- 1Department of Chemistry, College of Science, University of Hail, Ha’il, Saudi Arabia
- 2Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Hail, Ha’il, Saudi Arabia
- 3Chemistry Program, New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
- 4Centre for Interdisciplinary Research in Basic Sciences, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India
- 5Translational Bioinformatics Group, International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), New Delhi, India
Introduction: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that significantly impacts the cognitive function and memory of a person. Despite the significant research efforts, the ability to completely prevent or effectively treat AD and its related dementias remains limited. Protein kinases are integral to AD pathology and represent promising targets for therapeutic intervention.
Methods: A series of pyrimidine-based compounds 4-(4-(arylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidine derivatives (8-14) were synthesized and characterised. ATPase inhibition was carried out against the MARK4 enzyme. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation at 500 ns was carried out against MARK4 (PDB: 5ES1). The drug-likeness feature and toxicity of the molecules were evaluated using QikProp and other tools.
Results: Compounds were synthesized following a multi-step approach and characterized using multi-nuclear magnetic resonance (1H/13C-NMR) and mass spectrometry. ATPase inhibition assay of the compounds against MARK4 showed an IC50 value in the micromolar (μM) range. The results of the docking studies were consistent with the in-vitro experiments and identified (9) and (14) as the candidates with the highest affinity towards MARK4. MD simulation further supported these results, showing that the binding of ligands stabilises the target protein.
Conclusion: Using experimental and theoretical approaches, we demonstrated that the reported class of pyrimidine derivatives are an excellent starting point for developing the next-generation anti-AD drugs.
Introduction
Heterocyclic compounds are ubiquitous in both synthetic and natural chemical spaces, forming the essential backbone for a diverse array of applications (Reymond, 2015). The significance of heterocyclic compounds is immense as they are essential to humans, plants, and animals (Katritzky et al., 2010). Among wide-ranging small and medium-sized heterocycles, pyrimidine nuclei constitute an important group of pharmacologically active compounds (Das et al., 2022). The importance of this core is well supported by the fact that it serves as the fragment of nucleobases (cytosine, thymine, uracil) as well as numerous clinically approved drugs. For example, pyrimidine nucleus is present in 5-fluorouracil, imatinib (anti-cancer), rilpivirine (anti-viral), iclaprim (antibiotic), trimethoprim (anti-bacterial), and many others (Nammalwar and Bunce, 2024). Besides, its ability to serve as bioisostere (for aromatic cores) and to interact with biological targets through non-covalent interactions (NCIs) makes it an excellent candidate in drug discovery programs (Nammalwar and Bunce, 2024). A plethora of research demonstrates that pyrimidine is a promising scaffold for developing drugs against chronic and infectious diseases (Nadar and Khan, 2022). In recent years, several 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidines have been identified with anti-protozoal (Rahman et al., 2024; Singh et al., 2024), anti-inflammatory (Fatima et al., 2023), anti-neuroinflammatory (Manzoor et al., 2023) and carbonic anhydrase inhibitory (Manzoor et al., 2021a) activity.
Reported over a century ago, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has now become the most widespread cause of dementia, with millions of cases reported worldwide. This has led to a significant economic and manpower burden (Bell, 2023; Gustavsson et al., 2023). The number of people suffering from AD and other dementias is estimated to surpass 152 million by 2050 (Nichols et al., 2022). To combat this debilitating condition, researchers are adopting various approaches and one of them is developing small molecules that target one or more AD machinery (e.g., β-amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles) (Takahashi et al., 2017). Among different classes of small molecules identified to date, pyrimidine-based compounds emerged as a promising candidate (Singh et al., 2021; Das et al., 2022). For example, Nain and coworkers (Pant et al., 2024) reported a series of substituted pyrimidine derivatives with interesting anti-AD results. The compounds were safe at high dosages (1000 mg/kg), did not cause toxicity, and inhibited acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in animal models. Biological assay results indicated that the compound a (Figure 1) exhibits neuroprotective effects better than donepezil, a clinically used drug. By adopting a multitarget-directed ligand (MTDL) strategy, Hoda and coworkers (Manzoor et al., 2021b) reported compound b (Figure 1) that was found to be active against esterases in the nanomolar (nM) concentration. It was reported that functional groups guided the activity of the compounds with methoxy and chloro substituents showing the best activity. Since kinases contribute to the production of abnormal and hyperphosphorylated microtubule-associated tau proteins, pyrimidine-based compounds have also been studied as kinase inhibitors (Luo et al., 2016; Naz et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2016; Jameel et al., 2017; Hartz et al., 2023). Hartz et al. (2023) reported that introducing pyrimidine provides bioactive conformation to the hinge binder and is better than the pyridine counterpart c (Figure 1). Nevertheless, the clinical success of dasatinib d (Figure 1) in CML and ALL is well known (Ayala-Aguilera et al., 2021). These studies support the idea that pyrimidine-based compounds can target multiple pathways related to Alzheimer’s disease. However, we noticed a gap, especially concerning 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidines, which have been poorly studied in relation to AD pathology, particularly regarding their interaction with kinases. Therefore, in the quest for new compounds with application in AD (Haque et al., 2024a; Haque et al., 2024b), we adopted the concept of molecular hybridization and designed hybrid compounds (8-14, Figure 1) containing a central pyrimidine ring flanked by different substituents at fourth and sixth positions. The designed molecule can be divided into three areas/regions: a fixed left-hand side electron-rich region (thiophene), and a central pyrimidine scaffold, and varying aryl (sulfonyl)piperazine fragments on the right hand. To optimize the activity of the compounds, we varied functional groups on the aromatic ring and introduced electron donor and acceptor groups of varying strength. The rationale behind the selection of these groups stems from their common use in medicinal chemistry and established bioactivity (Kilbile et al., 2023; Thakur et al., 2024). The synthesized compounds were evaluated for their activity against the microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 (MARK4) enzyme. This ser/thr enzyme has been reported to be over-expressed in AD and serves as the potential target for anti-AD drug development (Naz et al., 2013). The in-vitro biological results were complemented by molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation studies. Attempts have been made to correlate the MARK4 activity with physicochemical characteristics, drug-likeness, toxicity, and frontier molecular orbitals of the molecules.
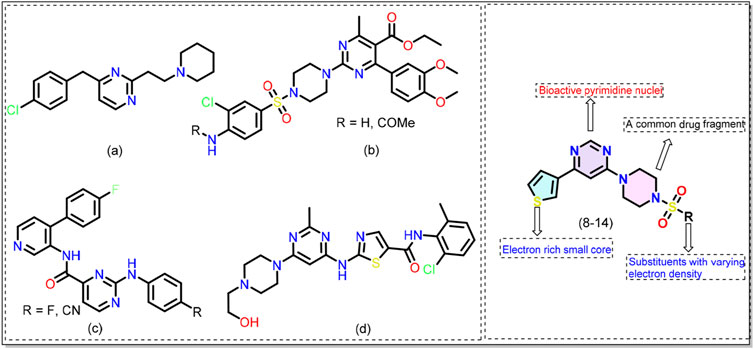
Figure 1. Chemical structures of previously reported pyrimidine-based kinase inhibitors (see text for more details). General structure of the 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidine derivatives (8-14) reported in this work.
Materials and methods
General
All chemicals were procured from Sigma Aldrich and were used as received. All manipulations, except otherwise stated, were performed under a nitrogen (N2) atmosphere. Dichloromethane (DCM) was dried over calcium hydride (Armarego, 2017). Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (200–400 mesh) while thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis was carried out on aluminium plates pre-coated with silica gel GF254. Melting points were determined by using the open capillary method and are uncorrected. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker Spectrospin DPX 300 MHz spectrometer (Bruker Analytic GmbH, Berlin, Germany). The splitting patterns are denoted as follows: s for singlet, d for doublet, and m for multiplet. Chemical shift values are reported in parts per million (ppm). High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) was performed using an Agilent 1290 Infinity II UPLC/HRMS instrument, equipped with a Q-TOF (UHD Accurate-Mass) and a photodiode array detector.
General procedure for the synthesis of compounds
Synthesis of tbutyl 4-(6-chloropyrimidin-4-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (3)
In a 50 mL round-bottom flask containing 15 mL of iso-propanol under N2 atmosphere, 4,6-dichloropyrimidine (1, 1.0 mmol) was added followed by 1.2 equivalents of N-Boc piperazine (2) at 0°C. To the resulting mixture, triethylamine (TEA, 1.2 mmol) was added dropwise, and the mixture was stirred. The reaction mixture was removed from the ice bath and placed at room temperature for 5–6 h and monitored by TLC. Upon the completion of the reaction, the reaction was quenched by adding 10 mL of cold water. The crude reaction mixture was extracted using DCM (3 × 30 mL) and the separated organic layer was washed with brine solution (20 mL). Afterwards, the organic layer was dried over anhyd. Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), concentrated, and the crude product was purified using column chromatography (ethyl acetate/hexane = 8:2) to obtain intermediate tbutyl 4-(6-chloropyrimidin-4-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylate 3.
Synthesis of tbutyl 4-(6-(thiophen-3-yl) pyrimidin-4-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (5)
In a 50 mL sealed Schlenk tube tbutyl 4-(6-chloropyrimidin-4-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (3, 1.0 mmol), thiophene-boronic acid (4, 1.5 equiv.) and potassium carbonate (K2CO3, 6.0 equiv.) were added. To this mixture, the solvent (8.0 mL dioxane and 2.0 mL water) was added followed by flushing with N2 gas for 2 min (three times). The catalyst (Pd(PPh3)4 = 5 mol%) was then added while maintaining the N2 atmosphere. The reaction mixture was heated at 100°C for 3 h. Upon the completion of the reaction (as confirmed by the TLC), the mixture was cooled to room temperature and the solvent was then evaporated using rotary evaporator. The resulting crude product was purified using column chromatography (ethyl acetate/hexane = 8:2) to obtain tbutyl 4-(6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylate (5).
Synthesis of 4-(piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidine (6)
To a 100 mL round-bottom flask containing compound 5 (1.0 mmol) dissolved in 15.0 mL DCM under a N2 atmosphere, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA, 1.0 mL) was added dropwise at 0°C. The reaction mixture was warmed to room temperature and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Following the completion of the reaction, the mixture was basified using dilute sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). The organic layer was extracted with DCM (3 × 50 mL), followed by washing with water (10 mL) and brine solution (10 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhy. Na2SO4, and the solvent was evaporated using the rotary evaporator. The crude product was purified using column chromatography (DCM/MeOH = 8:3) yielding 4-(piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidine (6).
Synthesis of 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidine derivatives (8-14)
In a 50 mL two-neck round-bottom flask containing 4-(piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)-pyrimidine (6, 1.0 mmol) dissolved in 15 mL of dry DCM, different aryl sulfonyl chloride (7, 1.5 equiv.) was added slowly in portions while maintaining a nitrogen atmosphere at 0°C. Then, TEA (2.0 equiv.) was added dropwise to the mixture and stirred for 6 h. Once the reaction was complete, it was neutralized with 20 mL of a sat. NaHCO3 solution. The crude product was extracted using DCM (3 × 30 mL) and the combined organic layer was subsequently washed with 20 mL of cold water and 20 mL of brine solution and dried over anhyd. Na2SO4. The organic layer was evaporated on rotatory evaporator and purified by column chromatography (ethyl acetate/hexane = 8:2) to obtain 8–14 in moderate to good yields.
4-(4-((3-Chlorothiophen-2-yl)-sulfonyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)-pyrimidine (8)
Synthesised as described above. White solid; yield = 78%, m. p. = 158°C; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.61 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.02 (dd, J = 3.0, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 6.98 (d, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 3.86 (t, J = 5.1 Hz, 4H), 3.18 (t, J = 5.1 Hz, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.07, 159.40, 158.52, 140.56, 138.06, 133.59, 132.19, 127.30, 126.70, 125.90, 125.68, 98.06, 45.66, 43.23. Exact mass = 426.00 amu for C16H15ClN4O2S3; observed mass (m/z): 427.01 amu [M + 1]+.
4-(4-((2,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-sulfonyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)-pyrimidine (9)
Synthesised as described above. Off-white solid; yield = 75%, m. p. = 172°C; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.60 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 8.01 (dd, J = 3.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.83 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.48 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.78 (t, J = 5.1 Hz, 4H), 3.36–3.25 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.97, 162.25, 159.17, 158.51, 158.46, 140.67, 133.60, 126.61, 125.76, 125.72, 117.90, 104.53, 99.56, 98.08, 56.03, 55.73, 45.58, 43.96. Exact mass = 446.11 amu for C20H22N4O4S2; observed mass (m/z): 447.11 amu [M + 1]+.
4-(4-((4-Fluorophenyl)-sulfonyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)-pyrimidine (10)
Synthesised as described above. White solid; yield = 73%, m. p. = 162°C; 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.59 (s, 1H), 8.00 (dd, J = 3.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.82–7.72 (m, 2H), 7.56 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (m, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.71 (s, 1H), 3.82 (t, J = 5.0 Hz, 4H), 3.11 (t, J = 5.0 Hz, 4H); 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.70, 164.16, 162.07, 159.34, 158.49, 140.57, 131.48, 131.45, 130.49, 130.40, 126.67, 125.84, (d, J = 22.0 Hz), 116.70, 116.48, 98.04, 45.64, 43.34. Exact mass = 404.08 amu for C18H17FN4O2S2; observed mass (m/z): 405.09 amu [M + 1]+.
4-(4-((4-Nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidine (11)
Synthesised as described above. White solid; yield = 83%, m. p. = 155°C, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.62 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 8.05–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.72 (ddd, J = 7.0, 4.6, 1.9 Hz, 2H), 7.66–7.56 (m, 2H), 7.40 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (t, J = 5.2 Hz, 4H), 3.43 (t, J = 5.2 Hz, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.3, 158.5, 158.4, 140.80, 135.51, 132.93, 130.87, 127.65, 126.87, 126.68, 124.67, 98.95, 45.75, 43.55. Exact mass = 431.07 amu for C18H17N5O4S2; observed mass (m/z): 432.08 amu [M + 1]+.
4-(4-(Pyridin-3-ylsulfonyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)-pyrimidine (12)
Synthesised as described above. Light cream solid; yield = 65%, m. p. = 172°C, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 9.01 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.84 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 8.60 (s, 1H), 8.03 (dd, J = 23.7, 5.6 Hz, 2H), 7.60–7.46 (m, 2H), 7.39 (dd, J = 5.2, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 6.72 (s, 1H), 3.85 (t, J = 5.1 Hz, 4H), 3.18 (t, J = 5.0 Hz, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.09, 159.44, 158.51, 153.79, 140.52, 135.34, 132.40, 126.70, 125.90, 125.65, 123.86, 98.06, 45.54, 43.37. Exact mass = 387.08 amu for C17H17N5O2S2; observed mass (m/z): 388.09 amu [M + 1]+.
4-((4-(6-(Thiophen-3-yl)-pyrimidin-4-yl)-piperazin-1-yl)-sulfonyl)-morpholine (13)
Synthesised as described above. Light color solid; yield = 85%, m. p. = 163°C, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.65 (s, 1H), 8.04 (dd, J = 3.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 6.78 (s, 1H), 3.79 (dd, J = 6.4, 3.9 Hz, 4H), 3.77–3.70 (m, 4H), 3.38 (dd, J = 6.2, 4.0 Hz, 4H), 3.30–3.23 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.37, 159.35, 158.51, 140.63, 126.68, 125.86, 125.71, 98.16, 66.36, 46.63, 46.12, 43.69. Exact mass = 395.11 amu for C16H21N5O3S2; observed mass (m/z): 396.12 amu [M +1]+.
4-(4-(Naphthalen-1-ylsulfonyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)-pyrimidine (14)
Synthesised as described above. White solid; yield = 70%, m. p. = 160°C, 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.55 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.34 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.99–7.94 (m, 3H), 7.90 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (m, J = 6.9, 1.5 Hz, 2H), 7.53 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 3.94–3.75 (m, 4H), 3.17 (t, J = 5.1 Hz, 4H); 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 162.02, 159.24, 158.44, 140.58, 135.02, 132.43, 132.21, 129.48, 129.23, 129.20, 129.09, 127.98, 127.77, 126.61, 125.78, 125.67, 122.78, 98.00, 45.77, 43.39. Exact mass = 436.10 amu for C22H20N4O2S2; observed mass (m/z): 437.11 amu [M + 1]+.
Biological studies
Enzyme inhibition assay
The inhibitory potential of the synthesized compounds against MARK4 was analysed using the malachite green based enzyme inhibition assay. The malachite green kinase inhibition assay is a colorimetric technique designed to assess kinase activity by detecting the release of inorganic phosphate (Pi) during phosphorylation. When a kinase transfers a phosphate group from ATP to its substrate, Pi is generated as a byproduct. The malachite green reagent interacts with Pi to produce a green-colored complex, which can be quantified using a spectrophotometer. This assay is modified to evaluate enzyme inhibition by measuring the reduction in Pi release in the presence of potential inhibitors. The concentration of ligands was gradually increased against the pure MARK4 in order to determine the inhibitory effect of the produced compounds on the kinase activity of MARK4. The protein’s highest activity, MARK4 (ligand-free), was utilised as a reference, and various ligand concentrations were added to determine the IC50 value. MARK4 (5 μM) and freshly made ATP were combined, and a final volume (100 μL) of the reaction mixture was created. It was then incubated for 1 hour at 25°C. To stop the reaction, we added 200 μL of Malachite green solution to the mixture. After that, we incubated the samples at room temperature to allow the color to develop. Finally 96 well plates were filled with 100 μL of the reaction mixture, which was then scanned at 620 nm using a multiscan ELISA reader. All the reactions were carried out in triplicates.
Computational studies
Modeling of MARK4 structure
The 3D structure of the MARK4 protein (PDB ID: 5ES1) was downloaded from the protein data bank (Sack et al., 2016). The crystal structure of MARK4 lacks amino acid residues between 205 and 218. Therefore, it was modelled prior to the docking and simulation studies. The missing residues were reconstructed using a web-based SWISS-Model server (Schwede et al., 2003). The sequence of the missing region was input into the SWISS-Model server, which used homologous structures to predict and build the missing loop. The quality of the modeled region was assessed by comparing it to the original crystal structure through structural alignment and validation techniques, such as a Ramachandran plot. The combined structure, incorporating both the crystallographic data and the modeled residues, was used for further computational studies.
Ligand and target preparation
The 2D chemical structures were drawn and converted to 3D using ChemDraw. Energy minimisation and geometry optimisation were then performed to ensure stable conformations. Non-ionic form of the ligands was employed in the docking studies. Input files were prepared using AutoDock Tools (ADT, v1.5.7) and the docking was performed using AutoDock Vina (v1.1.2) (Huey et al., 2012). Docking was performed using a grid box of dimension 70 × 88 × 84 Å3, a default grid spacing of 0.375 Å and default parameters for the rest of the variables. The output file produced were analysed in PyMol (DeLano, 2002). A 2D interaction plot of the best-docked conformation was generated using Schrödinger Visualizer (Schrödinger Release 2024-4: Maestro, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2024).
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation
MD simulations of the docked ligand-MARK4 complexes were conducted using the Desmond module in Schrödinger (Bowers et al., 2006). Initially, the docked ligand and target MARK4 complexes were merged within the Maestro interface (Friesner et al., 2006). The system setup involved embedding the merged complex into an orthorhombic water box, ensuring a 10 Å buffer distance from the protein. The water was modeled using the TIP4P model, which provides a realistic representation of water’s properties in MD simulations (Release, 2017). To achieve electrostatic neutrality, counterions (Na⁺/Cl⁻) were added. This step is crucial for maintaining proper ionic strength and mimicking physiological conditions within the simulation environment. The OPLS_2005 force field was employed to describe atomic interactions within the system accurately (Shivakumar et al., 2010). The ensemble class was set to NPT (constant pressure and temperature) with the temperature maintained at 300 K using the Nose-Hoover thermostat, while the pressure was stabilized and at 1 atm using the Martyna-Tobias-Klein barostat (Lippert et al., 2013). A pre-production equilibration phase lasting 10 ns was performed, during which the system’s trajectory was recorded at intervals of 4.8 ps to monitor initial adjustments. Following equilibration, a production run of 500 ns was executed to explore the dynamic stability of the ligand-MARK4 complex comprehensively. Post-simulation analysis involved calculating the root mean square deviation (RMSD), root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) and evaluating secondary structure elements (SSE) along with protein-ligand interaction plots.
Drug-likeness, bioavailability, and toxicity prediction
To evaluate the physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties of the compounds, we employed both free and commercial computational tools, each offering unique strengths. For freely accessible resources, we used SwissADME (Daina et al., 2017) and pKCSM (Pires et al., 2015), for predicting drug-likeness, solubility, absorption, and other key pharmacokinetic parameters. SwissADME provides insights into lipophilicity, water solubility, and bioavailability, while pKCSM models complex ADMET (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity) properties, enhancing our understanding of the compounds’ safety and efficacy profiles. For a more refined analysis, we used the commercially available QikProp (Shahbazi et al., 2017; Omoboyowa, 2022), which offers high-precision predictions of molecular properties and ADMET profiles.
Density functional theory (DFT) study
Quantum chemical calculations were performed using Spartan 20 software (Hehre and Huang, 1995) using the B3LYP/6-31G* level of theory. This DFT analysis yielded chemical descriptors, including total energy (E), chemical hardness (η), chemical potential (μ), and electrophilicity (ω).
Results and discussion
Synthesis and characterization of 4-(4-(arylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidine derivatives (8-14)
Target compounds 4-(4-aryl piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidine derivatives (8–14) were synthesised following the steps given in Scheme 1. Nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) reaction between 4,6-dichloropyrimidine (1) with the tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc)-protected piperazine (2) in the presence of triethylamine (TEA) in iso-propanol afforded Boc-protected intermediate (3). Suzuki–Miyaura coupling between 3-thienylboronic acid (4) and (3) using Pd(PPh3)4 catalyst and K2CO3 as the base in aqueous dioxane under reflux afforded (5). Finally, Boc was deprotected using trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) in dichloromethane (DCM). The resulting product (6) underwent reaction with different substituted arylsulfonyl chloride (7) using TEA in DCM to afford 4-(4-(arylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)-6-(thiophen-3-yl)pyrimidine derivatives (8–14) in 65%–80% yield.
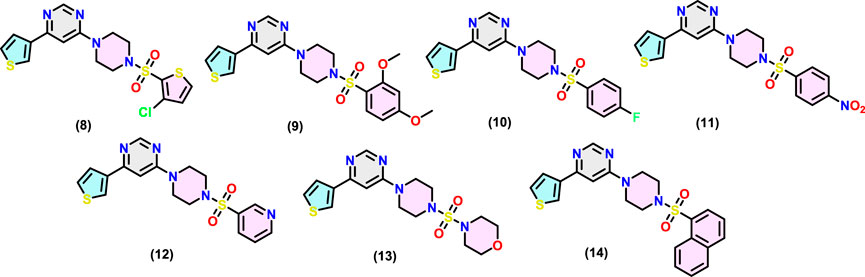
The chemical structure of the final compounds (Figure 2) was confirmed by proton (1H-NMR), carbon (13C-NMR), and mass spectrometry. All spectral data are given in Supplementary Figures SF1–SF7 (supporting information). Characteristics resonances observed in 1H-NMR include signals for the piperidine ring, thienyl ring, methylene of piperazine, and aromatic core attached to it through sulfonyl core. For instance, the 1H-NMR spectrum of (8–14) showed multiplet at δ 3.17–3.43 ppm and δ 3.38–3.94 ppm integrated for eight hydrogens of piperazine core. Two protons of the pyrimidine ring appeared at δ 7.36-7.58 and δ 8.59–8.65 ppm (Gong et al., 2017). Another characteristic signal (e.g., methoxy protons at δ 3.85–3.88 ppm as a singlet in compound 9) equalled the number of different protons and are in agreement with the formula. Similarly, in 13C-NMR, carbon of the aromatic rings and others was observed at expected chemical shift values. For instance, the 13C-NMR spectrum of (8–14) shows a characteristic peak for piperazine at δ 43.23–43.96 ppm and δ 45.54–46.12 ppm. In the case of compound (9), two carbons resonating at δ 66.36 ppm and δ 46.63 ppm can be attributed to C-O and C-N, respectively of the morpholine moiety. Finally, the MS results further provided the identification of compounds. All compounds showed (M + 1) molecular ion peaks at m/z 427.01, 447.11, 405.09, 432.08, 388.09, 396.12 and 437.11 amu for (8–14), respectively, confirming formulations for the final compounds.
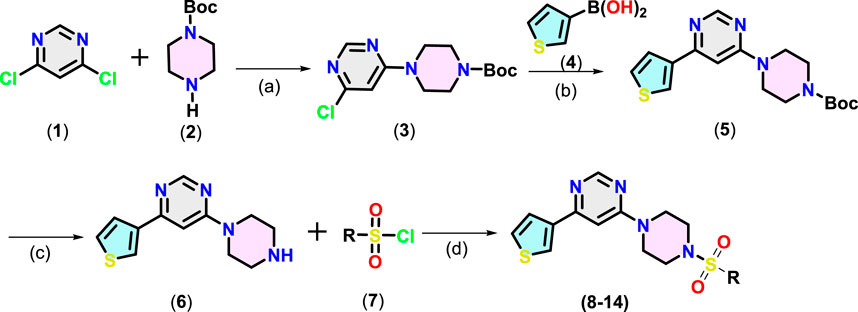
Scheme 1. Synthesis of pyrimidine derivatives (8-14). Reaction conditions: (a): 1 (1.0 mmol), 2 (1.2 equiv.), isopropanol, TEA, 0°C to RT, 5-6 h, (b): 3 (1.0 mmol), 4 (1.5 equiv.), K2CO3 (6.0 equiv.), dioxane/H2O (8:2), 100°C, 3 h, (c): 5 (1.0 mmol), TFA (1.0 mL), 0°C to RT, 6 h (d) 6 (1.0 mmol), 7 (1.5 equiv.), Et3N (2 equiv.), 0°C to RT, 6 h
Biological assay
Enzyme (MARK4) inhibition assay
MARKs, or microtubule-affinity regulating kinases, are a group of serine/threonine kinases found in mammals and other organisms (Naz et al., 2013). These kinases play a critical role in phosphorylating microtubule-associated proteins, which then go on to regulate important processes like cell cycle progression and cytoskeletal dynamics. These kinases are quite abundant in the human brain and are known to be key players in the development and progression of various diseases including cancer and ADs (Alam et al., 2023). Despite their high importance, there has been limited research on the development of synthetic small molecules (inhibitors) against MARK4 (Li et al., 2020; Voura et al., 2022). In the present study, we selected MARK4 as the target and assessed our compounds against it. The kinase inhibitory potential of the compounds against MARK4 was examined using an ATPase inhibition assay (Yousuf et al., 2015; Yousuf et al., 2022). Figure 3 displays the kinase activity profile of the inhibitors (8-14) against MARK4. We found that compounds with electron rich aryl substituents exhibited relatively higher activity. For example, compound (14), with naphthyl substituents, exhibited the best activity (IC50 = 7.52 ± 0.33 μM) followed by (9) (IC50 = 12.98 ± 0.63, Figure 3A) containing 2,4-dimethoxyphenyl substituent. However, the other five compounds displayed relatively lower activity with IC50 between 14.92 ± 0.53-37.99 ± 0.62 μM (activity order: 14 > 9 > 12 > 10 > 13 > 11 > 8). It is also notable that as the concentration of compound (14) increases, the activity of MARK4 decreases significantly (Figure 3B), underscoring their potential as MARK4 inhibitors. Following this, attempts have been made to collect the fluorescence quenching of MARK4 in the presence of the best inhibitor (14). However, to our surprise, it did not show appreciable quenching of the emission (data not included). The rationale behind the behaviour is currently under investigation.
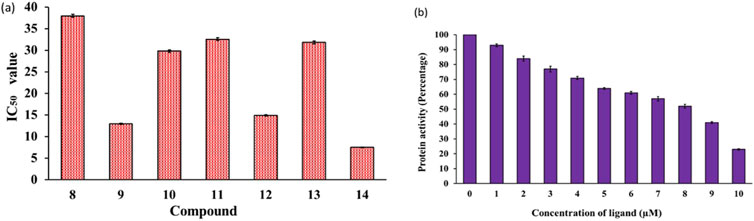
Figure 3. (A) Enzyme inhibition assay of compounds (8–14) and (B) variation of MARK4 activity with the ligand (14) concentration.
In-silico assay
Molecular modeling and validation
The analysis of the MARK4 crystal structure (PDB ID: 5ES1) indicated some missing regions (205-218) in the available structure. Therefore, using 5ES1 as a template and the web-based platform SWISS-Model server, missing residues were modeled (Figure 4A). The accuracy of the modeled structure was verified using a Ramachandran plot. The analysis revealed that 85.9% of the residues are located in the most favored regions, 12.6% in the additional allowed regions, 0.7% in the generously allowed regions, and only 0.7% in the disallowed regions (Figure 4B). The modeled structure showed that the structure is reliable for further studies.
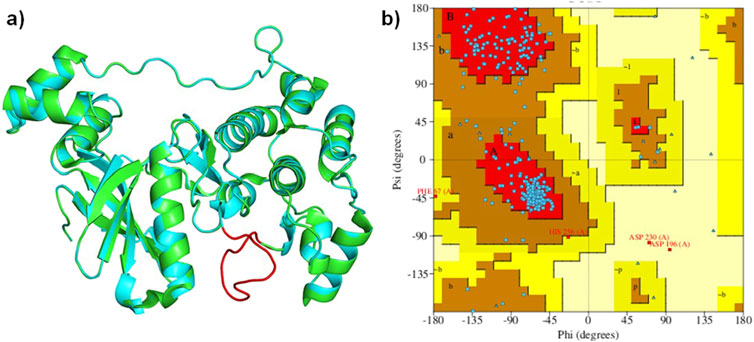
Figure 4. (A): Ribbon diagram displaying the superimposed MARK4 (PDB ID: 5ES1) alongside the modeled MARK4, and (B) the Ramachandran plot of the modeled structure.
Molecular docking
Molecular docking was carried out using AutoDock Vina program (v1.1.2) using compounds (8–14) as the ligands and MARK4 receptor (PDB: 5ES1) as the target. The findings of the study are shown in Figure 5 and Supplementary Figure SF8 (supporting information). The binding energy of the compounds (Table 1) varies slightly as compounds share high structural similarity. Among the studied series, compound (14) demonstrated the highest binding score (ΔG = −8.3 kcal/mol) and interacted through H-bonds with Tyr137 and Glu142 residues, as well as hydrophobic interactions. Compound (10) also showed similar value (ΔG = −8.3 kcal/mol), establishing H-bonds with Lys67 and Glu185 residues of MARK4. Compounds (11) and (12) had a slightly lower values (ΔG = −8.2 kcal/mol for both), despite interacting with different partners in H-bonding. Additionally, compounds (9) (ΔG = −8.0 kcal/mol), (8) (ΔG = −7.6 kcal/mol), and (13) (ΔG = −7.3 kcal/mol) displayed appreciable binding affinity and formed H-bonds with residues such as Ala138, Glu142, and Tyr137 (Supplementary Figure SF8).
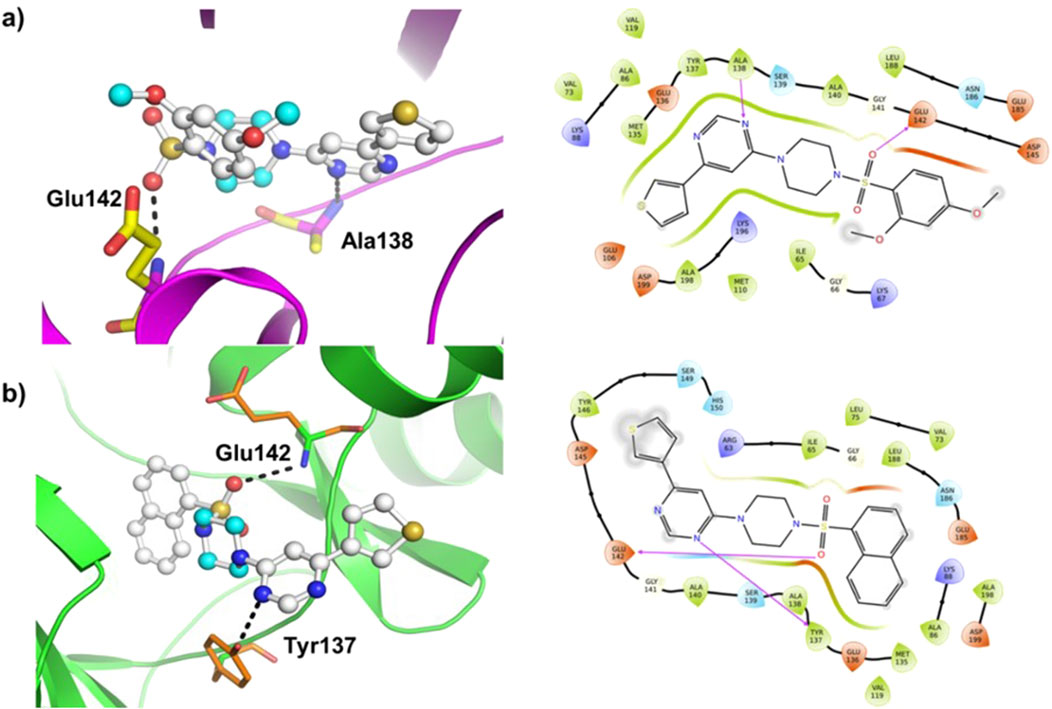
Figure 5. Molecular docking results of (A) ligand (9) and (B) ligand (14) with the MARK4 enzyme (PDB: 5ES1). The protein is depicted as a cartoon model, while the ligands are shown in a ball-and-stick representation.
MD simulation
Root mean square deviation (RMSD) and root mean fluctuation (RMSF) analysis
To assess the stability and dynamic characteristics of the MARK4 protein-ligand complexes, molecular dynamics (MD) simulation at 500 ns scale was carried out for the complexes containing compounds (9) and (14). The stability profiles were assessed through RMSD and RMSF analysis, comparing the native MARK4 structure and its complexes with the two ligands. The RMSD result provides insights into the overall conformational stability of the protein-ligand complex (Du et al., 2016; Ahamad et al., 2024), while the RMSF highlights the flexibility of individual residues throughout the simulation (Martínez, 2015), contributing to a thorough understanding of the dynamic behaviour of the complex. The RMSD plot indicated that the native MARK4 and its complex with compound (9) reached equilibrium within the first 25 ns of the simulation (Figure 6A). However, the same complex showed significant fluctuations between 25 and 75 ns, with an RMSD value peaking at 3.5 Å. The inspection of the trajectory indicated that it stabilized between 75 ns and 200 ns with minimal fluctuations. Beyond 200 ns, an increase in RMSD fluctuations was observed, indicating a less stable complex. In contrast, the MD trajectory of compound (14) with MARK4 exhibited a different pattern. Up to 125 ns, the RMSD of the (14)-MARK4 complex closely resembled that of the native MARK4 structure. After 125 ns, some deviations were noted, but the trajectory for compound (14) remained stable throughout the simulation time, showing fewer fluctuations and better stability than compound (9). The average RMSD values of the native MARK4 and (9)-MARK4 complex were approximately 2.64 Å and 2.91 Å, respectively. On the other hand, the (14)-MARK4 complex maintained a lower average RMSD of 2.21 Å, indicating greater structural stability. These findings suggest that compound (14) forms a more stable complex with the MARK4 receptor compared to compound (9), maintaining better equilibrium and fewer deviations throughout the simulation period. The lower average RMSD of the compound (14) underscores its potential to stabilize the MARK4 protein structure more effectively, thereby enhancing its role as a promising MARK4 inhibitor. The MD simulation results indicate that the average RMSD values for ligands (9) and (14) in complex with the MARK4 protein were 11.97 Å and 8.85 Å, respectively (Figure 6B). Notably, compound (14) demonstrated greater structural stability within the MARK4 binding pocket, as indicated by its lower RMSD compared to compound (9). This lower RMSD suggests that compound (14) maintains a more stable binding conformation over the course of the simulation, highlighting its potential as a MARK4 inhibitor.
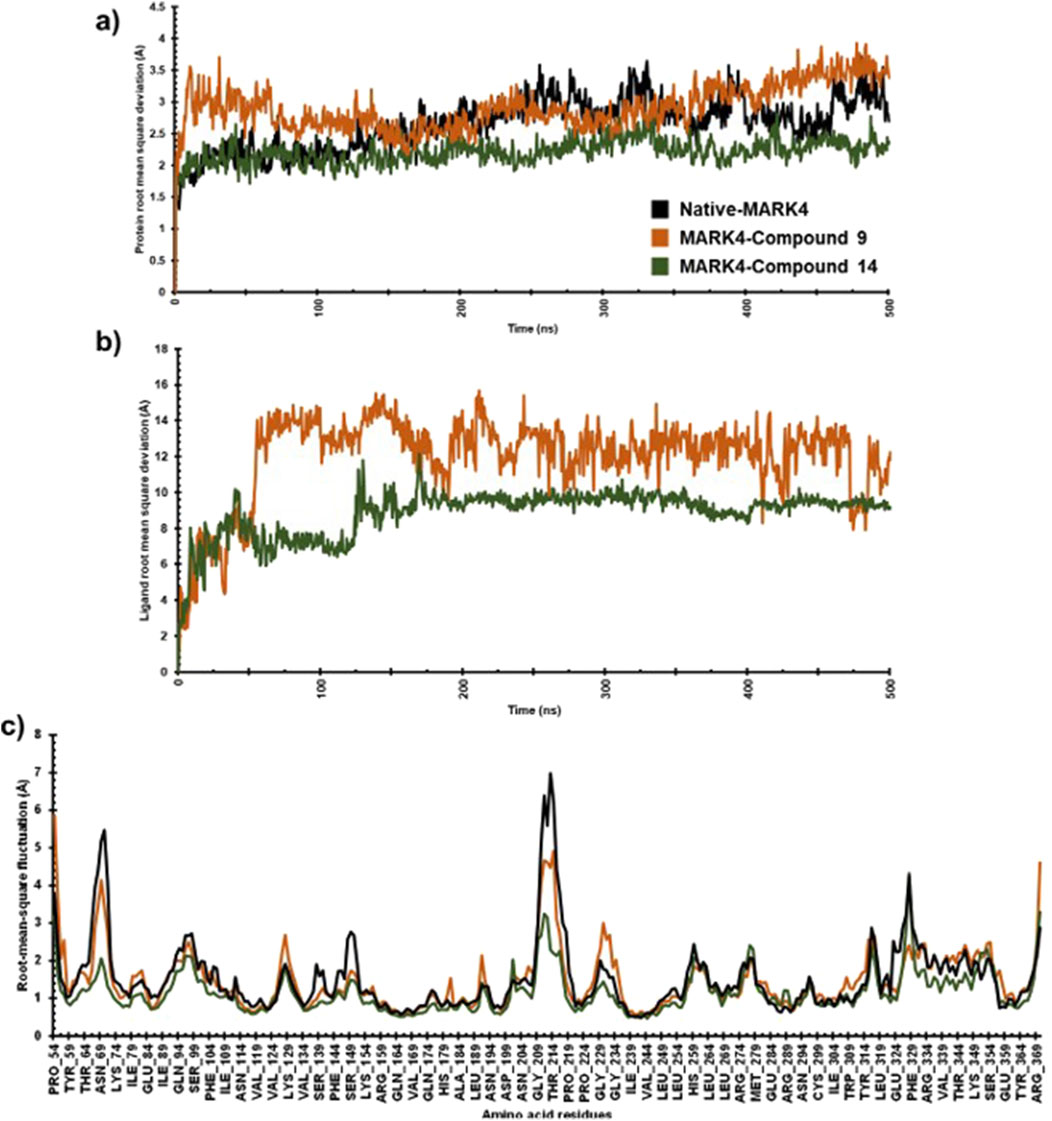
Figure 6. The protein RMSD (A), ligand RMSD (B), and RMSF (C) plots comparing the native MARK4 structure with its complexes with compounds (9) and (14).
For both the native MARK4 and the (9)-MARK4 complex, several regions (Thr64-Lys74, Asn204-Pro219, Pro224-Gly234, Glu324-Phe329, Tyr364-Arg369) showed fluctuations. These regions, particularly in loops and surface-exposed areas, exhibited notable flexibility, potentially indicating instability or conformational changes affecting the overall structural integrity of the protein. In contrast, the (14)-MARK4 complex demonstrated reduced fluctuations across these regions, suggesting that compound (14) effectively stabilized the protein structure. The lower RMSF values indicate that it restricts the flexibility of key residues, contributing to a more rigid and stable conformation of the MARK4 protein compared to the native structure and the complex with compound (9). The RMSF values were calculated for the native MARK4 protein, as well as for the MARK4 complexes with compounds (9) and (14). The RMSF values for the native MARK4, (9)-MARK4, and (14)-MARK4 complexes were approximately 1.46 Å, 1.52 Å, and 1.15 Å, respectively (Figure 6C). The higher RMSF value in the (9)-MARK4 complex indicates tighter binding at specific sites but with higher flexibility in other regions. On the other hand, the (14)-MARK4 complex demonstrates a balanced profile, providing stability across the protein structure. Consequently, the RMSF analysis strongly supports the finding that compound (14) offers greater stabilization to the MARK4 receptor, limiting the flexibility of key regions and maintaining a more consistent structural conformation throughout the simulation.
Secondary structure elements (SSE)
The SSE of the native MARK4, (9)-MARK4, and (14)-MARK4 complexes were evaluated to analyse the structural integrity and stability of the enzyme in the presence of ligands. The SSE was calculated as the percentage of helix and strand content, which are crucial indicators of stability (Swain et al., 2023). For the native MARK4 protein, the SSE values were calculated to be 45.08% SSE (31.97% helix and 13.11% strand) (Figure 7A). This reflects the inherent structural stability of the protein in its unbound state, with a balanced distribution between α-helical and β-strand regions. In the case of the (9)-MARK4 complex, the SSE values were slightly reduced (SSE = 43.18%) with 30.44% helix and 12.74% strand (Figure 7B). A decrease in helical and strand content suggests that compound (9) induces subtle conformational changes in the protein, leading to destabilisation, particularly in regions critical for maintaining the protein’s overall fold (Daggett, 2006). In contrast, the (14)-MARK4 complex exhibited improved structural stability with 45.64% SSE (31.51% helix and 14.13% strand) (Figure 7C). These values are higher than those observed for the 9-MARK4 complex and the native MARK4, indicating that compound (14) preserves and even enhances the SSEs of the MARK4 receptor. The increased strand content in the presence of compound (14) is a significant factor contributing to the overall stability of the protein-ligand complex. The analysis of SSE confirms that compound (14) stabilises the MARK4 protein more effectively compared to compound (9), maintaining a robust secondary structure throughout the MD simulation.
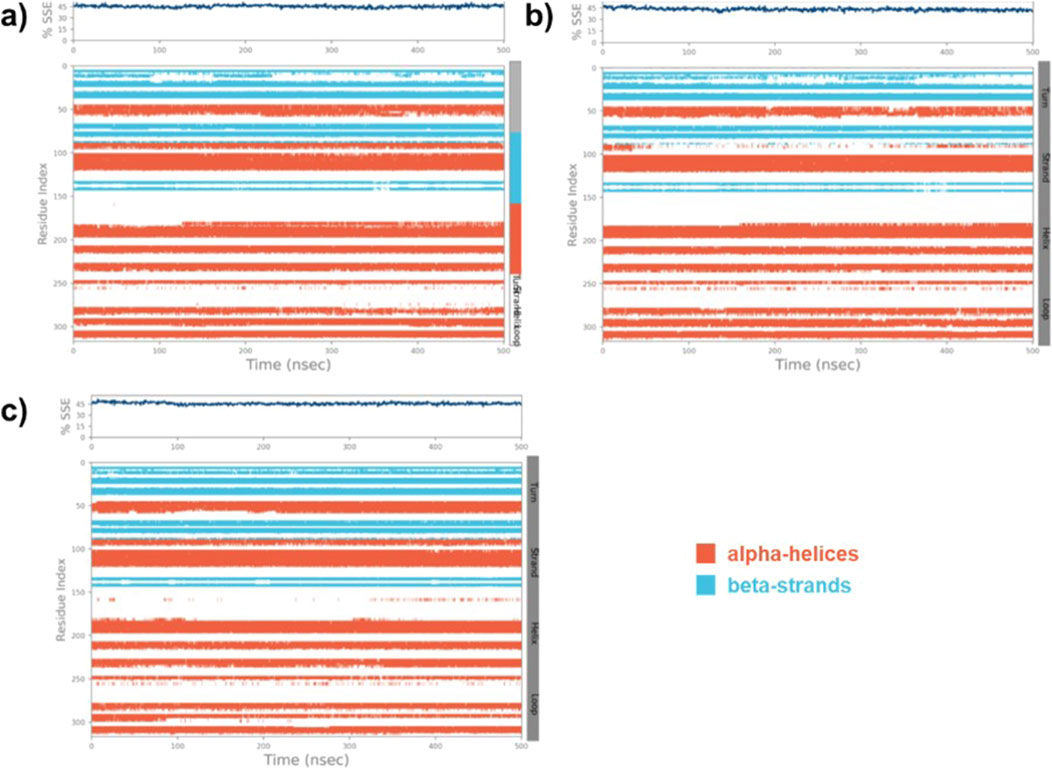
Figure 7. The SSE plot of the native MARK4 (A) and its complexes with compounds (9) and (14) (B, C), displays the distribution of SSE by residue index and their composition over time.
Protein-ligand interactions during simulations of (9)-MARK4 and (14)-MARK4 complexes were monitored. Key interactions, including H-bonds, hydrophobic interactions, ionic interactions, and water bridges, were the main contributors throughout the simulation period (Figure 8). Analysis of the ligand (9)-MARK4 complex during the simulation revealed stabilizing interactions, particularly with the following residues: Arg63, Ile65, Lys88, Thr137, Ala138, Ala140, Glu185, Asn186, and Asp199 (Figure 8A). (Kristiansen, 2004) These residues play an important role in maintaining binding within the active site pocket. Similarly, the MD simulation of the ligand (14)-MARK4 complex demonstrated H-bonding with residues Lys67, Lys88, Thr137, Glu142, Asp145, Lys211, and Asp213. This underscores their significance in anchoring the ligand within the active site.
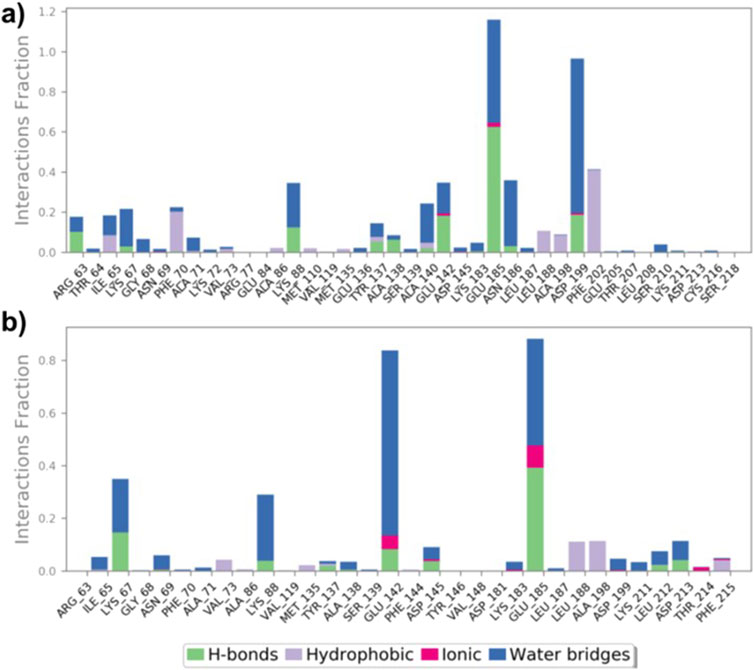
Figure 8. Interactions (hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic, ionic, and water bridges) between MARK4 and ligands (9) and (14) throughout the MD simulation (A, B).
Pharmacokinetic properties
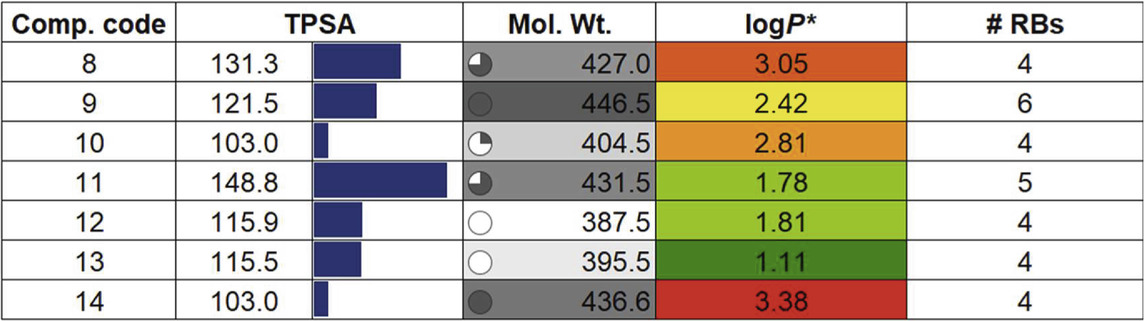
To assess whether a compound is suitable for pharmaceutical use, it is essential to evaluate several critical factors. These include the drug-likeness and examination of its absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) properties. Such evaluation helps determine the possible fate of the compound within the body, ensuring it can be safely and effectively utilized in medical treatments (Jia et al., 2020). Besides, it also aids researchers in guiding the design of new molecules with desired characteristics and establishing correlations with biological outcomes (Wager et al., 2016). Following the molecular docking and dynamics studies, we assessed the drug-likeness, bioavailability, and toxicity profiles of compounds (8–14). Table 2 presents some of the results obtained from SwissADME (Ritchie et al., 2011). It is quite clear that the compounds under investigation align well with Lipinski’s drug-likeness parameters (Lipinski et al., 2012), with all compounds exhibiting TPSA within the defined range of 20–130 Å (Daina and Zoete, 2016). The top three compounds, (14, TPSA = 103 Ǻ), (9, TPSA = 121.5 Ǻ), and (12, TPSA = 115.9 Ǻ), which displayed lower TPSA values, also exhibited low IC50 values. Conversely, compounds (11, TPSA = 148.8 Ǻ) and (8, TPSA = 131.3 Ǻ) with higher TPSA values showed higher IC50 values. We observed an inverse relationship between activity and the logP value, suggesting that the compounds may be interacting with the receptor through hydrophobic interactions.
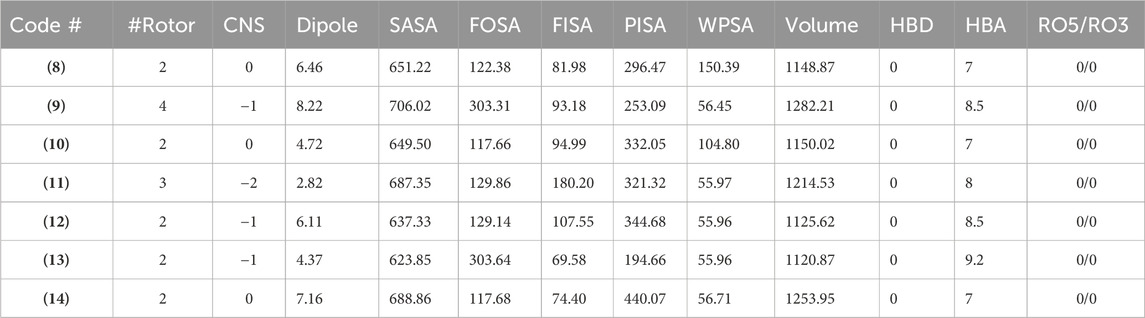
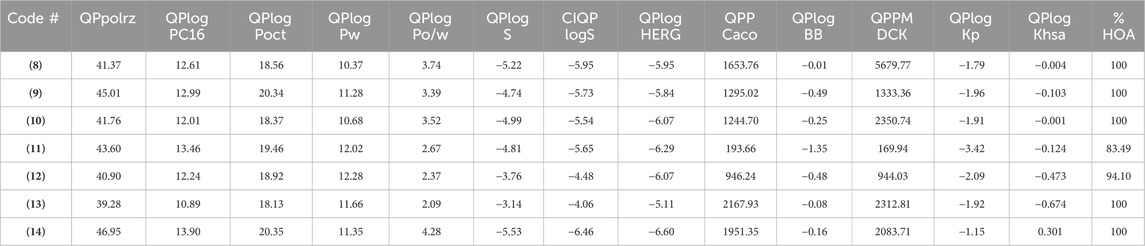
Additional drug-like properties of the compounds were studied using the QikProp (Schrödinger) tool (Shahbazi et al., 2017; Omoboyowa, 2022). This tool is valuable for calculating various drug-likeness parameters, especially for CNS drug development (Ghose et al., 2012). The results (Tables 3, 4) obtained aligned well with both experimental and computed values discussed earlier. For instance, the compounds exhibited 2-4 rotatable bonds (within the limit of 0–15) and dipole moments ranging from 2.82 to 8.22, falling within the specified range of 1–12.5. Additionally, none of the compounds deviated from Ro5/Ro3 parameters. Furthermore, the CNS activity predicted using this tool indicated that all compounds, with the exception of (11) (CNS = −2), displayed moderate activity towards the CNS (CNS = −1 to 0). This is a crucial consideration for drugs intended for CNS applications. This compound also has highest also exhibited the highest TPSA value and relatively lower human oral absorption (%HOA). The compounds screened showed similar values for total solvent-accessible surface area (SASA = 623.85-706.02) and related hydrophobic (FOSA = 117.66-303.64), hydrophilic (FISA = 69.58-180.20), π (PISA = 194.66-440.07), and weakly (55.96-150.39) surface area components (Haque et al., 2024a; Haque et al., 2024b). The octanol/water partition coefficient (QPlogPo/w) for the compounds evaluated fell within the generally accepted range of −2.0 to 6.5, with measured values spanning from 2.09 to 4.28. Additionally, the negative brain–blood partition coefficient (QPlogBB value) was acceptable for all the compounds except (11) (QPlogBB = −1.35), which was the lowest among all. Also, compound (11) showed the lowest Caco-2 permeability rate (good if > 500 nm s−1), indicating its weak drug-likeliness (Nunes et al., 2013). The results of the toxicity prediction studies (Supplementary Table ST1, supporting information) (Pires et al., 2015) reveal that compounds (8), (11), and (12)exhibited AMES toxicity, while compound (14), identified as the most active within the series, displayed the highest maximum tolerated dose (MTD = 0.308 log mg/kg/day). Additionally, none of the compounds were anticipated to act as inhibitors of hERG I/II inhibitor, except for compound (10), which demonstrated potential as an hERG II inhibitor. While the compounds are not expected to induce skin sensitization, there is a possibility of hepatotoxicity. It is essential to emphasize that the aforementioned predicted values are projected, and further research is necessary to obtain an accurate representation.
Density functional theory (DFT) study
Density functional theory (DFT) calculation is a routine but important technique used to understand structural, chemical, photo-physical, and many other underlying properties at atomic and molecular levels (Van Mourik et al., 2014). For example, chemical hardness, based on the HOMO-LUMO energy gap, reflects stability and resistance to charge transfer in molecules. These descriptors help understand molecular electronic properties and potential reactivity.
Considering this, we performed structural optimization followed by frontier orbital calculations for the compounds (8-14). All calculations were performed using B3LYP/6-31G* in the gas phase, and the results are depicted in Figure 9, Supplementary Figure SF9, and Supplementary Table ST2 (supporting information). The energy levels of the highest occupied molecular orbital (EHOMO) ranged from −5.99 to −6.43 eV, while the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (ELUMO) levels were observed between −1.08 and −3.17 eV. This resulted in a band gap (ΔE) between 3.26 and 5.00 eV, which is consistent with previously small molecules (Arshad et al., 2022; Guerraoui et al., 2023). Figure 9 shows that HOMO was localized over the 4-thienyl group with little contribution from the pyrimidine core. On the other hand, the 6-aryl group contributed to the LUMO only, and piperazine served as the conjugation break. This observation clearly explains why there were no major changes in the HOMO energy levels while LUMO level varied with change in aryl group. The introduction of a strong electron-withdrawing nitro group significantly deepens the LUMO (−3.17 eV) level with considerable change in the HOMO level (−6.43 eV), too, leading to the smallest energy gap (ΔE = 3.26 eV). It is also notable that the two most active compounds also had higher HOMO levels.
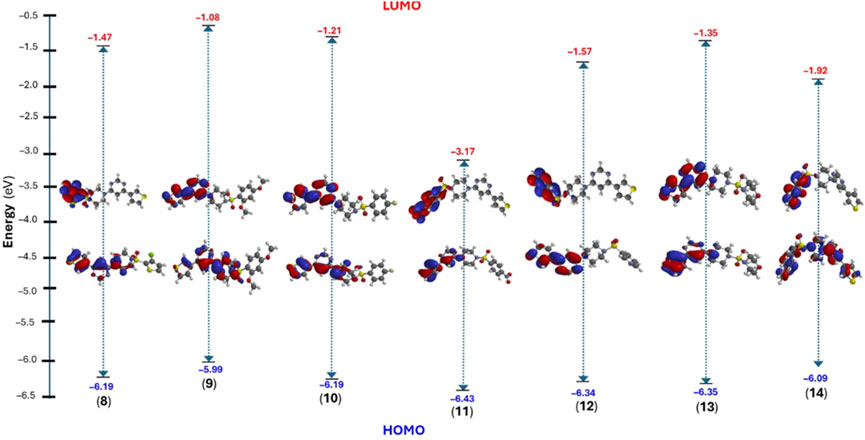
Figure 9. DFT calculated frontier molecular orbitals (HOMO/LUMO) energy level and their distribution in compounds (8–14).
Once the energy level of the molecules is in hand, we then proceed to compute chemical descriptors as they can be correlated with the biological activity of the molecule and underpins several properties of a molecule (Sánchez-Bojorge et al., 2009; Kawakami et al., 2013; Mushtaque et al., 2016; Frau and Glossman-Mitnik, 2017). For example, the HOMO energy level of a molecule impacts its electron-donating ability, with higher levels indicating greater ability. A smaller ΔE value corresponds to a lower energy requirement for electronic excitation, resulting in increased chemical reactivity and softer molecule (Mermer et al., 2020). According to the data obtained, the ionization energy (I) ranged between 5.99 and 6.43 eV while the electron affinity (A) of the compounds were in the range of 1.08–3.17 eV. Other descriptors, such as negative μ value (−2 to −4.80 eV) and reasonable ω (0.85–7.06 eV) indicate the stable nature of the molecule (Parr et al., 1999). Finally, the electrostatic potential (ESP) map showed the expected distribution of the electron-deficient and rich regions over carbocycles and heteroatoms, respectively.
Conclusion
The development of new drug candidates for application in chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and AD continues to be an exciting area of research. In this paper, we presented the chemical and biological properties of a series of 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidine-based small molecules. The synthesised compounds have been synthesized and fully characterised using NMR and MS spectrometry. Final compounds were then assessed in-vitro against the MARK4 enzyme, which has emerged as a potential target to combat neurodegenerative diseases. The biological findings were supported by computational studies, including molecular docking, MD simulation, and ADME/T analysis. We demonstrated that compounds are efficient against MARK4, and the binding of the most potent compound (14) stabilises the protein. The results of the MD simulation studies indicated that compound (14) showed reduced RMSD and RMSF value while enhancing the SSE, especially strands. This enhanced stability could play a crucial role in the efficacy of compound (14) as a potential inhibitor of MARK4, making it a promising candidate for further drug development. We also found that, to some extent, the activity of the compound is directly proportional to the TPSA while inversely proportional to the logP values.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing–review and editing. KA: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Writing–original draft. MRs: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Validation. MRh: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. SaA: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. ShA: Data curation, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. DG: Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors extend their appreciation to the King Salman Center for Disability Research for funding this work through Research Group no KSRG-2023-387.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the King Salman center For Disability Research for funding this work through Research Group no KSRG-2023-387.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1517504/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahamad, S., Junaid, I. T., and Gupta, D. (2024). Computational design of novel tau-tubulin kinase 1 inhibitors for neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmaceuticals 17, 952. doi:10.3390/ph17070952
Alam, M., Ahmed, S., Abid, M., Hasan, G. M., Islam, A., and Hassan, M. I. (2023). Therapeutic targeting of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Cell. Biochem. 124, 1223–1240. doi:10.1002/jcb.30468
Arshad, R., Khan, M. A., Mutahir, S., Hussain, S., Al-Hazmi, G. H., and Refat, M. S. (2022). DFT, molecular docking and ADME studies of thiazolidinones as tyrosinase inhibitors. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 43, 6750–6765. doi:10.1080/10406638.2022.2124286
Ayala-Aguilera, C. C., Valero, T., Lorente-Macias, A., Baillache, D. J., Croke, S., and Unciti-Broceta, A. (2021). Small molecule kinase inhibitor drugs (1995–2021): medical indication, pharmacology, and synthesis. J. Med. Chem. 65, 1047–1131. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00963
Bell, J. (2023). Alzheimer’s crisis in the GCC: urgent calls for action at Saudi summit. Al Arab. Engl.
Bowers, K. J., Chow, E., Xu, H., Dror, R. O., Eastwood, M. P., Gregersen, B. A., et al. (2006). “Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters,” in Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on supercomputing, 84–es.
Daina, A., Michielin, O., and Zoete, V. (2017). SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 7, 42717. doi:10.1038/srep42717
Daina, A., and Zoete, V. (2016). A boiled-egg to predict gastrointestinal absorption and brain penetration of small molecules. ChemMedChem 11, 1117–1121. doi:10.1002/cmdc.201600182
Das, S., Akbar, S., Ahmed, B., Dewangan, R. P., Iqubal, A., Pottoo, F. H., et al. (2022). Structural activity relationship based medicinal perspectives of pyrimidine derivatives as anti-Alzheimer’s agents: a comprehensive review. CNS and Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets Formerly Curr. Drug Targets-CNS and Neurological Disord. 21, 926–939. doi:10.2174/1871527320666210804161400
Delano, W. L. (2002). Pymol: an open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 40, 82–92.
Du, X., Li, Y., Xia, Y.-L., Ai, S.-M., Liang, J., Sang, P., et al. (2016). Insights into protein–ligand interactions: mechanisms, models, and methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 144. doi:10.3390/ijms17020144
Fatima, S., Zaki, A., Madhav, H., Khatoon, B. S., Rahman, A., Manhas, M. W., et al. (2023). Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of morpholinopyrimidine derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. RSC Adv. 13, 19119–19129. doi:10.1039/d3ra01893h
Frau, J., and Glossman-Mitnik, D. (2017). Chemical reactivity theory study of advanced glycation endproduct inhibitors. Molecules 22, 226. doi:10.3390/molecules22020226
Friesner, R. A., Murphy, R. B., Repasky, M. P., Frye, L. L., Greenwood, J. R., Halgren, T. A., et al. (2006). Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein− ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 49, 6177–6196. doi:10.1021/jm051256o
Ghose, A. K., Herbertz, T., Hudkins, R. L., Dorsey, B. D., and Mallamo, J. P. (2012). Knowledge-based, central nervous system (CNS) lead selection and lead optimization for CNS drug discovery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 3, 50–68. doi:10.1021/cn200100h
Gong, Z., Xie, Z., Qiu, J., and Wang, G. (2017). Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking study of 2-substituted-4, 6-diarylpyrimidines as α-glucosidase inhibitors. Molecules 22, 1865. doi:10.3390/molecules22111865
Guerraoui, A., Goudjil, M., Direm, A., Guerraoui, A., Şengün, İ. Y., Parlak, C., et al. (2023). A rhodanine derivative as a potential antibacterial and anticancer agent: crystal structure, spectral characterization, DFT calculations, Hirshfeld surface analysis, in silico molecular docking and ADMET studies. J. Mol. Struct. 1280, 135025. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.135025
Gustavsson, A., Norton, N., Fast, T., Frölich, L., Georges, J., Holzapfel, D., et al. (2023). Global estimates on the number of persons across the Alzheimer's disease continuum. Alzheimer's and Dementia 19, 658–670. doi:10.1002/alz.12694
Haque, A., Alenezi, K. M., and Rasheed, M. S. M. A. (2024a). Identification of imidazole-based small molecules to combat cognitive disability caused by Alzheimer’s disease: a molecular docking and MD simulations based approach. Comput. Biol. Chem. 112, 108152. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2024.108152
Haque, A., Alenezi, K. M., and Rasheed, M. S. M. A. (2024b). Structural and molecular features of acetylcholinesterase targeting small molecules: leveraging in-silico tools to combat Alzheimer's disease. New J. Chem. 48, 16387–16396. doi:10.1039/d4nj02065k
Hartz, R. A., Ahuja, V. T., Luo, G., Chen, L., Sivaprakasam, P., Xiao, H., et al. (2023). Discovery of 2-(anilino) pyrimidine-4-carboxamides as highly potent, selective, and orally active glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 66, 7534–7552. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00364
Hehre, W. J., and Huang, W. W. (1995). Chemistry with computation: an introduction to SPARTAN. Incorporated: Wavefunction.
Huey, R., Morris, G. M., and Forli, S. (2012). Using AutoDock 4 and AutoDock vina with AutoDockTools: a tutorial. Scripps Res. Inst. Mol. Graph. Laboratory 10550, 1000.
Jameel, E., Naz, H., Khan, P., Tarique, M., Kumar, J., Mumtazuddin, S., et al. (2017). Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of pyrimidine derivatives as potential inhibitors of human calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV. Chem. Biol. and drug Des. 89, 741–754. doi:10.1111/cbdd.12898
Jia, C.-Y., Li, J.-Y., Hao, G.-F., and Yang, G.-F. (2020). A drug-likeness toolbox facilitates ADMET study in drug discovery. Drug Discov. today 25, 248–258. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2019.10.014
Katritzky, A. R., Ramsden, C. A., Joule, J. A., and Zhdankin, V. V. (2010). Handbook of heterocyclic chemistry. Elsevier.
Kawakami, J., Kakinami, H., Matsushima, N., Nakane, A., Kitahara, H., Nagaki, M., et al. (2013). Structure–activity relationship analysis for Antimicrobial activities of Tryptanthrin derivatives using quantum chemical calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 12, 109–112. doi:10.2477/jccj.2012-0026
Kilbile, J. T., Tamboli, Y., Gadekar, S. S., Islam, I., Supuran, C. T., and Sapkal, S. B. (2023). An insight into the biological activity and structure-based drug design attributes of sulfonylpiperazine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 1278, 134971. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.134971
Kristiansen, K. (2004). Molecular mechanisms of ligand binding, signaling, and regulation within the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors: molecular modeling and mutagenesis approaches to receptor structure and function. Pharmacol. and Ther. 103, 21–80. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.05.002
Li, F., Liu, Z., Sun, H., Li, C., Wang, W., Ye, L., et al. (2020). PCC0208017, a novel small-molecule inhibitor of MARK3/MARK4, suppresses glioma progression in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 10, 289–300. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2019.09.004
Lipinski, C. A., Lombardo, F., Dominy, B. W., and Feeney, P. J. (2012). Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 4–17. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.019
Lippert, R. A., Predescu, C., Ierardi, D. J., Mackenzie, K. M., Eastwood, M. P., Dror, R. O., et al. (2013). Accurate and efficient integration for molecular dynamics simulations at constant temperature and pressure. J. Chem. Phys. 139, 164106. doi:10.1063/1.4825247
Luo, G., Chen, L., Burton, C. R., Xiao, H., Sivaprakasam, P., Krause, C. M., et al. (2016). Discovery of isonicotinamides as highly selective, brain penetrable, and orally active glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 59, 1041–1051. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01550
Manzoor, S., Almarghalani, D. A., James, A. W., Raza, M. K., Kausar, T., Nayeem, S. M., et al. (2023). Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel triazole-pyrimidine hybrids as potential neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory agents. Pharm. Res. 40, 167–185. doi:10.1007/s11095-022-03429-1
Manzoor, S., Petreni, A., Raza, M. K., Supuran, C. T., and Hoda, N. (2021a). Novel triazole-sulfonamide bearing pyrimidine moieties with carbonic anhydrase inhibitory action: design, synthesis, computational and enzyme inhibition studies. Bioorg. and Med. Chem. Lett. 48, 128249. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128249
Manzoor, S., Prajapati, S. K., Majumdar, S., Raza, M. K., Gabr, M. T., Kumar, S., et al. (2021b). Discovery of new phenyl sulfonyl-pyrimidine carboxylate derivatives as the potential multi-target drugs with effective anti-Alzheimer’s action: design, synthesis, crystal structure and in-vitro biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 215, 113224. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113224
Martínez, L. (2015). Automatic identification of mobile and rigid substructures in molecular dynamics simulations and fractional structural fluctuation analysis. PloS one 10, e0119264. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119264
Mermer, A., Bayrak, H., Alyar, S., and Alagumuthu, M. (2020). Synthesis, DFT calculations, biological investigation, molecular docking studies of β-lactam derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 1208, 127891. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.127891
Mushtaque, M., Ahamad, S., Jahan, M., Hussain, K., and Khan, M. S. (2016). Azole-based compounds as antiamoebic agents: a perspective using theoretical calculations. RSC Adv. 6, 815–824. doi:10.1039/c5ra20552b
Nadar, S., and Khan, T. (2022). Pyrimidine: an elite heterocyclic leitmotif in drug discovery-synthesis and biological activity. Chem. Biol. and Drug Des. 100, 818–842. doi:10.1111/cbdd.14001
Nammalwar, B., and Bunce, R. A. (2024). Recent advances in pyrimidine-based drugs. Pharmaceuticals 17, 104. doi:10.3390/ph17010104
Naz, F., Anjum, F., Islam, A., Ahmad, F., and Hassan, M. I. (2013). Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4: structure, function, and regulation. Cell Biochem. biophysics 67, 485–499. doi:10.1007/s12013-013-9550-7
Naz, H., Jameel, E., Hoda, N., Shandilya, A., Khan, P., Islam, A., et al. (2016). Structure guided design of potential inhibitors of human calcium–calmodulin dependent protein kinase IV containing pyrimidine scaffold. Bioorg. and Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 782–788. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.12.098
Nichols, E., Steinmetz, J. D., Vollset, S. E., Fukutaki, K., Chalek, J., Abd-Allah, F., et al. (2022). Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 7, e105–e125. doi:10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00249-8
Nunes, A., Marques, S. M., Quintanova, C., Silva, D. F., Cardoso, S. M., Chaves, S., et al. (2013). Multifunctional iron-chelators with protective roles against neurodegenerative diseases. Dalton Trans. 42, 6058–6073. doi:10.1039/c3dt50406a
Omoboyowa, D. A. (2022). Exploring molecular docking with E-pharmacophore and QSAR models to predict potent inhibitors of 14-α-demethylase protease from Moringa spp. Pharmacol. Research-Modern Chin. Med. 4, 100147. doi:10.1016/j.prmcm.2022.100147
Pant, S., Kumar K, R., Rana, P., Anthwal, T., Ali, S. M., Gupta, M., et al. (2024). Novel substituted pyrimidine derivatives as potential anti-alzheimer’s agents: synthesis, biological, and molecular docking studies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 15, 783–797. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00662
Parr, R. G., Szentpály, L. V., and Liu, S. (1999). Electrophilicity index. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 1922–1924. doi:10.1021/ja983494x
Pires, D. E., Blundell, T. L., and Ascher, D. B. (2015). pkCSM: predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J. Med. Chem. 58, 4066–4072. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00104
Rahman, A., Anjum, S., Bhatt, J. D., Dixit, B. C., Singh, A., Fatima, S., et al. (2024). Sulfonamide based pyrimidine derivatives combating Plasmodium parasite by inhibiting falcipains-2 and falcipains-3 as antimalarial agents. RSC Adv. 14, 24725–24740. doi:10.1039/d4ra04370g
Release, S. (2017). 3: Desmond molecular dynamics system, DE Shaw research, New York, NY, 2017. New York, NY: Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools, Schrödinger.
Reymond, J.-L. (2015). The chemical space project. Accounts Chem. Res. 48, 722–730. doi:10.1021/ar500432k
Ritchie, T. J., Ertl, P., and Lewis, R. (2011). The graphical representation of ADME-related molecule properties for medicinal chemists. Drug Discov. Today 16, 65–72. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2010.11.002
Sack, J. S., Gao, M., Kiefer, S. E., Myers, J. E., Newitt, J. A., Wu, S., et al. (2016). Crystal structure of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 catalytic domain in complex with a pyrazolopyrimidine inhibitor. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F. Struct. Biol. Commun. 72, 129–134. doi:10.1107/S2053230X15024747
Sánchez-Bojorge, N.-A., Flores-Holguín, N., Glossman-Mitnik, D., and Rodríguez-Valdez, L. M. (2009). Computational note on the chemical reactivity of pyrrole derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 912, 119–120. doi:10.1016/j.theochem.2009.07.037
Schwede, T., Kopp, J., Guex, N., and Peitsch, M. C. (2003). SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic acids Res. 31, 3381–3385. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg520
Shahbazi, S., Kaur, J., Kuanar, A., Kar, D., Singh, S., and Sobti, R. C. (2017). Risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease by plasma cholesterol: rational in silico drug investigation of pyrrole-based HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 15, 342–351. doi:10.1089/adt.2017.804
Shivakumar, D., Williams, J., Wu, Y., Damm, W., Shelley, J., and Sherman, W. (2010). Prediction of absolute solvation free energies using molecular dynamics free energy perturbation and the OPLS force field. J. Chem. theory Comput. 6, 1509–1519. doi:10.1021/ct900587b
Singh, A., Beg, M. A., Jamal, S., Khan, A., Rahman, A., Selvapandiyan, A., et al. (2024). Robust leishmanicidal upshot of some new diphenyl triazine-based molecules. RSC Adv. 14, 22587–22597. doi:10.1039/d4ra01904k
Singh, S., Dhanawat, M., Gupta, S., Kumar, D., Kakkar, S., Nair, A., et al. (2021). Naturally inspired pyrimidines analogues for alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 19, 136–151. doi:10.2174/1570159X18666201111110136
Swain, S. P., Ahamad, S., Samarth, N., Singh, S., Gupta, D., and Kumar, S. (2023). In silico studies of alkaloids and their derivatives against N-acetyltransferase EIS protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 42, 10950–10964. doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2259487
Takahashi, R. H., Nagao, T., and Gouras, G. K. (2017). Plaque formation and the intraneuronal accumulation of β-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Pathol. Int. 67, 185–193. doi:10.1111/pin.12520
Thakur, S., Kumar, D., Goel, K. K., Rawat, P., Srivastava, V., Dhiman, S., et al. (2024). Medicinal chemistry-based perspective on thiophene and its derivatives: exploring the structural insights to discover plausible druggable leads. RSC Med. Chem. doi:10.1039/D4MD00450G
Van Mourik, T., Bühl, M., and Gaigeot, M.-P. (2014). Density functional theory across chemistry, physics and biology. Philosophical Trans. R. Soc. A-Mathematical Phys. Eng. Sci. 372, 20120488. doi:10.1098/rsta.2012.0488
Voura, M., Anwar, S., Thysiadis, S., Κhan, P., Dalezis, P., Trafalis, D. T., et al. (2022). Synthesis and biological activity of bisindole derivatives as novel MARK4 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 6, 100076. doi:10.1016/j.ejmcr.2022.100076
Wager, T. T., Hou, X., Verhoest, P. R., and Villalobos, A. (2016). Central nervous system multiparameter optimization desirability: application in drug discovery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 7, 767–775. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00029
Yousuf, I., Arjmand, F., Tabassum, S., Toupet, L., Khan, R. A., and Siddiqui, M. A. (2015). Mechanistic insights into a novel chromone-appended Cu(II) anticancer drug entity: in vitro binding profile with DNA/RNA substrates and cytotoxic activity against MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cells. Dalton Trans. 44, 10330–10342. doi:10.1039/c5dt00770d
Yousuf, M., Shamsi, A., Mohammad, T., Azum, N., Alfaifi, S. Y., Asiri, A. M., et al. (2022). Inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinase 6 by taurine: implications in anticancer therapeutics. ACS omega 7, 25844–25852. doi:10.1021/acsomega.2c03479
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, kinase inhibitors, mark 4, pyrimidine, synthesis
Citation: Haque A, Alenezi KM, Rasheed MSMA, Rahman MA, Anwar S, Ahamad S and Gupta D (2025) 4,6-Disubstituted pyrimidine-based microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 (MARK4) inhibitors: synthesis, characterization, in-vitro activity and in-silico studies. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1517504. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1517504
Received: 29 October 2024; Accepted: 17 December 2024;
Published: 20 January 2025.
Edited by:
Vinícius Gonçalves Maltarollo, Federal University of Minas Gerais, BrazilReviewed by:
Saulo Fehelberg Pinto Braga, Federal University of Ouro Preto, BrazilStefânia Neiva Lavorato, Federal University of Western Bahia, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Haque, Alenezi, Rasheed, Rahman, Anwar, Ahamad and Gupta. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ashanul Haque, YS5oYXF1ZUB1b2guZWR1LnNh, aGFxdWVfY2hlbUB5YWhvby5jb20=
 Ashanul Haque
Ashanul Haque Khalaf M. Alenezi1
Khalaf M. Alenezi1 Mohd. Saeed Maulana Abdul Rasheed
Mohd. Saeed Maulana Abdul Rasheed Saleha Anwar
Saleha Anwar Shahzaib Ahamad
Shahzaib Ahamad Dinesh Gupta
Dinesh Gupta