- 1Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology, Clinical Medicine Research Center, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 2College of Life Sciences, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 3Thoracic Surgery Department, Inner Mongolia Hospital of Peking University Cancer Hospital, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
- 4Ultrasonic Department, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic endocrine and metabolic disorder characterized by persistent hyperglycemia that poses serious threats to human health and quality of life. The morbidity, disability, and mortality rates of cardiovascular complications stemming from chronic hyperglycemia are primary factors affecting the lifespan of patients with diabetes. Currently, there is no cure for DM. Standard biomedical treatments mostly control the symptoms using insulin injections or oral hypoglycemic drugs. Although the effect of standard biomedical therapy is remarkable, its long-term use is prone to toxic side effects. Numerous studies have recently found that Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has strong advantages in the prevention and treatment of DM and cardiovascular complications (DACC). The collection, processing, preparation and clinical use of TCM are guided by the theory of TCM and follow the “holistic concept.” Multiple components, pathways, and targets form the basis for the use of TCM in treating multiple parts and organs of the body simultaneously. TCM is mainly derived from natural medicines and their processed products and has fewer side effects. TCM is clinically used as compound prescriptions, botanical drugs, and monomers. TCM, either independently or in combination with standard biomedical treatments, has shown unique therapeutic advantages. This review aimed to explore the recently reported mechanisms of action of TCM in the prevention and treatment of DACC. These findings will aid the optimization of the current therapy or formation of a therapeutic schedule for integrated TCM and standard biomedical treatments.
1 Introduction
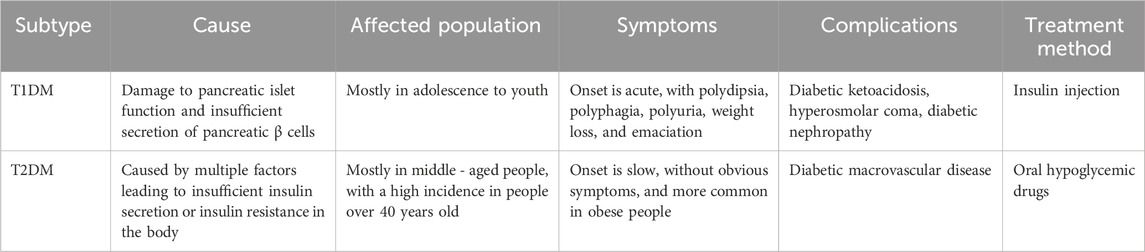
Diabetes mellitus (DM) encompasses a group of clinical syndromes caused by genetic, environmental, and other factors, primarily characterized by hyperglycemia. This condition arises from insufficient insulin secretion and/or impaired insulin action, caused by glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism disorders. Diabetes can be categorized into type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), based on differences in pathogenesis, symptoms, complications, and treatment strategies (Table 1). With increasing population aging and lifestyle changes, the prevalence of DM is increasing dramatically worldwide (Diabetesatlas, 2021). Based on projections, the number of individuals with DM will increase to 642.8 million by 2030 and 783.7 million by 2045 (Collaborators, 2023). Patients with DM face a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease compared with those without DM, and they often experience these complications earlier in life (Heather et al., 2022). In addition, extensive cohort observational studies conducted over the last 30 years have confirmed that 49% of DM-related deaths are due to cardiovascular disease (Chiquette and Chilton, 2002; Tamayo et al., 2023). Patients with T2DM exhibited a considerably increased lifetime risk of various cardiovascular conditions, which may include coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and peripheral artery disease (Marx et al., 2023). The rising morbidity associated with DM, coupled with cardiovascular complications resulting from long-term hyperglycemia, leads to disability and mortality among patients. This situation has become a pressing public health issue, posing a serious threat to human health (Lopez-Diez et al., 2021).
Cardiomyocytes and vascular endothelial cells are important structural components of the heart and blood vessels. The mechanisms by which long-term hyperglycemia induces cardiomyopathy in DM include at least three key aspects: 1) hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress promotes the excessive release of reactive oxygen species, which in turn induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis, 2) the oxidative stress may also result in persistent inflammatory damage to blood vessels, thereby increasing the risk of diabetic cardiomyopathy, and 3) hyperglycemia adversely affects protein structure. Studies have shown that hyperglycemia can alter protein structures, leading to the cross-linking of collagen molecules. This alteration impairs the degradation ability of collagen, resulting in increased myocardial fibrosis and infarction (Dal Canto et al., 2023; Stultz and Edelman, 2003). The mechanisms underlying DM-induced chronic hyperglycemia and its associated cardiovascular complications are complex. First, the normal vascular endothelium serves as the body’s natural physical barrier, which can weaken the adhesion of substances such as leukocytes and platelets. However, when endothelial cells are damaged, adhesion molecules become highly expressed, and chemokines are secreted, promoting the adhesion, rolling, and infiltration of leukocytes and platelets into the intimal layer, thus inducing atherosclerosis (Li Y. et al., 2023). Second, high levels of blood glucose are catalyzed by aldose reductase and other enzymes, resulting in the production of fructose and sorbitol, which accumulate outside the endothelial cells. This increase in extracellular osmotic pressure disrupts the internal environment, leading to endothelial cell degeneration, edema, and vascular diseases (Katakami, 2018). In addition, high blood glucose levels damage the inhibitory effect of the renin-angiotensin system, promoting sodium retention, causing insulin resistance (IR), and resulting in hyperinsulinemia. These changes activate the sympathetic nervous system, contributing to hypertension (Jia and Sowers, 2021). Studies have found that the incidence of hypertension in patients with DM is approximately two to six times higher than in those without DM (Lithovius et al., 2020; Wang B. et al., 2022). Chronic hyperglycemia in DM results in a decrease in insulin efficiency in promoting glucose uptake and utilization, alongside a reduction in insulin sensitivity, also known as IR. IR can decrease endothelium-dependent vasodilation response (Fan et al., 2024). The role of vascular endothelium in regulating blood vessel movement is impaired when vascular endothelial dysfunction occurs. Consequently, blood vessel wall elasticity decreases and plaques gradually form on the vessel walls, exacerbating conditions such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, myocardial infarction, stroke, and congestive heart failure. Furthermore, DM is a recognized risk factor for coronary artery disease and is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease and mortality among patients (Association, 2019; Baena-Diez et al., 2016). Statistically, the mortality rate from coronary heart disease in patients with T2DM is two to four times higher than that in patients without DM (Benjamin et al., 2019). In terms of treatment, compared with patients with non-DM-related cardiovascular complications, patients with DM-related cardiovascular complications are less likely to opt for surgical interventions. This is primarily because of the limitations posed by anesthesia evaluation and surgical contraindications. Therefore, exploring and identifying suitable drugs for the prevention and treatment of DM and cardiovascular complications (DACC) is essential.
Currently, several drugs are used to treat DACC. For example, statins, antilipids, and antiplatelet drugs (such as aspirin and clopidogrel) can delay further narrowing of the coronary arteries. When angina symptoms arise from coronary ischemia, nitrates can be used to dilate the blood vessels and improve symptoms. However, each of these medications has various side effects, which may exacerbate long-term complications associated with chronic conditions such as DACC (Table 2). Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for DM globally. Studies have shown that metformin causes serious gastrointestinal side effects (Dixon et al., 2023). Statins used to treat DACC are associated with an increased risk of developing T2DM (Laakso and Fernandes Silva, 2023). Table 2 outlines the side effects of other commonly used medications. Therefore, it is crucial to identify effective drugs, have fewer side effects, and can contribute to optimizing treatment plans.
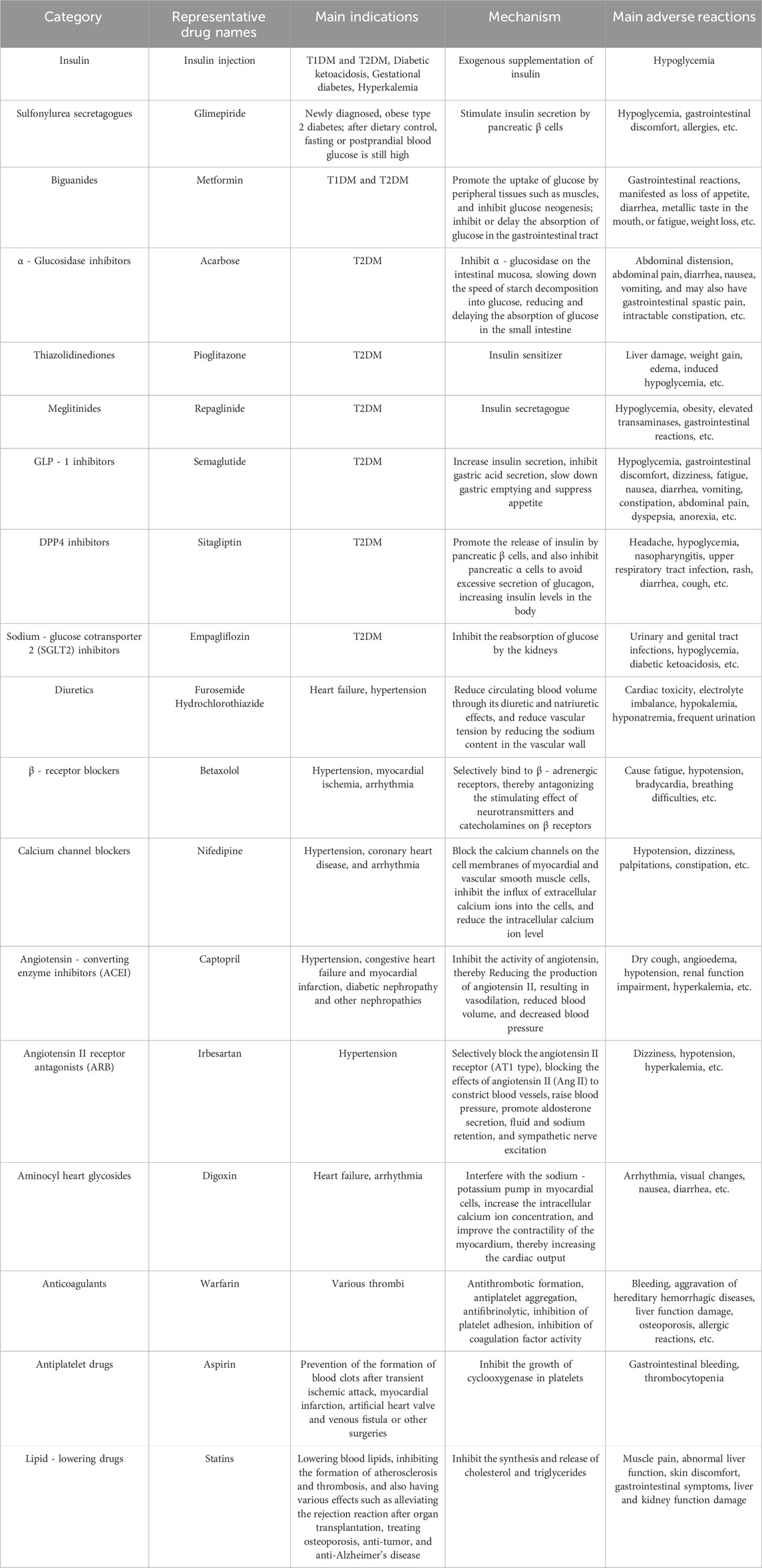
Table 2. Adverse reactions or side effects of commonly used drugs for diabetes and its cardiovascular complications.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has gained popularity as a treatment method for chronic diseases in recent years. TCM typically includes TCM compound prescriptions, botanical drugs, and individual botanical drugs components. Compared with standard biomedical treatments, patients benefit from TCM’s “holistic concept,” as well as the characteristics of natural products and lower toxicity. Numerous basic studies have explored TCM’s efficacy in treating DACC (Liu et al., 2023; Song Z. et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2022). Studies have confirmed that TCM can be used as a complementary treatment method for patients with DM and coronary heart disease (Wei Y. et al., 2022). Although high-quality clinical studies on TCM for the treatment of DACC remain limited, some key studies have provided valuable and compelling evidence for its application. For instance, the MUST-D study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IV trial, enrolled 716 patients with DM-related coronary heart disease from 97 tertiary hospitals in China (Zhou J. et al., 2023). The study found that the treatment group with Shexiang Baoxin pills was highly effective in reducing the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Compared with the control group, the incidence of MACEs in the Shexiang Baoxin pill treatment group decreased by 45.8%. Moreover, at 24 months, the overall incidence of secondary endpoints (composite outcome of all-cause death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, hospitalization due to unstable angina or heart failure, and coronary angioplasty) significantly decreased by 32.3%. In addition, the incidence of cardiovascular adverse events in the Shexiang Baoxin pill group (4.4%) was lower than that in the placebo group (7.7%), demonstrating its safety. TCM has also shown remarkable potential in pre-DM intervention. The FOCUS randomized clinical trial included 885 patients with impaired glucose tolerance, abdominal obesity, or any abnormal index of metabolic syndrome (Ji et al., 2024). The results revealed that the risk of DM in the Jinlida Granule group significantly decreased by 41% and had prominent advantages in improving multiple metabolic indices (waist circumference, body mass index, blood glucose, blood lipids, and insulin resistance index). These results reveal the potential of TCM in pre-DM intervention and the improvement of metabolic disorders, providing solid evidence for the further application of TCM for DM prevention and treatment. Furthermore, regarding the treatment of DM complicated by coronary heart disease, a treatment regimen combining Tongxinluo, Jinlida, and metoprolol also presents promising application prospects. One study indicated that the total effective rate of the combined treatment group was significantly higher than that of the single metoprolol treatment group and surpassed the control group in terms of improving cardiac function indices (such as cardiac stroke volume and left ventricular ejection fraction) and blood glucose control (Yujun et al., 2020). Numerous small-sample clinical trials have demonstrated that TCM plays a crucial role in the treatment of DACC (Lili and Yan, 2025; Zhaolong, 2025). For instance, in a study investigating the impact of Danhu Tongbi Decoction on patients with T2DM complicated by coronary heart disease and angina pectoris, the control group received conventional treatment. In contrast, the observation group received Danhu Tongbi Decoction. The results showed that the observation group showed more significant improvements in glycometabolic and lipid-metabolic indices (including blood glucose and lipid levels). Furthermore, there was a notable enhancement in cardiac function, as measured by the left ventricular ejection fraction, and both the frequency and severity of angina attacks were better alleviated (Lili and Yan, 2025). Another study evaluating the efficacy of naoxintong in treating diabetes mellitus complicated by stroke classified patients into control and treatment groups. In addition to the conventional treatment, the treatment group received naoxintong. After a period of treatment, this group showed more substantial improvements in the neurological deficit score, better blood glucose control, and an increase in the daily activity of living ability scores (Zhaolong, 2025). A large number of small-sample clinical studies are sufficient to confirm the therapeutic value of TCM. These findings established a solid foundation for the promotion and communication of TCM in the international DACC field. To reduce the side effects of standard biomedical treatments and increase their efficacy, some studies have used a combination of TCM and standard biomedical treatments. Wang et al. (Wang H. et al., 2024) selected Jinghong Decoction combined with metformin sustained-release tablets for the syndrome differentiation treatment of T2DM. They found that patients’ symptoms improved significantly and adverse reactions were reduced. In summary, by consolidating research progress on TCM compound prescriptions, botanical drugs, and individual monomers aimed at treating DACC in recent years, we aimed to contribute to the development of new effective prevention and treatment strategies.
2 The application of TCM compound prescriptions in DACC
TCM compound prescriptions show the characteristics of multiple targets and mechanisms in the treatment of diseases owing to their complex components. In this study, we summarized the mechanisms through which TCM compound prescriptions function in DACC, including reducing inflammation, regulating immunity, modulating gut microbiota, inhibiting islet cell or cardiovascular cell apoptosis, anti-oxidative stress, regulating glucose and lipid metabolism, and other mechanisms (Table 3).
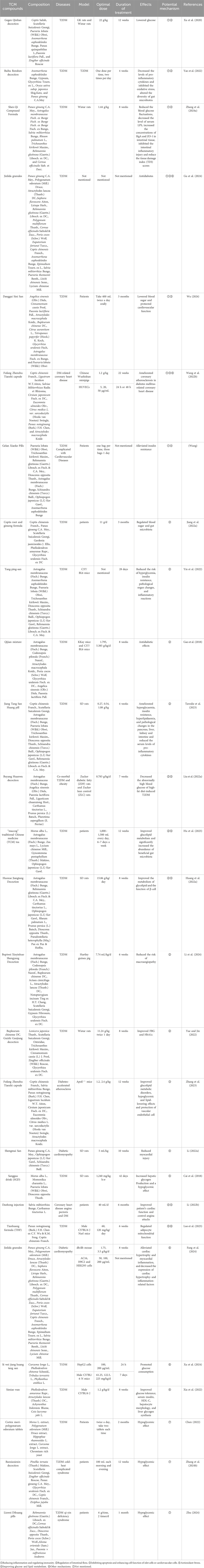
Table 3. Lists of TCM compounds with potential anti-diabetes and its cardiovascular complications action.
2.1 Reducing inflammation and regulating immunity
T1DM arises from an autoimmune attack on the pancreas, leading to the destruction of insulin-secreting β-cells. Immune system cells contribute to β-cell death through various mechanisms, including triggering inflammation. Some researchers describe T1DM as a “chronic anti-auto-inflammatory response,” and there is a theory suggesting that pancreatic inflammation may be the most important cause of T1DM (Committee, 2024; Gearty et al., 2022). Once T1DM develops, it can cause inflammation in other parts of the body, which may result from immune response to hyperglycemia (Qi et al., 2022). T2DM has a complex bidirectional relationship with inflammation. T2DM, characterized by IR, can lead to chronic inflammation, which further exacerbates IR, creating a vicious cycle. Chronic and systemic inflammation are the prominent features of T2DM. Excessive cytokines and signaling proteins generated to control inflammation can inadvertently lead to heightened inflammatory responses. In both T1DM and T2DM diabetes, chronic inflammation can lead to DACC such as cardiomyopathy, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and other cardiovascular diseases (Lorenzo-Almoros et al., 2022; Peng et al., 2023; Poznyak et al., 2020). This underscores the rationale behind targeting inflammation or regulating the immune system as therapeutic strategies for DM. Several TCM compound prescriptions have demonstrated efficacy in addressing these issues. For example, GegenQinlian Decoction, BaihuRenshen Decoction, and Shen-Qi Compound Formula promote glucose absorption and exert hypoglycemic effects in diabetic rats by inhibiting small intestinal inflammation (Xu et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2022; Zhang and Liu, 2024). Jinlida granules and Danggui SiniSan can inhibit islet cell inflammation, enhance islet cell function, and play hypoglycemic roles (Gu et al., 2024; Wu, 2024). The Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi capsule can reduce vascular endothelial inflammation and alleviate DACC (Wang L. et al., 2022). Gelan Xiaoke Pills can enhance the immune function in patients with diabetes, reduce IR, and alleviate diabetes symptoms (Wang M.-C. et al., 2024).
2.2 Regulation of intestinal flora
The intestinal flora is often referred to as the “hidden organ” of the human body, that is involved in regulating various biological processes such as energy metabolism and immune inflammatory response, and plays an irreplaceable role in the metabolic health of the body and the occurrence and development of diseases (Drozdz et al., 2021). Under normal physiological conditions, the gut maintains a complete immune barrier. However, this barrier is broken down once hyperglycemia occurs. An imbalance in the intestinal microecology is an important factor that accelerates the occurrence, development, and outcomes of various endocrine and metabolic diseases. Several studies have found that T2DM is often accompanied by intestinal flora disturbances and multiple organ dysfunctions (Mao et al., 2023; Nesci et al., 2023; Zhang and Xie, 2024). The intestinal leakage theory suggests that when the intestinal flora is disturbed, intestinal permeability increases, endotoxin and pro-inflammatory cytokine production increases, energy intake increases, and systemic inflammation and IR are induced (Cristofori et al., 2021; Gonzalez et al., 2019). The “gut-islet axis” is an important endocrine regulation axis of intestinal microecology and intestinal neuroendocrine dialogue with islets. Therefore, it is important to explore functional protective strategies for islet cells within the gut.
Several TCM compound prescriptions, including Gegen Qinlian decoction, Shen Qi compound formula, Coptis saliva root and Ginseng Alph. Wood formula, Tang-ping-san, Qijian mixture, JiangTang San Huang pill, Buyang Huanwu decoction, Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang decoction, “maccog” TCM tea, Huoxue Jiangtang Decoction and Bupiwei Xieyinhuo Shengyang Decoction can increase the proportion of beneficial bacteria by regulating intestinal flora, and play a role in lowering blood glucose or alleviating diabetes symptoms (Gao et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2023; Huang Q. et al., 2022; Jiang L. et al., 2022; Liu M. et al., 2022; Tawulie et al., 2023; Wang B. et al., 2022; Zhang F. et al., 2024). From the perspective of TCM, the small intestine and the heart are similar to the “gut - spindle.” Long-term dietary changes in patients with pre-DM lead to a structural imbalance of the intestinal flora, which aggravates the changes in metabolic products (mainly trimethylamine oxide, short-chain fatty acids, bile acids, and lipopolysaccharides) of the flora (Bielka et al., 2022; Bondy, 2023). These substances can enter systemic circulation, damaging the intestinal barrier, and leading to complications such as myocardial fibrosis, vascular inflammation, and other diabetic cardiovascular diseases. This progression can result in poor management of the patient’s condition, uncontrollably and substantially accelerating mortality rates among patients with DM. Therefore, protecting the integrity of the intestinal barrier, improving imbalance of the intestinal flora, and regulating the metabolites of the flora can inhibit inflammatory responses in cardiomyocytes, delaying myocardial fibrosis, and protect cardiomyocytes. Such strategies represent novel auxiliary approaches for the treatment of DACC. Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction has been shown to reduce blood glucose levels in diabetic rats by adjusting the absorption of short-chain fatty acids (Li et al., 2024). Bupiwei Xieyinhuo Shengyang Decoction exerts its effect by regulating the metabolites of intestinal flora to lower blood glucose (Yue et al., 2022).
2.3 Inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing the function of islet cells or cardiovascular cells
Islet cells form the basis of insulin secretion, and dysfunction in these cells, including the abnormal apoptosis of islet cells caused by various factors, occurs in most patients with DM. Therefore, the development of inhibitors of islet cell apoptosis is considered one of the most effective strategies for the prevention and treatment of DM. According to the TCM theory, jinlidagranules can tonify the spleen and push qi, a fundamental substance or driving force that sustains human life activities in the effect of TCM theory (Gu et al., 2024). Several studies have shown that jinlidagranules exert hypoglycemic effects by inhibiting islet cell apoptosis and enhancing islet function (Gu et al., 2024). Abnormal death of cardiovascular cells, such as cardiomyocytes and vascular endothelial cells, is a major cause of cardiovascular complications in patients with DM. Danggui SiniSan has the functions of nourishing blood and warming the meridian, namely, dispelling cold air in TCM theory (Wu, 2024). Standard biomedical treatment suggests that Danggui SiniSan can promote blood circulation by increasing vital energy, enhancing resistance, and regulating endocrine function. Some studies have shown that it not only enhances islet function by inhibiting islet cell apoptosis, but also protects cardiovascular function (Wu, 2024). Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi capsules can inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis induced by DM, thereby safeguarding cardiovascular function in patients with diabetes (Wang L. et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023).
2.4 Antioxidant stress
Oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between oxidation and antioxidant activity, leaning toward oxidative damage. Oxidative stress is mainly involved in DM development through at least three ways: 1) blocking of the insulin action pathway, which leads to IR (Masenga et al., 2023), 2) reducing insulin gene expression, resulting in reduced insulin synthesis and secretion (Hoseini et al., 2022), and 3) promoting islet cell apoptosis (Zhao et al., 2023). Gel XiaokePills can enhance antioxidant capacity and thus reduce IR (Wang J. et al., 2024). In addition, hyperglycemia can induce or aggravate cardiovascular complications in several ways: 1) it directly increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) by aggravating mitochondrial load and the diabetic vascular inflammatory response (Ma X. M. et al., 2023), 2) non-enzyme-catalyzed glycosylation of proteins is enhanced during hyperglycemia. Therefore, the glycosylation of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase, inevitably leads to changes in enzyme activity, a decrease in free radical scavenging ability, induction of oxidative stress, and aggravation of DACC (Perrone et al., 2020), 3) hyperglycemia directly induces angiotensin production in muscle cells. Ang II can produce superoxide ions by activating the NADPH/NADH system (Zhang L. et al., 2024). Induction of oxidative stress results in vascular endothelial cell dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases, and 4) it promotes the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (Chen J. W. et al., 2020). Previous studies have shown that the proliferation and migration of these muscle cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (Gong X. et al., 2021; Yan Y. et al., 2021). Recent studies have used TCM to treat different cell types and alleviate DM by affecting the mitochondrial oxidative respiratory chain, showing that oxidative stress has a bidirectional regulatory effect on DACC (Gong X. et al., 2021; Zhang Y. et al., 2024). ShengmaiSan is a combination of three important components that alleviate DM-induced myocardial damage by improving oxidative stress response (Li Y.-Y., 2022). Danhong injection has been reported to improve myocardial function in patients with DM through its anti-oxidative stress properties (Li D. L., 2022).
2.5 Improving glucose and lipid metabolism
Abnormal glucose metabolism is a well-known underlying cause of DM. The metabolic abnormalities that lead to DM include reduced glycogen synthesis and increased glycogen breakdown. Sangguadrink directly lower blood sugar levels by promoting liver glycogen synthesis (Cai et al., 2018). There exists a close relationship between glucose and lipid metabolism. When adipose tissue absorbs glucose, fat synthesis diminishes. Simultaneously, the mobilization and decomposition of stored fat are accelerated, resulting in a heightened level of free fatty acids and triglycerides in the bloodstream. Elevated levels of fatty acids can inhibit the synthesis of liver glycogen, promoting the production of more glucose and further aggravating hyperglycemic symptoms. Moreover, high concentrations of free fatty acids and triglycerides in the bloodstream increase the susceptibility of the myocardium to ischemic damage, thus inducing or aggravating DACC (Park, 2021). Lipid metabolism disorders result in fat accumulation in the liver, muscles, and blood vessel walls, affecting the normal role of insulin and resulting in IR, which is more likely to induce or aggravate hyperglycemia (Yan B. F. et al., 2023). Therefore, a research team found that Buyang Huanwu decoction can reduce the symptoms of T2DM in mice on a high-fat diet by improving lipid metabolism (Liu M. et al., 2022). Similar to the results of “maccog,” a kind of TCM tea, can improve the glucolipid metabolism and improve the symptoms of T2DM (Hu et al., 2023). In addition, HuoxueJiangtang decoction could enhance the function of islet β-cells by improving glucose and lipid metabolism (Huang Q. et al., 2022). Danhong injection, a certified Chinese medical product made from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge and Carthamus tinctorius L., is prescribed to patients with coronary heart disease in China and can improve cardiac function and control angina attacks by improving glucolipid metabolism (Li D. L., 2022). The Tianhuang formula can improve the mitochondrial function of adipocytes by regulating glycolipid metabolism and alleviating diabetes symptoms (Luo et al., 2023).
2.6 Other mechanisms
The development and progression of DACC involve multiple genes and signaling pathways (Graczyk et al., 2024; Wang H. et al., 2024). Jinlid granules may mitigate DACC by modulating signal transduction or the TP53 pathway (Fang et al., 2024; Gu et al., 2024). Tianhuang formula improves glycolipid metabolism in diabetic mice through the AMPK/MICU1 pathway (Luo et al., 2023). Si wei jiang huang tang san promotes glucose consumption by activating the ERK signaling pathway and inhibiting HIF-1α, so as to alleviate the symptoms of T1DM (Xu et al., 2024). Furthermore, Simiao Wan improved glucose tolerance, serum insulin, high density lipid cholesterol, hepatocyte morphology, and liver glycogen synthesis in T2DM mice by regulating the insulin receptor substrate-1/AKT2/FOXO1/glucose transported type (GLUT) 2 pathway (Xia et al., 2022).
Endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) refers to the process by which endothelial cells lose their original characteristics and transform into mesenchymal cells (myofibroblasts and smooth muscle cells) under the action of various stimulus factors. This transformation results in significant changes in their polarity, morphology, and function of endothelial cells. In the context of diabetes, vascular endothelial cells promote fibrosis after EndMT treatment, subsequently becoming more permeable to promote white blood cell and lipid accumulation in the arterial intima, resulting in plaque formation (You et al., 2022). Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi capsules have been shown to inhibit EndMT and prevent or reduce cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes (Wang L. et al., 2022).
In addition, several other TCM prescriptions, such as Cortex mori-polygonatum odoratum tablets, Liuwei Dihuang Pills (Tang), and Banxiaxiexin Decoction, are used to prevent or treat DACC; however, the specific mechanism of this treatment remains unclear (Chen, 2022; Zhang F. et al., 2024; Zhu, 2024). Therefore, elucidating the specific mechanisms of action is essential for future studies.
3 Application of TCM botanical drugs in DACC
TCM botanical drugs are composed of plant extracts and are widely used in treatment, healthcare, skincare, and other fields because of their natural and nontoxic characteristics. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have shown that many botanical TCM drugs and their extracts play crucial roles in combatting DACC (Prasopthum et al., 2022; Zhang L. et al., 2024; Zhou G. et al., 2023). TCM botanical drugs extracts from different solvents can prevent and treat DACC via multiple mechanisms (Table 4). These mechanisms mainly include reducing inflammation and regulating the immune system; properly regulating the intestinal flora; inhibiting the apoptosis or death of islet and cardiovascular cells, thereby enhancing their functions; affecting cellular stress, including endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER) and oxidative stress; and regulating glucose and lipid metabolism, thereby reducing IR.
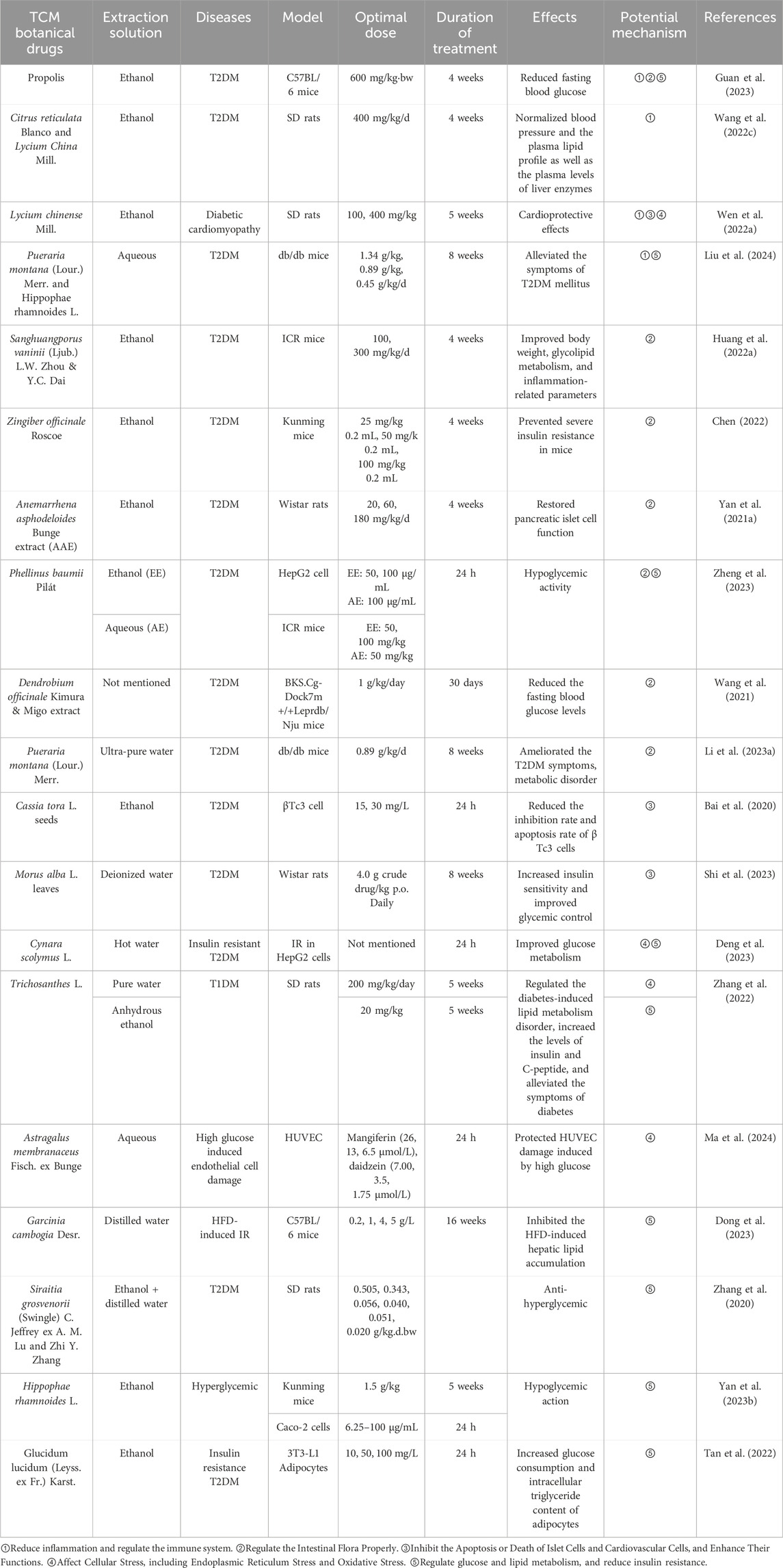
Table 4. Lists of TCM botanical drugs with potential anti-diabetes and its cardiovascular complications action.
3.1 Reducing inflammation and regulating immunity
Studies have found that propolis alcohol extract and Propolis water extracts can alleviate IR by reducing inflammation and regulating glucose metabolism, thereby alleviating DM symptoms (Guan et al., 2023). Inflammation also plays an important role in DACC (Spinetti et al., 2023). Citrus reticulata Blanco and Lycium Chinense Mill. alcohol extracts can inhibit vascular endothelial and myocardial cell inflammation, thus preventing or easing DACC (Wang Y. et al., 2022; Wen et al., 2022a).
3.2 Regulation of gut flora
Gut flora also plays an important role in DACC (Alka et al., 2022). Pueraria montana (Lour.) Merr. aqueous extract and Sanghuangporus vaninii (Ljub.) L.W. Zhou and Y.C. Dai, Zingiber officinale Roscoe, Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge (AAE) alcohol extract, Phellinus baumii Pilát water and alcohol extract, and Dendrobium officinale Kimura and Migo extract, Pueraria montana (Lour.) Merr. water extracts can improve IR and blood sugar levels by regulating intestinal flora (Chen, 2022; Huang Z. R. et al., 2022; Li J. et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2021; Yan D. et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2024).
3.3 Inhibiting islet or cardiovascular cell death and enhancing cell function
Cell death usually occurs in various forms, such as apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and other forms discovered so far. The death of islets and cardiovascular cells is one of the major contributing factors to DACC. In recent years, TCM botanical drugs have gained popularity as treatment for DACC. The alcohol extract of Lycium chinense Mill. was used to treat diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats (Wen et al., 2022a). The results showed that inhibiting the apoptosis of heart cells is one of the main mechanisms for improving diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cassia obtusifolia L. is commonly used in clinical medicine to treat eye diseases, constipation, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and DM. Studies have found that the use of Cassia tora L. seeds in the treatment of DM is mainly related to the inhibition of islet cell apoptosis (Bai et al., 2020). Ferroptosis, a new type of programmed cell death that is iron-dependent and differs from apoptosis, cell necrosis, and autophagy, was first proposed by Dr. Brent R. Stockwell of Columbia University in 2012 (Zeng et al., 2023). Morus alba L. leaves, an herb with high medicinal and economic value, possesses an aqueous extract capable of inhibiting ferroptosis in islet cells (Shi et al., 2023).
3.4 Effects of cellular stress (ER and oxidative stress)
The ER plays an important role in protein folding and is highly sensitive to changes in cellular homeostasis. Changes in the environment in which proteins fold can lead to the aggregation of unfolded or misfolded proteins and affect normal cell function (Chen and Zhang, 2023). When the ER is stressed, the unfolded protein response alleviates protein misfolding and restores cell homeostasis through a series of adaptive responses or induces apoptosis if homeostasis cannot be reshaped (Wiseman et al., 2022). ROS production has been confirmed to be closely related to ER stress and the unfolded protein response (Zeeshan et al., 2016). Although ROS are toxic, they can also mediate physiological processes as messenger molecules. The cytoplasm and various organelles, including the ER and mitochondria, produce ROS (Liu X. et al., 2022). Changes in the redox state of the ER can cause ER stress, which in turn induces ROS in the ER and mitochondria. Sustained oxidative and ER stress initiate apoptosis (Sahu et al., 2023). Lycium chinense Mill. attenuated cardiac oxidative stress and protected the myocardium (Wen et al., 2022a). Cynara scolymus L. improves IR in HepG2 cells by inhibiting ER stress (Deng et al., 2023). Astragalus membranaceus Fisch. ex Bunge and Trichosanthes L. aqueous extracts improve DACC through their anti-oxidant effects (Ma et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2022).
3.5 Regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism and reduction in IR
Several botanical TCM drugs do not depend on a single mechanism of action to exert their effects. For example, Propolis ethanol extracts and Phellinus baumii Pilát have been shown to reduce IR by regulating glucose and lipid metabolism (Spinetti et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2023). Different extraction solvents may exhibit different mechanisms of action. In addition to the antioxidant activity of the alcohol extract, Trichosanthes L. water extract improved the symptoms of type 1 diabetic rats by improving the liver glycogen content (Zhang et al., 2022). Garcinia cambogia Desr. aqueous extracts alleviate diabetes symptoms by improving lipid metabolism (Dong et al., 2023). Water extract of Siraitia grosvenorii (Swingle) C. Jeffrey ex A. M. Lu andand Zhi Y. Zhang promotes Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion, reduces insulin secretion, and has a hypoglycemic function. Hippophae rhamnoides L. is a plant that shares medicinal and dietary roles, has an alcohol extract that inhibits glucose absorption in the small intestine (Zhang et al., 2020). Glucidum lucidum (Leyss. ex Fr.) Karst. a type of fungus that reduces IR by increasing glucose consumption and intracellular triglyceride content in fat cells (Tan et al., 2022). Hypoglycemic effects of Pueraria montana (Lour.) Merr. and Hippophae rhamnoides L. are associated with reduced IR (Liu et al., 2024; Yan C.-Y. et al., 2023).
4 Application of TCM monomers in DACC
Natural pharmaceutical chemicals consist of both inorganic and organic components. In TCM, the content of inorganic components such as minerals and metals, is relatively low compared with organic components Alkaloids, saponins, polysaccharides, flavonoids, phenanthrene quinones, phenols, and terpenoids are important organic components. Notably, compounds belonging to the same class can exhibit different mechanisms of action. The mechanisms of action of these organic compounds in DACC include: 1) reducing inflammation and regulating immunity; 2) regulating intestinal mass; 3) inhibiting apoptosis or death of islet cells or cardiovascular cells; 4) affecting cellular stress (ER and oxidative stress); 5) regulating glycolipid metabolism and alleviating IR; 6) other mechanisms (affecting cell microenvironment, ion channels, and activation of autophagy) (Table 5).
Table 5. Lists of TCM monomers with potential anti-diabetes and its cardiovascular complications action.
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid found in plants such as Coptis Salisb. and Phellodendron Rupr. Clinically, its hydrochloride form, known as berberine hydrochloride, is widely used to treat intestinal infections. With the deepening of pharmacological research, berberine hydrochloride has been reported to have numerous pharmacological effects, including anticancer, antitumor, bactericidal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and lipid-lowering properties (Song et al., 2020). Early studies have demonstrated that berberine not only shows potential in hypoglycemic studies in animals and humans but also has considerable therapeutic effects in DACC (Coppinger et al., 2024). In addition, studies have shown that berberine can improve diabetic complications without causing substantial side effects (Chang et al., 2015; Dai et al., 2021). Compared with other first-line drugs and treatments, berberine is relatively inexpensive and suitable for long-term management of T2DM and related complications. Numerous studies have shown that berberine can considerably reduce blood sugar in rats by regulating the intestinal flora, alleviating intestinal inflammation, and increasing the absorption and utilization of glucose in the small intestine (Nematollahi et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020). Furthermore, berberine can improve cardiometabolic status and myocardial inflammation, as well as improve blood sugar levels and protect the myocardium of diabetic patients (Nematollahi et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020).
Matrine, an alkaloid extracted from the dried roots, plants, and fruits of Sophora flavescens Aiton, has a wide range of physiological activities, including antibacterial, antiviral, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, anti-tumor, anti-fibrosis, and protective effects on multiple organs and tissues (Lin et al., 2022). As one of the effective active compounds, matrine increases insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, and ameliorates DACC. IR can lead to impaired endothelial function, including barrier dysfunction, impaired nitric oxide (NO) activity, excessive production of ROS, oxidative stress, and inflammatory dysregulation. NO acts through eNOS-regulated biosynthesis, and is a potent vasodilator and an important vascular endothelial protective factor. The PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway is widely present in vascular endothelial cells and plays an important role in the regulation of vasodilation and contraction (Wen et al., 2022b). Activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway enhances eNOS expression and plays a regulatory role in eNOS. Astragaloside IV activates the PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway and promotes eNOS expression to improve myocardial function in diabetic rats (Wu S. et al., 2023). Astragaloside IV can also enhance pancreatic beta cell dysfunction induced by uric acid through the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway, anti-apoptotic effects, and activation of autophagy (Jiang Z. et al., 2022). Astragaloside IV can regulate intestinal flora, remove ROS free radicals, and reverse abnormal levels of blood lipids, blood sugar, IR, and antioxidant stress in Kunming mice (Gong P. et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021). Anemoside B4, a natural saponin extracted from Pulsatilla chinensis of the goldenseal family, has good efficacy as anti-tumor, anti-inflammation, and neuroprotective effects (Li Y. F. J. et al., 2020). Recent studies have found that Anemoside B4 also plays a role in lowering blood glucose levels by promoting glucose uptake by muscle cells, facilitating the transport and utilization of grape sleeves, enhancing GLUT4 expression, and regulating various mechanisms of the PI3K/AKT pathway (Gong, 2023a; Gong, 2023b; Gong et al., 2023). These studies provided data for the prevention and treatment of DM and its associated cardiovascular complications.
Polysaccharides from botanical drugs in TCM are complex sugars with complex molecular structures that are extracted from botanical drugs. An increasing number of studies have shown that polysaccharides have considerable efficacy in treating cardiovascular complications in diabetes (Zhang et al., 2019). Dendrobium offiHerbalcinale Kimura and Migo polysaccharides may regulate glycogen synthesis and glucose metabolism through the insulin/PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, improve sugar metabolic disorder in mice with T2DM, and exert hypoglycemic activity (Liu, 2019). The Lycium Chinense Mill. polysaccharide was derived from the medicine-edible plant Lycium Chinense Mill. LBP also reduces blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity in diabetic mice by regulating gut flora (Ma et al., 2022). The purified RG polysaccharide was extracted from Rehmannia Libosch. ex Fisch. and C.A.Mey. can also lower blood sugar levels by affecting glucose metabolism (Zhou et al., 2015). Coix lacryma L., a TCM, has many health benefits, and Coix lacryma L. polysaccharides are its main active compounds. In a mouse model of DM, Coix lacryma L. polysaccharides were found to reduce blood sugar levels by improving the intestinal flora (Xia et al., 2021). Polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum Redouté have a substantial hypoglycemic effect in T2DM (Chen et al., 2023). Plant polysaccharides not only have significant efficacy in DM but also show good prospects for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Astragalus L. inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic mice by improving ER stress, providing strong evidence for the prevention and treatment of diabetic cardiomyopathy (Sun et al., 2019).
Flavonoids are a class of natural compounds characterized by a 2-phenylchromogen (flavone) structure. They can be classified into various structural types depending on the degree of oxidation of the central carbon, ring formation, and the junction site of the B ring. These structural types include flavones, isoflavones, flavonols, dihydroflavones, dihydroflavonols, dihydroisoflavones, chalcones, aurones, flavanes, anthocyanidins, anthocyanidins, and biflavones. Flavonoids are widely distributed in nature, and exhibit various biological activities. Many studies have shown that they have high application value in DM and cardiovascular diseases (Hou et al., 2013; Jin and Arroo, 2023).
Mangiferin, a compound derived from mangoes, possesses various pharmacological and nutritional properties. Upregulation of MMP-2 and downregulation of MMP-9 reduce myocardial collagen accumulation, protein expression of IRE1, ASK1, and JNK in cardiomyocytes, and ER stress in cardiomyocytes, thus inhibiting the progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy (Hou et al., 2013; Jin and Arroo, 2023). Puerarin, a derivative extracted from TCM, plays an active anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidation, anti-myocardial hypertrophy, and anti-myocardial fibrosis and is closely related to programmed cell death. Studies have shown that puerarin can improve or prevent cardiomyopathy in diabetic rats by inhibiting ROS production, pyroptosis, and the inflammation of cardiomyocytes and vascular endothelial cells (Bai et al., 2021; Wei et al., 2024). Luteolins are a class of flavonoids widely found in TCM botanical drugs and are natural antioxidants. Chen et al. found that luteolin reduced oxidative stress and myocardial tissue inflammation, thereby improving myocardial function in rats with diabetic cardiomyopathy (Chen, 2023). Flavonoid components of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb (Rosaceae) alleviates oxidative stress injury through the c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK)/PI3K/Akt pathway, reduces the expression and secretion of inflammatory cytokines while improving glucose metabolism, and alleviating fatty IR (Guo et al., 2023). Naringin is derived from the Rutaceae plant, Citrus maxima (Burm.) Merr. fruit and is a natural flavonoid compound. Grapefruit is a popular fruit worldwide (Li Y. F. J. et al., 2020). However, it is also a TCM that can serve as both medicine and food in China and has a variety of biological activities, including promoting digestion, anti-inflammatory effects, and relieving hangovers. The total flavonoids in Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack leaves relieve inflammation mediated by free-radical lipid peroxidation, strengthen the pancreatic beta cell secretion index, improve lipid metabolism disorders, and diabetic cardiomyopathy (Sun, 2020).
Phenanthraquinone is a quinone containing compound. Several studies have indicated that tanshinone IIA is the most fat-soluble component of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, which can improve the symptoms of diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis mediated by ER stress (Tao et al., 2019; Wu S. et al., 2023). Tanshinone I is a natural phenanthrene quinone extracted from Salviorrhiza that can regulate glycogen metabolism and improve blood sugar levels and IR in T2DM rats (Wei et al., 2017).
Phenolic compounds are a diverse group of natural compounds commonly found in TCM. Curcumin is a natural polyphenolic compound extracted from ginger plants, which imparts a unique color and flavor to food. In addition, curcumin has significant medicinal value as it can improve human immunity, accelerate body metabolism, and have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidant, lipid-lowering, gallbladder, and other biological activities. It has been applied in food, medicine, animal production, and other fields. Studies have shown that curcumin can reduce lipid levels, enhance anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capacities, activate IR signaling pathways, considerably prevent blood sugar rise in mice, reduce IR, and improve insulin sensitivity (Chen, 2022). Furthermore, curcumin can reduce ferroptosis and associated myocardial damage in diabetic mice via the NRF2-glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathway (Wei Z. et al., 2022). Curcumin analogs can also inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway, myocardial inflammation, and improve diabetic cardiomyopathy (Wang M. et al., 2022). Moreover, curcumin inhibits the glycosylation of myocardial proteins in mice induced by a high-fructose diet (Leon-Garcia et al., 2022), improves the cardiomyopathy of diabetic rats induced by STZ combined with a high-fat and high-sugar diet, and activates the silencing information regulator 1(Sirt1)-fork head transcription factor (FoxO1) and PI3K-AKT pathways, alleviating myocardial oxidative stress and inhibiting apoptosis (Ren et al., 2020). C66, a derivative mentioned in the literature, has been shown to ameliorate obesity-related cardiomyopathy induced by a high-fat diet and palmitic acid-stimulated cardiomyocyte injury in H9c2 rats by inhibiting the JNK signaling pathway (Ye et al., 2021). The rose is the dried bud of the Rosaceae family, which has high ornamental, edible, and medicinal value. Rosa rugosa Thunb. polyphenol extract, a polyphenol-rich rose extract, inhibits the activity of α-glucosidase, an enzyme that breaks down complex carbohydrates into absorbable monosaccharides in the small intestine, improving glycogen metabolism and regulating the blood glucose of T2DM rats (Liu et al., 2017). Resveratrol attenuates diabetic cardiac microvascular injury through antioxidative stress (Cai, 2024).
Terpenoids represent the largest group of natural compounds. Volatile oils, resins, rubber, and carotenes are terpenoids, most of which have various physiological activities. Diterpenoids extracted from rock sugar grass can protect islets and alleviate IR (Sun et al., 2020). Euscaphic acid, Tormentic acid, Corosolic acid, Maslinic acid, Oleanolic acid, and Ursolic acid belong to terpenoids and can inhibit alpha glycosidic enzyme activity in vitro and inhibit the absorption of glucose (Chen J. W. et al., 2020). These findings suggest that it may offer promising avenues for treating DM and its related cardiovascular complications.
In addition, based on the principle that structure determines function, the derivatives of these compounds may be used for the prevention and treatment of diabetes and its cardiovascular complications. TPX, derived from the mangiferin derivative 1,3,6,7-tetraallylloxy ketone, can restore the insulin signaling pathway, increase liver glycogen synthesis, and protect against IR caused by glucose metabolism disorders in liver cells (Fan et al., 2023).
5 Discussion
The number of people diagnosed with DM is increasing (Collaborators, 2023). The risk of cardiovascular disease in people with DM is approximately 2.5 times that in people without DM, contributing to the impaired life expectancy of patients with DM (Bragg et al., 2017; Bragg et al., 2016). Although numerous standard biomedical drugs are currently being researched for the treatment of DM and related diseases. However, owing to the side effects and toxicity of these drugs (Table 2), it appears that the single use of standard biomedical treatment drugs is not the optimal plan for patients with chronic diseases who need to take them for a long time. As research into DACC advances, the preventive and therapeutic effects of TCM have been increasingly affirmed. TCM compound prescriptions, botanical drugs, and monomer components have been shown to have positive effects on DACC prevention and treatment. The pathogenesis of includes mainly multiple factors (such as intestinal flora disorders, inflammation, oxidative stress, ER stress, and metabolic disorders) induced by impaired islet function, insufficient insulin secretion, or a decreased ability to perceive glucose (Figure 1). Long-term high-sugar stimulation causes inflammation and damages the normal physiological functions of vascular endothelial cells and cardiomyocytes. In addition, high sugar levels cause oxidative stress in the myocardium and cardiovascular cells, resulting in cardiovascular damage. Hyperglycemia stimulates the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and collagen synthesis, leading to fibrosis and hardening of the vascular wall, causing blood vessels to lose their elasticity, increasing vascular resistance and pressure, and inducing diabetic cardiovascular disease. Long-term high sugar consumption stimulates intestinal flora disorder, which can destroy the normal metabolism of the body, enhance the oxidative stress response in the body, and through the secretion of harmful bacterial endotoxins, shift to cardiovascular circulation and aggravate cardiovascular system inflammation. This review explores the relevant mechanisms of TCM compound prescriptions, TCM botanical drugs, and active compounds in the prevention and treatment of DACC in recent years. Also, it provides the necessary theoretical basis for the modern development of TCM. An increasing number of studies have suggested that the effect of integrated Chinese and standard biomedical treatments on the treatment of DM yields better outcomes than standard biomedical treatments alone (Gu et al., 2018; Ma K. et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2019). Studies have shown that Liuwei Dihuang Pill (decoction) combined with metformin for the treatment of T2DM may reduce the adverse effects of metformin (Zhao et al., 2019). Gu Yuming (Gu et al., 2018) reported that the common adverse events in the TCM group were gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea/vomiting, bloating, and diarrhea), nervous system symptoms, and hypoglycemia. However, no significant abnormalities in blood, liver, or kidney functions were observed in any of these studies. This may provide ideas for promoting combined treatments for DACC. Therefore, the use of TCM, either independently or in combination with standard biomedical therapies, represents a viable alternative for the prevention and treatment of DACC.
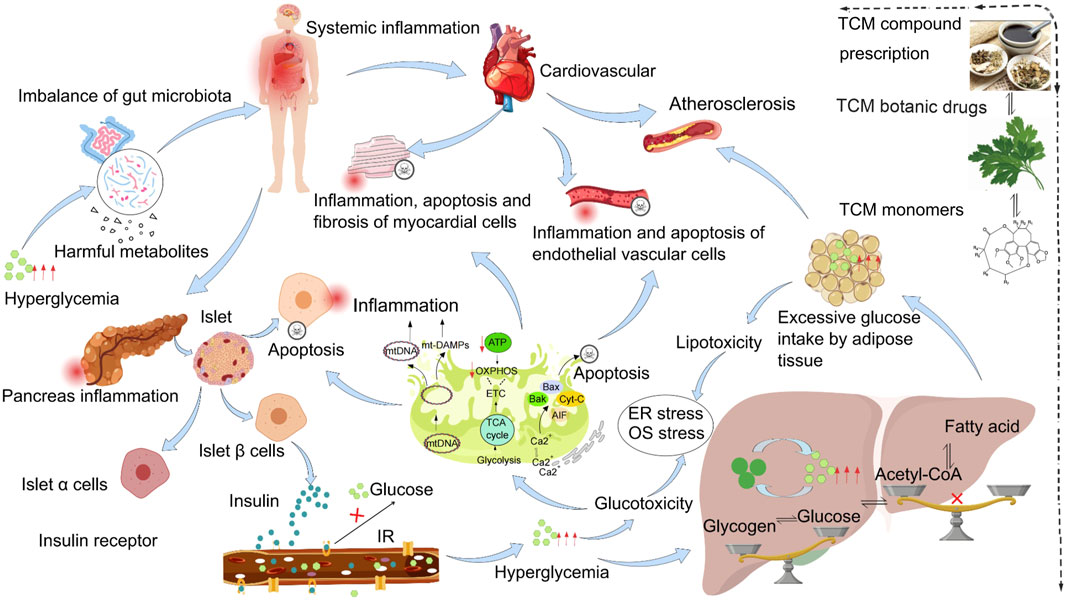
Figure 1. Schematic Diagram of the Pathogenesis of DACC. The pathogenesis of DACC involves multiple interconnected mechanisms, including insulin resistance, gut microbiota dysbiosis, oxidative stress, disorders of glucose and lipid metabolism, inflammation, and apoptosis. These factors interact synergistically, contributing to the initiation and progression of DACC. In the diagram, the red upward arrow (↑) indicates an elevation or increase in a specific factor. The red downward arrow (↓) signifies a reduction or decrease. The red “×” denotes an inhibitory effect. The blue curved arrow represents promotion or generation of a process. The black arrow illustrates the occurrence of a biochemical process. The red halo symbolizes inflammation, while the skull icon represents apoptosis. This schematic highlights the complex interplay of these mechanisms, providing a comprehensive overview of the multifactorial nature of DACC pathogenes.
TCM has demonstrated unique advantages in the prevention and treatment of DACC, offering novel therapeutic approaches through its multicomponent, multitarget mechanisms of action. However, the clinical application of TCM for the management of DACC poses substantial challenges. First, the complexity of TCM components and issues related to standardization remain major hurdles. Each TCM botanical drug is a complex mixture of natural compounds that often contain various chemical constituents such as alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, and polysaccharides. For instance, ginseng alpha wood contains multiple ginsenosides as well as volatile oils, polysaccharides, and amino acids, which interact synergistically. In compound formulations, the chemical complexity is further amplified, making it difficult to precisely elucidate pharmacological mechanisms. This complexity poses a challenge for quality control and drug development. For instance, when studying the mechanisms of action of a TCM formulation for DM treatment, it is challenging to identify the specific components that exert hypoglycemic effects and how they interact. Standardization issues also hinder the clinical application of TCM. The quality of TCM botanic materials varies considerably due to differences in geographical origin, cultivation environment, harvesting season, and processing methods. For instance, Angelica sinensis from Min County, Gansu Province, China, differs in its active component content from those in other regions. Even within the same region, variations in the climate and other factors can lead to inconsistent quality. In addition, the lack of uniform and precise standards in TCM processing further complicates quality control, because different processing techniques can yield products with varying efficacies. In the process of TCM preparations, the absence of standard quality control systems results in substantial variability in the composition and efficacy of products from different manufacturers, which undermines the accuracy and effectiveness for clinical applications. Second, the safety and adverse effects of TCM cannot be overlooked. Although TCM is often perceived to be natural and safe, this is not always the case. Some TCM herbs contain toxic components such as aconitine in Aconitum species, which can cause severe poisoning if improperly processed or overdosed. Moreover, the adverse effects of TCM may be insidious and delayed, making prompt detection difficult. Hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity were the most common adverse effects. For example, long-term use of certain compound formulations containing Astragalus L., Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, and Coptis Salisb. Is associated with liver injury. A case study reported that a patient with diabetes developed abnormal liver function 6 months after using a TCM formulation, which resolved after discontinuation (Pan et al., 2020). Similarly, herbs such as Polygonum multiflorum and Tripterygium wilfordii have been linked to hepatotoxicity, potentially causing irreversible liver damage (Song J. et al., 2023). Mechanistically, certain TCM components such as anthraquinones and alkaloids may induce oxidative stress or directly damage hepatocytes. Chronic use of herbs containing aristolochic acid, such as Aristolochia manshuriensis Kom. and Aristolochia fangchi Y. C. Wu ex L. D. Chow and S. M. Hwang has been associated with nephrotoxicity, potentially leading to chronic renal failure (Omer Mohamed et al., 2020). Aristolochic acid may induce apoptosis and fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. In addition, the combination of TCM with standard biomedical treatments, owing to their complex composition, may lead to drug interactions and increase the risk of adverse effects. For instance, the concurrent use of hypoglycemic herbs, such as Ginseng Alpha Wood and Lycium barbarum Mill. With standard biomedical treatments, antidiabetic drugs may increase the risk of severe hypoglycemia (Ni et al., 2024). This may be attributed to active components such as ginsenosides, which enhance insulin sensitivity or promote glucose utilization. However, current research on TCM safety remains limited and lacks a comprehensive safety evaluation system, making it difficult for clinicians and patients to accurately assess and manage potential risks. Furthermore, most existing studies have been limited to animal experiments or small-scale clinical trials, with a lack of large-scale, high-quality, multicenter, randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Future research should focus on elucidating the mechanisms of TCM, conducting high-quality multicenter RCTs, and investigating the synergistic effects and potential risks of combining TCM with standard biomedical treatments to advance the modernization and global recognition of TCM. Modern scientific techniques, such as network pharmacology and metabolomics, should be employed to investigate the active components and multi-target mechanisms of TCM to provide safer and more effective therapeutic options for DACC.
Despite the systematic review of TCM applications in DACC presented in this study, several limitations persist. Mechanistic studies addressing anti-inflammatory and gut microbiota regulation lack depth in molecular biology and cellular signaling pathways, making it difficult to precisely delineate the synergistic actions of complex components. Clinically, the scarcity of high-quality, large-sample, multicenter RCTs limits the reliability and generalizability of these findings. In addition, there is a notably deficiency in studies investigating the combined use of TCM with standard biomedical treatments, failing to provide adequate guidance for clinical practice. Otherwise, the methodological rigor of the studies incorporated in this review calls for careful and critical examination. In the realm of study design standardization, there seem to be several prevalent concerns. A significant number of studies have not adopted standardized approaches for estimating sample sizes. This lack of standardization can potentially lead to underpowered studies, which may in turn impact the general applicability of the findings, particularly when attempting to discern differences in treatment effects across various patient subgroups. Furthermore, the documentation of randomization protocols appears to be somewhat insufficient, and the setup of control groups could be optimized. When assessing the interventions of TCM in the context of DACC, the potential synergistic or antagonistic interactions between conventional therapies and TCM botanical drugs formulations have yet to be comprehensively evaluated. In addition, the over - reliance on subjective patient - reported outcomes raises some questions regarding data reliability. Since these outcomes are susceptible to recall bias and placebo effects, they might not provide the most robust basis for drawing firm conclusions. As for traditional pre - clinical models, there are certain aspects that could be improved. Rodent models exhibit species - specific variations in glucose homeostasis mechanisms and cardiovascular drug metabolism pathways, and traditional in - vitro islet cell models struggle to fully replicate the intricate paracrine signaling networks and three - dimensional niche architecture characteristic of the human pancreatic microenvironment. These gaps require further investigation.
Future research on the use of TCM for the prevention and treatment of DACC is both challenging and promising. Modern separation technologies, such as chromatography-mass spectrometry, should be employed to isolate and identify active TCM components and elucidate their mechanisms of action to establish a solid theoretical foundation for clinical applications. However, large-scale, high-quality, multicenter RCTs are urgently required to validate the efficacy and safety of TCM. Exploring the synergistic effects and potential risks of combining TCM with standard biomedical treatments will enable the development of scientifically sound treatment protocols and offer patients better therapeutic options. Future research should adopt prospective designs and employ validated methods to ensure high - level effectiveness of the studies. Furthermore, leveraging modern scientific techniques, such as network pharmacology and metabolomics, will drive the modernization of TCM and enhance its global recognition and application. This will enable TCM to play a pivotal role in the global prevention and treatment of diabetes, thereby contributing substantially to this field.
In summary, TCM has made remarkable progress in the prevention and treatment of DACC. With the continuous development of biomedicine, science, and technology, the mechanism of action of TCM in the treatment of DACC is expected to improve. More advanced modern bioscience technologies are expected to help researchers identify targets and apply TCM with multiple components, mechanisms, and targets for the prevention and treatment of DACC. In addition, research on the combination of TCM and standard biomedical treatments in the treatment of DACC will be continuously deepened, and basic research and clinical trials of TCM will also achieve a comprehensive transformation. New related technologies may be the primary tool for overcoming the problems associated with the prevention and treatment of various diseases, further promoting the application of TCM in clinical settings.
Author contributions
CC: Writing – original draft. HG: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. YiW: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. YaW: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82104474), the Projetc of Inner Mongolia Medical University Innovation Team (YKD2022TD025) and the Project of Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University Youth backbone (2023NYFYGG009).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alka, A., Saraswathy, M., Nandakumar, S., Prakash, F. A., Kn, G., and Um, D. (2022). Role of the gut microbiome in diabetes and cardiovascular diseases including restoration and targeting approaches- A review. Drug Metab. Bioanal. Lett. 15, 133–149. doi:10.2174/2949681015666220615120300
Association, A. D. (2019). 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: Standards of medical Care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 42, S103–S123. doi:10.2337/dc19-S010
Baena-Diez, J. M., Penafiel, J., Subirana, I., Ramos, R., Elosua, R., Marin-Ibanez, A., et al. (2016). Risk of cause-specific death in individuals with diabetes: a competing risks analysis. Diabetes Care 39, 1987–1995. doi:10.2337/dc16-0614
Bai, L., Zhang, Y.-Q., Zhang, X.-Y., Xiao, J.-Y., and Zhang, J. (2020). Effect and mechanism of alcohol extract of Cassia seed on apoptosis of pancreatic islet β cells. J. Mudanjiang Med. Univ. (China) 41, 1–3. doi:10.13799/j.cnki.mdjyxyxb.2020.06.001
Bai, Y. L., Han, L. L., Qian, J. H., and Wang, H. Z. (2021). Molecular mechanism of puerarin against diabetes and its complications. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 780419. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.780419
Benjamin, E. J., Muntner, P., Alonso, A., Bittencourt, M. S., Callaway, C. W., Carson, A. P., et al. (2019). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation 139, e56–e528. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659
Bielka, W., Przezak, A., and Pawlik, A. (2022). The role of the gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 480. doi:10.3390/ijms23010480
Bondy, S. C. (2023). Relationships between diabetes and the intestinal microbial population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 566. doi:10.3390/ijms24010566
Bragg, F., Holmes, M. V., Iona, A., Guo, Y., Du, H., Chen, Y., et al. (2017). Association between diabetes and cause-specific mortality in rural and urban areas of China. Jama 317, 280–289. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.19720
Bragg, F., Li, L., Yang, L., Guo, Y., Chen, Y., Bian, Z., et al. (2016). Risks and population burden of cardiovascular diseases associated with diabetes in China: a prospective study of 0.5 million adults. PLoS Med. 13, e1002026. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002026
Cai, S. (2024). Study on the effect and mechanism of resveratrol on diabetic cardiac microvascular injury. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. (China) 37, 7–11. doi:10.13401/j.cnki.jsumc.2024.01.002
Cai, Y., Wang, Y., Zhi, F., Xing, Q. C., and Chen, Y. Z. (2018). The effect of sanggua drink extract on insulin resistance through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 9407945. doi:10.1155/2018/9407945
Chang, W. G., Chen, L., and Hatch, G. M. (2015). Berberine as a therapy for type 2 diabetes and its complications: from mechanism of action to clinical studies. Biochem. Cell Biol. 93, 479–486. doi:10.1139/bcb-2014-0107
Chen, D., Wang, Y., Xu, B., Wang, H. Y., and Zhang, C.-K. (2022). Analysis of the human trial effect of Morus alba and Polygonatum odoratum tablets on lowering blood sugar. Henan J. Prev. Med. (China) 33, 431–434. doi:10.13515/j.cnki.hnjpm.1006-8414.2022.06.008
Chen, J. W., Lü, H., Jian, T. Y., Ding, X.-Q., Li, J.-W., Liu, Y., et al. (2020a). Study on the in vitro activity of triterpenoid acids in loquat leaves against diabetes and its complications. J. Plant Resour. Environ. (China) 29, 78–80.
Chen, M.-X. (2022). Isolation of gingerols from ginger and their preventive effect on type 2 diabetes in mice. master's thesis (Nanjing, Jiangsu, China: Nanjing Agricultural University).
Chen, M.-Y. (2023). “Luteolin alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy and is related to inhibiting SHP2/STAT3,”. master's thesis (Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China: Zhejiang Academy of Medical Sciences).
Chen, X., Tong, Y. L., Ren, Z. M., Chen, S. S., Mei, X. Y., Zhou, Q. Y., et al. (2023). Hypoglycemic mechanisms of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide in db/db mice via regulation of glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathway and alteration of gut microbiota. Heliyon 9, e15484. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15484
Chen, Y., Zhao, X., and Wu, H. (2020b). Arterial stiffness: a focus on vascular calcification and its link to bone mineralization. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 40, 1078–1093. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.313131
Chen, Z., and Zhang, S. L. (2023). Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a key regulator of cardiovascular disease. DNA Cell Biol. 42, 322–335. doi:10.1089/dna.2022.0532
Chiquette, E., and Chilton, R. (2002). Cardiovascular disease: much more aggressive in patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 4 (4), 134–142. doi:10.1007/s11883-002-0037-z
Collaborators, G. B. D. D. (2023). Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 402, 203–234. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6
Committee, A. D. A. P. P. (2024). 2. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 47, S20–S42. doi:10.2337/dc24-S002
Coppinger, C., Pomales, B., Movahed, M. R., Marefat, M., and Hashemzadeh, M. (2024). Berberine: a multi-target natural PCSK9 inhibitor with the potential to treat diabetes, alzheimer's, cancer and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Rev. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. 19, 312–326. doi:10.2174/0127724328250471231222094648
Cristofori, F., Dargenio, V. N., Dargenio, C., Miniello, V. L., Barone, M., and Francavilla, R. (2021). Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: a door to the body. Front. Immunol. 12, 578386. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386
Dai, Q., He, X. M., Yu, H., Bai, Y., Jiang, L., Sheng, H. L., et al. (2021). Berberine impairs coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis through the inhibition of virus replication and host pro-inflammatory response. J. Med. Virology 93, 3581–3589. doi:10.1002/jmv.26747
Dal Canto, E., van Deursen, L., Hoek, A. G., Elders, P. J. M., den Ruijter, H. M., van der Velden, J., et al. (2023). Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in skin is associated with higher risk of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in women with type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Diabetes Care System Cohort. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 22, 234. doi:10.1186/s12933-023-01935-z
Deng, A., Wang, Y., Huang, K., Xie, P., Mo, P., Liu, F., et al. (2023). Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) water extract alleviates palmitate-induced insulin resistance in HepG2 hepatocytes via the activation of IRS1/PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 and GSK-3β signaling pathway. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23, 460. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-04275-3
Diabetesatlas (2021). International diabetes federation. Available online at: https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/world/January 10, 2022).
Dixon, S. A., Mishra, S., Dietsche, K. B., Jain, S., Mabundo, L., Stagliano, M., et al. (2023). The effects of prebiotics on gastrointestinal side effects of metformin in youth: a pilot randomized control trial in youth-onset type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 14, 1125187. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1125187
Dong, J., Li, W., Du, X., He, X., Deng, B., Zheng, H., et al. (2023). Garcinia cambogia water extract alleviates insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Nutr. Res. 67. doi:10.29219/fnr.v67.8977
Drozdz, K., Nabrdalik, K., Hajzler, W., Kwiendacz, H., Gumprecht, J., and Lip, G. Y. H. (2021). Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), diabetes, and cardiovascular disease: associations with fructose metabolism and gut microbiota. Nutrients 14, 103. doi:10.3390/nu14010103
Fan, X., Jiao, G., Pang, T., Wen, T., He, Z., Han, J., et al. (2023). Ameliorative effects of mangiferin derivative TPX on insulin resistance via PI3K/AKT and AMPK signaling pathways in human HepG2 and HL-7702 hepatocytes. Phytomedicine 114, 154740. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154740
Fan, Y., Yan, Z., Li, T., Li, A., Fan, X., Qi, Z., et al. (2024). Primordial drivers of diabetes heart disease: comprehensive insights into insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. J. 48, 19–36. doi:10.4093/dmj.2023.0110
Fang, T., Wang, J., Sun, S., Deng, X., Xue, M., Han, F., et al. (2024). JinLiDa granules alleviates cardiac hypertrophy and inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating TP53. Phytomedicine 130, 155659. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155659
Gao, K., Yang, R., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Jia, C., Zhang, F., et al. (2018). Effects of Qijian mixture on type 2 diabetes assessed by metabonomics, gut microbiota and network pharmacology. Pharmacol. Res. 130, 93–109. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.01.011
Gearty, S. V., Dundar, F., Zumbo, P., Espinosa-Carrasco, G., Shakiba, M., Sanchez-Rivera, F. J., et al. (2022). An autoimmune stem-like CD8 T cell population drives type 1 diabetes. Nature 602, 156–161. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04248-x
Gong, P., Xiao, X., Wang, S., Shi, F., Liu, N., Chen, X., et al. (2021a). Hypoglycemic effect of astragaloside IV via modulating gut microbiota and regulating AMPK/SIRT1 and PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 281, 114558. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114558
Gong, Q. (2023a). Efficacy analysis of Banxia Xiexin Decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes with syndrome of intermingled cold and heat. dissertation thesis.
Gong, Q. (2023b). Study on the hypoglycemic effect and mechanism of pulsatilla saponin B4 on hyperglycemic rats. dissertation thesis.
Gong, Q., Yin, J., Wang, M., Zha, C., Yu, D., Yang, S., et al. (2023). Anemoside B4 exerts hypoglycemic effect by regulating the expression of GLUT4 in HFD/STZ rats. Molecules 28, 968. doi:10.3390/molecules28030968
Gong, X., Tian, M., Cao, N., Yang, P., Xu, Z., Zheng, S., et al. (2021b). Circular RNA circEsyt2 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell remodeling via splicing regulation. J. Clin. Invest. 131, e147031. doi:10.1172/JCI147031
Gonzalez, A., Krieg, R., Massey, H. D., Carl, D., Ghosh, S., Gehr, T. W. B., et al. (2019). Sodium butyrate ameliorates insulin resistance and renal failure in CKD rats by modulating intestinal permeability and mucin expression. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 34, 783–794. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfy238
Graczyk, P., Dach, A., Dyrka, K., and Pawlik, A. (2024). Pathophysiology and advances in the therapy of cardiomyopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 5027. doi:10.3390/ijms25095027
Gu, H., Zhong, L., Zhang, Y., Sun, J., Liu, L., and Liu, Z. (2024). Exploring the mechanism of Jinlida granules against type 2 diabetes mellitus by an integrative pharmacology strategy. Sci. Rep. 14, 10286. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-61011-8
Gu, Y., Xu, X., Wang, Z., Xu, Y., Liu, X., Cao, L., et al. (2018). Chromium-containing traditional Chinese medicine, tianmai xiaoke tablet, for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 3708637. doi:10.1155/2018/3708637
Guan, R., Ma, N., Liu, G., Wu, Q., Su, S., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Ethanol extract of propolis regulates type 2 diabetes in mice via metabolism and gut microbiota. J. Ethnopharmacol. 310, 116385. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116385
Guo, T., Pan, Y., Yang, L., Chen, G., Deng, J., and Zhu, L. (2023). Flavonoid compound from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb improves adipose insulin resistance by alleviating oxidative stress and inflammation. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23, 322. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-04114-5
Heather, L. C., Hafstad, A. D., Halade, G. V., Harmancey, R., Mellor, K. M., Mishra, P. K., et al. (2022). Guidelines on models of diabetic heart disease. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 323, H176–H200. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00058.2022
Hoseini, R., Rahim, H. A., and Ahmed, J. K. (2022). Concurrent alteration in inflammatory biomarker gene expression and oxidative stress: how aerobic training and vitamin D improve T2DM. Bmc Complementary Med. Ther. 22, 165. doi:10.1186/s12906-022-03645-7
Hou, J., Zheng, D., Zhong, G., and Hu, Y. (2013). Mangiferin mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 91, 759–763. doi:10.1139/cjpp-2013-0090
Hu, B., Yin, T., Zhang, J., Liu, M., Yun, H., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Effect of “maccog” TCM tea on improving glucolipid metabolism and gut microbiota in patients with type 2 diabetes in community. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 14, 1134877. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1134877
Huang, Q., Meng, L., Li, H., Xiong, N., Zeng, L., Wang, G., et al. (2022a). Huoxue Jiangtang decoction alleviates type 2 diabetes mellitus by regulating the oral microbiota and food preferences. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 15, 3739–3751. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S391226
Huang, Z. R., Zhao, L. Y., Zhu, F. R., Liu, Y., Xiao, J. Y., Chen, Z. C., et al. (2022b). Anti-diabetic effects of ethanol extract from sanghuangporous vaninii in high-fat/sucrose diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by modulating gut microbiota. Foods 11, 974. doi:10.3390/foods11070974
Ji, H., Zhao, X., Chen, X., Fang, H., Gao, H., Wei, G., et al. (2024). Jinlida for diabetes prevention in impaired glucose tolerance and multiple metabolic abnormalities: the FOCUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 184, 727–735. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.1190
Jia, G., and Sowers, J. R. (2021). Hypertension in diabetes: an update of basic mechanisms and clinical disease. Hypertension 78, 1197–1205. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17981
Jiang, L., Fu, Q., Wang, S., Chen, Y., Li, J., Xiao, Y., et al. (2022a). Effect of RG (Coptis root and ginseng) formula in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a study protocol for a randomized controlled and double-blinding trial. Trials 23, 305. doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06229-5
Jiang, Z., Wang, G., Meng, L., Tang, Y., Yang, M., and Ni, C. (2022b). Protective effects of astragaloside IV on uric acid-induced pancreatic β-cell injury through PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2429162. doi:10.1155/2022/2429162
Jin, Y., and Arroo, R. (2023). The protective effects of flavonoids and carotenoids against diabetic complications-A review of in vivo evidence. Front. Nutr. 10, 1020950. doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1020950
Katakami, N. (2018). Mechanism of development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 25, 27–39. doi:10.5551/jat.RV17014
Kong, L.-J., Ji, X.-Q., Liu, Y., Liu, H., and Gao, Z.-X. (2023). Puerarin alleviates myocardial injury in diabetic rats by regulating the AMPK/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Chin. Medi. Mater. 46, 476–478. doi:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2023.02.035
Laakso, M., and Fernandes Silva, L. (2023). Statins and risk of type 2 diabetes: mechanism and clinical implications. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 14, 1239335. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1239335
Leon-Garcia, M. C., Silva-Gaona, O. G., Hernandez-Ortiz, M., Vargas-Ortiz, K., Ramirez-Emiliano, J., Garay-Sevilla, M. E., et al. (2022). Curcumin prevents the glycation of tricarboxylic acid cycle and cell respiration proteins in the heart of mice fed with a high-fructose diet. Curr. Pharm. Des. 28, 1769–1778. doi:10.2174/1381612828666220331160501
Li, D. L. (2022a). Observation on the curative effect of Danhong injection combined with ticagrelor in the treatment of angina pectoris of coronary heart disease complicated with diabetes and its influence on glucose and lipid metabolism. J. Hubei Univ. Chin. Med. (China) 24, 24–27.
Li, J., Zhang, H., Ouyang, H., Xu, W., Sun, Y., Zhong, Y., et al. (2023a). Pueraria thomsonii radix water extract alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus in db/db mice through comprehensive regulation of metabolism and gut microbiota. Molecules 28, 7471. doi:10.3390/molecules28227471
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Gao, M., Wang, W., Chen, K., et al. (2023b). Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8, 152. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01400-z
Li, Y. F. J., Xie, F.-J., Deng, L., Li, Y.-F., and You, L.-P. (2020a). Naringenin alleviates myocardial injury in diabetic mice by regulating the AMPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. (China) 36, 38–46. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/44.1187.r.20200115.1410.012.
Li, Y. H., Zou, M., Han, Q., Deng, L. R., and Weinshilboum, R. M. (2020b). Therapeutic potential of triterpenoid saponin anemoside B4 from Pulsatilla chinensis. Pharmacol. Res. 160, 105079. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105079
Li, Y.-Y. (2022b). Study on the improvement effect and mechanism of Shengmai Powder on diabetic cardiomyopathy through oxidative stress pathway. master's thesis. (Jinan, Shandong, China: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine). doi:10.27282/d.cnki.gsdzu.2022.000884
Li, Z., Yang, S.-Y., Chen, L.-L., Hu, L.-Z., Li, B.-L., and Lin, C.-T. (2024). Study on the effect of Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction on intestinal flora and short-chain fatty acids in rats with type 2 diabetes. Shaanxi J. Traditional Chin. Med. (China) 45, 757–762. doi:10.20056/j.cnki.ZNMDZK.20240507
Lili, J., and Yan, C. (2025). Study on the improving effects of Danhu Tongbi decoction on glucose and lipid metabolism and cardiac function of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by angina pectoris of coronary heart disease Chinese. J. General Pract. 23, 248–252. doi:10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.003878
Lin, Y. D., He, F. M., Wu, L., Xu, Y., and Du, Q. (2022). Matrine exerts pharmacological effects through multiple signaling pathways: a comprehensive review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 16, 533–569. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S349678
Lithovius, R., Harjutsalo, V., Mutter, S., Gordin, D., Forsblom, C., Groop, P. H., et al. (2020). Resistant hypertension and risk of adverse events in individuals with type 1 diabetes: a nationwide prospective study. Diabetes Care 43, 1885–1892. doi:10.2337/dc20-0170
Liu, H., L, R.-Z., Li, Y.-T., Chang, S.-Y., and Liu, Y.-H. (2024). Improvement effect and mechanism of water extract of Pueraria lobata on islet cell inflammatory injury in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Food Res. Dev. (China) 45, 34–42.
Liu, L., Tang, D., Zhao, H., Xin, X., and Aisa, H. A. (2017). Hypoglycemic effect of the polyphenols rich extract from Rose rugosa Thunb on high fat diet and STZ induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 200, 174–181. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.022
Liu, M., Zhao, Q., Liu, J., Huang, A., and Xia, X. (2022a). Buyang Huanwu decoction affects gut microbiota and lipid metabolism in a ZDF rat model of co-morbid type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: an integrated metabolomics analysis. Front. Chem. 10, 1036380. doi:10.3389/fchem.2022.1036380
Liu, X., Hussain, R., Mehmood, K., Tang, Z., Zhang, H., and Li, Y. (2022b). Mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum communication-mediated oxidative stress and autophagy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 6459585. doi:10.1155/2022/6459585
Liu, Y., Fu, B. M., and Zeng, Y. (2023). Targeting FoxO1 in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of diabetes. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 69, 44–51. doi:10.14715/cmb/2023.69.12.8
Liu, Y.-G. (2019). Study on the alleviating effect and mechanism of polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale on hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice. master's thesis. (Wuhan, Hubei, China: Huazhong University of Science and Technology).
Lopez-Diez, R., Egana-Gorrono, L., Senatus, L., Shekhtman, A., Ramasamy, R., and Schmidt, A. M. (2021). Diabetes and cardiovascular complications: the epidemics continue. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 23, 74. doi:10.1007/s11886-021-01504-4
Lorenzo-Almoros, A., Cepeda-Rodrigo, J. M., and Lorenzo, O. (2022). Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Rev. Clin. Esp. Barc. 222, 100–111. doi:10.1016/j.rceng.2019.10.012
Luo, D., Zhao, Y., Fang, Z., Zhao, Y., Han, Y., Piao, J., et al. (2023). Tianhuang formula regulates adipocyte mitochondrial function by AMPK/MICU1 pathway in HFD/STZ-induced T2DM mice. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23, 202. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-04009-5
Ma, K., Zhou, L., Zhang, Y., Zhao, J., Yao, C., Tian, C., et al. (2023a). Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicines combined with conventional Western medicines in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 14, 1134297. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1134297
Ma, P. L., Peng, M.-Z., Niu, Y.-T., Yang, M.-M., Xu, Y.-C., Liu, Z.-R., et al. (2024). Study on the protective effect and mechanism of three active components of Astragalus membranaceus water extract on endothelial cell injury induced by high glucose. J. Beijing Univ. Traditional Chin. Med. (China) 47, 188–198. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3574.R.20240115.1038.002.
Ma, Q., Zhai, R., Xie, X., Chen, T., Zhang, Z., Liu, H., et al. (2022). Hypoglycemic effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide in type 2 diabetes mellitus mice via modulating gut microbiota. Front. Nutr. 9, 916271. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.916271
Ma, X. M., Geng, K., Law, B. Y., Wang, P., Pu, Y. L., Chen, Q., et al. (2023b). Lipotoxicity-induced mtDNA release promotes diabetic cardiomyopathy by activating the cGAS-STING pathway in obesity-related diabetes. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 39, 277–299. doi:10.1007/s10565-021-09692-z
Mao, Z. H., Gao, Z. X., Liu, D. W., Liu, Z. S., and Wu, P. (2023). Gut microbiota and its metabolites - molecular mechanisms and management strategies in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 14, 1124704. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1124704
Marx, N., Federici, M., Schutt, K., Muller-Wieland, D., Ajjan, R. A., Antunes, M. J., et al. (2023). 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. Eur. Heart J. 44, 4043–4140. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehad192
Masenga, S. K., Kabwe, L. S., Chakulya, M., and Kirabo, A. (2023). Mechanisms of oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 7898. doi:10.3390/ijms24097898
Nematollahi, S., Pishdad, G. R., Zakerkish, M., Namjoyan, F., Ahmadi Angali, K., and Borazjani, F. (2022). The effect of berberine and fenugreek seed co-supplementation on inflammatory factor, lipid and glycemic profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double-blind controlled randomized clinical trial. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 14, 120. doi:10.1186/s13098-022-00888-9
Nesci, A., Carnuccio, C., Ruggieri, V., D'Alessandro, A., Di Giorgio, A., Santoro, L., et al. (2023). Gut microbiota and cardiovascular disease: evidence on the metabolic and inflammatory background of a complex relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 9087. doi:10.3390/ijms24109087
Ni, Y., Wu, X., Yao, W., Zhang, Y., Chen, J., and Ding, X. (2024). Evidence of traditional Chinese medicine for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: from molecular mechanisms to clinical efficacy. Pharm. Biol. 62, 592–606. doi:10.1080/13880209.2024.2374794
Omer Mohamed, H. A., Osman, O. M., Ali, H. H., Asiri, M. N., Hassan, A. A., Almangah, I. M., et al. (2020). A complicated Chinese herbal medicine nephrotoxicity. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 31, 533–536. doi:10.4103/1319-2442.284032
Pan, X., Zhou, J., Chen, Y., Xie, X., Rao, C., Liang, J., et al. (2020). Classification, hepatotoxic mechanisms, and targets of the risk ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine-induced liver injury. Toxicol. Lett. 323, 48–56. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.01.026
Park, J. J. (2021). Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of heart failure in diabetes. Diabetes Metab. J. 45, 796–157. doi:10.4093/dmj.2021.0239
Peng, C., Zhang, Y., Lang, X., and Zhang, Y. (2023). Role of mitochondrial metabolic disorder and immune infiltration in diabetic cardiomyopathy: new insights from bioinformatics analysis. J. Transl. Med. 21, 66. doi:10.1186/s12967-023-03928-8
Perrone, A., Giovino, A., Benny, J., and Martinelli, F. (2020). Advanced glycation end products (AGEs): biochemistry, signaling, analytical methods, and epigenetic effects. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 3818196. doi:10.1155/2020/3818196
Poznyak, A., Grechko, A. V., Poggio, P., Myasoedova, V. A., Alfieri, V., and Orekhov, A. N. (2020). The diabetes mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: the role of lipid and glucose metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1835. doi:10.3390/ijms21051835
Prasopthum, A., Insawek, T., and Pouyfung, P. (2022). Herbal medicine use in Thai patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with glycemic control: a cross-sectional evaluation. Heliyon 8, e10790. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10790
Qi, L., Wei, Q., Ni, M., Liu, D., Bao, J., Lv, Y., et al. (2022). Pancreatic and gut hormone responses to mixed meal test in post-chronic pancreatitis diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. 48, 101316. doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101316
Ren, B. C., Zhang, Y. F., Liu, S. S., Cheng, X. J., Yang, X., Cui, X. G., et al. (2020). Curcumin alleviates oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via Sirt1-Foxo1 and PI3K-Akt signalling pathways. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24, 12355–12367. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15725
Sahu, G., Patra, S. A., Lima, S., Das, S., Göerls, H., Plass, W., et al. (2023). Ruthenium(II)-Dithiocarbazates as anticancer agents: synthesis, solution behavior, and mitochondria-targeted apoptotic cell death. Chemistry-a Eur. J. 29, e202202694. doi:10.1002/chem.202202694
Shi, L., Wang, J., He, C., Huang, Y., Fu, W., Zhang, H., et al. (2023). Identifying potential therapeutic targets of mulberry leaf extract for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a TMT-based quantitative proteomic analysis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 23, 308. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-04140-3
Song, D., Hao, J., and Fan, D. (2020). Biological properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front. Med. 14, 564–582. doi:10.1007/s11684-019-0724-6
Song, J., He, G. N., and Dai, L. (2023a). A comprehensive review on celastrol, triptolide and triptonide: insights on their pharmacological activity, toxicity, combination therapy, new dosage form and novel drug delivery routes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 162, 114705. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114705
Song, Z., Chen, R., Wang, C., Pan, G., Yan, A., Xie, G., et al. (2023b). Effect and mechanism of Tangzhiqing in improving cardiac function in mice with hyperlipidaemia complicated with myocardial ischaemia. Heliyon 9, e15645. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15645
Spinetti, G., Mutoli, M., Greco, S., Riccio, F., Ben-Aicha, S., Kenneweg, F., et al. (2023). Cardiovascular complications of diabetes: role of non-coding RNAs in the crosstalk between immune and cardiovascular systems. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 22, 122. doi:10.1186/s12933-023-01842-3
Stultz, C. M., and Edelman, E. R. (2003). A structural model that explains the effects of hyperglycemia on collagenolysis. Biophysical J. 85, 2198–2204. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74645-1
Sun, J., Fu, W.-W., Li, M., Xu, H.-L., and Sui, D.-Y. (2020). Protective effect of ginsenoside from Panax ginseng fruit combined with total flavonoids from Murraya paniculata leaves on diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Ginseng Res. (China) 32, 2–5. doi:10.19403/j.cnki.1671-1521.2020.05.001
Sun, S., Yang, S., An, N., Wang, G., Xu, Q., Liu, J., et al. (2019). Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis during diabetic cardiomyopathy via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 238, 111857. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.111857
Sun, W.-Y. (2020). Study on the structure and hypoglycemic activity of diterpenoids in Lippia nodiflora, a traditional Li medicine. master's thesis (Haikou, Hainan, China: Hainan Medical University).
Tamayo, I., Librero-Lopez, J., Galbete, A., Cambra, K., Enguita-German, M., Forga, L., et al. (2023). Cohort profile: CArdiovascular risk in patients with DIAbetes in NAvarra (CARDIANA cohort). BMJ Open 13, e066052. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066052
Tan, M., Zhou, J.-L., Yang, L., and Liu, D.-B. (2022). Effect of ethanol extract of Ganoderma lucidum on improving insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Res. Dev. (China) 43, 22–29.
Tao, S., Chen, L., Song, J., Zhu, N., Song, X., Shi, R., et al. (2019). Tanshinone IIA ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting Grp78 and CHOP expression in STZ-induced diabetes rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 18, 729–734. doi:10.3892/etm.2019.7580
Tawulie, D., Jin, L. L., Shang, X., Li, Y. M., Sun, L., Xie, H. X., et al. (2023). Jiang-Tang-San-Huang pill alleviates type 2 diabetes mellitus through modulating the gut microbiota and bile acids metabolism. Phytomedicine 113, 154733. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154733
Wang, B., Yang, Y., and Li, X. (2022a). Interaction of hypertension and insulin resistance exacerbates the occurrence of diabetes mellitus in healthy individuals. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 9289812. doi:10.1155/2022/9289812
Wang, H., Chang, S. C., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y. Z., and Yang, D. Y. (2024a). Clinical observation on the treatment of type 2 diabetes with Jinghong Decoction combined with metformin sustained-release tablets. J. Mod. Med. Health 40, 2385–2392.
Wang, J., Song, X., Xia, Z., Feng, S., Zhang, H., Xu, C., et al. (2024c). Serum biomarkers for predicting microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn 24, 703–713. doi:10.1080/14737159.2024.2391021
Wang, L., Zhang, D., Zhan, W., Zeng, Z., Yin, J., Wang, K., et al. (2022b). Chinese medicine Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi capsule ameliorates coronary atherosclerosis in diabetes mellitus-related coronary heart disease minipigs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 156, 113831. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113831
Wang, M., Jin, L., Zhang, Q., Zhu, W., He, H., Lou, S., et al. (2022c). Curcumin analog JM-2 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy inflammation and remodeling by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 154, 113590. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113590
Wang, M.-C., Dong, L., Huang, R., Liu, M.-N., Liu, J.-L., Zheng, Y., et al. (2024b). Influence of Gelan Xiaoke Pills on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes and deficiency of kidney yin syndrome. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Materia Medica (China), 1–16. doi:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20240412.006
Wang, S., Li, X. Y., and Shen, L. (2021). Modulation effects of Dendrobium officinale on gut microbiota of type 2 diabetes model mice. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 368, fnab020. doi:10.1093/femsle/fnab020
Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Zhou, C., Khan, H., Fu, M., and Cheang, W. S. (2022d). Citri reticulatae pericarpium (chenpi) protects against endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation in diabetic rats. Nutrients 14, 5221. doi:10.3390/nu14245221
Wei, H., Sun, M., Wang, R., Zeng, H., Zhao, B., and Jin, S. (2024). Puerarin mitigated LPS-ATP or HG-primed endothelial cells damage and diabetes-associated cardiovascular disease via ROS-NLRP3 signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 28, e18239. doi:10.1111/jcmm.18239
Wei, Y., Ding, Q. Y., Yeung, C., Huang, Y. S., Zhang, B. X., Zhang, L. L., et al. (2022a). Evidence and potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine for the adjuvant treatment of coronary heart disease in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2545476. doi:10.1155/2022/2545476
Wei, Y., Gao, J., Qin, L., Xu, Y., Wang, D., Shi, H., et al. (2017). Tanshinone I alleviates insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats through IRS-1 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 93, 352–358. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.040
Wei, Z., Shaohuan, Q., Pinfang, K., and Chao, S. (2022b). Curcumin attenuates ferroptosis-induced myocardial injury in diabetic cardiomyopathy through the Nrf2 pathway. Cardiovasc Ther. 2022, 3159717. doi:10.1155/2022/3159717
Wen, C., Liu, C., Li, Y., Xia, T., Zhang, X., Xue, S., et al. (2022a). Ameliorative potentials of the ethanolic extract from Lycium chinense leaf extract against diabetic cardiomyopathy. Insight into oxido-inflammatory and apoptosis modulation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 154, 113583. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113583
Wen, C., Xue, F. S., Wang, Y. H., Jin, J. H., and Liao, X. (2022b). Hypercholesterolemia attenuates cardioprotection of ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning with α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist by enhancing inflammation and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 23, 342. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11272
Wiseman, R. L., Mesgarzadeh, J. S., and Hendershot, L. M. (2022). Reshaping endoplasmic reticulum quality control through the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell 82, 1477–1491. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.025
Wu, S., Lu, D., Gajendran, B., Hu, Q., Zhang, J., Wang, S., et al. (2023a). Tanshinone IIA ameliorates experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in cardiomyocytes via SIRT1. Phytother. Res. 37, 3543–3558. doi:10.1002/ptr.7831
Wu, Y.-H. (2024). Effect of Danggui Sini Powder combined with metformin on insulin-resistant diabetes and its influence on blood microcirculation and cardiovascular function of patients. Clin. Med. (China) 44, 120–123. doi:10.19528/j.issn.1003-3548.2024.02.039
Wu, Y. Z. H., Chen, Y.-H., Dong, X., Li, X., Zhang, L.-Y., Huang, W.-Y., et al. (2023b). Exploring the protective mechanism of astragaloside IV on cardiac function in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats based on the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res. (China) 34, 2329–2332.
Xia, T., Liu, C. S., Hu, Y. N., Luo, Z. Y., Chen, F. L., Yuan, L. X., et al. (2021). Coix seed polysaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus via gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids activation of IGF1/PI3K/AKT signaling. Food Res. Int. 150, 110717. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110717
Xia, T., Xu, W. J., Hu, Y. N., Luo, Z. Y., He, W., Liu, C. S., et al. (2022). Simiao Wan and its ingredients alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus via IRS1/AKT2/FOXO1/GLUT2 signaling. Front. Nutr. 9, 1012961. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1012961
Xu, T. S., He, P., Namwangdu, S., Xu, C. Y., Hou, B. Y., Ma, P., et al. (2024). Revealing the improvement of diabetes by Si Wei Jiang Huang Tang San through ERK/HIF1α signaling pathway via network pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319, 117254. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117254
Xu, X., Gao, Z., Yang, F., Yang, Y., Chen, L., Han, L., et al. (2020). Antidiabetic effects of gegen qinlian decoction via the gut microbiota are attributable to its key ingredient berberine. Genomics Proteomics Bioinforma. 18, 721–736. doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2019.09.007
Yan, B. F., Pan, L. F., Quan, Y. F., Sha, Q., Zhang, J. Z., Zhang, Y. F., et al. (2023a). Huangqin decoction alleviates lipid metabolism disorders and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by triggering Sirt1/NF-κB pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 29, 4744–4762. doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i31.4744
Yan, C.-Y., Ding, Z.-J., Li, X.-M., Mao, X.-L., Yu, Z.-S., Wang, Z.-F., et al. (2023b). Study on the chemical constituents and hypoglycemic activity of ethanol extract from Hippophae rhamnoides leaves. Acta Pharm. Sin. (China) 58, 396–404. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.2022-0840
Yan, D., Fan, P., Sun, W., Ding, Q., Zheng, W., Xiao, W., et al. (2021a). Anemarrhena asphodeloides modulates gut microbiota and restores pancreatic function in diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 133, 110954. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110954
Yan, Y., Li, T., Li, Z. H., He, M. Y., Wang, D. J., Xu, Y. Y., et al. (2021b). Metformin suppresses the progress of diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis by inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell migration through AMPK-pdlim5 pathway. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8, 690627. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.690627
Yao, B., Pan, B. C., Tian, T., Su, X. H., Zhang, S. F., Li, H. Z., et al. (2022). Baihu renshen decoction ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats through affecting gut microbiota enhancing gut permeability and inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12, 1051962. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.1051962
Ye, L., Chen, X., Wang, M., Jin, L., Zhuang, Z., Yang, D., et al. (2021). Curcumin analogue C66 attenuates obesity-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting JNK-mediated inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 143, 112121. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112121
Yin, W., Zhang, S. Q., Pang, W. L., Chen, X. J., Wen, J., Hou, J., et al. (2022). Tang-ping-san decoction remodel intestinal flora and barrier to ameliorate type 2 diabetes mellitus in rodent model. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 15, 2563–2581. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S375572
You, M., Liu, Y., Wang, B., Li, L., Zhang, H., He, H., et al. (2022). Asprosin induces vascular endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic lower extremity peripheral artery disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 21, 25. doi:10.1186/s12933-022-01457-0
Yue, Y. (2022). Study on Bupiwei Xieyinhuo Shengyang Decoction intervening in macrovascular lesions of type 2 diabetes based on TMAO intestinal flora metabolism pathway. master's thesis (Tianjin, China: Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine).
Yujun, R., Jianxue, B., Mingde, Z., and Yingjiang, C. (2020). The efficacy of Tongxinluo, Jinlida combined with Metoprolol in the treatment of patients with diabetes complicated by coronary heart disease and its effects on cardiac function and blood glucose indexes. Clin. Med. Eng. 27, 1199–1200.
Zeeshan, H. M., Lee, G. H., Kim, H. R., and Chae, H. J. (2016). Endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated ROS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 327. doi:10.3390/ijms17030327
Zeng, F., Nijiati, S., Tang, L., Ye, J., Zhou, Z., and Chen, X. (2023). Ferroptosis detection: from approaches to applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 62, e202300379. doi:10.1002/anie.202300379
Zhang, B., Yuan, Y., Xin, J., Chen, M., Wang, Z., Li, X., et al. (2022). Study of water- and organic-soluble extracts from Trichosanthes on type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 3250016. doi:10.1155/2022/3250016
Zhang, F., Zeng, Z. L., Zhang, J. H., Li, X. L., Yang, W. L., Wei, Y. M., et al. (2024a). Pterostilbene attenuates heart failure by inhibiting myocardial ferroptosis through SIRT1/GSK-3β/GPX4 signaling pathway. Heliyon 10, e24562. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24562
Zhang, L., Wang, P., Huang, J., Xing, Y., Wong, F. S., Suo, J., et al. (2024b). Gut microbiota and therapy for obesity and type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 15, 1333778. doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1333778
Zhang, R., and Liu, X. H. (2024). Efficacy analysis of Banxia Xiexin Decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes with syndrome of intermingled cold and heat. New World Diabetes (China) 27, 82–84+88. doi:10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2024.04.082
Zhang, Y., Jiao, X., Liu, J., Feng, G., Luo, X., Zhang, M., et al. (2024c). A new direction in Chinese herbal medicine ameliorates for type 2 diabetes mellitus: focus on the potential of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 321, 117484. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117484
Zhang, Y., Mao, X. D., Cao, A. L., Chu, S., Li, Z. J., Wang, Y. M., et al. (2021). Astragaloside IV prevents endothelial dysfunction by improving oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse aortas. Exp. Ther. Med. 22, 1197. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10631
Zhang, Y., Wang, R., Tan, H., Wu, K., Hu, Y., Diao, H., et al. (2023). Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi (FTZ) capsule ameliorates diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis via suppressing YTHDF2-mediated m(6)A modification of SIRT3 mRNA. J. Ethnopharmacol. 317, 116766. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116766
Zhang, Y., Zhou, G., Peng, Y., Wang, M., and Li, X. (2020). Anti-hyperglycemic and anti-hyperlipidemic effects of a special fraction of Luohanguo extract on obese T2DM rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 247, 112273. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.112273
Zhang, Y. Z., and Xie, C. G. (2024). Exploring the effect of Shenqi Compound on blood glucose fluctuation in diabetic GK rats based on intestinal flora and intestinal mucosal barrier. Liaoning J. Traditional Chin. Med. (China) 51, 197-200+225–226. doi:10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2024.05.052
Zhang, Z., Zhang, L., and Xu, H. (2019). Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide in treatment of diabetes mellitus: a narrative review. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 39, 133–138.
Zhao, D., Yin, D., Wang, X., Li, Y., He, M., Hu, J., et al. (2023). Taurine alleviates high-fat-high-glucose-induced pancreatic islet beta-cell oxidative stress and apoptosis in rat. Heliyon 9, e21879. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21879
Zhao, S. Y. H. F., Feng, Z. T., Xu, Y. P., Hong, J. S., Cheng, X. Y., Chen, G. Z., et al. (2019). Meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of Liuwei Dihuang Pills (Decoction) combined with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. (China) 39, 1158–1165. doi:10.13286/j.cnki.chinhosppharmacyj.2019.11.11
Zhaolong, Y. (2025). Clinical value of Naoxintong in the treatment of diabetes mellitus complicated with stroke. Med. Front. 15, 72–75.
Zheng, M., Wang, L., Sun, Y., Pi, X., Zhang, W., Gao, P., et al. (2023). Hypoglycemic effect of the Phellinus baumii extract with alpha-glucosidase-inhibited activity and its modulation to gut microbiota in diabetic patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 158, 114130. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114130
Zhou, G., Wang, C. Z., Mohammadi, S., Sawadogo, W. R., Ma, Q., and Yuan, C. S. (2023a). Pharmacological effects of ginseng: multiple constituents and multiple actions on humans. Am. J. Chin. Med. 51, 1085–1104. doi:10.1142/S0192415X23500507
Zhou, J., Shi, H., Ji, F., Wu, Y., Zhao, Y., Qian, J., et al. (2023b). Effectiveness and safety of Shexiang Baoxin Pill (MUSKARDIA) in patients with stable coronary artery disease and concomitant diabetes mellitus: a subgroup analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 136, 82–87. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000002527
Zhou, J., Xu, G., Yan, J., Li, K., Bai, Z., Cheng, W., et al. (2015). Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. polysaccharide ameliorates hyperglycemia, hyperlipemia and vascular inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 164, 229–238. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.026
Zhu, H., Rong, Z.-L., Li, Y.-T., Chang, S.-Y., and Liu, Y.-H. (2024). Improvement effect and mechanism of water extract of Pueraria lobata on inflammatory injury of islet cells in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Food Res. Dev. (China) 45, 34–42.
Zhu, J., Chen, H., Le, Y., Guo, J., Liu, Z., Dou, X., et al. (2022). Salvianolic acid A regulates pyroptosis of endothelial cells via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates diabetic atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1009229. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1009229
Keywords: traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular complications (DACC), TCM compound prescriptions, TCM botanical drugs, TCM monomers
Citation: Chen C, Gao H, Wei Y and Wang Y (2025) Traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention of diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular complications: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1511701. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1511701
Received: 16 October 2024; Accepted: 28 March 2025;
Published: 11 April 2025.
Edited by:
Wei Peng, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Runyu Miao, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaMeiyan Li, Shaanxi Institute of International Trade and Commerce, China
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Gao, Wei and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Wei, d2VpbW96aHVvQDE2My5jb20=; Yaxi Wang, dHR3YW5neWF4aUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Caixia Chen
Caixia Chen Hui Gao
Hui Gao Ying Wei
Ying Wei Yaxi Wang
Yaxi Wang