- 1Department of Thoracic Surgery, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
- 3Sichuan Province Revolutionary Disable Armyman Rehab, The First Veterans Hospital Of Sichuan Province, Chengdu, China
- 4School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China
- 5Department of Outpatient, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
Lung cancer has posed a significant challenge to global health, and related study has been a hot topic in oncology. This article focuses on metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells, a process to adapt to energy demands and biosynthetic needs, supporting the proliferation and development of tumor cells. In this study, the latest studies on lung cancer tumor metabolism were reviewed, including the impact of metabolic products and metabolic enzymes on the occurrence and development of lung cancer, as well as the progress in the field of lung cancer treatment targeting relevant metabolic pathways. This provides some promising potential directions into exploring lung cancer tumor metabolism and helps researchers to better understand lung cancer.
1 Introduction
In 2012, 14.1 million new cases of malignant tumors were diagnosed globally and 8.2 million people died from malignant tumors. The most commonly diagnosed types of cancer inlude lung (1.82 million cases), cancer (1.67 million cases), and colorectal (1.36 million cases); cancer (1.6 million deaths), cancer (745,000 deaths), and cancer (723,000 deaths from) were the leading causes of cancer-related deaths (Ferlay et al., 2015). Lung cancer poses a significant challenge to global health. Approximately 2.1 million people are diagnosed with lung cancer each year, and about 1.8 million people lose their lives as a result (Fr et al., 2017; Bray et al., 2018; Muscat et al., 1997). The global incidence of cancer continues to rise, despite a decline in the incidence of cancer in men in some Western countries. The diagnosis of lung cancer relies on histological examination, immunohistochemistry, and molecular analysis. Among all lung cancer cases, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for about 85%, while small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accounts for about 15%. The 5-year survival rate for cancer patients usually ranges from 15%–20%. The 5-year survival rate for patients with non-small cell lung cancer can reach 90% in stage 1A, but drops to less than 10% by stage 4. For patients with small cell lung cancer, the 5-year survival rate for limited-stage small cell lung cancer is about 30%, while the 5-year survival rate for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer is less than 10%. Treating lung cancer requires a multidisciplinary team effort, including surgery, radiation therapy, systemic therapies (e.g., chemotherapy, targeted therapies, immune checkpoint inhibitors), and supportive care including palliative care (Zappa and Mousa, 2016). Developing a treatment plan requires consideration of tumor characteristics, staging, and patient-specific circumstances. Although the rapid development of targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors has brought new hope for the treatment of lung cancer, lung cancer remains a clinical challenge that is difficult to cure completely. Therefore, the development of new treatment strategies is a key focus of current lung cancer research.
Cellular metabolism is essential for maintaining homeostatic redox balance and providing the necessary energy and substrates to support physiological functions in the human body. In the context of oncogenesis and tumor progression, cellular metabolism undergoes significant alterations to fulfill the bioenergetic and biosynthetic requirements of the unchecked proliferation of malignant cells (Ward and Thompson, 2012; Mg et al., 2009; Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011). A notable example of this phenomenon is the upregulation of glycolysis under aerobic conditions, known as the Warburg effect, which is observed in many cancer cells. Although the manifestation of tissue heterogeneity varies among different cancer types, a subset of common metabolic modifications is consistently observed, characterizing a fundamental aspect of cancer cell biology. This metabolic reprogramming is now recognized as one of the hallmarks of cancer (Hanahan, 2022; Pavlova et al., 2022; Kroemer and Pouyssegur, 2008). Here, our comprehension of the intricate mechanisms underlying tumor metabolic reprogramming remains incomplete. Therefore, there is a pivotal need to delineate the molecular underpinnings of these metabolic shifts since it is indispensable for developing novel therapeutic strategies targeting cancer cell metabolism.
In this work, advanced researches related to tumor metabolism in lung cancer were summarized, in which we briefly outlined the impact of metabolic products and enzymes on the occurrence and development of lung cancer, the predictive value of related metabolic products and enzymes for lung cancer prognosis, and the progress of targeting related metabolic pathways in the field of lung cancer treatment. This study provides some promising potential directions related to tumor metabolism in lung cancer research, helping researchers to better understand lung cancer.
2 Metabolic reprogramming in tumor
Tumor cells differ from normal tissue cells in their metabolic processes for energy and biomolecules during growth and proliferation, and this field has become a new hot topic in oncology research. Research on tumor metabolism can be traced back to the 1920s when German biochemist Otto Warburg first described that tumor cells tend to produce energy through glycolysis, even in the presence of sufficient oxygen, a phenomenon later known as the “Warburg effect” (Koppenol et al., 2011; Icard et al., 2018; Vaupel and Multhoff, 2021) (Figure 1). Tumor metabolic reprogramming refers to the process by which cancer cells regulate their own metabolic processes in various ways to meet the energy demands of rapid proliferation. This mode of metabolism is different from that of normal cells, which rely more on the process of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria for energy production. Over time, researchers have found that tumor metabolism involves the changes in energy production and the metabolic reprogramming of glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides, which support the rapid proliferation and survival of tumor cells. Tumor cells alter metabolic pathways to meet their needs for biosynthetic precursors, such as increasing the expression of certain metabolic enzymes, changing the regulation of metabolic pathways, and interacting with other cells in the tumor microenvironment.
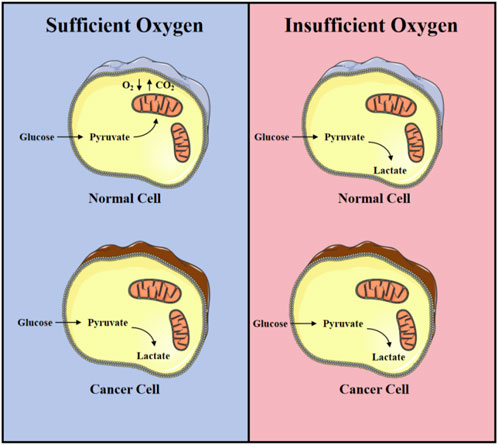
Figure 1. Warburg effect: Differences in energy metabolism between normal nuclear lung cancer cells under aerobic and hypoxic conditions.
Research on tumor metabolism not only helps us to better understand tumor biology but also provides new strategies for tumor diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. For example, by targeting tumor-specific metabolic pathways, new anticancer drugs can be developed that selectively inhibit the metabolic activity of tumor cells with minimal impact on normal cells. In addition, changes in tumor metabolic products can serve as the biomarkers for early detection of tumors and monitoring treatment effects.
3 Glucose metabolism in lung cancer
Glucose metabolism is fundamental to cellular function and is crucial for maintaining cell proliferation and determining cell fate (Zhu and Thompson, 2019). It not only provides the energy required by cells but also supplies the necessary carbon skeletons for cellular biosynthetic processes. Glucose, as the primary source of energy, is converted into pyruvate through the glycolytic process within the cell, and then under aerobic conditions, it enters the mitochondria for oxidative phosphorylation, producing approximately 30–32 molecules of ATP per glucose. In addition, glucose also provides the carbon precursors needed for synthesizing nucleic acids, fatty acids, and phospholipids in cell membranes through the pentose phosphate pathway and the serine synthesis pathway (Arren et al., 2012; Mulukutla et al., 2016; Mergenthaler et al., 2013). Even when oxygen is abundant, tumor cells tend to produce energy through the glycolytic process, which can rapidly produce a large amount of intermediates required for biosynthesis, with an appropriate ATP/ADP ratio. Hence the proliferation and malignant progression of tumor cells are more dependent on sugar metabolism (Walker-Samuel et al., 2013; Boroughs and DeBerardinis, 2015; Qin et al., 2020).
The metabolic diversity of tumor cells is perfectly demonstrated in lung cancer (Han et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2019) (Figure 2). In non-small cell lung cancer, Transforming Growth Factor (TGF-β) has a dual function in regulating glycolysis: under normal oxygen levels, TGF-β can inhibit glycolysis, but under hypoxic conditions, both in vitro and in vivo, TGF-β significantly promotes tumor cell glycolysis. This transition is due to the binding of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF-1α) to the MH2 domain of phosphorylated Smad3, leading to changes in Smad partners under hypoxic conditions (Huang et al., 2021).
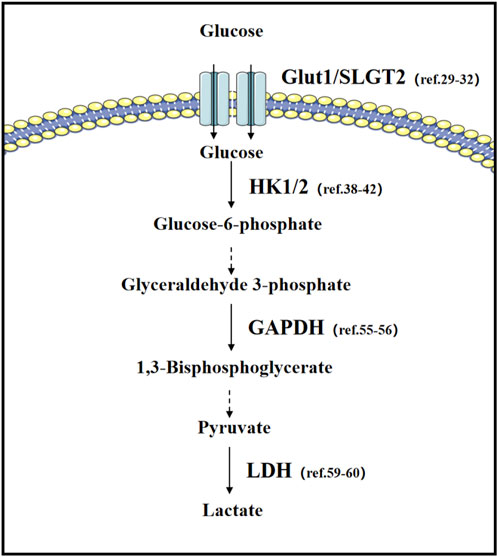
Figure 2. Glucose metabolism in lung cancer: important transporters and rate-limiting enzymes in glucose metabolism, as well as relevant literature in lung cancer research.
3.1 Glucose transporters
Glucose transporters (GLUTs) are a group of proteins located on the cell membrane that are responsible for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into the cell. Glucose is the primary energy source for cells and is essential for sustaining life activities. Dysfunction of glucose transporters is associated with a variety of diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. The role of GLUTs in cancer is extremely important as they are responsible for transporting glucose from the blood into cells, providing the necessary energy for the rapid proliferation of cancer cells. In many types of cancer, such as lung, liver, stomach, breast, ovarian, and colorectal cancers, the expression levels of GLUT1 are increased (Yadav et al., 2024; Zambrano et al., 2019; Macheda et al., 2005). This increased expression allows cancer cells to take up a large amount of glucose to maintain their growth and development; therefore, GLUT1 can serve as a marker for detecting cancerous changes and is used in clinical examinations (Barron et al., 2016). Studies have shown that in non-small cell lung cancer, anti-Glut1 antibodies can inhibit proliferation and also enhance the anti-proliferative effects of cisplatin, paclitaxel, and gefitinib (Rastogi et al., 2007). Certain types of lung cancer become refractory due to specific genetic changes, such as KEAP1-mutated lung cancer, which is resistant to most current treatment methods. However, research has found that the lack of KEAP1 promotes the dependency of lung cancer cells on glucose, and KEAP1-mutated/deficient lung cancer cells are more sensitive to glucose deprivation than their wild-type counterparts. Therefore, targeting metabolism may be a better solution for specific types of refractory lung cancer (Koppula et al., 2021a; Saggese et al., 2024). Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 (SGLT2) is another type of glucose transport protein that primarily functions in the kidneys. For example, SGLT2 inhibitors can improve the overall survival rate of non-small cell lung cancer patients with pre-existing diabetes (Luo et al., 2023).
3.2 Glycolysis-related enzymes
Hexokinase (HK) is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, the initial step of glycolysis and the rate-limiting step of the pathway. There are four hexokinase isoforms in the human body: HKI, HKII, HKIII, and HKIV. Among these isoforms, HKII has garnered significant attention due to its abnormally elevated expression levels in a variety of cancers, which is closely associated with the metabolic reprogramming and progression of tumors (Roberts and Miyamoto, 2015; Li R. et al., 2022; DeWaal et al., 2018; Ciscato et al., 2021; Lee et al., 2019). Specifically, the overexpression of HKII has been linked to the glycolysis-dependent metastasis of lung cancer cells (Wiel et al., 2019). Also, it is reported that HKII regulates proliferation of lung cancer cells and predicts poor prognosis in lung cancer patients (Duan et al., 2019; Yu et al., 2024; Yang L. et al., 2021). Those finding provides a theoretical basis for therapeutic strategies targeting HKII. Moreover, studies have identified selective inhibitors of HKII, which have shown significant effects in vivo, substantially suppressing the glycolytic process and cancer cell proliferation in lung cancer cells, with high inhibitory potency and low toxicity. Therefore, these HKII inhibitors are considered promising candidate drugs for future lung cancer therapy and are worth further development and research (Zhang et al., 2021).
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) is a class of enzymes widely present in various human tissues, playing a crucial role in the glycolysis process, particularly under anaerobic conditions, by catalyzing the conversion of pyruvate to lactate (Sharma et al., 2022). The role of LDH is especially significant in the occurrence and development of cancer. Cancer cells tend to produce energy through the glycolytic process, and LDH converts pyruvate to lactate in this process, promoting the proliferation and survival of cancer cells (Claps et al., 2022; Certo et al., 2021; Doherty and Cleveland, 2013). The expression patterns and roles of the two subunits, LDHA and LDHB, in tumors are not entirely the same. LDHA is overexpressed in many malignant tumors and is associated with tumor growth, maintenance, and invasion. The role of LDH in the tumor microenvironment is not limited to energy metabolism; the lactate it produces can promote, invasion (Dong et al., 2017; Brand et al., 2016), and metastasis (Dong et al., 2017), and may also affect immune responses (Brand et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2021). In addition, the expression level of LDH is closely related to the prognosis of cancer patients, with high levels of LDH usually being associated with poor prognosis (Zhang et al., 2016; Gu and Yang, 2023; Chen L. et al., 2024). Studies have found that 90% of patients diagnosed with non-small-cell lung cancer express LDH, which is not present in non-cancerous tissues. Analysis shows that LDH is also crucial for predicting lung cancer prognosis (Mezquita et al., 2018; Mathur et al., 2023); high levels of LDH in the serum of NSCLC and small-cell lung cancer patients before treatment are associated with lower survival rates, and LDH levels in NSCLC patients’ serum are negatively correlated with progression-free survival. Thus, high LDH expression in lung cancer is linked to poor prognosis and may be related to poor responses to standard chemotherapy (Zhang et al., 2016).
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) catalyzes the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, a key step in the metabolic pathway that generates energy for cells (Colell et al., 2009). GAPDH is commonly overexpressed in various cancers, indicates a poor prognosis, and is linked to immune cell infiltration and the expression of immune checkpoint genes (Wang J. et al., 2023). Studies have shown that GAPDH plays a crucial regulatory role in linking energy metabolism with the cell cycle network. Inducing senescence in LKB1-deficient non-small cell lung cancer cells through GAPDH depletion suggests a novel strategy for controlling the proliferation of tumor cells (Phadke et al., 2011). Furthermore, in the study of lung adenocarcinoma, bioinformatics analysis has revealed GAPDH as a prognostic marker associated with ferroptosis, whose expression level correlates with the tumor’s immune microenvironment. Combining immunotherapy with strategies targeting GAPDH to induce ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma may offer a novel therapeutic approach (Ouyang et al., 2023).
4 Lipid metabolism in lung cancer
Fatty acid metabolism plays a crucial role in the occurrence and development of cancer. Cancer cells tend to meet their increased demand for energy and biosynthetic precursors by enhancing fatty acid synthesis and oxidation. Key enzymes in fatty acid synthesis, such as Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN), Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC), and ATP Citrate Lyase (ACLY), are upregulated in various cancers and are closely associated with tumor progression (Paul et al., 2022; Menendez and Lupu, 2017; Menendez and Lupu, 2007; Wang Y. et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2015; Khwairakpam et al., 2015; Merino et al., 2017). Fatty acid metabolism not only affects the energy production of cancer cells but may also impact the tumor microenvironment and immune response. For instance, NADPH generated during fatty acid oxidation helps maintain redox balance, while intermediates produced in fatty acid synthesis can act as signaling molecules affecting cell proliferation and survival (Ju et al., 2020). In cancer therapy, targeting fatty acid metabolism offers a new strategy for cancer treatment. For example, inhibiting FASN can reduce the proliferation and survival of cancer cells, and FASN inhibitors have shown anti-tumor effects in preclinical models (Lupu and Menendez, 2006; Wang H. et al., 2022; Singha et al., 2020). Additionally, key enzymes in fatty acid oxidation (FAO), such as Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) and Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), also play significant roles in tumor growth and progression (Hu et al., 2023; Liu Z. et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2018; Liao et al., 2007; Evans and Kargman, 2004; Ma et al., 2024). Overall, fatty acid metabolism is vital for the occurrence, development, and metastasis of tumors and may become a new target for cancer therapy. Future research needs to be conducted to further explore the specific mechanisms of fatty acid metabolism in different types of cancers and develop targeted treatment methods.
4.1 Fatty acid transporter
CD36 is a scavenger receptor expressed in various cell types, involved in multiple processes such as lipid uptake, immune recognition, inflammatory responses, molecular adhesion, and cellular apoptosis. It plays an important role in the treatment of blood disorders and cancer, making it a potential therapeutic target (Abumrad et al., 2021). There is a high expression level of CD36 in tumor cells, and its expression in metastatic foci is often more significant than that in the primary tumor site. This finding suggests that CD36 plays an important role in the development of tumors and may indicate a poor prognosis (Yang et al., 2024; Ww et al., 2023; Wang and Li, 2019). Overweight and lipid metabolism disorders have become increased risk factors for lung cancer (Nath and Chan, 2016; Hale et al., 2014; Pascual et al., 2017). Studies have confirmed that palmitic acid (PA) or high-fat diet (HFD) promote the proliferation and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells in a CD36-dependent manner (Li et al., 2023; Liu L-Z. et al., 2023). Additionally, CD36 is also associated with the functional impairment of immune cells in the lung cancer tumor microenvironment. CD36-positive CD8-positive T cells exhibit compromised immune functions, and a high level of infiltration of CD36-positive CD8-positive T cells predicts poor prognosis and inferior response to chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (Ao et al., 2023). These research efforts have provided new insights into lung cancer research, suggesting that CD36 is a valid target for Lung Adenocarcinoma therapy (Bai et al., 2013; H et al., 2024).
Fatty Acid Binding Proteins (FABPs) are members of the lipid-binding protein superfamily with low molecular weights (14–15 kDa). They are expressed in various tissues and play crucial roles in the metabolism, transport, and signaling of fatty acids (Li et al., 2020). In cancer, the aberrant expression of FABPs has been found to be closely associated with the occurrence and progression of tumors (Greenhill, 2018; Elsherbiny et al., 2013; Nimptsch et al., 2023). For instance, the expression of FABP1 is reduced in hepatocellular adenomas (HCA). This phenomenon is linked to the decreased expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α (HNF-1α), a transcription factor that plays a central role in regulating hepatocyte growth and differentiation. In the absence of FABP1, an increase in the levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids and a decrease in saturated fatty acids are observed. Concurrently, changes in the levels of prostaglandins such as prostaglandin E2, which is regulated by FABP1, are associated with the occurrence and progression of colorectal cancer. These findings reveal the potential role of FABP1 in the development of liver tumors and highlight the significance of FABPs in cancer metabolism (McKillop et al., 2019). In a mouse model of lung cancer metastasis, FABP5-deficient mice were found to be more susceptible to tumor metastasis (Yang S. et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2013). Mutations in the Src gene are common in lung cancer, and the release of Src’s inhibitory effect leads to an increase in FABP4 levels. This elevated expression of FABP4 is closely associated with the decrease in lipid droplets and a slowdown in tumor growth. Furthermore, in paired samples from lung cancer patients, the upregulation of FABP4 has also been confirmed to correlate with better patient prognosis (Hua et al., 2019). These studies not only reveal how tumor cells can promote cancer progression by regulating metabolism but also provide new insights into the role of metabolic reprogramming in tumor development (Figure 3).
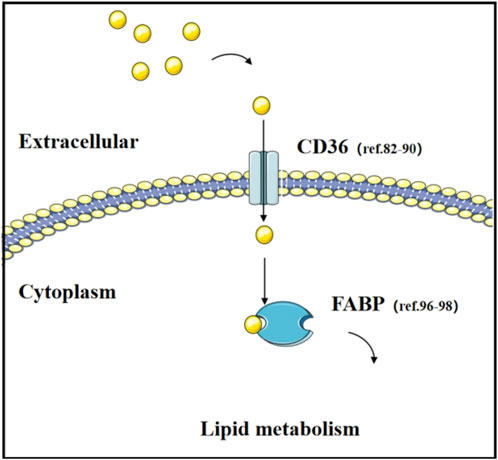
Figure 3. Transport of fatty acid and their transporters. The function of fatty acid transporters (CD36 and FABP) and relevant literature in lung cancer research.
4.2 Fatty acid synthesis
Fatty acid synthesis (FAS) is an important metabolic process within cells, involving the conversion of acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA into long-chain fatty acids. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of cells, primarily taking place in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. Fatty acid synthesis is crucial for physiological functions such as the construction of cell membranes, and signal transduction (Wedan et al., 2024; Bogie et al., 2020). The role of fatty acid synthesis in cancer cells is extremely important as it provides the necessary energy and biosynthetic precursors for the rapid proliferation of cancer cells. Compared to normal cells, cancer cells proliferate faster, require more energy, and their energy production is closely related to the metabolism of materials. Cancer cells tend to convert glucose into lactate through glycolysis. Nevertheless, fatty acid metabolism is closely related to tumor development, and the energy provided by fatty acids in cancer cells may promote the occurrence, development, and metastasis of tumors (La and Sr, 2021; Röhrig and Schulze, 2016; Currie et al., 2013; Ko et al., 2020) (Figure 4).
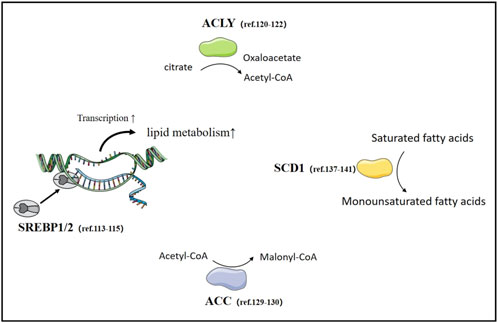
Figure 4. Fatty acid synthesis in lung Cancer. The important transcription factor SREBPs and rate-limiting enzymes in fatty acid synthesis, as well as relevant literature in lung cancer research.
Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Proteins (SREBPs) are a group of important transcription factors that regulate the endogenous synthesis of cholesterol, fatty acids, triglycerides, and phospholipids to maintain intracellular lipid balance. SREBP1 plays a particularly crucial role in this process, primarily responsible for regulating the synthesis of fatty acids (Shimano and Sato, 2017). Recent research indicates that the role of SREBPs in tumor is becoming increasingly significant (Cheng et al., 2022; Su and Koeberle, 2024; Cheng et al., 2015). Inhibiting SREBPs can affect the peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (Kawamura et al., 2022) which helps to overcome tumor resistance to therapy. The activity of SREBPs is regulated by various signaling pathways in tumor, including p53, Akt, ROS, microenvironmental pH, and so on (Kawamura et al., 2022; Rong et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2015; Yi et al., 2020). SREBP1 has been confirmed by numerous studies to be associated with the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells, among other biological behaviors (Jin et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2021). KRAS gene mutations are one of the main causes of lung adenocarcinoma, and the activation of KRAS in lung cancer can enhance the activity of SREBP through the ERK-mTORC1 pathway, thereby stimulating the synthesis of fatty acids (Gouw et al., 2017). Therefore, targeting SREBP-regulated fatty acid synthesis is a unique therapeutic target for KRAS-mutated lung cancer.
ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) is a key enzyme in the glycolipid metabolic pathway, catalyzing the breakdown of citrate into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate, thereby providing the necessary acetyl-CoA for the synthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol. Moreover, ACLY generates acetyl-CoA within the cell nucleus, a process essential for the acetylation of histones and the regulation of gene expression. By converting citrate into acetyl-CoA, ACLY supplies the necessary metabolic substrates for the proliferation and survival of cancer cells, thereby facilitating fatty acid synthesis and cholesterol biosynthesis. In cancer cells, the expression of ACLY is often upregulated, and it plays a significant role in the occurrence, development, and metastasis of tumors (Wen et al., 2019; Chen Y. et al., 2024; Granchi, 2018; Xiang et al., 2023). ARHGEF3, a member of the Rho GEFs family, is highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer, enhancing the protein stability of ACLY, thereby promoting the proliferation of NSCLC cells both in vitro and in vivo (Zhou et al., 2022). In contrast, in the A549 lung cancer cell line, the inhibition of ACLY leads to growth arrest both in vitro and in vivo (Migita et al., 2008). This suggests that ACLY is a promising target for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (Dong et al., 2023).
Acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that plays a crucial regulatory role in fatty acid synthesis. ACC controls the rate of long-chain fatty acid entry into the mitochondria by inhibiting carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT 1) through its production of malonyl CoA, which is the rate-limiting step for β-oxidation (Wang Y. et al., 2022). In cancer cells, the activity of ACC increases, promoting fatty acid synthesis, which is vital for the growth and survival of tumor cells (Chen G. et al., 2023; Svensson et al., 2016; Rios Garcia et al., 2017; Bacci et al., 2024). In the tumor microenvironment, ACC activity and expression may impact CD8+ T cell function. Inhibition of ACC in tumor microenvironment can enhance mitochondrial use of free fatty acids and bioenergetics, improving CD8+ T cell survival and antitumor effects in tumor microenvironment (Hunt et al., 2024). Due to its key role in tumor metabolism, ACC has become a potential target for cancer treatment. Targeting the metabolic pathways of ACC, such as by inhibiting its activity, may be effective for cancer treatment (Jsv et al., 2019). Studies have reported a novel lncRNA, CTD-2245E15.3, which promotes the occurrence of lung cancer by regulating the anabolic enzyme ACC1[(Wang C. et al., 2021)]. Non-small cell lung cancer cells rely on de novo fatty acid synthesis to promote growth, a process that requires ACC enzyme. Inhibiting ACC can restrict the growth of non-small cell lung cancer, suggesting that ACC inhibitors may become a new means of tumor treatment (Svensson et al., 2016). In addition, ACC is also associated with lung metastatic cancer, and relevant research data reveal a mechanism by which downregulation of ACC directs the formation of an immunosuppressive pre-metastatic niche (PMN) in the lungs for breast cancer (Huang et al., 2023). Therefore, ACC plays a significant role in the development of lung cancer and can become a very promising therapeutic target for lung cancer treatment.
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1), as a key enzyme, is responsible for converting saturated fatty acids into monounsaturated fatty acids, playing an essential role in maintaining the body’s metabolic and tissue homeostasis (Mauvoisin and Mounier, 2011; Sun et al., 2024). In cancer cells, the high activity of SCD1 is a crucial determinant of fatty acid composition, driving cancer cell metabolism towards more active lipogenesis and less lipid oxidation (Xuan et al., 2022). Furthermore, the activity of SCD1 also promotes cancer cell proliferation, survival, and invasiveness, partly by altering the lipid domains of the plasma membrane, which favors the activation of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling platforms (Sen et al., 2023; F et al., 2021; D et al., 2022). In lung cancer cell lines, upregulation of SCD1 expression is observed. Specifically, cells resistant to gefitinib have higher lipid droplet content and SCD1 expression levels than gefitinib-sensitive cells in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines and patient tissues (Q et al., 2019). A549 and H1573 cells with overexpressed SCD1 exhibit higher IC50 values for gefitinib, which is associated with the activation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and promotes the progression of lung tumors (She et al., 2019). Studies have confirmed that the expression of SCD1, enhanced by SNORD88C, promotes the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer both in vitro and in vivo (K et al., 2023). Additionally, a research team has demonstrated the involvement of SCD1 in the regulation of the Hippo pathway in lung cancer and pointed out that fatty acid metabolism is a key regulatory factor for lung cancer stem cells (Noto et al., 2017). Using CRISPR screening technology, scholars have confirmed that SCD1 is particularly important in STK11/KEAP1 co-mutated lung adenocarcinoma, representing a selective vulnerability. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of SCD1 enhances the ferroptosis induced by erastin and RSL3 [(Wohlhieter et al., 2020)], further highlighting the role of SCD1 in the development of lung cancer and its status as a key regulatory factor in lung cancer stem cells.
4.3 Fatty acid oxidation
Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) is an important process in cellular metabolism, involving the breakdown of fatty acids into energy-rich molecules such as Acetyl-CoA, which can further enter the citric acid cycle to produce a large amount of ATP, providing energy for the cell (Grabner et al., 2021; Lopaschuk et al., 2010). The rate-limiting enzyme for fatty acid oxidation is Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1). CPT1 is a key enzyme in the process of fatty acid oxidation, catalyzing the activation of long-chain fatty acids and transporting them into the mitochondria for beta-oxidation. Fatty acid oxidation plays a significant role in the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells, providing not only an energy source for cancer cells but also participating in the occurrence, development, metastasis, immune evasion, and response to treatment of tumors (Carracedo et al., 2013; Y et al., 2018; Li Y-J. et al., 2022).
Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) is a key rate-limiting enzyme in the process of fatty acid oxidation, playing an essential role in carnitine-dependent transport across the mitochondrial inner membrane. A deficiency in CPT1 leads to a decrease in the rate of fatty acid β-oxidation. Inhibition of CPT1 has been shown to suppress tumor growth, and CPT1 is overexpressed in various types of cancer, where it regulates gene expression and apoptosis in tumor cells. In the tumor microenvironment, CPT1 also plays a significant role in tumor neovascularization (Wang et al., 2018; Qu et al., 2016; Yang H. et al., 2021; Schlaepfer et al., 2014). A study shows that CPT1A significantly affects ferroptosis resistance in lung cancer stem cells and drives complex metabolic reprogramming. Additionally, a new feedback regulatory mechanism between CPT1A and c-Myc in the ferroptosis process of lung cancer stem cells was discovered, revealing how metabolic rewiring supports tumor cell survival during immune clearance (Ma et al., 2024).
5 Amino acid metabolism in lung cancer
Amino acids are not only the basic building blocks of proteins, but also play a crucial role in numerous biological processes such as cell structure construction, enzyme catalysis, signal transduction, and immune responses. Disorders in their metabolism are closely related to the occurrence and development of various diseases (Paulusma et al., 2022; Cibrian et al., 2020). In oncology, the role of amino acid metabolism is particularly significant, as tumor cells alter the uptake and metabolism of amino acids to meet their proliferative needs (Butler et al., 2021). Amino acids not only provide energy and biosynthetic precursors for the rapid growth of tumor cells (Vettore et al., 2020; Qiu et al., 2023), but also the high expression of certain amino acid metabolic enzymes, such as asparaginase, which plays a role in the treatment of leukemia, and the enhancement of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) metabolism, may promote the migration and invasion of tumor cells (Qian et al., 2023). Furthermore, amino acid metabolism shapes the tumor microenvironment and affects the function of immune cells, which may have an enhancing or inhibitory effect on immune surveillance (Yang et al., 2023). Therefore, amino acid metabolism has a profound impact not only on the biological behavior of tumor cells but also regulates immune responses within the tumor microenvironment.
5.1 Glutamine metabolism
Glutamine, a non-essential amino acid, is the most abundant free amino acid in the human body and plays a critical role in various metabolic processes. During periods of stress, illness, or injury, the body’s requirements for glutamine can exceed its production capacity, making it conditionally essential (Yoo et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2019; H and ussinger, 1990; Bodineau et al., 2022). Glutamine plays a central role in tumor cell metabolism; it is not only a key energy source for tumor growth and proliferation but also participates in maintaining the redox balance within tumor cells (Altman et al., 2016). In tumor cells, the expression levels of certain enzymes related to glutamine metabolism are significantly higher than in normal cells. For instance, high expression levels of glutamine synthetase and glutaminase are closely associated with the severity of the tumor and poor prognosis (Jin et al., 2023). Moreover, glutamine metabolism also affects the function of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, which may enhance or suppress the action of immune surveillance (Edwards et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2024). In the tumor microenvironment, glutamine metabolism is involved in regulating immune responses, and its metabolic products can modulate the activity of immune cells, thereby affecting their ability to attack the tumor (Leone et al., 2019). Therefore, glutamine metabolism is not only crucial for the survival of tumor cells but also has a significant impact on immune responses within the tumor microenvironment. The growth of lung cancer cells largely depends on the metabolism of glutamine (Kim et al., 2022; T et al., 2022). In particular, cancer cells with mutations in Keap1 or Nrf2 require enhanced glutamine catabolism to maintain their growth (Romero et al., 2017). These cells alleviate oxidative stress by increasing the conversion of glutamine to glutamate and subsequently synthesizing glutathione, thereby supporting the proliferation and survival of lung cancer cells (Han et al., 2024). Moreover, blocking glutamine metabolism not only enhances the anti-cancer immune response, but glutamine is also essential for the development and activation of effector T cells in the tumor microenvironment that have anti-tumor functions (Huang et al., 2022). Inhibitors of glutaminase may suppress the CD8 T cells activated by anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, indicating that the impact of glutamine metabolism should be carefully considered when designing anti-cancer strategies (Best et al., 2022).
5.2 Argine metabolism
Arginine, owning a central role in the urea cycle by aiding the liver in converting toxic ammonia into urea, is an essential amino acid for human health, which is the primary route for mammals to eliminate nitrogenous waste (Mangoni et al., 2019). Moreover, arginine is also crucial for reproductive health, as its deficiency may lead to reduced sperm production and thus affect fertility (Azhar et al., 2023). Arginine plays a crucial role in tumor metabolism and is closely associated with the development of cancer. In liver cancer, despite the reduced expression of arginine synthesis genes, tumor cells accumulate higher levels of arginine by enhancing its uptake and decreasing its conversion to polyamines. This accumulation of arginine further promotes tumor formation and triggers a series of metabolic reprogramming, including changes in glucose, amino acid, nucleotide, and fatty acid metabolism (Mossmann et al., 2023). Moreover, arginine metabolism, particularly the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids, may play a role in tumor progression, with increased metabolic activity potentially promoting the migration and invasion of tumor cells (Sciacovelli et al., 2022). Additionally, the inhibition of glutaminase has a negative impact on CD8 T cells activated by anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, indicating that the blockade of arginine metabolism might affect the efficacy of immunotherapy (Canale et al., 2021; Tharp et al., 2024). Arginine plays a crucial role in enhancing the proliferation, invasion, and metastatic capabilities of non-small cell lung cancer (Chen D. et al., 2023). In MYC-driven small cell lung cancer, tumors rely heavily on the arginine synthesis pathway, and depleting arginine using pegylated arginine deiminase can significantly inhibit tumor growth and improve survival rates in mouse tumor models (Chalishazar et al., 2019). In non-small cell lung cancer with KRAS mutations, the expression of arginine succinate synthetase is silenced, leading to a dependence on the arginine transporter SLC7A1 for arginine uptake from the extracellular environment. Thus, SLC7A1-mediated arginine uptake becomes a potential therapeutic vulnerability for the treatment of KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (Gai et al., 2024).
5.3 Serine metabolism
Serine is a non-essential amino acid that participates in a variety of biosynthetic processes, including the synthesis of purines, pyrimidines, and phospholipids, which are crucial for the construction and function of cell membranes. Restricting the intake of serine can suppress the growth of cancer cells by promoting the synthesis of toxic sphingolipids (Muthusamy et al., 2020). Relevant studies have shown that restricting serine and glycine in the diet significantly slows down the growth of intestinal cancer in mice. Colon cancer cells promote metastasis by enhancing the activity of key enzymes in serine synthesis, a process closely related to the generation of S-adenosylmethionine (Zhang Y. et al., 2021). Inhibiting serine metabolism in lung cancer cells leads to a decrease in cellular proliferation both in vitro and in vivo (He et al., 2022). In non-small cell lung cancer with wild-type IDH, increased serine synthesis disrupts the balance between glutathione and reactive oxygen species, supports pyrimidine biosynthesis, maintains tumor-initiating capacity, and enhances resistance to gemcitabine chemotherapy (Zhang et al., 2023). Furthermore, NRF2, a regulator of serine metabolism in non-small cell lung cancer, is associated with the invasiveness of lung cancer (Gm et al., 2015). Overall, the significance of serine in tumor metabolism offers new perspectives for cancer treatment.
5.4 Cystine metabolism
Cystine is a sulfur-containing amino acid formed by the oxidation of two cysteine molecules linked together by a disulfide bond. It is one of the important amino acids in the human body, known for its roles in enhancing immune function, promoting growth and development, improving liver function, and providing antioxidant effects (Figure 5). In cancer metabolism and cancer cell survival, cystine plays a crucial role in the redox regulation of cellular status and protein function. The cystine/cysteine redox cycle effectively protects cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death or ferroptosis by increasing intracellular cysteine levels and maintaining very high extracellular cysteine concentrations (Badgley et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020; Koppula et al., 2021b). Through metabolomic approaches, related studies have found that mutated and activated KRAS significantly increases intracellular cysteine levels and glutathione biosynthesis (Hu et al., 2020). The ablation of RBMS1 inhibits the translation of SLC7A11, reduces SLC7A11-mediated cysteine uptake, and promotes ferroptosis in lung cancer cells (Zhang W. et al., 2021). SOX2 also activates SLC7A11 in lung cancer cells, enhancing their cysteine uptake (Wang X. et al., 2021).
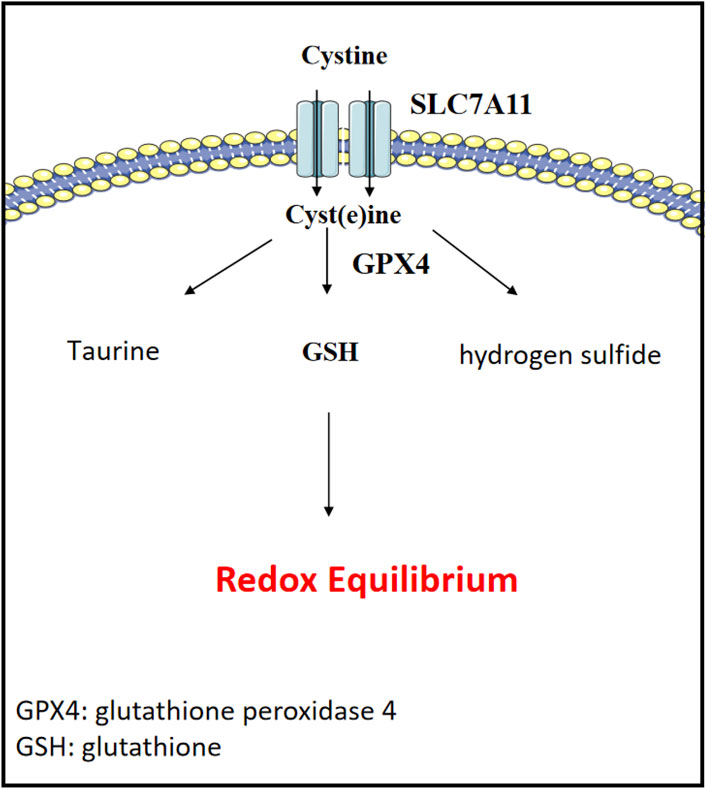
Figure 5. Cystine metabolism and redox equilibrium. Cystine is vital for redox regulation in cancer metabolism and cell survival.
6 Application of targeting metabolism in lung cancer
6.1 Targeting glucose metabolism
2-Deoxyglucose (2-DG) is converted into 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphate by the catalysis of hexokinase, a product that cannot be further metabolized by cells. As it cannot be broken down further, it accumulates within the cells and competitively binds to hexokinase, thereby inhibiting its activity and slowing down the glucose uptake process. Additionally, 2-DG increases oxidative stress, inhibits N-glycosylation, and induces autophagy. It can be combined with other therapeutic agents or radiotherapy to exhibit synergistic anticancer effects (Zhang et al., 2014). Lung cancer cells treated with 2-deoxyglucose show a significant decrease in cell viability, and this cytotoxicity may be closely related to the lung cancer genes LKB1 and IGF1R (Inge et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2018). The combination of 2-DG with other effective drugs for the treatment of lung cancer exhibits better toxicity than the use of compounds alone (Hou et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2024).
3-bromopyruvate is a small and highly reactive molecule that targets the overexpressed monocarboxylate transporters in cancer cells, leading to tumor cell death by depleting ATP through the inactivation of glycolysis and mitochondrial energy production pathways. 3-bromopyruvate can significantly inhibit the proliferation of A549 cells and induce apoptosis (Cunha et al., 2022; Dai et al., 2019).
6.2 Targeting lipid metabolism
The fatty acid synthase inhibitor TVB-2640 has shown strong anti-tumor effects and has demonstrated good therapeutic efficacy and manageable safety in clinical trials (Falchook et al., 2021). TVB-2640 significantly inhibited the lipogenic phenotype in lung cancer cells, and weakened the capabilities of self-renewal, chemoresistance, and tumorigenesis mediated by USP13 in small cell lung cancer (Wang J. et al., 2022).
Etomoxir is an irreversible inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (CPT-1a), which inhibits fatty acid oxidation by suppressing CPT-1a. By inhibiting lipolysis with Etomoxir, it can synergistically suppress the proliferation of drug-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells (Li et al., 2013).
ND-646 is an inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), which reduces fatty acid synthesis by inhibiting ACC1 and ACC2. In the non-small cell lung cancer cell line A549, ND-646 can decrease the production of palmitic acid and total fatty acid content within the cells, induce apoptosis, and trigger endoplasmic reticulum stress (Li et al., 2019). In a mouse xenograft model of A549 lung cancer, when administered at a dose of 25 mg/kg twice daily, ND-646 was able to inhibit tumor growth (Jsv et al., 2019).
6.3 Targeting acid amino metabolism
CB-839, also known as Telaglenastat, is a first-in-class, selective, reversible, and orally active glutaminase 1 inhibitor. In lung cancer cells, CB-839 can leads to increased levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and decreased levels of ATP, NADPH/NADP + ratio, and glutathione, thereby increasing energy and redox stress (Galan-Cobo et al., 2019).
NCT-503 is a phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) inhibitor. PHGDH catalyzes the first step in the de novo synthesis of L-serine from 3-phosphoglycerate. It has been identified as an inhibitor of PHGDH and was found to be inactive against a panel of other dehydrogenases and showed minimal cross-reactivity in a panel of G-protein-coupled receptors. In lung cancer, the combination of PKM2-IN-1 and NCT-503 has shown significant anti-cancer effects by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis (Wang K. et al., 2023).
7 Conclusion
Lung cancer is a globally common malignant tumor, with both incidence and mortality rates remaining high. The treatment of lung cancer requires the joint efforts of a multidisciplinary team, including surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Despite the development of targeted and immunotherapies offering new hope for the treatment of lung cancer, it remains a clinical challenge that is difficult to completely cure. Therefore, the development of new treatment strategies is one of the key focuses of current lung cancer research.
The metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells is a key driver of tumor development, involving significant changes in energy metabolism and biosynthetic pathways. These changes include glycolysis, amino acid metabolism, fatty acid metabolism, and more. These metabolic alterations not only support the rapid proliferation of tumor cells but also affect the tumor microenvironment and immune response. For example, lung cancer cells may meet energy demands by enhancing the glycolytic process, even under conditions of sufficient oxygen, a phenomenon known as the “Warburg effect.” Additionally, lung cancer cells may alter fatty acid synthesis and oxidation to meet their needs for energy and biosynthetic precursors.
The document also discusses the role of glucose transport proteins (such as GLUTs), glycolysis-related enzymes (such as hexokinase 2 and lactate dehydrogenase A), fatty acid metabolism-related proteins (such as CD36 and fatty acid-binding proteins), and some amino acids and their metabolic pathways in lung cancer. The expression levels of these proteins are often upregulated in lung cancer and are closely related to tumor proliferation, invasion, and prognosis. Targeted therapies against these metabolic pathways, such as inhibiting specific metabolic enzymes, may provide new opportunities for lung cancer treatment.
The manuscript in question primarily focuses on the three major metabolic pathways—glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism—which are indeed the most extensively studied and form the cornerstone of current research in the field. However, we acknowledge that this concentration inherently limits the scope of our review, as it does not encompass other significant metabolic pathways that may also play crucial roles in the development and progression of lung cancer. This omission is a recognized limitation of our study, and we hope that future research will address these gaps by delving into the less-explored metabolic avenues. We anticipate that with more articles dedicated to these areas, a more comprehensive understanding of the metabolic landscape in lung cancer can be achieved, ultimately contributing to the advancement of therapeutic strategies and patient outcomes.
Overall, this document provides a comprehensive perspective on how lung cancer cells adapt to their growth and survival needs through metabolic reprogramming and explores how these metabolic changes can serve as potential therapeutic targets. By gaining a deeper understanding of the metabolic characteristics of lung cancer, researchers can develop more effective treatment strategies to improve the prognosis of lung cancer patients.
Author contributions
QH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. LF: Writing–original draft, Investigation, Resources. MG: Writing–original draft, Formal Analysis. JR: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. CC: Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. SX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province - Key R&D project (2023YFS0305).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abumrad, N. A., Cabodevilla, A. G., Samovski, D., Pietka, T., Basu, D., and Goldberg, I. J. (2021). Endothelial cell receptors in tissue lipid uptake and metabolism. Circ. Res. 128, 433–450. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318003
Altman, B. J., Stine, Z. E., and Dang, C. V. (2016). From Krebs to clinic: glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 619–634. doi:10.1038/nrc.2016.71
Ao, Y.-Q., Gao, J., Zhang, L.-X., Deng, J., Wang, S., Lin, M., et al. (2023). Tumor-infiltrating CD36+CD8+T cells determine exhausted tumor microenvironment and correlate with inferior response to chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 23, 367. doi:10.1186/s12885-023-10836-z
Arren, B.-E., Avi, F., Elad, N., and Ron, M. (2012). Rethinking glycolysis: on the biochemical logic of metabolic pathways. Nat. Chem. Biol., 8. doi:10.1038/nchembio.971
Azhar, M., Xu, C., Jiang, X., Li, W., Cao, Y., Zhu, X., et al. (2023). The arginine methyltransferase Prmt1 coordinates the germline arginine methylome essential for spermatogonial homeostasis and male fertility. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, 10428–10450. doi:10.1093/nar/gkad769
Bacci, M., Lorito, N., Smiriglia, A., Subbiani, A., Bonechi, F., Comito, G., et al. (2024). Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 controls a lipid droplet-peroxisome axis and is a vulnerability of endocrine-resistant ER+ breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 16, eadf9874. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.adf9874
Badgley, M. A., Kremer, D. M., Maurer, H. C., DelGiorno, K. E., Lee, H.-J., Purohit, V., et al. (2020). Cysteine depletion induces pancreatic tumor ferroptosis in mice. Science 368, 85–89. doi:10.1126/science.aaw9872
Bai, L., Zhao, J., Yu, H., Zhao, N., Liu, D., Zhong, W., et al. (2013). The CD36 dynamic change after radiation therapy in lung cancer patients and its correlation with symptomatic radiation pneumonitis. Radiother. Oncol. 107, 389–391. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.04.014
Barron, C. C., Bilan, P. J., Tsakiridis, T., and Tsiani, E. (2016). Facilitative glucose transporters: implications for cancer detection, prognosis and treatment. Metabolism 65, 124–139. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2015.10.007
Best, S. A., Gubser, P. M., Sethumadhavan, S., Kersbergen, A., Negrón Abril, Y. L., Goldford, J., et al. (2022). Glutaminase inhibition impairs CD8 T cell activation in STK11-/Lkb1-deficient lung cancer. Cell Metab. 34, 874–887.e6. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2022.04.003
Bodineau, C., Tomé, M., Murdoch, P. D. S., and Durán, R. V. (2022). Glutamine, MTOR and autophagy: a multiconnection relationship. Autophagy 18, 2749–2750. doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2062875
Bogie, J. F. J., Haidar, M., Kooij, G., and Hendriks, J. J. A. (2020). Fatty acid metabolism in the progression and resolution of CNS disorders. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 159, 198–213. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2020.01.004
Boroughs, L. K., and DeBerardinis, R. J. (2015). Metabolic pathways promoting cancer cell survival and growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 17, 351–359. doi:10.1038/ncb3124
Brand, A., Singer, K., Koehl, G. E., Kolitzus, M., Schoenhammer, G., Thiel, A., et al. (2016). LDHA-associated lactic acid production blunts tumor immunosurveillance by T and NK cells. Cell Metab. 24, 657–671. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.011
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., and Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394–424. doi:10.3322/caac.21492
Butler, M., van der Meer, LT., and van Leeuwen, FN. (2021). Amino acid depletion therapies: starving cancer cells to death. Trends Endocrinol. metabolism TEM, 32. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2021.03.003
Canale, F. P., Basso, C., Antonini, G., Perotti, M., Li, N., Sokolovska, A., et al. (2021). Metabolic modulation of tumours with engineered bacteria for immunotherapy. Nature 598, 662–666. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04003-2
Carracedo, A., Cantley, L. C., and Pandolfi, P. P. (2013). Cancer metabolism: fatty acid oxidation in the limelight. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 227–232. doi:10.1038/nrc3483
Certo, M., Tsai, C.-H., Pucino, V., Ho, P.-C., and Mauro, C. (2021). Lactate modulation of immune responses in inflammatory versus tumour microenvironments. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 21, 151–161. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0406-2
Chalishazar, M. D., Wait, S. J., Huang, F., Ireland, A. S., Mukhopadhyay, A., Lee, Y., et al. (2019). MYC-driven small-cell lung cancer is metabolically distinct and vulnerable to arginine depletion. Clin. cancer Res. official J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res., 25. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-4140
Chen, P. H., Cai, L., Huffman, K., Yang, C., Kim, J., Faubert, B., et al. (2019). Metabolic diversity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. cell, 76. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.028
Chen, G., Bao, B., Cheng, Y., Tian, M., Song, J., Zheng, L., et al. (2023a). Acetyl-CoA metabolism as a therapeutic target for cancer. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 168, 115741. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115741
Chen, D., Fan, S., Wang, J., Liang, Y., Li, P., Lv, X., et al. (2023b). Cip2a induces arginine biosynthesis and promotes tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 62, 561–572. doi:10.1002/mc.23507
Chen, L., Xing, X., Zhu, Y., Chen, Y., Pei, H., Song, Q., et al. (2024a). Palmitoylation alters LDHA activity and pancreatic cancer response to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 587, 216696. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216696
Chen, Y., Shen, J., Yuan, M., Li, H., Li, Y., Zheng, S., et al. (2024b). Dehydrocostus lactone suppresses gastric cancer progression by targeting ACLY to inhibit fatty acid synthesis and autophagic flux. J. Adv. Res. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2024.01.028
Cheng, C., Ru, P., Geng, F., Liu, J., Yoo, J. Y., Wu, X., et al. (2015). Glucose-mediated N-glycosylation of SCAP is essential for SREBP-1 activation and tumor growth. Cancer cell, 28. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.021
Cheng, C., Geng, F., Li, Z., Zhong, Y., Wang, H., Cheng, X., et al. (2022). Ammonia stimulates SCAP/Insig dissociation and SREBP-1 activation to promote lipogenesis and tumour growth. Nat. Metab. 4, 575–588. doi:10.1038/s42255-022-00568-y
Cibrian, D., de la Fuente, H., and Sánchez-Madrid, F. (2020). Metabolic pathways that control skin homeostasis and inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 26, 975–986. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2020.04.004
Ciscato, F., Ferrone, L., Masgras, I., Laquatra, C., and Rasola, A. (2021). Hexokinase 2 in cancer: a prima donna playing multiple characters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4716. doi:10.3390/ijms22094716
Claps, G., Faouzi, S., and Quidville, V. (2022). The multiple roles of LDH in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol., 19. doi:10.1038/s41571-022-00686-2
Colell, A., Green, D. R., and Ricci, J.-E. (2009). Novel roles for GAPDH in cell death and carcinogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 16, 1573–1581. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.137
Cunha, A., Rocha, A. C., Barbosa, F., Baião, A., Silva, P., Sarmento, B., et al. (2022). Glycolytic inhibitors potentiated the activity of paclitaxel and their nanoencapsulation increased their delivery in a lung cancer model. Pharmaceutics 14, 2021. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14102021
Currie, E., Schulze, A., Zechner, R., Walther, T. C., and Farese, R. V. (2013). Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer. Cell Metab. 18, 153–161. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.017
D, D., C, L., M, Q., X, Z., T, X., S, Y., et al. (2022). Metabolic dysregulation and emerging therapeutical targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharm. Sin. B, 12. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.019
Dai, K., Radin, D. P., and Leonardi, D. (2019). PINK1 depletion sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer to glycolytic inhibitor 3-bromopyruvate: involvement of ROS and mitophagy. Pharmacol. Rep. 71, 1184–1189. doi:10.1016/j.pharep.2019.08.002
DeWaal, D., Nogueira, V., Terry, A. R., Patra, K. C., Jeon, S.-M., Guzman, G., et al. (2018). Hexokinase-2 depletion inhibits glycolysis and induces oxidative phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma and sensitizes to metformin. Nat. Commun. 9, 446. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02733-4
Doherty, J. R., and Cleveland, J. L. (2013). Targeting lactate metabolism for cancer therapeutics. J. Clin. Invest 123, 3685–3692. doi:10.1172/JCI69741
Dong, T., Liu, Z., Xuan, Q., Wang, Z., Ma, W., and Zhang, Q. (2017). Tumor LDH-A expression and serum LDH status are two metabolic predictors for triple negative breast cancer brain metastasis. Sci. Rep. 7, 6069. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06378-7
Dong, L., Dong, C., Wang, F., Wei Liu, C., Xing, J., Sheng, L.-Q., et al. (2023). Active post-transcriptional regulation and ACLY-mediated acetyl-CoA synthesis as a pivotal target of Shuang-Huang-Sheng-Bai formula for lung adenocarcinoma treatment. Phytomedicine Int. J. phytotherapy Phytopharm., 113. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154732
Duan, Q., Li, D., Xiong, L., Chang, Z., and Xu, G. (2019). SILAC quantitative proteomics and biochemical analyses reveal a novel molecular mechanism by which ADAM12S promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of small cell lung cancer cells through upregulating hexokinase 1. J. Proteome Res. 18, 2903–2914. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00208
Edwards, D. N., Ngwa, V. M., Raybuck, A. L., Wang, S., Hwang, Y., Kim, L. C., et al. (2021). Selective glutamine metabolism inhibition in tumor cells improves antitumor T lymphocyte activity in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Invest 131, 140100. doi:10.1172/JCI140100
Elsherbiny, M. E., Emara, M., and Godbout, R. (2013). Interaction of brain fatty acid-binding protein with the polyunsaturated fatty acid environment as a potential determinant of poor prognosis in malignant glioma. Prog. Lipid Res. 52, 562–570. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2013.08.004
Evans, J. F., and Kargman, S. L. (2004). Cancer and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibition. Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 627–634. doi:10.2174/1381612043453126
F, A., C, D. V., M, M.-S., C, N., G, C., and R, M. (2021). SCD1, autophagy and cancer: implications for therapy. J. Exp. and Clin. cancer Res. CR, 40. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-02067-6
Falchook, G., Infante, J., Arkenau, H.-T., Patel, M. R., Dean, E., Borazanci, E., et al. (2021). First-in-human study of the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of first-in-class fatty acid synthase inhibitor TVB-2640 alone and with a taxane in advanced tumors. EClinicalMedicine 34, 100797. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100797
Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Dikshit, R., Eser, S., Mathers, C., Rebelo, M., et al. (2015). Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 136, E359–E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
Fr, H., Gv, S., Jl, M., R, K., Wj, C., Yl, W., et al. (2017). Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet London, Engl., 389. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30958-8
Gai, X., Liu, Y., Lan, X., Chen, L., Yuan, T., Xu, J., et al. (2024). Oncogenic KRAS induces arginine auxotrophy and confers a therapeutic vulnerability to SLC7A1 inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 84, 1963–1977. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2095
Galan-Cobo, A., Sitthideatphaiboon, P., Qu, X., Poteete, A., Pisegna, M. A., Tong, P., et al. (2019). LKB1 and KEAP1/NRF2 pathways cooperatively promote metabolic reprogramming with enhanced glutamine dependence in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 79, 3251–3267. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3527
Gm, D., Ph, C., E, M., Ja, S., Z, H., D, W., et al. (2015). NRF2 regulates serine biosynthesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 47, 1475–1481. doi:10.1038/ng.3421
Gouw, AM., Eberlin, LS., Margulis, K., Sullivan, DK., Toal, GG, Tong, L., et al. (2017). “Oncogene KRAS activates fatty acid synthase, resulting in specific ERK and lipid signatures associated with lung adenocarcinoma,” in Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America, 114. doi:10.1073/pnas.1617709114
Grabner, G. F., Xie, H., Schweiger, M., and Zechner, R. (2021). Lipolysis: cellular mechanisms for lipid mobilization from fat stores. Nat. Metab. 3, 1445–1465. doi:10.1038/s42255-021-00493-6
Granchi, C. (2018). ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) inhibitors: an anti-cancer strategy at the crossroads of glucose and lipid metabolism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 157, 1276–1291. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.09.001
Greenhill, C. (2018). A-FABP links obesity and breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 14, 566. doi:10.1038/s41574-018-0085-2
Gu, S., and Yang, C. (2023). Serum lactate dehydrogenase level predicts the prognosis in bladder cancer patients. BMC Urol. 23, 65. doi:10.1186/s12894-023-01239-0
Guo, Z., Liu, Y., Li, X., Huang, Y., Zhou, Z., and Yang, C. (2024). Reprogramming hematopoietic stem cell metabolism in lung cancer: glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and the role of 2-DG. Biol. Direct 19, 73. doi:10.1186/s13062-024-00514-w
Hussinger, D. (1990). Liver glutamine metabolism. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 14, 14. doi:10.1177/014860719001400405
H, L., W, G., T, W., P, C., T, Z., Y, P., et al. (2024). CD36 inhibition reduces non-small-cell lung cancer development through AKT-mTOR pathway. Cell Biol. Toxicol., 40. doi:10.1007/s10565-024-09848-7
Hale, J. S., Otvos, B., Sinyuk, M., lvarado, A. G., Hitomi, M., Stoltz, K., et al. (2014). Cancer stem cell-specific scavenger receptor CD36 drives glioblastoma progression. Stem cells Dayt. Ohio, 32. doi:10.1002/stem.1716
Han, M., Bushong, E. A., Segawa, M., Tiard, A., Wong, A., Brady, M. R., et al. (2023). Spatial mapping of mitochondrial networks and bioenergetics in lung cancer. Nature 615, 712–719. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-05793-3
Han, X., Wang, D., Yang, L., Wang, N., Shen, J., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Activation of polyamine catabolism promotes glutamine metabolism and creates a targetable vulnerability in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 121, e2319429121. doi:10.1073/pnas.2319429121
Hanahan, D., and Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Hanahan, D. (2022). Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12, 31–46. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059
He, L., Endress, J., Cho, S., Li, Z., Zheng, Y., Asara, J. M., et al. (2022). Suppression of nuclear GSK3 signaling promotes serine/one-carbon metabolism and confers metabolic vulnerability in lung cancer cells. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm8786. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abm8786
Hou, X.-B., Li, T.-H., Ren, Z.-P., and Liu, Y. (2016). Combination of 2-deoxy d-glucose and metformin for synergistic inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer: a reactive oxygen species and P-p38 mediated mechanism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 84, 1575–1584. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.037
Hu, K., Li, K., Lv, J., Feng, J., Chen, J., Wu, H., et al. (2020). Suppression of the SLC7A11/glutathione axis causes synthetic lethality in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Invest 130, 1752–1766. doi:10.1172/JCI124049
Hu, A., Wang, H., Xu, Q., Pan, Y., Jiang, Z., Li, S., et al. (2023). A novel CPT1A covalent inhibitor modulates fatty acid oxidation and CPT1A-VDAC1 axis with therapeutic potential for colorectal cancer. Redox Biol. 68, 102959. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102959
Hua, T. N. M., Kim, M.-K., Vo, V. T. A., Choi, J.-W., Choi, J. H., Kim, H.-W., et al. (2019). Inhibition of oncogenic Src induces FABP4-mediated lipolysis via PPARγ activation exerting cancer growth suppression. EBioMedicine 41, 134–145. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.015
Huang, Y., Chen, Z., Lu, T., Bi, G., Li, M., Liang, J., et al. (2021). HIF-1α switches the functionality of TGF-β signaling via changing the partners of smads to drive glucose metabolic reprogramming in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40, 398. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-02188-y
Huang, M., Xiong, D., Pan, J., Qhang, Z., Sei, S., Robert, H., et al. (2022). Targeting glutamine metabolism to enhance immunoprevention of EGFR-driven lung cancer. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger. 9, 9. doi:10.1002/advs.202105885
Huang, Y.-C., Hou, M.-F., Tsai, Y.-M., Pan, Y.-C., Tsai, P.-H., Lin, Y.-S., et al. (2023). Involvement of ACACA (acetyl-CoA carboxylase α) in the lung pre-metastatic niche formation in breast cancer by senescence phenotypic conversion in fibroblasts. Cell Oncol. (Dordr) 46, 643–660. doi:10.1007/s13402-022-00767-5
Hunt, E. G., Hurst, K. E., Riesenberg, B. P., Kennedy, A. S., Gandy, E. J., Andrews, A. M., et al. (2024). Acetyl-CoA carboxylase obstructs CD8+ T cell lipid utilization in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. 36, 969–983.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2024.02.009
Icard, P., Shulman, S., Farhat, D., Steyaert, J.-M., Alifano, M., and Lincet, H. (2018). How the Warburg effect supports aggressiveness and drug resistance of cancer cells? Drug Resist Updat 38, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2018.03.001
Inge, L. J., Coon, K. D., Smith, M. A., and Bremner, R. M. (2009). Expression of LKB1 tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer determines sensitivity to 2-deoxyglucose. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc Surg. 137, 580–586. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.11.029
Jin, J., Byun, J. K., and Choi, Y. K. (2023). Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. Exp. and Mol. Med., 55. doi:10.1038/s12276-023-00971-9
Jin, Q., Qi, D., Zhang, M., Qu, H., Dong, Y., Sun, M., et al. (2024). CLDN6 inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis through SREBP1-mediated RAS palmitoylation. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 29, 112. doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00629-y
Jsv, L., S, G., Dk, D., O, M., L, W., R, M., et al. (2019). Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by phosphorylation or the inhibitor ND-654 suppresses lipogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell metab., 29. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.020
Ju, H.-Q., Lin, J.-F., Tian, T., Xie, D., and Xu, R.-H. (2020). NADPH homeostasis in cancer: functions, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 5, 231. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00326-0
K, W., S, W., Y, Z., L, X., and X, S. (2023). SNORD88C guided 2’-O-methylation of 28S rRNA regulates SCD1 translation to inhibit autophagy and promote growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell death Differ., 30. doi:10.1038/s41418-022-01087-9
Kawamura, S., Matsushita, Y., Kurosaki, S., Tange, M., Fujiwara, N., Hayata, Y., et al. (2022). Inhibiting SCAP/SREBP exacerbates liver injury and carcinogenesis in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. investigation 132, 132. doi:10.1172/JCI151895
Khwairakpam, A. D., Shyamananda, M. S., Sailo, B. L., Rathnakaram, S. R., Padmavathi, G., Kotoky, J., et al. (2015). ATP citrate lyase (ACLY): a promising target for cancer prevention and treatment. Curr. Drug Targets 16, 156–163. doi:10.2174/1389450115666141224125117
Kim, S., Jeon, J. S., Choi, Y. J., Baek, G. H., Kim, S. K., and Kang, K. W. (2022). Heterogeneity of glutamine metabolism in acquired-EGFR-TKI-resistant lung cancer. Life Sci. 291, 120274. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120274
Koundouros, N., and Poulogiannis, G. (2020). Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. cancer, 122. doi:10.1038/s41416-019-0650-z
Koppenol, W. H., Bounds, P. L., and Dang, C. V. (2011). Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11, 325–337. doi:10.1038/nrc3038
Koppula, P., Olszewski, K., Zhang, Y., Kondiparthi, L., Liu, X., Lei, G., et al. (2021a). KEAP1 deficiency drives glucose dependency and sensitizes lung cancer cells and tumors to GLUT inhibition. iScience 24, 102649. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.102649
Koppula, P., Zhuang, L., and Gan, B. (2021b). Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell 12, 599–620. doi:10.1007/s13238-020-00789-5
Kroemer, G., and Pouyssegur, J. (2008). Tumor cell metabolism: cancer’s Achilles’ heel. Cancer Cell 13, 472–482. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2008.05.005
La, S., and Sr, D. (2021). Fatty acid synthesis in prostate cancer: vulnerability or epiphenomenon? Cancer Res., 81. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1392
Lee, H.-J., Li, C.-F., Ruan, D., He, J., Montal, E. D., Lorenz, S., et al. (2019). Non-proteolytic ubiquitination of Hexokinase 2 by HectH9 controls tumor metabolism and cancer stem cell expansion. Nat. Commun. 10, 2625. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-10374-y
Leone, R. D., Zhao, L., Englert, J. M., Sun, I.-M., Oh, M.-H., Sun, I.-H., et al. (2019). Glutamine blockade induces divergent metabolic programs to overcome tumor immune evasion. Science 366, 1013–1021. doi:10.1126/science.aav2588
Li, J., Zhao, S., Zhou, X., Zhang, T., Zhao, L., Miao, P., et al. (2013). Inhibition of lipolysis by mercaptoacetate and etomoxir specifically sensitize drug-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cell to paclitaxel. PLoS One 8, e74623. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074623
Li, E.-Q., Zhao, W., Zhang, C., Qin, L.-Z., Liu, S.-J., Feng, Z.-Q., et al. (2019). Synthesis and anti-cancer activity of ND-646 and its derivatives as acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 137, 105010. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105010
Li, B., Hao, J., Zeng, J., and Sauter, E. R. (2020). SnapShot: FABP functions. Cell 182, 1066–1066.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.027
Li, R., Mei, S., Ding, Q., Wang, Q., Yu, L., and Zi, F. (2022a). A pan-cancer analysis of the role of hexokinase II (HK2) in human tumors. Sci. Rep. 12, 18807. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-23598-8
Li, Y.-J., Fahrmann, J. F., Aftabizadeh, M., Zhao, Q., Tripathi, S. C., Zhang, C., et al. (2022b). Fatty acid oxidation protects cancer cells from apoptosis by increasing mitochondrial membrane lipids. Cell Rep. 39, 110870. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110870
Li, M.-Y., Wang, M., Dong, M., Wu, Z., Zhang, R., Wang, B., et al. (2023). Targeting CD36 determines nicotine derivative NNK-induced lung adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis. iScience 26, 107477. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107477
Liao, Z., Mason, K. A., and Milas, L. (2007). Cyclo-oxygenase-2 and its inhibition in cancer: is there a role? Drugs 67, 821–845. doi:10.2165/00003495-200767060-00001
Liu, Q, Wang, S, Xu, H, and Zhang, S (2013). Expressions and significances of CRABPII and E-FABP in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo fei ai za zhi = Chin. J. lung cancer, 16. doi:10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2013.01.03
Liu, L., Zhang, K., Sandoval, H., Yamamoto, S., Jaiswal, M., Sanz, E., et al. (2015). Glial lipid droplets and ROS induced by mitochondrial defects promote neurodegeneration. Cell 160, 177–190. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.12.019
Liu, F., Liu, Y., Liu, X., Mao, K., Zhong, D., Marcus, A. I., et al. (2018). Inhibition of IGF1R enhances 2-deoxyglucose in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 123, 36–43. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.06.026
Liu, X., Olszewski, K., Zhang, Y., Lim, E. W., Shi, J., Zhang, X., et al. (2020). Cystine transporter regulation of pentose phosphate pathway dependency and disulfide stress exposes a targetable metabolic vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 22, 476–486. doi:10.1038/s41556-020-0496-x
Liu, L., Yan, H., Ruan, M., Yang, H., Wang, L., Lei, B., et al. (2021). An AKT/PRMT5/SREBP1 axis in lung adenocarcinoma regulates de novo lipogenesis and tumor growth. Cancer Sci. 112, 3083–3098. doi:10.1111/cas.14988
Liu, Z., Liu, W., Wang, W., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., Drum, D. L., et al. (2023a). CPT1A-mediated fatty acid oxidation confers cancer cell resistance to immune-mediated cytolytic killing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120, e2302878120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2302878120
Liu, L.-Z., Wang, B., Zhang, R., Wu, Z., Huang, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2023b). The activated CD36-Src axis promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and actin remodeling-involved metastasis in high-fat environment. Cell Death Dis. 14, 548. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06078-3
Lopaschuk, G. D., Ussher, J. R., Folmes, C. D. L., Jaswal, J. S., and Stanley, W. C. (2010). Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 90, 207–258. doi:10.1152/physrev.00015.2009
Luo, J., Hendryx, M., and Dong, Y. (2023). Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and non-small cell lung cancer survival. Br. J. Cancer 128, 1541–1547. doi:10.1038/s41416-023-02177-2
Lupu, R., and Menendez, J. A. (2006). Pharmacological inhibitors of Fatty Acid Synthase (FASN)-catalyzed endogenous fatty acid biogenesis: a new family of anti-cancer agents? Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 7, 483–493. doi:10.2174/138920106779116928
Ma, L., Chen, C., Zhao, C., Li, T., Ma, L., Jiang, J., et al. (2024). Targeting carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (CPT1A) induces ferroptosis and synergizes with immunotherapy in lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 9, 64. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01772-w
Macheda, M. L., Rogers, S., and Best, J. D. (2005). Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 202, 654–662. doi:10.1002/jcp.20166
Mangoni, A. A., Rodionov, R. N., McEvoy, M., Zinellu, A., Carru, C., and Sotgia, S. (2019). New horizons in arginine metabolism, ageing and chronic disease states. Age Ageing 48, 776–782. doi:10.1093/ageing/afz083
Mathur, D., Liao, C., Lin, W., La Ferlita, A., Alaimo, S., Taylor, S., et al. (2023). The ratio of key metabolic transcripts is a predictive biomarker of breast cancer metastasis to the lung. Cancer Res. 83, 3478–3491. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0153
Mauvoisin, D., and Mounier, C. (2011). Hormonal and nutritional regulation of SCD1 gene expression. Biochimie, 93. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.08.001
McKillop, I. H., Girardi, C. A., and Thompson, K. J. (2019). Role of fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) in cancer development and progression. Cell. Signal. 62, 109336. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.06.001
Menendez, J. A., and Lupu, R. (2007). Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 763–777. doi:10.1038/nrc2222
Menendez, J. A., and Lupu, R. (2017). Fatty acid synthase (FASN) as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 21, 1001–1016. doi:10.1080/14728222.2017.1381087
Mergenthaler, P., Lindauer, U., Dienel, G. A., and Meisel, A. (2013). Sugar for the brain: the role of glucose in physiological and pathological brain function. Trends Neurosci. 36, 587–597. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2013.07.001
Merino, S. M., Gómez de Cedrón, M., Moreno Rubio, J., Falagán Martínez, S., Sánchez Martínez, R., Casado, E., et al. (2017). Lipid metabolism and lung cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 112, 31–40. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.02.001
Mezquita, L., Auclin, E., Ferrara, R., Charrier, M., Remon, J., Planchard, D., et al. (2018). Association of the lung immune prognostic index with immune checkpoint inhibitor outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 4, 351–357. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.4771
Mg, V. H., Lc, C., and Cb, T. (2009). Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Sci. (New York, NY), 324. doi:10.1126/science.1160809
Migita, T., Narita, T., Nomura, K., Miyagi, E., Inazuka, F., Matsuura, M., et al. (2008). ATP citrate lyase: activation and therapeutic implications in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 68, 8547–8554. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1235
Mossmann, D., Müller, C., Park, S., Ryback, B., Colombi, M., Ritter, N., et al. (2023). Arginine reprograms metabolism in liver cancer via RBM39. Cell 186, 5068–5083.e23. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.011
Mulukutla, B. C., Yongky, A., Le, T., Mashek, D. G., and Hu, W.-S. (2016). Regulation of glucose metabolism - a perspective from cell bioprocessing. Trends Biotechnol. 34, 638–651. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.04.012
Muscat, J. E., Stellman, S. D., Zhang, Z. F., Neugut, A. I., and Wynder, E. L. (1997). Cigarette smoking and large cell carcinoma of the lung. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 6, 477–480.
Muthusamy, T., Cordes, T., Handzlik, M. K., You, L., Lim, E. W., Gengatharan, J., et al. (2020). Serine restriction alters sphingolipid diversity to constrain tumour growth. Nature 586, 790–795. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2609-x
Nath, A., and Chan, C. (2016). Genetic alterations in fatty acid transport and metabolism genes are associated with metastatic progression and poor prognosis of human cancers. Sci. Rep. 6, 18669. doi:10.1038/srep18669
Nimptsch, K., Aleksandrova, K., Pham, T. T., Papadimitriou, N., Janke, J., Christakoudi, S., et al. (2023). Prospective and Mendelian randomization analyses on the association of circulating fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP-4) and risk of colorectal cancer. BMC Med. 21, 391. doi:10.1186/s12916-023-03104-1
Noto, A., De Vitis, C., Pisanu, M. E., Roscilli, G., Ricci, G., Catizone, A., et al. (2017). Stearoyl-CoA-desaturase 1 regulates lung cancer stemness via stabilization and nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ. Oncogene 36, 4573–4584. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.75
Ouyang, X., Zhu, R., Lin, L., Wang, X., Zhuang, Q., and Hu, D. (2023). GAPDH is a novel ferroptosis-related marker and correlates with immune microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Metabolites 13, 142. doi:10.3390/metabo13020142
Pascual, G., Avgustinova, A., Mejetta, S., Martin, M., Castelanoos, A., Otto, C.-S., et al. (2017). Targeting metastasis-initiating cells through the fatty acid receptor CD36. Nature, 541. doi:10.1038/nature20791
Paul, B., Lewinska, M., and Andersen, J. B. (2022). Lipid alterations in chronic liver disease and liver cancer. JHEP Rep. 4, 100479. doi:10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100479
Paulusma, C., Lamers, W. H., and Sfj, van de G. (2022). Amino acid metabolism, transport and signalling in the liver revisited. Biochem. Pharmacol., 201. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115074
Pavlova, N. N., Zhu, J., and Thompson, C. B. (2022). The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: still emerging. Cell Metab. 34, 355–377. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2022.01.007
Phadke, M., Krynetskaia, N., Mishra, A., and Krynetskiy, E. (2011). Accelerated cellular senescence phenotype of GAPDH-depleted human lung carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 411, 409–415. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.165
Q, H., Q, W., D, L., X, W., Y, J., Z, Z., et al. (2019). Co-administration of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol (g-PPT) and EGFR-TKI overcomes EGFR-TKI resistance by decreasing SCD1 induced lipid accumulation in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. and Clin. cancer Res. CR, 38. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1120-4
Qian, L., Li, N., Lu, X. C., Liu, Y., Li, K., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Enhanced BCAT1 activity and BCAA metabolism promotes RhoC activity in cancer progression. Nat. Metab., 5. doi:10.1038/s42255-023-00818-7
Qin, C., Yang, G., Yang, J., Ren, B., Wang, H., Chen, G., et al. (2020). Metabolism of pancreatic cancer: paving the way to better anticancer strategies. Mol. Cancer 19, 50. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01169-7
Qiu, H., Shao, N., Liu, J., Zhao, J., Chen, C., Li, Q., et al. (2023). Amino acid metabolism in tumor: new shine in the fog? Clin. Nutr. 42, 1521–1530. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.06.011
Qu, Q., Zeng, F., Liu, X., Wang, Q. J., and Deng, F. (2016). Fatty acid oxidation and carnitine palmitoyltransferase I: emerging therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 7, e2226. doi:10.1038/cddis.2016.132
Rastogi, S., Banerjee, S., Chellappan, S., and Simon, G. R. (2007). Glut-1 antibodies induce growth arrest and apoptosis in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 257, 244–251. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.07.021
Rios Garcia, M., Steinbauer, B., Srivastava, K., Singhal, M., Mattijssen, F., Maida, A., et al. (2017). Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1-dependent protein acetylation controls breast cancer metastasis and recurrence. Cell Metab. 26, 842–855. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.018
Roberts, D. J., and Miyamoto, S. (2015). Hexokinase II integrates energy metabolism and cellular protection: akting on mitochondria and TORCing to autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 22, 248–257. doi:10.1038/cdd.2014.173
Röhrig, F., and Schulze, A. (2016). The multifaceted roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer, 16. doi:10.1038/nrc.2016.89
Romero, R., Sayin, V. I., Davidson, S. M., Bauer, M. R., Singh, S. X., LeBoeuf, S. E., et al. (2017). Keap1 loss promotes Kras-driven lung cancer and results in dependence on glutaminolysis. Nat. Med. 23, 1362–1368. doi:10.1038/nm.4407
Rong, S., Xia, M., Vale, G., Wang, S., Kim, C.-W., Li, S., et al. (2024). DGAT2 inhibition blocks SREBP-1 cleavage and improves hepatic steatosis by increasing phosphatidylethanolamine in the ER. Cell Metab. 36, 617–629.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2024.01.011
Saggese, P., Pandey, A., Alcaraz, M., Fung, E., Hall, A., Yanagawa, J., et al. (2024). Glucose deprivation promotes pseudohypoxia and dedifferentiation in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 84, 305–327. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1148
Schlaepfer, I. R., Rider, L., Rodrigues, L. U., Gijón, M. A., Pac, C. T., Romero, L., et al. (2014). Lipid catabolism via CPT1 as a therapeutic target for prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 13, 2361–2371. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0183
Sciacovelli, M., Dugourd, A., Jimenez, L. V., Yang, M., Nikitopoulou, E., Costa, A. S. H., et al. (2022). Dynamic partitioning of branched-chain amino acids-derived nitrogen supports renal cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 13, 7830. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-35036-4
Sen, U., Coleman, C., and Sen, T. (2023). Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase-1: multitasker in cancer, metabolism, and ferroptosis. Trends Cancer 9, 480–489. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2023.03.003
Sharma, D., Singh, M., and Rani, R. (2022). Role of LDH in tumor glycolysis: regulation of LDHA by small molecules for cancer therapeutics. Seminars cancer Biol., 87. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.11.007
She, K., Fang, S., Du, W., Fan, X., He, J., Pan, H., et al. (2019). SCD1 is required for EGFR-targeting cancer therapy of lung cancer via re-activation of EGFR/PI3K/AKT signals. Cancer Cell Int. 19, 103. doi:10.1186/s12935-019-0809-y
Shimano, H., and Sato, R. (2017). SREBP-regulated lipid metabolism: convergent physiology — divergent pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 13, 710–730. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.91
Singha, P. K., Mäklin, K., Vihavainen, T., Laitinen, T., Nevalainen, T. J., Patil, M. R., et al. (2020). Evaluation of FASN inhibitors by a versatile toolkit reveals differences in pharmacology between human and rodent FASN preparations and in antiproliferative efficacy in vitro vs. in situ in human cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 149, 105321. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105321
Su, F., and Koeberle, A. (2024). Regulation and targeting of SREBP-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 43, 673–708. doi:10.1007/s10555-023-10156-5
Sun, Q., Xing, X., Wang, H., Wan, K., Fan, R., Liu, C., et al. (2024). SCD1 is the critical signaling hub to mediate metabolic diseases: mechanism and the development of its inhibitors. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 170, 115586. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115586
Svensson, R. U., Parker, S. J., Eichner, L. J., Kolar, M. J., Wallace, M., Brun, S. N., et al. (2016). Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer in preclinical models. Nat. Med. 22, 1108–1119. doi:10.1038/nm.4181
T, L., C, H., P, F., Z, M., X, W., H, C., et al. (2022). Cancer-associated fibroblast-specific lncRNA LINC01614 enhances glutamine uptake in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Hematol. and Oncol., 15. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01359-4
Tharp, K. M., Kersten, K., Maller, O., Timblin, G. A., Stashko, C., Canale, F. P., et al. (2024). Tumor-associated macrophages restrict CD8+ T cell function through collagen deposition and metabolic reprogramming of the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat. Cancer 5, 1045–1062. doi:10.1038/s43018-024-00775-4
Vaupel, P., and Multhoff, G. (2021). Revisiting the Warburg effect: historical dogma versus current understanding. J. Physiology 599, 1745–1757. doi:10.1113/JP278810
Vettore, L., Westbrook, R. L., and Tennant, D. A. (2020). New aspects of amino acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 122, 150–156. doi:10.1038/s41416-019-0620-5
Walker-Samuel, S., Ramasawmy, R., Torrealdea, F., Rega, M., Rajkumar, V., Johnson, S. P., et al. (2013). In vivo imaging of glucose uptake and metabolism in tumors. Nat. Med. 19, 1067–1072. doi:10.1038/nm.3252
Wang, J., and Li, Y. (2019). CD36 tango in cancer: signaling pathways and functions. Theranostics 9 (9), 4893–4908. doi:10.7150/thno.36037
Wang, C., Ma, J., Zhang, N., Yang, Q., Jin, Y., and Wang, Y. (2015). The acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme: a target for cancer therapy? Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 15, 667–676. doi:10.1586/14737140.2015.1038246
Wang, Y.-N., Zeng, Z.-L., Lu, J., Wang, Y., Liu, Z.-X., He, M.-M., et al. (2018). CPT1A-mediated fatty acid oxidation promotes colorectal cancer cell metastasis by inhibiting anoikis. Oncogene 37, 6025–6040. doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0384-z
Wang, Y., Bai, C., Ruan, Y., Liu, M., Chu, Q., Qiu, L., et al. (2019). Coordinative metabolism of glutamine carbon and nitrogen in proliferating cancer cells under hypoxia. Nat. Commun. 10, 201. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-08033-9
Wang, C., Meng, X., Zhou, Y., Yu, J., Li, Q., Liao, Z., et al. (2021a). Long noncoding RNA CTD-2245e15.3 promotes anabolic enzymes ACC1 and PC to support non-small cell lung cancer growth. Cancer Res. 81, 3509–3524. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3806
Wang, X., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Tian, H., Wang, Y., Jin, J., et al. (2021b). Stem cell factor SOX2 confers ferroptosis resistance in lung cancer via upregulation of SLC7A11. Cancer Res., 81. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0567
Wang, Y., Weixing, Y., Sha, L., Dinguan, G., Jia, H., and Yugang, W. (2022a). Acetyl-CoA carboxylases and diseases. Front. Oncol. 12, 836058. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.836058
Wang, H., Zhou, Y., Xu, H., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Shang, R., et al. (2022b). Therapeutic efficacy of FASN inhibition in preclinical models of HCC. Hepatology 76, 951–966. doi:10.1002/hep.32359
Wang, J., Lin, W., Li, R., Cheng, H., Sun, S., Shao, F., et al. (2022c). The deubiquitinase USP13 maintains cancer cell stemness by promoting FASN stability in small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 12, 899987. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.899987
Wang, J., Yu, X., Cao, X., Tan, L., Jia, B., Chen, R., et al. (2023a). GAPDH: a common housekeeping gene with an oncogenic role in pan-cancer. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 21, 4056–4069. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2023.07.034
Wang, K., Lu, H., Wang, X., Liu, Q., Hu, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2023b). Simultaneous suppression of PKM2 and PHGDH elicits synergistic anti-cancer effect in NSCLC. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1200538. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1200538
Wang, B., Pei, J., Xu, S., Liu, J., and Yu, J. (2024). A glutamine tug-of-war between cancer and immune cells: recent advances in unraveling the ongoing battle. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43, 74. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-02994-0
Ward, P. S., and Thompson, C. B. (2012). Metabolic reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 21, 297–308. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.014
Wedan, R. J., Longenecker, J. Z., and Nowinski, S. M. (2024). Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis is an emergent central regulator of mammalian oxidative metabolism. Cell Metab. 36, 36–47. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2023.11.017
Wen, J., Min, X., Shen, M., Hua, Q., Han, Y., Zhao, L., et al. (2019). ACLY facilitates colon cancer cell metastasis by CTNNB1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38, 401. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1391-9
Wiel, C., Le Gal, K., Ibrahim, M. X., Jahangir, C. A., Kashif, M., Yao, H., et al. (2019). BACH1 stabilization by antioxidants stimulates lung cancer metastasis. Cell 178, 330–345. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.005
Wohlhieter, C. A., Richards, A. L., Uddin, F., Hulton, C. H., Quintanal-Villalonga, À., Martin, A., et al. (2020). Concurrent mutations in STK11 and KEAP1 promote ferroptosis protection and SCD1 dependence in lung cancer. Cell Rep. 33, 108444. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108444
Ww, F., Ht, Z., and M, K. (2023). The role of CD36 in cancer progression and its value as a therapeutic target. Cells, 12. doi:10.3390/cells12121605
Xiang, W., Lv, H., Xing, F., Sun, X., Ma, Y., Wu, L., et al. (2023). Inhibition of ACLY overcomes cancer immunotherapy resistance via polyunsaturated fatty acids peroxidation and cGAS-STING activation. Sci. Adv. 9, eadi2465. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adi2465
Xu, K., Yin, N., Peng, M., Stamatiades, E. G., Shyu, A., Li, P., et al. (2021). Glycolysis fuels phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling to bolster T cell immunity. Sci. (New York, NY), 371. doi:10.1126/science.abb2683
Xuan, Y., Wang, H., Yung, M. M., Chen, F., Chan, W.-S., Chan, Y.-S., et al. (2022). SCD1/FADS2 fatty acid desaturases equipoise lipid metabolic activity and redox-driven ferroptosis in ascites-derived ovarian cancer cells. Theranostics 12, 3534–3552. doi:10.7150/thno.70194
Y, M., Sm, T., Am, H., C, G., W, W., Xy, W., et al. (2018). Fatty acid oxidation: an emerging facet of metabolic transformation in cancer. Cancer Lett., 435. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.006
Yadav, D., Yadav, A., Bhattacharya, S., Dagar, A., Kumar, V., and Rani, R. (2024). GLUT and HK: two primary and essential key players in tumor glycolysis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 100, 17–27. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2024.03.001
Yang, L., Yan, X., Chen, J., Zhan, Q., Hua, Y., Xu, S., et al. (2021a). Hexokinase 2 discerns a novel circulating tumor cell population associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118, e2012228118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2012228118
Yang, S., Kobayashi, S., Sekino, K., Kagawa, Y., Miyazaki, H., Kumar Shil, S., et al. (2021b). Fatty acid-binding protein 5 controls lung tumor metastasis by regulating the maturation of natural killer cells in the lung. FEBS Lett. 595, 1797–1805. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.14106
Yang, H., Deng, Q., Ni, T., Liu, Y., Lu, L., Dai, H., et al. (2021c). Targeted Inhibition of LPL/FABP4/CPT1 fatty acid metabolic axis can effectively prevent the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis to liver cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci., 17. doi:10.7150/ijbs.64714
Yang, L., Chu, Z., Liu, M., Zou, Q., Li, J., Liu, Q., et al. (2023). Amino acid metabolism in immune cells: essential regulators of the effector functions, and promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 16, 59. doi:10.1186/s13045-023-01453-1
Yang, Y., Liu, X., Yang, D., Li, L., Li, S., Lu, S., et al. (2024). Interplay of CD36, autophagy, and lipid metabolism: insights into cancer progression. Metabolism 155, 155905. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2024.155905
Yi, J., Zhu, J., Wu, J., Thompson, C. B., and Jiang, X. (2020). Oncogenic activation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling suppresses ferroptosis via SREBP-mediated lipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 31189–31197. doi:10.1073/pnas.2017152117
Yoo, H. C., Yu, Y. C., Sung, Y., and Han, J. M. (2020). Glutamine reliance in cell metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 52, 1496–1516. doi:10.1038/s12276-020-00504-8
Yu, Y., Nie, Q., Wang, Z., Di, Y., Chen, X., and Ren, K. (2023). Targeting acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 for cancer therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1129010. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1129010
Yu, S.-K., Yu, T., Wang, Y.-M., Sun, A., Liu, J., and Lu, K.-H. (2024). CCT6A facilitates lung adenocarcinoma progression and glycolysis via STAT1/HK2 axis. J. Transl. Med. 22, 460. doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05284-7
Zambrano, A., Molt, M., Uribe, E., and Salas, M. (2019). Glut 1 in cancer cells and the inhibitory action of resveratrol as A potential therapeutic strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 3374. doi:10.3390/ijms20133374
Zappa, C., and Mousa, S. A. (2016). Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 5, 288–300. doi:10.21037/tlcr.2016.06.07
Zhang, D., Li, J., Wang, F., Hu, J., Wang, S., and Sun, Y. (2014). 2-Deoxy-D-glucose targeting of glucose metabolism in cancer cells as a potential therapy. Cancer Lett. 355, 176–183. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.003
Zhang, X., Guo, M., Fan, J., Lv, Z., Huang, Q., Han, J., et al. (2016). Prognostic significance of serum LDH in small cell lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Cancer Biomark. 16, 415–423. doi:10.3233/CBM-160580
Zhang, Y., Yu, H., Zhang, J., Gao, H., Wang, S., Li, S., et al. (2021a). Cul4A-DDB1-mediated monoubiquitination of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via increased S-adenosylmethionine. J. Clin. investigation 131, 131. doi:10.1172/JCI146187
Zhang, W., Sun, Y., Bai, L., Zhi, L., Yang, Y., Zhao, Q., et al. (2021b). RBMS1 regulates lung cancer ferroptosis through translational control of SLC7A11. J. Clin. Invest 131, e152067. doi:10.1172/JCI152067
Zhang, C., Yu, J.-J., Yang, C., Yuan, Z.-L., Zeng, H., Wang, J.-J., et al. (2023). Wild-type IDH1 maintains NSCLC stemness and chemoresistance through activation of the serine biosynthetic pathway. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eade4113. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.ade4113
Zheng, M, Wu, C, Yang, K, Yang, Y, Liu, Y, Gao, S, et al. (2021). Novel selective hexokinase 2 inhibitor Benitrobenrazide blocks cancer cells growth by targeting glycolysis. Pharmacol. Res., 164. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105367
Zhou, F., Ai, W., Zhang, Y., Hu, Q., Gan, M., Wang, J.-B., et al. (2022). ARHGEF3 regulates the stability of ACLY to promote the proliferation of lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 13, 870. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05297-4
Keywords: metabolic reprogramming, lung cancer, glucose, lipid metabolism, amino acid metabolism
Citation: Huang Q, Fan L, Gong M, Ren J, Chen C and Xie S (2024) Metabolic reprogramming in lung cancer and its clinical implication. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1516650. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1516650
Received: 24 October 2024; Accepted: 28 November 2024;
Published: 18 December 2024.
Edited by:
Xuelin Zhou, Capital Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
William W. Feng, Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, United StatesXiao Zhang, Washington University in St. Louis, United States
Vrushank Bhatt, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, United States
Jin-Ming Zhang, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, United States
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Fan, Gong, Ren, Chen and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chen Chen, MTg1ODM4MzA2NzZAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Shenglong Xie, eGllc2hlbmdsb25nQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Qingqiu Huang
Qingqiu Huang Lisha Fan2†
Lisha Fan2†