
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol., 26 February 2025
Sec. Translational Pharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1509259
This article is part of the Research TopicAnti-cancer Nanomedicines: From Design to Clinical ApplicationsView all 10 articles
Background: Nanomedicine has received much attention for its potential applications in the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer. However, no bibliometric evaluation has been conducted to present an assessment of scientific progress in the field. The aim of this study is to comprehensively catalog the cooperation and influence of journals, countries, institutions, and authors in the field of nanomedicine in liver cancer from the perspective of bibliometrics, evaluate the clustering evolution of knowledge structure, and uncover hot topics and emerging themes.
Methods: Articles and reviews related to nanomedicine and liver cancer were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Literature Library using Topic Search. #1 T= (“Hepatic Neoplasm*” OR “Liver Neoplasm” OR “Liver Cancer*” OR “Hepatocellular Cancer*” OR “Hepatic Cancer*“), #2 T= “nano*“, the search strategy is set as #1 AND #2 limited to Science Citation Index Expanded database source, with no limitation of publication types and language/time. Bibliometric studies were conducted using CiteSpace and VOSviewer.
Results: 2,648 articles and reviews were included from 2000 to 2024. The number of articles regarding nanomedicine in liver cancer showed an increasing trend. Analysis of the most productive journals shows that most are specialized in nanoscience and nanotechnology, pharmacology and pharmacy, and chemistry and multidisciplinary. These publications mainly come from 8,782 institutions in 297 countries led by China and the United States of America. Shao D published the most papers among the publications, while Jemal A had the most co-citations. The macroscopical sketch and micro-representation of the whole knowledge field are realized through co-citation analysis. Hepatocellular carcinoma, targeted delivery, sorafenib nanoparticles, and others are current and developing areas of study. The keywords “nanocrystals,” “biodistribution,” and “particles” also may be the focus of new trends and future research.
Conclusion: In this study, bibliometrics and visual methods were used to review the research of nanomedicine in liver cancer comprehensively. The article will help scholars to gain a better understanding of the dynamic evolution of nanomedicine applications in liver cancer and point the directions for future research.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, also called primary liver cancer) was the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death worldwide in 2020, with approximately 906,000 new cases and 830,000 deaths, with a 5-year survival rate of only 18% (Sung et al., 2021). Operative resection, liver grafting, local radiotherapy or chemotherapy, and combination therapy are the mainstay of treatment for HCC. However, due to the insidious onset of HCC and the lack of any specific early markers, most patients are diagnosed with HCC at an advanced stage, which is generally not amenable to operative treatment. Immunotherapy to reverse the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment shows potential to improve antitumor therapy for patients with HCC. This involves chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, vaccines, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) like programmed death receptor 1/programmed death receptor ligand 1 (PD-1/PD-L1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) (Donne and Lujambio, 2023). Despite promising advances in immunotherapies (e.g., approved activating cytokines and checkpoint-blocking drugs), limited efficacy and safety are still tremendous challenges for HCC immunotherapies (Liu and Webster, 2007). Consequently, there is an urgent need for better therapeutic alternatives that inhibit tumorigenesis and/or restore sensitivity to immunotherapy-resistant tumors with liver cancer that cannot have surgery.
Nanomedicine has become a highly promising branch of nanotechnology in the 21st century (Liu and Webster, 2007). This growth is particularly significant in medical fields where traditional methods are suboptimal, such as cancer management, or treatments have been outstripped by illnesses like antibiotic-resistant bacteria (Halbus et al., 2017; Perko and Mousa, 2022). Within pharmaceutical delivery, nanomedicines are therapeutic agents formulated with polymers, lipids, or inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) with dimensions of about 100 nm or less. Several NPs have an intrinsic therapeutic effect, and nearly all types of NPs can be used as carriers for nanodrug delivery systems (NDS). These characteristics have been applied increasingly in HCC immunotherapies to improve the effectiveness and diminish the toxicity of immune-modulating drugs (Upaganlawar et al., 2022). For example, nab-paclitaxel (albumin nanoparticles of paclitaxel) and atezolizumab (PD-L1 blocker) are used to treat patients with advanced HCC. Qiu et al. reported a nanosized ultrasound contrast agent (arsenic trioxide (ATO)/PFH NPs@Au-cRGD) that integrates diagnostic and therapeutic properties for efficient ultrasound imaging and liver cancer treatment (Qiu et al., 2023). Multifunctional Janus nanocomposites with magnetic Fe3O4 heads and mesoporous SiO2 bodies contain doxorubicin (DOX) “nanobullets” (M-MSNs-DOX) that significantly inhibit tumor growth and reduce systemic toxicity (Shao et al., 2016). Immunotherapy with nanotechnology not only enables the precise release of medications but also further improves the therapeutic effect of antitumor agents by regulating the microenvironment (alleviating immunosuppression, reversing interstitial cell phenotypes, up-regulating or down-regulating the level of chemokines or cytokines, alleviating hypoxia, improving the level of antigen presentation, inhibiting neovascularization or improving the morphological form of existing vascularization, and tumor vaccines, etc.). Due to the great potential of nanomedicine in liver cancer, scholars have a strong interest in further understanding the role and application of nanomedicine in liver cancer, with published articles having increased rapidly. In recent years, studies on nanomedicine in liver cancer have been reviewed from various aspects. Although there is a very small amount of literature addressing this issue (Fan et al., 2024), but it is limited to nanomaterials. However, no comprehensive and impartial assessment of trends in publication, research fields, countries/regions, institutions, or authors has been undertaken in nanomedicine in liver cancer, affecting research areas and their cooperation, knowledge base, hotspots, and frontiers.
Such an exponentially visible increase in documents requires new approaches to analyse trends in the field of knowledge. Bibliometrics enables researchers to see how evidence is linked to reveal the structure and evolution of an area through two kinds of different methodologies, namely, performance analysis and bibliometric mapping, while systematic mapping offers a landscape of the current knowledge and identifies fields that need further attention and full integration (Zupic and Čater, 2015; Haddaway et al., 2016). The scientometric analysis, combining bibliometric analyses and systematic mapping, focuses on the system and features of research literature and has been applied widely to qualitative and quantitative analysis of scientific documents to understand the relationship between knowledge structure and research hotspots (Nakagawa et al., 2019). The contributions of different countries/regions, organizations, scholars, and publications can be compared to describe and predict the future progress of a specific research topic through scientometric analysis (Garcia-Fuentes et al., 2022). Many scholars have applied scientometric analysis to various fields of medicine, such as cardiovascular disease (Chen C. et al., 2020), cancer (Shen J. et al., 2022), psychopharmacology (Sabe et al., 2022), biological signaling molecule (Fang et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2021), ferroptosis (Zhang et al., 2021), and pyroptosis (Ma et al., 2021b). They are evaluating the research frontiers of nanomedicines for the treatment of liver cancer and developing treatment options. This study used CiteSpace and VOSviewer as research tools, summarized the research hotspots and frontier trends of nanomedicine in liver cancer over the past several years, and formed the corresponding knowledge map. This study will provide the current research status, clustering evolution path, frontier hotspots, and future research trends of nanomedicine in liver cancer for basic research and clinical application.
Several databases have unique advantages and limitations in literature retrieval, such as Web of Science (WoS), PubMed, and Scopus (Mongeon and Paul-Hus, 2015). This study used the Expanded (SCI-Expanded) of the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) catalog database developed by Thomson Scientific to conduct literature retrieval, data extraction, and scientometric analysis (Leydesdorff et al., 2013). The WoSCC is considered one of the most standardized, comprehensive, consistent, and practicable scientific literature sources with the highest qualitative index (Bettencourt and Kaur, 2011). Its diversification, capacity to analyse productivity across journals, countries/regions, institutions and authors, and better compatibility with critical data analysis tools, further increase its availability. #1 TS= (“Hepatic Neoplasm*” OR “Liver Neoplasm” OR “Liver Cancer*” OR “Hepatocellular Cancer*” OR “Hepatic Cancer*“), #2 TS= “nano*“, the search strategy is set as #1 AND #2 limited to Science Citation Index Expanded database source, with no limitation of publication types and language/time. The “nano*” uses a truncated word retrieval method, which can not only save the number of characters entered, but also achieve a higher recall ratio. For example, “nano*” denotes nanomedicine, nanomaterials, nanotechnology, etc.
The retrieved papers were extracted from WoSCC within 1 day (1 June 2024) to avoid bias errors in the form of “Full Record and Cited References” and saved in tag-delimited “Plain Text” files named “download_.txt.“2,863 articles were retrieved, including seven types of literature among them. We import the retrieved literature into CiteSpace for data cleaning. Only English articles and reviews are eligible for inclusion; 2,648 papers were obtained after deleting duplicate literature. The two researchers (SDL and DPC) independently searched the raw data, then discussed possible disagreements, and eventually reached an agreement of 0.96 (Landis and Koch, 1977) with considerable consistency. We finally obtained 2,648 papers; the detailed screening flowchart is shown in Figure 1.
Presently, the commonly used scientometric software includes CiteSpace, VOSViewer, Bibliometric R packages, SCI2, NetDraw, Ucinet, and HistCite (Leydesdorff et al., 2013; Mongeon and Paul-Hus, 2016). Considering their advantages and characteristics, this study used CiteSpace (version 6.3. R1) (Chen, 2004) and VOSviewer (1.6.17) (van Eck and Waltman, 2010) to conduct the data analysis and visualization.
Developed by Professor Chaomei Chen, CiteSpace is a scientometric and visual analysis tool dedicated to exploring collaborations, internal structures, hotspots, and possible trends in a field. Furthermore, CiteSpace also provides various significant metrics, including temporal metrics such as structure metrics (e.g., betweenness centrality, modularity, and silhouette), burstiness, and their combination, the sigma metric values. The specific parameters used in CiteSpace were set as follows: link retaining factor of 3.0, look back years (5), time slicing (from January 2001 to June 2024 years per slice = 1), text processing (author keywords, keywords plus, title and abstract), node type (one option chosen at a time from country, institution, author, keyword, co-cited author, and co-cited reference), links (strength: cosine, scope: within slices), pruning (Minimum et al. Sliced Networks) and others followed the default. Specifically, the g-Index is an author-level metric based on the citation frequency distribution, which inherits all the sound characteristics of the h-index, better considers the citation scores of top papers, and mitigates the bias of highly cited articles (Egghe, 2006). The magnified value of the g-Index gives credit to the low-cited or non-cited papers as similar to the high-cited papers, making the co-cited analysis clusters more comprehensive and professional. The value g-Index was adjusted to 25 for all analyses in CiteSpace. Nodes with high betweenness centrality typically connect different clusters, suggesting essential hubs in the network (in addition to closeness centrality, degree centrality, etc.) (Can et al., 2021). CiteSpace uses this indicator to find and quantify the value of literature, and a purple circle is used to emphasize such literature (or countries/regions, institutions, authors, etc.). Burstness measures the rate of variation, with the frequency of an emergent term over time indicating a specific duration when an abrupt change in the frequency takes place (Kleinberg, 2003). Using the likelihood ratio test (LLR), the cluster labels are obtained from the noun terms of the citing literature titles in the corresponding clusters (p < 0.001). Each cluster is scrutinized, and if needed, the labels formed by the automatic clustering are relabeled based on the author’s professional knowledge.
VOSviewer, developed by Leiden University, does fantastic work in creating, visualizing, and exploring maps with network-based data (Can et al., 2021). VOSviewer (version 1.6.20.0) generated scientific categories, keyword co-occurrence, and clustering maps for text-based data. We used natural linguistic algorithms to extract terms from the title and summary segments and supplemented the VOSviewer corpus files. We cleaned the data by combining “hepatocellular-carcinoma”, “liver cancer”, and “liver cancer” as “hepatocellular carcinoma” and excluding nominal terms such as “in vitro”, “in vivo”, and “roles” in keywords co-occurrence analysis.
Microsoft Office Excel 2021 was used to manage the number of articles published in the year. CiteSpace and VOSviewer software were used to analyze the distribution of journals, countries/regions, institutions, authors, and co-cited authors, as well as the dual map of journals, cluster map, and keyword co-occurrence. Besides, the latest impact factor (IF) and JCR partitions of journals were obtained from Web of Science.
The change in the number of annual publications reflects the speed and progress of this research and the degree of research emphasis on this topic (Feng et al., 2024). Figure 2 shows 2,648 articles on nanomedicine in liver cancer, showing an annual increasing trend from 2001 to 2023 (Figure 2). Between 2001 and 2010, there was a gradual and steady upward trend in the number of publications. A more significant publication increase occurred after 2011. The logistic growth curve f (x) = 0.2802*x2.2556 for the global publication accumulation. This area is predicted to maintain favorable development over an extended period. While the data for 2024 are incomplete, it was estimated that the eventual number of publications in 2024 will rapidly increase to over 350.
In the WoSCC database, classifying journals into scientific categories provides insight into the scientific discipline and field on which the papers published in journals are concerned (Wang Y. et al., 2022). To search for the most productive and influential journals, we used VOSviewer software to visualize published journals related to nanomedicine in liver cancer (Figure 3A). The results showed that 2,648 articles were published in 702 academic journals. As shown in Table 4, the International Journal of Nanomedicine (90 publications, IF: 6.600) published the most articles concerning nanomedicine in liver cancer, followed by Biomaterials (52 publications, IF: 12.800) and ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (75 publications, IF: 8.300). Through the analysis of the co-citation of periodicals, we can see the contribution of each periodical to this field. Among 32,196 co-cited journals, two journals had citations of over 1,000. As presented in Table 1, the Biomaterials had the most citations (citations: 1,247, IF:14.000), followed by the Journal of Controlled Release, International Journal of Nanomedicine, and ACS Nano. According to the 2023 Journal citation reports (JCR), all were at the Q1 JCR division. Five of the top ten cited journals had an IF of more than ten, and eight were from the United States.

Figure 3. (A) The visualization map of journals publishing papers on nanomedicine applications in liver cancer. (B) The dual-map overlay of the relevant journals. Cross-flow of information between scientific categories and journals. The citing journals on the left, cited journals on the right, colored paths represent citation relationships.
To further explore the flow of knowledge between journals, especially between citing and cited journals, a dual-map overlay of the journals was developed to analyze the connection of scientific categories to nanomedicine in liver cancer, as shown (Figure 3B). This approach is designed to identify patterns of knowledge flow from cited to citing journals and provides high-level insights into innovative research output in the field of nanomedicine in liver cancer (Goerlandt et al., 2022). Designed by Chen and Leydesdorff L, the map portraying the interconnectedness of over 10,000 scientific journals is further classified into regions representing discipline-level publication and citation activity (Chen and Leydesdorff, 2014). For better interpretation, labels are presented on the dual-map overlay, which indicates clusters of journals similar to this topic. Figure 3B shows a dual-map overlay concerning nanomedicine in liver cancer articles published between 2001 and 2024. All colored curves starting from the citing (the left) map and ending at the cited (the right) map represented the paths of the citation links. Four dominant citation paths were identified. It indicated that papers published in “Physics, Materials, Chemistry” journals and “Molecular, Biology, Immunology” journals were often cited in papers published in “Molecular, Biology, Genetics” journals and “Physics, Materials, Chemistry” journals.
This study analyzed 8,782 institutions from 297 different countries/regions contributing to the publications in the field of nanomedicine in liver cancer. As shown in Figure 4, this visualized map allowed us to identify the impact and burstness of the most critical countries/regions and institutions with significant hotspots. We ranked the ten foremost productive countries/regions and institutions according to Table 2. China (1,559/58.87%) and the USA (345/13.03%) published the most articles, which even approach seven times higher than those of other countries, followed by India (235/8.87%), Egypt (165/6.23%), and Saudi Arabia (164/6.19%). Among the top 10 productive countries, Germany (0.53), the USA (0.42), China (0.14), and Italy (0.12) were colored purple in Figure 4A with high betweenness centrality, which was generally regarded as an essential turning point, which served as a bridge structure and may lead to revolutionary discoveries. Furthermore, the Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB) (163, 6.16%) published the most papers, followed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (155, 5.85%) and Fudan University (68, 2.57%). China occupied eight of the top ten fruitful institutions and was the seat of most institutions. Additionally, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (0.34), Fudan University (0.21), and King Saud University (0.17) showed high centrality, circled in purple in Figure 5. Each circle in the map represents a nation, with the size of the circle indicating the country’s number of publications. The lines connecting circles represent international collaboration, and the broader the lines, the stronger the collaboration. However, most countries and research affiliations are dispersed, and more consistent and extensive cooperation is needed.
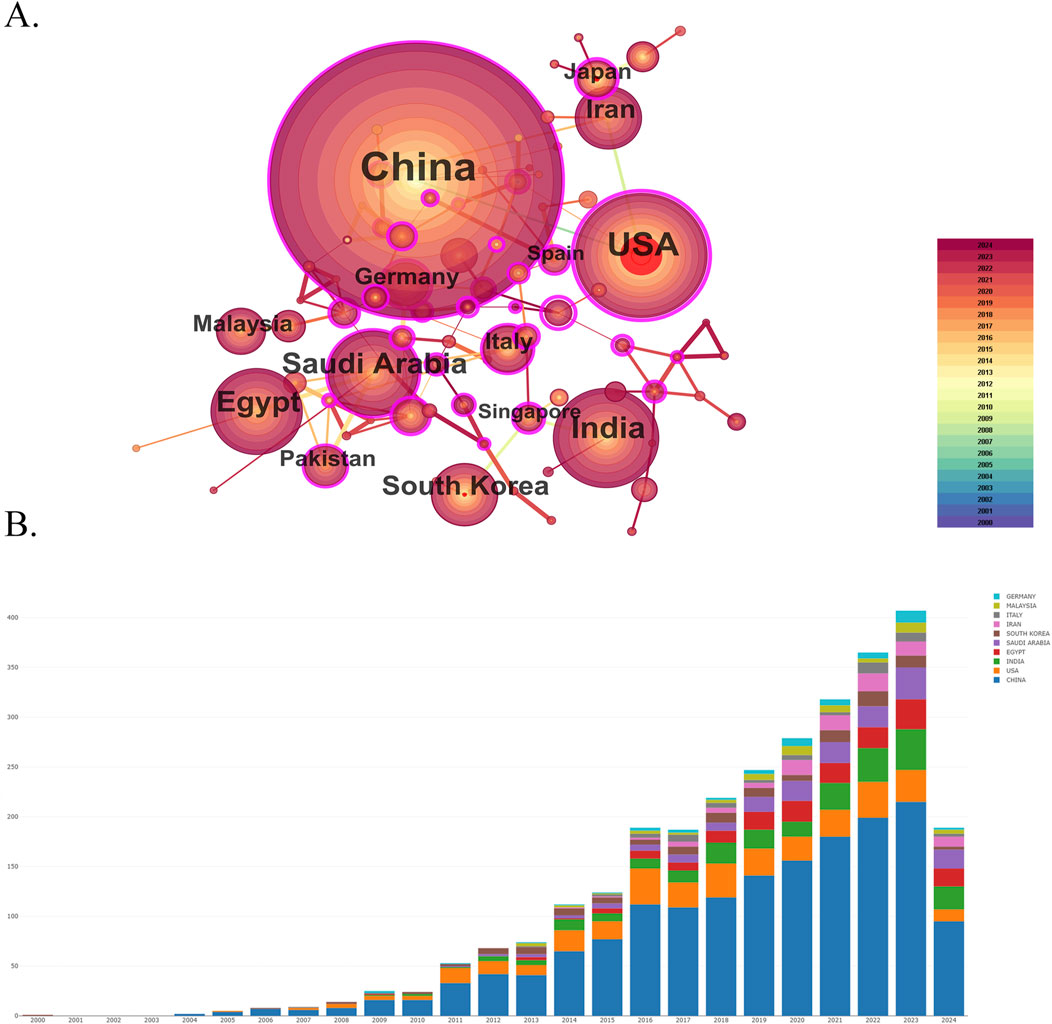
Figure 4. Spatial collaboration map of countries/regions. (A) The visualization map of leading countries contributing to research on nanomedicine applications in liver cancer. (B) Annual publication of leading countries contributing to research on nanomedicine applications in liver cancer.
Analyzing and visualizing influential researchers, such as authors of many citing or cited papers in specific domains of science, can help researchers advance along the path and provide further opportunities and guidelines for collaboration (Ma et al., 2021a; Xue et al., 2021). There are a total of 14,773 authors and 63,989 co-cited authors associated with nanomedicine in liver cancer. The author network visualized scientific cooperation between authors using co-authors' frequency (Figure 6A). The top ten productive authors are listed in Table 3. Shao Dan of South China University of Technology for the School of Biomedical Sciences and Engineering tied for the top place in nanomedicine research toward liver cancer with the most publications published (n = 15), followed by Hussein Mohd Zobir (n = 14), Li Jing (n = 14), and Fakurazi Sharida (n = 14). Notably, the betweenness centrality was relatively slight (≤0.01), indicating that the authors had little influence on each other‘s works. The node dimension represented the number of documents published by authors, with more prominent nodal points representing more published research papers. The stronger the cooperative relationship between the two researchers, the shorter the distance between the two nodes. The purple nodes represented the authors of early published articles, while the red nodes represented the authors of recently published articles. Co-citation analysis is an essential part of scientometric analysis and visualization, and co-cited authors are referred to as two or more authors cited by another or more papers simultaneously, constituting a co-cited relationship. CiteSpace was used to analyze and visualize the co-cited author’s cooperation network regarding nanomedicine in liver cancer research. Among the top 10 co-cited authors who have been cited more than 100 times, Jemal A (271) was the most frequently cited author, followed by Llovet JM (262), Zhang Y (201), and Wang Y (196) (Figure 6B).
Small and Marshakova first advanced the concept of co-citations in 1973, and it was then integrated into literature co-citation analysis to indicate that scientific literature is not an isolated resource but a system of mutual connections and continuous development (Small, 1973; Marshakova-shaikevich, 2009; Bashir, 2022). Assuming that two or more references are often cited together, it is evident that these references are associated in specific ways. It has been proved that the network map formed in this approach captures the focus of potential scientific research because the network of influential cited articles provides a knowledge basis including the main theories, concepts, and approaches, which collectively drive the generation and development of new research domain (Chen et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2014). Network clustering also provides deep insights into the degree of integration of the entire research domain since it can identify subdomains within the entire research field, which are relatively isolated from knowledge clusters based on the development of other subfields (Chen L. et al., 2020). The mapping co-citation analysis of references is the core function of CiteSpace, which characterizes knowledge structure and dynamic evolution in such networks through various visual attributes (Leydesdorff et al., 2016). Citing and cited articles represent the research frontier and knowledge base (Zhang et al., 2020). Moreover, analyzing typical clusters can help us understand nanomedicine’s knowledge structure and dynamic evolution in liver cancer. Based on the analysis of 2,648 cited articles and 106,400 valid references, the homogenous clustering of highly cited articles related to the treatment of liver cancer with nanomedicine was determined.
The co-citation network mapping of the nanomedicine in the liver cancer research landscape was shown in Figure 7A, with the first author and the year of the top 10 most cited references. Each research article generally cited several references represented as nodes in the co-citation network map. The size of a node was proportional to the cited frequency. The links among these nodes of such reference documents represented the frequency of their references cited by the same article. Similarly, line thickness was positively correlated with co-citation frequency. More information on the top 10 cited references is presented in Table 4. The most co-cited reference performed by Sung et al. (2021) was an original article published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, entitled “Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries”, followed by an article entitled “Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches”. Additionally, “Functional alginate nanoparticles for efficient intracellular release of doxorubicin and hepatoma carcinoma cell targeting therapy” (0.18) showed high centrality, circled in purple in Figure 7A.
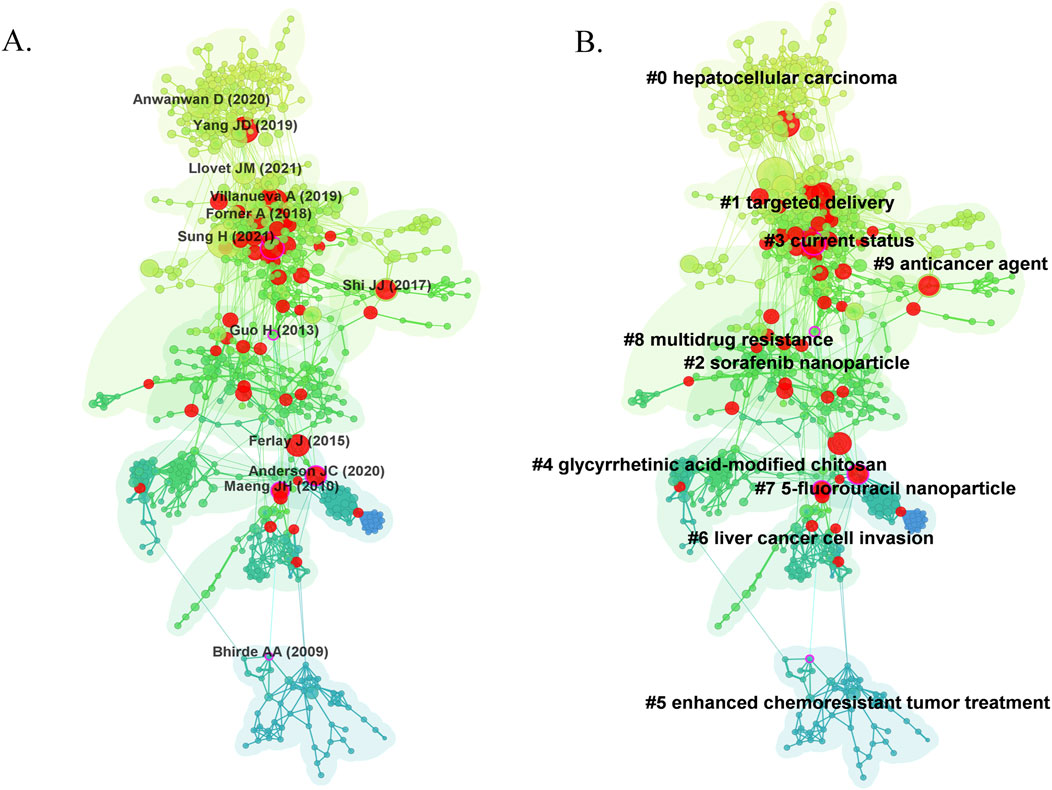
Figure 7. Visual analysis of co-citation (A) and clustering network (B). The nodes in the graph represent co-cited literature and the links between the nodes represent co-citation relations. Large nodes or with red tree rings are either highly cited or exploded. All clustering labels were extracted from the titles of cited articles with a log-likelihood ratio algorithm.
Clustering network analysis can excavate the knowledge structure of the research domain (Chen, 2017). Based on the co-citation state of 106,400 references to articles cited in CiteSpace software, a hierarchical clustering network is generated if the two publications have many similar references and are often homogeneous. The most significant ten clusters extracted from the references of the 2,648 citing articles are shown in Figure 7B. Cluster labels were well-known noun phrases extracted from the title of citing articles using the logarithmic likelihood ratio (LLR) algorithm, including #0 hepatocellular carcinoma, #1 targeted delivery, #2 sorafenib nanoparticle, #3 current status, #4 glycyrrhetinic acid-modified chitosan, #5 enhanced chemoresistant tumor treatment, #6 liver cancer cell invasion, #7 5-fluorouracil nanoparticle, #8 multidrug resistance, #9 anticancer agent (Figure 7B). The number of cluster tags is inversely related to the number of articles per cluster included. A clustering network’s modularity (Q value) indicates the extent to which a network can be divided into clusters. In contrast, the silhouette (S value) is a metric of validation and interpretation of consistency within clusters (Shibata et al., 2008). As shown in Figure 7B, the total Q value was 0.8455, indicating a well-structured network, and each cluster had a weighted mean S value of 0.9191 or higher, suggesting that the cluster quality was highly credible. Moreover, the generic clusters, #0 hepatocellular carcinoma, #6 liver cancer cell invasion, and #3 current status, addressed more challenges and current status in liver cancer. At the same time, two applications focused clusters, #1 targeted delivery, #2 sorafenib nanoparticle, #4 glycyrrhetinic acid-modified chitosan, #7 5-fluorouracil nanoparticle, and #9 anticancer agent, concentrating the application of nanomedicine in liver cancer.
We conducted a timeline view of co-cited references to reveal the research trends and hotspots over time (Figures 8A, B). Cluster #1 has a high concentration of nodes with citation bursts from 2014. Cluster #0 has a sustained period of about 5 years from 2006 to 2011, whereas cluster # 5 is short lived, with an associated period of 5 years from 2008 to 2015. The results showed that clusters #0 and 1 have the largest nodes scattered along the timeline and contain 4 of the 10 most frequently cited references. Besides, it is obvious that the research on 5-fluorouracil nanoparticle (cluster #7) with the size of 21 publications started earlier and relevant studies has a certain interruption period. To further explore the flow of knowledge between clustering networks, we conducted a clustering of dependency analysis of co-cited references (Figure 8C). #0 Hepatocellular carcinoma is built on #7 5-fluorouracil nanoparticle, #3 current status. Meanwhile, #1 targeted delivery, #2 sorafenib nanoparticles, #4 glycyrrhetinic acid-modified chitosan, and #9 anticancer agents provide the basis for #8 multidrug resistance. However, #5 enhanced chemoresistant tumor treatment and #6 liver cancer cell invasion are independent of the two main pathways.

Figure 8. The timeline view of co-citation clusters (A) and (B). The dependency analysis of co-cited references (C).
The author keywords are the core of papers, covering the main topics. In the study of scientific knowledge structure, keywords can accurately identify the research front and hotspots, which is an effective methodology of bibliometric analysis (Yu et al., 2022). The term co-occurrence (Table 5; Figure 9) and bursting keywords analysis (Figure 10) were presented using the VOSviewer and CiteSpace software, showing mutually relevant topics of nanomedicine in liver cancer. A total of 5,581 terms were extracted, among which 300 appeared more than 5 times, and 126 appeared more than 10 times. The density visualization of terms could find high frequency co-occurrence keywords, revealing research hotspots of the nanomedicine in liver cancer. As we can see from Figure 9 and Table 5, hepatocellular carcinoma is the most critical term with 1,061 co-occurrences, followed by nanoparticles, drug delivery, cancer, apoptosis, and therapy.
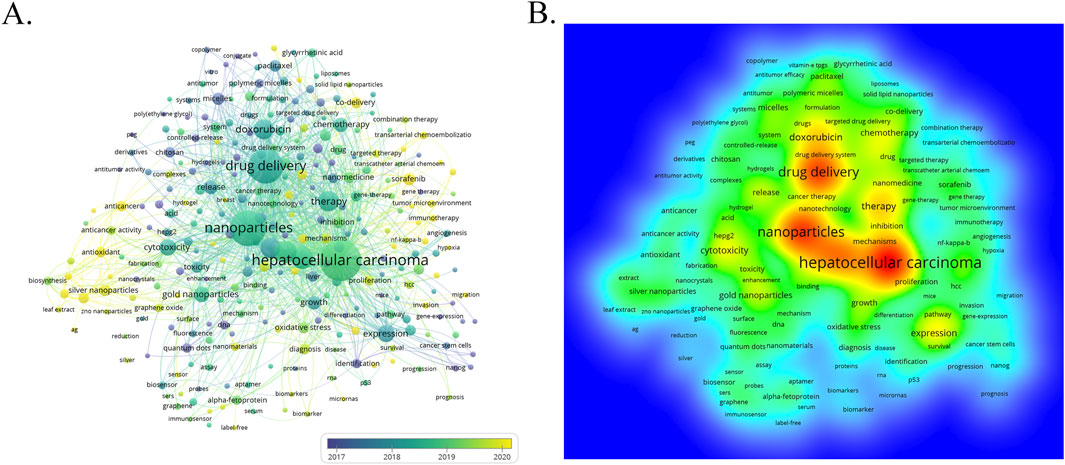
Figure 9. Keyword evolution over time (A) and keyword co-occurrence heat map analysis (B). The color of each keyword indicates the average publication time of articles containing that keyword.
Furthermore, burst detection of keywords contributes to finding keywords that have not yet reached the frequency threshold but may have academic contributions, thereby providing a more comprehensive analysis of hot spots and fronts of the nanomedicine in liver cancer (Zhu et al., 2020). As an essential metric for researching leading-edge topics, CiteSpace detects bursting keywords (Tang et al., 2021). The timeline is represented by a line in blue, and the time span of bursting keywords is shown by the red section of the blue timeline. Figure 10 shows the top 20 keywords with the most robust citation bursts. “Nanocrystals” was the strongest burst keyword in this field from 2004 to 2015 and was followed by “biodistribution”, “particles”, and “in vivo”. The results suggested that studies in recent decades had increasingly focused on the relationships between the nanomaterials and antitumor drugs (e.g., chitosan, selenium nanoparticles, and Vitamin E TPGS), as well as the underlying potential applications.
In this study, we proposed a scientometric analysis of nanomedicine’s knowledge structure and dynamic evolution in liver cancer. The WoSCC database indicated that as of 1 June 2024, 5,630 authors from 8,782 institutions in 297 countries had published 2,648 articles about nanomedicine in liver cancer. The temporal trend, scientific categories, spatial distribution, and author contributions of 2,648 retrieved articles were evaluated using CiteSpace and VOSviewer. Regarding nanomedicine in liver cancer research, we utilized literature co-citation, keyword co-occurrence, and clustering network analysis to identify the research knowledge base, hotspots, and frontiers in each period and define the topic’s evolutionary trajectory. Additionally, we identified the current research frontiers in the field of nanomedicine in liver cancer.
Feng Z et al. included a total of 1,641 literature on the research of nanomaterials in liver cancer (Fan et al., 2024), while we expanded the scope of research to the whole nanomedicine without limiting the time condition, and included a total of 2,648 literature on the research of nanomedicine in liver cancer. Therefore, we consider this study to be more comprehensive and novel. Changing annual output is a vital indicator of how a particular field is developing (Jiang et al., 2022). To address this problem, many researchers turned to the field of nanotechnology. The term was first used by Norio Taniguchi in 1974 (nanotechnology) and again by K. Eric Drexler in 1981 (nanotechnology) (Szczyglewska et al., 2023). The dramatic increase in the number of nanomedicine papers published globally in liver cancer research between 2001 and 2023. Prior to 2010, worldwide papers on nanomedicine in liver cancer research grew incrementally, but the number of these papers has increased dramatically over the past decade. According to the logistic growth model, the global turning point will likely occur in 2025. It has brought nanomedicine to the forefront and has attracted participation and support from research organizations in various countries. Consequently, there has been a progressive increase in research on the relationship between nanomedicines and liver cancer.
The overview of nanomedicine in the liver cancer research domain was initiated by analyzing the contributions of diverse scientific fields and journals. Nanoscience & Nanotechnology was the most prominent category in the field of the nanomedicine in liver cancer. Having the second highest frequency and centrality, the cross-domain of Nanoscience & Nanotechnology was highly comprehensive, indicating a revolution in multidisciplinary research on the nanomedicine in liver cancer. However, Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology, Electrochemistry, Biophysics, and Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging were also breakthrough points with relatively high centrality. Additionally, the dual-map overlay of journals suggested a strong predominant pattern in knowledge flow between publications and that most of the literature on nanomedicine in liver cancer was published in a relatively limited set of journals (Shen Z. et al., 2022; Wang C. et al., 2022). Four major citation trajectories, indicating that nanomedicine-related research in liver cancer favors translational medicine and cross-disciplinary-oriented categories. Journal and cited journal analyses can provide a significant amount of information, which can assist researchers in choosing appropriate journals for submission. Our study showed that nearly two-fifths of the papers published in the top ten most active journals covered the topic of nanomedicine in liver cancer, indicating that the distribution of the literature is relatively concentrated. International Journal of Nanomedicine (90 publications, IF: 6.60) published the most papers, while Biomaterials received the most significant number of citations. Both were journals concerning nanomedicine, consistent with the dual-map overlay of journals. Additionally, it can be concluded that the study of the clinical translation of nanomedicine in liver cancer is a current hot topic and a direction for future research.
Regarding the geographic distribution of countries, regions, and institutions, China, Unite States, and India were among the top 3 most productive countries. South Korea was the first country to carry out nanomedicine studies in liver cancer, followed by China, the United States, Italy, Germany, and India; these countries were among the ten countries with the highest production. In a network structure, the betweenness centrality is typically applied to measure the significance of the bridge function of nodes (Iacobucci et al., 2018). Germany and the United States had the highest betweenness centrality, which represented one of the critical bridges in national cooperation networks worldwide. Interestingly, China ranked first in the literature published. However, the betweenness centrality was just 0.14, indicating that although the number of publications in China has grown, high-quality articles still need to be available. China accounted for about 60% of those institutions in the top ten. The Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Fudan University, and the Jilin University published the most, and we found considerable collaboration and significant betweenness centrality among these institutions, indicating their substantial contribution to nanomedicine in liver cancer-related research.
Emphasizing the influential authors through a comprehensive analysis of the authors of many citing or cited papers in a specific domain can help researchers identify potential collaborators and provide further guidance and direction (Huang et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2024). Shao Dan (15 papers) published the most papers, while Jemal A (times cited 271) had the most co-citations. Additionally, we identified two scholars, Li Jing, and Zhang Yu, who were not only the top 10 prolific authors but were also the top 10 co-cited authors, which implied that all three authors had made significant contributions in the field of the nanomedicine in liver cancer. In 2016, Dan Shao and his colleagues designed multifunctional Janus nanocomposites, which are characterized by magnetic Fe3O4 in the head and mesoporous SiO2 in the body, and contain doxorubicin (DOX) as a “nanobullet” (M-MSNs-DOX). It is found that under the effect of the magnetic field, M-MSNs-DOX can selectively inhibit the growth of cancer cells instead of inhibiting the growth of normal cells in the human body, utilizing nanotechnology to treat liver cancer safely and efficiently (Shao et al., 2016). Hussein Mohd Zobir has contributed significantly to the development of therapeutics and theranostic nanodrug delivery systems for liver cancer (Ruman et al., 2020). The nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems (NDDS) may provide a novel treatment approach to deliver drugs selectively to cancerous regions and reduce the chance of nonspecific delivery to healthy tissues, thereby reducing drug side effects (Zhang et al., 2019). Tang, et al identified that compared with free sorafenib (SFB), the SFB-loaded biodegradable d-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1,000 succinate polycaprolactone nanoparticles (TPGS-b-PCL NPs) were more efficiently inhibited the growth of HepG2 cells and retarded tumor growth in HCC xenograft models (Yang T. et al., 2019). It is expected that these pioneering academic scientists will continue to have an impact on the future development of nanomedicine in liver cancer and encourage young researchers to enter them in the clinical translation of nanomedicine in liver cancer.
Co-citation analysis is a methodology that reveals intrinsic patterns that are considered to be the basis of research in a particular field (Yang L. et al., 2019). This suggests that scientists are paying close attention to this literature, which may highlight the evolving changes and emerging trends in nanomedicine in liver cancer research. The co-citation analysis for the nanomedicine in liver cancer was mainly focused on ten research areas in this case: “hepatocellular carcinoma”, “targeted delivery”, “sorafenib nanoparticles”, “current status”, “glycyrrhetinic acid-modified chitosan”, “enhanced chemoresistant tumor treatment”, “liver cancer cell invasion”, “5-fluorouracil nanoparticle”, “multidrug resistance”, and “anticancer agents”. Early co-citation clustering in the literature focused on the nanomaterials research, e.g., #2 sorafenib nanoparticle, #4 glycyrrhetinic acid-modified chitosan, and #7 5-fluorouracil nanoparticle. Caputo TM et al. developed a biodegradable and biocompatible amino-polymeric Poly (D, L-Lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticle loaded with sorafenib by an emulsion-solvent evaporation process. Their high stability confirmed the enhanced cytotoxic effect of the nanoparticles on liver cancer cells, sustained release properties and rapid cellular uptake (Caputo et al., 2023). Chitosan nanoparticles are biodegradable cationic polysaccharide polymers synthesized by partial deacetylation of chitin (Hong et al., 2017). Many studies have focused on chitosan nanoparticles applied to liver cancer drug delivery for therapeutic purposes. Cheng et al, evaluated chitosan-coated 5-fluorouracil nanocarriers in hepatocellular carcinoma where it had promising inhibitory effects on liver cancer (Cheng et al., 2013). Loutfy et al. also synthesized chitosan nanoparticles for in vitro human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model evaluation (Loutfy et al., 2016). They found that chitosan nanoparticles had better cytotoxic effects on liver cancer cells and suggested the chitosan nanoparticles are suitable as a drug delivery option for liver cancer. Besides, other nanoparticles such as micelles (Hanafy et al., 2018), liposome (Quagliariello et al., 2019), dendrimer (Noriega-Luna et al., 2014), graphene oxide-based nanocarriers (Pan et al., 2016), polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) nanoparticles (Danhier et al., 2012), carbon nanotubes (Ravi Kiran et al., 2020), superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles (Depalo et al., 2017), are also used in the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer.
Co-citation determined the knowledge base and clustering evolution, keyword co-occurrence analysis revealed the research frontiers and hotspots; keyword clustering analysis showed the knowledge structure, and the timeline view visualized the hotspot evolution of the keywords. All these keywords in VOSviewer are labeled with a different color according to the average year of publication. The earlier keywords are represented by blue, while the later keywords are represented by yellow. The keywords of “hepatocellular carcinoma”, “nanoparticles”, “drug delivery” and “therapy” are the main topics in the early stage. The keywords of “silver nanoparticles”, “antioxidant”, “sorafenib” and “mechanisms” exhibit relatively recent average publication years, demonstrating that this topic is potentially of great interest and concern to clinicians and scientists.
Despite encouraging results in preclinical and clinical trials, the successful clinical translation of nanomedicine for liver cancer treatment still faces several obstacles: (1) The behavior of nanomaterials is not fully understood in vivo, which seriously hinders the design and optimization of nanomedicines. Further study of the behavior of nanomedicines will help to better evaluate and further improve the bioavailability, biocompatibility and pharmacokinetics of nanomedicines, thereby improving anticancer efficacy and development efficiency; (2) At present, the loading efficiency of most nanomedicines is moderate, which greatly limits the efficacy of nanomedicines. This challenge can be solved by improving existing nanocarriers or preparing new nanocarriers; (3) The performance of targeted localization of nanomaterials is far from satisfactory and needs further improvement. This problem can be solved by developing new ligands for known targets or finding new targets in liver cancer biomarkers; (4) The characterization and evaluation of nanomedicine has always been a test, which requires a revolutionary means to replace the current evaluation; (5) In the promotion of nanomedicine, industrial manufacturing is still a difficult task. The large-scale production of nanomedicines remains very difficult and requires the collaborative efforts of nanotechnology experts, engineers, oncologists and chemists to overcome this challenge by developing new technologies; Despite these challenges, we believe that these problems will be adequately addressed in the future through multidisciplinary collaboration of medicine, materials science, biology, physics, chemistry, as well as engineering. A new era is awaiting us in which nanomedicine will become an important modality for liver cancer treatment.
The bibliometric analysis and visualization provide some insight into the structural and temporal dynamics of the field, but this study still has some limitations. The raw data was retrieved from the WoSCC database only, and may miss some relevant records published in other databases (e.g., Google Scholar or PubMed). However, WoSCC data represent to some extent the majority of studies and provide comprehensive and detailed information for references (Campbell et al., 1988; Fang et al., 2023). Also, WoSCC is the most widely utilized database for bibliometric analysis (Ling et al., 2023). In addition, given the limitations of literature types, terms, and languages, our retrieval strategy might not identify all relevant references; therefore, our findings needed to be more comprehensive. However, our study has thoroughly analyzed the current status of the nanomedicine in liver cancer research and its progress between 2000 and 2024, contributing to development of future research directions.
The application of nanomedicines in the diagnostic and therapeutic process of liver cancer has become a focus of attention. The bibliometric analysis presents an objectively quantifiable method for understanding the roles and molecular mechanisms and evaluating trends and frontiers of the nanomedicine in liver cancer. Publications in this field have increased rapidly since 2011, and there is strong international scientific cooperation, but more collaborations may be necessary among researchers. Many articles have been published in international core journals, showing great prominence. Nanoscience & Nanotechnology, Pharmacology & Pharmacy, and Chemistry & Multidisciplinary will highlight future research. This study could provide important insights for researchers into the structural and dynamic evolution of nanomedicine in liver cancer.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
SL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. DC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. BS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. ZK: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. GY: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants to DPC from the Key R&D Program of Hebei Province (223777101D).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Bashir, M. F. (2022). Oil price shocks, stock market returns, and volatility spillovers: a bibliometric analysis and its implications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 29 (16), 22809–22828. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-18314-4
Bettencourt, L. M., and Kaur, J. (2011). Evolution and structure of sustainability science. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (49), 19540–19545. doi:10.1073/pnas.1102712108
Campbell, C. T., Harris, R. C., Cook, M. H., and Reines, H. D. (1988). A new device for emergency percutaneous transtracheal ventilation in partial and complete airway obstruction. Ann. Emerg. Med. 17 (9), 927–931. doi:10.1016/s0196-0644(88)80674-7
Can, G., Wang, R., Zhang, L., and Yue, C. (2021). Visualization analysis of CRISPR gene-editing knowledge map based on citespace. Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 48 (6), 705–720. doi:10.1134/S1062359021060108
Caputo, T. M., Cusano, A. M., Principe, S., Cicatiello, P., Celetti, G., Aliberti, A., et al. (2023). Sorafenib-loaded PLGA carriers for enhanced drug delivery and cellular uptake in liver cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomedicine 18, 4121–4142. doi:10.2147/IJN.S415968
Chen, C. (2004). Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101 (Suppl. 1), 5303–5310. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307513100
Chen, C. (2017). Science mapping: a systematic review of the literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2, 1–40. doi:10.1515/jdis-2017-0006
Chen, C., Dubin, R., and Kim, M. C. (2014). Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: a scientometrics update (2000 - 2014). Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 14 (9), 1295–1317. doi:10.1517/14712598.2014.920813
Chen, C., Hu, Z., Liu, S., and Tseng, H. (2012). Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometrics analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 12 (5), 593–608. doi:10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
Chen, C., and Leydesdorff, L. (2014). Patterns of connections and movements in dual-map overlays: a new method of publication portfolio analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 65, 334–351. doi:10.1002/asi.22968
Chen, C., Lou, Y., Li, X. Y., Lv, Z. T., Zhang, L. Q., and Mao, W. (2020a). Mapping current research and identifying hotspots on mesenchymal stem cells in cardiovascular disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11 (1), 498. doi:10.1186/s13287-020-02009-7
Chen, L., Wei, Q., Li, J., Liao, D., and Feng, D. (2020b). A scientometrics visualization analysis for global toxicology and pharmacology research of natural products from 1962 to 2018. Phytomedicine 68, 153190. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153190
Cheng, M., Gao, X., Wang, Y., Chen, H., He, B., Xu, H., et al. (2013). Synthesis of glycyrrhetinic acid-modified chitosan 5-fluorouracil nanoparticles and its inhibition of liver cancer characteristics in vitro and in vivo. Mar. Drugs 11 (9), 3517–3536. doi:10.3390/md11093517
Danhier, F., Ansorena, E., Silva, J. M., Coco, R., Le Breton, A., and Preat, V. (2012). PLGA-based nanoparticles: an overview of biomedical applications. J. Control Release 161 (2), 505–522. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043
Depalo, N., Iacobazzi, R. M., Valente, G., Arduino, I., Villa, S., Canepa, F., et al. (2017). Sorafenib delivery nanoplatform based on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles magnetically targets hepatocellular carcinoma. Nano Res. 10 (7), 2431–2448. doi:10.1007/s12274-017-1444-3
Donne, R., and Lujambio, A. (2023). The liver cancer immune microenvironment: therapeutic implications for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 77 (5), 1773–1796. doi:10.1002/hep.32740
Egghe, L. (2006). Theory and practise of the g-index. Scientometrics 69 (1), 131–152. doi:10.1007/s11192-006-0144-7
Fan, Y., Xiao, H., Wang, Y., Wang, S., and Sun, H. (2024). Global research on nanomaterials for liver cancer from 2004 to 2023: a bibliometric and visual analysis. Discov. Oncol. 15 (1), 838. doi:10.1007/s12672-024-01735-1
Fang, H., Xu, J., Ma, H., Liu, J., Xing, E., Cheng, Y. Y., et al. (2023). Functional materials of 3D bioprinting for wound dressings and skin tissue engineering applications: a review. Int. J. Bioprint 9 (5), 757. doi:10.18063/ijb.757
Fang, J., Pan, L., Gu, Q. X., Juengpanich, S., Zheng, J. H., Tong, C. H., et al. (2020). Scientometric analysis of mTOR signaling pathway in liver disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 8 (4), 93. doi:10.21037/atm.2019.12.110
Feng, Z., Hao, Z., Zhao, B., Feng, Z., Huang, D., and Huo, J. (2024). Fluorescent probe applications and prospects in gastrointestinal cancer: a bibliometric analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 50 (10), 108565. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2024.108565
Garcia-Fuentes, W., Espinoza-Rodriguez, L., Munive-Degregori, A., Mauricio-Vilchez, C., Guerrero, M. E., Pacheco-Mendoza, J., et al. (2022). A 10-year scientometrics analysis of brain tumors treated with gamma knife radiosurgery: visualization, characteristics, and scientific trends. J. Cancer Epidemiol. 2022, 7136868. doi:10.1155/2022/7136868
Goerlandt, F., Li, J., and Reniers, G. (2022). The landscape of safety management systems research: a scientometrics analysis. J. Saf. Sci. Resil. 3 (3), 189–208. doi:10.1016/j.jnlssr.2022.02.003
Haddaway, N. R., Bernes, C., Jonsson, B. G., and Hedlund, K. (2016). The benefits of systematic mapping to evidence-based environmental management. Ambio 45 (5), 613–620. doi:10.1007/s13280-016-0773-x
Halbus, A. F., Horozov, T. S., and Paunov, V. N. (2017). Colloid particle formulations for antimicrobial applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 249, 134–148. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2017.05.012
Hanafy, N. A. N., Quarta, A., Ferraro, M. M., Dini, L., Nobile, C., De Giorgi, M. L., et al. (2018). Polymeric nano-micelles as novel cargo-carriers for LY2157299 liver cancer cells delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (3), 748. doi:10.3390/ijms19030748
Hong, S. C., Yoo, S. Y., Kim, H., and Lee, J. (2017). Chitosan-based multifunctional platforms for local delivery of therapeutics. Mar. Drugs 15 (3), 60. doi:10.3390/md15030060
Huang, W., Liu, S., Zhang, T., Wu, H., and Pu, S. (2024). Bibliometric analysis and systematic review of electrochemical methods for environmental remediation. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 144, 113–136. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2023.08.003
Huang, X., Yang, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, R., Fan, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). A bibliometric analysis based on Web of science: current perspectives and potential trends of SMAD7 in oncology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 712732. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.712732
Iacobucci, D., McBride, R., Popovich, D., and Rouziou, M. (2018). Confidence intervals for assessing sizes of social network centralities.
Jiang, H., Li, Y., Liu, Y., and Dong, W. (2022). Bibliometric analysis of N6-methyladenosine in cancer: landscapes, highlights and trending topics. Future Oncol. 18 (17), 2141–2153. doi:10.2217/fon-2022-0086
Kleinberg, J. (2003). Bursty and hierarchical structure in streams. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 7 (4), 373–397. doi:10.1023/A:1024940629314
Landis, J. R., and Koch, G. G. (1977). The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33 (1), 159–174. doi:10.2307/2529310
Leydesdorff, L., Carley, S., and Rafols, I. (2013). Global maps of science based on the new Web-of-Science categories. Scientometrics 94 (2), 589–593. doi:10.1007/s11192-012-0784-8
Leydesdorff, L., Comins, J. A., Sorensen, A. A., Bornmann, L., and Hellsten, I. (2016). Cited references and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) as two different knowledge representations: clustering and mappings at the paper level. Scientometrics 109 (3), 2077–2091. doi:10.1007/s11192-016-2119-7
Ling, L. X., Ouyang, Y., and Hu, Y. (2023). Research trends on nanomaterials in gastric cancer: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2023. J. Nanobiotechnology 21 (1), 248. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02033-8
Liu, H., and Webster, T. J. (2007). Nanomedicine for implants: a review of studies and necessary experimental tools. Biomaterials 28 (2), 354–369. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.08.049
Loutfy, S. A., Alam El-Din, H. M., Elberry, M. H., Allam, N. G., Hasanin, M. T. M., and Abdellah, A. M. (2016). Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxic evaluation of chitosan nanoparticles: in vitro liver cancer model. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7 (3), 035008. doi:10.1088/2043-6262/7/3/035008
Ma, D., Guan, B., Song, L., Liu, Q., Fan, Y., Zhao, L., et al. (2021a). A bibliometric analysis of exosomes in cardiovascular diseases from 2001 to 2021. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 8, 734514. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.734514
Ma, D., Yang, B., Guan, B., Song, L., Liu, Q., Fan, Y., et al. (2021b). A bibliometric analysis of pyroptosis from 2001 to 2021. Front. Immunol. 12, 731933. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.731933
Mongeon, P., and Paul-Hus, A. (2015). The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 106, 213–228. doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5
Mongeon, P., and Paul-Hus, A. (2016). The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 106 (1), 213–228. doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5
Nakagawa, S., Samarasinghe, G., Haddaway, N. R., Westgate, M. J., O'Dea, R. E., Noble, D. W. A., et al. (2019). Research weaving: visualizing the future of research synthesis. Trends Ecol. Evol. 34 (3), 224–238. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2018.11.007
Noriega-Luna, B., Godínez, L., Rodriguez, F., Rodríguez-García, A., Larrea, G., Sosa-Ferreyra, C.-F., et al. (2014). Applications of dendrimers in drug delivery agents, diagnosis, therapy, and detection. J. Nanomater. 2014, 19. doi:10.1155/2014/507273
Pan, Q., Lv, Y., Williams, G. R., Tao, L., Yang, H., Li, H., et al. (2016). Lactobionic acid and carboxymethyl chitosan functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposites as targeted anticancer drug delivery systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 151, 812–820. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.024
Perko, N., and Mousa, S. A. (2022). Management of pancreatic cancer and its microenvironment: potential impact of nano-targeting. Cancers (Basel) 14 (12), 2879. doi:10.3390/cancers14122879
Qiu, Y., Wu, Z., Chen, Y., Liao, J., Zhang, Q., Wang, Q., et al. (2023). Nano ultrasound contrast agent for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy and enhanced immunotherapy against liver cancer and metastasis. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10 (21), e2300878. doi:10.1002/advs.202300878
Quagliariello, V., Masarone, M., Armenia, E., Giudice, A., Barbarisi, M., Caraglia, M., et al. (2019). Chitosan-coated liposomes loaded with butyric acid demonstrate anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Oncol. Rep. 41 (3), 1476–1486. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6932
Ravi Kiran, A. V. V. V., Kusuma Kumari, G., and Krishnamurthy, P. T. (2020). Carbon nanotubes in drug delivery: focus on anticancer therapies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 59, 101892. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101892
Ruman, U., Fakurazi, S., Masarudin, M. J., and Hussein, M. Z. (2020). Nanocarrier-based therapeutics and theranostics drug delivery systems for next generation of liver cancer nanodrug modalities. Int. J. Nanomedicine 15, 1437–1456. doi:10.2147/IJN.S236927
Sabe, M., Pillinger, T., Kaiser, S., Chen, C., Taipale, H., Tanskanen, A., et al. (2022). Half a century of research on antipsychotics and schizophrenia: a scientometrics study of hotspots, nodes, bursts, and trends. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 136, 104608. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104608
Shao, D., Li, J., Zheng, X., Pan, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., et al. (2016). Janus “nano-bullets” for magnetic targeting liver cancer chemotherapy. Biomaterials 100, 118–133. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.05.030
Shen, J., Shen, H., Ke, L., Chen, J., Dang, X., Liu, B., et al. (2022a). Knowledge mapping of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a bibliometric study. Front. Immunol. 13, 815575. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.815575
Shen, Z., Wu, H., Chen, Z., Hu, J., Pan, J., Kong, J., et al. (2022b). The global research of artificial intelligence on prostate cancer: a 22-year bibliometric analysis. Front. Oncol. 12, 843735. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.843735
Shibata, N., Kajikawa, Y., Takeda, Y., and Matsushima, K. (2008). Detecting emerging research fronts based on topological measures in citation networks of scientific publications. Technovation 28 (11), 758–775. doi:10.1016/j.technovation.2008.03.009
Small, H. (1973). Co-citation in the scientific literature: a new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 24, 265–269. doi:10.1002/asi.4630240406
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Szczyglewska, P., Feliczak-Guzik, A., and Nowak, I. (2023). Nanotechnology-general aspects: a chemical reduction approach to the synthesis of nanoparticles. Molecules 28 (13), 4932. doi:10.3390/molecules28134932
Tang, C., Liu, D., Fan, Y., Yu, J., Li, C., Su, J., et al. (2021). Visualization and bibliometric analysis of cAMP signaling system research trends and hotspots in cancer. J. Cancer 12 (2), 358–370. doi:10.7150/jca.47158
Upaganlawar, A., Polshettiwar, S., Raut, S., Tagalpallewar, A., and Pande, V. (2022). Effective cancer management: inimitable role of phytochemical based nano- formulations. Curr. Drug Metab. 23 (11), 869–881. doi:10.2174/1389200223666220905162245
van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84 (2), 523–538. doi:10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Wang, C., Guan, D., Li, Z., Yang, Y., and Yang, K. (2022a). Emerging trends and frontier research on recurrent implantation failure: a bibliometric analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 10 (6), 307. doi:10.21037/atm-22-703
Wang, Y., Jiang, L., Li, B., and Zhao, Y. (2022b). Management of chronic myeloid leukemia and pregnancy: a bibliometric analysis (2000-2020). Front. Oncol. 12, 826703. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.826703
Xue, J., Reniers, G., Li, J., Yang, M., Wu, C., and van Gelder, P. (2021). A bibliometric and visualized overview for the evolution of process safety and environmental protection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (11), 5985. doi:10.3390/ijerph18115985
Yang, H., Niu, S., Guo, M., and Xue, Y. (2024). Applications of 3D organoids in toxicological studies: a comprehensive analysis based on bibliometrics and advances in toxicological mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 98, 2309–2330. doi:10.1007/s00204-024-03777-4
Yang, L., Han, L., and Liu, N. (2019a). A new approach to journal co-citation matrix construction based on the number of co-cited articles in journals. Scientometrics 120, 507–517. doi:10.1007/s11192-019-03141-9
Yang, T., Lan, Y., Cao, M., Ma, X., Cao, A., Sun, Y., et al. (2019b). Glycyrrhetinic acid-conjugated polymeric prodrug micelles co-delivered with doxorubicin as combination therapy treatment for liver cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 175, 106–115. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.11.082
Yu, N., Wang, R., Liu, B., and Zhang, L. (2022). Bibliometric and visual analysis on metabolomics in coronary artery disease research. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 9, 804463. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.804463
Zhang, F., Jia, Y., Zheng, X., Shao, D., Zhao, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2019). Janus nanocarrier-based co-delivery of doxorubicin and berberine weakens chemotherapy-exacerbated hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Acta Biomater. 100, 352–364. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.09.034
Zhang, J., Song, L., Xu, L., Fan, Y., Wang, T., Tian, W., et al. (2021). Knowledge domain and emerging trends in ferroptosis research: a bibliometric and knowledge-map analysis. Front. Oncol. 11, 686726. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.686726
Zhang, X. L., Zheng, Y., Xia, M. L., Wu, Y. N., Liu, X. J., Xie, S. K., et al. (2020). Knowledge domain and emerging trends in vinegar research: a bibliometric review of the literature from WoSCC. Foods 9 (2), 166. doi:10.3390/foods9020166
Zhu, X., Hu, J., Deng, S., Tan, Y., Qiu, C., Zhang, M., et al. (2020). Bibliometric and visual analysis of research on the links between the gut microbiota and depression from 1999 to 2019. Front. Psychiatry 11, 587670. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.587670
Keywords: nanomedicine, liver cancer, bibliometric analysis, visualization, citespace, VOSviewer
Citation: Li S, Cui D, Shao B, Kang Z and Yan G (2025) Knowledge structure and dynamic evolution of nanomedicine in liver cancer research: a scientometric analysis and visualization. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1509259. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1509259
Received: 10 October 2024; Accepted: 07 February 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Sujan K. Mondal, Michigan State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Tarik Aanniz, Mohammed V University in Rabat, MoroccoCopyright © 2025 Li, Cui, Shao, Kang and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoqiang Yan, eWFuZ3VvcWlhbmdAamx1LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.