inhibitory effect and mechanism of luteolin 7-glucoside on rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 29 (1), 67–72. doi:10.1007/bf02977471
Ko, G., Kim, J., Jeon, Y. J., Lee, D., Baek, H. M., and Chang, K. A. (2023). Salvia miltiorrhiza alleviates memory deficit induced by ischemic brain injury in a transient MCAO mouse model by inhibiting ferroptosis. Antioxidants (Basel) 12 (4), 785. doi:10.3390/antiox12040785
Kong, P., Cui, Z. Y., Huang, X. F., Zhang, D. D., Guo, R. J., and Han, M. (2022). Inflammation and atherosclerosis: signaling pathways and therapeutic intervention. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 131. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00955-7
Konturek, P. C., Haziri, D., Brzozowski, T., Hess, T., Heyman, S., Kwiecien, S., et al. (2015). Emerging role of fecal microbiota therapy in the treatment of gastrointestinal and extra-gastrointestinal diseases. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 66 (4), 483–491.
Koppula, P., Lei, G., Zhang, Y., Yan, Y., Mao, C., Kondiparthi, L., et al. (2022). A targetable CoQ-FSP1 axis drives ferroptosis- and radiation-resistance in KEAP1 inactive lung cancers. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 2206. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29905-1
Krittanawong, C., Maitra, N. S., Qadeer, Y. K., Wang, Z., Fogg, S., Storch, E. A., et al. (2023). Association of depression and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Med. 136 (9), 881–895. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.04.036
Kumfu, S., Chattipakorn, S., Fucharoen, S., and Chattipakorn, N. (2012). Mitochondrial calcium uniporter blocker prevents cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction induced by iron overload in thalassemic mice. Biometals 25 (6), 1167–1175. doi:10.1007/s10534-012-9579-x
La Carpia, F., Wojczyk, B. S., Annavajhala, M. K., Rebbaa, A., Culp-Hill, R., D'Alessandro, A., et al. (2019). Transfusional iron overload and intravenous iron infusions modify the mouse gut microbiota similarly to dietary iron. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 5 (1), 26. doi:10.1038/s41522-019-0097-2
Laskar, A., Eilertsen, J., Li, W., and Yuan, X. M. (2013). SPION primes THP1 derived M2 macrophages towards M1-like macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 441 (4), 737–742. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.115
Lasunción, M. A., Martínez-Botas, J., Martín-Sánchez, C., Busto, R., and Gómez-Coronado, D. (2022). Cell cycle dependence on the mevalonate pathway: role of cholesterol and non-sterol isoprenoids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 196, 114623. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114623
Lei, G., Zhuang, L., and Gan, B. (2022). Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 22 (7), 381–396. doi:10.1038/s41568-022-00459-0
Lei, J., Luo, D., Xiong, J., and Li, M. (2023). Using Mendelian randomization analysis to determine the causal connection between unpleasant emotions and coronary atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 10, 1126157. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2023.1126157
Lei, P., Bai, T., and Sun, Y. (2019). Mechanisms of ferroptosis and relations with regulated cell death: a review. Front. Physiol. 10, 139. doi:10.3389/fphys.2019.00139
Li, B., Wang, C., Lu, P., Ji, Y., Wang, X., Liu, C., et al. (2022a). IDH1 promotes foam cell formation by aggravating macrophage ferroptosis. Biol. (Basel) 11 (10), 1392. doi:10.3390/biology11101392
Li, B., Yan, Y., Zhang, T., Xu, H., Wu, X., Yao, G., et al. (2024a). Quercetin reshapes gut microbiota homeostasis and modulates brain metabolic profile to regulate depression-like behaviors induced by CUMS in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1362464. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1362464
Li, C., Woo, T., and Ganesananthan, S. (2020a). What is the association between depression and cardiovascular disease? JAMA Psychiatry 77 (12), 1307–1308. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.3219
Li, E., Yin, H., Su, M., Li, Q., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2023a). Inhibition of ferroptosis alleviates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression in mice via tsRNA-3029b. Brain Res. Bull. 204, 110773. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.110773
Li, F. J., Long, H. Z., Zhou, Z. W., Luo, H. Y., Xu, S. G., and Gao, L. C. (2022b). System X(c) (-)/GSH/GPX4 axis: an important antioxidant system for the ferroptosis in drug-resistant solid tumor therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 910292. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.910292
Li, H., Cao, Z., Liu, C., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Tang, Y., et al. (2024b). Quercetin inhibits neuronal pyroptosis and ferroptosis by modulating microglial M1/M2 polarization in atherosclerosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72 (21), 12156–12170. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01134
Li, J., Cao, F., Yin, H. L., Huang, Z. J., Lin, Z. T., Mao, N., et al. (2020b). Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 11 (2), 88. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
Li, J., Ding, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Cui, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024c). Iron overload suppresses hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice: implication for iron dysregulation-linked neurological diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (2), e14394. doi:10.1111/cns.14394
Li, L., Wang, H., Zhang, J., Chen, X., Zhang, Z., and Li, Q. (2021). Effect of endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles on endothelial cell ferroptosis and atherosclerotic vascular endothelial injury. Cell Death Discov. 7 (1), 235. doi:10.1038/s41420-021-00610-0
Li, X., Hu, J., Zang, X., Xing, J., Mo, X., Hei, Z., et al. (2023b). Etomidate improves the antidepressant effect of electroconvulsive therapy by suppressing hippocampal neuronal ferroptosis via upregulating BDNF/Nrf2. Mol. Neurobiol. 60 (11), 6584–6597. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03499-1
Li, Y., Liu, A., Chen, K., Li, L., Zhang, X., Zou, F., et al. (2024d). Sodium butyrate alleviates lead-induced neuroinflammation and improves cognitive and memory impairment through the ACSS2/H3K9ac/BDNF pathway. Environ. Int. 184, 108479. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2024.108479
Lian, X. Y., and Stringer, J. L. (2004). Energy failure in astrocytes increases the vulnerability of neurons to spreading depression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 19 (9), 2446–2454. doi:10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03289.x
Liang, L., Liu, Y., Wu, X., and Chen, Y. (2023). Artesunate induces ferroptosis by inhibiting the nuclear localization of SREBP2 in myeloma cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 20 (12), 1535–1550. doi:10.7150/ijms.86409
Liao, X. X., Hu, K., Xie, X. H., Wen, Y. L., Wang, R., Hu, Z. W., et al. (2023). Banxia Xiexin decoction alleviates AS co-depression disease by regulating the gut microbiome-lipid metabolic axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 313, 116468. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116468
Liu, L., Wang, H., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., and Xie, P. (2023a). Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: from pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine 90, 104527. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104527
Liu, P., Chen, W., Kang, Y., Wang, C., Wang, X., Liu, W., et al. (2023b). Silibinin ameliorates STING-mediated neuroinflammation via downregulation of ferroptotic damage in a sporadic Alzheimer's disease model. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 744, 109691. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2023.109691
Liu, S., Gao, X., and Zhou, S. (2022a). New target for prevention and treatment of neuroinflammation: microglia iron accumulation and ferroptosis. ASN Neuro 14, 17590914221133236. doi:10.1177/17590914221133236
Liu, W., Östberg, N., Yalcinkaya, M., Dou, H., Endo-Umeda, K., Tang, Y., et al. (2022b). Erythroid lineage Jak2V617F expression promotes atherosclerosis through erythrophagocytosis and macrophage ferroptosis. J. Clin. Invest 132 (13), e155724. doi:10.1172/jci155724
Liu, Y., Wan, Y., Jiang, Y., Zhang, L., and Cheng, W. (2023c). GPX4: the hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1878 (3), 188890. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188890
Liu, Z., Zou, Y., He, M., Yang, P., Qu, X., and Xu, L. (2022c). Hydroxysafflor yellow A can improve depressive behavior by inhibiting hippocampal inflammation and oxidative stress through regulating HPA axis. J. Biosci. 47, 7. doi:10.1007/s12038-021-00246-3
Lomeli, N., Pearre, D. C., Cruz, M., Di, K., Ricks-Oddie, J. L., and Bota, D. A. (2024). Cisplatin induces BDNF downregulation in middle-aged female rat model while BDNF enhancement attenuates cisplatin neurotoxicity. Exp. Neurol. 375, 114717. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114717
Long, Q., Li, T., Zhu, Q., He, L., and Zhao, B. (2024). SuanZaoRen decoction alleviates neuronal loss, synaptic damage and ferroptosis of AD via activating DJ-1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 323, 117679. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117679
Lou, T., Wu, H., Feng, M., Liu, L., Yang, X., Pan, M., et al. (2024). Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics reveals that Da Chuanxiong Formula improves vascular cognitive impairment via ACSL4/GPX4 mediated ferroptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 325, 117868. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117868
Lu, X., Ji, Q., Pan, H., Feng, Y., Ye, D., Gan, L., et al. (2024). IL-23p19 deficiency reduces M1 macrophage polarization and improves stress-induced cardiac remodeling by alleviating macrophage ferroptosis in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 222, 116072. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116072
Luo, X., Wang, Y., Zhu, X., Chen, Y., Xu, B., Bai, X., et al. (2024). MCL attenuates atherosclerosis by suppressing macrophage ferroptosis via targeting KEAP1/NRF2 interaction. Redox Biol. 69, 102987. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102987
Ma, J., Zhang, H., Chen, Y., Liu, X., Tian, J., and Shen, W. (2022). The role of macrophage iron overload and ferroptosis in atherosclerosis. Biomolecules 12 (11), 1702. doi:10.3390/biom12111702
Ma, X., Wang, J., Quan, Q., Zhang, H., Tian, Y., Wang, L., et al. (2024). Sestrin2 attenuates depressive-like behaviors and neuroinflammation in CUMS mice through inhibiting ferroptosis. Neuroreport 35 (3), 143–151. doi:10.1097/wnr.0000000000001988
Maguire, E. M., Pearce, S. W. A., and Xiao, Q. (2019). Foam cell formation: a new target for fighting atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 112, 54–71. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2018.08.002
Maheshwari, S. (2023). Ferroptosis signaling pathways: Alzheimer's disease. Horm. Metab. Res. 55 (12), 819–826. doi:10.1055/a-2084-3561
Malhi, G. S., and Mann, J. J. (2018). Depression. Lancet 392 (10161), 2299–2312. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31948-2
Mao, C., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Lei, G., Yan, Y., Lee, H., et al. (2021). DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nature 593 (7860), 586–590. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03539-7
Mao, L., You, J., Xie, M., Hu, Y., and Zhou, Q. (2024). Arginine methylation of β-catenin induced by PRMT2 aggravates LPS-induced cognitive dysfunction and depression-like behaviors by promoting ferroptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 61, 7796–7813. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04019-5
Mao, M., Deng, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, G., Qi, R., Gong, H., et al. (2023). Chronic unpredictable mild stress promotes atherosclerosis via adipose tissue dysfunction in ApoE(-/-) mice. PeerJ 11, e16029. doi:10.7717/peerj.16029
Matin, S., and Dadkhah, M. (2024). BDNF/CREB signaling pathway contribution in depression pathogenesis: a survey on the non-pharmacological therapeutic opportunities for gut microbiota dysbiosis. Brain Res. Bull. 207, 110882. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.110882
Mavrides, N., and Nemeroff, C. (2013). Treatment of depression in cardiovascular disease. Depress Anxiety 30 (4), 328–341. doi:10.1002/da.22051
Mayer, E. A., Nance, K., and Chen, S. (2022). The gut-brain Axis. Annu. Rev. Med. 73, 439–453. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042320-014032
Miura, H., Mizuguchi, H., Amano-Iwashita, M., Maeda-Kogure, R., Negishi, A., Sakai, A., et al. (2021). Clofibric acid increases molecular species of phosphatidylethanolamine containing arachidonic acid for biogenesis of peroxisomal membranes in peroxisome proliferation in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1866 (8), 158963. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158963
Modica-Napolitano, J. S., and Renshaw, P. F. (2004). Ethanolamine and phosphoethanolamine inhibit mitochondrial function in vitro: implications for mitochondrial dysfunction hypothesis in depression and bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 55 (3), 273–277. doi:10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00784-4
Monroe, S. M., and Harkness, K. L. (2022). Major depression and its recurrences: life course matters. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 18, 329–357. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-072220-021440
Moujalled, D., Strasser, A., and Liddell, J. R. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of cell death in neurological diseases. Cell Death Differ. 28 (7), 2029–2044. doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00814-y
Mousa, R. F., Smesam, H. N., Qazmooz, H. A., Al-Hakeim, H. K., and Maes, M. (2022). A pathway phenotype linking metabolic, immune, oxidative, and opioid pathways with comorbid depression, atherosclerosis, and unstable angina. CNS Spectr. 27 (6), 676–690. doi:10.1017/s1092852921000432
Ng, S. M., Yin, M. X. C., Chan, J. S. M., Chan, C. H. Y., Fong, T. C. T., Li, A., et al. (2022). Impact of mind-body intervention on proinflammatory cytokines interleukin 6 and 1β: a three-arm randomized controlled trial for persons with sleep disturbance and depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 99, 166–176. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2021.09.022
Nishida Xavier da Silva, T., Friedmann Angeli, J. P., and Ingold, I. (2022). GPX4: old lessons, new features. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 50 (3), 1205–1213. doi:10.1042/bst20220682
Novakovic, M. M., Korshunov, K. S., Grant, R. A., Martin, M. E., Valencia, H. A., Budinger, G. R. S., et al. (2023). Astrocyte reactivity and inflammation-induced depression-like behaviors are regulated by Orai1 calcium channels. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 5500. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40968-6
Otoki, Y., Hennebelle, M., Levitt, A. J., Nakagawa, K., Swardfager, W., and Taha, A. Y. (2017). Plasma phosphatidylethanolamine and triacylglycerol fatty acid concentrations are altered in major depressive disorder patients with seasonal pattern. Lipids 52 (6), 559–571. doi:10.1007/s11745-017-4254-1
Paranthaman, R., Greenstein, A., Burns, A. S., Heagerty, A. M., Malik, R. A., and Baldwin, R. C. (2012). Relationship of endothelial function and atherosclerosis to treatment response in late-life depression. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 27 (9), 967–973. doi:10.1002/gps.2811
Parry, S. D., Barbatzas, C., Peel, E. T., and Barton, J. R. (2002). Sulphasalazine and lung toxicity. Eur. Respir. J. 19 (4), 756–764. doi:10.1183/09031936.02.00267402
Peng, L., Lei, Z., Rao, Z., Yang, R., Zheng, L., Fan, Y., et al. (2021). Cardioprotective activity of ethyl acetate extract of Cinnamomi Ramulus against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Phytomedicine 93, 153798. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153798
Peng, Q., Liu, H., Luo, Z., Zhao, H., Wang, X., and Guan, X. (2022). Effect of autophagy on ferroptosis in foam cells via Nrf2. Mol. Cell Biochem. 477 (5), 1597–1606. doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04347-3
Petrisor, G., Motelica, L., Craciun, L. N., Oprea, O. C., Ficai, D., and Ficai, A. (2022). Melissa officinalis: composition, pharmacological effects and derived release systems-A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (7), 3591. doi:10.3390/ijms23073591
Pizzi, C., Manzoli, L., Mancini, S., Bedetti, G., Fontana, F., and Costa, G. M. (2010). Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors. Atherosclerosis 212 (1), 292–298. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.04.038
Puylaert, P., Roth, L., Van Praet, M., Pintelon, I., Dumitrascu, C., van Nuijs, A., et al. (2023). Effect of erythrophagocytosis-induced ferroptosis during angiogenesis in atherosclerotic plaques. Angiogenesis 26 (4), 505–522. doi:10.1007/s10456-023-09877-6
Qian, Y., Chen, L., Gao, B., and Ye, X. (2023). Sestrin2 levels in patients with anxiety and depression myocardial infarction was up-regulated and suppressed inflammation and ferroptosis by LKB1-mediated AMPK activation. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 45 (1), 2205049. doi:10.1080/10641963.2023.2205049
Ran, S., Peng, R., Guo, Q., Cui, J., Chen, G., and Wang, Z. (2024). Bupleurum in treatment of depression disorder: a comprehensive review. Pharm. (Basel) 17 (4), 512. doi:10.3390/ph17040512
Rana, T., Behl, T., Sehgal, A., Srivastava, P., and Bungau, S. (2021). Unfolding the role of BDNF as a biomarker for treatment of depression. J. Mol. Neurosci. 71 (10), 2008–2021. doi:10.1007/s12031-020-01754-x
Ravingerová, T., Kindernay, L., Barteková, M., Ferko, M., Adameová, A., Zohdi, V., et al. (2020). The molecular mechanisms of iron metabolism and its role in cardiac dysfunction and cardioprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (21), 7889. doi:10.3390/ijms21217889
Ren, D. D., Li, J., Chang, B., Li, C. S., and Yang, J. H. (2017). Early intervention with Didang decoction delays macrovascular lesions in diabetic rats through regulating AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 15 (11), 847–854. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(18)30018-9
Rochette, L., Dogon, G., Rigal, E., Zeller, M., Cottin, Y., and Vergely, C. (2022). Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (1), 449. doi:10.3390/ijms24010449
Rong, J., Li, C., Zhang, Q., Zheng, G., Fan, W., Pan, Z., et al. (2023). Hydroxysafflor yellow A inhibits endothelial cell ferroptosis in diabetic atherosclerosis mice by regulating miR-429/SLC7A11. Pharm. Biol. 61 (1), 404–415. doi:10.1080/13880209.2023.2225543
Scaini, G., Mason, B. L., Diaz, A. P., Jha, M. K., Soares, J. C., Trivedi, M. H., et al. (2022). Dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy and apoptosis in major depressive disorder: does inflammation play a role? Mol. Psychiatry 27 (2), 1095–1102. doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01312-w
Shakt, G., Tsao, N. L., Levin, M. G., Walker, V., Kember, R. L., Klarin, D., et al. (2024). Major depressive disorder impacts peripheral artery disease risk through intermediary risk factors. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 13 (4), e030233. doi:10.1161/jaha.123.030233
Shen, J., Hao, C., Yuan, S., Chen, W., Tong, T., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). Acupuncture alleviates CUMS-induced depression-like behaviors of rats by regulating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and ferroptosis. Brain Res. 1826, 148715. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148715
Shen, J. D., Zhang, Y. W., Wang, B. Y., Bai, L., Lu, S. F., Zhu, L. L., et al. (2020). Effects of resveratrol on the levels of ATP, 5-HT and GAP-43 in the hippocampus of mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Neurosci. Lett. 735, 135232. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135232
Shi, J., Yang, M. M., Yang, S., Fan, F., Zheng, G., Miao, Y., et al. (2024). MaiJiTong granule attenuates atherosclerosis by reducing ferroptosis via activating STAT6-mediated inhibition of DMT1 and SOCS1/p53 pathways in LDLR(-/-) mice. Phytomedicine 128, 155489. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155489
Shi, X., Wu, H., Liu, Y., Huang, H., Liu, L., Yang, Y., et al. (2022). Inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation mediated by osteopontin via regulating gut microbial lipopolysaccharide: a novel mechanism for paeonol in atherosclerosis treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 936677. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.936677
Shi, X., Xie, X., Sun, Y., He, H., Huang, H., Liu, Y., et al. (2020). Paeonol inhibits NLRP3 mediated inflammation in rat endothelial cells by elevating hyperlipidemic rats plasma exosomal miRNA-223. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 885, 173473. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173473
Shimada, K., Skouta, R., Kaplan, A., Yang, W. S., Hayano, M., Dixon, S. J., et al. (2016). Global survey of cell death mechanisms reveals metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 12 (7), 497–503. doi:10.1038/nchembio.2079
So, H. C., Chau, C. K., Cheng, Y. Y., and Sham, P. C. (2021). Causal relationships between blood lipids and depression phenotypes: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. Psychol. Med. 51 (14), 2357–2369. doi:10.1017/s0033291720000951
Song, Y., Cao, H., Zuo, C., Gu, Z., Huang, Y., Miao, J., et al. (2023a). Mitochondrial dysfunction: a fatal blow in depression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 167, 115652. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115652
Song, Y. H., Lei, H. X., Yu, D., Zhu, H., Hao, M. Z., Cui, R. H., et al. (2023b). Endogenous chemicals guard health through inhibiting ferroptotic cell death. Biofactors 50, 266–293. doi:10.1002/biof.2015
Stockwell, B. R. (2022). Ferroptosis turns 10: emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell 185 (14), 2401–2421. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.003
Su, G., Yang, W., Wang, S., Geng, C., and Guan, X. (2021). SIRT1-autophagy axis inhibits excess iron-induced ferroptosis of foam cells and subsequently increases IL-1Β and IL-18. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 561, 33–39. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.05.011
Su, L., Cai, Y., Xu, Y., Dutt, A., Shi, S., and Bramon, E. (2014). Cerebral metabolism in major depressive disorder: a voxel-based meta-analysis of positron emission tomography studies. BMC Psychiatry 14, 321. doi:10.1186/s12888-014-0321-9
Susser, L. I., and Rayner, K. J. (2022). Through the layers: how macrophages drive atherosclerosis across the vessel wall. J. Clin. Invest 132 (9), e157011. doi:10.1172/jci157011
Trachtenberg, F., Vichinsky, E., Haines, D., Pakbaz, Z., Mednick, L., Sobota, A., et al. (2011). Iron chelation adherence to deferoxamine and deferasirox in thalassemia. Am. J. Hematol. 86 (5), 433–436. doi:10.1002/ajh.21993
Tsao, C. W., Aday, A. W., Almarzooq, Z. I., Anderson, C. A. M., Arora, P., Avery, C. L., et al. (2023). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation 147 (8), e93–e621. doi:10.1161/cir.0000000000001123
Ursini, F., and Maiorino, M. (2020). Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 152, 175–185. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
Wang, A., Wan, X., Zhuang, P., Jia, W., Ao, Y., Liu, X., et al. (2023a). High fried food consumption impacts anxiety and depression due to lipid metabolism disturbance and neuroinflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120 (18), e2221097120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2221097120
Wang, D., Wang, J., Yu, Z., Yao, R., Zhang, J., and Zhao, X. (2024a). Quercetin alleviates perimenopausal depression induced by ovariectomy combined with chronic unpredictable mild stress through regulating serum elements and inhibiting ferroptosis in prefrontal cortex of rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 202, 5596–5611. doi:10.1007/s12011-024-04106-7
Wang, D., Ye, P., Kong, C., Chao, Y., Yu, W., Jiang, X., et al. (2021a). Mitoferrin 2 deficiency prevents mitochondrial iron overload-induced endothelial injury and alleviates atherosclerosis. Exp. Cell Res. 402 (1), 112552. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112552
Wang, H., He, Y., Sun, Z., Ren, S., Liu, M., Wang, G., et al. (2022a). Microglia in depression: an overview of microglia in the pathogenesis and treatment of depression. J. Neuroinflammation 19 (1), 132. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02492-0
Wang, L., Cai, J., Qiao, T., and Li, K. (2023b). Ironing out macrophages in atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 55 (1), 1–10. doi:10.3724/abbs.2022196
Wang, M., Wei, X., Jia, Y., Wang, C., Wang, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2024b). Quercetin alleviates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior by inhibiting NMDAR1 with α2δ-1 in rats. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30 (4), e14724. doi:10.1111/cns.14724
Wang, S., Guo, Q., Zhou, L., and Xia, X. (2024c). Ferroptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Death Discov. 10 (1), 265. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-02037-9
Wang, X., Li, S., Yu, J., Wang, W., Du, Z., Gao, S., et al. (2023c). Saikosaponin B2 ameliorates depression-induced microglia activation by inhibiting ferroptosis-mediated neuroinflammation and ER stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 316, 116729. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116729
Wang, X., Xiao, A., Yang, Y., Zhao, Y., Wang, C. C., Wang, Y., et al. (2022b). DHA and EPA prevent seizure and depression-like behavior by inhibiting ferroptosis and neuroinflammation via different mode-of-actions in a pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling model in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 66 (22), e2200275. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202200275
Wang, X., Zhang, M., Mao, C., Zhang, C., Ma, W., Tang, J., et al. (2023d). Icariin alleviates ferroptosis-related atherosclerosis by promoting autophagy in xo-LDL-induced vascular endothelial cell injury and atherosclerotic mice. Phytother. Res. 37 (9), 3951–3963. doi:10.1002/ptr.7854
Wang, Y., Jia, Y., Liu, X., Yang, K., Lin, Y., Shao, Q., et al. (2024d). Effect of Chaihu-Shugan-San on functional dyspepsia and gut microbiota: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 322, 117659. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117659
Wang, Y., Wang, S., Xin, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, S., Yang, Z., et al. (2021b). Hydrogen sulfide alleviates the anxiety-like and depressive-like behaviors of type 1 diabetic mice via inhibiting inflammation and ferroptosis. Life Sci. 278, 119551. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119551
Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Ye, T., Yang, L., Shen, Y., and Li, H. (2021c). Ferroptosis signaling and regulators in atherosclerosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 809457. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.809457
Wang, Y. L., Han, Q. Q., Gong, W. Q., Pan, D. H., Wang, L. Z., Hu, W., et al. (2018). Microglial activation mediates chronic mild stress-induced depressive- and anxiety-like behavior in adult rats. J. Neuroinflammation 15 (1), 21. doi:10.1186/s12974-018-1054-3
Wang, Y. L., Wu, H. R., Zhang, S. S., Xiao, H. L., Yu, J., Ma, Y. Y., et al. (2021d). Catalpol ameliorates depressive-like behaviors in CUMS mice via oxidative stress-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome and neuroinflammation. Transl. Psychiatry 11 (1), 353. doi:10.1038/s41398-021-01468-7
Wei, E., Gao, A., Mu, X., Qu, S., Yang, C., Li, F., et al. (2023). Paeonol ameliorates hippocampal neuronal damage by inhibiting GRM5/GABBR2/β-arrestin2 and activating the cAMP-PKA signaling pathway in premenstrual irritability rats. Brain Res. Bull. 205, 110830. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.110830
WHO (2017). Depression and other common mental disorders global health estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Woodward, N. C., Haghani, A., Johnson, R. G., Hsu, T. M., Saffari, A., Sioutas, C., et al. (2018). Prenatal and early life exposure to air pollution induced hippocampal vascular leakage and impaired neurogenesis in association with behavioral deficits. Transl. Psychiatry 8 (1), 261. doi:10.1038/s41398-018-0317-1
Wu, X., Guan, Y., Wang, J., Song, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2024a). Co-catalpol alleviates fluoxetine-induced main toxicity: involvement of ATF3/FSP1 signaling-mediated inhibition of ferroptosis. Phytomedicine 126, 155340. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155340
Wu, X., Pan, J., Yu, J. J., Kang, J., Hou, S., Cheng, M., et al. (2023a). DiDang decoction improves mitochondrial function and lipid metabolism via the HIF-1 signaling pathway to treat atherosclerosis and hyperlipidemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 308, 116289. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116289
Wu, Y., Liu, L., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Hu, J., Li, H., et al. (2024b). Xiaoyaosan promotes neurotransmitter transmission and alleviates CUMS-induced depression by regulating the expression of Oct1 and Oct3 in astrocytes of the prefrontal cortex. J. Ethnopharmacol. 326, 117923. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117923
Wu, Z., Chen, T., Qian, Y., Luo, G., Liao, F., He, X., et al. (2023b). High-dose ionizing radiation accelerates atherosclerotic plaque progression by regulating P38/NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy/ferroptosis of endothelial cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 117 (1), 223–236. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.04.004
Xiang, P., Chen, Q., Chen, L., Lei, J., Yuan, Z., Hu, H., et al. (2023). Metabolite Neu5Ac triggers SLC3A2 degradation promoting vascular endothelial ferroptosis and aggravates atherosclerosis progression in ApoE(-/-)mice. Theranostics 13 (14), 4993–5016. doi:10.7150/thno.87968
Xie, L. H., Fefelova, N., Pamarthi, S. H., and Gwathmey, J. K. (2022). Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and relevance to cardiovascular disease. Cells 11 (17), 2726. doi:10.3390/cells11172726
Xu, C., Xiong, Q., Tian, X., Liu, W., Sun, B., Ru, Q., et al. (2022a). Alcohol exposure induces depressive and anxiety-like behaviors via activating ferroptosis in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (22), 13828. doi:10.3390/ijms232213828
Xu, X. D., Chen, J. X., Zhu, L., Xu, S. T., Jiang, J., and Ren, K. (2022b). The emerging role of pyroptosis-related inflammasome pathway in atherosclerosis. Mol. Med. 28 (1), 160. doi:10.1186/s10020-022-00594-2
Xue, X., Deng, Y., Wang, J., Zhou, M., Liao, L., Wang, C., et al. (2021). Hydroxysafflor yellow A, a natural compound from Carthamus tinctorius L with good effect of alleviating atherosclerosis. Phytomedicine 91, 153694. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153694
Yan, B., Belke, D., Gui, Y., Chen, Y. X., Jiang, Z. S., and Zheng, X. L. (2023). Pharmacological inhibition of MALT1 (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1) induces ferroptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Death Discov. 9 (1), 456. doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01748-9
Yang, J., Du, C., Li, Y., Liu, R., Jing, C., Xie, J., et al. (2024a). Contrasting iron metabolism in undifferentiated versus differentiated MO3.13 oligodendrocytes via IL-1β-induced iron regulatory protein 1. Neurochem. Res. 49 (2), 466–476. doi:10.1007/s11064-023-04047-y
Yang, R., Shi, L., Si, H., Hu, Z., Zou, L., Li, L., et al. (2023). Gallic acid improves comorbid chronic pain and depression behaviors by inhibiting P2X7 receptor-mediated ferroptosis in the spinal cord of rats. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 14 (4), 667–676. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00532
Yang, W. S., Kim, K. J., Gaschler, M. M., Patel, M., Shchepinov, M. S., and Stockwell, B. R. (2016). Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113 (34), E4966–E4975. doi:10.1073/pnas.1603244113
Yang, Y., Huang, H., Cui, Z., Chu, J., and Du, G. (2021). UPLC-MS/MS and network pharmacology-based analysis of bioactive anti-depression compounds in betel nut. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 15, 4827–4836. doi:10.2147/dddt.S335312
Yang, Z., He, Y., Wu, D., Shi, W., Liu, P., Tan, J., et al. (2024b). Antiferroptosis therapy alleviated the development of atherosclerosis. MedComm (2020) 5 (4), e520. doi:10.1002/mco2.520
Yang, Z., Jiang, Y., Xiao, Y., Qian, L., Jiang, Y., Hu, Y., et al. (2024c). Di-Huang-Yin-Zi regulates P53/SLC7A11 signaling pathway to improve the mechanism of post-stroke depression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 2), 117226. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117226
Ye, Z., Huang, W., Li, J., Tang, Y., Shao, K., and Xiong, Y. (2024). Association between atherogenic index of plasma and depressive symptoms in US adults: results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2005 to 2018. J. Affect Disord. 356, 239–247. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2024.04.045
You, J., Ouyang, S., Xie, Z., Zhi, C., Yu, J., Tan, X., et al. (2023). The suppression of hyperlipid diet-induced ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells protests against atherosclerosis independent of p53/SCL7A11/GPX4 axis. J. Cell Physiol. 238 (8), 1891–1908. doi:10.1002/jcp.31045
Zaafar, D., Khalil, H. M. A., Elnaggar, R., Saad, D. Z., and Rasheed, R. A. (2024). Protective role of hesperetin in sorafenib-induced hepato- and neurotoxicity in mice via modulating apoptotic pathways and mitochondrial reprogramming. Life Sci. 336, 122295. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122295
Zeng, N. X., Li, H. Z., Wang, H. Z., Liu, K. G., Gong, X. Y., Luo, W. L., et al. (2022). Exploration of the mechanism by which icariin modulates hippocampal neurogenesis in a rat model of depression. Neural Regen. Res. 17 (3), 632–642. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.320993
Zeng, T., Li, J., Xie, L., Dong, Z., Chen, Q., Huang, S., et al. (2023). Nrf2 regulates iron-dependent hippocampal synapses and functional connectivity damage in depression. J. Neuroinflammation 20 (1), 212. doi:10.1186/s12974-023-02875-x
Zhang, G., Lv, S., Zhong, X., Li, X., Yi, Y., Lu, Y., et al. (2023a). Ferroptosis: a new antidepressant pharmacological mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1339057. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1339057
Zhang, H. L., Hu, B. X., Li, Z. L., Du, T., Shan, J. L., Ye, Z. P., et al. (2022a). PKCβII phosphorylates ACSL4 to amplify lipid peroxidation to induce ferroptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 24 (1), 88–98. doi:10.1038/s41556-021-00818-3
Zhang, J., Wang, X., Guan, B., Wang, X., An, X., Wang, T., et al. (2023b). Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule inhibits ferroptosis and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the GPX4/xCT signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 301, 115852. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115852
Zhang, J., Xie, S. A., Wang, J., Liu, J., Liu, Y., Zhou, S., et al. (2023c). Echinatin maintains glutathione homeostasis in vascular smooth muscle cells to protect against matrix remodeling and arterial stiffening. Matrix Biol. 119, 1–18. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2023.03.007
Zhang, M., Mao, C., Dai, Y., Xu, X., and Wang, X. (2024). Qixian granule inhibits ferroptosis in vascular endothelial cells by modulating TRPML1 in the lysosome to prevent postmenopausal atherosclerosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 328, 118076. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118076
Zhang, W., Yu, M., Zhang, Q., Yang, Z., and Zhang, T. (2022b). DFO treatment protects against depression-like behaviors and cognitive impairment in CUMS mice. Brain Res. Bull. 187, 75–84. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.06.016
Zhou, S. N., Zhang, J., Ren, Q. Y., Yao, R. F., Liu, P., and Chang, B. (2020). Early intervention with Di-Dang Decoction prevents macrovascular fibrosis in diabetic rats by regulating the TGF-β1/Smad signalling pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 18 (8), 612–619. doi:10.1016/s1875-5364(20)30073-x
Zhou, Y., Huang, Y., Ye, W., Chen, Z., and Yuan, Z. (2024). Cynaroside improved depressive-like behavior in CUMS mice by suppressing microglial inflammation and ferroptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 173, 116425. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116425
Zhou, Y., Que, K. T., Zhang, Z., Yi, Z. J., Zhao, P. X., You, Y., et al. (2018). Iron overloaded polarizes macrophage to proinflammation phenotype through ROS/acetyl-p53 pathway. Cancer Med. 7 (8), 4012–4022. doi:10.1002/cam4.1670
Zhu, L., Bao, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, J., Li, Z., Sun, X., et al. (2024a). Gualou-Xiebai herb pair ameliorate atherosclerosis in HFD-induced ApoE(-/-) mice and inhibit the ox-LDL-induced injury of HUVECs by regulating the Nrf2-mediated ferroptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 326, 117892. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.117892
Zhu, Q., Han, Y., He, Y., Meng, P., Fu, Y., Yang, H., et al. (2024b). Quercetin inhibits neuronal Ferroptosis and promotes immune response by targeting lipid metabolism-related gene PTGS2 to alleviate breast cancer-related depression. Phytomedicine 130, 155560. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155560
Keywords: ferroptosis, atherosclerosis, depression, comorbid, pathogenesis, therapy
Citation: Zhao Y, Ren P, Luo Q, Li X, Cheng X, Wen Y, Wu X and Zhou J (2025) Ferroptosis, pathogenesis and therapy in AS co-depression disease. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1516601. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1516601
Received: 24 October 2024; Accepted: 04 February 2025;
Published: 24 February 2025.
Edited by:
Ewa Litwa, Polish Academy of Sciences, PolandReviewed by:
Stefano Comai, University of Padua, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Ren, Luo, Li, Cheng, Wen, Wu and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoyun Wu, eXVueGlhb3d1MTE4QDEyNi5jb20=; Junjie Zhou, emhvdWp1bmppZUBnbXUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.