- 1The Third School of Clinical Medicine, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 2School of Clinical Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 4Office of Human Research, Memorial Healthcare System, Florida, United States
- 5School of Basic Medical Sciences, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
Background: Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) is potentially the most valuable water-soluble active component in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Its chemical formula contains multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups, so it has a strong antioxidant capacity.
Objective: We aim to investigate the efficacy and the potential mechanism of Sal B in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke injury.
Materials and methods: CNKI, VIP, WanFang, SinoMed, PubMed and Web of Science were searched for all the literature related to Sal B in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke before August 2024. The methodological quality was assessed using an inspection scale combining the CAMARADES checklist and the new STAIR criteria. Data were analyzed using RevMan5.4 software.
Results: A total of 14 articles were included. Sal B could effectively reduce infarct size, neurological deficit score, brain edema index, and brain water content in cerebral ischemic animals. Sal B could not only increase the content of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and decrease the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) to achieve anti-oxidative stress, but also reduce the level of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) protein to achieve anti-inflammatory response, and reduce the number of TUNEL cells to reflect its anti-apoptosis effect. In addition, Sal B can improve energy metabolism by increasing the content of energy charge (EC) and phosphocreatine (PCr), and maintaining ion balance via Na+/K+ ATPase activity, resulting in the neuroprotective effects against acute ischemic stroke injury.
Conclusion: This study showed that Sal B could significantly protect against acute ischemic stroke injury, mainly through anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory response, anti-apoptosis, improving energy metabolism, and stabilizing ion balance.
1 Introduction
Salvia miltiorrhiza is the dried root and rhizome of Salvia miltiorrhiza in the Labiatae family, which has the effects of vasodilation, myocardial protection, anti-atherosclerosis and anti-thrombosis (Giugliano et al., 2020; Wang G. et al., 2022; He and Chen, 2020; Rosińska et al., 2017), and is widely used in clinical treatment of various cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, including coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction and stroke caused by cerebral ischemia, dementia (Fang et al., 2018; Qin et al., 2021; Guo and Wang, 2022). Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 edition) stipulated that the total amount of tanshinone-containing tanshinone I, IIA and cryptotanshinone should not be less than 0.25%, and salvianolic acid B (Sal B) should not be less than 3.0% as the quality evaluation standard of salvianolic acid. Sal B is a water-soluble compound, while tanshinone I, tanshinone IIA and cryptotanshinone are lipid-soluble compounds (Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, 2020). Therefore, Sal B is potentially the most valuable water-soluble active component in Salvia miltiorrhiza.
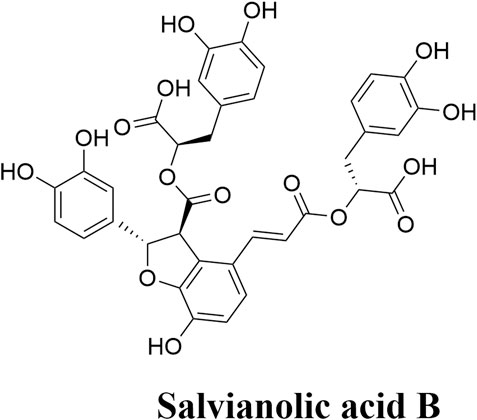
Sal B is a monomer compound formed by the condensation of three molecules of 3,4-dihydroxyphenyllactic acid and one molecule of caffeic acid (Figure 1) (He et al., 2023). There are several phenolic hydroxyl groups in the molecular structure of Sal B, indicating strong antioxidant activity property (Loaiza-Cano et al., 2020). Recently, research results show that Sal B possesses various pharmacological characteristics, such as anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects contributing to improve the injury of acute ischemic stroke (Lee et al., 2023; Xiao et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2021). Sal B has minor side effects with a higher margin of safety (Ding et al., 2017).
Several studies have reported the neuroprotective effects of Sal B on acute ischemic stroke injury (Zhu et al., 2022). The mechanisms underlying its neuroprotective effects have been investigated in animal models of acute ischemic stroke in recent years. In this study, we conducted a systematical review and meta-analysis of studies in animals, aiming at evaluating the therapeutic effects of Sal B against acute ischemic stroke and determining the relevant mechanisms of Sal B in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke, hopefully providing scientific evidence for the clinical application of Sal B in protecting against acute ischemic stroke injury.
2 Materials and methods
This study was reported in accordance with the PRISMA principles (Moher et al., 2009) and the Cochrane Collaboration guidance (Cumpston et al., 2019).
2.1 Literature retrieval strategy
In this study, the Chinese Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) of the National Library of Medicine was used to determine the item term of “ischemic stroke” (DeMars and Perruso, 2022), and the following search strategies were established according to the results: (Sal B) AND (ischemic stroke OR cerebral ischemia OR cerebrovascular disease OR cerebral infarction OR cerebral infarction OR cerebral embolism). Six databases including CNKI, VIP, WanFang, SinoMed, PubMed and Web of Science were searched by two researchers independently. The search period was up to August 2024, and the language of the publications was not restricted. The search results were imported into reference management software.
2.2 Study inclusion and exclusion criteria
Experimental studies in animal models of acute ischemic stroke were included, with no restrictions on animal species, strain, sex, or modeling methods. The experimental group was the acute ischemic stroke model injected with Sal B, and the control group was the acute ischemic stroke model without Sal B injection.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Duplicate or irrelevant literature; (2) Reviews, conference proceedings, dissertations, informal journals, catalogs, etc.; (3) Clinical and other in vitro studies; (4) Animal models unrelated to acute ischemic stroke; (5) Studies involving combination therapies; (6) Studies with incomplete or missing data; (7) Outcome measures could not be extracted or combined.
2.3 Outcome measures
All indicators were divided into primary indicators and secondary indicators according to whether they could directly reflect the efficacy (Li and Zhang, 2021; Zhang et al., 2005). Primary outcome measures included infarct size, neurological deficit score, and brain edema index (brain index, brain water content). Secondary indicators included oxidative stress markers (SOD, MDA), inflammatory markers (IL-1β protein level), apoptosis index (number of TUNEL-positive cells), and cytotoxic edema markers (EC, PCr, Na+/K+ ATPase activity, lactate).
2.4 Literature screening and data extraction
Two researchers searched independently according to strict inclusion and exclusion criteria, and all data were screened and extracted in Noteexpress software. Any disagreements on the eligibility of studies were resolved by discussing with the third investigator.
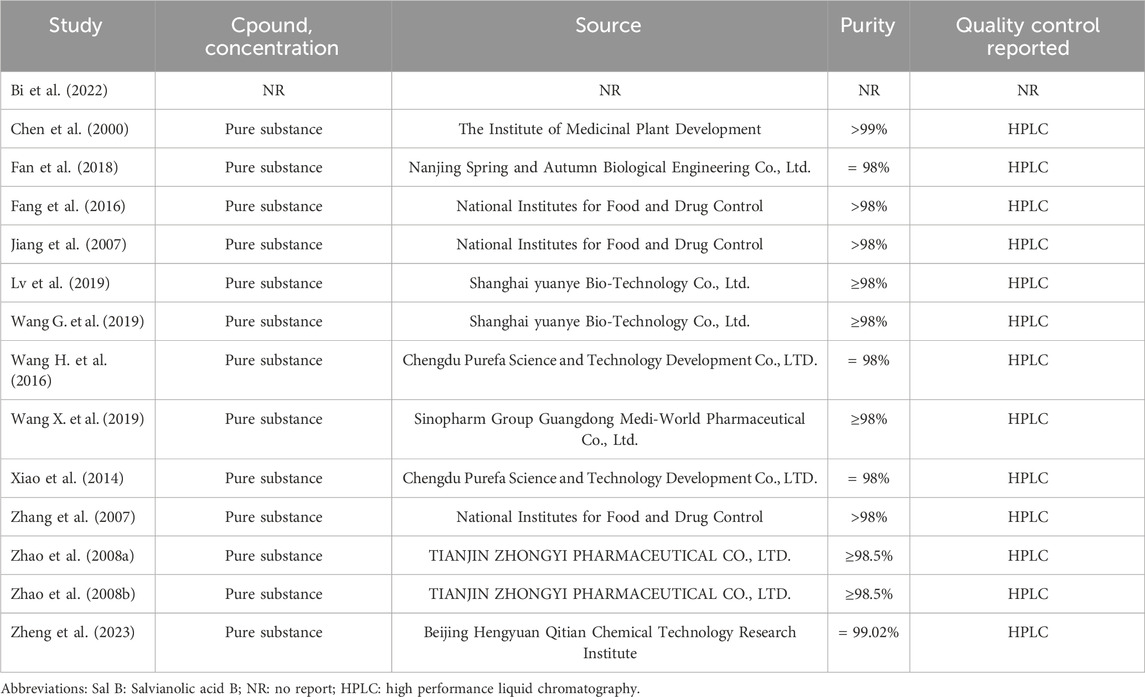
Data were extracted from original text, tables, figures, supplementary materials and methods, and references. GetData Graph Digitizer software was used to extract data in literature that only presented data in the form of images. The experimental part included intervention design, administration route, administration dose, treatment time, and outcome indicators, in which the outcome indicator was the difference of Sal B before and after intervention. The model part included animal species, strain, sex, age, weight, ischemia type and modeling method. The material section included drug purity, source, etc. In addition, general information such as author, country, and year of publication was collected.
2.5 Quality assessment and risk of bias
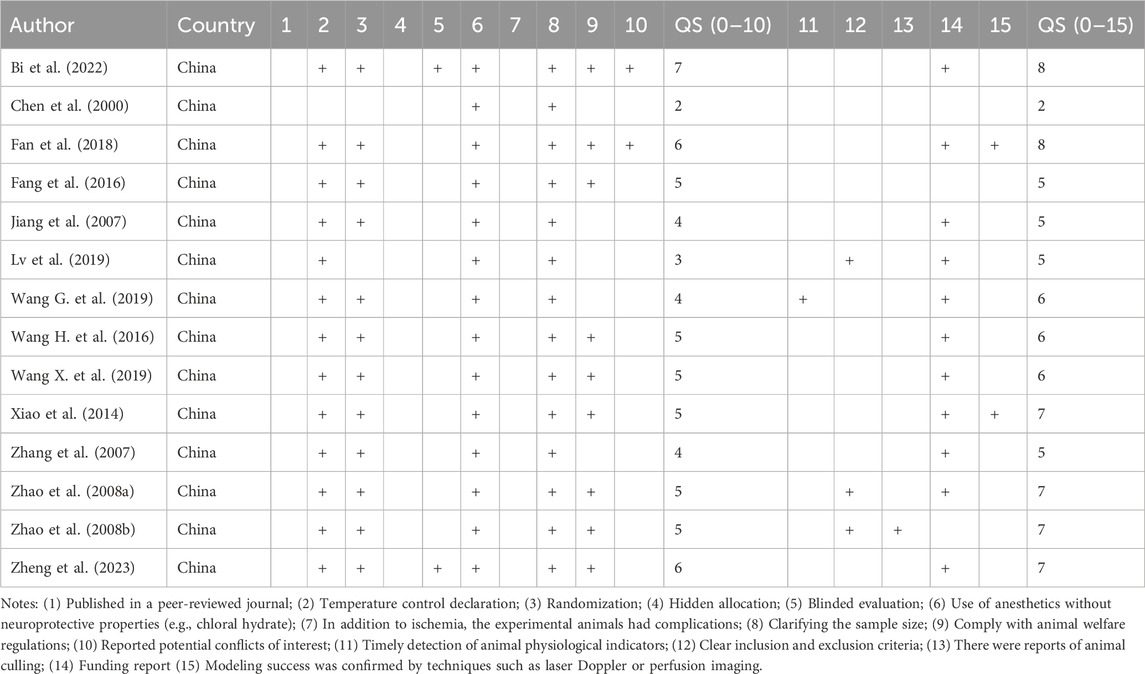
An inspection scale (Aliena-Valero et al., 2021) including the CAMARADES (Sena et al., 2007) criteria and the STAIR criteria (Fisher et al., 2009) was used for quality assessment: (1) Published in a peer-reviewed journal; (2) Temperature control declaration; (3) Randomization; (4) Hidden allocation; (5) Blinded evaluation; (6) Use of anesthetics without neuroprotective properties (e.g., chloral hydrate); (7) In addition to ischemia, the experimental animals had complications; (8) Clarifying the sample size; (9) Comply with animal welfare regulations; (10) Reported potential conflicts of interest; (11) Timely detection of animal physiological indicators; (12) Clear inclusion and exclusion criteria; (13) There were reports of animal culling; (14) Funding report (15) Modeling success was confirmed by techniques such as laser Doppler or perfusion imaging.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical software Rev man 5.4 was used to analyze the collected data. The mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD) was used to report the pooled effect estimate for continuous variables with their 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity among studies was categorized by the I2 statistic as follows: I2<50% indicated low or non-significant heterogeneity, and the fixed effect models were used, and I2 > 50%, represented high heterogeneity, and the random effect models were used. For the literature with high heterogeneity, subgroup analysis or sensitivity analysis was further analyzed according to the actual situation to determine the source of heterogeneity.
3 Result
3.1 Included literature
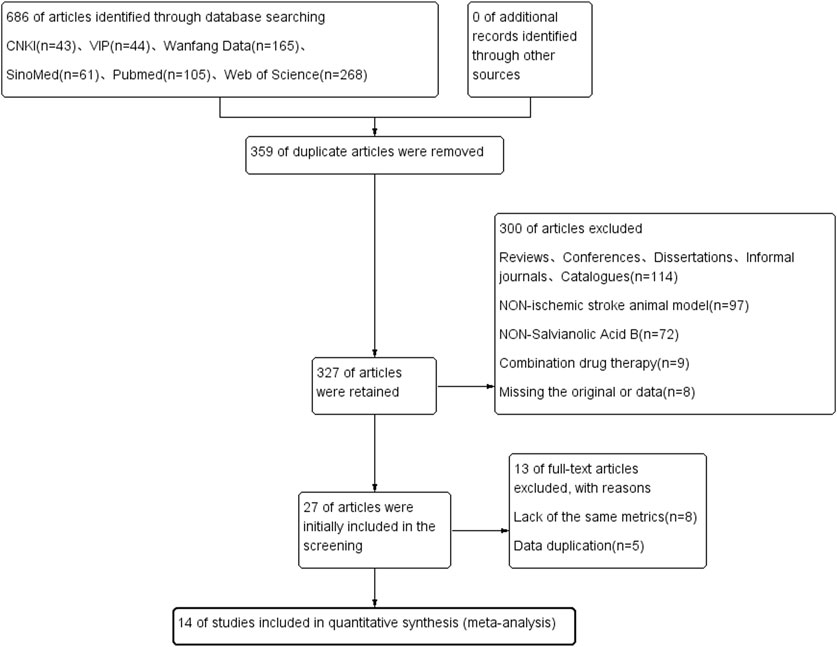
A total of 686 literatures were retrieved from six databases including CNKI and Wanfang. Among these, 359 duplicates and 114 reviews, conferences, dissertations, unofficial journals, and catalog literature were excluded. We screened the literature according to the title and abstract of the literature, and excluded the literature of non-non-animal models (n = 97), non-salvianolic acid B (n = 72), combination drugs (n = 9), and loss of original text and incomplete data reporting (n = 9), leaving 27 literatures were reviewed, and a further 13 excluded. The remaining 14 articles finally met the inclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. The study selection flow chart is shown in Figure 2.
3.2 Study characteristics and quality assessment
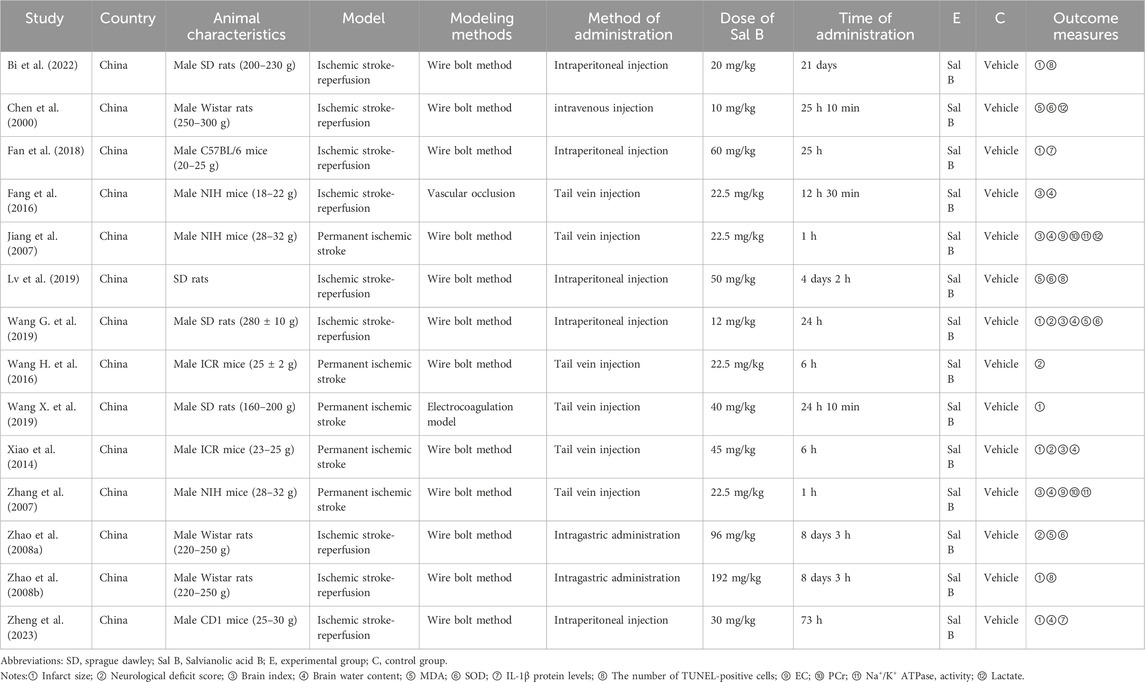
Tables 1, 2 summarize the characteristics of the included studies. Of the 14 studies, 7 studies were conducted in rats and 7 in mice. The dosage of Sal B ranged from 10 mg/kg to 192 mg/kg, and was administrated via the tail veins or intraperitoneal injections. All studies used anesthetics with no apparent intrinsic neuroprotective properties. Two studies did not explicitly mention the non-randomized controls, and the rest of the studies were randomized controlled trials. In the study design, two studies mentioned the use of a blinded method to assess outcomes, three studies had pre-specified inclusion and exclusion criteria, and one study reported the exclusion of animals for analysis. One study did not mention temperature control during ischemia induction. In addition, nine studies explicitly issued statements of compliance with animal welfare requirements, and eleven studies explicitly reported research funding. The results are shown in Table 3.
3.3 Included literature
3.3.1 Infarct size
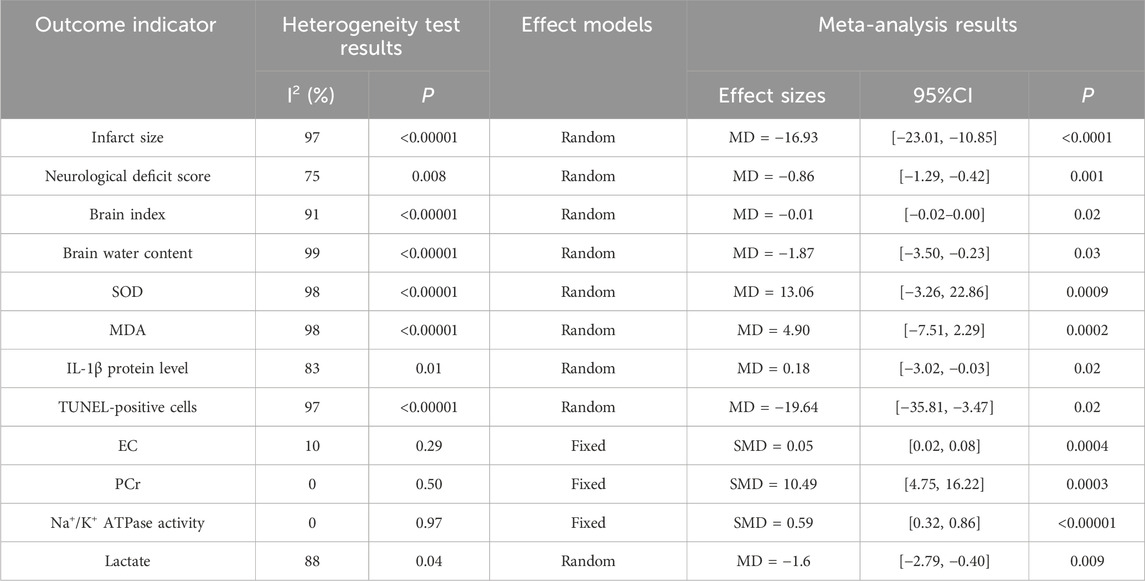
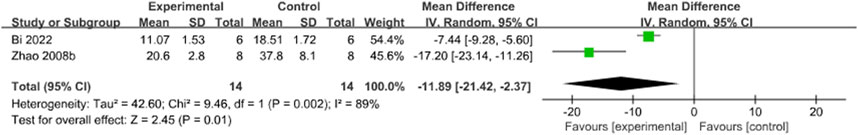
Seven studies (Bi et al., 2022; Fan et al., 2018; Wang G. et al., 2019; Wang X. et al., 2019; Xiao et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2008b; Zheng et al., 2023) reported the effects of Sal B on infarct size following acute ischemic stroke injury. The results showed that Sal B could effectively reduce infarct size (MD = −16.93, 95%CI = [−23.01, −10.85]; I2 = 97%, P < 0.0001) (Table 4).
3.3.2 Neurological deficit score
Four studies reported the effects of Sal B on neurological deficit score (Wang G. et al., 2019; Wang H. et al., 2016; Xiao et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2008a). The results showed that Sal B could effectively reduce neurological deficit score (MD = −0.86, 95% CI = [−1.29, −0.42]; I2 = 75% P = 0.001) (Table 4).
3.3.3 Brain index
Five studies reported the effects of Sal B on brain index following acute ischemic stroke injury (Fang et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2007; Wang G. et al., 2019; Xiao et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2007). The results showed that Sal B could effectively reduce the brain index (MD = −0.01, 95%CI = [-0.02, −0.00]; I2 = 91%; p = 0.02) (Table 4).
3.3.4 Brain water content
Six studies (Fang et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2007; Wang G. et al., 2019; Xiao et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2007; Zheng et al., 2023) reported the effects of Sal B on brain water content following acute ischemic stroke injury. The results showed that Sal B could effectively reduce brain water content (MD = −1.87, 95%CI = [−3.50, −0.23]; I2 = 99%; P = 0.03) (Table 4).
3.3.5 SOD
Four studies (Chen et al., 2000; Lv et al., 2019; Wang G. et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2008a) reported the effects of Sal B on brain SOD content following acute ischemic stroke injury. The results showed that Sal B could significantly increase the activity of SOD (MD = 13.06, 95%CI = [−3.26, 22.86]; I2 = 98%; P = 0.0009) (Table 4).
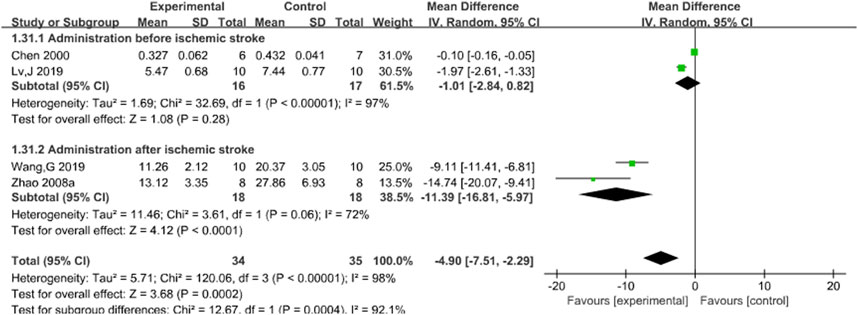
3.3.6 MDA
Four studies (Chen et al., 2000; Lv et al., 2019; Wang G. et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2008a) reported the effects of Sal B on brain MDA content following acute ischemic stroke injury. The results showed that Sal B could significantly increase the activity of MDA (MD = 4.90, 95%CI = [−7.51, 2.29]; I2 = 98%; P = 0.0002) (Table 4).
3.3.7 IL-1β protein levels
Two studies reported the effects of Sal B on IL-1β protein levels following cerebral ischemic injury (Fan et al., 2018; Zheng et al., 2023). The results showed that Sal B could effectively increase the content of IL-1β protein (MD = 0.18, 95%CI = [−3.02, −0.03]; I2 = 83%; P = 0.02) (Table 4).
3.3.8 The number of TUNEL-positive cells
Three articles [24, 29, 36] reported the effects of Sal B on the number of TUNEL-positive cells in the ischemic brain tissues. The results showed that Sal B could effectively reduce the number of TUNEL-positive cells (MD = −19.64, 95%CI = [−35.81, −3.47]; I2 = 97%; P = 0.02) (Table 4).
3.3.9 Energy charge
Two articles (Jiang et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2007) reported the effects of Sal B on EC. The results showed that Sal B could effectively improve EC (SMD = 0.05, 95%CI = [0.02, 0.08]; I2 = 10%; P = 0.0004) (Table 4).
3.3.10 Phosphocreatine
Two articles (Jiang et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2007) reported the effects of Sal B on brain PCr activity. The results showed that Sal B could effectively improve the PCr content (SMD = 10.49, 95%CI = [4.75, 16.22]; I2 = 0%; P = 0.0003) (Table 4).
3.3.11 Na+/K+ ATPase activity
Two studies reported the effects of Sal B on brain Na+/K+ ATPase activity (Jiang et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2007). The results showed that Sal B could effectively improve Na+/K+ ATPase activity (SMD = 0.59, 95%CI = [0.32, 0.86]; I2 = 0%; P < 0.00001) (Table 4).
3.3.12 Lactate
Two articles reported the effects of Sal B on brain lactate content (Chen et al., 2000; Jiang et al., 2007). The results showed that Sal B could effectively reduce brain lactate content (MD = −1.6, 95%CI = [−2.79, −0.40]; I2 = 88%; P = 0.009) (Table 4).
3.4 Sensitivity analysis
3.4.1 Infarct size
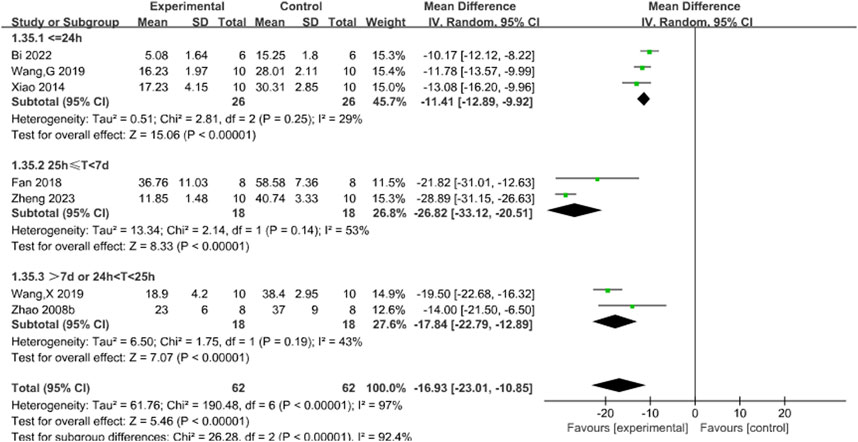
Subgroup analyses used the duration of treatment as the grouping criterion. We found that the I2 decreased to 29% for treatment duration of less than 24 h (P < 0.00001), 53% for treatment duration of 25 h to 7 days (P < 0.00001), and 43% for treatment duration of more than 7 days or more than 24 h or less than 25 h, suggesting that differences in treatment duration may be the main source of heterogeneity. The new pooled results showed that Sal B was effective in reducing infarct size (Figure 3).
3.4.2 Neurological deficit score
Subgroup analyses were conducted using the duration of treatment as the grouping criterion (<24 or ≥24 h). The results showed that Sal B could effectively reduce the neurological deficit score (Figure 4).
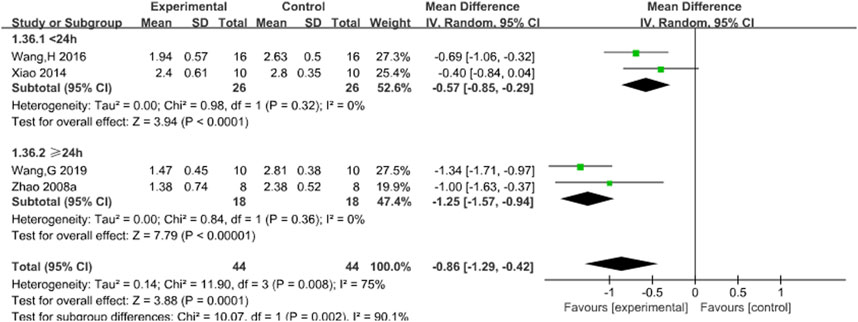
Figure 4. Forest chart of neurological deficit score divided into subgroups according to the treatment time.
3.4.3 Brain index
Subgroup analysis was conducted based on the timing of administration. The results showed that there was still a significant difference in the pre-ischemia group, and the difference was not statistically significant (I2 = 87%, P = 0.20). However, I2 decreased significantly to 48% (P = 0.0003) in the post-ischemia group, suggesting that timing of administration may be a potential source of brain index heterogeneity. The results support that Sal B can effectively reduce brain index. See Figure 5.
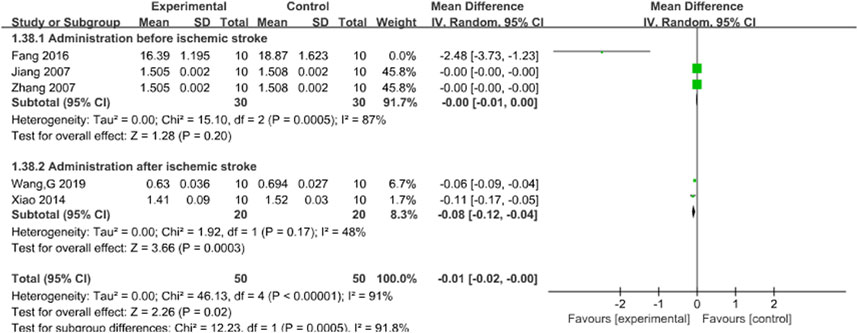
Figure 5. Forest chart of brain index divided into subgroups according to administration time point.
3.4.4 Brain water content
The timing of administration was used as the criterion for subgroup analysis. In subgroup analysis of brain water content, It was observed that I2 decreased to 73% (P = 0.007) in the pre-ischemia group, whereas I2 remained at 99% after ischemia. Thus, different timing of administration may be the primary source of heterogeneity, and the results support the efficacy of Sal B in reducing brain water content after ischemia. See Figure 6.
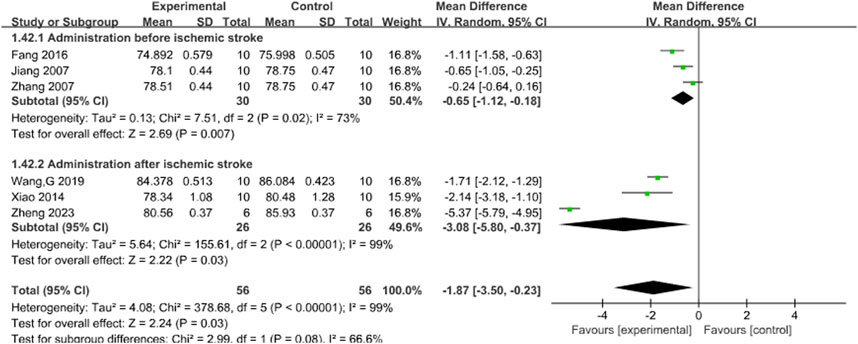
Figure 6. Forest plot of brain water content divided into subgroups according to the timing of administration.
3.4.5 SOD
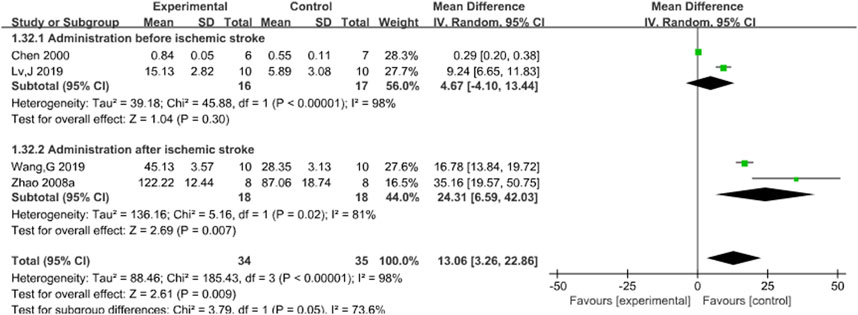
Subgroup analysis was conducted based on the timing of administration. Results indicated no statistical significance in administration before acute ischemic stroke (P = 0.30), but I2 decreased to 81% after acute ischemic stroke (P = 0.007), which was statistically significant, suggesting that different timing of administration may be the potential source of heterogeneity. Nevertheless, the results support the ability of Sal B to increase SOD content after acute ischemic stroke. See Figure 7.
3.4.6 MDA
Subgroup analysis was conducted based on the timing of administration. The results showed that there was no statistical significance in preischemic stroke administration (P = 0.28), but Z was 4.12 (P < 0.00001) after ischemic stroke administration. This finding was statistically significant, suggesting that different timing of administration might be a potential source of heterogeneity. However, the results still support the efficacy of Sal B in reducing MDA content after acute ischemic stroke. See Figure 8.
3.4.7 The number of TUNEL-positive cells
After systematically excluding individual studies, it was found that The study by Lv et al. (2019), may be the primary source of heterogeneity, and I2 decreased from 97% to 89% after removing the literatures. Due to the limited number of studies included in this analysis, it is speculated that this study had drug administration before ischemia, while the other two studies were administered after ischemia, which ultimately led to heterogeneity. Nonetheless, the findings continue to support the ability of Sal B to decrease the number of TUNEL-positive cells following acute ischemic stroke. See Figure 9.
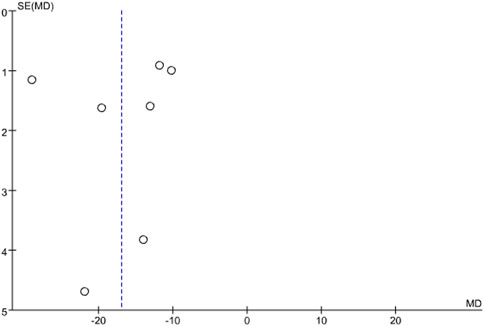
3.5 Publication bias
Publication bias was assessed for infarct size using a funnel plot. The results showed that the points on the funnel plot were asymmetrically distributed along the centerline, indicating the presence of publication bias. See Figure 10.
4 Discussion
This meta-analysis demonstrated the effectiveness of Sal B in reducing infarct size and neurological deficit score in animal models of acute ischemic stroke. In addition, the decrease in both brain index and brain water content also reflected that Sal B was effective in alleviating brain edema. This meta-analysis has shown that Sal B can achieve neuroprotective effects through a variety of actions, including:
① Anti-oxidative stress: When the brain tissue is subjected to ischemic injury, a lot of free radicals would be produced and oxidative stress reaction would occur, which results in brain tissue damage. SOD and MDA are common indicators of oxidative stress (Yang et al., 2022; Fu et al., 2022). SOD is a major antioxidant enzyme, which can capture highly active free radicals produced during various chemical reactions and make them inactivate or inert. MDA is the final product of free radicals acting on lipid peroxidation, which has cytotoxicity. Sal B can alleviate brain injury by manipulating the level of SOD and MDA, scavenging oxygen free radicals and inhibiting oxidative stress;
② Anti-inflammatory response: IL-1 is an important pro-inflammatory factor, and IL-1β is the main existing form in brain tissue. Under normal physiological conditions, IL-1β is only expressed at a low level in the brain. After acute ischemic stroke, IL-1β will be released considerably, inducing the production of other inflammatory mediators and resulting in damaging neurons (Yu et al., 2022; Zeng et al., 2022). Sal B can low the level of IL-1β and the expression of inflammatory factors, resulting in reducing the inflammatory response in the brain.
③ Anti-apoptosis: TUNEL staining is often used to evaluate the apoptosis of nerve cells during acute ischemic stroke (Resnick-Silverman, 2021). Sal B could reduce the number of TUNEL-positive cells.
④ Improve energy metabolism: Under aerobic conditions, ADP in the body can react with phosphocreatine (PCr) to generate ATP (Brewster, 2018). Energy charge (EC) is an important parameter that dynamically reflects the state of mutual conversion between ADP and ATP, and a high value of EC indicates active ATP production in cells (Wilson and Matschinsky, 2022). When acute ischemic stroke occurs, aerobic oxidation is impaired, anaerobic glycolysis is enhanced, and the end product lactate is increased and accumulated in tissues, leading to acidosis (Xu et al., 2020). Sal B can increase the EC value and PCr content of ischemic brain tissue, thus inhibiting the production of lactate and improving energy metabolism disorders.
⑤ Stable ion balance: In the early stage of ischemia, energy depletion first affects the function of ion pump. Na+/K+ ATPase cannot maintain the ion balance in and out of cells when energy is scarce, which leads to the accumulation of sodium in cells (Li et al., 2021; Alquisiras-Burgos et al., 2020). The results showed that Sal B could increase the Na+/K+ ATPase activity, maintaining ion balance inside and outside the cells.
In addition, we analyzed and summarized other studies that met the criteria for “Sal B in acute ischemic stroke” but could not be combined for analysis. The results showed that Sal B also ameliorated acute ischemic stroke damage by: ① Anti-excitotoxicity: Excessive accumulation of glutamate in the intercellular space is the main source of neurotoxic reactions. The results showed that Sal B can significantly reduce the content of glutamate in brain tissue to inhibit excitatory amino acid toxicity and play a neuroprotective role. ② Anti-platelet aggregation: Platelets are activated and aggregated to form a large number of thrombi to block blood vessels, resulting in insufficient blood and oxygen supply to brain tissue. The results showed that Sal B can effectively combat acute ischemic stroke by inhibiting platelet aggregation and reducing thrombosis. ③ Promoting angiogenesis: VEGF and its receptor molecule VEGFR can improve vascular permeability, promote the generation of cerebral blood vessels by promoting the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells. The results showed that Sal B can promote angiogenesis in time by up-regulating the expression of VEGFR2 and VEGFA, thereby reducing acute ischemic stroke injury.
According to the included studies, 8 studies were administered 7 days to 10 min before cerebral ischemia, and 6 studies were administered immediately or 1 h after cerebral ischemia, both of which had a significant therapeutic effect. The concentration of Sal B between 10 and 192 mg/kg will play a better therapeutic effect, and the longer the treatment time, the more significant the effect. However, more studies are needed to confirm the optimal timing, dosage and duration of administration.
Limitations and future directions: (1) Some studies included in the meta-analysis were downgraded in quality due to lack of blinding during induction and uncontrolled temperature. (2) Given the limited sample size, further research is warranted. (3) It is necessary to further study the mechanism of Sal B. (4) At the same time, better administration timing, the optimal dose and treatment time of Sal B should be understood to improve the efficacy of anti-ischemic stroke.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study highlights the significant therapeutic potential of Sal B in treating acute ischemic stroke. Sal B can reduce infarct size, improve neurological deficit symptoms and reduce brain edema by anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory response, anti-apoptosis, improving energy metabolism and stabilizing ion balance, thus achieving neuroprotection. It has great potential in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
Author contributions
JW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. PS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. CW: Data curation, Validation, Writing–original draft. YX: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing–original draft. JH: Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing–original draft. JN: Writing–review and editing. ZJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 81774010.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aliena-Valero, A., Baixauli-Martín, J., Castelló-Ruiz, M., Torregrosa, G., Hervás, D., and Salom, J. B. (2021). Effect of uric acid in animal models of ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 41 (4), 707–722. doi:10.1177/0271678X20967459
Alquisiras-Burgos, I., Ortiz-Plata, A., Franco-Pérez, J., Millán, A., and Aguilera, P. (2020). Resveratrol reduces cerebral edema through inhibition of de novo SUR1 expression induced after focal ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 330, 113353. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113353
Bi, S. J., Dong, X. Y., Wang, Z. Y., Fu, S. J., Li, C. L., Wang, Z. Y., et al. (2022). Salvianolic acid B alleviates neurological injury by upregulating stanniocalcin 1 expression. Ann. Transl. Med. 10 (13), 739. doi:10.21037/atm-21-4779
Brewster, L. M. (2018). Creatine kinase, energy reserve, and hypertension: from bench to bedside. Ann. Transl. Med. 6 (15), 292. doi:10.21037/atm.2018.07.15
Chen, Y. H., Du, G. H., and Zhang, J. T. (2000). Salvianolic acid B protects brain against injuries caused by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 21 (5), 463–466.
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2020). The pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2020 Edition. Available at: https://ydz.chp.org.cn/#/main.
Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M. J., Chandler, J., Welch, V. A., Higgins, J. P., et al. (2019). Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane database Syst. Rev. 10 (10), ED000142. doi:10.1002/14651858.ED000142
DeMars, M. M., and Perruso, C. (2022). MeSH and text-word search strategies: precision, recall, and their implications for library instruction. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 110 (1), 23–33. doi:10.5195/jmla.2022.1283
Ding, S. S., Yao, J., Ling, Z., and Li, Y. Y. (2017). Safety study of salvianolic acid B. West China J. Pharm. Sci. 1, 49–51. doi:10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2017.01.016
Fan, Y., Luo, Q., Wei, J., Lin, R., Lin, L., Li, Y., et al. (2018). Mechanism of salvianolic acid B neuroprotection against ischemia/reperfusion induced cerebral injury. Brain Res. 1679, 125–133. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2017.11.027
Fang, J., Little, P. J., and Xu, S. (2018). Atheroprotective effects and molecular targets of tanshinones derived from herbal medicine danshen. Med. Res. Rev. 38 (1), 201–228. doi:10.1002/med.21438
Fang, L., Yang, M., and Jiang, Y. (2016). Protective effect of salvianolic acid B on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med. 34 (12), 3060–3062. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2016.12.069
Fisher, M., Feuerstein, G., Howells, D. W., Hurn, P. D., Kent, T. A., Savitz, S. I., et al. (2009). Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable preclinical recommendations. Stroke 40 (6), 2244–2250. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.541128
Fu, C., Wu, Y., Liu, S., Luo, C., Lu, Y., Liu, M., et al. (2022). Rehmannioside A improves cognitive impairment and alleviates ferroptosis via activating PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 and SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling pathway after ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 289, 115021. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115021
Giugliano, R. P., Pedersen, T. R., Saver, J. L., Keech, P. S., Sever, A. C., Bohula, E. A., et al. (2020). Stroke prevention with the PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9) inhibitor evolocumab added to statin in high-risk patients with stable atherosclerosis. Stroke 51 (5), 1546–1554. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027759
Guo, S. S., and Wang, Z. G. (2022). Salvianolic acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge: a potential antitumor agent. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1042745. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1042745
He, D., and Chen, Y. (2020). Study on the mechanism of tanshinone IIA in the treatment of atherosclerosis through 5-lipoxygenase/leukotriene pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-/Cerebrovascuiar Dis. 18 (23), 3959–3962. doi:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2020.23.010
He, G., Chen, G., Liu, W., Ye, D., Liu, X., Liang, X., et al. (2023). Salvianolic acid B: a review of pharmacological effects, safety, combination therapy, new dosage forms, and novel drug delivery routes. Pharmaceutics 15 (9), 2235. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15092235
Jiang, Y., Liu, Z. Q., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. Z., Wang, Q., Liu, S., et al. (2007). Effect of salvianolic acid B on high-energy phosphate compounds and lactate in mice with cerebral ischemia. J. Beijing Univ. Traditional Chin. Med. 8, 522–524. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1006-2157.2007.08.005
Lee, H. G., Kwon, S., Moon, S. K., Cho, S. Y., Park, S. U., Jung, W. S., et al. (2023). Neuroprotective effects of geopung-chunghyuldan based on its salvianolic acid B content using an in vivo stroke model. Curr. issues Mol. Biol. 45 (2), 1613–1626. doi:10.3390/cimb45020104
Li, L. L., Ke, X. Y., Jiang, C., Qin, S. Q., Liu, Y. Y., Xian, X. H., et al. (2021). Na+, K+ -ATPase participates in the protective mechanism of rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion through the interaction with glutamate transporter-1. Fundam. and Clin. Pharmacol. 35 (5), 870–881. doi:10.1111/fcp.12652
Li, Y., and Zhang, J. (2021). Animal models of stroke. Anim. Model Exp. Med. 4 (3), 204–219. doi:10.1002/ame2.12179
Loaiza-Cano, V., Monsalve-Escudero, L. M., Filho, CDSMB., Martinez-Gutierrez, M., and Sousa, D. P. (2020). Antiviral role of phenolic compounds against dengue virus: a review. Biomolecules 11 (1), 11. doi:10.3390/biom11010011
Lv, J., Zhao, H. M., Sun, G. F., and Wang, R. Q. (2019). The protective effect of salvianolic acid B on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inducing angiogenesis and alleviating oxidative stress. Chin. J. Immunol. 35 (10), 1174–1178. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2019.10.005
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G.PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 6 (7), e1000097. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Qin, W., Xing, L., Yang, Z., Jia, Y., Jin, J., Guo, M., et al. (2021). Research progress on the role and mechanism of active components of Salvia miltiorrhiza in anti-atherosclerosis. Shaanxi J. Traditional Chin. Med. 42 (07), 977–979. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2021.07.044
Resnick-Silverman, L. (2021). Using TUNEL assay to quantitate p53-induced apoptosis in mouse tissues. Methods Mol. Biol. 2267, 181–190. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-1217-0_12
Rosińska, J., Łukasik, M., and Kozubski, W. (2017). The impact of vascular disease treatment on platelet-derived microvesicles. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 31 (5-6), 627–644. doi:10.1007/s10557-017-6757-7
Sena, E., van der Worp, H. B., Howells, D., and Macleod, M. (2007). How can we improve the pre-clinical development of drugs for stroke? Trends Neurosci. 30 (9), 433–439. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2007.06.009
Wang, G., Ma, L., Wang, B., Gao, F., Li, J., Cai, H., et al. (2022). Tanshinone IIA accomplished protection against radiation-induced cardiomyocyte injury by regulating the p38/p53 pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 1478181. doi:10.1155/2022/1478181
Wang, G., Zhang, L., Chen, B., Zhang, Y. Y., Kong, L., and Han, J. (2019). Protective effect of salvianolic acid B in salvia miltiorrhiza on volume -reperfusion injury in rats. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med. 37 (07), 1566–1568. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2019.07.006
Wang, H., Zhong, X. M., Chen, M., Lou, Y. L., Gong, X. Y., Xiao, W. X., et al. (2016). Effect of salvianolic acid B on TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in mice with acute cerebral ischemia. Acta Univ. Tradit. Medicalis Sin. Pharmacol. Shanghai 30 (02), 57–61. doi:10.16306/j.1008-861x.2016.02.014
Wang, X., Song, J., and Wang, J. (2019). Effect and mechanism of salvianolic acid B on cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Bengbu Med. Coll. 44 (06), 705–707+711. doi:10.13898/j.cnki.issn.1000-2200.2019.06.002
Wilson, D., and Matschinsky, F. (2022). Integration of eukaryotic energy metabolism: the intramitochondrial and cytosolic energy states ([ATP]f/[ADP]f[Pi]). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (10), 5550. doi:10.3390/ijms23105550
Xiao, W. X., Wang, H., Zhong, X. M., and Huang, Z. (2014). Neuroprotective effect of salvianolic acid B on acute focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Chin. J. Exp. Traditional Med. Formulae 20 (17), 163–166. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2014170163
Xiao, Z., Liu, W., Mu, Y. P., Zhang, H., Wang, X. N., Zhao, C. Q., et al. (2020). Pharmacological effects of salvianolic acid B against oxidative damage. Front. Pharmacol. 11, 572373. doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.572373
Xu, J., Zheng, Y., Lv, S., Kang, J., Yu, Y., Hou, K., et al. (2020). Lactate promotes reactive astrogliosis and confers axon guidance potential to astrocytes under oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neuroscience 442, 54–68. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.06.041
Yang, L., Tao, Y., Luo, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., and Meng, X. (2022). Dengzhan Xixin injection derived from a traditional Chinese herb Erigeron breviscapus ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via modulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 288, 114988. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.114988
Yu, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, Q., He, Y., Zhou, H., Wan, H., et al. (2022). Formononetin protects against inflammation associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by targeting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 149, 112836. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112836
Zeng, X., Zhang, Y. D., Ma, R. Y., Chen, Y. J., Xiang, X. M., Hou, D. Y., et al. (2022). Activated Drp1 regulates p62-mediated autophagic flux and aggravates inflammation in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via the ROS-RIP1/RIP3-exosome axis. Mil. Med. Res. 9 (1), 25. doi:10.1186/s40779-022-00383-2
Zhang, J. H., Song, H. J., and Li, S. Y. (2005). Protective effect and mechanism of daisies gentienone on focal cerebral ischemia injury. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 21 (2), 220–224. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1001-1978.2005.02.024
Zhang, Y., Jiang, Y. F., Liu, Z. Q., Ren, L. W., Wang, Q., Wang, W. R., et al. (2007). Effects of salvianolic acid B on brain energy metabolism and brain edema at different times of cerebral ischemia in mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. 12, 1250–1253. doi:10.16438/j.0513-4870.2007.12.002
Zhao, X., Fan, Y., and Du, Y. (2008a). Effect of salvianolic acid B on serum superoxide dismutase activity and malondialdehyde content in rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Tianjin J. Traditional Chin. Med. 1, 63–65.
Zhao, X., Fan, Y., Xu, X., and Guo, M. J. (2008b). Pathological changes of brain tissue in rats with ischemic brain injury and the intervention effect of salvianolic acid B. Chin. J. Stroke 2, 109–113. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5765.2008.02.007
Zheng, X., Liu, H., Ma, M., Ji, J., Zhu, F., and Sun, L. (2021). Anti-thrombotic activity of phenolic acids obtained from Salvia miltiorrhiza f. alba in TNF-α-stimulated endothelial cells via the NF-κB/JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Arch. Pharm. Res. 44 (4), 427–438. doi:10.1007/s12272-021-01325-7
Zheng, X. F., Zhang, X. J., Dong, L. P., Zhao, J. R., Zhang, C., and Chen, R. (2023). Neuroprotective mechanism of salvianolic acid B against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice through downregulation of TLR4, p-p38MAPK, p-JNK, NF-κB, and IL-1β. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 11 (10), e1030. doi:10.1002/iid3.1030
Keywords: salvianolic acid B, acute ischemic stroke injury, MCAO, Neuroprotection, meta-analysis
Citation: Wang J, Su P, Wan C, Xu Y, Huang J, Niu J and Jin Z (2024) Role of salvianolic acid B in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal models. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1479765. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1479765
Received: 12 August 2024; Accepted: 04 December 2024;
Published: 24 December 2024.
Edited by:
Alessandra Durazzo, Council for Agricultural Research and Economics, ItalyCopyright © 2024 Wang, Su, Wan, Xu, Huang, Niu and Jin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhuqing Jin, amluenFAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jiashan Wang1†
Jiashan Wang1† Pingping Su
Pingping Su Zhuqing Jin
Zhuqing Jin