- 1Shandong Engineering and Technology Research Center for Pediatric Drug Development, Shandong Medicine and Health Key Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacy, Department of Clinical Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining, China
- 3Center for Big Data Research in Health and Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital, Jinan, China
- 4Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
The β-Lactam antibiotics represent a widely used class of antibiotics, yet the latent and often overlooked risk of coagulation dysfunction associated with their use underscores the need for proactive assessment. Machine learning methodologies can offer valuable insights into evaluating the risk of coagulation dysfunction associated with β-lactam antibiotics. This study aims to identify the risk factors associated with coagulation dysfunction related to β-lactam antibiotics and to develop machine learning models for estimating the risk of coagulation dysfunction with real-world data. A retrospective study was performed using machine learning modeling analysis on electronic health record data, employing five distinct machine learning methods. The study focused on adult inpatients discharged from 1 January 2018, to 31 December 2021, at the First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University. The models were developed for estimating the risk of coagulation dysfunction associated with various β-lactam antibiotics based on electronic health record feasibility. The dataset was divided into training and test sets to assess model performance using metrics such as total accuracy and area under the curve. The study encompassed risk-factor analysis and machine learning model development for coagulation dysfunction in inpatients administered different β-lactam antibiotics. A total of 45,179 participants were included in the study. The incidence of coagulation disorders related to cefazolin sodium, cefoperazone/sulbactam sodium, cefminol sodium, amoxicillin/sulbactam sodium, and piperacillin/tazobactam sodium was 2.4%, 5.4%, 1.5%, 5.5%, and 4.8%, respectively. Machine learning models for estimating coagulation dysfunction associated with each β-lactam antibiotic underwent validation with 5-fold cross-validation and test sets. On the test set, the optimal models for cefazolin sodium, cefoperazone/sulbactam sodium, cefminol sodium, amoxicillin/sulbactam sodium, and piperacillin/tazobactam sodium yielded AUC values of 0.798, 0.768, 0.919, 0.783, and 0.867, respectively. The study findings suggest that machine learning classifiers can serve as valuable tools for identifying patients at risk of coagulation dysfunction associated with β-lactam antibiotics and intervening based on high-risk predictions. Enhanced access to administrative and clinical data could further enhance the predictive performance of machine learning models, thereby expanding pharmacovigilance efforts.
Introduction
β-Lactam antibiotics, renowned for their safety, efficacy, and widespread availability (Shenoy et al., 2019), stand as the cornerstone of antimicrobial prescriptions. While generally well-tolerated, a subset of patients encounters diverse adverse reactions following clinical application. Notably, these adverse reactions span a spectrum, including severe renal or hepatic toxicity, neurotoxicity, hemocytopenia, and Clostridium difficile infections (Vardakas et al., 2018). A particularly noteworthy adverse effect of this class of drugs is coagulation dysfunction. Drug-Related Coagulation dysfunction (DRCD) is usually characterized by drug-induced prothrombin time prolongation and partial thromboplastin time activation. Over recent decades, global reports have documented instances of bleeding and diminished prothrombin levels associated with β-lactam antibiotics (Nguyen et al., 2015). In 2013, a multicenter clinical study established an association between cefoperazone and coagulopathy (Xin et al., 2013). Subsequently, in January 2014, the China Drug and Food Administration issued a notice regarding serious adverse reactions to cefazolin injections, underscoring the imperative for vigilant monitoring and clinically rational drug use.
Despite a wealth of case reports and small uncontrolled studies on β-lactam antibiotics-related coagulation dysfunction, controlled studies exploring the risks associated with these antibiotics remain limited (Sattler et al., 1988; Wang et al., 2020; Turner et al., 2022; Bai et al., 2023). Given the potential variation in chemical structures among β-lactams, which may influence coagulation dysfunction differently, thorough analyses of individual antibiotics become imperative.
This study aims to address this gap by investigating the incidence and risk factors associated with coagulation dysfunction linked to several β-lactams, including cefazolin sodium, cefoperazone/sulbactam sodium, cefminol sodium, amoxicillin/sulbactam sodium, and piperacillin/tazobactam sodium, utilizing electronic medical record data. Additionally, our objective is to develop machine learning models for estimating the risk of coagulation dysfunction in hospitalized patients receiving these β-lactam antibiotics.
Materials and methods
Ethical approval
This study received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University (Approval No. YXLL-KY-2022-024). The requirement for informed consent was granted a waiver due to the retrospective nature and minimal risk of this study.
Study design and data source
This retrospective investigation focused on patients discharged between 1 January 2018, and 31 December 2021, who received treatment with cefazolin sodium, cefoperazone/sulbactam sodium, cefminol sodium, amoxicillin/sulbactam sodium, or piperacillin/tazobactam sodium. We utilized clinical data extracted from electronic medical records at the First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University. The data for this study was collected from Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital Healthcare Big Data Platform (SPQHHBDP). The SPQHHBDP integrates multi-source data from hospital information system (HIS), electronic medical records (EMR), laboratory information management system (LIS), picture archiving and communication system (PACS), nursing information system. The encrypted personal identification number was used as a unique identifier to interlink each person’s data information in the above-mentioned database. The patient’s identification number, name, address, and telephone number were encrypted and not accessible to the investigators. Therefore, this study fully adhered to ethical principles and protected patients' privacy.
Data were retrieved from patient medical records via the hospital management systems and healthcare big data platforms. This comprehensive dataset included patient demographics, surgical details, laboratory test results, and diagnostic information, as shown in Supplementary Table S1. For missing data, we employed two strategies: (1) If the proportion of subjects with missing values was less than 5% of the total, those records were removed. (2) For variables with a missing rate below 10%, the missing values were filled using the patient’s information from other hospitalizations within our institution. The dataset was obtained from the hospital’s EHR system, capturing patients from various departments and covering a diverse patient population in terms of age, gender, and clinical diagnoses. To minimize selection bias, random sampling was employed, and bias analysis was conducted to ensure the generalizability of the results.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria comprised patients with a hospital stay of ≥48 h, aged ≥18 years, and two or more tests for prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thrombin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), and platelet (PLT) during hospitalization. Exclusion criteria included patients with an unclear route of administration, non-intravenous administration, those receiving heparin, low molecular weight heparin, warfarin, or other anticoagulants, patients lacking baseline parameters or presenting baseline abnormalities, and those with underlying diseases predisposing to coagulation dysfunction.
Case definition
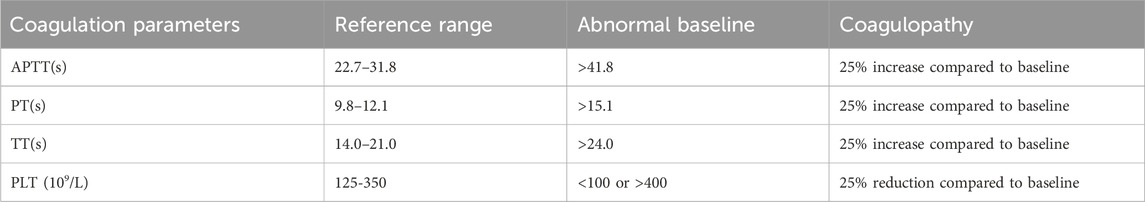
Baseline values for drug-related coagulation dysfunction (DRCD) definition were determined from the last test before the initial medication use. As shown in Table 1, the baseline abnormalities were defined as TT or PT exceeding the normal upper limit by 3 s or APTT surpassing the normal upper limit by 10 s. Coagulation parameter abnormalities were identified as a 25% increase in APTT, PT, or TT post-medication compared to baseline.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using R software (version 3.6.3) on the healthcare big data platform at the First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University. Data with normal distribution were presented as mean ± standard deviation, analyzed by t-test or analysis of variance. Non-normally distributed data were expressed as median and interquartile range, assessed by the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Categorical data were represented as counts or percentages and compared using the Chi-square test. Multivariate logistic regression analysis reported odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). A two-sided p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Development and validation of machine learning models
Five machine learning methods including logistic regression (LR), random forest (RF), gradient boosting machine (GBM), extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), and light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM), were employed for predictive model development. The advantages of Logistic Regression are strong explanatory power and high computational efficiency; Random Forest has strong anti-overfitting ability and can perform feature importance evaluation; XGBoost and LightGBM are both improved algorithms based on GBM. XGBoost has better performance, while LightGBM has faster training speed. Therefore, we have selected these five algorithms for the construction of the prediction model and selected the optimal model from them. Patient inclusion involved random division into training and validation sets at a 4:1 ratio. Models underwent 5-fold cross-validation (5-CV) on training sets and independent validation on separate validation sets. To prevent overfitting, univariate analysis screened significantly correlated variables (p < 0.05). The features used in the machine learning models were selected based on the results of multivariate logistic regression analysis, where parameters with statistically significant associations (p < 0.05) were included. The optimal penalty coefficient (λ) was determined by ten-fold cross-validation, identifying characteristic variables with predictive value. Model performance was evaluated using area under the subject operating characteristic curve (AUC), accuracy (ACC), sensitivity (SEN), and specificity (SPE). ACC gauged overall correctness, while SEN and SPE assessed positive and negative sample prediction accuracy, respectively.
Results
Incidence and clinical features of coagulation disorders in patients receiving β-lactam antibiotics
The study analyzed and modeled a cohort of 9,529 participants. The incidence of coagulation dysfunction in patients receiving cefazolin sodium, cefoperazone/sulbactam sodium, cefminox sodium, amoxicillin/sulbactam sodium, and piperacillin/tazobactam sodium was found to be 2.4% (51/2,161), 5.4% (102/1,900), 1.5% (25/1,626), 5.5% (139/2,535), and 4.8% (61/1,282), respectively.
Analysis of DRCD related factors of study drugs
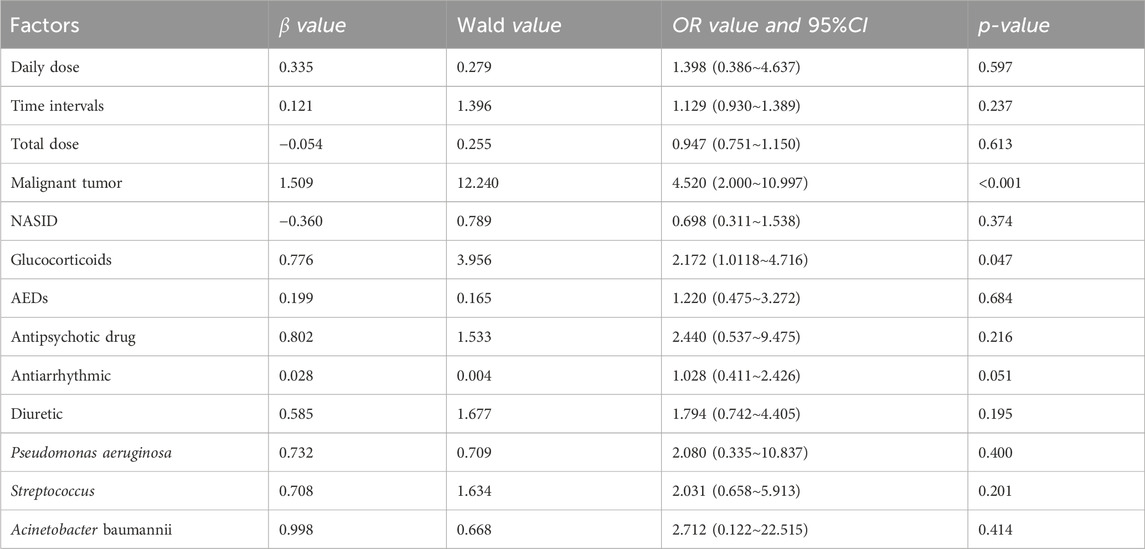
The study conducted both single-factor (as shown in Supplementary Tables S2–S6) and multi-factor analysis (as shown in Table 2–6) for each β-lactam antibiotic. In the case of cefazolin sodium (CAS), independent factors associated with DRCD included malignant tumors (OR: 4.52, 95% CI 2.000–10.997) and glucocorticoids (OR: 2.172, 95% CI 1.0118–4.716).
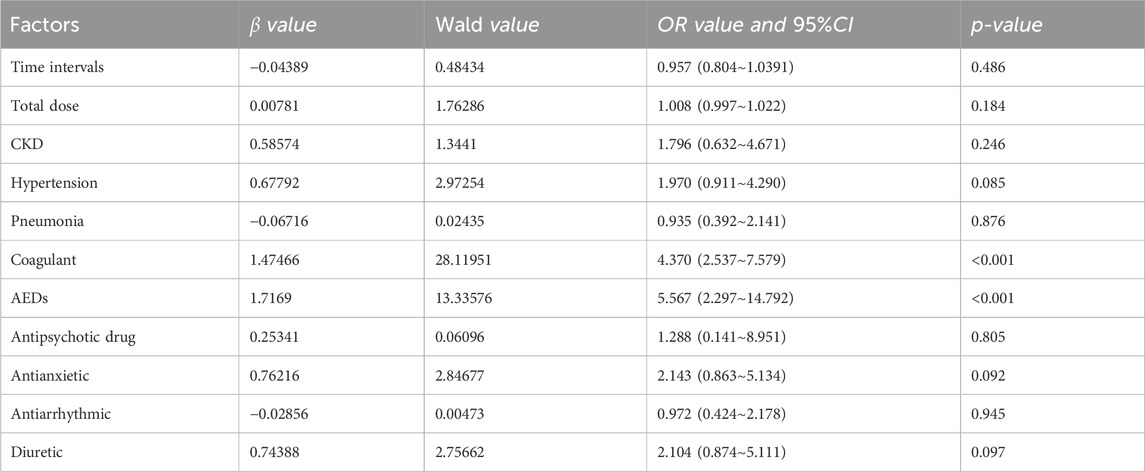
Table 6. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of DRCD occurrence received Mezlocillin Sodium and Sulbactam
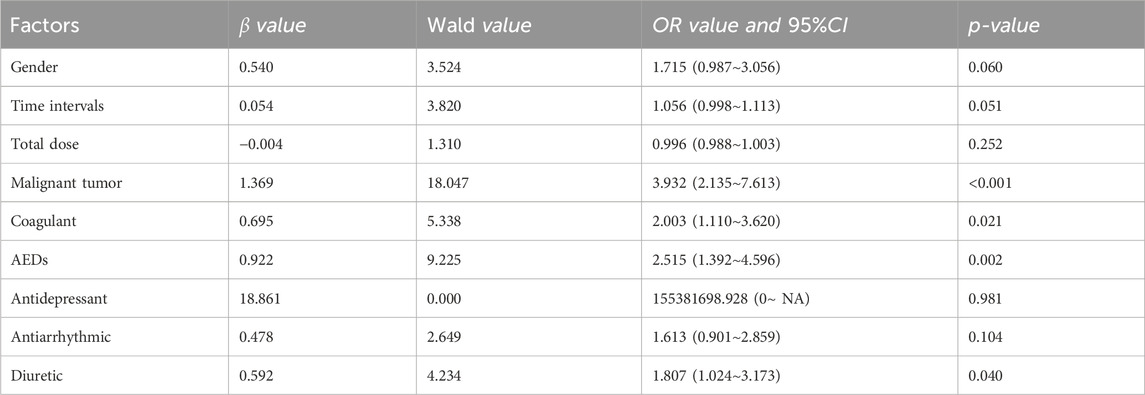
For cefoperazone/sulbactam sodium (CSSS), independent factors for DRCD were malignant tumors (OR: 3.932, 95% CI 2.135–7.613), anticoagulants (OR: 2.00, 95% CI 1.110–3.620), antiepileptic drugs (OR: 2.515, 95% CI 1.392–4.596), and diuretics (OR: 1.807, 95% CI 1.024–3.173).
The risk factors for DRCD associated with cefminox sodium (CMS) included daily dose (OR: 0.487, 95% CI 0.258–0.865), anticoagulants (OR: 5.267, 95% CI 1.774–15.458), antiepileptics (OR: 3.213, 95% CI 1.046–10.081), anxiolytics (OR: 3.225, 95% CI 1.089–9.070), and proton pump inhibitors (OR: 0.162, 95% CI 0.034–0.909).
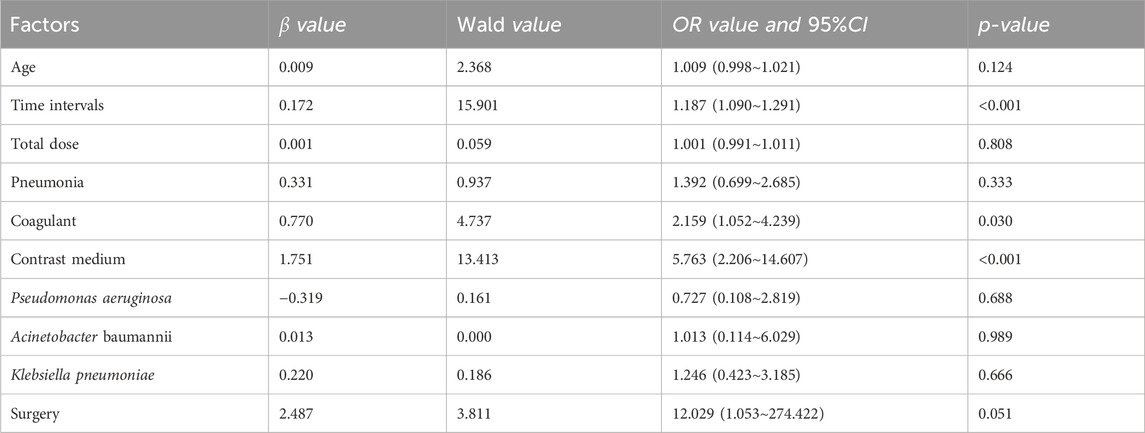
Mezlocillin/sulbactam sodium (MMS) DRCD independent risk factors comprised drug use time (OR: 1.187, 95% CI 1.090–1.291), contrast agents (OR: 5.763, 95% CI 2.206–14.607), and coagulants (OR: 2.159, 95% CI 1.052–4.239).
Piperacillin/tazobactam sodium (PTS) independent risk factors for DRCD were anticoagulants (OR: 4.370, 95% CI 2.537–7.579) and antiepileptic drugs (OR: 5.567, 95% CI 2.297–14.792).
Validation and evaluation of DRCD prediction models for study drugs
Internal and external verification results for each β-lactam antibiotic revealed optimal AUC and ACC values, as shown in Figures 1–5. For CAS, the AUC was 0.798. CSSS had an AUC of 0.768, CMS 0.919, MMS 0.783, and PTS 0.867. Validation results illustrated the robustness of the prediction models, with key factors impacting DRCD risk elucidated through ROC curve analyses.
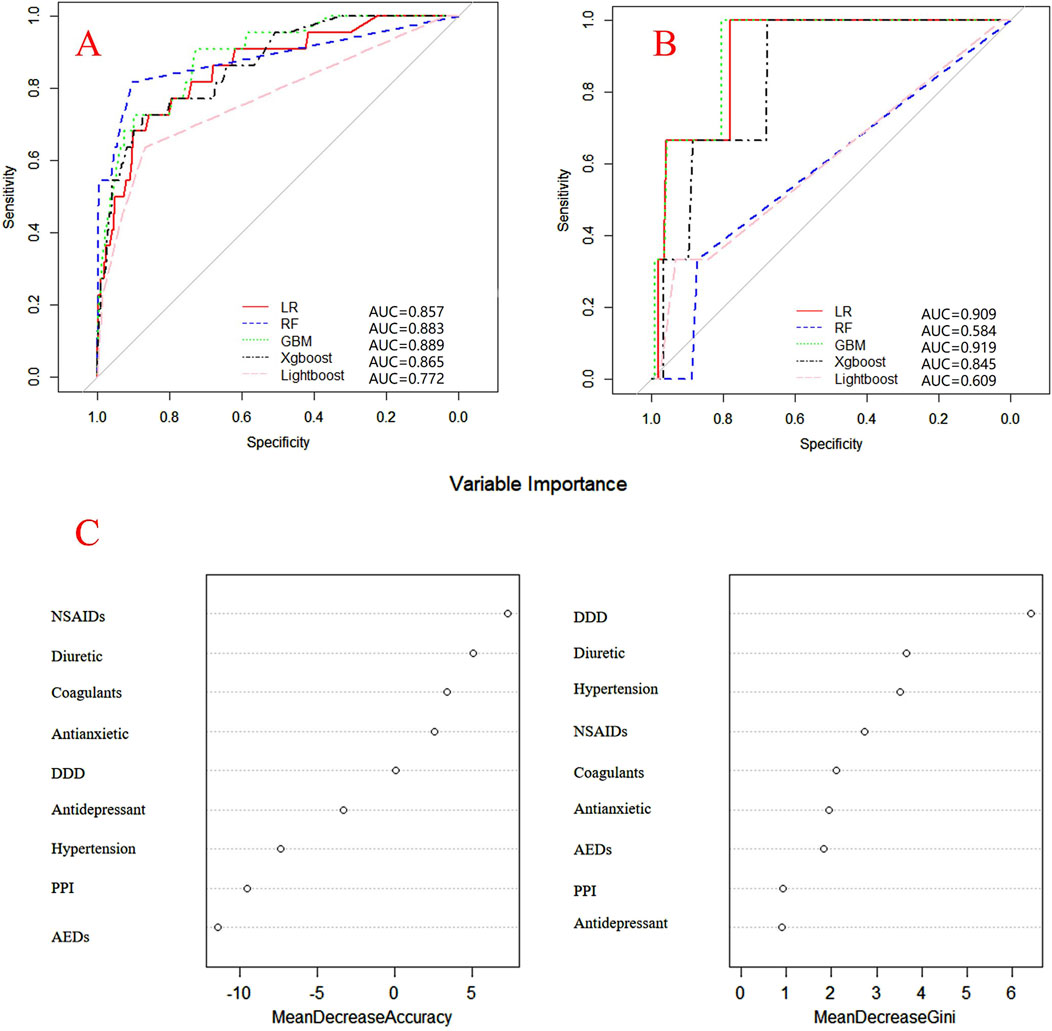
Figure 1. ROC curves of models for cefazolin sodium associated DRCD and the results of the importance of related factors. (A) internal validation; (B) external validation; (C) analysis on the importance of DRCD related factors of cefazolin sodium.
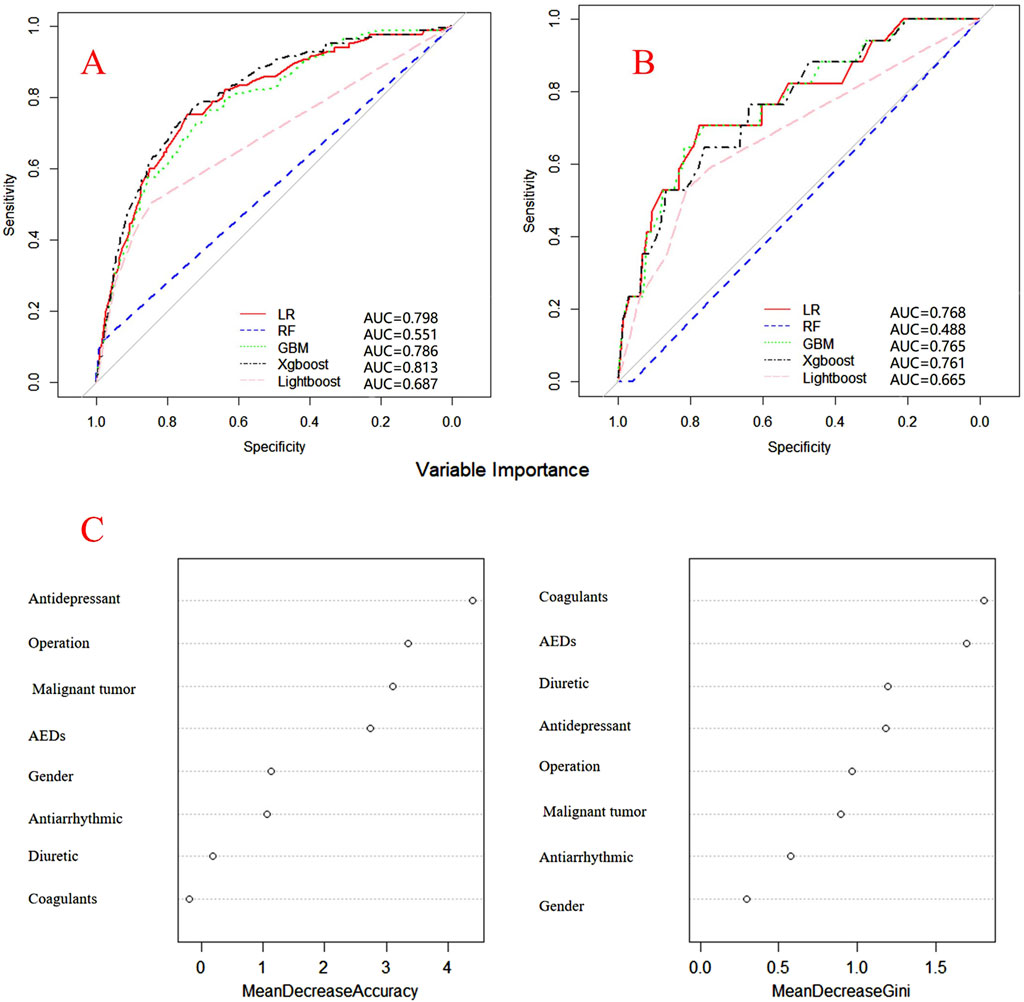
Figure 2. ROC curves of models for cefoperazone associated DRCD and the results of the importance of related factors. (A) internal validation; (B) external validation; (C) analysis on the importance of DRCD related factors of cefoperazone.
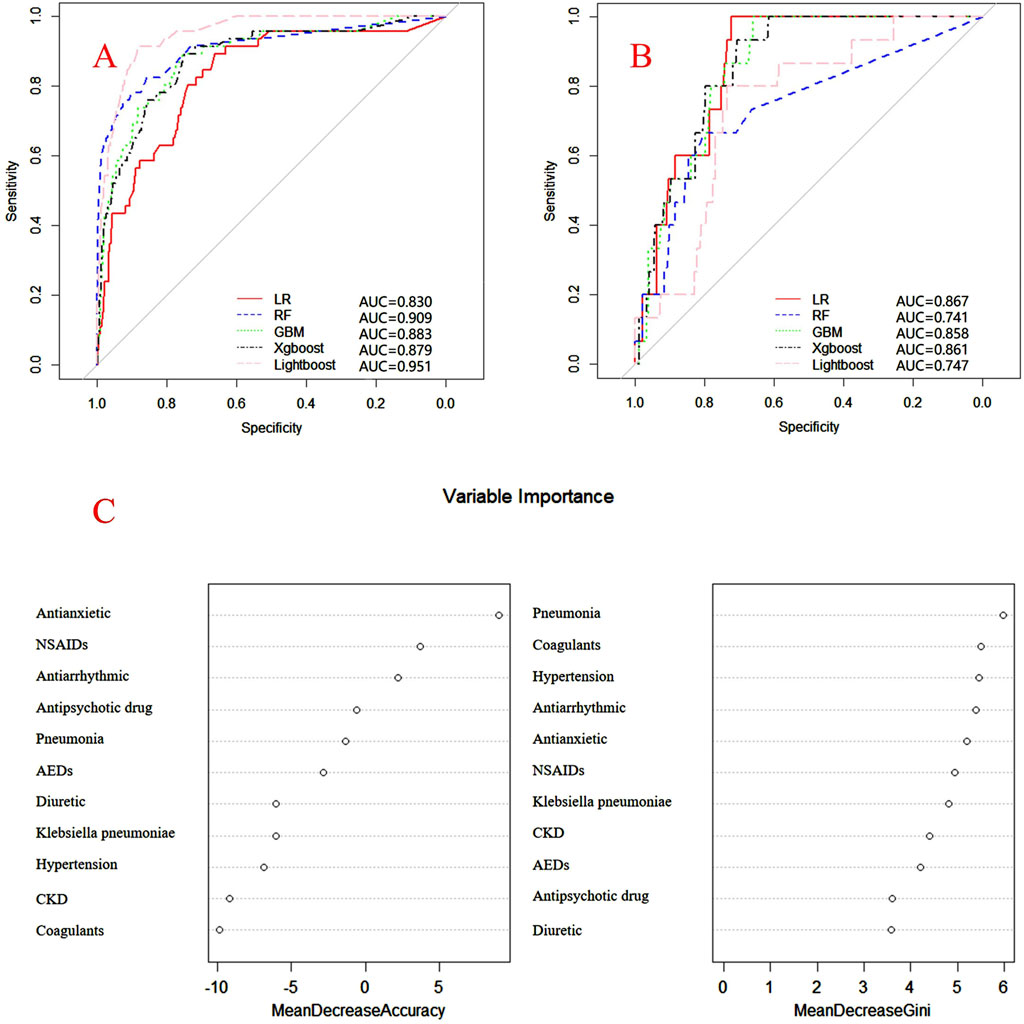
Figure 3. ROC curves of models for cefminox sodium associated DRCD and the results of the importance of related factors. (A) internal validation; (B) external validation; (C) analysis on the importance of DRCD related factors of cefminox sodium.
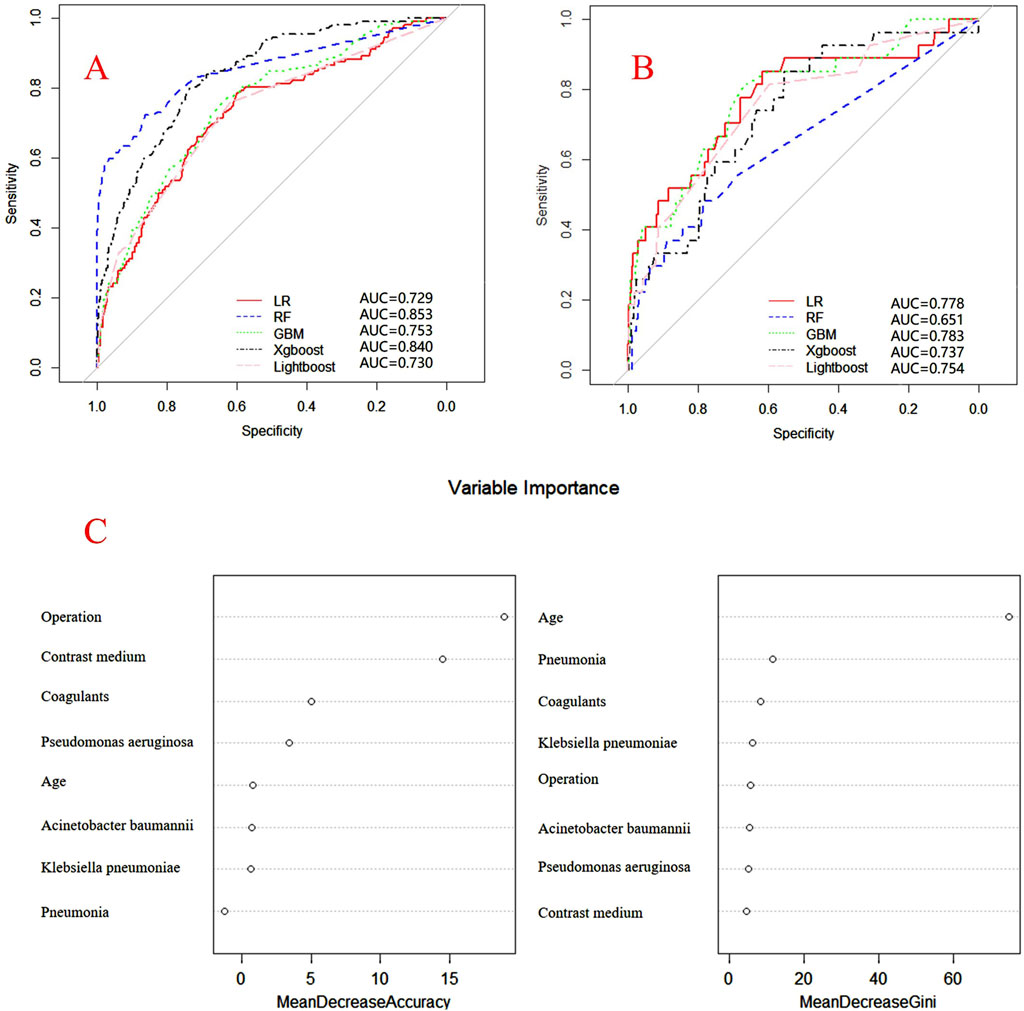
Figure 4. ROC curves of models for mezlocillin associated DRCD and the results of the importance of related factors. (A) internal validation; (B) external validation; (C) analysis on the importance of DRCD related factors of mezlocillin.
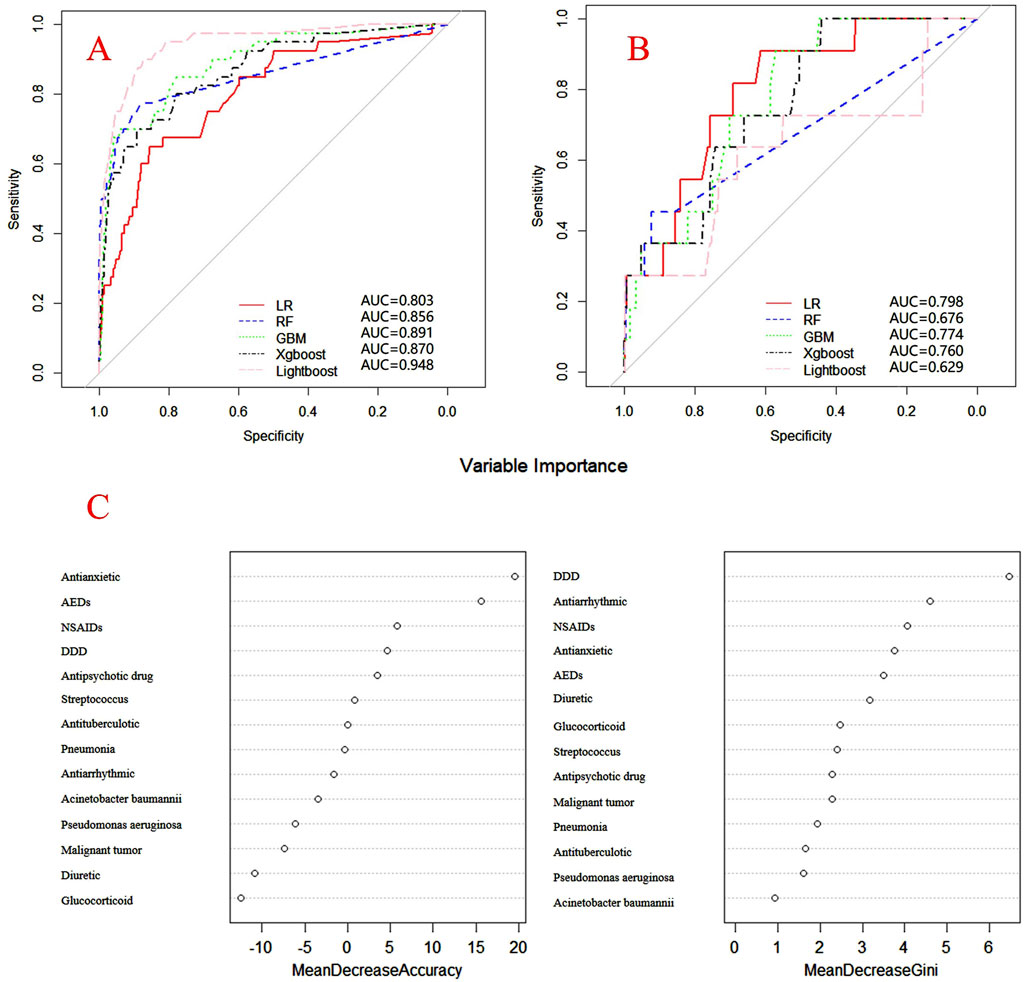
Figure 5. ROC curves of models for piperacillin associated DRCD and the results of the importance of related factors. (A) internal validation; (B) external validation; (C) analysis on the importance of DRCD related factors of piperacillin.
For CAS, factors such as daily dose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anxiolytics, antiepileptics, antipsychotics, and antiarrhythmic drugs were identified as highly correlated with DRCD in cefazolin sodium. For CSSS, major factors affecting the DRCD risk model of cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium included surgery, antiepileptic drugs, antidepressants, diuretics, and malignant tumors. Similarly, for CMS, significant factors impacting the occurrence of DRCD in cefminox sodium included non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, daily dose, diuretics, anxiolytics, and hypertension. In MMS, factors such as age, surgery, contrast agent, pneumonia, procoagulants, and others were found to have a considerable impact on the production of DRCD of mezlocillin/sulbactam sodium. For PTS, the occurrence of DRCD in injectable piperacillin/tazobactam was significantly influenced by risk factors such as anxiolytics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiarrhythmic drugs, pneumonia, anticoagulants, and hypertension.
The predictive models can be integrated into clinical decision support systems to identify patients at high risk of DRCD, enabling timely intervention and personalized medication adjustments, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Discussion
The emergence of coagulation disorders related to β-lactam antibiotics poses a multifaceted challenge, necessitating a nuanced exploration of contributing factors. Our study delves into the intricate web of associations, shedding light on the complexity of determinants influencing DRCD in this antibiotic class. The random forest algorithm assesses the importance of variables through two primary methods: Mean Decrease in Gini and Mean Decrease in Accuracy. These two methods determine the importance of variables by calculating the impact of each factor on the impurity of all decision tree nodes in the forest, as well as the impact of randomly adding noise to a certain feature on the accuracy of the model. The larger the value, the more important the variable.
Molecular mechanisms and patient demographics
Cephalosporin-induced DRCD can be attributed to the molecular structure containing the N-methylthiotetrazolium side (NMTT), directly impacting vitamin K participation in carboxylation reactions and heightening the risk of bleeding (Lipsky, 1983). In contrast, penicillin-related DRCD may result from penicillin binding to platelet surface proteins, rendering them antigenic and triggering an immune response, leading to decreased platelet count and DRCD (Chong et al., 2013). The stronger association between cefminox and piperacillin with coagulation dysfunction may be related to their specific molecular structures that affect clotting pathways. For instance, cefminox has been associated with reduced prothrombin activity, leading to increased risk of coagulation disorders (Wu et al., 2022).
Analyzing patient demographics, age emerges as a contributing factor to DRCD related to β-lactam antibiotics, with a higher incidence in the elderly. Age-related factors such as diminished immunity, organ aging, poor renal excretion, and drug accumulation elevate the risk of adverse reactions. Thus, caution is warranted to ensure medication safety for the elderly (Fu and Perloff, 2022). Furthermore, our findings underscore a positive correlation between total dosage and DRCD risk, emphasizing the importance of adhering to recommended antibiotic doses in clinical applications (Rochoy et al., 2022).
Gender disparities and underlying diseases
Gender appears to influence DRCD occurrence, particularly evident in a higher likelihood among men receiving cefoperazone injection. These gender-related differences may be linked to body fat composition and hydrophilic drug combinations, suggesting the necessity for personalized clinical guidance (Karamian et al., 2022).
Patients with underlying diseases, particularly those with malignant tumors, exhibited a significantly higher incidence of DRCD. This association might be linked to circulating tumor cells affecting the coagulation system, extending APTT, TT, or PT times, and elevating DRCD risk (Ward et al., 2021). Chronic kidney disease patients, particularly in the study of piperacillin/tazobactam sodium for injection, demonstrated a heightened susceptibility to DRCD, possibly due to alterations in coagulation system interactions under metabolic conditions in renal failure, as suggested by studies on the impact of microparticles on coagulation (Lutz et al., 2014).
Unexpected findings and medication interactions
Contrary to general expectations, our study revealed higher DRCD incidence in hypertensive patients treated with cefminox sodium for injection and piperacillin for injection. This unexpected finding prompts further investigation to explore potential connections between hypertension and DRCD, especially in the context of diuretic use (Antza et al., 2018; Kearsley and Stocks, 2021).
Analyzing concurrent medications, anticoagulant use was associated with an increased DRCD risk, seemingly contradictory to the expected therapeutic effects. However, this association was likely influenced by the inclusion of patients undergoing surgeries that required anticoagulants. Similarly, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs exhibited a significant impact, affecting COX-1 activity and transiently influencing platelet function (Scharf, 2012).
Glucocorticoids and protective effects
Inconsistencies arose in the relationship between glucocorticoid use and DRCD, with our study indicating a higher incidence, contrary to previous research (Graversen et al., 2012; Coelho et al., 2015; Isidori et al., 2015). This unexpected outcome suggests the need for a more nuanced exploration of the potential liver-related effects of glucocorticoids on DRCD occurrence.
Surprisingly, the inclusion of proton pump inhibitors appeared to inhibit DRCD occurrence, suggesting a potential protective effect. This aligns with their clinical use in alleviating gastrointestinal bleeding, underscoring the importance of considering the comprehensive medication profile (Lanas et al., 2018).
Bacterial associations and surgery
Examining bacterial associations, Streptococcus and Gram-negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, were linked to increased DRCD risk. The interaction between these bacteria and the coagulation system components was identified as a potential contributor to DRCD (Herwald et al., 2003; Bergmann and Hammerschmidt, 2007).
Surgery emerged as a significant related factor, supporting existing research on postoperative patients being more prone to DRCD (Ranucci, 2015; Bolliger and Tanaka, 2017). The local trauma and mechanical bleeding associated with surgery might contribute to DRCD, necessitating vigilant monitoring during antibiotic administration in surgical settings.
Limitations
One of the limitations of this study is its retrospective design, which limits the ability to infer causal relationships between β-lactam antibiotic use and coagulation dysfunction. Additionally, since the data were collected from a single hospital, the generalizability of the findings to other populations or healthcare settings may be limited. Future studies should aim to validate the model on external datasets from different regions or healthcare systems to enhance its applicability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our study unravels the intricate interplay of factors influencing DRCD in β-lactam antibiotics. Individualized clinical medication plans, considering patient demographics, comorbidities, and concurrent medications, are pivotal to mitigate the risk of DRCD. Further research is imperative to delve into nuanced relationships and unexpected outcomes, providing a more comprehensive understanding of DRCD determinants.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
YH: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing–original draft. NL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. JL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing–original draft. ZC: Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing–original draft. SM: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Validation, Writing–review and editing. XL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Research project of disease treatment and rational use of drugs of Shandong Pharmaceutical Association (DRM2022007), Shandong Pharmaceutical Association Hospital Pharmacy Special Scientifc Research Project (yyyx2021zd-03), Shandong Pharmaceutical Association Hospital Rational Drug Use Young and Middle-aged Scientific Research (hlyy-2024-01), Shandong Pharmaceutical Association Medical Institution Pharmacovigilance Young and Middle-aged Project (ywjj-2024-01), Shanghai sailing program (22YF1440300), and Shanghai Jiaotong University “Jiaotong University Star” program (medical-engineering cross-research, YG2022QN015).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the staff at the Center for Big Data Research in Health and Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital, for their valuable contribution. We gratefully acknowledge Ms. Chaoyue Yang for the encouragement.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1503713/full#supplementary-material
References
Antza, C., Cifkova, R., and Kotsis, V. (2018). Hypertensive complications of pregnancy: a clinical overview. Metabolism - Clin. Exp. 86, 102–111. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2017.11.011
Bai, H., Li, H., Nie, X., Yao, Y., Han, X., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting cefoperazone/sulbactam-induced hypoprothrombinaemia in Hospitalized adult patients. PLOS ONE 18 (9), e0291658. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0291658
Bergmann, S., and Hammerschmidt, S. (2007). Fibrinolysis and host response in bacterial infections. Thromb. Haemost. 98 (3), 512–520. doi:10.1160/th07-02-0117
Bolliger, D., and Tanaka, K. A. (2017). Point-of-Care coagulation testing in cardiac surgery. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 43 (4), 386–396. doi:10.1055/s-0037-1599153
Chong, B. H., Young-Ill Choi, P., Khachigian, L., and Perdomo, J. (2013). Drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia. Hematology/Oncology Clin. N. Am. 27 (3), 521–540. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2013.02.003
Coelho, M. C. A., Santos, C. V., Neto, L. V., and Gadelha, M. R. (2015). Adverse effects of glucocorticoids: coagulopathy. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 173 (4), M11–M21. doi:10.1530/EJE-15-0198
Fu, J. L., and Perloff, M. D. (2022). Pharmacotherapy for spine-related pain in older adults. Drugs and Aging 39 (7), 523–550. doi:10.1007/s40266-022-00946-x
Graversen, D., Vestergaard, P., Stochholm, K., Gravholt, C. H., and Jørgensen, J. O. L. (2012). Mortality in Cushing's syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 23 (3), 278–282. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2011.10.013
Herwald, H., Mörgelin, M., Dahlbäck, B., and Björck, L. (2003). Interactions between surface proteins of Streptococcus pyogenes and coagulation factors modulate clotting of human plasma. J. Thrombosis Haemostasis 1 (2), 284–291. doi:10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00105.x
Isidori, A. M., Minnetti, M., Sbardella, E., Graziadio, C., and Grossman, A. B. (2015). Mechanisms in endocrinology: the spectrum of haemostatic abnormalities in glucocorticoid excess and defect. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 173 (3), R101–R113. doi:10.1530/EJE-15-0308
Karamian, B. A., Toci, G. R., Lambrechts, M. J., Siegel, N., Sherman, M., Canseco, J. A., et al. (2022). Cefazolin prophylaxis in spine surgery: patients are frequently underdosed and at increased risk for infection. Spine J. 22 (9), 1442–1450. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2022.05.018
Kearsley, R., and Stocks, G. (2021). Venous thromboembolism in pregnancy—diagnosis, management, and treatment. BJA Educ. 21 (3), 117–123. doi:10.1016/j.bjae.2020.10.003
Lanas, A., Dumonceau, J.-M., Hunt, R. H., Fujishiro, M., Scheiman, J. M., Gralnek, I. M., et al. (2018). Non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 4 (1), 18020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2018.20
Lipsky, J. (1983). N-methyl-thio-tetrazole inhibition of the gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid: possible mechanism for antibiotic-associated hypoprothrombinaemia. Lancet 322 (8343), 192–193. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(83)90174-5
Lutz, J., Menke, J., Sollinger, D., Schinzel, H., and Thürmel, K. (2014). Haemostasis in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 29 (1), 29–40. doi:10.1093/ndt/gft209
Nguyen, V. D., Tourigny, J.-F., Roy, R., and Brouillette, D. (2015). Rapid-onset thrombocytopenia following piperacillin-tazobactam reexposure. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 35 (12), e326–e330. doi:10.1002/phar.1675
Ranucci, M. (2015). Hemostatic and thrombotic issues in cardiac surgery. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 41 (1), 84–90. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1398383
Rochoy, M., Danel, A., Chazard, E., Gautier, S., and Berkhout, C. (2022). Doping with aromatase inhibitors and oestrogen receptor modulators in steroid users: analysis of a forum to identify dosages, durations and adverse drug reactions. Therapies 77 (6), 683–691. doi:10.1016/j.therap.2022.03.004
Sattler, F. R., Weitekamp, M. R., Seyegh, A., and Ballard, J. O. (1988). Impaired hemostasis caused by beta-lactam antibiotics. Am. J. Surg. 155 (5), 30–39. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(88)80209-5
Scharf, R. E. (2012). Drugs that affect platelet function. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 38 (08), 865–883. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1328881
Shenoy, E. S., Macy, E., Rowe, T., and Blumenthal, K. G. (2019). Evaluation and management of penicillin allergy: a review. JAMA 321 (2), 188–199. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.19283
Turner, J., Muraoka, A., Bedenbaugh, M., Childress, B., Pernot, L., Wiencek, M., et al. (2022). The chemical relationship among beta-lactam antibiotics and potential impacts on reactivity and decomposition. Front. Microbiol. 13, 807955. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.807955
Vardakas, K. Z., Kalimeris, G. D., Triarides, N. A., and Falagas, M. E. (2018). An update on adverse drug reactions related to β-lactam antibiotics. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 17 (5), 499–508. doi:10.1080/14740338.2018.1462334
Wang, W., Liu, Y., Yu, C., Tan, J., Xiong, W., Dong, D., et al. (2020). Cefoperazone-sulbactam and risk of coagulation disorders or bleeding: a retrospective cohort study. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 19 (3), 339–347. doi:10.1080/14740338.2020.1713090
Ward, M. P., Kane, L. A., Norris, L., Mohamed, B. M., Kelly, T., Bates, M., et al. (2021). Platelets, immune cells and the coagulation cascade; friend or foe of the circulating tumour cell? Mol. Cancer 20 (1), 59. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01347-1
Wu, S., Bi, X., Lin, Y., Yang, L., Li, M., and Xie, Y. (2022). Severe coagulopathy caused by cefminox sodium in a liver cirrhosis patient: a case report. Infect. Agents Cancer 17 (1), 30. doi:10.1186/s13027-022-00446-y
Xin, X., Jian, L., Xia, X., Jia, B., Huang, W., Li, C., et al. (2013). A multicentre clinical study on the injection of ceftriaxone/sulbactam compared with cefoperazone/sulbactam in the treatment of respiratory and urinary tract infections. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 12 (1), 38. doi:10.1186/1476-0711-12-38
Keywords: β-lactam antibiotics, coagulation disorders, risk factors, machine learning, pharmacovigilance
Citation: Hua Y, Li N, Lao J, Chen Z, Ma S and Li X (2024) Machine learning models for coagulation dysfunction risk in inpatients administered β-lactam antibiotics. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1503713. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1503713
Received: 29 September 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 26 November 2024.
Edited by:
Zhi-Chun Gu, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yinyin Wang, China Pharmaceutical University, ChinaXun Yu, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, China
Xuelin Sun, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Hua, Li, Lao, Chen, Ma and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiao Li, bGl4aWFvMTY4OEAxNjMuY29t, eC5saUBzZHUuZWR1LmNu
†ORCID: Xiao Li, orcid.org/0000-0002-1148-9898
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yuqing Hua1,2‡
Yuqing Hua1,2‡ Na Li
Na Li Jiahui Lao
Jiahui Lao Xiao Li
Xiao Li