
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Pharmacol. , 06 January 2025
Sec. Ethnopharmacology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1505851
Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. (C. trichotomum) is a shrub or tree of the genus Clerodendrum, family Lamiaceae, which is widely distributed in China, Korea, India, Japan and Philippines. C. trichotomum is a kind of medicinal and edible plant which integrates ecological afforestation, garden greening, herbal medicine and flavor wild vegetable. As a traditional Chinese medicine, C. trichotomum is used to treat various diseases and conditions, which has inspired research on the pharmacological activities of its different parts, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. These studies have revealed many biological properties of C. trichotomum, such as antihypertensive, antitumor, antioxidant, antiinflammatory, antibacterial, analgesic, sedative, anti-HIV-1 and whitening. A total of 164 secondary metabolites were isolated from C. trichotomum, and their structural types were mainly terpenoids, flavonoids, steroids, phenylpropanoids and phenylpropanoid glycosides, phenylethanosides, phenolic glycosides, anthraquinones, polyketones, cyclohexylethanoids, alkaloids and acid amides. The presence of a variety of phytochemicals, especially abietane diterpenes, clerodane diterpenes, phenylpropanoid glycosides and flavonoid glycosides, plays an important role in the activity diversity of this plant. The current study is attempt to comprehensively compile information regarding the phytochemicals and pharmacological activities of C. trichotomum, provide the chemotaxonomic proof for the taxonomic classification of the plant, and also highlight the current gaps and propose possible bridges for the development of C. trichotomum as a therapeutic against important diseases.
Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. is a deciduous shrub or small tree widely distributed in China, Korea, India, Japan and the northern Philippines (Figure 1), and can be mostly found in hillside scrub below 2,400 m above sea level (Chen and Michael, 1994). The first mentioning of C. trichotomum was recorded in the book of Bencao Tujing of Song Dynasty. Historically, due to its origin in Haizhou area of Lianyungang, Jiangsu province, it was once used as Changshan (another kind of Chinese medicine Dichroa febrifuga Lour.), so it is named Haizhou Changshan in China. It is also known as “Chou Wu Tong,” “Di Wu Tong,” “Ai Tong Zi” and so on (Chinese Materia Medica editorial board, 1999). The flowering period of C. trichotomum is from June to October, and the fruiting period is from August to November (Peng and Chen, 1982). The inflorescence is large, the flowers and fruits are gorgeous. Especially, the white flowers, the red calyx and the blue fruit can coexist on the same tree at the same time, and the three colors complement each other. The flowers and fruits can reach a half-year long ornamental period, so it is one of the rare summer flower plants and owes high ornamental value. C. trichotomum has strong resistance and large absorption to sulfur dioxide (SO2) (Zheng et al., 2006), strong tolerance and enrichment ability to heavy metal arsenic (Mahmud et al., 2008). In addition, it has strong stress resistance to drought, salt, waterlogging, barren, high temperature and so on (Xie et al., 2008; Wei et al., 2009; Xie et al., 2012; Zeng et al., 2013). Therefore, it is a suitable tree for urban landscaping, saline-alkali land greening and abandoned land vegetation restoration.
C. trichotomum is mainly used as a folk remedy for the treatment of rheumatism, hemiplegia, hypertension, migraine, malaria and dysentery (Xie, 1996; Chinese Materia Medica editorial board, 1999). Its roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits can be used as medicine (Table 1). What’s more, the young leaves of C. trichotomum are a kind of green woody wild vegetable favoured by local residents in Guizhou, Hubei, Sichuan, Yunnan and other places of China because of their unique flavor, fresh taste and slightly sweet aftertaste. The leaves are non-toxic, bitter and cold in taste, with special flavor and rich in pectin, vegetable protein and a variety of amino acids. They are essential raw materials for Enshi Tujia to make “fairy tofu,” and have been favored by the majority of consumers because of their unique flavor and natural pollution-free (Wang, 2002), and can also be made into special drinks (Zheng et al., 2013).
C. trichotomum is a kind of medicine homologous food which integrates ecological afforestation, garden greening, traditional Chinese medicine and flavor wild vegetable. Despite the existence of many bioactive phytochemicals and some potential biological properties, only one recent review of C. trichotomum has been published and only 50 references have been reviewed (Gomulski and Grzegorczyk-Karolak, 2024). A complete and comprehensive compilation of the phytochemicals and pharmacological activities of C. trichotomum is still absent in the literature. This may be an important reason for the underutilization of this medicinal and edible plant. Hence, in the current study, the comprehensive compilation of phytochemicals as well as pharmacological activities of C. trichotomum has been attempted, which also highlights the current gaps and proposes possible bridges for the development of C. trichotomum as a therapeutic against important diseases. C. trichotomum belongs to the genus Clerodendrum. However, it is still debated whether the genus Clerodendrum belongs to the Labiaceae family or the Verbenaceae family. Genus Clerodendrum was assigned to family Verbenaceae traditionally by Engler and Prantl (Briquet, 1895). This classification method is also adopted in Flora of China (Peng and Chen, 1982; Chen and Michael, 1994). But modern taxonomic systems mostly put it in the family Lamiaceae (Latta, 2008). Therefore, a review of its chemical constituents is of great significance in chemotaxonomy for the scientific definition of its placement in the plant classification system.
Information for this review was collected through several popular search engines and databases such as Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Springer, Google Scholar, PubMed, Taylor and Francis, Wiley, ProQuest, CNKI, and classic texts of Chinese herbal medicines (e.g., Bencao Tujing), and other websites, such as the Flora of China, the Plant List, YaoZh website (https://db.yaozh.com/). The selection criteria of this article were: 1) Research involves the botany, toxicity and adverse reactions, and the traditional application of C. trichotomum; 2) research involves the preparation of crude extract and the separation and identification of monomer compounds; 3) research involves the pharmacological activity of the crude extracts and isolated compounds; 4) research involves the mechanism of action and so on. Keywords used in the literature search were “C. trichotomum,” “海州常山,” “phytochemistry,” “chemical constituents,” “pharmacology,” “biological activity,” “traditional uses,” “medicinal uses,” “toxicology,” “safety,” and other related search terms. We searched all eligible literature up to July 2024, with no time and language restrictions. The sources of the literature database were shown in Figure 2. The chemical structures of these compounds isolated from C. trichotomum were drawn using the software ChemDraw 22.
C. trichotomum is a deciduous shrub or tree that belongs to genus Clerodendrum family Verbenaceae, 1.5–10 m tall (Figure 3). The branchlets are lenticellate. The leaves of the plant are ovate-elliptic, triangular-ovate or ovate, with a size of around 5–16 cm × 2–13 cm. Their base is broadly cuneate, truncate, or rarely cordate, margin is entire or rarely undulate, apex is acuminate. The leaf blade is greenish abaxially and dark green adaxially. The veins are 3–5 pairs and the petiole is 2–8 cm long. The inflorescences are axillary or terminal, lax, corymbose cymes, dichotomous. The length of inflorescence is 8 and 18 cm and the peduncle is 3–6 cm long. The bracts are elliptic and the flowers are fragrant. The calyx is greenish firstly, then becoming purple, deeply 5-lobed; the lobes are triangular-lanceolate to ovate. The corolla is white or pinkish, with about 2 cm long, its tube is slender; its lobes are oblong, with the size of around 5–10 mm × 3–5 mm. The style is shorter than stamens, both exserted. The drupes are blue-purple, subglobose, ca. 6–8 mm in diam (Peng and Chen, 1982; Chen and Michael, 1994).
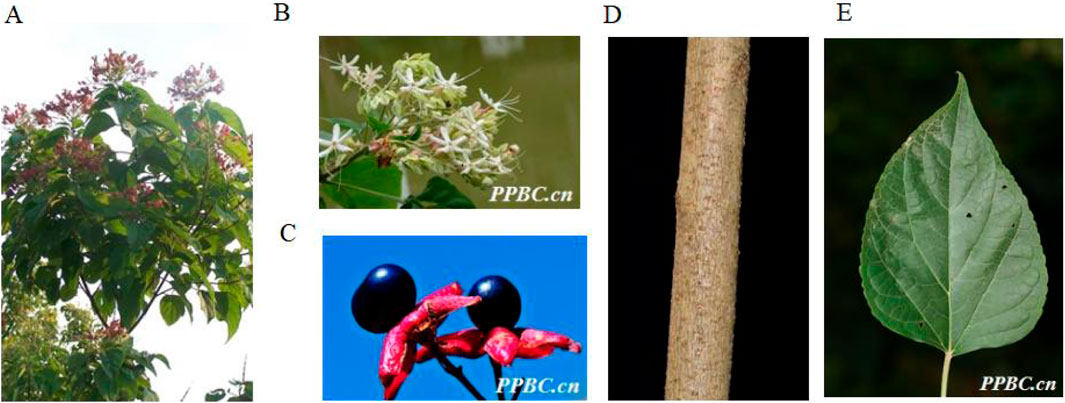
Figure 3. The aerial parts (A), Plant flowers (B), Plant fruits (C), Plant stems (D) and Plant leaves (E) of Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb (http://ppbc.iplant.cn/).
Limited toxicity research on C. trichotomum has been conducted in the literature, although C. trichotomum leaves and stems have been used as a medicine in different populations. The median lethal dose (LD50) of C. trichotomum water extract in mice was 20.6 g/kg by intraperitoneal injection (Yan et al., 1957). Rats were given 150 g/kg hot water (80°C) maceration extract by intragastric administration, and no animal death was observed within 72 h; The LD50 for intravenous injection was 19.4 g/kg (Xu and Xing, 1962). Mice were intraperitoneally injected with clerodendronin A (an active compound of C. trichotomum), the LD50 was 1.84 g/kg (equivalent to crude drug 370 g/kg); Intraperitoneally injected mice with clerodendronin B (another active compound of C. trichotomum), the LD50 was 3.21 g/kg (equivalent to crude drug 550 g/kg) (Xu et al., 1960a). The rats were given 0.25 g/(kg·d) and 2.5 g/(kg·d) hot water (80°C) maceration extract of C. trichotomum by intragastric administration for 60 days, separately, no abnormal changes were observed in growth, blood, urine and pathology except for quiet, reduced activity and loose stool in a few animals (Xu and Xing, 1962). When dogs were given 10 g/(kg·d) for 3 consecutive weeks, there were no significant effects on liver function, blood image, electrocardiogram and pathological examination of heart, liver and kidney, but the dose above 20 g/kg could induce vomiting (Wang et al., 1960).
The roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits of C. trichotomum can be used as medicinal parts. 164 phytochemicals have been reported in the roots and aerial parts of C. trichotomum (Table 2). Most of these studies were focused on leaves, stems, roots and fruits, while few papers have been done on the flowers so far. The prime objective behind the phytochemical identification in C. trichotomum was the discovery of phytochemicals responsible for the reported biological activities. Hence, in several studies, further biological properties were also analyzed after the phytochemical studies. Various important phytochemicals discovered in these studies may explain the reported biological properties of C. trichotomum. Among 164 secondary metabolites, there were 74 terpenoids (including 4 monoterpenes, 3 sesquiterpenes, 51 diterpenes and 16 triterpenes), 11 flavonoids, 16 steroids, 24 phenylpropanoids, 3 phenylethanosides, 2 phenolic glycosides, 3 anthraquinones, 2 polyketones, 7 cyclohexylethanoids, 7 alkaloids, 2 acid amides, and 13 other compounds (including 3 acids, 3 alcohols, 3 aldehydes, 2 esters, 1 alkane and 1 peroxide). In addition, the volatile oils from different parts of C. trichotomum also have been analyzed and reported.
Terpenoids are the most commonly reported types of compounds isolated from C. trichotomum, with a total of 74 compounds (Figure 4), including monoterpenes (1–4) (Nagao et al., 2001; Lee et al., 2016; Li et al., 2022a), sesquiterpenes (5–7) (Xu et al., 2015), diterpenes (8–58) and triterpenoids (59–74) (Choi et al., 2012; Hu et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2015; Li et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022a; Zhang et al., 2022). Among the diterpenes, there were 39 abietane-type diterpenes (8–46) (Wang et al., 2013a; Li et al., 2014a; Li et al., 2014b; Xu et al., 2015; Hu et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022a; Li et al., 2022b; Zhang et al., 2022), 9 clerodane-type diterpene (47–55) (Nishida et al., 1989; Kawai et al., 1998; Kawai et al., 1999; Ono et al., 2013), a chained diterpene (56) (Hu et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2015), a monocyclic diterpene (57) (Xu et al., 2015) and a dimeric diterpene (58) (Wang et al., 2013b). Abietane-type diterpenes are also the most abundant of all isolated secondary metabolites. Due to the limitation of science and technology at that time, there were some errors in some literatures. Li et al. discovered and revised the NMR data and chemical system names of some compounds in the literatures (Li et al., 2022a; Li et al., 2014b).
Flavonoids are mainly found in the leaves of C. trichotomum. Up to now, only 11 flavonoids (75–85, Figure 5) (Zeng et al., 1963; Okigawa et al., 1970; Morita et al., 1977; Chen et al., 1988; Min et al., 2005; Yao and Guo, 2010; Ono et al., 2013; Xu and Shi, 2015; Tian, 2017; Li et al., 2019) have been isolated from C. trichotomum. The only difference is the substituents in the 6, 7, 3′ and 4′ positions of the flavonoid, the linked sugar group is mostly glucuronic acid (GlcA).
There were 16 steroid compounds (86–101, Figure 6) (Choi et al., 2012; Ono et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2013; Hu et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2014; Xu and Shi, 2015; Tian, 2017; Li et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020) isolated from C. trichotomum. Interestingly, there are nine steroids with a side chain of C10H17 and two double bonds at C-22 and C-25.
There were 24 phenylpropanoid compounds (102–125, Figure 7) reported in the literature (Kim et al., 2001; Kang et al., 2003; Chae et al., 2004; Chae et al., 2005; Chae et al., 2006; Chae et al., 2007; Kim et al., 2009; Lee D. G. et al., 2011; Ono et al., 2013; Li et al., 2014a; Xu and Shi, 2015; Lee et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022b; Zhang et al., 2022). The isolated phenylpropanoids were second only to terpenoids in quantity. They are more polar, mostly in the form of glycosides, and often contain caffeoyl groups in the molecule.
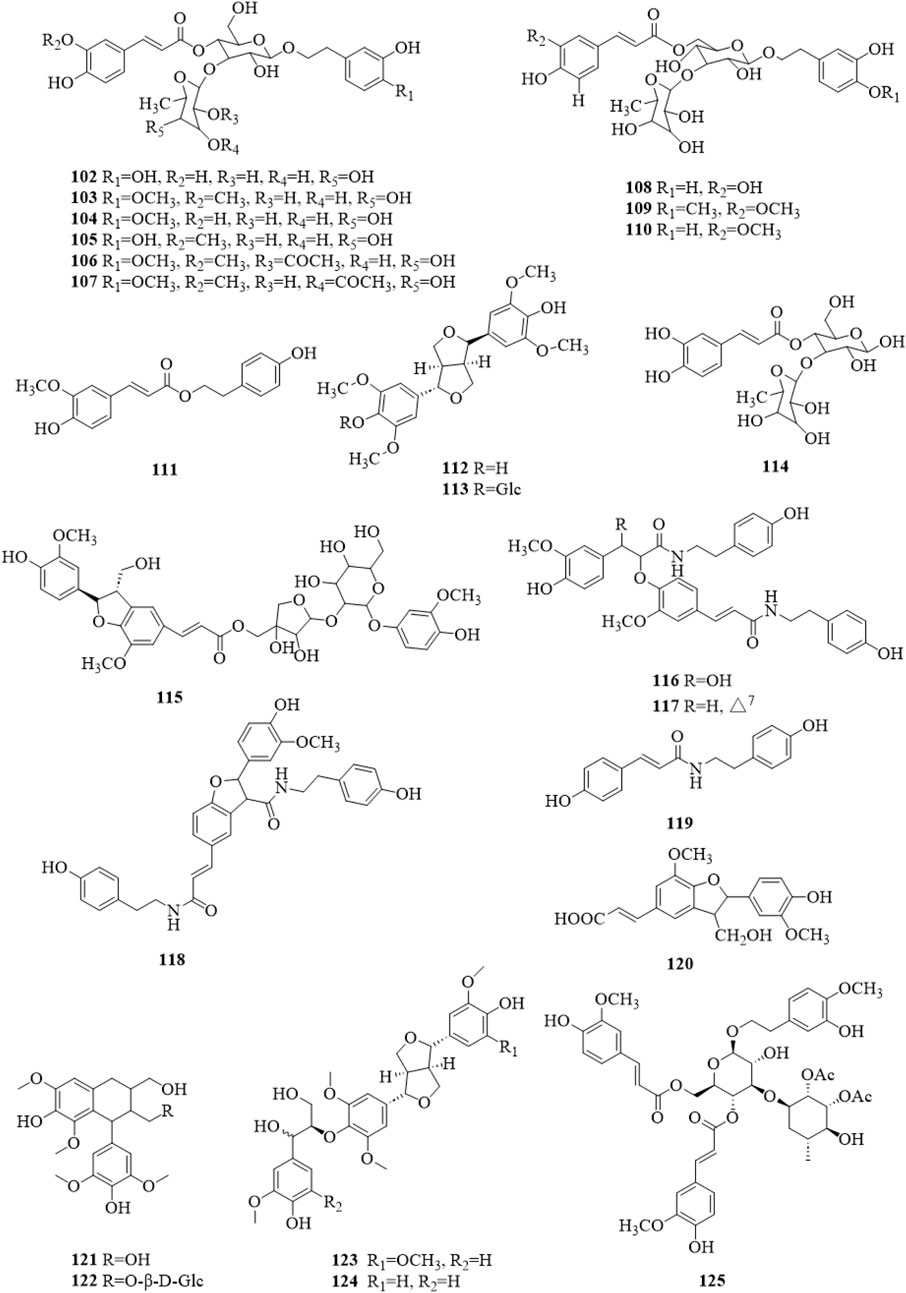
Figure 7. The chemical structure of phenylpropanoids 102–125 isolated from Clerodendrum trichotomum.
Three phenylethanosides, decaffeoylverbascoside (126), 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) ethanol-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (127) and deacylisomartynoside (128) were isolated from the stems of C. trichotomum (Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022b). Compound 126 was also yielded from the leaves (Kim et al., 2009). The structure of compounds 126–128 is shown in Figure 8.
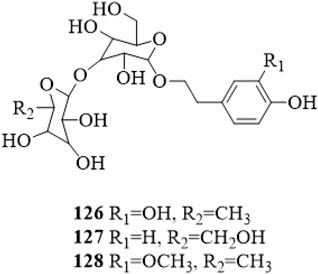
Figure 8. The chemical structure of phenylethanosides 126–128 isolated from Clerodendrum trichotomum.
3,4-dimethoxyphenyl-1-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl (1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside (129) and 2,6-dimethoxy-4-hydroxy-1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (130) have been isolated from the stems, and both of them are phenolic glycosides (Li et al., 2022b). The structures are shown in Figure 9.
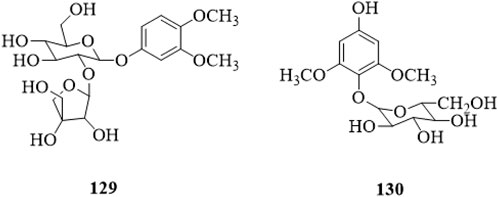
Figure 9. |The chemical structure of phenolic glycosides 129,130 isolated from Clerodendrum trichotomum.
Three anthraquinones (131–133, Figure 10) were isolated from the stems of C. trichotomum (Li et al., 2014a). They were reported from the genus Clerodendrum for the first time.
Two polyketones (Figure 11), Clerodendruketone A (134) and Clerodendruketone B (135), from the leaves and twigs of C. trichotomum were reported (Gao et al., 2022).
Cyclohexylethanoids are rarely isolated from C. trichotomum. In 2014, 7 cyclohexylethanoids (Figure 12), including rengyolone (136), 5-O-butyl cleroindin D (137), cleroindin C (138), 1-hydroxy-1-(8-palmitoyloxyethyl) cyclohexanone (139), cleroindin B (140), rengyol (141) and isorengyol (142), were isolated from the leaves and reported (Xu et al., 2014).
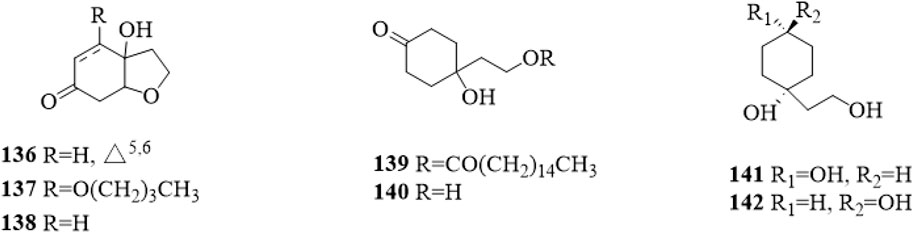
Figure 12. The chemical structure of cyclohexylethanoids 136–142 isolated from Clerodendrum trichotomum.
So far, a total of 8 alkaloids (143–149, Figure 13) have been found from C. trichotomum. In the 1960s, Xu et al. isolated three quinoline alkaloids (Xu and Xing, 1962), namely, orixine (146), orixidine (147) and iso-orixine (148). Then, 1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid (145) (Hu et al., 2014), trichotomine (143) and trichotomine G1 (144) (Iwadare et al., 1974) have been discovered, which were all indole alkaloids. In recent years, 1H-imidazole-4-carboxylate (149) (Wang et al., 2021) were reported, and they belong to purine and imidazole, respectively.
Two acid amides, including (2S,3S,4R,23E)-2-[(2′R)-2′-hydroxyl-octacosane amino]-hexacosane-1,3,4-triol (150) (Tian, 2017) and aurantiamide acetate (151) (Xu and Shi, 2015) have been isolated and reported. The structures of the two compounds are shown in Figure 14.
Other types of compounds (152–164, Figure 15) include acids (152–154) (Yao and Guo, 2010; Xu and Shi, 2015; Tian, 2017; Liu et al., 2020), alcohols (155–157) (Xu et al., 2015; Xu and Shi, 2015; Tian, 2017), aldehydes (158–160) (Xu and Shi, 2015; Li et al., 2019), esters (161,162) (Xu and Shi, 2015; Li et al., 2019), a alkane (163) (Tian, 2017), and a peroxide (164) (Liu et al., 2020).
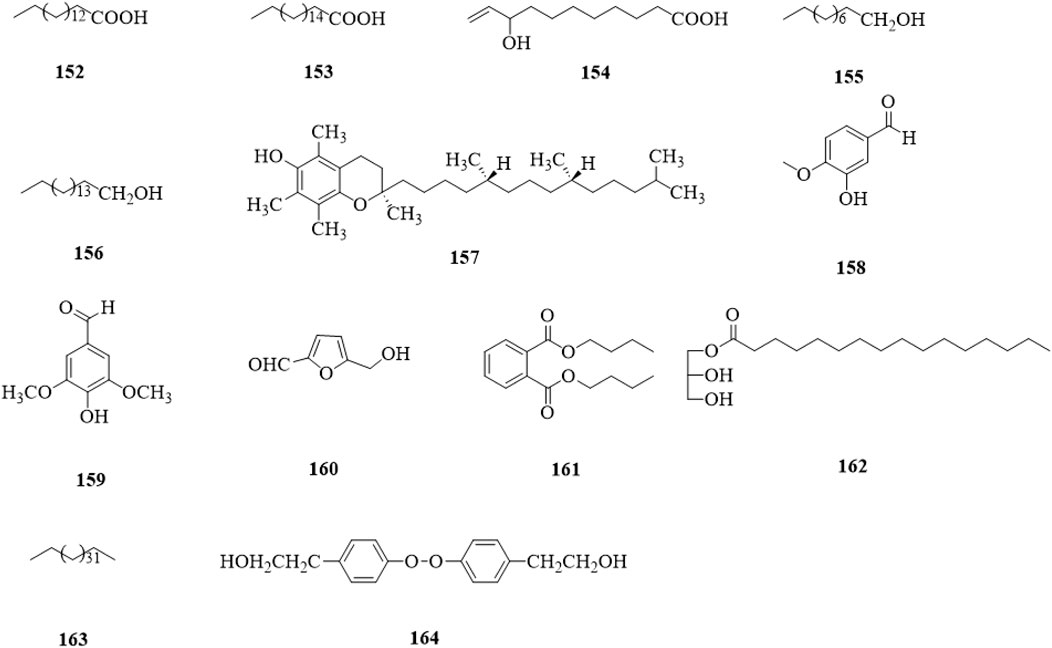
Figure 15. The chemical structure of other compounds 152–164 isolated from Clerodendrum trichotomum.
Volatile compounds of C. trichotomum have been analyzed and reported by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and most of these studies were focused on the leaves, flowers and fruits (Table 3). Yan et al. extracted volatile oil from the leaves of C. trichotomum by steam distillation, analyzed and identified 47 compounds (Yan and Tian, 2003). Among them, (E,E,E)-9,12,15-octadecatrienoate methyl ester and (E,E,E) −9,12,15-octadecatrienol accounted for the higher content, accounting for 12.65% and 13.4% of the total components respectively. Lee et al. used GC-MS to analyse the volatile components of the leaves, and identified 50 compounds (Lee J. Y. et al., 2011), of which the main components were 2,6,10,15-tetramethylheptadecane (23.83%) and linalool (29%). The volatiles of the flowers were analyzed by headspace solid phase microextraction coupled with GC-MS (HS-SPME-GC-MS) for the first time (Tian et al., 2011). Twenty-seven compounds were identified, 2,6,10,14-tetramethylhexadecane, hexadecanal, octen-3-ol, benzaldehyde and n-hexadecanoic acid were the dominant components. Li et al. used GC-MS to analyse the volatile oil components in the fruits of C. trichotomum in 2020, and identified a total of 31 compounds (Li et al., 2020). The analysis showed that the components of volatile oil were different with different parts of plant, origin and extraction methods.
C. trichotomum is widely used in the folk to nourish the liver and reduce blood pressure, dispell wind and eliminate dampness. Pharmacological studies have shown that it has a variety of pharmacological activities. In China, relevant studies mainly focus on the mechanism of reducing blood pressure, sedation and analgesia, most of which were in the 1950s and 1960s. Studies in other countries mainly concentrated in antiinflammatory, antioxidant and other mechanisms of action, with more reports in South Korea and Japan, and most of the studies were carried out in the 21st century. The chemical constituents isolated from the C. trichotomum have abundant pharmacological activities, the most important ones are antihypertensive, antitumour, antioxidant, antiinflammatory, antibacterial, sedative and analgesic. The pharmacological activities of all the compounds are shown in Table 4.
The study on the antihypertensive pharmacology of C. trichotomum first began in China in the 1950s and 1960s. The water extracts of the leaves and twigs of C. trichotomum (“Chou Wu Tong” in Chinese) showed different degrees of hypotensive effect on anesthetized or awake rats and dogs, as well as renal hypertensive rats and dogs, regardless of oral administration or injection (Xu and Xing, 1962). Xu and Peng reported that the antihypertensive effects are closely related to the central nervous and endovascular receptors (Xu and Peng, 1960). Other research have shown that its antihypertensive mechanism is closely related to the direct dilation of blood vessels and the blocking of ganglia (Xu, 1962). Lu et al. found that C. trichotomum is effective in lowering blood pressure by increasing renal blood flow and promoting urinary water and sodium excretion (Lu et al., 1994).
Kang et al. isolated a series of phenylpropanoid glycosides from the stems of C. trichotomum and found that these compounds acteoside (102), martynoside (103), leucosceptoside A (104), isoacteoside (108), and isomartynoside (109) had significant angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity, with IC50 values were 373.3 ± 9.3 µg/mL, 524.4 ± 28.1 µg/mL, 423.7 ± 18.8 µg/mL, 376.0 ± 15.6 µg/mL, 505.9 ± 26.7 µg/mL, respectively. The antihypertensive effect of C. trichotomum may be, at least in part, due to ACE inhibitory effect of the phenylpropanoid glycosides (Kang et al., 2003).
Morita et al. isolated a flavonoid glycoside, clerodendroside (82), from the leaves of C. trichotomum, which proved to have a hypotensive effect on anaesthetised rats (Morita et al., 1977).
The large number of compounds in C. trichotomum has a variety of anti-tumour activities, including breast cancer cells MCF-7, 4T1, lung cancer cells A549, hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2, cervical cancer cells Hela, melanoma cells B16, haematological leukemia cells K562, acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells CEM, acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells HL-60, intestinal cancer cells HCT-8 and so on.
Li et al. isolated nine abietane diterpenoids from the EtOAc part of the stems of C. trichotomum, and cyrtophyllone B (9), villosin B (14), villosin C (15), teuvincenone A (19), uncinatone (26) were found to have remarkable cytotoxicity against four cancer cell lines (A549, HepG-2, MCF-7 and 4T1) with IC50 values ranging from 8.79 to 35.46 µM (Li et al., 2014b). Then, 4 abietane diterpenoids were obtained from the n-butanol portion by the same research group, and villosin C (15), teuvincenone B (20) and ucinatcone (26) were found to have good antitumour activity (Li et al., 2022b). Ucinatcone (26) inhibited the proliferation of MCF-7, A549 and HepG2 cells most strongly, with the IC50 of 25.00, 22.34, and 12.50 μM, respectively. Only villosin C (15) had inhibitory activity on the proliferation of K562 cells, with an IC50 of 28.41 μM. Teuvincenone B (20) had some inhibitory activity on the proliferation of MCF-7 and HepG2 cells, with IC50 of 43.18 and 29.74 μM, respectively. Wang et al. isolated and characterized 14 rearranged abietane diterpenoids from the roots of C. trichotomum (Wang et al., 2013a). All isolates were tested for their cytotoxicities against five human cancer cell lines (BGC-823, Huh-7, KB, KE-97, and Jurkat), only uncinatone (26), mandarone E (27), teuvincenone E (29), (10R,16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-18-oxo-17(15→16),18(4→3)-diabeo-abieta-3,5,8,11,13-pentaene-7-one (31), (3S,4R,10R,16S)-3,4:12,16-diepoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15→16),18(4→3)-diabeo-abieta-5,8,11,13-tetraene-7-one (44) and 12,16-epoxy-17(15→16),18(4→3)-diabeo-abieta-3,5,8,12,15-pentaene7,11,14-trione (45) were found to show cytotoxic effects with IC50 values of 0.83–50.99 μM. The study of structure-activity relationship (SAR) shows that the rearranged A-ring and an intact 2-methyl-2-dihydrofuran moiety are supposed to be necessary to demonstrate cytotoxicity. A dimeric diterpene trichotomone (58) was isolated from the roots and inhibited in vitro cytotoxicities against several human cancer cell lines (A549, Jurkat, BGC-823 and 293TWT) with IC50 values ranging from 7.51 to 19.38 μM (Wang et al., 2013b).
Five steroids were isolated from the leaves of C. trichotomum (Xu et al., 2013), of which (20R,22E,24R)-3β-hydroxy-stigmasta-5,22,25-trien-7-one (97) and (20R,22E,24R)-stigmasta-5,22,25-trien-3β,7β-diol (98) exhibited moderate cytotoxicity in vitro against HeLa cell line, with IC50 at 35.67 and 28.92 μg/mL, respectively. The same research group (Xu et al., 2014) also isolated seven cyclohexylethanoids from the leaves. 5-O-butyl cleroindin D (137) and 1-hydroxy-1-(8-palmitoyloxyethyl) cyclohexanone (139) were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against A549 human tumor cell line, but there were no obvious cytotoxicity.
Nagao et al. regarded acteoside (102) and isoacteoside (108) as the antiproliferative constituents and found that the content of active compounds was higher in the bark of C. trichotomum (ca. 4.6%) than in leaves (ca. 0.6%). The GI50 of acteoside (102) against three tumor cell lines (MK-1: human gastric adenocarcinoma, HeLa: human uterus carcinoma, and B16F10: murine melanoma) were 40, 66 and 8 μM, while GI50 of isoacteoside (108) were 40, 61, 8 μM, respectively. SAR study suggests that the antiproliferative activities of phenylpropanoids depend on the 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl group with some contribution of the 3,4-dihydroxycinnamoyl (caffeoyl) group (Nagao et al., 2001).
Phenylpropanoid glycosides 2″-acetylmartynoside (106) and 3″-acetylmartynoside (107), isolated from the stems of C. trichotomum, showed antioxidant activity in terms of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging effects (Chae et al., 2007). Jionoside D (105), isoacteoside (108) and trichotomoside (125), also isolated from the stems, exhibited scavenging activity of intracellular ROS and of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical, as well as lipid peroxidation inhibitory activity. This radical scavenging activity of them protected the cell viability of Chinese hamster lung fibroblast (V79-4) cells exposed H2O2 (Chae et al., 2004; Chae et al., 2005; Chae et al., 2006). Furthermore, jionoside D (105) and isoacteoside (108) increased the activities of cellular antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) (Chae et al., 2004; Chae et al., 2005). Gao et al. isolated ecdysanols D (123) and ecdysanols E (124) from the leaves and twigs, which had moderate antioxidant activity with respective IC50 values of 66.07 and 53.60 μM (Gao et al., 2022). Lee et al. isolated five compounds from the flowers and found that acteoside (102), martynoside (103), leucosceptoside A (104), isoacteoside (108) exhibited strong DPPH antioxidant activity (Lee et al., 2016). Yoon et al. isolated acteoside (102) and isoacteoside (108) from C. trichotomum, both of which dose-dependently inhibited silica-induced ROS production in B16 melanoma cells (Yoon et al., 2009). Ono et al. also reported that among six isolated compounds, acteoside (102) showed the strongest activity with EC50 values of 22.2, 80.2, 23.4 μM in the scavenging of DPPH radical, H2O2 and O2− radical (Ono et al., 2013). Taken together, these findings suggest that phenylpropanoid glycosides isolated from C. trichotomum exhibits antioxidant properties.
A flavonoid glycoside apigenin 7-galacturonide (81) was isolated from the leaves of C. trichotomum and exhibited moderate NO scavenging activity, with the EC50 452 μM (Ono et al., 2013).
Choi et al. used carrageenan-induced rat paw oedema model to study the antiinflammatory effect of methanol extracts from C. trichotomum leaves and found that the antiinflammatory activity of 60% methanol extract was higher than indomethacin, and that this extract also inhibited the production of PGE2 in RAW 264.7 cells (Choi et al., 2004). Park et al. found that methanol extract of C. trichotomum leaves inhibited the production and expression of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in mononuclear macrophages in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (Park and Kim, 2007). Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) showed that the activity of NF-κB was also inhibited, which means that C. trichotomum inhibits the expression of the pro-inflammation gene through the inhibition of NF-κB dependent pathway in RAW 264.7 cells.
Hu et al. discovered a range of diterpenoids from the roots of C. trichotomum and assessed their abilities to inhibit NO production in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Villosin C (15) 15,16-dehydroteuvincenone G (23), 2α-hydrocaryopincaolide F (35) and trichotomin A (46) exerted inhibitory effects at noncytotoxic concentrations with IC50 values of 15.5, 6.0, 6.5 and 10.6 μM, respectively, better than the positive control. Compounds 15α-hydroxyteuvincenone E (37) and trichotomin B (38) showed moderate or weak activities with IC50 values of 28.9–38.6 μM (Hu et al., 2018).
Lee et al. reported that acteoside (102) inhibited histamine release in RBL-2H3 mast cells stimulated by melittin, arachidonic acid and toxocarotene regardless of the presence of extracellular Ca2+ (Lee et al., 2006). The anti-asthmatic effect on the aerosolized ovalbumin (OA) challenge in the OA-sensitized guinea-pigs of acteoside (102) was also evaluated (Lee J. Y. et al., 2011). 102 inhibited specific airway resistance in immediate asthmatic response, inhibited protein content at a dose of 25 mg/kg, and histamine content and PLA2 activity at a dose of 50 mg/kg, in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Kim et al. isolated three phenylpropanoid compounds from the leaves of C. trichotomum, the 80% methanol fraction and acteoside (102) were found to have in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity (Kim et al., 2009).
Min et al. found that apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside (84) was more effective than omeprazole on reflux esophagitis and gastritis in mice (Min et al., 2005). Yang et al. isolated four 24-ethylcholestane derivatives from the roots of C. trichotomum; in vitro screening for anti-inflammatory activity showed that 24-ethyl-7-oxocholesta-5,22(E),25-trien-3β-ol (91) could dose-dependently inhibit IL-8 production in colon cancer HT-29 cells induced by IL-1β (Yang et al., 2014).
Choi et al. tested the antibacterial activity of the MeOH extract from C. trichotomum. The n-hexane and methylene chloride (MC) fractions showed antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori at a concentration of 1.7 mg/mL and showed inhibition zones of 10 and 11 mm in disc assay, respectively. β-Amyrin (70) and 22-dehydroclerosterol (93), isolated from the MC fraction, revealed moderate antibacterial effects against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and H. pylori. 70 showed clear zones of 12 and 13 mm against E. coli and H. pylori, respectively (Choi et al., 2012).
Gao et al. isolated two polyketides clerodendruketone A (134) and clerodendruketone B (135) from the leaves and twigs of C. trichotomum. The antibacterial activity evaluated by turbidimetry assay demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity of 134 (50 µg/mL) with the inhibition rate between 30%∼60% against E. coli and 60%∼80% against S. aureus, while the rates of 135 (50 µg/mL) were both between 30% and 60% (Gao et al., 2022).
Electric shock rat tail method (Wang and Shen, 1957) showed that the analgesic effect was shown when the injection of Chou Wu Tong (leaves and twigs of C. trichotomum) decoction into the abdominal cavity of mice was above 1.65 g/kg, and the peak value appeared 20–40 min after administration, and then gradually decreased, which could be maintained for 2 h. The effect before flowering was better than after flowering. The analgesic effect in mice was observed by hot plate and found that clerodendronin B, an acid soluble granular crystal of Chou Wu Tong, had a significant analgesic effect, and the effect was stronger and longer than that of morphine at a dose of 10–20 mg/Kg when injected into mice peritoneally at a dose of 400–800 mg/Kg (Xu et al., 1960b).
Oral administration or intraperitoneal injection of the Chou Wu Tong decoction was found to have a mild sedative effect on mice, and increased doses did not induce sleep (Shen and Wang, 1957). Clerodendronin A, a water-soluble acicular crystal of Chou Wu Tong, has a strong sedative effect and has a synergistic effect with pentobarbital sodium (Xu et al., 1960b).
Kim et al. isolated seven phenylethanoid glycosides from the stems of C. trichotomum. Acteoside (102) and isoacteoside (108) showed inhibitory activities against HIV-1 integrase with IC50 values of 7.8 and 13.7 μM, respectively (Kim et al., 2001).
Acteoside (102) and isoacteoside (108), isolated from C. trichotomum, showed whitening activity by the inhibition of tyrosinase activity and tyrosinase expression (Yoon et al., 2009). Clerodane-type diterpenes clerodendrin B (48), clerodendrin D (49), clerodendrin H (53) and clerodendrin I (54), were found to have insect feeding stimulant activity of the turnip sawflies, Athalia rosae ruficornis (Nishida et al., 1989; Nishida and Fukami, 1990; Kawai et al., 1998; Kawai et al., 1999). In addition, the sodium phosphate buffer extract of C. trichotomum leaves inhibited the growth of Eichhornia crassipes, causing the leaves dry, rot or even decline, which can be used for biological control of E. crassipes (Zheng and Lu, 2012).
C. trichotomum is endemic to East Asia and has been studied mainly in Japan, Korea and China. At present, the research of chemical composition mainly focus on terpenoids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids and steroids. Most of the terpenoids are diterpenoids, and the main structural types are abietane-type and clerodane-type. Phenylpropanoids exist mainly in the form of glycosides. The quantity and category of volatile oil components in the literature reports are different, which may be related to different origin and extraction methods. The extracts and isolated compounds of C. trichotomum have showed many pharmacological effects such as antihypertensive, antitumor, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory, but their toxicological studies have rarely been reported.
It has been a matter of debate whether C. trichotomum belongs to the family Verbenaceae or the family Lamiaceae (Briquet, 1895; Latta, 2008). This review briefly summarises the secondary metabolites isolated from C. trichotomum reported in the literature. Among the 164 compounds, the largest number was abietane diterpenoids, with 39. Abietane diterpenoids are abundant in C. trichotomum, both in the aerial parts and the roots. From a chemotaxonomical point of view, the abundant presence of abietane diterpenoids supports the view that C. trichotomum transfers Verbenaceae to Labiaceae.
Studies on the chemical components of the plant mainly focus on leaves, stems, roots and fruits. So far, only one paper (Lee et al., 2016) has reported the isolation of four phenylpropanoid glycosides and a monoterpene glycoside from the flowers. However, Xu et al. found that the antihypertensive, analgesic and other activities of C. trichotomum were better before flowering than after flowering (Wang and Shen, 1957; Xu and Xing, 1962), and the reason is still unclear. Therefore, it is a very interesting and meaningful work to study the chemical compositions and pharmacological activities of flower parts and the difference between pre-flowering and post-flowering. In addition, early studies of C. trichotomum were focused on the isolation and identification of individual or several compounds from the extracts, or the pharmacological activity of crude extracts. Future research on chemical and pharmacological activities should be further closely combined to clarify the bioactive compounds of C. trichotomum. On this basis, one or several active compounds should be determined and the quality control standard of C. trichotomum will be established.
The active compounds isolated from C. trichotomum mainly included abietane diterpenoids, phenylpropanoid glycosides, flavonoid glycosides, clerodane diterpenoids and steroidal compounds, which showed excellent activities of reducing blood pressure, antitumor, antioxidant, antiinflammatory, anti-HIV-1 and promoting insect feeding. Among these ingredients, the plant’s major phytochemical is acteoside (102), which has rich pharmacological activities, such as anti-hypertension, antitumor, antioxidant, antiviral and whitening. Relevant studies have shown that it exists in various stages of clinical trials for anti-nephritic, hepatoprotective, and osteoarthritic activity (Srivastava and Shanker, 2022). Some of the isolates are structurally similar to the more highly active phytocompounds. However, they have not been tested for their potential biological activities. The study of the activity of analogues as well as other types of secondary metabolites is an important area for further research, as infectious diseases and civilizational diseases such as cancer require the search for new therapeutic active structures. At the same time, the active substances responsible for analgesic (Wang and Shen, 1957) and sedative (Shen and Wang, 1957) effects of C. trichotomum are still unclear, and Clerodendronin A (Xu et al., 1960a) and Clerodendronin B (Xu et al., 1960b), as reported crystals, need to be further purified and identified. Additionly, SAR studies were in focus of only 2 literatures (Nagao et al., 2001; Wang et al., 2013a) in the past. Therefore, the study of SAR is one of the future research directions. Of course, the chemical modifications of the isolated compounds are necessary in order to obtain semi-synthetic analogues with enhanced biological activity and improved bioavailability or safety. Recent studies have shown that there are abundant secondary metabolites associated with diverse biological activities in C. trichotomum. However, in numerous studies, the excellent pharmacological activity of C. trichotomum was established through cell culture and in vitro experiments. Still, an effective study through in vivo experiments is missing in the scientific literature. Future studies should employ appropriate animal models to elucidate the mechanism of action.
C. trichotomum is a kind of medicinal and edible plant which integrates ecological afforestation, garden greening, herbal medicine and flavor wild vegetable. But the practical application of C. trichotomum is still limited, and its pharmacological potential is also underutilized. In this paper, a comprehensive review of the literature was carried out, the information about extraction, isolation and pharmacological experiments were listed, and the isolated compounds were critically collated. The summary of the chemical compositions of C. trichotomum supports its attribution in plant classification. Compiled information on phytochemicals and pharmacological activities, as well as highlighted gaps and suggested precise directions, may contribute to the development of C. trichotomum as a drug for the treatment of disease, a Chinese herbal preparation, a plant pesticide or a functional food.
LL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing–original draft. SX: Data curation, Resources, Software, Writing–original draft. XD: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. YW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing–original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.81860689 and 82260752).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Au, D. T., Wu, J., Jiang, Z., Chen, H. B., Lu, G. H., and Zhao, Z. Z. (2008). Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by Hakka in Guangdong, China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 117 (1), 41–50. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2008.01.016
Bae, J. Y., Ahn, M. J., and Park, J. H. (2012). Pharmacognostical studies on the Korean folk medicine. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 43 (2), 95–97.
Briquet, J. (1895). in Verbenaceae. Editors A. Engler,, and K. Prantl (Leipzig: Wilhelm Engelmann: Die natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien), IV, 132–182.
Chae, S., Kang, K. A., Kim, J. S., Hyun, J. W., and Kang, S. S. (2006). Trichotomoside: a new antioxidative phenylpropanoid glycoside from Clerodendron trichotomum. Chem. Biodivers. 3 (1), 41–48. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200690005
Chae, S., Kim, J. S., Kang, K. A., Bu, H. D., Lee, Y., Hyun, J. W., et al. (2004). Antioxidant activity of jionoside D from Clerodendron trichotomum. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27 (10), 1504–1508. doi:10.1248/bpb.27.1504
Chae, S., Kim, J. S., Kang, K. A., Bu, H. D., Lee, Y., Seo, Y. R., et al. (2005). Antioxidant activity of isoacteoside from Clerodendron trichotomum. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, Part A 68 (5), 389–400. doi:10.1080/15287390590900750
Chae, S. W., Kang, K. A., Kim, J. S., Kim, H. K., Lee, E. J., Hyun, J. W., et al. (2007). Antioxidant activities of acetylmartynosides from Clerodendron trichotomum. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 50 (4), 270–274.
Chen, S. L., and Michael, G. G. (1994). Verbenaceae: Flora of China, 17, 42. Beijing: Science Press.
Chen, Z. N., Xu, P. J., and Yao, T. R. (1988). Spectral analysis of clerodendrin from Clerodendron trichotomum. Acta Pharm. Sinca 23 (10), 789–791. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.1988.10.013
Chinese Materia Medica editorial board, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (1999). Chinese Materia Medica, Vol. 6. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 576–579.
Choi, J. H., Whang, W. K., and Kim, H. J. (2004). Studies on the anti-inflammatory effects of Clerodendron trichotomum Thunberg leaves. Arch. Pharm. Res. 27 (2), 189–193. doi:10.1007/BF02980105
Choi, J. W., Cho, E. J., Lee, D. G., Choi, K., Ku, J., Park, K. W., et al. (2012). Antibacterial activity of triterpenoids from Clerodendron trichotomum. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 55 (3), 169–172. doi:10.3839/jabc.2012.026
Gao, Y. N., Wei, J. C., Qi, Z. B., Gao, X. Y., and Wang, A. H. (2022). Two novel polyketones from the leaves and twigs of Clerodendrum trichotomum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 24 (3), 245–251. doi:10.1080/10286020.2021.1914598
Gomulski, J., and Grzegorczyk-Karolak, I. (2024). Clerodendrum trichotomum thunberg—an ornamental shrub with medical properties. Molecules 29 (14), 3272. doi:10.3390/molecules29143272
Hu, H. J., Liu, Q., Yang, Y. B., Yang, L., and Wang, Z. T. (2014). Chemical constituents of Clerodendrum trichotomum leaves. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 37 (09), 1590–1593. doi:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2014.09.021
Hu, H. J., Zhou, Y., Han, Z. Z., Shi, Y. H., Wang, Z. T., Li, Y., et al. (2018). Abietane diterpenoids from the roots of Clerodendrum trichotomum and their nitric oxide inhibitory activities. J. Nat. Prod. 81 (7), 1508–1516. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00814
Iwadare, S., Shizuri, Y., Sasaki, K., and Hirata, Y. (1974). Isolation and structure of trichotomine and trichotomine G1. Tetrahedron 30, 4105–4111. doi:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)97392-2
Kang, D. G., Lee, Y. S., Kim, H. J., Lee, Y. M., and Lee, H. S. (2003). Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory phenylpropanoid glycosides from Clerodendron trichotomum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 89 (1), 151–154. doi:10.1016/s0378-8741(03)00274-5
Kawai, K., Amano, T., Nishida, R., Kuwahara, Y., and Fukami, H. (1998). Clerodendrins from Clerodendron trichotomum and their feeding stimulant activity for the turnip sawfly. Phytochemistry 49 (7), 1975–1980. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(98)00431-2
Kawai, K., Nishida, R., and Fukami, H. (1999). Clerodendrin I, a new neoclerodane diterpenoid from Clerodendron trichotomum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63 (10), 1795–1797. doi:10.1271/bbb.63.1795
Kim, H. J., Woo, E. R., Shin, C. G., Hwang, D. J., Park, H., and Lee, Y. S. (2001). HIV-1 integrase inhibitory phenylpropanoid glycosides from Clerodendron trichotomum. Arch. Pharm. Res. 24 (4), 286–291. doi:10.1007/BF02975093
Kim, K. H., Kim, S., Jung, M. Y., Han, I. H., and Whang, W. K. (2009). Anti-inflammatory phenylpropanoid glycosides from Clerodendron trichotomum leaves. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 7–13. doi:10.1007/s12272-009-1112-6
Latta, J. (2008). Changing to APG II:. Sibbaldia J. Botanic Gard. Hortic. 6, 133–153. doi:10.24823/sibbaldia.2008.39
Lee, D. G., Choi, K., and Lee, S. H. (2011). GC/MS analysis of volatile constituents from woody plants. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 38 (4), 723–730. doi:10.7744/cnujas.2011.38.4.723
Lee, J. H., Lee, J. Y., Kang, H. S., Jeong, C. H., Moon, H., Whang, W. K., et al. (2006). The effect of acteoside on histamine release and arachidonic acid release in RBL-2H3 mast cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 29 (6), 508–513. doi:10.1007/BF02969425
Lee, J. W., Bae, J. J., and Kwak, J. H. (2016). Glycosides from the flower of Clerodendrum trichotomum. Kor. J. Pharmacogn. 47 (4), 301–306.
Lee, J. Y., Lee, J. G., Sim, S. S., Whang, W. K., and Kim, C. J. (2011). Anti-asthmatic effects of phenylpropanoid glycosides from Clerodendron trichotomum leaves and Rumex gmelini herbes in conscious Guinea-pigs challenged with aerosolized ovalbumin. Phytomedicine 18 (2-3), 134–142. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2010.06.014
Li, L. Z., Liu, L., Wang, D. P., Yang, X. S., and Liang, J. Y. (2020). GC-MS analysis of volatile oil from the fruit of Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb. Strait Pharm. J. 32 (04), 44–46. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2020.04.015
Li, L. Z., Wang, M. H., Sun, J. B., and Liang, J. Y. (2014a). Abietane diterpenoids and other constituents from Clerodendrum trichotomum. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 56, 218–220. doi:10.1016/j.bse.2014.06.002
Li, L. Z., Wei, X., Liu, L., Li, Y. J., and Liang, J. Y. (2019). Chemical constituents from the stems of Clerodendron trichotomum. J. China Pharm. Univ. 50 (05), 544–548. doi:10.11665/j.issn.1000-5048.20190506
Li, L. Z., Wu, L., Wang, M. H., Sun, J. B., and Liang, J. Y. (2014b). Abietane diterpenoids from Clerodendrum trichotomum and correction of NMR data of villosin C and B. Nat. Prod. Commun. 9 (7), 907–910. doi:10.1177/1934578x1400900706
Li, L. Z., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Cen, Y. Z., Tu, Y. L., Yang, X. S., et al. (2022a). Two new abietane diterpenes from the stems of Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. Nat. Prod. Commun. 17 (9), 1–8. doi:10.1177/1934578x221125053
Li, L. Z., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Cen, Y. Z., Tu, Y. L., Yang, X. S., et al. (2022b). Chemical constituents of the n-butanol fraction from the stems of Clerodendrum trichotomum and their antitumor activities in vitro. China Pharm. 33 (21), 2578–2583+2589. doi:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2022.21.04
Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Wei, X., Li, Y. J., Yang, X. S., and Li, L. Z. (2020). Chemical constituents of Clerodendrum trichotomum fruits. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 43 (07), 1622–1625. doi:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2020.07.016
Lu, G. W., Miura, K., Yukimura, T., Yukimura, T., and Yamamoto, K. (1994). Effects of extract from Clrodendron trichotomum on blood pressure and renal fuction in rats and dogs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 4 (2), 77–82. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(94)90100-7
Mahmud, R., Inoue, N., Kasajima, S. Y., and Shaheen, R. (2008). Assessment of potential indigenous plant species for the phytoremediation of arsenic-contaminated areas of Bangladesh. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 10 (2), 117–130. doi:10.1080/15226510801913884
Min, Y. S., Yim, S. H., Bai, K. L., Choi, H. J., Jeong, J. H., Song, H. J., et al. (2005). The effects of apigenin-7-O-β-d-glucuronopyranoside on reflux oesophagitis and gastritis in rats. Auton. Autacoid Pharmacol. 25, 85–91. doi:10.1111/j.1474-8673.2005.00332.x
Morita, N., Arisawa, M., Ozawa, H., Chen, C. S., and Kan, W. S. (1977). Clerodendroside, a new glycoside from the leaves of Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb. var fargesii Rehd.(Verbenaceae). Yakugaku zasshi 97 (9), 976–979. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.97.9_976
Nagao, T., Abe, F., and Okabe, H. (2001). Antiproliferative constituents in the plants 7. Leaves of Clerodendron bungei and leaves and bark of C. trichotomum. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 24 (11), 1338–1341. doi:10.1248/bpb.24.1338
Nishida, R., and Fukami, H. (1990). Sequestration of distasteful compounds by some pharmacophagous insects. J. Chem. Ecol. 16, 151–164. doi:10.1007/BF01021276
Nishida, R., Fukami, H., Miyata, T., Miyata, T., and Takeda, M. (1989). Clerodendrins: feeding stimulants for the adult turnip sawfly, Athalia rosae ruficornis, from Clerodendron trichotomum (Verbenaceae). Agric. BioI. Chem. 53 (6), 1641–1645. doi:10.1271/bbb1961.53.1641
Ogunlakin, A. D., Akinwumi, I. A., and Ambali, O. A. (2023). Ethnomedicinal application, phytochemistry and therapeutic effects of genus clerodendrum. Funct. Food Sci. 3 (10), 228–247. doi:10.31989/ffs.v3i10.1151
Okigawa, M., Hatanaka, H., Kawano, N., Matsunaga, I., and Tamura, Z. (1970). A new glycoside, acacetin-7-glucurono-(1→2)-glucuronide from the leaves of Clerodendron trichotomum. Tetrahedron Lett. 11 (33), 2935–2936. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)98377-7
Ono, M., Furusawa, C., Matsumura, K., Noguchi, S., Yasuda, S., Okawa, M., et al. (2013). A new diterpenoid from the leaves of Clerodendron trichotomum. J. Nat. Med. 67, 404–409. doi:10.1007/s11418-012-0690-7
Park, M. A., and Kim, H. J. (2007). Anti-inflammatory constituents isolated from Clerodendron trichotomum Tunberg leaves (CTL) inhibits pro-inflammatory gene expression in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing NF-kappaB activation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 30 (6), 755–760. doi:10.1007/BF02977639
Shen, J. L., and Wang, Y. R. (1957). The antihypertensive effect of the leaves and twigs from Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (04), 5–10. doi:10.16305/j.1007-1334.1957.04.002
Shrivastava, N., and Patel, T. (2007). Clerodendrum and healthcare: an overview. Med. aromatic plant Sci. Biotechnol. 1 (1), 142–150.
Srivastava, M., and Shanker, K. (2022). Duranta erecta Linn: a critical review on phytochemistry, traditional uses, pharmacology, and toxicity from phytopharmaceutical perspective. J. Ethnopharmacol. 293, 115274. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115274
Subba, B., Srivastav, C., and Kandel, R. C. (2016). Scientific validation of medicinal plants used by Yakkha community of Chanuwa VDC, Dhankuta, Nepal. Springerplus 5, 155–214. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-1821-5
Tian, K. (2017). Studies on anti-inflammatory activities and chemical constituents of Clerodendron trichotomum Tunberg leaves. Wuhan: HuBei University.
Tian, P. Y., Li, C. Q., Wang, J. M., and Kang, W. Y. (2011). Volatiles in Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb. By head-space solid micro-extraction coupled with GC-MS. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 23 (06), 1077–1079. doi:10.16333/j.1001-6880.2011.06.042
Wang, D. S. (2002). Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. Leaves—a wild woody vegetable with promising development prospects. Panzhihua Sci-Tech and Inf. 27 (2), 49.
Wang, N., Cai, Q., Shan, J. J., Pang, X. H., and Zhu, Y. (2021). Chemical constituents from fruit of Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. ShanDong Chem. Ind. 50 (10), 86–88. doi:10.19319/j.cnki.issn.1008-021x.2021.10.027
Wang, W. X., Xiong, J., Tang, Y., Zhu, J. J., Li, M., Zhao, Y., et al. (2013a). Rearranged abietane diterpenoids from the roots of Clerodendrum trichotomum and their cytotoxicities against human tumor cells. Phytochemistry 89, 89–95. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.01.008
Wang, W. X., Zhu, J. J., Zou, Y., Hong, Z. L., Liu, S. T., Li, M., et al. (2013b). Trichotomone, a new cytotoxic dimeric abietane-derived diterpene from Clerodendrum trichotomum. Tetrahedron Lett. 54 (20), 2549–2552. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2013.03.048
Wang, X. L., Li, X. Y., and Ding, G. S. (1960). Studies on drugs for treatment of hypertension—XI. Therapy with the decoction of Clerodendrum trichotomum in dogs. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. (02), 88–94. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.1960.02.005
Wang, Y. R., and Shen, J. L. (1957). Analgesic effect of the leaves and twigs from Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (04), 11–13. doi:10.16305/j.1007-1334.1957.04.004
Wei, J., Xie, F., Wang, H. T., Chen, C. Y., Yu, W. S., Song, L., et al. (2009). Effect of water stress on growth and physiological characteristicsof Clerodendrum trichotonum Thumb. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 40 (3), 371–376. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2009.03.011
Xie, F. C., Qin, D., and Wang, H. T. (2012). Effects of several environmental stress on morphological and physiological characteristics of Clerodendrum trichotomum. North. Hortic. (4), 55–59.
Xie, F. C., Zhang, W. T., Liu, F. Q., Wang, H. T., Yu, W. S., Chen, C. Y., et al. (2008). Effect of soil NaCl stress on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Clerodendrum trichotonum Thumb. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 30 (5), 839–844. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2008.05.017
Xie, Z. W. (1996). National compilation of Chinese herbal medicine. 2nd edition, 732. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House.
Xu, R. L., Jiang, H. L., Wang, R., and Yan, P. S. (2015). Diverse terpenoids from the leaves of Clerodendrum trichotomum. Chem. Nat. Compd+ 51, 999–1000. doi:10.1007/s10600-015-1477-3
Xu, R. L., and Shi, Y. P. (2015). A study on chemical constituents of Clerodendrum trichotomum. J. Nanchang Inst. Technol. 34 (04), 15–19. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-4869.2015.04.005
Xu, R. L., Wang, R., Ding, L., and Shi, Y. P. (2013). New cytotoxic steroids from the leaves of Clerodendrum trichotomum. Steroids 78 (7), 711–716. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2013.03.002
Xu, R. L., Wang, R., Ha, W., and Shi, Y. P. (2014). New cyclohexylethanoids from the leaves of Clerodendrum trichotomum. Phytochem. Lett. 7, 111–113. doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2013.10.010
Xu, S. Y. (1962). Pharmacological studies on the Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb—Ⅱ. Study on the antihypertensive mechanism of C. trichotomum Thunb. Acta Physiol. Sin. (04), 272–277.
Xu, S. Y., and Peng, H. M. (1960). Pharmacological studies on Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb—III. Further studies on the antihypertensive mechanism of C. trichotomum Thunb. J. Anhui Med. Univ. 3 (2,3), 1–7. doi:10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.1960.z1.001
Xu, S. Y., Peng, H. M., and Gu, Y. Z. (1960a). Pharmacological studies on Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb—V. Analgesic and antihypertensive effects of Clerodendronin B. J. Anhui Med. Univ. 3 (2,3), 14–17. doi:10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.1960.z1.003
Xu, S. Y., Peng, H. M., Gu, Y. Z., and Xing, W. R. (1960b). Pharmacological study of Clerodendrum trichotomum—Ⅳ. Sedative and antihypertensive effects of Clerodendronin A. J. Anhui Med. Univ. 3 (2,3), 8–13. doi:10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.1960.z1.002
Xu, S. Y., and Xing, W. R. (1962). Pharmacological study of Clerodendrum trichotomum—I. Toxicity and antihypertensive effects of C. trichotomum՚s hot water impregnation and its extract. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. (12), 734–740. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.1962.12.005
Yan, S. C., and Tian, X. (2003). Study on the volatile chemical constituents of Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb. leaves. J. Lanzhou Univ. (03), 105–106. doi:10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2003.03.029
Yan, Y. J., Jiang, H. J., and Zou, T. F. (1957). Comparison of several dosage forms of Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb. in lowering blood pressure. J. Qingdao Med. Coll. (01), 5–8.
Yang, G. X., Wang, W. X., Hu, C. L., Lou, B., Xiong, J., and Hu, J. F. (2014). Sterols from roots of Clerodendrum trichotomum and their anti-inflammatory activity. Chin. Traditional Herb. Drugs 45 (18), 2597–2601. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2014.18.004
Yang, Y. B., Zhang, Q., Wang, J., Hu, H. J., Wang, M., Wang, Z. T., et al. (2024). Bioactive constituents from Clerodendrum trichotomum and their α-glucosidase inhibitory and PPAR-γ agonist activities. Fitoterapia 2024, 106266. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106266
Yao, Z. Q., and Guo, Q. (2010). Studies on the chemical composition of the leaves of Clerodendron trichotomum Thunb.(Ⅰ). Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 16 (06), 103–104. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2010.06.065
Yoon, M. Y., Sim, S. S., Whang, W. K., and Choi, B. C. (2009). Antioxidant activity and whitening effects of acteoside and isoacteoside. Yakhak Hoeji 53 (1), 1–5.
Zeng, D. J., Wang, C., Liu, J., and Yin, L. J. (2013). Effect of high temperature stress on morphological and physiological characteristics of Clerodendrum trichotomum. J. Northeast For. Univ. 41 (3), 90–94. doi:10.13759/j.cnki.dlxb.2013.03.031
Zeng, G. F., Zhou, B. N., and Zhao, Z. Y. (1963). Research on flavonoids in traditional Chinese medicine Ⅹ. Studies on the constituents of Clerodendron trichotomum—isolation of a new flavonoid glycoside, Clerodendrin, and its chemical structure. Acta Pharm. Sinca 10 (08), 480–488. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.1963.08.005
Zhang, Y., Cen, Y. Z., Chen, L., Li, Y. J., Sun, J. B., and Li, L. Z. (2022). Chemical constituents from the stems of Clerodendrum trichotomum (Ⅱ). J. Chin. Med. Mater. 45 (04), 857–861. doi:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2022.04.016
Zheng, B., and Lu, J. B. (2012). Inhibitory effects of harlequin glory-bower (Clerodendrum trichotomum) extract on growth of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. and Life Sci.) 38 (03), 279–287. doi:10.3785/j.issn.1008-9209.2012.03.007
Zheng, L. W., Hu, D. M., Liu, W. F., Yang, W. J., and Sun, M. G. (2006). Adaptability of eleven ornamental tree species to sulfur dioxide stress treatment. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 37 (3), 363–368. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2006.03.010
Keywords: Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb., phytochemicals, pharmacological activities, diterpenes, phenylpropanoid glycosides
Citation: Li L, Tang Z, Xiao S, Dai X, Wang Y and Wei X (2025) Clerodendrum trichotomum Thunb.: a review on phytochemical composition and pharmacological activities. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1505851. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1505851
Received: 03 October 2024; Accepted: 03 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Mozaniel Oliveira, Emílio Goeldi Paraense Museum, BrazilReviewed by:
Ljuboš Ušjak, University of Belgrade, SerbiaCopyright © 2025 Li, Tang, Xiao, Dai, Wang and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Linzhen Li, bGlsaW56aGVuOUAxNjMuY29t; Xi Wei, NDY0MzE4Nzg3QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.