
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Pharmacol. , 25 November 2024
Sec. Pharmacology of Anti-Cancer Drugs
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1486742
Background: This study aims to improve the solubility and the toxicity of Bufonis venenum, and finally enhance the therapeutic outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: The cholesterol-free liposomes simultaneously encapsulate bufadienolides and indolealkylamines (Non-Cholesterol-Bufonis Venenum Extract-Liposome, Non-Chol-BVE-LP) was prepared by the thin-film evaporation technique. In vitro, the cytotoxicity, cell apoptosis study, cellular uptake and hemolysis studies were evaluated in HepG2 cells. In vivo, the biodistribution and anti-tumor activity studies were conducted in BALB/C mice with HepG2 cells.
Results: The liposomes showed good size distribution, encapsulation efficiency drug loading capacity and slower drug release. Non-Chol-BVE-LP had higher cytotoxicity on HepG2 cells and induced more apoptosis on HepG2 Cells compared with BVE. In addition, the liposomes could accumulate in tumor by passive targeting, thus facilitating the anti-tumor effects. In vivo, Non-Chol-BVE-LP showed equivalent anti-tumor efficacy to the first-line anti-HCC drug sorafenib.
Conclusion: The study provided new ideas for the development and clinical application of Bufonis venenum related formulation and offered new drug for the treatment of HCC.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancer with mortality rate ranking the third among all cancer (Sung et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2023). HCC is susceptible to intrahepatic and extrahepatic metastases. This makes the clinical prognosis of patients worse (Jia et al., 2023). Currently, the main diagnostic methods of HCC are ultrasounds, enhanced CT or MRI, tissue biopsy, and identification of biomarkers (Zhang et al., 2022). The treatment of HCC are modalities urgical resection, liver transplantation, local ablation, hepatic artery chemoembolization (TACE) and systemic therapy (Ajoolabady et al., 2023; Forner et al., 2018; Vogel et al., 2019; Vogel and Saborowski, 2022). Since most patients are diagnosed with advanced HCC and not suitable for surgical treatment, systemic therapy is usually the only chance for them. However, there are few options for systemic therapy for advanced HCC with only two first-line drug, Sorafenib and Lenvatinib, available. But both Sorafenib and Lenvatinib have poor effects on improving the survival rate of HCC patients, and it has been found that many HCC patients show resistance to these drug (Lu et al., 2022; Tang W. et al., 2020). Consequently, the development of innovative therapeutic modalities is imperative to enhance the therapeutic outcomes for patients diagnosed with HCC. Modern pharmacological researches show that some traditional Chinese medicine can act in all aspects of tumor occurrence and development, and has unique advantages in the treatment of tumors (Chen et al., 2022; Ge et al., 2018; Li et al., 2018; Luo et al., 2020; Tang K. Y. et al., 2020).
Bufonis venenum, which is the dried secretion of Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor or Bufo melanostictus, has been widely used in the treatment of malignant tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma, lung carcinoma, gastric carcinoma and other malignant tumors (Nalbantsoy et al., 2016; Wei et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2018). The extract of Bufonis venenum mainly contains bufadienolides and indolealkylamines (Bi et al., 2016; Tao et al., 2023) (Figures 1A, B). In recent years, studies have shown that bufadienolides has certain anti-tumor effects. It can promote the apoptosis of tumor cells and reverse the drug resistance of tumor cells (Dai et al., 2023; Yun et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2012). It has been reported that Cinobufagin and Bufalin can induce apoptosis via Fas- and mitochondria-mediated pathways (Qi et al., 2011). Gamabufotalin can improves the suppressive tumour immune microenvironment by inhibiting PD-L1 (Fan et al., 2024). Angiogenesis is proven to be an inhibitor of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis (Li et al., 2012). Resibufogenin can inducing reactive oxygen species accumulation and thus kill tumour cells (Han et al., 2018). Indolealkylamines has anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting effects (Xu et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2019). It has been reported that 5-hydroxytryptamine can promote liver regeneration and immune cell activation (Fang et al., 2018; Karmakar and Lal, 2021). Bufotenine and bufotenidine have analgesic activilities (Xu et al., 2021). Both the Huachansu capsules (which mainly contain bufadienolides) and Huachansu injection (which primarily contains indolealkylamines) have exhibited significant anti-HCC activities in clinic. However, bufadienolides has poor solubility in water and tends to be rapidly distributed and eliminated in vivo. Furthermore, it may induce adverse reactions such as accelerated heart rate, convulsions, nausea and vomiting. Since the hydrophobicity limits the clinical use of bufadienolides to some extent. It is of great importance to improve the bioavailability and reduce the toxicity of these compounds through advancements in pharmaceutical technology.
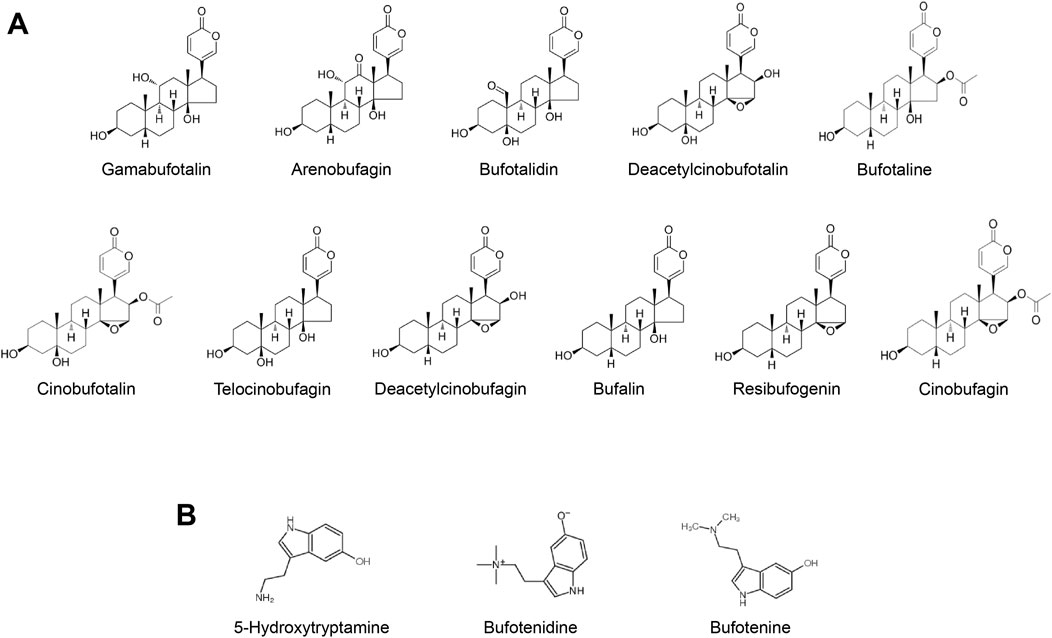
Figure 1. (A) Typical bufadienolides in Bufonis venenum (B) Typical indolealkylamines in Bufonis venenum.
Nanotechnology has demonstrated significant ability to delivery insoluble drug in vivo and reduce the toxicity of drug (Farokhzad and Langer, 2009). Liposomes, as a kind of drug carriers, have been widely used in clinic. They have biofilm-like properties with good tissue permeability and targeting. Besides, they can encapsulate lipophilic drug in the phospholipid bilayer and hydrophilic drug in the hydrophilic core, which can protect the encapsulated macromolecules from degradation, play a role in reducing the toxicity and improve the therapeutic efficacy of the drug (Abu Lila and Ishida, 2017; Mazur et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2009). Liposomes are generally composed of phospholipids and cholesterol (Maeda et al., 2017). Cholesterol can regulate the fluidity of the phospholipid bilayer membrane and retard the lateral flow of oxidized phospholipids (Kaddah et al., 2018). The above mechanism prevents the deformation of liposomes and the creation of air pockets, which can keep a relatively robust bilayer structure of liposomes even after a certain degree of oxidation. However, taking too much cholesterol may cause cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis and other health problems (Folkerd and Dowsett, 2010; Nelson et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2019). Steroids and saponins, which have similar structure to cholesterol, are capable of replacing cholesterol at right proportions without damaging the structure of liposomes (Hong et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2018). The bufadienolides in Bufonis venenum extract is such a kind of steroid.
In this study, we aim to prepare the cholesterol-free liposomes by replacing cholesterol with bufadienolides, which has a similar chemical structure to cholesterol, and co-encapsulate indolealkylamines in the hydrophilic core of the liposomes. The characterization, uptake ability, in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor effects and in vivo biodistribution of the liposome was investigated, This study is expected to provide new ideas for the development and clinical application of Bufonis venenum related formulation and to offer new drug for the treatment of HCC.
DSPC, DSPE-mPEG2000 and cholesterol were obtained from AVT (Shanghai) Pharmaceutical Tech Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). Bufonis Venenum Extract was extracted and isolated according to an established procedure. Chloroform, methanol, rhodamine B (RB), indocyanine green (ICG) and Phosphotungstic acid were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). Sephadex G-50 Dextran Gel was obtained from Pharmacia LKB Biotechnology Inc., (Uppsala, Sweden). MEM medium, FBS and Penicillin-Streptomycin solution were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, United States of America). Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was obtained from Shanghai Biyuntian Biological Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). Gamabufotalin, Arenobufagin, Bufotalidin, Deacetylcinobufotalin, Bufotaline, Cinobufotalin, Telocinobufagin, Deacetylcinobufagin, Bufalin, Resibufogenin, Cinobufagin and 5-Hydroxytryptamine were obtained from Shanghai Hongyong Biological Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). Bufotenidine and Bufotenine were obtained from Anhui Xiqingguo Biological Co., Ltd., (Anhui, China).
HepG2 cells were obtained from the Cell Bank of Typical Culture Preservation Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China) and cultivated in complete MEM medium (containing 10% FBS and 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin solution). The cells were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 incubator for subsequent experiments.
Male Sprague Dawley rats were obtained from Shanghai Sippr bk laboratory animal Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). Male BALB/C mice were obtained from SLAC Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Agilent 1290 series UPLC with a column (Agilent Eclipse Plus C18 RRHD, 100 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm) and an ultraviolet detector (300 nm) was used to quantify the bufadienolides concentration. The column temperature was maintained at 35°C. The separation system was consisted of 0.1% phosphoric acid in water (A) and methanol (B). The solvent gradient was set as follows: 0–5 min, 15% B; 5–10 min, 15%–18% B; 10–15 min, 18% B; 15–17 min, 18%–40% B; 17–25 min, 40%–55% B; 25–28 min, 55%–75% B; 28–30 min, 75%–90% B and 30–35 min, 90% B. The injection volume was 2 μL, and the flow rate was approximately 0.4 mL/min.
Agilent 1200 series HPLC with a column (Diamonsil Plus C18, 250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) and an ultraviolet detector (275 nm) was used to quantify the indolealkylamines concentration. The column temperature was maintained at 30°C. The separation system was consisted of 0.5% potassium dihydrogen phosphate in water (A) and methanol (B). The solvent gradient was set as follows: 0–5 min, 8% B; 5–20 min, 8%–12% B; 20–25 min, 12%–80% B and 25–35 min, 80% B. The injection volume was 10 μL, and the flow rate was approximately 1 mL/min.
Bufonis Venenum Extract (BVE) was extracted and isolated according to an established procedure (Lee et al., 2012). We have improved on this method. Bufonis venenum was added to 70% ethanol (ratio 1:120) and refluxed for 140 min 2 times. After filtration and evaporation, the final BVE was obtained. The content of main components of extract was test by HPLC and supplied in SI (Supplementary Table S1).
Non-Cholesterol-BVE-Liposome (Non-Chol-BVE-LP) was prepared by the thin-film evaporation technique. After a preliminary prescribing study (Supplementary Figures S1, S2), Non-Chol-BVE-LP was consisted of 28.16 mg of DSPC, 25 mg of DSPE-mPEG2000 and 4.28 mg of Bufonis Venenum extract (BVE). The above mixture was dissolved respectively in chloroform/methanol (1:1, v/v) and evaporated to get a thin lipid film under 60°C by rotatory evaporator. To ensure organic reagents were completely removed, the lipid film was kept in a vacuum dryer overnight. 4 mL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 6.8) was added to hydrate the lipid film. The above hydrated mixture solution was probe-sonicated in an ice-water for 10 min (80 W, 3S on/3S off) to get Non-Chol-BVE-LP.
Rhodamine B (RB) and Indocyanine Green (ICG) liposomes were prescribed by loading RB or ICG into the Non-Chol-LP. The rest of the steps were the same as the preparation of Non-Chol-BVE-LP.
The particle size and zeta potential of the liposomes were characterized using a Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments Ltd, United Kingdom). 50 μL of liposome suspension was diluted with 1 mL of double-distilled water before measuring. The morphology of the liposomes was visualized under a transmission electron microscope (TEM). The encapsulation efficiency (EE) and drug loading (DL) of the liposomes were determined by dextran gel G-50 column chromatography. The concentration of components in Non-Chol-BVE-LPs was determined by ultraperformance liquid chromatography (UPLC) at 300 nm. The following equations were used for the calculations:
All measurements were performed in triplicate respectively.
The stability of liposomes was investigated by particle size and EE. The liposomes prepared were stored in dark at 4°C. Samples were collected at 1, 7, 14, 21 and 30 d to determine the above indicators.
The in vitro drug release of liposomes was examined by dialysis method. 2 mL of Non-Chol-BVE-LP and BVE solution were added into a dialysis bag (molecular weight: 7 KDa) and sealed respectively. The dialysis bags were immersed into 200 mL of PBS with 0.5% Tween-80 and placed on a magnetic stirrer (37°C, 100 rpm). After measuring the volume of liposomes in the dialysis bags, 0.1 mL of the solution in the bag was taken to determine the drug concentration by UPLC. Samples were collected at the time point of 10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 120, 240, 360 and 480 min. The drug release profiles of preparation and free drug were plotted and compared by calculating the cumulative percentage of drug release ratio at each sampling time.
The cytotoxicity of Non-Chol-BVE-LP and BVE was evaluated by CCK8 assay. 100 μL of HepG2 cell or LO2 cell suspension (1 × 105 cells/mL) was inoculated into 96-well plates and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 incubator overnight. Different concentrations of BVE solution and Non-Chol-BVE-LP were added into 96-well plates in three replicates. After 48 h of incubation, 10 μL of CCK-8 solution was added into per well. After incubating for another 2 h in the 5% CO2 incubator, the optical density (OD) of each well was measured at 450 nm by a microplate reader. The cell inhibition rate was calculated as following equation:
Flow cytometer was used to detect the apoptosis of HepG2 cells. 2 mL of HepG2 cell suspension (3 × 105 cells/mL) was inoculated into 6-well plates and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 incubator overnight. After discarding the culture medium, 2 mL of BVE solution or Non-Chol-BVE-LP was added into each well. The concentration of BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP were 0.18 μg/mL and 0.10 μg/mL. Cells were incubated for 48 h and then washed with 2 mL of PBS (containing 1% FBS). Cells in each well were digested with 200 μL of trypsin (without EDTA) and resuspended into 100 μL of Binding Buffer. 5 μL of Annexin V-FITC was added into the cell solutions followed by incubating in dark at 4°C for 30 min 5 min before testing by flow cytometry, 400 μL of Binding Buffer and 5 μL of PI were added.
The flow cytometry and confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) were employed to analyze the cellular uptake of preparations by HepG2 cells. For flow cytometry study, HepG2 cell suspension (1 × 105 cells/mL) was inoculated into 6-well plates in three replicates and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 incubator overnight. After discarding the culture medium, 2 mL of culture medium with RB or Non-Chol-RB-LP solution was added. The concentration of RB and BVE was 5 μg/mL and 0.5 μg/mL. After 2 h of incubation, the culture medium was discarded, and cells were washed three times with PBS. Cells in each well were digested with trypsin and resuspended into 1 mL of PBS. The cell suspensions were transferred into a flow tube for detection.
For CLSM study, HepG2 cell suspension (1 × 105 cells/mL) was inoculated into glass-bottom Petri dishes in three replicates and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 incubator overnight. After discarding the culture medium, 2 mL of culture medium with RB or Non-Chol-RB-LP solution was added. The concentration of RB and BVE was 5 μg/mL and 0.5 μg/mL. After 2 h of incubation, the culture medium was discarded, and cells were washed three times with PBS. 1 mL of 4% paraformaldehyde solution was used to fix the cells for 10 min. After washing three times with PBS, 500 μL of Hoechst 33342 was used to perform nuclear staining for 20 min. The fluorescent dyes were discarded, washed three times with PBS and 500 μL of PBS was added to each dish. Finally, the cells were observed and photographed with a CLSM.
The erythrocytes of SD rats were collected. Pure water (positive control), PBS solution (negative control), BVE solution, and Non-Chol-BVE-LP was added respectively to centrifuge tubes containing 20 μL of erythrocytes. After mixing, the mixtures were centrifuged at 3,500 rpm for 10 min to get the supematant after keeping at room temperature for 30 min. A UV-visible spectrophotometry was used to measure the absorbance of the supematant at a wavelength of 540 nm and the hemolysis rates were calculated.
A HepG2 subcutaneous tumor mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma was established to investigate the biodistribution and anti-tumor activity of the preparations. Healthy male BALB/C mice with a body weight of approximately 20 ± 2 g were kept in the laboratory for 7 days to adapt before the study. HepG2 cells were digested with trypsin and resuspended into serum-free medium (3 × 106 cells/mL). 125 μL of HepG2 cell suspension were subcutaneously injected into the right axilla of each BALB/c mouse.
The biodistribution study was conducted on tumor-bearing BALB/c mice. When the tumor volume reached about 100 mm3, the mice were randomly divided into free ICG group and Non-Chol-ICG-LP group. Free ICG or Non-Chol-ICG-LP were intravenously administrated at an equal ICG dose of 2 mg/kg and BVE dose of 0.08 mg/kg, followed by anesthetizing the mice with 1.5% isoflurane, and the fluorescence distribution and intensity of ICG in the mice was recorded at 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 h post injection using the IVIS Lumina in vivo imaging system. After 24 h of the administration, the mice were sacrificed. Tumors, hearts, livers, spleens, lungs, and kidneys were removed and flushed by saline for ex vivo fluorescence imaging.
The in vivo anti-tumor study was conducted on tumor-bearing BALB/c mice. When the tumor volume reached about 50 mm3, the mice were randomly divided into the following five groups: control (saline), sorafenib, Chansu injection, BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP. The dose of sorafenib, Chansu injection and BVE were 30 mg/kg, 20 μL/g and 0.08 mg/kg. All groups were treated every other day. The body weights and tumor volumes of the mice were recorded every other day. The tumor volume was calculated as the following equation:
After 2 weeks of the treatment, the mice were sacrificed 24 h after the last treatment. The tumors and hearts were excised. After weighing the tumor, the tumor inhibition rate was calculated by the following equation:
All the tissues were flushed by saline and stored at 4% paraformaldehyde fix solution for 48 h. Samples were fixed in paraffin and sliced into 3–5 µm sections then. After dehydrating overnight, hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) was conducted. Then perform histological observations with light microscope.
Data were expressed as mean value ± standard deviation (SD). Differences among groups were performed with a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The appearance of Non-Chol-BVE-LP was a slightly yellowish clarified solution (Figure 2A). Non-Chol-BVE-LP was prepared with the particle size of 81.51 ± 1.10 nm and the zeta potential of −20.1 ± 0.76 (Figures 2B, C). The concentration of Gamabufotalin, Arenobufagin, Bufotalidin, Deacetylcinobufotalin, Bufotaline, Cinobufotalin, Telocinobufagin, Deacetylcinobufagin, Bufalin, Resibufogenin, Cinobufagin, 5-Hydroxytryptamine, Bufotenidine, Bufotenine in Non-Chol-BVE-LP were 11.12 ± 0.10 μg/mL, 18.22 ± 0.43 μg/mL, 6.25 ± 1.85 μg/mL, 0.45 ± 0.03 μg/mL, 18.76 ± 1.30 μg/mL, 20.82 ± 0.86 μg/mL, 8.94 ± 0.77 μg/mL, 1.99 ± 0.09 μg/mL, 29.83 ± 2.40 μg/mL, 40.25 ± 0.80 μg/mL, 56.40 ± 3.44 μg/mL, 0.62 ± 0.21 μg/mL, 3.89 ± 0.97 μg/mL and 0.09 ± 0.04 μg/mL respectively.
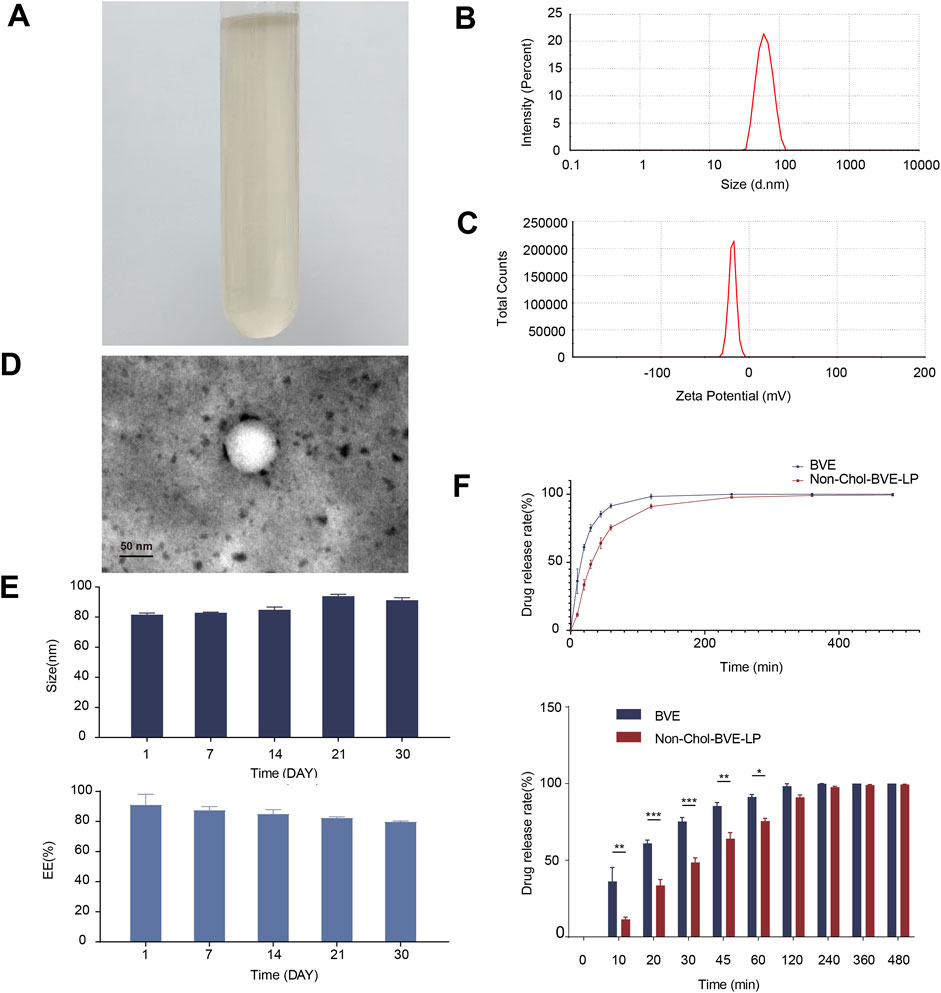
Figure 2. (A) The appearance of Non-Chol-BVE-LP (B) Particle size of Non-Chol-BVE-LP (C) Zeta potential of Non-Chol-BVE-LP (D) TEM images of Non-Chol-BVE-LP (E) Changes in particle size and EE of Non-Chol-BVE-LP during 30 days (n = 3). (F) In vitro drug release of BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP (n = 3).
The EE of Non-Chol-LP was 91.20% ± 6.80% and the DL was 2.87% ± 0.11%. TEM was used to evaluate the appearance and shape of the liposomes. The micrograph showed that the Non-Chol-BVE-LP was spherical with relatively uniform size. And no aggregation or fusion was observed (Figure 2D). The stability of the Non-Chol-BVE-LP in PBS during 30 days was investigated by particle size and encapsulation efficiency (Figure 2E). The stability of the Non-Chol-BVE-LP in saline and DMEM during 7 days was investigated either (Supplementary Figure S3). The particle size of Non-Chol-BVE-LP in saline was 76.66 ± 0.27 nm. The particle size of Non-Chol-BVE-LP in MEM was 80.27 ± 0.42 nm. The EE of Non-Chol-BVE-LP in saline was 93.59% ± 1.91%. The particle size of Non-Chol-BVE-LP in MEM was 93.66% ± 3.38%. The particle size and EE of the liposomes in saline and MEM during 7 days were stable. In general, the stability of Non-Chol-BVE-LP was good. There was no significant difference between 1 d and 30 d in particle size or encapsulation efficiency, which indicated that liposomes did not aggregate or degrade under a certain time of storage.
The in vitro release profiles of free drug and liposomes over 480 min were shown (Figure 2F). After 30 min, 75.3% ± 2.6% of free drug was released, while in Non-Chol-BVE-LP, only 48.5% ± 3.1% of the drug was released. In 60 min, 75.6% ± 1.9% of the drug was released from Non-Chol-BVE-LP. These results indicated that liposome had a certain sustained-release effect on the encapsulated drug, which could lower the Cmax of the drug in blood after injection and reduce the toxicity caused by high blood concentration of Bufonis venenum extract.
Bufonis venenum extract has been reported to be able to kill various tumor cells and induce apoptosis in tumor cells, which is also its main mechanism of anti-tumor activity. In vitro cytotoxicity of BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP on HepG2 cells was measured by CCK8 assay (Figure 3A). After 48 h of incubation, the cell viability of HepG2 cells was negatively correlated with the concentration of the drug. According to the results of cytotoxicity, IC50 values of BVE solution and Non-Chol-BVE-LP were 0.24 μg/mL and 0.17 μg/mL respectively. Compared with BVE solution, Non-Chol-BVE-LP group showed higher cytotoxicity on HepG2 cells. In vitro cytotoxicity of BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP on LO2 cells was measured by CCK8 assay (Supplementary Figure S4). The result indicated that BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP does not cause significant toxicity to normal liver cells even at four times the therapeutic doses on HepG2 cells. Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining was used to detect apoptosis on HepG2 cells (Figures 3B, C). For BVE group and Non-Chol-BVE-LP group, the total apoptosis rates were 20.46% ± 0.35% and 27.26% ± 2.10% respectively. The early apoptosis rate, late apoptosis rate and total apoptosis rates of BVE group were lower than Non-Chol-BVE-LP, which was consistent with the results of cytotoxicity.
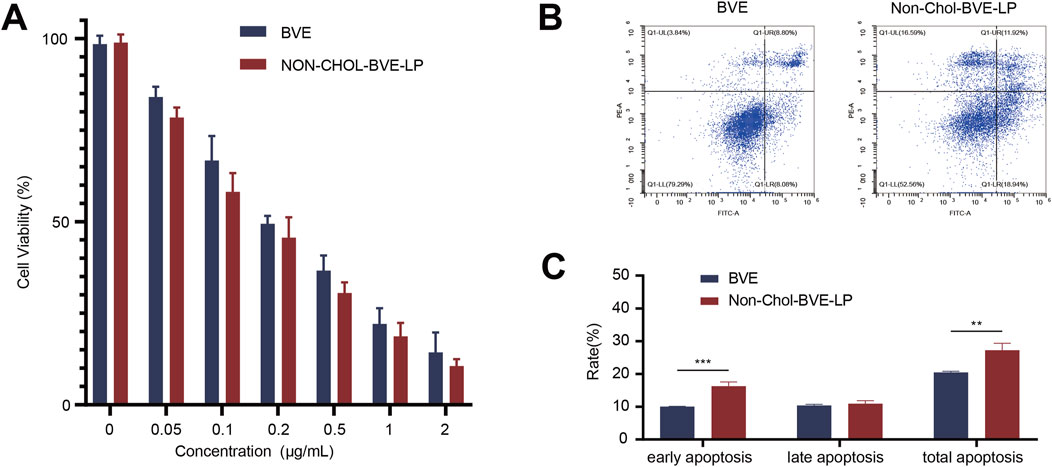
Figure 3. (A) Cytotoxicity of BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP on HepG2 cells (B) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis on HepG2 cells (C) The quantitative analysis results according to the flow cytometry analysis (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
RB was used to mark the liposome for cellular uptake studies. The analysis results of flow cytometry were shown (Figures 4A, B). The uptake of Non-Chol-RB-LP by HepG2 cells was significantly higher than that of RB. The results were further verified by CLSM (Figures 4C, D). The red fluorescence was the staining of RB and blue fluorescence was the nucleus after being stained by Hoechst 33342. The increased intracellular red fluorescence indicated the increased uptake of RB by HepG2 cells. The uptake of Non-Chol-RB-LP by HepG2 cells was also higher than that of RB, which was in agreement with those obtained by flow cytometry.
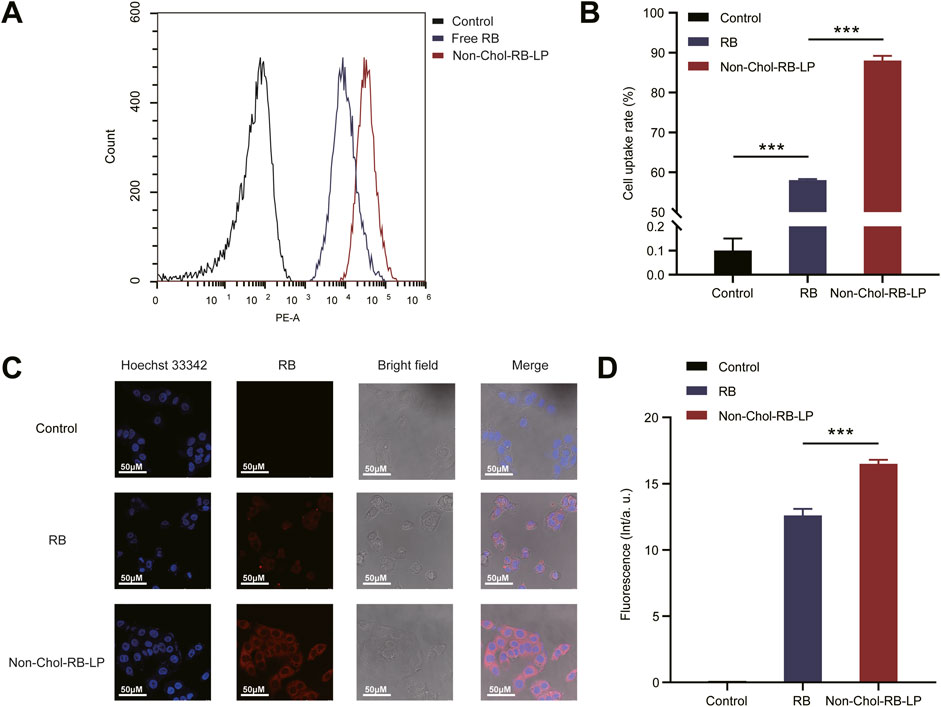
Figure 4. (A) In vitro cellular uptake of BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP by HepG2 cells (B) The quantitative analysis results according to the uptake (C) CLSM images of cells incubated with RB and Non-Chol-BVE-LP (D) The quantitative analysis results according to the CLSM analysis Data is expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
Before in vivo studies, we first investigated the hemolytic activity of the formulations. As it was shown (Figure 5A), the hemolysis rates of BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP were less than 5% at the actual in vivo dose, meeting the requirements for intravenous injection. BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP demonstrated good blood safety when administered in vivo. ICG was used to mark the liposome for in vivo distribution studies. The in vivo distribution of free ICG and Non-Chol-ICG-LP in nude mice was examined by an IVIS Lumina in vivo imaging system. Equal doses of ICG solution and Non-Chol-ICG-LP were injected via tail vein. As it was shown (Figures 5B, C), the fluorescence intensity was positively correlated with time within 4 h after administration, and then declined. Comparing with ICG group, Non-Chol-ICG-LP was distributed more widely in vivo 4 h after administration, which indicated liposomes could prolong the in vivo circulation of drug. In isolated tumors of the mice (Figure 5D), the fluorescence intensity of ICG group was weaker than that of Non-Chol-ICG-LP group. And in isolated organs, fluorescence intensity was almost absent except in livers. Because the liver, which was rich in reticuloendothelial cells distributed throughout, was capable of ingesting liposomes and was also the primary organ for drug metabolism. These results indicated that Non-Chol-ICG-LP exhibited higher tumor accumulation.
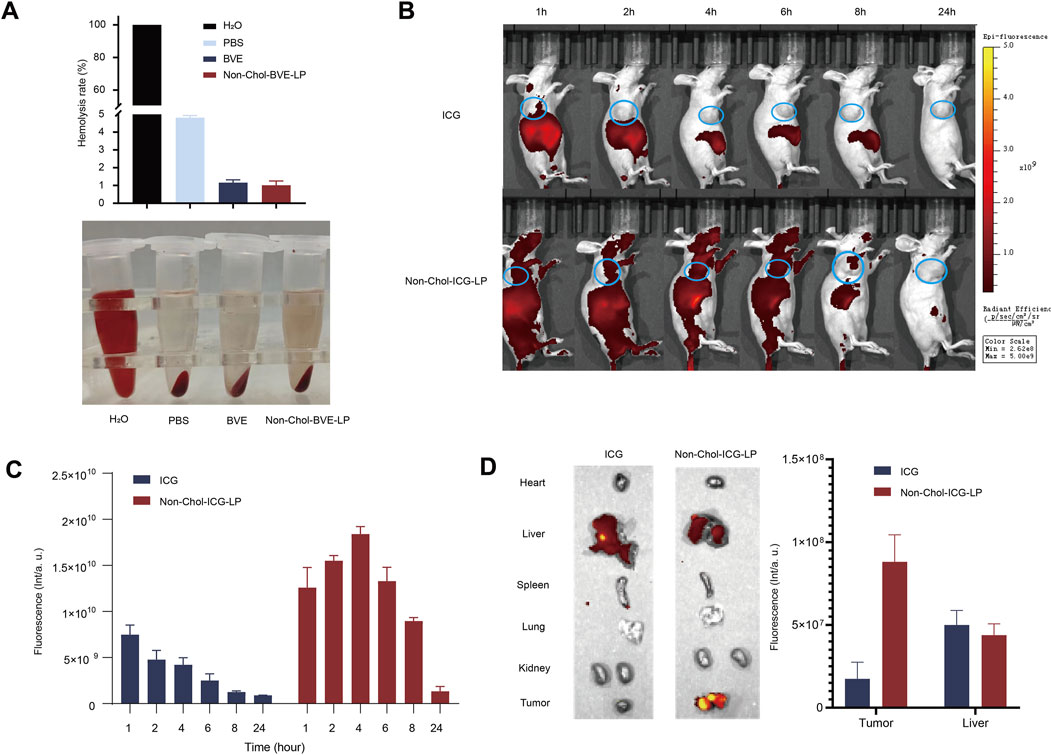
Figure 5. (A) Hemolysis in each group (B) In vivo biodistribution images of ICG and Non-Chol-BVE-LP (C) The fluorescence semi-quantification analysis results of tumor during 24 h after the administration (D) Ex vivo fluorescence images of organs and tumors at 24 h after administration and the fluorescence semi-quantification analysis results according to the biodistribution analysis. Data is expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
The anti-tumor effect on HepG2 subcutaneous tumor mice was investigated. As it was shown (Figures 6A–C), the tumor volumes in control, sorafenib, Chansu injection, BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP groups were 1511.02 ± 230.39 mm3, 326.34 ± 81.82 mm3, 816.84 ± 100.70 mm3, 577.72 ± 106.90 mm3 and 454.93 ± 76.43 mm3. The tumor weights were 1.34 ± 0.22 g, 0.28 ± 0.11 g, 0.65 ± 0.18 g, 0.46 ± 0.11 g and 0.26 ± 0.10 g respectively. And the tumor inhibition rates in sorafenib, Chansu injection, BVE and Non-Chol-BVE-LP groups were 79.75% ± 4.98%, 52.20% ± 6.70%, 65.75% ± 3.75% and 80.42% ± 5.69%. The above results indicated that liposomes had significant tumor suppressor effects with equivalent anti-tumor efficacy to the first-line anti-HCC drug sorafenib. Moreover, no significant changes in body weight of mice after treatment (Figure 6D). H&E staining results showed significant apoptosis and necrosis in the tumor tissue of the sorafenib and Non-Chol-BVE-LP groups, with typical features such as cell shrinkage and deepening of nuclear staining (Figure 6E). Therefore, Non-Chol-BVE-LP has achieved efficient anti-tumor effects by loading bufadienolides and indolealkylamines.
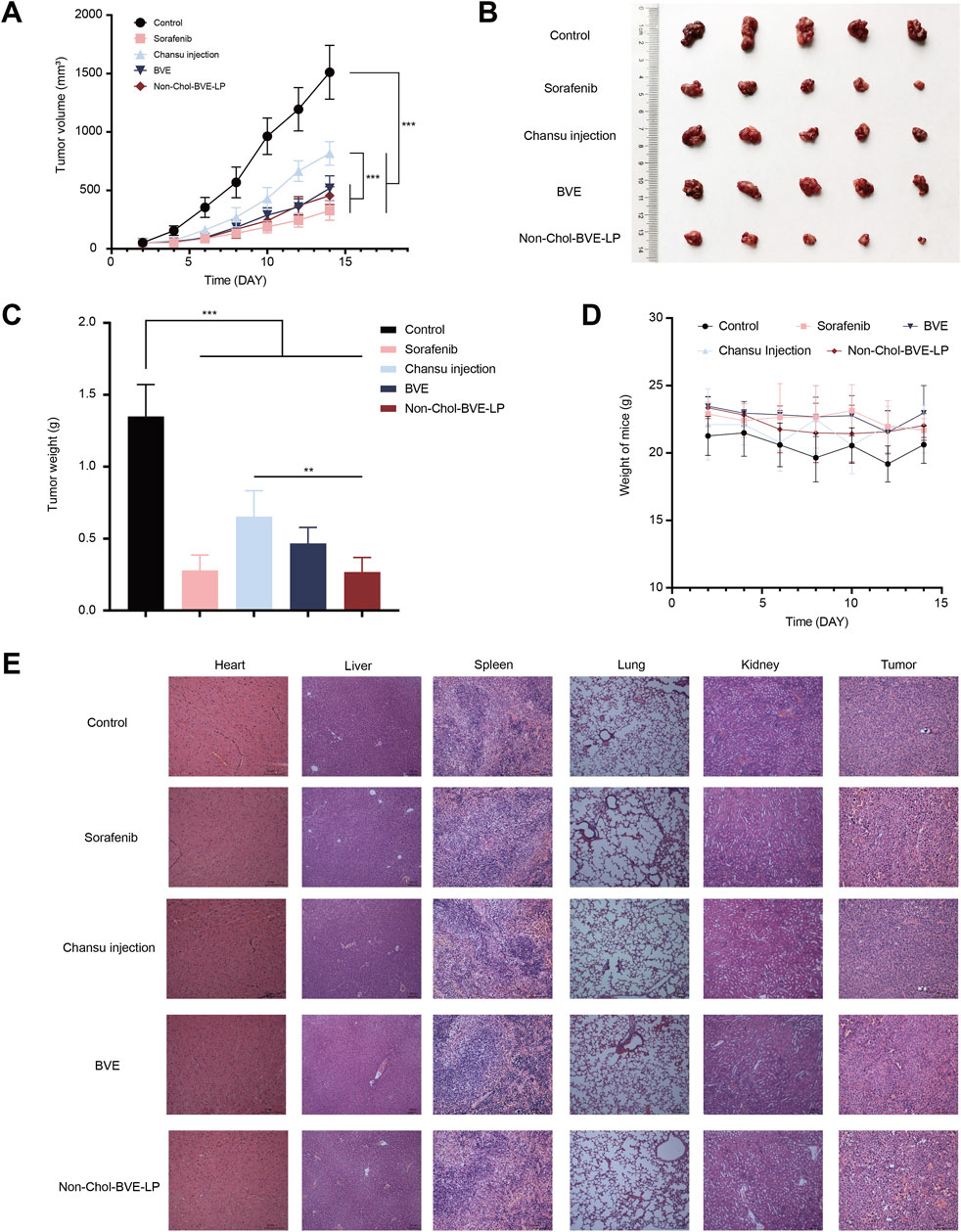
Figure 6. (A) Tumor growth curves of each group of tumors (B) Photographs of each group of tumors (C) Weight of each group of tumors (D) Body weight change curves (E) Histopathology sections of mice treated with various groups. Data is expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
The presented studies provided a strong evidence of the likelihood of preparing cholesterol-free liposomes by replacing cholesterol with anti-tumor steroid such as bufadienolides. The liposome showed good size distribution, encapsulation efficiency drug loading capacity and slower drug release. Compared to BVE, Non-Chol-BVE-LP had higher cytotoxicity on HepG2 cells and induced more apoptosis on HepG2 cell. In addition, the liposomes had better intracellular uptake by HepG2 cells than the free drug, enhancing the drug accumulation in tumor, which facilitated the anti-tumor effects. In vivo, Non-Chol-BVE-LP showed high tumor accumulation and equivalent anti-tumor efficacy to the first-line anti-HCC drug sorafenib. The study provided new ideas for the development and clinical application of Bufonis venenum related formulation and offered new drug for the treatment of HCC.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The animal study was approved by Ethics Committee of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
SY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review and editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. ML: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing–review and editing. YW: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. LS: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. TZ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YD: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Programs of the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 82274066, 82374002 and 82204777]; Shanghai Leading Talent [grant number 2019100]; Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader [grant number 22XD1423000]; “Shuguang Program” supported by Shanghai Education Development Foundation and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission [grant number 20SG43]; Project from Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology [grant number 20S21902500, 22S21901200 and 21010504200]; Youth Talent Program from the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission [grant number 2022YQ030]; Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai [grant number 22ZR1459000]; National Key Research and Development Program of China [grant number 2022YFC3501705], China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [grant number 2022M712155].
We thank the ElectronMicroscopy Laboratory of Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences for their assistance with the TEM support. We also thank the Flow Cytometry Laboratory of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine for their help with the flow cytometry experiments.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1486742/full#supplementary-material
Abu Lila, A. S., and Ishida, T. (2017). Liposomal delivery systems: design optimization and current applications. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 40 (1), 1–10. doi:10.1248/bpb.b16-00624
Ajoolabady, A., Tang, D., Kroemer, G., and Ren, J. (2023). Ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: mechanisms and targeted therapy. Br. J. Cancer 128 (2), 190–205. doi:10.1038/s41416-022-01998-x
Bi, Q. R., Hou, J. J., Qi, P., Ma, C. H., Shen, Y., Feng, R. H., et al. (2016). Venenum Bufonis induces rat neuroinflammation by activiating NF-κB pathway and attenuation of BDNF. J. Ethnopharmacol. 186, 103–110. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.049
Chen, W., Ma, Z., Yu, L., Mao, X., Ma, N., Guo, X., et al. (2022). Preclinical investigation of artesunate as a therapeutic agent for hepatocellular carcinoma via impairment of glucosylceramidase-mediated autophagic degradation. Exp. Mol. Med. 54 (9), 1536–1548. doi:10.1038/s12276-022-00780-6
Dai, C. L., Zhang, R. J., An, P., Deng, Y. Q., Rahman, K., Zhang, H., et al. (2023). Cinobufagin: a promising therapeutic agent for cancer. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 75 (9), 1141–1153. doi:10.1093/jpp/rgad059
Fan, J., Qin, Y., Qiu, W., Liang, J., Xiao, C., Xie, Q., et al. (2024). Gamabufotalin loaded micro-nanocomposites for multimodal therapy of metastatic TNBC by efficiently inducing ICD. Biomaterials 314, 122851. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122851
Fang, Y., Liu, C., Shu, B., Zhai, M., Deng, C., He, C., et al. (2018). Axis of serotonin -pERK-YAP in liver regeneration. Life Sci. 209, 490–497. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2018.08.047
Farokhzad, O. C., and Langer, R. (2009). Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano 3 (1), 16–20. doi:10.1021/nn900002m
Folkerd, E. J., and Dowsett, M. (2010). Influence of sex hormones on cancer progression. J. Clin. Oncol. 28 (26), 4038–4044. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.27.4290
Forner, A., Reig, M., and Bruix, J. (2018). Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 391 (10127), 1301–1314. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30010-2
Ge, W., Chen, X., Han, F., Liu, Z., Wang, T., Wang, M., et al. (2018). Synthesis of cucurbitacin B derivatives as potential anti-hepatocellular carcinoma agents. Molecules 23 (12), 3345. doi:10.3390/molecules23123345
Han, Q., Ma, Y., Wang, H., Dai, Y., Chen, C., Liu, Y., et al. (2018). Resibufogenin suppresses colorectal cancer growth and metastasis through RIP3-mediated necroptosis. J. Transl. Med. 16 (1), 201. doi:10.1186/s12967-018-1580-x
Hong, C., Wang, D., Liang, J., Guo, Y., Zhu, Y., Xia, J., et al. (2019). Novel ginsenoside-based multifunctional liposomal delivery system for combination therapy of gastric cancer. Theranostics 9 (15), 4437–4449. doi:10.7150/thno.34953
Jia, W., Liang, S., Lin, W., Li, S., Yuan, J., Jin, M., et al. (2023). Hypoxia-induced exosomes facilitate lung pre-metastatic niche formation in hepatocellular carcinoma through the miR-4508-RFX1-IL17A-p38 MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 19 (15), 4744–4762. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86767
Kaddah, S., Khreich, N., Kaddah, F., Charcosset, C., and Greige-Gerges, H. (2018). Cholesterol modulates the liposome membrane fluidity and permeability for a hydrophilic molecule. Food Chem. Toxicol. 113, 40–48. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2018.01.017
Karmakar, S., and Lal, G. (2021). Role of serotonin receptor signaling in cancer cells and anti-tumor immunity. Theranostics 11 (11), 5296–5312. doi:10.7150/thno.55986
Lee, H. J., Koung, F. P., Kwon, K. R., Kang, D. I., Cohen, L., Yang, P. Y., et al. (2012). Comparative analysis of the bufonis venenum by using TLC, HPLC, and LC-MS for different extraction methods. J. Pharmacopuncture 15 (4), 52–65. doi:10.3831/kpi.2012.15.012
Li, M., Wu, S., Liu, Z., Zhang, W., Xu, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2012). Arenobufagin, a bufadienolide compound from toad venom, inhibits VEGF-mediated angiogenesis through suppression of VEGFR-2 signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 83 (9), 1251–1260. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.023
Li, R., Zhang, L. Y., Li, Z. J., Xue, C. H., Dong, P., Huang, Q. R., et al. (2020). Characterization and absorption kinetics of a novel multifunctional nanoliposome stabilized by sea cucumber saponins instead of cholesterol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68 (2), 642–651. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06460
Li, S. G., Shi, Q. W., Yuan, L. Y., Qin, L. P., Wang, Y., Miao, Y. Q., et al. (2018). C-Myc-dependent repression of two oncogenic miRNA clusters contributes to triptolide-induced cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 37 (1), 51. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0698-2
Lu, L., Ding, Y., Zhang, Y., Ho, R. J., Zhao, Y., Zhang, T., et al. (2018). Antibody-modified liposomes for tumor-targeting delivery of timosaponin AIII. Int. J. Nanomedicine 13, 1927–1944. doi:10.2147/ijn.S153107
Lu, Y., Chan, Y. T., Tan, H. Y., Zhang, C., Guo, W., Xu, Y., et al. (2022). Epigenetic regulation of ferroptosis via ETS1/miR-23a-3p/ACSL4 axis mediates sorafenib resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 41 (1), 3. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-02208-x
Luo, Y., Song, L., Wang, X., Huang, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, Q., et al. (2020). Uncovering the mechanisms of cryptotanshinone as a therapeutic agent against hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 1264. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01264
Maeda, N., Ikeda, K., Matsumoto, M., and Namba, Y. (2017). Advanced lipid technology. J. Liposome Res. 27 (3), 221–227. doi:10.1080/08982104.2016.1224898
Mazur, F., Bally, M., Städler, B., and Chandrawati, R. (2017). Liposomes and lipid bilayers in biosensors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 249, 88–99. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2017.05.020
Nalbantsoy, A., Karış, M., Yalcin, H. T., and Göçmen, B. (2016). Biological activities of skin and parotoid gland secretions of bufonid toads (Bufo bufo, Bufo verrucosissimus and Bufotes variabilis) from Turkey. Biomed. Pharmacother. 80, 298–303. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.03.034
Nelson, E. R., Chang, C. Y., and McDonnell, D. P. (2014). Cholesterol and breast cancer pathophysiology. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 25 (12), 649–655. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2014.10.001
Qi, F., Inagaki, Y., Gao, B., Cui, X., Xu, H., Kokudo, N., et al. (2011). Bufalin and cinobufagin induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Fas- and mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cancer Sci. 102 (5), 951–958. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01900.x
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71 (3), 209–249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
Tang, K. Y., Du, S. L., Wang, Q. L., Zhang, Y. F., and Song, H. Y. (2020). Traditional Chinese medicine targeting cancer stem cells as an alternative treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Integr. Med. 18 (3), 196–202. doi:10.1016/j.joim.2020.02.002
Tang, W., Chen, Z., Zhang, W., Cheng, Y., Zhang, B., Wu, F., et al. (2020). The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 5 (1), 87. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-0187-x
Tao, C., Wang, J., Gu, Z., Ni, H., Luo, Y., Ling, J., et al. (2023). Network pharmacology and metabolomics elucidate the underlying mechanisms of Venenum Bufonis in the treatment of colorectal cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 317, 116695. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116695
Vogel, A., Cervantes, A., Chau, I., Daniele, B., Llovet, J. M., Meyer, T., et al. (2019). Correction to: hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 30 (5), 871–873. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy510
Vogel, A., and Saborowski, A. (2022). Medical therapy of HCC. J. Hepatol. 76 (1), 208–210. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.017
Wang, N., Wang, T., Li, T., and Deng, Y. (2009). Modulation of the physicochemical state of interior agents to prepare controlled release liposomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 69 (2), 232–238. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2008.11.033
Wei, W. L., Hou, J. J., Wang, X., Yu, Y., Li, H. J., Li, Z. W., et al. (2019). Venenum bufonis: an overview of its traditional use, natural product chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 237, 215–235. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.042
Wu, Q., Wang, Q., Fu, J., and Ren, R. (2019). Polysaccharides derived from natural sources regulate triglyceride and cholesterol metabolism: a review of the mechanisms. Food Funct. 10 (5), 2330–2339. doi:10.1039/c8fo02375a
Xie, D., Shi, J., Zhou, J., Fan, J., and Gao, Q. (2023). Clinical practice guidelines and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: a Chinese perspective. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 29 (2), 206–216. doi:10.3350/cmh.2022.0402
Xu, D., Wang, J., Chen, W., Yang, X., Zhou, J., Ma, H., et al. (2021). Evaluation of analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions of indolealkylamines from toad venom in mice using lipidomics and molecular docking. J. Ethnopharmacol. 269, 113677. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113677
Yun, H. R., Yoo, H. S., Shin, D. Y., Hong, S. H., Kim, J. H., Cho, C. K., et al. (2009). Apoptosis induction of human lung carcinoma cells by Chan Su (Venenum Bufonis) through activation of caspases. J. Acupunct. Meridian. Stud. 2 (3), 210–217. doi:10.1016/s2005-2901(09)60057-1
Zhang, L., Su, W., Liu, S., Huang, C., Ghalandari, B., Divsalar, A., et al. (2022). Recent progresses in electrochemical DNA biosensors for MicroRNA detection. Phenomics 2 (1), 18–32. doi:10.1007/s43657-021-00032-z
Zhang, Y., Takagi, N., Yuan, B., Zhou, Y., Si, N., Wang, H., et al. (2019). The protection of indolealkylamines from LPS-induced inflammation in zebrafish. J. Ethnopharmacol. 243, 112122. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2019.112122
Zhu, L., Chen, Y., Wei, C., Yang, X., Cheng, J., Yang, Z., et al. (2018). Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of cinobufagin on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells and its molecular mechanism. Nat. Prod. Res. 32 (4), 493–497. doi:10.1080/14786419.2017.1315575
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, Bufonis venenum, liposomes, cell apoptosis, traditional Chinese medicine
Citation: Yang S, Lan J, Li Z, Li M, Wu Y, Sun L, Zhang T and Ding Y (2024) Bufonis venenum extract loaded novel cholesterol-free liposome for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1486742. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1486742
Received: 26 August 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 25 November 2024.
Edited by:
Chen Ling, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Nemany A.N. Hanafy, Kafrelsheikh University, EgyptCopyright © 2024 Yang, Lan, Li, Li, Wu, Sun, Zhang and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tong Zhang, emhhbmd0b25nc2h1dGNtQGhvdG1haWwuY29t; Yue Ding, ZGluZ3l1ZS0yMDAxQGhvdG1haWwuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.