- 1Department of Nephrology and Institute of Nephrology, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Sichuan Clinical Research Centre for Kidney Diseases, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Health Management, Damian Honghe Community Health Service Center of Longquanyi District, Chengdu, China
- 3Department of Nephrology, Zhongjiang County People’s Hospital, Deyang, China
- 4Cancer Center, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
Background: To summarize current evidence on kidney related adverse events (AEs) following targeted therapies in lung cancer from trial settings.
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane Central Library. Randomized controlled trials that had reported kidney related AEs following targeted therapies in lung cancer were eligible. Outcomes included renal dysfunction as reported, increased serum creatinine, proteinuria, urinary tract infection (UTI), and electrolyte disorders. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane guidelines. The incidence of the examined outcomes, along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs), were combined using a random-effects model. Network analysis was applied if the comparisons had passed the consistency test. Publication bias was assessed using Funnel plot analysis.
Results: 57 studies encompassing 11,497 patients were included. The pooled incidences (95% CI) of acute kidney injury (AKI), increased serum creatinine, proteinuria, and UTI following targeted therapies in lung cancer were 1% (0%, 2%), 4% (1%, 8%), 9% (6%, 13%), and 6% (2%, 12%), respectively. Targeted therapies did not increase the risk of AKI, yet were associated with higher incidence of proteinuria, particularly vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors containing therapies. Multiple electrolyte disorders could be observed following targeted treatments, with the pooled incidences ranging from 4% to 21%; however, most electrolytes disorders had limited number of reports. Most of the reported kidney related AEs were of Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grade 1 or 2. Publication bias was present for kidney related AEs excluding AKI.
Conclusion: Kidney related adverse events are not uncommon following targeted therapies in lung cancer in trial settings. In comparison to chemotherapy alone, targeted therapies did not increase the risk of AKI, yet were associated with higher risk of proteinuria. Proteinuria and electrolytes disorders are more often observed than renal dysfunction and UTI. All types of AEs were mostly mild in severity.
Systematic Review Registration: PROSPERO CRD42023441979.
Introduction
Lung cancer accounts for 11.6% of all cancers globally and is the reason of approximately one-fifths of the cancer related deaths (Sung et al., 2021). Early targeted therapies provide hope for advances in the treatment of lung cancer, particularly for patients with surgically unresectable lesions or distant metastasis (Hirsch et al., 2017; Lahiri et al., 2023; Miller and Hanna, 2021). However, early and intensive targeted therapies are associated with adverse events (AEs) in multiple organs, among which the most reported are gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, vomit, and nausea, as well as skin reactions including rash, acne, or injection site reaction (Ruiz et al., 2014).
Notably, adverse kidney related outcomes also occur subsequent to targeted therapies, sometimes even causing delay or suspension in the anti-cancer treatments. Kidney related AEs following targeted therapies include impaired renal function evidenced by elevated serum creatinine, proteinuria, urinary tract infection, and electrolyte disorders (Ruiz et al., 2014). We have even observed a few cases who even advanced to dialysis-dependent stage after targeted therapies in our own practice. Understanding the profile of kidney related AEs following targeted therapies help communications between patients and healthcare professionals for clinical decision making and might aid to reduce the chance of AEs in high-risk patients. However, the incidence, severity and outcomes of kidney related AEs are only sporadically reported in individual clinical trials, lacking a summary of existing evidence in this field.
Therefore, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to elucidate the incidences of unfavorable kidney related outcomes following targeted therapies in lung cancer patients, to enhance the understanding of this subject and provide references for clinical practice.
Materials and methods
Data sources and searches
We conducted a comprehensive search identify eligible studies published until 19 August 2023 in EMBASE via Ovid, Cochrane Central Library via Ovid, and MEDLINE via PubMed, adhering to the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (Liberati et al., 2009). The search terms included appropriate text terms related to the names and targeted molecules of commercially available pharmaceuticals for targeted therapies in lung cancers, randomized controlled trial, and lung cancer (Supplementary Table 1). No restrictions were imposed on publication date or language. The systematic review was prospectively registered on PROSPERO (Identifier# CRD42023441979).
Study selection
Eligible studies were randomized controlled trial (RCTs) that had reported pairwise comparison among different targeted therapies, combination of targeted therapies and conventional chemotherapy, and chemotherapy alone in lung cancers as well as kidney related AEs following treatments. Only studies in adults were considered. No restriction was applied to the category of targeted agents or targeted molecules of treatment.
Two reviewers (S.R. and W.W.) independently conducted the screening process using a standardized approach. The titles and abstracts of all retrieved records from the database search were carefully examined. Duplicates, pediatric studies, reviews, editorials, commentaries, case reports, study protocols, conference abstracts lacking sufficient information, non-human studies, studies irrelevant to lung cancer, non-RCT studies, secondary analysis or pooled analysis of RCT trials, studies that had not reported kidney related outcomes or any targeted therapy, and studies that had not compared different categories of pharmaceutical treatment were excluded. Additionally, the reference lists of included studies or important reviews were also reviewed to identify any relevant studies. Any discrepancy was adjudicated by a third reviewer (Y.L.F.).
Outcomes
All kidney related AEs were considered as study outcomes in this systematic review and were classified into four categories. The first category was renal dysfunction, including the diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) or acute kidney failure and increased serum creatinine evidenced by laboratory examinations. The second category was proteinuria as indicated by abnormal urine findings. The third category was urinary tract infection (UTI). The fourth category was electrolytes disorders, including abnormalities in serum levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium.
All adverse events were recorded as per the reporting in individual studies and quantified using their respective incidences reported in the corresponding studies.
Data extraction and quality assessment
The extracted data included authors’ names, publication year, geographical location, total sample size of the study population, details of treatments employed, number of patients in both control and interventional groups, numbers of study outcomes in both control and interventional groups, and the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grade of the adverse events (if reported). Treatments were classified into conventional chemotherapy and different categories of targeted therapies based on the targeted molecules.
Two reviewers (S.R. and W.W.) independently extracted data from included studies and compiled them into a shared document. Any discrepancy was resolved by the third reviewer (Y.L.F.).
Critical appraisal
Two reviewers (S.R. and Y.L.F.) independently assessed the risk of bias of included studies based on the 7-item criteria in the RevMan analysis software provided by the Cochrane Collaboration (2022) (Higgins et al., 2019). Any discrepancy was resolved by consensus.
Data synthesis and analysis
Data analysis and synthesis were performed using Stata (version 17.0; Stata Corporation, TX, United States) and Review Manager (RevMan 5.35) software.
The pooled occurrences of the examined outcomes, along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs), were combined using a random-effects model, with each study group in the RCT studies treated as an independent arm. Additionally, the meta-analysis for study outcomes for which the assumption of consistency in the network analysis was verified using a design-by-treatment approach (Higgins et al., 2012) included direct comparisons for each pair of treatments and the network meta-analysis for multiple comparisons including indirect comparisons via pooled odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using a random-effects model. Network map was used to shown the interactions among different treatments and the treatments were sorted in rank based on surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) (Salanti et al., 2011) and graphically illustrated using the ranking panel plots. The higher the rank, the superior the treatment effect. Subgroup analyses were performed based on the category of treatments and the severity of adverse events evaluated by the CTCAE grade. Statistical heterogeneity was estimated using the I2 statistic, for which an I2 value of ≤25%, between 26% and 75%, and >75% represents low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively (Ioannidis, 2008). A two-sided p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Publication bias was assessed by visual inspection of funnel plots and comparison adjusted funnel plots.
Results
Search findings
A total of 6,827 records were initially identified through literature searching and after removing duplicates. 6,600 records were excluded after screening the titles and abstracts, and another 170 publications were further excluded after full text review. Finally, 57 RCT studies were included in this systematic review (see Figure 1).
Study characteristics
57 RCT studies encompassing 11,497 patients were included in this systematic review (Ahn et al., 2012; Argiris et al., 2017; Ciuleanu et al., 2018; Ciuleanu et al., 2013; Crinò et al., 2008; Doebele et al., 2015; Du et al., 2013; Ellis et al., 2014; Gaafar et al., 2011; Garon et al., 2014; Goldman et al., 2020; Herbst et al., 2018; Johnson et al., 2013; Karayama et al., 2016; Kenmotsu et al., 2022; Lara et al., 2016; Leighl et al., 2017; Lynch et al., 2009; Miller et al., 2012; Nakagawa et al., 2019; Niho et al., 2012; Paz-Ares et al., 2015; Paz-Ares et al., 2017; Pérol et al., 2012; Pujol et al., 2015; Ramlau et al., 2012; Reck et al., 2016; Reck et al., 2009; Sandler et al., 2006; Scagliotti et al., 2012; Schuler et al., 2016; Sequist et al., 2011; Seto et al., 2014; Shaw et al., 2017; Shi et al., 2017; Socinski et al., 2010; Spigel et al., 2018; Spigel et al., 2013; Spigel et al., 2017a; Spigel et al., 2017b; Steendam et al., 2021; Stephenson et al., 2014; Stinchcombe et al., 2019; Tada et al., 2022; Takeda et al., 2010; Takeda et al., 2016; Thatcher et al., 2015; von Pawel et al., 2018; Wakelee et al., 2017a; Wakelee et al., 2017b; Witta et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2015; Yoh et al., 2016; Yoshioka et al., 2015; Zhong et al., 2018; Zhou et al., 2015). The majority of studies had been registered. The maximum follow-up duration was 108 months. Therapeutic regimens substantially varied among the studies, including combinations of two targeted therapies and chemotherapy, combination of one targeted therapy and chemotherapy, one or two targeted therapies, and chemotherapy alone. Detailed characteristics of the included studies are shown in Supplementary Table 2.
Acute kidney injury following targeted treatments
The pooled incidence of AKI in the 10 RCT studies that had reported the occurrence of AKI following targeted therapies was 1% (95% CI: 0%, 2%) (Supplementary Figure 1). The treatment regimens encompassed one combination of two different targeted therapies and chemotherapy, three combinations of one targeted therapy and chemotherapy, and chemotherapy alone. The direct comparison of AKI following different treatment regimens did not reveal a significantly increased risk of AKI after any specific therapy (Supplementary Figure 2). Network meta-analysis was conducted after verification of consistency (Supplementary Table 3) and the results also indicated none of the four combination treatments significantly increased the risk of AKI compared to chemotherapy alone or each other (Figure 2). The subgroup analysis based on CTCAE grade indicated most of the AKI events were of CTCAE grade 1–2 (Supplementary Figure 3).
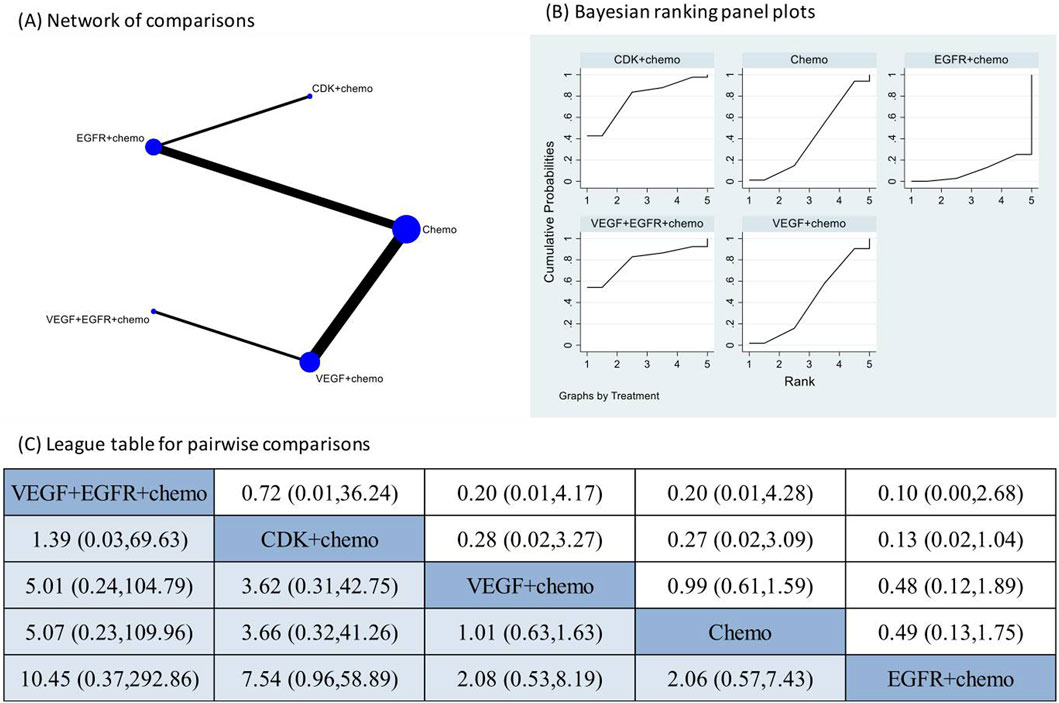
Figure 2. Network meta-analysis of AKI subsequent to the administration of targeted therapies in lung cancer. Note: (A) In the network of comparisons, the size of nodes is proportional to the total sample size of each treatment, and the width of lines is proportional to the number of studies in each pair of comparison. (B) Bayesian ranking panel plots indicate the higher the rank reflected by the area under curve, the superior the treatment to increase the risk of AKI. (C) The league table of pairwise comparison for the risk of AKI following treatments. All treatments are ordered based on AKI ranking.
Increased serum creatinine following targeted treatments
20 studies reported the occurrence of increased serum creatinine following targeted treatments. Network meta-analysis was not conducted due to the lack of verified consistency. The pooled incidence of increased serum creatinine following targeted treatments was 4% (95% CI: 1%, 8%), with a high degree of heterogeneity among the studies (I2 = 97.0%, p < 0.01) (Figure 3). Notably, the pooled incidence of increased serum creatinine in the chemotherapy groups in these studies was 4% (95% CI: 1%, 6%), having no significant difference compared to that following targeted therapies (p = 0.724) (Supplementary Figure 4). A further breaking down of targeted therapies revealed the pooled incidence of increased serum creatinine varied substantially across different targeted regimens, ranging from 2% (95% CI: 0%, 10%) in the combination of EGFR inhibitors and chemotherapy group to 12% (95% CI: 10%, 14%) in the combination of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors and chemotherapy group (Supplementary Figure 5). The pooled incidence of increased serum creatinine of CTCAE grade 1–2 was 6% (95% CI: 2%, 11%) (Supplementary Figure 6). Increased serum creatinine of CTCAE grade 3–4 was rarely observed (Supplementary Figure 7).
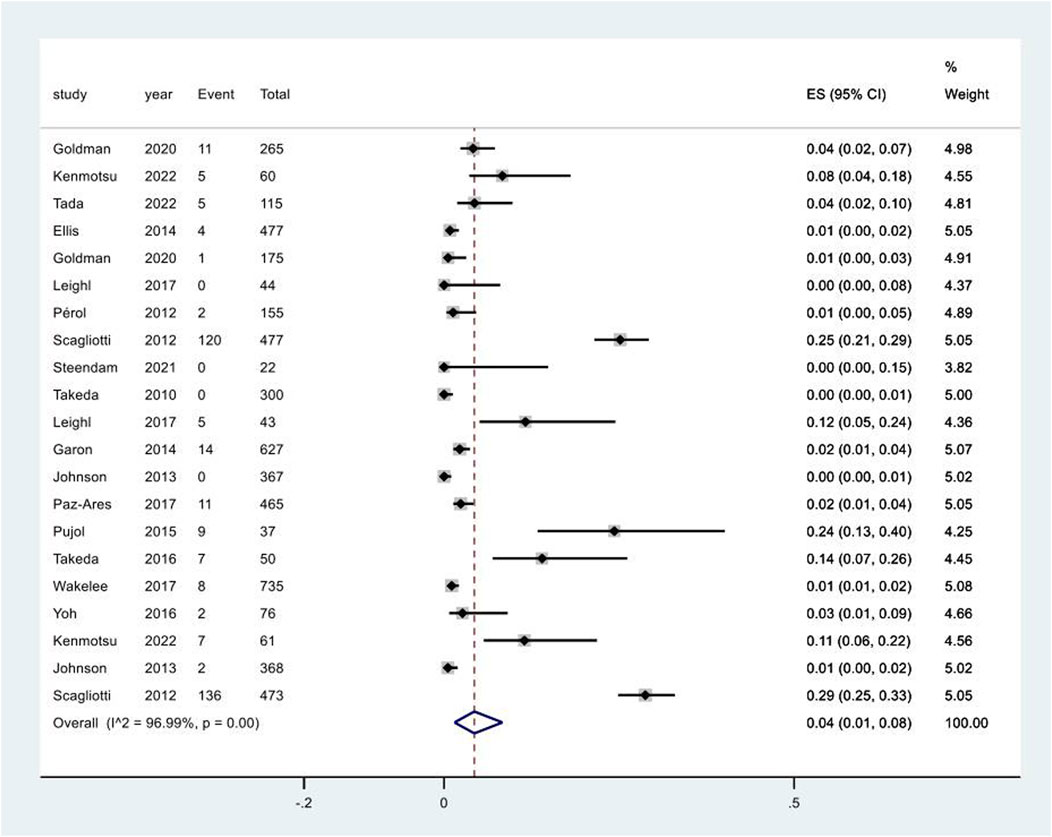
Figure 3. Aggregated occurrence rate of increased serum creatinine subsequent to the administration of targeted therapies in lung cancer. Notes: The pooled incidence of proteinuria was 5% (95% CI: 2%, 8%), with a high degree of heterogeneity observed among the studies (I2 = 96.3%, p < 0.01).
Proteinuria following targeted treatments
The pooled incidence of proteinuria in the 23 studies that had reported this outcome was 9% (95% CI: 6%, 13%) (Supplementary Figure 8). The treatments examined in these studies included one combination of two targeted therapies and chemotherapy, two combinations of one targeted therapy and chemotherapy, one combination of two different targeted therapies, two targeted monotherapies, and chemotherapy alone. The direct comparison showed that three regimens that contained VEGFR inhibitors had significantly higher risk of proteinuria in comparison to chemotherapy alone (Supplementary Figure 9). Network meta-analysis was conducted after verification of consistency (Supplementary Table 4) and the results again revealed increased risk of proteinuria following the VEGFR inhibitors containing regimens in comparison to chemotherapy alone (Figure 4). The combination of IGF-1R targeted therapy and chemotherapy had the lowest risk of proteinuria. The subgroup analysis based on CTCAE grade indicated most of the proteinuria events were of CTCAE grade 1–2 (Supplementary Figure 10).
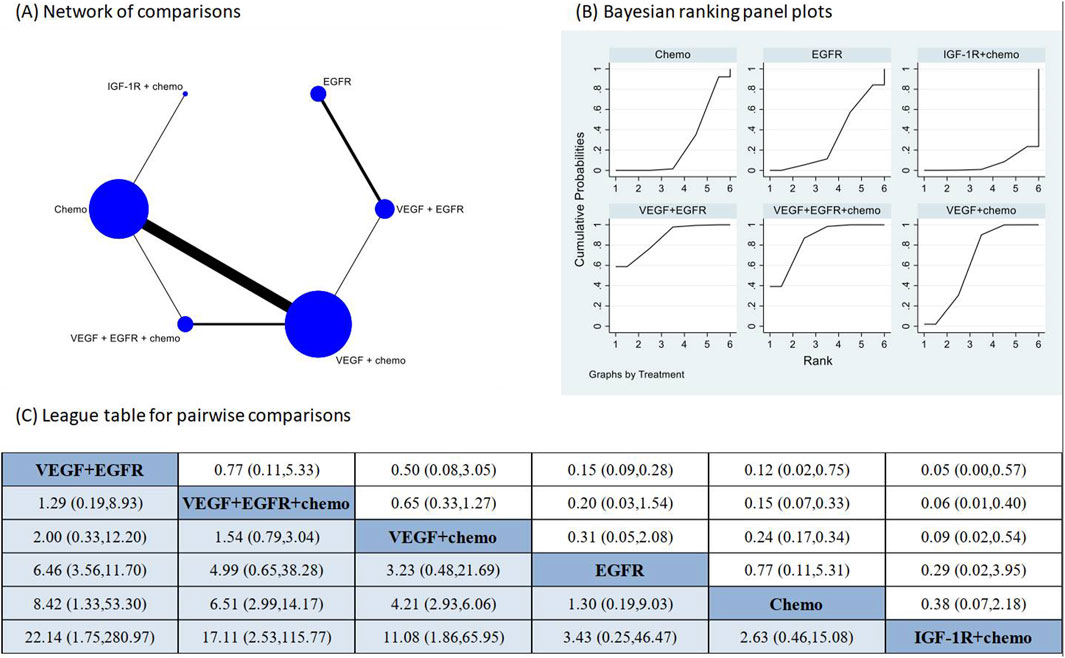
Figure 4. Network meta-analysis of proteinuria subsequent to the administration of targeted therapies in lung cancer. Note: (A) In the network of comparisons, the size of nodes is proportional to the total sample size of each treatment, and the width of lines is proportional to the number of studies in each pair of comparison. (B) Bayesian ranking panel plots indicate the higher the rank reflected by the area under curve, the superior the treatment to increase the risk of proteinuria. (C) The league table of pairwise comparison for the risk of proteinuria following treatments. All treatments are ordered based on proteinuria ranking. * Statistical significance.
Urinary tract infection following treatments
Five studies reported the adverse event of UTI following different regimens containing targeted therapies. The meta-analysis for UTI only included direct comparisons due to the limited number of studies. The pooled incidence was 6% (95% CI: 2%, 12%), with a high degree of heterogeneity observed among the studies (I2 = 84.6%, p < 0.01) (Figure 5). The pooled incidence of UTI in chemotherapy groups in these studies was 1% (95% CI: 0%, 1%), significantly lower than that following targeted therapy groups (p = 0.002) (Supplementary Figure 11).
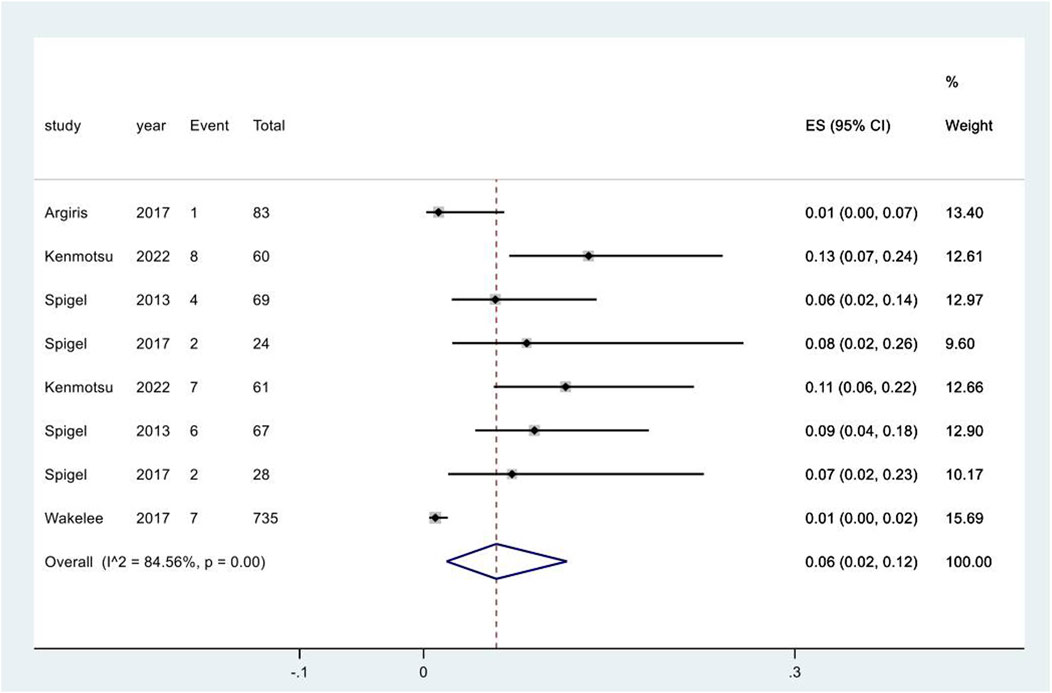
Figure 5. Urinary tract infection subsequent to the administration of targeted therapies in lung cancer. Notes: The pooled incidence of UTI was 7% (95% CI: 2%, 13%), with a high degree of heterogeneity observed among the studies (I2 = 91.7%, p < 0.01).
Electrolytes disorders following treatments
17 studies reported the adverse event of hypokalemia, of which the pooled incidence was 6% (95% CI: 3%, 9%) (Supplementary Figure 12). The pooled incidence of hypokalemia in the chemotherapy groups in these studies was 4% (95% CI: 2%, 6%), having no significant difference compared to that in the targeted therapy groups (p = 0.351) (Supplementary Figure 13). Analysis based on the types of targeted therapies indicated the pooled incidence of hypokalemia varied from 1% (95% CI: 0%, 3%) in the EGFR inhibitors group to 26% (95% CI: 23%, 29%) in the combination of VEGF and EGFR inhibitors and chemotherapy group (heterogeneity between groups: p < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure 14). The pooled incidence of hyperkalemia in the targeted therapy groups in four studies was 4% (95% CI: 1%, 8%) (Supplementary Figure 15), which was significantly higher than that in the chemotherapy groups in two studies (p = 0.037) (Supplementary Figure 16).
15 studies reported the adverse event of hyponatremia, of which the pooled incidence was 7% (95% CI: 4%, 11%) (Supplementary Figure 17). The pooled incidence of hyponatremia in the chemotherapy groups in these studies was 6% (95% CI: 3%, 11%), having no significant difference compared to that in the targeted therapy groups (p = 0.854) (Supplementary Figure 18).
The pooled incidence of hypocalcemia following targeted therapies in four studies was 12% (95% CI: 4%, 23%) (Supplementary Figure 19), which was significantly higher than that following chemotherapy alone reported in 22 studies (p < 0.01) (Supplementary Figure 20). The pooled incidence of hypercalcemia following targeted therapies in two studies was 4% (95% CI: 1%, 10%) (Supplementary Figure 21).
Other reported electrolyte disorders following targeted therapies included hypophosphatemia reported in four studies and hypomagnesemia reported in eight studies, of which the pooled incidences were 12% (95% CI: 1%, 30%) (Supplementary Figure 22) and 26% (95% CI: 15%, 39%), respectively (Supplementary Figure 23). The summary of pooled incidences for all electrolytes disorders is shown in Figure 6.
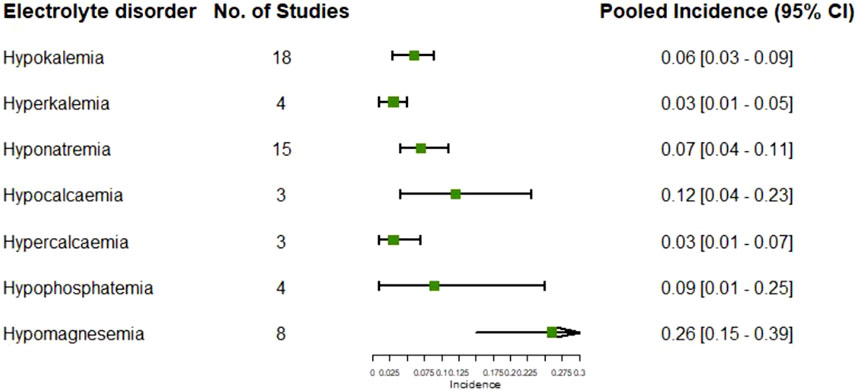
Figure 6. Pooled incidences of electrolytes disorders subsequent to the administration of targeted therapies in lung cancer.
Risk of bias assessment
Critical appraisal indicated 16, 14, and 27 studies were rated as having low, high, and unclear risk of bias based on the 7-item Cochrane criteria (Supplementary Figure 24). The domain with the highest proportion of high risk was the performance bias (Supplementary Figure 25).
Publication bias
Visual inspections of the funnel plot revealed absence of asymmetry for the outcome of AKI (Supplementary Figure 26); however, the presence of asymmetry was observed in the funnel plots for the outcomes of increased serum creatinine (Supplementary Figure 27), proteinuria (Supplementary Figure 28), UTI (Supplementary Figure 29), and electrolyte disorders (Supplementary Figure 30).
Discussion
Our findings showed adverse kidney related outcomes are not uncommon following targeted therapies in lung cancer. The pooled incidences of AKI and proteinuria following targeted therapies in lung cancer were 1% (95% CI: 0%, 2%) and 7% (95% CI: 5%, 10%), respectively. The network meta-analysis indicated targeted therapies, either alone or in combination, did not increased the risk of AKI compared to chemotherapy alone, whereas VEGFR inhibitors containing therapies are associated with higher risk of proteinuria. The pooled incidences of increased serum creatinine and UTI following targeted therapies in lung cancer were 5% (95% CI: 2%, 8%) and 7% (95% CI: 2%, 13%), respectively, without significant differences in comparison with chemotherapy alone. Various electrolytes disorders could be observed following targeted treatments, with pooled incidences ranging from 4% to 21%; however, most electrolyte disorders had limited number of reports. Most of the reported events were of CTCAE grade 1–2.
Kidney injury following targeted treatment can manifests in various forms, among which renal function impairment, proteinuria, and electrolyte disorders are the most reported. The underlying histopathological diagnoses include thrombotic microangiography, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, acute interstitial nephritis, and acute tubular necrosis (den Deurwaarder et al., 2012). Our findings that the pooled incidence of proteinuria was higher than that of renal function impairment reflected by the diagnosis of AKI or increased serum creatinine and also higher in VEGFR inhibitors containing therapies compared to chemotherapy alone are consistent with literature on glomerular injury caused by targeted agents, particularly VEGFR inhibitors (den Deurwaarder et al., 2012; Estrada et al., 2019; Izzedine et al., 2010). Notably, the pooled incidence of AKI in this study was lower than that associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in non-small cell lung cancer (Zhu et al., 2022). Meanwhile, AKI and renal failure had been reported to top the ranking of kidney related AEs following ICIs treatment (Hu et al., 2021), again confirming a different toxicity spectrum compared with targeted therapies. Although proteinuria and electrolyte disorders were more often observed than AKI and UTI in this systematic review, proteinuria, UTI, and electrolyte disorders have gained far less attention than renal dysfunction in the literature, reflected by the fewer number of studies.
Our findings indicated all types of kidney related outcomes were minor in severity, necessitating no pharmaceutical interventions. These findings are consistent with our clinical observations. The timing of onset also matters. Therefore, close surveillance and regular examinations of renal function and urine analysis play a significant role in the follow up of lung cancer patients who are receiving targeted therapies, to monitor both the onset and outcomes of kidney related AEs. In addition, the assessment of renal function in these cases should be comprehensive, monitoring not only serum creatinine, but also urinary protein and electrolytes.
To our acknowledgment, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis on the kidney related AEs following targeted therapies in lung cancer so far. This study benefited from a comprehensive literature search and unbiased comparisons of RCTs. In contrast to previous reports that focused on AKI or renal failure, this systematic review investigated the occurrence of all types of kidney related AEs, providing a full picture of relevant studies in this field. Future research on the mechanisms of nephrotoxicity caused by targeted agents will help to minimize the risk of adverse kidney related outcomes and improve patients’ survival.
There are still some limitations worth mentioning. First, the report bias should be considered when interpretate the results. Since the kidney related AEs are not the mainstay of adverse events following targeted therapies, they may be underestimated due to report bias. Second, the kidney related outcomes examined here were reported as adverse event without consensus definition, which might be an important source for the observed high heterogeneity. For example, for increased creatine, we were unable to know the increased amount or if the increased creatinine accounted for a diagnosis of AKI. Third, the chemotherapy was considered as a single group in the meta-analysis; however, the regimens substantially varied across different studies, from a single agent to combination of multiple agents, and the sequence of drug administration might also be different even for the same agents. Fourth, we cannot rule out the renal injury caused by lung cancer per se in this study. Although we tried to reduce the effect of this confounder by including RCT studies; however, network meta-analysis was only feasible for AKI and proteinuria. Fifth, this systematic review investigated the kidney related AEs in the clinical trial settings. Future studies and accumulative data from real-world cohorts will further help us gain more insight into this field.
Conclusion
In summary, the findings suggested adverse kidney related outcomes are not uncommon following targeted therapies in lung cancer in trial settings. In comparison to chemotherapy alone, targeted therapies did not increase the risk of AKI, yet were associated with higher incidence of proteinuria, particularly VEGFR inhibitors containing therapies. Proteinuria and electrolytes disorders are more often observed than renal dysfunction and UTI. All types of AEs were mild in severity. Future studies and accumulative data from real-world cohorts will further help us to understand the whole picture.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
SR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. WW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. XY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing–original draft. WF: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. GL: Investigation, Project administration, Validation, Writing–review and editing. YF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. MX: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Software, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was partly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81800613) and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2023YFSY0027).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1511171/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahn, M. J., Yang, J. C. H., Liang, J., Kang, J. H., Xiu, Q., Chen, Y. M., et al. (2012). Randomized phase II trial of first-line treatment with pemetrexed-cisplatin, followed sequentially by gefitinib or pemetrexed, in East Asian, never-smoker patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 77 (2), 346–352. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.03.011
Argiris, A., Lee, J. W., Stevenson, J., Sulecki, M. G., Hugec, V., Choong, N. W., et al. (2017). Phase II randomized trial of carboplatin, paclitaxel, bevacizumab with or without cixutumumab (IMC-A12) in patients with advanced non-squamous, non-small-cell lung cancer: a trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E3508). Ann. Oncol. 28 (12), 3037–3043. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx534
Ciuleanu, T., Socinski, M. A., Obasaju, C., Luft, A. V., Szczesna, A., Szafrański, W., et al. (2018). Efficacy and safety of necitumumab continuation therapy in the phase III SQUIRE study of patients with stage IV squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 19 (2), 130–138. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2017.10.004
Ciuleanu, T., Tsai, C. M., Tsao, C. J., Milanowski, J., Amoroso, D., Heo, D. S., et al. (2013). A phase II study of erlotinib in combination with bevacizumab versus chemotherapy plus bevacizumab in the first-line treatment of advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 82 (2), 276–281. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.08.002
Crinò, L., Cappuzzo, F., Zatloukal, P., Reck, M., Pesek, M., Thompson, J. C., et al. (2008). Gefitinib versus vinorelbine in chemotherapy-naive elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (INVITE): a randomized, phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (26), 4253–4260. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.0672
den Deurwaarder, E. S., Desar, I. M. E., Steenbergen, E. J., Mulders, P. F., Wetzels, J. F. M., and van Herpen, C. M. L. (2012). Kidney injury during VEGF inhibitor therapy. Neth J. Med. 70 (6), 267–271.
Doebele, R. C., Spigel, D., Tehfe, M., Thomas, S., Reck, M., Verma, S., et al. (2015). Phase 2, randomized, open-label study of ramucirumab in combination with first-line pemetrexed and platinum chemotherapy in patients with nonsquamous, advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 121 (6), 883–892. doi:10.1002/cncr.29132
Du, N., Li, X., Li, F., Zhao, H., Fan, Z., Ma, J., et al. (2013). Intrapleural combination therapy with bevacizumab and cisplatin for non-small cell lung cancer-mediated malignant pleural effusion. Oncol. Rep. 29 (6), 2332–2340. doi:10.3892/or.2013.2349
Ellis, P. M., Shepherd, F. A., Millward, M., Perrone, F., Seymour, L., Liu, G., et al. (2014). Dacomitinib compared with placebo in pretreated patients with advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NCIC CTG BR.26): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15 (12), 1379–1388. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70472-3
Estrada, C. C., Maldonado, A., and Mallipattu, S. K. (2019). Therapeutic inhibition of VEGF signaling and associated nephrotoxicities. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 30 (2), 187–200. doi:10.1681/ASN.2018080853
Gaafar, R. M., Surmont, V. F., Scagliotti, G. V., Van Klaveren, R. J., Papamichael, D., Welch, J. J., et al. (2011). A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III intergroup study of gefitinib in patients with advanced NSCLC, non-progressing after first line platinum-based chemotherapy (EORTC 08021/ILCP 01/03). Eur. J. Cancer 47 (15), 2331–2340. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.045
Garon, E. B., Ciuleanu, T. E., Arrieta, O., Prabhash, K., Syrigos, K. N., Goksel, T., et al. (2014). Ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel for second-line treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer after disease progression on platinum-based therapy (REVEL): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 384 (9944), 665–673. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60845-X
Goldman, J. W., Mazieres, J., Barlesi, F., Dragnev, K. H., Koczywas, M., Göskel, T., et al. (2020). A randomized phase III study of abemaciclib versus erlotinib in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer with a detectable KRAS mutation who failed prior platinum-based therapy: JUNIPER. Front. Oncol. 10, 578756. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.578756
Herbst, R. S., Redman, M. W., Kim, E. S., Semrad, T. J., Bazhenova, L., Masters, G., et al. (2018). Cetuximab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without bevacizumab versus carboplatin and paclitaxel with or without bevacizumab in advanced NSCLC (SWOG S0819): a randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 19 (1), 101–114. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30694-0
Higgins, J. P., Jackson, D., Barrett, J. K., Lu, G., Ades, A. E., and White, I. R. (2012). Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: concepts and models for multi-arm studies. Res. Synth. Methods 3 (2), 98–110. doi:10.1002/jrsm.1044
J. P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas, J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Pageet al. (Editors) (2019). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2nd Edn. Chichester, United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons.
Hirsch, F. R., Scagliotti, G. V., Mulshine, J. L., Kwon, R., Curran, W. J., Wu, Y. L., et al. (2017). Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 389 (10066), 299–311. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30958-8
Hu, F., Zhai, Y., Yuan, L., Liang, J., Xu, J., Guo, X., et al. (2021). Renal toxicities in immune checkpoint inhibitors with or without chemotherapy: an observational, retrospective, pharmacovigilance study leveraging US FARES database. Cancer Med. 10 (24), 8754–8762. doi:10.1002/cam4.4343
Ioannidis, J. P. (2008). Interpretation of tests of heterogeneity and bias in meta-analysis. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 14 (5), 951–957. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2753.2008.00986.x
Izzedine, H., Massard, C., Spano, J. P., Goldwasser, F., Khayat, D., and Soria, J. C. (2010). VEGF signalling inhibition-induced proteinuria: mechanisms, significance and management. Eur. J. Cancer 46 (2), 439–448. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.11.001
Johnson, B. E., Kabbinavar, F., Fehrenbacher, L., Hainsworth, J., Kasubhai, S., Kressel, B., et al. (2013). ATLAS: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIIB trial comparing bevacizumab therapy with or without erlotinib, after completion of chemotherapy, with bevacizumab for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 31 (31), 3926–3934. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.47.3983
Karayama, M., Inui, N., Fujisawa, T., Enomoto, N., Nakamura, Y., Kuroishi, S., et al. (2016). Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed and bevacizumab versus pemetrexed monotherapy after induction therapy with carboplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-squamous non small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 58, 30–37. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2016.01.013
Kenmotsu, H., Wakuda, K., Mori, K., Kato, T., Sugawara, S., Kirita, K., et al. (2022). Randomized phase 2 study of osimertinib plus bevacizumab versus osimertinib for untreated patients with nonsquamous NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations: WJOG9717L study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 17 (9), 1098–1108. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2022.05.006
Lahiri, A., Maji, A., Potdar, P. D., Singh, N., Parikh, P., Bisht, B., et al. (2023). Lung cancer immunotherapy: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol. Cancer 22 (1), 40. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01740-y
Lara, P. N., Moon, J., Hesketh, P. J., Redman, M. W., Williamson, S. K., Akerley, W. L., et al. (2016). SWOG S0709: randomized phase II trial of erlotinib versus erlotinib plus carboplatin/paclitaxel in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and impaired performance status as selected by a serum proteomics assay. J. Thorac. Oncol. 11 (3), 420–425. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2015.11.003
Leighl, N. B., Rizvi, N. A., de Lima, L. G., Arpornwirat, W., Rudin, C. M., Chiappori, A. A., et al. (2017). Phase 2 study of erlotinib in combination with linsitinib (OSI-906) or placebo in chemotherapy-naive patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Clin. Lung Cancer 18 (1), 34–42. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2016.07.007
Liberati, A., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gøtzsche, P. C., Ioannidis, J. P. A., et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339, b2700. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2700
Lynch, T. J., Fenton, D., Hirsh, V., Bodkin, D., Middleman, E. L., Chiappori, A., et al. (2009). A randomized phase 2 study of erlotinib alone and in combination with bortezomib in previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 4 (8), 1002–1009. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181aba89f
Miller, M., and Hanna, N. (2021). Advances in systemic therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Bmj 375, n2363. doi:10.1136/bmj.n2363
Miller, V. A., Hirsh, V., Cadranel, J., Chen, Y. M., Park, K., Kim, S. W., et al. (2012). Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): a phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 13 (5), 528–538. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70087-6
Nakagawa, K., Garon, E. B., Seto, T., Nishio, M., Ponce Aix, S., Paz-Ares, L., et al. (2019). Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20 (12), 1655–1669. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30634-5
Niho, S., Kunitoh, H., Nokihara, H., Horai, T., Ichinose, Y., Hida, T., et al. (2012). Randomized phase II study of first-line carboplatin-paclitaxel with or without bevacizumab in Japanese patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 76 (3), 362–367. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.12.005
Paz-Ares, L., Mezger, J., Ciuleanu, T. E., Fischer, J. R., von Pawel, J., Provencio, M., et al. (2015). Necitumumab plus pemetrexed and cisplatin as first-line therapy in patients with stage IV non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (INSPIRE): an open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 16 (3), 328–337. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70046-X
Paz-Ares, L. G., Pérol, M., Ciuleanu, T. E., Kowalyszyn, R. D., Reck, M., Lewanski, C. R., et al. (2017). Treatment outcomes by histology in REVEL: a randomized phase III trial of Ramucirumab plus docetaxel for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 112, 126–133. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.05.021
Pérol, M., Chouaid, C., Pérol, D., Barlési, F., Gervais, R., Westeel, V., et al. (2012). Randomized, phase III study of gemcitabine or erlotinib maintenance therapy versus observation, with predefined second-line treatment, after cisplatin-gemcitabine induction chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 (28), 3516–3524. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.39.9782
Pujol, J. L., Lavole, A., Quoix, E., Molinier, O., Souquet, P. J., Barlesi, F., et al. (2015). Randomized phase II-III study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive small-cell lung cancer: results from the IFCT-0802 trial†. Ann. Oncol. 26 (5), 908–914. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv065
Ramlau, R., Gorbunova, V., Ciuleanu, T. E., Novello, S., Ozguroglu, M., Goksel, T., et al. (2012). Aflibercept and Docetaxel versus Docetaxel alone after platinum failure in patients with advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized, controlled phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 (29), 3640–3647. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.42.6932
Reck, M., Socinski, M. A., Luft, A., Szczęsna, A., Dediu, M., Ramlau, R., et al. (2016). The effect of necitumumab in combination with gemcitabine plus cisplatin on tolerability and on quality of life: results from the phase 3 SQUIRE trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 11 (6), 808–818. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.002
Reck, M., von Pawel, J., Zatloukal, P., Ramlau, R., Gorbounova, V., Hirsh, V., et al. (2009). Phase III trial of cisplatin plus gemcitabine with either placebo or bevacizumab as first-line therapy for nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAil. J. Clin. Oncol. 27 (8), 1227–1234. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.5466
Ruiz, J. N., Belum, V. R., Creel, P., Cohn, A., Ewer, M., and Lacouture, M. E. (2014). Current practices in the management of adverse events associated with targeted therapies for advanced renal cell carcinoma: a national survey of oncologists. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 12 (5), 341–347. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2014.04.001
Salanti, G., Ades, A. E., and Ioannidis, J. P. (2011). Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64 (2), 163–171. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.03.016
Sandler, A., Gray, R., Perry, M. C., Brahmer, J., Schiller, J. H., Dowlati, A., et al. (2006). Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 355 (24), 2542–2550. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061884
Scagliotti, G. V., Krzakowski, M., Szczesna, A., Strausz, J., Makhson, A., Reck, M., et al. (2012). Sunitinib plus erlotinib versus placebo plus erlotinib in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 (17), 2070–2078. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.39.2993
Schuler, M., Wu, Y. L., Hirsh, V., O'Byrne, K., Yamamoto, N., Mok, T., et al. (2016). First-Line afatinib versus chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and Common epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and brain metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 11 (3), 380–390. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2015.11.014
Sequist, L. V., von Pawel, J., Garmey, E. G., Akerley, W. L., Brugger, W., Ferrari, D., et al. (2011). Randomized phase II study of erlotinib plus tivantinib versus erlotinib plus placebo in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 29 (24), 3307–3315. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.34.0570
Seto, T., Kato, T., Nishio, M., Goto, K., Atagi, S., Hosomi, Y., et al. (2014). Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 15 (11), 1236–1244. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70381-X
Shaw, A. T., Kim, T. M., Crinò, L., Gridelli, C., Kiura, K., Liu, G., et al. (2017). Ceritinib versus chemotherapy in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer previously given chemotherapy and crizotinib (ASCEND-5): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18 (7), 874–886. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30339-X
Shi, Y. K., Wang, L., Han, B. H., Li, W., Yu, P., Liu, Y. P., et al. (2017). First-line icotinib versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (CONVINCE): a phase 3, open-label, randomized study. Ann. Oncol. 28 (10), 2443–2450. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx359
Socinski, M. A., Scappaticci, F. A., Samant, M., Kolb, M. M., and Kozloff, M. F. (2010). Safety and efficacy of combining sunitinib with bevacizumab + paclitaxel/carboplatin in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 5 (3), 354–360. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181c7307e
Spigel, D. R., Burris, H. A., Greco, F. A., Shih, K. C., Gian, V. G., Lipman, A. J., et al. (2018). Erlotinib plus either pazopanib or placebo in patients with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial with correlated serum proteomic signatures. Cancer 124 (11), 2355–2364. doi:10.1002/cncr.31290
Spigel, D. R., Ervin, T. J., Ramlau, R. A., Daniel, D. B., Goldschmidt, J. H., Blumenschein, G. R., et al. (2013). Randomized phase II trial of Onartuzumab in combination with erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 31 (32), 4105–4114. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.47.4189
Spigel, D. R., Luft, A., Depenbrock, H., Ramlau, R., Khalil, M., Kim, J. H., et al. (2017a). An open-label, randomized, controlled phase II study of paclitaxel-carboplatin chemotherapy with necitumumab versus paclitaxel-carboplatin alone in first-line treatment of patients with stage IV squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 18 (5), 480–488. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2017.02.002
Spigel, D. R., Rubin, M. S., Gian, V. G., Shipley, D. L., Burris, H. A., Kosloff, R. A., et al. (2017b). Sorafenib and continued erlotinib or sorafenib alone in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer progressing on erlotinib: a randomized phase II study of the Sarah Cannon Research Institute (SCRI). Lung Cancer 113, 79–84. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.09.007
Steendam, C. M. J., Peric, R., van Walree, N. C., Youssef, M., Schramel, F. M. N. H., Brocken, P., et al. (2021). Randomized phase III study of docetaxel versus docetaxel plus intercalated erlotinib in patients with relapsed non-squamous non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 160, 44–49. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.08.002
Stephenson, J. J., Nemunaitis, J., Joy, A. A., Martin, J. C., Jou, Y. M., Zhang, D., et al. (2014). Randomized phase 2 study of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor dinaciclib (MK-7965) versus erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 83 (2), 219–223. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.11.020
Stinchcombe, T. E., Jänne, P. A., Wang, X., Bertino, E. M., Weiss, J., Bazhenova, L., et al. (2019). Effect of erlotinib plus bevacizumab vs erlotinib alone on progression-free survival in patients with advanced EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 5 (10), 1448–1455. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.1847
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Tada, H., Mitsudomi, T., Misumi, T., Sugio, K., Tsuboi, M., Okamoto, I., et al. (2022). Randomized phase III study of gefitinib versus cisplatin plus vinorelbine for patients with resected stage II-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer with EGFR mutation (IMPACT). J. Clin. Oncol. 40 (3), 231–241. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01729
Takeda, K., Hida, T., Sato, T., Ando, M., Seto, T., Satouchi, M., et al. (2010). Randomized phase III trial of platinum-doublet chemotherapy followed by gefitinib compared with continued platinum-doublet chemotherapy in Japanese patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results of a west Japan thoracic oncology group trial (WJTOG0203). J. Clin. Oncol. 28 (5), 753–760. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.23.3445
Takeda, M., Yamanaka, T., Seto, T., Hayashi, H., Azuma, K., Okada, M., et al. (2016). Bevacizumab beyond disease progression after first-line treatment with bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer (West Japan Oncology Group 5910L): an open-label, randomized, phase 2 trial. Cancer 122 (7), 1050–1059. doi:10.1002/cncr.29893
Thatcher, N., Hirsch, F. R., Luft, A. V., Szczesna, A., Ciuleanu, T. E., Dediu, M., et al. (2015). Necitumumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin versus gemcitabine and cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in patients with stage IV squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (SQUIRE): an open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 16 (7), 763–774. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00021-2
von Pawel, J., Spigel, D. R., Ervin, T., Losonczy, G., Barlesi, F., Juhász, E., et al. (2018). Randomized phase II trial of parsatuzumab (Anti-EGFL7) or placebo in combination with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab for first-line nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 23 (6), 654–e58. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0690
Wakelee, H., Zvirbule, Z., De Braud, F., Kingsley, C. D., Mekhail, T., Lowe, T., et al. (2017a). Efficacy and safety of onartuzumab in combination with first-line bevacizumab- or pemetrexed-based chemotherapy regimens in advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 18 (1), 50–59. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2016.09.013
Wakelee, H. A., Dahlberg, S. E., Keller, S. M., Tester, W. J., Gandara, D. R., Graziano, S. L., et al. (2017b). Adjuvant chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab in patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer (E1505): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18 (12), 1610–1623. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30691-5
Witta, S. E., Jotte, R. M., Konduri, K., Neubauer, M. A., Spira, A. I., Ruxer, R. L., et al. (2012). Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib with and without entinostat in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed on prior chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 30 (18), 2248–2255. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.9411
Wu, Y. L., Lu, S., Lu, Y., Zhou, J., Shi, Y. K., Sriuranpong, V., et al. (2018). Results of PROFILE 1029, a phase III comparison of first-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in East asian patients with ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 13 (10), 1539–1548. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2018.06.012
Wu, Y. L., Zhou, C., Liam, C. K., Wu, G., Liu, X., Zhong, Z., et al. (2015). First-line erlotinib versus gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: analyses from the phase III, randomized, open-label, ENSURE study. Ann. Oncol. 26 (9), 1883–1889. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv270
Yoh, K., Hosomi, Y., Kasahara, K., Yamada, K., Takahashi, T., Yamamoto, N., et al. (2016). A randomized, double-blind, phase II study of ramucirumab plus docetaxel vs placebo plus docetaxel in Japanese patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer after disease progression on platinum-based therapy. Lung Cancer 99, 186–193. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.07.019
Yoshioka, H., Azuma, K., Yamamoto, N., Takahashi, T., Nishio, M., Katakami, N., et al. (2015). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial of erlotinib with or without a c-Met inhibitor tivantinib (ARQ 197) in Asian patients with previously treated stage IIIB/IV nonsquamous nonsmall-cell lung cancer harboring wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor (ATTENTION study). Ann. Oncol. 26 (10), 2066–2072. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv288
Zhong, W. Z., Wang, Q., Mao, W. M., Xu, S. T., Wu, L., Shen, Y., et al. (2018). Gefitinib versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin as adjuvant treatment for stage II-IIIA (N1-N2) EGFR-mutant NSCLC (ADJUVANT/CTONG1104): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 19 (1), 139–148. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30729-5
Zhou, C., Wu, Y. L., Chen, G., Liu, X., Zhu, Y., Lu, S., et al. (2015). BEYOND: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, phase III study of first-line carboplatin/paclitaxel plus bevacizumab or placebo in Chinese patients with advanced or recurrent nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 33 (19), 2197–2204. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.59.4424
Keywords: renal dysfunction, proteinuria, urinary tract infection, electrolyte disorder, targeted therapy, lung cancer, meta-analysis
Citation: Ren S, Wang W, Yao X, Fang W, Li G, Feng Y and Xia M (2025) Adverse kidney related events following targeted therapies in lung cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1511171. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1511171
Received: 14 October 2024; Accepted: 25 February 2025;
Published: 13 March 2025.
Edited by:
Seema Kumari, Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management (GITAM), IndiaReviewed by:
Yuma Shibutani, National Cancer Center Hospital East, JapanRakesh MP, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham University, India
Copyright © 2025 Ren, Wang, Yao, Fang, Li, Feng and Xia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Xia, NTY4MTgzNTIwQHFxLmNvbQ==; Yunlin Feng, ZmVuZ3l1bmxpbkBtZWQudWVzdGMuZWR1LmNu; Guisen Li, Z3Vpc2VubGlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Song Ren
Song Ren Wei Wang1†
Wei Wang1† Xiaoxiu Yao
Xiaoxiu Yao Guisen Li
Guisen Li Yunlin Feng
Yunlin Feng