- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Xiangtan Central Hospital (The Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University), Xiangtan, China
- 2Department of Pharmacy, People’s Hospital of Ningxiang City, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
Background: Sulfasalazine (SSZ) is commonly prescribed for the treatment of ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. However, it can also trigger a severe drug reaction known as Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) or Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome (DIHS). This article aims to analyze the clinical characteristics of DRESS/DIHS induced by SSZ and provide evidence for clinical diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Methods: We gathered relevant literature on SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS published from 1 January 2005, to 21 July 2024, by searching both English and Chinese databases.
Results: Thirty-nine patients (15 males and 24 females) were included in the study, with a median age of 47 years (range: 11–82 years). Following SSZ administration, the median onset time of DRESS/DIHS was 28 days (range: 10–60 days). These patients exhibited clinical symptoms such as fever (100%), rash (100%), digestive system responses (38.5%), and edema (35.9%). Organ involvement was observed in 38 patients, with commonly affected organs being lymph nodes (78.9%), liver (94.7%), kidney (15.8%), heart (13.2%), and lung (7.9%). All patients had hematological abnormalities, primarily eosinophilia (69.2%) and atypical lymphocytosis (35.9%). Additional hematological changes included agranulocytosis (5.1%), hemophagocytic syndrome (5.1%), and pancytopenia (2.6%). Virus reactivation occurred in 21 patients (53.8%). The primary treatment for DRESS/DIHS due to SSZ is the immediate cessation of the drug, followed by systemic corticosteroid administration. Alternative treatments such as cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab require further investigation to establish their efficacy.
Conclusion: SSZ may lead to DRESS/DIHS. To make a conclusive diagnosis, healthcare providers should conduct a thorough assessment by examining the patient’s clinical presentation, conducting physical evaluations, and analyzing laboratory findings. Immediate discontinuation of SSZ is recommended, and corticosteroids are often considered an efficacious treatment for DRESS/DIHS.
Introduction
Sulfasalazine (SSZ), a drug with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties, undergoes breakdown in the ileocolonic tract to produce two main components: 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), the active therapeutic compound, and sulfapyridine, which serves as a carrier molecule (Azad Khan et al., 1977). SSZ is recommended for the treatment of autoimmune disorders such as ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (Ye et al., 2024). The most frequently reported adverse drug reactions related to SSZ include nausea, vomiting, rash, headache, and abdominal pain, generally of mild intensity and well-tolerated. However, in recent years, it has been reported that SSZ may cause drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) or drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS) (Shimada et al., 2023). SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS is a severe adverse drug reaction characterized by multiorgan manifestations and reactivation of human herpesvirus-6 (Miyagawa and Asada, 2021). Clinical features of these syndromes encompass fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, internal organ involvement, and hematologic abnormalities such as lymphocytosis and eosinophilia (Yildirim Arslan et al., 2024). Despite the infrequent occurrence of DRESS/DIHS, its mortality rate can reach up to 10% (Mitsuno et al., 2024). Therefore, the early identification, diagnosis, and treatment of DRESS/DIHS are crucial to mitigate mortality rates. Of note, the understanding of SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS is primarily based on case reports, which exhibit inconsistent and variable clinical features. Consequently, the diagnosis and treatment of SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS present a significant challenge for healthcare professionals. The purpose of this study was to explore the characteristics of SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS and provide insights for the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS.
Methods
Search strategy
We searched the literature related to SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS by searching English databases (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science) and Chinese databases (Wanfang Data, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)) from 1 January 2005, to 21 July 2024. The search keywords were “salazosulfapyridine” OR “sulfasalazine” OR “sulphasalazine” OR “SASP” OR “SSZ” AND “DRESS” OR “Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms” OR “Drug rash eosinophilia systemic symptoms” OR “DIHS” OR “Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome”.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: case report and case series of SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS. Exclusion criteria: reviews, mechanism studies, animal studies, duplicate cases, articles with insufficient data.
Data extraction
Two researchers conducted an initial literature screening independently, adhering to predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Subsequently, a group discussion was held to finalize the selection of literature. Patient data extracted for analysis included region, gender, age, medical history, medication regimen, onset timing, clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, treatment modalities, and prognostic outcomes, facilitated through a self-designed data extraction table.
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Count data were presented as numbers and percentages, while measurement data were expressed as the median (minimum, maximum).
Results
Basic information
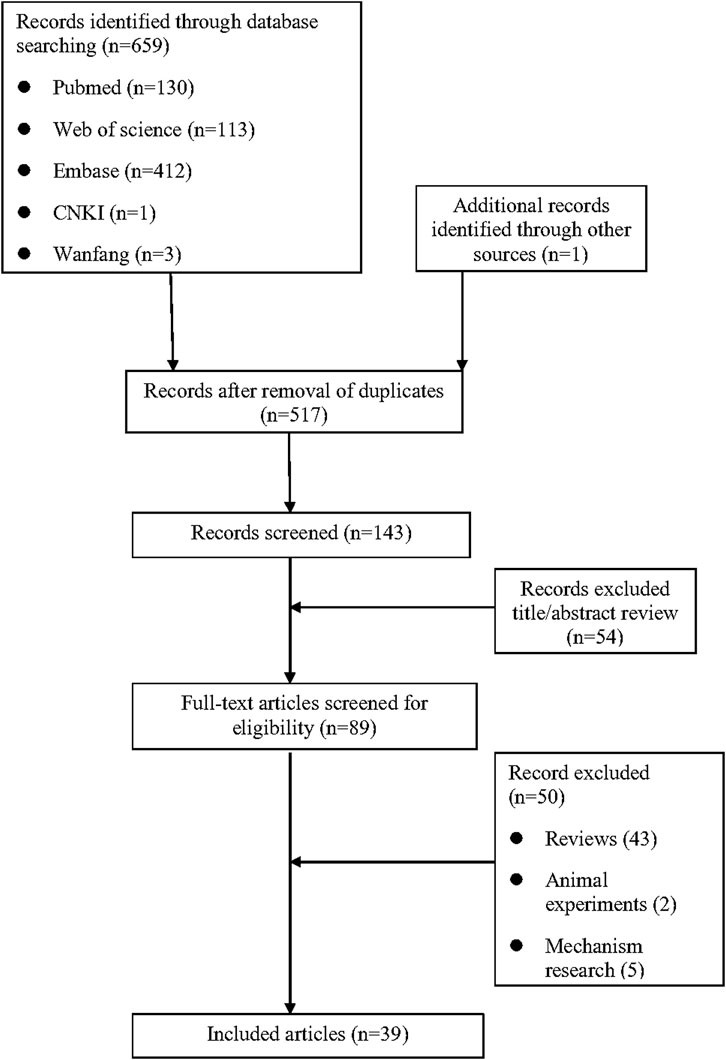
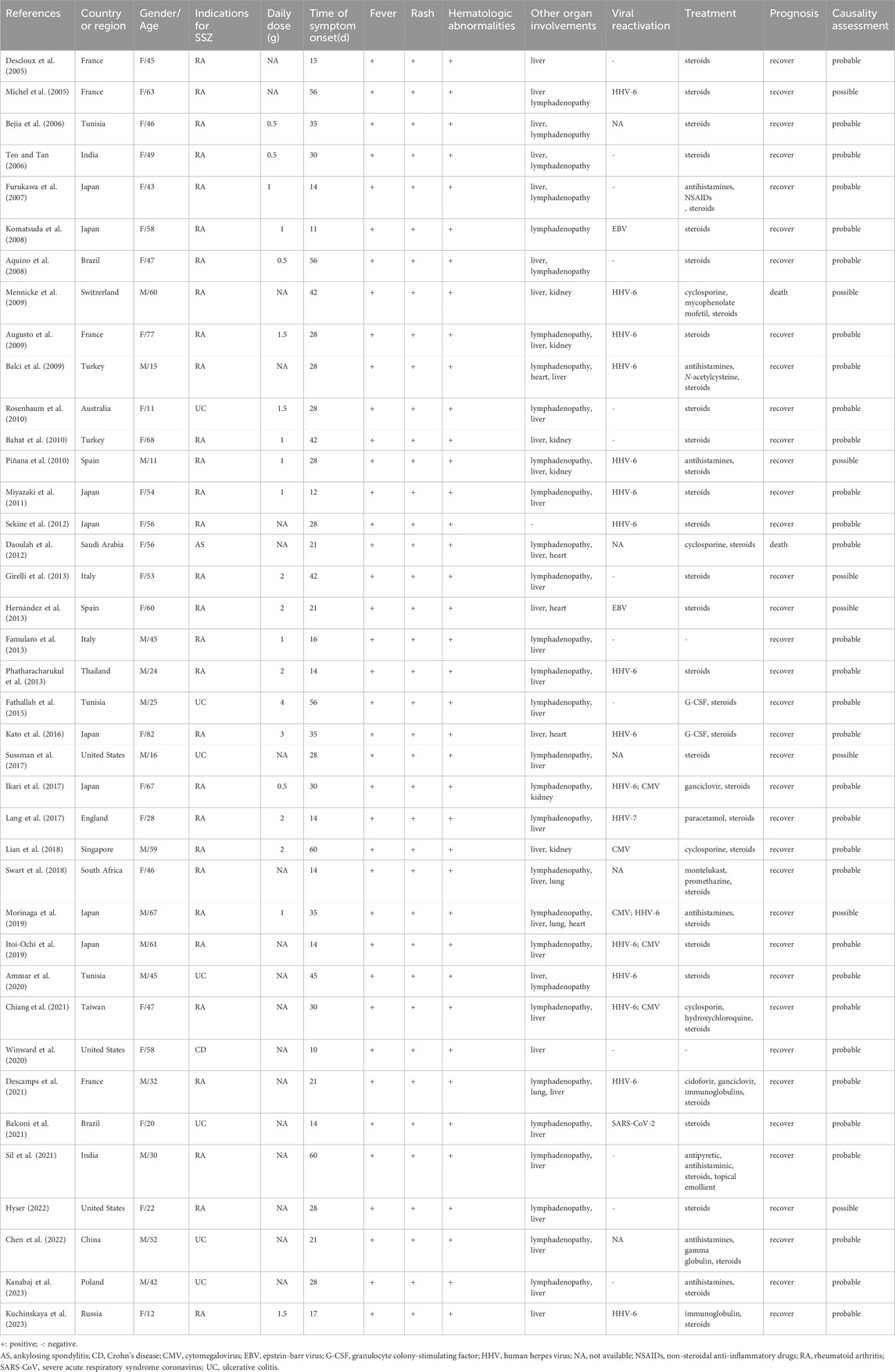
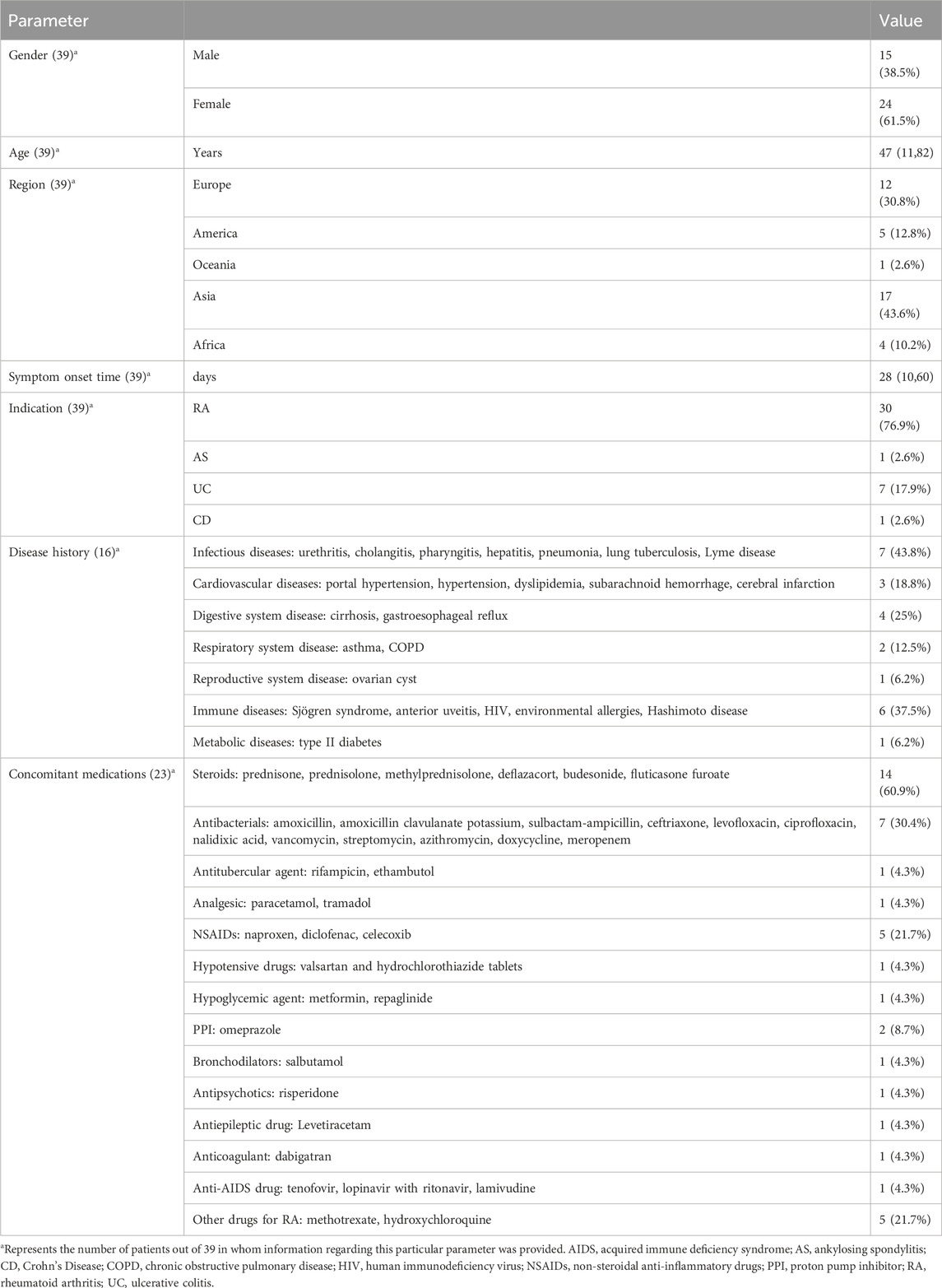
As shown in Figure 1, a total of 659 relevant studies were initially identified. After removing duplicate documents and screening the titles and abstracts, 39 studies were identified for a full-text assessment. The basic information of these 39 patients was summarized in Table 1 and the assessment of causality was carried out using the Naranjo scale (Naranjo et al., 1981). Furthermore, general data of patients was analyzed in Table 2. The study included 39 patients, comprising 15 males (38.5%) and 24 females (61.5%), with a median age of 47 years (range 11–82). The geographical distribution of these patients was as follows: 12 (30.8%) from Europe, 17 (43.6%) from Asia, 5 (12.8%) from America, 1 (2.6%) from Oceania, and 4 (10.2%) from Africa. The median onset time for DRESS/DIHS induced by sulfasalazine was 28 days (range 10–60). Among these patients, 30 cases (76.9%) were diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 7 cases (17.9%) with ulcerative colitis (UC), 1 case (2.6%) with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and 1 case (2.6%) with Crohn’s disease (CD). Medical history data were available for 16 patients (41.0%), of whom seven had a history of infectious diseases and had taken antibiotics.
Clinical manifestations
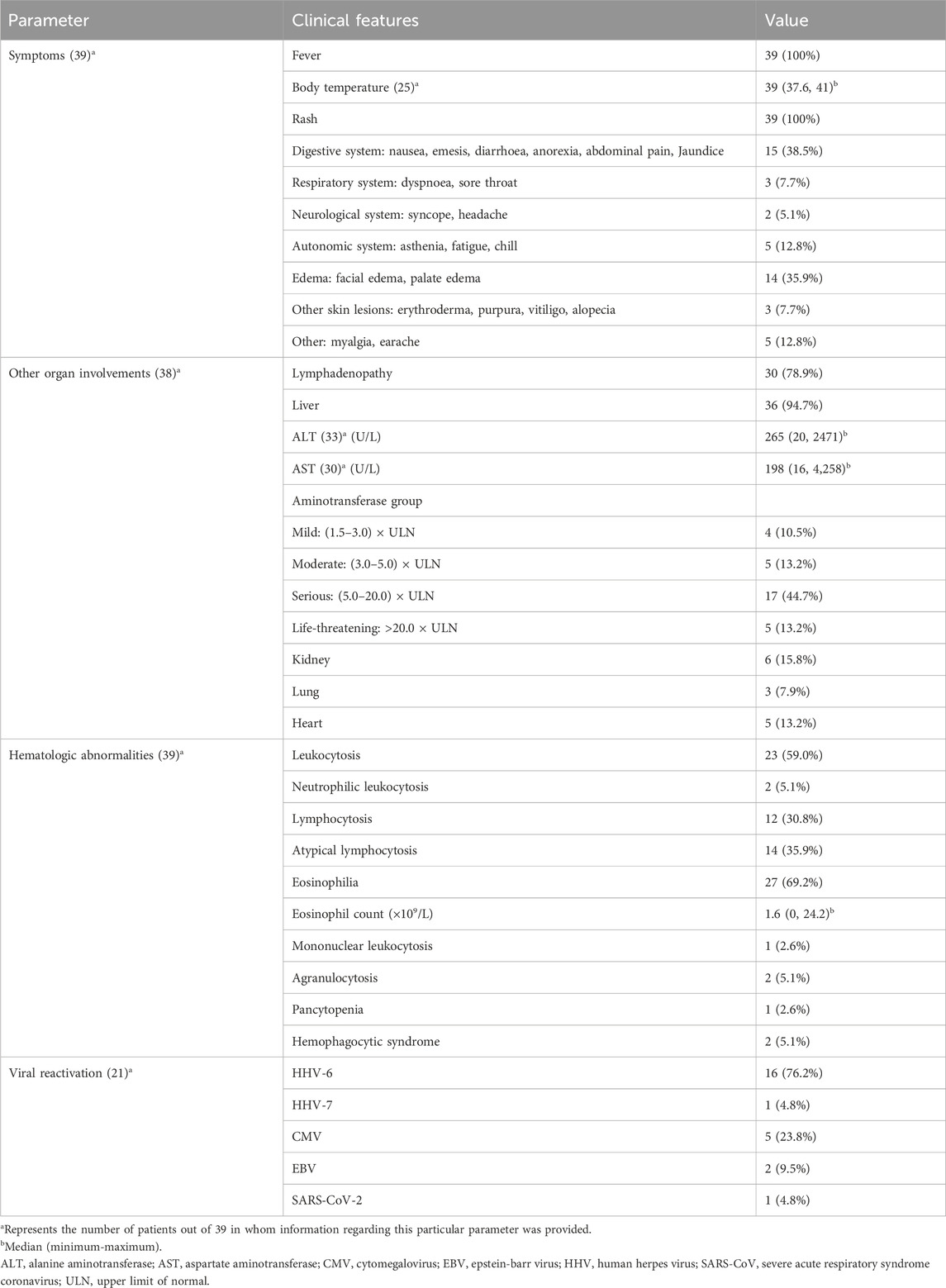
The clinical symptoms of the 39 patients are detailed in Table 3. All these patients displayed fever and rash, with primary clinical manifestations including gastrointestinal symptoms in 15 cases (38.5%), comprising nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, abdominal pain, and jaundice; and edema in 14 cases (35.9%), including facial and palate edema. Other symptoms consisted of autonomic system responses in 5 cases (12.8%), like asthenia, fatigue, and chills; severe skin involvement in 3 cases (7.7%), such as erythroderma, purpura, vitiligo, and alopecia; respiratory system responses in 3 cases (7.7%), like dyspnea and sore throat; neurological system responses in 2 cases (5.1%), such as syncope and headache; and myalgia in 4 cases (10.3%) and earache in 1 case (2.6%).
Physical examination and laboratory examination
The physical examination and laboratory examination of 39 DRESS/DIHS patients are summarized in Table 3. Physical examination revealed lymphadenopathy in 30 patients (78.9%) and laboratory tests revealed abnormal liver function in 36 patients (94.7%), including abnormal elevations of aminotransferase, bilirubin, or alkaline phosphatase. Six patients (15.8%) had abnormal renal function, including creatinine elevation, tubular dysfunction, or renal failure. Five patients (13.2%) had cardiac involvement, including pericardial effusion, tachycardia, heart failure, or acute ST-elevated myocardial infarction. And three patients (7.9%) developed lung disease, presenting with pneumonia or interstitial pneumonia. Furthermore, all 39 patients included in the study exhibited hematological abnormalities. Among them, 23 patients (59.0%) presented leukocytosis, 27 patients (69.2%) exhibited eosinophilia, 14 patients (35.9%) showed atypical lymphocytosis, 2 patients (5.1%) displayed neutrophilic leukocytosis, 1 patient (2.6%) manifested mononucleosis, 2 patients (5.1%) demonstrated agranulocytosis, and 2 (5.1%) patients developed hemophagocytic syndrome. Additionally, one patient (2.6%) presented with pancytopenia. Viral reactivations were experienced in 21 patients, including HHV-6 (16 cases, 76.2%), HHV-7 (1 case, 4.8%), CMV (5 cases, 23.8%), EBV (2 cases, 9.5%), and SARS-CoV-2 (1 case, 4.8%).
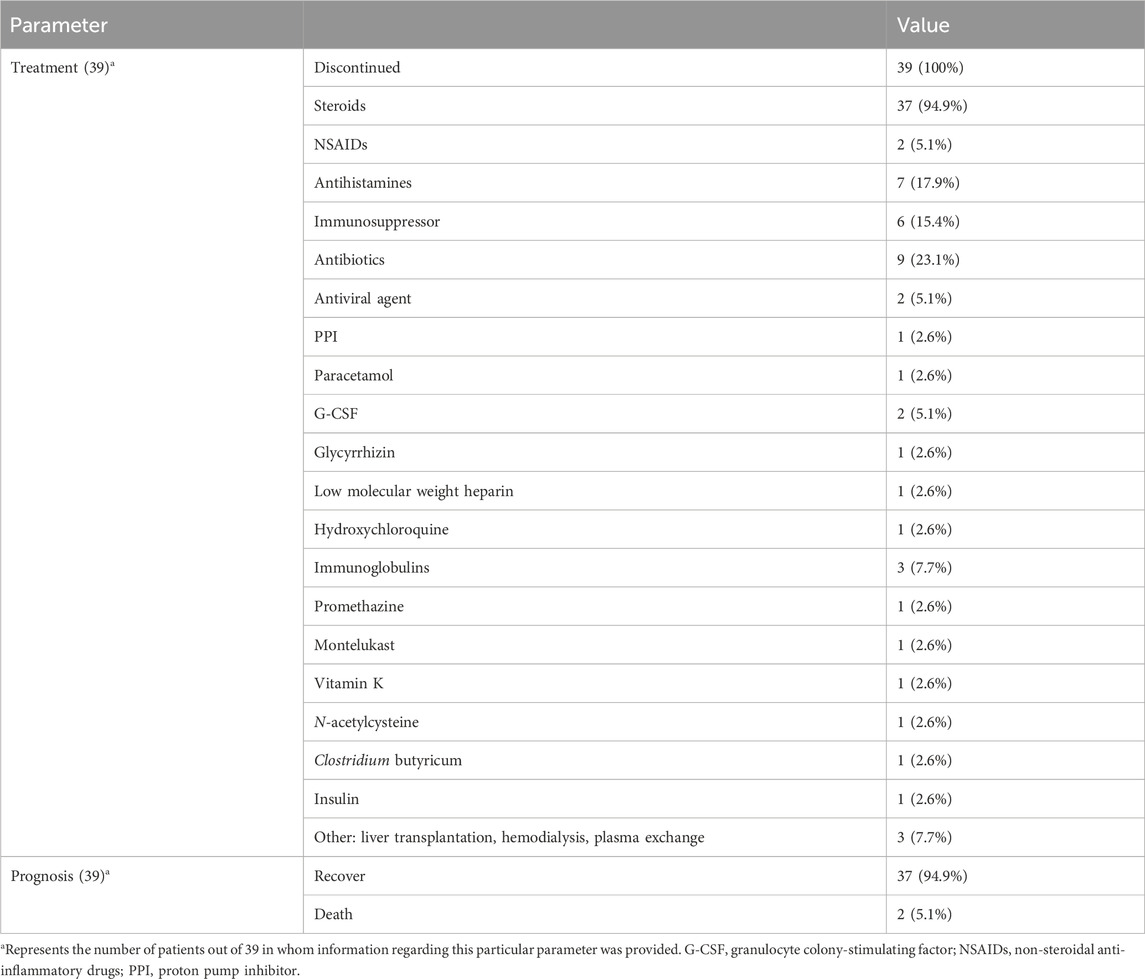
Treatment and prognosis
The treatment and prognosis of the 39 DRESS/DIHS patients are summarized in Table 4. All patients promptly discontinued SSZ following the onset of symptoms. Furthermore, 37 patients (94.9%) were administered steroids, nine (23.1%) received antibiotics, seven (17.9%) were prescribed antihistamines, six (15.4%) were given immunosuppressants, three (7.7%) received immunoglobulins, and three (7.7%) underwent liver transplantation or hemodialysis or hemofiltration. Additionally, other drugs involved include antiviral drugs (2 cases, 5.1%), G-CSF (2 cases, 5.1%), NSAIDs (2 cases, 5.1%), PPI (1 case, 2.6%), paracetamol (1 case, 2.6%), glycyrrhizin (1 case, 2.6%), low molecular weight heparin (1 case, 2.6%), hydroxychloroquine (1 case, 2.6%), promethazine (1 case, 2.6%), montelukast (1 case, 2.6%), vitamin K (1 case, 2.6%), N-acetylcysteine (1 case, 2.6%), clostridium butyricum (1 case, 2.6%) and insulin (1 case, 2.6%). Ultimately, 37 patients (94.9%) achieved recovery while two (5.1%) died.
Discussion
SSZ is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) used for treating and managing autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (Choi et al., 2024). It is also the second most common cause of DRESS/DIHS among drugs prescribed for rheumatic diseases (Adwan, 2017). In our analysis, the higher prevalence of SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS in women compared to men may be attributed to gender-specific differences in the incidence of underlying conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. The onset of DRESS/DIHS is generally believed to occur between 2 and 8 weeks after starting the drug (Salame et al., 2019); however, we have observed cases with onset within 2 weeks (Komatsuda et al., 2008; Miyazaki et al., 2011; Winward et al., 2020). The reported mortality rate for DRESS/DIHS ranges from 3.8% to 10% (Chen et al., 2010; Hiransuthikul et al., 2016), which is consistent with our results (5.1%).
Initially associated with aromatic antiepileptic drugs, the DRESS/DIHS syndrome is now known to be induced by approximately 50 different drugs, including allopurinol, β-lactams, vancomycin, minocycline, fluoroquinolones, and sulfonamides (Cacoub et al., 2011; Wolfson et al., 2019). DRESS/DIHS is characterized by fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, elevated liver enzyme levels, and leukocytosis with eosinophilia. Previous studies have shown that 90% of DRESS/DIHS patients experience fever, although body temperature rarely exceeds 38.5°C (Ramirez et al., 2023). However, our analysis indicated that 100% of patients exhibited fever, with a median body temperature of 39°C. Additionally, 75% of patients presented with lymphadenopathy. The liver is the most commonly affected internal organ (75%), as evidenced by abnormal liver function tests. Kidney involvement was observed in 30% of patients, whereas lung involvement occurred in 25% (Calle et al., 2023; Kardaun et al., 2013). Similar to previous studies, our findings revealed that 78.9% of patients with DRESS/DIHS caused by SSZ exhibited lymph node involvement. However, in terms of internal organ involvement, our review showed that SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS more frequently impacted the liver, with a prevalence of 94.7%. Liver function test results demonstrated median ALT and AST levels elevated by more than five times the normal limits, reaching 265 IU/L and 198 IU/L, respectively. In addition, we have clustered aminotransferase into groups according to the most recent version of the National Cancer Institute’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (v5.0). According to our statistical analysis, among the cases in which specific data of aminotransferase were provided, abnormal elevation of aminotransferase was found in 31 patients, including 4 patients with mild liver damage, 5 patients with moderate liver damage, 17 patients with severe liver damage, and 5 patients with life-threatening condition. The risks of kidney, lung, and heart injuries were significantly lower. Previous reports indicate that the most common drugs causing kidney damage are allopurinol, carbamazepine, and dapsone. Minocycline is most frequently associated with lung injury, while heart involvement is more commonly linked to minocycline and ampicillin (Husain et al., 2013; Kardaun et al., 2013). Consequently, we suspect that different drugs induce DRESS/DIHS with varying manifestations of organ involvement, with SSZ more frequently affecting the liver. Furthermore, there are diverse hematological abnormalities than those previously reported in DRESS/DIHS. Kardaun et al. (2013) reported eosinophilia (95%) and atypical lymphocytes (67%) as the main characteristics of hematological abnormalities. However, our review indicated a prevalence of 69.2% for eosinophilia and 35.9% for atypical lymphocytes. Additionally, we discovered that 5.1% of patients had agranulocytosis, 5.1% had hemophagocytic syndrome, and 2.6% had pancytopenia. Although the proportion of patients with cytopenia is small, it warrants attention. Therefore, a complete blood cell count examination is indispensable when diagnosing DRESS/DIHS. Previous studies have demonstrated that herpes virus reactivation, especially HHV-6, is frequently depicted in DRESS/DIHS and has even been regarded as a criterion of DIHS by Japanese experts. It is considered to cause a more severe and/or prolonged course of the disease (Descamps et al., 2001; Kano et al., 2006; Picard et al., 2010; Shiohara et al., 2007; Shiohara et al., 2006; Suzuki et al., 1998; Tohyama et al., 2007). However, among the 39 cases we investigated, virus reactivation was involved in 21 cases. These included 16 cases of HHV-6 reactivation, 5 cases of CMV reactivation, 2 cases of EBV reactivation, 1 case of HHV-7 reactivation, and 1 case of SARS-CoV-2 reactivation. The rate of HHV-6 reactivation (41%) is lower than previously reported, particularly in Japan, where the probability exceeds 60% (Tohyama et al., 2007). This discrepancy may be due to incomplete information or the lack of examinations in some cases. Besides HHV-6 reactivation, we assert that the reactivation of viruses like CMV, EBV, or HHV-7 should also be considered at the time of diagnosis.
In the treatment of DRESS/DIHS resulting from SSZ, the immediate cessation of SSZ is paramount. Following this, systemic administration of corticosteroids is essential (Brüggen et al., 2024). It is recommended to start with a dose of at least 1 mg/kg/day of prednisone or its equivalent, and tapering should be implemented over 3–6 months (Gottlieb et al., 2022). If this regimen proves insufficient, intravenous pulse methylprednisolone may be considered (Ramirez et al., 2023). In a case presented by Augusto et al. (2009), the patient discontinued corticosteroids after 20 days, leading to secondary renal failure. Therefore, rapid dose reduction of corticosteroids is not advised to prevent disease recurrence. In fact, the latest international consensus recommends that mild and moderate DRESS should have steroids reduced gradually over a period of 6 weeks to 3 months; severe DRESS should have steroids reduced gradually over a period of 3–6 months (Brüggen et al., 2024). Regular follow-up visits after discharge are also crucial. Additionally, case reports suggest alternative treatments including cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (Stirton et al., 2022). However, further research is needed to establish the efficacy of these alternative medications.
Conclusion
DRESS/DIHS is a rare but serious adverse effect of SSZ. Patients receiving SSZ treatment must consistently monitor their symptoms. If adverse reactions such as unexplained rash, fever, abdominal pain, jaundice, facial edema, or lymph node enlargement occur, they should immediately seek medical attention for timely intervention and early treatment, thereby minimizing the detrimental effects of SSZ-induced DRESS/DIHS. Clinicians should promptly diagnose DRESS/DIHS when these symptoms arise and immediately discontinue SSZ use, employing corticosteroids for treatment. A complete blood cell count, examinations of the liver, kidney, heart, and lungs, as well as tests for viral reactivation should be performed.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing–original draft. DW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. SW: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XL: Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. CX: Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the research project of Health Commission of Hunan Province (No. D202313018969) and the research project of Chinese Medical Association (No. Z-2021-46-2101).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adwan, M. H. (2017). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome and the rheumatologist. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 19 (1), 3. doi:10.1007/s11926-017-0626-z
Ammar, H., Azouzi, A., Fathallah, N., Boujelben, M. A., Ouni, B., Boussarsar, M., et al. (2020). Fatal sulfasalazine-induced DRESS complicated by HHV-6 reactivation and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 76 (3), 467–468. doi:10.1007/s00228-019-02809-8
Aquino, R. T., Vergueiro, C. S., Magliari, M. E., and de Freitas, T. H. (2008). Sulfasalazine-induced DRESS syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). Sao Paulo Med. J. 126 (4), 225–226. doi:10.1590/s1516-31802008000400006
Augusto, J. F., Sayegh, J., Simon, A., Croue, A., Chennebault, J. M., Cousin, M., et al. (2009). A case of sulphasalazine-induced DRESS syndrome with delayed acute interstitial nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 24 (9), 2940–2942. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfp277
Azad Khan, A. K., Piris, J., and Truelove, S. C. (1977). An experiment to determine the active therapeutic moiety of sulphasalazine. Lancet 2 (8044), 892–895. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90831-5
Bahat, G., Celik, H. G., Tufan, F., and Saka, B. (2010). Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome induced by sulfasalazine. Jt. Bone Spine 77 (1), 87–88. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2009.08.003
Balci, D. D., Peker, E., Duran, N., and Dogramaci, C. A. (2009). Sulfasalazine-induced hypersensitivity syndrome in a 15-year-old boy associated with human herpesvirus-6 reactivation. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 28 (1), 45–47. doi:10.1080/15569520802696250
Balconi, S. N., Lopes, N. T., Luzzatto, L., and Bonamigo, R. R. (2021). Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in a case of DRESS by sulfasalazine: could there be a relationship with clinical importance? Int. J. Dermatol. 60 (1), 125–126. doi:10.1111/ijd.15316
Bejia, I., Ben Hammouda, S., Riahi, K., Zinelabidine, F., Mediouni, B., Touzi, M., et al. (2006). DRESS syndrome induced by sulphasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 73 (6), 764–765. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2006.01.006
Brüggen, M. C., Walsh, S., Ameri, M. M., Anasiewicz, N., Maverakis, E., French, L. E., et al. (2024). Management of adult patients with drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: a delphi-based international consensus. JAMA Dermatol 160 (1), 37–44. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.4450
Cacoub, P., Musette, P., Descamps, V., Meyer, O., Speirs, C., Finzi, L., et al. (2011). The DRESS syndrome: a literature review. Am. J. Med. 124 (7), 588–597. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2011.01.017
Calle, A. M., Aguirre, N., Ardila, J. C., and Cardona Villa, R. (2023). DRESS syndrome: a literature review and treatment algorithm. World Allergy Organ. J. 16 (3), 100673. doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2022.100673
Chen, D. H., Zhou, H. R., Zhang, Y. G., Shen, G. Y., Xu, C., and Guan, C. L. (2022). Drug hypersensitivity syndrome induced by sulfasalazine: a case report. Med. Baltim. 101 (33), e30060. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000030060
Chen, Y. C., Chiu, H. C., and Chu, C. Y. (2010). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: a retrospective study of 60 cases. Arch. Dermatol. 146 (12), 1373–1379. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.198
Chiang, P. H., Ng, C. Y., Kuo, T. T., Hui, R. C., Chen, C. B., Lu, C. W., et al. (2021). Case of vitiligo universalis as a sequela of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. J. Dermatol. 48 (1), 92–95. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15562
Choi, J., Patel, P., and Fenando, A. (2024). “Sulfasalazine,” in StatPearls (StatPearls Publishing). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557809/.
Daoulah, A., Alqahtani, A. A., Ocheltree, S. R., Alhabib, A., and Ocheltree, A. R. (2012). Acute myocardial infarction in a 56-year-old female patient treated with sulfasalazine. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 30 (4), 638.e1–638.e6383. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2011.02.018
Descamps, V., Gautheret-Dejean, A., Pelletier, A. L., Bonnafous, P., Deschamps, L., and Prusty, B. K. (2021). Chronic persistent HHV-6B infection after sulfasalazine-induced DRESS with demonstration of HHV-6 encoded small noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs) in Crohn's-like colitis: case report. Clin. Case Rep. 9 (2), 841–844. doi:10.1002/ccr3.3680
Descamps, V., Valance, A., Edlinger, C., Fillet, A. M., Grossin, M., Lebrun-Vignes, B., et al. (2001). Association of human herpesvirus 6 infection with drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Arch. Dermatol. 137 (3), 301–304.
Descloux, E., Argaud, L., Dumortier, J., Scoazec, J. Y., Boillot, O., and Robert, D. (2005). Favourable issue of a fulminant hepatitis associated with sulfasalazine DRESS syndrome without liver transplantation. Intensive Care Med. 31 (12), 1727–1728. doi:10.1007/s00134-005-2846-3
Famularo, G., Bravi, M. C., Gasbarrone, L., and Minisola, G. (2013). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an atypical case during treatment with sulfasalazine. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 31 (2), 326–327.
Fathallah, N., Slim, R., Rached, S., Hachfi, W., Letaief, A., and Ben Salem, C. (2015). Sulfasalazine-induced DRESS and severe agranulocytosis successfully treated by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 37 (4), 563–565. doi:10.1007/s11096-015-0107-2
Furukawa, K., Ohtani, T., Furukawa, F., and Suzuki, Y. (2007). Infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome induced by salazosulfapyridine in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 17 (6), 492–495. doi:10.1007/s10165-007-0615-6
Girelli, F., Bernardi, S., Gardelli, L., Bassi, B., Parente, G., Dubini, A., et al. (2013). A new case of DRESS syndrome induced by sulfasalazine and triggered by amoxicillin. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2013, 409152. doi:10.1155/2013/409152
Gottlieb, M., Figlewicz, M. R., Rabah, W., Buddan, D., and Long, B. (2022). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: an emergency medicine focused review. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 56, 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.03.024
Hernández, N., Borrego, L., Soler, E., and Hernández, J. (2013). Sulfasalazine-induced linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis with DRESS. Actas. Dermosifiliogr. 104 (4), 343–346. doi:10.1016/j.adengl.2011.11.022
Hiransuthikul, A., Rattananupong, T., Klaewsongkram, J., Rerknimitr, P., Pongprutthipan, M., and Ruxrungtham, K. (2016). Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DIHS/DRESS): 11 years retrospective study in Thailand. Allergol. Int. 65 (4), 432–438. doi:10.1016/j.alit.2016.04.001
Husain, Z., Reddy, B. Y., and Schwartz, R. A. (2013). DRESS syndrome: Part I. Clinical perspectives. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 68 (5), 693.e1–708. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.01.033
Hyser, E. (2022). Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome masquerading as a lymphoproliferative disorder in a young adult on immunosuppressive therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 16 (1), 336. doi:10.1186/s13256-022-03526-0
Ikari, T., Nagai, K., Ohe, M., Harada, T., and Akiyama, Y. (2017). Multiple cavities with halo sign in a case of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis during therapy for drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 21, 124–128. doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2017.04.017
Itoi-Ochi, S., Nakagawa, Y., Tanemura, A., Hirao, M., and Fujimoto, M. (2019). A case of salazosulfapyridine-induced hypersensitivity syndrome in a rheumatoid arthritis patient with relapse of skin erythema. Case Rep. Dermatol 11 (3), 334–337. doi:10.1159/000504644
Kanabaj, K., Jenerowicz, D., Jankowska, L., and Żaba, Z. (2023). DRESS syndrome - a dermatological emergency - sulfasalazine-related acute drug reaction case report. Heliyon 9 (9), e20021. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20021
Kano, Y., Hiraharas, K., Sakuma, K., and Shiohara, T. (2006). Several herpesviruses can reactivate in a severe drug-induced multiorgan reaction in the same sequential order as in graft-versus-host disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 155 (2), 301–306. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07238.x
Kardaun, S. H., Sekula, P., Valeyrie-Allanore, L., Liss, Y., Chu, C. Y., Creamer, D., et al. (2013). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Br. J. Dermatol. 169 (5), 1071–1080. doi:10.1111/bjd.12501
Kato, M., Kano, Y., Sato, Y., and Shiohara, T. (2016). Severe agranulocytosis in two patients with drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Acta. Derm. Venereol. 96 (6), 842–843. doi:10.2340/00015555-2420
Komatsuda, A., Okamoto, Y., Hatakeyama, T., Wakui, H., and Sawada, K. (2008). Sulfasalazine-induced hypersensitivity syndrome and hemophagocytic syndrome associated with reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus. Clin. Rheumatol. 27 (3), 395–397. doi:10.1007/s10067-007-0753-4
Kuchinskaya, E. M., Chikova, I. A., and Kostik, M. M. (2023). Case report: sulfasalazine-induced hypersensitivity. Front. Med. 10, 1140339. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1140339
Lang, M., Fish, J., Covelli, C., and Schreiber, B. E. (2017). DRESS syndrome triple whammy: sulfasalazine, amoxicillin and HHV-7. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 78 (11), 648–649. doi:10.12968/hmed.2017.78.11.648
Lian, B. S., Busmanis, I., and Lee, H. Y. (2018). Relapsing course of sulfasalazine-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) complicated by alopecia universalis and vitiligo. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 47 (11), 492–493. doi:10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.v47n11p492
Mennicke, M., Zawodniak, A., Keller, M., Wilkens, L., Yawalkar, N., Stickel, F., et al. (2009). Fulminant liver failure after vancomycin in a sulfasalazine-induced DRESS syndrome: fatal recurrence after liver transplantation. Am. J. Transpl. 9 (9), 2197–2202. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02788.x
Michel, F., Navellou, J. C., Ferraud, D., Toussirot, E., and Wendling, D. (2005). DRESS syndrome in a patient on sulfasalazine for rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 72 (1), 82–85. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2004.06.002
Mitsuno, R., Nakayama, T., Uchiyama, K., Yoshimoto, N., Kusahana, E., Morimoto, K., et al. (2024). Hemodialysis treatment of vancomycin-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms/drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome in a patient undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Cen. Case Rep. 13, 339–345. doi:10.1007/s13730-023-00847-x
Miyagawa, F., and Asada, H. (2021). Current perspective regarding the immunopathogenesis of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DIHS/DRESS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (4), 2147. doi:10.3390/ijms22042147
Miyazaki, M., Tanaka, M., Ueda, A., Yoshimoto, T., Kato, M., Nakamuta, M., et al. (2011). Acute liver failure caused by drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome associated with hyperferritinemia. World. J. Gastroenterol. 17 (44), 4928–4931. doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4928
Morinaga, Y., Abe, I., Minamikawa, T., Ueda, Y., Nii, K., Sakamoto, K., et al. (2019). A case of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome induced by salazosulfapyridine combined with SIADH caused by interstitial pneumonia. Drug Discov. Ther. 13 (4), 232–238. doi:10.5582/ddt.2019.01045
Naranjo, C. A., Busto, U., Sellers, E. M., Sandor, P., Ruiz, I., Roberts, E. A., et al. (1981). A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 30 (2), 239–245. doi:10.1038/clpt.1981.154
Phatharacharukul, P., and Klaewsongkram, J. (2013). A case of sulfasalazine-induced hypersensitivity syndrome confirmed by enzyme-linked immunospot assay. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 5 (6), 415–417. doi:10.4168/aair.2013.5.6.415
Picard, D., Janela, B., Descamps, V., D'Incan, M., Courville, P., Jacquot, S., et al. (2010). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): a multiorgan antiviral T cell response. Sci. Transl. Med. 2 (46), 46ra62. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001116
Piñana, E., Lei, S. H., Merino, R., Melgosa, M., De La Vega, R., Gonzales-Obeso, E., et al. (2010). DRESS-syndrome on sulfasalazine and naproxen treatment for juvenile idiopathic arthritis and reactivation of human herpevirus 6 in an 11-year-old Caucasian boy. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 35 (3), 365–370. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01081.x
Ramirez, G. A., Ripa, M., Burastero, S., Benanti, G., Bagnasco, D., Nannipieri, S., et al. (2023). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): focus on the pathophysiological and diagnostic role of viruses. Microorganisms 11 (2), 346. doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020346
Rosenbaum, J., Alex, G., Roberts, H., and Orchard, D. (2010). Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms secondary to sulfasalazine. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 46 (4), 193–196. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1754.2009.01660.x
Salame, N., Chow, M. L., Ochoa, M. T., Compoginis, G., and Crew, A. B. (2019). Sorafenib toxicity mimicking drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome. J. Drugs Dermatol. 18 (5), 468–469.
Sekine, A., Saito, T., Ito, S., Tsunoda, Y., Sumazaki, Y., Tanaka, T., et al. (2012). Two cases of tuberculosis with multiple drug hypersensitivity after drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Respir. Investig. 50 (2), 70–75. doi:10.1016/j.resinv.2012.04.004
Shimada, Y., Suyama, Y., Koizumi, M., and Hagiwara, K. (2023). Laryngeal edema in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome due to sulfasalazine. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 26 (11), 2317–2319. doi:10.1111/1756-185x.14783
Shiohara, T., Iijima, M., Ikezawa, Z., and Hashimoto, K. (2007). The diagnosis of a DRESS syndrome has been sufficiently established on the basis of typical clinical features and viral reactivations. Br. J. Dermatol. 156 (5), 1083–1084. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07807.x
Shiohara, T., Inaoka, M., and Kano, Y. (2006). Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS): a reaction induced by a complex interplay among herpesviruses and antiviral and antidrug immune responses. Allergol. Int. 55 (1), 1–8. doi:10.2332/allergolint.55.1
Sil, A., Bhattacharjee, M. S., Chandra, A., and Pramanik, J. D. (2021). Sulfasalazine-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) with concomitant acute chikungunya virus infection: possible role of new viral trigger. BMJ. Case Rep. 14 (10), e244063. doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-244063
Stirton, H., Shear, N. H., and Dodiuk-Gad, R. P. (2022). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)/Drug-Induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS)-Readdressing the DRESS. Biomedicines 10 (5), 999. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10050999
Sussman, S., Devlin, V., and Dimitriades, V. R. (2017). A teenager with sulfasalazine-associated DRESS syndrome after the introduction of amoxicillin. Clin. Pediatr. (Phila). 56 (3), 290–291. doi:10.1177/0009922816656624
Suzuki, Y., Inagi, R., Aono, T., Yamanishi, K., and Shiohara, T. (1998). Human herpesvirus 6 infection as a risk factor for the development of severe drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch. Dermatol. 134 (9), 1108–1112. doi:10.1001/archderm.134.9.1108
Swart, L., Schapkaitz, E., and Baiden, A. (2018). A case of a drug reaction to sulfasalazine in a patient infected with HIV. South Afr. J. HIV. Med. 19 (1), 829. doi:10.4102/sajhivmed.v19i1.829
Tohyama, M., Hashimoto, K., Yasukawa, M., Kimura, H., Horikawa, T., Nakajima, K., et al. (2007). Association of human herpesvirus 6 reactivation with the flaring and severity of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 157 (5), 934–940. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08167.x
Winward, J., Lyckholm, L., Brown, S. M., and Mokadem, M. (2020). Case of relapsing sulfasalazine-induced hypersensitivity syndrome upon re-exposure. BMJ. Case Rep. 13 (9), e235803. doi:10.1136/bcr-2020-235803
Wolfson, A. R., Zhou, L., Li, Y., Phadke, N. A., Chow, O. A., and Blumenthal, K. G. (2019). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome identified in the electronic Health record allergy module. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 7 (2), 633–640. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2018.08.013
Ye, W., Ding, Y., Li, M., Tian, Z., Wang, S., and Liu, Z. (2024). Safety assessment of sulfasalazine: a pharmacovigilance study based on FAERS database. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1452300. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1452300
Yildirim Arslan, S., Sahbudak Bal, Z., Guner Ozenen, G., Bilen, N. M., Avcu, G., Erci, E., et al. (2024). Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome secondary to antimicrobial therapy in pediatric bone and joint infections. World Allergy Organ. J. 17 (2), 100850. doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2023.100850
Keywords: sulfasalazine, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS), HHV-6 reactivation, diagnosis
Citation: Liu Y, Wang D, Wu S, Liu X and Xiao C (2024) Literature review of the clinical features of sulfasalazine-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms/drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DRESS/DIHS). Front. Pharmacol. 15:1488483. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1488483
Received: 30 August 2024; Accepted: 18 November 2024;
Published: 02 December 2024.
Edited by:
Teresa Bellon, University Hospital La Paz Research Institute (IdiPAZ), SpainReviewed by:
Rosario Cabañas Moreno, University Hospital La Paz, SpainRannakoe Lehloenya, University of Cape Town, South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Wang, Wu, Liu and Xiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Can Xiao, eGlhb2NhbmxjeXhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Xiang Liu, bGl1eGlhbmc4NzZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Ya Liu1†
Ya Liu1† Can Xiao
Can Xiao