
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol. , 21 February 2025
Sec. Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1438760
The CYP2D6 plays critical roles in drug metabolism, and its inter-individual variability should be properly addressed in clinical practice. Our research aimed to assess the performance of single-point saliva metabolic ratio (MR) in a healthy Chinese Han population using dextromethorphan as the probe drug. MR was determined as the ratio of parent drug to metabolite in 3 h saliva, 3 h plasma, and 0–3 h urine post-ingestion. 416 healthy volunteers were enrolled, with 290 (69.7%) male participants and a median body mass index (BMI) of 23.1 kg/m2. The Spearman correlation coefficients were 0.876 between plasma and saliva MR, and 0.746 between plasma and urine MR. The population was clustered into four metabolizer classes with either plasma or saliva MR, but into two metabolizer classes with urine MR. The saliva-based clustering agreed well with plasma-based clustering (Cohen’s Kappa 0.689). A clear negative correlation was observed between Activity Score (AS) and saliva MR, and linear regression revealed that overweight population had significantly lower saliva MR than others. In conclusion, single-point saliva MR performed better than urine MR with satisfactory correlation with plasma MR and effective separation of four metabolizer classes. Predicting saliva MR with the AS system was more accurate when BMI was considered.
The highly polymorphic gene CYP2D6 encodes the enzyme cytochrome P450 2D6, and the alleles can be classified into increased, normal, decreased, and no function groups according to the observed enzymatic activity (Caudle et al., 2020). Commonly found in microsomes and other cytoplasmic structures in hepatocytes, CYP2D6 functions as a monooxygenase and takes part in the biotransformation of numerous clinically used drugs (Puszkiel et al., 2021; Muriel et al., 2023). When probed with dextromethorphan (DM) or other substrates, the CYP2D6 phenotype can be demonstrated with metabolic ratio (MR) and classified into poor (PM), intermediate (IM), normal (NM), or ultrarapid (UM) metabolizers accordingly (Gaedigk et al., 2008).
Determining the drug metabolism phenotype is of critical importance to select the proper medication and dose in clinical practice. Based on previously confirmed data, the Activity Score (AS) system was developed in order to deduce related drug metabolism phenotype based on CYP2D6 genotyping information (Gaedigk et al., 2008). Though continually evolving, the latest version of AS system merely explained 40% of variability in DM metabolizing rates, and could not replace the direct phenotyping methods yet (Dalton et al., 2020; Hertz et al., 2015).
Traditional pharmacokinetic analysis requires a time series of plasma drug concentration to demonstrate the whole plasma concentration-time profile. For CYP2D6 phenotyping specifically, our previous study has shown that single-point plasma MR from 1 to 30 h post-ingestion is a satisfactory substitute for traditional MR by area-under-curve method, but its application is still limited by the necessity of venous puncture (Chen et al., 2016). Another classical method, urine MR analysis, requires urine collection during a long period of time, which precludes urine method from routine clinical practice (Gaedigk et al., 2008). Also, urine MR can be influenced by urinary pH (Labbé et al., 2000), and is not applicable in anuric patients with renal failure (Hou et al., 1996).
Saliva is an easily accessible body fluid and a suitable specimen for drug concentration determination, and has been investigated as a proper substitute for plasma and urine since 1990s (Hou et al., 1996; Hou et al., 1991). Its convenience has drawn attention from clinicians, pharmacists, and pharmacologists, and the usefulness of saliva in anticonvulsant monitoring has been firmly established (Kim et al., 2020). For cytochrome P450 phenotyping, the time series of saliva drug concentration has been used in phenotyping of CYP2D6, CYP3A, and CYP1A2 with satisfactory results up till now (Link et al., 2008; Perera et al., 2011; Chen et al., 2017; Jin et al., 2022). However, the usefulness of single-point saliva MR has not been fully investigated in a large enough representative healthy East Asian population. Our study aims to demonstrate the performance of single-point saliva MR in phenotyping, to compare it with plasma and urine counterparts, and to confirm its correlation with the AS system and other factors.
This study was performed in accordance with the Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki. The research protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee of Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China. In total, 421 healthy unrelated subjects of Han people from Chinese mainland were voluntarily enrolled to clarify the CYP2D6 phenotyping performance of different body fluid samples, and written informed consent was obtained from each subject (Chen et al., 2017). Subjects had a detailed physical examination including routine urinalysis, complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and 12-lead electrocardiography in order to exclude the ones with any of the following situations: a history of hematologic, gastrointestinal, renal, or hepatic abnormalities; human immunodeficiency virus, syphilis, hepatitis C or B infection; allergy to dextromethorphan; other acute or chronic diseases that were not cured at recruitment. Consuming grapefruit juice, caffeinated beverages, or alcohol was not allowed in the last 24 h before DM administration, nor until all samples were collected. Subjects were also instructed to refrain from ingesting herbal remedies or medications for a minimum of 1 week before the study, and to refrain from smoking for a minimum of 3 days before the study. All the collected data were later introduced into regression analysis, and those subjects with items missing were excluded.
Whole genomic DNA was extracted from white blood cells in peripheral blood samples using a Wizard TM Genomic Purification Kit (Promega, United States), and then different alleles were detected with Sanger sequencing (Chen et al., 2017). To be concise, the genomic region including CYP2D6 gene and its 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (M33388 positions −2,182–4,482) was amplified. As the whole DNA segment flanking CYP2D6 gene was too long for one single Sanger sequencing, six different primers evenly scattered across the gene were designed to perform six independent Sanger sequencing from the respective starting points. Since the six sequenced sub-segments overlapped with each other at the juncture, the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of complete CYP2D6 gene were determined successfully. After cleansing with the PCR purification Kit (Capitalbio, China), Sanger sequencing was performed with BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, United States) under the following program: 96°C/1 min for denaturing, 25 cycles of 96°C/10 s–50°C/5 s–60°C/4 s. The final reaction product was purified via ethanol/ammonium acetate precipitation, and then analyzed using the ABI 3730XL Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, United States) and Sequence Variation Analysis v1.2 (Capitalbio, China). Deletion (*5) as well as duplication were detected using a duplex long polymerase chain reaction-based method (DLPCR) originally developed by Løvlie et al. (1996) and Hersberger et al. (Hersberger et al., 2000), with minor modifications. Briefly, the CYP2D6 flanking region changes due to deletion or duplication resulted in length variation of DNA clones amplified with elaborately designed primers, which was then visualized using 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. In case of duplication, the whole duplicated segment was specifically cloned and sequenced with the above Sanger method to determine which allele it was. The naming of alleles, genotypes, AS and metabolizer subgroups were determined according to SNPs from Sanger sequencing, deletion and duplication from DLPCR, latest allele scoring in Pharmacogenomics Knowledgebase (Whirl-Carrillo et al., 2021), and the 2020 consensus recommendations from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium and Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (Caudle et al., 2020), which had been validated in our (Jin et al., 2022) and Wang et al. (2024) studies. Since the specific allele duplication number was not determined, all duplicated alleles were attributed with twice the original activity value as Gaedigk et al. originally reported when developing the AS system (Gaedigk et al., 2008): activity value = 2 for *1xN and *2xN, activity value = 0.5 for *10xN and *41xN (Duarte et al., 2024). The rare alleles with uncertain function, including *90, were assigned with 0 activity value. The potential bias from this manual assignment was limited according to the sensitivity analysis, in which the main findings were found unaffected.
Each subject was provided with 15 mg of DM (Tylenol Cold Tablet containing DM, Johnson and Johnson Investment Ltd., Shanghai, China), along with 300 mL water (Chen et al., 2017). Saliva (2–3 mL each) and peripheral venous blood samples (8–9 mL each) were collected at 3 h post-ingestion, while all urine were collected during the 0–3-hour interval post-ingestion, which was proved effective in a previous study by Chládek et al. (2000). Saliva samples were collected into test tubes directly from the oral cavity using sterile pipettes, and were then centrifuged at 4,000 rpm, 4°C for 15 min to separate the supernatants for further experiments. Concentrations of DM and unconjugated dextrorphan (DX) in all samples were determined with a sensitive and validated high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay using established standards without hydrolysis (Hou et al., 1991; Hu et al., 1998). To be specific, DM and DX were detected using fluorescence detectors (Millipore, United States) at wavelengths of 200/310 nm (excitation/emission), and the lower limit of quantification was 0.05 ng/mL for both DM and DX in all samples. The MR of DM over DX was adopted to assess the CYP2D6 enzymatic activity in plasma, saliva, or urine samples.
Data were displayed as median (lower quantile, higher quantile). To enhance the readability of the results and the performance of statistical analyses, MR underwent log transformation (base 10) in part of the results. The strength of correlation was measured with Spearman’s correlation coefficient, and the agreement between different classification systems was measured with Cohen’s kappa coefficient. Model-based clustering by R package “mclust” was performed to divide log10 of MR into mixtures of univariate normal distributions using R commands formatted as “clusters < - Mclust (data, modelNames = “V”)”, and the related statistical principles are demonstrated in the book composed by Scrucca et al. (2016). Both-direction (forward and backward) stepwise linear regression was performed to investigate the impact of AS and other factors on MR, and variable inclusion/exclusion was determined with Akaike information criteria. All statistical analyses were performed with R statistics (version 4.2.0, https://www.R-project.org/).
In total, 416 subjects with complete data record were included in the final analysis with 290 males and 126 females (Table 1). These subjects comprised a representative population, with a median age of 29 (Jukić et al., 2021; Krogstad et al., 2021) years and a median body mass index (BMI) of 23.1 (21.5, 24.8) kg/m2. Of all CYP2D6 alleles, *10 was the most frequent allele (45.4%) in the study population, and the second and third most frequent ones were *1 (25.1%) and *2 (13.2%). Allele duplication was detected in 11 subjects, including 1 *1xN, 3 *2xN, 5 *10xN, and 2 *41xN. The top three most frequent genotypes were *1/*10 (22.4%), *10/*10 (20.4%), and *2/*10 (13.0%), respectively. Over four-fifths of all subjects (84.6%) were attributed with an AS less than 2, and the majority of participants were classified into NM (54.1%) and IM (43.5%). The CYP2D6 genotype of all 416 participants was presented in Supplementary Table S1.
We plotted the histogram of log-transformed MR in saliva, plasma, and urine, and performed model-based clustering accordingly (Figure 1). As the classical PM/IM/NM/UM system proposed, both single-point saliva (cutoff values for saliva MR: 0.520, 1.644, 33.884) and single-point plasma (cutoff values for plasma MR: 0.223, 0.577, 8.375) could separate the study population into 4 clusters with fair uncertainty level (Figures 1A–F), and the agreement between saliva- and plasma-based clustering was satisfactory with a Cohen’s kappa of 0.689. In contrast, MR in 0–3 h urine could merely identify the poorest metabolizers from the others with significantly lower kurtosis than saliva and plasma (Figures 1G–I). Moreover, the correlation between plasma and saliva MR (r = 0.876) was closer than that between plasma and urine (r = 0.746), and urine MR seemed more dispersed than saliva MR with a given plasma MR (Figure 2). All these findings indicated that compared with urine MR, saliva MR was a relatively better noninvasive specimen to phenotype CYP2D6 in the Chinese Han population.
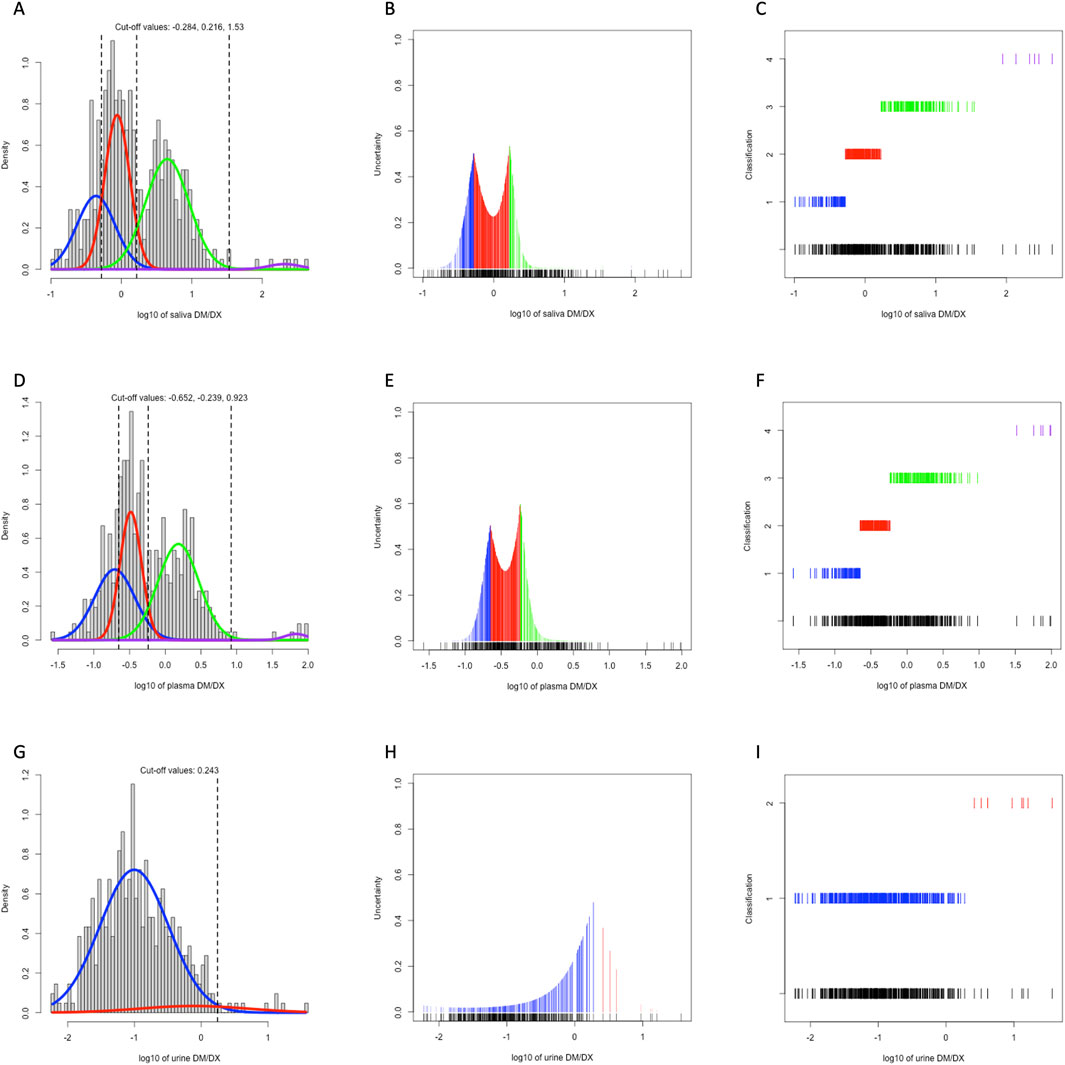
Figure 1. Model-based clustering of the study population based on 3h saliva MR (A–C), 3 h plasma MR (D–F), and 0–3 h urine MR (G–I). The histograms with density curves (A, D, G), the uncertainty plots (B, E, H), and the classification plots (C, F, I) were displayed. Colors of all lines represented metabolizer class by AS, with blue for PM, red for IM, green for NM, and purple for UM, respectively.
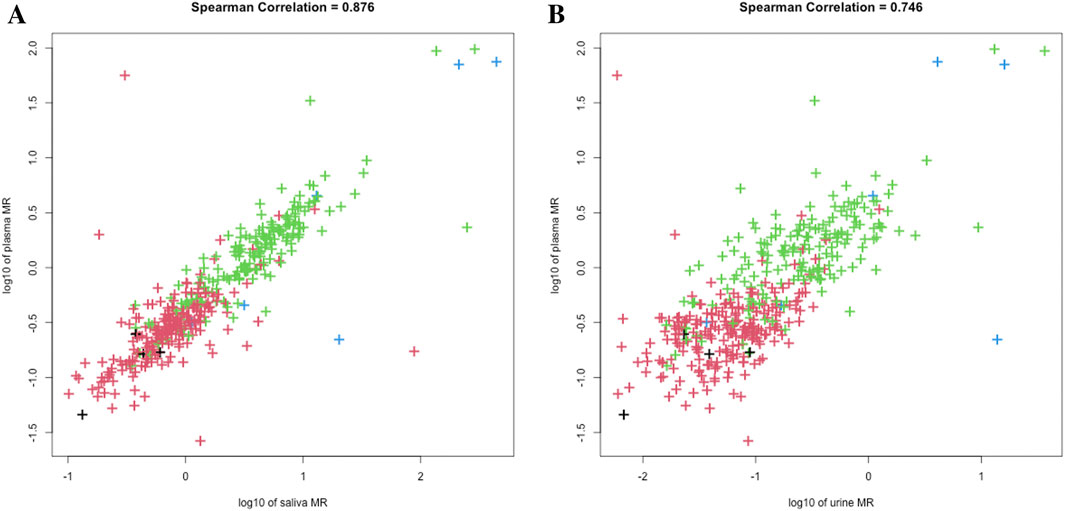
Figure 2. Scatterplots of saliva-plasma MR (A) and urine-plasma MR (B). Colors of the dots represented metabolizer class by AS, with black for UM, red for NM, green for IM, and blue for PM, respectively.
A clear monotonic relationship was displayed between AS and single-point saliva MR (r = −0.801, Figure 3A). Fair separation of single-point saliva MR was observed between AS-based UM, NM, and IM metabolizer classes, while the MR distribution was largely intermingled between PM and IM subgroups (Figure 3B). As reported in the confusion matrix (Table 2), the saliva MR-based clustering tended to overstate CYP2D6 phenotype compared with AS-based metabolizer classes, with the Cohen’s kappa of 0.477 between the two systems.
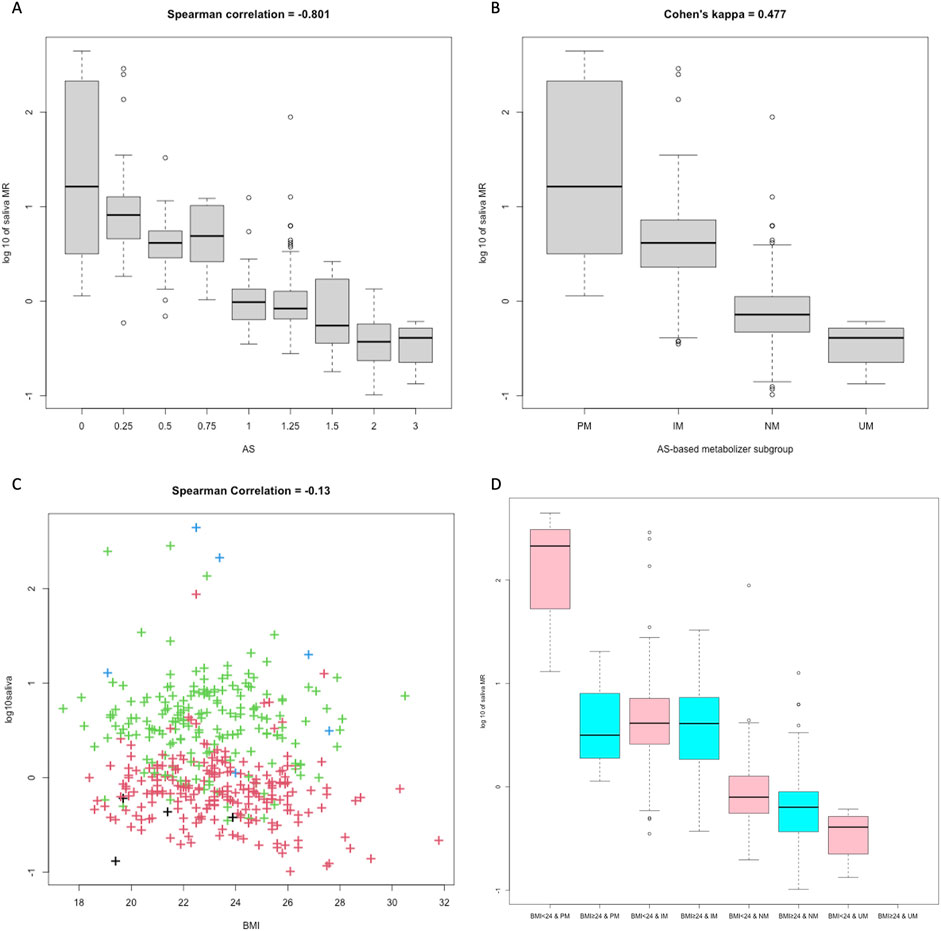
Figure 3. The impact of AS and BMI on 3h saliva MR. Boxplots compared 3h saliva MR between subjects with different AS values (A) and different AS-based metabolizer classes (B). The scatterplot showed distribution of 3h saliva MR-BMI (C), and the grouped boxplot (D) compared 3h saliva MR of different BMI categories and AS-based metabolizer classes. Colors of the dots represented metabolizer class by AS, with black for UM, red for NM, green for IM, and blue for PM, respectively. In Figure 3D, colors of the graphs distinguish the BMI, as pink for BMI <24, and blue for BMI >24.
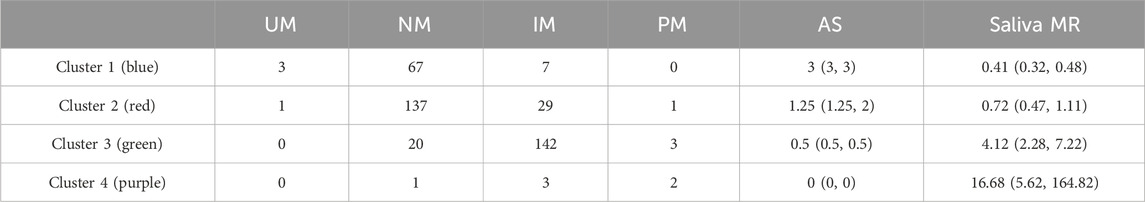
Table 2. The confusion matrix comparing saliva MR-based clustering and metabolizer classes by AS, and the AS and saliva MR distribution of different clusters.
To identify measurable factors other than CYP2D6 genotype that influence single-point saliva MR, we performed multivariable linear regression for log-transformed 3 h saliva MR (Table 3). When considering BMI, the adjusted R2 of the regression model increased significantly compared with the model with AS alone. Overweight subjects with BMI >24 seemed to have lower log-transformed saliva MR compared with others (−0.045 [-0.284, 0.519] vs. 0.132 [-0.147, 0.618], P = 0.003 by t-test), and the differences were most apparent in PM subjects (Figures 3C,D).
Our study was the first one to demonstrate the performance of single-point saliva for CYP2D6 phenotyping in a large healthy East Asian population. We demonstrated that CYP2D6 phenotyping with single-point saliva MR was as good as CYP2D6 phenotyping with single-point plasma MR for separating different metabolizer subgroups, while the performance of 0–3 h urine MR was not satisfactory. Close correlation was observed between saliva and plasma MR, suggesting that saliva could serve as a satisfactory substitute for plasma in CYP2D6 phenotyping. The AS system showed fair prediction for single-point saliva-based phenotype, and the prediction could be further improved when taking BMI into consideration.
In order to address interindividual variability in pharmacokinetics in clinical practice, dose adjustment is commonly carried out in two ways: to predict the metabolizer phenotype and prescribe proper dose, or to monitor the drug concentration and titrate the dose (Abdullah-Koolmees et al., 2020). Pharmacogenetic methods, displayed as various AS systems, are expected to define metabolizer subgroups in advance (Jukić et al., 2021). Potato diet-derived solanidine and other metabolic biomarkers have shown promising roles in identifying CYP2D6 PM subjects (Magliocco et al., 2021; Behrle et al., 2022; Wollmann et al., 2023), and linearity was observed between solanidine and risperidone metabolism in certain metabolizer classes (Wollmann et al., 2024). Since not all medical centers have access to the methodology mentioned above, drug concentration monitoring remains irreplaceable up till now, and a non-invasive specimen would be preferrable over plasma.
Saliva should serve as a non-invasive substitute for plasma in most situations other than Sjögren’s syndrome, and should replace urine in patients with kidney dysfunction (Hou et al., 1996). The role of saliva in cytochrome P450 phenotyping and pharmacokinetic monitoring has been confirmed in multiple small-scaled previous studies, and our study is the first to present single-point saliva MR as a suitable measurement for CYP2D6 phenotype for East Asians (Link et al., 2008; Perera et al., 2011; Chen et al., 2017; Jin et al., 2022). Some drugs like tacrolimus require close monitoring, and drug concentration beyond therapeutic range can lead to detrimental effects including seizure and sinusoidal obstructive syndrome (Xie et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2021). We believe that saliva might be a solution to drug monitoring in pediatric liver transplantation as well as other clinical situations (Yang et al., 2015).
Compared with CYP2D6 genotyping, single-point saliva MR featured lower cost, lower risk of “genetic identity” exposure, but higher phenotyping uncertainty, which somehow composed a trade-off. There could be a couple of factors underlying the discrepancies between single-point saliva MR-based clustering and CYP2D6 AS-based metabolizer classification. Although being widely accepted as a CYP2D6 phenotyping probe, DM is metabolized via CYP3A as well (Tian et al., 2013), which could contribute to the CYP2D6 phenotype-overstating tendency of saliva MR-based clustering compared with AS. In agreement with a previous study concerning risperidone pharmacokinetics, our study demonstrated the negative impact of BMI on MR of CYP2D6-dependent medication (Paulzen et al., 2016). However, another recent study demonstrated that only CYP3A, not CYP2D6, had its activity significantly correlated with body composition, making things controversial (Krogstad et al., 2021). Further studies with wider BMI distribution should be conducted to analyze the effect of BMI on pharmacokinetics as well as the underlying mechanisms.
Our research had some limitations. The urine collection period was relatively short, which might influence the CYP2D6 phenotyping performance of urine compared with saliva and plasma. The exclusion of subjects with any morbidity could prevent the widespread application of our data in real clinical settings, and further studies among specific patient groups with clinical endpoints should make up for it. The relatively small number of UM and PM subjects in our cohort might influence the statistical performance of model-based clustering as well as linear regression, and a larger cohort with more UM and PM subjects is expected. Since our phenotyping method, regardless of the sample type, requires chromatography and mass spectrometry equipment that is hard to acquire in most hospitals, a more convenient methodology shall be developed in the future.
In conclusion, our study showed that single-point saliva MR could separate the study population into four metabolizer clusters, and was a convenient and reliable phenotyping method for CYP2D6 compared with single-point plasma MR and period urine MR. Single-point saliva MR could be predicted with the latest AS system, and the prediction accuracy was improved when taking BMI into account.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethical Committee of Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants themselves.
YH: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZH: Writing–original draft. XG: Project administration, Writing–review and editing. PH: Conceptualization, Software, Writing–review and editing. RC: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Software, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The work was funded by National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding grant number (2022-PUMCH-A-060), Clinical Research Fund from WU JIEPING Medical Foundation grant number (320.6750.19090-12) and the Drug Development and Application Fund from Chinese Pharmacological Society grant number (2018DL001).
We acknowledge all volunteers and working staff who have contributed to the study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1438760/full#supplementary-material
Abdullah-Koolmees, H., van Keulen, A. M., Nijenhuis, M., and Deneer, V. H. M. (2020). Pharmacogenetics Guidelines: overview and comparison of the DPWG, CPIC, CPNDS, and RNPGx Guidelines. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 595219. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.595219
Behrle, A. C., Douglas, J., Leeder, J. S., and van Haandel, L. (2022). Isolation and identification of 3,4-Seco-Solanidine-3,4-dioic acid (SSDA) as a urinary biomarker of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) activity. Drug Metab. Dispos. 50 (10), 1342–1351. doi:10.1124/dmd.122.000957
Caudle, K. E., Sangkuhl, K., Whirl-Carrillo, M., Swen, J. J., Haidar, C. E., Klein, T. E., et al. (2020). Standardizing CYP2D6 genotype to phenotype translation: consensus recommendations from the clinical Pharmacogenetics implementation Consortium and Dutch Pharmacogenetics working group. Clin. Transl. Sci. 13 (1), 116–124. doi:10.1111/cts.12692
Chen, R., Rostami-Hodjegan, A., Wang, H., Berk, D., Shi, J., and Hu, P. (2016). Application of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for the evaluation of single-point plasma phenotyping method of CYP2D6. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 92, 131–136. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2016.07.001
Chen, R., Zheng, X., and Hu, P. (2017). CYP2D6 phenotyping using urine, plasma, and saliva metabolic ratios to assess the impact of CYP2D6(*)10 on interindividual variation in a Chinese population. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 239. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00239
Chládek, J., Zimová, G., Beránek, M., and Martínková, J. (2000). In-vivo indices of CYP2D6 activity: comparison of dextromethorphan metabolic ratios in 4-h urine and 3-h plasma. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 56 (9-10), 651–657. doi:10.1007/s002280000218
Dalton, R., Lee, S. B., Claw, K. G., Prasad, B., Phillips, B. R., Shen, D. D., et al. (2020). Interrogation of CYP2D6 structural variant alleles improves the correlation between CYP2D6 genotype and CYP2D6-mediated metabolic activity. Clin. Transl. Sci. 13 (1), 147–156. doi:10.1111/cts.12695
Duarte, J. D., Thomas, C. D., Lee, C. R., Huddart, R., Agundez, J. A. G., Baye, J. F., et al. (2024). Clinical Pharmacogenetics implementation Consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6, ADRB1, ADRB2, ADRA2C, GRK4, and GRK5 genotypes and beta-blocker therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 116 (4), 939–947. doi:10.1002/cpt.3351
Gaedigk, A., Simon, S. D., Pearce, R. E., Bradford, L. D., Kennedy, M. J., and Leeder, J. S. (2008). The CYP2D6 activity score: translating genotype information into a qualitative measure of phenotype. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 83 (2), 234–242. doi:10.1038/sj.clpt.6100406
Hersberger, M., Marti-Jaun, J., Rentsch, K., and Hänseler, E. (2000). Rapid detection of the CYP2D6*3, CYP2D6*4, and CYP2D6*6 alleles by tetra-primer PCR and of the CYP2D6*5 allele by multiplex long PCR. Clin. Chem. 46 (8 Pt 1), 1072–1077. doi:10.1093/clinchem/46.8.1072
Hertz, D. L., Snavely, A. C., McLeod, H. L., Walko, C. M., Ibrahim, J. G., Anderson, S., et al. (2015). In vivo assessment of the metabolic activity of CYP2D6 diplotypes and alleles. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 80 (5), 1122–1130. doi:10.1111/bcp.12665
Hou, Z. Y., Chen, C. P., Yang, W. C., Lai, M. D., Buchert, E. T., Chung, H. M., et al. (1996). Determination of dextromethorphan metabolic phenotype by salivary analysis with a reference to genotype in Chinese patients receiving renal hemodialysis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 59 (4), 411–417. doi:10.1016/S0009-9236(96)90109-5
Hou, Z. Y., Pickle, L. W., Meyer, P. S., and Woosley, R. L. (1991). Salivary analysis for determination of dextromethorphan metabolic phenotype. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 49 (4), 410–419. doi:10.1038/clpt.1991.48
Hu, O. Y., Tang, H. S., Lane, H. Y., Chang, W. H., and Hu, T. M. (1998). Novel single-point plasma or saliva dextromethorphan method for determining CYP2D6 activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 285 (3), 955–960. doi:10.1016/s0022-3565(24)37524-x
Jin, Y., Zhang, S., Hu, P., Zheng, X., Guan, X., Chen, R., et al. (2022). The impact of CYP2D6*41 on CYP2D6 enzyme activity using phenotyping methods in urine, plasma, and saliva. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 940510. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.940510
Jukić, M. M., Smith, R. L., Molden, E., and Ingelman-Sundberg, M. (2021). Evaluation of the CYP2D6 haplotype activity scores based on metabolic ratios of 4,700 patients treated with three different CYP2D6 substrates. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 110 (3), 750–758. doi:10.1002/cpt.2246
Kim, D. Y., Moon, J., Shin, Y. W., Lee, S. T., Jung, K. H., Park, K. I., et al. (2020). Usefulness of saliva for perampanel therapeutic drug monitoring. Epilepsia 61 (6), 1120–1128. doi:10.1111/epi.16513
Krogstad, V., Peric, A., Robertsen, I., Kringen, M. K., Vistnes, M., Hjelmesæth, J., et al. (2021). Correlation of body weight and composition with hepatic activities of cytochrome P450 enzymes. J. Pharm. Sci. 110 (1), 432–437. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2020.10.027
Labbé, L., Sirois, C., Pilote, S., Arseneault, M., Robitaille, N. M., Turgeon, J., et al. (2000). Effect of gender, sex hormones, time variables and physiological urinary pH on apparent CYP2D6 activity as assessed by metabolic ratios of marker substrates. Pharmacogenetics 10 (5), 425–438. doi:10.1097/00008571-200007000-00006
Link, B., Haschke, M., Grignaschi, N., Bodmer, M., Aschmann, Y. Z., Wenk, M., et al. (2008). Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral midazolam in plasma and saliva in humans: usefulness of saliva as matrix for CYP3A phenotyping. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 66 (4), 473–484. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03201.x
Liu, Y., Sun, L. Y., Zhu, Z. J., Wei, L., Qu, W., and Zeng, Z. G. (2021). Is sinusoidal obstructive syndrome a recurrent disease after liver transplantation? A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 9 (2), 489–495. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.489
Løvlie, R., Daly, A. K., Molven, A., Idle, J. R., and Steen, V. M. (1996). Ultrarapid metabolizers of debrisoquine: characterization and PCR-based detection of alleles with duplication of the CYP2D6 gene. FEBS Lett. 392 (1), 30–34. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)00779-x
Magliocco, G., Desmeules, J., Matthey, A., Quirós-Guerrero, L. M., Bararpour, N., Joye, T., et al. (2021). Metabolomics reveals biomarkers in human urine and plasma to predict cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 178 (23), 4708–4725. doi:10.1111/bph.15651
Muriel, J., Barrachina, J., Del Barco, G., Carvajal, C., Escorial, M., Margarit, C., et al. (2023). Impact of CYP2D6 genotype on opioid use disorder deprescription: an observational prospective study in chronic pain with sex-differences. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1200430. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1200430
Paulzen, M., Haen, E., Stegmann, B., Hiemke, C., Gründer, G., Lammertz, S. E., et al. (2016). Body mass index (BMI) but not body weight is associated with changes in the metabolism of risperidone; A pharmacokinetics-based hypothesis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 73, 9–15. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.07.009
Perera, V., Gross, A. S., Xu, H., and McLachlan, A. J. (2011). Pharmacokinetics of caffeine in plasma and saliva, and the influence of caffeine abstinence on CYP1A2 metrics. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 63 (9), 1161–1168. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01326.x
Puszkiel, A., Arellano, C., Vachoux, C., Evrard, A., Le Morvan, V., Boyer, J. C., et al. (2021). Model-based quantification of impact of genetic polymorphisms and Co-medications on pharmacokinetics of tamoxifen and six metabolites in breast cancer. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 109 (5), 1244–1255. doi:10.1002/cpt.2077
Scrucca, L., Fop, M., Murphy, T. B., and Raftery, A. E. (2016). Mclust 5: clustering, classification and density estimation using Gaussian finite mixture models. R. J. 8 (1), 289–317. doi:10.32614/rj-2016-021
Tian, X., Cheng, Z. Y., He, J., Jia, L. J., and Qiao, H. L. (2013). Concentration-dependent inhibitory effects of baicalin on the metabolism of dextromethorphan, a dual probe of CYP2D and CYP3A, in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 203 (2), 522–529. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2013.02.005
Wang, X., Huang, J., Lu, J., Li, X., Tang, H., and Shao, P. (2024). Risperidone plasma level, and its correlation with CYP2D6 gene polymorphism, clinical response and side effects in chronic schizophrenia patients. BMC Psychiatry 24 (1), 41. doi:10.1186/s12888-023-05488-z
Whirl-Carrillo, M., Huddart, R., Gong, L., Sangkuhl, K., Thorn, C. F., Whaley, R., et al. (2021). An evidence-based framework for evaluating Pharmacogenomics knowledge for personalized medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 110 (3), 563–572. doi:10.1002/cpt.2350
Wollmann, B. M., Smith, R. L., Kringen, M. K., Ingelman-Sundberg, M., Molden, E., and Størset, E. (2024). Evidence for solanidine as a dietary CYP2D6 biomarker: significant correlation with risperidone metabolism. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 90 (3), 740–747. doi:10.1111/bcp.15721
Wollmann, B. M., Størset, E., Kringen, M. K., Molden, E., and Smith, R. L. (2023). Prediction of CYP2D6 poor metabolizers by measurements of solanidine and metabolites-a study in 839 patients with known CYP2D6 genotype. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 79 (4), 523–531. doi:10.1007/s00228-023-03462-y
Xie, M., Rao, W., Sun, L. Y., Zhu, Z. J., Deng, Y. L., Shen, Z. Y., et al. (2014). Tacrolimus-related seizure after pediatric liver transplantation--a single-center experience. Pediatr. Transpl. 18 (1), 58–63. doi:10.1111/petr.12198
Keywords: CYP2D6, saliva metabolic ratio, activity score, non-invasive phenotyping, dextromethorphan
Citation: Huang Y, He Z, Guan X, Hu P and Chen R (2025) The CYP2D6 phenotyping performance of single-point saliva metabolic ratio in a healthy Chinese Han population. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1438760. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1438760
Received: 26 May 2024; Accepted: 03 February 2025;
Published: 21 February 2025.
Edited by:
Amit V. Pandey, University of Bern, SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Youssef Daali, University of Geneva, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2025 Huang, He, Guan, Hu and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rui Chen, Y2hlbnJ1aTA0QDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.