
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol., 26 March 2025
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1508290
 Wenjie Dong1,2†
Wenjie Dong1,2† Yao Mou1,2†
Yao Mou1,2† Qiuyu Li1,2†
Qiuyu Li1,2† Min Li1,2
Min Li1,2 Hao Su1,2
Hao Su1,2 Longyang Jiang1,2
Longyang Jiang1,2 Jie Zhou1,2
Jie Zhou1,2 Kun Tu1,2
Kun Tu1,2 Xuping Yang1,2
Xuping Yang1,2 Yuexi Huang3
Yuexi Huang3 Changjing Xu1
Changjing Xu1 Liaoyun Zhang4*
Liaoyun Zhang4* Yilan Huang1,2*
Yilan Huang1,2*Background: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is the most common cause of acute liver injury. Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. (AR) and its polysaccharide fractions (ARPs) have been shown to have effective therapeutic effects with minimal side effects on a wide range of diseases including hepatopathy. This study aims to determine the therapeutic effects of ARPs on acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver injury and to explore the mechanistic pathways involved.
Methods: C57BL/6J male mice at 8 weeks were used to construct a model of APAP-induced liver injury. The acute hepatic injury was induced by oral administration of APAP (300 mg/kg) before 16 h fasting. For therapeutic experiment, mice were gavaged with the water extract of AR (AR.WE) or the purified ARPs before and after APAP administration. Biochemical analyses, ELISA analyses, H&E staining, RT-PCR, and Quantitative proteomic analysis were used to investigate the effects and mechanisms of AR on DILI.
Results: Both AR.WE. and the purified ARPs treatment reduced APAP-induced liver injury, decreased hepatic glutathione and TNF-α levels, alleviated oxidative stress and inflammation. Quantitative proteomic analysis revealed that ARPs downregulated the protein levels involved in apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, necroptosis, while upregulated the protein levels involved in autophagy. These protective effects of ARPs are possibly related to the downregulation of vATPase activity and thus participating in the autophagic process and ferroptosis.
Conclusion: ARPs can protect mice against APAP-induced liver injury, alleviate oxidative stress and inflammation. Our study reveals a potential therapeutic effect for ARPs in protecting APAP-induced liver injury.
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is the most common cause of acute liver injury (Kumachev and Wu, 2021). In the USA, more than 50% of all cases of acute liver failure are attributed to DILI, among which idiosyncratic DILI accounts for over 10% of the reported cases (Li et al., 2022). Acetaminophen (APAP) is one of the most commonly used antipyretic and analgesic drugs (Yan et al., 2018) and the Food and Drug Administration has recommended a maximum daily dose of 4 g per day for adults (Orandi et al., 2023). Today, overdose of APAP is the leading cause of pharmacological acute liver injury worldwide (Lee, 2017; Reuben et al., 2016). In the body, most of the APAP is metabolized to nontoxic compounds that are ultimately excreted out of the body via the kidneys or bile, and no more than 10% of APAP is activated by cytochrome P450 enzymes (mainly CYP2E1) to an active product (n-acetyl-p-benzoquinone-imine (NAPQI)) (Chiew et al., 2023; McGill et al., 2012), which binds to glutathione (GSH) to deplete the amount of glutathione in the liver (Cai et al., 2022). In addition, binding of NAPQI to intracellular proteins in the hepatocyte leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and ultimately to hepatocyte necrosis (Yan et al., 2018). To date, n-acetylcysteine (NAC) is the only antidote used for APAP poisoning. However, its therapeutic timeframe is narrow (it is effective only within 12 h of APAP poisoning) (Chowdhury et al., 2020; Licata et al., 2022). Therefore, there is an urgent need to find new targets as well as to develop new drugs for clinical treatment to improve survival.
In recent years, with the in-depth study of traditional Chinese medicines, some of them have been found to have detoxifying and hepatoprotective effects, provide unique advantages in the treatment of liver injury. Zhou et al. found that baicalein could ameliorate APAP-induced liver injury by a mechanism involving the Jak2/Stat3 and MAPK signaling pathways (Zhou et al., 2018). Meanwhile, Jing et al. found that celastrol-loaded biomimetic nanodrug ameliorated APAP-induced liver injury by modulating macrophage polarization (Zheng et al., 2023). In addition, Zhong et al. found that ginsenoside Rc treatment prevented inflammatory responses induced by APAP and oxidative stress in primary mouse hepatocytes and corresponding changes in related genes (Zhong et al., 2022). Recently, in a comprehensive review of clinical trials of natural products as hepatoprotective agents, it was noted that Chinese herbal medicines such as berberine, turmeric, schizandra, and silymarin, as well as natural products such as artichoke, chlorella, and spirulina, improved some measures of liver outcomes after treatment of liver injury (Służały et al., 2024). Therefore, there is a need to explore more potential agents for hepatic injury treatment, and natural products derived from traditional Chinese herbal medicines may provide alternative treatment options for liver injury.
Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. (AR), a traditional herbal medicine belonging to the family of Orchidaceae, is widely distributed in Southeast Asia (Cui et al., 2023). The polysaccharides of AR polysaccharides (ARPs) are the main water-soluble constituents of the plant, which have various pharmacological activities such as improvement of immunity, glycemic control, blood circulation, and anti-oxidation (Qiu et al., 2023). Previously, our research group found that the ARPs treatment can inhibit hepatic lipid deposition and liver steatosis, increase fatty acid oxidation, thereby improving liver lipid metabolism in diet-induced fatty liver (Fu et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2022). Similarly, Huang et al. found that AR oral liquid exerted a protective effect against alcoholic liver injury in rats by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory infiltration (Huang et al., 2023). In addition to this, it has been found that ARPs can reduce serum ALT and AST by decreasing oxidative stress and inhibit the production of hepatic malondialdehyde in a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic injury (Yang et al., 2017). However, whether AR is effective against acute liver injury caused by acetaminophen is less clear. In the present study, we found that aqueous extracts of AR and its polysaccharide fractions ARPs has preventive and therapeutic effects on acute liver injury caused by APAP, the hepatoprotective effect of this herb is at least partially connected with hepatocyte autophagy.
Medicinal herbs of AR was purchased from Sichuan Tianzhi Co. The extraction method was performed according to the previous study of our research group (Fu et al., 2022). Briefly, AR.WE was prepared with distilled water (1:50, w/v), and the ARPs fractions were collected by water extraction and alcohol precipitation. The polysaccharide content was determined by the phenol-sulfuric acid method (sulfuric acid: phenol: polysaccharide = 5:1:2). Concentrated sulfuric acid (95%) was added and left in a water bath at 100°C for 10 min and the absorbance was measured at 490 nm. Finally, for further study, the precipitate was washed with distilled water and freeze-dried. The ARPs fractions were identified by High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, United States) and separated on a Shiseido C18 column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm, pore size). The molecular weights of the fractions were determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) on a Viscotek GPCmax VE2001 (Malvern Instruments, UK) chromatograph.
C57BL/6J male mice, 6–8 weeks old were purchased from HFK Biological Technology Co. Ltd, and all mice were housed in standard procedures in the Animal Experiment Center of Southwest Medical University. They were kept in the Animal Experiment Center of Southwest Medical University with 12 h of light and dark cycles, 20°C–25°C, 50%–70% humidity, and free access to food and water. For ALIL model construction, APAP was dissolved in lukewarm water at 50°C and used as it was prepared. In this study, the drug was administered by gavage. In the prevention experiment, a total of 18 C57BL/6J mice were gavaged with AR.WE (250 mg/kg) (n = 6) or ARPs (250 mg/kg) (n = 6) for three consecutive days, and on the last day, the mice were fasted for 16 h and then given 300 mg/kg APAP to induce acute liver injury. In the treatment experiments, mice were gavaged with 300 mg/kg APAP to induce acute liver injury after 16 h of fasting. One hour later, mice were gavaged with AR.WE. (250 mg/kg) (n = 6). Ten hours after administration, mice were anaesthetised with isoflurane and blood and liver were taken for testing. All experimental designs were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Animal Experiment Center of Southwest Medical University.
HepG2 cells were cultured using medium containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin and were incubated at 37°C in an incubator containing 5% CO2. After pretreatment with ARPs (0.5 μg/mL and 1 μg/mL) for 1 h, APAP (2.5 mM) was given for stimulation for 24 h before subsequent experiments.
Blood was taken from mice after anesthesia and execution, and whole blood samples were centrifuged at 4°C at 6,000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was taken in a new tube. Next, the supernatant was centrifuged again at 4°C at 6,000 rpm for 10 min to remove impurities, and then plasma was collected. Plasma was stored in a refrigerator at 80°C and assayed with ALT and AST kits (Zhongsheng Technologies, China). 200 μL of assay solution was added to 5 µL of serum/standard/PBS (blank control) and immediately subjected to enzyme kinetic assay at 37°C.
The surface of mouse liver was washed with PBS, then added with saline homogenate, centrifuged at 4°C, 4,000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was taken for measurement. The GSH content in the supernatant was detected using a GSH kit (Nanjing Jiancheng, China).
The surface of mouse liver was washed with PBS, then added with saline homogenization, centrifuged at 4°C, 4000rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was taken for measurement. The SOD content in the supernatant was detected by using SOD kit (Nanjing Jiancheng, China).
The same leaf of mouse liver was taken and immediately fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, then the dehydrated liver tissue was embedded in paraffin, and the tissue wax block was cut into sections of about 4 μm thickness. Each section was dewaxed, rehydrated and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Microscope equipped with a DFC350FX digital camera (Leica, Milano, Leica) was used to observe the tissue morphology.
Whole blood samples were centrifuged at 4°C, 6,000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was taken in a new tube next, and the supernatant was centrifuged again at 4°C, 6,000 rpm for 10 min to remove impurities, and then plasma was collected. The plasma was stored in a refrigerator at 80°C, and the concentration levels of serum IL-6, TNF-α (ml002095, mlbio, China) were determined using ELISA kits according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Add 10 µL of biotin labelled antibody and 50 µL of enzyme reagent to 40 µL of serum/standard/PBS. Warm bath at 37°C for 30 min and then washed with washing solution. Finally the absorbance was measured after adding the colour developer.
Total RNA from liver and HepG2 cells were extracted using TRIzol reagent (Vazyme, Nanjing, China), and 1,000 ng of RNA was reverse transcribed to complementary DNA using a PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (Takara RR037A). 1,000 ng of RNA was extracted using SYBR® Green Realtime PCR Master Mix (Novizan, Nanjing, China) was used to perform real-time quantitative PCR on a Bio-Rad CFX ConnectTM Real-Time system (Bio-Rad, United States). The following procedure was used: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, denaturation at 95°C for 20 s, annealing at 60°C for 20 s, and extension at 72°C for 20 s, for a total of 39 cycles. The relative gene expression levels were assessed using the 2−ΔΔCT method with 18s or GAPDH as control. Primer sequences are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
Liver samples were first grinded by liquid nitrogen and then the powder was transferred to a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube and sonicated three times on ice, using a high intensity ultrasonic processor in a lysis buffer (8M urea including 1mM PMSF, 2 mM EDTA). Then, the remaining debris was removed by centrifugation at 15,000 g at 4°C for 10 min. Finally, the protein concentration was determined with a BCA kit according to the instructions of the manufacturer.
Equal amount of proteins from each sample were used for tryptic digestion. Add 8M urea to 200ul to the supernatants, then reduced with 10 mM DTT for 45 min at 37°C and alkylated with 50 mM iodoacetamide (IAM) for 15 min in a dark room at room temperature. 4×volume of chilled acetone was added and precipitated at −20°C for 2 h. After centrifugation, the protein precipitate was air-dried and resuspended in 200ul of 25 mM ammonium bicarbonate solution and 3 μL of trypsin (Promega) and digested overnight at 37°C. After digestion, peptides were desalted using C18 Cartridge followed by drying with Vacuum concentration meter, concentrated by vacuum centrifugation and redissolved in 0.1% (v/V) formic acid.
LC-MS/MS analysis was performed on an Orbitrap Astral MS coupled to a Thermo ScientificTM VanquishTM Neo UHPLC system, and interfaced online using an EASYSprayTM Nano source. Sample was injected via autosampler and trapped on an PepMap Neo Trap Cartridge column (300 μm × 5 mm, 5 μm), and then separated on an Easy-SprayTM PepMapTM Neo UHPLC column (150 μm × 15 cm, 2 μm) with a gradient time of 6.9 min. For the DIA experiments, the Orbitrap Astral MS was operated at a full MS resolution of 240,000 at 200 m/z with a full scan range of 380–980 m/z when stated. The full MS AGC was set to 500%. Fragmention scans were recorded at a resolution of 80,000 and Maximum lnjection Time (ms) of 3 ms. 299 windows of 2-Th scanning from 380 to 980 m/z were used. The isolated ions were fragmented using HCD with 25% NCE.
MS raw data were analyzed using DIA-NN (v1.8.1) with library-free method. The uniprot-proteome_UP000000589_Mus_musculus.fasta database (A total of 55,319 sequences), iRT2.fasta database (A total of 1 sequences) was uesed to creat a spectra library with deep learning algrithms of neural networks. The option of MBR was employed to create a spectral library from DIA data and then reanlyse using this library. FDR of search results was adjusted to <1% at both protein and precursor ion levels, the remaining identifications were used for further quantification analysis.
Besides the data from DIA-based quantitative proteomics, other data were statistically analyzed using Graph Pad Prism 9.5 software (San Diego, CA, USA). Student's t-test was used for comparisons between two groups. Comparisons between multiple groups were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, and post hoc test adjustments were made using Bonferroni correction. Post hoc tests were performed only when F reached p < 0.05 and there was no significant heteroscedasticity.
APAP-induced liver injury is mainly characterized by histopathological changes and hepatic necrosis (Chen et al., 2023). We assessed the preventive effects of AR.WE on acute liver injury induced by APAP using a dose of 250 mg/kg (Figure 1A). The hallmark of APAP-induced liver injury is centrilobular liver necrosis (Yan et al., 2018). H&E results showed that pretreatment of AR.WE significantly reduced pathological changes and necrotic area of mouse liver (Figures 1B,C). Furthermore, ALT and AST expression in serum AST and ALT are specific aminotransferases in the liver. When hepatocytes are damaged, ALT and AST are released in large amounts into the blood, and serum ALT and AST levels are increased (Lv et al., 2019). APAP-treated mice showed high ALT and AST levels in the blood test, the biochemical outcomes demonstrated that the AR.WE pretreatment considerably decreased the blood ALT and AST levels induced by APAP (Figure 1D).
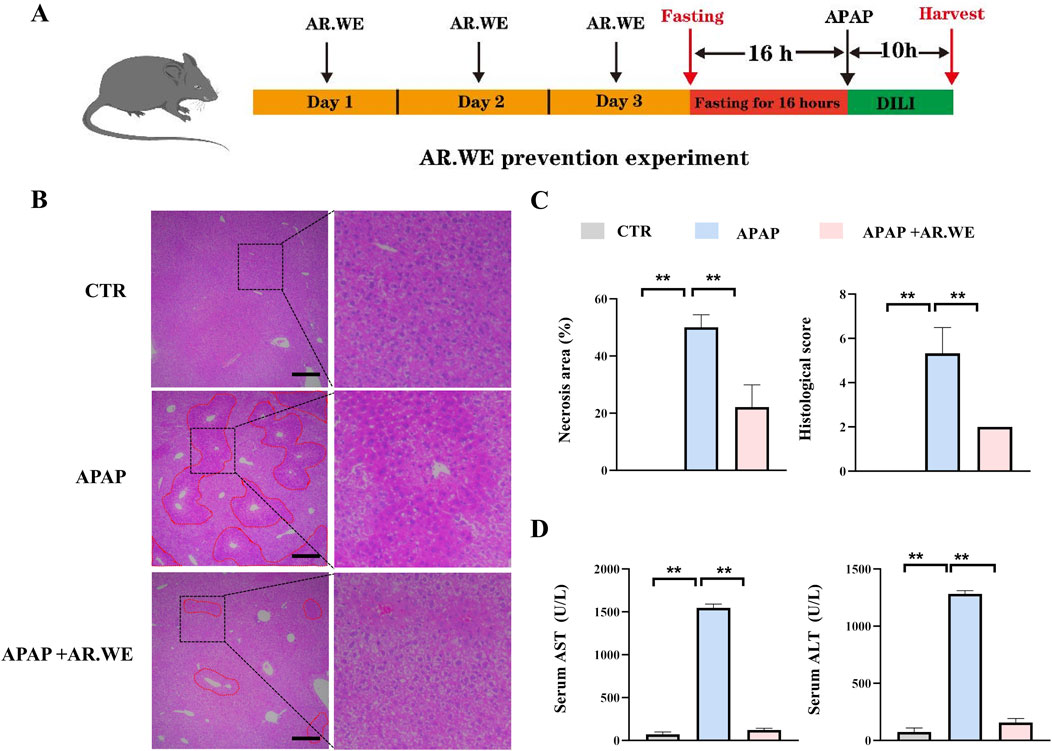
Figure 1. Anoectochilus roxburghii water extract (AR.WE) can prevent hepatotoxicity induced by APAP. (A) The time schedule for the AR.WE for the prevention of APAP-induced liver injury. Mice were gavaged with AR.WE (250 mg/kg) for 3 days continuously, and fasting was initiated for 16 h after the end of gavage on the third day. Acute liver injury was induced by administration of 300 mg/kg APAP at the end of fasting. Then, blood and liver samples were collected after 10 h (B) H&E staining of mouse liver sections after prophylaxis with AR.WE The dotted line indicates central lobular necrosis. Scale bars, 100 μm, n = 3. (C) Percentage of necrotic areas (left) and liver histological scores (right), n = 3 (D) Serum ALT (left) and AST (right) levels. All group data subjected to statistical analysis were repeated in at least three independent experiments, n = 5–6. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) is an important antioxidant enzyme that clears harmful free radicals. APAP-induced liver injury often leads to reduced SOD levels, which triggers oxidative stress in the body (Li et al., 2023a). However, we found that AR.WE pretreatment significantly increased hepatic SOD levels, thereby reducing the occurrence of oxidative stress (Figure 2A). Meanwhile, Glutathione (GSH) depletion is a critical step in APAP-induced liver injury. We detected variations in liver GSH activity in mice. The results demonstrated that APAP significantly reduced the activity of hepatic GSH compared to the control group, whereas AR.WE preconditioning significantly increased the activity of hepatic GSH (Figure 2A). APAP-induced liver injury is often accompanied by a powerful inflammatory response (Xu L. et al., 2022). To assess the inflammatory state in the liver, enzyme activity and protein expression levels of a certain factor involved in the inflammatory pathway were detected. We examined the serum pro-inflammatory cytokine protein and mRNA levels such as TNF-α by using ELISA analysis (Figure 2B) and RT-PCR analysis (Figure 2C), respectively. APAP significantly increased serum IL-6 and TNF-α levels and expression of genes involved in inflammation compared to controls. As expected, AR.WE pretreatment prevent inflammatory response induced by APAP.
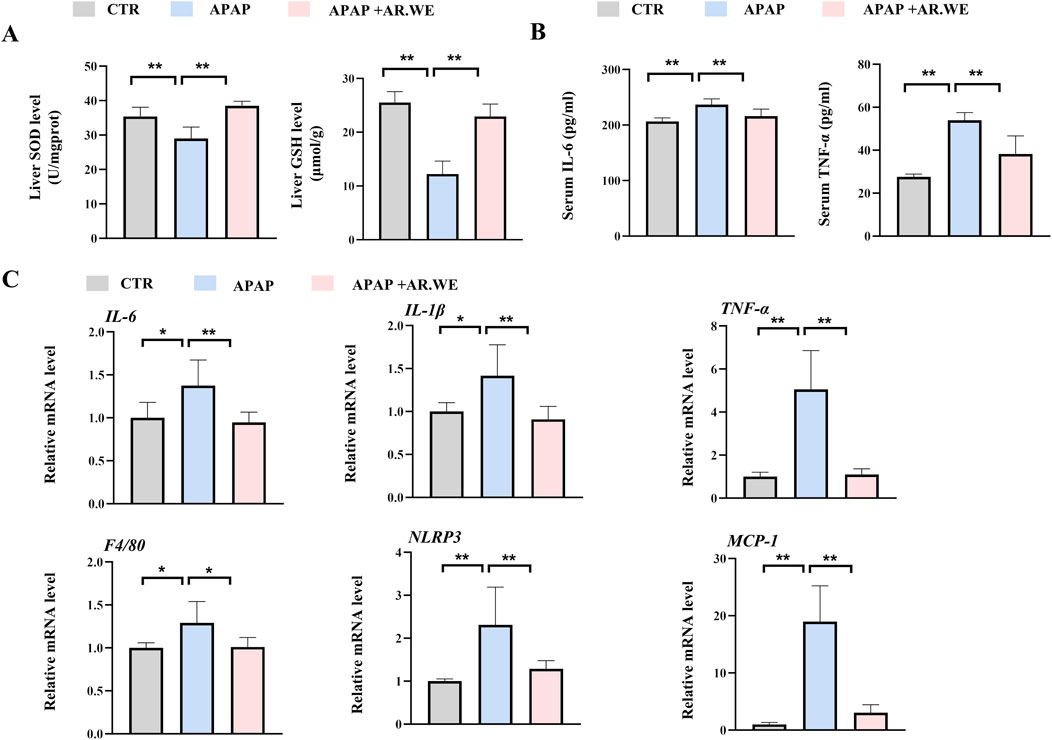
Figure 2. AR.WE can prevent APAP-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. (A) ELISA analysis of serum IL-6 (left) and TNF-α (right), n = 6. (B) The level of liver SOD (left) and GSH (right), n = 5–6 (C) RT-PCR analysis of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, F4/80, NLRP3, MCP-1, n = 5–6. All group data subjected to statistical analysis were repeated in at least three independent experiments. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Our previously results have shown that pretreatment of AR.WE for 3 days significantly prevent against APAP-induced liver injury, whether this herb is effective against the liver damage that has been caused is still unclear. Thus, mice were gavaged with AR.WE at 1 h after APAP administration, and were sacrificed 10 hour later (Figure 3A). Similarly, AR.WE treatment after APAP administration significantly reduced pathological changes and necrotic area of mouse liver, as revealed by H&E analysis (Figures 3B, C). Meanwhile, the liver function markers ALT and AST were also improved by AR.WE treatment (Figure 3D). Moreover, we found that AR.WE treatment significantly increased hepatic SOD levels and decreased the activity of hepatic GSH compared to the control group, therefore play an important role in antioxidant defense and stress resistance (Figure 4A). We then examined serum pro-inflammatory cytokine expression levels and the mRNA expression of genes related to inflammatory response. Consistently, APAP-induced inflammatory response in liver and circulation was significantly abolished by AR.WE (Figures 4B, C). Thus, we may conclude that AR.WE treatment after APAP administration mitigated APAP-induced liver injury.
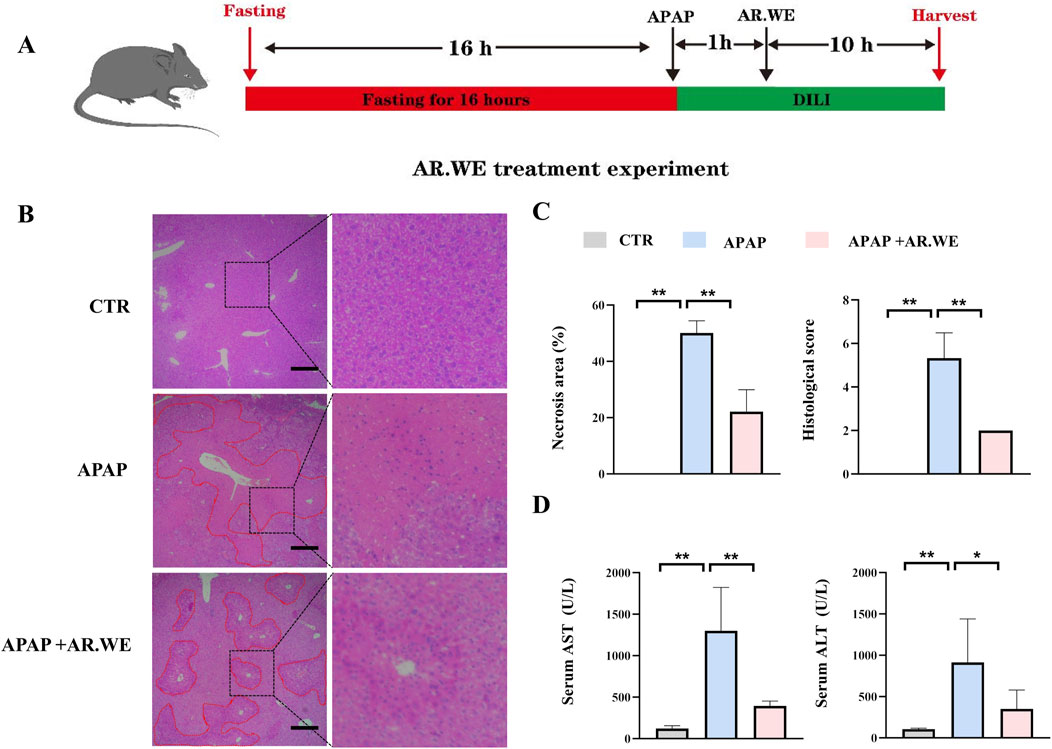
Figure 3. AR.WE can treat APAP-induced hepatotoxicity. (A) The time schedule fothe AR.WE for the treatment of APAP-induced liver injury. After fasting for 16 h, the mice were given APAP (300 mg/kg) to induce acute liver injury. After 1 h, a single dose of AR.WE (250 mg/kg) was administered intragastric. Then, blood and liver samples were collected after 10 h (B) H&E staining of mouse liver sections after treatment with AR.WE The dotted line indicates central lobular necrosis. Scale bars, 100 μm, n = 3. (C) Percentage of necrotic areas (left) and liver histological scores (right), n = 3. (D) Serum ALT (left) and AST (right) levels, n = 5–6. All group data subjected to statistical analysis were repeated in at least three independent experiments. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
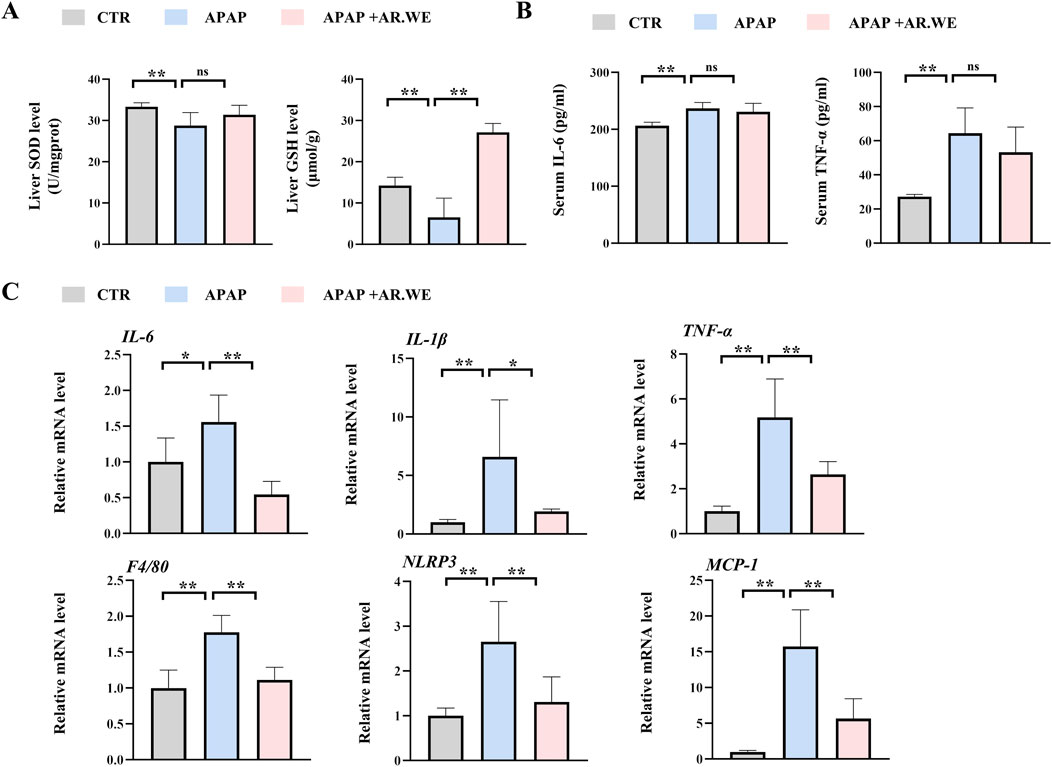
Figure 4. AR.WE can treat APAP-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. (A) Elisa analysis of serum IL-6 (left) and TNF-α (right), n = 5–6. (B) The level of liver SOD (left) and GSH (right), n = 5–6. (C) RT-PCR analysis of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, F4/80, NLRP3, MCP-1, n = 5–6. All group data subjected to statistical analysis were repeated in at least three independent experiments. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
ARPs is the main water-soluble component of AR, have been proved to play a significant role in antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antivirus, antihyperglycemic, anti-aging and anticoagulant activities (Liu et al., 2020). We then performed experiment to determine whether ARPS was the main component of AR.WE that exerts hepatoprotective effects. Polysaccharides from AR were usually extracted by the method of water extract and alcohol precipitate, followed by protein removal using the Sevag method, as shown in our previous research (Figure 5A). Before APAP administration, Mice were pretreated with ARPs at a dose of 250 mg/kg for 3 days (Figure 5B). As revealed by H&E analysis, ARPs preconditioning for 3 days ameliorated APAP-induced liver injury, much less hepatocellular injury and necrosis was observed in ARPs-treated group, indicating the protection of ARPs against APAP-induced liver toxicity (Figures 5C, D). Meanwhile, ARPs treatment reduced both ALT and AST levels significantly (Figure 6A). In addition, ARPs preconditioning significantly improved hepatic SOD and GSH activities compared to the APAP group (Figure 6B). Then, RT-PCR and ELISA assays were conducted to detect the expression change of the angiogenic factor and inflammatory factors at the mRNA levels and protein levels. ARPs-treated mice also exhibited significantly decreased pro-inflammatory factor expression levels which were consistent with the previous experimental results (Figures 6C–E). The above findings indicated that ARPs pretreatment effectively prevented acute liver damage induced by APAP.
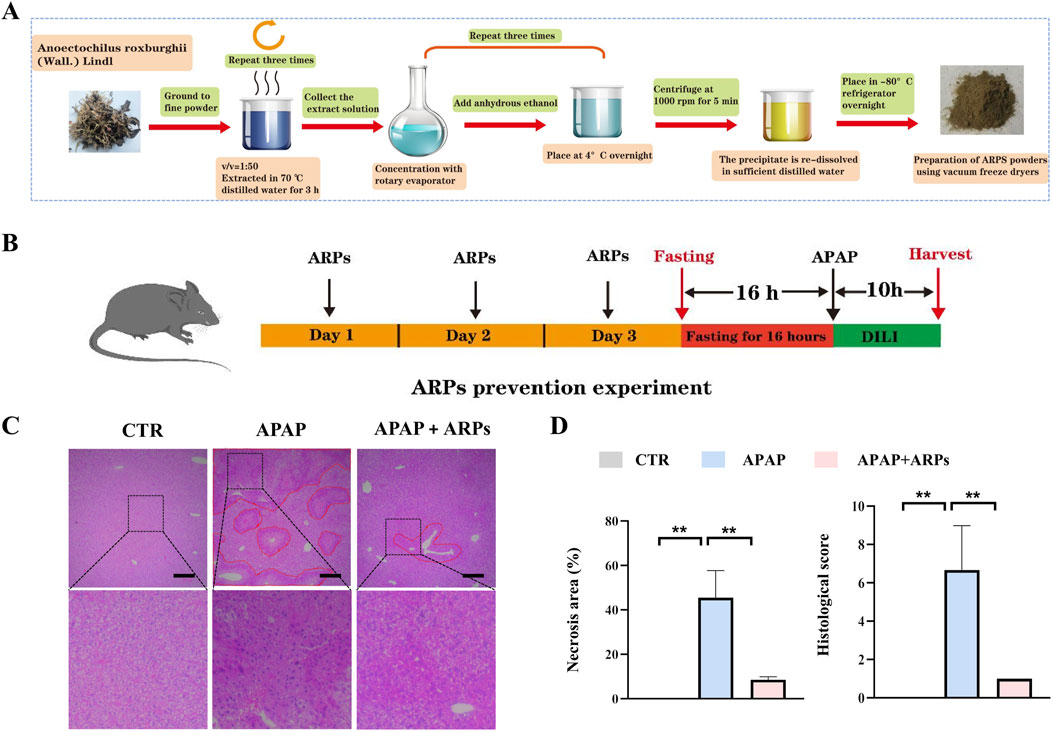
Figure 5. ARPs can prevent APAP-induced hepatotoxicity. (A) Flowchart for extracting ARPs. (B) The time schedule for ARPs for the prevention of APAP-induced liver injury. Mice were gavaged with ARPs (250 mg/kg) for 3 days continuously, and fasting was initiated for 16 h after the end of gavage on the third day. Acute liver injury was induced by administration of 300 mg/kg APAP at the end of fasting. Then, blood and liver samples were collected after 10 h (C) H&E staining of mouse liver sections after treatment with AR.WE. The dotted line indicates central lobular necrosis. Scale bars, 100 μm, n = 3. (D) Percentage of necrotic areas (left) and liver histological scores (right), n = 3. All group data subjected to statistical analysis were repeated in at least three independent experiments. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
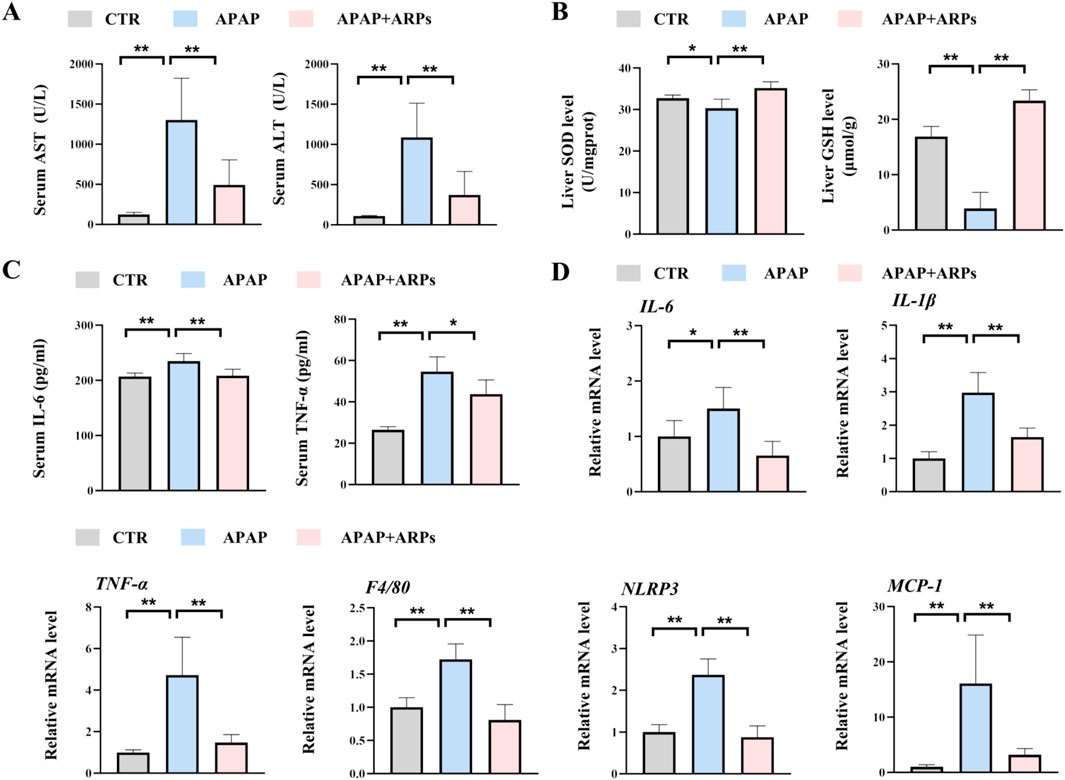
Figure 6. ARPs can prevent APAP-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. (A) Serum ALT (left) and AST (right) levels, n = 5–6. (B) ELISA analysis of serum IL-6 (left) and TNF-α (right), n = 5–6. (C) The levels of liver SOD (left) and GSH (right). (D) RT-PCR analysis of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, F4/80, NLRP3, MCP-1, n = 5–6. All group data subjected to statistical analysis were repeated in at least three independent experiments. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns p ≥ 0.05.
To further test the potential effect of ARPs on hepatocytes, we performed in vitro experiment. HepG2 cell lines were preconditioned with ARPs for 1 h and then stimulated with APAP for 24 h. As revealed by RT-PCR analysis, ARPs preconditioning significantly upregulated genes involved in inflammation such as TNF-α, F4/80, and il-1β in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 7). The NLRP3 inflammasome is a cytosolic complex for early inflammatory responses, increasing evidence shows that the NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in APAP-induced liver injury in mice. Consistently, APAP exposure significantly increased the expression of NLRP3 in HepG2 cell, while the treatment of ARPs effectively reversed this phenotype (Figure 7). Thus, these in vitro results further verified the hepatoprotective effect in APAP-induced liver injury.
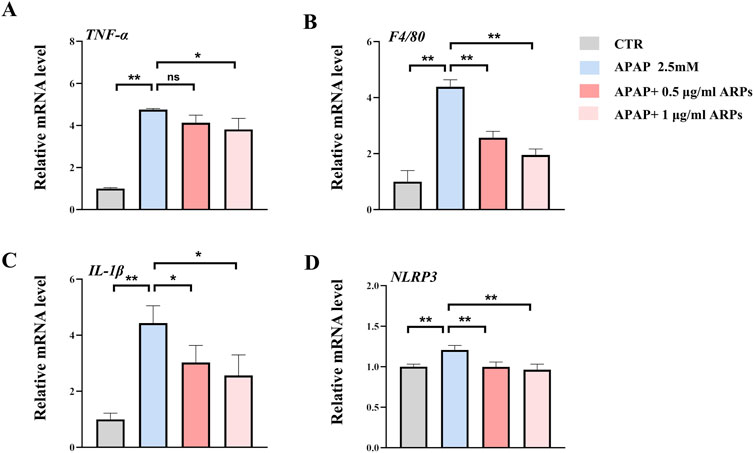
Figure 7. ARPs ameliorates APAP-induced inflammation in HEPG2 cells. APAP (2.5 mM) was given after pretreatment with ARPs (0.5 µg/ml and 1 µg/ml) for 1 h, then stimulated for 24 h before subsequent experiments. (A–D) RT-PCR analysis of IL-1β, TNF-α, F4/80, NLRP3, n=3. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns p ≥ 0.05.
To further explore the potential mechanisms by which ARPs ameliorates liver injury, we conducted a Data-independent acquisition (DIA)-based quantitative proteomics research. PCA analysis showed that the three patterns were distinct (Figure 8A). In total, 74,977 peptide fragments and 6,257 quantitative proteins were identified (Figure 8B). A total of 729 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) (356 upregulated proteins and 373 downregulated proteins) were found between the APAP and ARPs groups (Figure 8C). The DEPs screening criteria was as follows: fold change (FC) ≥1.5 or ≤0.67 and P < 0.05. Volcano plot showing differential expressed genes between APAP and ARPs groups (Figure 8D).
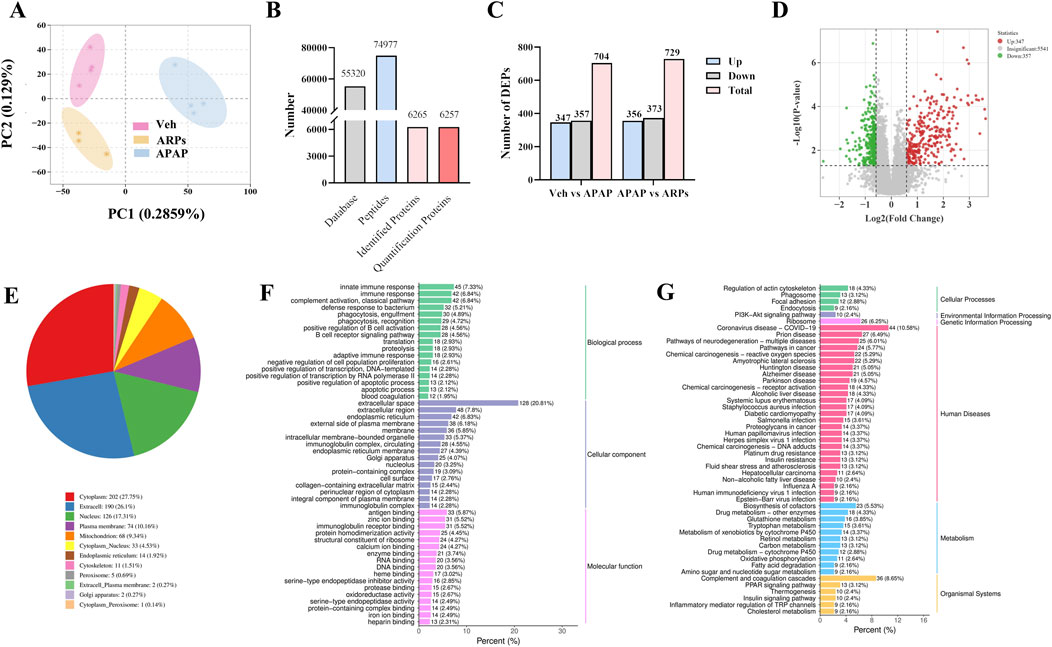
Figure 8. DIA-based quantitative proteomic analysis of mouse liver. (A) Principal Componen Analysis (PCA) results. The horizontal and vertical coordinates represent the first and second principal components, respectively, and the percentage in parentheses represents the contribution of the principal component to the sample variance; each point in the graph represents a sample, and different colours represent different groups of samples. (B) Statistical map of identification results. (C) The number of DEPs in Veh group vs APAP group, APAP group vs ARPs group, Veh group vs ARPs group. (D) Volcano plots of DEPs in APAP group vs ARPs group. Red points represented upregulated proteins and blue points represented downregulated proteins. (E) Pie graph of results of subcellular localization of differentially expressed proteins. (F) Bar graph of GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed proteins. Horizontal coordinates represent the percentage of the number of differentially expressed proteins annotated to the entry; vertical coordinates represent the name of the GO entry. (G) Bar graph of the classification of the differentially expressed protein KEGG. The horizontal coordinate represents the ratio of differentially expressed proteins annotated to the pathway to the total number of proteins with annotations, and the vertical coordinate represents the name of the KEGG pathway.
We conducted subcellular localization of DEPs between the APAP group and the ARPs group and demonstrated the top 12 most enriched. In the first place was the cytoplasm, indicating that 27.75% of DEPs were located in the cytoplasm, followed by extracell (26.1%), nucleus (17.31%), and plasma membrane (10.16%), respectively (Figure 8E). Then Gene Ontology (GO) annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment were performed based on these DEPs. The GO annotation divides these DEPs into three sections: biological processes, cellular component, and molecular function. For biological processes, DEPs in the APAP and ARPs groups were mainly enriched in innate immune response (Figure 8F). For cell contents, DEPs were mainly enriched in extracellular components. In terms of molecular function, DEPs were mainly enriched in antigen binding (Figure 8F). KEGG enrichment revealed that these DEPs were most enriched in regulation of actin cytoskelenon, and phagosome pathway (Figure 8G). We further analysed the phagosome pathway based on animal model and research direction. KEGG pathway map demonstrated that vacuolar H+-ATPases (vATPases) played an important role in the phagosome pathway (Figure 9). We therefore speculated that downregulation of vATPase activity was a potential target of ARPs for the treatment of liver injury.
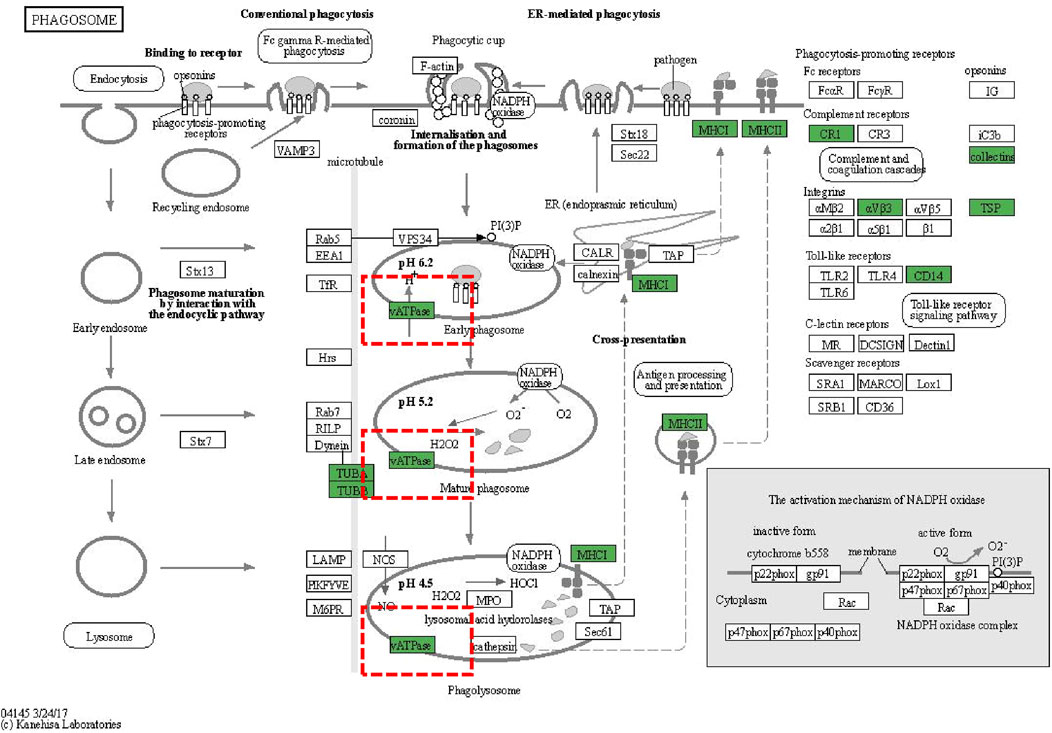
Figure 9. KEGG pathway diagrams of DEGs. KEGG pathway diagrams of DEGs. Green represents downregulation.
We next assess the protein levels involved in apoptosis, inflammation, necroptosis, and oxidative stress, all of which important pathogenesis of APAP-induced liver injury. As shown in heatmaps, APAP exposure significantly upregulated the protein levels involved in pro-apoptosis, pro-inflammation, pro-necroptosis, and oxidative stress, while these phenotypes were prevented by ARPs treatment (Figures 10A–D). Hepatic autophagy is an essential mechanism for liver regeneration, and impaired autophagy is found to be related to dysfunction of various processes of hepatic regeneration (Wang et al., 2024). Thus, improving autophagy is an important therapeutic method to alleviate hepatic injury. Our data showed that ARPs could promote autophagy by transcriptionally activating autophagy-related genes, which indicated that ARPs may ameliorate APAP-induced liver injury by restoring autophagy (Figure 10E). APAP can aggravate oxidative stress and induce ferroptosis, a mode of cell death mediated by lipid peroxidation and cellular free iron when protective mechanisms such as glutathione peroxidase activity have been compromised (Jaeschke et al., 2021). In our data, ferroptosis-related genes were significantly regulated by ARPs treatment (Figure 10F). Consequently, we could speculate ARPs protects against drug-induced liver injury by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis. To validate this conjecture, we performed RT-PCR analysis and found that Liver P62 gene expression level was significantly higher in APAP group mice compared to control group (P = 0.01). After ARPs administration, P62 gene expression level decreased (P = 0.17). Whereas, APAP stimulation resulted in decreased hepatic LC3B expression level in mice (P = 0.03). After ARPs administration, LC3B gene expression level increased (P = 0.004) (Figures 11A, B). In addition, the gene expression levels of GPX4, FTH1, ATG5, and XCT were reduced in the livers of mice in the APAP group compared to the control group, and the administration of ARPs reversed these trends (Figures 11C–F). All these data suggest that ARPs may ameliorate liver injury by regulating autophagy and ferroptosis.
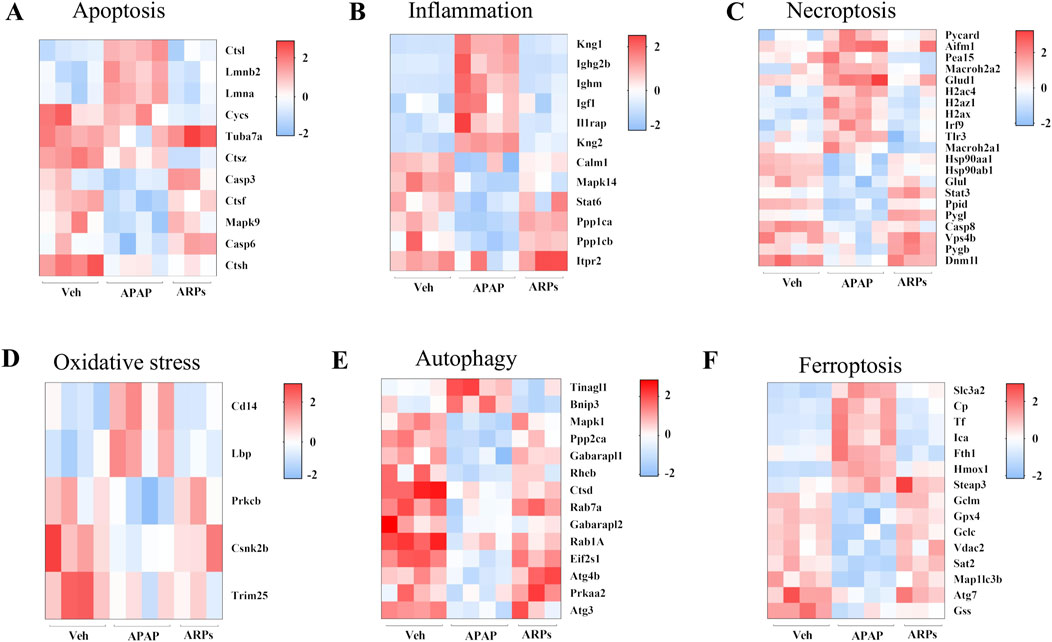
Figure 10. The protein levels involved in apoptosis, inflammation, necroptosis, and oxidative stress, autophagy, and ferroptosis (A) Heatmap of differential protein clustering involved in apoptosis. (B) Heatmap of differential protein clustering involved in inflammation. (C) Heatmap of differential protein clustering involved in necroptosis. (D) Heatmap of differential protein clustering involved in oxidative stress. (E) Heatmap of differential protein clustering involved in autophagy. (F) Heatmap of differential protein clustering involved in ferroptosis.
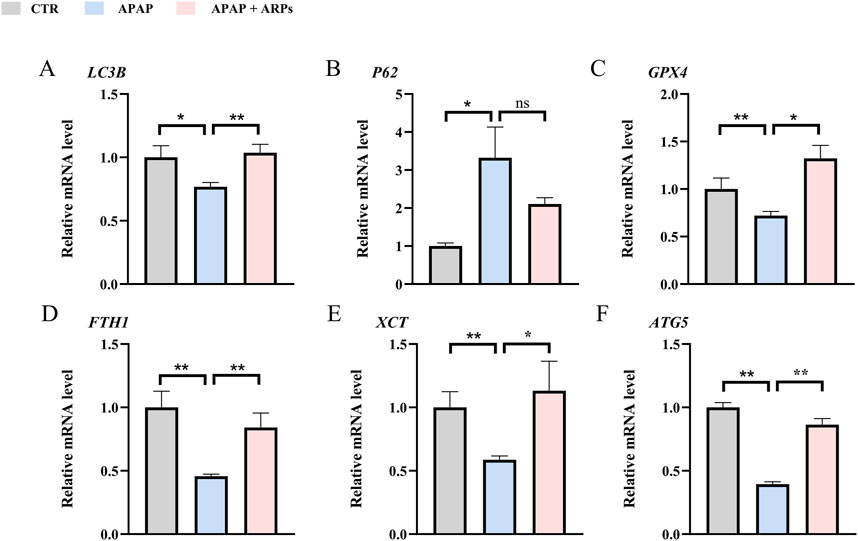
Figure 11. RT-PCR confirms that ARPs ameliorate liver injury by regulating genes involved in hepatocyte autophagy and ferroptosis. (A) RT-PCR analysis of LC3B; (B) RT-PCR analysis of P62; (C) RT-PCR analysis of GPX4; (D) RT-PCR analysis of FTH1; (E) RT-PCR analysis of XCT; (F) RT-PCR analysis of ATG5. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns p ≥ 0.05, n = 6.
AR is a traditional medicinal plant in China with a variety of pharmacological effects such as liver protection, cancer prevention, treatment of cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus (Han et al., 2008; Ye et al., 2017). A study has reported the hypoglycaemic and antioxidant effects of water extract from AR on diabetic mice (Cui et al., 2013). It has also been shown that AR may alleviate aging and aging-related learning and memory impairment (Xiao et al., 2024). Meanwhile, Yan et al. found that AR ameliorates D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury by modulating inflammatory vesicles. AR also showed a protective effect against isoniazid-induced drug-induced liver injury (Lin et al., 2024). In addition, multiple ameliorative effects of this herb on hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, inflammatory infiltration, hepatocyte apoptosis and fibrosis in experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have been identified (Deng et al., 2022). Our study demonstrated that AR and its polysaccharide fractions can effectively ameliorate inflammatory infiltration and oxidative stress in acute liver injury induced by APAP, and the mechanism may be related to the hepatocyte autophagy, and downregulation of vATPase activity is likely to participate in this progress.
Oxidative stress has been implicated as an important factor in the development of various diseases such as liver disease, chronic kidney disease, neurodegenerative diseases, etc. (Samarghandian et al., 2017). Excess APAP leads to increased mitochondrial oxidative stress, generating large amounts of reactive oxygen species thereby damaging hepatocytes (Xu P. et al., 2022). It has been shown that AR protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced L02 cell damage, and the mechanism may involve oxidative stress. Moreover, Kinsenoside (an extract of AR) can ameliorate alcoholic liver injury in mice by reducing oxidative stress (Gao et al., 2021). Furthermore, Luo et al. found that AR protected the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis while reducing apoptosis-associated neovascularisation (Luo et al., 2018). In this study, we observed that AR exhibited significant anti-oxidative stress in APAP -induced liver injury, including increased GSH and SOD levels in the liver. These data were in line with the functional and phenotypic results described previously.
Chronic inflammation is a major cause of liver cirrhosis (Koyama and Brenner, 2017). Macrophage plays an important role in inflammation and liver injury (Saha et al., 2018). Activated Kupffer cells (hepatic Macrophages) secrete pro-inflammatory factors, including IL-6 and TNF-α, which ultimately lead to liver injury (Voican et al., 2011; Kurihara et al., 1997). APAP-induced hepatotoxicity involves sterile inflammation, macrophage modulates innate immune signaling stimulating factor (STING) mediated inflammation (Yang et al., 2023). Hsiao et al. found that AR alleviated acute inflammation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokine (TNF-α, IL-6) release and enhancing SOCS - 3 mediated release of anti-inflammatory cytokines via the NF-κB signaling pathway (Hsiao et al., 2011). Uniformly, AR also ameliorated rheumatoid arthritis in rats by inhibiting the phosphorylation of IkB and P65 and down-regulating LPS-induced IL-1β and IL-6 (Guo et al., 2019). In this study, we found that AR reduced the expression of inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, which highlight the therapeutic potential of AR for APAP -induced liver injury.
To further reveal the underlying mechanisms of AR amelioration of APAP-induced liver injury, we performed a DIA-based quantitative proteomics study. A total of 729 DEPs were identified between ARPs the APAP and group. In further biological analyses, KGEE enrichment showed that these DEPs were significantly enriched in the phagosome pathway. Phagosome is involved in the autophagy process and binds to lysosome in the final stage of autophagy, which becomes the final site of degradation (Zhou et al., 2023). Autophagy is closely linked to liver homeostasis (Gao et al., 2020). LC3 is a key molecule in the process of autophagy and can bind to the membrane surface of autophagosomes to become a marker of autophagosomes (Fan et al., 2021). P62 was the first selective autophagy receptor discovered and plays an important role in autophagosome formation (Huang et al., 2024). In this study, APAP exposure led to decreased LC3 expression and increased P62 expression, while ARPs inhibition these aberrant expressions. The modulation by AR on autophagy have been verified in other diseases models. Gao et al. found that AR activated AMPK-dependent autophagic pathway to attenuate liver injury in alcoholic liver-injured mice (Gao et al., 2021). In addition, Wang et al. demonstrated that AR upregulated GPX4 expression to ameliorate myocardial injury, a process that was accompanied by the regulation of Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 signalling (Wang et al., 2023).
Referring to the results of KEGG enrichment, we found that vATPase is involved in the biological process of phagosome. vATPase is a multisubunit protein complex that primarily functions to acidify lysosomes and promote autophagosomal degradation (Hooper et al., 2022). Meanwhile, vATPase activity is an indispensable component of the process of LC3 lipidation and distribution (Florey et al., 2015). In addition to its role in conventional autophagy, the researchers found that vATPase inhibits ferroptosis by activating TFEB-dependent SOD production, and may participate in iron death by affecting autophagy activity because the selective activation of autophagy mediates the degradation of antiferroptosis regulators, including ferritin (Chen F. et al., 2022). In conclusion, our study concluded that AR reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory infiltration by regulating vATPase activity and thus participating in the autophagic process and ferroptosis.
There are some limitations in our study. Firstly, although we found that AR can ameliorate APAP-induced liver injury, it has only been validated in mice due to the conditions. Therefore, clinical trials are needed to assess the effectiveness and safety of AR in humans. Second, AR contains a variety of bioactive components, including polysaccharides, glycosides, steroids, triterpenes, amino acids, and alkaloids. ARPs, one of the main components of AR, not only reduce blood glucose levels in diabetic mice by improving glucolipid metabolism, enhancing immunoprotection and reducing oxidative stress (Zhang et al., 2015). Although we demonstrated that ARPs can prevent liver injury, we cannot rule out that there are other components that play a role. Further experiments are needed in the future to determine the key active components of AR for the treatment of liver injury. Thirdly, the gut-liver axis plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of drug-induced liver injury (Chen Q. W. et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2024), and it has been demonstrated that many natural polysaccharides can improve the intestinal flora diversity (Liu et al., 2024; Li et al., 2023b; Xu et al., 2023; Fu et al., 2023). Given that ARPs are administered orally, and we can not rule out the effect of microbial flora and its metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have been proven to act as molecular regulators in multiple liver diseases (Zhang et al., 2021).
In conclusion, we acknowledge that this study has some limitations, including the lack of human clinical trial data and the further investigation of detailed molecular mechanisms.
While this research also preliminarily clarified that AR as a promising new treatment for drug induced liver injury. This will broaden the potential applications of AR in liver diseases.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
The animal study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Southwest Medical University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
WD: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YM: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. QL: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. ML: Software, Writing–review and editing. HS: Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. LJ: Software, Writing–review and editing. JZ: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. KT: Validation, Writing–review and editing. XY: Investigation, Writing–original draft. YH: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. CX: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. LZ: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. YH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Science and Technology Program of Luzhou City (2024SYF169), Natural Science Foundation of Southwest Medical University (2024ZKY014 and 2024ZKY079), Special Fund Project for Medical Scientific Research of Chengdu Municipal Health Commission (No. 2022024). In-Hospital Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Sichuan Maternal and Child Health Hospital (No. CXPJ2023-02).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1508290/full#supplementary-material
DILI, Drug-induced liver injury; AR, Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.); ARPs, Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharides; APAP, Acetaminophen; AR.WE, water extract of Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.); NAPQI, n-acetyl-p-benzoquinone-imine; GSH, glutathione; NAC, n-acetylcysteine; GPC, gel permeation chromatography; ELISA, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay; SOD, Superoxide Dismutase; DEPs, differentially expressed proteins; NAFLD, non-alcoholicfatty liver disease; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; STING, innate immune signaling stimulating factor; (v-ATPases), vacuolar H+-ATPases; DIA, Data-independent acquisition; HPLC, High-performance liquid chromatography; IAM, iodoacetamide; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; GO, Gene Ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Cai, X., Cai, H., Wang, J., Yang, Q., Guan, J., Deng, J., et al. (2022). Molecular pathogenesis of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its treatment options. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 265–285. doi:10.1631/jzus.B2100977
Chen, F., Kang, R., Liu, J., and Tang, D. (2022a). The V-ATPases in cancer and cell death. Cancer gene Ther. 29, 1529–1541. doi:10.1038/s41417-022-00477-y
Chen, Q. W., Li, Q. R., Cao, M. W., Yan, J. H., and Zhang, X. Z. (2022b). Hierarchy-assembled dual probiotics system ameliorates cholestatic drug-induced liver injury via gut-liver Axis modulation. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger. 9, e2200986. doi:10.1002/advs.202200986
Chen, S., Lu, Z., Jia, H., Yang, B., Liu, C., Yang, Y., et al. (2023). Hepatocyte-specific Mas activation enhances lipophagy and fatty acid oxidation to protect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J. hepatology 78, 543–557. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.10.028
Chiew, A. L., Isbister, G. K., Stathakis, P., Isoardi, K. Z., Page, C., Ress, K., et al. (2023). Acetaminophen metabolites on presentation following an acute acetaminophen overdose (ATOM-7). Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 113, 1304–1314. doi:10.1002/cpt.2888
Chowdhury, A., Nabila, J., Adelusi Temitope, I., and Wang, S. (2020). Current etiological comprehension and therapeutic targets of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 161, 105102. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105102
Cui, M., Liang, Z., Liu, Y., Sun, Q., Wu, D., Luo, L., et al. (2023). Flavonoid profile of Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. Under short-term heat stress revealed by integrated metabolome, transcriptome, and biochemical analyses. Plant physiology Biochem. PPB 201, 107896. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107896
Cui, S. C., Yu, J., Zhang, X. H., Cheng, M. Z., Yang, L. W., and Xu, J. Y. (2013). Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant activity of water extract from Anoectochilus roxburghii in experimental diabetes. Exp. Toxicol. pathology official J. Gesellschaft fur Toxikologische Pathologie 65, 485–488. doi:10.1016/j.etp.2012.02.003
Deng, Y. F., Xu, Q. Q., Chen, T. Q., Ming, J. X., Wang, Y. F., Mao, L. N., et al. (2022). Kinsenoside alleviates inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH mice by suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 104, 154241. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154241
Fan, S., Yue, L., Wan, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., Otomo, C., et al. (2021). Inhibition of autophagy by a small molecule through covalent modification of the LC3 protein. Angewandte Chemie Int. ed. Engl. 60, 26105–26114. doi:10.1002/anie.202109464
Florey, O., Gammoh, N., Kim, S. E., Jiang, X., and Overholtzer, M. (2015). V-ATPase and osmotic imbalances activate endolysosomal LC3 lipidation. Autophagy 11, 88–99. doi:10.4161/15548627.2014.984277
Fu, L., Zhu, W., Tian, D., Tang, Y., Ye, Y., Wei, Q., et al. (2022). Dietary supplement of Anoectochilus roxburghii (wall.) Lindl. Polysaccharides ameliorates cognitive dysfunction induced by high fat diet via “Gut-Brain” Axis. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 16, 1931–1945. doi:10.2147/dddt.S356934
Fu, Y. P., Peng, X., Zhang, C. W., Jiang, Q. X., Paulsen, B. S., et al. (2023). Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharide and its related metabolite 5-methoxyindole-3-carboxaldehyde ameliorate experimental colitis by regulating Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 306, 120626. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120626
Gao, J., Wei, B., de Assuncao, T. M., Liu, Z., Hu, X., Ibrahim, S., et al. (2020). Hepatic stellate cell autophagy inhibits extracellular vesicle release to attenuate liver fibrosis. J. hepatology 73, 1144–1154. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.044
Gao, L., Chen, X., Fu, Z., Yin, J., Wang, Y., Sun, W., et al. (2021). Kinsenoside alleviates alcoholic liver injury by reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress, and regulating AMPK-dependent autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 747325. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.747325
Guo, Y., Ye, Q., Yang, S., Wu, J., Ye, B., Wu, Y., et al. (2019). Therapeutic effects of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 122, 882–892. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.015
Han, M. H., Yang, X. W., and Jin, Y. P. (2008). Novel triterpenoid acyl esters and alkaloids from Anoectochilus roxburghii. Phytochem. Anal. PCA 19, 438–443. doi:10.1002/pca.1070
Hooper, K. M., Jacquin, E., Li, T., Goodwin, J. M., Brumell, J. H., Durgan, J., et al. (2022). V-ATPase is a universal regulator of LC3-associated phagocytosis and non-canonical autophagy. J. cell Biol. 221, e202105112. doi:10.1083/jcb.202105112
Hsiao, H. B., Wu, J. B., Lin, H., and Lin, W. C. (2011). Kinsenoside isolated from Anoectochilus formosanus suppresses LPS-stimulated inflammatory reactions in macrophages and endotoxin shock in mice. Shock (Augusta, Ga.) 35, 184–190. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181f0e7a3
Huang, T., Wu, Y., Huang, L., Lin, R., Li, Z., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Mechanism of the effect of compound Anoectochilus roxburghii (wall.) Lindl. Oral liquid in treating alcoholic rat liver injury by metabolomics. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 17, 3409–3428. doi:10.2147/dddt.S427837
Huang, X., Liu, L., Yao, J., Lin, C., Xiang, T., and Yang, A. (2024). S-acylation regulates SQSTM1/p62-mediated selective autophagy. Autophagy 20, 1467–1469. doi:10.1080/15548627.2023.2297623
Jaeschke, H., Adelusi, O. B., and Ramachandran, A. (2021). Ferroptosis and acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: are we going down another rabbit hole? Gene Expr. 20, 169–178. doi:10.3727/105221621x16104581979144
Koyama, Y., and Brenner, D. A. (2017). Liver inflammation and fibrosis. J. Clin. investigation 127, 55–64. doi:10.1172/jci88881
Kumachev, A., and Wu, P. E. (2021). Drug-induced liver injury. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. = J. de l'Association medicale Can. 193, E310. doi:10.1503/cmaj.202026
Kurihara, T., Warr, G., Loy, J., and Bravo, R. (1997). Defects in macrophage recruitment and host defense in mice lacking the CCR2 chemokine receptor. J. Exp. Med. 186, 1757–1762. doi:10.1084/jem.186.10.1757
Lee, W. M. (2017). Acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity-Isn't it time for APAP to go away? J. hepatology 67, 1324–1331. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.005
Li, Q., Liu, W., Zhang, H., Chen, C., Liu, R., Hou, H., et al. (2023b). α-D-1,3-glucan from Radix Puerariae thomsonii improves NAFLD by regulating the intestinal flora and metabolites. Carbohydr. Polym. 299, 120197. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120197
Li, Q., Zhang, W., Cheng, N., Zhu, Y., Li, H., Zhang, S., et al. (2023a). Pectolinarigenin ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory response in Nrf2 and PPARa dependent manners. Phytomedicine 113, 154726. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154726
Li, X., Tang, J., and Mao, Y. (2022). Incidence and risk factors of drug-induced liver injury. Liver Int. official J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 42, 1999–2014. doi:10.1111/liv.15262
Licata, A., Minissale, M. G., Stankevičiūtė, S., Sanabria-Cabrera, J., Lucena, M. I., Andrade, R. J., et al. (2022). N-acetylcysteine for preventing acetaminophen-induced liver injury: a comprehensive review. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 828565. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.828565
Lin, R., Wu, P., Wu, Y., Huang, L., Lin, B., and Huang, L. (2024). Effects of compound Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. oral liquid on relative metabolic enzymes and various biochemical indices in Wistar rats with isoniazid-induced liver injury. J. Pharm. Biomed. analysis 248, 116249. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116249
Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Zheng, M., Ye, Y., Shi, M., Wang, X., et al. (2024). Polysaccharides in Medicinal and Food Homologous Plants regulate intestinal flora to improve type 2 diabetes: systematic review. Phytomedicine 134, 156027. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156027
Liu, Y., Tang, T., Duan, S., Li, C., Lin, Q., Wu, H., et al. (2020). The purification, structural characterization and antidiabetic activity of a polysaccharide from Anoectochilus roxburghii. Food & Funct. 11, 3730–3740. doi:10.1039/c9fo00860h
Lu, J., Gao, Y., Gong, Y., Yue, Y., Yang, Y., Xiong, Y., et al. (2024). Lycium barbarum L. Balanced intestinal flora with YAP1/FXR activation in drug-induced liver injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 130, 111762. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111762
Luo, X., Gu, S., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, J. (2018). Kinsenoside ameliorates oxidative stress-induced RPE cell apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis via erk/p38/NF-κB/VEGF signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 240. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00240
Lv, H., Hong, L., Tian, Y., Yin, C., Zhu, C., and Feng, H. (2019). Corilagin alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via enhancing the AMPK/GSK3β-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 17 (2), 2. doi:10.1186/s12964-018-0314-2
McGill, M. R., Sharpe, M. R., Williams, C. D., Taha, M., Curry, S. C., and Jaeschke, H. (2012). The mechanism underlying acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in humans and mice involves mitochondrial damage and nuclear DNA fragmentation. J. Clin. investigation 122, 1574–1583. doi:10.1172/jci59755
Orandi, B. J., McLeod, M. C., MacLennan, P. A., Lee, W. M., Fontana, R. J., Karvellas, C. J., et al. (2023). Association of FDA mandate limiting acetaminophen (paracetamol) in prescription combination opioid products and subsequent hospitalizations and acute liver failure. Jama 329, 735–744. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.1080
Qiu, Y., Song, W., Yang, Y., Zhou, G., Bai, Y., Akihisa, T., et al. (2023). Isolation, structural and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl.: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 236, 123883. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123883
Reuben, A., Tillman, H., Fontana, R. J., Davern, T., McGuire, B., Stravitz, R. T., et al. (2016). Outcomes in adults with acute liver failure between 1998 and 2013: an observational cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 164, 724–732. doi:10.7326/m15-2211
Saha, B., Momen-Heravi, F., Furi, I., Kodys, K., Catalano, D., Gangopadhyay, A., et al. (2018). Extracellular vesicles from mice with alcoholic liver disease carry a distinct protein cargo and induce macrophage activation through heat shock protein 90. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 67 (67), 1986–2000. doi:10.1002/hep.29732
Samarghandian, S., Azimi-Nezhad, M., Farkhondeh, T., and Samini, F. (2017). Anti-oxidative effects of curcumin on immobilization-induced oxidative stress in rat brain, liver and kidney. Biomed. Pharmacother. 87, 223–229. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.105
Służały, P., Paśko, P., and Galanty, A. (2024). Natural products as hepatoprotective agents-A comprehensive review of clinical trials. Plants Basel, Switz. 13, 1985. doi:10.3390/plants13141985
Tian, D., Zhong, X., Fu, L., Zhu, W., Liu, X., Wu, Z., et al. (2022). Therapeutic effect and mechanism of polysaccharides from Anoectochilus Roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. in diet-induced obesity. Phytomedicine 99, 154031. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154031
Voican, C. S., Perlemuter, G., and Naveau, S. (2011). Mechanisms of the inflammatory reaction implicated in alcoholic hepatitis: 2011 update. Clin. Res. hepatology gastroenterology 35, 465–474. doi:10.1016/j.clinre.2011.01.017
Wang, R., Dong, S., Xia, R., Sun, M., Sun, Y., Ren, H., et al. (2023). Kinsenoside mitigates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced ferroptosis via activation of the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 956, 175985. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175985
Wang, Z. Y., Chen, R. X., Wang, J. F., Liu, S. C., Xu, X., Zhou, T., et al. (2024). Apolipoprotein A-1 accelerated liver regeneration through regulating autophagy via AMPK-ULK1 pathway. Cell. Mol. gastroenterology hepatology 17, 539–551. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.12.004
Xiao, Y., Duan, C., Gong, P., Zhao, Q., Wang, X. H., Geng, F., et al. (2024). Kinsenoside from Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. suppressed oxidative stress to attenuate aging-related learning and memory impairment via ERK/Nrf2 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319, 117152. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117152
Xu, H., Wang, S., Jiang, Y., Wu, J., Chen, L., Ding, Y., et al. (2023). Poria cocos polysaccharide ameliorated antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice via regulating the homeostasis of the gut microbiota and intestinal mucosal barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 1423. doi:10.3390/ijms24021423
Xu, L., Yang, Y., Wen, Y., Jeong, J. M., Emontzpohl, C., Atkins, C. L., et al. (2022a). Hepatic recruitment of eosinophils and their protective function during acute liver injury. J. hepatology 77, 344–352. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.02.024
Xu, P., Xi, Y., Wang, P., Luka, Z., Xu, M., Tung, H. C., et al. (2022b). Inhibition of p53 sulfoconjugation prevents oxidative hepatotoxicity and acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 162, 1226–1241. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.260
Yan, M., Huo, Y., Yin, S., and Hu, H. (2018). Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol. 17, 274–283. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2018.04.019
Yang, T., Qu, X., Zhao, J., Wang, X., Wang, Q., Dai, J., et al. (2023). Macrophage PTEN controls STING-induced inflammation and necroptosis through NICD/NRF2 signaling in APAP-induced liver injury. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 21, 160. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01175-4
Yang, Z., Zhang, X., Yang, L., Pan, Q., Li, J., Wu, Y., et al. (2017). Protective effect of Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharide against CCl(4)-induced oxidative liver damage in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 96, 442–450. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.039
Ye, S., Shao, Q., and Zhang, A. (2017). Anoectochilus roxburghii: a review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications. J. Ethnopharmacol. 209, 184–202. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2017.07.032
Zhang, J. G., Liu, Q., Liu, Z. L., Li, L., and Yi, L. T. (2015). Antihyperglycemic activity of Anoectochilus roxburghii polysaccharose in diabetic mice induced by high-fat diet and streptozotocin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 164, 180–185. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.050
Zhang, S., Zhao, J., Xie, F., He, H., Johnston, L. J., Dai, X., et al. (2021). Dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids: a potential therapeutic target to alleviate obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes. Rev. official J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 22, e13316. doi:10.1111/obr.13316
Zheng, J., Yang, N., Wan, Y., Cheng, W., Zhang, G., Yu, S., et al. (2023). Celastrol-loaded biomimetic nanodrug ameliorates APAP-induced liver injury through modulating macrophage polarization. J. Mol. Med. Berlin, Ger. 101, 699–716. doi:10.1007/s00109-023-02321-8
Zhong, Y., Chen, Y., Pan, Z., Tang, K., Zhong, G., Guo, J., et al. (2022). Ginsenoside Rc, as an FXR activator, alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via relieving inflammation and oxidative stress. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1027731. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1027731
Zhou, H. C., Wang, H., Shi, K., Li, J. M., Zong, Y., and Du, R. (2018). Hepatoprotective effect of baicalein against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Mol. Basel, Switz. 24, 131. doi:10.3390/molecules24010131
Zhou, Y., Huang, X., Yu, H., Shi, H., Chen, M., Song, J., et al. (2023). TMT-based quantitative proteomics revealed protective efficacy of Icariside II against airway inflammation and remodeling via inhibiting LAMP2, CTSD and CTSS expression in OVA-induced chronic asthma mice. Phytomedicine 118, 154941. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154941
Keywords: drug-induced liver injury, acetaminophen, anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.), polysaccharides, oxidative stress and inflammation
Citation: Dong W, Mou Y, Li Q, Li M, Su H, Jiang L, Zhou J, Tu K, Yang X, Huang Y, Xu C, Zhang L and Huang Y (2025) DIA-based quantitative proteomics explores the mechanism of amelioration of APAP-induced liver injury by anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1508290. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1508290
Received: 30 October 2024; Accepted: 04 March 2025;
Published: 26 March 2025.
Edited by:
Javier Echeverria, University of Santiago, ChileReviewed by:
Wei Zhong, University of Kansas Medical Center, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Dong, Mou, Li, Li, Su, Jiang, Zhou, Tu, Yang, Huang, Xu, Zhang and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yilan Huang, aHlsMzE2MDEzMUAxMjYuY29t; Liaoyun Zhang, emhhbmdsaWFveXVuMTk4NEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.