- 1State Key Laboratory for Macromolecule Drugs and Large-Scale Manufacturing, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng, China
- 2Liaocheng Key Laboratory of Quality Control and Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Ganoderma Lucidum, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng, Shandong, China
A series of para-quinone methide derivatives were evaluated their anti-inflammatory activity. Through the screening of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory cell model in Raw264.7 cells, it was found that the inhibitory activity of meta-substituted derivatives on NO production was superior to that of ortho- and para-substituted derivatives. Among them, in the inflammatory cell model, the meta-trifluoromethyl substituted para-quinone methide derivative 1i had the best activity in inhibiting LPS-induced excess generation of NO. And 1i could effectively inhibit the increase of ROS in inflammatory cells, the expression of iNOS related to the production of NO, and the expressions of inflammation related initiating protein TLR4, pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α, inflammasome NLRP3 and Caspase1. In the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced ulcerative colitis (UC) mouse model, the active derivative 1i could inhibit DSS-induced colon shortening, and reverse DSS-induced pathological changes in colon tissue, such as inflammatory infiltration, structural destruction and crypt disappearance. 1i could effectively inhibit oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in UC mice. Moreover, through the determination of serum biochemical indicators, tissue pathologies and tissue organ indexes, 1i could effectively reverse the damage to mouse liver and kidney caused by DSS, playing a protective role in liver and kidney of mice. In summary, 1i was an effective anti-inflammatory reagent and could be developed as a potential drug for anti-UC.
1 Introduction
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) characterized by pathological mucosal damage and ulcers. At present, the treatment of UC can achieve clinical relief for most patients, but it is prone to recurrence and has poor long-term efficacy. UC is known as “green cancer”; Patients with UC face a higher risk of developing colon cancer (Eaden et al., 2001; Jess et al., 2012). In addition, most drugs used for its treatment can lead to serious side effects (Li et al., 2023; Harbord et al., 2017; Kawalec and Malinowski, 2015).
The structure-activity relationship (SAR) of drugs refers to the relationship between chemical structures and physiological activities, and is one of the main research topics in medicinal chemistry. Studying the relationship between the chemical structures and biological activities of derivatives can help identify which chemical modifications to the structure can enhance their activity or reduce their toxic effects. Structural analogues dominated by natural active products or known drugs have made significant contributions to the development of drugs.
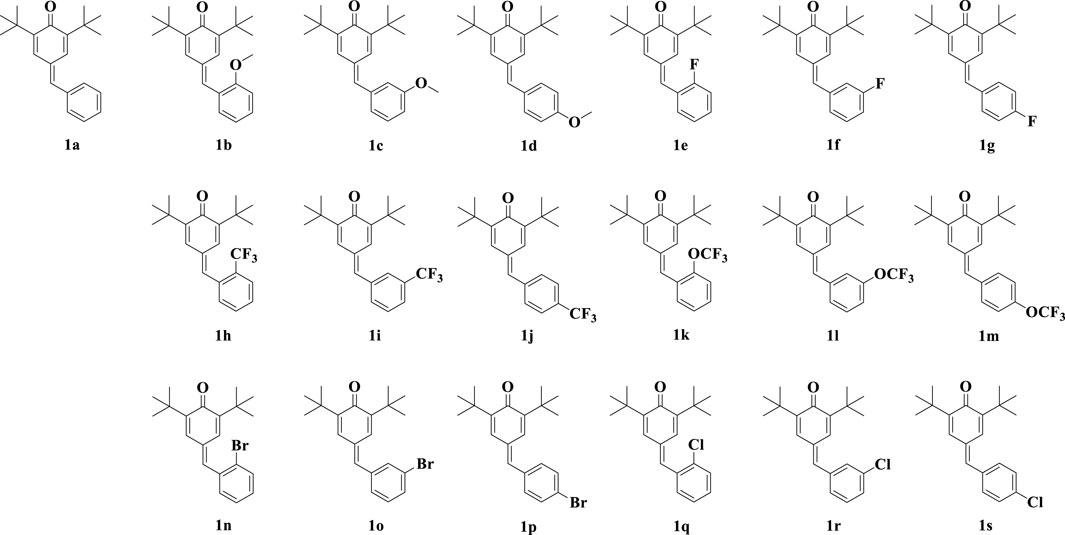
Quinone methides are a class of biologically active compounds that can be used as antiviral, antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents in medicine (Kula et al., 2023). In our previous work (Li et al., 2022), we synthesized a series of para-quinone methide derivatives with different electron withdrawing/donating groups (methoxy, fluorine, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, bromine or chlorine) in the ortho-, meta-, or para-positions of the benzene ring (Figure 1), and systematically studied their SAR. Among them, the derivatives with ortho-substitution showed the best anti-proliferation activity in several cancer cells. Especially, the active ortho-trifluoromethyl substituted para-quinone methide derivative 1h showed certain safety in vivo and could exhibit potential anti-tumor activity by inhibiting thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) in vivo and in vitro.
Additionally, we found that ortho-fluorine, trifluoromethyl, and methoxy substituted hybrid derivatives of curcumin and β-ionone exhibited stronger anti-cancer activity than their corresponding meta and para-substituted compounds (Yang et al., 2020). While, the hybrid derivatives with meta-substitutions exhibited good anti-inflammatory activity in both the inflammatory Raw264.7 cell model induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and the UC mouse model induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) (Ma et al., 2022).
Therefore, in this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory activity of these synthesized para-quinone methide derivatives. Exploring the SAR of nitric oxide (NO) inhibitory activity in the LPS-induced inflammatory Raw264.7 cell model; And investigating the in vivo activity of active hybrid derivatives in the DSS-induced UC mouse model.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 LPS induced NO generation in RAW264.7 cells
Inoculate 100 μL of Raw264.7 cells (SCSP-5036, Center for excellence in molecular cell science of the Chinese academy of sciences) into a 96 well plate at a density of 1 × 106 cells/mL. After 24 h of incubation, discard the original culture medium and add fresh culture medium DMEM (C3113-0500, Hyclone) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (C04001-500, Gibco) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution (C0222, Beyotime) containing LPS (1 μg/mL, S1732, Beyotime) and corresponding concentrations of compounds. After continue incubation for 24 h, take 75 μL of culture medium supernatant and 75 μL of freshly prepared Griess reagent (0.1% N-(1-naphthyl)-ethylenediamine dihydrochloride, 1% sulfonamide, and 2.5% phosphate) (B010348, B010385 and W810039, Energy Chemical) to a new 96 well plate. Measure the OD value of the mixture solution at 540 nm using a microplate reader (Tecan, Infinite 200 pro). The experiment was performed in triplicate.
2.2 Reactive oxygen species (ROS) determination
Inoculate 2 mL of Raw264.7 cells at a density of 1.5 × 106 cells/mL into a 6-well plate. After 24 h of incubation, discard the original culture medium and add fresh culture medium containing LPS (1 μg/mL) and corresponding concentrations of compounds. After incubation for 24 h, collect cells by centrifugation and wash twice with PBS. Add 0.5 mL of DCFH-DA (3 μM) (T88220, Yuanye) solution to each group of cells and incubate at 37°C for 30 min. After washing with PBS three times, the fluorescence intensity (λEx = 495 nm and λEm = 529 nm) of each group of samples was measured using a fluorescence spectrophotometer (Hitachi High-Tech Science, F-7000).
2.3 Modeling and drug intervention of UC in mice
After Balb/c mice (8-week-old, 18–20 g, male; Jinan Pengyue experimental animal breeding Co., Ltd.) were adapted for 7 days, they were randomly assigned into five groups (n = 8). Eight normal mice were randomly selected as the normal group. Except for the mice in the normal group, the mice were free to drink 3% DSS (MB5535-2, Meilunbio) aqueous solution for 10 days. For the model group, mice were only free to drink 3% DSS aqueous solution. For the 1i-treatment groups, starting from the fifth day, mice were orally administered with different concentrations of active derivatives 1i (50, 100 or 200 mg/kg/day) in carboxymethylcellulose sodium (0.5%) solution (P1346637, Adamas-beta). On the tenth day, after gavage, the mice were fasted for 12 h and were euthanized by cervical dislocation. All operations were strictly carried out in accordance with the National Laboratory Animal Care and Use Guidelines. The animal experiment of this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Liaocheng University (2022111013).
2.4 Determination of serum biochemical indicators
Blood was collected by removing the eyeball and placed in an anticoagulant centrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C and 1,000 g for 10 min, and take the supernatant to obtain serum. Use the aspartate transaminase (AST)/glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) activity detection kit (E2023, Applygen), the alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/glutamate pyruvate transaminase (GPT) activity detection kit (E2021, Applygen), the urea (BUN) assay kit (C013-1-1, Nanjing Jiancheng), and the creatinine (CRE) assay kit (C011-2-1, Nanjing Jiancheng) for detection. The content of AST, ALT, BUN and CRE are represented by U/L, U/L, mmol/L and μmol/L, respectively.
2.5 Determination of malonic dialdehyde (MDA) content in colon tissue
Mix 50 μL of colon tissue supernatant and 100 μL of working solution (0.4% thiobarbituric acid (w/v) (V900387, Vetec), 0.5% SDS (w/v) (ST627, Beyotime), 9.4% acetic acid (w/v)) (B020052, Energy Chemical). After heating at 100°C for 15 min, the mixture was cooled using the ice bath. After centrifugation, 100 μL of supernatant were placed in a 96 well plate and the absorbance at 532 nm was measured using a microplate reader. The MDA content was expressed in nmol/mg pro.
2.6 Determination of myeloperoxidase (MPO) level in colon tissue
Mix 40 μL of colon tissue supernatant and 60 μL of working solution (0.0005% o-diaminodiphenylenediamine dihydrochloride (A17175, Alfa Aesar) and PBS (50 mM, pH 6.0) solution of 0.1% hydrogen peroxide). Measure the absorbance change at 460 nm using a microplate reader at 25°C. A change of 5.65 × 10−3 in absorbance was equivalent to one unit of MPO activity. MPO activity is expressed in U/mg pro.
2.7 Determination of catalase (CAT) level in colon tissue
The CAT level in the colon tissue was detected by the catalase assay kit (A007-2-1, Nanjing Jiancheng). CAT activity was expressed in U/g pro.
2.8 Histopathology
Colon tissue was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde fix solution (P0099, Beyotime), embedded in paraffin, and sliced. Stained with the hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining kit (C0105S, Beyotime), photographed under an Olympus microscope (BX53 + DP80). Then Colon sections were scored according to the histological scoring system (Wang et al., 2021).
2.9 Immunohistochemical analysis
The immunohistochemical (IHC) experiment used conventional methods. The primary antibodies F4/80 (GB113373) was purchased from Servicebio. The slides were stained with DAB (G1212, Servicebio) and counter-stained with hematoxylin (G1004, Servicebio).
2.10 Western blotting
2.10.1 Whole cell extraction
Inoculate 2 mL of Raw264.7 cells into a 6-well plate at a density of 1.5 × 106 cells/mL. After 24 h of incubation, discard the original culture medium and add fresh culture medium containing LPS (1 μg/mL) and corresponding concentrations of compounds. After incubation for 24 h, collect cells by centrifugation and wash twice with PBS. Cell lysis buffer for Western and IP (P0013, Beyotime) and protease inhibitor cocktail for general use (P1005, Beyotime) were added to each group of cells for cell lysis. After sufficient lysis, centrifuge at 12,000 g for 5 min, take the supernatant, and measure the protein concentration using the enhanced BCA protein assay kit (P0010, Beyotime). The entire experiment process was conducted under ice bath or 4°C conditions.
2.10.2 Nuclear protein extraction
Inoculate 2 mL of Raw264.7 cells into a 6-well plate at a density of 1.5 × 106 cells/mL. After 24 h of incubation, discard the original culture medium and add fresh culture medium containing LPS (1 μg/mL) and corresponding concentrations of compounds. After incubation for 24 h, collect cells by centrifugation and wash twice with PBS. Each group of cells was used to extract nuclear protein using the nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extraction kit (R0050, Solarbio), and the protein concentration was measured using the enhanced BCA protein assay kit. The entire experiment process was conducted under ice bath or 4°C conditions.
2.10.3 Colon tissue protein extraction
Weigh a certain amount of colon tissue and use the cell lysis buffer for Western and IP and tissue crusher (Shanghai Jingxin) for fragmentation. After sufficient lysis, centrifuge at 12,000 g for 5 min, take the supernatant, and measure the protein concentration using the enhanced BCA protein assay kit. The entire experiment process was conducted under ice bath or 4°C conditions.
2.10.4 The WB experiments used conventional methods
The primary antibodies were as follows: the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) (WL00196, Wanleibio), interleukin (IL)-6 (WL02841, Wanleibio), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (WL01581, Wanleibio), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (WL0992a, Wanleibio), NLR family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) (WL02635, Wanleibio), Caspase1 (WL03450, Wanleibio), B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X (Bax) (WL01637, Wanleibio), Caspase3 (WL02117, Wanleibio), Ki-67 (WL01384a, Wanleibio), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) p65 (bs-0465R, Bioss), β-actin (81115-1-RR, Proteintech), β-tubulin (WL01931, Wanleibio), Histone H3 (68345-1-IG, Proteintech). The secondary antibodies were as follows: HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse and anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) (A0216 and A0208, Beyotime).
2.11 Molecular docking simulation calculation
Simulation calculation of molecular docking between active drug molecule 1i and myeloid differentiation factor 2 (MD2) (PBD ID, 3VQ2) or cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) (PBD ID, 4GLP) using the Libdock module of the discovery studio (DS) software. The entire C-chain of MD2 (x = −32.237392, y = −17.019290, z = 31.671505; radius = 27.117655) or the N-terminal hydraulic pocket of the A-chain of CD14 (x = 48.350000, y = 51.480000, z = 0.970000; radius = 29.370001) was used as the calculation range.
2.12 Statistical analysis
Data were expressed using the average and standard deviation values of at least three independent experiments. Statistical significances were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Dunns test in the GraphPad Prism software.
3 Results
3.1 NO production
We measured the inhibitory activity of para-quinone methide and eighteen derivatives (Figure 1) modified with methoxy, fluorine, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, bromine or chlorine in the ortho-, meta-, or para-positions of the benzene ring on the NO production in the LPS-induced inflammatory Raw264.7 cell model. These synthesized derivatives were prepared and structurally identified according to our previously reported methods, as shown in Supplementary Material.
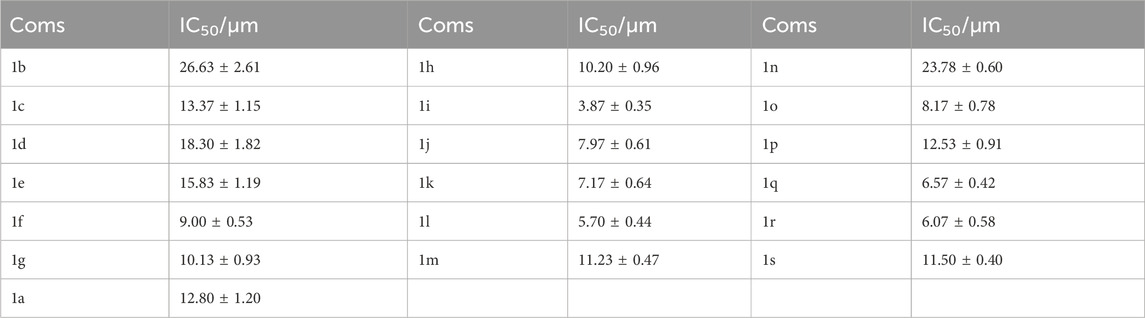
According to the results in Table 1, for derivatives modified with the same substituent, the meta-substituted derivative had the best NO inhibitory activity compared to ortho- and para-substituted derivatives. For meta-substituted derivatives, meta-trifluoromethyl modified derivative had the highest anti-inflammatory activity, which was selected for subsequent research. In addition, we measured the cytotoxicity of the derivatives on Raw264.7 cells (Supplementary Table S1). Some derivatives had certain cytotoxic activity. However, the cytotoxic activity of most compounds didn’t affect their ability to inhibit NO production, including 1i (Supplementary Figure S1).
3.2 ROS production
As shown in Figure 2, LPS induced excessive accumulation of ROS in Raw264.7 macrophage cells. The intervention of the active derivative 1i can reduce the production of ROS in a dose-dependent manner.
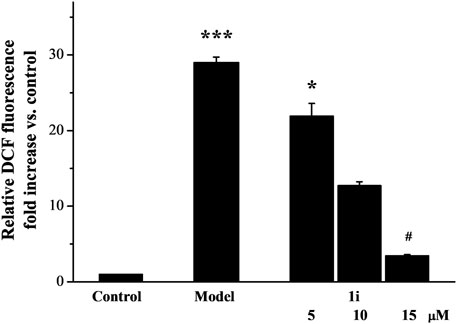
Figure 2. The effect of active derivative 1i on LPS-induced excess production of ROS. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001, compared with the control group. #p < 0.05, compared with the model group. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
3.3 Expressions of inflammatory related proteins
We evaluated the effects of 1i on the expressions of inflammation related proteins TLR4, IL-6, TNF-α, NLRP3, and Caspase 1. In addition, we also measured the expression of inducible iNOS, a regulatory factor for inflammatory NO synthesis. As shown in Figure 3, LPS induced overexpressions of TLR4, IL-6, TNF-α, iNOS, NLRP3, and Caspase 1 in Raw264.7 macrophage cells. And the intervention of 1i resulted in a decrease in these overexpressions in a dose-dependent manner.
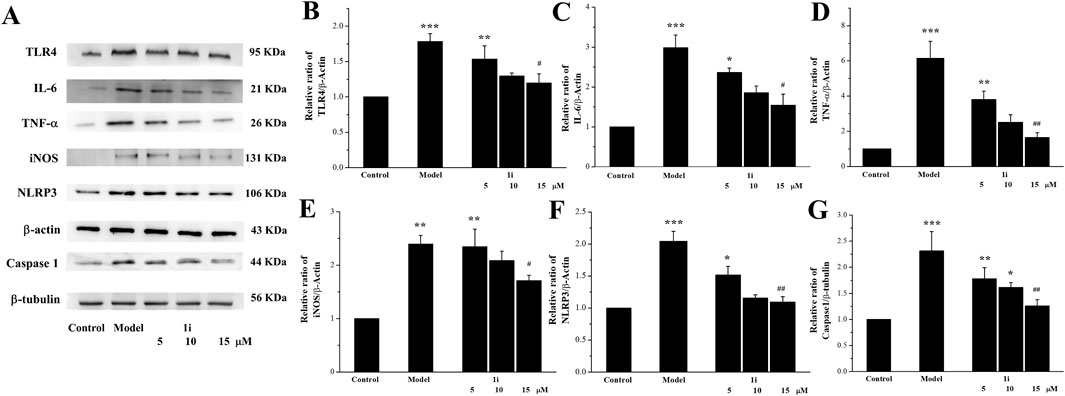
Figure 3. Effects of the active derivative 1i on expressions of inflammatory related proteins in LPS-induced Raw264.7 cells. (A) Representative protein bands. Quantitative analysis of (B) TLR4, (C) IL-6, (D) TNF-α, (E) iNOS, (F) NLRP3 and (G) Caspase 1 grayscale using the ImageJ software. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, compared with the control group. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01, compared with the model group. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
The nuclear transfer of NF-κB protein expression was also determined. As shown in Figure 4, LPS induced the increase in NF-κB expression in the nucleus. And the intervention of 1i reduced the nuclear transfer of NF-κB.
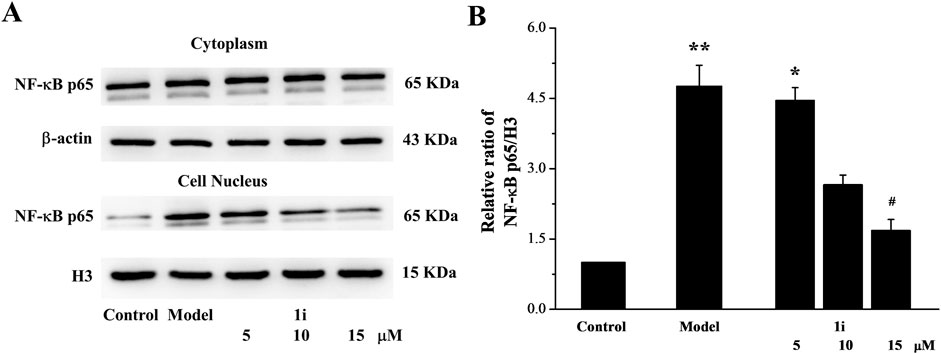
Figure 4. The effect of 1i on nuclear transfer of NF-κB protein. (A) Representative protein bands. (B) Perform grayscale quantitative analysis of NF-κB in nuclear proteins using the ImageJ software. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, compared with the control group. #p < 0.05, compared with the model group. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
3.4 Molecular simulation calculations
TLR4-NF-κB is a key pathway for initiating inflammatory responses. TLR4 is a key receptor or promoter for transmembrane signal transduction of LPS. The recognition of TLR4 and LPS involves the binding of LPS to the CD14 receptor, and the transmitting LPS to the TLR4-MD2 complex. TLR4 recognizes LPS with the help of CD14 and MD2. In order to better understand the intervention effect of 1i on the TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway, we used the Libdock module of DS to perform molecular docking simulation calculations between 1i and CD14 or MD2. The N-terminal hydrophobic pocket of the A-chain of CD14 and the C-chain of the MD2 were defined as binding sites for calculation.
As shown in Figure 5, 1i can form molecular docking with both CD14 and MD2. 1i formed the conventional hydrogen bond, halogen, pi-cation, pi-sigma, alkyl, and pi-alkyl with CD14. While, 1i formed pi-sigma, pi-stacked, pi-T-shaped, alkyl, and pi-alkyl with MD2. There were more interactions between 1i and CD14 than MD2, and there was the stable conventional hydrogen bond. Additionally, the Libdockscore for molecular docking between 1i and CD14 was 108.131, higher than the Libdockscore of 86.2821 for molecular docking between 1i and MD2. These results suggested that the inhibition of CD14 by 1i may have a more effective anti-inflammatory effect.
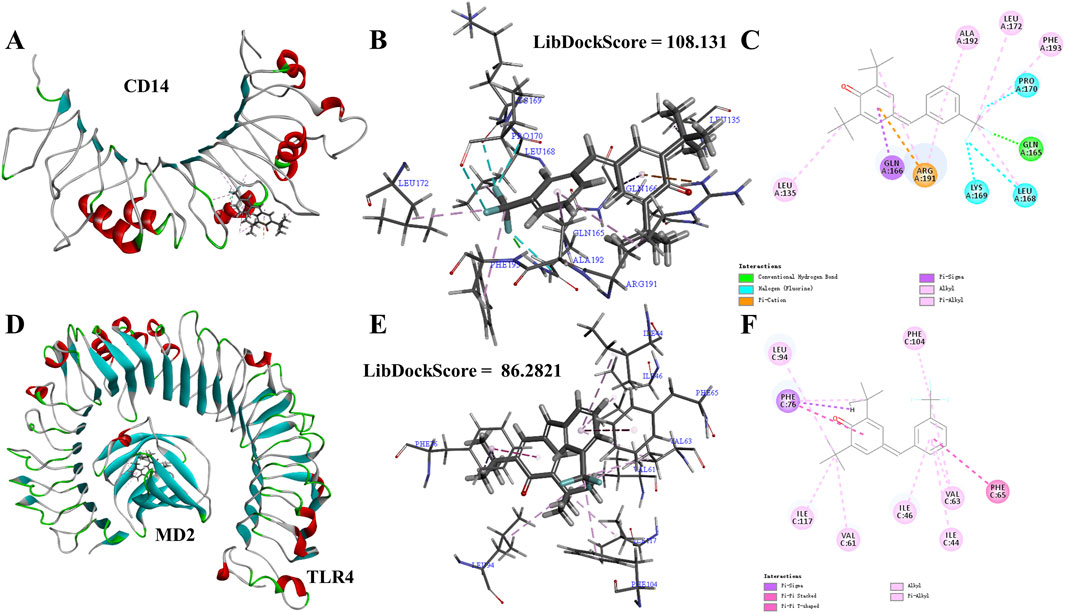
Figure 5. Molecular simulation calculations of 1i and CD14 and TLR4-MD2. (A–C) 1i-CD14 interactions on 3D and 2D diagrams. (D–F) 1i-MD2 interactions on 3D and 2D diagrams.
3.5 In vivo study
3.5.1 Effects of symptoms on the mouse model of UC
Further study on the anti-inflammatory activity of 1i in vivo using DSS-induced UC mouse model. The experimental mice were free to drink 3% DSS solution for 10 days; And starting from the fifth day, the experimental mice were treated with the active derivative 1i by gavage for 6 days. As shown in Figure 6A, as the drinking time of DSS increased, the weight of mice decreased in the model group. In the drug treatment group, the weight loss of mice slightly decreased after gavage with 1i. For the length of the colon, as shown in Figures 6B, C, DSS significantly shortened the length of the colon; After gavage, the length of the colon increased in a dose-dependent manner. For the pathological tissue sections of the colon, as shown in Figures 6D, E, compared with the normal group, the pathological tissue sections of the colon in the model group showed obvious inflammatory reactions, such as disappearance of crypts, inflammatory infiltration and structural destruction. When treated with 1i by gavage, a dose of 50 mg/kg of 1i can alleviate these inflammatory reactions; 100 mg/kg of 1i significantly improved these inflammatory responses; 200 mg/kg of 1i can basically reverse these inflammatory reactions. IHC staining of colon tissue with F4/80, a recognized biomarker for mouse macrophages, showed that DSS induced massive macrophage infiltration in the colon of UC mice; While, the intervention of 1i significantly inhibited macrophage infiltration, as shown in Figure 6F. These results suggested that 1i can protect colon tissue from damage caused by DSS.
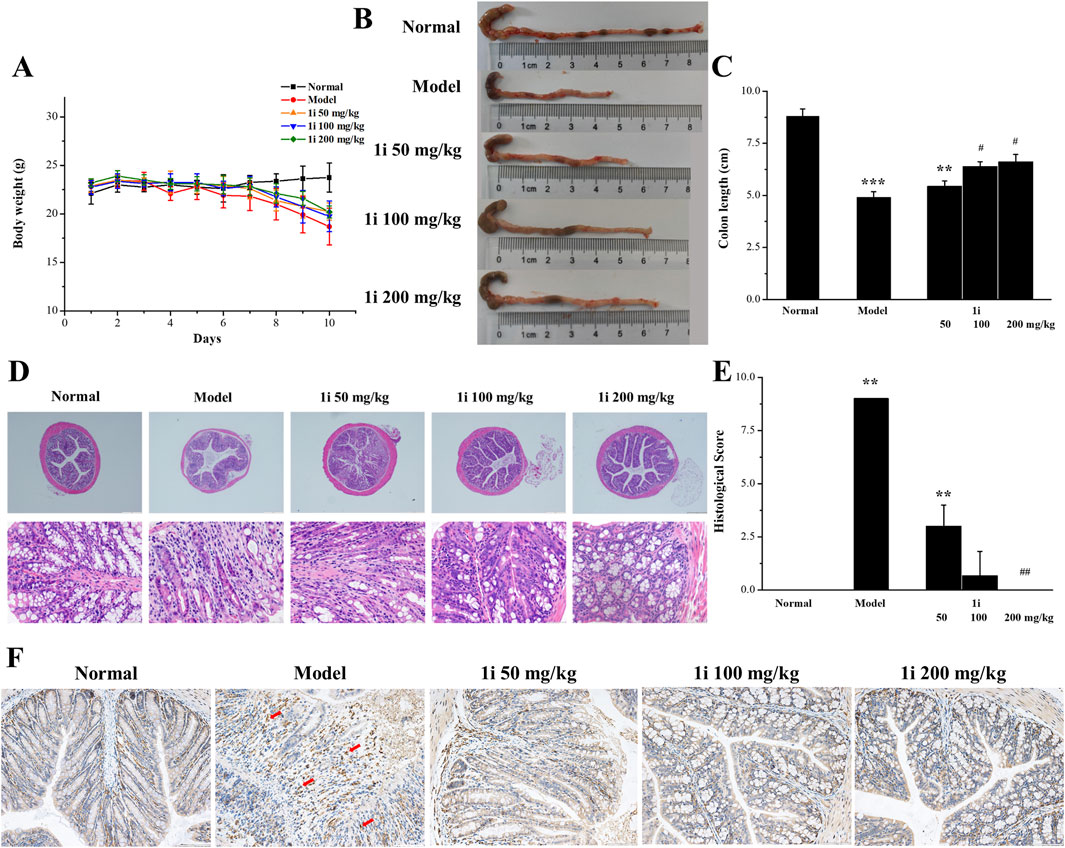
Figure 6. The anti-inflammatory activity of 1i in mice with UC. (A) Changes in mouse body weight; (B, C) colon length; (D) Representative images of histopathological analysis of colon tissue stained with HE. (E) Colon sections were scored according to the histological scoring system. (F) Representative images of histopathological analysis of colon tissue stained with F4/80. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, compared with the normal group. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01, compared with the model group. Scale bar: D, 500 μm and 50 μm; F, 100 μm. The number of mice per group was 8.
3.5.2 Effects of oxidative stress on the mouse model of UC
As shown in Figure 7, in the model group, the MDA and MPO levels in the colon tissue of UC mice were significantly increased; However, the expressions of CAT were significantly reduced. This meant that the oxidative stress level in the colon tissue of UC mice was increased. Oral administration of the active derivative 1i to UC mice can reverse these changes in a dose-dependent manner.
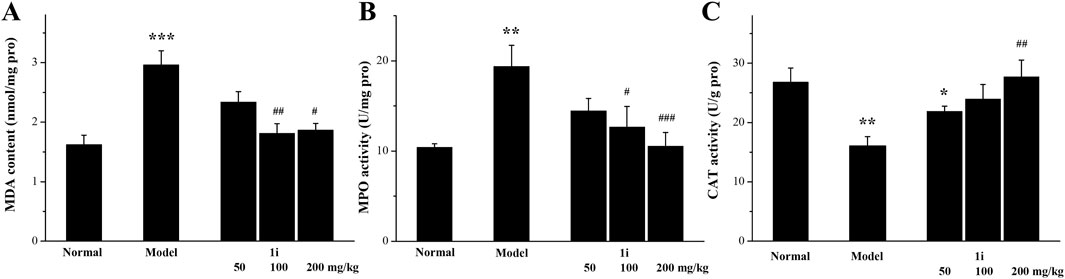
Figure 7. Determination of oxidative stress indicators in colon tissue. (A) MDA, (B) MPO and (C) CAT. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, compared with the normal group. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001, compared with the model group. The number of mice per group was 8. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
3.5.3 Regulation of inflammatory related proteins in colon tissue
We measured the expressions of inflammation related proteins TLR4, IL-6, TNF-α, and iNOS in colon tissue. As shown in Figures 8A–E, compared with normal mice, the expressions of TLR4, IL-6, TNF-α, and iNOS in UC mice were significantly increased, while the active derivative 1i could reduce these expressions of these inflammation related proteins.
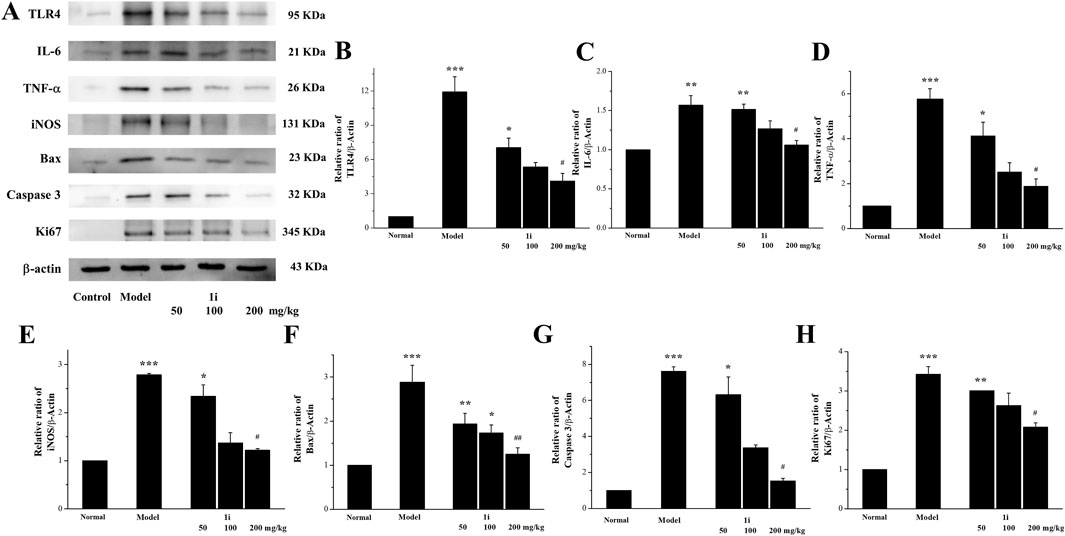
Figure 8. Effects of the active derivative 1i on expressions of inflammatory related proteins in DSS-induced UC mice. (A) Representative protein bands. Quantitative analysis of (B) TLR4, (C) IL-6, (D) TNF-α, (E) iNOS, (F) Bax, (G) Caspase 3 and (H) Ki67 grayscale using the ImageJ software. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, compared with the normal group. ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001, compared with the model group. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
3.5.4 Regulation of apoptosis related proteins in colon tissue
We further detected the expression of two pro-apoptotic proteins, Bax and Caspase 3, to confirm whether the active derivative 1i can regulate the expression of apoptosis related proteins to resist damage caused by UC. As shown in Figures 8A, F, G, the expressions of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Caspase 3 in the colon tissue of UC mice were indeed increased, consistent with literature reports. The intervention of the active derivative 1i can effectively reduce the expressions of these two pro-apoptotic proteins. The effect of 1i on cell apoptosis has also been confirmed by the cell system, that 1i can reverse LPS-induced apoptosis in Raw264.7 cells (Supplementary Figure S2).
3.5.5 Regulation of Ki67 in colon tissue
In addition, we measured the expression of Ki67 in mouse colon tissue. As shown in Figures 8A, H, compared with the normal group, the colon tissue of UC mice showed high expression of Ki67; However, the expression of Ki67 was decreased with increasing 1i concentration. This result indicated that 1i can reduce DSS-induced colon tissue damage in UC mice by inhibiting the expression of Ki67.
3.5.6 Evaluation of liver and kidney function
We further used serum biochemical indicators (AST, ALT, BUN and CRE), pathological tissue analyses, and the organ indexes to evaluate the liver and kidney function damage. As shown in Figure 9, in the UC model group, the levels of AST, ALT, BUN, and CRE in the serum of the model mice were higher than those of normal mice, indicating that DSS caused damage to liver and kidney function in the UC model mice. The treatment of the active derivative 1i resulted in the decreases in AST, ALT, BUN and CRE levels, indicating that the intervention of 1i can effectively reverse the liver and kidney function damages caused by DSS.
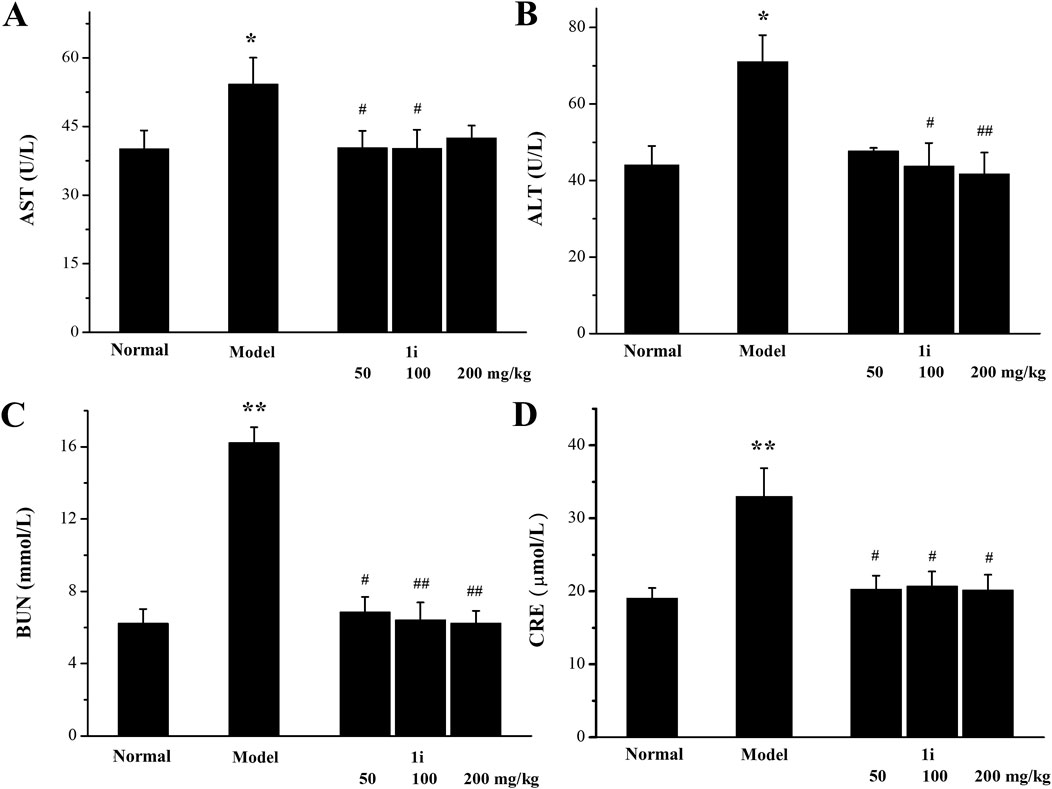
Figure 9. Evaluation of biochemical indicators of liver and kidney function in serum. (A) AST level. (B) ALT level. (C) BUN level. (D) CRE level. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared with the normal group. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01, compared with the model group. The number of mice per group was 8. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
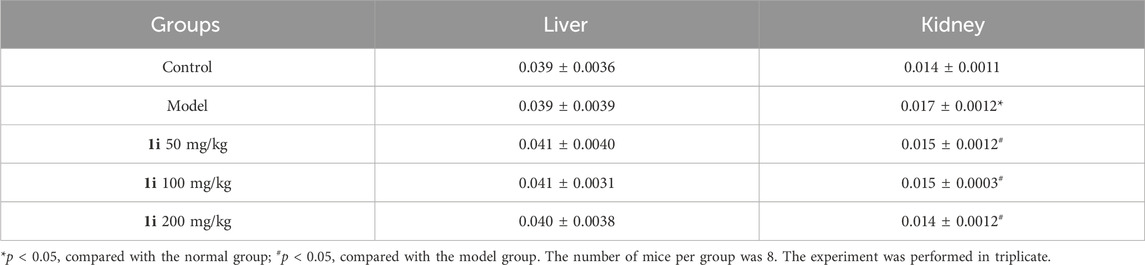
However, as shown in Figure 10, there was no significant change in the pathological examination of liver tissue between the groups; As shown in Table 2, there was no statistically significant difference in the liver organ index between the groups.
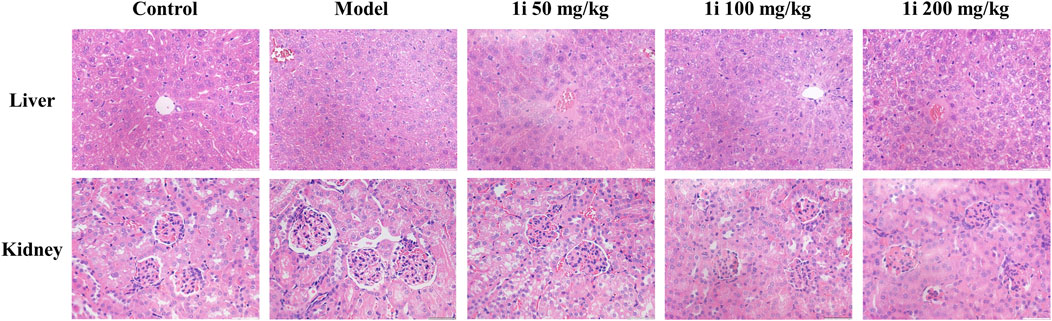
Figure 10. Representative images of pathological tissue sections of liver and kidney. Scale bar: 50 and 50 μm. The number of mice per group was 8.
For the kidneys, as shown in Figure 10, pathological examination revealed an increase in glomerular volume in the UC model group; As shown in Table 2, the organ index of the kidney in the UC model group significantly increased. And the intervention of 1i can reverse these changes.
4 Discussion
The research on natural products has shown great potential in the field of new drug development. Quinones are natural organic compounds that are widely present in nature, and possess various biological activities. Numerous studies have shown that quinones and their derivatives have clear anti-inflammatory effects, and their development potential as anti-inflammatory drugs are enormous (Guo et al., 2024). Quinone methides are the derivatives of quinones, in which one oxygen atom is replaced by carbon; Quinone methides have stronger polarity and higher reactivity. Most quinone methides exhibit significant biological activity. For example, celastrol, a quinone methide triterpenoid, can inhibit the inflammatory response of macrophages and resist the invasion of skin inflammation, enteritis, arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, and so on (Zhao et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2009; Allison et al., 2001).
In this study, a series of synthesized para-quinone methide derivatives were investigated their anti-inflammatory activity in the LPS-induced inflammatory Raw264.7 cell model. The LPS-induced inflammatory Raw264.7 cell model is a commonly used cell model in vitro for anti-inflammatory activity research. LPS can induce excessive production of NO in Raw264.7 cells. NO is an important regulatory molecule in the inflammatory response (Wang et al., 2013). Through the screening of LPS-induced inflammatory cell models in Raw264.7 cells, it was found that the inhibitory activity of meta-substituted derivatives on NO production was superior to that of ortho- and para-modified derivatives. Among them, in the inflammatory cell model, the meta-trifluoromethyl substituted para-quinone methide derivative 1i had the best activity in the inhibiting LPS-induced excess generation of NO.
In our previous work (Li et al., 2022), derivatives with ortho-modification showed the best anti-proliferation activity against cancer cells. This was consistent with the SAR of hybrid derivatives of curcumin and β-ionone discovered in previous work (Yang et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2022), where ortho-substituted derivatives exhibited good anti-cancer activity, while meta-substituted derivatives exhibited good anti-inflammatory activity.
Inflammation can cause oxidative stress, which can also cause inflammation. The excessive production of ROS and cellular redox imbalance play a core role in the pathophysiology of inflammatory response (Lee and Yang, 2012). A large amount of evidence suggests that oxidative stress is an important pathogenic factor in the inflammatory response (Barrett et al., 2017). In the LPS-induced Raw264.7 macrophage cells, excessive production of ROS is closely related to pathological states such as inflammation. In the LPS-induced Raw264.7 macrophage cells, 1i can effectively reduce the excessive accumulation of ROS induced by LPS, which means that 1i can reduce the degree of oxidative stress of the cellular redox imbalance.
In the LPS-induced inflammatory Raw264.7 cell model, LPS first recognizes and forms complexes with the lipopolysaccharide binding protein in the cytoplasm. Further deliver LPS to the leukocyte differentiation antigen CD14 on the cell membrane and decompose complexes into monomeric LPS, which is then presented to the TLR4-MD2. The binding of TLR4-MD2 complex to LPS induces activation of NF-κB, which is a key nuclear factor in the initiation and regulation of inflammatory responses. Activated NF-κB undergoes nuclear transfer, further promoting transcription and translation of cytokines (such as IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α) and NLRP3. After NLRP3 inflammasome is activated, it further activates Caspase 1, which is mainly involved in the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the process of cell apoptosis.
1i can effectively inhibit the expressions of inflammation related initiating protein TLR4, pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α, inflammasome NLRP3 and Caspase1, and can reduce the nuclear transfer of NF-κB. These results suggested that 1i can resist LPS-induced inflammation in Raw264.7 macrophage cells. These results suggested that 1i can resist LPS-induced inflammation in Raw264.7 macrophage cells.
The DSS-induced UC mouse model is selected for the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity evaluation of 1i. The DSS-induced UC mouse model can simulate the clinical characteristics of human UC, including weight loss, diarrhea, hematochezia, colon shortening, intestinal mucosal damage, and elevated inflammatory markers.
In the DSS-induced UC mouse model, the active derivative 1i can inhibit DSS-induced colon shortening, and reverse DSS-induced pathological changes in colon tissue, such as inflammatory infiltration, structural destruction, and crypt disappearance. In addition, like the LPS-induced inflammatory Raw264.7 cell model in vitro, 1i can effectively inhibit inflammation related proteins TLR4, IL-6, TNF-α and iNOS in the colon tissue of the DSS-induced UC mouse model. These indicates that 1i can effectively resist DSS-induced colon inflammation in UC mice.
The pathogenesis of UC is related to increased inflammation and weaken antioxidant capacity. Oxidative stress metabolites are potential inflammatory mediators of IBD (Sheethal et al., 2020). MDA, MPO, and CAT were measured to evaluate the oxidative stress levels in colon tissue. MDA is the final product of lipid peroxidation and an indirect indicator of oxidative stress (Jentzsch et al., 1996). MPO is a peroxidase present in the phenylalanine blue granules of myeloid cells (neutrophils and monocytes) (Palla et al., 2016). Under physiological conditions, MPO is a part of the natural immune system; While, under specific conditions, MPO can catalyze the production of excess oxidants leading to oxidative stress (Bo et al., 2017). CAT protects cells from oxidative stress by catalyzing the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen (Sepasi Tehrani and Moosavi-Movahedi, 2018). The active derivative 1i can effectively reverse the increases of MDA and MPO caused by oxidative stress, as well as the decrease of CAT. These indicates that 1i can effectively resist oxidative stress in UC mice, thereby exhibiting anti-UC effects.
According to literature reports, UC is associated with apoptosis. Excessive apoptosis of colonic epithelial tissue can lead to structural damage and intestinal mucosal barrier damage, thereby inducing inflammation of the colon (Wei et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2021; Cai et al., 2022; Li et al., 2020). The Bcl-2/Bax cell signaling pathway and its downstream caspase family are important proteins related to cell apoptosis. 1i can reduce the increased expressions of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Caspase 3 in the colon tissue of UC mice, which indicates that 1i can resist UC damage by inhibiting colon apoptosis in UC mice. It is interesting that in our previous work (Li et al., 2022), meta-trifluoromethyl modified derivative 1h, a structural analogue of 1i, can exert anti-cancer effects by promoting cancer cell apoptosis via targeting TrxR.
UC is one of the triggering factors for colon cancer, and UC patients face a higher risk of developing colon cancer. Ki67 is a proliferating cell related antigen and a commonly used tumor proliferation index in clinical practice. The expression level of Ki67 usually indicates the activity level of cell proliferation (Ilyas and Talbot, 1995). In clinical practice, the higher the expression of Ki67, the more active the proliferation of cells and the higher the degree of malignancy. 1i can decrease the high expression of Ki67 caused by UC, thereby reducing the colon tissue damage caused by UC.
In the UC mouse model induced by DSS, in addition to causing UC, DSS can also accumulate and cause damage in other organs of the mouse (Yang and Merlin, 2024). AST and ALT are serum biochemical indicators used to evaluate liver damage, while BUN and CRE are serum biochemical indicators used to evaluate kidney damage. Through serum biochemical index measurement, it is found that 1i can reduce the elevation of AST, ALT, BUN, and CRE caused by UC, thereby reversing DSS-induced liver and kidney damage. Both the histopathological examination and organ index of the kidney tissue show that 1i can effectively reverse the kidney damage caused by DSS. These results indicate that 1i can effectively protect against liver and kidney damages caused by DSS, and also confirms the safety of 1i as the potential anti-UC reagent.
In summary, 1i is an effective anti-inflammatory reagent and could be developed as a potential drug for anti-UC. Further research will focus on the evaluation of the activity of the active derivative 1i in other inflammatory models, more detailed mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and evaluations of acute and chronic toxicity.
In addition, the SAR between the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties of this series of para-quinone methides derivatives shows that ortho-substituted derivatives have good anti-cancer activity, while, meta-substitued derivatives have good anti-inflammatory activity. This type of SAR had also been observed in previous studies of hybrid derivatives of curcumin and β-ionone (Yang et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2022). This provides some guidances for the design of drugs containing Michael receptor structures attached to the benzene ring. Further research is needed on computer simulation calculations related to this SAR.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Liaocheng University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YQ: Investigation, Writing–original draft, Data curation. XL: Writing–original draft, Validation, Investigation. XZ: Writing–original draft, Validation, Investigation. XiW: Writing–original draft, Investigation. XuW: Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition. JY: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft, Project administration, Data curation. GL: Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2023MB089), the Research Fund of Liaocheng University (318012106), “Guangyue Young Scholar Innovation Team” of Liaocheng University (LCUGYTD2022-04), and “Youth Innovation Team Plan” of Shandong Province Higher Education (2022KJ111).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1474678/full#supplementary-material
References
Allison, A. C., Cacabelos, R., Lombardi, V. R., Alvarez, X. A., and Vigo, C. (2001). Celastrol, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug, as a possible treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 25, 1341–1357. doi:10.1016/s0278-5846(01)00192-0
Barrett, C. W., Short, S. P., and Williams, C. S. (2017). Selenoproteins and oxidative stress-induced inflammatory tumorigenesis in the gut. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 74, 607–616. doi:10.1007/s00018-016-2339-2
Bo, L., Shan, J. G., and Zhao, Z. W. (2017). Research progress of myeloperoxidase in cardiovascular diseases. Lab. Med. 32, 738–743. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-8640.2017.08.018
Cai, B. X., Cai, X. Y., Xu, T., Wang, J. T., and Yu, Y. (2022). Structures and anti-inflammatory evaluation of phenylpropanoid derivatives from the aerial parts of Dioscorea polystachya. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 10954. doi:10.3390/ijms231810954
Eaden, J. A., Abrams, K. R., and Mayberry, J. F. (2001). The risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Gut 48, 526–535. doi:10.1136/gut.48.4.526
Guo, Y. J., Peng, X. L., Liu, F. F., Zhang, Q., Ding, L. Q., Li, G., et al. (2024). Potential of natural products in inflammation: biological activities, structure-activity relationships, and mechanistic targets. Arch. Pharm. Res. 47, 377–409. doi:10.1007/s12272-024-01496-z
Harbord, M., Eliakim, R., Bettenworth, D., Karmiris, K., Katsanos, K., Kopylov, U., et al. (2017). Third european evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 2: current management. J. Crohn’s Colitis 11, 769–784. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx009
Ilyas, M., and Talbot, I. C. (1995). p53 expression in ulcerative colitis: a longitudinal study. Gut 37, 802–804. doi:10.1136/gut.37.6.802
Jentzsch, A. M., Bachmann, H., Furst, P., and Biesalski, H. K. (1996). Improved analysis of malondialdehyde in human body fluids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 20, 251–256. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(95)02043-8
Jess, T., Rungoe, C., and Peyrin-Biroulet, L. (2012). Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis of population based cohort studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 10, 639–645. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.01.010
Kawalec, P., and Malinowski, K. P. (2015). Indirect health costs in ulcerative colitis and crohn’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Pharm. Outcomes Res. 15, 253–266. doi:10.1586/14737167.2015.1011130
Kim, D. H., Shin, E. K., Kim, Y. H., Lee, B. W., Jun, J. G., Park, J. H. Y., et al. (2009). Suppression of inflammatory responses by celastrol, a quinone methide triterpenoid isolated from Celastrus regelii. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 39, 819–827. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02186.x
Kula, K., Nagatsky, R., Sadowski, M., Siumka, Y., and Demchuk, O. M. (2023). Arylcyanomethylenequinone oximes: an overview of synthesis, chemical transformations, and biological activity. Molecules 28, 5229. doi:10.3390/molecules28135229
Lee, I. T., and Yang, C. M. (2012). Role of NADPH oxidase/ROS in pro-inflammatory mediators-induced airway and pulmonary diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 84, 581–590. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2012.05.005
Li, C., Ai, G. X., Wang, Y. F., Lu, Q., Luo, C. D., Tan, L. H., et al. (2020). Oxyberberine, a novel gut microbiota-mediated metabolite of berberine, possesses superior anti-colitis effect: impact on intestinal epithelial barrier, gut microbiota profile and TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 152, 104603. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104603
Li, H. M., Ruan, J. Y., Huang, J. Y., Yang, D. S., Yu, H. Y., Wu, Y. Z., et al. (2023). Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) and its rich ellagitannins as potential inhibitors in ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 17538. doi:10.3390/ijms242417538
Li, P. X., Ma, Y. Z., Wang, K., Shi, X. H., Yang, J., and Liu, G. Y. (2022). Design, synthesis and antitumor activity of potent and safe para-quinone methides derivatives in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 156, 113893. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113893
Liu, L., Li, H. B., Hu, K. W., Xu, Q. L., Wen, X. A., Cheng, K. G., et al. (2021). Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of saponin derivatives of δ-oleanolic acid. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 209, 112932. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112932
Ma, Y. Z., Guo, X. Y., Wang, Q., Liu, Q., Yang, M. N., Jia, A. X., et al. (2022). Anti-inflammatory effects of β-ionone-curcumin hybrid derivatives against ulcerative colitis. Chem-Biol. Interact. 367, 110189. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110189
Palla, A. H., Iqbal, N. T., Minhas, K., and Gilani, A. H. (2016). Flaxseed extract exhibits mucosal protective effect in acetic acid induced colitisin mice by modulating cytokines, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Int. Immunopharmacol. 38, 153–166. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.043
Sepasi Tehrani, H., and Moosavi-Movahedi, A. A. (2018). Catalase and its mysteries. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 140, 5–12. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2018.03.001
Sheethal, S., Ratheesh, M., Jose, S. P., Asha, S., Krishnakumar, I. M., Sandya, S., et al. (2020). Anti-ulcerative effect of curcumin-galactomannoside complex on acetic acid-induced experimental model by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Inflammation 43, 1411–1422. doi:10.1007/s10753-020-01218-9
Wang, Y., Jiang, Z., Kim, D., Ueno, M., Okimura, T., Yamaguchi, K., et al. (2013). Stimulatory effect of the sulfated polysaccharide ascophyllan on the respiratory burst in Raw264.7 macrophages. Inter. J. Biol. Macromol. 52, 164–169. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.09.008
Wang, Z. Q., Mu, W. W., Gong, Z. T., Liu, G. Y., and Yang, J. (2021). Meta-substituted piperlongumine derivatives attenuate inflammation in both Raw264.7 macrophages and a mouse model of colitis. Bioorg. Chem. 117, 105465. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105465
Wei, Q., Wu, B., Wang, X., Buchanan, M. E., Lin, Z., Hartman, D. J., et al. (2011). PUMA-mediated intestinal epithelial apoptosis contributes to ulcerative colitis in humans and mice. J. Clin. Invest. 121, 1722–1732. doi:10.1172/JCI42917
Yang, C. H., and Merlin, D. (2024). Unveiling colitis: a journey through the dextran sodium sulfate-induced model. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 30, 844–853. doi:10.1093/ibd/izad312
Yang, J., Mu, W. W., Cao, Y. X., and Liu, G. Y. (2020). Synthesis and biological evaluation of β-ionone oriented proapoptosis agents by enhancing the ROS generation. Bioorg. Chem. 104, 104273. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104273
Keywords: anti-inflammatory, ulcerative colitis, para-quinone methides, oxidative stress, apoptosis
Citation: Qiu Y, Li X, Zhang X, Wang X, Wang X, Yang J and Liu G (2024) Anti-inflammatory effects of para-quinone methide derivatives on ulcerative colitis. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1474678. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1474678
Received: 02 August 2024; Accepted: 18 October 2024;
Published: 29 October 2024.
Edited by:
Ahmed Esmat Abdel Moneim, Helwan University, EgyptReviewed by:
Qinghe Meng, Upstate Medical University, United StatesPatricia Teixeira Santana, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Atsushi Kitani, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH), United States
Copyright © 2024 Qiu, Li, Zhang, Wang, Wang, Yang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuekun Wang, eHVla3Vud2FuZzA2MTBAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Jie Yang, eWFuZ2ppZTExMTBAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Guoyun Liu, Z3VveXVubGl1QDEyNi5jb20=
 Yue Qiu1
Yue Qiu1 Xuekun Wang
Xuekun Wang Jie Yang
Jie Yang