
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol. , 07 January 2025
Sec. Cardiovascular and Smooth Muscle Pharmacology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1515172
This article is part of the Research Topic Cardiometabolic Diseases: Therapeutic Targets Discovery and Mechanism Study View all 16 articles
 Xiao-Lan Zhao1
Xiao-Lan Zhao1 Zhang-Jing Cao1
Zhang-Jing Cao1 Ke-Di Li1
Ke-Di Li1 Fei Tang1
Fei Tang1 Li-Yue Xu1
Li-Yue Xu1 Jing-Nan Zhang1
Jing-Nan Zhang1 Dong Liu1
Dong Liu1 Cheng Peng1*
Cheng Peng1* Hui Ao1,2*
Hui Ao1,2*Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) causes significant morbidity and mortality globally. Most of the chemicals specifically target certain pathways and minimally impact other diseases associated with ASCVD. Moreover, interactions of these drugs can cause toxic reactions. Consequently, the exploration of multi-targeted and safe medications for treating and preventing ASCVD has become an increasingly popular trend. Gallic acid (GA), a natural secondary metabolite found in various fruits, plants, and nuts, has demonstrated potentials in preventing and treating ASCVD, in addition to its known antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. It alleviates the entire process of atherosclerosis (AS) by reducing oxidative stress, improving endothelial dysfunction, and inhibiting platelet activation and aggregation. Additionally, GA can treat ASCVD-related diseases, such as coronary heart disease (CHD) and cerebral ischemia. However, the pharmacological actions of GA in the prevention and treatment of ASCVD have not been comprehensively reviewed, which limits its clinical development. This review primarily summarizes the in vitro and in vivo pharmacological actions of GA on the related risk factors of ASCVD, AS, and ASCVD. Additionally, it provides a comprehensive overview of the toxicity, extraction, synthesis, pharmacokinetics, and pharmaceutics of GA,aimed to enhance understanding of its clinical applications and further research and development.
According to the latest statistics, the absolute number of CVD incident cases and deaths remains an increasing worldwide (Li et al., 2023). It is projected that by 2050, In the United States, 61% of adults will have some form of cardiovascular disease, primarily due to increases in hypertension, obesity, and diabetes (Joynt Maddox et al., 2024). And ischaemic heart disease will remain the leading cause of cardiovascular deaths (20 million deaths) (Chong et al., 2024). Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is a major type of cardiovascular disease (CVD), with risk factors that include hypertension, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity. Preventive measures should involve lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking, as well as pharmacological interventions to control blood pressure, blood glucose, and lipid levels (Al Rifai et al., 2022; Pasquel et al., 2018; Qiao et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2023).
However, traditional risk assessment tools tend to underestimate the risk for high-risk populations, while the application of emerging technologies, lifestyle interventions, and personalized treatments is hindered by issues such as cost, resources, and adherence to treatment. There is an urgent need for innovative, safer, and more accessible strategies to improve prevention and management. However, the treatment of acute cardiovascular diseases often involves multiple medications, which can lead to side effects and toxicity (Barkas et al., 2024). In this context, natural multi-target drugs such as quercetin, berberine, and curcumin exhibit significant commercial potential (Chen et al., 2020; Deng et al., 2020; Lv et al., 2024). These natural products, distinguished from synthetic chemicals, hold promise as alternative options for the prevention and treatment of ASCVD, owing to their low toxicity and multifunctional effects. Therefore, exploring natural compounds for the prevention and treatment of ASCVD is of critical importance, as it holds the potential to offer substantial benefits in managing this condition.
GA (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid), first identified by Scheele in 1786 and derived from oak apple extract, is a natural secondary metabolite predominantly extracted from various fruits, plants, and nuts (Wianowska and Olszowy-Tomczyk, 2023). This compound is extensively utilized as a food preservative, in brewing, cosmetics, and food packaging (Limpisophon and Schleining, 2017).
GA exhibited multi-target and multi-level pathophysiological effects, demonstrating significant therapeutic potential in several key pathological processes of ASCVD. In addition to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, GA regulated lipid metabolism to lower cholesterol levels, improved insulin sensitivity, reduced blood glucose levels, and decreased systolic blood pressure, thereby mitigating the risk of acute cardiovascular events. Furthermore, GA enhanced endothelial function, inhibited platelet aggregation and thrombosis, reduced abnormal vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and stabilized atherosclerotic plaques, comprehensively addressing the pathological processes of ASCVD. These characteristics underscored GA’s immense potential in the prevention and treatment of ASCVD, positioning it as a promising natural candidate for further research and development (Choubey et al., 2018; Lekakis et al., 2005).However, these findings have not been systematically summarized, which will limit the clinical application and further development of GA.
Consequently, this review systematically assesses the research on the therapeutic potential of GA across various stages of ASCVD progression, pointing out that GA is a promising drug candidate applied in the prevention and treatment of ASCVD. We anticipate that this comprehensive review will further facilitate development and application of GA as a therapeutic agent against ASCVD.
GA possesses a wide range of pharmacological effects and has demonstrated potential therapeutic value in various aspects of ASCVD. In this section, the availability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of GA were summarized.
GA, a phenolic compound, is found in various plants, including black tea, green tea, quince, pomegranate, oranges, grapes, and berries. Given the wide range of sources containing GA, various extraction techniques, including hot water extraction, supercritical CO2 extraction, solid-phase extraction, and ultrasonic-assisted extraction, have been developed (Du et al., 2009; Murga et al., 2000; Palma et al., 1999; Pawar and Surana, 2010).
Researchers have found that hot water extraction is the primary method for extracting antioxidants. Pawar et al. optimized the extraction parameters forextracting GA from Caesalpinia decapetala. The ideal conditions were an extraction temperature of 65–70°C, an extraction period of 48 h, and a solvent mixture of ethanol to water (70:30). Under these optimal conditions, the maximum yield of GA was 17.85% (Pawar and Surana, 2010). However, the extraction of GA from Emblica officinalis, by the preparation of molecularly imprinted microspheres and nanoparticles through precipitation polymerization and subsequent elution with hot water, significantly increased the extraction yield to 28% (Pardeshi et al., 2014). Additionally, GA was extracted from pomegranate rind using solid-phase extraction with surface-imprinted polymers on magnetic carbon nanotubes with a yield of 3.16 mg/g (Hao et al., 2015). The optimum extraction yield of GA (8.57 mg/g) was achieved by preparing hydrophilic molecularly imprinted chitosan and employing solid-phase microextraction methods, using the response surface methodology strategy (Li and Row, 2019). Khodaie et al. successfully extracted GA (50.54%) from the seeds of the sumac species Rhus coraria using supercritical CO2 with ethanol as a co-solvent (Khodaie and Ghoreishi, 2021). In addition, when GA was extracted from the leaves of Ficus auriculata, alkaline water and ultrasonic-assisted extraction were used. This method was environmentally friendly and safe. The results showed that the extraction yield with weak alkaline water was 284.2 mg/L, second only to 50% methanol (Baite et al., 2021).
It have been found that GA was synthesized through the shikimic acid pathway (Fernandes and Salgado, 2016; Wu et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2009). Researches showed that shikimate dehydrogenase (SDH) was an essential enzyme in the shikimate pathway for GA synthesis. The aroE mutant strain of Escherichia coli could produce GA through functional complementation with plant-derived SDH. In transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) expressing SDH from walnut (Juglans regia), accumulation of GA was increased by 500% (Muir et al., 2011). Additionally, with the high-yield, high-titer synthesis of 3-dehydroshikimic acid from glucose using recombinant E. coli, GA was efficiently synthesized from 3-dehydroshikimic acid by choosing the appropriate solvent (such as acetic acid) and optimizing the catalytic system (such as using Cu (OAc)2 and ZnO). And the yield of GA was significantly increased to 67% (Kambourakis and Frost, 2000).
Additionally, in nature or within plants, GA was synthesized through the degradation of tannic acid via tannase, a glycoprotein esterase. This enzyme was produced by fermentation with various microorganisms, particularly fungi from the Aspergillus and Penicillium genera (Aguilar-Zárate et al., 2015; Dhiman et al., 2018). For example, the novel Penicillium roqueforti strain could produce both tannase and GA simultaneously (Andrade et al., 2018). Moreover, the marine Aspergillus awamori strain BTMFW032, under deep fermentation conditions, was able to simultaneously produce GA and tannase, resulting in a 15-fold increase in the yields of both tannase and GA (Beena et al., 2011). Furthermore, other microorganisms such as Rhodotorula pilimanae A45.2 and Bacillus spheroides have also been noted for their abilities to co-produce GA and tannase, with the latter achieving high efficiency in converting tannic acid to GA (90.80% crystallization), making it the most potent bacterial tannase producer for GA synthesis (Kanpiengjai et al., 2020; Raghuwanshi et al., 2011). Recent research discovered that a high-activity PobA variant, Y385F/T294A-PobA, was developed from the hydroxyphenylacetic acid hydroxylase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This variant exhibited a molar conversion rate of up to 93%, providing a promising pathway for the biomanufacturing of GA and its derivatives (Chen et al., 2017). In summary, GA is primarily synthesized through the shikimic acid pathway, and in some cases, it is also produced as a by-product of tannic acid decomposition.
It is well known that GA has a wide range of sources, and different forms of GA exhibit significant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters. Studies found that compared to pure GA, the half-life (T1/2) (93.72–128.52 min) and time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) (40–100 min) of GA in P. capitatum extracts were prolonged (Ma et al., 2015). After oral administration of Japanese toad venom extract SD in rats, the pharmacokinetics parameters for GA were determined using a single-compartment model. It was found that Tmax, maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) T1/2, AUC0-∞, in SD rats were 1.40 ± 1.13 h, 35.5 ± 10.2 ng/mL, 3.21 ± 4.56 h, 199.7 ± 43.9 ng/mL*h (Yu X.-A. et al., 2018). After oral administration of Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract to SD rats, the T1/2, Cmax and AUC0–∞ of GA were 1.54 ± 0.43h, 919.48 ± 35.03 ng/mL, 8213.20 ± 733.40 ng•h/mL (Chen et al., 2018a). Additionally, after administration of a single oral dose of tea (containing 0.3 mmol of GA) to 10 volunteers, T1/2 was 1.06 ± 0.06 h, and Cmax was 2.09 ± 0.22 μmol/L (Shahrzad et al., 2001). Pharmacokinetic differences between GA and GA-loaded carboxymethylchitosan nanoparticles (GANPs) were examined in SD rats after gastric administration. Nanoparticles significantly improved area under the curve (AUC) (13.8 mg/min/mL and 5.2 mg/min/mL) and T1/2 (2.0 h and 2.7 h) of GA (Y. Zhao et al., 2020a). Additionally, dosage also affected GA absorption. Repeated daily exposure to grape seed polyphenol extract (GSPE) significantly increased the bioavailability of GA. When the GSPE dose reached 100 mg/kg BW, AUC0–8h of GA significantly was increased from 512.7 to 673 ng/mL•h (Ferruzzi et al., 2009). The AUC0–8h (area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 8 h) was used to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of the compound (Alpízar et al., 2024). Yu et al. found that pathological conditions can alter the pharmacokinetics of GA. In the study, compared to normal rats, the absorption rate of GA in rats with myocardial infarction was slower. When the dose of GA was 100 mg/kg, the AUC decreased by approximately 23%. The Cmax was reduced by 2.5 times, and the half-life was significantly prolonged (Yu Z. et al., 2018). In summary, absorption of GA was altered by different administration route, dosage, and health status.
Also, GA was extensively distributed across various tissues, predominantly in the kidneys, followed by the heart, liver, spleen, and lungs (Chen et al., 2018b). Notably, it was primarily localized in the kidneys and liver (Liu et al., 2019). FW et al. reported that GA showed a targeted distribution in renal tissues, achieving a concentration of 1218.62 ng/g 1 hour post-administration of 60 mg/kg of Cephalonia extract (equivalent to 12 mg/kg GA)(Ma et al., 2016; Wei et al., 2020).In addition, researches found that the metabolites of GA underwent typical methylation reactions in the liver, which increased the polarity of the molecules, thereby facilitating their excretion in the kidneys. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis revealed that GA was metabolized into several structurally similar compounds, including pyrogallol, 2-O-methyl-phenylenetriol, and 4-O-methylgallic acid (Yasuda et al., 2000). Additional researches by FW et al. on the urinary excretion of Pseudomonas cephalosporium extracts indicated that GA underwent significant metabolism, primarily to 4-methyl GA (4-Ω) and 4-methyl protocatechuic acid (4-OMePCA) (Hsu C.-L. et al., 2007). Other predominant mammalian metabolites included 3-O-methyl GA, 4-O-methyl GA, and 3,4-O-dimethyl GA (Hodgson et al., 2000). High-performance liquid chromatography analyses demonstrated that GA was predominantly metabolized into 4-O-methyl GA in peripheral blood and urine (Shahrzad and Bitsch, 1998). Overall, GA was absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, primarily distributed in the kidneys, then metabolized in the liver, and excreted by the kidneys.
The development of various formulations has enhanced the controlled release, bioavailability, and therapeutic efficacy of GA under different disease conditions. The utilization of contemporary technologies and encapsulation methodologies has facilitated the development of an array of formulations of GA, encompassing nanoparticles, hydrogels, gels, inclusion complexes, microcapsules, nanoemulsions and liposomes.
Killedar et al. found that nanoparticles effectively controlled drug release, thereby enhancing the bioavailability of GA. Formulating GA into chitosan nanoparticles effectively controls the release of the drug, achieving an accumulative in vitro release rate of 77.16% for GA (Patil and Killedar, 2021a). The modification of chitosan nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid resulted in the creation of HA@CS-GA NPs, which proved to be an effective treatment for recalcitrant skin diseases such as psoriasis (Sheikh et al., 2023). Further studies developed a lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle system (LPHNs) containing GA, which penetrated deeper layers of the skin more effectively, demonstrating a higher drug release rate of 79% ± 0.001% (Hazari et al., 2023). Encapsulating GA into nanoparticles using gum arabic (GANPs) enhanced its bioavailability (Hassani et al., 2020). Additionally, the combination of GA with magnetite nanoparticles constituted an innovative nanotechnology-based drug formulation that, with the assistance of an external magnetic field, crossed the blood-brain barrier (Azarmi et al., 2023).
In addition, gels and hydrogels effectively control drug release and are mostly used for dermal administration. Research has found that the gel formulations of GA were commonly used in cosmetics, reducing lipid peroxidation by 33.97%, which confirmed their antioxidant effects in the skin’s stratum corneum (Monteiro E Silva et al., 2017). Additionally, research has developed and characterized a poloxamer gel containing the antioxidant molecule GA, capable of precisely controlling drug release and enhancing the local concentration of the drug at the target site, typically used for topical administration in melanoma skin treatments (Sguizzato et al., 2020). Additionally, Hydrogels based on chitosan (CS) and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (AMPS) were prepared using free radical polymerization techniques for the controlled release of GA (Yu et al., 2022). Hydrogel films based on sodium alginate and a polyvinyl alcohol-acrylic acid copolymer loaded with GA were also used for skin wound healing (Naeem et al., 2022). Furthermore, the water absorption rate of hydrogels loaded with GA-based carbon nanoparticles (GACNPs) was significantly higher than that of blank hydrogels, demonstrating a desirable characteristic for wound dressing applications (Dechsri et al., 2024).
Besides this, other GA-related formulations can also control drug release and enhance drug delivery efficiency and bioavailability. Inclusion complexes formed by ferulic acid (FA) and GA with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) through spray drying techniques have enhanced drug release and bioavailability (Patil and Killedar, 2021b). Erik and colleagues found that encapsulating GA in a polymer matrix composed of sodium alginate and pectin provided an alternative method for protecting and controlling the release of GA (Nájera-Martínez et al., 2023). Furthermore, the developed self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) loaded with GA offered an effective method for enhancing the transdermal delivery efficiency of poorly soluble drugs (Khan et al., 2024). Moreover, GA was encapsulated in stealth liposomes, which were functionalized with transferrin (Tf) to deliver the drug directly to the brain for sustained release (Andrade et al., 2022). A novel co-loaded nanoliposome system containing GA and quercetin was developed, enhancing the stability and bioavailability of the drugs in the body (Al-Samydai et al., 2023).
In summary, the use of various formulation technologies has enabled the precise and effective application of GA across different areas, adding significant value to its clinical use.
Hyperlipidemia, arterial stiffening, and AS collectively constitute the core pathological basis of ASCVD (Dutta et al., 2024; Hoshino et al., 2024; Szołtysek-Bołdys et al., 2024). This process begins with early lipid metabolism abnormalities, gradually leading to vascular dysfunction and structural changes, ultimately resulting in the onset and progression of ASCVD. GA, through its inhibitory effects on hepatic cholesterol synthesis, multifaceted vascular protection, and its role in suppressing atherosclerosis, offered a novel strategy for the comprehensive intervention of ASCVD.
Recent studies have revealed that hyperlipidemia, characterized by elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B (ApoB), directly promotes the onset and progression of atherosclerosis, making it a key pathogenic factor in ASCVD (Correction, 2023). Studies have demonstrated that GA, a natural compound, effectively improves lipid profiles by inhibiting lipid synthesis, promoting lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation, and inducing adipocyte apoptosis, thereby exerting a substantial lipid-lowering effect (Figure 1).
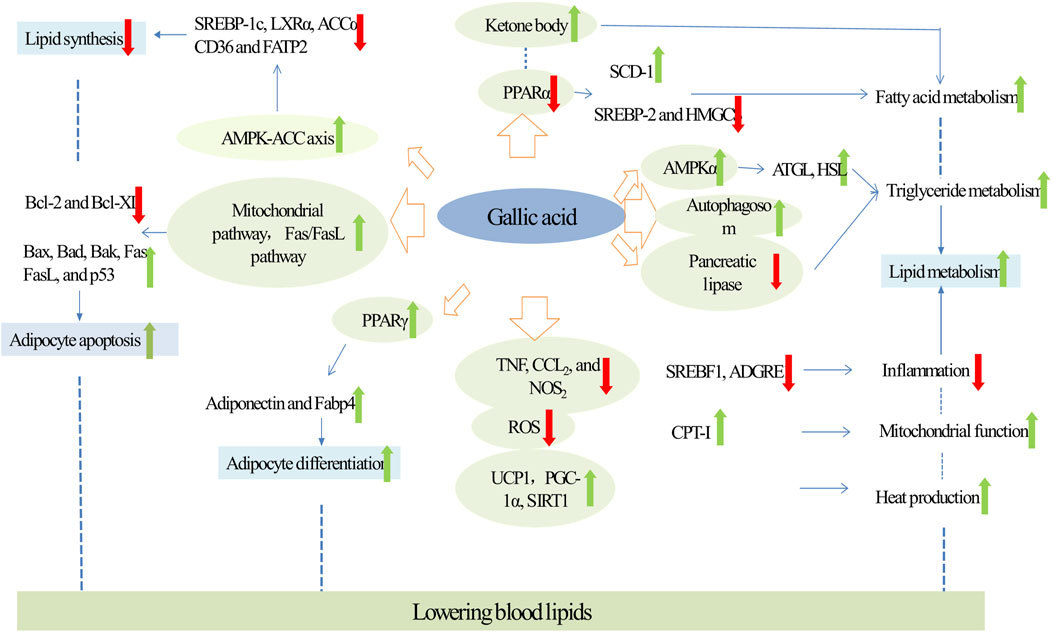
Figure 1. Molecular targets and mechanism of action of GA in hyperlipidemia. Green arrows and red arrows indicate promotion and inhibition, respectively. Description: This figure illustrates how GA regulates lipid metabolism in patients with hyperlipidemia. GA inhibits lipid synthesis by activating the AMPK pathway, downregulating SREBP-1c, SREBP-2, and ACCα. Simultaneously, it promotes fatty acid oxidation by decreasing PPARα expression and increasing ketone body levels. GA also reduces triglyceride accumulation by activating AMPKα, promoting autophagy, and inhibiting HSL and pancreatic lipase. Furthermore, GA suppresses inflammation by reducing TNF, CCL-2, and NOS levels, while enhancing mitochondrial function through UCP1, PGC-1α, and SIRT1. Additionally, GA induces adipocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL and promotes adipocyte differentiation, leading to increased production of adipokines such as adiponectin and Fabp4, thereby indirectly influencing lipid levels. These combined effects underscore GA’s potential for effective control of hyperlipidemia. Green arrows indicate promoting effects, while red arrows represent inhibitory actions.
It has been established that GA can ameliorate lipid accumulation by inhibiting lipogenesis, a critical strategy for lowering lipid levels. GA reduced the activity of transcription factors involved in lipid synthesis. Particularly noteworthy is its targeting of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) family, which acts as a rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid metabolism, thereby reducing overall lipid synthesis (Chen et al., 2019; Yeudall et al., 2022). GA strongly activated the AMPK-ACC axis in a dose-dependent manner, thereby inhibiting lipid synthesis. In mice fed high-fat diet (HFD), GA reduced the mRNA expressions of the lipidogenesis marker ACC, FAS (Fatty Acid Synthase)/B-actin, ACC/B-actin and Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Beta (Sousa et al., 2020). Futhermore, in HepG2 cells, GA treatment activated AMPK signaling and reduced mRNA expression of key transcription factors in fatty acid synthesis, including SREBP-1c, LXRα, and ACCα, as well as fatty acid transporter proteins such as CD36 and FATP2, which mitigated palmitic acid-induced lipid accumulation (Tanaka et al., 2020a). In summary, GA primarily inhibited lipogenesis and improved lipid profiles through the AMPK pathway.
Researches have demonstrated that GA mitigated lipid accumulation by enhancing lipid metabolism which involved s several key pathways.
On one hand, GA directly promoted lipid metabolism. Firstly, GA treatment promoted fatty acid metabolism. Specifically, GA increased beta-oxidation of fatty acids and elevated levels of ketone body metabolites which are produced during fatty acid catabolism. This process enhanced lipolysis, thereby reducing hepatic cholesterol accumulation. In mice with HFD-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), GA treatment raised ketone body levels in both serum and urine, enhanced beta-oxidation in the liver, and reduced excessive fat accumulation in intracellular vacuoles. Additionally, GA treatment decreased liver triglyceride (TG), cholesterol, and fatty acid levels (Chao et al., 2014a). Peroxisome proliferator-activatedve receptor alpha (PPARα) regulates genes involved in lipid metabolism, influencing lipid homeostasis (Bougarne et al., 2018). In HFD mice, GA could also significantly reduce the expression of PPARα. It downregulated the expression of the lipogenic enzyme monounsaturated fatty acid synthase (SCD-1) and upregulated the expressions of key genes for triglyceride synthesis, such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP-2) and the cholesterol synthesis gene β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase (HMGCS), which led to the inhibition of cholesterol synthesis and the reduction of lipid accumulation (Chao et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2021).
Secondly, GA treatment enhanced triglyceride metabolism. Pancreatic lipase was essential for breaking down triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids, which prevented the absorption and digestion of triglycerides (Modanwal et al., 2024). In diet-induced obese mice, GA inhibited triglyceride uptake and digestion by decreasing pancreatic lipase activity (Oi et al., 2012). Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) and hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) are key enzymes in lipolysis (Grabner et al., 2021). Studies have shown that GA increased ATGL expression in the perirenal adipose tissue of HFD rats, leading to decreased hypertriglyceridemia and fat accumulation (Huang et al., 2018). In bovine subcutaneous adipocytes, GA reduced TG levels b increasing the expression of lipolysis-related genes such as ATGL and HSL, and activating the metabolic regulator AMPKα (Jin et al., 2022). Moreover, GA promoted triglyceride metabolism by inducing autophagy. According to Singh et al., autophagy is a critical pathway for regulating cellular lipid levels by digesting lipid droplets in autophagic lysosomes, thus reducing TG storage (Grabner et al., 2021). In HepG2 cells, an increase in autophagosome formation, marked by the conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II, led to a reduction in oleic acid (OA)-induced TG accumulation (Doan et al., 2015).
On the other hand, GA treatment can also indirectly enhance lipid metabolism. Firstly, GA treatment can indirectly enhance lipid metabolism by inhibiting inflammation. Increasing evidences suggested that inflammation in adipose tissue triggered lipolysis, leading to the excessive release of free fatty acids and subsequent hepatic lipid accumulation (Badmus et al., 2022; van Dierendonck et al., 2022). By reducing inflammatory responses, GA potentially lowered the risk of abnormal lipid metabolism and related diseases. In dust-exposed HFD-induced rats, GA pretreatment notably reduced the expression of NF-κB, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and the serum levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (Fanaei et al., 2021). In the white adipose tissue of diet-induced obese mice, GA diminished the expressions of Il6, Nos2, Ptgs2, Adgre1 and Srebf1. Moreover, in a co-culture of 3T3-L1 adipocytes and RAW 264 macrophages, treatment with GA resulted in a significant reduction in the expression of TNF, CCl2 and NOS2. Consequently, GA may be mitigate adipose tissue inflammation by suppressing the expression of inflammatory mediators, either within the white adipose tissue or in macrophages (Tanaka et al., 2020b).
Secondly, GA treatment can enhance lipid metabolism by improving mitochondrial function. Mitochondria are crucial for cellular energy production and lipid metabolism (Pernas, 2024). Moreover, GA can promote lipid metabolism by improving mitochondrial function, a key factor in cellular energy production and lipid metabolism. Specifically, GA significantly increased the expression of PGC1α target genes such as mitochondrial transcription factor A, nuclear respiratory factor-1, and nuclear respiratory factor-2, thereby upregulating fatty acid β-oxidation enzymes like carnitine palmitoyltransferase-I, and promoting fatty acid oxidative metabolism in mitochondria (Doan et al., 2015). Furthermore, in rats induced with HFD, GA reduced body weight, adipose tissue weight (peritoneal and epididymal), triglyceride (TAG) level, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level, phospholipids, and total cholesterol level by enhancing antioxidant activity (Hsu and Yen, 2007). For example, in db/db mice fed with a high-fiber diet, GA enhanced intracellular antioxidant defenses, inhibited reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and boosted hepatic antioxidant enzymes (GSH, SOD, GST), thereby promoting lipid metabolism (Hsu and Yen, 2007; Lee et al., 2021; Punithavathi V. et al., 2011).
Thirdly, GA improved lipid metabolism by increasing thermogenesis, which was associated with the AMPK/Sirt1/PGC1α pathway. Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is integral to lipid metabolism as it increased heat production through enhanced energy metabolism (Jung et al., 2019). Bioinformatics analyses have identified SIRT1 as a significant player in thermogenesis. PGC-1α is known to regulate thermogenesis in BAT (Rao et al., 2014; Zhang J. et al., 2022). In the BAT of HFD-fed mice, treatment with GA elevated the expression of SIRT1 and PGC1-alpha mRNA, enhancing thermogenesis and improving overall body metabolism (Paraíso et al., 2019). Furthermore, GA regulated key thermogenic factors primarily by activating the AMPK pathway. GA treatment activated this pathway and significantly upregulated the expression of UCP1, a crucial regulator of heat production in BAT. It also increased the expression of energy expenditure-related genes such as UCP3, PGC1β, and β3-Adr, contributing to body weight reduction in HFD-induced obese mice (Doan et al., 2015).
In conclusion, GA significantly promoted lipid metabolism both directly, by enhancing fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism, and indirectly, through the inhibition of inflammation, improvement of mitochondrial function, and stimulation of thermogenesis.
GA has been demonstrated to reduce lipid accumulation by inducing adipocyte apoptosis, a process that entails the regulated, active death of adipocytes through apoptosis pathways. GA triggers adipocyte apoptosis via two primary pathways, outlined as follows:
GA can induce adipocyte apoptosis through the intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway. In 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, GA increased the expression and release of mitochondrial cytochrome c into the cytoplasm, which significantly upregulated the expression of apoptosis-related enzymes, such as caspase-3 and caspase-9, thereby reducing cell viability (Hsu F.-L. et al., 2007). Additionally, in subcutaneous preadipocytes, GA altered the expression ratio of pro- and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family, decreasing anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL, and markedly increasing pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bax, Bad, and Bak, which reduces the viability of these cells (Jin et al., 2022). Indeed, the extrinsic apoptosis pathway, activated by death receptors, is crucial for cellular apoptosis. This pathway is primarily mediated by fas cell surface death receptor/fas ligand (Fas/FasL) and significantly modulated by the p53 protein (Mustafa et al., 2021; R. Zhao et al., 2020). Similarly, GA modulated the Fas/FasL pathway, contributing to p53-mediated induction of apoptosis in adipocytes. In 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, GA elevated the expressions of Fas, FasL, and p53, diminished adipocyte viability, and decreased lipid accumulation (Hsu C.-L. et al., 2007).In summary, GA disrupted adipocyte viability and induces apoptosis via both the mitochondrial and death receptor pathways.
GA indirectly regulated lipid levels by promoting adipocyte differentiation. Torres et al. have found that this is a process that increases the production of adipokines (such as lipocalin) and enhances oxidase activity (Pérez-Torres et al., 2021). A key factor in this process is PPARγ, a ligand-activated transcription factor from the nuclear receptor family, pivotal in adipocyte differentiation (Hernandez-Quiles et al., 2021). In diet-induced obese mice, GA reduced serum triglyceride concentrations and significantly increased PPARγ protein level in white adipose tissue, thereby enhancing adipocyte differentiation (Bak et al., 2013). Additionally, in GA-treated mouse 3T3-L1 cells, expressions and levels of both adiponectin, a crucial protein hormone for this process—and fatty acid-binding protein-4 (Fabp4), a target of PPARγ and a marker of adipocyte differentiation were increased. Furthermore, GA treatment boosted the secretion and expression of lipocalin, reduced adipocyte viability, and ameliorated lipid accumulation (Makihara et al., 2016; Tanaka et al., 2020b).
In conclusion, it was evident that GA promoted adipocyte differentiation, leading to enhanced production of adipokine, which in turn indirectly influenced lipid levels.
AS is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease and the basis of ASCVD (Hafiane and Daskalopoulou, 2022). The pathology of atherosclerosis involves damage to arterial endothelial cells, typically caused by factors such as hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes. This damage leads to the oxidation of LDL within the vessel walls, initiating an inflammatory response and the formation of foam cells. These foam cells gradually develop into plaques. As these plaques grow, they cause significant changes in vascular function and structure, including platelet activation, proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle, and thickening and hardening of the arterial walls with narrowing of the lumen (Jiang et al., 2022). These changes decrease blood flow, increase the risk of thrombosis, and can ultimately lead to various cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease (Dasagrandhi et al., 2022). Studies have demonstrated that GA exhibited multiple biological activities and showed significant potential in the treatment of AS. GA enhanced endothelial cell viability through its antioxidant properties and by regulating apoptosis-related enzymes. It also reduced platelet activation and aggregation by inhibiting P-selectin on platelets. Additionally, GA effectively regulated the proliferation and migration of VSMCs by modulating key cell cycle signals and pathways (Appeldoorn et al., 2005; Chang et al., 2012a; Chung et al., 2020). In conclusion, GA could intervene in the pathogenesis of AS through multiple mechanisms, slowing disease progression and improving prognosis, making it a promising candidate for AS treatment (Figure 2).
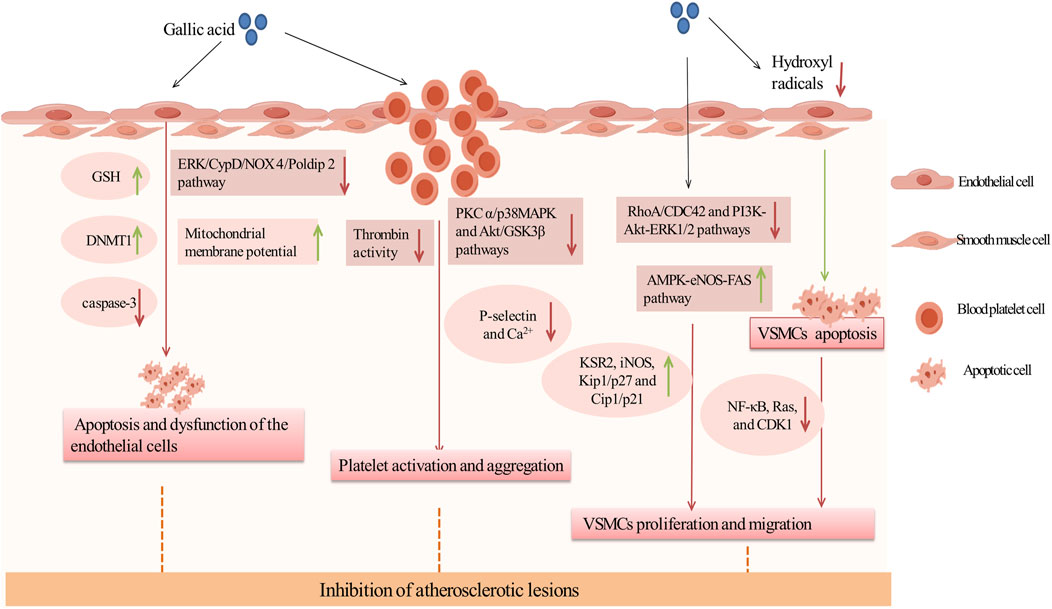
Figure 2. Inhibition of atherosclerotic lesions by GA. Green arrows and red arrows indicate promotion and inhibition, respectively. Description: This figure illustrates how GA inhibits atherosclerotic lesions through multiple mechanisms. GA protects endothelial cells by increasing GSH levels and DNMT1 expression to reduce apoptosis, while improving mitochondrial function by inhibiting the ERK/CypD/NOX4 pathway. It also inhibits platelet activation and aggregation by suppressing thrombin activity, downregulating the PKC and p38/MAPK pathways, reducing Ca2⁺ influx, and decreasing P-selectin expression. Additionally, GA suppresses VSMC proliferation and migration by inhibiting the RhoA/CDC42 and PI3K-Akt-ERK1/2 pathways, while promoting VSMC apoptosis through the AMPK-eNOS-FAS pathway and mitigating oxidative stress caused by hydroxyl radicals (•OH). These effects collectively stabilize atherosclerotic plaques and prevent their progression. Green arrows indicate promotion, while red arrows represent inhibition.
Research showed that GA preserved vascular health by preventing endothelial cell apoptosis and dysfunction, making it a key strategy against AS. Initially, GA can directly reduce apoptosis. In various mouse models, DNA (Cytosine-5)-Methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) was crucial for cell survival, and proteasome inhibitors can prevent endothelial cell apoptosis and reduce mortality, significantly aiding in endothelial protection (Wesley et al., 2024; Zhao et al., 2024). In EAhy926 and HBEC-5i cells exposed to a mixture of homocysteine, adenosine, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) (DL Hcy Ado TNF), GA effectively restored DNMT1 expression, reduced the activity of the chymotrypsin-like proteasome, significantly inhibited caspase-3 expression, and alleviated apoptotic effects and granule formation (Kam et al., 2014).
Secondly, GA can damage endothelial cells by reducing oxidative stress. Endothelial dysfunction, a precursor in atherosclerosis pathogenesis, was primarily driven by oxidative stress (Panda et al., 2022). GA acted as an antioxidant to counteract oxidants generated in the peroxidase cycle. In human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) exposed to high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, GA reduced oxidants produced in the peroxidase cycle, and significantly enhanced cell viability (Serrano et al., 2010). Furthermore, in a cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cell model of oxidative stress (o-toluene-3-phenol), GA at relatively low concentrations enhanced endothelial cell viability and significantly reduced o-toluene-3-phenol-induced cytotoxicity. This was primarily attributable to an elevation in total intracellular GSH levels in the presence of low concentrations of GA. However, no enhancement in SOD or catalase activity was observed (Goszcz et al., 2017). In addition, recent studies have shown that GA can also ameliorate endothelial cell injury by inhibiting endothelial cell mitochondrial dysfunction, mainly through the ERK/CypD/NOX 4/Poldip 2 pathway. In Ang II-induced HUVECs, GA inhibited Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) phosphorylation, Cyclophilin D (CypD) expression, the interaction of NOX4 and Poldip 2, and lowered mitochondrial ROS levels, resulting in an increase in the mitochondrial membrane potential of the HUVECs cells, thereby alleviating endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction (Sun et al., 2023). Thus, GA may inhibit oxidative stress and ameliorate endothelial cell dysfunction by increasing total GSH levels and mitochondrial membrane potential.
Inhibition of platelet activation and aggregation constituted a key anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of GA in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.This effect was primarily associated with platelet P-selectin. In both normolipidemic C57/Bl6 and aged atherosclerotic ApoE-deficient mice, GA improved vascular cell adhesion molecule function and inhibit platelet activation prior to platelet activation. Further research has found that GA inhibited the interaction between P-selectin and platelets in HL60 cells, thereby preventing platelet activation (Appeldoorn et al., 2005). Futhermore, in platelet-rich plasma stimulated by ADP or U46619 (a thromboxane A2 analog), GA reduced the adherence of platelets to white blood cells and inhibited the formation of platelet-leukocyte aggregates. It was shown that GA reduced intracellular Ca2+ level by inhibiting phosphorylation of Protein Kinase C alpha (PKCα) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) in platelets, as well as phosphorylation of Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), leading to a significant reduction in ADP- and U46619-induced platelet aggregation and platelet P-selectin expression in a concentration-dependent manner (Chang et al., 2012b). In conclusion, GA improves platelet aggregation by inhibiting the expression of P-selectin, which may be related to PKC α/p38 MAPK and Akt/GSK3β pathways.
Additionally, GA could reduce the initial activation of platelets by inhibiting thrombin activity. Negrier et al. identified thrombin as a key regulatory factor in platelet activation and aggregation, enhancing adhesion and aggregation between platelets by promoting fibrin formation (Negrier et al., 2019). In platelet aggregation assays involving thrombin-stimulated platelets, GA demonstrated a reduction in aggregation by approximately 35%. Subsequent studies confirmed that GA significantly inhibited thrombin by directly binding to the thrombin protein, thereby rapidly stabilizing its conformation and reducing platelet aggregation (Zhang et al., 2022b).
In summary, GA reduces platelet activation and aggregation by inhibiting P-selectin and thrombin activity.
Firstly, GA inhibited the proliferation of VSMCs by inducing their apoptosis. In cultured VSMCs from rat aortas, GA treatment inhibited oxidative stress caused by hydroxyl radicals and promoted apoptosis, characterized by cytoplasmic shrinkage, vesicle formation, and nuclear condensation, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (Qiu et al., 2000). Secondly, Clark et al. have demonstrated that GA decelerated cell cycle progression in VSMCs through reducing signaling pathways associated with growth, mobility, and senescence, thereby inhibiting the over-proliferation of VSMCs (Clark et al., 2022). In TNF-α-stimulated A7r5 rat aortic VSMC, GA inhibited the expression and phosphorylation of the cytoskeletal proteins ras homolog family member A (RhoA), Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1), and cell division cycle 42 (CDC42). This resulted in a reduction in TNF-α-induced cell migration. Furthermore, GA inhibited the phosphorylation of PI3K, Akt and ERK, and regulated the expression of inflammatory proteins (reducing the activation of NF-κB and Ras, and increasing the expression of iNOS and Kinase Suppressor of Ras 2), and increased the expression of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog deleted on Chromosome 10 (PTEN), thereby inhibiting TNF-α-induced cell proliferation (Chung et al., 2020). Furthermore, in OA-treated VSMC, GA treatment activated AMPK and eNOS, and inhibited fatty acid synthase (FAS), decreased the levels of cytokinin B1 and cytokinin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), and increased the levels of Kip1/p27 and Cip1/p21, which led to the accumulation of the G2/M phase of the cell cycle, thereby slowing down cell cycle progression and inhibiting VSMC proliferation. The specific inhibitor of AMPK, Compound C, was observed to reduce GA-induced eNOS activation and nitric oxide production, thereby underscoring the pivotal role of AMPK in this process (Ou et al., 2013). In summary, GA inhibited the RhoA/CDC42 and PI3K-Akt-ERK1/2 pathways and activated the AMPK-eNOS-FAS signaling pathway, thereby suppressing the migration and proliferation of VSMCs (Figure 3).
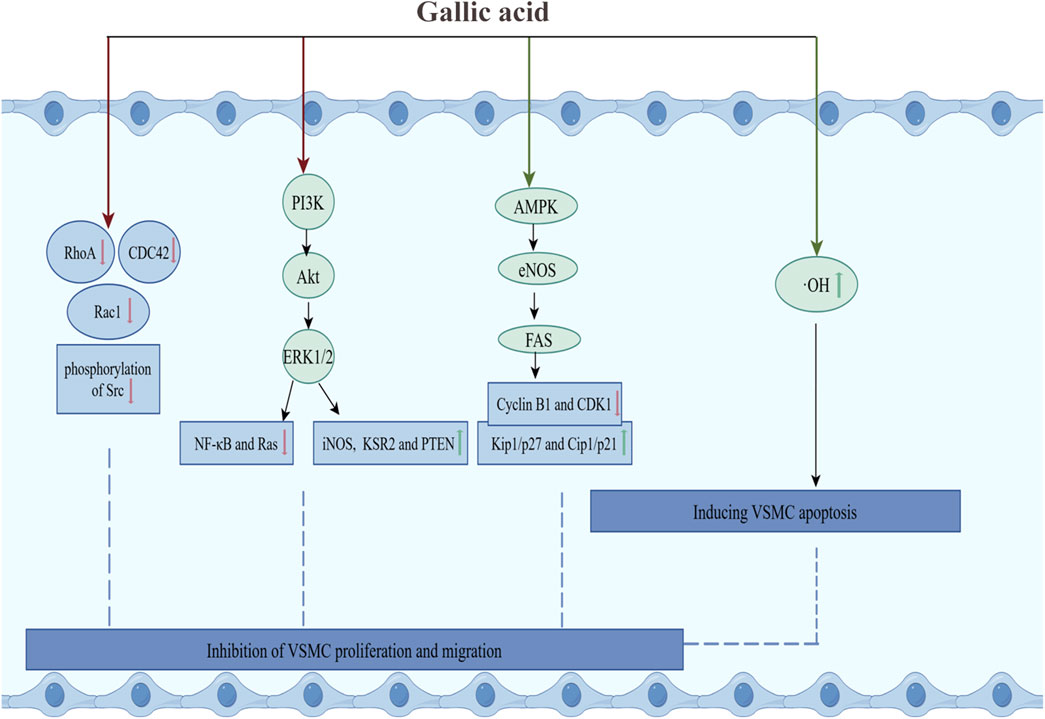
Figure 3. GA inhibited the proliferation and migration of VSMCs. Green arrows and red arrows indicate promotion and inhibition, respectively. Description: This figure illustrates how GA inhibits VSMC proliferation and migration while inducing apoptosis. GA suppresses the RhoA/CDC42 and PI3K-Akt-ERK1/2 pathways, reduces the activation of NF-κB and Ras, and increases the expression of iNOS and KSR2. Additionally, GA promotes the AMPK-eNOS-FAS pathway, enhances Kip1/p27 and Cip1/p21 levels, and inhibits the expression of cyclin B1 and CDK1. Moreover, GA reduces hydroxyl radicals and alleviates oxidative stress to induce apoptosis. Green arrows indicate promoting effects, while red arrows represent inhibitory effects.
Arterial stiffness refers to the loss of elasticity and hardening of the arteries, typically measured by pulse wave velocity (PWV) (Aimagambetova et al., 2024). Vascular stiffening is a complex process driven by multiple factors, including vascular calcification, elastic fiber degradation, and collagen deposition (Ribeiro-Silva et al., 2021). It is not only a consequence of AS but also an important risk factor and a predictor of ASCVD (Szołtysek-Bołdys et al., 2024).
Recent studies demonstrated that GA exhibited significant vascular protective effects and alleviated arterial stiffness. Firstly, GA inhibited vascular calcification by blocking the BMP2-Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway.In vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) induced by inorganic phosphate (Pi), GA inhibited vascular calcification by interfering with the osteogenic signaling pathway through suppressing BMP2 upregulation and Smad1/5/8 phosphorylation (Kee et al., 2014). Secondly, GA inhibited arterial stiffness by preventing the degradation of elastic fibers and suppressing collagen deposition. Studies have shown that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) degrade elastic fibers, while transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) induces collagen deposition by activating fibrosis-related genes (Giachelli et al., 2024; Vallée and Lecarpentier, 2019). In rats induced by advanced glycation end products (AGEs), GA downregulated expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9, and TGF-β, thereby inhibiting extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and calcification and protecting vascular elasticity. Furthermore, additional studies found that this effect was associated with GA’s ability to inhibit ROS generation, as well as the expression of NF-κB and the level of TNF-α, which was further validated in AGEs-induced H9C2(2–1) (Umadevi et al., 2014; 2013). In conclusion, GA mitigated arterial stiffness by inhibiting vascular calcification through the suppression of the BMP2-Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway and protecting elastic fibers as well as reducing collagen deposition via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Hyperglycemia and hypertension are key modifiable risk factors in the prevention and management of ASCVD. These metabolic disorders not only accelerate arterial hardening and damage to the vascular walls but also significantly increase the incidence of cardiovascular events. Borghi et al. have found that comprehensive control of these factors, through lifestyle changes or pharmacological interventions, can significantly reduce the incidence and mortality rates of ASCVD (Borghi et al., 2022; Haas and McDonnell, 2018). Traditional medications are primary interventions but often have adverse side effects, driving the search for natural product-based alternatives. Indeed, GA improves glucose metabolism, which is beneficial for controlling high blood sugar. Specifically, GA enhances insulin sensitivity by regulating the signaling pathways involved in glucose uptake and utilization. This not only helps in controlling blood sugar levels but also addresses insulin resistance (Sousa et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2024). Also, it impairs vasodilatory function through oxidative stress and inflammation, reducing blood pressure level.Therefore, by targeting fundamental risk factors such as hypertension and diabetes, GA not only addresses the root cause of ASCVD deterioration but also provides diverse disease management strategies.
Researches indicate that the onset of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) involves significant islet dysfunction, β cell failure, and the emergence of insulin resistance (Burillo et al., 2021; Lawlor et al., 2017); Consequently, enhancing the quantity of pancreatic islet β cells and reducing insulin resistance are crucial in diabetes management (Prasad et al., 2023). GA, recognized for its hypoglycemic properties, plays a beneficial role in both the prevention and treatment of diabetes (Xu et al., 2021). The efficacy of GA is largely due to its ability to stimulate insulin secretion from β cells, reduce insulin resistance, and inhibit the intestinal absorption of glucose (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Molecular targets and mechanism of action of GA in T2DM. Green arrows and red arrows indicated promotion and inhibition, respectively. Description: This figure illustrates the molecular mechanisms by which GAexerts therapeutic effects in T2DM. GA enhances insulin secretion by inhibiting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and the formation of SFRP4. Simultaneously, GA improves insulin resistance by activating the PPARγ-PI3K/Akt-GLUT4 signaling pathway, thereby increasing glucose uptake. Additionally, GA delays glucose absorption by inhibiting the activities of SGLT1, GLUT2, and α-amylase. In the figure, green arrows indicate processes or pathways promoted by GA, while red arrows highlight inhibitory effects.
Gerst et al. identified that mitigating β cell damage and fostering β cell regeneration significantly boosts insulin secretion from these cells (Gerst et al., 2021; Rady et al., 2022).Thus, strategies to restore β cell functionality typically involved promoting cell proliferation and minimizing damage (Lewis and Wells, 2021; Lu et al., 2020; Tomita, 2017). Researches have demonstrated that GA primarily enhanced regeneration of β cells and reduced β cell damage, thereby augmenting insulin secretion. The detailed mechanisms are elaborated below.
Initially, GA promoted the regeneration of pancreatic β cells and enhance insulin secretion. In diabetes rats, GA treatment resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in blood glucose level, as evidenced by lowered AUCglucose, insulin levels, and Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) indices (Abdel-Moneim et al., 2017; Variya et al., 2020). Additionally, in male Wistar rats with diabetes induced by streptozotocin (STZ), GA improved pathological alterations in pancreatic islet cells, promoted β-cell regeneration, and boosted insulin output. From a mechanistic standpoint, GA promoted pancreatic β-cell regeneration through its antioxidant properties (Latha and Daisy, 2011). In STZ-induced diabetic male albino rats, GA enhanced antioxidant capacity by altering biochemical conditions in pancreatic tissues. It decreased the activity of pancreatic peroxidases, purinergic enzymes, detoxifying enzymes (GST), heme biosynthesizing enzymes (δ-ALA-D), and glycolysis enzymes (LDH), which led to reduced level of blood glucose and decreased pancreatic weight (Kade et al., 2014). Furthermore, in a rat model of STZ-induced diabetes, GA significantly reduced thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and lipid hydroperoxides, enhanced activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). Histopathological analysis showed that GA restored pancreatic beta cells and increased insulin secretion (Punithavathi V. R. et al., 2011).
Secondly, GA enhanced insulin secretion by ameliorating damage of β-cells. Recent studies have demonstrated that secreted frizzled-related protein 4 (SFRP4) is a potential biomarker for β-cell dysfunction in type II diabetes, associated with reduced insulin secretion (Bukhari et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020). In diabetic mice induced by a high-calorie diet, oral administration of GA significantly lowered serum SFRP4 level, which led to reductions in body weight and blood glucose level (Bukhari et al., 2022). Furthermore, in RINm5F β cells exposed to high glucose, palmitate esters, or both, GA enhanced cellular survival pathways by upregulating Bcl-2 activity, downregulating caspase-3 activity, reducing DNA damage, weakening nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling, and increasing the expression of insulin mRNA, thereby promoting insulin secretion (Sameermahmood et al., 2010). Fibrin deposition (also known as islet amyloid polypeptide) has been identified as one of the factors leading to the death of islet β cells (Salazar Vazquez et al., 2020). Also, GA prevented the formation of pancreatic amyloid fibrils, thereby protecting pancreatic β cells and enhancing insulin secretion. In vitro, GA could interacted with natural insulin, inhibiting the key nucleation process essential for the growth of fibrils, thus hindering the formation of amyloid fibers and safeguarding the insulin structure and curtailing protofibril formation (Jayamani and Shanmugam, 2014).
Caturano et al. showed that addressing insulin resistance could significantly improve blood glucose control and was a feasible strategy for diabetes management (Caturano et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2019). In streptozotocin-induced experimental type 2 diabetic rats fed a high-fat diet, GA significantly reduced plasma insulin and HOMA-IR levels and normalised changes in insulin resistance levels, thereby reducing body weight and fasting blood glucose (Gandhi et al., 2014). Therefore, GA can lower blood glucose by alleviating insulin resistance GA attenuated insulin resistance primarily by activating the protein kinase B (Akt) signalling pathway. In fructose-induced diabetic rats, GA increased the expression of proteins related to hepatic insulin signalling, including insulin receptor (IR), insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt and glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) (Huang et al., 2016). Furthermore, in experimental type 2 diabetic rats induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocin, GA treatment lowered the levels of glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, facilitating glucose absorption. This was associated with a significant increase in the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) mRNA. Molecular docking studies showed that PPARγ interacted well with GLUT4, GLUT1, PI3K and p-Akt, indicating that GA could attenuate insulin resistance by activating the PPARγ-PI3K/p-Akt -GLUT4 signalling pathway (Gandhi et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2018; Variya et al., 2020). It was noteworthy that in fructose-induced diabetic rat model, treatment with GA increased expressions of Glut4, PPAR-γ and pAkt proteins, but not phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase (pAMPK) in the epithelial white adipose tissue, suggesting that GA attenuated insulin resistance through the Akt signalling pathway (Variya et al., 2020). However, pAMPK was not restored, which further suggested that GA attenuated insulin resistance through the Akt signalling pathway.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that type 2 diabetes could be therapeutically managed by reducing intestinal glucose absorption, primarily through the inhibition of intestinal carbohydrate hydrolases such as α-amylase, and sodium-dependent glucose transporter protein 1 (SGLT1) (Cefalo et al., 2019; Gong et al., 2020). GA has been shown to be effective in inhibiting and delaying intestinal absorption of glucose. In diabetic albino rats, GA treatment significantly decreased α-amylase activity, thereby disrupting the hydrolytic absorption of starch-like compounds, which led to a marked reduction in situ intestinal glucose absorption (Abdel-Moneim et al., 2022). In addition, in a glucose transport assay using Caco-2 cell monolayers, GA demonstrated specific inhibitory effects on SGLT1, reducing intestinal glucose absorption primarily by suppressing the transport of low concentrations of glucose (5 mM). This effect was further validated in a 2DG transport assay (Wang et al., 2021). In conclusion, GA effectively reduced in situ intestinal glucose absorption, primarily by suppressing the activity of the intestinal carbohydrate hydrolase α-amylase and by downregulating the levels of glucose transporter proteins in the gastrointestinal tract.
Hypertension is a cardiovascular disease that is characterized by persistently elevated arterial blood pressure. Blood pressure is usually represented by two numerical values, namely, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure (McEvoy et al., 2024). Studies have demonstrated that GA could ameliorate hypertension through multiple mechanisms, including reducing systolic blood pressure, decreasing the thickness and weight of the aortic wall, and mitigating cardiac fibrosis (Jin et al., 2017a; 2017b). The specific mechanism is as follows.
GA improved endothelial cell damage and reduced blood pressure by inhibiting activities of NO-related enzymes, such as the NADPH Oxidase (Nox) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). In spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs), GA inhibited components of the renin angiotensin II system and lowered systolic blood pressure. In addition, GA relaxed blood vessels and also reduced the thickness and weight of the aortic wall, thereby regulating blood pressure in the vascular system. This may be related to the inhibition of Nox and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in cardiac tissue by GA. Furthermore, this was confirmed in Ang II-induced H9c2 cells (Jin et al., 2017b). Lind et al. discovered that eNOS was an enzyme responsible for producing NO, and was crucial for cardiovascular health and blood pressure regulation (Lind et al., 2017). In Ang II-induced C57BL/6J mice, GA inhibited immunoproteasome, trypsin, and chymotrypsin activities, thereby increasing eNOS degradation and NO levels. To verifiy the blood pressure-lowering effect of the eNOS/NO pathway, a specific inhibitor Nω-Nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) was used to block eNOS activity, which significantly eliminated the GA-mediated beneficial effects, such as the reduction in SBP, aortic thickening, and collagen deposition (Yan et al., 2020). In SHRs, GA significantly reduced both SBP and DBP. Subsequent studies demonstrated that pretreatment with the eNOS inhibitor L-NAME resulted in a reduction in NO production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). GA treatment resulted in increased phosphorylation of eNOS and Akt, which subsequently induced NO production and inhibited angiotensin I converting enzyme (Kang et al., 2015). Therefore, GA reduced blood pressure by activating the eNOS/NO pathway, which may be related to the Akt pathway. Furthermore, studies have found that HDAC (histone deacetylase), epigenetic regulators that remove acetyl groups from histones, are closely associated with endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and myocardial fibrosis through their epigenetic regulatory actions (Bahl and Seto, 2021). In NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester-induced hypertensive mice, GA significantly inhibited the expression of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC2) and atrial natriuretic peptide, which reduced SBP levels in chronic L-NAME-induced hypertensive mice, LV (left ventricle) posterior wall, septum thickness and cardiac fibrosis (Jin et al., 2017a). Additionally, recent studies demonstrated that GA was an effective dietary HDAC inhibitor with strong inhibitory effects on the activity of HDAC8 and class IIa/b HDACs. These findings suggested that GA exhibited antihypertensive and antifibrotic effects, highlighting its significant potential for clinical translation (Choi et al., 2018). In summary, GA alleviated symptoms of hypertension by increasing the level of NO.
Additionally, GA treated hypertension by inhibiting the expression of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), which was related to apoptosis. CaMKII is a key protein kinase that regulates the contraction and relaxation processes of cardiomyocytes (Carlson et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022c). In SHRs, GA significantly reduced the expression of four CaMKII isoforms: α, β, δ, γ, and the expressions of caspase-3, Bax, p53, and p300 proteins, thereby reducing angiotensin II-induced angiotensin II-induced apoptosis (Jin et al., 2018).
Overall, GA lowered blood pressure mainly by ameliorating endothelial cell damage and inhibiting apoptosis.
Atherosclerosis contributes to ASCVD by narrowing arteries or forming thrombi, thereby obstructing blood flow to the heart (coronary artery disease), brain (ischemic stroke), or lower limbs (peripheral vascular disease). The main areas affected by ASCVD are 1) CHD, 2) cerebrovascular disease, and 3) peripheral vascular disease (Tannu et al., 2024). Studies showed that GA, due to its antioxidant properties, helped prevent and treat CHD and cerebrovascular diseases, contributing to the management of ASCVD. Specifically, GA reduced serum the levels of LDH, creatine phosphokinase (CPK), and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), regulated hemodynamic parameters, and offered protection against CHD (Ramezani-Aliakbari et al., 2017; Souri et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023). Moreover, GA enhanced neuroprotective proteins, improved cerebral blood flow, and lowered blood-brain barrier permeability, providing potential therapeutic benefits for ischemic brain diseases (Praveen Kumar et al., 2021). Consequently, GA emerges as a promising drug for treating ASCVD.
CHD, caused by coronary atherosclerosis, leads to myocardial ischemia and hypoxia due to lipid metabolism disorders, oxidative stress, and inflammation (Donia and Khamis, 2021; Han et al., 2024). Berezin et al. emphasize the importance of cardiac markers and function indices for diagnosing myocardial ischemia and infarction, with evaluations relying on cardiac hemodynamic and electrocardiogram parameters (Berezin and Berezin, 2020; Liu et al., 2022; Sarda and Thute, 2022). GA was a phenolic compound with a protective effect against CHD through its antioxidant properties. In ischemia-reperfused rat hearts, GA reduced histological damage in the heart, showing less edema, collagen fibers, and necrosis, and improved myocardial structure (Dianat et al., 2014). GA also lowered levels of serum cardiac markers like CK-MB and LDH, indicating cardioprotection (Shackebaei et al., 2022; Stanely Mainzen Prince et al., 2009). CK-MB is a specific marker for early myocardial injury, while LDH, a glycolytic enzyme, helps assess the extent of myocardial damage (Feng et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024). Notably, in an isoproterenol (ISO)-induced ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury model, GA not only decreased the activity of cardiac biomarkers (CK-MB, CPK, and LDH) but also increased the activity of lysosomal enzymes such as β-glucuronidase and cathepsin D (Shackebaei et al., 2022), and in ISO induced MI in rats, GA also reduced serum cardiac troponin T (cTnT) level and the intensity of LDH-1 and LDH-2 isoenzyme bands (Priscilla and Prince, 2009).
Additionally, GA improved hemodynamic parameters, enhancing vasodilation, blood flow, and overall cardiac function. These changes collectively contributed to significant improvements in myocardial injury and infarction outcomes. In a rat model of four-vessel occlusion (4VO) I/R induced by PM, GA significantly enhanced cardiac function post-I/R by reducing hemodynamic parameters such as left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP), rates of pressure development (±dp/dt), and the rate-pressure product (RPP)(Radan et al., 2019). These findings demonstrated the effectiveness of GA in reducing myocardial cell damage (Dianat et al., 2014; Shackebaei et al., 2022; Stanely Mainzen Prince et al., 2009). This was linked to the antioxidant properties of GA, which specifically lowered cardiac Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS) level and enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, CAT, and GPX (Patel and Goyal, 2011; Ramezani-Aliakbari et al., 2017; Shackebaei et al., 2022). It is noteworthy that neutrophil activity plays a crucial role in improving the prognosis of myocardial infarction (Cristinziano et al., 2022). Calycosin and GA synergistically induced the expression of Leukotriene B4 12-Hydroxydehydrogenase (LTB4DH) in HepG2 cells and human neutrophils, which can be used to limit neutrophil infiltration and subsequent myocardial injury. Further confirmation was obtained in an isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction mouse model, where these two LTB4DH inducers—namely calycosin and GA—significantly reduced the levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and MDA in cardiac tissues, thereby attenuating the cardiac morphological changes induced by isoproterenol (Cheng et al., 2015).
Cerebral ischemia, caused by a loss of blood supply, leads to harmful processes like glutamate excitotoxicity, calcium overload, oxidative stress, and inflammation, resulting in cell death (Kaur and Sharma, 2022; Suzuki et al., 2021). Effective treatment targets hypoxia/reoxygenation injury and aims to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress (Geng et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2019). In fact, GA offered potential benefits for ischemic brain diseases by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.
Firstly, as a natural antioxidant, GA has shown potential in the prevention and treatment of ischemic brain diseases. In rats with I/R induced by bilateral common carotid artery (BCCA) occlusion, GA enhanced passive avoidance memory and tail-flick latency, thereby improving outcomes in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. This was primarily due to GA pretreatment enhancing antioxidant defenses, inhibiting the functions of neurotoxicity-related proteins (Bax, TNF-α and caspase-3), and improving cerebral I/R injury in rats, thereby exhibiting neuroprotective properties (Abdelsalam et al., 2023; Farbood et al., 2013; Nabavi et al., 2016; Praveen Kumar et al., 2021). GA alleviated behavioral and electrophysiological deficits induced by cerebral hypoperfusion ischemia (CHI) through its antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties, providing significant neuroprotection. For example, in a rat model of CHI induced by permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (2VO), GA significantly restored spatial memory, increased time spent in the target quadrant, and improved memory consolidation (Sarkaki et al., 2014). It is noteworthy that cerebral ischemic injury can lead to vascular dementia (VD). Studies have found that GA also has therapeutic effects on VD. In a VD model induced by 2VO, GA demonstrated beneficial effects on 2VO-induced cognitive deficits. It significantly improved spatial memory in the Morris water maze by increasing non-enzymatic (total thiols) and GPx antioxidant levels (Korani et al., 2014).
Secondly, GA exerted neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia by reducing inflammation. In a rat model involving four-vessel occlusion (4VO)-induced I/R, GA significantly mitigated I/R-induced cognitive impairments and hippocampal long-term potentiation damage. This protective effect was associated with an increase in miR-146a expression and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, along with a reduction in the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α levels (Bavarsad et al., 2023). Additionally, GA inhibited the levels of inflammatory mediators by activating microglia. In an experimental ischemic stroke model, GA treatment significantly reduced brain edema and infarct volume, thereby improving neurological function in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (MCAO) mice, including motor skills, sensory sensitivity, balance, and reflexes. Furthermore, GA treatment decreased the levels of the microglial marker Iba-1 mRNA in the ipsilateral hemisphere, indicating microglial activation. Importantly, during the acute phase of ischemic injury, GA significantly reduced the levels of M1 markers (iNOS, COX-2, MCP-1) while increasing the levels of M2 markers (Arg-1, CD206, IL-10). This dual action not only inhibited the transition of microglia to the pro-inflammatory M1 subtype but also promoted their shift to the anti-inflammatory M2 subtype. As a result, GA significantly lowers the levels of inflammatory mediators (IL-1β, MCP-1, TNFα, IL-6, MIP-2) while the expression of tight junction proteins (ZO-1 and claudin) was increased (Qu et al., 2022).
Finally, GA alleviated cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting apoptosis in brain microvascular endothelial cells. In Na₂S₂O₄-induced MCAO rats, GA significantly increased the expression of cytochrome C in mitochondria while reducing its expression in the cytoplasm. This led to a marked decrease in neurological deficit scores, total infarct volume, and TUNEL-positive cells in each infarct region. In Na₂S₂O₄-induced SH-SY5Y cells, GA inhibited mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opening and prevented the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential, significantly increasing ATP levels. As a result, GA mitigated mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby protecting cells from apoptosis or necrosis (Sun et al., 2014). Further research revealed that GA inhibited the opening of MPTP by regulating the ERK-CypD axis, thereby preventing apoptosis. In BCCA-induced I/R rats, GA reduced neurological deficit scores and the percentage of cleaved-caspase-9 positive cells (relative to DAPI + cells). In H2O2-induced SH-SY5Y cells, GA treatment inhibited the binding of CypD to adenine nucleotide translocase and enhanced the phosphorylation of ERK, leading to reduced expression of CypD. This resulted in desensitization to MPTP-induced permeability transition, thereby suppressing the expression of mitochondrial apoptosis signals, including initiator Cyto C, mediator caspase-9, and effector caspase-3. Consequently, the apoptosis rate of SH-SY5Y cells was significantly reduced (Sun et al., 2017).
Collectively, GA possessed anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-hypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-CHD, and anti-cerebral ischemia properties (Table 1). In Table 1 we list detail information, models, dosage and application.
Acute toxicity tests indicated that albino mice with a single oral dose of 2,000 mg/kg of GA did not exhibit any toxicological conditions. Furthermore, subacute toxicity findings revealed that daily oral administration of 900 mg/kg of GA for 28 days did not significantly affect morphological and behavioral parameters, nor did it significantly alter hematological and histopathological parameters (Variya et al., 2019). In F344 rats, the administration of high doses of GA orally for a period of 14 weeks, at a dosage of 357 mg/kg/day for males and 384 mg/kg/day for females, resulted in the induction of significant toxic effects in both sexes. These effects included weight loss, signs of anemia (such as reduced red blood cell count), and pathological changes in the spleen, liver, and kidneys (Niho et al., 2001).
Furthermore, studies in both animals and cells had shown that high doses of GA potentially exhibited embryotoxic, neurotoxic, and reproductive toxicities. In the Chicken Embryo Model, concentrations of GA at or above 6 μM (1.02 mg/kg) found to induce significant embryotoxic effects, characterized by the dissolution of cerebral blood, degeneration of adipose tissue in neck muscles, and developmental disorders. These effects were linked to GA’s capacity to suppress levels of PPAR-α, elevate concentrations of NO, H2O2, and malondialdehyde, and activate the Ras/Raf/JAK/STAT signaling pathways. Moreover, supplementation with GSH, vitamin E, and N-acetylcysteine showed to alleviate these adverse reactions (Hsieh C. L. et al., 2015; Hsieh C.-L. et al., 2015). Furthermore, in zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio), GA (200 μg/mL) significantly inhibited embryo hatching and cardiac development (Harishkumar et al., 2019). Using zebrafish larvae that had hatched 72 h prior, brief exposure (30 min) to GA induced over-excitation of the central nervous system and behavioral changes in the larvae. This was characterized by increased activity of fosab neuronal markers and cumulative motor responses, and impaired GABA-glutamate balance, revealing GA’s potential neurotoxicity (Annona et al., 2021).
Furthermore, GA (25–100 μM) reduced the cell viability of mouse spermatogonia, mouse spermatocytes, and mouse Sertoli cells, suggesting that GA might have adverse effects on male reproductive health, which was associated with an increase in H2O2 levels (Park et al., 2008). The latest research showed that GA had reproductive toxicity by causing oxidative stress and inflammation. Studies have found that oral administration of GA (100 mg/kg/d) for four consecutive weeks reduced the quantity of sperm output, sperm quality, and testicular testosterone levels, while inhibiting the activity of steroidogenic enzymes (3β-HSD and 17β-HSD) and antioxidants (GSH, GPx, and SOD). Treatment of primary Sertoli cells with GA (25–100 μM) stimulated the expression of Tgf-β1 and CD-14, activated NF-κB and degraded IκBα, suggesting that it triggers inflammation through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Notably, curcumin can mitigate these adverse effects of GA (Abarikwu et al., 2014).
The extraction and synthesis of GA have laid a solid foundation for its widespread application. Research on GA extraction has developed various efficient methods (ultrasound-assisted, molecular blotting and supercritical CO2 extraction), significantly improving extraction efficiency by optimizing parameters such as solvent ratios, extraction temperature, and time (Baite et al., 2021; Khodaie and Ghoreishi, 2021; Pawar and Surana, 2010). In addition, the synthetic pathways of GA, including tannin degradation or synthesis via the shikimic acid pathway, have expanded the possibilities for its industrial-scale production. However, existing methods are costly and lack environmental sustainability, necessitating the development of more efficient, eco-friendly, and cost-effective technologies to meet industrial production demands.
Current studies indicated that GA has low bioavailability, primarily due to rapid metabolism and excretion in the gastrointestinal tract, with significant accumulation in organs such as the kidneys and liver. Repeated dosing and specific health conditions significantly alter its pharmacokinetics, highlighting the need for personalized dose adjustments (Ferruzzi et al., 2009; Yu X.-A. et al., 2018). However, researchers have synthesized GA derivatives and formulations to address these issues. The derivatives of GA, such as propyl gallate (E310), octyl gallate (E311) and dodecyl gallate (E312) are commonly used as preservatives in food and can be easily hydrolyzed to GA, helping to enhance the bioavailability of GA (Dhiman and Mukherjee, 2021). Studies showed that short-chain derivatives like E310 had higher hydrolysis and absorption efficiency, whereas long-chain derivatives such as E311 and E312 exhibited significantly lower absorption efficiency (Badhani et al., 2015; van der Heijden et al., 1986). Additionally, in Western societies, due to dietary habits, differences in gut flora, and their rapid metabolism and clearance, the actual bioavailability of GA and its derivatives was low (Randeni et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2020). This phenomenon suggested that further researches are needed to enhance GA’s absorption efficiency through optimized delivery systems, such as nanocarriers.
Studies have demonstrated that innovative formulations of GA, including nanoparticles, gels, colloids, nanoemulsions, and liposomes, significantly enhance its bioavailability, solubility, and transmembrane transport. For example, GA-loaded nanoparticles have been shown to prolong the half-life, increase plasma concentrations, and enhance overall bioavailability (Hassani et al., 2020; Patil and Killedar, 2021a; Y. Zhao et al., 2020b). Although advanced delivery systems, such as GA-loaded nanoparticles, hydrogels, and nanoemulsions, have significantly improved bioavailability and therapeutic outcomes, these technologies face challenges. Nanoparticle formulations involve complex preparation processes. Hydrogel and colloidal formulations are largely limited to topical use. Encapsulated compounds may interact with the encapsulating materials. And emulsions tend to be unstable. Therefore, future research should focus on optimizing these formulation technologies to improve their effectiveness and safety in clinical applications.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (ASCVDs) are inflammatory conditions, manifested as aortic, coronary, and cerebrovascular diseases due to plaque instability or thrombosis. ASCVD is often associated with hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obesity, highlighting the importance of managing these risk factors for prevention (Nayor et al., 2021). Traditional treatments for cardiovascular sequelae typically include cholesterol-lowering drugs, antihypertensives, antiplatelets, thrombolytics, and anticoagulants. However, these treatments usually target specific conditions and may not address the broader spectrum of atherosclerotic complications, often leading to drug interactions and significant patient burden. Despite the variety of drugs available, there is still a lack of treatments that cover multiple atherosclerosis-related conditions (Bhatia et al., 2023; Ip et al., 2023; Kónyi et al., 2016).
GA, as a natural multi-target compound, is widely used in the food industry, aligning with the current trend towards developing safer, more comprehensive treatment strategies. Compared to traditional single-target drugs, GA possesses antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, blood lipid-regulating, blood sugar-reducing, and endothelial function-improving properties, allowing it to more comprehensively intervene in the pathological processes associated with acute cardiovascular diseases. This review explored the availability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacology, and safety of GA, which aimed to enhance its clinical applications. It also highlighted GA’s significant potential against ASCVD and related risk factors. Research indicated that GA exhibited preventive and therapeutic effects on ASCVD, including diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, atherosclerosis, cerebral ischemia, and myocardial infarction. Furthermore, the paper emphasized that GA’s pharmacological actions involved multiple key signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt, AMPK/Sirt1/PGC1α, ERK/CypD/NOX4/Poldip2, PKCα/p38MAPK, Akt/GSK3β, PI3K-Akt-ERK1/2, and AMPK-eNOS-FAS. Its effects were also associated with the regulation of ATGL, GLUT4, PPARα, PPARγ, NO, Ca2+, and MDA levels. Notably, PPARα and PPARγ, two nuclear receptors, play distinct roles in metabolic regulation. PPARγ is crucial for adipocyte differentiation and lipid storage, while PPARα is essential for lipid metabolism (Bougarne et al., 2018; Hernandez-Quiles et al., 2021). In HFD mice, GA suppressed the expression of PPARα and increased the expression of PPARγ, highlighting GA’s potential for metabolic disorders (Chao et al., 2020; Makihara et al., 2016). By influencing glucose metabolism and lipid homeostasis, GA emerges as a promising candidate for managing metabolic syndrome.
Furthermore, in a series of therapeutic studies targeting these metabolic diseases, literature reports indicated that the dosage of GA was usually high. For example, in these disease models, the dosage of GA ranged from 50 to 100 mg/kg per day, with treatment periods lasting from 4 to 24 weeks. This dosage was significantly higher than that used in studies for treating atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and cerebral ischemia, which ranged from 7 to 50 mg/kg over 3–10 days (Table 1). Although GA has shown potential in the prevention and treatment of ASCVD, there are still some limitations in the existing research. Future research needs to further explore whether GA can lower blood glucose through non-insulin-dependent pathways and its specific effects on different types of fat cells. Additionally, it is worth investigating whether GA involves other mechanisms in regulating blood pressure and the direct clinical evidence for GA treatment of arterial stiffness. In the context of atherosclerosis, the regulatory effects of GA on foam cells and macrophages require more detailed investigation, especially as the specific mechanisms of its anti-ASCVD actions have not been fully elucidated.
Acute toxicity studies showed that a single oral dose of GA up to 2,000 mg/kg in mice did not exhibit significant toxicity, suggesting that GA was sufficiently safe for the prevention and treatment of ASCVD (Variya et al., 2019). However, prolonged high doses (357–384 mg/kg over 14 weeks) led to cumulative toxicity (Niho et al., 2001). GA demonstrated notable embryotoxicity and neurotoxicity in animal embryo models such as chicken embryos and zebrafish (Annona et al., 2021; Hsieh C. L. et al., 2015). Current research, however, primarily focused on the toxic effects of short-term exposure. Additionally, the potential threat of high concentrations of GA (25–100 μM or 100 mg/kg/day) to male reproductive health, particularly its impact on male fertility, deserved special attention (Abarikwu et al., 2014). Further in vivo studies were needed to determine whether GA posed reproductive toxicity risks for females. In conclusion, GA has a relatively high safety profile, but potential risks associated with high doses or long-term use warrant attention. Future research should further evaluate its long-term safety and reproductive toxicity to ensure safe application.
In conclusion, GA, as a natural multi-target compound, demonstrates significant clinical value in the prevention and treatment of ASCVD, addressing the current demand for safer and more comprehensive therapeutic strategies. In particular, it is potentially beneficial for patients with metabolic disorders or those seeking complementary approaches to traditional drug therapy. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-regulating, glucose-lowering, and endothelial function-improving properties enable a holistic intervention in ASCVD-related pathological processes, making it a promising adjunctive therapy to traditional treatments. Given the lack of a systematic review on the role and mechanisms of GA in ASCVD, this paper provides a comprehensive summary on the topic, offering valuable insights for future research and paving the way for its validation through mechanistic studies and clinical trials. With further evidence, GA is expected to emerge as a safe, affordable, and effective adjunctive therapy for ASCVD prevention and management.
X-LZ: Writing–original draft. Z-JC: Investigation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. K-DL: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Data curation. FT: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. L-YX: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. J-NZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. DL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. CP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. HA: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We acknowledge the funding supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 81503272, 81630101, and 81891012), Application Foundation Research Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology (Grant number: 2017JY0187 and 23NSFSC2057), Xinglin Scholar Research Premotion Project of Chengdu University of TCM (Grant number: 2018016), the Regional Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China: Study on the Geoherbalism of Medicinal Materials from Sichuan Tract (Grant number: U19A2010), National Interdisciplinary Innovation Team of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Multi-dimensional evaluation and multidisciplinary cross-innovation team of traditional Chinese medicine resources with Southwest characteristics (Grant number: ZYYCXTD-D-202209), Sichuan Traditional Chinese Medicine Technology Industry Innovation Team: Multidimensional Evaluation of Characteristic Traditional Chinese Medicine Resources and Product Development Innovation Team (Grant number: 2022C001), and Sichuan Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration Project (Grant number: 2020JC0031).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abarikwu, S. O., Akiri, O. F., Durojaiye, M. A., and Alabi, A. F. (2014). Combined administration of curcumin and gallic acid inhibits gallic acid-induced suppression of steroidogenesis, sperm output, antioxidant defenses and inflammatory responsive genes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 143, 49–60. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.02.008
Abdel-Moneim, A., Abd El-Twab, S. M., Yousef, A. I., Ashour, M. B., Reheim, E. S. A., and Hamed, M. A. A. (2022). New insights into the in vitro, in situ and in vivo antihyperglycemic mechanisms of gallic acid and p-coumaric acid. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 128, 1188–1194. doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1762659
Abdel-Moneim, A., Yousef, A. I., Abd El-Twab, S. M., Abdel Reheim, E. S., and Ashour, M. B. (2017). Gallic acid and p-coumaric acid attenuate type 2 diabetes-induced neurodegeneration in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 32, 1279–1286. doi:10.1007/s11011-017-0039-8
Abdelsalam, S. A., Renu, K., Zahra, H. A., Abdallah, B. M., Ali, E. M., Veeraraghavan, V. P., et al. (2023). Polyphenols mediate neuroprotection in cerebral ischemic stroke-an update. Nutrients 15, 1107. doi:10.3390/nu15051107
Aguilar-Zárate, P., Cruz, M. A., Montañez, J., Rodríguez-Herrera, R., Wong-Paz, J. E., Belmares, R. E., et al. (2015). Gallic acid production under anaerobic submerged fermentation by two bacilli strains. Microb. Cell. Fact. 14, 209. doi:10.1186/s12934-015-0386-2
Aimagambetova, B., Ariko, T., Merritt, S., and Rundek, T. (2024). Arterial stiffness measured by pulse wave velocity correlated with cognitive decline in hypertensive individuals: a systematic review. BMC Neurol. 24, 393. doi:10.1186/s12883-024-03905-8
Alpízar, M., de Jesús Reséndiz, J., García Martínez, E., Dwivedi, S., and Trejo, M. A. (2024). Pharmacokinetic simulation and area under the curve estimation of drugs subject to enterohepatic circulation. Pharmaceutics 16, 1044. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16081044
Al Rifai, M., Blaha, M. J., Nambi, V., Shea, S. J. C., Michos, E. D., Blumenthal, R. S., et al. (2022). Determinants of incident atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events among those with absent coronary artery calcium: multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Circulation 145, 259–267. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056705
Al-Samydai, A., Al Qaraleh, M., Al Azzam, K. M., Mayyas, A., Nsairat, H., Abu Hajleh, M. N., et al. (2023). Formulating co-loaded nanoliposomes with gallic acid and quercetin for enhanced cancer therapy. Heliyon 9, e17267. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17267
Andrade, P. M. L., Baptista, L., Britto, J. S., Uetenabaro, A. P. T., and da, A. M. (2018). Co-production of tannase and gallic acid by a novel Penicillium rolfsii (CCMB 714). Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 48, 700–706. doi:10.1080/10826068.2018.1487853
Andrade, S., Loureiro, J. A., and Pereira, M. C. (2022). Transferrin-functionalized liposomes for the delivery of gallic acid: a therapeutic approach for alzheimer’s disease. Pharmaceutics 14, 2163. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14102163
Annona, G., Tarallo, A., Nittoli, V., Varricchio, E., Sordino, P., D’Aniello, S., et al. (2021). Short-term exposure to the simple polyphenolic compound gallic acid induces neuronal hyperactivity in zebrafish larvae. Eur. J. Neurosci. 53, 1367–1377. doi:10.1111/ejn.15021
Appeldoorn, C. C. M., Bonnefoy, A., Lutters, B. C. H., Daenens, K., van Berkel, T. J. C., Hoylaerts, M. F., et al. (2005). Gallic acid antagonizes P-selectin-mediated platelet-leukocyte interactions: implications for the French paradox. Circulation 111, 106–112. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000151307.10576.02
Azarmi, M., Maleki, H., Nikkam, N., and Malekinejad, H. (2023). Novel neurolisteriosis therapy using SPION as a drivable nanocarrier in gallic acid delivery to CNS. J. Control Release 353, 507–517. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.12.006
Badavi, M., Sadeghi, N., Dianat, M., and Samarbafzadeh, A. (2014). Effects of gallic Acid and cyclosporine a on antioxidant capacity and cardiac markers of rat isolated heart after ischemia/reperfusion. Iran. Red. Crescent Med. J. 16, e16424. doi:10.5812/ircmj.16424
Badhani, B., Sharma, N., and Kakkar, R. (2015). Gallic acid: a versatile antioxidant with promising therapeutic and industrial applications. RSC Adv. 5, 27540–27557. doi:10.1039/C5RA01911G
Badmus, O. O., Hillhouse, S. A., Anderson, C. D., Hinds, T. D., and Stec, D. E. (2022). Molecular mechanisms of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): functional analysis of lipid metabolism pathways. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 136, 1347–1366. doi:10.1042/CS20220572
Bahl, S., and Seto, E. (2021). Regulation of histone deacetylase activities and functions by phosphorylation and its physiological relevance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 427–445. doi:10.1007/s00018-020-03599-4
Baite, T. N., Mandal, B., and Purkait, M. K. (2021). Ultrasound assisted extraction of gallic acid from Ficus auriculata leaves using green solvent. Food Bioprod. Process. 128, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.fbp.2021.04.008
Bak, E.-J., Kim, J., Jang, S., Woo, G.-H., Yoon, H.-G., Yoo, Y.-J., et al. (2013). Gallic acid improves glucose tolerance and triglyceride concentration in diet-induced obesity mice. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 73, 607–614. doi:10.3109/00365513.2013.831470
Barkas, F., Sener, Y. Z., Golforoush, P. A., Kheirkhah, A., Rodriguez-Sanchez, E., Novak, J., et al. (2024). Advancements in risk stratification and management strategies in primary cardiovascular prevention. Atherosclerosis 395, 117579. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2024.117579
Bavarsad, K., Farbood, Y., Mard, S. A., Khoshnam, S. E., Dianat, M., Jahangiri, H. M., et al. (2023). Effects of gallic acid on memory deficits and electrophysiological impairments induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats following exposure to ambient dust storm. Neurochem. Res. 48, 2911–2923. doi:10.1007/s11064-023-03953-5
Beena, P. S., Basheer, S. M., Bhat, S. G., Bahkali, A. H., and Chandrasekaran, M. (2011). Propyl gallate synthesis using acidophilic tannase and simultaneous production of tannase and gallic acid by marine Aspergillus awamori BTMFW032. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 164, 612–628. doi:10.1007/s12010-011-9162-x
Berezin, A. E., and Berezin, A. A. (2020). Adverse cardiac remodelling after acute myocardial infarction: old and new biomarkers. Dis. Markers 2020, 1215802. doi:10.1155/2020/1215802
Bhatia, K., Ladd, L. M., Carr, K. H., Di Napoli, M., Saver, J. L., McCullough, L. D., et al. (2023). Contemporary antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapies for secondary stroke prevention: a narrative review of current literature and guidelines. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 23, 235–262. doi:10.1007/s11910-023-01266-2
Borghi, C., Fogacci, F., Agnoletti, D., and Cicero, A. F. G. (2022). Hypertension and dyslipidemia combined therapeutic approaches. High. Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 29, 221–230. doi:10.1007/s40292-022-00507-8
Bougarne, N., Weyers, B., Desmet, S. J., Deckers, J., Ray, D. W., Staels, B., et al. (2018). Molecular actions of PPARα in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Endocr. Rev. 39, 760–802. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00064
Bukhari, S. A., Yasmin, A., Rasul, A., Zahoor, M. A., Mustafa, G., Al Farraj, D. A., et al. (2022). Identification of ascorbic acid and gallic acid as novel inhibitors of secreted frizzled-related protein for the treatment of obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. Dose Response 20, 15593258211069707. doi:10.1177/15593258211069707
Bukhari, S. A., Yasmin, A., Zahoor, M. A., Mustafa, G., Sarfraz, I., and Rasul, A. (2019). Secreted frizzled-related protein 4 and its implication in obesity and type-2 diabetes. IUBMB Life 71, 1701–1710. doi:10.1002/iub.2123
Burillo, J., Marqués, P., Jiménez, B., González-Blanco, C., Benito, M., and Guillén, C. (2021). Insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in alzheimer’s disease. Cells 10, 1236. doi:10.3390/cells10051236
Carlson, C. R., Aronsen, J. M., Bergan-Dahl, A., Moutty, M. C., Lunde, M., Lunde, P. K., et al. (2022). AKAP18δ anchors and regulates CaMKII activity at phospholamban-SERCA2 and RYR. Circ. Res. 130, 27–44. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317976
Caturano, A., Galiero, R., Rocco, M., Tagliaferri, G., Piacevole, A., Nilo, D., et al. (2024). Modern challenges in type 2 diabetes: balancing new medications with multifactorial care. Biomedicines 12, 2039. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12092039
Cefalo, C. M. A., Cinti, F., Moffa, S., Impronta, F., Sorice, G. P., Mezza, T., et al. (2019). Sotagliflozin, the first dual SGLT inhibitor: current outlook and perspectives. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 18, 20. doi:10.1186/s12933-019-0828-y
Chang, S.-S., Lee, V. S. Y., Tseng, Y.-L., Chang, K.-C., Chen, K.-B., Chen, Y.-L., et al. (2012a). Gallic acid attenuates platelet activation and platelet-leukocyte aggregation: involving pathways of Akt and GSK3β. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 683872. doi:10.1155/2012/683872
Chang, S.-S., Lee, V. S. Y., Tseng, Y.-L., Chang, K.-C., Chen, K.-B., Chen, Y.-L., et al. (2012b). Gallic acid attenuates platelet activation and platelet-leukocyte aggregation: involving pathways of Akt and GSK3β. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 683872. doi:10.1155/2012/683872
Chao, J., Cheng, H.-Y., Chang, M.-L., Huang, S.-S., Liao, J.-W., Cheng, Y.-C., et al. (2020). Gallic acid ameliorated impaired lipid homeostasis in a mouse model of high-fat diet-and streptozotocin-induced NAFLD and diabetes through improvement of β-oxidation and ketogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 606759. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.606759
Chao, J., Huo, T.-I., Cheng, H.-Y., Tsai, J.-C., Liao, J.-W., Lee, M.-S., et al. (2014a). Gallic acid ameliorated impaired glucose and lipid homeostasis in high fat diet-induced NAFLD mice. PLoS One 9, e96969. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096969
Chao, J., Huo, T.-I., Cheng, H.-Y., Tsai, J.-C., Liao, J.-W., Lee, M.-S., et al. (2014b). Gallic acid ameliorated impaired glucose and lipid homeostasis in high fat diet-induced NAFLD mice. PLoS One 9, e96969. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096969
Chen, H., Zhang, F., Li, R., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2020). Berberine regulates fecal metabolites to ameliorate 5-fluorouracil induced intestinal mucositis through modulating gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 124, 109829. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109829
Chen, L., Duan, Y., Wei, H., Ning, H., Bi, C., Zhao, Y., et al. (2019). Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) as a therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome and recent developments in ACC1/2 inhibitors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 28, 917–930. doi:10.1080/13543784.2019.1657825
Chen, X., Zhu, P., Liu, B., Wei, L., and Xu, Y. (2018a). Simultaneous determination of fourteen compounds of Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract in rats by UHPLC-MS/MS method: application to pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 159, 490–512. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.07.023
Chen, X., Zhu, P., Liu, B., Wei, L., and Xu, Y. (2018b). Simultaneous determination of fourteen compounds of Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract in rats by UHPLC-MS/MS method: application to pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 159, 490–512. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.07.023
Chen, Z., Shen, X., Wang, J., Wang, J., Yuan, Q., and Yan, Y. (2017). Rational engineering of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase to enable efficient gallic acid synthesis via a novel artificial biosynthetic pathway. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 114, 2571–2580. doi:10.1002/bit.26364
Cheng, Y., Zhao, J., Tse, H. F., Le, X. C., and Rong, J. (2015). Plant natural products calycosin and gallic acid synergistically attenuate neutrophil infiltration and subsequent injury in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction: a possible role for Leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 434052. doi:10.1155/2015/434052
Choi, S. Y., Kee, H. J., Jin, L., Ryu, Y., Sun, S., Kim, G. R., et al. (2018). Inhibition of class IIa histone deacetylase activity by gallic acid, sulforaphane, TMP269, and panobinostat. Biomed. Pharmacother. 101, 145–154. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.071
Chong, B., Jayabaskaran, J., Jauhari, S. M., Chan, S. P., Goh, R., Kueh, M. T. W., et al. (2024). Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: projections from 2025 to 2050. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. zwae281, zwae281. doi:10.1093/eurjpc/zwae281
Choubey, S., Goyal, S., Varughese, L. R., Kumar, V., Sharma, A. K., and Beniwal, V. (2018). Probing gallic acid for its broad spectrum applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 18, 1283–1293. doi:10.2174/1389557518666180330114010
Chung, D.-J., Wu, Y.-L., Yang, M.-Y., Chan, K.-C., Lee, H.-J., and Wang, C.-J. (2020). Nelumbo nucifera leaf polyphenol extract and gallic acid inhibit TNF-α-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration involving the regulation of miR-21, miR-143 and miR-145. Food Funct. 11, 8602–8611. doi:10.1039/d0fo02135k
Clark, M., Centner, A. M., Ukhanov, V., Nagpal, R., and Salazar, G. (2022). Gallic acid ameliorates atherosclerosis and vascular senescence and remodels the microbiome in a sex-dependent manner in ApoE(-/-) mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 110, 109132. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109132
Correction (2023). Correction to: 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 148, e5. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001172
Cristinziano, L., Modestino, L., Antonelli, A., Marone, G., Simon, H.-U., Varricchi, G., et al. (2022). Neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 79, 91–104. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.07.011
Dasagrandhi, D., Muthuswamy, A., and Swaminathan, J. K. (2022). Atherosclerosis: nexus of vascular dynamics and cellular cross talks. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 477, 571–584. doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04307-x
Dechsri, K., Suwanchawalit, C., Patrojanasophon, P., Opanasopit, P., Pengnam, S., Charoenying, T., et al. (2024). Photodynamic antibacterial therapy of gallic acid-derived carbon-based nanoparticles (GACNPs): synthesis, characterization, and hydrogel formulation. Pharmaceutics 16, 254. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16020254
Deng, Q., Li, X. X., Fang, Y., Chen, X., and Xue, J. (2020). Therapeutic potential of quercetin as an antiatherosclerotic agent in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 5926381. doi:10.1155/2020/5926381
Dhiman, S., and Mukherjee, G. (2021). “Gallic acid (GA): a multifaceted biomolecule transmuting the biotechnology era,” in Recent developments in microbial technologies. Editors R. Prasad, V. Kumar, J. Singh, and C. P. Upadhyaya (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore), 163–202. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-4439-2_8
Dhiman, S., Mukherjee, G., and Singh, A. K. (2018). Recent trends and advancements in microbial tannase-catalyzed biotransformation of tannins: a review. Int. Microbiol. 21, 175–195. doi:10.1007/s10123-018-0027-9
Dianat, M., Sadeghi, N., Badavi, M., Panahi, M., and Taheri Moghadam, M. (2014). Protective effects of Co-administration of gallic acid and cyclosporine on rat myocardial morphology against ischemia/reperfusion. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 9, e17186. doi:10.17795/jjnpp-17186
Doan, K. V., Ko, C. M., Kinyua, A. W., Yang, D. J., Choi, Y.-H., Oh, I. Y., et al. (2015). Gallic acid regulates body weight and glucose homeostasis through AMPK activation. Endocrinology 156, 157–168. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1354
Donia, T., and Khamis, A. (2021). Management of oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular diseases: mechanisms and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 28, 34121–34153. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-14109-9
Du, F.-Y., Xiao, X.-H., Luo, X.-J., and Li, G.-K. (2009). Application of ionic liquids in the microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from medicinal plants. Talanta 78, 1177–1184. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2009.01.040
Dutta, S., Singhal, A. K., Suryan, V., and Chandra, N. C. (2024). Obesity: an impact with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 39, 168–178. doi:10.1007/s12291-023-01157-w
Fanaei, H., Mard, S. A., Sarkaki, A., Goudarzi, G., and Khorsandi, L. (2021). Gallic acid protects the liver against NAFLD induced by dust exposure and high-fat diet through inhibiting oxidative stress and repressing the inflammatory signaling pathways NF-kβ/TNF-α/IL-6 in Wistar rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed 11, 527–540. doi:10.22038/AJP.2021.17835
Farbood, Y., Sarkaki, A., Hashemi, S., Mansouri, M. T., and Dianat, M. (2013). The effects of gallic acid on pain and memory following transient global ischemia/reperfusion in Wistar rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed 3 (4), 329–340.
Feng, J., Liu, R., and Chen, X. (2024). Association between Lactate dehydrogenase and 28-day all-cause mortality in patients with non-traumatic Intracerebral hemorrhage: a retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database. Biomol. Biomed. doi:10.17305/bb.2024.11189
Fernandes, F. H. A., and Salgado, H. R. N. (2016). Gallic acid: review of the methods of determination and quantification. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 46, 257–265. doi:10.1080/10408347.2015.1095064
Ferruzzi, M. G., Lobo, J. K., Janle, E. M., Cooper, B., Simon, J. E., Wu, Q.-L., et al. (2009). Bioavailability of gallic acid and catechins from grape seed polyphenol extract is improved by repeated dosing in rats: implications for treatment in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 18, 113–124. doi:10.3233/JAD-2009-1135
Gandhi, G. R., Jothi, G., Antony, P. J., Balakrishna, K., Paulraj, M. G., Ignacimuthu, S., et al. (2014). Gallic acid attenuates high-fat diet fed-streptozotocin-induced insulin resistance via partial agonism of PPARγ in experimental type 2 diabetic rats and enhances glucose uptake through translocation and activation of GLUT4 in PI3K/p-Akt signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 745, 201–216. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.10.044
Geng, C., Wei, J., and Wu, C. (2020). Yap-Hippo pathway regulates cerebral hypoxia-reoxygenation injury in neuroblastoma N2a cells via inhibiting ROCK1/F-actin/mitochondrial fission pathways. Acta Neurol. Belg 120, 879–892. doi:10.1007/s13760-018-0944-6
Gerst, F., Kemter, E., Lorza-Gil, E., Kaiser, G., Fritz, A.-K., Nano, R., et al. (2021). The hepatokine fetuin-A disrupts functional maturation of pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 64, 1358–1374. doi:10.1007/s00125-021-05435-1
Giachelli, C. M., Donato, M., and Scatena, M. (2024). Matrix metalloproteinase-3 joins a growing list of proteases that regulate vascular calcification. Cardiovasc Res. 120, 565–566. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvae064
Gong, L., Feng, D., Wang, T., Ren, Y., Liu, Y., and Wang, J. (2020). Inhibitors of α-amylase and α-glucosidase: potential linkage for whole cereal foods on prevention of hyperglycemia. Food Sci. Nutr. 8, 6320–6337. doi:10.1002/fsn3.1987
Goszcz, K., Deakin, S. J., Duthie, G. G., Stewart, D., and Megson, I. L. (2017). Bioavailable concentrations of delphinidin and its metabolite, gallic acid, induce antioxidant protection associated with increased intracellular glutathione in cultured endothelial cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 9260701. doi:10.1155/2017/9260701
Grabner, G. F., Xie, H., Schweiger, M., and Zechner, R. (2021). Lipolysis: cellular mechanisms for lipid mobilization from fat stores. Nat. Metab. 3, 1445–1465. doi:10.1038/s42255-021-00493-6
Guo, S., Zhang, Y.-Y., Peng, J.-J., Li, Y.-Q., Liu, W.-N., Tang, M.-X., et al. (2019). Natural compound methyl protodioscin protects rat brain from ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulation of Mul1/SOD2 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 849, 50–58. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.01.057
Haas, A. V., and McDonnell, M. E. (2018). Pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 47, 51–63. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2017.10.010
Hafiane, A., and Daskalopoulou, S. S. (2022). Targeting the residual cardiovascular risk by specific anti-inflammatory interventions as a therapeutic strategy in atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Res. 178, 106157. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106157
Han, R., Huang, H., Zhu, J., Jin, X., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., et al. (2024). Adipokines and their potential impacts on susceptibility to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 23, 372. doi:10.1186/s12944-024-02357-w
Hao, Y., Gao, R., Liu, D., Tang, Y., and Guo, Z. (2015). Selective extraction of gallic acid in pomegranate rind using surface imprinting polymers over magnetic carbon nanotubes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 407, 7681–7690. doi:10.1007/s00216-015-8930-9
Harishkumar, R., Reddy, L. P. K., Karadkar, S. H., Murad, M. A., Karthik, S. S., Manigandan, S., et al. (2019). Toxicity and selective biochemical assessment of quercetin, gallic acid, and curcumin in zebrafish. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 42, 1969–1976. doi:10.1248/bpb.b19-00296
Hassani, A., Azarian, M. M. S., Ibrahim, W. N., and Hussain, S. A. (2020). Preparation, characterization and therapeutic properties of gum Arabic-stabilized gallic acid nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 10, 17808. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71175-8
Hazari, S. A., Sheikh, A., Abourehab, M. A. S., Tulbah, A. S., and Kesharwani, P. (2023). Self-assembled Gallic acid loaded lecithin-chitosan hybrid nanostructured gel as a potential tool against imiquimod-induced psoriasis. Environ. Res. 234, 116562. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.116562
Hernandez-Quiles, M., Broekema, M. F., and Kalkhoven, E. (2021). PPARgamma in metabolism, immunity, and cancer: unified and diverse mechanisms of action. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 12, 624112. doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.624112
Hodgson, J. M., Morton, L. W., Puddey, I. B., Beilin, L. J., and Croft, K. D. (2000). Gallic acid metabolites are markers of black tea intake in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 2276–2280. doi:10.1021/jf000089s
Hoshino, T., Ishizuka, K., Seki, M., Hosoya, M., Toi, S., Mizuno, T., et al. (2024). Effect of pemafibrate on cerebrovascular atherosclerosis in patients with stroke and hypertriglyceridemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb., 65277. doi:10.5551/jat.65277
Hsieh, C. L., Lin, C.-H., Chen, K. C., Peng, C.-C., and Peng, R. Y. (2015a). The teratogenicity and the action mechanism of gallic acid relating with brain and cervical muscles. PLoS One 10, e0119516. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119516
Hsieh, C.-L., Lin, C.-H., Wang, H.-E., Peng, C.-C., and Peng, R. Y. (2015b). Gallic acid exhibits risks of inducing muscular hemorrhagic liposis and cerebral hemorrhage--its action mechanism and preventive strategy. Phytother. Res. 29, 267–280. doi:10.1002/ptr.5249
Hsu, C.-L., Lo, W.-H., and Yen, G.-C. (2007a). Gallic acid induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes via a Fas- and mitochondrial-mediated pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 55, 7359–7365. doi:10.1021/jf071223c
Hsu, C.-L., and Yen, G.-C. (2007). Effect of gallic acid on high fat diet-induced dyslipidaemia, hepatosteatosis and oxidative stress in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 98, 727–735. doi:10.1017/S000711450774686X
Hsu, F.-L., Yang, L.-M., Chang, S.-F., Wang, L.-H., Hsu, C.-Y., Liu, P.-C., et al. (2007b). Biotransformation of gallic acid by Beauveria sulfurescens ATCC 7159. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74, 659–666. doi:10.1007/s00253-006-0692-z
Huang, D.-W., Chang, W.-C., Wu, J.S.-B., Shih, R.-W., and Shen, S.-C. (2016). Gallic acid ameliorates hyperglycemia and improves hepatic carbohydrate metabolism in rats fed a high-fructose diet. Nutr. Res. 36, 150–160. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2015.10.001
Huang, D.-W., Chang, W.-C., Yang, H.-J., Wu, J.S.-B., and Shen, S.-C. (2018). Gallic acid alleviates hypertriglyceridemia and fat accumulation via modulating glycolysis and lipolysis pathways in perirenal adipose tissues of rats fed a high-fructose diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 254. doi:10.3390/ijms19010254
Ip, Y. M. B., Lau, K. K., Ko, H., Lau, L., Yao, A., Wong, G.L.-H., et al. (2023). Association of alternative anticoagulation strategies and outcomes in patients with ischemic stroke while taking a direct oral anticoagulant. Neurology 101, e358–e369. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000207422
Jayamani, J., and Shanmugam, G. (2014). Gallic acid, one of the components in many plant tissues, is a potential inhibitor for insulin amyloid fibril formation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 85, 352–358. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.07.111
Jiang, H., Zhou, Y., Nabavi, S. M., Sahebkar, A., Little, P. J., Xu, S., et al. (2022). Mechanisms of oxidized LDL-mediated endothelial dysfunction and its consequences for the development of atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 9, 925923. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.925923
Jin, L., Lin, M. Q., Piao, Z. H., Cho, J. Y., Kim, G. R., Choi, S. Y., et al. (2017a). Gallic acid attenuates hypertension, cardiac remodeling, and fibrosis in mice with NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester-induced hypertension via regulation of histone deacetylase 1 or histone deacetylase 2. J. Hypertens. 35, 1502–1512. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000001327
Jin, L., Piao, Z. H., Liu, C. P., Sun, S., Liu, B., Kim, G. R., et al. (2018). Gallic acid attenuates calcium calmodulin-dependent kinase II-induced apoptosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 22, 1517–1526. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13419
Jin, L., Piao, Z. H., Sun, S., Liu, B., Kim, G. R., Seok, Y. M., et al. (2017b). Gallic acid reduces blood pressure and attenuates oxidative stress and cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 7, 15607. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-15925-1
Jin, Q., Liu, G., Tan, X., Zhang, X., Liu, X., and Wei, C. (2022). Gallic acid as a key substance to inhibit proliferation and adipogenesis in bovine subcutaneous adipocyte. Anim. Biotechnol. 33, 657–663. doi:10.1080/10495398.2020.1822370
Joynt Maddox, K. E., Elkind, M. S. V., Aparicio, H. J., Commodore-Mensah, Y., de Ferranti, S. D., Dowd, W. N., et al. (2024). Forecasting the burden of cardiovascular disease and stroke in the United States through 2050-prevalence of risk factors and disease: a presidential advisory from the American heart association. Circulation 150, e65–e88. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001256
Jung, S. M., Sanchez-Gurmaches, J., and Guertin, D. A. (2019). Brown adipose tissue development and metabolism. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 251, 3–36. doi:10.1007/164_2018_168
Kade, I. J., Ogunbolude, Y., Kamdem, J. P., and Rocha, J. B. T. (2014). Influence of gallic acid on oxidative stress-linked streptozotocin-induced pancreatic dysfunction in diabetic rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 25, 35–45. doi:10.1515/jbcpp-2012-0062
Kam, A., Li, K. M., Razmovski-Naumovski, V., Nammi, S., Chan, K., and Li, G. Q. (2014). Gallic acid protects against endothelial injury by restoring the depletion of DNA methyltransferase 1 and inhibiting proteasome activities. Int. J. Cardiol. 171, 231–242. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.12.020
Kambourakis, S., and Frost, J. W. (2000). Synthesis of gallic acid: Cu(2+)-mediated oxidation of 3-dehydroshikimic acid. J. Org. Chem. 65, 6904–6909. doi:10.1021/jo000335z
Kang, N., Lee, J.-H., Lee, W., Ko, J.-Y., Kim, E.-A., Kim, J.-S., et al. (2015). Gallic acid isolated from Spirogyra sp. improves cardiovascular disease through a vasorelaxant and antihypertensive effect. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 39, 764–772. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2015.02.006
Kanpiengjai, A., Khanongnuch, C., Lumyong, S., Haltrich, D., Nguyen, T.-H., and Kittibunchakul, S. (2020). Co-production of gallic acid and a novel cell-associated tannase by a pigment-producing yeast, Sporidiobolus ruineniae A45.2. Microb. Cell. Fact. 19, 95. doi:10.1186/s12934-020-01353-w
Kaur, M. M., and Sharma, D. S. (2022). Mitochondrial repair as potential pharmacological target in cerebral ischemia. Mitochondrion 63, 23–31. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2022.01.001
Kee, H. J., Cho, S.-N., Kim, G. R., Choi, S. Y., Ryu, Y., Kim, I. K., et al. (2014). Gallic acid inhibits vascular calcification through the blockade of BMP2-Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. Vasc. Pharmacol. 63, 71–78. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2014.08.005
Khan, M. S., Fatima, M., Wahab, S., Khalid, M., and Kesharwani, P. (2024). Gallic acid loaded self-nano emulsifying hydrogel-based drug delivery system against onychomycosis. Nanomedicine (Lond) 19, 2065–2083. doi:10.1080/17435889.2024.2386923
Khodaie, F., and Ghoreishi, S. M. (2021). Experimental extraction of gallic acid from brown sumac seed (Rhus coriaria) using supercritical carbon dioxide and ethanol as co-solvent: modeling and optimization. J. Supercrit. Fluids 175, 105266. doi:10.1016/j.supflu.2021.105266
Kónyi, A., Sárszegi, Z., Hild, G., and Gaszner, B. (2016). Safety and effectiveness of combined antihypertensive and cholesterol-lowering therapy in high-/very high-risk patients. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 5, 355–364. doi:10.2217/cer-2016-0003
Korani, M. S., Farbood, Y., Sarkaki, A., Fathi Moghaddam, H., and Taghi Mansouri, M. (2014). Protective effects of gallic acid against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced cognitive deficit and brain oxidative damage in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 733, 62–67. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.03.044
Latha, R. C. R., and Daisy, P. (2011). Insulin-secretagogue, antihyperlipidemic and other protective effects of gallic acid isolated from Terminalia belerica Roxb. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 189, 112–118. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2010.11.005
Lawlor, N., Khetan, S., Ucar, D., and Stitzel, M. L. (2017). Genomics of islet (Dys)function and type 2 diabetes. Trends Genet. 33, 244–255. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2017.01.010
Lee, A.-T., Yang, M.-Y., Lee, Y.-J., Yang, T.-W., Wang, C.-C., and Wang, C.-J. (2021). Gallic acid improves diabetic steatosis by downregulating MicroRNA-34a-5p through targeting NFE2L2 expression in high-fat diet-fed db/db mice. Antioxidants (Basel) 11, 92. doi:10.3390/antiox11010092
Lekakis, J., Rallidis, L. S., Andreadou, I., Vamvakou, G., Kazantzoglou, G., Magiatis, P., et al. (2005). Polyphenolic compounds from red grapes acutely improve endothelial function in patients with coronary heart disease. Eur. J. Cardiovasc Prev. Rehabil. 12, 596–600. doi:10.1097/00149831-200512000-00013
Lewis, P. L., and Wells, J. M. (2021). Engineering-inspired approaches to study β-cell function and diabetes. Stem Cells 39, 522–535. doi:10.1002/stem.3340
Li, G., and Row, K. H. (2019). Hydrophilic molecularly imprinted chitosan based on deep eutectic solvents for the enrichment of gallic acid in red ginseng tea. Polym. (Basel) 11, 1434. doi:10.3390/polym11091434
Li, Y., Cao, G.-Y., Jing, W.-Z., Liu, J., and Liu, M. (2023). Global trends and regional differences in incidence and mortality of cardiovascular disease, 1990-2019: findings from 2019 global burden of disease study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 30, 276–286. doi:10.1093/eurjpc/zwac285
Limpisophon, K., and Schleining, G. (2017). Use of gallic acid to enhance the antioxidant and mechanical properties of active fish gelatin film. J. Food Sci. 82, 80–89. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.13578
Lind, M., Hayes, A., Caprnda, M., Petrovic, D., Rodrigo, L., Kruzliak, P., et al. (2017). Inducible nitric oxide synthase: good or bad? Biomed. Pharmacother. 93, 370–375. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.036
Liu, F., Song, L., Lu, Z., Sun, T., Lun, J., Zhou, C., et al. (2022). Isosteviol improves cardiac function and promotes angiogenesis after myocardial infarction in rats. Cell. Tissue Res. 387, 275–285. doi:10.1007/s00441-021-03559-9
Liu, Y., Sun, C., Li, W., Adu-Frimpong, M., Wang, Q., Yu, J., et al. (2019). Preparation and characterization of syringic acid-loaded TPGS liposome with enhanced oral bioavailability and in vivo antioxidant efficiency. AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 98. doi:10.1208/s12249-019-1290-6
Lu, C.-L., Liao, M.-T., Hou, Y.-C., Fang, Y.-W., Zheng, C.-M., Liu, W.-C., et al. (2020). Sirtuin-1 and its relevance in vascular calcification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1593. doi:10.3390/ijms21051593
Lv, F., Fang, H., Huang, L., Wang, Q., Cao, S., Zhao, W., et al. (2024). Curcumin equipped nanozyme-like metal-organic framework platform for the targeted atherosclerosis treatment with lipid regulation and enhanced magnetic resonance imaging capability. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11, e2309062. doi:10.1002/advs.202309062
Ma, F., Gong, X., Zhou, X., Zhao, Y., and Li, M. (2015). An UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid in rat plasma after oral administration of Polygonum capitatum extract and its application to pharmacokinetics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 162, 377–383. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.12.044
Ma, F.-W., Deng, Q.-F., Zhou, X., Gong, X.-J., Zhao, Y., Chen, H.-G., et al. (2016). The tissue distribution and urinary excretion study of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid after oral administration of polygonum capitatum extract in rats. Molecules 21, 399. doi:10.3390/molecules21040399
Makihara, H., Koike, Y., Ohta, M., Horiguchi-Babamoto, E., Tsubata, M., Kinoshita, K., et al. (2016). Gallic acid, the active ingredient of Terminalia bellirica, enhances adipocyte differentiation and adiponectin secretion. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 39, 1137–1143. doi:10.1248/bpb.b16-00064
McEvoy, J. W., McCarthy, C. P., Bruno, R. M., Brouwers, S., Canavan, M. D., Ceconi, C., et al. (2024). 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 45, 3912–4018. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehae178
Modanwal, S., Maurya, A. K., Mulpuru, V., and Mishra, N. (2024). Exploring flavonoid derivatives as potential pancreatic lipase inhibitors for obesity management: an in silico and in vitro study. Mol. Divers. doi:10.1007/s11030-024-11005-5
Monteiro E Silva, S. A., Calixto, G. M. F., Cajado, J., De Carvalho, P. C. A., Rodero, C. F., Chorilli, M., et al. (2017). Gallic acid-loaded gel formulation combats skin oxidative stress: development, characterization and ex vivo biological assays. Polym. (Basel) 9, 391. doi:10.3390/polym9090391
Muir, R. M., Ibáñez, A. M., Uratsu, S. L., Ingham, E. S., Leslie, C. A., McGranahan, G. H., et al. (2011). Mechanism of gallic acid biosynthesis in bacteria (Escherichia coli) and walnut (Juglans regia). Plant Mol. Biol. 75, 555–565. doi:10.1007/s11103-011-9739-3
Murga, R., Ruiz, R., Beltrán, S., and Cabezas, J. L. (2000). Extraction of natural complex phenols and tannins from grape seeds by using supercritical mixtures of carbon dioxide and alcohol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 3408–3412. doi:10.1021/jf9912506
Mustafa, N., Mitxelena, J., Infante, A., Zenarruzabeitia, O., Eriz, A., Iglesias-Ara, A., et al. (2021). E2f2 attenuates apoptosis of activated T lymphocytes and protects from immune-mediated injury through repression of fas and FasL. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 311. doi:10.3390/ijms23010311
Nabavi, S. F., Habtemariam, S., Di Lorenzo, A., Sureda, A., Khanjani, S., Nabavi, S. M., et al. (2016). Post-stroke depression modulation and in vivo antioxidant activity of gallic acid and its synthetic derivatives in a murine model system. Nutrients 8, 248. doi:10.3390/nu8050248
Naeem, A., Yu, C., Zhu, W., Chen, X., Wu, X., Chen, L., et al. (2022). Gallic acid-loaded sodium alginate-based (polyvinyl alcohol-Co-acrylic acid) hydrogel membranes for cutaneous wound healing: synthesis and characterization. Molecules 27, 8397. doi:10.3390/molecules27238397
Nájera-Martínez, E. F., Flores-Contreras, E. A., Araújo, R. G., Iñiguez-Moreno, M., Sosa-Hernández, J. E., Iqbal, H. M. N., et al. (2023). Microencapsulation of gallic acid based on a polymeric and pH-sensitive matrix of pectin/alginate. Polym. (Basel) 15, 3014. doi:10.3390/polym15143014
Nayor, M., Brown, K. J., and Vasan, R. S. (2021). The molecular basis of predicting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk. Circ. Res. 128, 287–303. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315890
Negrier, C., Shima, M., and Hoffman, M. (2019). The central role of thrombin in bleeding disorders. Blood Rev. 38, 100582. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2019.05.006
Niho, N., Shibutani, M., Tamura, T., Toyoda, K., Uneyama, C., Takahashi, N., et al. (2001). Subchronic toxicity study of gallic acid by oral administration in F344 rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 39, 1063–1070. doi:10.1016/s0278-6915(01)00054-0
Oi, Y., Hou, I.-C., Fujita, H., and Yazawa, K. (2012). Antiobesity effects of Chinese black tea (Pu-eh tea) extract and gallic acid. Phytother. Res. 26, 475–481. doi:10.1002/ptr.3602
Ou, T.-T., Lin, M.-C., Wu, C.-H., Lin, W.-L., and Wang, C.-J. (2013). Gallic acid attenuates oleic acid-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell through regulation of AMPK-eNOS-FAS signaling. Curr. Med. Chem. 20, 3944–3953. doi:10.2174/09298673113209990175
Palma, M., Taylor, L. T., Varela, R. M., Cutler, S. J., and Cutler, H. G. (1999). Fractional extraction of compounds from grape seeds by supercritical fluid extraction and analysis for antimicrobial and agrochemical activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 47, 5044–5048. doi:10.1021/jf990019p
Panda, P., Verma, H. K., Lakkakula, S., Merchant, N., Kadir, F., Rahman, S., et al. (2022). Biomarkers of oxidative stress tethered to cardiovascular diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 9154295. doi:10.1155/2022/9154295
Paraíso, A. F., Sousa, J. N., Andrade, J. M. O., Mangabeira, E. S., Lelis, D. de F., de Paula, A. M. B., et al. (2019). Oral gallic acid improves metabolic profile by modulating SIRT1 expression in obese mice brown adipose tissue: a molecular and bioinformatic approach. Life Sci. 237, 116914. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116914
Pardeshi, S., Dhodapkar, R., and Kumar, A. (2014). Molecularly imprinted microspheres and nanoparticles prepared using precipitation polymerisation method for selective extraction of gallic acid from Emblica officinalis. Food Chem. 146, 385–393. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.084
Park, W., Chang, M. S., Kim, H., Choi, H. Y., Yang, W. M., Kim, D. R., et al. (2008). Cytotoxic effect of gallic acid on testicular cell lines with increasing H2O2 level in GC-1 spg cells. Toxicol Vitro 22, 159–163. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2007.08.010
Pasquel, F. J., Gregg, E. W., and Ali, M. K. (2018). The evolving epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in people with diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 47, 1–32. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2017.11.001
Patel, S. S., and Goyal, R. K. (2011). Cardioprotective effects of gallic acid in diabetes-induced myocardial dysfunction in rats. Pharmacogn. Res. 3, 239–245. doi:10.4103/0974-8490.89743
Patil, P., and Killedar, S. (2021a). Chitosan and glyceryl monooleate nanostructures containing gallic acid isolated from amla fruit: targeted delivery system. Heliyon 7, e06526. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06526
Patil, P., and Killedar, S. (2021b). Improving gallic acid and quercetin bioavailability by polymeric nanoparticle formulation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 47, 1656–1663. doi:10.1080/03639045.2022.2043353
Pawar, C. R., and Surana, S. J. (2010). Optimizing conditions for gallic acid extraction from Caesalpinia decapetala wood. Pak J. Pharm. Sci. 23 (4), 423–425.
Pérez-Torres, I., Castrejón-Téllez, V., Soto, M. E., Rubio-Ruiz, M. E., Manzano-Pech, L., and Guarner-Lans, V. (2021). Oxidative stress, plant natural antioxidants, and obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 1786. doi:10.3390/ijms22041786
Pernas, L. (2024). Division of labour: mitochondria split to meet energy demands. Nature 635, 557–558. doi:10.1038/d41586-024-03469-0
Prasad, M. K., Mohandas, S., and Ramkumar, K. M. (2023). Dysfunctions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies of pancreatic β-cells in diabetes. Apoptosis 28, 958–976. doi:10.1007/s10495-023-01854-0
Praveen Kumar, P., D, M., Siva Sankar Reddy, L., Dastagiri Reddy, Y., Somasekhar, G., Sirisha, N. V. L., et al. (2021). A new cerebral ischemic injury model in rats, preventive effect of gallic acid and in silico approaches. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 28, 5204–5213. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.05.044
Priscilla, D. H., and Prince, P. S. M. (2009). Cardioprotective effect of gallic acid on cardiac troponin-T, cardiac marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants in experimentally induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 179, 118–124. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.12.012
Punithavathi, V. R., Prince, P. S. M., Kumar, R., and Selvakumari, J. (2011a). Antihyperglycaemic, antilipid peroxidative and antioxidant effects of gallic acid on streptozotocin induced diabetic Wistar rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 650, 465–471. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.08.059
Punithavathi, V. R., Stanely Mainzen Prince, P., Kumar, M. R., and Selvakumari, C. J. (2011b). Protective effects of gallic acid on hepatic lipid peroxide metabolism, glycoprotein components and lipids in streptozotocin-induced type II diabetic Wistar rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 25, 68–76. doi:10.1002/jbt.20360
Qiao, Y.-N., Zou, Y.-L., and Guo, S.-D. (2022). Low-density lipoprotein particles in atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 13, 931931. doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.931931
Qiu, X., Takemura, G., Koshiji, M., Hayakawa, Y., Kanoh, M., Maruyama, R., et al. (2000). Gallic acid induces vascular smooth muscle cell death via hydroxyl radical production. Heart Vessels 15, 90–99. doi:10.1007/s003800070038
Qu, Y., Wang, L., and Mao, Y. (2022). Gallic acid attenuates cerebral ischemia/re-perfusion-induced blood-brain barrier injury by modifying polarization of microglia. J. Immunotoxicol. 19, 17–26. doi:10.1080/1547691X.2022.2043494
Radan, M., Dianat, M., Badavi, M., Mard, S. A., Bayati, V., and Goudarzi, G. (2019). Gallic acid protects particulate matter (PM(10)) triggers cardiac oxidative stress and inflammation causing heart adverse events in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 26, 18200–18207. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-05223-w
Rady, B., Liu, J., Huang, H., Bakaj, I., Qi, J., Lee, S. P., et al. (2022). A FFAR1 full agonist restores islet function in models of impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and diabetic non-human primates. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 1061688. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1061688
Raghuwanshi, S., Dutt, K., Gupta, P., Misra, S., and Saxena, R. K. (2011). Bacillus sphaericus: the highest bacterial tannase producer with potential for gallic acid synthesis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 111, 635–640. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.02.008
Ramezani-Aliakbari, F., Badavi, M., Dianat, M., Mard, S. A., and Ahangarpour, A. (2017). Effects of gallic acid on hemodynamic parameters and infarct size after ischemia-reperfusion in isolated rat hearts with alloxan-induced diabetes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 96, 612–618. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.014
Randeni, N., Bordiga, M., and Xu, B. (2024). A comprehensive review of the triangular relationship among diet-gut microbiota-inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 9366. doi:10.3390/ijms25179366
Rao, R. R., Long, J. Z., White, J. P., Svensson, K. J., Lou, J., Lokurkar, I., et al. (2014). Meteorin-like is a hormone that regulates immune-adipose interactions to increase beige fat thermogenesis. Cell. 157, 1279–1291. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.065
Ribeiro-Silva, J. C., Nolasco, P., Krieger, J. E., and Miyakawa, A. A. (2021). Dynamic crosstalk between vascular smooth muscle cells and the aged extracellular matrix. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 10175. doi:10.3390/ijms221810175
Salazar Vazquez, S., Blondeau, B., Cattan, P., Armanet, M., Guillemain, G., and Khemtemourian, L. (2020). The flanking peptides issue from the maturation of the human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP) slightly modulate hIAPP-fibril formation but not hIAPP-induced cell death. Biochimie 170, 26–35. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2019.12.005
Sameermahmood, Z., Raji, L., Saravanan, T., Vaidya, A., Mohan, V., and Balasubramanyam, M. (2010). Gallic acid protects RINm5F beta-cells from glucolipotoxicity by its antiapoptotic and insulin-secretagogue actions. Phytother. Res. 24 (Suppl. 1), S83–S94. doi:10.1002/ptr.2926
Sarda, A. K., and Thute, P. (2022). Importance of ecg in the diagnosis of acute pericarditis and myocardial infarction: a review article. Cureus 14, e30633. doi:10.7759/cureus.30633
Sarkaki, A., Fathimoghaddam, H., Mansouri, S. M. T., Korrani, M. S., Saki, G., and Farbood, Y. (2014). Gallic acid improves cognitive, hippocampal long-term potentiation deficits and brain damage induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Pak J. Biol. Sci. 17, 978–990. doi:10.3923/pjbs.2014.978.990
Serrano, J., Cipak, A., Boada, J., Gonzalo, H., Cacabelos, D., Cassanye, A., et al. (2010). Double-edged sword behaviour of gallic acid and its interaction with peroxidases in human microvascular endothelial cell culture (HMEC-1). Antioxidant and pro-oxidant effects. Acta Biochim. Pol. 57, 193–198. doi:10.18388/abp.2010_2394
Sguizzato, M., Valacchi, G., Pecorelli, A., Boldrini, P., Simelière, F., Huang, N., et al. (2020). Gallic acid loaded poloxamer gel as new adjuvant strategy for melanoma: a preliminary study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 185, 110613. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110613
Shackebaei, D., Hesari, M., Ramezani-Aliakbari, S., Hoseinkhani, Z., and Ramezani-Aliakbari, F. (2022). Gallic acid protects against isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 41, 9603271211064532. doi:10.1177/09603271211064532
Shahrzad, S., Aoyagi, K., Winter, A., Koyama, A., and Bitsch, I. (2001). Pharmacokinetics of gallic acid and its relative bioavailability from tea in healthy humans. J. Nutr. 131, 1207–1210. doi:10.1093/jn/131.4.1207
Shahrzad, S., and Bitsch, I. (1998). Determination of gallic acid and its metabolites in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 705, 87–95. doi:10.1016/s0378-4347(97)00487-8
Sheikh, A., Hazari, S. A., Molugulu, N., Alshehri, S. A., Wahab, S., Sahebkar, A., et al. (2023). Hyaluronic acid engineered gallic acid embedded chitosan nanoparticle as an effective delivery system for treatment of psoriasis. Environ. Res. 238, 117086. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2023.117086
Souri, F., Badavi, M., Dianat, M., Mard, S. A., and Sarkaki, A. (2023). Protective effects of gallic acid and SGK1 inhibitor on oxidative stress and cardiac damage in an isolated heart model of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 26, 308–315. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68045.14874
Sousa, J. N., Paraíso, A. F., Andrade, J. M. O., Lelis, D. F., Santos, E. M., Lima, J. P., et al. (2020). Oral gallic acid improve liver steatosis and metabolism modulating hepatic lipogenic markers in obese mice. Exp. Gerontol. 134, 110881. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2020.110881
Stanely Mainzen Prince, P., Priscilla, H., and Devika, P. T. (2009). Gallic acid prevents lysosomal damage in isoproterenol induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 615, 139–143. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.05.003
Sun, J., Li, Y.-Z., Ding, Y.-H., Wang, J., Geng, J., Yang, H., et al. (2014). Neuroprotective effects of gallic acid against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced mitochondrial dysfunctions in vitro and cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo. Brain Res. 1589, 126–139. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.039
Sun, J., Liu, Y., Chen, C., Quarm, A. K., Xi, S., Sun, T., et al. (2023). Cyclophilin D-mediated angiotensin II-induced NADPH oxidase 4 activation in endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction that can be rescued by gallic acid. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 940, 175475. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175475
Sun, J., Ren, D.-D., Wan, J.-Y., Chen, C., Chen, D., Yang, H., et al. (2017). Desensitizing mitochondrial permeability transition by ERK-cyclophilin D Axis contributes to the neuroprotective effect of gallic acid against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 184. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00184
Suzuki, H., Kanamaru, H., Kawakita, F., Asada, R., Fujimoto, M., and Shiba, M. (2021). Cerebrovascular pathophysiology of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Histol. Histopathol. 36, 143–158. doi:10.14670/HH-18-253
Szołtysek-Bołdys, I., Zielińska-Danch, W., Łoboda, D., Gołba, K. S., and Sarecka-Hujar, B. (2024). Do photopletysmographic parameters of arterial stiffness differ depending on the presence of arterial hypertension and/or atherosclerosis? Sensors (Basel) 24, 4572. doi:10.3390/s24144572
Tanaka, M., Sato, A., Kishimoto, Y., Mabashi-Asazuma, H., Kondo, K., and Iida, K. (2020a). Gallic acid inhibits lipid accumulation via AMPK pathway and suppresses apoptosis and macrophage-mediated inflammation in hepatocytes. Nutrients 12, 1479. doi:10.3390/nu12051479
Tanaka, M., Sugama, A., Sumi, K., Shimizu, K., Kishimoto, Y., Kondo, K., et al. (2020b). Gallic acid regulates adipocyte hypertrophy and suppresses inflammatory gene expression induced by the paracrine interaction between adipocytes and macrophages in vitro and in vivo. Nutr. Res. 73, 58–66. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2019.09.007
Tannu, M., Hess, C. N., Gutierrez, J. A., Lopes, R., Swaminathan, R. V., Altin, S. E., et al. (2024). Polyvascular disease: a narrative review of risk factors, clinical outcomes and treatment. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 26, 505–520. doi:10.1007/s11886-024-02063-0
Tomita, T. (2017). Apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells in Type 1 diabetes. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 17, 183–193. doi:10.17305/bjbms.2017.1961
Umadevi, S., Gopi, V., and Elangovan, V. (2014). Regulatory mechanism of gallic acid against advanced glycation end products induced cardiac remodeling in experimental rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 208, 28–36. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2013.11.013
Umadevi, S., Gopi, V., and Vellaichamy, E. (2013). Inhibitory effect of gallic acid on advanced glycation end products induced up-regulation of inflammatory cytokines and matrix proteins in H9C2 (2-1) cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 13, 396–405. doi:10.1007/s12012-013-9222-2
Vallée, A., and Lecarpentier, Y. (2019). TGF-β in fibrosis by acting as a conductor for contractile properties of myofibroblasts. Cell. Biosci. 9, 98. doi:10.1186/s13578-019-0362-3
van der Heijden, C. A., Janssen, P. J., and Strik, J. J. (1986). Toxicology of gallates: a review and evaluation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 24, 1067–1070. doi:10.1016/0278-6915(86)90290-5
van Dierendonck, X. A. M. H., Vrieling, F., Smeehuijzen, L., Deng, L., Boogaard, J. P., Croes, C.-A., et al. (2022). Triglyceride breakdown from lipid droplets regulates the inflammatory response in macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119, e2114739119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2114739119
Variya, B. C., Bakrania, A. K., Madan, P., and Patel, S. S. (2019). Acute and 28-days repeated dose sub-acute toxicity study of gallic acid in albino mice. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 101, 71–78. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.11.010
Variya, B. C., Bakrania, A. K., and Patel, S. S. (2020). Antidiabetic potential of gallic acid from Emblica officinalis: improved glucose transporters and insulin sensitivity through PPAR-γ and Akt signaling. Phytomedicine 73, 152906. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152906
Wang, H., Fowler, M. I., Messenger, D. J., Ordaz-Ortiz, J. J., Gu, X., Shi, S., et al. (2021). Inhibition of the intestinal postprandial glucose transport by gallic acid and gallic acid derivatives. Food Funct. 12, 5399–5406. doi:10.1039/d1fo01118a
Wang, H., Lu, Y., Yan, Y., Tian, S., Zheng, D., Leng, D., et al. (2019). Promising treatment for type 2 diabetes: fecal microbiota transplantation reverses insulin resistance and impaired islets. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 9, 455. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2019.00455
Wei, L., Zhu, P., Chen, X., Wang, Y., and Xu, Y. (2020). An ultra high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of thirteen components extracted from Radix Puerariae in rat plasma and tissues: application to pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution study. J. Sep. Sci. 43, 418–437. doi:10.1002/jssc.201900824
Wesley, C. D., Sansonetti, A., Neutel, C. H. G., Krüger, D. N., De Meyer, G. R. Y., Martinet, W., et al. (2024). Short-term proteasome inhibition: assessment of the effects of carfilzomib and bortezomib on cardiac function, arterial stiffness, and vascular reactivity. Biol. (Basel) 13, 844. doi:10.3390/biology13100844
Wianowska, D., and Olszowy-Tomczyk, M. (2023). A concise profile of gallic acid-from its natural sources through biological properties and chemical methods of determination. Molecules 28, 1186. doi:10.3390/molecules28031186
Wu, S., Chen, W., Lu, S., Zhang, H., and Yin, L. (2022). Metabolic engineering of shikimic acid biosynthesis pathway for the production of shikimic acid and its branched products in microorganisms: advances and prospects. Molecules 27, 4779. doi:10.3390/molecules27154779
Xu, B., Li, W., You, Z., Yang, N., Lin, L., and Li, Y. (2024). Risk factors for left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis. Med. Baltim. 103, e40496. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000040496
Xu, Y., Tang, G., Zhang, C., Wang, N., and Feng, Y. (2021). Gallic acid and diabetes mellitus: its association with oxidative stress. Molecules 26, 7115. doi:10.3390/molecules26237115
Yan, X., Zhang, Q.-Y., Zhang, Y.-L., Han, X., Guo, S.-B., and Li, H.-H. (2020). Gallic acid attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction by inhibiting the degradation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 1121. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01121
Yang, K., Zhang, L., Liao, P., Xiao, Z., Zhang, F., Sindaye, D., et al. (2020). Impact of gallic acid on gut health: focus on the gut microbiome, immune response, and mechanisms of action. Front. Immunol. 11, 580208. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.580208
Yang, R., Shi, L., Si, H., Hu, Z., Zou, L., Li, L., et al. (2023). Gallic acid improves comorbid chronic pain and depression behaviors by inhibiting P2X7 receptor-mediated ferroptosis in the spinal cord of rats. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 14, 667–676. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00532
Yasuda, T., Inaba, A., Ohmori, M., Endo, T., Kubo, S., and Ohsawa, K. (2000). Urinary metabolites of gallic acid in rats and their radical-scavenging effects on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical. J. Nat. Prod. 63, 1444–1446. doi:10.1021/np0000421
Yeudall, S., Upchurch, C. M., Seegren, P. V., Pavelec, C. M., Greulich, J., Lemke, M. C., et al. (2022). Macrophage acetyl-CoA carboxylase regulates acute inflammation through control of glucose and lipid metabolism. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq1984. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abq1984
Yu, C., Chen, X., Zhu, W., Li, L., Peng, M., Zhong, Y., et al. (2022). Synthesis of gallic acid-loaded chitosan-grafted-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid hydrogels for oral controlled drug delivery: in vitro biodegradation, antioxidant, and antibacterial effects. Gels 8, 806. doi:10.3390/gels8120806
Yu, X.-A., Teye Azietaku, J., Li, J., Wang, H., Zheng, F., Hao, J., et al. (2018a). Simultaneous quantification of gallic acid, bergenin, epicatechin, epicatechin gallate, isoquercitrin, and quercetin-3-rhamnoside in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS method and its application to pharmacokinetics after oral administration of Ardisia japonica extract. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 4964291. doi:10.1155/2018/4964291
Yu, Z., Song, F., Jin, Y.-C., Zhang, W.-M., Zhang, Y., Liu, E.-J., et al. (2018b). Comparative pharmacokinetics of gallic acid after oral administration of gallic acid monohydrate in normal and isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 328. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00328
Zhang, D., Zhou, Q., Yang, X., Zhang, Z., Wang, D., Hu, D., et al. (2024). Gallic acid can promote low-density lipoprotein uptake in HepG2 cells via increasing low-density lipoprotein receptor accumulation. Molecules 29, 1999. doi:10.3390/molecules29091999
Zhang, J., Li, L., Kim, S.-H., Hagerman, A. E., and Lü, J. (2009). Anti-cancer, anti-diabetic and other pharmacologic and biological activities of penta-galloyl-glucose. Pharm. Res. 26, 2066–2080. doi:10.1007/s11095-009-9932-0
Zhang, J., Liang, R., Wang, K., Zhang, W., Zhang, M., Jin, L., et al. (2022a). Novel CaMKII-δ inhibitor hesperadin exerts dual functions to ameliorate cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury and inhibit tumor growth. Circulation 145, 1154–1168. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055920
Zhang, Y., Guan, H., Fu, Y., Wang, X., Bai, L., Zhao, S., et al. (2020). Effects of SFRP4 overexpression on the production of adipokines in transgenic mice. Adipocyte 9, 374–383. doi:10.1080/21623945.2020.1792614
Zhang, Y., Li, T., Pan, M., Wang, W., Huang, W., Yuan, Y., et al. (2022b). SIRT1 prevents cigarette smoking-induced lung fibroblasts activation by regulating mitochondrial oxidative stress and lipid metabolism. J. Transl. Med. 20, 222. doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03408-5
Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Lu, B., Gao, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2022c). Functional and binding studies of gallic acid showing platelet aggregation inhibitory effect as a thrombin inhibitor. Chin. Herb. Med. 14, 303–309. doi:10.1016/j.chmed.2021.09.001
Zhao, R., Liu, W., Wang, M., Zhang, Y., Pan, L., Feng, F., et al. (2020). Lysyl oxidase inhibits TNF-α induced rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via regulating Fas/FasL pathway and the p53 pathways. Life Sci. 260, 118483. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118483
Zhao, S., Cui, H., Fang, X., Xia, W., Tao, C., and Li, J. (2024). Increased DNMT1 acetylation leads to global DNA methylation suppression in follicular granulosa cells during reproductive aging in mammals. BMC Genomics 25, 1030. doi:10.1186/s12864-024-10957-0
Zhao, Y., Li, D., Zhu, Z., and Sun, Y. (2020a). Improved neuroprotective effects of gallic acid-loaded chitosan nanoparticles against ischemic stroke. Rejuvenation Res. 23, 284–292. doi:10.1089/rej.2019.2230
Zhao, Y., Li, D., Zhu, Z., and Sun, Y. (2020b). Improved neuroprotective effects of gallic acid-loaded chitosan nanoparticles against ischemic stroke. Rejuvenation Res. 23, 284–292. doi:10.1089/rej.2019.2230
Zhou, F., Li, K., and Yang, K. (2023). Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes and related microRNAs in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J. Cardiovasc Transl. Res. 16, 453–462. doi:10.1007/s12265-022-10329-7
ASCVD Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
AS atherosclerosis
CHD coronary heart disease
GA Gallic acid
T2DM type 2 diabetes
HOMA-IR Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance
STZ streptozotocin
SFRP4 secreted frizzled-related protein 4
IR insulin receptor
IRS-1 insulin receptor substrate 1
PI3K Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase
Akt Protein Kinase B
NF-κB Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
IL-6 Interleukin-6
TNF-α Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
GLUT2 glucose transporter 2
SGLT1 sodium-dependent glucose transporter protein 1
ACC acetyl-CoA carboxylase
LDL low-density lipoprotein
HFD high-fat diet
TG triglyceride
FAS Fatty Acid Synthase
pAMPK phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase
OA oleic acid
NAFLD non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ATGL Adipose triglyceride lipase
HSL hormone-sensitive lipase
PPARγ Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma
PPARα Peroxisome proliferator-activatedve receptor alpha
BAT Brown adipose tissue
Fas/FasL Fas Cell Surface Death Receptor/Fas Ligand
Fabp4 fatty acid-binding protein-4
L-NAME Nω-Nitro-L-arginine methyl ester
ERK Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase
CypD Cyclophilin D
HDAC1 histone deacetylase 1
HDAC2 histone deacetylase 2
HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells
HMEC-1 human microvascular endothelial cells
Nox NADPH Oxidase
eNOS endothelial nitric oxide synthase
LV left ventricle
SHRs spontaneously hypertensive rats
CaMKII calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
ISO isoproterenol
I/R ischemia/reperfusion
ROS Reactive Oxygen Species
MDA malondialdehyde
MPO myeloperoxidase
SOD superoxide dismutase
CAT catalase
GPx glutathione peroxidase
GST purinergic enzymes, detoxifying enzymes
δ-ALA-D heme biosynthesizing enzymes
LDH lactate dehydrogenase
TBARS Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances
LTB4DH Leukotriene B4 12-Hydroxydehydrogenase
PTEN Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog deleted on Chromosome 10
RhoA Ras Homolog Family Member A
Rac1 Ras-related C3 Botulinum Toxin Substrate 1
CDC42 Cell Division Cycle 42
CDK1 cytokinin-dependent kinase 1
TGF-β transforming growth factor-β
LVDP left ventricular developed pressure
±dp/dt rates of pressure development
RPP rate-pressure product
cTnT cardiac troponin T
VD vascular dementia
2VO permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion
CHI cerebral hypoperfusion ischemia
MCAO Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
MPTP mitochondrial permeability transition pore
MMPs matrix metalloproteinases
BBB blood-brain barrier
SDH shikimate dehydrogenase
BCCA bilateral common carotid artery
GSPE grape seed polyphenol extract
Cmax maximum plasma concentration
Tmax time to reach maximum concentration
T1/2 half-life
AUC the area under the curve
HPLC High-performance liquid chromatography
LPHNs lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle system
GANPs GA into nanoparticles
4-Ω 4-methyl GA
4-OMePCA 4-methyl protocatechuic acid
MNPs Magnesium ferrite nanoparticles
CS Hydrogels based on chitosan
AMPS 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid
GACNPs GA-based carbon nanoparticles
FA ferulic acid
HPβCD 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
SNEDDS self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system
SREBP-2 sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2
HMGCS β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase
TAG triglyceride
PWV pulse wave velocity
VSMCs vascular smooth muscle cells
AGEs advanced glycation end products
DNMT1 DNA (Cytosine-5)-Methyltransferase 1
PKCα Protein Kinase C alpha
p38 MAPK p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
GSK3β Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 beta
CPK creatine phosphokinase
CK-MB creatine kinase-MB
4VO four-vessel occlusion.
Keywords: gallic acid, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, ASCVD, cardio-vascular diseases
Citation: Zhao X-L, Cao Z-J, Li K-D, Tang F, Xu L-Y, Zhang J-N, Liu D, Peng C and Ao H (2025) Gallic acid: a dietary metabolite’s therapeutic potential in the management of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1515172. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1515172
Received: 22 October 2024; Accepted: 20 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Di Yang, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Monika E. Czerwińska, Medical University of Warsaw, PolandCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Cao, Li, Tang, Xu, Zhang, Liu, Peng and Ao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Ao, YW9odWkyMDA1QDEyNi5jb20=; Cheng Peng, cGVuZ2NoZW5nY3h5QDEyNi5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.