
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol., 24 January 2025
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1492517
This article is part of the Research TopicPlant Polyphenols: New Chemical and Pharmacological ApproachesView all 3 articles
 Maroua Jalouli1
Maroua Jalouli1 Md Ataur Rahman2
Md Ataur Rahman2 Partha Biswas3
Partha Biswas3 Hasanur Rahman4
Hasanur Rahman4 Abdel Halim Harrath5
Abdel Halim Harrath5 In-Seon Lee6,7
In-Seon Lee6,7 Sojin Kang8
Sojin Kang8 Jinwon Choi8
Jinwon Choi8 Moon Nyeo Park8
Moon Nyeo Park8 Bonglee Kim8,9*
Bonglee Kim8,9*Polyphenols, naturally occurring phytonutrients found in plant-based foods, have attracted significant attention for their potential therapeutic effects in neurological diseases and neuroinflammation. These compounds possess diverse neuroprotective capabilities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-amyloid properties, which contribute to mitigating the progression of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease (PD), Dementia, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Stroke, and Huntington’s Disease (HD). Polyphenols have been extensively studied for their ability to regulate inflammatory responses by modulating the activity of pro-inflammatory genes and influencing signal transduction pathways, thereby reducing neuroinflammation and neuronal death. Additionally, polyphenols have shown promise in modulating various cellular signaling pathways associated with neuronal viability, synaptic plasticity, and cognitive function. Epidemiological and clinical studies highlight the potential of polyphenol-rich diets to decrease the risk and alleviate symptoms of neurodegenerative disorders and neuroinflammation. Furthermore, polyphenols have demonstrated their therapeutic potential through the regulation of key signaling pathways such as Akt, Nrf2, STAT, and MAPK, which play critical roles in neuroprotection and the body’s immune response. This review emphasizes the growing body of evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of polyphenols in combating neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation, as well as enhancing brain health. Despite the substantial evidence and promising hypotheses, further research and clinical investigations are necessary to fully understand the role of polyphenols and establish them as advanced therapeutic targets for age-related neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammatory conditions.
Neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease, provide a substantial difficulty for healthcare systems worldwide since they worsen over time and there are no effective remedies available (Giri et al., 2024). These incapacitating ailments are distinguished by the slow degeneration of neurons and neural activity, resulting in cognitive deterioration, motor disabilities, and, finally, a substantial fall in the overall wellbeing of the affected persons (Singh K. et al., 2024). Despite extensive research spanning several decades, the hunt for effective treatments for neurodegenerative disorders continues to be a challenging endeavor.
Neuroinflammation is an essential element in the advancement of neurodegenerative disorders, marked by the stimulation of microglia, the main immune cells comprising the central nervous system (Adamu et al., 2024). Microglia, under normal physiological circumstances, offer neuroprotection by the release of neurotrophic factors and the maintenance of an anti-inflammatory milieu, therefore promoting the wellbeing and optimal functioning of neurons (Maugeri et al., 2021). Nevertheless, when exposed to inflammatory triggers such tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-κ), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), microglia have the ability to assume a pro-inflammatory configuration (Barry-Carroll and Gomez-Nicola, 2024). These activations trigger the synthesis of cytokines and other inflammatory substances that worsen the damage to neurons, therefore contributing to the death of neurons and the advancement of neurodegenerative disorders (Mesci et al., 2024). Degenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis are frequently characterized by chronic activation of microglia and persistent inflammation (Thomas et al., 2024). In these conditions, neurodegeneration is driven by a continuous cycle of inflammation and neuronal death. Elucidating the dual function of microglia is crucial for the development of treatments that may alleviate neuroinflammation and enhance neuroprotection in neurodegenerative diseases (Han et al., 2024). Figure 1 depicts the equilibrium between these two microglial immune responses, emphasizing how their level of activation might impact the progression of neuroinflammation and contribute to the development of neurodegenerative disorders.
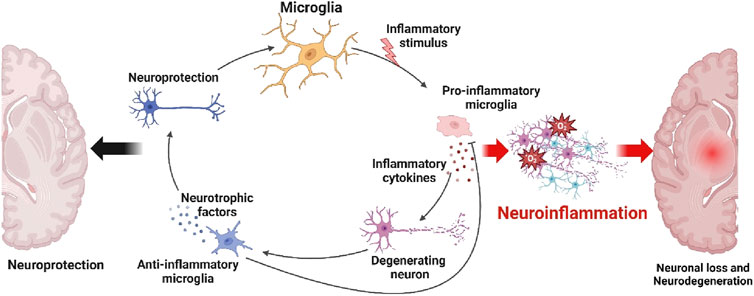
Figure 1. Formation of neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Microglia function as both neuroprotective and neurodegenerative agents in the brain’s response to injury and disease. Microglia play a neuroprotective role by promoting neuronal survival and repair by releasing neurotrophic substances and exhibiting an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Microglia, on the other hand, have the ability to become activated in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli like TNF-κ, IL-1β, and IL-6. Neuronal loss and an increasing number of neurodegenerative conditions have been associated with this transformation. Figure drawn by BioRender.com at 26 August 2024.
Polyphenolic compounds, a varied class of naturally occurring bioactive substances, have attracted considerable interest owing to their possible neuroprotective effects (Shi et al., 2024). These chemicals are extensively found in plants, functioning as secondary metabolites that aid in defense systems and coloring. Polyphenols are categorized as flavonoids, phenolic acids, lignans, and stilbenes, each defined by unique structural characteristics (Sejbuk et al., 2024). Flavonoids are categorized as flavones, flavonols, and isoflavones, which are present in fruits, vegetables, tea, and wine (Billowria et al., 2024). Caffeic and ferulic acids, types of phenolic acids, are prevalent in coffee and grains (Kumar et al., 2024). Lignans, found in seeds and whole grains, and stilbenes such as resveratrol, located in grapes and berries, illustrate the structural diversity of polyphenols (Majedi and Ahamad, 2024). This extensive variety of structural kinds highlights their intricate biological functions. Comprehending the origins and structural variety of polyphenolic compounds is crucial for recognizing their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties, presenting new therapeutic options for neurodegenerative disorders.
There has been an increasing focus on the possible impact of polyphenols in reducing the advancement of neurodegenerative diseases and enhancing brain function (Shi et al., 2024). Polyphenols are inherent substances present in a variety of plant-derived foods, including fruits, vegetables, tea, coffee, and red wine (Thakur and Kumar, 2024). Their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective characteristics have attracted attention due to their potential therapeutic benefits in the treatment of neurodegeneration (Shi et al., 2024). Studying plant polyphenols to prevent degeneration and age-related disorders like NDs is part of the search for natural ways to age healthily (Song et al., 2024). In vitro, cell-based, animal, and human studies have investigated how dietary polyphenols protect the brain (Figueira et al., 2017).
This research aims to explore the current understanding of the mechanisms through which polyphenols act in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases, as well as their potential as therapeutic agents. Current preclinical and clinical data that supports the effectiveness of polyphenols in reducing the advancement of diseases, boosting cognitive abilities, and promoting overall brain health (Mayer et al., 2024). In addition, the difficulties and restrictions involved in applying these discoveries to actual medical treatment and suggest future research paths to better understand the healing capabilities of polyphenols in neurodegenerative disorders (Socała et al., 2024). This review aims to provide a clear understanding of how polyphenols and neurodegeneration interact, with the goal of helping to create new treatment approaches to combat these debilitating diseases and enhance the quality of life for millions of affected individuals globally.
Neuroinflammation is a pathological process that involves the activation of glial cells and the subsequent production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, resulting in neuronal damage and impaired functionality (Biswas, 2023). The neuroprotective effects of polyphenols are mediated by many pharmacological mechanisms. One of the principal mechanisms by which polyphenols provide protection against neuroinflammation is the modulation of microglia and astrocytes, which are the immune cells that dwell in the brain (Al Mamun et al., 2024). Polyphenolic compounds, including resveratrol, curcumin, and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), have been found to possess inhibitory effects on microglial activation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-κ, IL-1β, and IL-6 (Liu et al., 2023). Additionally, these substances facilitate the synthesis of anti-inflammatory cytokines, so fostering a greater equilibrium in the immunological response within the brain (Tayab et al., 2022). Moreover, polyphenols possess robust antioxidant characteristics that greatly contribute to the mitigation of oxidative stress, a state that frequently intensifies neuroinflammation (Figure 2) (Chatterjee et al., 2024). Polyphenols have a crucial role in mitigating oxidative damage to neurons by effectively scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and augmenting the activity of intracellular antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) (Hu et al., 2024). In addition, polyphenols have been observed to engage with signaling pathways implicated in neuroinflammation. One example of its ability is the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation, which is a crucial transcription factor responsible for regulating the expression of genes associated with inflammation (Vaghari-Tabari et al., 2024). Moreover, polyphenols effectively regulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, which play a crucial role in cellular reactions to stress and inflammation (Islam et al., 2024). In brief, polyphenols present a potentially effective therapeutic strategy for addressing neuroinflammation through their ability to modulate immunological responses, mitigate oxidative stress, and modulate crucial inflammatory signaling pathways (Dama et al., 2024). Due to their diverse range of effects, they possess the potential to serve as viable candidates in the prevention or deceleration of neurodegenerative disorders. Polyphenols have great potential in preventing and treating neurological conditions because of their diverse pharmacological properties, which include antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. Their possible neuroprotective properties, especially in the context of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases, have attracted considerable study. Table 1 is a representation of the pharmacological function of polyphenols under different neurodegenerative diseases.
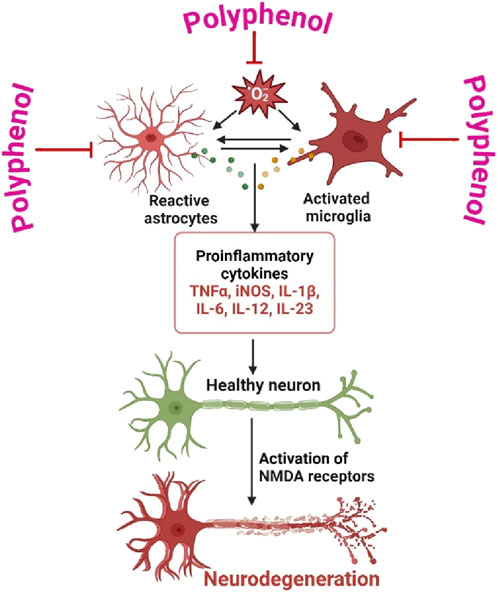
Figure 2. Roles of Astrocytes and Microglia in Neurodegeneration is prevented by polyphenol. The dual functions of astrocytes and microglia in the process of neurodegeneration and the potentially neuroprotective properties of polyphenols. Through the modulation of immunological responses, reduction of oxidative stress, and regulation of inflammatory signaling pathways, polyphenols protect neurodegeneration indicate that polyphenols have the potential to be used as therapeutic agents for neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Figure drawn by BioRender.com at 26 August 2024.
Table 1. The tabular representation of the pharmacological role of polyphenols in neurodegenerative diseases.
In AD and Dementia, polyphenols have been demonstrated as a vital neuroprotective characteristic evolving the therapeutic option. Green tea and White tea extracts have been used as a therapeutic goal in treating neurodegenerative age-medicated diseases like AD and dementia to inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity (Afzal et al., 2022). In the Aβ-mediated cytotoxicity in the rat model, the polyphenols of green tea regulated the expression of initial rat cortical neurons (Albadrani et al., 2024). A research study has demonstrated that the grape’s polyphenols enhanced the cognitive efficacy in the mouse research model developed of AD (Tavan et al., 2024). The synaptic transmission was enhanced by the epicatechin metabolite 3′-O-methyl-epicatechin-5-O-β-glucuronide via the response binding protein of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) (Jaeger et al., 2018). A research study has revealed that in the transgenic mice research model, the suppression of oligomerization of Aβ peptides has been exhibited by the polymeric polyphenol of grape seed and regulated cognitive losses neuronal reduction cells (Jadidian et al., 2024). The same research study also reported that the grape’s polyphenols showed the potential activity to minimize the abnormality for tau protein folding (Jadidian et al., 2024). Many experiments with animal models have reported that grape seed polyphenols suggested anti-Aβ activity (Al Amin et al., 2024; Vicente-Zurdo et al., 2024).
Resveratrol, an enormous polyphenol in the red wines and grapes, suppressed the expression of Aβ 42 fibril and regulated the Aβ neurotoxicity through suppressing the inhibition of the induceable nitric oxide synthase (Shah et al., 2024). In AD, the Resveratrol exhibited high therapeutic’s activity in the lipid core nanocapsules. It has been observed that the flavonoid fisetin suppressed Aβ fibril expression, and this evidence indicated that the flavonoid fisetin has appeared as a potential therapeutics for the treatment of AD (Al Amin et al., 2024; Bagchi et al., 2020). Morin formed by 2′,3,4′,5,7-pentahydroxyflavone has revealed a potent neuroprotective activity to inhibit neurons’ death by suppressing the tau hyperphosphorylation initiated by the Aβ (Yilmazer et al., 2024). Likewise, a research study on the transgenic mouse model, the tannic acid, has been noted to inhibit Aβ deposition by reducing the fission of β carboxyl-terminal amyloid precursor protein (APP) complex and regulated the inflammation of neuron cells (Manoharan et al., 2024). A research study in the 5XFAD transgenic mouse research model, A flavonoid named 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, has been identified to develop the cognitive efficacy to decrease the secretion of β-secretase enzyme and the synthesis of amyloid-beta (Aβ through the activation of receptor tyrosine kinase B (Emili et al., 2022). Moreover, the polyphenol liquiritigenin developed memory in the Tg2376 mice research model with AD (Zhong et al., 2024). It also minimized the astrocytosis and reduced the activation of Notch-2 for that it can regulate neuron death (Onciul et al., 2024). Figure 3 represents the overall mechanism of polyphenol in AD.
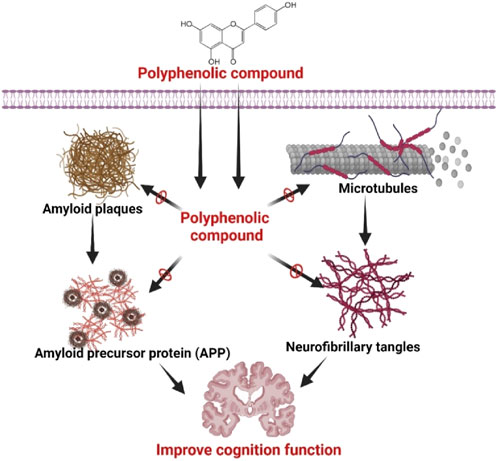
Figure 3. Effects of polyphenolic compounds in AD to improve cognition function. Polyphenolic substances have been found to possess inhibitory effects on the production of amyloid plaques, microtubule stabilization, and modulation of amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing, resulting in a reduction in neurofibrillary tangle deposition. The aforementioned acts collectively lead to the enhancement of cognitive function in individuals with neurodegenerative diseases by which polyphenolic compounds demonstrate their neuroprotective properties, emphasizing their potential as therapeutic interventions in the treatment of cognitive decline linked to conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. Figure drawn by BioRender.com at 26 July 2024.
Curcumin protects against peroxynitrite-mediated nitrosative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in N27 dopaminergic neuronal cell cultures exposed to 0–1,000 μM concentrations, mitigating the inhibition of mitochondrial complexes (Chithra et al., 2023). Curcumin in neurodegenerative diseases: In a study on neurotoxicity in rats induced by homocysteine, curcumin administered at doses of 5 and 50 mg/kg demonstrated protective effects (Plascencia-Villa and Perry, 2023). It alleviated homocysteine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress, reduced lipid peroxidation, and improved memory and learning in rats (Banji and Banji, 2024). Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) enhances resistance to oxidative damage induced by glucose oxidase in immortalized rat neurons (H 19-7) at concentrations ranging from 10 to 200 mM, demonstrating its potential in addressing oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases (Singh S. et al., 2024). EGCG was tested in an immortalized hippocampal neuronal cell line derived from mice to study its effects on Parkinson’s disease. At a concentration of 0.36 mM, EGCG was found to reduce oxidative cytotoxicity, inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway, and counteract neurodegeneration and levodopa methylation (Kang et al., 2010). EGCG helps mitigate age-related oxidative damage in the rat brain. Administered at a dose of 2 mg/kg body weight per day, it alleviates senescence-induced oxidative stress and enhances the activity of antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (Mokra et al., 2022) (Ye et al., 2024). Mangiferin (2.5 mg/mL) has been shown to inhibit neuronal damage, oxidative stress, and depolarization in a rat model of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in cortical neurons, suggesting its potential therapeutic effects in neurodegenerative disorders (Walia et al., 2021). Mangiferin in a murine neuroblastoma cell line (N2A) at a concentration of 0.25 mM protects against oxidative stress-induced toxicity caused by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium. It restores GSH levels and reduces the expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) as well as the mRNA levels of catalase (Amazzal et al., 2007). Mangiferin and morin reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation and activate the enzyme antioxidant system in primary rat neuron cultures exposed to glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. At a concentration of 100 nM, they help mitigate ischemic brain damage by stimulating the antioxidant enzyme mechanisms (Alberdi et al., 2018). Resveratrol has been shown to reduce dopaminergic neurodegeneration in rats induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at concentrations ranging from 15 to 60 μM. It mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity by decreasing ROS-mediated NADPH oxidase activity and delaying the activation of MAPK and NF-kB pathways (Teijido and Cacabelos, 2018). Resveratrol protects dopaminergic neurons in midbrain slice cultures from damage induced by MPP(+), by preventing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cellular oxidative damage, through modulation of ROS signaling and maintaining cellular glutathione levels at concentrations of 30 and 100 μM (Feng et al., 2024). Tea polyphenol (60 mg/kg/day) reduces synaptosomal ROS development and mitigates brain excitotoxic injury, including NMDA-induced neurotoxicity in mice (Niinuma et al., 2024).
In AD, it has been noted that the quercetin and rutin decreased the Aβ formation and also inhibited the aggregation of Aβ fibrils (Monteiro et al., 2024). The animal model studies revealed that both compounds also inhibited scopolamine-mediated amnesia. Research with flavonoid rutin has been shown in neuroblastoma cells SH-SY5Y, which can regulate oxidative stress, malondialdehyde and glutathione disulfide (Amiri et al., 2024). It also reduced the activation of inflammatory cascade by reducing cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β. Ferulic acid is a phenolic acid that has been revealed as a higher neuroprotective agent to regulate the Aβ toxicity than the polyphenol quercetin (Mugundhan et al., 2024). Many research studies have recently documented that polyphenols provide therapeutic potential in both the cell line and the animal research model. Polyphenols are proposed as a treatment target for age-related diseases such as AD and dementia for their efficiency to develop synaptic transmission by regulating cAMP, Aβ toxicity, and various signaling pathways (Dhapola et al., 2024).
Predominantly, Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation that decreases the number of dopaminergic neurons (Watanabe et al., 2024). Polyphenols have been recognized as a therapeutic target for treating PD to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress (Gahtani et al., 2024). Resveratrol can regulate the reduction of dopaminergic neurons in the rat research model with PD (Zhang Y. et al., 2024). The research studies have noted that in PD, through reducing the mRNA expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and the mRNA of TNF-α in substantia nigra, the resveratrol has been exhibited to inhibit the neural inflammation (Xue et al., 2024). Besides, in the rat research model of PD, resveratrol has shown the potential activity to reduce oxidative stress, protein carbonyl (PC), and lipid peroxidation (Khan et al., 2024). Many research studies have shown that the action of oxyresveratrol also reduces neuronal loss in SH-SY5Y cells by reducing SIRT1 and caspase-3, c-jun transcription factors and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) (Rahman et al., 2017; Rahman et al., 2021). Likewise, oxyresveratrol, the ferulic acid, also exhibited the potential neuroprotective activity through down-regulating the JNK pathway (Caban et al., 2023). The reduction of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyrimidinium (MMP) regulated the microglia activation used as a precursor for PD’s pathogenesis, and these abnormalities were overcome by quercetin (Bournival et al., 2012). Studies have demonstrated that quercetin can show the potential neuroprotective activity in mice model with PD through augmenting glutathione peroxidase (G{X), Na (+), K (+) -ATPase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Gugliandolo et al., 2020; Biswas et al., 2022). Other studies have shown that quercetin has prevented cell death in the PD mice research model, however, when quercetin is used as its metabolite known as quercetin-3-O-β-glucuronide due to its lower absorption rate (Muñoz-Reyes et al., 2022). Many other research studies in PD have demonstrated that the high neuroprotective activity can be induced by the other polyphenols known as kaempferol, baicalein, EGCG, and caffeic acid (Tavan et al., 2024; Bhullar and Rupasinghe, 2013). Identically, the polyphenols derived from various plant extracts have also shown the neuroprotective pharmacological role in PD research studies (Figure 4).
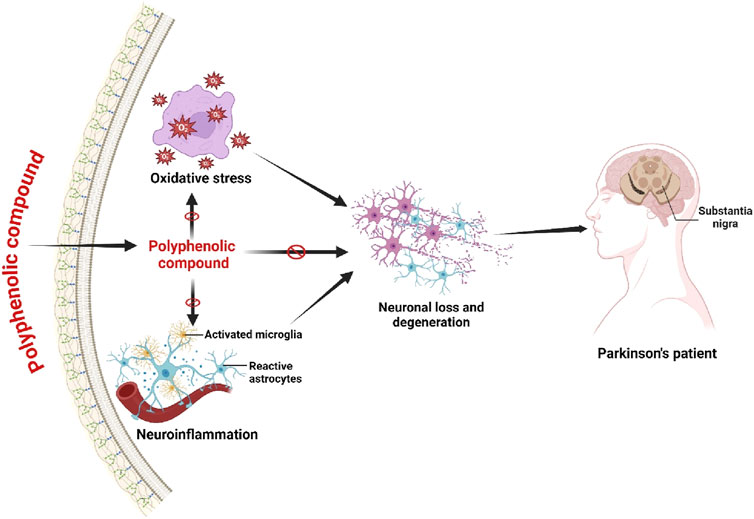
Figure 4. Effects on polyphenolic compound in Parkinson’s Disease. Polyphenolic chemical exerts inhibitory effects on oxidative stress, hence inducing the activation of microglia, thereby mitigating neuronal death. The mechanism by which Parkinson’s Disease progression is inhibited involves the lowering of oxidative stress and the protective function of activated microglia. Figure drawn by BioRender.com at 26 July 2024.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by autoimmune-related demyelination of the central nervous system (CNS), which can result in cognitive impairment and paralysis. The inflammation and downregulation of immunity can be attenuated by MS therapies (Zeng et al., 2024). In the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) research model of MS, the inhibition of neuron cell loss without any immunosuppression has been exerted by the polyphenol resveratrol through tracing the 2 homolog1 (SIRT1) activator (Azam et al., 2019). The formulation of therapeutic’s standard of resveratrol SRT501 was shown to reduce the neuron cell damage in the EAE cell line by activating SIRT1 (Chen et al., 2024a). Cell culture-based research studies by resveratrol have revealed SIRT1-associated neuroprotective activity (Yahia et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2013). The polyphenol quercetin showed the immune regulation activity through regulating the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β and also decreased the proliferation rate in a peripheral based mononuclear cell which derived from the various sclerosis patient’s body (Ferreira et al., 2024). The epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) noted the strong neuroprotective activity via controlling the neuro-inflammation and reducing the damage of neuron cells (Tripathi et al., 2024). Moreover, the other polyphenols like piceatannol, apple polyphenols 222, myricetin, and quercetin have regulated the activation of SIRT1 and shown effective therapeutic potential in MS treatment (Rudrapal et al., 2024). Polyphenols have been suggested as a strong therapeutic target for the treatment of age-related multiple sclerosis (MS) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) due to their potential properties (ALS) (Chatterjee et al., 2024).
Polyphenols, a heterogeneous collection of naturally derived substances present in plants, have attracted interest due to their possible therapeutic properties, specifically in the context of neurodegenerative disorders. The molecular mechanism of polyphenols in neurodegenerative diseases is based on cell signalings are presented in Table 2 is a list of frequently encountered polyphenols, along with their respective plant origins, usual levels of concentration, and their molecular mechanisms involved in neurodegeneration. Their modes of operation frequently entail the regulation of cell signaling pathways that are vital for cellular function and survival. These are the main factors by which polyphenols can affect these pathways.
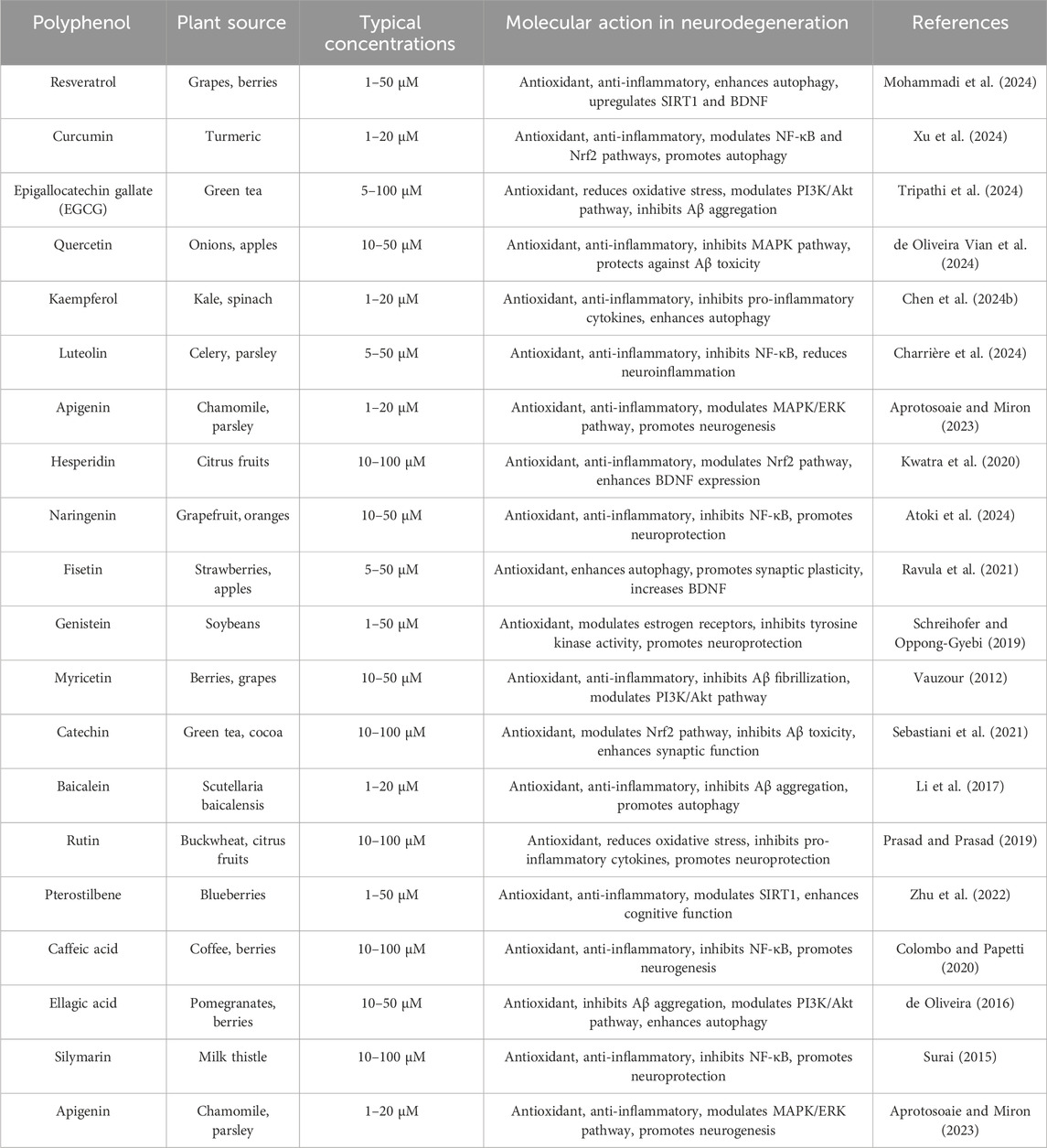
Table 2. Polyphenols are a varied collection of naturally existing chemicals present in plants, renowned for their antioxidant characteristics and possible therapeutic impacts on neurodegenerative disorders.
Polyphenols possess the ability to eliminate harmful free radicals and enhance the activity of natural antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase (Jomova et al., 2024; Dzah et al., 2024). This decreases oxidative stress, which is involved in the development of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (Gahtani et al., 2024; Wang J. et al., 2024).
Neurodegenerative diseases are significantly influenced by inflammation. Polyphenols have the ability to hinder pro-inflammatory substances including NF-κB, COX-2, and iNOS, and decrease the generation of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (Prakash et al., 2024; Nery-Flores et al., 2024). This action aids in regulating the neuroinflammatory response, which has the potential to decelerate the progression of the disease.
Polyphenols exert an impact on various signaling pathways, encompassing.
The MAPK pathway involves the regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which can have an impact on cell survival, differentiation, and apoptosis (Ampadu et al., 2024). Both the nervous system and other tissues benefit from the ERK1/2 and PI3K pathways. The ERK is found in several involving physiological functions such as proliferation, differentiation, and controlling various growth factors’ response (Islam et al., 2024). With the aid of upstream activator kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK), phosphorylation of threonine and tyrosine residues activates ERK1/2. ERK1/2 changes its position after activation and phosphorylates a variety of molecules, including transcription regulatory and cytoskeletal protein. Some phenolic compounds activate the ERK1/2, which enhances cell survival in several cell lines. The protection of PC12 cell against apoptosis was observed upon the activation of ERK1/2 by lutein (Hu et al., 2021). Furthermore, the viability of PC12 cells treated with U0126, an ERK1/2 kinase inhibitor, was decreased. ERK1/2 is important to understand the neuronal differentiation and activation of the released cytoskeleton and synaptic protein (Waetzig et al., 2017). Luteolin has been identified to improve outgrowing neuritis and expression of GAP-43 protein, known as neuronal biomarkers, and (HO-1) oxygenase1 expression in PC12 cells (Jain and Jain, 2019). The pharmacological inhibition of ERK 1/2 can block both of these effects. This research study has also shown that both ERE and PKC are involved in the production of PC12 neuritis (Bhuia et al., 2024). Simmilarly, the involvement of ERK and PKC pathways in the neurogenesis phase in PC12 cells also leads to a curcurrination response. The ERK and P38MAPK also inhibit Artepillin C-induced neutric outgrowth of PC12m3 cells (Motoda et al., 2019).
The activation of P38 MARK by ERK was also shown to be responsible for the c-inducing artepillin neuritis outgrowth of PC12m3 cells (Kano et al., 2008) (Figure 5). Finally, fisetin has been demonstrated that works efficiently during PC12 differentiation, while MEK inhibitors have reduced the fisetin induced ERK and neuritis outgrowth (Anwar et al., 2021).
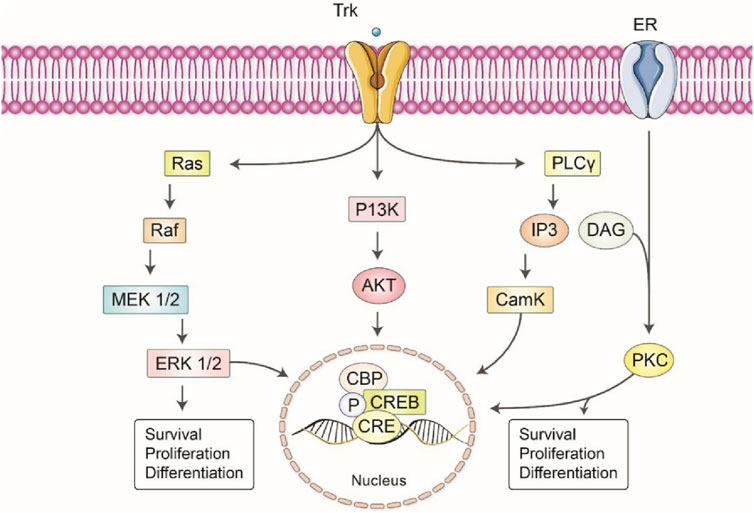
Figure 5. Principal signals that mediate the neurotrophic effects of different polyphenols. The neuromodulatory effects of different polyphenols are facilitated by several intracellular signaling pathways. The activation of the RAS/Raf/MEK pathway by polyphenols results in the modulation of neuronal survival and differentiation. Furthermore, the PI3K/AKT pathway is activated, hence facilitating cellular viability and proliferation. The IP3/PKC signaling cascade is of paramount importance in the mechanism of calcium signaling and the preservation of neuronic integrity. The combined actions of these pathways play a significant role in the neuroprotective effects of polyphenols, underscoring their potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.
Stimulating this route can enhance cell viability and protect against neurodegeneration, which is essential for preventing neuronal death (Manju and Bharadvaja, 2024). Recent studies suggest that PI3K and AKt (PI3K downstream effector) are involved in the survival of neurons (Ma et al., 2024). It also enhances the outgrowth of neurite and other neurotropic effects of polyphenols (Tavan et al., 2024). A research study has demonstrated that PI3K/AKt was responsible in Aβ induced cognitive impairment in mice (Liu G. et al., 2024). By increasing the neurotrophins via PCREB and pAKt signaling, it may be possible to protect neurons against hypoxia (Tregub et al., 2024). Methyl 3, 4-dihydroxybenzoate, a chemical compound derived from phenolic acid, can improve survival and neuronal outgrowth in cultivated cortical neurons via PI3K/AKt signaling pathway (Gopathy et al., 2024). The promotion of neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth may be interrupted by a PI3K specific inhibitor (Ma et al., 2024). The effects of NGF in PC12 cells were also potentiated by puerarin by activating the ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKt pathway (Gopathy et al., 2024). The natural flavonoid, astilbin has been found to reduce depressive behavior by activating MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKt pathways in mouse models (Gopathy et al., 2024).
Polyphenols stimulate the activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), which in turn increases the production of detoxifying enzymes and proteins that play a role in the cellular antioxidant response (Laddha et al., 2024). Neuronal cells respond to oxidative stress through the Nrt2 pathway and the enzyme including glutathione peroxidase, γ-glutamylcystine synthetase, gluta-thione s-transferase, Ho-1, NADPH quinine oxireductase-1, thlo redoxin, sulfiredoxin, peroxiredoxin and theoredoxin reductase plays a critical role in cell defense (Cadenas-Garrido et al., 2024; Anjo et al., 2024). The Nrf2 pathway and these enzymes mainly have a role in regulating CNS disease (Xiang et al., 2024). The luteolin and puerarin are phenolic compounds that enhance HO-1 expression in PC12 cells and CAPE dopaminergic neurons by promoting Nrf2 binding to ARE (Li J. et al., 2024) (Figure 6). Through the activation of the transcription factor Nrf2, the expression of HO-1 can be increased, the EGCG was capable of protecting cells against oxidative stress (Chi et al., 2024). The neuroprotective effect of puerarin on lesioned substantia nigra caused by 6-OHDA was protested neurons in the substantia nigra by modulating BDNF expression and triggering the Nrt2/ARE pathway (Li et al., 2023). The conventional sage plants and carnosic acid have been found in neuroprotective effects by activating Nrt2 and PC125 cells (Mirza et al., 2023).
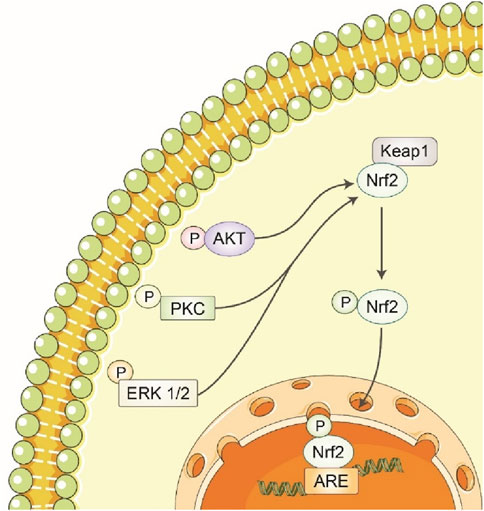
Figure 6. Polyphenols increase the expression of detoxification/antioxidant enzymes by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway. Polyphenols stimulate detoxification and antioxidant enzymes via the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway. Nrf2 moves to the nucleus when Keap1 changes conformation after polyphenol contact. Nrf2 increases detoxification and antioxidant defense enzyme expression by binding to the antioxidant response element (ARE) in target gene promoters. This mechanism helps polyphenols protect cells from oxidative damage and promote health.
Polyphenols, a heterogeneous collection of naturally occurring chemicals present in plants, have a substantial impact on regulating proteostasis and autophagy, which are essential mechanisms in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative disorders (Rahman et al., 2023). Protein homeostasis is the equilibrium of protein levels maintained by the processes of synthesis, folding, and degradation (Lippi and Krisko, 2024). In order to improve proteostasis, polyphenols stimulate the correct folding of proteins and trigger autophagy pathways, which are cellular mechanisms responsible for breaking down and recycling damaged proteins and organelles (Rahman et al., 2022). Polyphenols facilitate the removal of misfolded proteins and aggregates by autophagy, therefore mitigating neuroinflammation and slowing down the advancement of neurodegenerative disorders (Niu et al., 2024). By regulating important signaling pathways, polyphenols have therapeutic potential in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (Li L. et al., 2024).
Polyphenols have the ability to increase the production of neurotrophic factors, specifically BDNF, which promotes the development, survival, and differentiation of neurons (Carito et al., 2015). Polyphenols may modulate neurotrophic factors, which could potentially impact cognitive performance and mood control (Morton et al., 2024). For instance, elevated levels of BDNF are linked to enhanced cognitive function and decreased symptoms of depression (Kong et al., 2024). Moreover, the gut-brain axis significantly mediates the impact of polyphenols on neurotrophic factors (Liu H. et al., 2024). The gut microbiota can convert polyphenols into bioactive compounds that traverse the blood-brain barrier and affect central nervous system (CNS) functioning (Domínguez-López et al., 2024). These interactions may alleviate cognitive decline and mood problems by enhancing BDNF expression and diminishing neuroinflammation (Rahmati-Dehkordi et al., 2024). Recent evidence indicates that polyphenols enhance BDNF synthesis in conjunction with physical exercise and calorie restriction. This combinatorial method presents a viable way to postpone or avert age-related cognitive deterioration and mood disorders (Aziz et al., 2024). Consequently, polyphenols embody a natural, multifarious strategy for preserving neuronal health and augmenting neurotrophic factor function. Continued investigation of their particular molecular targets and enduring effects on cerebral health is an essential area of emphasis.
Polyphenols have the ability to affect the way genes are expressed by using epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation and histone modification (Castillo-Ordoñez et al., 2024). These mechanisms can change the expression of genes that are related to the protection and degeneration of the nervous system. The diverse effects of polyphenols on cell signaling as well as cellular processes make them highly attractive for the development of therapeutic approaches to combat neurodegenerative disorders (Islam et al., 2024). Besides, DNA methylation, polyphenols can also affect histone alterations, including acetylation and methylation. Histones are proteins that encase DNA, and their alteration can either facilitate or obstruct gene transcription (Sabi, 2024). Polyphenols such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and resveratrol have been documented to influence histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases (HDACs), the enzymes that regulate the acetylation status of histones (Bontempo et al., 2024). Through the regulation of these enzymes, polyphenols facilitate chromatin relaxation, hence enhancing accessibility for transcription factors to activate genes that contribute to cellular repair and neuroprotection.
Additionally, polyphenols may control non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs, which are essential for the regulation of gene expression (Wu et al., 2024). Polyphenols can affect the expression of particular microRNAs implicated in neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy, thus offering a method to regulate pathways related to neurodegeneration (Prasanth et al., 2024). Notwithstanding the encouraging outcomes from in vitro and animal research, clinical trials investigating the epigenetic effects of polyphenols remain scarce. Future study must concentrate on determining the ideal dosages, bioavailability, and long-term impacts of polyphenols on human health. Ultimately, comprehending the manner in which polyphenols alter the epigenome may facilitate the creation of innovative, non-invasive treatments for the prevention or postponement of neurological diseases.
Neuropathic inflammation, a prevalent characteristic observed in several neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis, is distinguished by the stimulation of glial cells, the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and consequent impairment of neuronal function (Abd-Nikfarjam et al., 2023). Polyphenols possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant characteristics, rendering them highly promising contenders for the amelioration of these harmful processes (Sun et al., 2024). One of the principal mechanisms via which polyphenols exert their neuroprotective effects is by modulating oxidative stress, a significant contributor to neuroinflammation (Tavan et al., 2024). Polyphenols exhibit robust antioxidant characteristics, enabling them to counteract the harmful effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitigate excessive oxidative harm to neurons (Hu et al., 2024; Yahia et al., 2024). Through the process of scavenging free radicals, these entities contribute to the preservation of neuronal cell integrity and the inhibition of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways activity. Table 3 that is provided presents a comprehensive overview of several polyphenols, including their natural origins, experimental models employed for investigating their impacts, and the molecular mechanisms through which they exert neuroprotective benefits. It is becoming more widely acknowledged that these chemicals provide promising therapeutic promise in the management of neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders.
Curcumin, derived from turmeric (Curcuma longa), provides neuroprotection by inhibiting amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, reducing oxidative stress, and modulating microglial activity (Azzini et al., 2024). Resveratrol, found in grapes and red wine, activates SIRT1, enhances mitochondrial function, and reduces inflammation. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), from green tea (Camellia sinensis), inhibits apoptosis while also reducing oxidative stress and inflammation (Tao et al., 2024). Quercetin, sourced from apples, onions, and berries, reduces inflammation, inhibits excitotoxicity, and decreases oxidative stress (Shi et al., 2024). Luteolin, present in celery, parsley, and thyme, suppresses microglial activation and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines (Madhubala et al., 2024). Kaempferol, available in green leafy vegetables and tea, exhibits antioxidant activity and inhibits the NF-κB pathway (Silva dos Santos et al., 2021). Apigenin, from chamomile and parsley, modulates GABAergic activity, reduces amyloid plaques, and has anti-inflammatory effects (Charrière et al., 2024). Anthocyanins, found in berries like blueberries and raspberries, inhibit oxidative stress, reduce neuroinflammation, and enhance synaptic plasticity (Tran and Tran, 2021). Hesperidin, abundant in citrus fruits such as oranges and lemons, increases antioxidant defenses, inhibits neuroinflammation, and improves cognition (Pontifex et al., 2021). Baicalein, derived from Scutellaria baicalensis (Baikal skullcap), inhibits α-synuclein aggregation, reduces oxidative stress, and has anti-inflammatory properties (Melrose, 2023). Fisetin, found in strawberries, apples, and onions, exhibits antioxidant activity, reduces inflammation, and modulates pathways involved in aging (Rauf et al., 2023). Genistein, sourced from soybeans and legumes, reduces oxidative stress, modulates estrogen receptors, and inhibits neuroinflammation (Dogra et al., 2023). Naringenin, present in grapefruit and citrus fruits, inhibits Aβ aggregation, reduces oxidative stress, and inflammation (Choi et al., 2023). Pterostilbene, found in blueberries and grapes, enhances antioxidant defenses, modulates sirtuins, and reduces neuroinflammation (Qu et al., 2023). Catechin, sourced from green tea and cocoa, reduces oxidative stress, inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines, and protects neurons (Özduran et al., 2023). These polyphenols contribute to neuroprotection by acting as antioxidants, reducing inflammation, and modulating pathways implicated in neurodegenerative diseases.
It is recommended that future investigations prioritize the elucidation of the precise molecular targets associated with polyphenols, the enhancement of their bioavailability, and the comprehension of their interactions with the gut-brain signaling pathway (Gong et al., 2024). Furthermore, the advancement of treatments based on polyphenols, potentially in conjunction with nanotechnology for precise dosage administration, has the potential to significantly transform the management of neuroinflammatory disorders (Fang et al., 2024). Furthermore, it is imperative to conduct clinical research in order to ascertain the effectiveness and safety of polyphenols in human populations, particularly when considering their long-term usage (Bolat et al., 2024). The potential incorporation of polyphenols into dietary guidelines or as dietary supplements may emerge as a pivotal approach in mitigating or decelerating the advancement of neuroinflammatory disorders, hence fostering enhanced aging outcomes and an elevated standard of living.
Recent research indicates that polyphenols have the ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, which is an essential characteristic for any substance that protects the brain (Isabel et al., 2024). Studies have demonstrated that they can regulate important signaling pathways linked to neurodegeneration, such as diminishing oxidative stress and inflammation, which play a crucial role in the advancement of neurodegenerative diseases (Nájera-Maldonado et al., 2024). In addition, polyphenols have the ability to prevent the clumping together of amyloid-beta peptides, which is a characteristic feature of Alzheimer’s disease (Gujarathi et al., 2024). They also improve autophagy, which helps in the removal of damaged proteins and organelles. Subsequent investigations are expected to prioritize the examination of the bioavailability and delivery mechanisms of polyphenols, given that their inadequate absorption and quick metabolism presently restrict their medicinal efficacy (Abbasi et al., 2024). Nanotechnology-based delivery methods and synthetic analogs that enhance bioavailability show great potential (Lv et al., 2024). Furthermore, comprehending the synergistic impacts of mixtures of polyphenols and their interaction with other elements in the diet could improve their effectiveness (Zhang W. et al., 2024). Additionally, clinical trials are necessary to determine the safety, effectiveness, and most effective doses of polyphenols in people (Chen et al., 2024c). As our knowledge of the molecular pathways that cause neurodegeneration increases, polyphenols may become essential elements of treatment efforts that target several factors. Therefore, the potential of polyphenols in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases shows promise for the future. Further investigation is necessary to completely understand and utilize their benefits in clinical applications.
Polyphenols, while showing potential in the treatment of neuroinflammation, encounter limitations such as low bioavailability, instability in the gastrointestinal tract, and fast metabolism, which minimize their therapeutic effectiveness. Moreover, the presence of inconsistent absorption and distribution patterns across individuals, the possibility of toxicity at high dosages, and the scarcity of clinical data on the long-term effects present obstacles for the application of these substances in neuroinflammatory disorders. Although they possess encouraging neuroprotective effects, their clinical application is hindered by various obstacles. A major obstacle that needs to be addressed is the issue of bioavailability. Polyphenols frequently exhibit limited absorption rates and undergo rapid metabolism within the human body, hence constraining their capacity to reach and exert their effects on specific regions within the brain (Grabska-Kobyłecka et al., 2023). The blood-brain barrier, a selective membrane, exacerbates this problem by limiting the passage of certain therapeutic substances, such as polyphenols, into the central nervous system (Carecho et al., 2024). Another issue to consider is the variety in polyphenol concentration among various plant sources, which might result in inconsistencies in dosage and effectiveness (Wang C.-W. et al., 2024). The efficacy of polyphenols can be influenced by variables such as the composition of the diet, the process of digestion, and variations in individual metabolism, which complicates the establishment of uniform treatment (Martemucci et al., 2024). In addition, although polyphenols possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory characteristics, the intricate nature of neurodegenerative disorders, which encompass multiple pathological factors, may necessitate more focused and precise therapies beyond the capabilities of polyphenols alone (Islam et al., 2024). Further research is required to examine the interplay between polyphenols and other medications, as well as their possible adverse effects, especially in the context of prolonged usage. Translating findings from in vitro and animal models to clinical practice has been difficult due to the lack of replication of identified effects in human studies. To overcome these constraints, it is essential to enhance the delivery systems, conduct thorough clinical trials, and get a deeper understanding of the interactions of polyphenols. These efforts are critical in exploring the potential of polyphenols in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Future research should concentrate on enhancing the bioavailability and stability of polyphenols to overcome their limitations in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. A possible strategy involves the creation of sophisticated delivery methods, such as nanoencapsulation or liposomal formulations, which can improve the absorption of polyphenols and enable their passage across the blood-brain barrier. By safeguarding polyphenols from fast metabolism and degradation, these systems can enhance the concentration of active chemicals in the brain, hence augmenting their therapeutic efficacy.
Another research option is identifying particular polyphenols that have enhanced bioavailability and more targeted effects on neuroinflammatory pathways. Integrating polyphenols with additional substances or therapies may enhance their effectiveness, providing a more holistic approach to treating neurodegenerative disorders. Furthermore, it is imperative to examine the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of polyphenols in clinical studies to enhance comprehension of their interactions with other drugs and long-term safety profiles.
Standardizing polyphenol dosages according to clinical evidence from rigorously conducted human trials may mitigate variations in their efficacy. Moreover, emphasizing personalized medicine strategies that account for individual genetic variations and metabolic discrepancies may result in more accurate and efficacious treatments for neurodegenerative disorders. Ultimately, surmounting these hurdles necessitates a cooperative endeavor among academics, physicians, and pharmaceutical corporations to realize the complete therapeutic potential of polyphenols for neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.
Polyphenols, naturally occurring plant metabolites, are powerful antioxidants with anti-inflammatory properties. They act on several signaling pathways, including ERK, PI3K, Nrf2/HO, PPAR, HIF, and STAT, while inhibiting pro-inflammatory biomarkers. Polyphenols also reduce oxidative stress by upregulating antioxidant enzymes like catalase and superoxide dismutase and downregulating pro-apoptotic proteins, thereby supporting neuron survival. Furthermore, polyphenols suppress acetylcholinesterase, a key enzyme involved in Alzheimer’s pathology, and chelate metals, which helps manage prion diseases. These compounds are promising for their neuroprotective effects, low toxicity, and potential to prevent neurodegenerative disorders.
MJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. PB: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HR: Data curation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. AH: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. I-SL: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. SK: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. JC: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. MP: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. BK: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2020R1I1A2066868), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2020R1A5A2019413), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. RS-2024-00350362), the Starting Growth Technological R&D Program (TIPS Program, No. RS-2024-00507224) funded by the Ministry of SMEs and Startups (MSS, Korea) in 2024, and a grant of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (RS-2023-00279315).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbasi, A., Hashemi, M., Samadi Kafil, H., Abbasi Astamal, M., Lahouty, M., Ghorbani Tajani, A., et al. (2024). A critical review on the bioavailability promotion of the food bioactive compounds: nano lipid carriers perspective. Pharm. Sci. doi:10.34172/ps.2024.11
Abd-Nikfarjam, B., Dolati-Somarin, A., Baradaran Rahimi, V., and Askari, V. R. (2023). Cannabinoids in neuroinflammatory disorders: focusing on multiple sclerosis, Parkinsons, and Alzheimers diseases. BioFactors 49 (3), 560–583. doi:10.1002/biof.1936
Adamu, A., Li, S., Gao, F., and Xue, G. (2024). The role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: current understanding and future therapeutic targets. Front. Aging Neurosci. 16, 1347987. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2024.1347987
Afzal, O., Dalhat, M. H., Altamimi, A. S. A., Rasool, R., Alzarea, S. I., Almalki, W. H., et al. (2022). Green tea catechins attenuate neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive deficits. Molecules 27 (21), 7604. doi:10.3390/molecules27217604
Al Amin, M., Dehbia, Z., Nafady, M. H., Zehravi, M., Kumar, K. P., Haque, M. A., et al. (2024). Flavonoids and Alzheimer’s disease: reviewing the evidence for neuroprotective potential. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 480, 43–73. doi:10.1007/s11010-023-04922-w
Albadrani, H. M., Chauhan, P., Ashique, S., Babu, M. A., Iqbal, D., Almutary, A. G., et al. (2024). Mechanistic insights into the potential role of dietary polyphenols and their nanoformulation in the management of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 174, 116376. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116376
Alberdi, E., Sánchez-Gómez, M. V., Ruiz, A., Cavaliere, F., Ortiz-Sanz, C., Quintela-López, T., et al. (2018). Mangiferin and morin attenuate oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neurocytotoxicity, induced by amyloid beta oligomers. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018 (1), 2856063. doi:10.1155/2018/2856063
Al Mamun, A., Shao, C., Geng, P., Wang, S., and Xiao, J. (2024). Polyphenols targeting NF-κB pathway in neurological disorders: what we know so far? Int. J. Biol. Sci. 20 (4), 1332–1355. doi:10.7150/ijbs.90982
Amazzal, L., Lapôtre, A., Quignon, F., and Bagrel, D. (2007). Mangiferin protects against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium toxicity mediated by oxidative stress in N2A cells. Neurosci. Lett. 418 (2), 159–164. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.03.025
Amiri, B., Yazdani Tabrizi, M., Naziri, M., Moradi, F., Arzaghi, M., Archin, I., et al. (2024). Neuroprotective effects of Flavonoids: endoplasmic reticulum as the target. Front. Neurosci. 18, 1348151. doi:10.3389/fnins.2024.1348151
Ampadu, F., Awasthi, V., and Joshi, A. D. (2024). Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 signaling in liver and metabolic diseases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 390 (2), 233–239. doi:10.1124/jpet.124.002065
Anjo, S. I., He, Z., Hussain, Z., Farooq, A., McIntyre, A., Laughton, C. A., et al. (2024). Protein oxidative modifications in neurodegenerative diseases: from advances in detection and modelling to their use as disease biomarkers. Antioxidants 13 (6), 681. doi:10.3390/antiox13060681
Anwar, H., Rasul, A., Iqbal, J., Ahmad, N., Imran, A., Malik, S. A., et al. (2021). Dietary biomolecules as promising regenerative agents for peripheral nerve injury: an emerging nutraceutical-based therapeutic approach. J. Food Biochem. 45 (12), e13989. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13989
Aprotosoaie, A. C., and Miron, A. (2023). “Apigenin: chemistry and pharmacology,” in Handbook of dietary flavonoids (Springer), 1–32.
Atoki, A. V., Aja, P. M., Shinkafi, T. S., Ondari, E. N., and Awuchi, C. G. (2024). Naringenin: its chemistry and roles in neuroprotection. Nutr. Neurosci. 27 (6), 637–666. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2023.2243089
Azam, S., Jakaria, M., Kim, I. S., Kim, J., Haque, M. E., and Choi, D. K. (2019). Regulation of toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway by polyphenols in the treatment of age-linked neurodegenerative diseases: focus on TLR4 signaling. Front. Immunol. 10, 1000. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01000
Aziz, N., Wal, P., Patel, A., and Prajapati, H. (2024). A comprehensive review on the pharmacological role of gut microbiome in neurodegenerative disorders: potential therapeutic targets. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives Pharmacol. 397, 7307–7336. doi:10.1007/s00210-024-03109-4
Azzini, E., Peña-Corona, S. I., Hernández-Parra, H., Chandran, D., Saleena, L. A. K., Sawikr, Y., et al. (2024). Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in Alzheimer's disease: targeting neuroinflammation strategies. Phytotherapy Res. 38, 3169–3189. doi:10.1002/ptr.8200
Bagchi, A., Swain, D. K., and Mitra, A. (2020). Neuroprotective effect of organic and inorganically grown tea on oxidative damage in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Traditional Med. 20 (3), 439–450. doi:10.1007/s13596-020-00428-8
Banji, D., and Banji, O. J. (2024). “Impact of curcumin on aging: its manifestations and limitations,” in Curcumin and neurodegenerative diseases: from traditional to translational medicines (Springer), 253–291.
Barry-Carroll, L., and Gomez-Nicola, D. (2024). The molecular determinants of microglial developmental dynamics. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 25, 414–427. doi:10.1038/s41583-024-00813-1
Bhuia, M. S., Chowdhury, R., Ara, I., Mamun, M., Rouf, R., Khan, M. A., et al. (2024). Bioactivities of morroniside: a comprehensive review of pharmacological properties and molecular mechanisms. Fitoterapia 175, 105896. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.105896
Bhullar, K. S., and Rupasinghe, H. V. (2013). Polyphenols: multipotent therapeutic agents in neurodegenerative diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013 (1), 891748. doi:10.1155/2013/891748
Billowria, K., Ali, R., Rangra, N. K., Kumar, R., and Chawla, P. A. (2024). Bioactive flavonoids: a comprehensive review on pharmacokinetics and analytical aspects. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 54 (5), 1002–1016. doi:10.1080/10408347.2022.2105641
Biswas, K. (2023). Microglia mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: a review on the cell signaling pathways involved in microglial activation. J. Neuroimmunol. 383, 578180. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2023.578180
Biswas, P., Dey, D., Biswas, P. K., Rahaman, T. I., Saha, S., Parvez, A., et al. (2022). A comprehensive analysis and anti-cancer activities of quercetin in ROS-mediated cancer and cancer stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (19), 11746. doi:10.3390/ijms231911746
Bolat, E., Sarıtaş, S., Duman, H., Eker, F., Akdaşçi, E., Karav, S., et al. (2024). Polyphenols: secondary metabolites with a biological impression. Nutrients 16 (15), 2550. doi:10.3390/nu16152550
Bontempo, P., Capasso, L., De Masi, L., Nebbioso, A., and Rigano, D. (2024). Therapeutic potential of natural compounds acting through epigenetic mechanisms in cardiovascular diseases: current findings and future directions. Nutrients 16 (15), 2399. doi:10.3390/nu16152399
Bournival, J., Plouffe, M., Renaud, J., Provencher, C., and Martinoli, M. G. (2012). Quercetin and sesamin protect dopaminergic cells from MPP+-induced neuroinflammation in a microglial (N9)-neuronal (PC12) coculture system. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 921941. doi:10.1155/2012/921941
Caban, M., Owczarek, K., and Lewandowska, U. (2023). Effects of polyphenol-rich extracts on inflammatory bowel diseases. Food Rev. Int. 40, 2448–2485. doi:10.1080/87559129.2023.2273929
Cadenas-Garrido, P., Schonvandt-Alarcos, A., Herrera-Quintana, L., Vázquez-Lorente, H., Santamaría-Quiles, A., Ruiz de Francisco, J., et al. (2024). Using redox proteomics to gain new insights into neurodegenerative disease and protein modification. Antioxidants 13 (1), 127. doi:10.3390/antiox13010127
Carecho, R., Marques, D., Carregosa, D., Masuero, D., Garcia-Aloy, M., Tramer, F., et al. (2024). Circulating low-molecular-weight (poly) phenol metabolites in the brain: unveiling in vitro and in vivo blood–brain barrier transport. Food and Funct. 15, 7812–7827. doi:10.1039/d4fo01396d
Carito, V., Ceccanti, M., Chaldakov, G., Tarani, L., De Nicolò, S., Ciafrè, P., et al. (2015). “Polyphenols, nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and the brain,” in Bioactive nutraceuticals and dietary supplements in neurological and brain disease (Elsevier), 65–71.
Castillo-Ordoñez, W. O., Cajas-Salazar, N., and Velasco-Reyes, M. A. (2024). Genetic and epigenetic targets of natural dietary compounds as anti-Alzheimer’s agents. Neural Regen. Res. 19 (4), 846–854. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.382232
Charrière, K., Schneider, V., Perrignon-Sommet, M., Lizard, G., Benani, A., Jacquin-Piques, A., et al. (2024). Exploring the role of apigenin in neuroinflammation: insights and implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (9), 5041. doi:10.3390/ijms25095041
Chatterjee, A., Kumar, S., Roy Sarkar, S., Halder, R., Kumari, R., Banerjee, S., et al. (2024). Dietary polyphenols represent a phytotherapeutic alternative for gut dysbiosis associated neurodegeneration: a Systematic review. J. Nutr. Biochem. 129, 109622. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109622
Chen, M., Tan, J., Jin, Z., Jiang, T., Wu, J., and Yu, X. (2024a). Research progress on Sirtuins (SIRTs) family modulators. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 174, 116481. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116481
Chen, M., Xiao, J., El-Seedi, H. R., Woźniak, K. S., Daglia, M., Little, P. J., et al. (2024b). Kaempferol and atherosclerosis: from mechanism to medicine. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64 (8), 2157–2175. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2121261
Chen, X., Walton, K., Brodaty, H., and Chalton, K. (2024c). Polyphenols and diets as current and potential nutrition senotherapeutics in Alzheimer’s disease: findings from clinical trials. J. Alzheimer's Dis. (s1), 1–23. doi:10.3233/JAD-231222
Chen, Z., Shentu, T. P., Wen, L., Johnson, D. A., and Shyy, J. Y. J. (2013). Regulation of SIRT1 by oxidative stress-responsive miRNAs and a systematic approach to identify its role in the endothelium. Antioxidants and redox Signal. 19 (13), 1522–1538. doi:10.1089/ars.2012.4803
Chi, F., Cheng, C., Zhang, M., Su, B., Hou, Y., and Bai, G. (2024). Resveratrol targeting NRF2 disrupts the binding between KEAP1 and NRF2-DLG motif to ameliorate oxidative stress damage in mice pulmonary infection. J. Ethnopharmacol. 332, 118353. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118353
Chithra, Y., Dey, G., Ghose, V., Chandramohan, V., Gowthami, N., Vasudev, V., et al. (2023). Mitochondrial complex I inhibition in dopaminergic neurons causes altered protein profile and protein oxidation: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 48 (8), 2360–2389. doi:10.1007/s11064-023-03907-x
Choi, G.-Y., Kim, H. B., Hwang, E. S., Park, H. S., Cho, J. M., Ham, Y. K., et al. (2023). Naringin enhances long-term potentiation and recovers learning and memory deficits of amyloid-beta induced Alzheimer’s disease-like behavioral rat model. Neurotoxicology 95, 35–45. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2022.12.007
Colombo, R., and Papetti, A. (2020). An outlook on the role of decaffeinated coffee in neurodegenerative diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 60 (5), 760–779. doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1550384
Dama, A., Shpati, K., Daliu, P., Dumur, S., Gorica, E., and Santini, A. (2024). Targeting metabolic diseases: the role of nutraceuticals in modulating oxidative stress and inflammation. Nutrients 16 (4), 507. doi:10.3390/nu16040507
de Oliveira, M. R. (2016). The effects of ellagic acid upon brain cells: a mechanistic view and future directions. Neurochem. Res. 41 (6), 1219–1228. doi:10.1007/s11064-016-1853-9
de Oliveira Vian, C., Marinho, M. A. G., da Silva Marques, M., Hort, M. A., Cordeiro, M. F., and Horn, A. P. (2024). Effects of quercetin in preclinical models of Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Basic and Clin. Pharmacol. and Toxicol. 135 (1), 3–22. doi:10.1111/bcpt.14011
Dhapola, R., Beura, S. K., Sharma, P., Singh, S. K., and HariKrishnaReddy, D. (2024). Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: current knowledge of signaling pathways and therapeutics. Mol. Biol. Rep. 51 (1), 48. doi:10.1007/s11033-023-09021-z
Dogra, S. K., Kajla, V., Garg, H., Singh, D., Kumar, G. R., Puri, M., et al. (2023). Genistein as a neuroprotective agent: a comprehensive review of its potential in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Pharma Insights Res. 1 (1), 50–60.
Domínguez-López, , López-Yerena, A., Vallverdú-Queralt, A., Pallàs, M., Lamuela-Raventós, R. M., and Pérez, M. (2025). From the gut to the brain: the long journey of phenolic compounds with neurocognitive effects. Nutr. Rev. 83, e533–e546.
Dzah, C. S., Zhang, H., Gobe, V., Asante-Donyinah, D., and Duan, Y. (2024). Anti-and pro-oxidant properties of polyphenols and their role in modulating glutathione synthesis, activity and cellular redox potential: potential synergies for disease management. Adv. Redox Res. 11, 100099. doi:10.1016/j.arres.2024.100099
Emili, M., Guidi, S., Uguagliati, B., Giacomini, A., Bartesaghi, R., and Stagni, F. (2022). Treatment with the flavonoid 7, 8-Dihydroxyflavone: a promising strategy for a constellation of body and brain disorders. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 62 (1), 1–38. doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1810625
Fan, Y., He, X., Chen, M., Guo, S., and Dong, Z. (2024). Pterostilbene alleviates MPTP-induced neurotoxicity by targeting neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun. 729, 150358. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150358
Fang, S., Zhang, K., Liu, D., Yang, Y., Xi, H., Xie, W., et al. (2024). Polyphenol-based polymer nanoparticles for inhibiting amyloid protein aggregation: recent advances and perspectives. Front. Nutr. 11, 1408620. doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1408620
Feng, S., Gui, J., Qin, B., Ye, J., Zhao, Q., Guo, A., et al. (2024). Resveratrol inhibits VDAC1-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction to mitigate pathological progression in Parkinson’s disease model. Mol. Neurobiol., 1–19. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04234-0
Ferreira, C., Vieira, P., Sá, H., Malva, J., Castelo-Branco, M., Reis, F., et al. (2024). Polyphenols: immunonutrients tipping the balance of immunometabolism in chronic diseases. Front. Immunol. 15, 1360065. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1360065
Figueira, I., Menezes, R., Macedo, D., Costa, I., and Dos Santos, C. N. (2017). Polyphenols beyond barriers: a glimpse into the brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 15 (4), 562–594. doi:10.2174/1570159X14666161026151545
Gahtani, R. M., Shoaib, S., Hani, U., Jayachithra, R., Alomary, M. N., Chauhan, W., et al. (2024). Combating Parkinson’s disease with plant-derived polyphenols: targeting oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Neurochem. Int. 178, 105798. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105798
Giri, P. M., Banerjee, A., Ghosal, A., and Layek, B. (2024). Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: current knowledge and therapeutic implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (7), 3995. doi:10.3390/ijms25073995
Gong, G., Ganesan, K., Wan, Y., Liu, Y., Huang, Y., Luo, Y., et al. (2024). Unveiling the neuroprotective properties of isoflavones: current evidence, molecular mechanisms and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., 1–37. doi:10.1080/10408398.2024.2357701
Gopathy, S., Seshadri, S., Amudha, P., Vidya, R., Jayalakshmi, M., Kulanthaivel, L., et al. (2024). “Phytochemicals and natural extracts, secondary metabolites of plants and improvement of brain function,” in Neuroprotective effects of phytochemicals in brain ageing (Springer), 199–219.
Grabska-Kobyłecka, I., Szpakowski, P., Król, A., Książek-Winiarek, D., Kobyłecki, A., Głąbiński, A., et al. (2023). Polyphenols and their impact on the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases and development. Nutrients 15 (15), 3454. doi:10.3390/nu15153454
Gugliandolo, E., Peritore, A. F., D'Amico, R., Licata, P., and Crupi, R. (2020). Evaluation of neuroprotective effects of quercetin against aflatoxin B1-intoxicated mice. Animals 10 (5), 898. doi:10.3390/ani10050898
Gujarathi, N. A., Aher, A. A., Sukhia, A., Patil, T. S., Goyal, Y. S., and Keservani, R. K. (2024). “Nutraceutical interventions in Alzheimer's disease,” in Nutraceutical fruits and foods for neurodegenerative disorders (Elsevier), 379–404.
Han, T., Xu, Y., Sun, L., Hashimoto, M., and Wei, J. (2024). Microglial response to aging and neuroinflammation in the development of neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 19 (6), 1241–1248. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.385845
Hu, B., Ouyang, Y., Zhao, T., Wang, Z., Yan, Q., Qian, Q., et al. (2024). Antioxidant hydrogels: antioxidant mechanisms, design strategies, and applications in the treatment of oxidative stress-related diseases. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (11), 2303817. doi:10.1002/adhm.202303817
Hu, Y., Zhang, X., Lian, F., Yang, J., and Xu, X. (2021). Combination of lutein and DHA alleviate H2O2 induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by regulating the MAPK pathway. J. Nutr. Sci. vitaminology 67 (4), 234–242. doi:10.3177/jnsv.67.234
Isabel, U.-V., Belén, A. d.l.R. M., Elena, G.-B., and Elena, G. B. (2024). A new frontier in neuropharmacology: recent progress in natural products research for blood–brain barrier crossing. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 8, 100235. doi:10.1016/j.crbiot.2024.100235
Islam, F., Roy, S., Zehravi, M., Paul, S., Sutradhar, H., Yaidikar, L., et al. (2024). Polyphenols targeting MAP kinase signaling pathway in neurological diseases: understanding molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Mol. Neurobiol. 61 (5), 2686–2706. doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03706-z
Jadidian, F., Amirhosseini, M., Abbasi, M., Hamedanchi, N. F., Zerangian, N., Erabi, G., et al. (2024). Pharmacotherapeutic potential of Vitis vinifera (grape) in age-related neurological diseases. Bol. Latinoam. del Caribe Plantas Med. Aromáticas 23 (3), 349–370. doi:10.37360/blacpma.24.23.3.24
Jaeger, B. N., Parylak, S. L., and Gage, F. H. (2018). Mechanisms of dietary flavonoid action in neuronal function and neuroinflammation. Mol. aspects Med. 61, 50–62. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2017.11.003
Jain, K. K., and Jain, K. K. (2019). Neuroprotective agents. Handb. Neuroprotection, 45–173. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-9465-6_2
Jomova, K., Alomar, S. Y., Alwasel, S. H., Nepovimova, E., Kuca, K., and Valko, M. (2024). Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Archives Toxicol. 98 (5), 1323–1367. doi:10.1007/s00204-024-03696-4
Kang, K. S., Wen, Y., Yamabe, N., Fukui, M., Bishop, S. C., and Zhu, B. T. (2010). Dual beneficial effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on levodopa methylation and hippocampal neurodegeneration: in vitro and in vivo studies. PloS one 5 (8), e11951. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011951
Kano, Y., Horie, N., Doi, S., Aramaki, F., Maeda, H., Hiragami, F., et al. (2008). Artepillin C derived from propolis induces neurite outgrowth in PC12m3 cells via ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Neurochem. Res. 33, 1795–1803. doi:10.1007/s11064-008-9633-9
Khan, A. N., Jawarkar, R. D., Zaki, M. E. A., and Al Mutairi, A. A. (2024). Natural compounds for oxidative stress and neuroprotection in schizophrenia: composition, mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. Nutr. Neurosci. 27, 1306–1320. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2024.2325233
Kong, L., Miu, L., Yao, W., and Shi, Z. (2024). Effect of regular aerobic exercise on cognitive function, depression level and regulative role of neurotrophic factor: a prospective cohort study in the young and the middle-aged sample. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 17, 935–943. doi:10.2147/RMHP.S456765
Kumar, M., Kaushik, D., Shubham, S., Kumar, A., Kumar, V., Oz, E., et al. (2024). Ferulic acid: extraction, estimation, bioactivity and applications for human health and food. J. Sci. Food Agric. doi:10.1002/jsfa.13931
Kwatra, M., Ahmed, S., Gawali, B., Panda, S. R., and Naidu, V. (2020). Hesperidin alleviates chronic restraint stress and lipopolysaccharide-induced Hippocampus and Frontal cortex damage in mice: role of TLR4/NF-κB, p38 MAPK/JNK, Nrf2/ARE signaling. Neurochem. Int. 140, 104835. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104835
Laddha, A. P., Wu, H., and Manautou, J. E. (2024). Deciphering acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: the crucial role of transcription factors like nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 as genetic determinants of susceptibility to drug-induced liver injury. Drug Metabolism Dispos. 52 (8), 740–753. doi:10.1124/dmd.124.001282
Li, J., Long, Q., Ding, H., Wang, Y., Luo, D., Li, Z., et al. (2024a). Progress in the treatment of central nervous system diseases based on nanosized traditional Chinese medicine. Adv. Sci. 11 (16), 2308677. doi:10.1002/advs.202308677
Li, L., Wang, L., and Zhang, L. (2024b). Therapeutic potential of natural compounds from herbs and nutraceuticals in alleviating neurological disorders: targeting the wnt signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72 (5), 2411–2433. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07536
Li, Q., Li, S., Fang, J., Yang, C., Zhao, X., Wang, Q., et al. (2023). Artemisinin confers neuroprotection against 6-OHDA-induced neuronal injury in vitro and in vivo through activation of the ERK1/2 pathway. Molecules 28 (14), 5527. doi:10.3390/molecules28145527
Li, S., Wang, Z., Liu, G., and Chen, M. (2024c). Neurodegenerative diseases and catechins:(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate is a modulator of chronic neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Front. Nutr. 11, 1425839. doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1425839
Li, Y., Zhao, J., and Hölscher, C. (2017). Therapeutic potential of baicalein in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. CNS drugs 31, 639–652. doi:10.1007/s40263-017-0451-y
Liang, H., Ma, Z., Zhong, W., Liu, J., Sugimoto, K., and Chen, H. (2024). Regulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial function: natural compounds as potential therapeutic strategies for Parkinson's disease. Phytotherapy Res. 38 (4), 1838–1862. doi:10.1002/ptr.8156
Lippi, A., and Krisko, A. (2024). Protein aggregation: a detrimental symptom or an adaptation mechanism? J. Neurochem. 168 (8), 1426–1441. doi:10.1111/jnc.15955
Liu, G., Xie, R., Tan, Q., Zheng, J., Li, W., Wang, Q., et al. (2024a). Pharmacokinetic study and neuropharmacological effects of Atractylenolide Ⅲ to improve cognitive impairment via PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway in intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 333, 118420. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118420
Liu, H., Guo, X., Jiang, K., Shi, B., Liu, L., Hou, R., et al. (2024b). Dietary polyphenols regulate appetite mechanism via gut-brain axis and gut homeostasis. Food Chem. 446, 138739. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138739
Liu, W., Cui, X., Zhong, Y., Liu, B., and Xia, Y. (2023). Phenolic metabolites as therapeutic in inflammation and neoplasms: molecular pathways explaining their efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 193, 106812. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106812
Lv, Y., Li, W., Liao, W., Jiang, H., Liu, Y., Cao, J., et al. (2024). Nano-drug delivery systems based on natural products. Int. J. Nanomedicine 19, 541–569. doi:10.2147/IJN.S443692
Lymperopoulos, D., Dedemadi, A. G., Voulgari, M. L., Georgiou, E., Dafnis, I., Mountaki, C., et al. (2024). Corinthian currants promote the expression of paraoxonase-1 and enhance the antioxidant status in serum and brain of 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomolecules 14 (4), 426. doi:10.3390/biom14040426
Ma, Q., Chen, G., Li, Y., Guo, Z., and Zhang, X. (2024). The molecular genetics of PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in the malformations of cortical development. Genes and Dis. 11 (5), 101021. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2023.04.041
Madhubala, D., Patra, A., Khan, M. R., and Mukherjee, A. K. (2024). Phytomedicine for neurodegenerative diseases: the road ahead. Phytotherapy Res. 38, 2993–3019. doi:10.1002/ptr.8192
Majedi, S., and Ahamad, J. (2024). “Flavonoids and polyphenols,” in Bioactive compounds from food (CRC Press), 88–102.
Manju, , and Bharadvaja, N. (2024). Exploring the potential therapeutic approach using ginsenosides for the management of neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Biotechnol. 66 (7), 1520–1536. doi:10.1007/s12033-023-00783-2
Manoharan, S. D., Abdul Hamid, H., Md Hashim, N. F., Cheema, M. S., Chiroma, S. M., Mustapha, M., et al. (2024). Could protein phosphatase 2A and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta be targeted by natural compounds to ameliorate Alzheimer’s pathologies? Brain Res. 1829, 148793. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2024.148793
Martemucci, G., Khalil, M., Di Luca, A., Abdallah, H., and D'Alessandro, A. G. (2024). Comprehensive strategies for metabolic syndrome: how nutrition, dietary polyphenols, physical activity, and lifestyle modifications address diabesity, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative conditions. Metabolites 14 (6), 327. doi:10.3390/metabo14060327
Maugeri, G., D'Agata, V., Magrì, B., Roggio, F., Castorina, A., Ravalli, S., et al. (2021). Neuroprotective effects of physical activity via the adaptation of astrocytes. Cells 10 (6), 1542. doi:10.3390/cells10061542
Mayer, E., Horn, J., Mayer, D., and Randolph, E. (2024). “Dietary polyphenols to maintain healthier brain measures and cognitive function, as mediated by gut microbiota metabolites,” in The gut-brain Axis (Elsevier), 341–360.
Melrose, J. (2023). The potential of flavonoids and flavonoid metabolites in the treatment of neurodegenerative pathology in disorders of cognitive decline. Antioxidants 12 (3), 663. doi:10.3390/antiox12030663
Mesci, P., LaRock, C. N., Jeziorski, J. J., Nakashima, H., Chermont, N., Ferrasa, A., et al. (2024). Human microglial cells as a therapeutic target in a neurodevelopmental disease model. Stem Cell Rep. 19 (8), 1074–1091. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.06.013
Mirza, F. J., Zahid, S., and Holsinger, R. D. (2023). Neuroprotective effects of carnosic acid: insight into its mechanisms of action. Molecules 28 (5), 2306. doi:10.3390/molecules28052306
Mohammadi, S., Moghadam, M. D., Nasiriasl, M., Akhzari, M., and Barazesh, M. (2024). Insights into the therapeutic and pharmacological properties of resveratrol as a nutraceutical antioxidant polyphenol in health promotion and disease prevention. Curr. Rev. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Former. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 19 (4), 327–354. doi:10.2174/0127724328268507231218051058
Mokra, D., Adamcakova, J., and Mokry, J. (2022). Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): a time for a new player in the treatment of respiratory diseases? Antioxidants 11 (8), 1566. doi:10.3390/antiox11081566
Monteiro, K. L. C., de Aquino, T. M., and da Silva-Júnior, E. F. (2024). Natural compounds as inhibitors of Aβ peptide and tau aggregation. CNS and Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS and Neurological Disorders.
Morton, L., Paton, C., and Braakhuis, A. (2024). The effects of polyphenol supplementation on BDNF, cytokines and cognition in trained male cyclists following acute ozone exposure during high-intensity cycling. Nutrients 16 (2), 233. doi:10.3390/nu16020233
Motoda, H., Hiragami, F., Kawamura, K., Inoue, S., Gomita, Y., and Kano, Y. (2019). Contrast bath-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12m3 cells via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Heliyon 5 (10), e02656. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02656
Mugundhan, V., Arthanari, A., and Parthasarathy, P. R. (2024). Protective effect of ferulic acid on acetylcholinesterase and amyloid beta peptide plaque formation in Alzheimer’s disease: an in vitro study. Cureus 16 (2), e54103. doi:10.7759/cureus.54103
Muñoz-Reyes, D., Casanova, A. G., González-Paramás, A. M., Martín, Á., Santos-Buelga, C., Morales, A. I., et al. (2022). Protective effect of quercetin 3-O-glucuronide against cisplatin cytotoxicity in renal tubular cells. Molecules 27 (4), 1319. doi:10.3390/molecules27041319
Nájera-Maldonado, J. M., Salazar, R., Alvarez-Fitz, P., Acevedo-Quiroz, M., Flores-Alfaro, E., Hernández-Sotelo, D., et al. (2024). Phenolic compounds of therapeutic interest in neuroprotection. J. Xenobiotics 14 (1), 227–246. doi:10.3390/jox14010014
Nery-Flores, S. D., Castro-López, C. M., Martínez-Hernández, L., García-Chávez, C. V., Palomo-Ligas, L., Ascacio-Valdés, J. A., et al. (2024). Grape pomace polyphenols reduce acute inflammatory response induced by carrageenan in a murine model. Chem. and Biodivers. 21 (7), e202302065. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202302065
Niinuma, S. A., Khudair, A. D., Habib, H., Khudair, A. D., MacKenzie, G., Atkin, S. L., et al. (2024). Unearthing nature's remedy: an exploration into Lycopodium's medicinal and therapeutic potential. Appl. Mater. Today 38, 102197. doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2024.102197
Niu, C., Dong, M., and Niu, Y. (2024). Natural polyphenol: their pathogenesis-targeting therapeutic potential in Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 269, 116359. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116359
Onciul, R., Brehar, F. M., Toader, C., Covache-Busuioc, R. A., Glavan, L. A., Bratu, B. G., et al. (2024). Deciphering glioblastoma: fundamental and novel insights into the biology and therapeutic strategies of gliomas. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 46 (3), 2402–2443. doi:10.3390/cimb46030153
Özduran, G., Becer, E., and Vatansever, H. S. (2023). The role and mechanisms of action of catechins in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 42 (1), 67–74. doi:10.1080/07315724.2021.1981487
Plascencia-Villa, G., and Perry, G. (2023). Roles of oxidative stress in synaptic dysfunction and neuronal cell death in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 12 (8), 1628. doi:10.3390/antiox12081628
Pontifex, M. G., Malik, M. M. A. H., Connell, E., Müller, M., and Vauzour, D. (2021). Citrus polyphenols in brain health and disease: current perspectives. Front. Neurosci. 15, 640648. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021.640648
Prakash, O., Singh, R., Bajpai, P., and Kumari, M. (2024). Signaling pathways and molecular process of natural polyphenols in the amelioration of inflammatory bowel disease: a privileged scaffold in new drug discovery. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. Former. Curr. Drug Abuse Rev. 16 (1), 57–72. doi:10.2174/2589977515666230502153206
Prasad, R., and Prasad, S. B. (2019). A review on the chemistry and biological properties of Rutin, a promising nutraceutical agent. Asian J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 5 (1), 1–20. doi:10.31024/ajpp.2019.5.s1.1
Prasanth, M. I., Sivamaruthi, B. S., Cheong, C. S. Y., Verma, K., Tencomnao, T., Brimson, J. M., et al. (2024). Role of epigenetic modulation in neurodegenerative diseases: implications of phytochemical interventions. Antioxidants 13 (5), 606. doi:10.3390/antiox13050606
Qu, X., Zhang, L., and Wang, L. (2023). Pterostilbene as a therapeutic alternative for central nervous system disorders: a review of the current status and perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71 (40), 14432–14457. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c06238
Rahman, M. A., Ahmed, K. R., Haque, F., Park, M. N., and Kim, B. (2023). Recent advances in cellular signaling interplay between redox metabolism and autophagy modulation in cancer: an overview of molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Antioxidants 12 (2), 428. doi:10.3390/antiox12020428
Rahman, M. A., Bishayee, K., Sadra, A., and Huh, S. O. (2017). Oxyresveratrol activates parallel apoptotic and autophagic cell death pathways in neuroblastoma cells. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subj. 1861 (2), 23–36. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.10.025
Rahman, M. A., Cho, Y., Nam, G., and Rhim, H. (2021). Antioxidant compound, oxyresveratrol, inhibits APP production through the AMPK/ULK1/mTOR-mediated autophagy pathway in mouse cortical astrocytes. Antioxidants 10 (3), 408. doi:10.3390/antiox10030408
Rahman, M. A., Mamun-Or-Rashid, A. N. M., Hwang, H., Chung, S., Kim, B., et al. (2022). Autophagy modulation in aggresome formation: emerging implications and treatments of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 10 (5), 1027. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10051027
Rahmati-Dehkordi, F., Khanifar, H., Najari, N., Tamtaji, Z., Talebi Taheri, A., Aschner, M., et al. (2024). Therapeutic potential of Fingolimod on psychological symptoms and cognitive function in Neuropsychiatric and Neurological disorders. Neurochem. Res. 49 (10), 2668–2681. doi:10.1007/s11064-024-04199-5
Rauf, A., Abu-Izneid, T., Imran, M., Hemeg, H. A., Bashir, K., Aljohani, A. S. M., et al. (2023). Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms of the multitargeted flavonoid fisetin. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 23 (21), 2075–2096. doi:10.2174/1568026623666230710162217
Ravula, A. R., Teegala, S. B., Kalakotla, S., Pasangulapati, J. P., Perumal, V., and Boyina, H. K. (2021). Fisetin, potential flavonoid with multifarious targets for treating neurological disorders: an updated review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 910, 174492. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174492
Rudrapal, M., Rakshit, G., Singh, R. P., Garse, S., Khan, J., and Chakraborty, S. (2024). Dietary polyphenols: review on chemistry/sources, bioavailability/metabolism, antioxidant effects, and their role in disease management. Antioxidants 13 (4), 429. doi:10.3390/antiox13040429
Sabi, E. M. (2024). The role of genetic and epigenetic modifications as potential biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of thyroid cancer. Front. Oncol. 14, 1474267. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1474267
Schreihofer, D. A., and Oppong-Gyebi, A. (2019). Genistein: mechanisms of action for a pleiotropic neuroprotective agent in stroke. Nutr. Neurosci. 22 (6), 375–391. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2017.1391933
Sebastiani, G., Almeida-Toledano, L., Serra-Delgado, M., Navarro-Tapia, E., Sailer, S., Valverde, O., et al. (2021). Therapeutic effects of catechins in less common neurological and neurodegenerative disorders. Nutrients 13 (7), 2232. doi:10.3390/nu13072232
Sejbuk, M., Mirończuk-Chodakowska, I., Karav, S., and Witkowska, A. M. (2024). Dietary polyphenols, food processing and gut microbiome: recent findings on bioavailability, bioactivity, and gut microbiome interplay. Antioxidants 13 (10), 1220. doi:10.3390/antiox13101220
Shah, M. A., Faheem, H. I., Hamid, A., Yousaf, R., Haris, M., Saleem, U., et al. (2024). The entrancing role of dietary polyphenols against the most frequent aging-associated diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 44 (1), 235–274. doi:10.1002/med.21985
Shi, R., Gao, D., Stoika, R., Liu, K., Sik, A., and Jin, M. (2024). Potential implications of polyphenolic compounds in neurodegenerative diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64 (16), 5491–5514. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2155106
Silva dos Santos, J., Gonçalves Cirino, J. P., de Oliveira Carvalho, P., and Ortega, M. M. (2021). The pharmacological action of kaempferol in central nervous system diseases: a review. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 565700. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.565700
Singh, K., Sethi, P., Datta, S., Chaudhary, J. S., Kumar, S., Jain, D., et al. (2024a). Advances in gene therapy approaches targeting neuro-inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 98, 102321. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2024.102321
Singh, S., Ahuja, A., Agrawal, N., Sharma, S., and Varshney, D. S. (2024b). “Antioxidant properties of nutraceuticals,” in Immune-boosting nutraceuticals for better human health (Apple Academic Press), 205–244.
Socała, K., Żmudzka, E., Lustyk, K., Zagaja, M., Brighenti, V., Costa, A. M., et al. (2024). Therapeutic potential of stilbenes in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders: a comprehensive review of preclinical and clinical evidence. Phytotherapy Res. 38 (3), 1400–1461. doi:10.1002/ptr.8101
Song, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Wu, C., and Li, Y. (2024). The influence of food matrix and processing methods on the bioaccessibility of lutein: a review. J. Food Bioact. 26, 7–23. doi:10.31665/jfb.2024.18376
Sun, S., Liu, Z., Lin, M., Gao, N., and Wang, X. (2024). Polyphenols in health and food processing: antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant insights. Front. Nutr. 11, 1456730. doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1456730
Surai, P. F. (2015). Silymarin as a natural antioxidant: an overview of the current evidence and perspectives. Antioxidants 4 (1), 204–247. doi:10.3390/antiox4010204
Tao, W., Zhang, H., Jiang, X., and Chen, N. (2024). Resveratrol combats chronic diseases through enhancing mitochondrial quality. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 13 (2), 597–610. doi:10.26599/fshw.2022.9250140
Tavan, M., Hanachi, P., de la Luz Cádiz-Gurrea, M., Segura Carretero, A., and Mirjalili, M. H. (2024). Natural phenolic compounds with neuroprotective effects. Neurochem. Res. 49 (2), 306–326. doi:10.1007/s11064-023-04046-z
Tayab, M. A., Islam, M. N., Chowdhury, K. A. A., and Tasnim, F. M. (2022). Targeting neuroinflammation by polyphenols: a promising therapeutic approach against inflammation-associated depression. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 147, 112668. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112668
Teijido, O., and Cacabelos, R. (2018). Pharmacoepigenomic interventions as novel potential treatments for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19 (10), 3199. doi:10.3390/ijms19103199
Thakur, A., and Kumar, A. (2024). Polyphenols for dyes application. Sci. Eng. Polyphenols Fundam. Industrial Scale Appl., 157–210. doi:10.1002/9781394203932.ch7
Thomas, S. D., Abdalla, S., Eissa, N., Akour, A., Jha, N. K., Ojha, S., et al. (2024). Targeting microglia in neuroinflammation: H3 receptor antagonists as a novel therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and autism spectrum disorder. Pharmaceuticals 17 (7), 831. doi:10.3390/ph17070831
Tran, P. H., and Tran, T. T. (2021). Blueberry supplementation in neuronal health and protective technologies for efficient delivery of blueberry anthocyanins. Biomolecules 11 (1), 102. doi:10.3390/biom11010102
Tregub, P. P., Kulikov, V. P., Ibrahimli, I., Tregub, O. F., Volodkin, A. V., Ignatyuk, M. A., et al. (2024). Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotection after the intermittent exposures of hypercapnic hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (7), 3665. doi:10.3390/ijms25073665
Tripathi, S., Mishra, R., Shrivastava, R., Srivastava, V., and Singh, G. (2024). “Neuroprotection induced by epigallocatechin-3-gallate,” in Natural molecules in neuroprotection and neurotoxicity (Elsevier), 1321–1339.
Vaghari-Tabari, M., Alemi, F., Zokaei, M., Moein, S., Qujeq, D., Yousefi, B., et al. (2024). Polyphenols and inflammatory bowel disease: natural products with therapeutic effects? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64 (13), 4155–4178. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2139222
Vauzour, D. (2012). Dietary polyphenols as modulators of brain functions: biological actions and molecular mechanisms underpinning their beneficial effects. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012 (1), 914273. doi:10.1155/2012/914273
Vicente-Zurdo, D., Gómez-Mejía, E., Rosales-Conrado, N., and León-González, M. E. (2024). A comprehensive analytical review of polyphenols: evaluating neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (11), 5906. doi:10.3390/ijms25115906
Waetzig, V., Belzer, M., Haeusgen, W., Boehm, R., Cascorbi, I., and Herdegen, T. (2017). Crosstalk control and limits of physiological c-Jun N-terminal kinase activity for cell viability and neurite stability in differentiated PC12 cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 82, 12–22. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2017.04.004
Walia, V., Chaudhary, S. K., and Sethiya, N. K. (2021). Therapeutic potential of mangiferin in the treatment of various neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem. Int. 143, 104939. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104939
Wang, C.-W., Yang, C.-T., and Liang, C. (2024b). Evaluation of soil mixing with carpet grasses for polyphenol reductive degradation of 1, 3-dinitrobenzene contaminated soils. Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 235 (8), 499–517. doi:10.1007/s11270-024-07284-1
Wang, J., Zhang, J., Yu, Z. L., Chung, S. K., and Xu, B. (2024a). The roles of dietary polyphenols at crosstalk between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease in ameliorating oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction via PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Ageing Res. Rev. 99, 102416. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2024.102416
Watanabe, H., Dijkstra, J. M., and Nagatsu, T. (2024). Parkinson’s disease: cells succumbing to lifelong dopamine-related oxidative stress and other bioenergetic challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (4), 2009. doi:10.3390/ijms25042009
Wu, X., Wu, H., Zhong, M., Chen, Y., Su, W., and Li, P. (2024). Epigenetic regulation by naringenin and naringin: a literature review focused on the mechanisms underlying its pharmacological effects. Fitoterapia 181, 106353. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106353
Xiang, Y., Song, X., and Long, D. (2024). Ferroptosis regulation through Nrf2 and implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Archives Toxicol. 98 (3), 579–615. doi:10.1007/s00204-023-03660-8
Xu, G., Chen, H., Cong, Z., Wang, R., Li, X., Xie, Y., et al. (2024). Promotion of transcription factor EB-dependent autophagic process by curcumin alleviates arsenic-caused lung oxidative stress and inflammation in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 125, 109550. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109550
Xue, J., Tao, K., Wang, W., and Wang, X. (2024). What can inflammation tell us about therapeutic strategies for Parkinson’s disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (3), 1641. doi:10.3390/ijms25031641
Yahia, I. B. H., Baccouri, O., Jalouli, M., Boujelbene, N., Rahman, M. A., Harrath, A. H., et al. (2024). The small phytomolecule resveratrol: a promising role in boosting tumor cell chemosensitivity. Pharmacia 71, 1–9. doi:10.3897/pharmacia.71.e122169
Ye, X., Fung, N. S. K., Lam, W. C., and Lo, A. C. Y. (2024). Nutraceuticals for diabetic retinopathy: recent advances and novel delivery systems. Nutrients 16 (11), 1715. doi:10.3390/nu16111715
Yilmazer, U. T., Pehlivan, B., Guney, S., Yar-Saglam, A. S., Balabanli, B., Kaltalioglu, K., et al. (2024). The combined effect of morin and hesperidin on memory ability and oxidative/nitrosative stress in a streptozotocin-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 471, 115131. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115131
Zeng, L., Yang, K., Yu, G., Hao, W., Zhu, X., Ge, A., et al. (2024). Advances in research on immunocyte iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and their regulatory roles in autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. Cell Death and Dis. 15 (7), 481. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06807-2
Zhang, W., Zhang, Q. Y., Li, J., Ren, X. N., Zhang, Y., and Niu, Q. (2024b). Study on the digestive behavior of chlorogenic acid in biomimetic dietary fiber and the antioxidative synergistic effect of polysaccharides and chlorogenic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72 (5), 2634–2647. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c08886
Zhang, Y., Guo, H., and Fu, H. (2024a). Protective effect of resveratrol combined with levodopa against oxidative damage in dopaminergic neurons. Cell Biochem. Biophysics 82, 817–826. doi:10.1007/s12013-024-01233-9
Zhong, M. Z., Peng, T., Duarte, M. L., Wang, M., and Cai, D. (2024). Updates on mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 19 (1), 23. doi:10.1186/s13024-024-00712-0
Keywords: polyphenols, neurodegenerative diseases, neuroinflammatory, signal transduction pathways, therapeutic applications
Citation: Jalouli M, Rahman MA, Biswas P, Rahman H, Harrath AH, Lee I-S, Kang S, Choi J, Park MN and Kim B (2025) Targeting natural antioxidant polyphenols to protect neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases: a comprehensive review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1492517. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1492517
Received: 07 September 2024; Accepted: 07 January 2025;
Published: 24 January 2025.
Edited by:
Malgorzata Kozyra, Medical University of Lublin, PolandReviewed by:
Mithun Rudrapal, Vignan’s Foundation for Science, Technology and Research, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Jalouli, Rahman, Biswas, Rahman, Harrath, Lee, Kang, Choi, Park and Kim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bonglee Kim, Ym9uZ2xlZWtpbUBraHUuYWMua3I=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.