- 1Department of Biomedicine, Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences (ASAB), National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Islamabad, Pakistan
- 2School of Interdisciplinary Engineering and Sciences (SINES), National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Islamabad, Pakistan
- 3Crop Sciences Institute, National Agriculture Research Center (NARC), Islamabad, Pakistan
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by synovial infiltration and pannus formation, and its rising incidence is significantly contributing to the global disability rate. Despite advances in biological drugs, no treatment has successfully cured or averted its progression. Consequently, natural drugs are being explored as alternative therapeutic strategies.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Pennisetum glaucum (pearl millet) and to identify its bioactive compounds to assess their effectiveness against RA targets.
Methods: The therapeutic potential of P. glaucum extracts was evaluated by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory assays. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was utilized to identify the compounds in P. glaucum extract. The pharmacokinetics and safety profile of these compounds were studied by absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) analysis. Network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation were employed to identify the active compounds and their therapeutic targets in P. glaucum for RA treatment.
Results: Acidified methanol (AM) extract of P. glaucum showed the highest phenolic (213 ± 0.008 mg GAE/g DW) and flavonoid content (138.1 ± 0.03 mg RE/g DW), demonstrating significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential. GC-MS of AM extract identified 223 compounds. Lipinski and toxicity parameters screened out 17 compounds. Protein–protein interaction (PPI) analysis shortlisted 20 key targets in RA pathways, nine of which were upregulated in five microarray datasets. Molecular docking and MD simulations revealed that compound-7 (benzenesulfonamide, 2-nitro-N-phenyl-) and compound-9 (Pregnane-3,20-diamine, (3.beta.,5.alpha.,20S)-) bind strongly with MMP9, JAK2, PTGS2, and HIF1a compared to the reference, predicting stable interaction with these upregulated genes. Finally, PASS (prediction of activity spectra for biological active substances) analysis further validated the anti-arthritic potential of these compounds based on their chemical structure.
Conclusion: This study uncovered a therapeutic drug candidate against HIF1a, MMP9, JAK2, and PTGS2 for RA from P. glaucum active compounds, laying the groundwork for future research.
1 Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a persistent autoimmune condition characterized by intense pain, inflammation, synovial hyperplasia, and the infiltration of various immune cells. It poses a higher disability rate than other joint diseases and affects about 0.5%–1% of the global population (Akram et al., 2021). Notably, women are two to three times more prone to developing RA than men. According to Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort (BAPC) analysis, it is expected that by 2030, 18.23 women per 100,000 will develop RA each year, compared to only 8.34 men (Cai et al., 2023). Despite its prevalence, effective clinical treatments for RA are limited. For instance, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and glucocorticoids relieve inflammatory symptoms but take a long time to kick in, and they have severe side effects. On the other hand, biologics—advanced therapies derived from living organisms—are highly effective in controlling inflammation and disease progression by specifically targeting immune system components like cytokines (e.g., tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) interleukin-6 (IL-6)) or immune cells (e.g., B-cells, T-cells), but they are expensive and generally target only a single molecule or pathway (Bullock et al., 2018).
The complex pathogenesis of RA, which involves the continuous breakdown of bone and cartilage by matrix metalloproteases (MMPs), leads to the increased activation of proinflammatory cytokines, activating various signaling cascade like Janus kinase and signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) and cyclooxygenase pathways. Both pathways further stimulate proinflammatory cytokines, the rapid proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), and the activation of MMPs (Hu et al., 2022) (Ma et al., 2021). Similarly, hypoxia inducible factors (HIF) play a crucial role in exacerbating the pathogenesis of RA by stimulating the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) which leads to rapid angiogenesis. A hypoxic environment also favors rapid glycolysis, resulting in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which further leads to extra-cellular matrix (ECM) degradation by MMPs and inflammatory cytokines (Figure 1) (Li et al., 2023). Such complex pathogenesis requires multitargeted therapy to manage the disease. Given these constraints and the high disability rate of RA, there is a global effort to develop new drugs with fewer side effects and greater therapeutic potential. The search for novel biomarkers to alleviate RA symptoms remains a key focus.
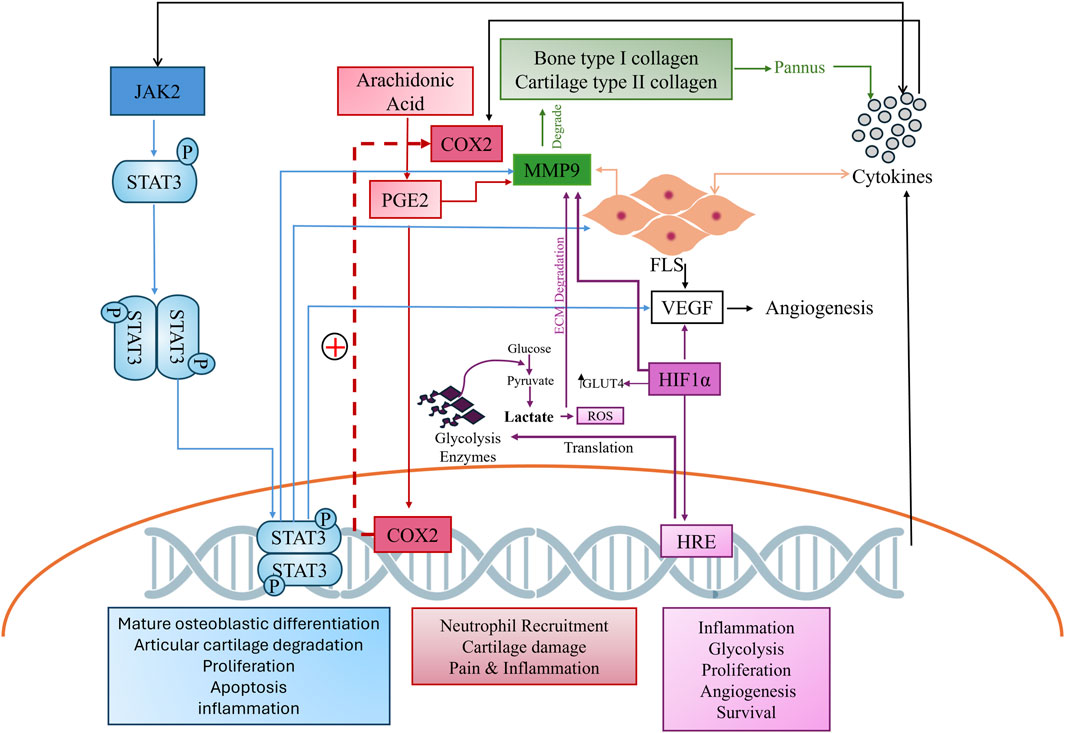
Figure 1. Complex cross-talk of hyper stimulated pathways in arthritis. The JAK2 pathway, shown in blue, cyclooxygenase pathway in red, MMP in green, and HIF in purple, depict the comprehensive interconnectedness of these pathways and their role in RA pathogenesis.
The safety and effectiveness of medicinal plants in enhancing human health are well-supported. Pearl millet, formally known as Pennisetum glaucum, is a member of the Paniceae family that is frequently consumed in tropical areas, particularly in Africa and Asia, to manage various ailments. Millet-based diets are anti-oxidant rich and have the potential to reduce inflammation in chronic alignments such as cancer and cardiovascular pathologies (Bhattacharya, 2023). Nani et al. demonstrated that P. glaucum consumption can significantly reduce the severity of diabetes in experimental models (Nani et al., 2015). Hegde et al. found that the inclusion of kodo millet in the diet alleviates hyperglycemia and cholesterol levels (Hegde et al., 2005). P. glaucum is also recommended for alleviating stomach ulcers due to its alkalizing nature. Antioxidants such as lignin and phytonutrients make them cardioprotective, and the presence of significant magnesium content helps modulate blood pressure, stress, and the respiratory symptoms of asthma. Moreover, the presence of elevated phosphorus content aids in bone growth and ATP production. It is notably safe for lactating women, the elderly, and convalescents (Pei et al., 2022). P. glaucum has been utilized in Moroccan ethnopharmacology for treating pain, bone fractures, and trauma, but it has not been evaluated scientifically (Ali et al., 2018). Ali et al. (2018) studied the effects of an aqueous extract of P. glaucum (AEPG) on the lumbar vertebrae of experimental models fed on a high-calorie diet, their findings suggesting that AEPG has the potential to be a viable and cost-effective alternative for treating bone loss and osteoporosis with no repercussions. P. glaucum is a natural repository of dietary antioxidants—mainly phenolics (melilotic acid, syringic acid, salicylic acid, para-hydroxyl benzoic acid, and vanilic acid) and flavonoids (tricin, 3, 4 Di-OMe luteolin, acacetin, and 4-OMe tricin) (Nambiar et al., 2012). The presence of these phytochemicals characterizes pearl millet as a nutraceutical. The bioactive constituents found in P. glaucum make it a promising candidate for drug discovery due to their considerable therapeutic potential. Our research focuses on exploring plant-based bioactive compounds to mitigate side effects associated with conventional RA treatments. This study aims to identify potential bioactive compounds from P. glaucum for RA through “computer-aided drug design” (CADD) to contribute to the development of novel and targeted therapies. These findings are intended to lay the groundwork for developing novel RA therapies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 In vitro evaluation of therapeutic potential of bioactive compounds in Pennisetum glaucum
2.1.1 Plant collection and extract preparation
Super bajra-1, an approved variety of P. glaucum (Munawwa et al., 2007), was obtained from the maize sorghum and millet program of the National Agriculture Research Center (NARC), Pakistan. Four extracts were prepared: ethanolic (E), hydro-alcoholic (HA), 1% AM, and aqueous (Aq). The AM extract was prepared by refluxing at 60 ℃ for 2 h, while E, HA, and Aq extracts were macerated for 24 h in a mechanical shaker at 37 ℃ and then filtered through Whatman filter paper no. 1.
2.1.2 Total phenolic and total flavonoid content
Total phenolic content (TPC) was determined using Folin–Ciocalteu (FC) reagent. First, 1 mL of extract (10–90 μg/mL) was mixed with 2.5 mL of 10% (w/v) FC reagent. Then, 2 mL of Na2CO3 (7.5%) was added and incubated at room temperature for 30 min. Absorbance was measured by a UV-spectrophotometer at 765 nm against blank. The results were quantified as milligrams of gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per gram of dried weight of extract (mg GAE/g DW) (Truong et al., 2019).
Total flavonoid content (TFC) was determined using the aluminum chloride method. Extract/rutin of 1 mL (10–90 μg/mL) was mixed with 0.2 mL of 10% (w/v) AlCl3 solution, 0.2 mL (1M) potassium acetate, and 5.6 mL distilled water. The mixture was incubated for 15 min at room temperature. Absorbance was measured at 415 nm against blank. TFC was expressed as mg of rutin equivalent (RE) per gram of dried weight of extract (mg RE/g DW) (Truong et al., 2019).
2.1.3 Antioxidant potential
Added to 1 mL of 0.1 mM DPPH solution was 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay 3 mL of extract. Different concentrations of extracts were made at 10–90 μg/mL. The reaction mixture (RM) was incubated for 30 min in the dark. The absorbance was taken at 517 nm with a UV-VIS spectrophotometer. Ascorbic acid was taken as a positive control. Percentage inhibition was calculated by the given formula (15):
To reduce the power assay, we employed the protocol of Oyaizu (1986), where 1 mL of extract was added to 2.5 mL of 0.2M PBS (pH 6.6) and 2.5 mL of 1% (w/v) potassium ferricyanide (K3Fe (CN) 6) solution. The mixture was vortexed, followed by the addition of 2.5 mL of 10% (w/v) trichloroacetic acid and centrifugation at 3000rpm for 10 min. The supernatant (2.5 mL) was then mixed with 2.5 mL of deionized water and 0.5 mL of 0.1% (w/v) ferric chloride (FeCl3). The absorbance of the resulting solution was measured at 700 nm using a UV-VIS spectrophotometer, and the results were analyzed. Increased absorbance indicated higher reducing capability. Ascorbic acid was used as a standard (Aryal et al., 2019).
2.1.4 Anti-inflammatory potential
The anti-inflammatory potential was analyzed via albumin denaturation and anti-proteinase assay (Truong et al., 2019). For albumin denaturation assay, 0.2 mL of egg albumin, 2.8 mL of PBS (pH 6.4), and 0.6 mL of extract at five different concentrations (10, 30, 50, 70, and −90 μg/mL) were used. RM was incubated for 10 min at 37 ℃ and then heated at 70 ℃ for 20 min to denature the albumin. After cooling, the absorbance was measured at 660 nm.
The proteinase assay RM contained 25uL of trypsin, 1 mL of 25 mM Tris-HCl buffer, and 1 mL of extract (10–90 μg/mL), and it was incubated for 5 min at 37 ℃. Then, 1 mL of 0.8% (w/v) casein was added and the mixture was incubated for 20 min, then 2 mL of 70% (v/v) perchloric acid was added to terminate the reaction. It was then centrifuged, and the absorbance of supernatant was determined at 280 nm against buffer as a blank. Aspirin was used as positive control for both assays. The percentage inhibition of both assays was measured by the following formula:
2.1.5 Statistical analysis
All the analyses for in vitro assays were performed in triplicate, the results presented in mean ± SD. IC-50 values were calculated by the percentage inhibition in Microsoft Excel, and the statistical difference between the IC-50 values was determined via one-way ANOVA in GraphPad prism.
2.2 In silico evaluation of Pennisetum glaucum bioactive compounds and their potential targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
2.2.1 Phytocompound library generation
Gas chromatography–mass spectroscopy (GC/MS) analysis of the AM extract of Super Bajra-1 was performed to generate a plant compound library. Samples were injected in split mode at a 1:25 ratio, using helium as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1.00 mL/min. The oven temperature was programmed from 60 ℃ to 260 ℃, with specific hold times. The mass spectrometer operated at 70 eV, with temperatures set at 260 ℃ and 280 ℃ for the interface and ion source, respectively, and a mass scan range of 40–550 (Khan, 2017). This library of compounds was then used for further in silico studies.
2.2.2 Drug likeness and ADME-toxicity prediction
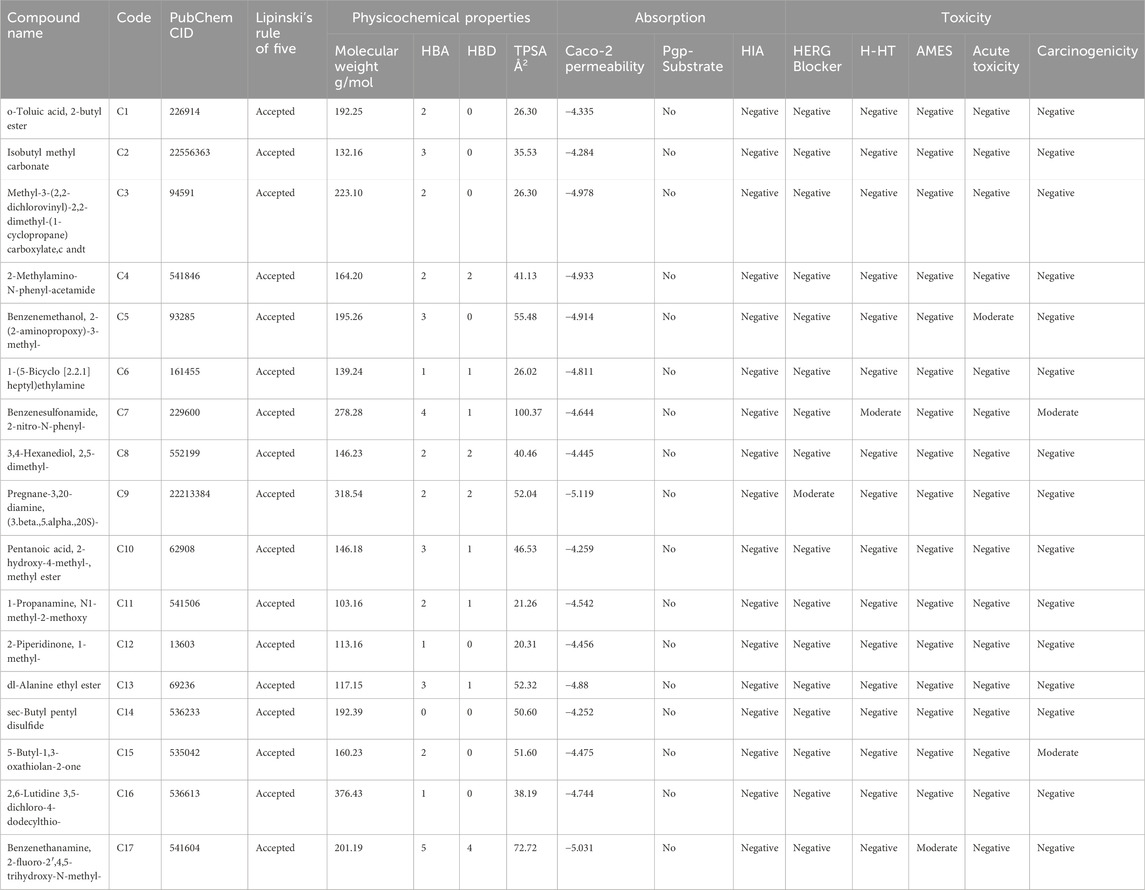
The retrieved compounds were evaluated based on pharmacokinetics parameters using SWISSadme and ADMETlab, such as Lipinski’s rule of five, cacao permeability, human intestinal absorption (HIA), oral bioavailability (OB), molar reflectivity (MR), rotatable bonds (RB), protein-glycoprotein-substrate (Pgp-S), and toxicity parameters—hepatotoxicity (H-HT), carcinogenicity, AMES, hERG, and acute toxicity. Compounds that fulfill all these parameters were shortlisted for target prediction (Maradesha et al., 2023).
2.2.3 Target prediction of disease and active compounds
Potential targets for active compounds of P. glaucum were retried from Super-PRED with a ≥50 probability and Swiss target prediction ≥0 probability, resulting in the shortlisting of targets with high confidence (Gallo et al., 2022).
To further explore the molecular mechanism of P. glaucum for RA, disease genes were retrieved from the CTD (Comparative Toxicogenomics Database), GeneCard, and OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) databases and literature using the keyword “rheumatoid arthritis”. Standard names were retrieved from universal protein resource by employing the selection “Homo sapiens” after deduplication (Zaru et al., 2023). Genes shared between RA and P. glaucum targets were identified using a Venn diagram and selected for further analysis.
2.2.4 Gene ontology, enrichment analysis, and network construction
The Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) performed functional annotation and enrichment analysis to determine the core mechanism and pathways of common targets (Huang et al., 2007). Gene functions were predicted at three levels: biological process (BP), molecular function (MF), and cellular component (CC). The species “H. sapiens” was chosen. From KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) enrichment analysis, top pathways were selected to establish a compound-target-pathways network to gain a clearer grasp of how P. glaucum exerts a multi-target effect against RA.
2.2.5 Protein–protein interactions (PPI)
A PPI network was built from common genes using a STRING database. “H. sapiens” was employed as a reference organism. Genes exhibiting a confidence level >0.7 were selected and exported to Cytoscape 3.10.0 for hub gene identification by employing the degree algorithm of cytohubba (Chin et al., 2014). Twenty genes with the highest degree were selected.
2.2.6 Microarray data analysis
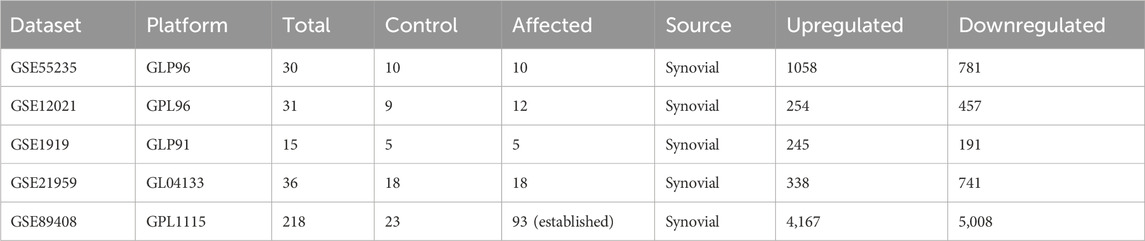
To determine the clinical relevance of the hub genes, we obtained five microarray datasets (GSE55235, GSE12021, GSE 1919, GSE21959, and GSE89408) from the Gene Expression Omnibus database (Clough et al., 2024). R studio 4.3.1 was employed to explore the differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The cut-off criteria for DEGs was set at “adj. p Val <0.05 and |log(FC)| ≥ 1” or “|log(FC)| < - 1.0”. A volcano plot was generated by employing the “ggplot2” package of R to showcase both significant and nonsignificant genes. Lastly, upregulated hub genes were selected for further in-depth analysis.
2.2.7 Molecular docking
Autodock was employed to perform molecular docking (Goodsell et al., 2021). Protein structures were retrieved from the protein data bank (PDB) and were refined via BIOVIA Discovery Studio. Kollmann-united and Gasteiger charges were assigned for the energy minimization of protein and ligand. Literature-reported residues were used for binding-site prediction and to position of the grid box (Supplementary Table S1). A generic algorithm with 20 runs was employed. The first binding poses with zero RMSD of atomic positions were considered highly valid, indicating strong binding affinity. BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer 2021 was utilized for visualization.
2.2.8 Molecular dynamic simulation
For the MD simulation, docked complexes with higher binding affinity than the reference drugs were selected. GROMACS-2020.1 software was employed for protein–ligand MD simulation. A CHARMM36 force field was utilized. CGenFF server (accessed in February 2024) was utilized to construct the ligand topology (Vanommeslaeghe and MacKerell, 2012). In total, 24 MD simulations were executed, with only those complexes that showed stability in a 30 ns timeframe being extended to 100ns. Trajectory analyses of the hydrogen-bond (H-bond), solvent-accessible surface area (SASA), radius of gyration (RoG), root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF), and root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) were conducted by XMGRACE.
2.2.9 Prediction of biological activity
The biological properties of active compounds were analyzed using PASS (Prediction of Activity Spectra for biological active Substances) (Poroikov et al., 2003) with a threshold where pharmacological activity (Pa) exceeded pharmacological inactivity (Pi). Biological activities related to RA were identified from the comprehensive array of attributes.
3 Results
3.1 In vitro evaluation of the therapeutic potential of Pennisetum glaucum extracts
3.1.1 Total phenolic and flavonoid content
The quantitative assessment of TPC and TFC was accessed by employing linear equations derived from the calibration curves of gallic acid (y = 0.0003x + 0.0904, R2 = 0.9906) for TPC and rutin (y = 0.008x + 0.005, R2 = 0.9996) for TFC. The results showed a significant amount of phenolics and flavonoids in all extracts. The TPC in different extracts were ranked in descending order as AM > E > Aq > HA (Figure 3A). A similar trend was noted for TFC: AM > Aq > E > HA (Figure 3B). The AM extract exhibited the highest TPC (213 ± 0.008 mg GAE/g DW) and TFC (138.1 ± 0.03 mg RE/g DW) of all extracts.
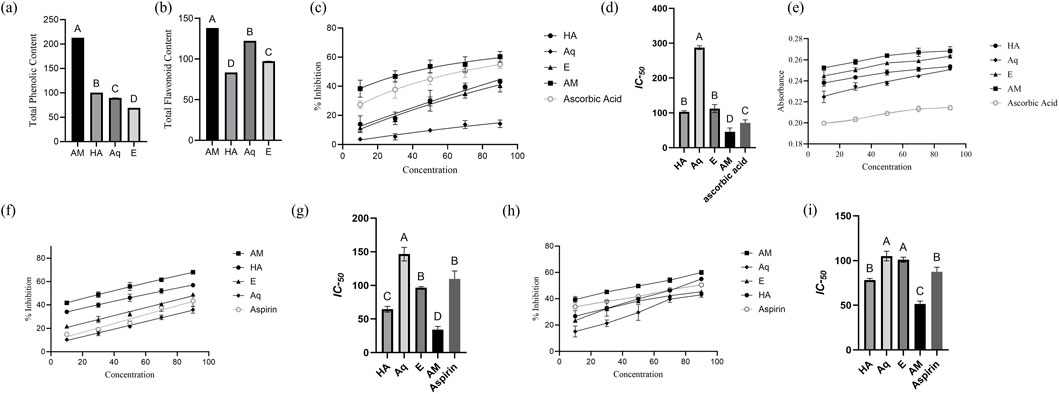
Figure 3. Characterization of Pennisetum glaucum extract. (A) TPC, (B) TFC, (C) percentage Inhibition of DPPH assay, (D) IC50 of extracts for DPPH assay, (E) absorbance of reducing power assay, (F) percentage inhibition of albumin denaturation assay, (G) IC50 of extracts for albumin denaturation assay, (H) percentage Inhibition of proteinase assay, and (I) IC50 of extracts for proteinase assay. IC50 were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, with different letters representing the statistical difference between different extracts. All experiments were conducted in triplicates and reported in mean ± SD.
3.1.2 Antioxidant potential
The result of the DPPH assay demonstrated the significant antioxidant potential of P. glaucum extracts. All extracts showed a significant dose-dependent inhibition of the free radicals, and maximum inhibition was observed by AM extract—60.7% at a concentration of 90 μg/mL (Figure 3C). The IC-50 of AM was recorded as 45.68 μg/mL—more statistically significant than other extracts (Figure 3D).
The result of reducing the power assay also demonstrated the significant antioxidant potential of P. glaucum extracts. AM extract showed the maximum absorbance, which correlates with the extract’s electron transfer ability, thus serving as a significant indicator of antioxidant potential (Figure 3E). All the extracts showed higher absorbance than the standard ascorbic acid. The EC-50 of AM extract was recorded as 38.50 μg/mL, while for ascorbic acid it was recorded as 45.60 μg/mL.
AM extract showed significant antioxidant potential in both assays (Supplementary Table S2).
3.1.3 Anti-inflammatory potential
The albumin denaturation assay demonstrated the anti-inflammatory potential of P. glaucum extracts. Dose-dependent inhibition was observed for all extracts, with the AM extract showing the highest percentage inhibition, surpassing aspirin (Figure 3F). Similarly, IC-50 of AM extract showed more statistically significant results than aspirin: 34.09 μg/mL and 109.47 μg/mL, respectively (Figure 3G).
Proteinase inhibition assay also demonstrated the anti-inflammatory potential of P. glaucum extracts. Dose-dependent inhibition was observed for all extracts where AM extract exhibited higher inhibition than aspirin (Figure 3H). The IC-50 for the AM extract and aspirin were 51.36 μg/mL and 87.60 μg/mL, respectively, indicating the greater inhibitory potential of the AM extract than the positive control (Figure 3I).
Both assays indicated the AM extract as potentially anti-inflammatory Supplementary Table S2.
3.2 In silico evaluation of Pennisetum glaucum active compounds and their potential targets for treating rheumatoid arthritis
3.2.1 P. glaucum active compound screening
Some 223 compounds were identified from P. glaucum GC-MS analysis. Active compounds were screened using various ADMET, drug-likeliness, and physiochemical parameters (Table 1). Based on these, 17 compounds were selected for further analysis.
3.2.2 Target prediction and network analysis
Potential targets of active compounds were identified, with 448 targets screened from the Swiss Target Prediction database and 594 from Super-PRED. A total of 819 targets was obtained after deduplication (Supplementary Figure S1A). CTD, GeneCard, OMIM, and the literature were employed to acquire 481, 412, 184, and 22 disease targets, respectively. A total of 855 disease targets were predicted after deduplication (Supplementary Figure S1B). Common targets of RA and compounds were predicted using a Venn diagram. A total of 160 anti-arthritic targets of P. glaucum were selected and considered as key therapeutic targets (Figure 4A).
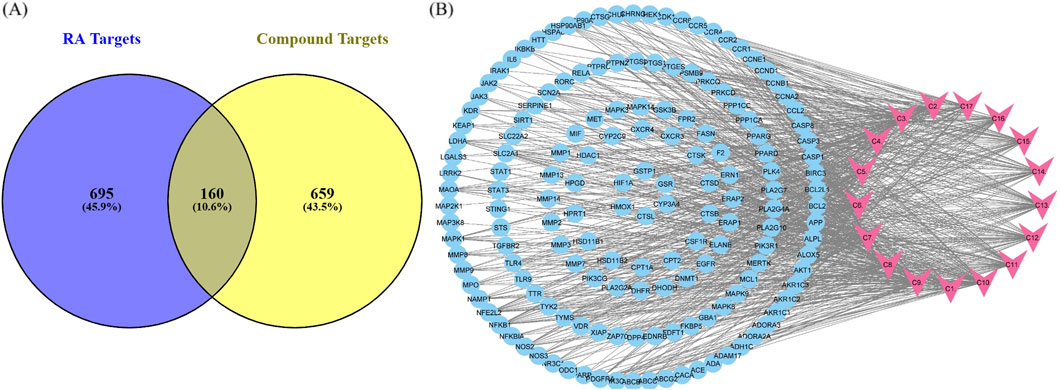
Figure 4. (A) Common targets between compounds and disease shown by a Venn diagram. (B) Compound–target pathway blue nodes represent the targets, while pink nodes represent the bioactive compound.
Cytoscape was employed to construct a compound–target (C-T) network from 17 compounds and 160 common targets to comprehend the multi-target effect of P. glaucum in RA (Figure 4B). The C-T network had 177 nodes and 800 edges. The degree of 17 compounds was analyzed; the higher the degree, the higher the connectivity, where compound 9 (C9) had the highest degree of connectivity—60 followed by C7 (degree:58) and C10 (degree:57). Therefore, these compounds were considered key nodes, suggesting the multi-component therapeutic role of P. glaucum on RA. The degree of all the compounds, along with the MCC, MNC, betweenness, and closeness are displayed in Supplementary Table S3.
3.2.3 Hub gene identification by the PPI network
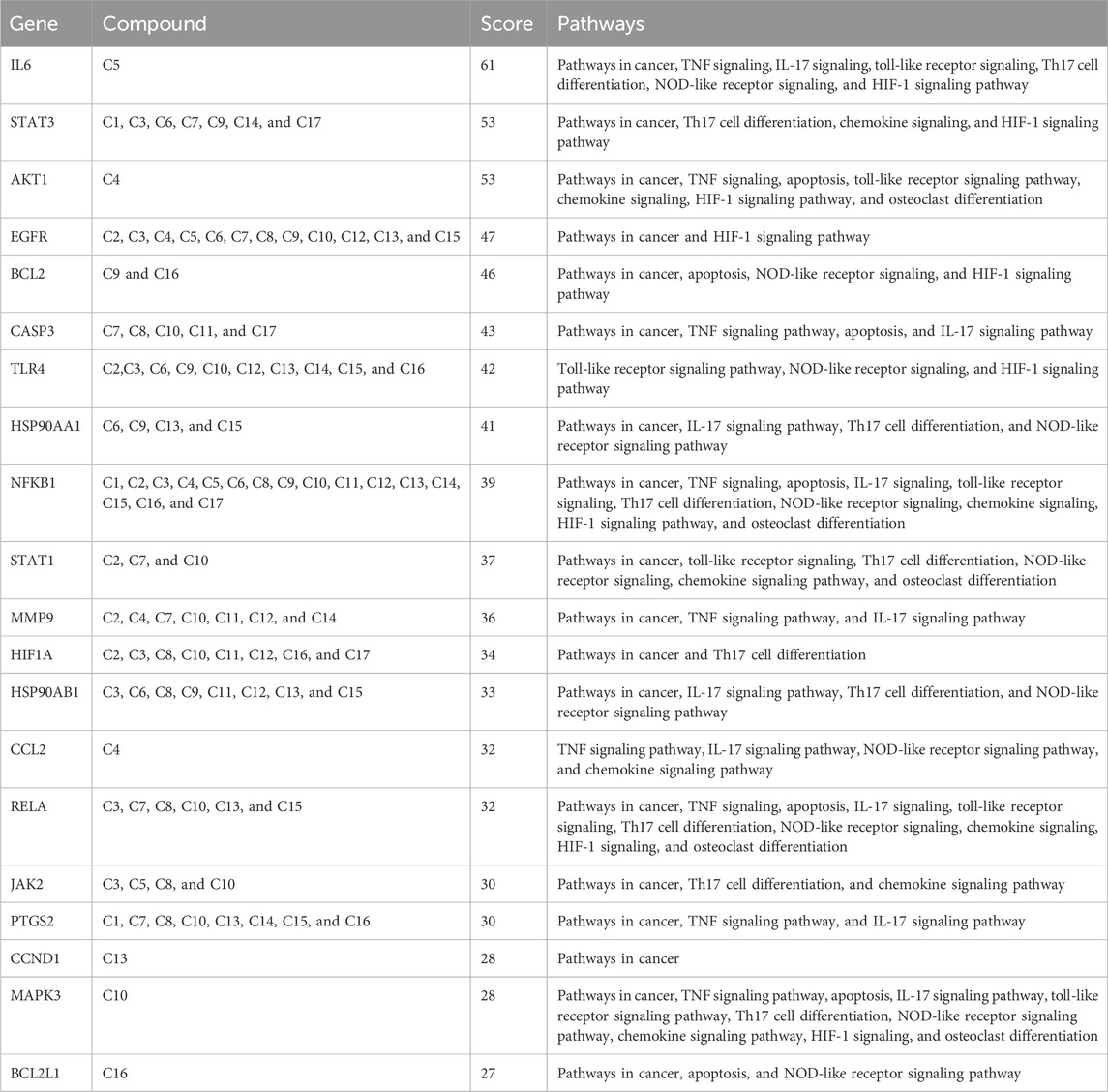
The STRING database was employed to construct the PPI network of 160 common targets. The PPI network had 949 edges (Figures 5A, B) and was exported to Cytoscape, where CytoHubba was employed to screen the top 20 hub genes based on degree connectivity (Figure 5C). The highest degree showed that the targets had stronger correlation among them and are the potential target. IL6, STAT3, AKT1, EGFR, BCL2, CASP3, TLR4, HSP90AA1, NFKB1, STAT1, MMP9, HIF1A, HSP90AB1, CCL2, RELA, JAK2, PTGS2, CCND1, MAPK3, and BCL2L1 showed the highest degree and were considered as the hub genes. The degree value of all these targets is shown in Figure 5D.
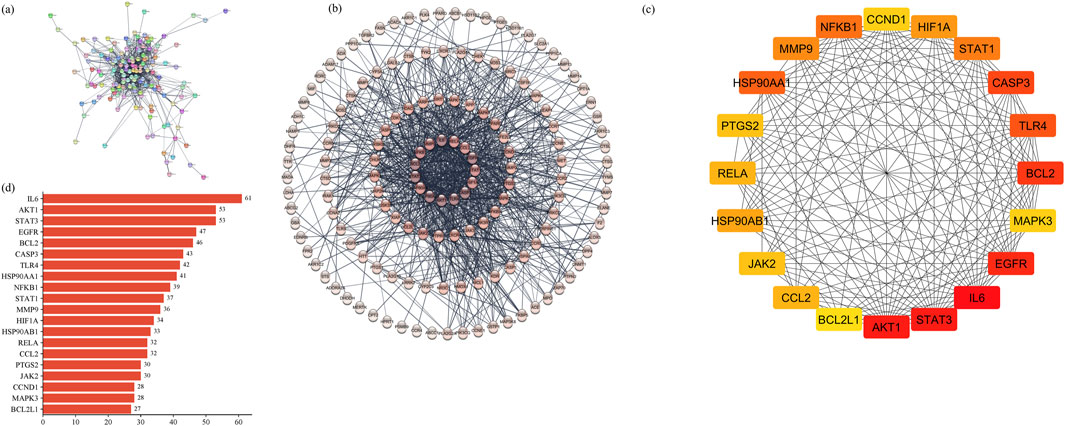
Figure 5. (A) PPI network of common 160 genes. (B) Degree sorted PPI network; darker color shows a higher degree. (C) Degree-based ranking of top 20 genes. (D) Bar plot of top 20 genes from the PPI network.
3.2.4 Gene ontology and KEGG enrichment analysis
Enrichment analysis and functional annotation revealed that P. glaucum targets were enriched in 518 BP, 74 CC, 123 MF, and 155 KEGG statistically significant pathways. The top ten enriched terms based on counts and p-value were visualized using a bubble plot (Figure 6). GO BP revealed that the targets of P. glaucum were enriched in protein phosphorylation, inflammatory response, the negative regulation of apoptotic process, extracellular matrix disassembly, collagen catabolism, and related processes (Figure 6A). GO CC analysis revealed that the targets were enriched in cytoplasm, cytosol, plasma membrane, nucleoplasm, and so forth (Figure 6B). GO MF analyses indicated that the targets were enriched in identical protein binding, ATP binding, protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinases, protein kinase, protein serine/threonine kinases, and related activities (Figure 6C).
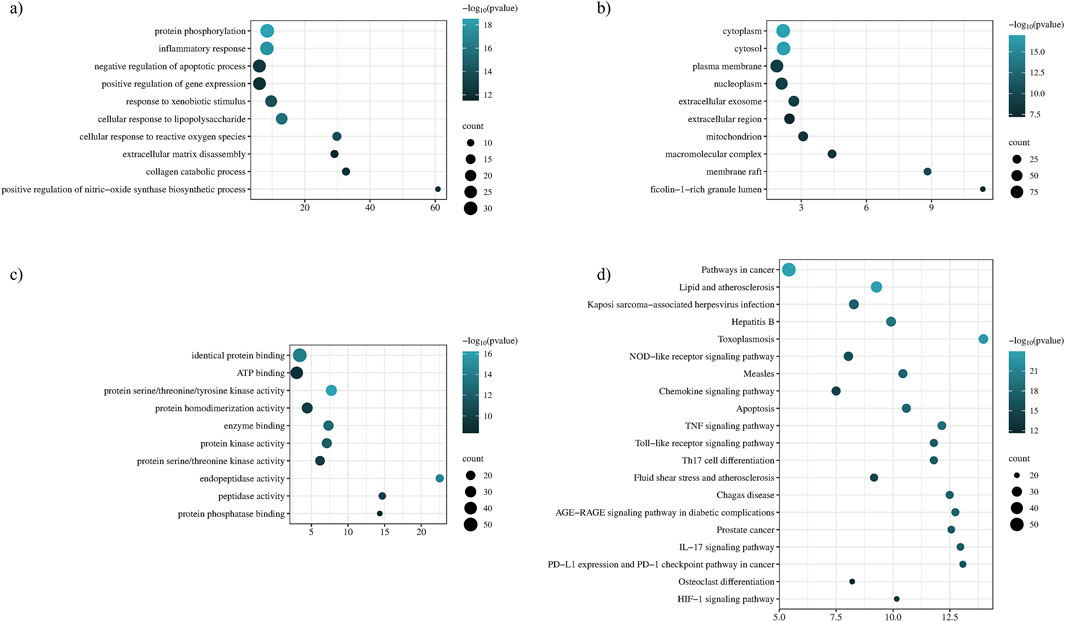
Figure 6. Functional annotation and enrichment analysis. (A) Gene ontology of BP, (B) gene ontology of CC, (C) gene ontology of MF, and (D) KEGG enrichment analysis.
KEGG pathway exploration was conducted to investigate the most significant signaling pathway (Figure 6D). Notably, most of the genes were enriched in pathways in cancer, TNF-alpha signaling pathway, apoptosis, IL17 signaling pathway, Th17 cell differentiation, toll-like signaling pathway, HIF1 signaling pathway, and osteoclast differentiation (Table 2). The compound-target-pathway network in Figure 7 shows the enrichment of KEGG pathways and hub genes in association with the bioactive compounds.
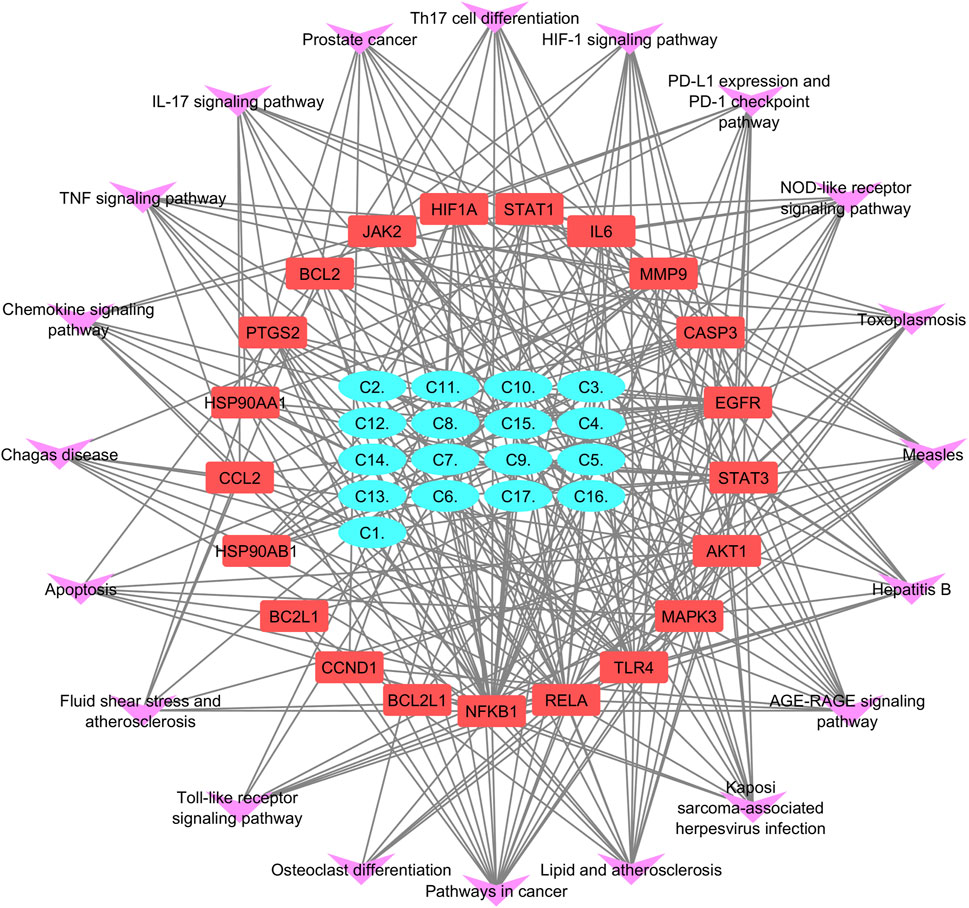
Figure 7. Compound–target-pathway network purple errors show pathways, red represents target gene, and cyan shows lead compounds of Pennisetum glaucum.
3.2.5 Microarray data analysis
The top 20 shortlisted hub genes were further validated by microarray data analysis (Figure 8). Five microarray datasets of RA and healthy control were selected to identify whether the selected hub genes were upregulated in RA. By concentrating on upregulated genes, we ensured a targeted and reliable strategy to identify the potential targets. Of the 20 hub genes, only nine were upregulated in these datasets: JAK2, STAT1, PTGS2, IL-6, MMP9, TLR4, CASP3, HIF1A, and CCL2 (Table 3). STAT1 was upregulated in all five datasets. MMP9 and JAK2 were upregulated in two datasets: GSE55235 and GSE89408. IL-6 was also upregulated in two datasets: GSE21959 and GSE89408. PTGS2, HIF1A, CCL2, CASP3, and TLR4 were upregulated in GSE89408. The nine upregulated genes were then selected for molecular docking.
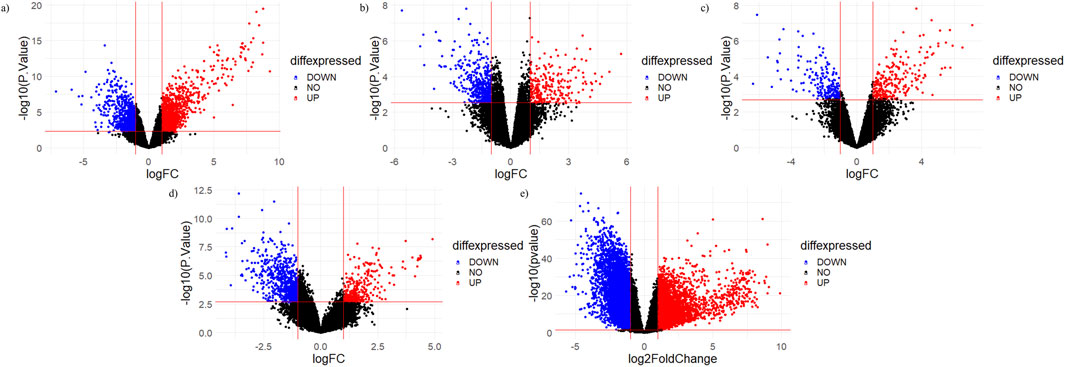
Figure 8. Volcano plots of micro array datasets. Red dots show upregulated genes, while blue dots show downregulated genes: (A) GSE55235, (B) GSE12021, (C) GSE 1919, (D) GSE21959, and (E) GSE89408 datasets.
3.2.6 Molecular docking
Molecular docking was performed for nine hub genes with 17 active compounds. Docking analysis predicted strong interactions between the binding pocket of proteins and active compounds, as shown in the heatmap in Figure 9B. The findings were compared with the FDA approved standard drugs: fludarabine phosphate (for STAT1), fostamatinib (for JAK2), minocycline (for MMP9), nifulmic acid (for PTGS2), bazedoxifene (for IL-6) chondroitin 4-sulfate (for CCL2), aspirin (for CASP3), vadadustat (for HIF1A), and cyclobenzaprine (for TLR4). C7 and C9 exhibited significantly higher binding affinities for target genes, as illustrated by box plot (Figure 9A).
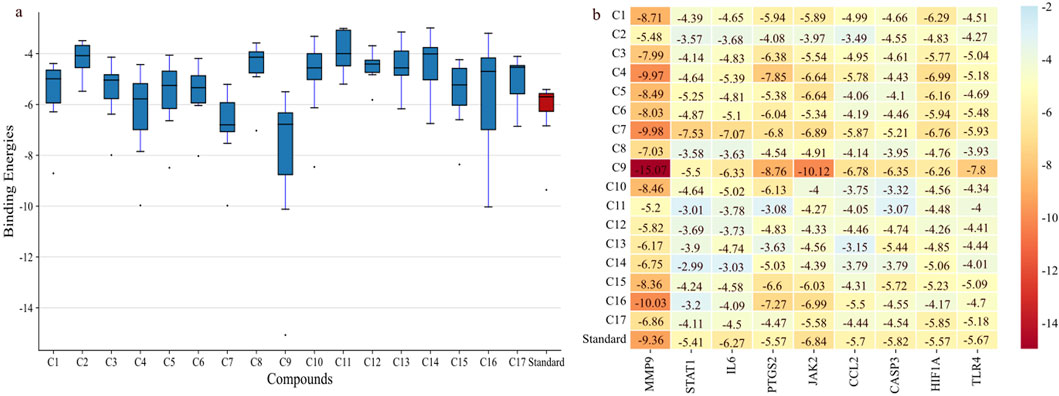
Figure 9. Binding affinities of shortlisted proteins with 17 compounds. (A) Boxplot showing that C9 and C7 have the best binding affinity among all the lead compounds; the red bar shows the binding affinity of different standards against each target. (B) Heatmap showing the binding affinities of proteins with the lead compounds.
C9 showed much stronger binding affinities than the reference drugs, with values of −15.07, −5.5, −6.33, −8.76, −10.12, −6.78, −6.56, −6.26, and −7.8 kcal/mol for MMP9, STAT1, IL-6, PTGS2, JAK2, CCL2, CASP3, HIF1α, and TLR4, respectively. The reference drugs (minocycline, fluradibine phosphate, bazedoxifene, niflumic acid, fostamatinib, chondroitin 4-sulfate, aspirin, vadadustat, and cyclobenzaprine) showed lower affinities, with values of −9.36, −5.41, −6.27, −5.57, −6.84, −5.7, −5.82, −5.57, and −5.67 kcal/mol for the same targets. Similarly, C7 demonstrated higher binding affinities for eight targets, with values of −9.98, −7.53, −7.07, −6.8, −6.89, −5.87, −6.76, and −5.93 kcal/mol for MMP9, STAT1, IL-6, PTGS2, JAK2, CCL2, HIF1A, and TLR4, respectively. These findings confirm the strong binding capabilities of C7 and C9 to target proteins, outperforming the references. Each drug candidate demonstrated significant interactions with receptor proteins (Supplementary Figures S2–10). C7 bound stably with the MMP9 binding pocket and formed H-bonds with Tyr245, His226, and Arg249 and hydrophobic interaction with Val223; the same interaction pattern was observed with the reference drug. However, C9 formed H-bonds with Arg249 and Ala189 and hydrophobic interactions with His226, Val223, Leu1s88, Tyr248, Pro255, Leu222, and Leu243. The common interacting residues between the standard and C9 were Tyr245, His226, Arg249 and Arg249, His226, Leu243, Leu222, and Tyr248. Figure 10 shows the binding interaction of the top eight targets with C7, C9, and the references. Supplementary Table S4 displays the detailed interaction of all the ligands and proteins in comparison with the reference drugs along with the binging affinities and inhibition constant (Ki).
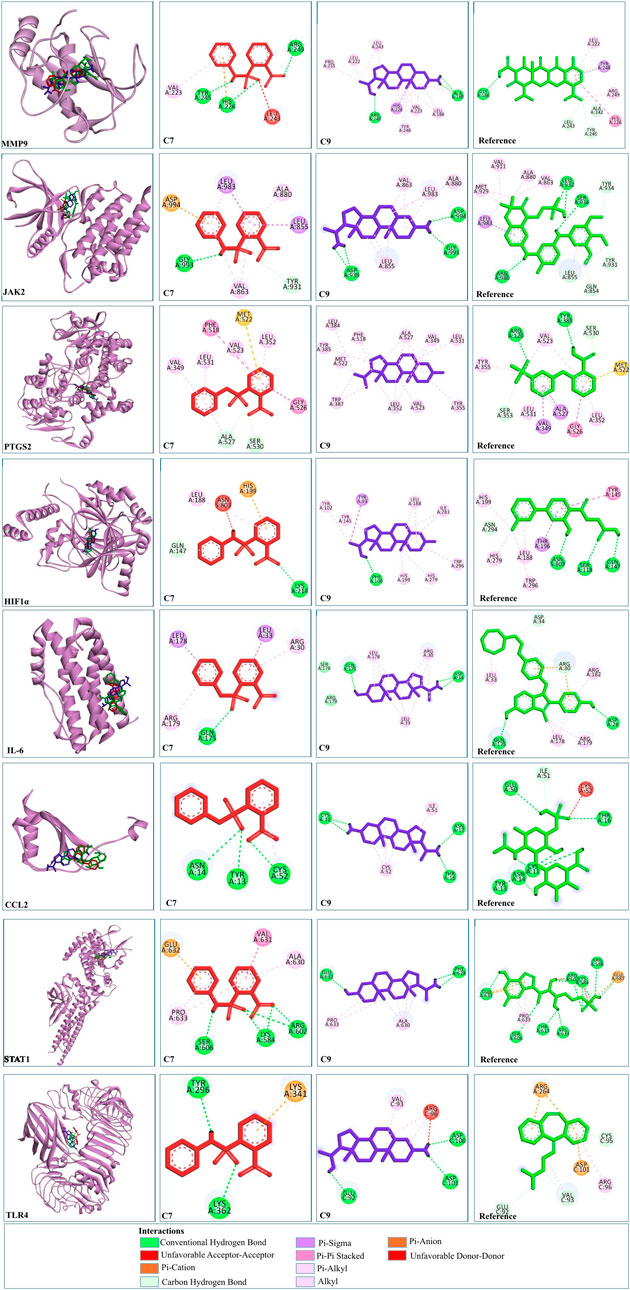
Figure 10. 2D and 3D visualization of docked complexes of C7, C9, and reference with the shortlisted targets—MMP9, JAK2, PTGS2, HIF1A, IL-6, CCL2, STAT1, and TLR4. Red depicts C7, blue represents C9, and green represents the reference structure. Key indicates the types of interaction between compounds and targets.
3.2.7 Molecular dynamic simulations
Molecular dynamic (MD) simulation was conducted to elucidate the stability of protein–ligand interactions and assess protein structural flexibility within the docked complexes. Complexes involving MMP9, JAK2, PTGS2, and HIF1α demonstrated consistent stability during the initial 30 ns period, thus warranting extension to 100 ns.
First, RMSD values were calculated to estimate the structural stability of docked complexes. Throughout the 100 ns MD simulation, RMSD values for all complexes remained stable (Figure 11). For MMP9 protein, C7 complex exhibited the most stable RMSD, with an average value of 0.26 nm and experiencing minor fluctuations after 75 ns. This demonstrated greater stability than the C9 complex (0.396 nm). Both compounds showed better RMSD values than the reference (0.792 nm). For JAK2 and HIF1A, C7 displayed a very stable RMSD without significant fluctuations, outperforming both C9 and reference. The JAK2-C9 complex showed an increased trend after 25 ns. The JAK2–Reference complex showed a fluctuation at 25 ns and then stabilized with minor fluctuations throughout the 100 ns. HIF1A-C9 showed an increasing trend with slight fluctuations before 50 ns, then stabilized with minimal fluctuations until 100 ns. The HIF1A–Reference showed a comparable RMSD to C7. For PTGS2, both the C9 and C7 complexes exhibited a very stable RMSD. PTGS2–Reference showed slight fluctuations at 38 ns and 83 ns, but its average RMSD remained within the acceptable range at 0.239 nm (Table 4).
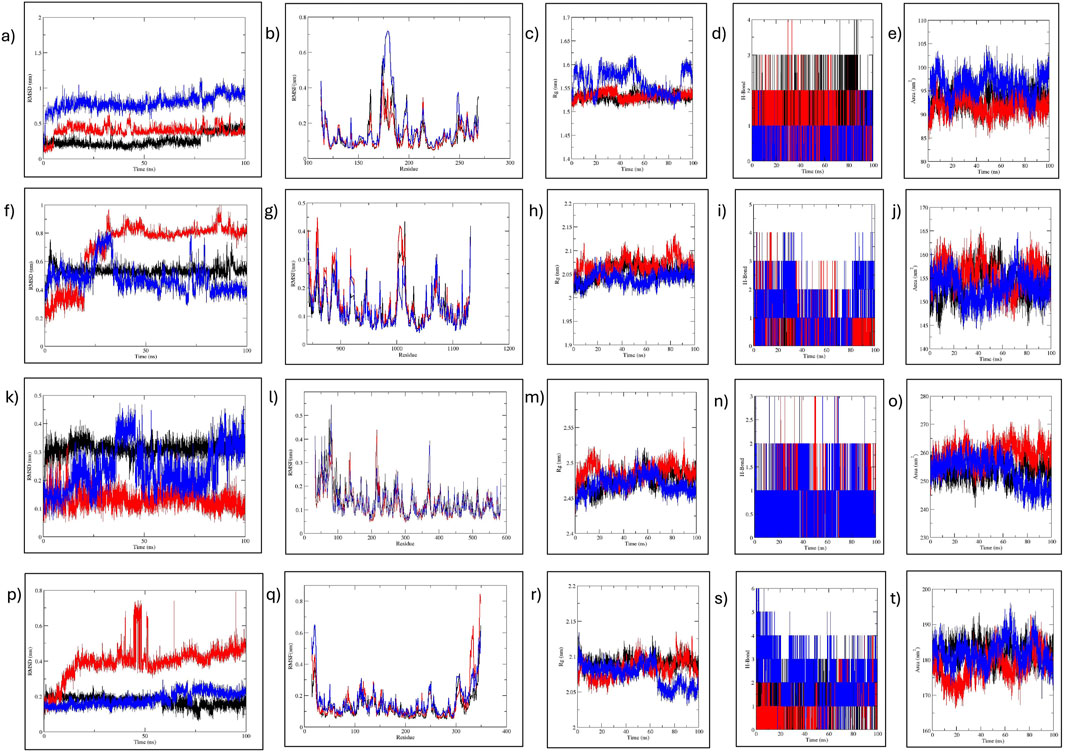
Figure 11. MD simulation analysis of MMP9, JAK2, PTGS2, and HIF1α. (A–E) MMP9-C7, C9, and reference analysis: (A) RMSD, (B) RMSF, (C) RoG, (D) H-bond, and (E) SASA analysis. (F–J) JAK2-C7, C9, and reference analysis: (F) RMSD, (G) RMSF, (H) RoG, (I) H-bond, and (J) SASA analysis. (K–O) PTGS2-C7, C9, and reference analysis: (K) RMSD, (L) RMSF, (M) RoG, (N) H-bond, and (O) SASA analysis. (P–T) HIF1a-C7, C9, and reference analysis: (P) RMSD, (Q) RMSF, (R) RoG, (S) H-bond, and (T) SASA analysis. Black represents C7; red, C9; and blue the reference.
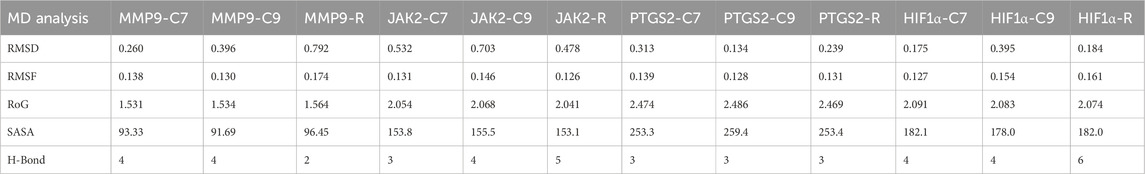
Table 4. Average values of RMSD, SASA, RoG, and H-Bonds formed during MD simulation of MMP9, JAK2, and PTGS2 with C7, C9, and R.
RMSF for the complexes were analyzed to assess flexibility at the residue level (Figure 11). For MMP9, minimal fluctuations were observed for both C7 and C9, while MMP9–Reference fluctuated slightly residues 173–184 at the C-terminus. The flexibility in all MMP9 complexes was noted in β-strands, indicating the dynamic nature of the binding pocket as it adapts to the bound ligand. In the case of JAK2, C7 and reference had comparable fluctuations while C9 had higher fluctuation at the same residues: 1006-1015 located in the protein kinase domain. Nonetheless, JAK2 complexes exhibited minimal fluctuation. For PTGS2, reference showed more fluctuation than the compounds, particularly at residues 81 and 373. PTGS2–C7 and –C9 showed stable RMSF, with C9 fluctuating at 83 residues in the helical region. For HIF1A, C7 and reference showed minimal fluctuation, whereas C9 fluctuated at the C-terminal residues 347 and 349. Overall, all complexes exhibited acceptable residue fluctuations, demonstrating high structural stability and rigidity (Table 4).
The compactness of the protein structure was analyzed by RoG, revealing that all complexes were stable (Figure 11). For MMP9, the RoG of the reference complex fluctuated between 1.5 and 1.6 nm, while the RoGs for MMP9–C7 and–C9 were nearly identical, indicating that both compounds preserved the MMP9 conformation much more stably than the reference. For JAK2, C9 and C7 RoGs were comparable to that of reference, showing that both compounds stabilized the protein effectively. Similarly, PTGS2–C9 and –C7 exhibited better RoG values (2.474 and 2.486 nm, respectively) than the reference (2.469 nm). The RoG of the HIF1α reference complex fluctuated 2.05–2.1 nm, while C7 and C9 had comparable RoG values, indicating that both compounds maintained the protein conformation better than the reference. Overall, the RoG data indicated that all complexes of C7 and C9 were structurally compact, with improved folding behavior compared to the reference complexes.
The H-bond analysis determined the stability of complex interactions. For MMP9, both C9 and C7 formed four H-bonds, while the reference formed two H-bonds. For JAK2, the reference formed five H-bonds while C7 and C9 formed three and four H-bonds, respectively. For PTGS2, all complexes formed three H-bonds. For HIF1α, both C7 and C9 formed four H-bonds, while reference formed six H-bonds (Figure 11).
Estimating SASA values is beneficial for predicting the protein-interactable surface with the solvent (Figure 11). For MMP9, the reference SASA ranged 90–100 nm2, while for C7 and C9 it ranged 90–95 nm2. For JAK2, C7 ranged 150–155 nm2, while C9 and reference showed fluctuation at approximately 155 nm2, suggesting similar surface accessibility for both. For PTGS2, all complexes displayed similar surface accessibility until 60 ns. Thereafter, reference and C7 showed a decrease, while C9 remained stable with minor fluctuations. In the case of HIF1α, C7 remained stable at 180–185 nm2, and C9 fluctuated 170–185 nm2. The reference fluctuated 185–190 nm2.
3.2.8 PASS prediction of biological activity
The identification of molecular interactions between compounds and their targets is important for in silico and toxicity analysis. The PASS tool uses structure–activity relationship analysis (SAR) to predict various biological targets, hence reducing the possibility of failure while performing in vitro and wet-lab testing. The PASS tool showed 1130 and 482 biological activities of C7 and C9, respectively, primarily focusing on anti-inflammatory signaling pathways and potential targets for RA. The tool successfully identified C7 and C9 as potential JAK2 (Pa = 0.267 for C7 and Pa = 0.322 for C9) and prostaglandin (Pa = 0.279 for C7 and Pa = 0.226 for C9) inhibitors. C7 was reported as a non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent (Pa = 0.188) with an anti-inflammatory Pa of 0.206 and was also reported to inhibit IL6 (Pa = 0.155), CC chemokine 9 and 10 receptor (Pa = 0.119), CXC chemokine 2 and 1 receptor (Pa = 0.051), and transcription factor NFKβ (Pa = 0.282). C9 was reported as steroidal anti-inflammatory (Pa = 0.308) and an antagonist of IL-2 and 10 (Pa = 0.448), interferons (Pa = 0.159)—particularly interferon gamma (Pa = 0.153)—and transcription factor NFKα (Pa = 0.229). C7 was also reported to inhibit MMPs (Pa = 0.053), particularly MMP1, 2, and 9 (Pa = 0.030, 0.054 and 0.032 respectively). C7 was also recognized as a collagenase inhibitor (Pa = 0.138). All biological activities of C7 and C9 predicted by the PASS are detailed in Supplementary File S2. These diverse arrays of biological activities suggest that C7 and C9 hold promise as multifaceted treatment candidates for RA.
4 Discussion
RA is a complex autoimmune condition characterized by hyperinflammatory and abnormal proteolytic activity. The limitations of current therapeutic options have demanded a shift toward medical plants, leading to a move from traditional methods to computer-based assessments with the aim of improving drug discovery, such as network pharmacology. These can offer insights into compound interactions and address concerns about research costs and drugs that lack ADME qualities (Cai et al., 2020).
Research on natural-compounds-based therapeutics has increased due to their safer profile in the efficient management of the various pathologies (Jha et al., 2023). Pennisetum glaucum has been reported to play a significant role in bone metabolism and osteoimmunology (Nani et al., 2020). This highly nutritious cereal crop has garnered significant global attention, leading the UN Food and Agriculture Organization to recognize 2023 as the “International Millet Year” (Harish et al., 2024). Acknowledged as a “nutri-cereal” by the Government of India, pearl millet stands out for its elevated nutrient content, particularly in unsaturated and omega-3 fatty acids (Deka et al., 2024), and it has been reported that these fatty acids modulate the pathogenesis of arthritis (Kostoglou-Athanassiou et al., 2020). The phytochemical diversity of pearl millet, including polyphenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tannins, and anthraquinones, underpins its various pharmacological properties, such as antioxidative, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, anticholesterolemic, and bone protecting effects, offering protection against numerous disorders (Ahmed et al., 2023). The aim of this study is to identify the potential bioactive compounds of P. glaucum to alleviate RA.
This study accessed the phenolic, flavonoid, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties of P. glaucum extracts. The AM extract showed the highest levels of phenols and flavonoids, likely due to the effectiveness of the acidified solvent in extracting maximum polyphenols that resulted in stronger antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential. Our results are more or less similar to previous studies (Siroha et al., 2016). Chethan and Malleshi (2007) reported that millet polyphenols are more stable in acidic conditions than alkaline. Consequently, the acidified extract underwent GCMS analysis to generate a compound library. Compounds that met all ADMET criteria to ensure that they were non-toxic, non-mutagenic, and orally effective were selected for further investigation, adopting an approach similar to Maradesha et al. (2023). The study utilized a network pharmacology approach to identify 160 anti-RA targets of P. glaucum. These were subjected to PPI and KEGG enrichment analysis where pathways such as TNF, IL-17, TH-17, toll-like receptor, NOD-like receptor, chemokine signaling, apoptosis, and osteoclast differentiation exhibited significant enrichment; dysregulation of these signaling pathways plays a pivotal role in RA (Baier et al., 2003). Compound–target network analysis revealed that all compounds exhibited strong interactions, especially C7 and C9, indicating potential anti-RA properties and validating our hypothesis that P. glaucum can effectively alleviate RA. The top 20 hub genes were selected from a PPI network by employing the degree algorithm of cytohubba. All 20 genes play a crucial role in RA pathogenesis, but to ensure their clinical relevance, they were assessed across five microarray datasets. Only nine genes were upregulated, revealing their significant role in disease progression and severity; a similar approach was utilized by Sadaqat et al. (2023). This finding was corroborated by docking nine genes with 17 compounds, which indicated significant docking energies (Figure 6). Importantly, C7, C9, and C4 emerged as particularly promising candidates in contrast to the reference drugs—minocycline was reported to cause hyperpigmentation (Fay et al., 2008) and other severe side effects in RA (Suresh et al., 2004), niflumic acid has reported nephrotoxic effect (Aronson JKBT-MSE of D and 16th, 2016), fostamatinib is associated with cardiovascular risk (Chen Y. et al., 2021), and vadadustat has reported to increase thrombosis events (Chen H. et al., 2021). Furthermore, ADMET profiles of the reference drugs revealed that they all exhibited some form of toxicity, including hepatotoxicity, acute toxicity, and carcinogenicity, except vadadustat (S2).
C7 and C9 complexes, which showed better binding energy than the reference drugs, were subjected to MD simulation. Initially, all complexes underwent a 30 ns MD simulation, during which complexes of STAT1 and TLR4 were unstable. In the case of IL-6, C7 initially deviated from the binding pocket but returned by the end of the 30 ns MD simulation, while both C9 and the reference left the binding pocket. Similar observations were made for CCL2 and thus were not extended further (Supplementary Figure S11). However, MMP9, JAK2, PTGS2, and HIF1A complexes were extended to 100 ns, demonstrating stability as strong inhibitors within the binding pocket of proteins. C7, an aromatic sulfur-containing compound, has also been reported in the GCMS analysis of soya bean extract (Chukeatirote et al., 2017), while its derivatives have been reported in the extracts of various medicinal plants (Ejiofor et al., 2022; Al-Rajhi et al., 2022). C9, an alkaloid steroid compound, is a pregnane derivative and has also been reported in many medical plants (Kadam and Gaykar, 2018; Nadar, 2015) and as exhibiting potential biological activities (Si et al., 2022). Finally, the PASS analysis confirmed the biological potential of C7 and C9 as promising targets for RA treatment, showing higher Pa values for inhibiting cyclooxygenase (responsible for pain and inflammation), MMPs (involved in cartilage destruction and bone erosion), JAK/STAT (crucial for aberrant signaling pathways), cytokines and chemokines (pivotal in RA pathogenesis), and specific inhibitors of the TCA cycle (facilitating the conversion of lactate in hypoxic environments, leading to increase inflammation) (Cai et al., 2020). The collective results of MD simulation and PASS analyses highlight C7 and C9 as potent inhibitors for MMP9, JAK2, PTGS2, and HIF1α proteins, warranting further exploration in therapeutic development.
These four genes play an intricate role in RA pathogenesis and collectively orchestrate a complex network of interactions. MMP9 secreted by FLS and neutrophiles lead to the degradation of cartilage/bone collagen and ECM membrane, facilitating the stimulation of angiogenic factors and cytokines in RA (Bian et al., 2023). JAK2, stimulated by various cytokines, stimulates angiogenesis (Cheng et al., 2020), hinders fibroblast apoptosis (Krause et al., 2002), induces MMP expression, and stimulates osteoblastic activity in RA. PTGS2 stimulated the synthesis of PEG2, which modulates bone resorption, pain, and inflammation and is associated with MMP secretion in RA (Ozen et al., 2019). HIF1a induced hypoxic environment and increased glycolysis which stimulates cytokines, VEGF, and rapid proliferation of RA-FLS (Ahmed et al., 2023). Therefore, the ability of C7 and C9 to interact with HIF1α, JAK2, PTGS2, and MMP9 suggests a multi-target approach that could effectively regulate inflammation, RA-FLS, immune response, and tissue degradation associated with RA.
This multi-faceted strategy holds great promise for managing RA by addressing various aspects of the disease’s complex pathophysiology. In previous studies on protein–ligand systems, Alsaif et al. (2024) and Yu et al. (2024) utilized molecular docking analysis, identifying significant binding affinities between target proteins and their respective compounds. In contrast, our research employed a more comprehensive set of techniques, incorporating molecular docking, MD simulation, and PASS analysis. This multifaceted approach allowed a thorough understanding of protein–ligand interactions and provided greater confidence in the results. Our study lays the groundwork for considering P. glaucum compounds as a potential treatment for RA.
5 Conclusion
This study identified the plant-based bioactive compounds of Pennisetum glaucum against RA by in vitro and in silico approaches. It concluded that P. glaucum and its bioactive compounds hold significant anti-rheumatic potential. In vitro analysis revealed a significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of P. glaucum extracts, which are crucial for anti-rheumatic therapies. In silico analysis, utilizing CADD techniques such as network pharmacology, microarray validation, molecular docking, and MD simulations, identified the potential bioactive compound and targets that influence biological processes such as inflammation, apoptosis, and collagen degradation, as well as pathways like TNF signaling, HIF1 signaling, and osteoclast differentiation, which are crucial in managing RA. Two bioactive compounds—C7 and C9—were identified with therapeutic potential against the key RA targets MMP9, JAK2, PTGS2, and HIF1A. The insights gained from this study could guide the future application and development of P. glaucum as a treatment for RA.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
MS: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. PJ: conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. AB: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, and writing–review and editing. RP: data curation, resources, software, supervision, validation, and writing–review and editing. AM: project administration, resources, supervision, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the technical staff of ASAB and SINES for their constant support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1488790/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmed, I., John, P., and Bhatti, A. (2023). Association analysis of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A (VEGF-A) polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis using computational approaches. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 21957. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-47780-8
Akram, M., Daniyal, M., Sultana, S., Owais, A., Akhtar, N., Zahid, R., et al. (2021). Traditional and modern management strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 512, 142–155. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.11.003
Ali, K., Meddah, B., Badraoui, R., Elblidi, O., Cherrah, Y., Chokairi, O., et al. Comparative effect of Pennisetum glaucum and alendronate on biochemical and histological analyses of lumbar vertebrae and liver for rats fed cafeteria diet associated with glucocorticoid therapy. 2018;
Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Mashraqi, A., Al Abboud, M. A., Shater, A.-R. M., Al Jaouni, S. K., Selim, S., et al. (2022). Screening of bioactive compounds from Endophytic marine-derived fungi in Saudi arabia: antimicrobial and anticancer potential. Vol. , 12, 1182, doi:10.3390/life12081182
Alsaif, G., Tasleem, M., Rezgui, R., Alshaghdali, K., Saeed, A., and Saeed, M. (2024). Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis of Catharanthus roseus compounds: implications for non-small cell lung cancer treatment. J. King Saud. Univ. - Sci. 36 (4), 103134. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2024.103134
Aronson JKBT-MSE of D (2016). in Niflumic acid. Editor E. Sixteenth (Oxford: Elsevier), 173–174. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444537171011483.
Aryal, S., Baniya, M. K., Danekhu, K., Kunwar, P., Gurung, R., and Koirala, N. (2019). Total phenolic content, flavonoid content and antioxidant potential of wild vegetables from western Nepal. Plants 8, 96. doi:10.3390/plants8040096
Baier, A., Meineckel, I., Gay, S., and Pap, T. (2003). Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 15 (3), 274–279. doi:10.1097/00002281-200305000-00015
Bhattacharya, S. (2023). Cultivating health: millets’ potential in combating non-communicable diseases and future research avenues in India. Front. Nutr. 10, 1190111. doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1190111
Bian, Y., Xiang, Z., Wang, Y., Ren, Q., Chen, G., Xiang, B., et al. (2023). Immunomodulatory roles of metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1285455. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1285455
Bullock, J., Rizvi, S. A. A., Saleh, A. M., Ahmed, S. S., Do, D. P., Ansari, R. A., et al. (2018). Rheumatoid arthritis: a brief overview of the treatment. Med. Princ. Pract. 27 (6), 501–507. doi:10.1159/000493390
Cai, W., Yu, Y., Zong, S., and Wei, F. (2020). Metabolic reprogramming as a key regulator in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 69, 1087–1101. doi:10.1007/s00011-020-01391-5
Cai, Y., Zhang, J., Liang, J., Xiao, M., Zhang, G., Jing, Z., et al. (2023). The burden of rheumatoid arthritis: findings from the 2019 global burden of diseases study and forecasts for 2030 by Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis. J. Clin. Med. 12 (4), 1291. doi:10.3390/jcm12041291
Chen, H., Cheng, Q., Wang, J., Zhao, X., and Zhu, S. (2021b). Long-term efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in anaemia of chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis including 13,146 patients. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 46 (4), 999–1009. doi:10.1111/jcpt.13385
Chen, Y., Liu, H., Huang, Y., Lin, S., Yin, G., and Xie, Q. (2021a). The cardiovascular risks of fostamatinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 632551. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.632551
Cheng, W.-X., Huang, H., Chen, J.-H., Zhang, T.-T., Zhu, G.-Y., Zheng, Z.-T., et al. (2020). Genistein inhibits angiogenesis developed during rheumatoid arthritis through the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3/VEGF signalling pathway. J. Orthop. Transl. 22, 92–100. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2019.07.007
Chethan, S., and Malleshi, N. G. (2007). Finger millet polyphenols: optimization of extraction and the effect of pH on their stability. Food Chem. 105 (2), 862–870. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.02.012
Chin, C.-H., Chen, S.-H., Wu, H.-H., Ho, C.-W., Ko, M.-T., and Lin, C.-Y. (2014). cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 8, S11–S17. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11
Chukeatirote, E., Eungwanichayapant, P. D., and Kanghae, A. (2017). Determination of volatile components in fermented soybean prepared by a co-culture of Bacillus subtilis and Rhizopus oligosporus. Food Res. 1, 225–233. doi:10.26656/fr.2017.6.066
Clough, E., Barrett, T., Wilhite, S. E., Ledoux, P., Evangelista, C., Kim, I. F., et al. (2024). NCBI GEO: archive for gene expression and epigenomics data sets: 23-year update. Nucleic Acids Res. 52 (D1), D138–D144. doi:10.1093/nar/gkad965
Deka, G., Goyat, J., and Dutta, H. (2024). “Nutraceutical potential and techno-functional properties of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum),” in Nutri-cereals (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press), 91–117.
Ejiofor, E. U., Oyedemi, S. O., Onoja, S. O., and Omeh, N. Y. (2022). Amaranthus hybridus Linn. leaf extract ameliorates oxidative stress and hepatic damage abnormalities induced by thioacetamide in rats. South Afr. J. Bot. 146, 213–221. Available at:. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2021.10.029
Fay, B. T., Whiddon, A. P., Puumala, S., Black, N. A., Dell, J. R., and Mikuls, T. R. (2008). Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation in rheumatoid arthritis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 14 (1), 17–20. doi:10.1097/RHU.0b013e31816356d1
Gallo, K., Goede, A., Preissner, R., and Gohlke, B.-O. (2022). SuperPred 3.0: drug classification and target prediction—a machine learning approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (W1), W726–W731. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac297
Goodsell, D. S., Sanner, M. F., Olson, A. J., and Forli, S. (2021). The AutoDock suite at 30. Protein Sci. 30 (1), 31–43. doi:10.1002/pro.3934
Harish, M. S., Bhuker, A., and Chauhan, B. S. (2024). Millet production, challenges, and opportunities in the Asia-pacific region: a comprehensive review. Front. Sustain Food Syst. 8, 1386469. doi:10.3389/fsufs.2024.1386469
Hegde, P. S., Rajasekaran, N. S., and Chandra, T. S. (2005). Effects of the antioxidant properties of millet species on oxidative stress and glycemic status in alloxan-induced rats. Nutr. Res. 25 (12), 1109–1120. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2005.09.020
Hu, L., Liu, R., and Zhang, L. (2022). Advance in bone destruction participated by JAK/STAT in rheumatoid arthritis and therapeutic effect of JAK/STAT inhibitors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 111, 109095. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109095
Huang, D. W., Sherman, B. T., Tan, Q., Kir, J., Liu, D., Bryant, D., et al. (2007). DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (Suppl. l_2), W169–W175. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm415
Jha, S., Vaiphei, K. K., and Alexander, A. (2023). Plant-based therapeutics: current status and future perspectives. Phytopharm. Herb. Drugs, 3–11. doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-99125-4.00003-2
Kadam, A. B., and Gaykar, B. M. (2018). Pregnane - a parent of progesterone from trigonella foenum - graecum linn. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 5 (September), 188–194. doi:10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.8(12).5194-98
Khan, I. U. (2017). Evaluation and identification of volatile bio active compounds in methanol extract of pearl millet genotypes by gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 5 (2), 526–531. doi:10.18782/2320-7051.2800
Kostoglou-Athanassiou, I., Athanassiou, L., and Athanassiou, P. (2020). The effect of omega-3 fatty acids on rheumatoid arthritis. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 31 (2), 190–194. doi:10.31138/mjr.31.2.190
Krause, A., Scaletta, N., Ji, J.-D., and Ivashkiv, L. B. (2002). Rheumatoid arthritis synoviocyte survival is dependent on Stat3. J. Immunol. 169 (11), 6610–6616. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.169.11.6610
Li, H., Wu, Q.-Y., Teng, X.-H., Li, Z.-P., Zhu, M.-T., Gu, C.-J., et al. (2023). The pathogenesis and regulatory role of HIF-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 48 (1), 338–345. doi:10.5114/ceji.2023.134217
Ma, Y., Hong, F. F., and Yang, S. L. (2021). Role of prostaglandins in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 39 (1), 162–172. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/1jlh15
Maradesha, T., Martiz, R. M., Patil, S. M., Prasad, A., Babakr, A. T., Silina, E., et al. (2023). Integrated network pharmacology and molecular modeling approach for the discovery of novel potential MAPK3 inhibitors from whole green jackfruit flour targeting obesity-linked diabetes mellitus. PLoS One 18 (1), 1–24. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0280847
Munawwa, R. M. H. ani., Fateh, J., Javed, H. I., Malik, H. N., and Hussain, M. (2007). Stability analysis of millet varieties across diverse environments in Pakistan. Sarhad J. Agric. 23 (3), 645–648.
Nambiar, V. S., Sareen, N., Daniel, M., and Gallego, E. B. (2012). Flavonoids and phenolic acids from pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) based foods and their functional implications. Funct. Foods Heal Dis. 2 (7), 251–264. doi:10.31989/ffhd.v2i7.85
Nani, A., Belarbi, M., Khan, N. A., and Hichami, A. (2020). Nutritional properties and plausible benefits of Pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) on bone metabolism and osteoimmunology: a mini-review: pearl millet nutritional properties and plausible benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 4 (8), 336–342. doi:10.51745/najfnr.4.08.336-342
Nani, A., Belarbi, M., Ksouri-Megdiche, W., Abdoul-Azize, S., Benammar, C., Ghiringhelli, F., et al. (2015). Effects of polyphenols and lipids from Pennisetum glaucum grains on T-cell activation: modulation of Ca2+ and ERK1/ERK2 signaling. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 15 (1), 426. doi:10.1186/s12906-015-0946-3
Oyaizu, M. (1986). Studies on products of browning reaction antioxidative activities of products of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. Jpn. J. Nutr. Diet. 44 (6), 307–315. doi:10.5264/eiyogakuzashi.44.307
Ozen, G., Boumiza, S., Deschildre, C., Topal, G., Longrois, D., Jakobsson, P. J., et al. (2019). Inflammation increases MMP levels via PGE2 in human vascular wall and plasma of obese women. Int. J. Obes. 43 (9), 1724–1734. doi:10.1038/s41366-018-0235-6
Pei, J., Umapathy, V. R., Vengadassalapathy, S., Hussain, S. F., Rajagopal, P., Jayaraman, S., et al. (2022). A review of the potential consequences of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) for diabetes mellitus and other biomedical applications. Nutrients 14, 2932. doi:10.3390/nu14142932
Poroikov, V. V., Filimonov, D. A., Ihlenfeldt, W.-D., Gloriozova, T. A., Lagunin, A. A., Borodina, Y. V., et al. (2003). PASS biological activity spectrum predictions in the enhanced open NCI database browser. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 43 (1), 228–236. doi:10.1021/ci020048r
Sadaqat, M., Qasim, M., Tahir ul Qamar, M., Masoud, M. S., Ashfaq, U. A., Noor, F., et al. (2023). Advanced network pharmacology study reveals multi-pathway and multi-gene regulatory molecular mechanism of Bacopa monnieri in liver cancer based on data mining, molecular modeling, and microarray data analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 161 (2022), 107059. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107059
Si, Y., Sha, X.-S., Shi, L.-L., Wei, H.-Y., Jin, Y.-X., Ma, G.-X., et al. (2022). Review on pregnane glycosides and their biological activities. Phytochem. Lett. 47, 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2021.10.007
Siroha, A. K., Sandhu, K. S., and Kaur, M. (2016). Physicochemical, functional and antioxidant properties of flour from pearl millet varieties grown in India. J. Food Meas. Charact. 10 (2), 311–318. doi:10.1007/s11694-016-9308-1
Suresh, E., Morris, I. M., and Mattingly, P. C. (2004). Use of minocycline in rheumatoid arthritis: a district general hospital experience. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 63 (10), 1354–1355. doi:10.1136/ard.2003.017749
Truong, D. H., Nguyen, D. H., Ta, N. T. A., Bui, A. V., Do, T. H., and Nguyen, H. C. (2019). Evaluation of the use of different solvents for phytochemical constituents, antioxidants, and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of severinia buxifolia. J. Food Qual. 2019, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2019/8178294
Vanommeslaeghe, K., and MacKerell, Jr A. D. (2012). Automation of the CHARMM General Force Field (CGenFF) I: bond perception and atom typing. J. Chem. Inf. Model 52 (12), 3144–3154. doi:10.1021/ci300363c
Yu, X., Qin, W., Cai, H., Ren, C., Huang, S., Lin, X., et al. (2024). Analyzing the molecular mechanism of xuefuzhuyu decoction in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension with network pharmacology and bioinformatics and verifying molecular docking. Comput. Biol. Med. 169, 107863. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107863
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, Pennisetum glaucum, network pharmacology, microarray analysis, molecular dynamic simulation, drug discovery
Citation: Sharif M, John P, Bhatti A, Paracha RZ and Majeed A (2024) Evaluation of the inhibitory mechanism of Pennisetum glaucum (pearl millet) bioactive compounds for rheumatoid arthritis: an in vitro and computational approach. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1488790. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1488790
Received: 30 August 2024; Accepted: 21 October 2024;
Published: 21 November 2024.
Edited by:
Sanjeeb Kalita, DBT-APSCS&T CoE for Bioresources and Sustainable Development, IndiaReviewed by:
Angela Ostuni, University of Basilicata, ItalyTarik Aanniz, Mohammed V University at Souissi, Morocco
Copyright © 2024 Sharif, John, Bhatti, Paracha and Majeed. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peter John, cGpvaG5AYXNhYi5udXN0LmVkdS5waw==
 Maria Sharif
Maria Sharif Peter John
Peter John Attya Bhatti
Attya Bhatti Rehan Zafar Paracha
Rehan Zafar Paracha Abid Majeed3
Abid Majeed3