- 1Fengxian Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shanghai, China
- 2Sixth People’s Hospital South Campus, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China
- 3Fengxian Mental Health Center, Shanghai, China
Background: In the past few decades, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) became widely used antidepressants worldwide. Therefore, the adverse reactions of patients after SSRI administration became a public and clinical concern. In this study, we conducted a pharmacovigilance study using the Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database of the US Food and Drug Administration. Our main goal was to evaluate adverse events related to SSRIs, with a particular focus on abnormal weight gain and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders.
Method: The adverse event data for representative SSRIs (citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline) was extracted from the FAERS database from 2004Q1 to 2023Q4. The reporting odds ratio and proportional reporting ratio were employed to explore relevant adverse event reports (ADEs) signals. Univariate logistic regression analysis was utilized to explore factors associated with glucose/lipid metabolism abnormality following SSRIs treatment.
Results: We identified 143,744 ADE reports associated with SSRIs and revealed significant abnormal signals related to weight gain and glucose/lipid metabolism in depressed patients. Variations were observed among different SSRIs medications. Specifically, citalopram was associated with abnormal weight gain (ROR: 4, 95% CI: 3.1-5.2) and hepatic steatosis (ROR: 2.8, 95% CI: 2.1-3.6); escitalopram was correlated with gestational diabetes (ROR: 9.1, 95% CI: 6.6-12.4) and cholestasis (ROR: 2.4, 95% CI: 1.75-3.38); fluoxetine was associated with obesity (ROR: 2.8, 95% CI: 2.08-3.78); fluvoxamine was linked to arteriospasm coronary (ROR: 13.87, 95% CI: 4.47-43.1); and sertraline was implicated in neonatal jaundice (ROR: 16.1, 95% CI: 12.6-20.6). Females and younger age are important risk factors for the development of associated adverse effects.
Conclusion: Our study screened for adverse effects associated with abnormal glucose/lipid metabolism, such as abnormal body weight and fatty liver, in depressed patients taking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors by utilizing FAERS database. This provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals in accepting and managing patients treated with SSRIs.
Introduction
With the increase of life pressure, the incidence rate of depression in all age groups has increased (Thapar et al., 2022; Gundersen and Bensadon, 2023). There are various factors that can lead to depression, including school or work stress, physical illness, strained relationships with family members, and financial stress in the family (Hammen, 2018). According to statistics from the World Health Organization, depression is expected to become one of the leading causes of death worldwide by 2030 (Miret et al., 2013).
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are widely used antidepressants for the treatment of depression and other related mental health disorders. The research on the mechanism of action of SSRIs in treating depression is constantly evolving. Early studies have shown that the expression level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is significantly higher in patients with major depression after fluoxetine treatment (Ghosh et al., 2015). Some researchers have proposed that SSRIs exert their effects by increasing the concentration of the neurotransmitter serotonin between neurons, thereby regulating feelings and moods (Gothert et al., 2020). A study suggests that the use of sertraline significantly decrease interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor α in leukocytes of patients with depression (Galecki et al., 2018). In addition, some studies have shown that SSRIs improve mood disorders such as anxiety and depression by enhancing the neurotransmission of GABAA receptors (Pinna et al., 2009). Currently, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline are the most used representative SSRIs for the treatment of depression. Among them, escitalopram is the s-enantiomer of citalopram, which has higher therapeutic efficacy and faster onset rate of action (Yin et al., 2023).
With the increasing use of SSRIs, public and clinical professionals are increasingly concerned about the adverse reactions of these antidepressants. In general, the common early adverse reactions encompass nausea, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, anxiety, and sexual dysfunction (Marjoribanks et al., 2013). For example, a survey indicate that SSRIs not only reduce sperm quantity and vitality in male depressive patients but also stimulate the fallopian tubes in female depressive patients, therefore negatively impacting fertility (Milosavljevic et al., 2022). In addition, SSRIs induce severe and rare adverse reactions such as gastrointestinal and intracranial hemorrhage in patients with depression (Yuet et al., 2019). However, the potential metabolic disorders after SSRI administration, such as overweight, glucose/lipid metabolism disorder, dyslipidemia and pregnancy diabetes, are still poorly understood.
The FDA Adverse Event Reporting System is maintained and managed by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which supports the FDA’s post-marketing safety surveillance program for all marketed drug and therapeutic biologic products. It includes adverse event reports received by FDA from manufacturers as required by regulation along with reports directly received from consumers (such as patients, family members, lawyers) and healthcare professionals (such as doctors, pharmacists, nurses), and facilitates the monitoring of drug safety and evaluation of potential medication risks. In this study, ADE data associated with SSRIs was extracted and analyzed from FAERS from the first quarter of 2004 to the fourth quarter of 2023. We aim to uncover and evaluate signals indicative of overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders, and provide insights for clinical practitioners and researchers in the field.
Methods
Data source
ADE reporting data submitted to the FAERS from the first quarter of 2004 to the fourth quarter of 2023 was accessed and reviewed by authors. Each quarterly dataset includes information such as drug details (DRUG), patient demographics (DEMO), adverse events (REAC), and outcomes (OUTC).
Data processing
The generic name of the target drug was defined as citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline, and corresponding data are retrieved in FAERS. All quarterly DEMO, DRUG, REAC, and other report data were cleaned and organized. Subsequently, duplicate reports (retaining the latest version) were removed based on CaseID, patient name, age, country, generic names, brand names and primary suspected drug (PS). Finally, PT were identified by consulting MedDRA to further screen SSRIs-related adverse reaction reports, with emphasis on overweight, glucose/lipid metabolism disorder.
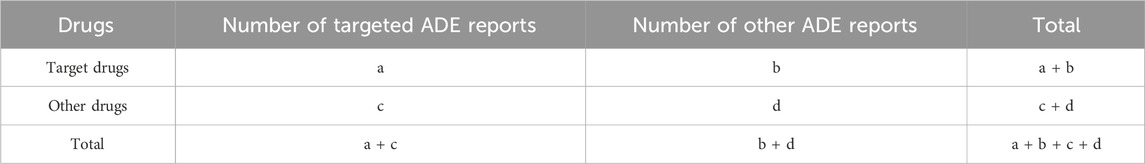
Signal mining and collation
This study utilized the Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) and Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR) methods for signal analysis, as delineated in Tables 1, 2. An adverse event signal was deemed significant if it met the following criteria: ADE reports >3, ROR >2, PRR >2, lower limit of the 95% confidence interval (CI) for ROR >1, lower limit of the 95% CI for PRR >1, and χ2 >4. Subsequently, manual screening was conducted to identify signals associated with overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders. All data processing and signal mining calculations were performed using R software (version 4.2.2). P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
ADE reports overview
Figure 1 illustrated the comprehensive data processing workflow of this study. A total of 20,755,634 ADE reports were extracted from FAERS. Following deduplication and data cleaning, a total of 143,746 reports were identified with SSRIs as the primary suspected (PS): 21,820 reports for citalopram, 19,288 for escitalopram, 21,456 for fluoxetine, 1,224 for fluvoxamine, 36,983 for paroxetine, and 42,975 for sertraline. After screening based on criteria such as ROR and PRR, a total of 6,588 PTs related to SSRIs were identified. Specifically, there were 1,227 PTs associated with citalopram, 1,091 with escitalopram, 1,248 with fluoxetine, 243 with fluvoxamine, 1,359 with paroxetine, and 1,420 with sertraline. Then, after reviewing the literature, 81 PTs related to weight and glucose/lipid metabolism were identified. Finally, we conducted a basic analysis of reports of PTs associated with SSRIs.
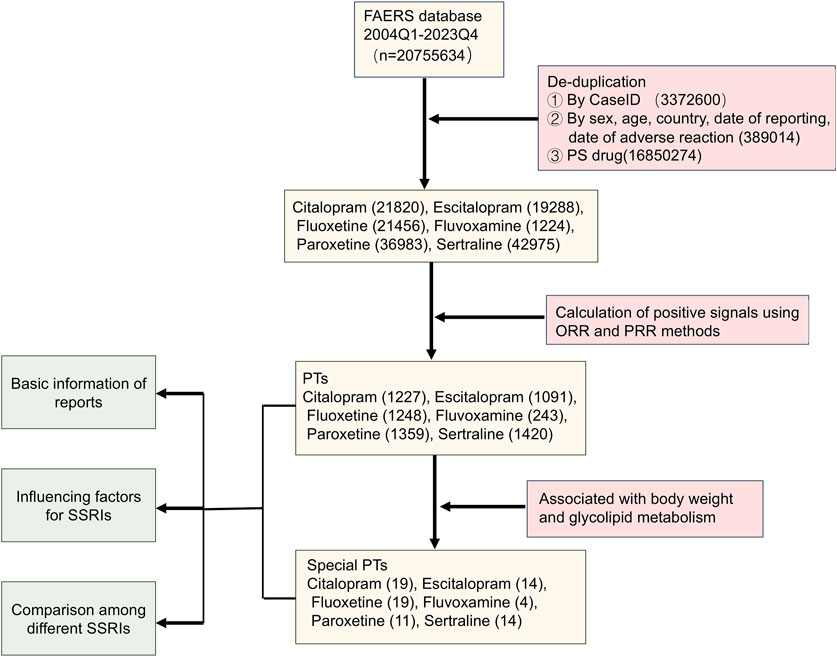
Figure 1. The flowchart for screening signals of overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders associated with SSRIs.
We visualized the number of reports for the 6 SSRIs by year (Figure 2A). The results showed a relatively smooth change in the number of ADE reports with escitalopram, citalopram, and fluvoxamine as the main suspected drugs. The number of ADE reports related to paroxetine showed an almost yearly decreasing trend. However, the number of ADE reports for sertraline increased and then decreased, with large fluctuations. We then counted the number of reports of all ADE to SSRIs and the number of reports of ADE associated with disorders of glucolipid metabolism separately (Figure 2B). Paroxetine had the highest number of adverse reaction reports, followed by sertraline. Fluvoxamine had the lowest number of adverse reactions. In addition, we calculated the percentage of the number of adverse reactions reports related to disorders of glucolipid metabolism (Figure 2C), with fluvoxamine having the highest percentage (13.28%) and paroxetine having the lowest (0.32%).
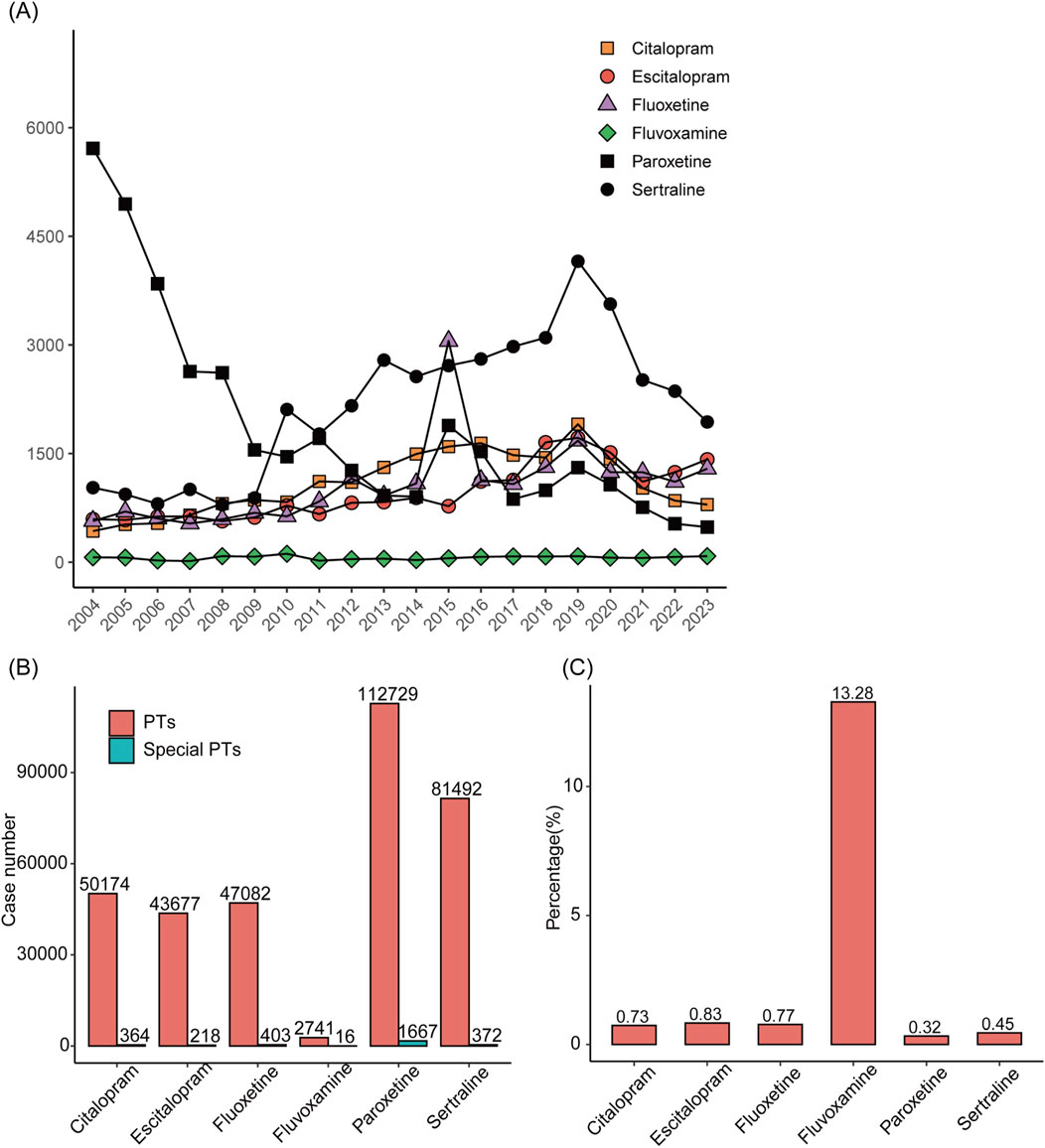
Figure 2. Statistics of reported diseases associated with abnormalities of glycolipid metabolism caused by treatment with SSRIs with and without SSRIs in FAERS between 2004 and 2023. (A) Annual ADE reports on SSRIs. (B) Total number of cases of adverse reactions after taking SSRIs and number of cases of adverse reactions related to disorders of glucolipid metabolism. (C) The proportions of reports with and without diseases associated with abnormalities of glycolipid metabolism for different SSRIs.
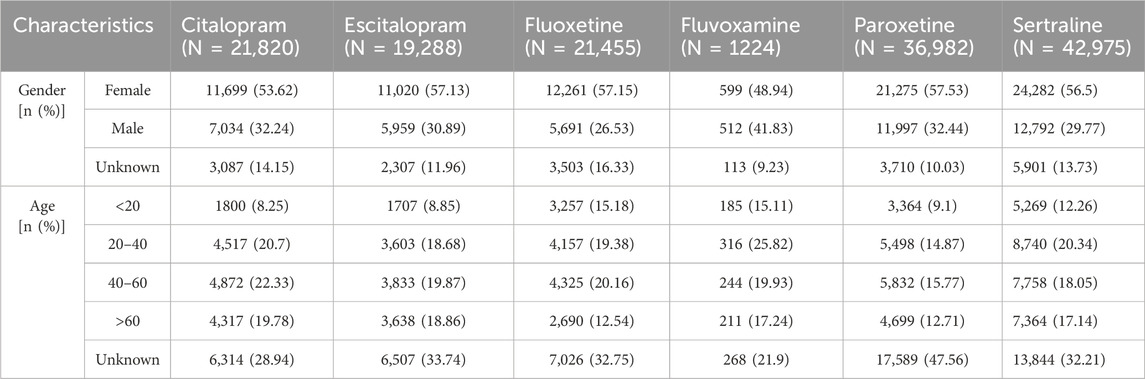
In all relevant ADE reports, the proportion of women was higher than that of men, indicating that women might be more prone to adverse reactions compared to men after taking SSRIs. The age distribution of reports was divided into four stages. Compared to the other two age groups, the number of ADE reports was higher in the 20-40 and 40-60 age groups (Table 3). Medical doctors (MD), occupational therapists (OT), and clinical nurses (CN) were the primary reporters. The majority of reports come from the United States (US), United Kingdom (GB), Denmark (DK), France (FR), Japan (JP), and Germany (DE) (Table 4).
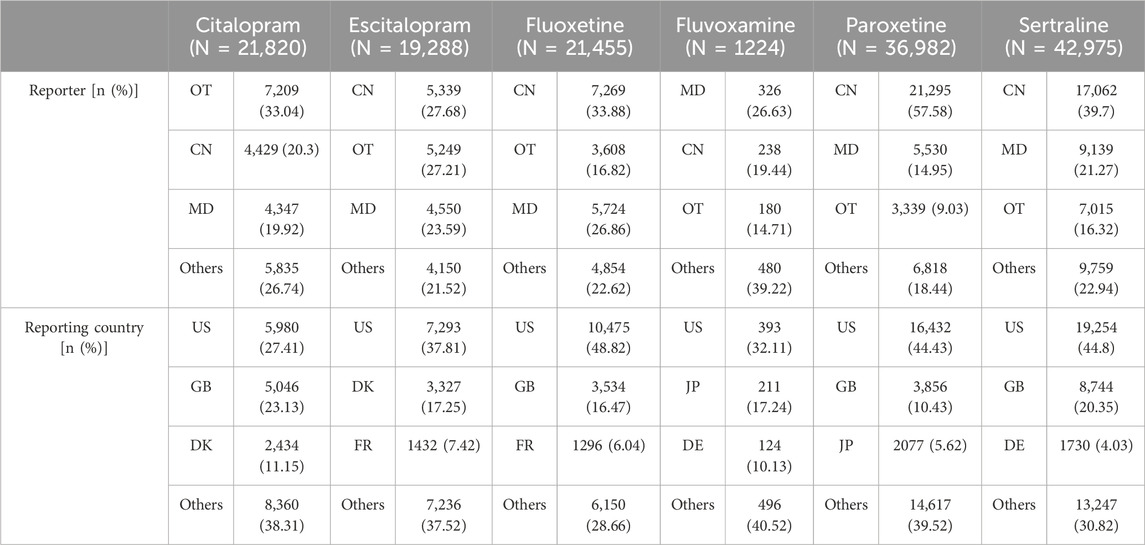
Table 4. The occupational distribution and national source distribution of SSRI related ADE reporters.
ADE signal detection
The top-ranking PTs in ADE signal intensity for citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline were shown in Figures 3A–F. The frequency of PT reports related to overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders for SSRIs were 364, 218, 403, 16, 1667, and 372, respectively, as delineated in Figures 4A–F. Specifically, with the exception of fluvoxamine, the remaining five SSRIs had a higher incidence of gestational diabetes in female patients. Citalopram, paroxetine and sertraline tend to cause abnormal weight gain in patients. In addition, hepatobiliary disorders such as “hepatic steatosis” and “cholestasis” caused by abnormalities in glucose and lipid metabolism were more common with citalopram, escitalopram and fluoxetine. For more details, please refer to Supplementary Tables S1–S6 (Sheet 1 and Special PTS, which respectively include all PTs related to citalopram, PTs related to glucose/lipid metabolism abnormality).
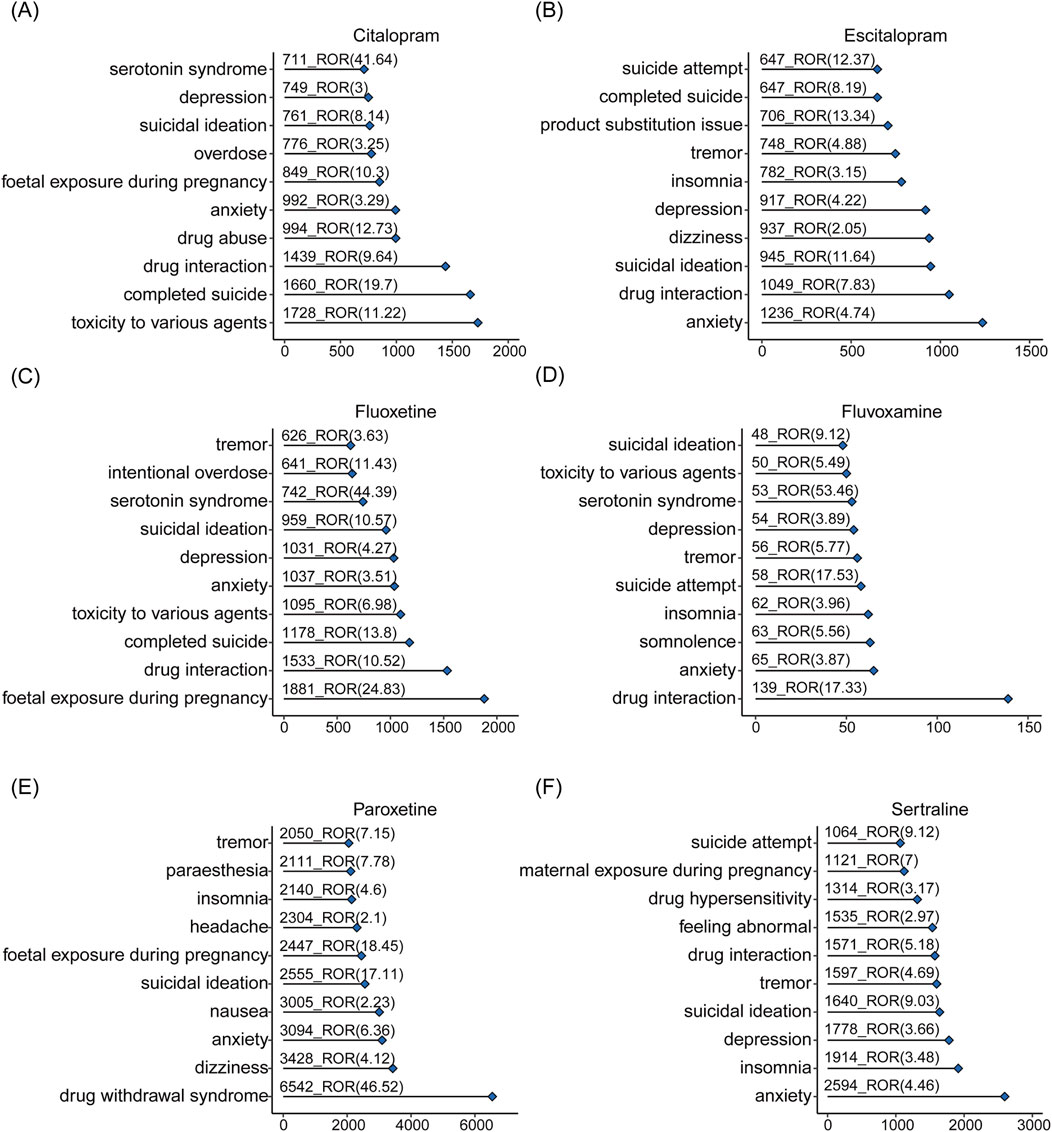
Figure 3. The overall signals of disorders associated with SSRIs. Adverse reactions related to citalopram (A), escitalopram (B), fluoxetine (C), fluvoxamine (D), paroxetine (E), sertraline (F) and occurring in the top 10 numbers.
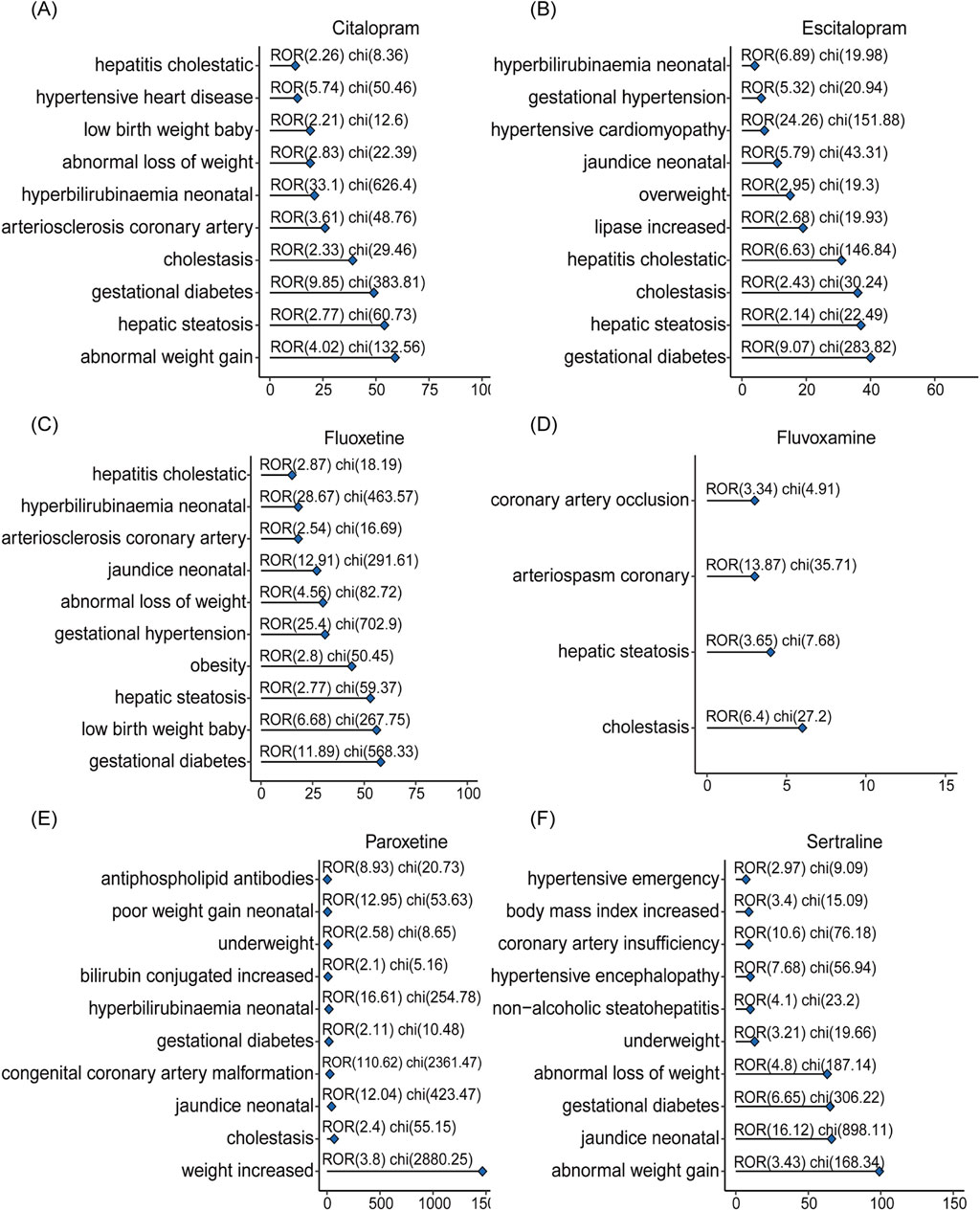
Figure 4. The signals of overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders associated with SSRIs. Adverse reactions related to citalopram (A), escitalopram (B), fluoxetine (C), fluvoxamine (D), paroxetine (E), sertraline (F) caused by abnormalities in glucolipid metabolism.
The number of adverse reactions caused by abnormalities in glucose/lipid metabolism was analyzed by gender (Figure 5). The results showed that, with the exception of “gestational diabetes”, “abnormal increase” and “hepatic steatosis” were more likely to occur in female depressed patients, and coronary atherosclerosis was more likely to occur in male depressed patients.
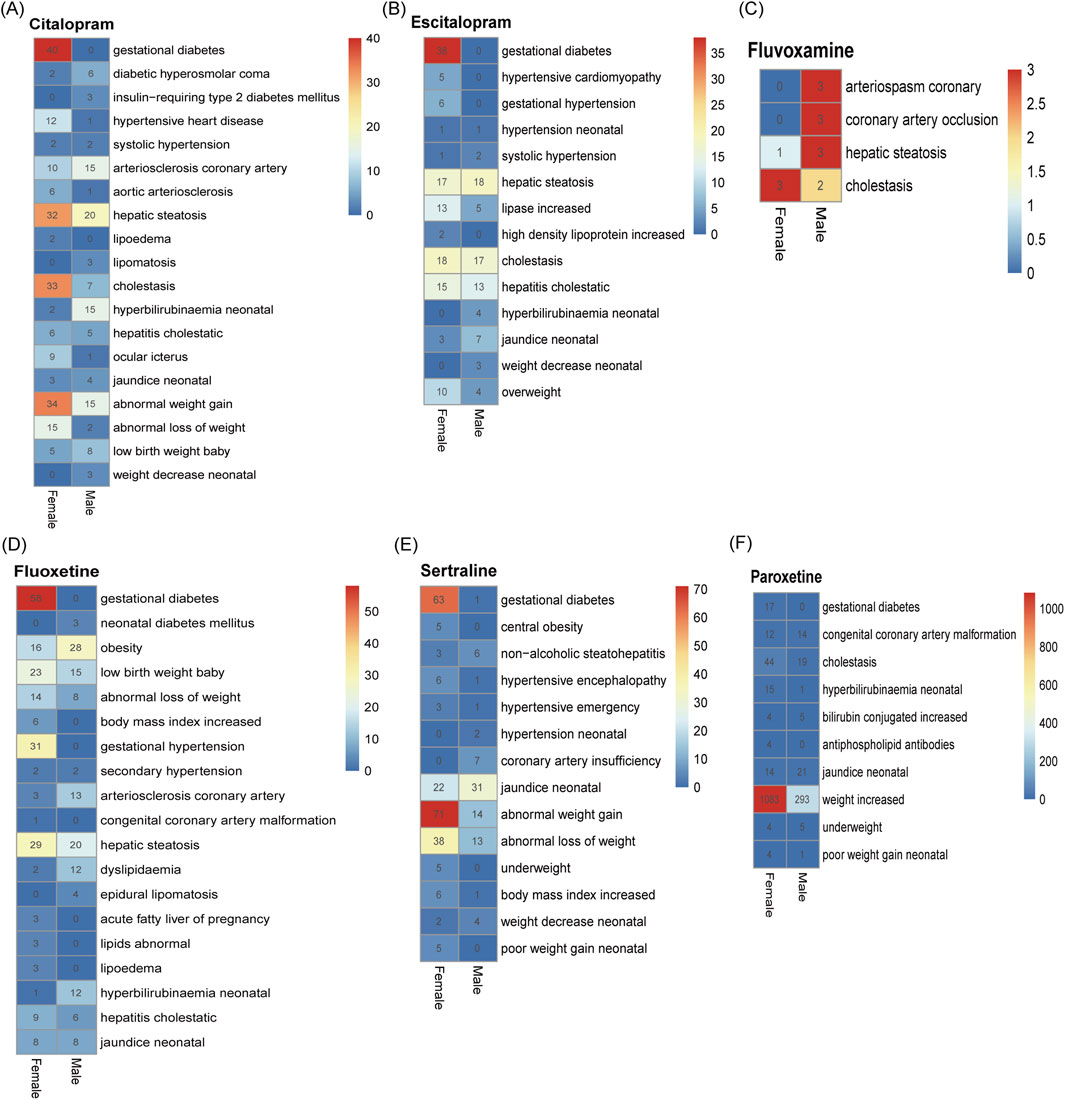
Figure 5. Differences in adverse reactions triggered by abnormalities in glucolipid metabolism in men and women after taking SSRIs. (A) Citalopram. (B) Escitalopram. (C) Fluvoxamine. (D) Fluoxetine. (E) Paroxetine. (F) Sertraline. The numerical values in the heatmap represent the number of specific PTs occurrences in males and females, respectively.
Influencing factors for SSRIs-related glucose/lipid metabolism disorders
We further investigated demographic factors that may influence the occurrence of disorders associated with glucose/lipid metabolism disorders using one-way logistic regression analyses based on case reports in which SSRIs were the primary suspected drug (Figure 6). Of these reports, only a total of 142,787 case reports of PTs associated with SSRIs all contained information on age, sex, and body weight, as detailed in Supplementary Table S7. Among all cases of SSRIs, female patients had a higher risk of glucose/lipid metabolism disorders-related disorders compared to males (OR = 1.63 [1.56, 1.71], P < 0.001). Patients aged 60–75 years were 1.27 times more likely to develop associated disorders compared to patients aged 75 years or older (OR = 1.27 [1.13, 1.42], P < 0.001), and patients younger than 60 years were 1.9 times more likely to develop associated disorders (OR = 1.90 [1.73, 2.09], P < 0.001). Patients weighing 60–75 kg and less than 60 kg had a reduced probability of developing the associated disease compared with patients weighing more than 75 kg. Subsequently, we analyzed each of the six SSRIs individually and showed that, consistent with the results of the overall analysis, both sex and age of the patients increased the probability of developing diseases associated with glucose/lipid metabolism disorders. We were unable to perform one-way logistic regression analyses for case reports in which fluvoxamine was the primary suspect drug because of the lack of information and the insufficient number of reports associated with the occurrence of diseases related to glucose/lipid metabolism disorders.
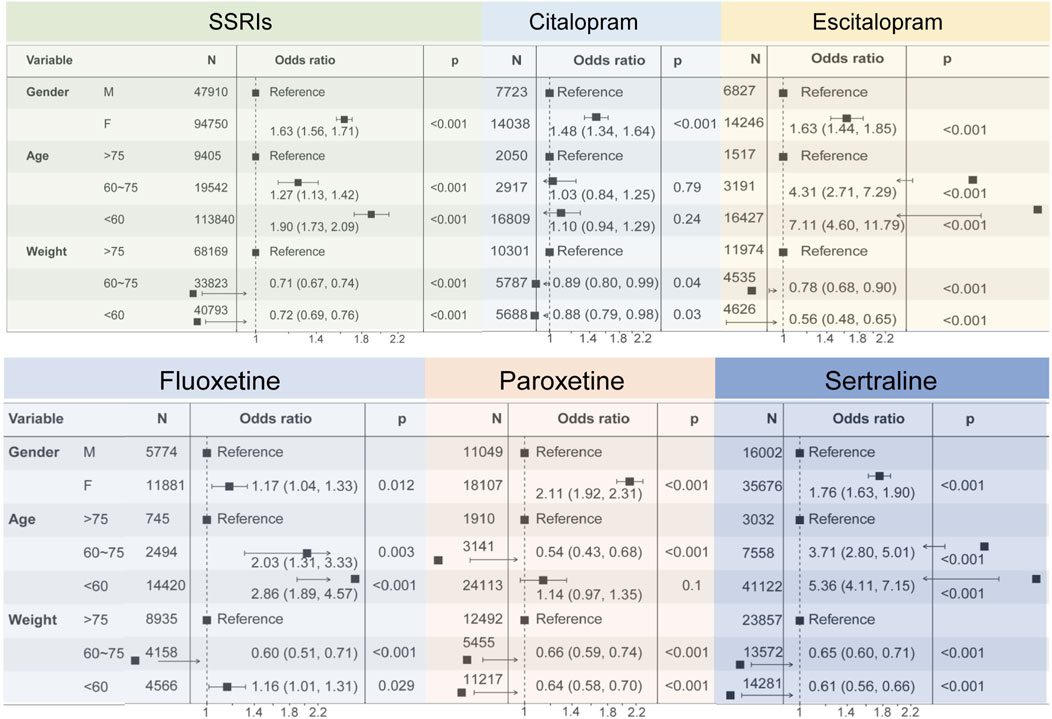
Figure 6. Forest plots showing the results of univariate logistic regression analyses regarding demographic factors affecting diseases caused by SSRIs-associated disorders of glucolipid metabolism.
Discussion
Number of ADE reports
In this work, we conducted a pharmacovigilance study using the Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database of the US Food and Drug Administration, focusing on representative SSRIs (citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline) as well as signals of overweight and glucose-lipid metabolism disorders. Among representative SSRIs, citalopram and escitalopram were the main antidepressants for the treatment of moderate to severe depression, with the latter exhibiting superior efficacy (Cipriani et al., 2012; Yin et al., 2023). In addition, fluoxetine was indicated for patients with moderate depression but might have unsatisfied efficacy in severe cases (Kishi et al., 2023). These three antidepressants were the most widely used in clinical practice. Our work confirmed that there are more reports in the real world about ADE related to overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism disorders associated with citalopram, escitalopram, and fluoxetine. Clinical application of fluvoxamine was late, therefore there were significantly fewer ADE reports for fluvoxamine compared to the other five SSRIs. Relatively speaking, both paroxetine and sertraline were effective in the treatment of moderate to severe depression, with significant efficacy and good tolerability, and fewer reports of adverse events (Sanchez et al., 2014).
Abnormal bodyweight change, overweight or obesity
In this work, we noticed that SSRIs have various abnormal signals related to body weight. Patients taking citalopram and escitalopram might experience abnormal bodyweight change, overweight, even obesity. However, fluoxetine displayed a contrary pattern, with ADE reports of weight loss. The ADE reports of paroxetine and sertraline showed that after taking these two antidepressants, some patients gained weight while others lost weight. Currently, the mechanisms underlying abnormal bodyweight change, overweight or obesity associated with SSRIs medication remained unclear and warranted extensive research exploration. It might have been related to uncontrolled eating during depressive episodes or improvement in depressive symptoms (McCuen-Wurst et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2023). As to weight loss, a research found that three serotonin receptors (5-HT1B, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT6) might have been associated with abnormal weight loss in patients (Halford et al., 2005). Activation of 5-HT1B and 5-HT2C receptors could have led to reduced appetite, with the latter especially believed to induce satiety through endogenous hypothalamic serotonin subtypes (Lam et al., 2010). In addition, a meta-analysis integrating data from 15 studies involving 1,977,446 subjects found that prenatal depression patients who took SSRIs medication experienced newborn weight loss (Zhao et al., 2018). Although this study did not eliminate the influence of other confounding factors, its findings deserve careful attention. However, another study analyzed 238 pregnant women (71 severe depression patients with SSRIs exposed, 36 severe depression patients with SSRIs unexposed, 131 non-severe depression patients with SSRIs unexposed) and concluded that SSRIs medication was not associated with neonatal weight loss (Wisner et al., 2013). In summary, based on our findings from FAERS data analysis and other work, large-sample real world investigation was further needed to determine whether there was an association between body overweight and SSRIs drugs.
Gestational diabetes
Pregnant women were highly susceptible to depression and were often prescribed by physician with antidepressants for treatment. Our results indicated a risk signal for gestational diabetes with all SSRIs except fluvoxamine. A study found that SSRIs not only activate the apoptosis of pancreatic β-cell, but also promote insulin resistance and thereby triggering diabetes (Isaac et al., 2018). Instead, a review summarized that SSRIs do not increase the risk of gestational diabetes (Lebin and Novick, 2022). Therefore, it should be vigilant to the risk of gestational diabetes for pregnant women with depression if they took SSRIs during pregnancy.
Gender differences
In this paper, our findings showed that gender was a risk factor for the occurrence of adverse reactions related to abnormalities of glycolipid metabolism after taking SSRIs. Women were more likely to experience adverse effects compared to men with depression. It was suggested that the high prevalence of depression in women may have been related to the interaction of a number of factors, including genetic, physiological, psychological, and social factors (Blanco et al., 2015; Sramek et al., 2016). These factors may have simultaneously affected women’s sensitivity and tolerance to SSRI drugs, thereby increasing their risk of adverse effects. For different SSRIs drugs, the mechanism of inducing adverse effects may have varied. For example, it was shown that fluoxetine may have induced a series of adverse reactions by affecting various neurotransmitter systems such as the 5-hydroxytryptamine system, the norepinephrine system, and the dopamine system (Kobayashi et al., 2012; Edinoff et al., 2021). As for sertraline, it may have caused adverse reactions in patients by affecting molecular targets such as 5-HT receptors and NMDA receptors (Izumi et al., 2024). Therefore, further clarification of the specific mechanisms of different SSRIs in the treatment of depression was beneficial for healthcare professionals to more accurately judge and manage the occurrence of adverse reactions.
Lipid metabolism
Lipid metabolism was crucial for life activity in maintaining energy balance and hormone synthesis. Disorders in lipid metabolism could lead to various diseases such as obesity, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular diseases (Banzi et al., 2015). From our analysis on ADE reports, we found that SSRIs medications were highly prone to cause lipid metabolism disorders, such as hepatic steatosis, arteriosclerosis, cholestasis, and neonatal jaundice. However, there were not many reports on the risk signals of neonatal jaundice related to SSRIs. Although the impact of SSRIs during pregnancy on maternal and infant health was very important, the relevant research was not sufficient up to now.
Limitations
Although the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System serves as a critical repository for regulatory oversight, pharmaceutical surveillance, and public health monitoring, its utility is tempered by inherent limitations. FAERS relies on voluntary reporting, which introduces potential biases and underreporting. In addition, the database may suffer from data duplication and inaccuracies. Moreover, FAERS lacks comprehensive patient data, including detailed medical histories and comorbid conditions. It is imperative to recognize and address these limitations for clinicians and researchers to derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions based on FAERS data.
Conclusion
We used real-world data from the FAERS database to screen for adverse reactions associated with abnormalities in glucose/lipid metabolism. Through the proportional imbalance method, we identified PTs that were highly associated with SSRIs. In addition, there were differences in adverse reactions associated with abnormalities in glucose/lipid metabolism elicited by different SSRIs. Specifically, the adverse reactions associated with abnormalities of glycolipid metabolism associated with paroxetine were relatively low in percentage, while the absolute lowest number was fluvoxamine. Therefore, healthcare professionals should consider factors such as inter-drug variability, patient age, and gender when selecting drugs for SSRIs in order to more effectively manage the occurrence of adverse reactions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JnC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZC: Data curation, Supervision, Resources, Writing–review and editing. YW: Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YM: Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. ZY: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing–review and editing. JaC: Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. ZX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. FX: Methodology, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the China Medical Education Association Grant (CMEA2024001).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1517546/full#supplementary-material
References
Banzi, R., Cusi, C., Randazzo, C., Sterzi, R., Tedesco, D., and Moja, L. (2015). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for the prevention of migraine in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 4 (4), CD002919. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002919.pub3
Blanco, C., Hanania, J., Petry, N. M., Wall, M. M., Wang, S., Jin, C. J., et al. (2015). Towards a comprehensive developmental model of pathological gambling. Addiction 110 (8), 1340–1351. doi:10.1111/add.12946
Cipriani, A., Purgato, M., Furukawa, T. A., Trespidi, C., Imperadore, G., Signoretti, A., et al. (2012). Citalopram versus other anti-depressive agents for depression. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 7 (7), CD006534. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006534.pub2
Edinoff, A. N., Akuly, H. A., Hanna, T. A., Ochoa, C. O., Patti, S. J., Ghaffar, Y. A., et al. (2021). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and adverse effects: a narrative review. Neurol. Int. 13 (3), 387–401. doi:10.3390/neurolint13030038
Galecki, P., Mossakowska-Wojcik, J., and Talarowska, M. (2018). The anti-inflammatory mechanism of antidepressants - SSRIs, SNRIs. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 80 (Pt C), 291–294. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.03.016
Ghosh, R., Gupta, R., Bhatia, M. S., Tripathi, A. K., and Gupta, L. K. (2015). Comparison of efficacy, safety and brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in patients of major depressive disorder, treated with fluoxetine and desvenlafaxine. Asian J. Psychiatr. 18, 37–41. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2015.10.006
Gothert, M., Bonisch, H., Malinowska, B., and Schlicker, E. (2020). Serotonin discovery and stepwise disclosure of 5-HT receptor complexity over four decades. Part II. Some contributions of Manfred Gothert. Pharmacol. Rep. 72 (2), 271–284. doi:10.1007/s43440-019-00047-4
Gundersen, E., and Bensadon, B. (2023). Geriatric depression. Prim. Care 50 (1), 143–158. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2022.10.010
Halford, J. C., Harrold, J. A., Lawton, C. L., and Blundell, J. E. (2005). Serotonin (5-HT) drugs: effects on appetite expression and use for the treatment of obesity. Curr. Drug Targets 6 (2), 201–213. doi:10.2174/1389450053174550
Hammen, C. (2018). Risk factors for depression: an autobiographical review. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 14, 1–28. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050817-084811
Isaac, R., Boura-Halfon, S., Gurevitch, D., Shainskaya, A., Levkovitz, Y., and Zick, Y. (2018). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) inhibit insulin secretion and action in pancreatic β cells. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (12), 4577–4578. doi:10.1074/jbc.AAC118.002476
Izumi, Y., Reiersen, A. M., Lenze, E. J., Mennerick, S. J., and Zorumski, C. F. (2024). Sertraline modulates hippocampal plasticity via sigma 1 receptors, cellular stress and neurosteroids. Transl. Psychiatry 14 (1), 474. doi:10.1038/s41398-024-03185-3
Kishi, T., Ikuta, T., Sakuma, K., Okuya, M., Hatano, M., Matsuda, Y., et al. (2023). Antidepressants for the treatment of adults with major depressive disorder in the maintenance phase: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 28 (1), 402–409. doi:10.1038/s41380-022-01824-z
Kobayashi, K., Haneda, E., Higuchi, M., Suhara, T., and Suzuki, H. (2012). Chronic fluoxetine selectively upregulates dopamine D₁-like receptors in the hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 37 (6), 1500–1508. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.335
Lam, D. D., Garfield, A. S., Marston, O. J., Shaw, J., and Heisler, L. K. (2010). Brain serotonin system in the coordination of food intake and body weight. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 97 (1), 84–91. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2010.09.003
Lebin, L. G., and Novick, A. M. (2022). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in pregnancy: an updated review on risks to mother, fetus, and child. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 24 (11), 687–695. doi:10.1007/s11920-022-01372-x
Marjoribanks, J., Brown, J., O'brien, P. M., and Wyatt, K. (2013). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for premenstrual syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013 (6), CD001396. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001396.pub3
Mccuen-Wurst, C., Ruggieri, M., and Allison, K. C. (2018). Disordered eating and obesity: associations between binge-eating disorder, night-eating syndrome, and weight-related comorbidities. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1411 (1), 96–105. doi:10.1111/nyas.13467
Milosavljevic, J. Z., Milosavljevic, M. N., Arsenijevic, P. S., Milentijevic, M. N., and Stefanovic, S. M. (2022). The effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on male and female fertility: a brief literature review. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 26 (1), 43–49. doi:10.1080/13651501.2021.1872647
Miret, M., Ayuso-Mateos, J. L., Sanchez-Moreno, J., and Vieta, E. (2013). Depressive disorders and suicide: epidemiology, risk factors, and burden. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 37 (10 Pt 1), 2372–2374. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.01.008
Pinna, G., Costa, E., and Guidotti, A. (2009). SSRIs act as selective brain steroidogenic stimulants (SBSSs) at low doses that are inactive on 5-HT reuptake. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 9 (1), 24–30. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2008.12.006
Sanchez, C., Reines, E. H., and Montgomery, S. A. (2014). A comparative review of escitalopram, paroxetine, and sertraline: are they all alike? Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 29 (4), 185–196. doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000023
Sramek, J. J., Murphy, M. F., and Cutler, N. R. (2016). Sex differences in the psychopharmacological treatment of depression. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 18 (4), 447–457. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2016.18.4/ncutler
Thapar, A., Eyre, O., Patel, V., and Brent, D. (2022). Depression in young people. Lancet 400 (10352), 617–631. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01012-1
Wisner, K. L., Bogen, D. L., Sit, D., Mcshea, M., Hughes, C., Rizzo, D., et al. (2013). Does fetal exposure to SSRIs or maternal depression impact infant growth? Am. J. Psychiatry 170 (5), 485–493. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11121873
Yin, J., Song, X., Wang, C., Lin, X., and Miao, M. (2023). Escitalopram versus other antidepressive agents for major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 23 (1), 876. doi:10.1186/s12888-023-05382-8
Yu, S., Zhang, Y., Shen, C., and Shao, F. (2023). Efficacy of pharmacotherapies for bulimia nervosa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 24 (1), 72. doi:10.1186/s40360-023-00713-7
Yuet, W. C., Derasari, D., Sivoravong, J., Mason, D., and Jann, M. (2019). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use and risk of gastrointestinal and intracranial bleeding. J. Am. Osteopath Assoc. 119 (2), 102–111. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2019.016
Keywords: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, FAERS, overweight, ADEs, glucose/lipid metabolism disorders
Citation: Cao J, Chen Z, Wang Y, Ma Y, Yang Z, Cai J, Xiao Z and Xu F (2025) Overweight and glucose/lipid metabolism abnormality associated with SSRIs: a pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA adverse event reporting system. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1517546. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1517546
Received: 26 October 2024; Accepted: 31 December 2024;
Published: 10 January 2025.
Edited by:
Yao Liu, Daping Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Joanna Gdula-Argasinska, Jagiellonian University Medical College, PolandLiz Girardi Müller, Regional Community University of Chapecó, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Chen, Wang, Ma, Yang, Cai, Xiao and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian Cai, NDU1MzIwMTA5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Zhijun Xiao, emhpanhpYW9AMTI2LmNvbQ==; Feng Xu, eHVmQHNtdS5lZHUuY24=
†ORCID: Jinming Cao, orcid.org/0000-0001-5946-4967; Zhicong Chen, orcid.org/0000-0002-3001-5567; Yan Wang, orcid.org/0009-0005-8206-268X; Yunpeng Ma, orcid.org/0009-0004-8048-5606; Zhen Yang, orcid.org/0000-0003-2105-3630; Jian Cai, orcid.org/0009-0009-4383-2767; Zhijun Xiao, orcid.org/0000-0001-6396-6820; Feng Xu, orcid.org/0000-0001-6215-8696
 Jinming Cao
Jinming Cao Zhicong Chen
Zhicong Chen Yan Wang2†
Yan Wang2† Zhen Yang
Zhen Yang Zhijun Xiao
Zhijun Xiao Feng Xu
Feng Xu