
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol. , 18 February 2025
Sec. Respiratory Pharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1516583
This article is part of the Research Topic Therapeutic Advances in Lung Cancer and Chronic Inflammatory Lung Disease View all 20 articles
A correction has been applied to this article in:
Corrigendum: Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targeting
 Min Qiang1,2
Min Qiang1,2 Zhe Chen1
Zhe Chen1 Hongyang Liu2
Hongyang Liu2 Junxue Dong3
Junxue Dong3 Kejian Gong1
Kejian Gong1 Xinjun Zhang1
Xinjun Zhang1 Peng Huo4
Peng Huo4 Jingjun Zhu5
Jingjun Zhu5 Yifeng Shao6
Yifeng Shao6 Jinazun Ma1
Jinazun Ma1 Bowei Zhang1
Bowei Zhang1 Wei Liu1*
Wei Liu1* Mingbo Tang1*
Mingbo Tang1*Owing to its high mortality rate, lung cancer (LC) remains the most common cancer worldwide, with the highest malignancy diagnosis rate. The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling (PAM) pathway is a critical intracellular pathway involved in various cellular functions and regulates numerous cellular processes, including growth, survival, proliferation, metabolism, apoptosis, invasion, and angiogenesis. This review aims to highlight preclinical and clinical studies focusing on the PAM signaling pathway in LC and underscore the potential of natural products targeting it. Additionally, this review synthesizes the existing literature and discusses combination therapy and future directions for LC treatment while acknowledging the ongoing challenges in the field. Continuous development of novel therapeutic agents, technologies, and precision medicine offers an increasingly optimistic outlook for the treatment of LC.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) predicts that in 2022, lung cancer (LC) will have the highest global rates of incidence at 12.4% and mortality at 18.7% (Bray et al., 2024). The 2022 report from the China National Cancer Center indicated that the number of LC cases in China will increase to 1,060,600, with 733,300 deaths. LC remains the leading cause of both incidence and mortality (Figure 1) (Han et al., 2024). Smoking is the most significant risk factor that markedly increases the incidence of LC. In China, smoking is responsible for approximately 44.7% of reported LC deaths in males and 6.4% in females (Xia et al., 2019). Based on the morphological characteristics of LC cells, LC is classified into small-cell lung cancer (SCLC, approximately 15%) and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC, approximately 85%) (Li et al., 2023). SCLC, with its small cellular morphology, is distinguished by its rapid proliferative kinetics and propensity for swift metastasis to organs, such as the liver and brain, through lymphatic and hematogenous routes. Consequently, the prognosis of SCLC is poor, with a 5-year survival rate less than 7% (Siegel et al., 2022). In contrast, the two predominant histological subtypes of NSCLC are adenocarcinoma (ADC; approximately 50%) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC; approximately 40%) (Davidson et al., 2013).
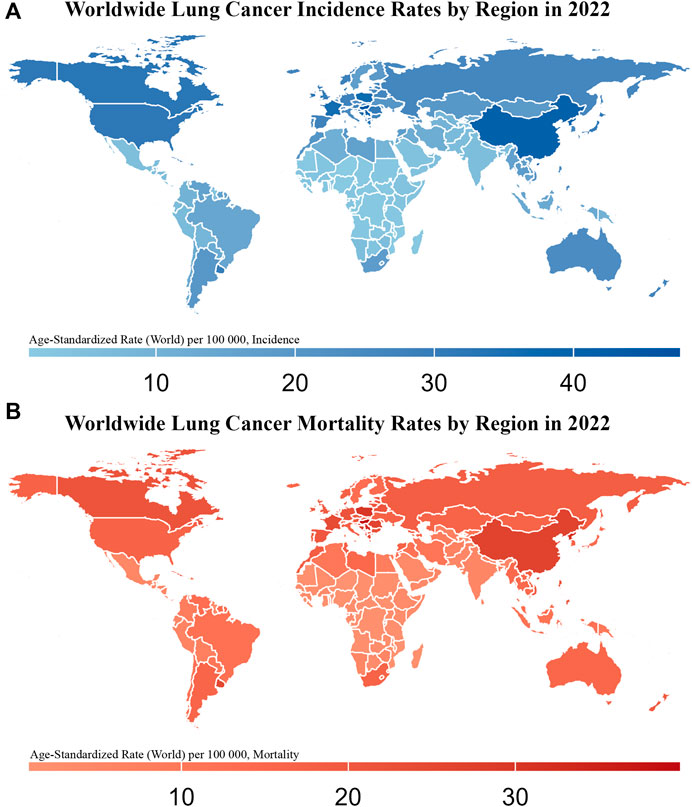
Figure 1. Worldwide Lung Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates by Region in 2022 This figure consists of two maps showing the age-standardized incidence (A) and mortality rates (B) of lung cancer (per 100,000 population) across different regions of the world in 2022. The color gradient in (A), from light blue to dark blue, represents increasing incidence rates, with darker blue regions indicating higher lung cancer incidence. In (B), the color gradient from light red to dark red represents increasing mortality rates, with darker red regions indicating higher lung cancer mortality.
The high incidence and mortality rates of LC pose significant global health challenges. Therefore, understanding these factors is essential to improve patient outcomes. The incidence of LC largely mirrors smoking rates with a latency period of several decades. Consequently, smoking cessation is considered the most effective strategy to reduce the risk of LC. Other important risk factors include environmental exposure to radon, occupational carcinogens, and preexisting nonmalignant lung diseases. Addressing this challenge requires a comprehensive approach to the various treatment modalities available for managing the complexities of LC.
Therapeutic strategies for LC can be classified into five main categories: surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. Multimodal treatment approaches have been used to improve patient survival. However, owing to the challenges of early diagnosis, the overall 5-year survival (OS) rate of LC remains low at only 19%, and therapeutic outcomes are unsatisfactory (Bray et al., 2024). In recent years, targeted therapy for LC has undergone rapid evolution with significant advancements. Given the high mutation rates in LC, progress in genetic and biomarker detection has made personalized, targeted therapies for individual patients increasingly feasible (Zappa and Mousa, 2016). As the treatment landscape evolves, personalized approaches driven by molecular and genetic insights have become pivotal in improving patient outcomes. Advances in molecular biology hold promise for developing chemopreventive agents that prevent the onset of LC (Bilello et al., 2002). Notably, the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling (PAM) pathway has emerged as a key target for the development of effective therapies.
The PAM signaling pathway is a key driver of carcinogenesis and drug resistance in patients with solid tumors. Abnormalities in the PAM signaling pathway are present in approximately 50% of tumors, making it the most frequently activated signaling pathway in human cancers (Martini et al., 2014). This pathway is regulated by various upstream signaling proteins and plays a crucial role in modulating downstream effectors through interactions with compensatory signaling pathways, particularly the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. The limited clinical success of targeted therapeutic agents highlights the importance of addressing alterations in the PAM signaling pathway when designing effective personalized treatment strategies (Ersahin et al., 2015). The use of inhibitors targeting key molecules within the PAM signaling pathway has garnered significant interest in targeted LC therapy. Indeed, several studies have developed promising inhibitors of this pathway, particularly for NSCLC (Fumarola et al., 2014). Several targeted therapies aimed at the PAM signaling pathway, including buparlisib (a PI3K inhibitor), MK2206 (an AKT inhibitor), sirolimus (an mTOR inhibitor), and perifosine (a dual PI3K/AKT inhibitor), are currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of LC (Moran et al., 2017; Primo N. et al., 2011; Novartis Pharmaceuticals, 2013a; AEterna Zentaris, 2006). Furthermore, several preclinical studies on natural compounds have garnered interest, with findings highlighting their potent inhibitory effects on the PAM signaling pathway (Zhang et al., 2021; Han et al., 2019; Niu et al., 2023). The high incidence and mortality rates of LC highlight the need for further research and treatment development.
In this review, we explored the role of the PAM signaling pathway in tumorigenesis and disease progression and reviewed recent advancements in preclinical studies and clinical trials targeting the PAM signaling pathway, focusing on the potential of natural products as therapeutic agents.
PI3K, an enzyme comprising a large family of lipid and serine/threonine kinases (Koundouros and Poulogiannis, 2020), is a heterodimeric protein comprising a p110 catalytic subunit and a p85 regulatory subunit (Figure 2) (Engelman et al., 2006). P110 catalytic subunits (p110α, p110β, p110δ, and p110γ) are encoded by PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, and PIK3CG, respectively (Fu et al., 2023). All p85 regulatory subunits (p85α, p85β, p55α, p55γ, p50α) are encoded by PIKR1 (Mazloumi Gavgani et al., 2018). Three types of PI3K (classes I, II, and III) have been identified in mammals. Class I PI3K is further divided into two subtypes: class 1A (p110α, p110β, p110δ) and 1B (p110γ), the most common type of cancer, is normally activated by RTKs, such as Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1-R), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/neu) (Higgins et al., 2016). Conversely, Class IB consists of one of the two regulatory subunits, p101 or p87, and the PIK3CG-encoded isoform, p110γ (Mazloumi Gavgani et al., 2018). Class II PI3K comprises three distinct enzymes: PI3K-C2α, PI3K-C2β, and PI3K-C2γ. In contrast, class III PI3K has only one known member, Vacuolar Protein Sorting 34 (Vps34, also known as PI3K-C3), the sole PI3 kinase expressed in all eukaryotes (Martini et al., 2014). PI3K signaling is one of the most commonly dysregulated pathways in cancer, promoting cell growth, proliferation, and survival (Koundouros and Poulogiannis, 2020). Activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase recruits PI3Kα to the plasma membrane, where it phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 triphosphate (PIP3). As a second messenger, PIP3 binds to and recruits various lipid-binding domains of downstream targets, such as the pleckstrin homology (PH), FYVE, phox (PX), C1, and C2 domains, to the cell membrane (Manning and Cantley, 2007). The PIK3CA mutation, which activates PI3K α, is one of the most common PI3K/AKT activation mechanisms in cancer. Distortion of NF1, MET, ERBB2, and RIT1 can also activate the PI3K signaling pathway (The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, 2014).

Figure 2. Schematic Representation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway. This figure illustrates the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway involved in cell growth, protein synthesis, lipid biogenesis, and autophagy regulation. Upon activation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) such as EGFR, IGF1-R, and HER2/neu, PI3K is activated, converting PIP2 to PIP3. This leads to the activation of AKT via phosphorylation at T308 by PDK1 and S473 by mTORC2. Activated AKT regulates the TSC1-TSC2 complex, which controls Rheb GTPase, thereby activating mTORC1. mTORC1 promotes protein synthesis (via 4E-BP1 and S6K), lipid biogenesis (via SREBP1 and PPARγ), and autophagy regulation (via ULK1).
The AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is initiated by PI3K activation. AKT, also known as PKB, is a 57-kDa serine/threonine kinase that is a key mediator of growth factor-nduced cell survival. In the mammalian genome, three AKT isoforms have been identified: AKT1, AKT2, and AKT3. AKT1 is the primary subtype crucial in regulating cell apoptosis (Datta et al., 1999). AKT1 binds to PIP3 and facilitates the activation of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) and mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2). PI3K activation leads to the phosphorylation of two critical residues in AKT1: threonine 308 (T308) in the activation loop and serine 473 (S473) in the C-terminal hydrophobic motif (Alessi et al., 1996). The phosphorylation of these two residues is a critical step in the maximal activation of AKT1. The corresponding residues in AKT2 (T309 and S474) and AKT3 (T305 and S472) regulated this activation process. PDK1 plays a key role in AKT activation by phosphorylating AKT1 at T308 (Alessi et al., 1997; Stokoe et al., 1997). Maximal activation of AKT requires phosphorylation at S473 in the hydrophobic motif, and mTORC2 is the primary kinase responsible for this phosphorylation (Sarbassov et al., 2005). Although AKT retained some activity without S473 phosphorylation, its activity was significantly reduced. Phosphorylation of S473 stabilizes T308 phosphorylation and maintains AKT in its fully active state (Alessi et al., 1996; Yang et al., 2002). EGFR-Y1068 self phosphorylates to provide a docking site for SH2 containing adaptor proteins, directly activating the PI3K/AKT pathway to maintain cell survival (Rodrigues et al., 2000). Phosphorylation of EGFR at Y992, Y1148, and Y1173 sites leads to recruitment of SHC to activate the MAPK/ERK pathway, thereby promoting cell proliferation (Okabayashi et al., 1994). IGF1R promotes cancer cell proliferation and differentiation by inducing phosphorylation of PI3K and AKT (Hua et al., 2022).
mTOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is the primary catalytic subunit of two protein complexes, mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2. mTOR was originally discovered as a cellular target of rapamycin and is involved in the checkpoint regulation of cell cycle regulation and regulates various biological processes, including cell proliferation, survival, autophagy, metabolism, and immunity (Saxton and Sabatini, 2017; Harwood et al., 2018). Inhibition of mTOR can effectively inhibit the growth, proliferation, cell cycle progression, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells, while inducing apoptosis activation (Yang et al., 2020).
The mTORC1 complex, which comprises mTOR, mLST8, Raptor, and PRAS40, is highly sensitive to rapamycin, making it a key target for mTOR inhibitors, particularly first-generation inhibitors (Hay and Sonenberg, 2004).
mTORC1 and mTORC2 are intricately linked. mTORC1 exerts feedback inhibition on mTORC2 through S6K1, one of its substrates. Upon activation by mTORC1, S6K1 phosphorylates Rictor at T1135 and mSin1 at T86 and T398, leading to the disruption of mTORC2 integrity (Dibble et al., 2009; Julien et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2013). mTORC2 activates the IGF-IR–AKT axis, thereby upregulating mTORC1 (Yin et al., 2016). Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a negative regulator of mTOR, which inhibits signal transduction via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Other regulatory factors include the tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) comprising TSC1 (hamartin) and TSC2 (tuberin) (Tewari et al., 2022). AKT inactivates the TSC1-TSC2 complex, thereby promoting the activation of RHEB GTPase, activating mTORC1 (Inoki et al., 2002). Subsequently, active mTORC1 promotes protein synthesis by inactivating the translation inhibitor 4E-BP1 and activating the kinase S6K; (ii) induces lipid biogenesis by activating the transcription factors SREBP1 and PPAR; (iii) inhibits autophagy by blocking ULK1 (Laplante and Sabatini, 2012; Ma and Blenis, 2009). mTORC2 directly activates AKT via phosphorylation at Ser-473 site (Dong et al., 2014; Benetatos et al., 2017).
Previous studies have identified non-coding RNA (ncRNA) as an essential regulatory factor in the PAM signaling pathway (Yang et al., 2019). ncRNAs function as both upstream and downstream effectors in regulating the PI3K pathway and, directly or indirectly, targets multiple key components of this pathway, including PI3K, AKT, and mTOR. However, the precise mechanisms by which ncRNAs exert these effects remain to be fully elucidated (Fumarola et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2018; Hong et al., 2020).
The PAM signaling pathway is a crucial intracellular signaling pathway that regulates various cellular processes, including cell growth, survival, proliferation, metabolism, apoptosis, invasion, and angiogenesis (King et al., 2015), and is one of the most commonly dysregulated pathways in cancers and pivotal in oncogenesis. Activation of the PAM signaling pathway can inhibit autophagy and apoptosis, which are typically associated with pro-survival effects (Luo et al., 2003; Xu et al., 2020). Most importantly, the excessive activation of key molecules within this pathway can unjustifiably promote cancer cell survival by inhibiting autophagy and apoptosis (Janku et al., 2018). The inhibition of this survival pathway induces autophagy and apoptosis in cancer cells (Yang et al., 2018).
The PAM signaling pathway is as a central signal transduction hub in response to extracellular stimuli, including insulin, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Li and Wang, 2014). Chemokine receptor 9 (CCR9), inflammation-associated cytokine Toll-like receptor (TLR), and interleukin (IL)-6 are key upstream regulatory factors of the PAM signaling pathway (Harashima et al., 2012; Axanova et al., 2010; Wegiel et al., 2008). High expression levels of CCR9 are associated with increased tumor proliferation and metastasis (Chai et al., 2022). IL6 promotes tumor cell survival through PI3K/AKT and cyclin A1 (Wegiel et al., 2008). The upregulation of TLR-4 coexists with the downregulation of PI3K, AKT, and mTOR, associated with reduced cell damage (Kamel et al., 2020).
Genetic alterations targeting the PAM signaling pathway are closely associated with cancer development. For example, the loss of PTEN in somatic cells represent the second most common oncogenic mutations in the human genome, second only to malignant p53 mutations (Yin and Shen, 2008). In recent years, the rising incidence of malignant tumors has been linked to abnormal activation of the PAM signaling pathway (Aziz et al., 2018). Mutations or overexpression of PI3K can result in hyperactivation of this pathway, driving cancer cell proliferation and survival. IL-7 upregulates PI3K expression and promotes AKT and mTOR phosphorylation, activating the PAM signaling pathway (Jian et al., 2019). Abnormal expression of KIF2A promotes malignant transformation of cell carcinoma. Different analytical approaches focusing on antitumor miRNAs and their specific targeting of oncogenes are of great significance for identifying the molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of lung squamous cell carcinoma (Uchida et al., 2019). AKT is constitutively active in many cancers, promotes resistance to apoptosis, and enhances tumor survival (Shariati and Meric-Bernstam, 2019). mTOR is often hyperactivated in cancer, leading to increased protein synthesis, cell growth, and angiogenesis, all essential for tumor progression (Noser et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023). Mutations in PI3K, loss of function of the PTEN tumor suppressor (a negative regulator of the pathway), and amplification or mutation of AKT can result in the constitutive activation of the PAM signaling pathway, driving uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival (Yehia et al., 2020). Owing to its pivotal role in cancer, the PAM signaling pathway is a major target for cancer therapies. Inhibitors targeting PI3K, AKT, and mTOR are undergoing clinical trials for various cancer types. However, drug resistance and feedback loops within the pathway remain major limitations that complicate the treatment strategies.
The PAM signaling pathway is involved in metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative diseases (Ramasubbu and Devi Rajeswari, 2023; Tan et al., 2023). For example, activation of the PAM signaling pathway alleviates ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic cardiomyopathy (Tan et al., 2023). This pathway also regulates insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis, making it a key focus of diabetes research (Zheng et al., 2023). Furthermore, applying plant-derived secondary metabolites in managing and treating various neurological diseases through modulation of the PAM signaling pathway is a promising neuroprotective strategy (Fakhri et al., 2021).
Understanding the biological complexities of the PAM signaling pathway is essential for elucidating its role in cancer progression and resistance mechanisms. Building on this foundation, the following section discusses therapeutic implications, focusing on how these insights can be applied to develop targeted treatment strategies for LC.
The PAM signaling pathway is one of the most frequently dysregulated networks in human cancers and plays a critical role in the proliferation and survival of LC cells. In LC cells, this pathway is often abnormally activated. For example, mutations in the PI3K gene or overexpression of AKT protein are common, which can cause uncontrolled proliferation, inhibited apoptosis, and enhanced migration and invasion ability of LC cells. Consequently, numerous drugs, most of which are small-molecule compounds, targeting these three key kinases---PI3K/AKT/mTOR have been developed and evaluated. Although these advances have contributed to significant progress, the effectiveness and future potential of these therapies require further exploration of specific inhibitors and their clinical applications.
In the following sections, we explore inhibitors targeting the PI3K, AKT, and mTOR components of the PAM signaling pathway, analyzing their mechanisms of action, outcomes of current clinical trials, and challenges in optimizing their use for LC therapy (Table 1) (Supplementary Images S1–S3). This in-depth analysis sheds light on how these small-molecule inhibitors shape the future of LC treatments.
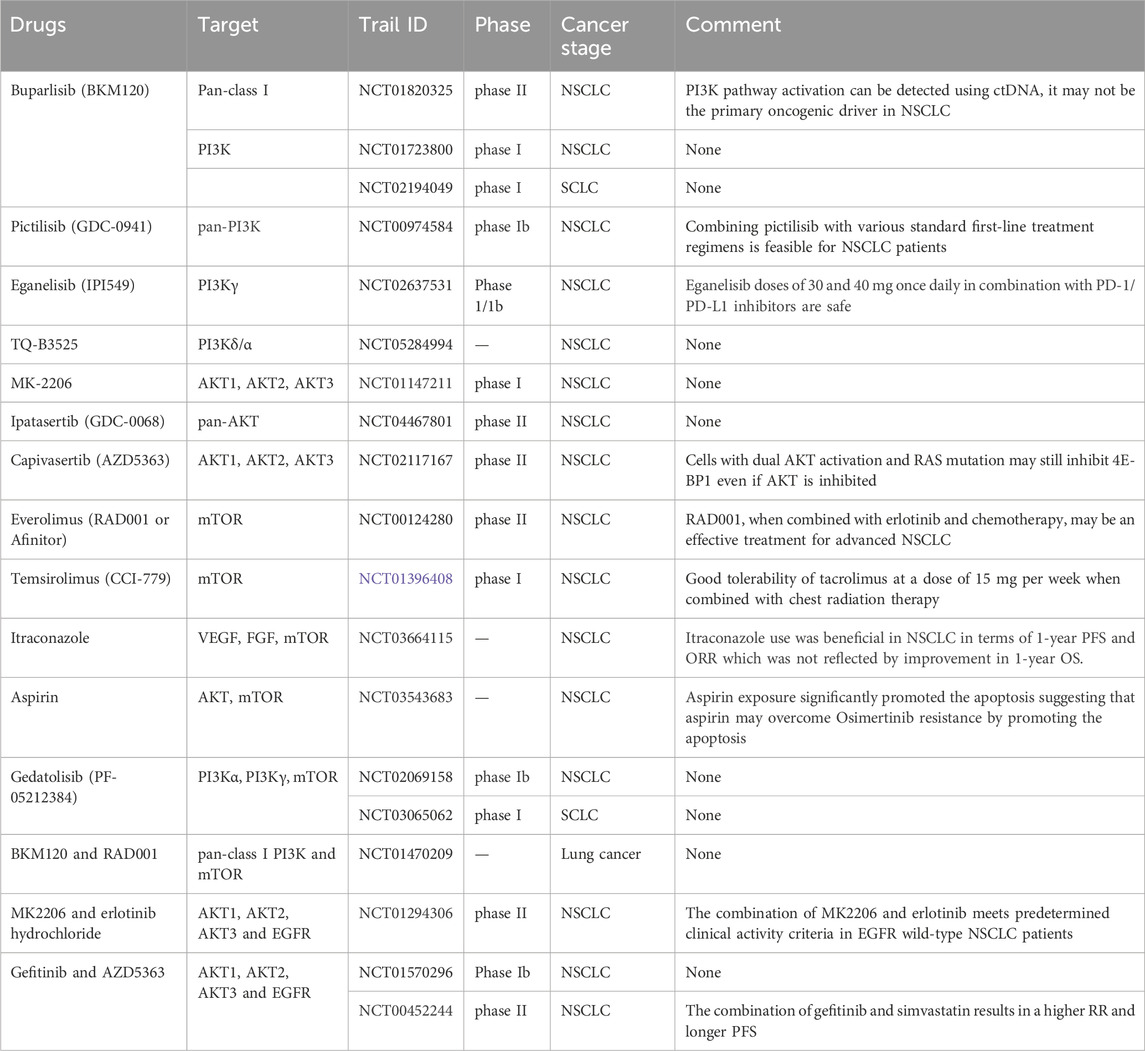
Table 1. Ongoing clinical trials of several drugs targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in lung cancer.
Within the PAM signaling pathway, PI3K is a primary drug target for cancer treatment since its hyperactivity is strongly associated with tumor progression, enhanced tumor microvascular formation, and increased cancer cell invasiveness (Liu et al., 2020a). Over the past few decades, several pharmaceutical companies have developed PI3K inhibitors to target this key pathway (Sirico et al., 2023; Bertucci et al., 2023). Although PI3K inhibitors have demonstrated significant therapeutic efficacy against human cancers, acquired and intrinsic resistance limit their clinical efficacy (Raith et al., 2023).
Buparlisib (BKM120), a 2,6-dimorpholino pyrimidine derivative, is a novel, potent, highly selective inhibitor of class I PI3K with confirmed anticancer effects in various solid tumor models (Hwang et al., 2022). However, it has not been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of specific cancer types (Emory University, 2011). Experimental studies have shown little correlation between mutations in K-Ras, p53, LKB1, PTEN, EGFR, or CDKN2A and the sensitivity of cells to BKM120. Therefore, BKM120 effectively inhibits the growth of NSCLC cells, regardless of genetic mutations (Ren et al., 2012). BKM120 has a rapid and effective inhibitory effect on the PAM signaling pathway in human NSCLC cells (Ren et al., 2012).
In SCLC and NSCLC, BKM120 may inhibit tumor cell growth by blocking key enzymes required for cell proliferation. Administering PI3K inhibitors, such as BKM120, in combination with chemotherapeutic agents, such as carboplatin, pemetrexed disodium, cisplatin, and etoposide, may enhance tumor cell killing (NCT01723800, NCT02194049) (Medifind, 2012; University of California, Davis, 2014). The open-label, two-stage, phase II study BASALT-1 (NCT01820325) evaluated the efficacy of the pan-PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in patients with recurrent NSCLC and PI3K pathway activation (Novartis Pharmaceuticals, 2013b). These results indicate that although PI3K pathway activation can be detected using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), it may not be the primary oncogenic driver in NSCLC. Therefore, combination therapies involving PI3K inhibitors and other agents may be more effective than monotherapy (Vansteenkiste et al., 2015).
Pictilisib (GDC-0941) is an efficient PI3K selective inhibitor. When combined with trastuzumab (an antitumor drug), pictilisib demonstrated significant therapeutic effects against cancer cells in vitro and on tumors in vivo (Junttila et al., 2009). One study investigated the treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC using pictilisib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin (with or without bevacizumab) or pemetrexed and cisplatin (with or without bevacizumab). The authors demonstrated that combining pictilisib with various standard first-line treatment regimens is feasible for NSCLC patients, and preliminary findings have indicated encouraging antitumor activity (NCT00974584) (Soria et al., 2017; Stephen et al., 2009).
Eganelisib (IPI549) is a first-in-class, orally administered, highly selective PI3Kγ inhibitor that has demonstrated anti-tumor activity in preclinical studies, both as a monotherapy and in combination with programmed cell death protein 1/ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) inhibitors. Eganelisib reshapes the tumor immune microenvironment and promotes cytotoxic T cell-mediated tumor regression without directly targeting the cancer cells (De Henau et al., 2016). The IPI-549–01 study was the first-in-human, multicenter, open-label, phase 1/1b dose-escalation trial.
The results indicated that eganelisib doses of 30 and 40 mg once daily in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors were selected for further evaluation in Phase II trials (NCT02637531) (Hong et al., 2023; Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 2015).
TQ-B3525, a novel PI3Kδ/α dual inhibitor developed by Zhengda Tianqing, induces cell apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation of malignant tumor cells by inhibiting the expression of PI3K protein and reducing the phosphorylation level of AKT protein (Li et al., 2024). TQ-B3525 selectively inhibits the PI3Kδ and PI3Kα subunits, overcoming drug resistance attributed to the upregulation of PI3Kα activity when PI3Kδ alone is inhibited. An ongoing single-arm, open-label, multi-cohort, multicenter clinical study is currently investigating the safety and efficacy of TQ-B3525 tablets combined with osimertinib for the treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC (NCT05284994) (Single-arm, 2022).
Alpelisib (BYL-719) is a potent, selective, orally active PI3Kα inhibitor with high efficacy in targeting PIK3CA-mutated cancersits anticancer activity against squamous cell LC cells with PIK3CA mutations in vitro and in vivo studies (Bonelli et al., 2015). BYL719 enhances the anticancer effects of gefitinib by inhibiting the p-AKT signaling pathway activated by PI3K/AKT in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells. The combination of BYL719 and gefitinib produced a synergistic effect on EGFR-mutant NSCLC cells via PI3K/AKT activation. Acquisition of PIK3CA mutations may contribute to cell proliferation and gefitinib resistance in NSCLC cells harboring EGFR mutations. Thus, combination therapy with gefitinib and BYL719 is a promising strategy to overcome EGFR-TKI resistance driven by PI3K/AKT activation (Yu Y. et al., 2023).
Candidate biomarkers for PI3K inhibitors have shown predictive value in preclinical models and exhibit tissue-specific changes in primary tumors (Spoerke et al., 2012).
Several drugs can specifically inhibit AKT protein, preventing excessive activation of downstream targets in the PAM signaling pathway. Ongoing clinical trials are investigating AKT inhibitors, such as capivasertib and ipatasertib, as monotherapy and in combination with other agents for treating advanced LC. In addition, MK-2206 has been evaluated in advanced solid and hematological malignancies. However, none of these drugs have received FDA approval. Notably, capivasertib is a promising new treatment option for these patients and is expected to gain Food and FDA approval in the near future (Alves and Ditzel, 2023).
MK-2206 is a potent, orally active allosteric inhibitor of human AKT1, AKT2, and AKT3, with demonstrated preclinical antitumor activity. A phase I study investigated the combination of MK-2206 and gefitinib in NSCLC patients who failed prior chemotherapy and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) (NCT01147211) (Lin et al., 2010).
Ipatasertib (GDC-0068) is an orally effective, highly selective, ATP-competitive pan-AKT inhibitor that activates FoxO3a and NF-κB through AKT inhibition, leading to p53-independent activation of PUMA. Ipatasertib also induces apoptosis in cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in xenograft mouse models (Sun et al., 2018; Blake et al., 2012).
Preclinical studies have suggested that ipatasertib enhances the therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy and immunotherapy by modulating the PI3K–AKT signaling pathway. Consequently, a multicenter phase II study is currently underway to evaluate the combination of ipatasertib and docetaxel for the treatment of patients with metastatic or advanced NSCLC who have failed or are intolerant to first-line immunotherapy (NCT04467801) (Clinical Research and Trials, 2020).
Capivasertib (AZD5363), a novel pyrrolopyrimidine-derived compound, inhibits all AKT isoforms and is an effective ATP-competitive AKT inhibitor with an IC50 of <10 nM for all three AKT subtypes. Using a GI50 critical value of <3 μM, 23% of a large panel of cell lines are sensitive to capivasertib inhibition, with three-quarters of these cell lines harboring PIK3CA mutations, PTEN deletions, or HER2 amplification. KRAS is a negative predictive biomarker of the capivasertib response (Davies et al., 2012). SAFIR02_Lung is an open-label, multicenter, randomized, phase II trial. Using high-throughput genomic analysis as a tool for treatment decision-making, this trial aims to identify actionable genetic abnormalities in NSCLC (NCT02117167) (UNICANCER, 2014). Cells with dual AKT activation and RAS mutations may inhibit 4E-BP1 even if AKT is inhibited (Middleton et al., 2015).
mTOR inhibitors were the first PAM-targeted drugs to enter clinical practice (Hudes et al., 2007). mTORC1 activation promotes the synthesis of proteins, lipids, and nucleotides while inhibiting autophagy, thereby enhancing cell survival, proliferation, and growth. In parallel, mTORC2 activation regulates protein kinases, including AKT, further supporting cell survival and proliferation (Sarbassov et al., 2005; Mao et al., 2022). Therefore, the functions of both mTORC1 and mTORC2 offer critical insights into the targeting of mTOR complexes to tumors. However, the effectiveness of some mTOR inhibitors may be limited by compensatory feedback loops that result in AKT activation (Machl et al., 2016).
Sirolimus is an effective and specific inhibitor of mTOR. In tissue culture studies, sirolimus at concentrations as low as 1 ng/mL inhibits mTOR signaling in cells. The first report on combining an mTOR inhibitor with radiotherapy in humans demonstrated that patients tolerated the combination well. Both clinical and animal data indicated that sirolimus can be safely combined with radiotherapy and cisplatin to treat LC (Sarkaria et al., 2007).
Everolimus (RAD001 or Afinitor) is a rapamycin analog that functions similarly by acting as a conformational inhibitor of mTOR. RAD001 is an FDA-approved drug used to treat kidney cancer. This prevents cancer cell proliferation and renders them susceptible to cell death. RAD001 improves progression-free survival in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma who previously received VEGF-targeted therapies (Motzer et al., 2008). Similar to rapamycin, everolimus induces AKT activation while inhibiting mTOR signaling in human cancer cells, including NSCLC cells, as well as in tumor biopsies (Wang et al., 2008; O'Reilly et al., 2006). This Phase II, nonrandomized, open-label, multicenter study evaluated the efficacy of everolimus monotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC previously undergone no more than two chemotherapy regimens (NCT00124280) (Open Label, 2005). Research has demonstrated that when administered at a daily dose of 10 mg, everolimus possesses favorable tolerability and safety within its pharmacological class. Additionally, preclinical evidence suggests that combining EGFRi and mTOR inhibitors can have cumulative or synergistic effects in NSCLC by sensitizing cells to DNA-damaging agents via mTOR inhibition. This indicates that everolimus, when combined with erlotinib and chemotherapy, may be an effective treatment for advanced NSCLC (Soria et al., 2009).
Temsirolimus (CCI-779) is an mTOR kinase inhibitor with antiproliferative and antiangiogenic properties. Temsirolimus activates autophagy and prevents cardiac function deterioration in animal models (Choi et al., 2012) and is a potential candidate for combination therapy with radiotherapy in NSCLC owing its established anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic activities in multiple epithelial tumors and its non-overlapping mechanisms with radiotherapy (Waqar et al., 2014). A phase I study evaluating the combination of tacrolimus and chest radiotherapy in patients with NSCLC demonstrated good tolerability of tacrolimus at a dose of 15 mg/week when combined with chest radiotherapy (NCT01396408) (Orphanet, 2011).
Itraconazole is an oral antifungal drug that has demonstrated anticancer effects in NSCLC by inhibiting angiogenesis. Circulating levels of angiogenic factors are associated with invasive tumor growth, metastasis, and prognosis in various solid tumors, including NSCLC. The FDA has approved itraconazole as an anti-angiogenic agent that targets factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and FGF. Itraconazole directly disrupts the production of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate (ATP), activating the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway and subsequent inhibition of the mTOR pathway. The results of the first randomized controlled trial evaluating itraconazole in combination with chemotherapy for newly diagnosed metastatic NSCLC demonstrated a significant improvement in overall response rate (ORR) compared with the control group. Additionally, the 1-year PFS in the itraconazole group was significantly improved, although this was not reflected in the 1-year OS (NCT03664115) (Mohamed et al., 2021; Asmaa et al., 2018).
Aspirin, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), not only possesses classic anti-inflammatory properties but also exhibits chemopreventive effects against various human cancers, including colon cancer, LC, breast cancer, and leukemia, making it a promising anticancer agent (Ulrich et al., 2006). Autophagy occurs frequently during tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy, and strategies to stimulate or inhibit autophagy have been proposed as potential cancer therapies (Yue et al., 2014). In LC cells, combination therapy with aspirin and ABT-737 (a Bcl-2 inhibitor) induces a stronger autophagic response than either drug alone. Autophagy triggered by this combination shifts the role of p38 from cell protection to death promotion, with p38 acting as a switch between two distinct types of cell death: autophagy and apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2015). In an in vivo study using a lung tumor model induced by 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) + lipopolysaccharide (LPS), nitric oxide-releasing aspirin (NO-aspirin) significantly reduced the number and size of lung tumors, as well as the expression of phosphorylated EGFR and AKT, and the pro-inflammatory molecules TNF-α and interferon-γ (Song et al., 2018).
Aspirin pretreatment disrupts the binding of the TATA-box and p300 at the initiation region of the mTOR promoter in cancer stem cells (CSCs), thereby inhibiting the binding of RNA polymerase II at these sites and suppressing mTOR gene transcription. Consequently, the downregulation of mTOR results in the phosphorylation of Akt at Ser473, leading to the activation of Gsk3β, which in turn causes the destabilization of Snail and β-catenin, thereby reversing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Khan et al., 2019). GSK-3 β is a serine/threonine protein kinase that plays an important role in regulating the degradation of cyclin D1 by phosphorylating Thr-286 (Yang et al., 2015). The dephosphorylation of GSK-3 β leads to the phosphorylation of cyclin D1, which is then degraded (Cross et al., 1995). Osimertinib-resistant cells exhibited abnormal activation of the PI3K/AKT/BIM pathway, and the classic drug aspirin has been shown to effectively reduce AKT phosphorylation and BIM activation. Consequently, aspirin may attenuate the PI3K/AKT/BIM signaling pathway, promoting apoptosis in osimertinib-resistant cells (NCT03543683) (Chung-Shien et al., 2018).
Gedatolisib (PF-05212384) is a potent dual inhibitor of PI3Kα, PI3Kγ, and mTOR, effectively targeting both mTORC1 and mTORC2 complexes. A Phase Ib, single-arm, open-label, dose-escalating study evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of gedatolisib in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with NSCLC. The results indicated that this combination was tolerable, with preliminary efficacy observed, particularly in clear cell ovarian carcinoma (CCOC) (NCT02069158) (Colombo et al., 2021; Medi find, 2014). An open-label Phase I clinical trial is currently evaluating the safety of gedatolisib in combination with palbociclib in patients with advanced SCLC. Although the FDA has approved palbociclib for other indications, palbociclib for this specific disease or gedatolisib alone or combined with palbociclib as a treatment option awaits approval. Palbociclib is an oral drug that inhibits the cell cycle, preventing cell growth. Gedatolisib is thought to modulate cell growth and survival by controlling key signaling events within tumor cells, potentially slowing or halting tumor activity (NCT03065062) (Dana-Farber, 2017).
Dactolisib (NVP-BEZ235) is an orally active, dual pan-class I PI3K and mTOR kinase inhibitor that targets p110α, p110γ, p110δ, p110β, mTORC1, and mTORC2 (Maira et al., 2008). Dactolisib induces significant antiproliferative effects in transgenic mice with carcinogenic KRAS-induced NSCLC, as well as in NSCLC cell lines expressing carcinogenic KRAS. Although dactolisib therapy alone cannot induce apoptosis, dual PI3K/mTOR blockade effectively sensitizes NSCLC cells expressing oncogenic KRAS to the pro-apoptotic effects of ionizing radiation (IR) in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, combining dual PI3K/mTOR blockade with IR may benefit patients with NSCLC expressing oncogenic KRAS (Konstantinidou et al., 2009). An abnormal vascular structure in the LC leads to hypoxia, which limits the effectiveness of radiotherapy. Dactolisib improves tumor oxygenation and vascular structure, contributing to effective vascular normalization. The significant therapeutic benefit of combining dactolisib and irradiation highlights its potential importance in cancer treatment (Fokas et al., 2012).
The combination of BKM120 and RAD001 has shown a synergistic inhibitory effect on LC cell growth in vitro and in vivo (NCT01470209) (Emory University, 2011; Wang et al., 2008; Sun et al., 2005). This combination not only eliminated RAD001-induced AKT and eIF4E phosphorylation but also enhanced the inhibitory effect on 4EBP1 phosphorylation and p21 induction (Ren et al., 2012).
Although this combination was tolerable when the doses of both drugs were reduced, it remained effective (Owonikoko et al., 2020).
MK2206 and erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) may inhibit tumor cell growth by blocking certain enzymes essential for cell proliferation. A phase II trial investigated the side effects and efficacy of MK2206 combined with erlotinib hydrochloride in treating patients with advanced NSCLC who previously responded to erlotinib hydrochloride but subsequently experienced disease progression (NCT01294306) (Primo N. et al., 2011). Studies have shown that the combination of MK2206 and erlotinib meets the predetermined clinical activity criteria in patients with wild-type EGFR NSCLC, necessitating further clinical investigation. Inhibition of the AKT pathway in wild-type EGFR NSCLC warrants additional clinical evaluation (Lara et al., 2015).
Gefitinib (ZD1839) is a potent, selective, and orally active EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits EGF-stimulated tumor cell growth by blocking EGF-induced EGFR autophosphorylation in tumor cells. In addition to its inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, gefitinib induces autophagy and apoptosis, making it a valuable agent for cancer research, particularly for LC and breast cancer (Wakeling et al., 2002; Pedersen et al., 2005; Piechocki et al., 2008). A Phase Ib trial investigated the combination therapy of gefitinib and the oral class I PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in patients with advanced NSCLC, focusing on those with alterations in PI3K pathway molecules and known overexpression of EGFR (NCT01570296) (National Cancer Centre, Singapore, 2012). A randomized Phase II trial compared treatment with either gefitinib alone or combined with simvastatin to treat patients with advanced NSCLC (NCT00452244) (Ji-Youn et al., 2007). The authors demonstrated that, in patients with wild-type EGFR non-adenocarcinoma, the combination of gefitinib and simvastatin results in a higher response rate (RR) and longer progression-free survival (PFS) than gefitinib alone. Therefore, simvastatin may enhance the efficacy of gefitinib in this subgroup of gefitinib-resistant NSCLC patients (Han et al., 2011).
EGFR inhibitors are generally ineffective in most NSCLC cases with wild-type EGFR, necessitating new treatment strategies. AKT signal transduction plays a crucial role in mediating EGFR survival in NSCLC. Combining gefitinib and AZD5363 demonstrated synergistic growth inhibition in EGFR-mutant (HCC-827 and PC-9) and wild-type (NCI-H522, NCI-H1651) NSCLC cell lines. Therefore, dual inhibition of EGFR and AKT is a potential early treatment strategy for patients with both EGFR mutant and wild-type NSCLC (Puglisi et al., 2014).
AZD6244 is an effective, selective, orally administered MEK1/2 inhibitor. The combination of NVP-BEZ235 and AZD6244 enhanced both antitumor and anti-angiogenic effects. Studies have shown that combining selective MEK and PI3K/mTOR inhibitors can effectively inhibit the growth of gefitinib-resistant tumors caused by EGFR T790M mutation, MET amplification, and KRAS/PIK3CA mutations (Qu et al., 2014). This new treatment strategy may offer a practical approach to treating these patients.
Although several drugs targeting the PAM signaling pathway have been developed, research on natural products demonstrated promising potential.
The next section explores the application of natural products in targeting the PAM signaling pathway and examines their underlying mechanisms.
Recently, drugs isolated and purified from natural products have garnered considerable interest. As a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) used in disease treatment, TCM offers several advantages, including minimal side effects, noninvasiveness, low cost, and broad accessibility to cancer therapy. Numerous studies have demonstrated the antitumor activity of various TCM ingredients, with clear benefits in reducing toxicity and enhancing efficacy when combined with other treatment modalities (Table 2) (Le-Xin et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2024).

Table 2. Preclinical investigation of several natural products targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in lung cancer.
For example, quercetin, kaempferol, and isorhamnetin demonstrated anti-NSCLC effects by targeting AKT1 and EGFR. Among these compounds, isorhamnetin exhibits the strongest binding affinity to EGFR, with a binding energy of −6.79 kcal/mol. The primary interactions between isorhamnetin and EGFR involve carbon-hydrogen bonds and Pi-sigma, Pi-sulfur, and Pi-alkyl interactions. Isorhamnetin inhibits the migration and invasion of A549 cells, induces cell apoptosis and G1 phase arrest, and reduces expression of P-PI3K and P-AKT in A549 cells (Tang et al., 2024). A drug may play a crucial role through multiple signaling pathways due to its multiple targets. For instance, Lanatoside C induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and inhibits cancer cell growth by weakening the MAPK, Wnt, JAK-STAT, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways (Reddy et al., 2019).
Napabucasin is a furanonaphthoquinone compound derived from plants of the Bignoniaceae family, with botanical sources including Tabebuia cassinoides (Rao and Kingston, 1982), Millettia versicolor (Fotsing et al., 2003), Ailanthus integrifolia (Kosuge et al., 1994), Ekmanian longiflora (Peraza-Sánchez et al., 2000), Newbouldia laevis (Eyong et al., 2015), and Handroanthus impetiginosus (Wagner et al., 1989). Previous studies have demonstrated that napabucasin and other compounds isolated from the roots of Ekmanianthe longiflora exhibit potent cytotoxicity against various cancer cell lines, including colon cancer, LC, and multidrug-resistant oral epidermoid carcinoma (Peraza-Sánchez et al., 2000). Napabucasin induces apoptosis and autophagy in LC cells by directly targeting AKT and Mtor. In the interaction with AKT, the key residues, Lys14, Glu17, Tyr18, and Arg23, in the PH domain play crucial roles in hydrogen bonding. In the NB-mTORC2 complex, napabucasin facilitated hydrophobic interactions with residues Leu2185, Lys2187, Glu2190, Asp2195, Ile2237, Trp2239, Val2240, Asn2343, Met2345, Leu2354, and Phe2358 and formed hydrogen bonds with Ile2356 and Asp2357. These results suggest that napabucasin disrupts the interactions between ATP complexes and mTOR catalytic targets. Inhibition of the AKT and mTOR pathways results in a reduction of the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, Mcl-1, and c-Myc, inducing apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation. This leads to autophagy, as evidenced by converting LC3B I to LC3B II (Petsri et al., 2022).
Ophiopogonin B, a bioactive compound derived from Radix Ophiopogon japonicus, is traditionally used in Chinese medicine to treat pulmonary diseases. NCI-H157 and H460 cells, representing the main subtypes of NSCLC originating from squamous and large cell carcinoma, respectively, have been used to investigate the effects of ophiopogonin B. In these cells, ophiopogonin B inhibited phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT) at the Ser308 and Thr473 sites and significantly induced autophagy without triggering apoptosis. Notably, in NCI-H460 cells, ophiopogonin B suppressed the PAM signaling pathway than in NCI-H157 cells, suggesting it as a potential inhibitor of the PI3K/AKT pathway for the treatment of NSCLC (Chen et al., 2013).
Fucoidan is a sulfated polysaccharide extracted from brown seaweed and is primarily composed of L-fucose and sulfate groups with an average molecular weight of approximately 20,000 Da. Fucoid polysaccharides exhibit a range of biological activities, including antibacterial effects (Zapopozhets et al., 1995), antioxidant (Wang et al., 2009), anti-inflammatory (Choi et al., 2010), anticoagulant (Dürig et al., 1997), and anti-tumor activities (Aisa et al., 2005). Fucoid polysaccharides significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of PI3K and its downstream target AKT in a concentration- and time-dependent manner and inhibited mTOR phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, two direct downstream targets of mTOR, 4E-BP1, and p70S6K, which are markers of mTOR activity, were significantly downregulated. In A549 LC cells, fucoid polysaccharides inhibited MMP-2 activity by suppressing the PAM signaling pathway, reducing cancer cell migration and invasion (Lee et al., 2012).
Sophflarine A, a novel alkaloid derived from Sophora flavescens, exhibits significant antiproliferative activity against NSCLC cells both in vitro and in vivo. Sophflarine A is characterized by a unique 6/8/6/6 four-ring system formed by the intramolecular half-bridge of 5,6-seco sophocarpine and inhibits NSCLC cell proliferation by inducing pyroptosis and impairs cell migration, invasion, colony formation, and angiogenesis through PAM-mediated autophagy. Sophflarine A also promotes reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by inhibiting the PAM signaling pathway and reducing p62 expression, thereby inducing autophagy and facilitating the conversion of LC3B-I to LC3B-II (Luo et al., 2023).
Euphorbia hirta is an herbaceous plant in the Euphorbiaceae family commonly found worldwide. E. hirta is well-known for its efficacy against various fungal and bacterial infections (Ogbulie et al., 2007) and contains secondary metabolites, including terpenoids, flavonoids, phenols, and essential oils. Currently, nanobiotechnology and nanomedicine are gaining increasing attention due to advancements in delivering targeted therapies that specifically destroy malignant cells (Gowda et al., 2013). Silver ions can inactivate invading pathogens and cancer cells, making them one of the most extensively studied metals for their activity against microbial pathogens and malignant cells (Iravani, 2011; Ebrahiminezhad et al., 2016). Over the past 20 years, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have garnered significant attention for their potent antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antiangiogenic, and anticancer properties, making them valuable for various biomedical applications (Lansdown, 2006). Additionally, AgNPs selectively destroy malignant cells while protecting normal cells through the controlled release of Ag ions (Jeong et al., 2014). In addition, some studies have shown that silver AgNPs selectively destroy malignant cells while protecting normal cells by releasing silver ions (Priya et al., 2011). This demonstrates that the application of Eh-AgNPs significantly reduces the phosphorylation of p-PI3K, p-AKT, p-mTOR, and p70S6K. The administration of Eh AgNPs specifically decreased the expression of PI3Kγ, without affecting other PI3K subtypes such as PI3Kα, β, and δ. These findings suggest that Eh AgNPs induce cell apoptosis by downregulating PI3Kγ, disrupting the PAM/p70S6K signaling pathway (Ramachandran et al., 2022).
Emodin (1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthraquinone) is a naturally occurring anthraquinone derivative isolated from the roots and bark of many plants, fungi, and lichens, including Rheum palmatum and Polygonam multiflorum (Shrimali et al., 2013). Emodin significantly downregulates the expression of AKT, p-AKT, I κ B- α, p-I κ B- α, p65, p-p65, mTOR, and p-mTOR in the AKT signaling pathway, thereby promoting apoptosis of HL-60 cells (Zheng et al., 2007). In cancer cells overexpressing Her2/neu, treatment with emodin inhibited MAPK and PI3K/AKT dependent pathways, thereby suppressing cell growth and inducing apoptosis. Research has shown for the first time that treatment with emodin leads to blocking the binding of Her2/neu to Hsp90, intracellular redistribution, and enhanced ubiquitination, thereby promoting the proteasomal degradation of Her2/neu. This may represent a new approach for targeted therapy of Her2/neu overexpressing cancer (Yan et al., 2011).
The PAM signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in the maturation, differentiation, recruitment, and survival of immune cells. The regulation of the immune system via the PAM signaling pathway is finely tuned, enabling the precise mobilization or inhibition of specific immune cell subsets through tightly controlled signaling mechanisms.
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIM), a critical site for tumor growth, invasion, and immune evasion, comprises various immune cells, tumor-associated cells, and signaling molecules. The PAM signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in mediating the interactions between tumor cells and their surrounding microenvironment, particularly affecting immune cells and influences immune response, cell survival, and dysfunction (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) Affecting Lung Cancer Progression. This figure illustrates the interactions within the tumor microenvironment (TME) that contribute to lung cancer progression. Various components, including stromal cells, tumor-associated macrophages (TAM M2), pro-tumorigenic macrophages (PAM), regulatory T cells (Treg), dendritic cells (DC), natural killer (NK) cells, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), play significant roles in modulating immune responses and tumor growth. Stromal cells provide structural support and secrete growth factors that promote tumor proliferation. TAM M2 cells release VEGFA, stimulating angiogenesis and increasing blood supply to the tumor. Pro-tumorigenic macrophages (PAM) also interact with immune cells, promoting an inflammatory environment that favors tumor survival. Regulatory T cells (Treg) produce IL-10, which suppresses the activity of effector T cells and other immune cells, facilitating tumor immune evasion. The mTOR pathways (mTOR1 and mTOR2) regulate Treg function and T cell differentiation, contributing to an immunosuppressive environment that supports tumor growth. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and dendritic cells (DC) secrete immunosuppressive cytokines such as IL-6 and TGF-β, which inhibit the anti-tumor activity of NK cells and T cells. miR-26a-5p further modulates these pathways, enhancing immune suppression. These complex interactions within the TME collectively create an environment that promotes immune escape, angiogenesis, and tumor progression.
The following outlines the interactions between key cells in the TIM and PAM signaling pathways: Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are among the most abundant cellular components in the tumor microenvironment and typically exhibit an M2-type immunosuppressive phenotype (Guo et al., 2013). TAMs are a significant source of angiogenic factors that promote vascular growth, and subsequently accelerate tumor invasion and metastasis. TAMs contribute to angiogenesis by activating and releasing these factors, and TAM-derived VEGFA plays a crucial role in driving tumor-associated angiogenesis (Riabov et al., 2014). Therefore, TAM-mediated angiogenesis is a potential therapeutic target for malignant tumors. The PAM signaling pathway plays a key role in regulating the differentiation, survival, and function of TAMs. Excessive activation of the PAM signaling pathway drives the transformation of TAMs toward the M2 phenotype, enhancing their pro-tumor activities, such as the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines like IL-10 and promoting angiogenesis, while simultaneously reducing the expression of M1-associated cytokines like TNF-α (Wang et al., 2018). Drugs that inhibit the PAM signaling pathway, such as PI3K inhibitors, may alter the phenotype of TAMs, transforming them from the M2 type to the antitumor M1 type, thereby enhancing the tumor immune response.
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are T cells and other immune cells that infiltrate tumor tissues and are typically associated with better antitumor immune responses. This indicates the parameters of the immune response to tumors (Riabov et al., 2014). Numerous studies have demonstrated that the quantity and composition of TILs are associated with an improved response to ICI therapy in various solid tumors (Cristescu et al., 2018). Activation of the PAM signaling pathway in TILs can influence their antitumor capabilities. The regulation of the PAM signaling pathway can enhance the infiltration and antitumor activity of TILs, particularly CD8+ T cells (Zhuang et al., 2020). Compared with normal T lymphocytes, tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes exhibited relatively low levels of miR-26a-5p. Experimental studies have shown that miR-26a-5p can inhibit the PAM signaling pathway, thereby reducing the ability of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating cells to eradicate tumors. Consequently, miR-26a-5p has emerged as a promising target for optimizing the efficacy of TIL therapy (Wang et al., 2023). For example, PI3Kδ-specific inhibitors can enhance the activity of TILs, thereby improving the immune-mediated clearance of tumors. Some tumor cells induce immunosuppressive signals by activating the PAM signaling pathway, which reduces the function (Chandrasekaran et al., 2021). This immune escape mechanism is a key focus of current research, with efforts to restore the antitumor activity of TILs by targeting the PAM signaling pathway.
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a critical class of immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment. They inhibit the function of effector T and NK cells, thereby promoting tumor growth (Budhwar et al., 2018). Granulocyte myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSCs) are the primary subpopulation of MDSCs and immature myeloid cells (IMCs) with immunosuppressive activity.
The role of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) is dependent on IFN-I signaling, which inhibits the activation of the PAM signaling pathway through a direct interaction with AKT. This suggests that the differentiation of immunosuppressive G-MDSCs involves a shift from immune activation to immune tolerance (Sun et al., 2022). The activation of the PAM signaling pathway enhances the immunosuppressive functions of MDSCs, leading to increased secretion of inhibitory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TGF-β, which suppress the anti-tumor activity of effector immune cells. Inhibition of the PAM signaling pathway can weaken the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs, thereby improving the effectiveness of tumor immunotherapy (Wu et al., 2020).
PI3K, particularly the PI3Kδ and PI3Kγ subtypes, predominant in white blood cells, are key regulators of immune homeostasis. Multiple studies have demonstrated that immunosuppressive regulatory T cells (Tregs) are highly dependent on PI3Kδ, as observed in human Tregs, mouse Tregs, and PI3Kδ-inactivated mouse models (Ahmad et al., 2017; Dong et al., 2019; Chellappa et al., 2019). PI3Kδ are involved in T cell receptor signaling, cell proliferation, and survival in Tregs. Notably, in a mouse model of LC, co-administration of PI3Kδ-specific inhibitors and tumor-specific vaccines reduced the number of inhibitory Tregs within the tumor microenvironment and increased the number of vaccine-induced CD8+ T cells, enhancing anti-tumor efficacy (Ahmad et al., 2017). Pharmacological inhibition of PI3Kδ effectively controls disease by significantly reducing the quantity, proliferation, and activation of CD25+ Tregs. However, this PI3Kδ-mediated reduction in Tregs did not improve CD8+ T cell function, as PI3Kδ inhibition also impairs T cell receptor signaling in CD8+ T cells, decreasing activation, effector differentiation, and proliferation (Hanna et al., 2019). Therefore, inhibiting PI3Kδ can suppress innate and adaptive immune systems, increasing patients’ susceptibility to severe infections. At the same time, the unique dependency of immunosuppressive regulatory T cells on PI3Kδ may explain the frequent occurrence of autoimmune conditions, such as pneumonia and colitis, in patients undergoing PI3Kδ inhibition (Tarantelli et al., 2021). Similar to PI3Kδ, the PI3Kγ subtype is active in lymphocytes. PI3Kγ, along with its regulatory subunits PIK3R5 and PIK3R6, is uniquely overexpressed in the bone marrow compartment, where PI3Kγ is the primary catalytic subunit for PI3K activity (Schmid et al., 2011). G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) activate p110γ through a Ras/p101-dependent mechanism, while receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and Toll-like/IL-1 receptors (TLR/IL1Rs) activate p110γ via a Ras/p87-dependent mechanism. Once activated, p110γ promotes the inside-out activation of the integrin α4β1, facilitating the invasion of bone marrow cells into tumors. Pharmacological or genetic blockade of p110γ inhibits inflammation, tumor growth, and metastasis in both implanted and spontaneous tumor models (Schmid et al., 2011).
AKT expression in most immune cells, both at the baseline and upon activation, underscores its critical role in immunity. AKT is essential for the regulation of both innate and adaptive immunity (Guerau-de-Arellano et al., 2022). AKT1 and AKT2, but not AKT3, promote terminal differentiation of CD8+ T cells while impairing the development of central and effector memory CD8+ T cell populations. These findings offer insights into adoptive cell transfer and vaccine-based cancer immunotherapies (Abu et al., 2015). In addition, AKT plays a critical role in CD4+ T cells by guiding helper T cell (Th) differentiation in a subtype-specific manner. AKT1 promotes antigen-specific Th1/Th17 responses by inhibiting the proliferation of thymes-derived T cells (Tregs). In contrast, AKT2 enhances tTreg proliferation in vitro and in vivo, while suppressing antigen-specific Th1/Th17 responses (Ouyang et al., 2019).
T cell activation through TCR and CD28 co-stimulation promotes the downstream induction of cytokines IL-2 and IFN-γ, mediated by T helper type 1 (Th1) cells in an AKT-dependent manner. In contrast, the regulation of IL-4 and IL-5 by T helper type 2 (Th2) cells occurs independently of AKT. FOXO is considered a tumor suppressor because they play an important role in inducing cell cycle arrest, DNA damage repair, and ROS clearance (Jiramongkol and Lam, 2020). AKT controls Treg homeostasis by inhibiting FOXO1 phosphorylation, enhancing Treg-mediated suppression (Ouyang et al., 2012). Treg cells expressing the transcription factor Foxp3 are essential for maintaining immune self-tolerance; however, excessive Treg activity can suppress antitumor immune responses. Low-dose expression of Foxo1 mutants has been shown to selectively deplete tumor-associated Treg cells, activate effector CD8+ T cells, and inhibit tumor growth without inducing autoimmunity. Inactivation of Foxo1 is crucial for migrating activated Tregs (aTregs), which play a key role in suppressing CD8+ T cell responses. FOXO4 activates the cell cycle dependent kinase inhibitor p27, which in turn inhibits the cell cycle dependent kinase (CDK) and blocks the G1 cell cycle progression in tumors. Silencing FOXO4 expression leads to an increase in cell cloning rate and migration enhancement (Yang et al., 2005). Modulating the FOXO signaling pathway in Treg cells offers a potential strategy for selectively disrupting tumor immune tolerance (Luo et al., 2016). Recent studies have demonstrated that Treg-mediated immune suppression is constrained in an AKT-dependent manner by PD-1 inhibition. Reduced signal transduction in the PI3K-AKT pathway is a key mechanism contributing to the enhanced suppressive capacity of PD-1-deficient Treg cells (Tan et al., 2021).
mTOR is the catalytic component of the mTORC1 and mTORC2 complexes, and its activation is essential for the proper activation and differentiation of effector CD4+ T cells (Zeng et al., 2013). These complexes collectively regulate cellular metabolism, the primary mechanism by which mTOR influences the immune system. mTORC1, in particular, plays a key role in regulating the differentiation of memory T cells (Araki et al., 2009); mTORC1 also partially sustains Treg cell function by inhibiting the mTORC2 pathway, linking immune signals from the TCR and IL-2 to adipogenesis pathways and functional adaptability. This highlights the central role of the Treg inhibitory activity in maintaining immune homeostasis and tolerance (Zeng et al., 2013). mTORC1 influences the effector response of CD8+ T cells, whereas mTORC2 regulates the memory of CD8+ T cells. mTORC2 inhibition leads to metabolic reprogramming driven by FOXO-mediated suppression of IL-15R expression, thereby enhancing the generation of CD8+ memory cells (Pollizzi et al., 2015). Importantly, mTORC1 and mTORC2 play direct roles in regulating innate immunity. mTOR is a key regulator of memory CD8+ T cell differentiation, and rapamycin, an immunosuppressive drug, has an immunostimulatory effect on the production of memory CD8+ T cells (Araki et al., 2009). mTORC1 regulates the production of inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting NF-κB, controlling monocyte/macrophage-mediated inflammation (Weichhart et al., 2008). mTORC2 complements this by modulating the chemotaxis of mast cells and neutrophils. Additionally, through FOXO1 inhibition, mTORC2 downregulates IL-12 production in dendritic cells and plays a key role in IL-4-dependent selective activation of M2 macrophages (Brown et al., 2011; Hallowell et al., 2017). mTOR regulates the expression of key inflammatory cytokines, including IL-10, IL-12, TGF-β, and TNF (Powell et al., 2012). mTOR-mediated inflammatory responses can also promote the recruitment of immune cells to TIM, which may exert antitumor effects or contribute to cancer cell growth, progression, and metastasis (Mafi et al., 2021). Activation of tumor-associated PAM signaling also promotes the expression of VEGF, a key mediator of angiogenesis and a chemokine that attracts immunosuppressive MDSCs and Tregs (Powell et al., 2012; Ostrand-Rosenberg and Fenselau, 2018; Goel and Mercurio, 2013). MDSCs accumulate in most cancer patients, promote tumor progression, suppress antitumor immunity, and impede the effectiveness of many cancer immunotherapies (Ostrand-Rosenberg and Fenselau, 2018).
In TIM, the PAM signaling pathway plays a crucial role in tumor immune escape and the efficacy of immunotherapy by regulating the activation, function, and inhibitory properties of various immune cells. Targeted therapies that inhibit the PAM signaling pathway not only directly suppress tumor cell growth but also enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy by modulating the immune microenvironment. The advent of immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatments, marking the beginning of the immune era. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4), along with cell-based therapies designed to target and destroy cancer cells, have demonstrated significant clinical efficacy.
Therefore, combining drugs that target the PAM signaling pathway with immunotherapies can significantly improve the survival rate of patients with LC. A randomized, prospective, multicenter, proof-of-concept Phase II clinical trial is currently evaluating the ORR of targeted therapy combined with the standard of care (SoC) in NSCLC (NCT04591431). Both immunotherapies, which leverage the body’s immune system to combat cancer, and targeted therapies are the cornerstones of personalized medicine. Ongoing research on gene mutations in tumor tissues or blood samples (e.g., circulating tumor cells [CTCs] or circulating free DNA [cfDNA]) is reshaping cancer treatment strategies. In the context of precision medicine, immuno-oncology is evolving into precision immuno-oncology with an emphasis on identifying predictive biomarkers that can optimize responses to ICIs (Annals of Oncology, 2020).
PI3K inhibition is a key target for antitumor therapy. While several inhibitors, including copanlisib, alpelisib, idelalisib, duvelisib, and umbralisib, have been approved by the FDA, challenges remain regarding drug resistance, identification of sensitivity markers, and toxicity (Yu M. et al., 2023).
Serious toxicities associated with PI3K inhibitors in clinical practice include hyperglycemia, skin reactions, diarrhea/colitis, pneumonia, and hypertension. Hyperglycemia typically occurs during the first two cycles of PI3K inhibitor treatment (Li et al., 2018; André et al., 2019). Hyperglycemia is regarded as an on-target effect of PI3K inhibitors and is linked to the critical role of the PI3K pathway in insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis (Juric et al., 2019). p110α and p110β regulate insulin-driven PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; inhibiting it can lead to hyperglycemia, rather than p110 δ and p110 γ (Moore et al., 2019). Additionally, the glucose-insulin feedback triggered by PI3K inhibitors is sufficient to reactivate PI3K signaling, thereby diminishing the effectiveness of the inhibitors (Horwitz et al., 2018). Skin reactions, such as rashes or papules, are among the most common toxicities observed with PI3K inhibitors in experimental studies. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is crucial in determining whether epidermal keratinocytes undergo differentiation or cell death (Liu et al., 2020b). Inhibition of this pathway suppressed keratinocyte proliferation and migration (Xenou and Papakonstanti, 2020). Additionally, activating the PAM signaling pathway inhibits autophagy and promotes inflammation in keratinocytes (Weidner et al., 2015). Diarrhea and colitis are common side effects of PI3K inhibitors, with severe cases often leading to treatment discontinuation (Curigliano and Shah, 2019). Histological examination via colonoscopy in patients with colitis revealed neutrophil infiltration, increased intraepithelial lymphocytes, and crypt cell apoptosis within the crypt epithelium (Wen et al., 2019).
The increased number of intraepithelial lymphocytes was predominantly CD8+ T cells, likely due to immune dysfunction. PI3Kδ inhibitors may disrupt B cell differentiation through immune dysregulation of Tregs, contributing to intestinal injury (Lynch et al., 2017). Fatal and severe pneumonia are common complications in patients receiving PI3K inhibitor treatments. Non-infectious pneumonia may be linked to the downstream inhibition of PI3K, whereas allergic and organizing pneumonia is more frequently observed in patients treated with mTOR inhibitors (Albiges et al., 2012). Pneumonia is also an immune-mediated disease, with a median increase in Th1-associated cytokines and chemokines observed in patient serum samples, including IFN-γ and IL-6, -7, and -8 (Barr et al., 2016). Hypertension is one of the most common adverse events associated with acute vasoconstriction (Mateo et al., 2017). The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway plays a key role in regulating classical endothelial functions, including the modulation of vascular tone and recruitment of white blood cells to the vascular wall (Molinaro et al., 2019). p110γ is a key factor in regulating blood pressure. p110γ alleviates hypertension and reduces vascular inflammation by lowering peripheral resistance; conversely, it may contribute to developing hypertension and related target organ damage by modulating T cell function (Pridham et al., 2018).
Somatic mutations in PIK3CA also display unique patterns with respect to sex- and tissue-specificity (Benvenuti et al., 2008). Amplification of chromosome regions containing the PIK3CA gene has been identified in several human cancers, including ovarian, cervical, head and neck, and gastric cancers (Engelman et al., 2006; Shayesteh et al., 1999). PIK3CB undergoes a missense substitution (E633K) that enhances cell proliferation, transformation, and membrane targeting, reducing its dependence on Ras activation (Dbouk et al., 2013). Overexpression of p110γ can induce oncogenic transformation in cell cultures, and its increased expression promotes cell proliferation. However, downregulation via siRNA reduces proliferation, underscoring the critical role of p110γ in pancreatic cancer progression (Kang et al., 2006; Edling et al., 2010). p110δ is primarily implicated in blood cancers, and somatic mutations in its catalytic subunit (E1021K) are associated with recurrent infections and progressive airway damage (Angulo et al., 2013). High-throughput mutation analysis identified novel somatic mutations affecting p110γ (N66K, D161E, R178L, S348I, K364N, T503M, R542W, E602V, and E740K) and p110δ (V397A) across various tumor types, including breast cancer, LC, ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer (Kan et al., 2010).
The therapeutic efficacy of PAM signaling pathway inhibitors is limited and often accompanied by significant treatment-related toxicity, particularly when used in combination with standard therapies or other targeted drugs. Consequently, most PAM signaling pathway inhibitors are not suitable as mainstream treatments for tumors. Recent trends have shifted toward combining multiple drugs with other treatment modalities, such as surgery, hormone therapy, and additional antitumor agents. Future studies should identify reliable biomarkers for patient stratification based on cancer type and genetic characteristics, allowing for a more effective use of PI3K inhibitors. Since the full mechanism of action of PI3K inhibitors is yet to be fully elucidated, further research is required to better understand their advantages and limitations in the context of personalized cancer treatment.
The AKT pathway is crucial for regulating cell proliferation, survival, and metabolism, making AKT inhibition a potentially powerful antitumor strategy. However, dose-limiting toxicities and an incomplete understanding of the different AKT subtypes have hindered the successful pharmacological application of AKT inhibitors.
Treatment with AKT inhibitors may also result in adverse reactions, including gastrointestinal discomfort, skin reactions, metabolic disorders, abnormal liver function, hematological abnormalities, cardiac toxicity, and immunosuppression (Glaviano et al., 2023). AKT1 amplification has been detected in gastric cancer and is associated with cisplatin resistance (Liu et al., 2007). Somatic mutations in AKT1 have been identified in breast, colorectal, ovarian, LC, and bladder cancer (Knowles et al., 2009). AKT1 E17K is an activating mutation that causes constitutive localization of the protein to the plasma membrane, leading to hyperphosphorylation of serine-473 and threonine-308 in a growth factor-independent manner (Carpten et al., 2007). AKT2 amplification is frequently detected in various tumors, including ovarian, breast, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers, and is positively correlated with increased invasion and poor prognosis (Bellacosa et al., 1995; Parsons et al., 2005; Cheng et al., 1996). Selective activation of the AKT3 subtype combined with PTEN loss has been observed in 43%–60% of sporadic melanomas, indicating elevated levels of active AKT3 in the late stages of the disease (Stahl et al., 2004).
The pharmacological markers of AKT inhibitors have demonstrated incomplete targeted regulation. Currently, there are no approved biomarkers that can predict treatment response to specific AKT inhibitors before their use. Consequently, predicting which patients will experience adverse reactions due to AKT inhibition is challenging. However, the AKT E17K mutation is a promising biomarker, as clinical data have shown a correlation between this mutation and the response to the AKT inhibitor capivasertib (Hyman et al., 2017). Mutations that confer resistance to one AKT inhibitor may not necessarily confer resistance to others. For example, the clinically relevant AKT1 Q79K mutation can induce resistance to certain miRNAs but not MK-2206, highlighting the importance of understanding AKT genotypes when selecting appropriate treatments (Shi et al., 2014). Targeting AKT is a key focus of clinical oncology research, and future studies may improve its clinical efficacy by combining AKT inhibitors with synergistic cytotoxic drugs.
Several mTOR inhibitors (mTORis) have been developed; however, only everolimus and temsirolimus have been approved for treating human tumors. Everolimus has shown acceptable safety in patients with neuroendocrine tumors, TSC-associated angiomyolipomas, renal cell carcinomas, and breast cancer. In patients with neuroendocrine tumors receiving everolimus monotherapy, grades 3–4 drug-related adverse events included stomatitis (9%), diarrhea (7%), infection (7%), anemia (4%), fatigue (3%), and hyperglycemia (3%). In renal cell carcinoma patients undergoing combination therapy with everolimus and lenvatinib, the most common grades 3–4 adverse events were constipation (37%) and diarrhea (20%) (Motzer et al., 2015; Janku et al., 2018). The most common grades 3–4 adverse reactions induced by temsirolimus included hypertriglyceridemia (44%), anemia (20%), hypophosphatemia (18%), lymphopenia (16%), hyperglycemia (16%), fatigue (11%), dyspnea (9%), neutropenia (5%), rash (5%), and pain (5%) (Kwitkowski et al., 2010). The clinical application of mTORi is often hindered by resistance driven by common molecular mechanisms across different drug categories. This suggests that co-targeting alternative pathways may be a more effective strategy than enhancing mTORi efficacy. Notably, preclinical and clinical data indicate that compared with other mTOR inhibitors, novel dual-space mTOR inhibitors can significantly promote cancer regression by inhibiting 4E-BP1 phosphorylation and reducing adaptive resistance by alleviating feedback inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) expression. Therefore, dual-space mTORC inhibitors are promising for treating cancers driven by activated mTORC1.
Additionally, developing new combination therapies may help to identify the molecular factors responsible for resistance to each drug class and improve patient selection for specific treatments. Optimizing the treatment sequences using different drugs may delay or overcome resistance to mTOR inhibitors.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), a class of ncRNAs longer than 200 nucleotides that regulate gene expression through various mechanisms, play critical roles in tumorigenesis (Hou et al., 2014). In recent years, many lncRNAs have been implicated in cancer progression by modulating the PAM signaling pathway. MALAT1, a well-known tumor-promoting lncRNA, competitively binds to microRNAs (miRNAs) such as miRNA-101 to relieve the inhibition of the PAM signaling pathway, thereby promoting tumor cell proliferation and migration (Goyal et al., 2021). Conversely, MEG3 is a tumor suppressor lncRNA that inhibits tumorigenesis by negatively regulating the PAM signaling pathway (He et al., 2021). The relative transcription level of colorectal cancer-related lncRNA colorectal cancer (OECC) was initially significantly upregulated in clinical LC tissues and cultured LC cells. Knocking down OECC in the LC cell line A549 led to a reduction in the mRNA levels of PI3K, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1, AKT, 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase, while increasing the expression of tumor protein 53, neurofibromatosis protein 1, and Cullin-1 regulatory factors. These molecules are components of the PAM signaling pathway and/or involved in crosstalk (Zou et al., 2019). Notably, several genes located on chromosome 8q24 are associated with an increased risk of LC. For instance, CCAT1 promotes cell metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma via epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activates the Wnt signaling pathway in NSCLC (Lin et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2017). The novel lncRNA OECC, located on chromosome 8q24, regulates the proliferation and metastasis of human LC. lncRNA OECC is a novel regulatory factor in LC progression, offering novel insights into clinical treatment strategies. miRNAs are small, non-coding RNAs, typically 20–22 nucleotides in length, that regulate gene expression by binding to the 3′untranslated region of mRNAs. Many miRNAs have been shown to influence tumor cell behavior by regulating key proteins in the PAM signaling pathway. MiR-21, a well-known pro-tumor miRNA, directly inhibits PTEN expression, thereby activating the PI3K/AKT pathway and promoting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and survival (Wang et al., 2020). MiR-29 promotes tumorigenesis by enhancing mTOR signaling through inhibition of the TSC1/TSC2 complex (Hu et al., 2021). Conversely, miR-126 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the expression of the PIK3R2 subunit of PI3K, thereby suppressing the PI3K/AKT pathway and reducing cell proliferation (Hu et al., 2021). Research has demonstrated that the overexpression of microRNA-520a-3p significantly reduces the ratios of p-AKT/AKT, p-PI3K/PI3K, and Bcl-2/Bax, as well as the levels of mTOR, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in NSCLC. Conversely, inhibition of microRNA-520a-3p expression enhances cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while suppressing apoptosis (Lv et al., 2018).
Overall, miRNAs and lncRNAs are promising therapeutic targets as regulatory molecules of the PAM signaling pathway. By designing miRNA mimetics or inhibitors or by interfering with lncRNA function, cancer-related signaling pathways can be modulated, offering new strategies for anti-cancer therapy. These approaches will facilitate the development of innovative cancer treatments.
Further research focusing on these molecules is expected to yield novel treatment options for cancer patients, and the outlook for LC treatment is optimistic. The PAM signaling pathway has demonstrated significant success in treating various tumors, and breakthroughs in LC therapy are anticipated. As more drugs targeting the PAM signaling pathway emerge, integrating multiple therapeutic approaches will play a crucial role in future treatment models. Multidisciplinary research may uncover increasingly effective strategies to gradually improve the survival rates of patients with LC. Additionally, advances in personalized precision medicine will offer more tailored and effective treatments, contributing to an overall improvement in the outcomes of this malignant disease.
In summary, the PAM pathway represents a critical target in the development of therapies for LC. Despite advances in identifying inhibitors and natural products targeting this pathway, challenges such as drug resistance, toxicity, and compensatory mechanisms persist. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive understanding of the PAM pathway’s role in cancer progression and its interaction with other signaling networks.
Recent advancements in precision medicine have provided new opportunities for the personalized treatment of LC, with combination therapies showing promise in overcoming resistance. By integrating insights from molecular biology, clinical trials, and natural product research, future therapeutic strategies can be optimized to improve outcomes for patients with LC. Continued exploration of biomarkers, alongside the development of innovative inhibitors and combination regimens, holds the potential to advance treatment efficacy and mitigate existing limitations. The road ahead necessitates collaborative efforts in research and clinical practice to fully realize the potential of PAM pathway-targeted therapies.
MQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. HL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. JD: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. KG: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XZ: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. PH: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. JZ: Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YS: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. JM: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. BZ: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. WL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. MT: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Development Plan Project, 20220204115YY; Jilin Province Medical and Health Personnel Special Fund (JLSWSRCZX2023). The funding source provided financial support for the project but had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, or writing of the manuscript.
We thank Xinliang Gao for his valuable effort in collecting the data.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1516583/full#supplementary-material
Abu, E. R., Friedman, K. M., Mkrtichyan, M., Walens, A., King, W., Janik, J., et al. (2015). Akt1 and -2 inhibition diminishes terminal differentiation and enhances central memory CD8(+) T-cell proliferation and survival. Oncoimmunology 4 (5), e1005448. doi:10.1080/2162402x.2015.1005448
Ahmad, S., Abu-Eid, R., Shrimali, R., Webb, M., Verma, V., Doroodchi, A., et al. (2017). Differential PI3Kδ signaling in CD4(+) T-cell subsets enables selective targeting of T regulatory cells to enhance cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 77 (8), 1892–1904. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-1839
Aisa, Y., Miyakawa, Y., Nakazato, T., Shibata, H., Saito, K., Ikeda, Y., et al. (2005). Fucoidan induces apoptosis of human HS-sultan cells accompanied by activation of caspase-3 and down-regulation of ERK pathways. Am. J. Hematol. 78 (1), 7–14. doi:10.1002/ajh.20182
Albiges, L., Chamming's, F., Duclos, B., Stern, M., Motzer, R. J., Ravaud, A., et al. (2012). Incidence and management of mTOR inhibitor-associated pneumonitis in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 23 (8), 1943–1953. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds115
Alessi, D. R., Andjelkovic, M., Caudwell, B., Cron, P., Morrice, N., Cohen, P., et al. (1996). Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. Embo J. 15 (23), 6541–6551. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb01045.x
Alessi, D. R., James, S. R., Downes, C. P., Holmes, A. B., Gaffney, P. R., Reese, C. B., et al. (1997). Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr. Biol. 7 (4), 261–269. doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00122-9
Alves, C. L., and Ditzel, H. J. (2023). Drugging the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in ER+ breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (5), 4522. doi:10.3390/ijms24054522
André, F., Ciruelos, E., Rubovszky, G., Campone, M., Loibl, S., Rugo, H. S., et al. (2019). Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 380 (20), 1929–1940. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1813904
Angulo, I., Vadas, O., Garçon, F., Banham-Hall, E., Plagnol, V., Leahy, T. R., et al. (2013). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ gene mutation predisposes to respiratory infection and airway damage. Science 342 (6160), 866–871. doi:10.1126/science.1243292
Annals of Oncology (2020). The Rome Trial from histology to target: the road to personalize target therapy and immunotherapy.;35(2):1–72. doi:10.1016/annonc/annonc1623
Araki, K., Turner, A. P., Shaffer, V. O., Gangappa, S., Keller, S. A., Bachmann, M. F., et al. (2009). mTOR regulates memory CD8 T-cell differentiation. Nature 460 (7251), 108–112. doi:10.1038/nature08155
Asmaa, W. M., Mohamed, E., Dalia Abdelghany, E., May Ahmed, S., and Amr Shafik, S. (2018). The effect of itraconazole on the clinical outcomes of patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer receiving platinum based chemotherapy. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03664115.
AEterna Zentaris (2006). A phase 1/2 trial of perifosine in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00399789.
Axanova, L. S., Chen, Y. Q., McCoy, T., Sui, G., and Cramer, S. D. (2010). 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) and PI3K/AKT inhibitors synergistically inhibit growth and induce senescence in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 70 (15), 1658–1671. doi:10.1002/pros.21201
Aziz, A. U. R., Farid, S., Qin, K., Wang, H., and Liu, B. (2018). PIM kinases and their relevance to the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the regulation of ovarian cancer. Biomolecules 8 (1), 7. doi:10.3390/biom8010007
Barr, P. M., Saylors, G. B., Spurgeon, S. E., Cheson, B. D., Greenwald, D. R., O'Brien, S. M., et al. (2016). Phase 2 study of idelalisib and entospletinib: pneumonitis limits combination therapy in relapsed refractory CLL and NHL. Blood 127 (20), 2411–2415. doi:10.1182/blood-2015-12-683516
Bellacosa, A., de Feo, D., Godwin, A. K., Bell, D. W., Cheng, J. Q., Altomare, D. A., et al. (1995). Molecular alterations of the AKT2 oncogene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 64 (4), 280–285. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910640412
Benetatos, L., Voulgaris, E., and Vartholomatos, G. (2017). The crosstalk between long non-coding RNAs and PI3K in cancer. Med. Oncol. 34 (3), 39. doi:10.1007/s12032-017-0897-2
Benvenuti, S., Frattini, M., Arena, S., Zanon, C., Cappelletti, V., Coradini, D., et al. (2008). PIK3CA cancer mutations display gender and tissue specificity patterns. Hum. Mutat. 29 (2), 284–288. doi:10.1002/humu.20648
Bertucci, A., Bertucci, F., and Gonçalves, A. (2023). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors and breast cancer: an overview of current achievements. Cancers (Basel) 15 (5), 1416. doi:10.3390/cancers15051416
Bilello, K. S., Murin, S., and Matthay, R. A. (2002). Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention of lung cancer. Clin. Chest Med. 23 (1), 1–25. doi:10.1016/s0272-5231(03)00057-1
Blake, J. F., Xu, R., Bencsik, J. R., Xiao, D., Kallan, N. C., Schlachter, S., et al. (2012). Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a selective ATP-competitive Akt inhibitor (GDC-0068) for the treatment of human tumors. J. Med. Chem. 55 (18), 8110–8127. doi:10.1021/jm301024w
Bonelli, M. A., Cavazzoni, A., Saccani, F., Alfieri, R. R., Quaini, F., La, M. S., et al. (2015). Inhibition of PI3K pathway reduces invasiveness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in squamous lung cancer cell lines harboring PIK3CA gene alterations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 14 (8), 1916–1927. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-14-0892
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2024). Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74 (3), 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Brown, J., Wang, H., Suttles, J., Graves, D. T., and Martin, M. (2011). Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) negatively regulates Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory response via FoxO1. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (52), 44295–44305. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.258053
Budhwar, S., Verma, P., Verma, R., Rai, S., and Singh, K. (2018). The yin and Yang of myeloid derived suppressor cells. Front. Immunol. 9, 2776. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02776
Carpten, J. D., Faber, A. L., Horn, C., Donoho, G. P., Briggs, S. L., Robbins, C. M., et al. (2007). A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature 448 (7152), 439–444. doi:10.1038/nature05933
Chai, S., Wen, Z., Zhang, R., Bai, Y., Liu, J., Li, J., et al. (2022). CCL25/CCR9 interaction promotes the malignant behavior of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. PeerJ 10, e13844. doi:10.7717/peerj.13844
Chandrasekaran, S., Funk, C. R., Kleber, T., Paulos, C. M., Shanmugam, M., and Waller, E. K. (2021). Strategies to overcome failures in T-cell immunotherapies by targeting PI3K-δ and -γ. Front. Immunol. 12, 718621. PubMed PMID: 34512641; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC8427697: Epub 20210826. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.718621
Chellappa, S., Kushekhar, K., Munthe, L. A., Tjønnfjord, G. E., Aandahl, E. M., Okkenhaug, K., et al. (2019). The PI3K p110δ isoform inhibitor idelalisib preferentially inhibits human regulatory T cell function. J. Immunol. 202 (5), 1397–1405. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1701703
Chen, M., Du, Y., Qui, M., Wang, M., Chen, K., Huang, Z., et al. (2013). Ophiopogonin B-induced autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 29 (2), 430–436. doi:10.3892/or.2012.2131
Cheng, J. Q., Ruggeri, B., Klein, W. M., Sonoda, G., Altomare, D. A., Watson, D. K., et al. (1996). Amplification of AKT2 in human pancreatic cells and inhibition of AKT2 expression and tumorigenicity by antisense RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93 (8), 3636–3641. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.8.3636
Choi, J. C., Muchir, A., Wu, W., Iwata, S., Homma, S., Morrow, J. P., et al. (2012). Temsirolimus activates autophagy and ameliorates cardiomyopathy caused by lamin A/C gene mutation. Sci. Transl. Med. 4 (144), 144ra102. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003875
Choi, J. I., Raghavendran, H. R., Sung, N. Y., Kim, J. H., Chun, B. S., Ahn, D. H., et al. (2010). Effect of fucoidan on aspirin-induced stomach ulceration in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 183 (1), 249–254. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.09.015
Chung-Shien, L., Matthew, M., and Nagashree, S. (2018). Prospective observational trial to evaluate the efficacy of the combination of osimertinib and aspirin in patients with disease progression to 1st generation EGFR-TKI due to acquisition of EGFR T790M. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03543683.
Clinical Research and Trials (2020). A multi-center phase II study of ipatasertib in combination with docetaxel in metastatic/advanced NSCLC patients who have failed or are intolerant to 1st line immunotherapy (Ipat-Lung). Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04467801.
Colombo, I., Genta, S., Martorana, F., Guidi, M., Frattini, M., Samartzis, E. P., et al. (2021). Phase I dose-escalation study of the dual PI3K-mTORC1/2 inhibitor gedatolisib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 27 (18), 5012–5019. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-21-1402
Cristescu, R., Mogg, R., Ayers, M., Albright, A., Murphy, E., Yearley, J., et al. (2018). Pan-tumor genomic biomarkers for PD-1 checkpoint blockade-based immunotherapy. Science 362 (6411), eaar3593. doi:10.1126/science.aar3593
Cross, D. A., Alessi, D. R., Cohen, P., Andjelkovich, M., and Hemmings, B. A. (1995). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378 (6559), 785–789. doi:10.1038/378785a0
Curigliano, G., and Shah, R. R. (2019). Safety and tolerability of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors in oncology. Drug Saf. 42 (2), 247–262. doi:10.1007/s40264-018-0778-4
Dana-Farber (2017). Phase I study of the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD-0332991) in combination with the PI3K/mTOR inhibitor gedatolisib (PF-05212384) for patients with advanced squamous cell lung. Pancreat. Head and Neck Other Solid Tumors. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03065062.
Datta, S. R., Brunet, A., and Greenberg, M. E. (1999). Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 13 (22), 2905–2927. doi:10.1101/gad.13.22.2905
Davidson, M. R., Gazdar, A. F., and Clarke, B. E. (2013). The pivotal role of pathology in the management of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 5 (Suppl. 5), S463–S478. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.08.43
Davies, B. R., Greenwood, H., Dudley, P., Crafter, C., Yu, D. H., Zhang, J., et al. (2012). Preclinical pharmacology of AZD5363, an inhibitor of AKT: pharmacodynamics, antitumor activity, and correlation of monotherapy activity with genetic background. Mol. Cancer Ther. 11 (4), 873–887. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-11-0824-t
Dbouk, H. A., Khalil, B. D., Wu, H., Shymanets, A., Nürnberg, B., and Backer, J. M. (2013). Characterization of a tumor-associated activating mutation of the p110β PI 3-kinase. PLoS One 8 (5), e63833. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063833
De Henau, O., Rausch, M., Winkler, D., Campesato, L. F., Liu, C., Cymerman, D. H., et al. (2016). Overcoming resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy by targeting PI3Kγ in myeloid cells. Nature 539 (7629), 443–447. doi:10.1038/nature20554
Dibble, C. C., Asara, J. M., and Manning, B. D. (2009). Characterization of Rictor phosphorylation sites reveals direct regulation of mTOR complex 2 by S6K1. Mol. Cell Biol. 29 (21), 5657–5670. doi:10.1128/mcb.00735-09
Dong, P., Konno, Y., Watari, H., Hosaka, M., Noguchi, M., and Sakuragi, N. (2014). The impact of microRNA-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness in endometrial cancer. J. Transl. Med. 12, 231. doi:10.1186/s12967-014-0231-0
Dong, S., Harrington, B. K., Hu, E. Y., Greene, J. T., Lehman, A. M., Tran, M., et al. (2019). PI3K p110δ inactivation antagonizes chronic lymphocytic leukemia and reverses T cell immune suppression. J. Clin. Invest. 129 (1), 122–136. doi:10.1172/jci99386
Dürig, J., Bruhn, T., Zurborn, K. H., Gutensohn, K., Bruhn, H. D., and Béress, L. (1997). Anticoagulant fucoidan fractions from Fucus vesiculosus induce platelet activation in vitro. Thromb. Res. 85 (6), 479–491. doi:10.1016/s0049-3848(97)00037-6
Ebrahiminezhad, A., Bagheri, M., Taghizadeh, S. M., Berenjian, A., and Ghasemi, Y. (2016). Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using microalgal secretory carbohydrates as a novel anticancer and antimicrobial. Adv. Nat. SCIENCES-NANOSCIENCE Nanotechnol. 7 (1), 015018. doi:10.1088/2043-6262/7/1/015018
Edling, C. E., Selvaggi, F., Buus, R., Maffucci, T., Di Sebastiano, P., Friess, H., et al. (2010). Key role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase class IB in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 16 (20), 4928–4937. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-10-1210
Emory University (2011). A phase I study of BKM120 and everolimus in advanced solid malignancies. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01470209.
Engelman, J. A., Luo, J., and Cantley, L. C. (2006). The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 7 (8), 606–619. doi:10.1038/nrg1879
Ersahin, T., Tuncbag, N., and Cetin-Atalay, R. (2015). The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway. Mol. Biosyst. 11 (7), 1946–1954. doi:10.1039/c5mb00101c
Eyong, K. O., Ketsemen, H. L., Ghansenyuy, S. Y., and Folefoc, G. N. (2015). Chemical constituents, the stereochemistry of 3-hydroxy furonaphthoquinones from the root bark of Newbouldialaevis Seem (Bignoniaceae), and screening against Onchocercaochengi parasites. Med. Chem. Res. 24 (3), 965–969. doi:10.1007/s00044-014-1173-z
Fakhri, S., Iranpanah, A., Gravandi, M. M., Moradi, S. Z., Ranjbari, M., Majnooni, M. B., et al. (2021). Natural products attenuate PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway: a promising strategy in regulating neurodegeneration. Phytomedicine 91, 153664. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153664
Fokas, E., Im, J. H., Hill, S., Yameen, S., Stratford, M., Beech, J., et al. (2012). Dual inhibition of the PI3K/mTOR pathway increases tumor radiosensitivity by normalizing tumor vasculature. Cancer Res. 72 (1), 239–248. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-11-2263
Fotsing, M. T., Yankep, E., Njamen, D., Fomum, Z. T., Nyasse, B., Bodo, B., et al. (2003). Identification of an anti-inflammatory principle from the stem bark of Millettia versicolor. Planta Med. 69 (8), 767–770. doi:10.1055/s-2003-42794
Fu, H., Liu, X., Shi, L., Wang, L., Fang, H., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Regulatory roles of Osteopontin in lung epithelial inflammation and epithelial-telocyte interaction. Clin. Transl. Med. 13 (8), e1381. doi:10.1002/ctm2.1381
Fumarola, C., Bonelli, M. A., Petronini, P. G., and Alfieri, R. R. (2014). Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 90 (3), 197–207. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2014.05.011
Glaviano, A., Foo, A. S. C., Lam, H. Y., Yap, K. C. H., Jacot, W., Jones, R. H., et al. (2023). PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 22 (1), 138. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01827-6
Goel, H. L., and Mercurio, A. M. (2013). VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13 (12), 871–882. doi:10.1038/nrc3627
Gowda, R., Jones, N. R., Banerjee, S., and Robertson, G. P. (2013). Use of nanotechnology to develop multi-drug inhibitors for cancer therapy. J. Nanomed Nanotechnol. 4 (6), 184. doi:10.4172/2157-7439.1000184
Goyal, B., Yadav, S. R. M., Awasthee, N., Gupta, S., Kunnumakkara, A. B., and Gupta, S. C. (2021). Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1875 (2), 188502. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188502
Guerau-de-Arellano, M., Piedra-Quintero, Z. L., and Tsichlis, P. N. (2022). Akt isoforms in the immune system. Front. Immunol. 13, 990874. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.990874
Guo, C., Buranych, A., Sarkar, D., Fisher, P. B., and Wang, X. Y. (2013). The role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor vascularization. Vasc. Cell 5 (1), 20. doi:10.1186/2045-824x-5-20
Hallowell, R. W., Collins, S. L., Craig, J. M., Zhang, Y., Oh, M., Illei, P. B., et al. (2017). mTORC2 signalling regulates M2 macrophage differentiation in response to helminth infection and adaptive thermogenesis. Nat. Commun. 8, 14208. doi:10.1038/ncomms14208
Han, B., Zheng, R., Zeng, H., Wang, S., Sun, K., Chen, R., et al. (2024). Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 4 (1), 47–53. doi:10.1016/j.jncc.2024.01.006
Han, J. Y., Lee, S. H., Yoo, N. J., Hyung, L. S., Moon, Y. J., Yun, T., et al. (2011). A randomized phase II study of gefitinib plus simvastatin versus gefitinib alone in previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 17 (6), 1553–1560. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-10-2525
Han, Y. H., Mun, J. G., Jeon, H. D., Kee, J. Y., and Hong, S. H. (2019). Betulin inhibits lung metastasis by inducing cell cycle arrest, autophagy, and apoptosis of metastatic colorectal cancer cells. Nutrients 12 (1), 66. doi:10.3390/nu12010066
Hanna, B. S., Roessner, P. M., Scheffold, A., Jebaraj, B. M. C., Demerdash, Y., Öztürk, S., et al. (2019). PI3Kδ inhibition modulates regulatory and effector T-cell differentiation and function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 33 (6), 1427–1438. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0318-3
Harashima, N., Inao, T., Imamura, R., Okano, S., Suda, T., and Harada, M. (2012). Roles of the PI3K/Akt pathway and autophagy in TLR3 signaling-induced apoptosis and growth arrest of human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 61 (5), 667–676. doi:10.1007/s00262-011-1132-1
Harwood, F. C., Klein Geltink, R. I., O'Hara, B. P., Cardone, M., Janke, L., Finkelstein, D., et al. (2018). ETV7 is an essential component of a rapamycin-insensitive mTOR complex in cancer. Sci. Adv. 4 (9), eaar3938. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aar3938
Hay, N., and Sonenberg, N. (2004). Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18 (16), 1926–1945. doi:10.1101/gad.1212704
He, Y., Dan, Y., Gao, X., Huang, L., Lv, H., and Chen, J. (2021). DNMT1-mediated lncRNA MEG3 methylation accelerates endothelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic retinopathy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 320 (3), E598–e608. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00089.2020
Higgins, G. S., Krause, M., McKenna, W. G., and Baumann, M. (2016). Personalized radiation oncology: epidermal growth factor receptor and other receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Recent Results Cancer Res. 198, 107–122. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-49651-0_5
Hong, D. S., Postow, M., Chmielowski, B., Sullivan, R., Patnaik, A., Cohen, E. E. W., et al. (2023). Eganelisib, a first-in-class PI3Kγ inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors: results of the phase 1/1b MARIO-1 trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 29 (12), 2210–2219. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-22-3313
Hong, F., Gao, Y., Li, Y., Zheng, L., Xu, F., and Li, X. (2020). Inhibition of HIF1A-AS1 promoted starvation-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis by reducing HIF-1α/mTOR-mediated autophagy. World J. Surg. Oncol. 18 (1), 113. doi:10.1186/s12957-020-01884-x
Horwitz, S. M., Koch, R., Porcu, P., Oki, Y., Moskowitz, A., Perez, M., et al. (2018). Activity of the PI3K-δ,γ inhibitor duvelisib in a phase 1 trial and preclinical models of T-cell lymphoma. Blood 131 (8), 888–898. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-08-802470
Hou, Z., Zhao, W., Zhou, J., Shen, L., Zhan, P., Xu, C., et al. (2014). A long noncoding RNA Sox2ot regulates lung cancer cell proliferation and is a prognostic indicator of poor survival. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 53, 380–388. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2014.06.004
Hu, B., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, F., Wei, H., and Li, L. (2017). LncRNA CCAT1/miR-130a-3p axis increases cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cell line by targeting SOX4. Cancer Biol. Ther. 18 (12), 974–983. doi:10.1080/15384047.2017.1385679
Hu, Y., Zhang, Y., Ding, M., and Xu, R. (2021). Long noncoding RNA TMPO-AS1/miR-126-5p/BRCC3 axis accelerates gastric cancer progression and angiogenesis via activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 36 (7), 1877–1888. doi:10.1111/jgh.15362
Hua, J., Wang, X., Ma, L., Li, J., Cao, G., Zhang, S., et al. (2022). CircVAPA promotes small cell lung cancer progression by modulating the miR-377-3p and miR-494-3p/IGF1R/AKT axis. Mol. Cancer 21 (1), 123. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01595-9
Hudes, G., Carducci, M., Tomczak, P., Dutcher, J., Figlin, R., Kapoor, A., et al. (2007). Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 356 (22), 2271–2281. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa066838
Hwang, Y., Kim, H. C., and Shin, E. J. (2022). BKM120 alters the migration of doublecortin-positive cells in the dentate gyrus of mice. Pharmacol. Res. 179, 106226. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106226
Hyman, D. M., Smyth, L. M., Donoghue, M. T. A., Westin, S. N., Bedard, P. L., Dean, E. J., et al. (2017). AKT inhibition in solid tumors with AKT1 mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 35 (20), 2251–2259. doi:10.1200/jco.2017.73.0143
Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (2015). A Phase 1/1b First-In-Human Dose-escalation study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of IPI-549 monotherapy and in combination with nivolumab in subjects with advanced solid tumors. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02637531.
Inoki, K., Li, Y., Zhu, T., Wu, J., and Guan, K. L. (2002). TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 4 (9), 648–657. doi:10.1038/ncb839
Iravani, S. (2011). Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. GREEN Chem. 13 (10), 2638–2650. doi:10.1039/c1gc15386b
Janku, F., Yap, T. A., and Meric-Bernstam, F. (2018). Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15 (5), 273–291. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.28
Jeong, Y., Lim, D. W., and Choi, J. (2014). Assessment of size-dependent antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties of silver nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1–6. doi:10.1155/2014/763807
Jian, M., Yunjia, Z., Zhiying, D., Yanduo, J., and Guocheng, J. (2019). Interleukin 7 receptor activates PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway via downregulation of Beclin-1 in lung cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 58 (3), 358–365. doi:10.1002/mc.22933
Jiramongkol, Y., and Lam, E. W. (2020). FOXO transcription factor family in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 39 (3), 681–709. doi:10.1007/s10555-020-09883-w
Ji-Youn, H., Soo-Hyun, L., Nam Jin, Y., Lee Suk, H., Yoon Joo, M., Tak, Y., et al. (2007). Randomized phase II trail comparing gefitinib plus simvastatin and gefitinib alone in patients with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00452244.
Julien, L. A., Carriere, A., Moreau, J., and Roux, P. P. (2010). mTORC1-activated S6K1 phosphorylates Rictor on threonine 1135 and regulates mTORC2 signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 30 (4), 908–921. doi:10.1128/mcb.00601-09
Junttila, T. T., Akita, R. W., Parsons, K., Fields, C., Lewis Phillips, G. D., Friedman, L. S., et al. (2009). Ligand-independent HER2/HER3/PI3K complex is disrupted by trastuzumab and is effectively inhibited by the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941. Cancer Cell 15 (5), 429–440. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.020
Juric, D., Janku, F., Rodón, J., Burris, H. A., Mayer, I. A., Schuler, M., et al. (2019). Alpelisib plus fulvestrant in PIK3CA-altered and PIK3CA-wild-type estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: a phase 1b clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 5 (2), e184475. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4475
Kamel, E. O., Hassanein, E. H. M., Ahmed, M. A., and Ali, F. E. M. (2020). Perindopril ameliorates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via regulation of NF-κB-p65/TLR-4, JAK1/STAT-3, nrf-2, and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Anat. Rec. Hob. 303 (7), 1935–1949. doi:10.1002/ar.24292
Kan, Z., Jaiswal, B. S., Stinson, J., Janakiraman, V., Bhatt, D., Stern, H. M., et al. (2010). Diverse somatic mutation patterns and pathway alterations in human cancers. Nature 466 (7308), 869–873. doi:10.1038/nature09208
Kang, S., Denley, A., Vanhaesebroeck, B., and Vogt, P. K. (2006). Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110beta, -gamma, and -delta isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103 (5), 1289–1294. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510772103
Khan, P., Bhattacharya, A., Sengupta, D., Banerjee, S., Adhikary, A., and Das, T. (2019). Aspirin enhances cisplatin sensitivity of resistant non-small cell lung carcinoma stem-like cells by targeting mTOR-Akt axis to repress migration. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 16913. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53134-0
King, D., Yeomanson, D., and Bryant, H. E. (2015). PI3King the lock: targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a novel therapeutic strategy in neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 37 (4), 245–251. doi:10.1097/mph.0000000000000329
Knowles, M. A., Platt, F. M., Ross, R. L., and Hurst, C. D. (2009). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway activation in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28 (3-4), 305–316. doi:10.1007/s10555-009-9198-3
Konstantinidou, G., Bey, E. A., Rabellino, A., Schuster, K., Maira, M. S., Gazdar, A. F., et al. (2009). Dual phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin blockade is an effective radiosensitizing strategy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer harboring K-RAS mutations. Cancer Res. 69 (19), 7644–7652. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-09-0823
Kosuge, K., Mitsunaga, K., Koike, K., and Ohmoto, T. (1994). Studies on the constituents of Ailanthus integrifolia. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 42 (8), 1669–1671. doi:10.1248/cpb.42.1669
Koundouros, N., and Poulogiannis, G. (2020). Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 122 (1), 4–22. doi:10.1038/s41416-019-0650-z
Kwitkowski, V. E., Prowell, T. M., Ibrahim, A., Farrell, A. T., Justice, R., Mitchell, S. S., et al. (2010). FDA approval summary: temsirolimus as treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Oncologist 15 (4), 428–435. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0178
Lansdown, A. B. (2006). Silver in health care: antimicrobial effects and safety in use. Curr. Probl. Dermatol 33, 17–34. doi:10.1159/000093928
Laplante, M., and Sabatini, D. M. (2012). mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149 (2), 274–293. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017
Lara, P. N., Longmate, J., Mack, P. C., Kelly, K., Socinski, M. A., Salgia, R., et al. (2015). Phase II study of the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 plus erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer who previously progressed on erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 21 (19), 4321–4326. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-14-3281
Lee, H., Kim, J. S., and Kim, E. (2012). Fucoidan from seaweed Fucus vesiculosus inhibits migration and invasion of human lung cancer cell via PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathways. PLoS One 7 (11), e50624. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050624
Le-Xin, C., Ming-Jun, L., Chun-Qi, X., Jia-Xin, Z., Jing-Ya, Y., Li-Xin, N., et al. (2024). Yi Qi Chu Tan Formula (YQCTF) inhibited the progress of lung cancer via regulating tumor-associated neutrophil: an integrated study of network pharmacology, proteomics and pharmacodynamics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 318 (Pt B), 116943. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116943
Li, M., Sala, V., De Santis, M. C., Cimino, J., Cappello, P., Pianca, N., et al. (2018). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma inhibition protects from anthracycline cardiotoxicity and reduces tumor growth. Circulation 138 (7), 696–711. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030352
Li, T., and Wang, G. (2014). Computer-aided targeting of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: toxicity reduction and therapeutic opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15 (10), 18856–18891. doi:10.3390/ijms151018856
Li, Y., Yan, B., and He, S. (2023). Advances and challenges in the treatment of lung cancer. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 169, 115891. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115891
Li, Z., Li, X., Li, S., Tao, R., Tian, X., Feng, F., et al. (2024). Preclinical evaluation and phase 1 study of the PI3Kα/δ inhibitor TQ-B3525 in Chinese patients with advanced cancers. Cancer 130, 3686–3698. doi:10.1002/cncr.35453
Lin, C.-C., Yu, C.-J., Ho, C.-C., Tsai, S.-H., and Yan, L. (2010). A phase I dose defining study for MK-2206 combined with gefitinib in NSCLC population enriched with EGFR mutation. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01147211.
Lin, H., Cheng, W., Yan, H., and Zhang, X. (2018). Overexpression of the long noncoding RNA CCAT1 promotes metastasis via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 16 (2), 1809–1814. doi:10.3892/ol.2018.8813
Liu, F., Gao, S., Yang, Y., Zhao, X., Fan, Y., Ma, W., et al. (2018). Antitumor activity of curcumin by modulation of apoptosis and autophagy in human lung cancer A549 cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Rep. 39 (3), 1523–1531. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6188
Liu, L. Z., Zhou, X. D., Qian, G., Shi, X., Fang, J., and Jiang, B. H. (2007). AKT1 amplification regulates cisplatin resistance in human lung cancer cells through the mammalian target of rapamycin/p70S6K1 pathway. Cancer Res. 67 (13), 6325–6332. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-4261
Liu, P., Gan, W., Inuzuka, H., Lazorchak, A. S., Gao, D., Arojo, O., et al. (2013). Sin1 phosphorylation impairs mTORC2 complex integrity and inhibits downstream Akt signalling to suppress tumorigenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 15 (11), 1340–1350. doi:10.1038/ncb2860
Liu, R., Chen, Y., Liu, G., Li, C., Song, Y., Cao, Z., et al. (2020a). PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 11 (9), 797. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6
Liu, R., Huang, J., Ge, Y., Liu, S., Huang, T., Cai, H., et al. (2020b). Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase γ by IPI-549 attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in mice. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 60 (2), 254–263. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2020.03.042
Luo, C. T., Liao, W., Dadi, S., Toure, A., and Li, M. O. (2016). Graded Foxo1 activity in Treg cells differentiates tumour immunity from spontaneous autoimmunity. Nature 529 (7587), 532–536. doi:10.1038/nature16486
Luo, D., Dai, X., Tian, H., Fan, C., Xie, H., Chen, N., et al. (2023). Sophflarine A, a novel matrine-derived alkaloid from Sophora flavescens with therapeutic potential for non-small cell lung cancer through ROS-mediated pyroptosis and autophagy. Phytomedicine 116, 154909. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154909
Luo, J., Manning, B. D., and Cantley, L. C. (2003). Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: rationale and promise. Cancer Cell 4 (4), 257–262. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(03)00248-4
Lv, X., Li, C. Y., Han, P., and Xu, X. Y. (2018). MicroRNA-520a-3p inhibits cell growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 22 (8), 2321–2327. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201804_14822
Lynch, J. T., Polanska, U. M., Delpuech, O., Hancox, U., Trinidad, A. G., Michopoulos, F., et al. (2017). Inhibiting PI3Kβ with AZD8186 regulates key metabolic pathways in PTEN-null tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 23 (24), 7584–7595. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-17-0676
Ma, X. M., and Blenis, J. (2009). Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10 (5), 307–318. doi:10.1038/nrm2672
Machl, A., Wilker, E. W., Tian, H., Liu, X., Schroeder, P., Clark, A., et al. (2016). M2698 is a potent dual-inhibitor of p70S6K and Akt that affects tumor growth in mouse models of cancer and crosses the blood-brain barrier. Am. J. Cancer Res. 6 (4), 806–818.
Mafi, S., Mansoori, B., Taeb, S., Sadeghi, H., Abbasi, R., Cho, W. C., et al. (2021). mTOR-mediated regulation of immune responses in cancer and tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 12, 774103. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.774103
Maira, S. M., Stauffer, F., Brueggen, J., Furet, P., Schnell, C., Fritsch, C., et al. (2008). Identification and characterization of NVP-BEZ235, a new orally available dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 7 (7), 1851–1863. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-08-0017
Manning, B. D., and Cantley, L. C. (2007). AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129 (7), 1261–1274. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009
Mao, B., Zhang, Q., Ma, L., Zhao, D. S., Zhao, P., and Yan, P. (2022). Overview of research into mTOR inhibitors. Molecules 27 (16), 5295. doi:10.3390/molecules27165295
Martini, M., De Santis, M. C., Braccini, L., Gulluni, F., and Hirsch, E. (2014). PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann. Med. 46 (6), 372–383. doi:10.3109/07853890.2014.912836
Mateo, J., Ganji, G., Lemech, C., Burris, H. A., Han, S. W., Swales, K., et al. (2017). A first-time-in-human study of GSK2636771, a phosphoinositide 3 kinase beta-selective inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 23 (19), 5981–5992. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-17-0725
Mazloumi Gavgani, F., Smith Arnesen, V., Jacobsen, R. G., Krakstad, C., Hoivik, E. A., and Lewis, A. E. (2018). Class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase PIK3CA/p110α and PIK3CB/p110β isoforms in endometrial cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (12), 3931. doi:10.3390/ijms19123931
Medifind (2012). Phase I trial of BKM120 in combination with carboplatin and pemetrexed in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01723800.
Medi find (2014). Dose finding study of pf-05212384 with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumor. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02069158.
Middleton, G., Crack, L. R., Popat, S., Swanton, C., Hollingsworth, S. J., Buller, R., et al. (2015). The National Lung Matrix Trial: translating the biology of stratification in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 26 (12), 2464–2469. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv394
Mohamed, A. W., Elbassiouny, M., Elkhodary, D. A., Shawki, M. A., and Saad, A. S. (2021). The effect of itraconazole on the clinical outcomes of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving platinum-based chemotherapy: a randomized controlled study. Med. Oncol. 38 (3), 23. doi:10.1007/s12032-021-01475-0
Molinaro, A., Becattini, B., Mazzoli, A., Bleve, A., Radici, L., Maxvall, I., et al. (2019). Insulin-driven PI3K-AKT signaling in the hepatocyte is mediated by redundant PI3Kα and PI3Kβ activities and is promoted by RAS. Cell Metab. 29 (6), 1400–1409. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.03.010
Moore, S. F., Smith, N. R., Blair, T. A., Durrant, T. N., and Hers, I. (2019). Critical roles for the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase isoforms p110β and p110γ in thrombopoietin-mediated priming of platelet function. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 1468. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-37012-9
Moran, T., Palmero, R., Provencio, M., Insa, A., Majem, M., Reguart, N., et al. (2017). A phase Ib trial of continuous once-daily oral afatinib plus sirolimus in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer and/or disease progression following prior erlotinib or gefitinib. Lung Cancer 108, 154–160. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.03.009
Motzer, R. J., Escudier, B., Oudard, S., Hutson, T. E., Porta, C., Bracarda, S., et al. (2008). Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet 372 (9637), 449–456. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(08)61039-9
Motzer, R. J., Hutson, T. E., Glen, H., Michaelson, M. D., Molina, A., Eisen, T., et al. (2015). Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 16 (15), 1473–1482. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(15)00290-9
National Cancer Centre, Singapore (2012). A phase Ib trial of gefitinib (EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, Iressa™) in combination with BKM120, an oral pan-class I PI3K inhibitor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer, with enrichment for patients whose tumours harbour molecular alterations of PI3K pathway and known to overexpress EGFR. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01570296.
Niu, H., Wang, D., Wen, T., Liu, H., Jie, J., Song, L., et al. (2023). Anwuligan inhibits the progression of non-small cell lung cancer via let-7c-3p/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. Cancer Med. 12 (5), 5908–5925. doi:10.1002/cam4.5382
Noser, A. A., Abdelmonsef, A. H., and Salem, M. M. (2023). Design, synthesis and molecular docking of novel substituted azepines as inhibitors of PI3K/Akt/TSC2/mTOR signaling pathway in colorectal carcinoma. Bioorg Chem. 131, 106299. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106299
Novartis Pharmaceuticals (2013a). A dose-finding phase Ib study followed by a randomized, double-blind phase II study of carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without buparlisib in patients with previously untreated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) of squamous histology. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01820325.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals (2013b). A phase Ib/II study of docetaxel with or without buparlisib as second line therapy for patients with advanced or metastatic squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01911325.
Ogbulie, J. N., Ogueke, C. C., Okoli, I. C., and Anyanwu, B. N. (2007). Antibacterial activities and toxicological potentials of crude ethanolic extracts of <i>Euphorbia hirta</i>. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 6 (13), 1544–1548. doi:10.4314/AJB.V6I13.57667
Okabayashi, Y., Kido, Y., Okutani, T., Sugimoto, Y., Sakaguchi, K., and Kasuga, M. (1994). Tyrosines 1148 and 1173 of activated human epidermal growth factor receptors are binding sites of Shc in intact cells. J. Biol. Chem. 269 (28), 18674–18678. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(17)32363-3
Open Label (2005). Non-randomized, phase 2 study investigating the effect of RAD001 monotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC previously treated with either chemotherapy only or with chemotherapy and EGFR inhibitor(s). Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00124280.
O'Reilly, K. E., Rojo, F., She, Q. B., Solit, D., Mills, G. B., Smith, D., et al. (2006). mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 66 (3), 1500–1508. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-05-2925
Orphanet (2011). A phase II study of sunitinib or temsirolimus in patients with advanced rare tumours. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01396408.
Ostrand-Rosenberg, S., and Fenselau, C. (2018). Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: immune-suppressive cells that impair antitumor immunity and are sculpted by their environment. J. Immunol. 200 (2), 422–431. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1701019
Ouyang, S., Zeng, Q., Tang, N., Guo, H., Tang, R., Yin, W., et al. (2019). Akt-1 and akt-2 differentially regulate the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by controlling proliferation of thymus-derived regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 202 (5), 1441–1452. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1701204
Ouyang, W., Liao, W., Luo, C. T., Yin, N., Huse, M., Kim, M. V., et al. (2012). Novel Foxo1-dependent transcriptional programs control T(reg) cell function. Nature 491 (7425), 554–559. doi:10.1038/nature11581
Owonikoko, T. K., Harvey, R. D., Carthon, B., Chen, Z., Lewis, C., Collins, H., et al. (2020). A phase I study of safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of concurrent everolimus and buparlisib treatment in advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 26 (11), 2497–2505. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-19-2697
Parsons, D. W., Wang, T. L., Samuels, Y., Bardelli, A., Cummins, J. M., DeLong, L., et al. (2005). Colorectal cancer: mutations in a signalling pathway. Nature 436 (7052), 792. doi:10.1038/436792a
Pedersen, M. W., Pedersen, N., Ottesen, L. H., and Poulsen, H. S. (2005). Differential response to gefitinib of cells expressing normal EGFR and the mutant EGFRvIII. Br. J. Cancer 93 (8), 915–923. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602793
Peraza-Sánchez, S. R., Chávez, D., Chai, H. B., Shin, Y. G., García, R., Mejía, M., et al. (2000). Cytotoxic constituents of the roots of Ekmanianthe longiflora. J. Nat. Prod. 63 (4), 492–495. doi:10.1021/np990528l
Petsri, K., Thongsom, S., Racha, S., Chamni, S., Jindapol, S., Kaekratoke, N., et al. (2022). Novel mechanism of napabucasin, a naturally derived furanonaphthoquinone: apoptosis and autophagy induction in lung cancer cells through direct targeting on Akt/mTOR proteins. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 22 (1), 250. doi:10.1186/s12906-022-03727-6
Piechocki, M. P., Dibbley, S. K., Lonardo, F., and Yoo, G. H. (2008). Gefitinib prevents cancer progression in mice expressing the activated rat HER2/neu. Int. J. Cancer 122 (8), 1722–1729. doi:10.1002/ijc.23231
Pollizzi, K. N., Patel, C. H., Sun, I. H., Oh, M. H., Waickman, A. T., Wen, J., et al. (2015). mTORC1 and mTORC2 selectively regulate CD8⁺ T cell differentiation. J. Clin. Invest. 125 (5), 2090–2108. doi:10.1172/jci77746
Powell, J. D., Pollizzi, K. N., Heikamp, E. B., and Horton, M. R. (2012). Regulation of immune responses by mTOR. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 30, 39–68. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075024
Pridham, K. J., Le, L., Guo, S., Varghese, R. T., Algino, S., Liang, Y., et al. (2018). PIK3CB/p110β is a selective survival factor for glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 20 (4), 494–505. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nox181
Primo N., L.Jr, Jeff, L., Philip C., M., Karen, K., Mark A., S., Ravi, S., et al. (2011). Phase II trial of the Akt inhibitor MK-2206 plus erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer who have progressed after previous response (including stable disease) with erlotinib therapy. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01294306.
Priya, M. M., Selvi, B. K., and Paul, J. A. J. (2011). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the leaf extracts of euphorbia hirta and nerium indicum. Dig. J. Nanomater. BIOSTRUCTURES 6 (2), 869–877.
Puglisi, M., Thavasu, P., Stewart, A., de Bono, J. S., O'Brien, M. E., Popat, S., et al. (2014). AKT inhibition synergistically enhances growth-inhibitory effects of gefitinib and increases apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Lung Cancer 85 (2), 141–146. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.05.008
Qu, Y., Wu, X., Yin, Y., Yang, Y., Ma, D., and Li, H. (2014). Antitumor activity of selective MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC xenograft models. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 33 (1), 52. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-33-52
Raith, F., O'Donovan, D. H., Lemos, C., Politz, O., and Haendler, B. (2023). Addressing the reciprocal crosstalk between the AR and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways for prostate cancer treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (3), 2289. doi:10.3390/ijms24032289
Ramachandran, R., Parthasarathy, R., and Dhayalan, S. (2022). Silver nanoparticles synthesized by Euphorbia hirta exhibited antibacterial activity and induced apoptosis through downregulation of PI3Kγ mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Environ. Toxicol. 37 (12), 2865–2876. doi:10.1002/tox.23643
Ramasubbu, K., and Devi Rajeswari, V. (2023). Impairment of insulin signaling pathway PI3K/Akt/mTOR and insulin resistance induced AGEs on diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative diseases: a perspective review. Mol. Cell Biochem. 478 (6), 1307–1324. doi:10.1007/s11010-022-04587-x
Rao, M. M., and Kingston, D. G. (1982). Plant anticancer agents. XII. Isolation and structure elucidation of new cytotoxic quinones from Tabebuia cassinoides. J. Nat. Prod. 45 (5), 600–604. doi:10.1021/np50023a014
Reddy, D., Kumavath, R., Ghosh, P., and Barh, D. (2019). Lanatoside C induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and suppresses cancer cell growth by attenuating MAPK, Wnt, JAK-STAT, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. Biomolecules 9 (12), 792. doi:10.3390/biom9120792
Ren, H., Chen, M., Yue, P., Tao, H., Owonikoko, T. K., Ramalingam, S. S., et al. (2012). The combination of RAD001 and NVP-BKM120 synergistically inhibits the growth of lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 325 (2), 139–146. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.06.018
Riabov, V., Gudima, A., Wang, N., Mickley, A., Orekhov, A., and Kzhyshkowska, J. (2014). Role of tumor associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Front. Physiol. 5, 75. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00075
Rodrigues, G. A., Falasca, M., Zhang, Z., Ong, S. H., and Schlessinger, J. (2000). A novel positive feedback loop mediated by the docking protein Gab1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 20 (4), 1448–1459. doi:10.1128/mcb.20.4.1448-1459.2000
Sarbassov, D. D., Guertin, D. A., Ali, S. M., and Sabatini, D. M. (2005). Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307 (5712), 1098–1101. doi:10.1126/science.1106148
Sarkaria, J. N., Schwingler, P., Schild, S. E., Grogan, P. T., Mladek, A. C., Mandrekar, S. J., et al. (2007). Phase I trial of sirolimus combined with radiation and cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2 (8), 751–757. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3180cc2587
Saxton, R. A., and Sabatini, D. M. (2017). mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 168 (6), 960–976. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.004
Schmid, M. C., Avraamides, C. J., Dippold, H. C., Franco, I., Foubert, P., Ellies, L. G., et al. (2011). Receptor tyrosine kinases and TLR/IL1Rs unexpectedly activate myeloid cell PI3kγ, a single convergent point promoting tumor inflammation and progression. Cancer Cell 19 (6), 715–727. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2011.04.016
Shariati, M., and Meric-Bernstam, F. (2019). Targeting AKT for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 28 (11), 977–988. doi:10.1080/13543784.2019.1676726
Shayesteh, L., Lu, Y., Kuo, W. L., Baldocchi, R., Godfrey, T., Collins, C., et al. (1999). PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet. 21 (1), 99–102. doi:10.1038/5042
Shi, H., Hong, A., Kong, X., Koya, R. C., Song, C., Moriceau, G., et al. (2014). A novel AKT1 mutant amplifies an adaptive melanoma response to BRAF inhibition. Cancer Discov. 4 (1), 69–79. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-13-0279
Shrimali, D., Shanmugam, M. K., Kumar, A. P., Zhang, J., Tan, B. K., Ahn, K. S., et al. (2013). Targeted abrogation of diverse signal transduction cascades by emodin for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer. Cancer Lett. 341 (2), 139–149. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.023
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E., and Jemal, A. (2022). Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 72 (1), 7–33. doi:10.3322/caac.21708
Single-arm, A. (2022). Open-label, multi-cohort, multi-center clinical study on the safety and efficacy of TQ-B3525 tablets combined with osimertinib in subjects with advanced non-small cell lung. Cancer. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05284994.
Sirico, M., D'Angelo, A., Gianni, C., Casadei, C., Merloni, F., and De Giorgi, U. (2023). Current state and future challenges for PI3K inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel) 15 (3), 703. doi:10.3390/cancers15030703
Song, J. M., Upadhyaya, P., and Kassie, F. (2018). Nitric oxide-donating aspirin (NO-Aspirin) suppresses lung tumorigenesis in vitro and in vivo and these effects are associated with modulation of the EGFR signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 39 (7), 911–920. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgy049
Soria, J. C., Adjei, A. A., Bahleda, R., Besse, B., Ferte, C., Planchard, D., et al. (2017). A phase IB dose-escalation study of the safety and pharmacokinetics of pictilisib in combination with either paclitaxel and carboplatin (with or without bevacizumab) or pemetrexed and cisplatin (with or without bevacizumab) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 86, 186–196. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2017.08.027
Soria, J. C., Shepherd, F. A., Douillard, J. Y., Wolf, J., Giaccone, G., Crino, L., et al. (2009). Efficacy of everolimus (RAD001) in patients with advanced NSCLC previously treated with chemotherapy alone or with chemotherapy and EGFR inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 20 (10), 1674–1681. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp060
Spoerke, J. M., O'Brien, C., Huw, L., Koeppen, H., Fridlyand, J., Brachmann, R. K., et al. (2012). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway alterations are associated with histologic subtypes and are predictive of sensitivity to PI3K inhibitors in lung cancer preclinical models. Clin. Cancer Res. 18 (24), 6771–6783. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-12-2347
Stahl, J. M., Sharma, A., Cheung, M., Zimmerman, M., Cheng, J. Q., Bosenberg, M. W., et al. (2004). Deregulated Akt3 activity promotes development of malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 64 (19), 7002–7010. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-04-1399
Stephen, L., Rebecca A, M., Daniel W, B., Joseph, A. W., Jing, Z., Jill, M. S., et al. (2009). A phase Ib dose-escalation study of the safety and pharmacology of GDC-0941 in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced solid tumors. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00975182.
Stokoe, D., Stephens, L. R., Copeland, T., Gaffney, P. R., Reese, C. B., Painter, G. F., et al. (1997). Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the activation of protein kinase B. Science 277 (5325), 567–570. doi:10.1126/science.277.5325.567
Sun, L., Huang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, Y., He, X., Zhang, L., et al. (2018). Ipatasertib, a novel Akt inhibitor, induces transcription factor FoxO3a and NF-κB directly regulates PUMA-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 9 (9), 911. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0943-9
Sun, S. Y., Rosenberg, L. M., Wang, X., Zhou, Z., Yue, P., Fu, H., et al. (2005). Activation of Akt and eIF4E survival pathways by rapamycin-mediated mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition. Cancer Res. 65 (16), 7052–7058. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-05-0917
Sun, Y., Han, X., Shang, C., Wang, Y., Xu, B., Jiang, S., et al. (2022). The downregulation of type I IFN signaling in G-MDSCs under tumor conditions promotes their development towards an immunosuppressive phenotype. Cell Death Dis. 13 (1), 36. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04487-w
Tan, C. L., Kuchroo, J. R., Sage, P. T., Liang, D., Francisco, L. M., Buck, J., et al. (2021). PD-1 restraint of regulatory T cell suppressive activity is critical for immune tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 218 (1), e20182232. doi:10.1084/jem.20182232
Tan, X., Chen, Y. F., Zou, S. Y., Wang, W. J., Zhang, N. N., Sun, Z. Y., et al. (2023). ALDH2 attenuates ischemia and reperfusion injury through regulation of mitochondrial fusion and fission by PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 195, 219–230. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.12.097
Tang, Y., Xian, Z., Wu, F., Cao, H., Wang, L., Tang, Q., et al. (2024). Traditional Chinese medicine combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: key drug screening and mechanism analysis. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 398, 843–854. doi:10.1007/s00210-024-03310-5
Tarantelli, C., Argnani, L., Zinzani, P. L., and Bertoni, F. (2021). PI3Kδ inhibitors as immunomodulatory agents for the treatment of lymphoma patients. Cancers (Basel) 13 (21), 5535. doi:10.3390/cancers13215535
Tewari, D., Patni, P., Bishayee, A., Sah, A. N., and Bishayee, A. (2022). Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: a novel therapeutic strategy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 80, 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.008
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2014). Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 511 (7511), 543–550. doi:10.1038/nature13385
Uchida, A., Seki, N., Mizuno, K., Yamada, Y., Misono, S., Sanada, H., et al. (2019). Regulation of KIF2A by antitumor miR-451a inhibits cancer cell aggressiveness features in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 11 (2), 258. doi:10.3390/cancers11020258
Ulrich, C. M., Bigler, J., and Potter, J. D. (2006). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: promise, perils and pharmacogenetics. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6 (2), 130–140. doi:10.1038/nrc1801
UNICANCER (2014). Evaluation of the efficacy of high throughput genome analysis as a therapeutic decision tool for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02117167.
University of California, Davis (2014). Phase I trial of Cisplatin and Etoposide Plus BKM120 in advanced solid tumors, with an emphasis on small cell lung cancer. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02194049.
Vansteenkiste, J. F., Canon, J. L., De Braud, F., Grossi, F., De Pas, T., Gray, J. E., et al. (2015). Safety and efficacy of buparlisib (BKM120) in patients with PI3K pathway-activated non-small cell lung cancer: results from the phase II BASALT-1 study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 10 (9), 1319–1327. doi:10.1097/jto.0000000000000607
Wagner, H., Kreher, B., Lotter, H., Hamburger, M. O., and Cordell, G. A. (1989). Structure determination of new isomeric naphtho[2,3-b]furan-4,9-diones from Tabebuia avellanedae by the selective-INEPT technique. Helvetica Chim. Acta 72 (4), 659–667. doi:10.1002/hlca.19890720406
Wakeling, A. E., Guy, S. P., Woodburn, J. R., Ashton, S. E., Curry, B. J., Barker, A. J., et al. (2002). ZD1839 (Iressa): an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 62 (20), 5749–5754.
Wang, C., Lin, H., Zhao, W., Liang, Y., Chen, Y., and Wang, C. (2023). MiR-26a-5p exerts its influence by targeting EP300, a molecule known for its role in activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in CD8+tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of colorectal cancer. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 69 (12), 232–241. PubMed PMID: 38063089: Epub 20231130. doi:10.14715/cmb/2023.69.12.37
Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., and Li, P. (2009). Synthesized phosphorylated and aminated derivatives of fucoidan and their potential antioxidant activity in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 44 (2), 170–174. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2008.11.010
Wang, P., Liu, S., Zhu, C., Duan, Q., Jiang, Y., Gao, K., et al. (2020). MiR-29 regulates the function of goat granulosa cell by targeting PTX3 via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Erk1/2 signaling pathways. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 202, 105722. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105722
Wang, X., Jiao, X., Meng, Y., Chen, H., Griffin, N., Gao, X., et al. (2018). Methionine enkephalin (MENK) inhibits human gastric cancer through regulating tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inside cancer cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 65, 312–322. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2018.10.023
Wang, X., Yue, P., Kim, Y. A., Fu, H., Khuri, F. R., and Sun, S. Y. (2008). Enhancing mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-targeted cancer therapy by preventing mTOR/raptor inhibition-initiated, mTOR/rictor-independent Akt activation. Cancer Res. 68 (18), 7409–7418. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-08-1522
Waqar, S. N., Robinson, C., Bradley, J., Goodgame, B., Rooney, M., Williams, K., et al. (2014). A phase I study of temsirolimus and thoracic radiation in non--small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 15 (2), 119–123. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2013.11.007
Wegiel, B., Bjartell, A., Culig, Z., and Persson, J. L. (2008). Interleukin-6 activates PI3K/Akt pathway and regulates cyclin A1 to promote prostate cancer cell survival. Int. J. Cancer 122 (7), 1521–1529. doi:10.1002/ijc.23261
Weichhart, T., Costantino, G., Poglitsch, M., Rosner, M., Zeyda, M., Stuhlmeier, K. M., et al. (2008). The TSC-mTOR signaling pathway regulates the innate inflammatory response. Immunity 29 (4), 565–577. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.012
Weidner, A.-S., Panarelli, N. C., Geyer, J. T., Bhavsar, E. B., Furman, R. R., Leonard, J. P., et al. (2015). Idelalisib-associated colitis: histologic findings in 14 patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathology 39 (12), 1661–1667. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000522
Wen, P. Y., Touat, M., Alexander, B. M., Mellinghoff, I. K., Ramkissoon, S., McCluskey, C. S., et al. (2019). Buparlisib in patients with recurrent glioblastoma harboring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway activation: an open-label, multicenter, multi-arm, phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 37 (9), 741–750. doi:10.1200/jco.18.01207
Wu, J., Zhao, X., Sun, Q., Jiang, Y., Zhang, W., Luo, J., et al. (2020). Synergic effect of PD-1 blockade and endostar on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy and angiogenesis in Lewis lung carcinoma mouse model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 125, 109746. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109746
Xenou, L., and Papakonstanti, E. A. (2020). p110δ PI3K as a therapeutic target of solid tumours. Clin. Sci. (Lond). 134 (12), 1377–1397. doi:10.1042/cs20190772
Xia, C., Zheng, R., Zeng, H., Zhou, M., Wang, L., Zhang, S., et al. (2019). Provincial-level cancer burden attributable to active and second-hand smoking in China. Tob. Control 28 (6), 669–675. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054583
Xu, C., Xiao, G., Zhang, B., Wang, M., Wang, J., Liu, D., et al. (2018). CCAT1 stimulation of the symmetric division of NSCLC stem cells through activation of the Wnt signalling cascade. Gene Ther. 25 (1), 4–12. doi:10.1038/gt.2017.98
Xu, Z., Han, X., Ou, D., Liu, T., Li, Z., Jiang, G., et al. (2020). Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104 (2), 575–587. doi:10.1007/s00253-019-10257-8
Yan, Y.-y., Zheng, L.-s., Zhang, X., Chen, L.-k., Singh, S., Wang, F., et al. (2011). Blockade of Her2/neu binding to Hsp90 by emodin azide methyl anthraquinone derivative induces proteasomal degradation of Her2/neu. Mol. Pharm. 8 (5), 1687–1697. doi:10.1021/mp2000499
Yang, H., Zhao, J., Zhao, M., Zhao, L., Zhou, L. N., Duan, Y., et al. (2020). GDC-0349 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth. Cell Death Dis. 11 (11), 951. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03146-w
Yang, H., Zhao, R., Yang, H. Y., and Lee, M. H. (2005). Constitutively active FOXO4 inhibits Akt activity, regulates p27 Kip1 stability, and suppresses HER2-mediated tumorigenicity. Oncogene 24 (11), 1924–1935. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208352
Yang, J., Cron, P., Good, V. M., Thompson, V., Hemmings, B. A., and Barford, D. (2002). Crystal structure of an activated Akt/protein kinase B ternary complex with GSK3-peptide and AMP-PNP. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9 (12), 940–944. doi:10.1038/nsb870
Yang, J., Nie, J., Ma, X., Wei, Y., Peng, Y., and Wei, X. (2019). Targeting PI3K in cancer: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 26. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0954-x
Yang, J., Pi, C., and Wang, G. (2018). Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 103, 699–707. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.072
Yang, Q., Meng, D., Zhang, Q., and Wang, J. (2024). Advances in research on the anti-tumor mechanism of Astragalus polysaccharides. Front. Oncol. 14, 1334915. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1334915
Yang, Y., Wu, J., Cai, J., He, Z., Yuan, J., Zhu, X., et al. (2015). PSAT1 regulates cyclin D1 degradation and sustains proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 136 (4), E39–E50. doi:10.1002/ijc.29150
Yang, Z., Guo, D., Zhao, J., Li, J., Zhang, R., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Aggf1 specifies hemangioblasts at the top of regulatory hierarchy via Npas4l and mTOR-S6K-Emp2-ERK signaling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 43 (12), 2348–2368. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.123.318818
Yehia, L., Keel, E., and Eng, C. (2020). The clinical spectrum of PTEN mutations. Annu. Rev. Med. 71, 103–116. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-052218-125823
Yin, Y., Hua, H., Li, M., Liu, S., Kong, Q., Shao, T., et al. (2016). mTORC2 promotes type I insulin-like growth factor receptor and insulin receptor activation through the tyrosine kinase activity of mTOR. Cell Res. 26 (1), 46–65. doi:10.1038/cr.2015.133
Yin, Y., and Shen, W. H. (2008). PTEN: a new guardian of the genome. Oncogene 27 (41), 5443–5453. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.241
Yu, M., Chen, J., Xu, Z., Yang, B., He, Q., Luo, P., et al. (2023b). Development and safety of PI3K inhibitors in cancer. Arch. Toxicol. 97 (3), 635–650. doi:10.1007/s00204-023-03440-4
Yu, Y., Xiao, Z., Lei, C., Ma, C., Ding, L., Tang, Q., et al. (2023a). BYL719 reverses gefitinib-resistance induced by PI3K/AKT activation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer 23 (1), 732. doi:10.1186/s12885-023-11243-0
Yue, W., Yang, C. S., DiPaola, R. S., and Tan, X. L. (2014). Repurposing of metformin and aspirin by targeting AMPK-mTOR and inflammation for pancreatic cancer prevention and treatment. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 7 (4), 388–397. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.Capr-13-0337
Zapopozhets, T. S., Besednova, N. N., and Loenko Iu, N. (1995). Antibacterial and immunomodulating activity of fucoidan. Antibiot. Khimioter 40 (2), 9–13.
Zappa, C., and Mousa, S. A. (2016). Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 5 (3), 288–300. doi:10.21037/tlcr.2016.06.07
Zeng, H., Yang, K., Cloer, C., Neale, G., Vogel, P., and Chi, H. (2013). mTORC1 couples immune signals and metabolic programming to establish T(reg)-cell function. Nature 499 (7459), 485–490. doi:10.1038/nature12297
Zhang, C., Shi, J., Mao, S. Y., Xu, Y. S., Zhang, D., Feng, L. Y., et al. (2015). Role of p38 MAPK in enhanced human cancer cells killing by the combination of aspirin and ABT-737. J. Cell Mol. Med. 19 (2), 408–417. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12461
Zhang, H. Q., Xie, X. F., Li, G. M., Chen, J. R., Li, M. T., Xu, X., et al. (2021). Erianin inhibits human lung cancer cell growth via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo. Phytother. Res. 35 (8), 4511–4525. doi:10.1002/ptr.7154
Zheng, H. Y., Hu, J. D., Zheng, Z. H., Huang, L. Y., Chen, Y. Y., Zheng, J., et al. (2007). Emodin induces leukemic HL-60 cells apoptosis probably by inhibiting Akt signal pathway. Yao Xue Xue Bao 42 (11), 1142–1146.
Zheng, L., Qin, R., Rao, Z., and Xiao, W. (2023). High-intensity interval training induces renal injury and fibrosis in type 2 diabetic mice. Life Sci. 324, 121740. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121740
Zhuang, H., Zhang, C., and Hou, B. (2020). FAM83H overexpression predicts worse prognosis and correlates with less CD8(+) T cells infiltration and Ras-PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 22 (12), 2244–2252. doi:10.1007/s12094-020-02365-z
Zou, Y., Zhang, B., Mao, Y., Zhang, H., and Hong, W. (2019). Long non-coding RNA OECC promotes cell proliferation and metastasis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 18 (3), 3017–3024. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.10644
LC lung cancer
PI3K phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
AKT protein kinase B
mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin
IARC International Agency for Research on Cancer
NSCLC non-small-cell lung cancer
SCLC small-cell lung cancer
ADC adenocarcinoma
KRT7 keratin 7
SOX2 SRY-box 2
TTF1 thyroid transcription factor 1
OS overall survival
PIP2 phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
PIP3 phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 triphosphate
T308 threonine 308
mTORC1 mTOR complex 1
TSC tuberous sclerosis complex
EGF epidermal growth factor
IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1
FGF fibroblast growth factor;
CCR9 Chemokine receptor 9
VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor
AMPK monophosphate-activated protein kinase
ATP adenosine triphosphate
NSAID nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
ORR overall response rate
LPS lipopolysaccharide
CSCs cancer stem cells
CCOC clear cell ovarian carcinoma
IR ionizing radiation
TCM traditional Chinese medicine
SFA Sophflarine A
ROS reactive oxygen species
TIM tumor immune microenvironment
TAMs Tumor-associated macrophages
MDSCs Myeloid-derived suppressor cells
G-MDSCs Granulocyte myeloid-derived suppressor cells
RTKs receptor tyrosine kinases
ICIs Immune checkpoint inhibitors
CTCs circulating tumor cells
MMP matrix metalloproteinase
ADC adenocarcinoma
SCC squamous cell carcinoma
TTF1 thyroid transcription factor 1
PH pleckstrin homology
PX phox
IGF-1 insulin-like growth factor-1
FGF fibroblast growth factor
EGF epidermal growth factor
CCR9 Chemokine receptor 9
TLR Toll-like receptor
IL interleukin
FDA Food and Drug Administration
AMPK adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
RR response rate
Tregs regulatory T cells
Th2 T helper type 2
RTKs receptor tyrosine kinases
GPCRs G protein-coupled receptors
Th1 helper type 1
CTLA-4 cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4
SoC standard of care
mTORis mTOR inhibitors
lncRNAs Long non-coding RNAs
PAM phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling
Keywords: PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, lung cancer, PI3K inhibitors, Akt inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors, natural products, combined therapy
Citation: Qiang M, Chen Z, Liu H, Dong J, Gong K, Zhang X, Huo P, Zhu J, Shao Y, Ma J, Zhang B, Liu W and Tang M (2025) Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in lung cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1516583. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1516583
Received: 24 October 2024; Accepted: 27 January 2025;
Published: 18 February 2025.
Edited by:
Prabhu Thirusangu, Mayo Clinic, United StatesReviewed by:
Jianbo Zhou, Sichuan University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Qiang, Chen, Liu, Dong, Gong, Zhang, Huo, Zhu, Shao, Ma, Zhang, Liu and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Liu, bF93MDFAamx1LmVkdS5jbg==; Mingbo Tang, bWJ0YW5nQGpsdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.