- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine Classics, Tai’an Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tai’an, China
Background: Despite the availability of multiple therapies for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), challenges remain due to side effects and efficacy limitations. Berberine (BBR) has shown broad anti-diabetic effects, prompting a systematic assessment of its efficacy and safety through a meta-analysis.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted across eight database and search engines from inception until 06/09/2024. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) meeting inclusion criteria were analyzed. The Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool and Jadad scale were used to evaluate study quality. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan v5.3 and Stata/SE v15.1.
Results: Fifty studies involving 4,150 participants were included. BBR alone significantly reduced fasting plasma glucose (FPG) (MD = −0.59 mmol/L, p = 0.048), 2-h postprandial blood glucose (2hPBG) (MD = −1.57 mmol/L, p < 0.01), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (MD = −0.30 mmol/L, p < 0.01), total cholesterol (TC) (MD = −0.30 mmol/L, p = 0.034), and triglycerides (TG) (MD = −0.35 mmol/L, p < 0.01). When combined with hypoglycemic drugs, BBR significantly improved FPG (MD = −0.99 mmol/L, p < 0.01), 2hPBG (MD = −1.07 mmol/L, p < 0.01), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (MD = −0.69%, p < 0.01), and other metabolic markers, including fasting insulin (Fins), homeostasis model assessment index for assessing insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), lipid profiles and inflammatory markers. The most common BBR dosage was 0.9–1.5 g/d, with treatment cycles typically lasting 1–3 months.
Conclusion: Current evidence suggests that BBR alone or in combination has significant potential for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Future research should encompass a broader scope, including not just the beneficial effects of BBR in head-to-head studies, but more crucially, delving into its mechanisms of action with hypoglycemic drugs to optimize T2DM treatment strategies.
1 Introduction
As per the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the global prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) among individuals aged 20–79 was estimated to be approximately 537 million in 2021, accounting for 10.5% of the global population. This figure is projected to increase to 643 million (11.3%) by 2030 and further to 783 million (12.2%) by 2045 (Sun et al., 2022). Among these cases, more than 90% are attributed to type 2 diabetes (T2DM) (Fan et al., 2024). T2DM is recognized as a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia (American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, 2024). Complications of T2DM, including various microvascular and macrovascular issues, severely impact patients’ quality of life and may lead to organ dysfunction and even death (Ahmad et al., 2022). Studies have shown that the risk of premature death in patients with T2DM is approximately 15% higher compared to the general population (Tancredi et al., 2015). Moreover, The impact of T2DM is further evidenced by the rising age-standardized mortality rates and the increasing disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), coupled with the substantial healthcare costs, particularly in high-income nations, posing a significant burden on the socioeconomic fabric and the quality of life of the population (Safiri et al., 2022; Ye et al., 2023; Butt et al., 2024). Consequently, there is an urgent need for more effective and safer strategies for prevention and treatment.
Conventional hypoglycemic agents administered orally, such as Metformin (Met), thiazolidinediones (TZDs), sulfonylureas (SU), and α-glucosidase inhibitors (AGI), are extensively utilized in the treatment of T2DM. However, they are associated with various adverse reactions, including gastrointestinal discomfort, hypoglycemia, and edema, as well as hepatic and renal impairment (Sanchez-Rangel and Inzucchi, 2017; Mehrpour et al., 2022; Derosa, 2010). Since the 21st century, a new class of hypoglycemic agents has emerged, agents like dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i), glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i), have been marketed. While these drugs exhibit promising outcomes in blood glucose control and complication reduction, they still harbor limitations and potential risks (Douros et al., 2020; Li et al., 2016). For instance, The osmotic diuretic effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors may lead to decreased blood volume and tissue perfusion, consequently increasing the risk of lower extremity complications, including amputations (Potier et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022; Yang T. et al., 2023); patients treated with DPP-4 inhibitors face a heightened incidence of cardiovascular events and adverse renal outcomes (Giugliano et al., 2022); GLP-1RA administration is intricate and may result in weight rebound post-discontinuation, significantly impacting patient tolerance and long-term compliance (Drucker et al., 2008; Weiss et al., 2022). Moreover, the high cost of these new hypoglycemic agents restricts their accessibility and affordability in certain regions (Ansari et al., 2022). Noteworthily, more researchers are turning to plant-derived traditional herbal medicines due to their significant efficacy, holistic regulation, and generally higher safety (Jovanovski et al., 2021; Samad et al., 2017; Zhang Y. et al., 2024).
Berberine (BBR), also known as Huangliansu, is a yellow crystalline isoquinoline alkaloid found in the roots, stems, leaves, and fruits of plants from the Ranunculaceae, Berberidaceae, Menispermaceae, Papaveraceae, and Rutaceae families (Neag et al., 2018). The Ranunculaceae herb Coptis chinensis has the highest BBR content, measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to be between 51.14 and 96.10 mg/g (Shrivastava et al., 2023). As a traditional medicine with a long history, BBR has been widely used to treat metabolic diseases, such as obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, and gout (Song et al., 2020). In the treatment of T2DM, although certain herbal therapies, such as okra, have shown certain potential, existing studies have demonstrated their limitations in reducing HbA1c (Mokgalaboni et al., 2023). In contrast, BBR not only significantly ameliorates glycemic control but also intervenes in the pathological state of T2DM through multiple molecular mechanisms, including improving insulin resistance, regulating gut microbiota, and exerting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (Kong et al., 2009; He et al., 2022; Utami et al., 2023). These features effectively address the limitations of existing treatment options and demonstrate promise as a new first-line therapeutic agent. Additionally, current systematic reviews have predominantly focused on BBR’s effectiveness in modulating blood glucose (Xie et al., 2022; Lan et al., 2015; Dong et al., 2012; Liang et al., 2019). Its holistic influence on glucose metabolism, insulin secretion, and lipid profiles in patients with T2DM remains incompletely validated. Thus, this study was conducted to perform a meta-analysis to thoroughly investigate the overall effects of BBR, either as a monotherapy or in combination with other hypoglycemic agents, on patients with T2DM, with the aim of providing insights and evidence for optimizing clinical treatment strategies.
2 Methods
Adhering to the PRISMA guidelines (Page et al., 2021), this study was conducted and registered with PROSPERO (ID: CRD42024519428).
2.1 Literature search
The search period spanned from the inception of database and search engines to 06/09/2024. An extensive search was done across the PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database (CNKI), Wan-Fang Database, Chinese Scientific Journals Full-text Database (VIP), and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (SinoMed) using the keywords: [“T2DM” or “Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus” or “insulin-independent diabetes mellitus” or “xiaokebing” or “tangniaobing”] AND [“Berberine” or “umbellatine” or “huangliansu”]. Detailed search strategies are available in Supplementary Table 1. Additionally, we manually reviewed the references of relevant articles to ensure that there was a thorough coverage of the literature.
2.2 Criteria for study inclusion/exclusion
2.2.1 Inclusion criteria
Population: Patients diagnosed with T2DM as per the 1999 World Health Organization criteria or the “Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (2020 Edition)”.
Intervention: BBR administered either alone or in combination with other oral hypoglycemic agents or probiotics.
Comparison: Control group subjects receiving interventions other than BBR, such as placebo, oral hypoglycemic agents, or probiotics.
Outcome: Primary outcome measures: 1) Fasting plasma glucose (FPG); 2) glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c); 3) fasting insulin (Fins). Secondary outcome measures: 1) 2-h postprandial glucose (2hPBG); 2) homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR); 3) lipid profiles (LDL-C, HDL-C, TC, TG); 4) inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6, TNF-α); 5) adverse events. Included studies should report at least one primary outcome and may include one or more secondary outcome measures.
Design: Only RCTs were deemed eligible for this study.
2.2.2 Exclusion criteria
Population: Studies involving patients with either acute or chronic complications, such as optic neuropathy, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, urinary tract infections, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, cerebral infarction, peptic ulcer disease, and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Intervention: Interventions with BBR-containing nutritional supplements or other pharmaceutical preparations such as Berberis vulgaris root extract or dried stem powder of Berberis aristata; the hypoglycemic medications used in combination interventions or the control group were not explicitly reported.
Comparison: Control measures that did not assess the effect of BBR, e.g., BBR + Met vs BBR or BBR + Met vs placebo.
Outcome: Insufficiently detailed, inaccessible, or incomplete baseline data for key outcome measures.
Study design: Self-controlled studies, animal experiments, reviews, unpublished conference abstracts, or duplicates.
2.3 Literature search and data extraction
All search results were imported into EndNote X9 (Thomson Reuters, New York, NY, United States). Following the removal of duplicate entries, the preliminary screening entailed evaluating titles and abstracts was conducted to filter out studies that did not align with the predefined criteria. Subsequently, full-text articles underwent a thorough review to finalize inclusion. Data extraction from the included studies encompassed the following categories: 1) Basic information: title, first author, publication year, and country; 2) Patient information: age, gender, disease type; 3) Drug information: intervention duration, number of participants, dosage, and outcomes for the intervention group and also the control group. Missing data were addressed by contacting the original study authors. As per the inclusion criteria, literature screening and data extraction were carried out independently by two researchers (Wang J.C., Bi C.H.). Any discrepancies were resolved through discussion with a senior researcher (Wei F.Q.).
2.4 Quality assessment concerning included studies
The quality assessment of the included RCTs was carried out using the modified Jadad scale (Moher et al., 2010). Expanding upon the original Jadad scale, this modified version evaluates random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding, and withdrawals and loss to follow-ups, providing a comprehensive assessment of study design and execution quality. Scores ranged from 0 to 7 points, with 4–7 indicating high-quality studies and 1–3 indicating low-quality studies. Additionally, we utilized the ROB to appraise the potential biases within the studies (Higgins et al., 2011). Random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, completeness of outcome data, selective reporting, and other potential sources of bias were all assessed via the tool. Each item was categorized as having a high, low, or unclear risk of bias. When details were insufficient to judge the conduct of the study, the risk was typically deemed unclear.
2.5 Statistical methods
We conducted qualitative and quantitative analyses of adjusted data using Revman v5.3 (Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom) and Stata/SE v15.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, United States) for meta-analysis. Revman 5.3 was utilized for bias risk assessment, while Stata/SE 15.1 was employed for statistical analyses. The I2 test was utilized for heterogeneity assessments across the studies. I2 between 0% and 40% suggest unimportant heterogeneity; 30%–60% may represent moderate heterogeneity; 50%–90% may represent substantial heterogeneity and 75%–100% indicate considerable heterogeneity. Therefore, a random-effects model would adopted when I2 was exceeded 40%, while a fixed-effects model would be selected if I2 was below 40% (Higgins et al., 2003). Continuous outcomes were evaluated using mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD), depending on whether the variables were measured with the same method and units (MD) or different methods/units (SMD) (Higgins et al., 2011). Effect sizes were reported with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). To identify potential publication bias among the included studies, funnel plots as well as Egger’s test were employed (Egger et al., 1997). If publication bias was identified, the trim-and-fill method was employed to make corresponding adjustments. Synthesized effects were calculated, with statistical significance defined when a two-sided p < 0.05. Exploratory subgroup and sensitivity analyses were undertaken to delve into the origins of heterogeneity and validate the robustness of the findings.
3 Results
3.1 Literature screening
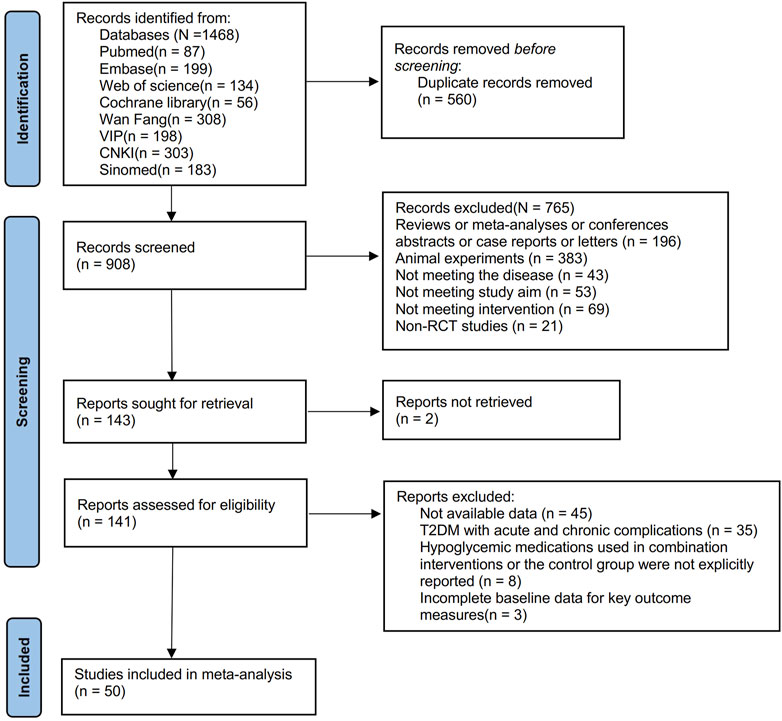
From the inception to 06/09/2024, searches were done across eight database and search engines: PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure Database (CNKI), Wan-Fang Database, Chinese Scientific Journals Full-text Database (VIP), and the Chinese Biomedical Literature Database (SinoMed), yielding a total of 1,468 articles. After removing 560 duplicates, 908 remained. Screening based on titles and abstracts further excluded 765 articles, resulting in 143 remaining articles. Two articles were inaccessible, leaving 141 articles. Following full-text review, 91 articles were then excluded, resulting in the inclusion of 50 articles (Rong et al., 1997; Zhang et al., 2000; Gao et al., 2002; Liu, 2004; Guo and Zhao, 2006; Li and Liu, 2007; Li et al., 2008; Li, 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Zhu et al., 2009; Sheng and Xie, 2010; Zhang et al., 2010; Meng et al., 2011; Xiang et al., 2011; Yin et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011; Liu, 2012; Wang et al., 2012; Xue et al., 2012; Zhang and Yuan, 2012; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Shu, 2014; Yao, 2015; Yu, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Du, 2016; Meng, 2016; Sun, 2016; Li, 2017; Sun, 2017; Wu, 2017; Xing, 2017; Zhang, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2018; Rashidi et al., 2018; Yao et al., 2018; Jiang and Wang, 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020; Chen C. et al., 2021; Chen, 2021). The flowchart of literature screening is plotted in Figure 1.
3.2 Characteristics of studies
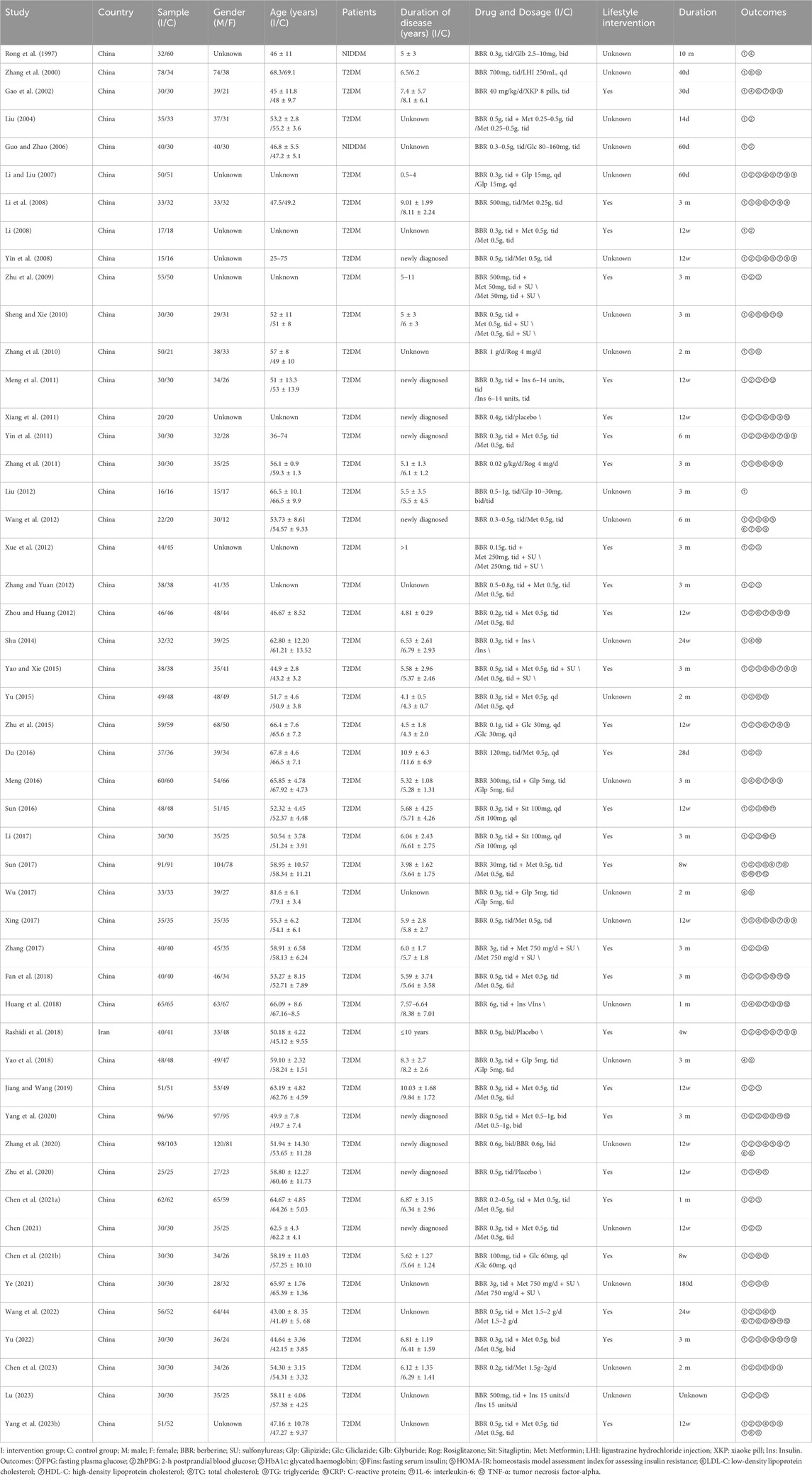
Basic characteristics of the studies are summarized in Table 1. A total of 50 studies were included, involving 4150 subjects: 2105 in the experimental group and 2045 in the control group. Participant numbers ranged from 31 to 201, with ages ranging from 25 to 75. All studies included subjects with uncomplicated T2DM. Four of the articles were published in English (Yin et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2010; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020), while the remaining studies appeared in Chinese, all of which were RCTs. Among these studies, one was conducted in Iran (Rashidi et al., 2018), whereas the others were conducted in China. Most studies used a two-arm parallel design, ten studies (Rong et al., 1997; Li and Liu, 2007; Li, 2008; Zhu et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2010; Xiang et al., 2011; Xue et al., 2012; Xing, 2017; Zhang, 2017; Ye, 2021) used a three-arm control design and one study (Zhang et al., 2020) used four-arm designs, where the most suitable paired groups were considered as independent studies, in a bid to reduce selection bias.
In 50 studies, 17 reported on the use of BBR alone, including 4 studies (Xiang et al., 2011; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020) that compared BBR to a placebo and 13 studies that conducted head-to-head trials of BBR with other medications. Among these, 3 studies (Rong et al., 1997; Guo and Zhao, 2006; Liu, 2012) compared BBR to SU (including glyburide, gliclazide, and glipizide), 6 studies (Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2012; Du, 2016; Xing, 2017; Chen et al., 2023) compared to Met, 2 studies (Zhang et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2011) contrasted with TZDs (rosiglitazone), and 2 studies (Zhang et al., 2000; Gao et al., 2002) compared to traditional Chinese medicine. Additionally, 33 studies compared BBR with one or two conventional medications used in combination, with the same conventional medication serving as the control. This included 15 studies (Liu, 2004; Li, 2008; Yin et al., 2011; Zhang and Yuan, 2012; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Yu, 2015; Sun, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Jiang and Wang, 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Chen C. et al., 2021; Chen, 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022; Yang B. et al., 2023) combining BBR with Met, 6 studies (Li and Liu, 2007; Zhu et al., 2015; Meng, 2016; Wu, 2017; Yao et al., 2018; Chen Z. et al., 2021) with SU (including gliclazide and glipizide), 2 studies (Sun, 2016; Li, 2017) with DPP-4 (sitagliptin), 4 studies (Meng et al., 2011; Shu, 2014; Huang et al., 2018; Lu, 2023) with insulin, and 6 studies (Zhu et al., 2009; Sheng and Xie, 2010; Xue et al., 2012; Yao, 2015; Zhang, 2017; Ye, 2021) combining Met and SU (including glyburide, gliclazide, and glipizide).
Treatment durations ranged from 14 days to 6 months. One trial (Liu, 2004) lasted 14 days, one trial (Rong et al., 1997) lasted 10 months, five trials (Gao et al., 2002; Du, 2016; Huang et al., 2018; Rashidi et al., 2018; Chen C. et al., 2021) lasted 1 month, five trials (Yin et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012; Shu, 2014; Ye, 2021; Wang et al., 2022) lasted 180 days, six trials (Zhang et al., 2010; Yu, 2015; Sun, 2017; Wu, 2017; Chen Z. et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023) lasted 2 months, one trial (Zhang et al., 2000) lasted 40 days and one trial (Lu, 2023) had an unknown duration; the remaining 30 studies lasted 3 months. The most common dosage of BBR was 0.9–1.5 g/d. One study (Sun, 2017) reported 0.09 g/d, while 6 trials (Xue et al., 2012; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Zhu et al., 2015; Du, 2016; Chen Z. et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023) used 0.3–0.6 g/d and 3 studies (Zhang et al., 2000; Liu, 2012; Zhang and Yuan, 2012) used 1.5–3 g/d. In two studies (Zhang, 2017; Ye, 2021), patients received 9.0 g/d, and one study (Huang et al., 2018) received 18.0 g/d. Two studies dosed by patients’ weight: one (Gao et al., 2002) at 40 mg/kg/d and the other (Zhang et al., 2011) at 0.02 g/kg/d; In the remaining 35 studies, the dosage of BBR ranged 0.9–1.5 g/d. The detailed information was shown in Table 1.
3.3 Risk assessment
The 50 RCTs included in this study ranged in quality from low to high. Four studies (Zhang, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020) were assessed as low risk, with detailed implementation of randomization and blinding, and reports on the number and reasons for withdrawals or terminations. 31 studies mentioned “random grouping” but did not detail the random sequence generation or allocation concealment methods, thus assessed as “unclear risk” of selection bias and one (Yao, 2015) used admission time to randomize the number of participants with high risk. 44 studies had insufficient descriptions of blinding for participants, personnel, and outcome assessment, thus assessed as “unclear risk” for performance bias or detection bias. One study (Zhou and Huang, 2012) was rated high risk for not reporting Fins outcomes. Other included studies were evaluated as having a low risk regarding the completeness of outcome data, selective reporting, or other biases. Detailed assessment of the risk of bias was illustrated in Figure 2.
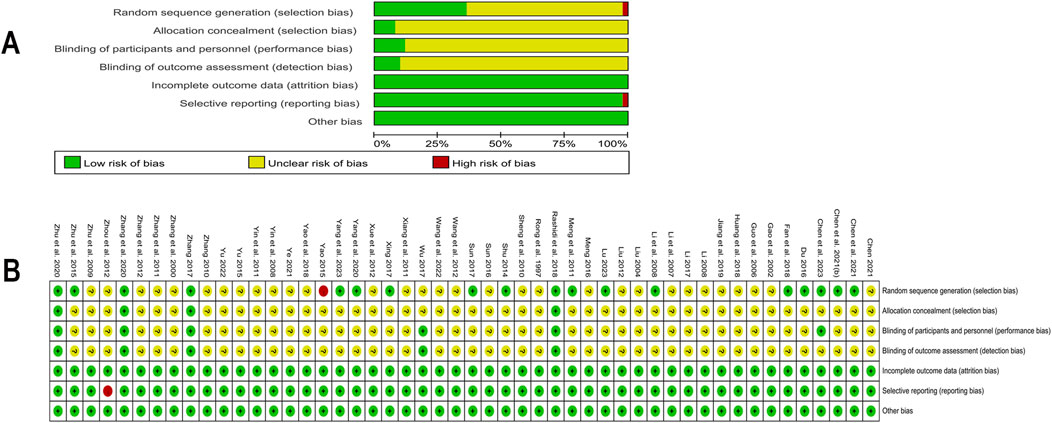
Figure 2. Risk of bias in included studies (A) Summary of risk of bias in included studies; (B) Detailed assessment of risk of bias in included studies.
We also evaluated the quality of the studies using modified Jadad scores. Scores varied from three to seven. A total of 31 studies were classified as low quality, with a minimum score of 2 (Yao, 2015). Although 19 other studies were of higher quality, the majority received a score of 4. One study (Chen et al., 2023) achieved a score of 5, two studies (Zhang, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018) were awarded 6 points, and two studies (Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020) received the full score of 7. Detailed information was shown in Supplementary Table 3.
3.4 Meta-analysis
3.4.1 BBR alone vs. conventional treatment or placebo
3.4.1.1 FPG
A total of 17 studies (Rong et al., 1997; Zhang et al., 2000; Gao et al., 2002; Guo and Zhao, 2006; Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2010; Xiang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011; Liu, 2012; Wang et al., 2012; Du, 2016; Xing, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023) were included. Meta-analysis utilizing a random effects model (I2 = 93.1%, p = 0.000) demonstrated that, compared to the control group, BBR’s effect on lowering FPG approached statistical significance (MD = −0.59 mmol/L, 95% CI: −1.18, −0.01, p = 0.048 < 0.05) (Figure 3A). However, it should be noted that this p-value was at the significance threshold, and its clinical relevance should be interpreted with caution. A subgroup analysis based on the control regimen revealed no significant difference in FPG reduction when BBR monotherapy was compared with SU (MD = −0.76 mmol/L, 95% CI (−3.17, 1.64), p = 0.533), Met (MD = −0.32 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.11, 0.47), p = 0.434), TZDs (MD = 0.28 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.24, 0.81), p = 0.292), or traditional Chinese medicinal products (MD = −1.28 mmol/L, 95% CI (−3.08, 0.52), p = 0.164). However, compared with placebo, the reduction was statistically significant (MD = −0.90 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.39, −0.42), p < 0.01) (Figure 3B). Meta-regression indicated no significant differences in FPG regarding sample size (p = 0.188), publication year (p = 0.599), intervention duration (p = 0.305), or patients’ baseline FPG levels (p = 0.054). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the disease course of T2DM, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were relatively robust (Figure 4A).

Figure 3. Forest plot for BBR alone vs conventional treatment or placebo: (A) FPG; (B) subgroup analysis of FPG by comparison regimen; (C) 2hPBG; (D) subgroup analysis of 2hPBG by baseline levels; (E) HbA1c; (F) subgroup analysis of HbA1c by comparison regimen; (G) Fins; (H) subgroup analysis of Fins by baseline levels; (I) HOMA-IR.
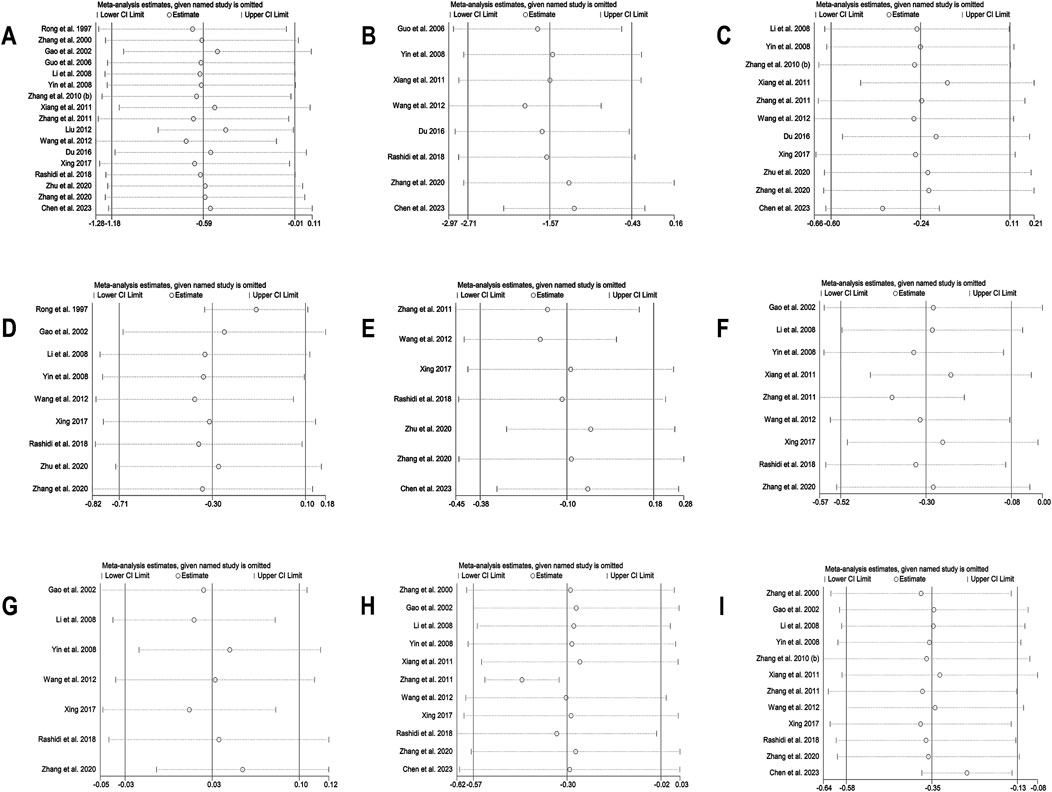
Figure 4. Sensitivity analysis for BBR alone vs conventional treatment or placebo: (A) FPG; (B) 2hPBG; (C) HbA1c; (D) Fins; (E) HOMA-IR; (F) LDL-C; (G) HDL-C; (H) TC; (I) TG.
3.4.1.2 2hPBG
Eight studies (Guo and Zhao, 2006; Yin et al., 2008; Xiang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012; Du, 2016; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023) reported 2hPBG. Using a random-effects model (I2 = 81.4, p = 0.000), the results revealed that the experimental group had significantly lower 2hPBG levels than the control group (MD = −1.57 mmol/L, 95% CI (−2.71, −0.43), p < 0.01) (Figure 3C). Meta-regression results showed a significant difference in baseline 2hPBG (p = 0.033 < 0.05). A subgroup analysis based on patients’ baseline average 2hPBG levels did not completely reduce the heterogeneity within the subgroups (Figure 3D). The results showed a significant difference in improvement in patients with baseline 2hPBG ≥14.5 mmol/L when treated with BBR monotherapy compared to controls (MD = −2.49 mmol/L, 95% CI (−3.71, −1.26), p < 0.01); conversely, there was no significant improvement in patients with baseline 2hPBG <14.5 mmol/L (MD = −0.80 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.72, 0.11), p = 0.086). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the disease course of T2DM, and further studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were relatively robust (Figure 4B).
3.4.1.3 HbA1c
11 studies (Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2010; Xiang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012; Du, 2016; Xing, 2017; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023), including 749 T2DM patients, were included. Utilizing a random-effects model (I2 = 81.3%, p = 0.000), The meta-analysis revealed no significant HbA1c level reduction in the experimental group compared to the control group (MD = −0.24%, 95% CI (−0.60, 0.11), p = 0.181) (Figure 3E). Subgroup analysis revealed that, compared to placebo, BBR alone significantly improved HbA1c levels (MD = −0.68%, 95% CI (−1.08, −0.28), p < 0.01). However, no statistically significant difference was observed in HbA1c reduction when compared with hypoglycemic agents such as Met (MD = 0.05%, 95% CI (−0.59, 0.69), p = 0.884) or TZDs (MD = −0.24%, 95% CI (−0.56, 0.08), p = 0.143) (Figure 3F). Sensitivity analysis indicated a deviation in the study by Chen et al. (2023) (Figure 4C). After excluding this study, the I2 value decreased from 81.3% to 48.5%, and the synthesized results were reversed (MD = −0.39%, 95% CI (−0.62, −0.17), p < 0.01), suggesting instability in the outcome. The relatively low BBR dosage in that study (Chen et al., 2023) may have influenced the overall results. Therefore, BBR monotherapy may be more effective than conventional treatment in improving HbA1c, although further high-quality studies are needed to confirm this finding.
3.4.1.4 Fins
A total of nine studies (Rong et al., 1997; Gao et al., 2002; Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2012; Xing, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020) were included. Meta-analysis utilizing a random effects model (I2 = 83.9%, p = 0.000) showed no significant difference in Fins improvement with BBR compared to the control group (SMD = −0.30, 95% CI (−0.71, 0.10), p = 0.136) (Figure 3G). Meta-regression showed a significant difference in baseline mean Fins (p = 0.001). Further subgroup analysis indicated that heterogeneity within subgroups was not completely reduced (Figure 3H). In addition, we conducted a sensitivity analysis (Figure 4D), which indicated a deviation in the study by Rong et al. (1997). After excluding this study, the I2 value decreased from 83.9% to 40.3%. The large difference in sample sizes between the experimental and control groups in this study (Rong et al., 1997) might have contributed to the overall heterogeneity. The synthesized results did not reverse (SMD = −0.12, 95% CI (−0.34, 0.11), p = 0.304), suggesting that the result was relatively robust.
3.4.1.5 HOMA-IR
In the meta-analysis, which encompassed seven studies (Zhang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012; Xing, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023) and utilized a random effects model (I2 = 60.0%, p = 0.020), no significant improvement in HOMA-IR was detected with BBR versus the control group (SMD = −0.10, 95% CI (−0.38, 0.18), p = 0.503) (Figure 3I). Meta-regression results indicated that significant differences in HOMA-IR were observed with respect to the publication year (p = 0.023). Further subgroup analysis showed reduced heterogeneity within each subgroup (I2 < 50), suggesting that publication year might be a source of heterogeneity (Figure 5A). Sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were robust (Figure 4E).
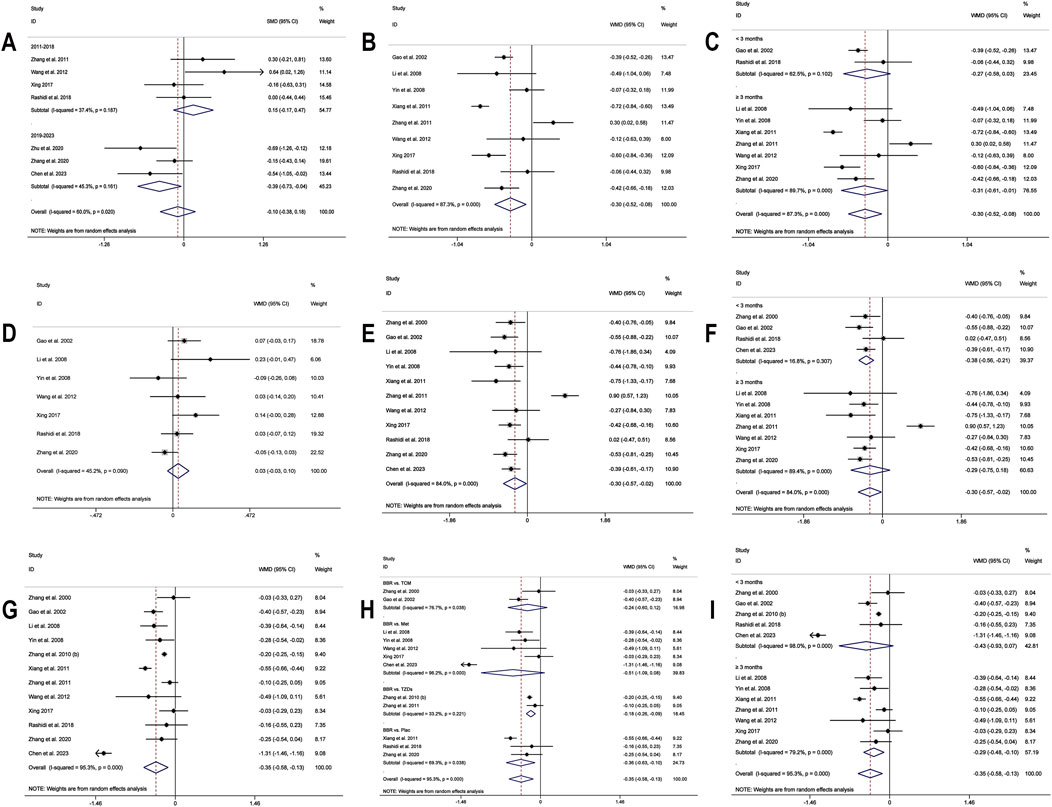
Figure 5. Forest plot for BBR alone vs conventional treatment or placebo: (A) subgroup analysis of HOMA-IR by publication year; (B) LDL-C; (C) subgroup analysis of LDL-C by intervention duration; (D) HDL-C; (E) TC; (F) subgroup analysis of TC by intervention duration; (G) TG; (H) subgroup analysis of TG by comparison regimen; (I) subgroup analysis of TG by intervention duration.
3.4.1.6 LDL-C
A total of 9 studies (Gao et al., 2002; Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Xiang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012; Xing, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020) reported data on LDL-C. A random-effects model was applied (I2 = 87.3%, p = 0.000), and the results showed that BBR alone significantly reduced LDL-C levels (MD = −0.30 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.52, −0.08), p < 0.01) (Figure 5B). Subgroup analysis based on intervention duration revealed that BBR monotherapy administered for ≥3 months significantly reduced LDL-C (MD = −0.31 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.61, −0.01), p < 0.05), whereas interventions lasting <3 months did not show a remarkable effect on LDL-C (MD = −0.27 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.58, 0.03), p = 0.082) (Figure 5C). Meta-regression showed no significant differences in LDL-C regarding publication year (p = 0.834), sample size (p = 0.802), or baseline FPG levels (p = 0.832). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the disease course of patients’ T2DM, and further research is needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the results were stable (Figure 4F).
3.4.1.7 HDL-C
A total of 7 studies (Gao et al., 2002; Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2012; Xing, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020) reported data on HDL-C. Through a random-effects model (I2 = 45.2%, p = 0.090), the results showed that BBR monotherapy did not significantly improve HDL-C levels compared to the control group (MD = 0.03 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.03, 0.10), p = 0.326) (Figure 5D). Sensitivity analysis indicated a deviation in the study by Zhang et al. (2020), and after excluding this study, the I2 value decreased from 45.2% to 23.2%. The re-synthesized results did not reverse (MD = 0.05 mmol/L, 95% CI (0.00, 0.11), p = 0.051), suggesting that the result was relatively robust (Figure 4G).
3.4.1.8 TC
A total of 11 studies (Zhang et al., 2000; Gao et al., 2002; Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Xiang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012; Xing, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023) reported data on TC, and a random-effects model was applied (I2 = 84.0%, p = 0.000). The results indicated that BBR monotherapy significantly reduced TC levels (MD = −0.30 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.57, −0.02), p = 0.034 < 0.05) (Figure 5E). A subgroup analysis was conducted based on intervention duration (Figure 5F), but heterogeneity within subgroups was not completely reduced. The results showed that BBR monotherapy significantly reduced TC when the intervention duration was <3 months (MD = −0.38 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.56, −0.21), p < 0.01). However, when the intervention duration was ≥3 months, the improvement in TC was not significant (MD = −0.29 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.75, 0.18), p = 0.226). Sensitivity analysis (Figure 4H) indicated a significant deviation in the study by Zhang et al. (2011), and after its exclusion, the I2 value decreased from 84% to 0%. This study had a relatively narrow confidence interval and small standard deviation, which may have significantly influenced overall heterogeneity. A fixed-effects model was used to re-synthesis the effect size, and the results did not reverse (MD = −0.43 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.54, −0.32), p < 0.01), suggesting that the result was relatively robust.
3.4.1.9 TG
A total of 12 studies (Zhang et al., 2000; Gao et al., 2002; Li et al., 2008; Yin et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2010; Xiang et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012; Xing, 2017; Rashidi et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023) reported data on TG. A random-effects model analysis was performed (I2 = 95.3%, p = 0.000), showing that BBR monotherapy significantly improved TG levels (MD = −0.35 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.58, −0.13), p < 0.01) (Figure 5G). A subgroup analysis based on the comparison regimen (Figure 5H) showed that compared to monotherapy with TZDs (MD = −0.18 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.26, −0.09), p < 0.01) or placebo (MD = −0.36 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.63, −0.10), p < 0.01), BBR demonstrated a statistically significant difference in improving TG levels. However, no significant differences in TG reduction were found when comparing BBR to traditional Chinese medicinal products (MD = −0.24 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.60, 0.12), p = 0.196) or Met (MD = −0.51 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.09, 0.08), p = 0.089). In addition, subgroup analysis based on intervention duration revealed that BBR monotherapy for ≥3 months significantly reduced TG levels (MD = −0.29 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.48, −0.10), p < 0.01), while interventions lasting <3 months did not show remarkable improvement in TG (MD = −0.43 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.93, 0.07), p = 0.091) (Figure 5I). Meta-regression showed no significant differences in TG levels concerning baseline FPG (p = 0.908), publication year (p = 0.460), or sample size (p = 0.075). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the disease course of T2DM, and further studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated a deviation in the study by Chen et al. (2023), and after its exclusion, the re-synthesized results did not reverse (MD = −0.26 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.38, −0.15), p < 0.01), suggesting that the result was relatively robust (Figure 4I).
3.4.1.10 Inflammatory markers
Only one study (Xiang et al., 2011) reported the effects of BBR monotherapy versus placebo on inflammatory markers. The results showed that compared to the control, BBR significantly improved levels of CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α (p < 0.05).
3.4.2 BBR combined with conventional treatment vs conventional treatment
3.4.2.1 FPG
30 studies (Liu, 2004; Li and Liu, 2007; Li, 2008; Zhu et al., 2009; Sheng and Xie, 2010; Meng et al., 2011; Yin et al., 2011; Xue et al., 2012; Zhang and Yuan, 2012; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Shu, 2014; Yao, 2015; Yu, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Sun, 2016; Li, 2017; Sun, 2017; Zhang, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2018; Jiang and Wang, 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Chen C. et al., 2021; Chen, 2021; Chen Z. et al., 2021; Ye, 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022; Lu, 2023; Yang B. et al., 2023) were included. Employing a random-effects model as per heterogeneity test results (I2 = 94.0%, p = 0.000), the meta-analysis revealed that the experimental group had remarkably lower FPG levels than the control group (MD = −0.99 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.28, −0.70), p < 0.01) (Figure 6A). Due to high heterogeneity, subgroup analysis was undertaken regarding interventions and mean baseline FPG levels (Figures 6B,C). However, heterogeneity within subgroups was not completely reduced. The results showed that BBR as an adjunct to DPP-4 inhibitors (MD = −1.28 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.64, −0.93), p < 0.01), insulin (MD = −1.14 mmol/L, 95% CI (−2.24, −0.03), p = 0.044 < 0.05), Met (MD = −1.19 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.57, −0.80), p < 0.01), and Met + SU (MD = −0.57 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.80, −0.34), p < 0.01) demonstrated a significant reduction in FPG compared to the use of these medications alone. In contrast, BBR + SU did not show a statistically significant reduction in FPG (MD = −0.48 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.96, 0.01), p = 0.053). Additionally, BBR significantly reduced FPG levels in patients with different baseline FPG levels: <9 mmol/L (MD = −0.79, 95% CI (−1.20, −0.39), p < 0.01), between 9 and 11 mmol/L (MD = −1.02, 95% CI (−1.51, −0.54), p < 0.01), and ≥11 mmol/L (MD = −1.21, 95% CI (−2.09, −0.33), p < 0.01), all showing statistical significance. A meta-regression was then conducted and found no significant differences in FPG reduction based on sample size (p = 0.503), publication year (p = 0.491), or BBR dosage (p = 0.615). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be associated with the dosage of the concomitant medications, and further research is needed for validation. According to the sensitivity analysis results, after sequentially excluding Zhou et al., 2012 (Zhou and Huang, 2012) (MD = −0.92 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.15, −0.69), p < 0.01) and Huang et al., 2018 (Huang et al., 2018) (MD = −0.92 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.20, −0.63), p < 0.01), the synthesized results did not reverse, suggesting that the result was relatively robust (Figure 8A).
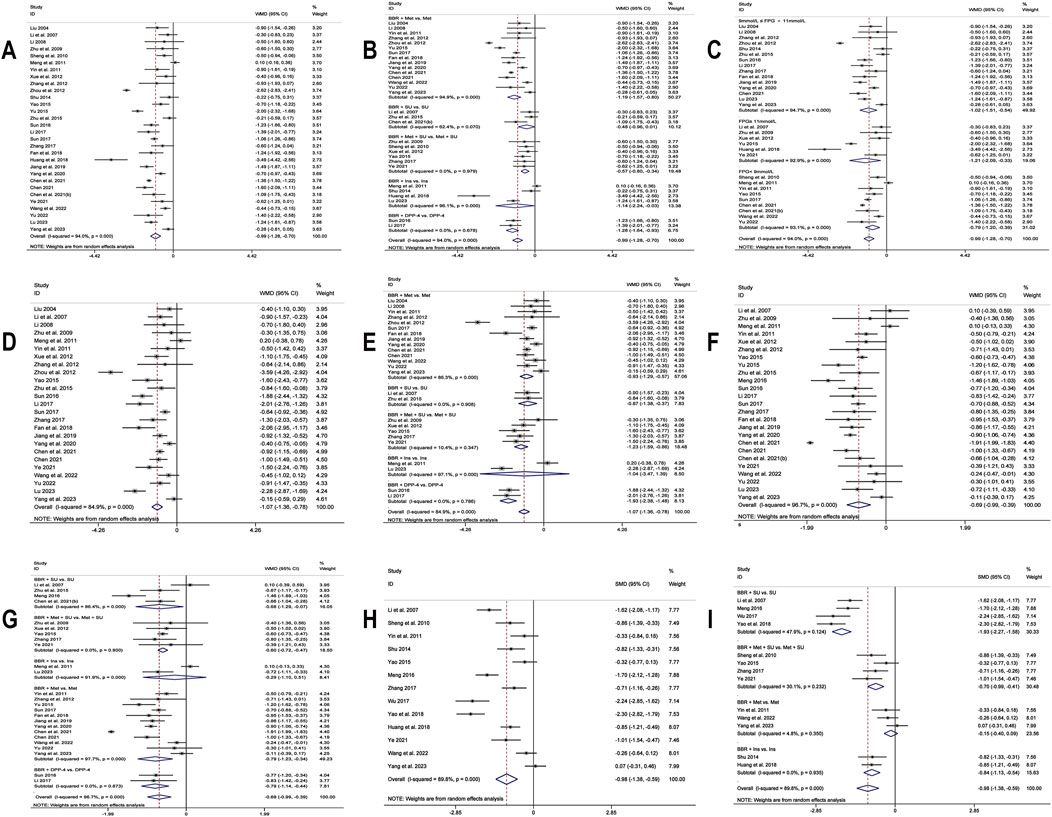
Figure 6. Forest plot for BBR combined with conventional treatment vs conventional treatment: (A) FPG; (B) subgroup analysis of FPG by comparison regimen; (C) subgroup analysis of FPG by baseline levels; (D) 2hPBG; (E) subgroup analysis of 2hPBG by comparison regimen; (F) HbA1c; (G) subgroup analysis of HbA1c by comparison regimen; (H) Fins; (I) subgroup analysis of Fins by comparison regimen.
3.4.2.2 2hPBG
25 studies (Liu, 2004; Li and Liu, 2007; Li, 2008; Zhu et al., 2009; Meng et al., 2011; Yin et al., 2011; Xue et al., 2012; Zhang and Yuan, 2012; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Yao, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Sun, 2016; Li, 2017; Sun, 2017; Zhang, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Jiang and Wang, 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Chen C. et al., 2021; Chen, 2021; Ye, 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022; Lu, 2023; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported 2hPBG. Through a random-effects model (I2 = 84.9, p = 0.000), the results demonstrate that the co-administration of BBR significantly reduces 2hPBG (MD = −1.07 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.36, −0.78), p < 0.01) (Figure 6D). We conducted a subgroup analysis based on different combination medication regimens. The results showed that BBR, when combined with DPP-4 inhibitors (MD = −1.93 mmol/L, 95% CI (−2.38, −1.48), p < 0.01), SU (MD = −0.87 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.38, −0.37), p < 0.01), Met (MD = −0.93 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.29, −0.57), p < 0.01), or Met + SU (MD = −1.23 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.59, −0.86), p < 0.01), significantly reduced 2hPBG compared to monotherapy. In contrast, the combination of BBR and insulin did not show a statistically significant improvement in 2hPBG (MD = −1.04, 95% CI (−3.47, 1.39), p = 0.402) (Figure 6E). Given that heterogeneity within subgroups was not completely reduced, we performed a meta-regression, which showed no significant differences in sample size (p = 0.178), publication year (p = 0.979), BBR dosage (p = 0.653), baseline mean FPG (p = 0.351), or baseline mean 2hPBG (p = 0.065). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the dosage of the co-medication, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated a deviation in the study by Zhou et al., 2012 (Zhou and Huang, 2012). After excluding this study, the re-synthesized results did not reverse (MD = −0.95 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.19, −0.72), p < 0.01), suggesting that the result was relatively robust (Figure 8B).
3.4.2.3 HbA1c
25 studies (Li and Liu, 2007; Zhu et al., 2009; Meng et al., 2011; Yin et al., 2011; Xue et al., 2012; Zhang and Yuan, 2012; Yao, 2015; Yu, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Meng, 2016; Sun, 2016; Li, 2017; Sun, 2017; Zhang, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Jiang and Wang, 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Chen C. et al., 2021; Chen, 2021; Chen Z. et al., 2021; Ye, 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022; Lu, 2023; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported HbA1c. By a random-effects model (I2 = 96.7%, p = 0.000), the meta-analysis revealed that the combination of BBR with hypoglycemic drugs significantly reduced HbA1c (MD = −0.69%, 95% CI (−0.99, −0.39), p < 0.01) (Figure 6F). To further explore the relationship between Co-administration of BBR and hypoglycemic drugs and improvement in HbA1c, a subgroup analysis was carried out (Figure 6G), which showed that the co-administration of BBR with DPP-4 (MD = −0.79%, 95% CI (−1.14, −0.44), p < 0.01), SU (MD = −0.68%, 95% CI (−1.29, −0.07), p = 0.028 < 0.05), Met (MD = −0.79%, 95% CI (−1.23, −0.34), p < 0.01) and Met + SU (MD = −0.60%, 95% CI (−0.72, −0.47), p < 0.01) demonstrated superior efficacy compared to the use of these medications alone. However, the combination with insulin showed no statistically significant difference in improving HbA1c levels (MD = −0.29%, 95% CI (−1.10, 0.51), p = 0.474). The meta-regression showed no significant differences regarding BBR dosage (p = 0.225), publication year (p = 0.145), and sample size (p = 0.391). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to different measurement times for HbA1c, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were relatively robust (Figure 8C).
3.4.2.4 Fins
13 studies (Li and Liu, 2007; Sheng and Xie, 2010; Yin et al., 2011; Shu, 2014; Yao, 2015; Meng, 2016; Wu, 2017; Zhang, 2017; Huang et al., 2018; Yao et al., 2018; Ye, 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported Fins. With a random-effects model (I2 = 89.8%, p = 0.000), the results indicated that BBR effectively decreased Fins levels in T2DM patients (SMD = −0.98, 95% CI (−1.38, −0.59), p < 0.01) (Figure 6H). We performed a subgroup analysis based on different co-medication regimens, and the heterogeneity within each subgroup decreased (I2 < 50%), suggesting that the combination regimen itself may be a source of heterogeneity (Figure 6I). Results showed that adding BBR to SU (SMD = −1.93, 95% CI (−2.27, −1.58), p < 0.01), Met + SU (SMD = −0.70, 95% CI (−0.99, −0.41), p < 0.01), or insulin therapy (SMD = −0.84, 95% CI (−1.13, −0.54), p < 0.01) significantly reduced Fins levels compared to the use of these drugs alone. In contrast, BBR + Met (SMD = −0.15, 95% CI (−0.40, 0.09), p = 0.227) did not show a significant reduction in Fins. A subgroup analysis based on the dosage of BBR (Figure 7A) revealed that both BBR ≤0.9 g/day (SMD = −1.50, 95% CI (−2.09, −0.90), p < 0.01) and BBR >0.9 g/day (SMD = −0.54, 95% CI (−0.84, −0.24), p < 0.01) significantly reduced Fins levels. Sensitivity analysis indicated that the result was robust (Figure 8D).
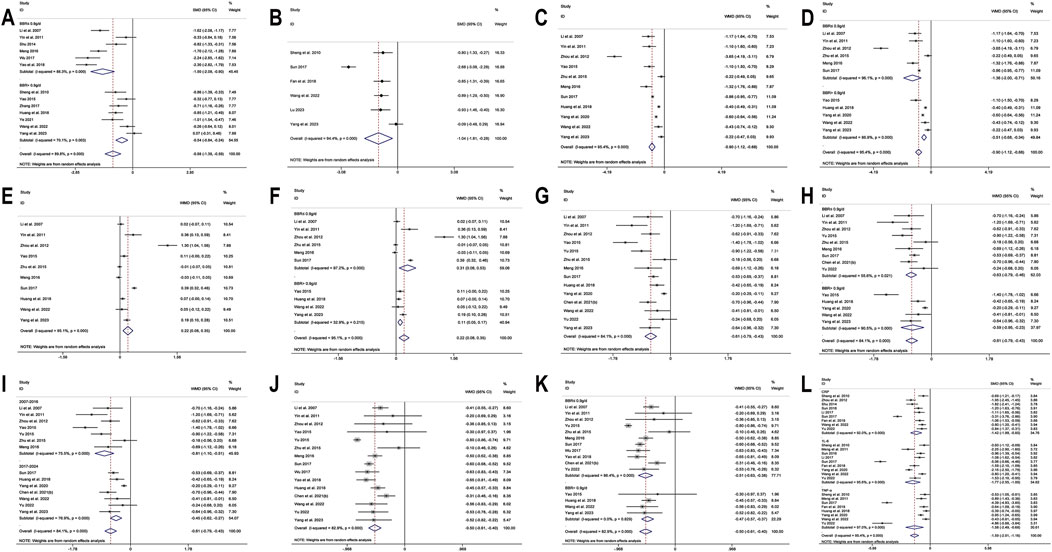
Figure 7. Forest plot for BBR combined with conventional treatment vs conventional treatment: (A) subgroup analysis of Fins by BBR dosage; (B) HOMA-IR; (C) LDL-C; (D) subgroup analysis of LDL-C by BBR dosage; (E) HDL-C; (F) subgroup analysis of HDL-C by BBR dosage; (G)TC; (H) subgroup analysis of TC by BBR dosage; (I) subgroup analysis of TC by publication year; (J) TG; (K) subgroup analysis of TG by BBR dosage; (L) Inflammatory markers.
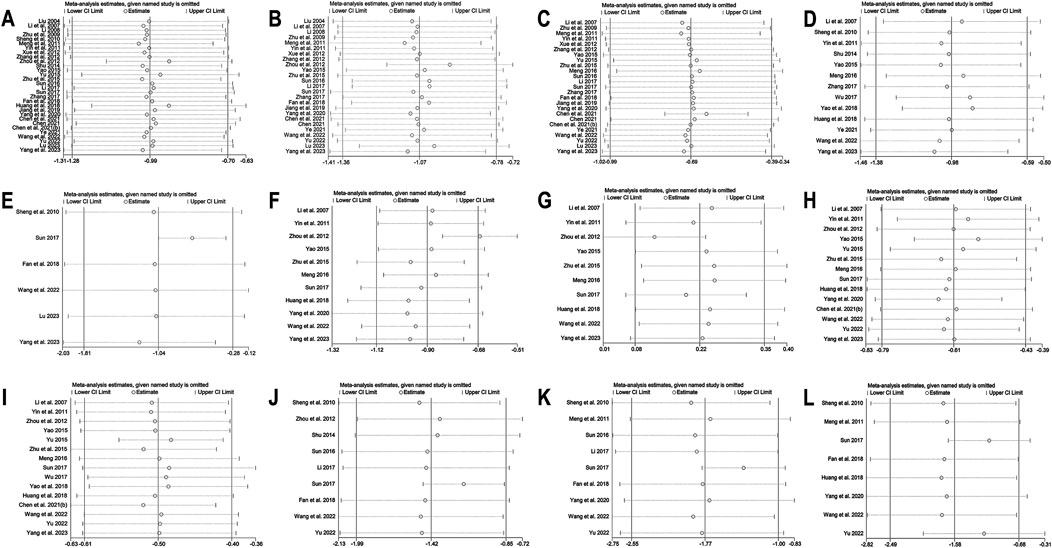
Figure 8. Sensitivity analysis for BBR combined with conventional treatment vs conventional treatment: (A) FPG; (B) 2hPBG; (C) HbA1c; (D) Fins; (E) HOMA-IR; (F) LDL-C; (G) HDL-C; (H) TC; (I) TG; (J) CRP; (K) 1L-6; (L) TNF-α.
3.4.2.5 HOMA-IR
Six studies (Sheng and Xie, 2010; Sun, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2022; Lu, 2023; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported HOMA-IR. With a random-effects model (I2 = 94.4, p = 0.000), the results indicated that BBR effectively decreased HOMA-IR levels in T2DM patients (SMD = −1.04, 95% CI (−1.81, −0.28), p < 0.01) (Figure 7B). The meta-regression found no significant differences in HOMA-IR regarding publication year (p = 0.226), sample size (p = 0.644), or interventions (p = 0.925). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the pancreatic function level of patients, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated a significant deviation in the study by Sun (2017). After excluding this study, the re-synthesized results did not reverse (SMD = −0.70, 95% CI (−1.04, −0.35), p < 0.01), suggesting that the result was relatively robust (Figure 8E).
3.4.2.6 LDL-C
A total of 11 studies (Li and Liu, 2007; Yin et al., 2011; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Yao, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Meng, 2016; Sun, 2017; Huang et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported data on LDL-C. Through a random-effects model (I2 = 95.4%, p = 0.000) for analysis, the results showed that BBR combined with hypoglycemic agents significantly reduced LDL-C levels (MD = −0.90 mmol/L, 95% CI (−1.12, −0.68), p < 0.01) (Figure 7C). A subgroup analysis based on BBR dosage (Figure 7D) revealed that BBR ≤0.9 g/day (MD = −1.36 mmol/L, 95% CI (−2.00, −0.71), p < 0.01) had a better effect on LDL-C improvement compared to BBR >0.9 g/day (MD = −0.51 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.68, −0.34), p < 0.01). The meta-regression showed no significant differences in LDL-C based on intervention duration (p = 0.960), publication year (p = 0.076), sample size (p = 0.301), or interventions (p = 0.766). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the dosage of the combined medications, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis identified a significant deviation in the study by Zhou and Huang (2012). After excluding this study, the re-synthesized results did not reverse (MD = −0.67 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.83, −0.51), p < 0.01), indicating that the result was relatively robust (Figure 8F).
3.4.2.7 HDL-C
A total of 10 studies (Li and Liu, 2007; Yin et al., 2011; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Yao, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Meng, 2016; Sun, 2017; Huang et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2022; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported data on HDL-C. Through a random-effects model for analysis (I2 = 95.1%, p = 0.000), the results showed that BBR combination therapy significantly increased HDL-C levels (MD = 0.22 mmol/L, 95% CI (0.08, 0.35), p < 0.01) (Figure 7E). A subgroup analysis based on BBR dosage (Figure 7F) indicated that daily BBR ≤0.9 g (MD = 0.31 mmol/L, 95% CI (0.08, 0.53), p < 0.01) had a better effect on improving HDL-C compared to BBR >0.9 g/day (MD = 0.11 mmol/L, 95% CI (0.05, 0.17), p < 0.01). A meta-regression was conducted and found no significant differences in HDL-C regarding the interventions (p = 0.807), publication year (p = 0.405), or intervention duration (p = 0.851). We hypothesized that the high heterogeneity may be related to the dosage of the combined medications, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis identified a significant deviation in the study by Zhou and Huang (2012). After excluding this study, the synthesized results did not reverse (MD = 0.12 mmol/L, 95% CI (0.01, 0.23), p < 0.05), indicating that the result was relatively robust (Figure 8G).
3.4.2.8 TC
A total of 14 studies (Li and Liu, 2007; Yin et al., 2011; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Yao, 2015; Yu, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Meng, 2016; Sun, 2017; Huang et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2020; Chen Z. et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported data on TC. Through a random-effects model (I2 = 84.1%, p = 0.000), the results showed that combination therapy with BBR significantly reduced TC (MD = −0.61 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.79, −0.43), p < 0.01) (Figure 7G). Subgroup analysis based on BBR dosage indicated that both BBR ≤0.9 g/day (MD = −0.63 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.79, −0.46), p < 0.01) and BBR >0.9 g/day (MD = −0.59 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.95, −0.23), p < 0.01) significantly reduced TC (Figure 7H). Meta-regression results showed a significant difference in TC with respect to the publication year (p = 0.026), and further subgroup analysis revealed that heterogeneity within subgroups was not completely reduced (Figure 7I). We hypothesized that the heterogeneity may be related to the dosage of the combined medications, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were relatively robust (Figure 8H).
3.4.2.9 TG
A total of 15 studies (Li and Liu, 2007; Yin et al., 2011; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Yao, 2015; Yu, 2015; Zhu et al., 2015; Meng, 2016; Sun, 2017; Wu, 2017; Huang et al., 2018; Yao et al., 2018; Chen Z. et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022; Yang B. et al., 2023) reported data on TG. Through a random-effects model (I2 = 82.9%, p = 0.000), the results showed that BBR in combination with other medications significantly reduced TG (MD = −0.50 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.61, −0.40), p < 0.01) (Figure 7J). A subgroup analysis based on BBR dosage indicated that both BBR ≤0.9 g/day (MD = −0.51 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.63, −0.38), p < 0.01) and BBR >0.9 g/day (MD = −0.47 mmol/L, 95% CI (−0.57, −0.37), p < 0.01) significantly reduced TG levels (Figure 7K). The meta-regression showed no significant differences in TG reduction concerning the type of intervention (p = 0.834), intervention duration (p = 0.456), publication year (p = 0.579), or sample size (p = 0.392). We hypothesized that the heterogeneity may be related to the dosage of the combined medications, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. Sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were relatively robust (Figure 8I).
3.4.2.10 Inflammatory markers
A total of 11 (Sheng and Xie, 2010; Meng et al., 2011; Zhou and Huang, 2012; Shu, 2014; Sun, 2016; Li, 2017; Sun, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022) studies reported on CRP and IL-6, and 8 studies (Sheng and Xie, 2010; Meng et al., 2011; Sun, 2017; Fan et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Yu, 2022) reported on TNF-α. We conducted a comprehensive evaluation of inflammatory markers using a random-effects model (I2 = 95.4%, p = 0.000) for the meta-analysis. The results showed that, compared to hypoglycemic agents alone, the addition of BBR significantly improved inflammatory markers (SMD = −1.59, 95% CI (−2.01, −1.16), p < 0.01) (Figure 7L). Specifically, BBR combination therapy significantly improved CRP (SMD = −1.42, 95% CI (−1.99, −0.85), p < 0.01), IL-6 (SMD = −1.77, 95% CI (−2.55, −1.00), p < 0.01), and TNF-α (SMD = −1.58, 95% CI (−2.49, −0.68), p < 0.01). Sensitivity analyses were performed separately, excluding Sun 2017 (Sun, 2017) for both CRP and IL-6, and re-synthesized the results. The results for CRP (SMD = −1.17, 95% CI (−1.48, −0.86), p < 0.01) and IL-6 (SMD = −1.36, 95% CI (−1.80, −0.92), p < 0.01) did not reverse, indicating that the results were relatively robust (Figures 8J,K,L).
3.5 Adverse events
A total of 16 studies reported detailed information on adverse events. The study by Du (2016) noted that the incidence of adverse events with BBR was significantly lower than that with metformin. Additionally, Jiang and Wang (2019) and Chen (2021) reported that the incidence of adverse reactions with BBR combined with hypoglycemic agents was significantly lower than that in the hypoglycemic agents alone group. The summary of adverse events can be found in Supplementary Table 2. No serious adverse events were reported during the treatment period in any of the studies, indicating that BBR is relatively safe.
3.6 Publication bias
For metrics with the number of studies ≥10, Egger’s test was utilized to assess the publication bias. For metrics with fewer than 10 studies, funnel plots were employed for the same purpose. Egger’s test revealed significant differences for HbA1c (p = 0.007), TC (p = 0.005), and TG (p = 0.016) (p < 0.05), suggesting potential publication bias. After performing the trim-and-fill method, the results did not reverse, indicating that the bias had little effect on the overall results, and the outcomes were relatively robust. In the funnel plot, we observed that the distributions of 2hPBG, Fins, HOMA-IR, and TNF-α were not completely symmetrical, and we conducted trim-and-fill analyses sequentially. The results showed that the meta-analyses for 2hPBG, HOMA-IR, and TNF-α did not undergo significant changes after trimming and filling, suggesting that the risk of bias was minimal for these markers. However, the effect for Fins changed significantly from not statistically significant to statistically significant, indicating that the meta-analysis result for Fins might be affected by publication bias. Therefore, BBR monotherapy may be superior to the control group in improving Fins, and further high-quality studies are needed for validation. We speculated that the source of bias might be related to the limited number of included studies and small sample sizes, which may have led to an overestimation of the effect sizes. Therefore, we recommend that future research include a broader range of data sources to improve the robustness of the meta-analysis and reduce the risk of bias. Other outcomes showed a relatively low risk of bias and had a certain level of reliability. Detailed data on publication bias are provided in Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
4 Discussion
The present meta-analysis systematically assessed both the efficacy and safety of BBR used alone or in combination for the treatment of T2DM. Our findings indicate that BBR holds significant potential in the management of T2DM, particularly when used in conjunction with existing hypoglycemic agents.
The meta-analysis results by Lan et al. (2015), Liang et al. (2019), Guo et al. (2021) indicated that BBR monotherapy significantly outperformed placebo in reducing FPG and HbA1c, but its efficacy may be comparable to that of oral hypoglycemic agents. This finding aligns with our subgroup analysis results. Additionally, we found that BBR monotherapy has a certain lipid-regulating effect, which significantly lowered LDL-C, TC, and TG levels, while its effect on HDL-C was not significant. A meta-analysis by Ye et al. (2021) suggested that BBR monotherapy also has a significant effect on improving HDL-C. Through in silico network pharmacology analysis, BBR was found to regulate 31 targets related to T2DM and 18 biological pathways associated with the condition. Among these, the PPAR pathway plays a crucial role in BBR’s enhancement of lipid metabolism in T2DM patients (Di et al., 2021). Further, Wu YY proposed that BBR primarily alleviates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by upregulating PPAR-α expression, reducing lipid accumulation, inhibiting cell apoptosis, and thereby promoting lipid oxidative metabolism while reducing lipotoxicity (Wu et al., 2019). While these findings have potential clinical significance, we believe that further high-quality head-to-head clinical trials are necessary to confirm the effects of BBR monotherapy considering the limited number and quality of studies included in the analysis.
Similar to previous research (Guo et al., 2021), our findings showed that, compared to the use of hypoglycemic agents alone, adjunctive BBR significantly improved glucose and lipid metabolism and enhanced insulin sensitivity, which may be attributed to the synergistic effects introduced by BBR (Tian et al., 2019). Studies have shown that BBR primarily improves glycemic control and reduces insulin resistance through various mechanisms, such as activating AMPK, upregulating insulin receptor (InsR) expression, regulating gut microbiota, and promoting GLP-1 secretion (Kong et al., 2009; He et al., 2022; Utami et al., 2023). A recent meta-analysis (Xie et al., 2022) assessing the impact of BBR on glucose metabolism in T2DM, published in 2022, conducted a subgroup analysis based on patients’ baseline FPG levels. The results demonstrated that post-treatment, the experimental group exhibited lower levels of FPG, 2hPBG, and HbA1c compared to the control group (p < 0.01). Our study found similar effects of BBR in reducing FPG levels. The distinction in our study lies in finding that the efficacy of BBR in reducing FPG increases with higher baseline FPG levels in patients. This may be linked to its mechanism of glucose concentration-dependent insulin secretion. BBR has been demonstrated to interact directly with the KCNH6 potassium channel, thereby promoting insulin secretion in a hyperglycemia-dependent manner while also contributing to a reduction in the incidence of hypoglycemic events, highlighting its potential application in the adjunctive treatment of diabetes (Zhao et al., 2021).
The meta-analysis by Liang et al. (2019) demonstrated that adding BBR to hypoglycemic agents produced the same improvement in HbA1c as using hypoglycemic agents alone, whereas the meta-analysis by Guo et al. (2021) indicated that the combination of BBR and hypoglycemic agents led to a significantly greater improvement in HbA1c than hypoglycemic agents alone. BBR has been shown to significantly enhance glycemic control through various synergistic mechanisms when used in combination with pioglitazone and metformin (Adil et al., 2017; Lyu et al., 2019). Furthermore, we conducted a more detailed subgroup analysis based on the combination regimens of BBR and found that BBR combined with Met, SU, and DPP-4 inhibitors exhibited a synergistic effect. However, its combination with insulin exhibited improvements in HbA1c comparable to insulin monotherapy. Additionally, our subgroup analysis revealed that BBR combined with SU may have an effect on FPG comparable to that of SU alone. Singh et al. (2020) found in in vitro experiments that when BBR is co-incubated with SU, it may interfere with the metabolism of SU, potentially weakening its hypoglycemic effect to some extent. We also observed that the combination of BBR with insulin for improving 2hPBG, as well as BBR combined with Met for improving Fins, did not exhibit a notable synergistic effect compared to monotherapy. This could be related to the alteration of the composition of certain gut microbiota by BBR, which in turn affects the pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy of the co-medication (Zhang et al., 2019; Laia et al., 2022). However, due to the limited number of included studies and the high heterogeneity in subgroup analyses, these conclusions remain uncertain. Therefore, future research should further explore the mechanisms of interaction between BBR and other hypoglycemic agents and validate these findings through clinical trials, to provide more precise therapeutic guidance for clinical practice.
In addition, in terms of improving insulin levels and lipid profiles (LDL-C, HDL-C, TC, and TG), we found that low-dose BBR (≤0.9 g/day) may have better effects than higher doses (>0.9 g/day). An animal study by Guo et al. (2011) indicated that high-dose BBR (300 mg/kg/day) significantly inhibited liver CYP enzyme activity during a 14-day dosing period, which might influence the effect of combined medication to some extent. In contrast, low-dose BBR (10–100 mg/kg/day) over the same period could regulate insulin and lipid metabolism more effectively without interfering with drug metabolism. Therefore, when considering the use of BBR in combination with hypoglycemic agents, determining the optimal dosage range to optimize therapeutic efficacy is particularly important.
Inflammatory biomarkers play a significant role in the pathogenesis of T2DM. They are closely associated with disease progression, the development of complications (Galantini et al., 2022; Du et al., 2023; Arif et al., 2024), and even increased mortality (Zhang J. et al., 2024). BBR exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway through an AMPK-dependent mechanism, thereby reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Yao et al., 2015). A recent umbrella meta-analysis (Nazari et al., 2024) showed that BBR supplementation effectively improves inflammatory markers in adults. We found that both BBR monotherapy and combination therapy significantly improved inflammatory markers, including reductions in CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α levels, further confirming the potential value of BBR in the comprehensive management of T2DM.
In this study, we observed significant statistical heterogeneity, which may be attributed to multiple factors, including the publication year of the studies, differences in baseline characteristics of patients, and genetic predispositions that may affect drug metabolism and therapeutic response. Additionally, different BBR combination regimens and treatment durations might also lead to inconsistent therapeutic effects. To explore the sources of heterogeneity in depth, subgroup analyses and meta-regression were conducted. Furthermore, we conducted sensitivity analyses to exclude studies with significant impacts on overall heterogeneity. However, considerable heterogeneity persisted in the glucose metabolism and lipid metabolism outcomes of BBR monotherapy and combination therapy with hypoglycemic agents. Through meta-regression and subgroup analyses, we were unable to identify specific sources of heterogeneity. We speculated that factors such as BMI, pancreatic function, differences in measurement times, the dosage of co-medication, and the dosage ratio of BBR may contribute to the high heterogeneity. Some studies did not specify the disease course of T2DM in the subjects or whether they received dietary and exercise interventions, which we believe may also contribute to the high heterogeneity. Moreover, the methodological limitations of the included studies, such as the lack of blinding and allocation concealment, may have contributed to the heterogeneity. Furthermore, we believed that there were interactions among factors contributing to heterogeneity. First, the limitations of study methodology may vary across research conducted in different years; earlier studies may have less rigorous designs, potentially introducing greater bias in results, whereas study designs may have improved over time. This interaction between methodological limitations and publication year could lead to discrepancies, influencing the overall assessment of BBR efficacy. Second, the timing of outcome measurements can affect the assessment of BBR’s efficacy in combination therapy. For instance, certain hypoglycemic agents have an optimal window of action within a specific period after treatment initiation; measurements taken outside this window may not accurately reflect the drug’s true effect. Additionally, the dosage of co-administered drugs and the dosage ratio of BBR to these drugs may influence both efficacy and side effects, and this impact may vary depending on the timing of the measurement. At last, obesity is a common comorbidity of T2DM. Patients with lower BMI often have a shorter T2DM course and may respond better to BBR. This interaction may introduce variability in overall results. From a multifactorial perspective, patients with higher BMI typically have a longer disease course and may require higher dosages or different dosage ratios in combination therapy to achieve optimal effects. Furthermore, these patients may need a longer time to exhibit treatment effects, and the timing of measurements during this period could influence efficacy assessment, contributing to overall heterogeneity. Future studies should further explore how these factors jointly influence outcomes and focus on controlling these variables to reduce heterogeneity.
Regarding safety, a total of 16 studies thoroughly evaluated adverse events. Typical side effects of BBR, such as gastrointestinal discomfort and hypoglycemia, can be anticipated due to its pharmacological actions and mechanisms. These side effects typically resolve spontaneously during the study period. In addition, no serious adverse drug reactions were observed. Hence, the appropriate use of BBR in treating T2DM is deemed safe. We performed funnel plots and Egger’s tests for all outcomes, and for those with potential publication bias, the trim-and-fill method was used to adjust the results. The robustness of the overall findings was confirmed. Although the effect size for Fins in BBR monotherapy was reversed after trimming and filling, overall, the results of our meta-analysis are considered reliable.
5 Strengths
This study has several strengths. This study conducted a comprehensive and systematic meta-analysis of BBR treatment for T2DM based on the use of BBR. Particularly, we performed in-depth subgroup analyses based on combination regimens to provide references for clinical treatment. To ensure robust and up-to-date findings, we established stringent inclusion criteria and employed meticulous search methods. Unlike previous meta-analyses (Guo et al., 2021), we excluded studies utilizing BBR fruit or Coptis extracts as interventions (Sanjari et al., 2020; Tahmasebi et al., 2019), as these dried root extracts contain additional alkaloids apart from BBR, potentially introducing bias to the outcomes. Additionally, unlike previous meta-analyses (Xie et al., 2022; Dong et al., 2012; Liang et al., 2019), our study incorporated analyses of lipid profiles, insulin levels and inflammatory markers, striving to present a thorough understanding of the effects of BBR on T2DM patients.
6 Limitations
Inevitably, certain limitations are presented in our study: First, our research is subject to geographical constraints, as the data predominantly derive from Asian populations. This may limit the broader generalizability of the findings to regions with genetic, lifestyle, and environmental differences from Asia. Therefore, we emphasize that when applying our results to different regions and countries, it is crucial to consider local medical facilities, patient compliance, and potential drug interactions. Second, due to the limited number of studies, certain parameters could not be subject to subgroup analysis, limiting the in-depth analysis of variables that might affect the efficacy of BBR. Third, despite conducting subgroup analyses and meta-regression, there remains significant heterogeneity in the study results, with the sources of some of this heterogeneity still not clearly identified. Hence, future studies should incorporate a more diverse geographical range, a broader array of literature resources, and more sophisticated methodological designs, in a bid to provide more robust evidence for the use of BBR in the treatment of T2DM.
7 Conclusion
Our study findings demonstrated the therapeutic potential of BBR in the management of T2DM, both as a monotherapy and in combination with conventional hypoglycemic agents. Nonetheless, the mechanisms of BBR in combination with other hypoglycemic agents still need to be further elucidated. Future research should adopt more diverse study designs and take into account factors such as the dosage of BBR, combination medications, treatment duration, and individual patient differences that may influence therapeutic outcomes. This will provide more precise guidance for clinical practice and help optimize treatment regimens for patients with T2DM.
Author contributions
JW: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing–original draft. CB: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. HX: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. FW: Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Zhang Zhenyu Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio Construction Project of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2010-112) and General Project of Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2022MH065).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2024.1455534/full#supplementary-material
References
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee (2024). 2. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 47 (Suppl. 1), S20–s42. doi:10.2337/dc24-S002
Adil, M., Mansoori, M. N., Singh, D., Kandhare, A. D., and Sharma, M. (2017). Pioglitazone-induced bone loss in diabetic rats and its amelioration by berberine: a portrait of molecular crosstalk. Biomed. Pharmacother. 94, 1010–1019. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.001
Ahmad, E., Lim, S., Lamptey, R., Webb, D. R., and Davies, M. J. (2022). Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 400 (10365), 1803–1820. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01655-5
Ansari, P., Akther, S., Hannan, J. M. A., Seidel, V., Nujat, N. J., and Abdel-Wahab, Y. H. A. (2022). Pharmacologically active phytomolecules isolated from traditional antidiabetic plants and their therapeutic role for the management of diabetes mellitus. Molecules 27 (13), 4278. doi:10.3390/molecules27134278
Arif, M., Nigoskar, S., Verma, M. K., and Amir, A. H. (2024). Screening type 2 Diabetes mellitus among Indians using inflammatory biomarkers. Bioinformation 20 (5), 515–519. doi:10.6026/973206300200515
Butt, M. D., Ong, S. C., Rafiq, A., Kalam, M. N., Sajjad, A., Abdullah, M., et al. (2024). A systematic review of the economic burden of diabetes mellitus: contrasting perspectives from high and low middle-income countries. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 17 (1), 2322107. doi:10.1080/20523211.2024.2322107
Chen, C., Sha, W. J., Xu, B. L., Zhu, J. Y., Zhang, C. P., Xia, J., et al. (2021a). Efficacy of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its effect on blood sugar, intestinal flora, and cystatin C, adiponectin, and free fatty acid levels. Hainan Med. J. 32 (20), 2596–2599. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2021.20.003
Chen, X. Y., Cao, H. M., Wang, J. J., and Cui, Y. Y. (2023). Effects of Huangliansu on T2DM. Chin. J. Urban Rural. Enter. Hyg. 38 (3), 160–162. doi:10.16286/j.1003-5052.2023.03.061
Chen, Y. (2021). Clinical study of berberine hydrochloride tablets combined with metformin in the treatment of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Care Health (16), 99–100.
Chen, Z. X., Wang, C. X., Xu, L. Q., and Liu, Y. Y. (2021b). Effect of Berberine on gastrointestinal hormones and glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with early type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. Mod. Med. 28 (34), 120–122. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2021.34.033
Derosa, G. (2010). Efficacy and tolerability of pioglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: comparison with other oral antihyperglycaemic agents. Drugs 70 (15), 1945–1961. doi:10.2165/11538100-000000000-00000
Di, S., Han, L., An, X., Kong, R., Gao, Z., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). In silico network pharmacology and in vivo analysis of berberine-related mechanisms against type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. J. Ethnopharmacol. 276, 114180. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114180
Dong, H., Wang, N., Zhao, L., and Lu, F. (2012). Berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 591654. doi:10.1155/2012/591654
Douros, A., Lix, L. M., Fralick, M., Dell'Aniello, S., Shah, B. R., Ronksley, P. E., et al. (2020). Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and the risk for diabetic ketoacidosis: a multicenter cohort study. Ann. Intern Med. 173 (6), 417–425. doi:10.7326/M20-0289
Drucker, D. J., Buse, J. B., Taylor, K., Kendall, D. M., Trautmann, M., Zhuang, D., et al. (2008). Eventide once weekly versus twice daily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority study. Lancet 372 (9645), 1240–1250. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61206-4
Du, J. (2016). Evaluation on efficacy and safety of berberine on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 8, 120–121. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2016.32.061
Du, Y. G., Zhang, Q., Zhang, X. L., Song, Y., Zheng, J., An, Y., et al. (2023). Correlation between inflammatory biomarkers, cognitive function and glycemic and lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Biochem. 121-122, 110683. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2023.110683
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M., and Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Bmj 315 (7109), 629–634. doi:10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Fan, C. L., Li, Y., Song, H. P., and Wang, Q. (2018). Effectiveness evaluation analysis on berberine tablets combination with metformin treating type Ⅱ diabetes. Mod. Hosp., 731–733. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-332X.2018.05.033
Fan, C., Zhang, J., and Qiu, D. (2024). Causal relationship between genetically predicted type 2 diabetes mellitus and male infertility. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 15, 1357279. doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1357279
Galantini, M. P. L., Ribeiro, I. S., Gonçalves, C. V., Muniz, I. P. R., Lima, P. H. B., Santos, G. S., et al. (2022). The sweet fuel of inflammation: new perspectives on the complex web that interconnects diabetes. Exp. Gerontol. 167, 111905. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2022.111905
Gao, F., Yue, G., and Wang, Q. (2002). Clinical study on berberine for improving insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. West J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 15 (6), 34–36. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-6852.2002.06.022
Giugliano, D., Longo, M., Signoriello, S., Maiorino, M. I., Solerte, B., Chiodini, P., et al. (2022). The effect of DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors on cardiorenal outcomes: a network meta-analysis of 23 CVOTs. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 21 (1), 42. doi:10.1186/s12933-022-01474-z
Guo, B., and Zhao, H. (2006). Hypoglycemic pharmacodynamics and clinical efficacy of berberine. Chin. Pharm. 15 (21), 30–31. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2006.21.025
Guo, J., Chen, H., Zhang, X., Lou, W., Zhang, P., Qiu, Y., et al. (2021). The effect of berberine on metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2074610. doi:10.1155/2021/2074610
Guo, Y., Pope, C., Cheng, X., Zhou, H., and Klaassen, C. D. (2011). Dose-response of berberine on hepatic cytochromes P450 mRNA expression and activities in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 138 (1), 111–118. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.058
He, Q., Dong, H., Guo, Y., Gong, M., Xia, Q., Lu, F., et al. (2022). Multi-target regulation of intestinal microbiota by berberine to improve type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 1074348. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1074348
Higgins, J. P., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Jüni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj 343, d5928. doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J., and Altman, D. G. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj 327 (7414), 557–560. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Huang, J., Hu, W., and Lin, X. (2018). Effect of berberine hydrochloride on improving insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and its mechanism. Chin. J. Gerontol. 38 (17), 4130–4132. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.17.013
Jiang, W., and Wang, H. (2019). Effect of berberine hydrochloride tablets combined with metformin on blood glucose control and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes. Chronic Pathol. J. 20 (8), 3. doi:10.16440/j.cnki.1674-8166.20190912.004
Jovanovski, E., Smircic-Duvnjak, L., Komishon, A., Au-Yeung, F. R., Sievenpiper, J. L., Zurbau, A., et al. (2021). Effect of coadministration of enriched Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng) and American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L) on cardiometabolic outcomes in type-2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. J. Ginseng Res. 45 (5), 546–554. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2019.11.005
Kong, W. J., Zhang, H., Song, D. Q., Xue, R., Zhao, W., Wei, J., et al. (2009). Berberine reduces insulin resistance through protein kinase C-dependent up-regulation of insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 58 (1), 109–119. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2008.08.013
Laia, N. L., Barko, P. C., Sullivan, D. R., McMichael, M. A., Williams, D. A., and Reinhart, J. M. (2022). Longitudinal analysis of the rectal microbiome in dogs with diabetes mellitus after initiation of insulin therapy. PLoS One 17 (9), e0273792. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0273792
Lan, J., Zhao, Y., Dong, F., Yan, Z., Zheng, W., Fan, J., et al. (2015). Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 161, 69–81. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.09.049
Li, J., Ma, X., and Ma, H. (2008). Xploring the efficacy of berberine combined with lifestyle interventions on type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. J. Liaoning Tradit. Chin. Med. 35 (12), 1858–1859. doi:10.13192/j.ljtcm.2008.12.69.lijh.071
Li, L., Li, S., Deng, K., Liu, J., Vandvik, P. O., Zhao, P., et al. (2016). Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and risk of heart failure in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and observational studies. Bmj 352, i610. doi:10.1136/bmj.i610
Li, M. (2008). Clinical observation of berberine combined with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hubei J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 30 (2), 34–35. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0704.2008.02.018
Li, P. (2017). The effects of berberine combined with sitagliptin on blood glucose and inflammatory markers in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Henan Med. Res. 26 (5), 903–904. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2017.05.096
Li, Z., and Liu, L. (2007). Therapeutic efficacy of combined berberine and glipizide on type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Res. 24 (1), 61–64. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2007.01.021
Liang, Y., Xu, X., Yin, M., Zhang, Y., Huang, L., Chen, R., et al. (2019). Effects of berberine on blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic literature review and a meta-analysis. Endocr. J. 66 (1), 51–63. doi:10.1507/endocrj.EJ18-0109
Liu, L. (2004). Observation of the efficacy of berberine in adjuvant treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Sichuan Tradit. Chin. Med. 22 (2), 46. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3649.2004.02.027
Liu, W. (2012). Clinical observation of BBR tablets in the treatment of 16 cases of T2DM. Qinghai Med. J. 42 (7), 5.
Lu, J. (2023). Clinical study of aspart insulin combined with berberine hydrochloride in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. North Pharm. 20 (7), 119–121. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2023.07.040
Lyu, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., Lin, L., Yang, X., Cheung, S. C. K., et al. (2019). Pharmacokinetic interactions between metformin and berberine in rats: role of oral administration sequences and microbiota. Life Sci. 235, 116818. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116818
Mehrpour, O., Saeedi, F., Hoyte, C., Hadianfar, A., Nakhaee, S., and Brent, J. (2022). Distinguishing characteristics of exposure to biguanide and sulfonylurea anti-diabetic medications in the United States. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 56, 171–177. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.03.023
Meng, L. (2016). Observation of the therapeutic effect of berberine combined with glipizide on type 2 diabetes. Diabetes New World (1), 19–21. doi:10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2016.01.019
Meng, X. J., Zeng, Y. J., Kong, H. J., and Shu, X. C. (2011). Research on the effect of berberine on the function of endothelial vessels, IL-6 and TNF-a in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. Prev. Contr Chron. Dis. 19 (5), 504–505. doi:10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2011.05.034
Moher, D., Hopewell, S., Schulz, K. F., Montori, V., Gøtzsche, P. C., Devereaux, P. J., et al. (2010). CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Bmj 340, c869. doi:10.1136/bmj.c869
Mokgalaboni, K., Lebelo, S. L., Modjadji, P., and Ghaffary, S. (2023). Okra ameliorates hyperglycaemia in pre-diabetic and type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical evidence. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1132650. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1132650
Nazari, A., Ghotbabadi, Z. R., Kazemi, K. S., Metghalchi, Y., Tavakoli, R., Rahimabadi, R. Z., et al. (2024). The effect of berberine supplementation on glycemic control and inflammatory biomarkers in metabolic disorders: an umbrella meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Ther. 46 (2), e64–e72. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.10.019
Neag, M. A., Mocan, A., Echeverría, J., Pop, R. M., Bocsan, C. I., Crişan, G., et al. (2018). Berberine: botanical occurrence, traditional uses, extraction methods, and relevance in cardiovascular, metabolic, hepatic, and renal disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 557. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00557
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj 372, n71. doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Potier, L., Mohammedi, K., Velho, G., and Roussel, R. (2021). SGLT2 inhibitors and lower limb complications: the diuretic-induced hypovolemia hypothesis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 20 (1), 107. doi:10.1186/s12933-021-01301-x
Rashidi, H., Namjoyan, F., Mehraban, Z., Zakerkish, M., Ghaderian, S. B., and Latifi, S. M. (2018). “The effects of active ingredients of barberry root (berberine) on glycemic control and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients,” in Jundishapur journal of natural pharmaceutical products. In Press.
Rong, W., Cai, L. S., Guo, S. B., and Dou, W. D. (1997). Glibenclamide combined with aspirin and berberine for the treatment of non-Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. New Drugs Clin. Rem. 16 (2), 109–110.
Safiri, S., Karamzad, N., Kaufman, J. S., Bell, A. W., Nejadghaderi, S. A., Sullman, M. J. M., et al. (2022). Prevalence, deaths and disability-adjusted-life-years (DALYs) due to type 2 diabetes and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 838027. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.838027
Samad, M. B., Mohsin, M., Razu, B. A., Hossain, M. T., Mahzabeen, S., Unnoor, N., et al. (2017). [6]-Gingerol, from Zingiber officinale, potentiates GLP-1 mediated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion pathway in pancreatic β-cells and increases RAB8/RAB10-regulated membrane presentation of GLUT4 transporters in skeletal muscle to improve hyperglycemia in Leprdb/db type 2 diabetic mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 17 (1), 395. doi:10.1186/s12906-017-1903-0
Sanchez-Rangel, E., and Inzucchi, S. E. (2017). Metformin: clinical use in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 60 (9), 1586–1593. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4336-x
Sanjari, M., Shamsinejad, B., Khazaeli, P., Safi, Z., Mirrashidi, F., and Naghibzadeh-Tahami, A. (2020). Safety and efficacy of Berberis integerrima root extract in patients with type 2 diabetes. A parallel intervention based triple blind clinical trial. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 19 (1), 71–80. doi:10.1007/s40200-019-00478-z
Sheng, Z., and Xie, D. (2010). Levels of inflammatory factors in patients with type 2 diabetes and the effect of berberine as adjuvant treatment. J. New Med. 41 (3), 177–180. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2010.03.012
Shrivastava, S., Sharma, A., Saxena, N., Bhamra, R., and Kumar, S. (2023). Addressing the preventive and therapeutic perspective of berberine against diabetes. Heliyon 9 (11), e21233. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21233
Shu, J. (2014). Effects of berberine on serum adiponectin and high sensitivity C reactive protein levels in type 2 diabetic patients. Chin. Pharm. 23 (15), 33–34.
Singh, A., Zhao, K., Bell, C., and Shah, A. J. (2020). Effect of berberine on in vitro metabolism of sulfonylureas: a herb-drug interactions study. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 34 (Suppl. 4), e8651. doi:10.1002/rcm.8651
Song, D., Hao, J., and Fan, D. (2020). Biological properties and clinical applications of berberine. Front. Med. 14 (5), 564–582. doi:10.1007/s11684-019-0724-6
Sun, H. (2016). Clinical observation of berberine hydrochloride combined with sitagliptin in treatment of diabesity type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs Clin. 31, 1020–1023. doi:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2016.07.022
Sun, H., Saeedi, P., Karuranga, S., Pinkepank, M., Ogurtsova, K., Duncan, B. B., et al. (2022). IDF Diabetes Atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 183, 109119. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
Sun, S. (2017). Effect of Berberine on the serum levels of IL-10, IL-6 and CRP in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Chang. Univ. Chin. Med. 33 (3), 431–433. doi:10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2017.03.028
Tahmasebi, L., Zakerkish, M., Golfakhrabadi, F., and Namjoyan, F. (2019). Randomised clinical trial of Berberis vulgaris root extract on glycemic and lipid parameters in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 32, 100998. doi:10.1016/j.eujim.2019.100998
Tancredi, M., Rosengren, A., Svensson, A. M., Kosiborod, M., Pivodic, A., Gudbjörnsdottir, S., et al. (2015). Excess mortality among persons with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 373 (18), 1720–1732. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1504347
Tian, X., Liu, F., Li, Z., Lin, Y., Liu, H., Hu, P., et al. (2019). Enhanced anti-diabetic effect of berberine combined with timosaponin B2 in goto-kakizaki rats, associated with increased variety and exposure of effective substances through intestinal absorption. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 19. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00019
Utami, A. R., Maksum, I. P., and Deawati, Y. (2023). Berberine and its study as an antidiabetic compound. Biol. (Basel). 12 (7), 973. doi:10.3390/biology12070973
Wang, F., Liu, J., Chen, Z. P., Ding, H. Y., Sheng, L., Xu, J., et al. (2012). The effects of berberine and metformin on lipid levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Intern Med. 29 (6), 384–386. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9057.2012.06.007
Wang, J., Hu, J. H., Wang, J. H., Yu, J. W., and Zhang, Q. L. (2022). Clinical effects of Berberine hydrochloride combined with Metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. Diabetes 30 (5), 5. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2022.05.006
Weiss, T., Yang, L., Carr, R. D., Pal, S., Sawhney, B., Boggs, R., et al. (2022). Real-world weight change, adherence, and discontinuation among patients with type 2 diabetes initiating glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the UK. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 10 (1), e002517. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002517
Wu, J. (2017). Analysis of the effects of berberine combined with glipizide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Dis. Electron J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West Med. 5 (35), 51–54. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-6681.2017.35.033
Wu, Y., Chen, F., Huang, X., Zhang, R., Yu, Z., Chen, Z., et al. (2019). Berberine (BBR) attenuated palmitic acid (PA)-Induced lipotoxicity in human HK-2 cells by promoting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPAR-α). Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 7702–7708. doi:10.12659/MSM.916686
Xiang, W., Huang, X., and Huang, G. (2011). Study on the treatment of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients with two anti-inflammatory medications. J. Pract. Diabetol. 7 (2), 51–52.
Xie, W., Su, F., Wang, G., Peng, Z., Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Glucose-lowering effect of berberine on type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1015045. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1015045
Xing, W. (2017). Observation of the efficacy of berberine combined with taurine in treating insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-Cerebrovasc Dis. 15 (1), 90–92. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2017.01.027
Xu, B., Li, S., Kang, B., and Zhou, J. (2022). The current role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus management. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 21 (1), 83. doi:10.1186/s12933-022-01512-w
Xue, S., Xu, J., and Ll, T. (2012). Clinical observation of sulfonylureas combined with berberine and metformin in the treatment of diabetes. J. Shanxi Tradit. Chin. Med. 33 (10), 1335–1336. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2012.10.046
Yang, B. Y., Yang, P., Wang, X. Y., and Zhang, Q. L. (2023b). Effect of berberine hydrochloride combined with metformin on intestinal GLP-1 level in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. Med. Health (12), 98–104.
Yang, T., Zhou, Y., and Cui, Y. (2023a). Urinary tract infections and genital mycotic infections associated with SGLT-2 inhibitors: an analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 23, 1035–1040. doi:10.1080/14740338.2023.2288897
Yang, X., Liu, Z., and Yang, H. (2020). Clinical study on berberine hydrochloride tablets combined with metformin in the treatment of primary type Ⅱ diabetes. Sh. J. TCM 54, 59–62. doi:10.16305/j.1007-1334.2020.03.017
Yao, H. Z., Gao, B. W., Wang, S.J., Li, X., and Lu, T. C. (2018). Effects of berberine combined with glipizide in the treatment of 48 cases of type Ⅱ diabetes. Diet. Health 005 (014), 74. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-8439.2018.14.086
Yao, J., and Xie, D. (2015). Clinical observation of triple therapy in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. Pharm. 26 (29), 4107–4109. doi:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2015.29.26
Yao, J., Kong, W., and Jiang, J. (2015). Learning from berberine: treating chronic diseases through multiple targets. Sci. China Life Sci. 58 (9), 854–859. doi:10.1007/s11427-013-4568-z
Ye, J., Wu, Y., Yang, S., Zhu, D., Chen, F., Chen, J., et al. (2023). The global, regional and national burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the past, present and future: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 14, 1192629. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1192629
Ye, L. (2021). Significance of sulfonylureas combined with berberine and metformin in the treatment of diabetes. Sci. Health Preserv. 24 (18), 263. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9714.2021.18.263
Ye, Y., Liu, X., Wu, N., Han, Y., Wang, J., Yu, Y., et al. (2021). Efficacy and safety of berberine alone for several metabolic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 653887. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.653887
Yin, J., Xing, H., and Ye, J. (2008). Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 57 (5), 712–717. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2008.01.013
Yin, S. L., Yin, H. Q., Li, Z. H., and Li, C. M. (2011). The effects of berberine hydrochloride on blood glucose, insulin levels, and lipids in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients. Acta Acad. Med. Xuzhou 31 (1), 40–41. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-2065.2011.01.014
Yu, Y. (2015). Clinical efficacy studies of berberine adjuvant treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes New World 35 (10), 34–35. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4062.2015.10.022
Yu, Y. (2022). Efficacy of BBR combined with metformin in the treatment of patients with T2DM. Chin. J. Med. Health (11), 139–141.
Zhang, H. (2017). Value analysis of sulfonylureas combined with berberine and metformin in the treatment of diabetes. Diabetes New World 20 (24), 82–83. doi:10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2017.24.082
Zhang, H., Wei, J., Xue, R., Wu, J. D., Zhao, W., Wang, Z. Z., et al. (2010). Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 59 (2), 285–292. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2009.07.029
Zhang, J., Fan, X., Xu, Y., Wang, K., Xu, T., Han, T., et al. (2024b). Association between inflammatory biomarkers and mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: NHANES 2005-2018. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 209, 111575. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2024.111575
Zhang, J. Y., Yang, Z. C., Li, H. F., Yang, G. L., Guo, M. S., Yang, R. P., et al. (2000). Clinical study on effect of high dose berberine on blood rheology in patients with type Ⅱ diabetes mellitus. Med. J. Chin. People’s Armed Police Forces 11 (11), 643–646. doi:10.14010/j.cnki.wjyx.2000.11.001
Zhang, R., Bai, R., and Wei, J. (2011). The therapeutic effects of berberine on 24 hour urinary albumin of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West Nephrol. 12 (1), 28–30. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2011.01.009
Zhang, W., Xu, J. H., Yu, T., and Chen, Q. K. (2019). Effects of berberine and metformin on intestinal inflammation and gut microbiome composition in db/db mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109131. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109131
Zhang, Y., Gu, Y., Ren, H., Wang, S., Zhong, H., Zhao, X., et al. (2020). Gut microbiome-related effects of berberine and probiotics on type 2 diabetes (the PREMOTE study). Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 5015. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18414-8
Zhang, Y., Li, L., Chai, T., Xu, H., Du, H. Y., and Jiang, Y. (2024a). Mulberry leaf multi-components exert hypoglycemic effects through regulation of the PI-3K/Akt insulin signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 319 (Pt 3), 117307. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117307
Zhang, Y., and Yuan, X. (2012). Clinical observation of Huangliansu in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Heze Med. Coll. 24 (2), 27–28. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-4118.2012.02.15
Zhao, M. M., Lu, J., Li, S., Wang, H., Cao, X., Li, Q., et al. (2021). Berberine is an insulin secretagogue targeting the KCNH6 potassium channel. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 5616. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25952-2
Zhou, Q., and Huang, S. (2012). Clinical study of berberine combined with metformin in the treatment of obese type 2 diabetes. J. Pract. Diabetol. 8 (4), 33–35.
Zhu, G., Zhang, C., and Kang, S. (2009). Observational study on the efficacy of berberine combined with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Chin. J. Misdiagn 9 (4), 788–789.
Zhu, J. X., Wang, X. Y., Lv, W. Q., and Ji, X. Z. (2015). Gliclazide combined with berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Zhejiang J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West Med. 25, 915–917. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4561.2015.10.008
Keywords: berberine, type 2 diabetes mellitus, traditional Chinese medicine, safety, meta-analysis
Citation: Wang J, Bi C, Xi H and Wei F (2024) Effects of administering berberine alone or in combination on type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1455534. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1455534
Received: 27 June 2024; Accepted: 05 November 2024;
Published: 21 November 2024.
Edited by:
Havagiray R. Chitme, Amity University, IndiaReviewed by:
Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla, South African Medical Research Council, South AfricaKabelo Mokgalaboni, University of South Africa, South Africa
Kaijian Hou, Shantou University, China
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Bi, Xi and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fengqin Wei, am53ZnFAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Jiacheng Wang
Jiacheng Wang Chenhao Bi
Chenhao Bi Hongbin Xi
Hongbin Xi Fengqin Wei
Fengqin Wei