- Department of Rheumatology, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
Objective: To evaluate efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) combined with Western medicine in treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome (SS).
Methods: CNKI, WanFang, VIP, CBM, Sinomed, PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science were searched to collect randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of TCM combined with conventional western medicine (CWM) in treating SS from the time of their estalishment to May 2023. The researchers independently screened the literature and extracted data for quality evaluation. Analyses were performed using Review Manager (version 5.4) and R-4.3.1.
Results: A total of 66 RCTs were included, with a sample size of 5,052, involving four kinds of TCM (total glucosides of paeony capsules, tripterygium glycosides tablet, Xinfeng capsule and Jinju Qingrun capsule) and three kinds of CWM(hydroxychloroquine sulfate, Iguratimod and glucocorticoid). The network meta-analysis results showed that IGU + HCQ + TGP ranked the highest in reducing ESR and IgG and improving the Schirmer test when the three drugs were combined. When the two drugs are combined, IGU + GC and TGT + TGP are good choices for reducing erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and Immunoglobulin G (IgG). Although TGP + HCQ vs. HCQ had the most studies, TGP combined with HCQ did not rank high in each outcome indicator. It is recommended to use TGT and XFG in decreasing ESR and IgG for a single drug. JJQR have an advantageous role in relieving xerostomia and dry eyes.
Conclusion: TCM combined with CWM has a very significant effect on treating SS compared with CWM alone. According to the network meta-analysis, the best intervention measures of different TCMs for different outcome indicators were obtained.
Systematic Review Registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/], identifier [CRD42023451845].
1 Introduction
Sjogren’s syndrome (SS) is a systemic autoimmune disease mainly involving exocrine glands. Its pathological feature is lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration (Ramos-Casals et al., 2012). The main clinical manifestations are dry mouth and dry eyes, and organ involvement can also occur, such as the digestive system, lung, kidney, etc (Mariette and Criswell, 2018). In addition, about 5%–10% of SS patients are associated with lymphoma (Beydon et al., 2024). The prevalence of the elderly in China is as high as 3.00%–4.00%; The prevalence of SS in Europe is about 0.23% (Brito-Zerón et al., 2016). The pathogenesis of PSS is complex, involving genetic, environmental factors and abnormal activation of the immune system. The activation of B cells and T cells plays an important role in maintaining and exacerbating the inflammatory response (Baldini et al., 2024).
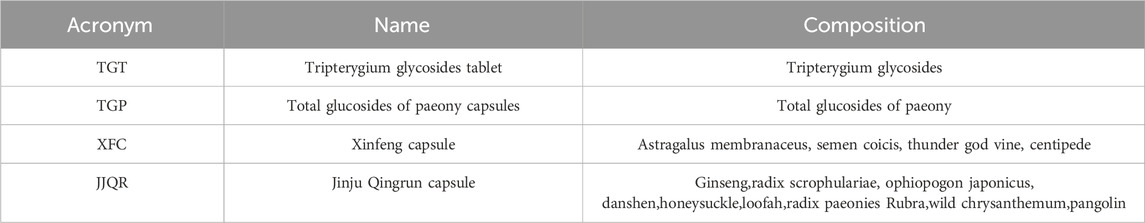
At present, the treatment options for SS are minimal, mainly immunosuppressive drugs and biological agents. In addition to symptomatic treatment to alleviate symptoms, there is no clear indication for drugs (Seror et al., 2021). Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has the advantage of multiple links, pathways, and targets, excelling in treating SS from a holistic perspective (Wang et al., 2024). With the development of TCM, the clinical application of TCM or the combination of TCM and Western medicine in treating SS is becoming increasingly widespread. For example, some studies have found that traditional Chinese medicine exerts therapeutic effects on SS mice and NOD mice by inhibiting inflammatory responses (Li et al., 2020). Other research indicates that total glycosides of white peony can improve the pathological damage of the submandibular glands in SS mice, possibly playing a therapeutic role in SS through the immune balance between Th17 and Treg mediated by RORγt/FoxP3 (Wu et al., 2021). There needs to be more comparison of the efficacy of different Chinese patents and Western medicines in treating SS. Network meta-analysis can quantitatively synthesize the results of multiple independent studies to enhance the strength and accuracy of evidence. In addition, in the absence of direct comparison, it can indirectly compare the effects of different interventions, so as to provide scientific basis for clinical practice and provide broader extrapolation (Higgins and Welton, 2015). Therefore, this study aims to conduct a network meta-analysis of Chinese and Western medicine interventions for Sjogren’s syndrome and to explore the efficacy and safety ranking of the current treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome to guide the best clinical treatment measures. The composition table of the traditional Chinese medicine is shown in Table 1.
2 Methods
2.1 Literature search strategy
The study has been registered in the International Registry of Prospective Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), and the registration number is CRD42023451845. Citations from the time of their estalishment to May 2023 were searched for in CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, CBM, Sinomed, PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases. The screening criteria were randomized controlled trials of TCM and CWM to treat SS. The included herbs included total glucosides of Paeony capsules, Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides tablets, Xinfeng capsules and Jinju Qingrun capsule. The included western drugs included hydroxychloroquine sulfate, methotrexate, iguratimod, leflunomide, methylprednisolone, prednisone. A literature search was conducted independently by two researchers, “Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides,” “total glucosides of paeony capsules,” “Pafflin capsules,” “Xinfeng capsules,” “Conventional western medicine,” “methotrexate,” “hydroxychloroquine,” “leflunomide,” “Iguratid,” “hormone,” “methylprednisolone,” “prednisone,” “hydrocortisone” and “Sjogren’s syndrome” were used for literature search in the database. A comprehensive search strategy is shown in Supplementary Table S1. Two researchers independently conducted the literature search. Weights were selected, and literature was screened based on title, abstract, and full-text reading for final inclusion.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
(1) The study type belonged to those above randomized controlled trials of Chinese patent medicine and Western medicine. it includes the treatment of SS with traditional Chinese medicine alone, Western medicine alone, or a combination of both, without any language restrictions. (2) The subjects should meet the classification criteria for primary Sjogren syndrome set by the 2002 American European Consensus Group (AECG) or the 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR) (Vitali et al., 2002; Shiboski et al., 2017). There were no special requirements for age, region, race, or gender.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
(1) Articles published were animal or cell experiments, academic conferences, reviews, or non-randomized controlled trials; (2) Duplicate published academic literature; (3) Interventions did not meet the requirements of the literature; (4) Literature for which complete data could not be obtained after contacting the authors.
2.4 Study extractions and quality assessment
Two researchers independently screened the literature according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, extracted the data using a pre-prepared Excel sheet, and assessed the risk of bias in the included literature. In the event of a disagreement, we will work towards a resolution through discussion or seek the assistance of a third-party mediator. The quality of the literature was assessed according to the bias risk tool of Cochrane assessment manual 5.1.0, and RevMan 5.4 software was used to draw the risk of bias map. The quality assessment criteria were as follows: random sequence generation of literature quality assessment; Assign hidden methods; Whether investigators, participants, and outcome assessors were blinded; The integrity of outcome data; Selective reporting of results; There were no other biases. The publication bias was evaluated by low, unclear, and high risks, and two researchers cross-checked the results.
2.5 Outcome measures
Based on the consensus experience of clinical experts and the pooled outcome measures in the RCT, we selected: erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), immunoglobulin G (IgG) level, Schirmer test, salivary flow rate, total response rate and adverse events as outcome measures. The total response rate was calculated as follows: (number of cured patients + number of improved patients)/total number of patients 100%. When the patient’s clinical symptoms and objective indicators disappear, the patient returns to normal. The patient had clinical symptoms and objective indicators, and the condition was considered to have improved. If the clinical symptoms and objective indicators were unchanged or aggravated, the patient was determined as having ineffective efficacy status.
2.6 Statistical analysis
The R-4.3.1 package “netmeta” was utilized to analyze the literature. Statistical heterogeneity was calculated using the I2 statistic, which describes the percentage of total variation across studies due to heterogeneity rather than chance. We defined an I2 greater than 50% as indicating substantial heterogeneity, in which case a random-effects model was used. Furthermore, given the common differences in population characteristics and study designs across studies, we ultimately reported only the results from the random-effects model. Odds ratio (OR) was used for binary variables, mean difference (MD) for continuous variables, and a 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated. The potential scale reduction factor (PSRF) indicated stability; the closer the value is to 1, the more stable the result. The “mtc. model ()” function established the consistency model. The “gelman. plot ()” function drew the convergence diagnosis and trajectory density maps. The “mtc. network ()” function drew the n network evidence diagram. The “forest ()” function was used to draw the forest plot of direct comparison between different interventions and conventional Western medicine. The “mtc. run ()” function was used to calculate the effect size of each intervention pairwise comparison and output the league table. The “rank. probability ()” function was used to calculate the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) of each intervention and draw the cumulative probability ranking graph. The intervention was considered more effective based on a higher SUCRA value (Yi et al., 2015).
3 Results
3.1 Literature search results
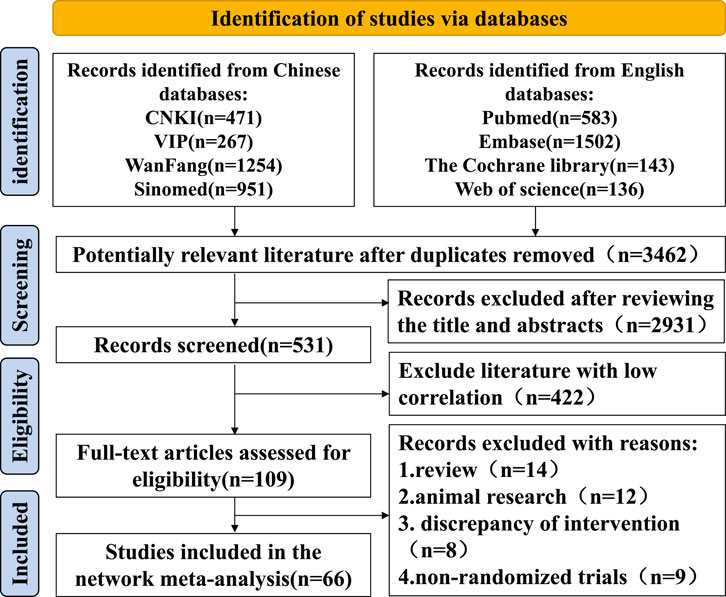
Five thousand three hundred seven articles were retrieved, and 3,462 remained after excluding duplicate articles using NoteExpress. A total of 2,931 articles were excluded after scanning titles and abstracts strictly according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and 66 articles were finally included after reading the full text (Chen and Chen, 2017; Chen et al., 2022; Chu, 2021; Ding et al., 2022; Fan et al., 2015; Feng et al., 2021; Gan et al., 2022; Gao, 2021; Gu, 2020; Gu, 2022; Guo et al., 2012; He, 2010; Ji and Cheng, 2019; Jia, 2020; Jiang et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2014; Ju et al., 2022; Li et al., 2018; Li, 2019; Li et al., 2020; Li et al., 2016; Li and Li, 2022; Liu, 2022; Liu and Yan, 2020; Liu et al., 2023; Liu J. et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2019; Lu and Zhang, 2021; Luo et al., 2019; Luo et al., 2018; Ma, 2012; Ma et al., 2021; Meng et al., 2023; Rao et al., 2022; Shao, 2016; Shi and Kong, 2023; Tang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2014; Wang, 2019; Wang, 2017; Wang, 2018; Wang et al., 2019; Wang and Wang, 2020; Wu et al., 2017; Xia et al., 2017; Xie et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2011; Ye et al., 2019; Yin, 2011; Yu, 2020; Zhang and Shen, 2019; Zhang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2009; Zhang, 2015; Zhang, 2019; Zhang, 2021; Zhao, 2013; Zhao, 2018; Zhao, 2020; Zhao, 2023; Zhao, 2019a; Zhao, 2019b; Zhu et al., 2016). The literature screening process was as follows Figure 1. A total of 5,052 cases were enrolled, including 2,529 cases in the experimental group and 2,523 cases in the control group. The sample size of a single study ranged from 29 to 200 cases, covering four kinds of Chinese patent medicine, including Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides tablets, total glucosides of paeony capsules, Xinfeng capsules, and Jinjuqingruncapsule.
3.2 Description of included trials
The essential characteristics of the included literature are shown in Table 2.
3.3 Risk of bias
Of the 66 included RCTS, 29 items (Chen et al., 2022; Chu, 2021; Fan et al., 2015; Gan et al., 2022; Gao, 2021; Gu, 2020; Gu, 2022; Jia, 2020; Jiang et al., 2016; Ju et al., 2022; Li et al., 2018; Liu and Yan, 2020; Liu et al., 2023; Liu M. et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2019; Lu and Zhang, 2021; Wang et al., 2013; Wang, 2017; Wang et al., 2019; Xie et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2011; Zhang and Shen, 2019; Zhao, 2018; Zhao, 2020; Zhao, 2019a; Zhao, 2019b; Zhu et al., 2016) using a random number table method, 3 items (Jiang et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2009) were SAS/SPSS statistical software, 5 items (Liu, 2022; Rao et al., 2022; Xia et al., 2017; Ye et al., 2019; Zhao, 2023) were lottery method, and the risk of bias was rated as low risk, 6 items (Li and Long, 2020; Luo et al., 2019; Shi and Kong, 2023; Tang et al., 2020; Wang, 2018; Wang and Wang, 2020) were grouped by different treatment regimens, 4 items (Ding et al., 2022; Li et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2017; Zhang, 2015) were grouped by admission or visit order. The risk of bias was rated as high, and the rest of the studies only mentioned the word “random,” and the risk of bias was rated as unclear. One article (Li et al., 2018) mentioned single-blind and allocation concealment, and the risk of bias was rated as low. All studies did not mention loss to follow-up/dropout reports, and there was no attrition bias. All studies had complete outcome data without selective reporting bias. Whether other biases are present is unclear. The quality evaluation of the included literature is shown in Figure 2.
3.4 ESR
3.4.1 Evidence network and network meta-analysis
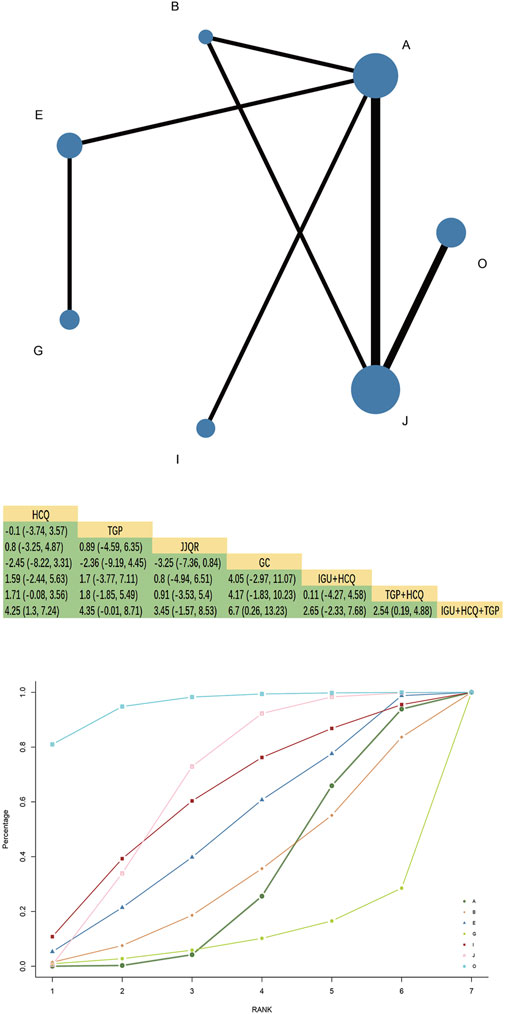
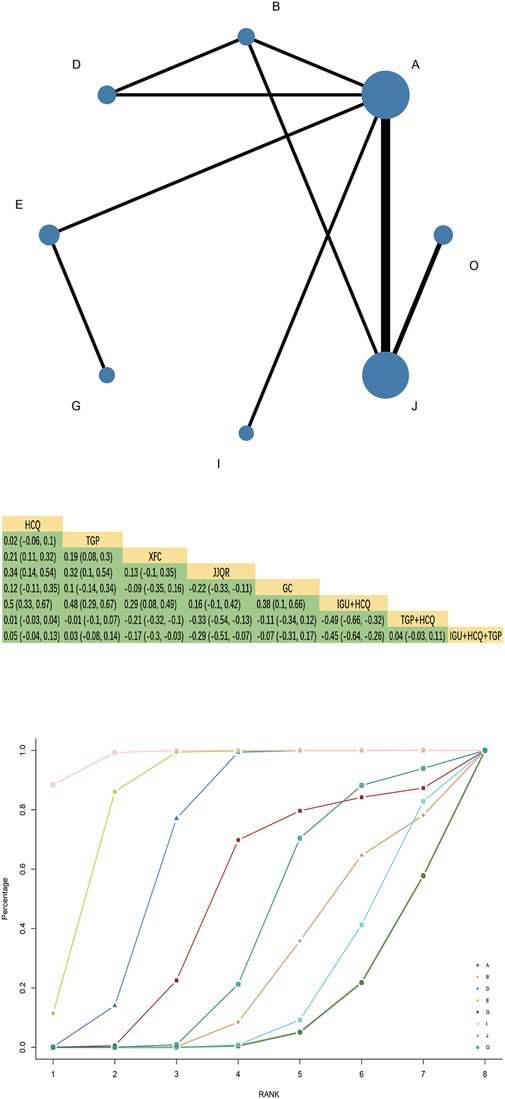
Forty-three RCTs reported ESR, involving 16 interventions, four kinds of Chinese patent medicine, 3,059 patients, and two closed loops. HCQ + TGPvsHCQ had the largest comparison with the thickest line segment and greater sample size. HCQ + GC had the largest nodes and sample size studied, with the most in direct comparison with IGU + GC.The results of the network meta-analysis showed that TGT had better efficacy than HCQ [MD = −6.63, 95%CI= (−12.78, −0.2)], TGP, XFC, JJQR had no significant difference compared with HCQ and IGU (p > 0.05). TGP combined with HCQ was superior to HCQ alone [MD = −9.13, 95%CI= (−12.52, −5.72)](Figure 3). The SUCRA ranking in the network graph of each outcome indicator is shown in Supplementary Table S2.
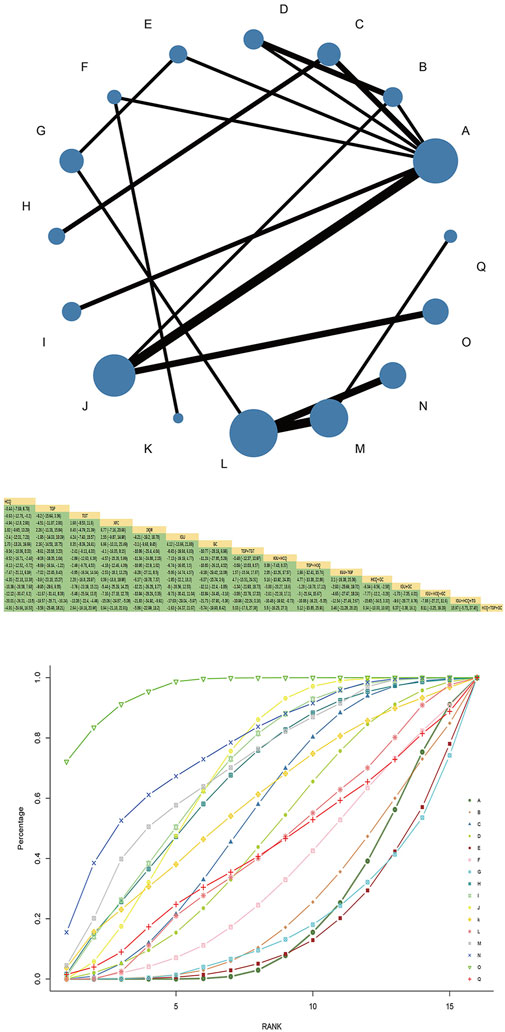
Figure 3. ESR network diagram, league diagram, SUCRA diagram.Note: A: HCQ; B: TGP; C: TGT; D: XFC; E: JJQR; F: IGU; G: GC; H: TGP + TGT; I: IGU + HCQ; J: TGP + HCQ; K: IGU + TGP; L: HCQ + GC; M: IGU + GC; N: IGU + HCQ + GC; O: IGU + HCQ + TGP; P: TGT + HCQ + GC; Q: HCQ + TGP + GC; In the evidence network drawn by different outcome indicators, the node size represents the study’s sample size, and the node connection’s thickness represents the number of included studies, the same as below.
3.4.2 SUCRA probability ranking
SUCRA probability values are ranked as:IGU + HCQ + TGP(SUCRA = 96.0)>IGU + HCQ + GC(SUCRA = 76.4)>IGU + GC(SUCRA = 69.5)>IGU + HCQ (SUCRA = 67.9)>TGP + HCQ (SUCRA = 67.6)>TGP + TGT (SUCRA = 65.5)>IGU + TGP(SUCRA = 57.4)>TGT (SUCRA = 53.7)>XFC(SUCRA = 46.4)>HCQ + GC(SUCRA = 42.8)>HCQ + TGP + GC(SUCRA = 42.2)>IGU(SUCRA = 33.6)>TGP(SUCRA = 24.2)>HCQ (SUCRA = 20.9)>GC(SUCRA = 18.7)>JJQR (SUCRA = 17.3).
3.5 IgG
3.5.1 Evidence network and network meta-analysis
Forty-six RCTs reported IgG, involving 16 interventions, 4 Chinese patent medicines, and 3,438 patients, forming one closed loop; HCQ and TGP combined with HCQ had the largest node and sample size. TGP + HCQvsHCQ was the most studied with the thickest line segment. The results of the network Meta-analysis showed that TGT was superior to HCQ [MD = −4.21, 95%CI= (−6.42, −1.89)], XFC was superior to TGP [MD = −2.89, 95%CI= (−5.03, −0.75)] under single treatment measure. TGP, XFC, and JJQR were not significantly different from HCQ and IGU (p > 0.05). TGP combined with HCQ was superior to HCQ alone [MD = −3.39, 95%CI= (−4.53, −2.23)] (Figure 4).
3.5.2 SUCRA probability ranking
SUCRA probability values are ranked as:IGU + HCQ + TGP(SUCRA = 96.0)>IGU + HCQ + GC(SUCRA = 76.2)>IGU + GC(SUCRA = 69.4)>IGU + HCQ (SUCRA = 68.0)>TGP + HCQ (SUCRA = 67.7)>TGP + TGT (SUCRA = 65.6)>IGU + TGP(SUCRA = 57.4)> TGT (SUCRA = 53.7) = XFC(SUCRA = 53.7)>HCQ + GC(SUCRA = 42.7)>HCQ + TGP + GC.
(SUCRA = 42.1)>IGU(SUCRA = 33.6)>TGP(SUCRA = 24.2)>HCQ (SUCRA = 20.9)>GC(SUCRA = 18.6)>JJQR (SUCRA = 17.2).
3.6 Schirmer trial
3.6.1 Evidence network and network meta-analysis
The Schirmer trial was reported in 18 RCTs, involving seven interventions, 2 Chinese patent medicines, and 1,387 patients, forming one closed loop; HCQ and TGP combined with HCQ had the largest node and sample size. TGP + HCQ vs. HCQ and IGU + TGP + HCQ vs. TGP + HCQ had the most studies and the thickest line segments. The network Meta-analysis results showed that the confidence intervals included 0 compared to a single treatment measure, suggesting no significant difference in improving Schirmer between Chinese patent medicine and Western medicine alone (p > 0.05). IGU + HCQ + TGP was superior to TGP + HCQ [MD = 2.54, 95%CI= (0.19, 4.88), P< 0.05] and HCQ alone [MD = 4.25, 95%CI= (1.30, 7.24), P< 0.05] (Figure 5).
3.6.2 SUCRA probability ranking
SUCRA probability values are ranked as:IGU + HCQ + TGP(SUCRA = 95.6)>TGP + HCQ (SUCRA = 66.2)>IGU + HCQ (SUCRA = 61.5)>JJQR (SUCRA = 50.6)>TGP(SUCRA = 33.7)>HCQ (SUCRA = 31.6)> GC(SUCRA = 10.7).
3.7 Salivary flow rate
3.7.1 Evidence network and network meta-analysis
Twenty-one RCTs reported a salivary flow rate involving eight interventions, 3 Chinese patent medicines, 1,642 patients, and forming two closed loops. HCQ and TGP combined with HCQ had the largest node and sample size. TGP + HCQ vs. HCQ had the most studies and the thickest line segments. The results of the network Meta-analysis showed that JJQR [MD = 0.34, 95%CI= (0.14, 0.54), P< 0.05] and XFC were superior to HCQ [MD = 0.21, 95%CI= (0.11, 0.32), P< 0.05], and TGP had the same efficacy as HCQ. There was no statistically significant difference [MD = 0.02, 95%CI= (−0.06, 0.1), P> 0.05] (Figure 6).
3.7.2 SUCRA probability ranking
SUCRA probability values are ranked as:IGU + HCQ (SUCRA = 98.2)>JJQR (SUCRA = 85.3)>XFC(SUCRA = 70.0)>GC(SUCRA = 49.2)>IGU + HCQ + TGP(SUCRA = 39.2)>TGP(SUCRA = 26.7)>TGP + HCQ (SUCRA = 19.2)>HCQ (SUCRA = 12.2).
3.8 Total effective rate
3.8.1 Evidence network and network meta-analysis
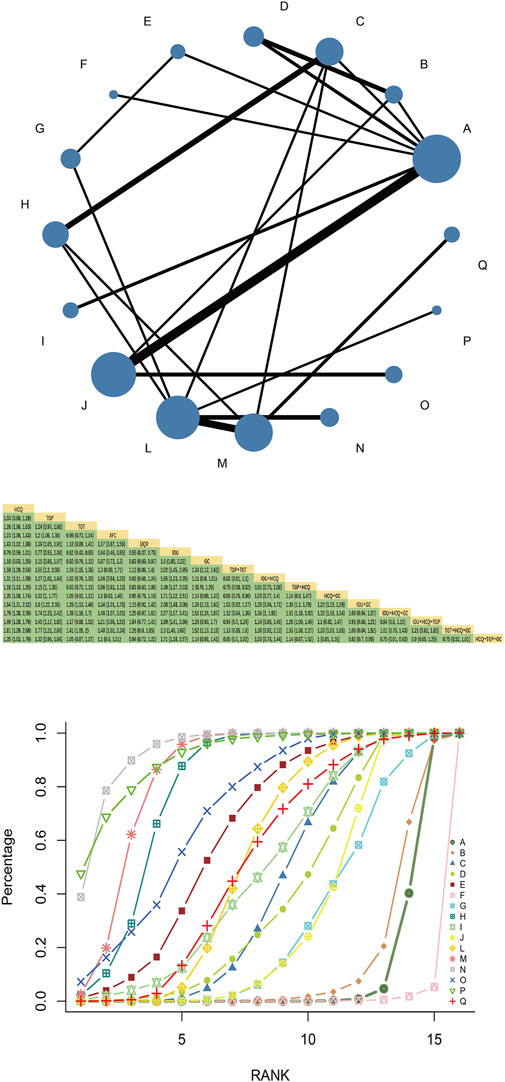
Fifty-four RCTs reported total response rates involving 16 interventions, 4 Chinese patent medicines, and 4,337 patients. Multiple closed loops were formed between the interventions. HCQ had the largest node and the largest sample size. TGP + HCQvsHCQ was the most studied with the thickest line segment. The results of the network Meta-analysis showed that TGT, XFC, and JJQR were superior to HCQ and IGU (p < 0.05), and there was no significant difference between TGP and HCQ or IGU (p > 0.05). TGP combined with HCQ was superior to HCQ alone [MD = 1.18, 95%CI= (1.13, 1.25)] (Figure 7).
3.8.2 SUCRA probability ranking
SUCRA probability values are ranked as: IGU + HCQ + GC (SUCRA = 93.6 > TGT + HCQ + GC (SUCRA = 91.0) > IGU + GC (SUCRA = 84.2 > TGP + TGT (SUCRA = 79.8)> IGU + HCQ + TGP (SUCRA = 71.1 > JJQR (SUCRA = 63.1 > HCQ + GC (SUCRA = 53.2 > HCQ + TGP + GC (SUCRA = 51.6 > IGU + HCQ (SUCRA = 48.3 > TGT (SUCRA = 43.0 > XFC (SUCRA = 38.4 > TGP + HCQ (SUCRA = 30.6 > GC (SUCRA = 28.8)> TGP (SUCRA = 12.8 > HCQ (SUCRA = 9.5 > IGU (SUCRA = 0.6).
3.9 Adverse events
Forty-two RCTs reported adverse events, as detailed in Supplementary Table S3. Four studies had no apparent discomfort, and 38 reported gastrointestinal discomfort, abnormal liver function, leukopenia, blurred vision, rash, and itching. Still, there was no dropout due to adverse events.
3.10 Consistency analysis
Bayesian P values generated by the node-splitting method were used to verify consistency between direct and indirect comparisons (Supplementary Figure S1). All P values exceeded 0.05, indicating a satisfactory level of consistency.
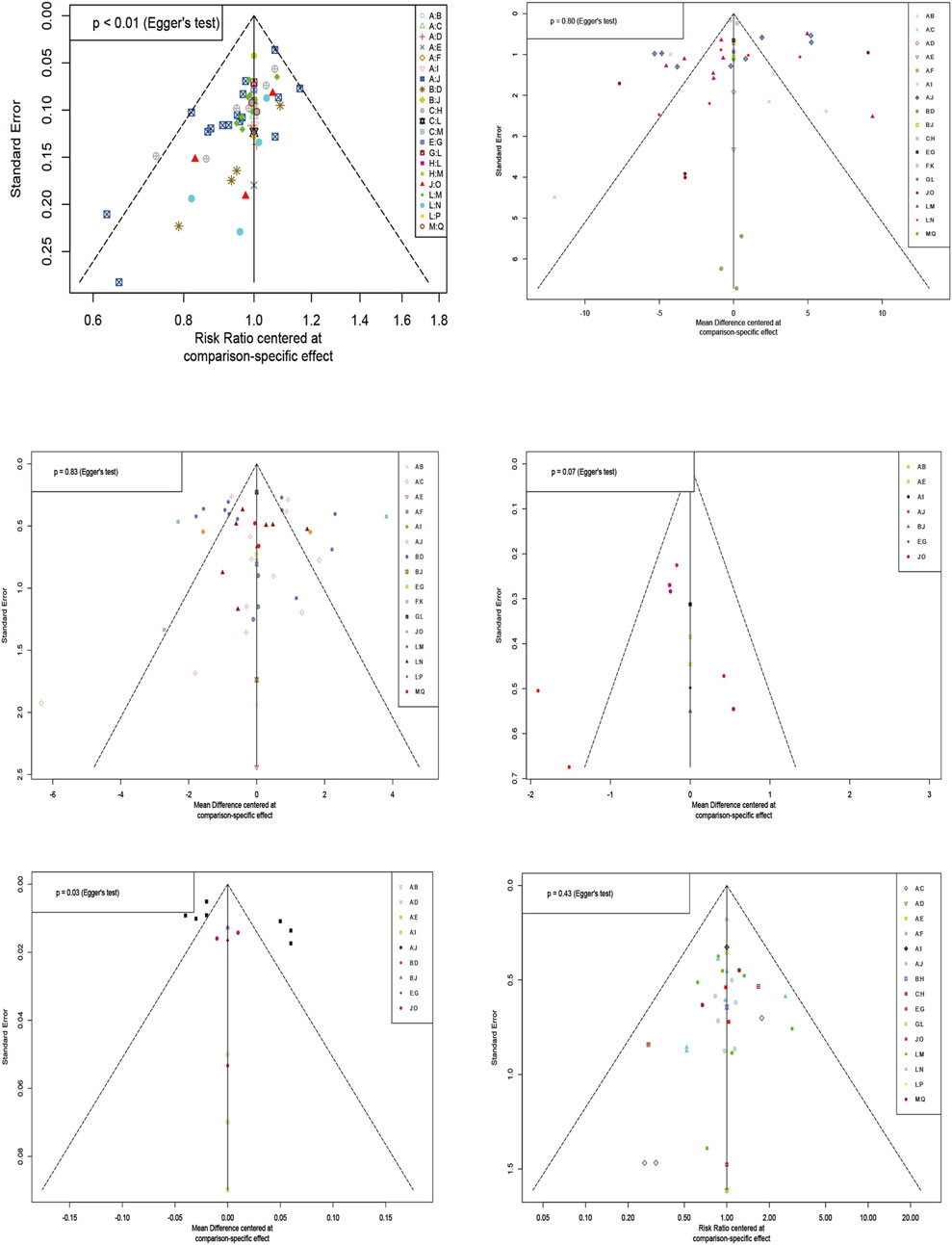
3.11 Publication bias
The results of the comparative-corrected funnel plot showed that most of the included literature was symmetrically distributed around the zero line. However, there was still a tiny part of the discrete distribution, indicating that there may be a certain degree of publication bias and a small sample effect (Figure 8).
4 Discussion
Western medicine treatments for SS usually rely on the extrapolation of the therapeutic effects of other autoimmune diseases, which are less selective. The treatment and management of patients often rely on experience, and there is a lack of evidence of treatment effects (Seror et al., 2021). With the gradual introduction of TCM, TCM is more and more widely used in the treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome. Natural drugs such as traditional Chinese medicine have strong pharmacological activities, anti-inflammatory and immune regulation effects.
In this study, various traditional Chinese medicines, such as TGT, TGP, radix scrophulariae, ophiopogon japonicus can be used to treat SS. A total of 66 RCTs were included in this study, which related 4 Chinese patent medicines, 3 Western medicines, and five outcome indicators, and achieved direct and indirect comparisons between different interventions used alone or in combination, and initially filled the academic gap of priority comparison of Chinese patent medicines commonly used in clinical treatment of SS. Of these 17 drug therapies, 4 were proprietary Chinese medicines, 3 were Western medicines (2 DMARDs and hormones), and 10 were different combinations of proprietary Chinese and Western medicines. The results of the study showed that IGU + HCQ + TGP tended to be recommended as the best treatment when the three drugs were used in combination because it ranked the highest in ESR (96.0%), IgG (96.0%), and Schirmer test (95.6%), and the risk of adverse events was relatively low. When the two drugs are combined, IGU + GC and TGT + TGP are good choices for reducing ESR and IgG. Although TGP + HCQ vs. HCQ had the most studies, TGP combined with HCQ ranked relatively low in each outcome indicator when the two drugs were compared. When a drug is used alone, TGT or XFC is better in reducing ESR or IgG, while JJQR alleviates dry mouth-eye, and improves Schirmer trial and Salivary flow rate.
However, some TCM will inevitably cause certain damage to the heart, liver, kidney, stomach and other organs, as well as common adverse reactions, such as blood system damage, gastrointestinal reaction, liver and kidney damage, skin itching, headache, constipation, amenorrhea,etc.For example, studies have shown that TGT has some reproductive toxicity (Zhang et al., 2023),which may lead to the risk of amenorrhea in female patients with Sjogren’s syndrome.
Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides are the components extracted from the root of the Eualaceae plant Tripterygium wilfordii. It has the effects of eliminating wind and dampness, reducing swelling, and relieving pain. It is widely used in autoimmune diseases due to its potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Consistent with the results of this study, a study (Liu J. et al., 2022) showed that TGT could alleviate inflammatory response and improve symptoms such as dry mouth and blood viscosity in SS model mice. Total paeony glucosides derived from the dried root of Paeonia lactiflora in the Ranunculaceae family are the most studied Chinese patent medicine for SS. Hanying Mei (Mei et al., 2021) found that total glucosides of paeony can reduce the inflammatory response in mice with Sjogren’s syndrome by regulating the activity of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and play an anti-inflammatory role. Both have been recommended by the “Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Sjogren’s Syndrome based on TCM Syndromes” (Jiang et al., 2024). The results of this study also showed that the combined IGU + HCQ + TGP regimen was significantly effective in reducing ESR, IgG and improving Schirmer trial, ranking first, but there is no study explaining the synergistic mechanism of TGP on IGU + HCQ.Desiccation affects more than 95% of patients with SS (Brito-Zerón et al., 2016). JJQR has a good effect on improving salivary flow, perhaps because its ingredients contain ginseng, ophiopogon and radix scrophulariae, which have the effect of nourishing qi and Yin, generating fluid and quenching thirst.
5 Limitation
There have been few indirect clinical studies on the treatment of SS by different TCMs combined with CWM; therefore, the differences in the therapeutic effects of different TCMs combined with CWM are not clear. In this study, network meta-analysis was used to clearly compare the efficacy of different TCMs combined with CWM to guide clinical treatment and provide certain suggestions and aid. However, there are still several shortcomings in this study. First,We found that not all studies specified the randomization process, which may have a particular publication bias; Second, Considering the large number of included studies, the differences between studies may affect the applicability of the network meta-analysis (transitivity assumption). Although all the studies we included were randomized controlled trials, there may still be significant inter-study differences in randomization methods, sample size settings, and intervention protocols. Additionally, the basic characteristics of the study populations are also important factors influencing the transitivity assumption. In the studies we included, the population’s age and disease duration were around 50 years and 5 years, respectively. We believe there are no significant differences in these two population characteristics between studies, thus meeting the transitivity assumption. However, some potential population characteristics, such as gender ratio and ethnicity, may still exhibit inter-study differences that could impact the robustness of our conclusions. Therefore, our conclusions will be interpreted and considered with caution. Next, some treatments had few papers, which may lead to statistical bias. Finally, TCMs are not widely used in other countries. Therefore, almost all selected papers in this NMA were from China, which may have caused regional, language,and racial biases. We hope that in the future there will be large-scale RCTs in different countries to further provide more reliable data.
6 Conclusion
Through the network meta-analysis concluded that TCMs combined with CWM had more significant clinical efficacy and safety in treating SS compared to only CWM, and also obtained the order of optimal interventions for different outcome measures. Among them, IGU + HCQ + TGP may be the best intervention. TGP + HCQ, TGP + TGT, IGU + TGP can be considered as an alternative to IGU + HCQ when reducing ESR and IgG. TGT and XFG decrease ESR and IgG with good clinical effects. JJQR may have an advantageous role in relieving xerostomia and dry eyes. The aim of the results of this study is to provide some advice and help for clinical application.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
XM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. TC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. CY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. YY: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft. BS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing–review and editing. JL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Software, Supervision, Writing–original draft. CX: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing–original draft. XG: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. QJ: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Innovation Engineering Team of the Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (Project number 461178).
Acknowledgments
Thanks to all the authors in this study for their contributions and to the advisors for their expert advice.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1455969/full#supplementary-material
References
Baldini, C., Fulvio, G., La Rocca, G., and Ferro, F. (2024). Update on the pathophysiology and treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 20 (8), 473–491. doi:10.1038/s41584-024-01135-3
Beydon, M., McCoy, S., Nguyen, Y., Sumida, T., Mariette, X., and Seror, R. (2024). Epidemiology of sjögren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 20 (3), 158–169. doi:10.1038/s41584-023-01057-6
Brito-Zerón, P., Baldini, C., Bootsma, H., Bowman, S. J., Jonsson, R., Mariette, X., et al. (2016). Sjögren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2, 16047. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.47
Chen, H., and Chen, Y. (2017). Clinical effect of Pavlin combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Contemp. Med. Symp. 15 (14), 37–38.
Chen, Y., Shen, P., and Sun, D. (2022). To analyze the efficacy of iguratimod in the treatment of elderly patients with pSS and its effect on B cell activity and immunoglobulin G secretion. J. Med. Theory Pract. 35 (02), 244–246. doi:10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2022.02.025
Chu, Y. (2021). Clinical effect of total glucosides of paeony capsule combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Med. Health (7).
Ding, L., He, S., Wang, M., Zou, C., and Wang, M. (2022). To investigate the efficacy of iguratimod in the treatment of elderly patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome and its influence on SSDAI and ESSPRI scores. Clin. Res. Pract. 7 (17), 78–80. doi:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202217020
Fan, H., Liu, J., Huang, C., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Wang, G., et al. (2015). Effect of Xinfeng capsule on lung function of Sjogren's syndrome and its mechanism. Rheunatism Arthritis 4 (01), 14–17. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4174.2015.01.003
Feng, L., Xu, Y., and Li, M. (2021). To investigate the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine sulfate in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome and its effect on serum IL-17, ESR, CRP and IgG levels. Hebei Med. 27 (02), 334–339. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6233.2021.02.034
Gan, M., Yu, J., and Deng, Y. (2022). To observe the clinical effect of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides combined with total glucosides of paeony in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome and its influence on serum ACL and RF. Chin. Archives Traditional Chin. Med. 40 (02), 94–96. doi:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2022.02.021
Gao, X. (2021). To evaluate the efficacy of total glucosides of paeony capsules combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Heilongjiang Med. Pharm. 44 (01), 164–165.
Gu, J. (2020). To investigate the clinical effect of methylprednisolone combined with iguratimod in the treatment of elderly patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Med. J. Chin. People's Health 32 (18), 1–2+5. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2020.18.001
Gu, J. (2022). Clinical effect of methylprednisolone combined with iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome and its influence on immunoglobulin levels. Contemp. Med. 28 (08), 158–160. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2022.08.057
Guo, Y., Ma, C., and Ji, W. (2012). Efficacy analysis of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides tablets in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome hyperglobulinemia. J. Zhejiang Chin. Med. Univ. 36 (07), 770–772. doi:10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2012.07.037
He, H. (2010). Clinical observation of total glucosides of paeony combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Hubei J. Traditional Chin. Med. 32 (11), 30–31.
Higgins, J. P., and Welton, N. J. (2015). Network meta-analysis: a norm for comparative effectiveness? Lancet London, Engl. 386 (9994), 628–630. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61478-7
Ji, J., and Cheng, J. (2019). To investigate the efficacy of iguratimod combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome and its effect on the expression of B cell surface molecules. J. Clin. Med. Pract. 23 (13), 14–17. doi:10.7619/jcmp.201913004
Jia, X. (2020). Efficacy of iguratimod combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Gansu Sci. Technol. 36 (18), 106–108. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0952.2020.18.038
Jiang, D., Bai, Y., Zhao, L., Zhang, Y., and Chen, Z. (2016). Clinical effect of iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Clin. Misdiagnosis and Mistherapy 29 (08), 90–93. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2016.08.029
Jiang, Q., Zhou, X., Tang, X., Jiao, J., Gong, X., and Han, M. (2024). Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of Sjogren's syndrome based on TCM syndromes. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 65 (04), 434–444.
Jiang, W., Zhao, Y., Lin, H., Liu, Y., and Chen, J. (2014). Efficacy of iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Med. J. West China 26 (06), 719–721+724. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2014.06.015
Ju, Y., Li, R., Zhou, S., Hu, J., and Guo, D. (2022). Clinical effect of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides tablets in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. China Mod. Med. 29 (03), 37–39.
Li, B., Liu, G., Liu, R., He, S., Li, X., Huang, L., et al. (2020). Total glucosides of paeony (TGP) alleviates Sjogren's syndrome through inhibiting inflammatory responses in mice. Phytomedicine Int. J. phytotherapy Phytopharm. 71, 153203. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153203
Li, C., Li, R., Liu, H., Cheng, C., and Zhao, T. (2018). Efficacy of methylprednisolone combined with iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome and its effect on immunoglobulin levels. China Pharm. 27 (14), 35–37. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2018.14.012
Li, Q. (2019). Clinical observation of total glucosides of paeony capsule combined with iguratimod in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Guangming J. Chin. Med. 34 (06), 930–932. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2019.06.048
Li, R., and Long, H. (2020). Efficacy of methylprednisolone combined with iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome and its effect on immunoglobulin levels. World J. Complex Med. 6 (05), 189–191. doi:10.11966/j.issn.2095-994x.2020.06.05.63
Li, T., Sun, H., and Shuai, S. (2016). Clinical observation of Pavlin in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Health World 6 (23), 70–71.
Li, Y., and Li, H. (2022). To investigate the efficacy of methylprednisolone combined with Iguratimod in the treatment of elderly patients with pSS and its effect on immunoglobulin levels. Liaoning J. Traditional Chin. Med. 36 (04), 64–67.
Liu, B. (2022). Effect of iguratimod in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Chin. Community Dr. 38 (13), 57–59. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2022.13.019
Liu, H., and Yan, Y. (2020). To investigate the clinical effect of tripterygium wilfordii polyglucosides combined with total glucosides of paeony in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome and its influence on anti-cardiolipin antibody and rheumatoid factor. Clin. Res. Pract. 5 (21), 128–129+135. doi:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202021044
Liu, J., Mei, R., Yang, L., Zhao, W., Han, C., Zhou, H., et al. (2022). Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides reduce inflammatory response in Sjogren's syndrome model mice. Basic and Clin. Med. 42 (09), 1362–1366. doi:10.16352/j.issn.1001-6325.2022.09.1362
Liu, L., Chen, Q., and You, X. (2023). To investigate the effect of iguratimod combined with methylprednisolone on the efficacy and ESSDAI score of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. J. Qiqihar Med. Univ. 44 (04), 317–320. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-1256.2023.04.005
Liu, M., Song, D., Wang, F., Tang, Q., and Sun, J. (2022). To investigate the application effect of hydroxychloroquine sulfate combined with total glucosides of paeony in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Health Required (23), 171–172.
Lu, D., Wang, L., Wang, G., and Zuo, Z. (2019). Clinical effect of total glucosides of paeony capsule combined with hydroxychloroquine sulfate in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. China Med. Her. 16 (36), 115–118.
Lu, T., and Zhang, W. (2021). Clinical efficacy of iguratimod combined with hydroxychloroquine sulfate in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 14 (31), 55–57. doi:10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2021.31.018
Luo, C., Shi, Y., Chen, X., and Wu, L. (2019). Clinical analysis of iguratimod in the treatment of 46 patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. J. Chin. Pract. Diagnosis Ther. 33 (12), 1232–1235. doi:10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2019.12.024
Luo, Y., Guo, D., Yu, Y., and Lin, J. (2018). Efficacy and safety of iguratimod and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 10 (24), 94–95. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2018.24.041
Ma, C. (2012). Effect of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides tablets on hyperglobulinemia in primary Sjogren's syndrome. Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (NanJing).
Ma, C., Sun, Q., and Qi, J. (2021). Effect analysis of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides tablets on hyperglobulinemia in primary Sjogren's syndrome. World Latest Med. Inf. 21 (2), 187–188. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-3141.2021.2.090
Mariette, X., and Criswell, L. A. (2018). Primary Sjögren's syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 378 (10), 931–939. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1702514
Mei, H., Liu, J., and Tang, Z. (2021). To investigate the mechanism of total glucosides of paeony on inhibiting inflammation in a mouse model of Sjogren's syndrome based on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Traditional Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 32 (09), 1293–1299.
Meng, D., Li, J., Li, Y., Liu, S., Liu, J., Wang, K., et al. (2023). Efficacy of iguratimod combined with methylprednisolone and hydroxychloroquine sulfate in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome complicated with interstitial lung disease. Chin. J. Clin. Res. 36 (01), 85–89. doi:10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2023.01.017
Ramos-Casals, M., Brito-Zerón, P., Sisó-Almirall, A., and Bosch, X. (2012). Primary sjogren syndrome. BMJ Clin. Res. ed. 344, e3821. doi:10.1136/bmj.e3821
Rao, Y., Zhang, W., Lu, T., and Xu, S. (2022). To investigate the effect of iguratimod in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome and its influence on immune function. J. Ningxia Med. Univ. 44 (02), 152–156. doi:10.16050/j.cnki.issn1674-6309.2022.02.008
Seror, R., Nocturne, G., and Mariette, X. (2021). Current and future therapies for primary Sjögren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 17 (8), 475–486. doi:10.1038/s41584-021-00634-x
Shao, N. (2016). Effect of Xinfeng capsule on Sjogren's syndrome. Chin. J. Mod. Drug Appl. 10 (18), 173–174. doi:10.14164/j.cnki.cn11-5581/r.2016.18.115
Shi, S., and Kong, H. (2023). Clinical effect of Pavlin capsule on Sjogren's syndrome. Women's Health Res. (4), 47–104.
Shiboski, C. H., Shiboski, S. C., Seror, R., Criswell, L. A., Labetoulle, M., Lietman, T. M., et al. (2017). 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren's syndrome: a consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Ann. Rhrum Dis. 76 (1), 9–16. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210571
Tang, Z., Chen, F., and Wu, T. (2020). Clinical effect of total glucosides of paeony capsule combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. World Chin. Med. 15 (16), 2443–2445+2449. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2020.16.018
Vitali, C., Bombardieri, S., Jonsson, R., Moutsopoulos, H. M., Alexander, E. L., Carsons, S. E., et al. (2002). Classification criteria for Sjögren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann. Rhrum Dis. 61 (6), 554–558. doi:10.1136/ard.61.6.554
Wang, F., Liu, J., and Ye, Y. (2013). To evaluate the efficacy and quality of life of Xinfeng capsule in 32 patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatism arthritis 2 (11), 15–19+22.
Wang, G., Liu, J., Huang, C., Fan, H., Wang, Y., Cao, Y., et al. (2014). 30 cases of Sjogren's syndrome were treated with Xinfeng capsule. Rheunatism Arthritis 3 (09), 5–9+13. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4174.2014.09.001
Wang, M. (2019). Analysis of the effect of total glucosides of paeony capsule in the adjuvant treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Contemp. Med. Symp. 17 (17), 3–4.
Wang, X. (2017). Effect of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides combined with total glucosides of paeony on salivary flow rate in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Shenzhen J. Integr. Traditional Chin. West. Med. 27 (13), 34–35. doi:10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2017.13.017
Wang, Y. (2018). Clinical efficacy of iguratimod combined with methylprednisolone in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome and its effect on serum IgG content. Health World 8 (27), 38–40. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1752.2018.27.025
Wang, Y., Zhao, F., Ai, X., Liu, Y., and Zhu, Z. (2019). To observe the efficacy and safety of iguratimod in the treatment of elderly patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Geriatrics and Health Care 25 (02), 209–213. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8296.2019.02.020
Wang, Z., and Wang, Y. (2020). To compare the efficacy and safety of iguratimod and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Electron. J. Clin. Med. Literature 7 (25), 160+168. doi:10.16281/j.cnki.jocml.2020.25.102
Wang, Z., Xu, Y., and Liang, S. (2024). Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on the mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook in the treatment of Sjögren syndrome. Med. Baltim. 103 (14), e37532. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000037532
Wu, G., Wang, Q., Lu, W., Xiong, F., Gao, L., and Bian, H. (2021). To investigate the effect of total glucosides of paeony on Sjogren's syndrome based on the regulation of RORγt, Foxp3 and their mRNA in submandibular gland of NOD mice. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 33 (03), 462–467.
Wu, T., Zhang, J., Su, J., Tian, C., and Long, W. (2017). Efficacy of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides combined with total glucosides of paeony and Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides alone in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Materia Medica 33 (01), 178–180. doi:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2017.01.050
Xia, Z., Liu, Y., Meng, F., Fang, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, C., et al. (2017). Analysis of clinical effect of iguratimod combined with treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. China Health Care and Nutr. 27 (34), 263. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-7484.2017.34.395
Xie, H., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Zeng, C., and Zhou, Y. (2020). Hydroxychloroquine sulfate combined with total glucosides of paeony and iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Med. J. West China 32 (09), 1358–1362. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2020.09.022
Xu, D., Lv, X., Cui, P., and Ma, S. (2017). To compare the efficacy and safety of iguratimod and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Chin. J. Difficult Complicat. Cases 16 (09), 915–918. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2017.09.013
Xu, L., Pang, L., and Li, X. (2022). Effect of pavlin combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Health World 12 (11), 15–21.
Yang, J., Liu, J., Wang, S., and Zhang, J. (2011). Clinical observation of Xinfeng capsule in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Clin. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 23 (06), 537–539. doi:10.16448/j.cjtcm.2011.06.020
Ye, J., Wang, R., Zhang, B., Li, L., and Huang, Y. (2019). To observe the curative effect of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides combined with total glucosides of paeony and Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides alone in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Electron. J. Clin. Med. Literature 6 (63), 140–141. doi:10.16281/j.cnki.jocml.2019.63.124
Yi, Y., Zhang, W., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Zhu, D., and Lv, Q. (2015). Interpretation of graphic results of network meta-analysis. Chin. J. Evidence-Based Med. 15 (01), 103–109.
Yin, B. (2011). Clinical observation of pavlin combined with hydroxychloroquine sulfate in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome with non-systemic involvement. Med. Innovation China 8 (35), 20–21.
Yu, W. (2020). Clinical analysis of iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Guide China Med. 18 (06), 150. doi:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2020.06.122
Zhang, J., and Shen, S. (2019). Efficacy and mechanism of iguratimod in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Shaanxi Med. J. 48 (04), 452–455. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7377.2019.04.012
Zhang, S., Guo, G., Liang, J., Li, H., Zhang, H., Zhu, X., et al. (2011). Clinical observation of 30 cases of primary Sjogren's syndrome treated with Jinju Qingrun capsule. Chin. J. Difficult Complicat. Cases 10 (11), 835–838. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2011.11.013
Zhang, S., Li, R., Zhu, X., Zhang, S., Wu, Z., Jiang, F., et al. (2009). Clinical observation of 50 cases of primary Sjogren's syndrome treated with Jinju Qingrun capsule. J. Traditional Chin. Med. 50 (08), 708–711. doi:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2009.08.026
Zhang, W., Xia, S., Ou, J., Cao, M., Cheng, G., Li, Z., et al. (2023). A single-cell landscape of triptolide-associated testicular toxicity in mice. J. Pharm. Anal. 13 (8), 880–893. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2023.04.006
Zhang, X. (2015). Efficacy of pavlin combined with hydroxychloroquine sulfate tablets in the treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome with both qi and yin deficiency. Master’s Thesis. Shenyang (China). Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Zhang, X. (2019). Comparison of iguratimod and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Guide China Med. 17 (32), 103. doi:10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2019.32.081
Zhang, Y. (2021). Effect of hydroxychloroquine sulfate combined with total glucosides of paeony and iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Contemp. Med. Symp. 19 (18), 97–99. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-7629.2021.18.048
Zhao, H., and Zhao, F. (2013). Clinical study of total glucosides of paeony combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 33 (04), 530–531. doi:10.16367/j.issn.1003-5028.2013.04.083
Zhao, J. (2018). To investigate the efficacy and safety of total glucosides of paeony capsules in the adjuvant treatment of xerostomia in Sjogren's syndrome. Strait Pharm. J. 30 (11), 174–175.
Zhao, J. (2020). To compare the efficacy and safety of iguratimod and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Chin. Remedies and Clin. 20 (21), 3627–3629. doi:10.11655/zgywylc2020.21.040
Zhao, J. (2023). Effect analysis of total glucosides of paeony capsule combined with hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Diet. Health (5), 1–4.
Zhao, L. (2019a). Effect of methylprednisolone combined with iguratimod in the treatment of primary Sjogren's syndrome. Med. J. Chin. People's Health 31 (17), 35–36. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2019.17.015
Zhao, L. (2019b). Effect of tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides combined with total glucosides of paeony in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome. Med. J. Chin. People's Health 31 (18), 127–128. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2019.18.053
Keywords: Sjogren’s syndrome, Chinese patent medicine, tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides tablets, total glucosides of paeony capsule, network meta-analysis, randomized controlled
Citation: Ma X, Liu Z, Chang T, Yao C, Yang Y, Shang B, Liu J, Xia C, Gong X and Jiang Q (2024) Network meta-analysis of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1455969. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1455969
Received: 17 July 2024; Accepted: 13 November 2024;
Published: 27 November 2024.
Edited by:
Rong-Rong He, Jinan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yuan Fan, Nanjing Medical University, ChinaYuzhou Gan, Peking University People’s Hospital, China
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Liu, Chang, Yao, Yang, Shang, Liu, Xia, Gong and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xun Gong, Z29uZ3h1bjgyNjlAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Quan Jiang, ZG9jdG9yanFAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xieli Ma
Xieli Ma Zixia Liu
Zixia Liu Tian Chang
Tian Chang Chuanhui Yao
Chuanhui Yao Yuchen Yang
Yuchen Yang Biyue Shang
Biyue Shang Jiameng Liu
Jiameng Liu Congmin Xia
Congmin Xia Xun Gong
Xun Gong Quan Jiang*
Quan Jiang*