- Department of Anesthesia, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin, China
Objective: Intertrochanteric femoral fracture (IFF) is a public issue in the old. Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia (CSEA) is commonly utilized for lower limb orthopedic surgery in elderly patients. Therefore, this study explored the application of dexmedetomidine (Dex) and ropivacaine (Rop) assisted CSEA in elderly IFF patients.
Methods: Totally 187 elderly IFF patients were assigned into the Rop assisted CSEA (Rop-CSEA), low-dose Dex-Rop assisted CSEA (low Dex and Rop-CSEA) and high-dose Dex-Rop assisted CSEA (high Dex and Rop-CSEA) groups. We compared block effects, hemodynamic indicators [heart rate (HR)/respiratory rate (RR)/mean arterial pressure (MAP)] at time before anesthesia (T0)/skin incision (T1)/10 min postoperatively (T2)/suture postoperatively (T3)/anesthesia recovery (T4), postoperative pain mediator release [substance P (SP)/prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)/5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)], neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), adverse reactions, delirium and cognitive dysfunction incidence.
Results: Compared with the Rop-CSEA group, low/high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups had shortened onset times, prolonged recovery times in sensory/motor block, elevated HR/RR/MAP, repressed pain mediator release, and reduced postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction incidences. HR/RR/MAP exhibited reductions followed by elevations at T2-T4, and SP/PGE2/5-HT levels revealed elevations in all groups postoperatively. NLR level displayed enhancement followed by reduction, and NLR in the low/high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups was abated on postoperative days 1–5. Total incidence of adverse reactions in the high Dex and Rop-CSEA group was enhanced.
Conclusion: Dex and Rop assisted CSEA shortens the onset time of anesthesia, maintains perioperative hemodynamic stability, inhibits pain mediator release, reduces postoperative NLR level and the incidence of delirium and cognitive dysfunction in IFF patients.
Introduction
The incidence of fractures in the elderly is on the rise and has emerged as a prominent health concern in numerous nations (Court-Brown and McQueen, 2016). Hip fractures in older individuals remarkably contributes to morbidity and mortality, exerting a substantial impact on society (Handoll et al., 2021). Among these, intertrochanteric femoral fracture (IFF) is prevalent among the elderly population and are linked with considerable morbidity, mortality, and a decline in life quality (Yoon et al., 2020). Surgery is acknowledged as a crucial tool in the management of IFF (Cheng and Sheng, 2020). Elderly patients commonly experience degenerative body functions, frequently accompanied by cardiovascular diseases, low tolerance to surgery, abnormal vital signs, and hemodynamic fluctuations during surgery. Besides, they are also susceptible to postoperative complications such as delirium, which places additional demands on nursing staff, extends hospital stays, raises hospitalization expenses, and elevates in-hospital mortality (Albanese et al., 2022; Basques et al., 2015; Neuman et al., 2014). The most frequently employed anesthesia protocol for hip surgery is combined spinal-epidural anesthesia (CSEA), which integrates the advantages of both lumbar and epidural anesthesia, providing effective analgesia, minimal respiratory and circulatory depression, and reduced complications (Chu et al., 2015; Johnson et al., 2016; McIsaac et al., 2018; Perlas et al., 2016). Previous studies have documented that the incorporation of sedative medications into standard anesthesia protocols can suppress sympathetic excitation and decrease catecholamine production, thereby promoting vital sign preservation, enhancing hemodynamic stability, and mitigating postoperative delirium (Shi et al., 2019; Shin et al., 2023; Su et al., 2016; Subramaniam et al., 2019; Yousef et al., 2015). Consequently, the choice of suitable anesthetic medications for aiding CSEA in IFF patients is a crucial consideration for mitigating postoperative pain and minimizing the incidence of complications such as delirium.
Postoperative delirium, which primarily impacts the elderly population, frequently leads to unfavorable patient outcomes, including prolonged hospital stays and clinically impaired functional recovery (Hshieh et al., 2017). The pathophysiology underlying postoperative delirium remains incompletely elicited and may encompass various physiological mechanisms of dysfunction, such as the impact of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation (Maldonado, 2013). Given the potential association between delirium and the inflammatory pathways, it is essential to probe specific inflammatory markers linked to postoperative delirium (Neerland et al., 2016). The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) serves as a biomarker for the systemic inflammatory response (Langley et al., 2021). Moreover, an elevated neutrophil count and an NLR ≥ 3.5 are identified as independent risk factors for postoperative delirium, and NLR may be a promising indicator for predicting delirium in elderly patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty for hip fracture (He et al., 2020). Hence, the quest for appropriate sedative drugs to help CSEA, with the aim of suppressing postoperative neutrophil function and reducing postoperative NLR, may yield advantageous therapeutic outcomes for postoperative delirium in IFF patients.
Ropivacaine (Rop) is an amide local anesthetic that is synthesized in its pure levorotatory form (Beilin and Halpern, 2010). Rop demonstrates anti-inflammatory properties by suppressing the expression and activity of the adhesion molecule CD11b in neutrophils (Zhu et al., 2010). Extensive research has been conducted on the application of Rop in postoperative management of fractures (Cheng et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Oura et al., 2023; Swennen et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2022). In addition, Rop may be bound up with a shorter time of motor function recovery (Malhotra et al., 2016). Nevertheless, further research is warranted to explore the use of Rop in CSEA in IFF patients. On the other hand, dexmedetomidine (Dex) is a highly selective agonist of the alpha2-adrenoceptor, known for its sedative, opioid-sparing, and analgesic effects and suitable for both short- and long-term sedation in the intensive care settings (Keating, 2015). Dex also modulates postoperative NLR (Du et al., 2021). Several studies have assessed the effectiveness and potential negative impacts of Dex as an adjunctive treatment for patients undergoing surgery for femur fractures (Dolma et al., 2018; Gopal and Krishnamurthy, 2018; Nwachukwu et al., 2020). The use of Dex as a local anesthetic adjuvant in femur fracture surgery is linked with a prolonged rescue analgesia (Deng and Yu, 2021). Dex has been shown to effectively decrease the need for narcotic drugs and abate the occurrence of postoperative delirium (Xie and Xie, 2018). Dex mitigates the neurotoxic effects induced by Rop (Xu et al., 2022). Nevertheless, the potential application of Dex and Rop in CSEA for elderly patients with IFF has not yet to be fully elucidated. Based on this context, the study aimed to examine the impacts of Dex and Rop assisted CSEA on postoperative block effect, hemodynamics, pain stress response, NLR, adverse effects, delirium, and cognitive dysfunction incidence in IFF patients, with the objective of identifying a suitable anesthetic drug for assisting CSEA in IFF patients.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
All participants provided their signed informed consent. This study adhered to the principles outlined in the Helsinki Declaration and its amendments, and received approval from the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Hospital (approved number: 2023202). This study was conducted without any disruption to the normal clinical practice.
Study subjects
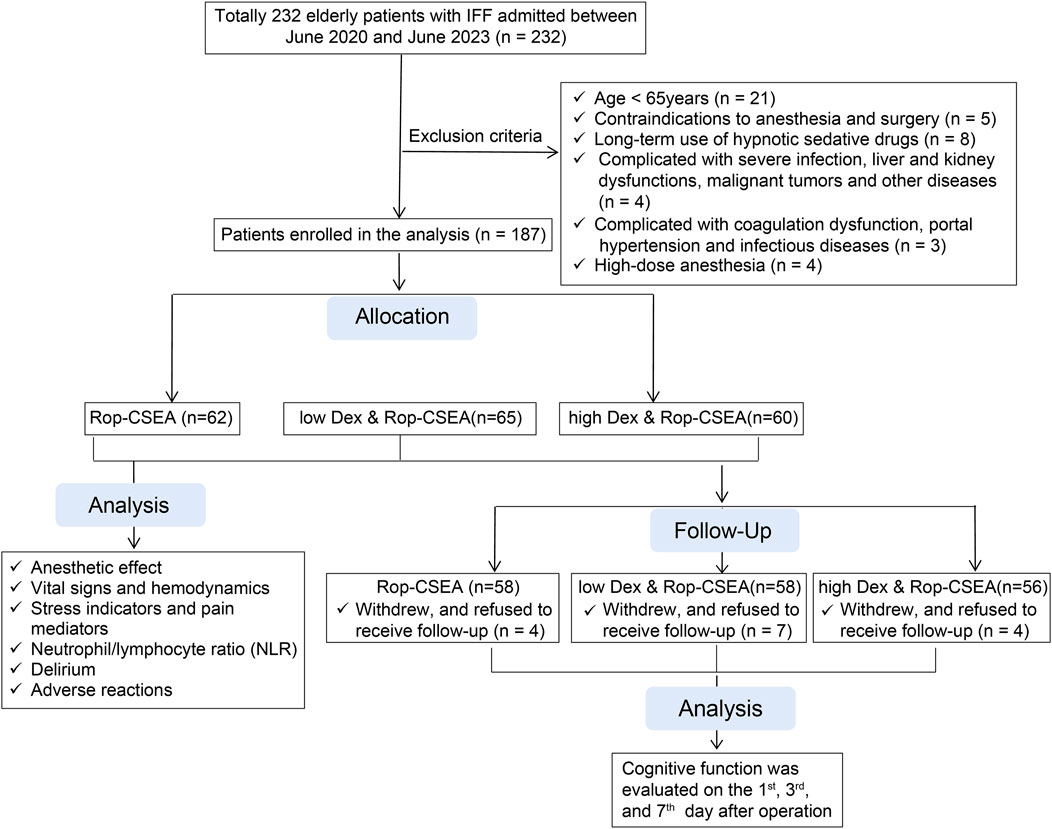
Totally 232 elderly IFF patients admitted to Tianjin Hospital (approved number: 2023202) between June 2020 and June 2023 were included in this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows (Court-Brown and McQueen, 2016): the presence of a well-defined cause of fracture and a confirmed diagnosis of IFF by computed tomography and X-ray examinations (Handoll et al., 2021); age ≥65 years (Yoon et al., 2020); American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class I ∼ II; and (Cheng and Sheng, 2020) the first onset. The exclusion criteria included (Court-Brown and McQueen, 2016): anesthesia and surgical contraindications (Handoll et al., 2021); mental illness, cognitive impairment, hearing impairment, or inability to communicate normally, preoperatively (Yoon et al., 2020); long-term use of hypnotic sedative drugs (Cheng and Sheng, 2020); complications of serious infections, liver and kidney function abnormalities, malignant tumors and other diseases (Albanese et al., 2022); complications of coagulation dysfunction, portal hypertension and infectious diseases (Basques et al., 2015); withdrew and did not accept follow-up (Neuman et al., 2014); high-dose anesthesia (Chu et al., 2015); allergic reaction to the study drugs. In the light of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 187 elderly patients with IFF were finally enrolled in the study (Figure 1 for the flow chart), and arranged into 3 groups (each received different anesthesia methods) using the random number table method, including the Rop assisted CSEA group (Rop-CSEA, n = 62; Rop-CSEA regimen was performed), the low-dose Dex-Rop assisted CSEA group (low Dex and Rop-CSEA, n = 65; low-dose Dex and Rop-CSEA regimen was implemented), and the high-dose Dex-Rop assisted CSEA group (high Dex and Rop-CSEA, n = 60; high-dose Dex and Rop-CSEA regimen was employed).
Anesthesia method
All patients underwent routine preoperative anesthesia risk detection and routine fasting prior to surgery.
Rop-CSEA group (n = 62): following the patient’s admission to the operating room, the venous access was established, and oxygen was administered via nasal catheter at a flow of 3 L/min. The blood oxygen saturation, electrocardiogram, and invasive arterial blood pressure were monitored. Next, the patients were in the lateral position, and routinely sterilized. Then, the towel was spread out. Under sterile conditions, a puncture was performed at the L3-4 intervertebral space using an 18 G epidural puncture needle. After penetrating to the epidural cavity, the arachnoid was punctured using a 25 G lumbar puncture needle via the aperture of the epidural puncture needle. The puncture was successful if the cerebrospinal fluid outflowed from the suction catheter was bloodless, airless, and clear. After the withdrawal of the needle core, the arachnoid was administered 3 mL of 0.375% Rop (H20060137, Hengrui Pharmaceuticals, Lianyungang, Jiangsu, China) at a uniform speed of 0.2 mL/s. The lumbar puncture needle was then retracted, and an epidural catheter was inserted through the epidural puncture needle, with a 3 cm catheter remaining in position towards the tip, followed by the removal of the epidural puncture needle. Subsequently, the puncture site was covered with sterilized gauze.
Low Dex and Rop-CSEA gruop (n = 65): after subarachnoid anesthesia, the patients were subjected to an intravenous injection of Dex (H20143195, Guorui Pharmaceutical, Leshan, Sichuan, China) at a rate of 0.5 μg/(kg⋅min) for 10 min, followed by a continuous infusion at 0.25 μg/(kg⋅h) until 10 min prior to the end of surgery (Xiong Jingwei, Li Liping, Zhang Lidong, Liu Yang. Effects of dexmedetomidine-assisted combined spinal and epidural anesthesia on hemodynamics and serum T lymphocyte subsets level in elderly patients with intertrochanteric fracture of femur [J]. Frontiers of Medicine (Electronic version), 2021, 13 (07): 104–108).
High Dex and Rop-CSEA group (n = 60): after subarachnoid anesthesia, the patients were subjected to intravenous infusion of Dex at a rate of 0.5 μg/(kg⋅min) for 10 min, followed by a continuous infusion at 0.40 μg/(kg⋅h). The administration was ceased 10 min before the end of the surgery (Xiong Jingwei, Li Liping, Zhang Lidong, Liu Yang. Effects of dexmedetomidine-assisted combined spinal and epidural anesthesia on hemodynamics and serum T lymphocyte subsets level in elderly patients with intertrochanteric fracture of femur [J]. Frontiers of Medicine (Electronic version), 2021, 13 (07): 104–108).
The adjustment of the anesthesia plane for the three groups was controlled at the T8-T10 level, and the surgery was carried out once the desired plane for the surgery was achieved. During the procedure, various measures such as mask oxygen inhalation, electrocardiogram monitoring, and fluid infusion were implemented to maintain the vital signs. The patients received regular administration of midazolam (H20031037, Nhwa, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China) for sedation, ephedrine (X20010406, Arker, Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China) to maintain central arterial pressure ≥30% of the baseline value and systolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg, and atropine (H34023679, Guorui Pharmaceutical) to maintain heart rate >55 beats/min.
Indicator observation
(1) Clinical baseline data such as age, sex, body mass index (BMI), comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and coronary artery disease), ASA classification, fracture Evans type [modified Evans (Kyle) type: Types 1–2 Stable and Types 3–4 Unstable (Bedrettin et al., 2022)], fracture cause (traffic accident injury, high fall injury, and fall injury) were acquired at enrollment of patients, as well as the general intraoperative conditions, including anesthesia time, surgery time, and intraoperative blood loss.
(2) Block effect: the onset/recovery time of sensory block, the onset/recovery time of motor block were observed in the three groups.
(3) Hemodynamic indicators such as heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) of the three groups at time of before anesthesia (T0), skin incision (T1), 10 min during the surgery (T2), suturing after surgery (T3) and anesthesia recovery (T4) were monitored and recorded using a PHILIPS patient monitor MX550 (Philips Medical Systems, Veenpluis, Netherlands).
(4) Pain stress response indicators: venous blood (3 mL) was acquired from the three groups of patients before (before anesthesia) and after (10 min after surgery) surgery and centrifuged routinely, and the serum and plasma were separated. Levels of plasma prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and serum substance P (SP) were measured utilizing a BioTek ELx808 absorption light microplate reader combined with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The kits were purchased from Sangon (Shanghai, China).
(5) NLR: venous blood (1.5 mL) was obtained from patients in the three groups on the 1st day before surgery and the 1st, 3rd, and 5th days after surgery. A whole blood cell count (NLR = neutrophil count/lymphocyte count) was performed using a Sysmex XE-5000 automatic blood cell analyzer (Sysmex, Kobe, Japan).
(6) The adverse reactions such as nausea/vomiting, bradycardia, transient hypotension, transient hypertension, and respiratory depression during the perioperative period were recorded in the three groups.
(7) Within 24 h postoperatively, patients were assessed for the occurrence of delirium using the Confusion Assessment Method Chinese Reversion, which consisted of 11 items, with 1-4 points for each item, and a total score of 11–44 points, with a score of >22 being the presence of delirium.
(8) The mental state and cognitive function of patients were evaluated utilizing Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) on the 1st day preoperatively and the 1st, 3rd, and 5th days postoperatively, and the total score of the scale was 0–30 points, with the higher score suggesting better mental state and cognitive function. The incidence of cognitive dysfunction was also calculated within 3 days postoperatively (MMSE score decreased by more than 3 points compared with that before surgery).
Statistical analysis
Data analysis and graphing in this study were conducted using SPSS 21.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, United States) and GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, United States). The normality of distribution in continuous variables was assessed by Shapiro-Wilk (W test). Data were categorized into counting data and measurement data, with counting data expressed as number of cases and percentages. The measurement data were tested for normal distribution using the W test, with measurement data that conformed to normal distribution presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and those that did not conform to normal distribution expressed as median [interquartile range]. Comparisons between two groups: the Chi-square test was employed for counting data, the independent sample t-test was utilized for measurement data that followed a normal distribution, and the Wilcoxon test was applied for measurement data that did not adhere to normal distribution. The diagnostic efficacy was assessed by measuring the sensitivity, specificity, and area under the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC). The analysis of the difference in AUC was conducted using Medcalc® version 15.0 software (Medcalc Software, Ostend, Belgium). Correlations between diagnostic findings and clinical characteristics were assessed using Chi-square test and linear regression analysis. The unpaired t-test or χ2 test was used to compare two groups of data. Multi-group data comparisons were conducted using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by post hoc analyses using Tukey’s test. p < 0.05 was accepted as indicative of significant differences.
Results
Comparative analyses of the clinical data of subjects
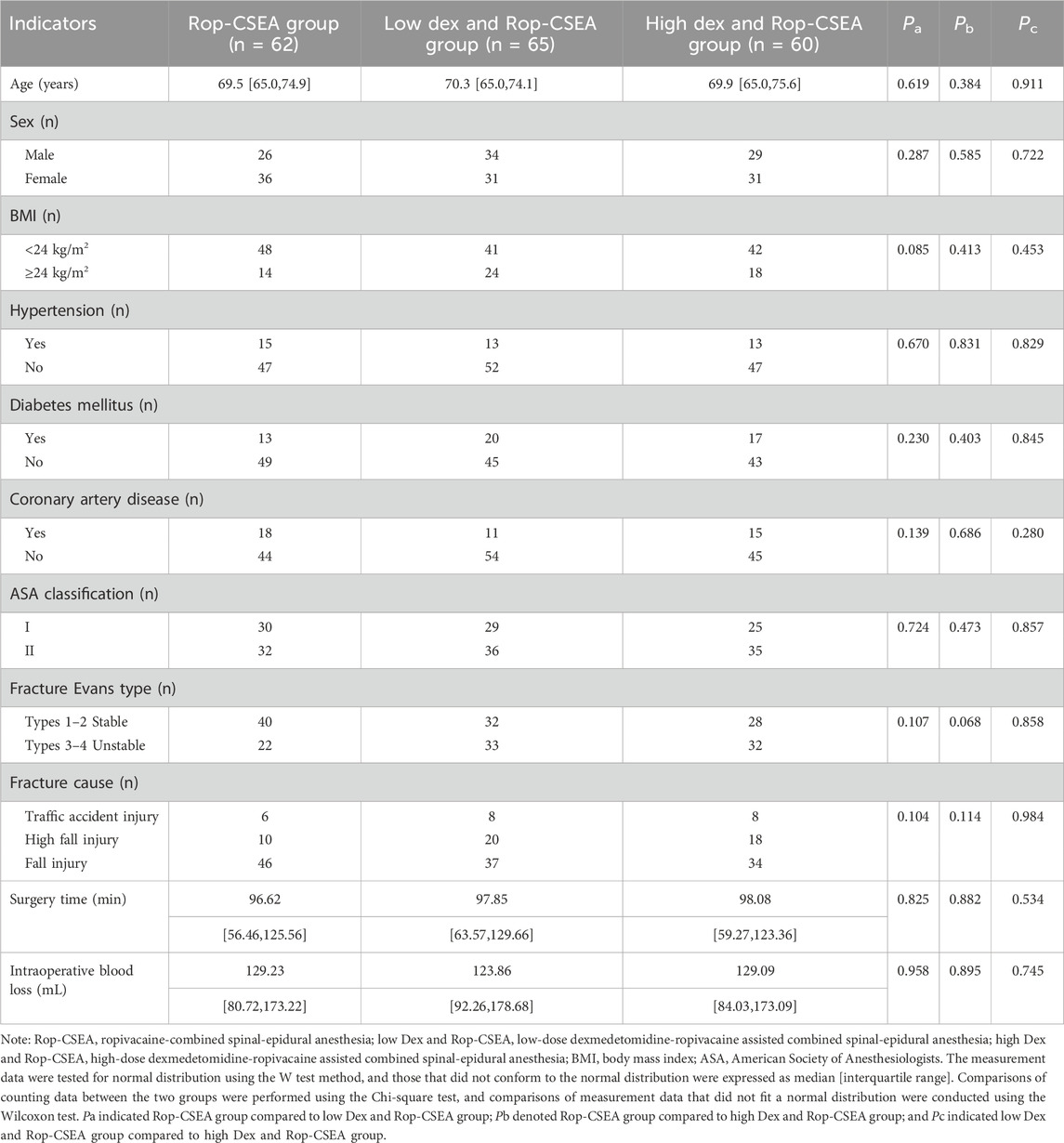
As shown in Table 1, no significant differences in the clinical baseline characteristics, including age, sex BMI, comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease), ASA classification, fracture Evans type, and fracture cause were observed among the three groups (all p > 0.05), and there were no notable differences in the intraoperative general conditions, such as operative time and intraoperative blood loss (all p > 0.05), which were comparable among the three groups.
Comparison of block effect among the three groups of patients
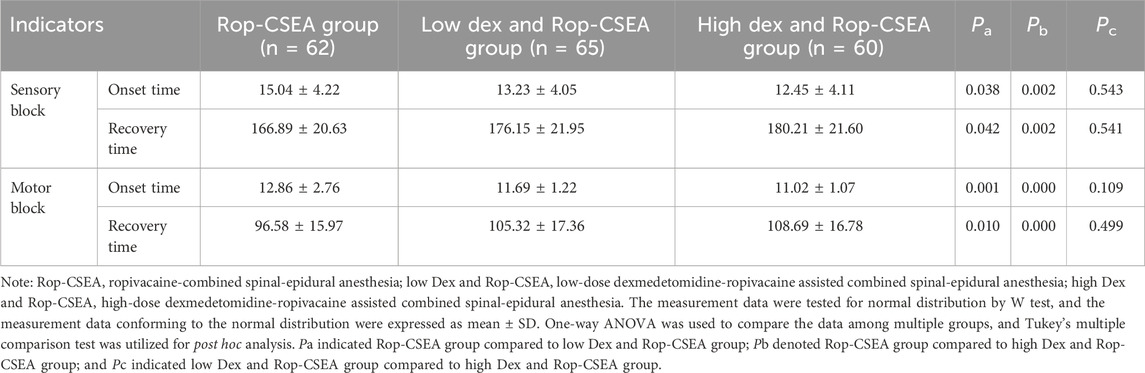
The low Dex and Rop-CSEA group and the high Dex and Rop-CSEA group exhibited shorter onset times for both sensory and motor block and longer recovery times for both sensory and motor blocks than the Rop-CSEA group (all p < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference noticed between the low Dex and Rop-CSEA group and the high Dex and Rop-CSEA group (all p > 0.05) (Table 2). Overall, Dex and Rop assisted CSEA shortened the onset time of anesthesia and prolonged the time of regional anesthesia.
Comparisons of perioperative hemodynamic indicators in three group of patients
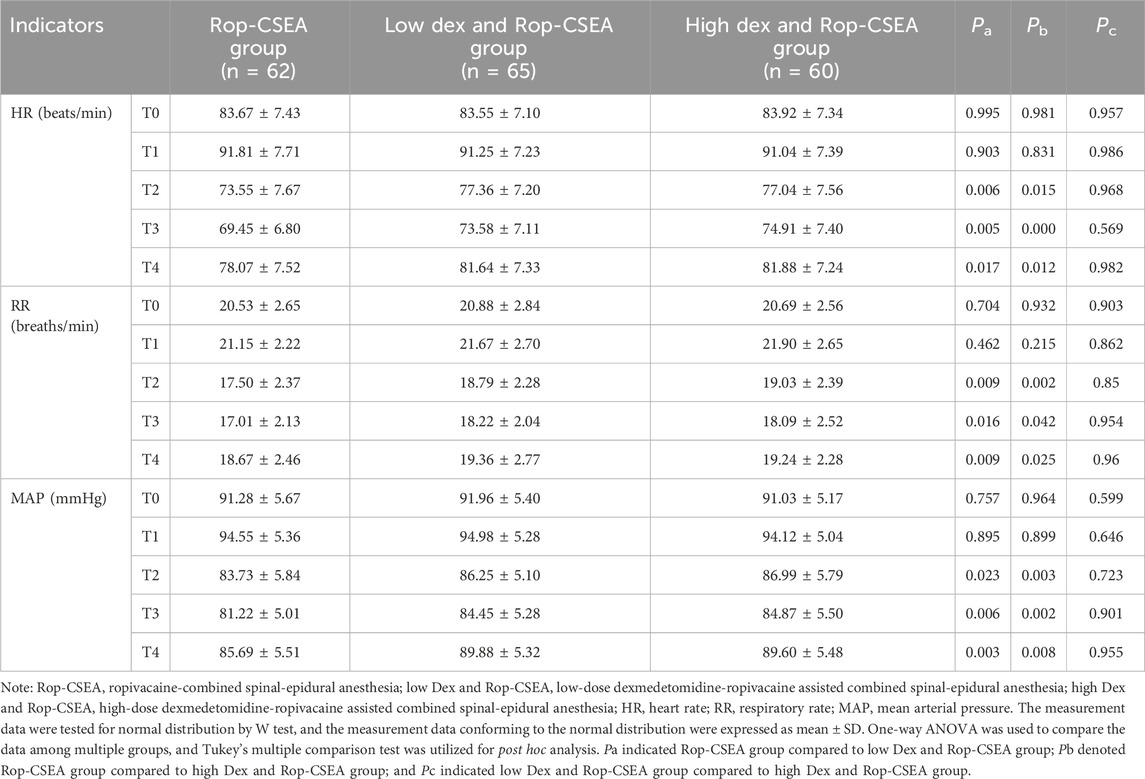
As presented in Table 3 and Figure 2, at T0, there were no substantial differences in HR, RR and MAP among the three groups (all p > 0.05). HR, RR and MAP of the three groups at T1 displayed elevations relative to at T0, with no significant differences in these indicators among the three groups (all p > 0.05). At T2-T4, HR, RR and MAP of the three groups revealed reductions followed by increments, and HR, RR and MAP of the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups were raised compared to the Rop-CSEA group (all p < 0.05), but with no significant differences noticed between the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop- CSEA groups (all p > 0.05). The aforementioned results revealed that Dex and Rop assisted CSEA was effective in stabilizing perioperative hemodynamic stability in IFF patients.

Figure 2. Comparisons of perioperative hemodynamic indicators among three groups of patients. Hemodynamic parameters (A) HR (B) RR and (C) MAP of the three groups at T0, T1, T2, T3 and T4 were compared. Data were presented as mean ± SD. Data comparisons among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s test.*p < 0.05 for comparisons with the Rop-CSEA group at the same time point, and **p < 0.01 for comparisons with the Rop-CSEA group at the same time point.
Comparisons of preoperative and postoperative pain stress indicators among three groups of patients
It has been documented that SP, PGE2, and 5-HT are pain mediators that have been linked to the initiation and exacerbation of pain and are frequently used to evaluate the pain stress response in individuals undergoing surgery (Ma et al., 2019). As reflected by ELISA results, there were no prominent differences in SP, PGE2 and 5-HT levels among the three groups before surgery (all p > 0.05), and the levels in the three groups were elevated compared to before surgery (all p < 0.05). Pain mediator release was suppressed in both the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups versus the Rop-CSEA group, postoperatively (all p < 0.01), whereas there were no observable differences between the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups (all p > 0.05) (Figure 3). Collectively, Dex and Rop assisted CSEA relieved the stress stimulation of pain on IFF patients.
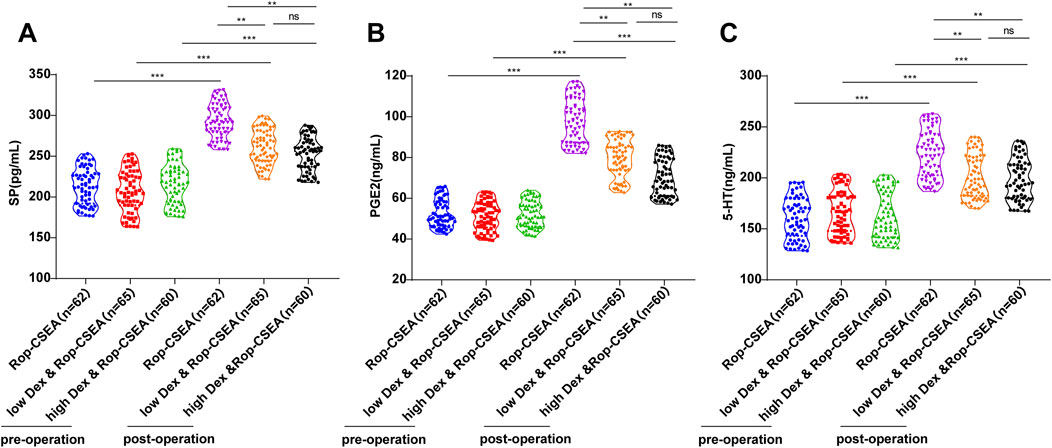
Figure 3. Comparisons of preoperative and postoperative pain stress response indicators in three groups of patients. Comparisons of pain stress response indicators (A) SP (B) PGE2 and (C) 5-HT preoperatively (Preop) and 10 min postoperatively (Postop) in the three groups. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA was conducted for data comparisons among multiple groups, and Tukey’s multiple comparison test for post hoc analysis. **p < 0.01.
Comparison of preoperative and postoperative NLR in three groups of patients
We compared the changes in NLR level in IFF patients in three groups preoperatively and postoperatively on days 1, 3, and 5 (Figure 4), with the results showing that there was no statistically significant difference observed in the preoperative level of NLR among the three groups (all p > 0.05). During postoperative days 1–5, NLR level demonstrated a pattern of initial enhancement followed by reduction in the three groups. Notably, the NLR value in the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups was reduced versus the Rop-CSEA group (all p < 0.05). There was no notable difference between the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups (all p > 0.05). The above results showed that Dex and Rop assisted CSEA was effective on reducing postoperative NLR level in IFF patients.
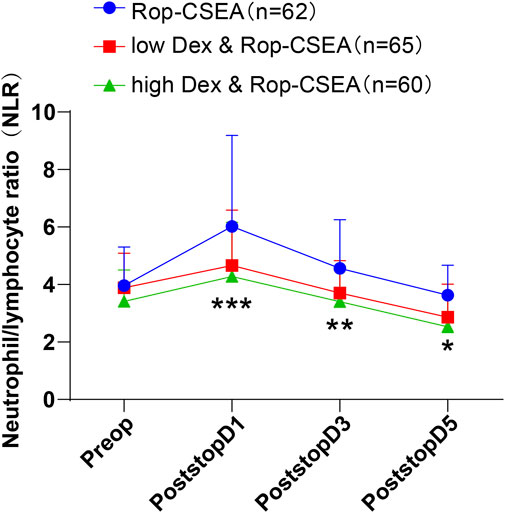
Figure 4. Comparisons of hemodynamic parameters at different times in three groups of patients. Changes in NLR level in the three groups Preop and Postop on days 1 (PostopD1), 3 (PostopD3), and 5 (PostopD5). Values were presented as mean ± SD, with data comparisons among multiple groups analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s test. *p < 0.05: compared with the Rop-CSEA group at the same time point, **p < 0.01: compared with the Rop-CSEA group at the same time point, and ***p < 0.001: compared with the Rop-CSEA group at the same time point.
Comparison of the incidence of perioperative adverse reactions among the three groups of patients
As listed in Table 4, there was no distinct disparity in the total incidence of adverse reactions in IFF patients in the Rop-CSEA and low Dex and Rop-CSEA groups (all p > 0.05), while the total incidence of adverse reactions in IFF patients in the high Dex and Rop-CSEA group was elevated relative to the Rop-CSEA and low Dex and Rop-CSEA groups (all p < 0.05).
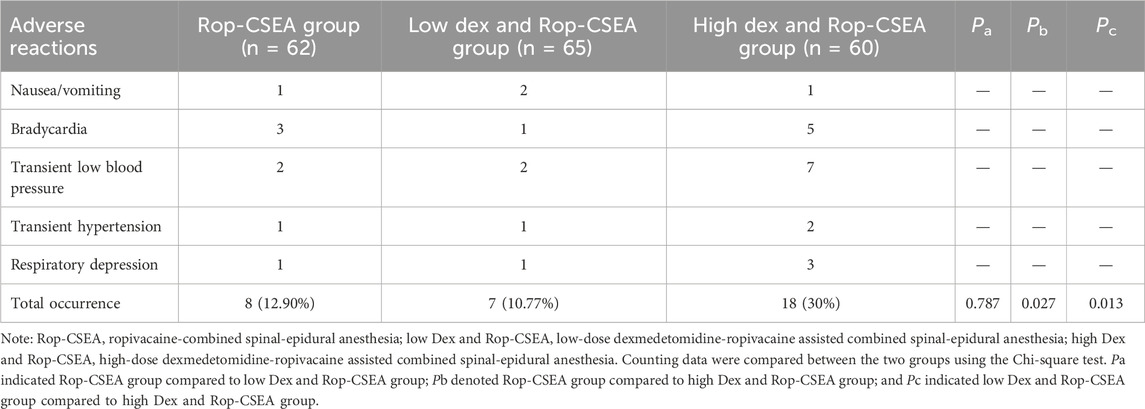
Table 4. Comparison of the incidence of perioperative adverse reactions among the three groups (n,%).
Comparisons of the incidence of postoperative delirium and cognitive function among three groups of patients
As shown in Table 5 and Figure 5, the incidence of postoperative delirium was decreased in both the low Dex and Rop-CSEA (7.69%) and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups (13.33%) versus the Rop-CSEA group (20.97%) (all p < 0.05), with no substantial difference between the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups (p > 0.05). Additionally, there was no significant difference in preoperative and postoperative day 1 MMSE score among the three IFF groups (all p > 0.05). On postoperative days 1, 3, and 5, the MMSE score of patients in the three groups presented a reduction followed by an elevation. On the 3rd and 5th days after surgery, the MMSE score of the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups were signally higher than that of the Rop-CSEA group (all p < 0.05), but the Low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups did not differ significantly (p > 0.05). The incidence of cognitive dysfunction within 3 days after surgery was reduced in both the low Dex and Rop-CSEA (7.69%) and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups (5.00%) compared with the Rop-CSEA group (24.19%) (all p < 0.05). Collectively, Dex and Rop-CSEA was effective on reducing the incidence of postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction in IFF patients.
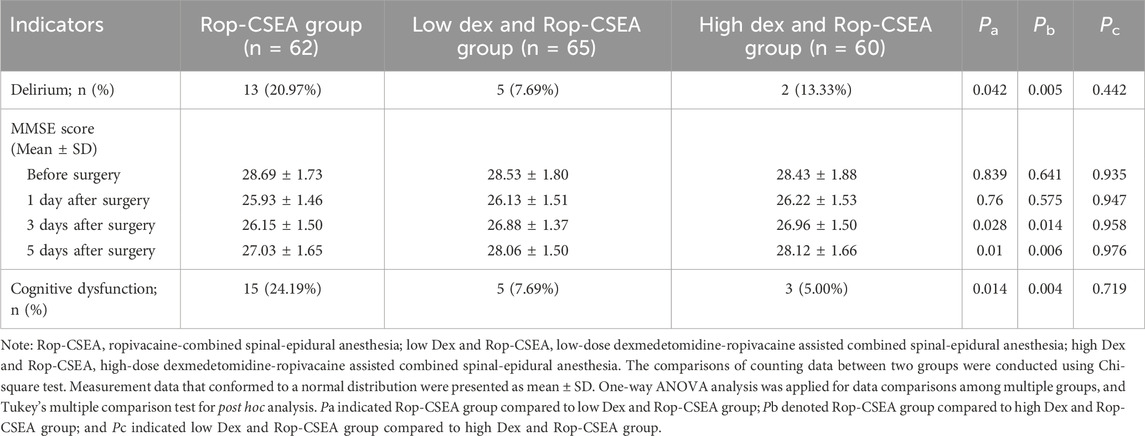
Table 5. Comparisons of the incidence of postoperative delirium and cognitive function among three groups of patients.
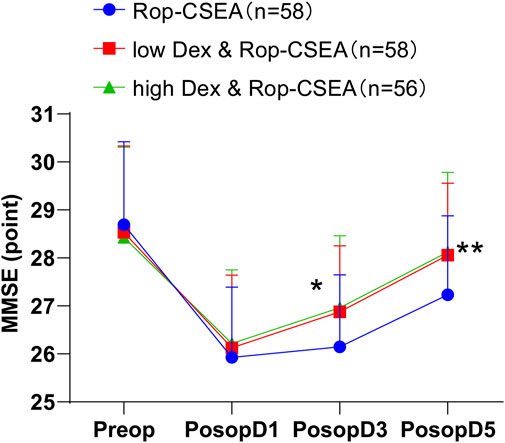
Figure 5. Comparison of postoperative cognitive function in three groups of patients. Changes in MMSE score of patients in the three groups Preop and Postop at PosopD1, PosopD3, and PosopD5. Data were expressed in the form of mean ± SD, and data comparisons among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s test. *p < 0.05: compared with the Rop-CSEA group at the same time point, and **p < 0.05: compared with the Rop-CSEA group at the same time point.
Discussion
Hip fractures have garnered considerable attention on a global scale due to the rapid increase in the geriatric population (Chang et al., 2020). IFF accounts for approximately half of all hip fractures, which are typically led by low-energy mechanisms, such as, a fall from standing height (Ahn and Bernstein, 2010). Surgical intervention is the most effective approach for managing IFF, as it facilitates prompt rehabilitation and functional restoration (Nherera et al., 2018). It is imperative to explore potential strategies for mitigating comorbidities and postoperative mortality of IFF patients (Borges et al., 2014). Our study emphasized that Dex and Rop assisted CSEA shortened the onset time of anesthesia, preserved perioperative hemodynamic stability, suppressed pain mediator release, and lowered postoperative NLR levels and incidence of delirium and cognitive dysfunction in IFF patients.
The intravenous administration of Dex has been linked to an extended sensory block during CSEA (Choi et al., 2020). Rop offers a more distinct block when administered epidurally, enabling a clearer differentiation between sensory and motor block (Chen et al., 2021; Pavlica et al., 2022). Notably, it has been reported that 5 μg Dex and 2.5 mL Rop results in earlier sensory blockade and prolongs both sensory and motor blockade durations in patients undergoing intrathecal anesthesia, without inducing sedation (Ravipati et al., 2017). The utilization of Dex as a supplementary agent in epidural anesthesia for orthopedic femoral fracture surgery has been demonstrated to reduce the onset time of sensory and motor block, extend the duration of analgesia, and prolong anesthesia (Akhondzadeh et al., 2023). The findings of our study indicated that individuals in the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups had reduced onset time for sensory and motor blocks, as well as extended recovery time for sensory and motor blocks, suggesting that Dex and Rop assisted CESA accelerated the onset of anesthesia and prolonged the duration of regional anesthesia.
Dex mitigates diverse stress responses during surgical procedures and sustains hemodynamic stability when employed as a supplement to general anesthesia (Chavan et al., 2016). Dex demonstrates superior clinical efficacy in enhancing perioperative hemodynamics among elderly gynecological patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery (Li Q. et al., 2023). Rop is effective in providing anesthesia for CSEA in caesarean sections, and is recommended due to its minimal impact on hemodynamics, shorter sensory and motor block time, and low occurrence of adverse reactions (Wang et al., 2019). MAP and HR in patients who received Dex and Rop were observably reduced relative to patients who received Rop alone (Lin et al., 2013). Consistently, our study found that HR, RR and MAP were higher in the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups than in the Rop-CSEA group, indicating that Dex and Rop assisted CSEA effectively stabilized perioperative hemodynamic stability in IFF patients.
SP, PGE2, and 5-HT are pain mediators implicated in the onset and exacerbation of pain (Ma et al., 2019). SP is a neuropeptide known for its injury-stimulating capability, which is widely distributed in the systemic system, and can exacerbate pain by facilitating 5-HT release and also contributes to the transmission of the pain signals (Saini et al., 2020). PGE2 is implicated in inflammation, fever, pain, and inflammatory diseases (Koeberle and Werz, 2015). 5-HT plays pivotal roles in the central nervous system, such as regulating pain tolerance and mood stability (Viguier et al., 2013). PGE2 level in the joint fluid of patients treated with Dex and Rop is abated at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h post-surgery (Li et al., 2017). The coadministration of Dex with Rop results in a notably extended period of postoperative analgesia and reduced need for postoperative analgesics (Balasubramaniam et al., 2023). Innovatively, our study results revealed that the low Dex and Rop-CSEA and high Dex and Rop-CSEA groups repressed SP, PGE2, and 5-HT releases, showing that Dex and Rop assisted CSEA relieved the stressful stimulus of pain in IFF patients.
It has been demonstrated that surgical stress produced by the surgery can cause cellular immunosuppression, disrupt the neuro-endocrine-immune network, and activate a great number of inflammation-associated cells in the body. NLR is a widely accessible, easily calculable, and replicable indicator of inflammation (Zhou et al., 2024). Upon activation, neutrophils can facilitate the release of myeloperoxidase, proteolytic enzymes, and oxygen, which in turn cause damage to the blood-brain barrier, inflict damage to brain, accelerate apoptotic rate, thereby inducing delirium (Wu et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2024). The increment of NLR postoperatively may serve as a predictive indicator for mortality in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery (Wu et al., 2023). Anesthesia can reduce the corresponding immunosuppression by reducing the surgical stress response. Our results suggested that Dex and Rop-CSEA was effective on reducing postoperative NLR level in IFF patients. The possible reason is that Dex can further reduce surgical stress-caused immunosuppression by inhibiting parasympathetic nerve, cell metabolism and immune response, which is conducive to reducing the increase of NLR. The utilization of various anesthesia techniques or adjuvant medications has the potential to alleviate stress response to surgical procedures, mitigate adverse reactions, and enhance overall clinical outcomes (Li Y. et al., 2023). Dex is a dextroisomer and is a highly selective α2 adrenergic receptor agonist. Upon action on the human body, Dex primarily exerts its effects through the medullary vasomotor center and so on, and its burden and effect on the liver and kidney are small. Therefore, it contributes to a low incidence of adverse reactions (Hong Xiaoya, Yao Bin, Li Yangyang. Effects of dexmedetomidine-assisted spinal epidural block anesthesia on stress response and cognitive function in elderly patients with intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Clinical Research and Practice, 2023, 8 (Zhu et al., 2010): 21–24). Additionally, Dex maintains hemodynamic equilibrium, reduces the requirement for anesthetic agents, and has a relatively mild impact on respiration (Hall et al., 2016). However, adverse reactions, specifically bradycardia and hypotension, were reported in patients who received Dex and Rop (Djaiani et al., 2016). Our study did not reveal a significant increase in the overall incidence of adverse reactions in IFF patients in the low Dex + Rop-CSEA group compared to Rop-CSEA, but the high Dex + Rop-CSEA group exhibited an elevated total incidence of adverse reactions, specifically an increase in the incidence of bradycardia and transient hypotension. The results suggested the risk of high-dose Dex in assisting CSEA applications. Caution is advised for patients with preexisting hypovolemia or cardiac conduction block, and co-administration should be considered if necessary.
Elderly patients with thoracolumbar fracture are affected by stress reactions during surgery, and the body will secrete a large amount of inflammatory mediators, which are prone to cause certain damage to the central nervous system to affect the recovery of postoperative cognitive function and induce delirium (Vasunilashorn et al., 2015; Hall et al., 2016). Dex not only decreases the frequency of postoperative delirium in elderly patients following cardiac surgery, but also delays its onset and shortens its duration (Djaiani et al., 2016). In elderly patients, the administration of intravenous Dex postoperatively for 12 h (0.2 μg/kg/h) potentially improves recovery quality and enhances postoperative cognitive function (Guo et al., 2015). Local Rop mitigates surgery-caused impairments in trace and context memory (Koyama et al., 2019). Dex and Rop treatment effectively improves cognitive function, alleviates pain, and reduces the inflammatory factor level (Liu et al., 2021). Intriguingly, our results suggested that Dex and Rop assisted CSEA was effective on reducing the incidence of postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction in IFF patients. The possible reason is that Dex can stimulate the α2 receptors on the medulla oblongata and pons and reduce the secretion of norepinephrine and the stress response of the patients’ organism, thereby reducing the release of inflammatory mediators and exerting a cerebroprotective effect that may prevent the onset of postoperative delirium (Tang et al., 2020; Bao and Tang, 2020). Furthermore, Dex has been shown to inhibit the expression levels of inflammatory factors and reduce the inhibitory effects of inflammatory mediators on neurons in the hippocampus, thus protecting patients’ cerebral nerves and lowering the incidence of postoperative delirium (Wang and Wang, 2021; Lv et al., 2020). It has been documented that Dex is involved in neuronal growth, proliferation and differentiation in the cerebral cortex, which contributes to the maintenance of neural function stability in patients’ brains, thus effectively preventing the occurrence of delirium, cognitive dysfunction and other related complications (Endesfelder et al., 2017).
Taken together, our study highlighted that Dex and Rop assisted CSEA shortened the onset time of anesthesia, maintained perioperative hemodynamic stability, inhibited pain mediator release, reduced postoperative NLR level and the incidence of delirium and cognitive dysfunction in IFF patients. Nevertheless, our study had certain limitations. Firstly, the sample size of this study was limited, especially in the detection of differences in adverse effects and rare outcomes, and further expansion of the sample size would enhance the generalizability of the findings. The single-center design of this study may restrict the generalizability of its findings to other hospitals or regions with different patient demographics and clinical practices. Multi-center studies are necessary to validate the generalizability of the results across diverse populations and healthcare environments. Secondly, further observations were needed to track changes in NLR levels at additional time points. Thirdly, Our study focuses on immediate and short-term postoperative outcomes; however, it does not provide data regarding long-term effects, such as chronic pain or persistent cognitive dysfunction. Long-term follow-up would be valuable in evaluating the sustained benefits or potential late-onset complications of Dex-Rop assisted CSEA. Furthermore, there was a need for further exploration of the use of alternative sedative-anesthetic drug combinations to aid in CSEA in IFF patients. Additionally, there were no significant differences in comorbidities or baseline cognitive function among the three groups of participants included in this study. Potential variability in patient characteristics may affect the reproducibility and reliability of the study results, and controlling for these variables or providing a more detailed analysis can strengthen the conclusions. While the study demonstrates beneficial effects of Dex on postoperative outcomes, the underlying mechanisms, particularly how Dex reduces NLR and the incidence of delirium, are not fully elucidated. Further research into the mechanistic pathways can provide deeper understanding and aid in refining anesthesia protocols.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LB: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing–review & editing. FJ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–review and editing. YL: Project administration, Validation, Writing–review and editing. PL: Investigation, Writing–review and editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahn, J., and Bernstein, J. (2010). Fractures in brief: intertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 468 (5), 1450–1452. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1263-2
Akhondzadeh, R., Olapour, A., Javaherforooshzadeh, F., Rashidi, M., Bakhtiari, N., and Hosseininejad, F. (2023). Dexmedetomidine or fentanyl, which one is better as an adjunct drug in epidural anesthesia and causes more postoperative pain reduction? A comparative study, a randomized clinical trial. Anesth. Pain Med. 13 (1), e134065. doi:10.5812/aapm-134065
Albanese, A. M., Ramazani, N., Greene, N., and Bruse, L. (2022). Review of postoperative delirium in geriatric patients after hip fracture treatment. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 13, 21514593211058947. doi:10.1177/21514593211058947
Balasubramaniam, A., Kumar Naggaih, S., Tarigonda, S., and Madhusudhana, R. (2023). Ultrasound-guided pericapsular nerve group block for hip surgery: a randomized controlled trial study comparing ropivacaine and ropivacaine with dexamethasone. Cureus 15 (1), e34261. doi:10.7759/cureus.34261
Bao, N., and Tang, B. (2020). Organ-protective effects and the underlying mechanism of dexmedetomidine. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 6136105. doi:10.1155/2020/6136105
Basques, B. A., Bohl, D. D., Golinvaux, N. S., Leslie, M. P., Baumgaertner, M. R., and Grauer, J. N. (2015). Postoperative length of stay and 30-day readmission after geriatric hip fracture: an analysis of 8434 patients. J. Orthop. Trauma 29 (3), e115–e120. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000000222
Bedrettin, A., Sahin, F., and Yucel, M. O. (2022). Treatment of intertrochanteric femur fracture with closed external fixation in high-risk geriatric patients: can it be the most reliable method that reduces mortality to minimum compared to proximal femoral nail and hemiarthroplasty? Med. Baltim. 101 (1), e28369. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000028369
Beilin, Y., and Halpern, S. (2010). Focused review: ropivacaine versus bupivacaine for epidural labor analgesia. Anesth. Analg. 111 (2), 482–487. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181e3a08e
Borges, A., Torres, J., Sao Simao, R., Cabral, A. T., and Pinto, R. (2014). Impact of preoperative analytical values on post-operative mortality rate of intertrochanteric fractures. Acta Med. Port. 27 (2), 218–222. doi:10.20344/amp.4280
Chang, S. M., Hou, Z. Y., Hu, S. J., and Du, S. C. (2020). Intertrochanteric femur fracture treatment in asia: what we know and what the world can learn. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 51 (2), 189–205. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2019.11.011
Chavan, S. G., Shinde, G. P., Adivarekar, S. P., Gujar, S. H., and Mandhyan, S. (2016). Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative monitoring parameters and recovery in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth. Essays Res. 10 (2), 278–283. doi:10.4103/0259-1162.171460
Chen, L., Zhang, J., He, W., and Liu, W. (2021). Comparative effects of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on dreaming of patients undergoing flexible bronchoscopy during general anesthesia. Med. Sci. Monit. 27, e929000. doi:10.12659/MSM.929000
Cheng, P., Ying, F., and Li, Y. (2022). Effects of different concentrations of ropivacaine lumbar plexus-sciatic nerve block on recovery from anesthesia, postoperative pain and cognitive function in elderly patients with femoral neck fracture. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 4096005. doi:10.1155/2022/4096005
Cheng, Y. X., and Sheng, X. (2020). Optimal surgical methods to treat intertrochanteric fracture: a Bayesian network meta-analysis based on 36 randomized controlled trials. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 15 (1), 402. doi:10.1186/s13018-020-01943-9
Choi, Y. M., Choi, E. J., Ri, H. S., Park, J. Y., You, J. A., and Byeon, G. J. (2020). The effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on combined spinal-epidural anesthesia in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Anesth. Pain Med. Seoul. 15 (1), 111–119. doi:10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.111
Chu, C. C., Weng, S. F., Chen, K. T., Chien, C. C., Shieh, J. P., Chen, J. Y., et al. (2015). Propensity score-matched comparison of postoperative adverse outcomes between geriatric patients given a general or a neuraxial anesthetic for hip surgery: a population-based study. Anesthesiology 123 (1), 136–147. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000000695
Court-Brown, C. M., and McQueen, M. M. (2016). Global forum: fractures in the elderly. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 98 (9), e36. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.00793
Deng, S., and Yu, Y. (2021). Effects of dexmedetomidine as an analgesic adjuvant for surgery of femur fracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacology 106 (9-10), 453–461. doi:10.1159/000515788
Djaiani, G., Silverton, N., Fedorko, L., Carroll, J., Styra, R., Rao, V., et al. (2016). Dexmedetomidine versus propofol sedation reduces delirium after cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology 124 (2), 362–368. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000000951
Dolma, L., Salhotra, R., Rautela, R. S., and Banerjee, A. (2018). Isobaric ropivacaine with or without dexmedetomidine for surgery of neck femur fracture under subarachnoid block. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 34 (4), 518–523. doi:10.4103/joacp.JOACP_226_18
Du, Z., Wei, S. W., Zhang, X. Y., Xiang, Z., and Qu, S. Q. (2021). The effect of dexmedetomidine premedication on postoperative systemic inflammatory response in children undergoing hernia repair surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Paediatr. Anaesth. 31 (7), 794–801. doi:10.1111/pan.14189
Endesfelder, S., Makki, H., von Haefen, C., Spies, C. D., Buhrer, C., and Sifringer, M. (2017). Neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine against hyperoxia-induced injury in the developing rat brain. PLoS One 12 (2), e0171498. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171498
Gopal, N. D., and Krishnamurthy, D. (2018). A clinical comparative study of fascia iliaca compartment block with bupivacaine and bupivacaine with dexmedetomidine for positioning and duration of postoperative analgesia in fracture femur under spinal anesthesia. Anesth. Essays Res. 12 (2), 528–534. doi:10.4103/aer.AER_56_18
Guo, Y., Sun, L., Zhang, J., Li, Q., Jiang, H., and Jiang, W. (2015). Preventive effects of low-dose dexmedetomidine on postoperative cognitive function and recovery quality in elderly oral cancer patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 8 (9), 16183–16190.
Hall, R. J., Watne, L. O., Idland, A. V., Raeder, J., Frihagen, F., MacLullich, A. M., et al. (2016). Cerebrospinal fluid levels of neopterin are elevated in delirium after hip fracture. J. Neuroinflammation 13 (1), 170. doi:10.1186/s12974-016-0636-1
Handoll, H. H., Cameron, I. D., Mak, J. C., Panagoda, C. E., and Finnegan, T. P. (2021). Multidisciplinary rehabilitation for older people with hip fractures. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 11 (11), CD007125. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007125.pub2
He, R., Wang, F., Shen, H., Zeng, Y., and Lijuan, Z. (2020). Association between increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and postoperative delirium in elderly patients with total hip arthroplasty for hip fracture. BMC Psychiatry 20 (1), 496. doi:10.1186/s12888-020-02908-2
Hshieh, T. T., Saczynski, J., Gou, R. Y., Marcantonio, E., Jones, R. N., Schmitt, E., et al. (2017). Trajectory of functional recovery after postoperative delirium in elective surgery. Ann. Surg. 265 (4), 647–653. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000001952
Johnson, R. L., Kopp, S. L., Burkle, C. M., Duncan, C. M., Jacob, A. K., Erwin, P. J., et al. (2016). Neuraxial vs general anaesthesia for total hip and total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of comparative-effectiveness research. Br. J. Anaesth. 116 (2), 163–176. doi:10.1093/bja/aev455
Keating, G. M. (2015). Dexmedetomidine: a review of its use for sedation in the intensive care setting. Drugs 75 (10), 1119–1130. doi:10.1007/s40265-015-0419-5
Koeberle, A., and Werz, O. (2015). Perspective of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 as drug target in inflammation-related disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 98 (1), 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2015.06.022
Koyama, T., Kawano, T., Iwata, H., Aoyama, B., Eguchi, S., Nishigaki, A., et al. (2019). Acute postoperative pain exacerbates neuroinflammation and related delirium-like cognitive dysfunction in rats. J. Anesth. 33 (3), 482–486. doi:10.1007/s00540-019-02635-3
Langley, B. O., Guedry, S. E., Goldenberg, J. Z., Hanes, D. A., Beardsley, J. A., and Ryan, J. J. (2021). Inflammatory bowel disease and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: a systematic scoping review. J. Clin. Med. 10 (18), 4219. doi:10.3390/jcm10184219
Li, J., Wang, H., Dong, B., Ma, J., and Wu, X. (2017). Adding dexmedetomidine to ropivacaine for femoral nerve block inhibits local inflammatory response. Minerva Anestesiol. 83 (6), 590–597. doi:10.23736/S0375-9393.17.11430-6
Li, Q., Fu, L. Y., Zhao, Y. H., Shi, W. G., Sun, W., Zhang, X. N., et al. (2023a). Effect of dexmedetomidine on perioperative haemodynamics and early cognitive function in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Wideochir Inne Tech. Maloinwazyjne 18 (3), 533–540. doi:10.5114/wiitm.2023.130329
Li, Y., Wang, L., Sun, J., Xie, T., Fu, J., Feng, C., et al. (2023b). Effects of subcostal anterior quadratus lumborum block with and without dexmedetomidine on postoperative rehabilitation in patients undergoing laparoscopic renal surgery: a prospective double-blinded randomized controlled study. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 17, 3281–3293. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S422356
Lin, Y. N., Li, Q., Yang, R. M., Mao, Z. X., and Liu, J. C. (2013). Addition of dexmedetomidine to ropivacaine improves cervical plexus block. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwan 51 (2), 63–66. doi:10.1016/j.aat.2013.06.001
Liu, Y., Xu, C., Wang, C., Gu, F., Chen, R., and Lu, J. (2022). Median effective analgesic concentration of ropivacaine in ultrasound-guided interscalene brachial plexus block as a postoperative analgesia for proximal humerus fracture: a prospective double-blind up-down concentration-finding study. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9, 857427. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.857427
Liu, Y., Zhang, H., and Zhang, W. (2021). Effect of dexmedetomidine combined with ropivacaine on cognitive dysfunction and inflammatory response in patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 4968300. doi:10.1155/2021/4968300
Lv, K., Yang, C., Xiao, R., Yang, L., Liu, T., Zhang, R., et al. (2020). Dexmedetomidine attenuates ethanol-induced inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis in neonatal mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 390, 114881. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2020.114881
Ma, W., Li, L., and Xing, S. (2019). PGE2/EP4 receptor and TRPV1 channel are involved in repeated restraint stress-induced prolongation of sensitization pain evoked by subsequent PGE2 challenge. Brain Res. 1721, 146335. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146335
Maldonado, J. R. (2013). Neuropathogenesis of delirium: review of current etiologic theories and common pathways. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 21 (12), 1190–1222. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2013.09.005
Malhotra, R., Johnstone, C., Halpern, S., Hunter, J., and Banerjee, A. (2016). Duration of motor block with intrathecal ropivacaine versus bupivacaine for caesarean section: a meta-analysis. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 27, 9–16. doi:10.1016/j.ijoa.2016.03.004
McIsaac, D. I., Wijeysundera, D. N., Huang, A., Bryson, G. L., and van Walraven, C. (2018). Association of hospital-level neuraxial anesthesia use for hip fracture surgery with outcomes: a population-based cohort study. Anesthesiology 128 (3), 480–491. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000001899
Neerland, B. E., Hall, R. J., Seljeflot, I., Frihagen, F., MacLullich, A. M., Raeder, J., et al. (2016). Associations between delirium and preoperative cerebrospinal fluid C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and interleukin-6 receptor in individuals with acute hip fracture. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 64 (7), 1456–1463. doi:10.1111/jgs.14238
Neuman, M. D., Rosenbaum, P. R., Ludwig, J. M., Zubizarreta, J. R., and Silber, J. H. (2014). Anesthesia technique, mortality, and length of stay after hip fracture surgery. JAMA 311 (24), 2508–2517. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.6499
Nherera, L., Trueman, P., Horner, A., Watson, T., and Johnstone, A. J. (2018). Comparison of a twin interlocking derotation and compression screw cephalomedullary nail (InterTAN) with a single screw derotation cephalomedullary nail (proximal femoral nail antirotation): a systematic review and meta-analysis for intertrochanteric fractures. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 13 (1), 46. doi:10.1186/s13018-018-0749-6
Nwachukwu, C., Idehen, H. O., Edomwonyi, N. P., and Umeh, B. (2020). Postoperative analgesic effect of intrathecal dexmedetomidine on bupivacaine subarachnoid block for open reduction and internal fixation of femoral fractures. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 23 (2), 172–178. doi:10.4103/njcp.njcp_142_19
Oura, P., Virtanen, A., Nurkkala, J., Kriikku, P., and Ojanpera, I. (2023). Postmortem concentrations of ropivacaine, bupivacaine, and lidocaine in femoral venous blood after hip fracture surgery. Int. J. Leg. Med. 137 (4), 1071–1076. doi:10.1007/s00414-023-03000-6
Pavlica, M., Krzan, M., Nemec, A., Kosjek, T., Bas, A., and Seliskar, A. (2022). Cardiopulmonary effects and pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine used as an adjunctive analgesic to regional anesthesia of the oral cavity with levobupivacaine in dogs. Anim. (Basel) 12 (9), 1217. doi:10.3390/ani12091217
Perlas, A., Chan, V. W., and Beattie, S. (2016). Anesthesia technique and mortality after total hip or knee arthroplasty: a retrospective, propensity score-matched cohort study. Anesthesiology 125 (4), 724–731. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000001248
Ravipati, P., Isaac, G. A., Reddy, P. N., Krishna, L., and Supritha, T. (2017). A comparative study between intrathecal isobaric ropivacaine 0.75% plus dexmedetomidine and isobaric ropivacaine 0.75% plus fentanyl for lower limb surgeries. Anesth. Essays Res. 11 (3), 621–626. doi:10.4103/0259-1162.206857
Saini, S., Singh, B., Prakash, S., Kumari, S., Kureel, A. K., Dube, A., et al. (2020). Parasitic load determination by differential expressions of 5-lipoxygenase and PGE2 synthases in visceral leishmaniasis. Prostagl. Other Lipid Mediat 147, 106390. doi:10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2019.106390
Shi, M., Miao, S., Gu, T., Wang, D., Zhang, H., and Liu, J. (2019). Dexmedetomidine for the prevention of emergence delirium and postoperative behavioral changes in pediatric patients with sevoflurane anesthesia: a double-blind, randomized trial. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 13, 897–905. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S196075
Shin, H. J., Woo Nam, S., Kim, H., Yim, S., Han, S. H., Hwang, J. W., et al. (2023). Postoperative delirium after dexmedetomidine versus propofol sedation in healthy older adults undergoing orthopedic lower limb surgery with spinal anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology 138 (2), 164–171. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000004438
Su, X., Meng, Z. T., Wu, X. H., Cui, F., Li, H. L., Wang, D. X., et al. (2016). Dexmedetomidine for prevention of delirium in elderly patients after non-cardiac surgery: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 388 (10054), 1893–1902. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30580-3
Subramaniam, B., Shankar, P., Shaefi, S., Mueller, A., O'Gara, B., Banner-Goodspeed, V., et al. (2019). Effect of intravenous acetaminophen vs placebo combined with propofol or dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium among older patients following cardiac surgery: the DEXACET randomized clinical trial. JAMA 321 (7), 686–696. doi:10.1001/jama.2019.0234
Swennen, C., Bredin, S., Eap, C., Mensa, C., Ohl, X., and Girard, V. (2017). Local infiltration analgesia with ropivacaine in acute fracture of thoracolumbar junction surgery. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 103 (2), 291–294. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2016.11.012
Tang, C., Hu, Y., Zhang, Z., Wei, Z., Wang, H., Geng, Q., et al. (2020). Dexmedetomidine with sufentanil in intravenous patient-controlled analgesia for relief from postoperative pain, inflammation and delirium after esophageal cancer surgery. Biosci. Rep. 40 (5). doi:10.1042/BSR20193410
Vasunilashorn, S. M., Ngo, L., Inouye, S. K., Libermann, T. A., Jones, R. N., Alsop, D. C., et al. (2015). Cytokines and postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing major elective surgery. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 70 (10), 1289–1295. doi:10.1093/gerona/glv083
Viguier, F., Michot, B., Hamon, M., and Bourgoin, S. (2013). Multiple roles of serotonin in pain control mechanisms--implications of 5-HT₇ and other 5-HT receptor types. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 716 (1-3), 8–16. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.074
Wang, H., Gao, Q., Xu, R., Dong, W., Zhang, Y., and Fan, J. (2019). The efficacy of ropivacaine and bupivacaine in the caesarean section and the effect on the vital signs and the hemodynamics of the lying-in women. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 26 (8), 1991–1994. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.07.014
Wang, J., and Wang, Y. (2021). Circular RNA cerebellar degeneration-related protein 1 antisense RNA (Circ-CDR1as) downregulation induced by dexmedetomidine treatment protects hippocampal neurons against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury through the microRNA-28-3p (miR-28-3p)/tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-3 (TRAF3) axis. Bioengineered 12 (2), 10512–10524. doi:10.1080/21655979.2021.1999369
Wang, Y., Zha, H., Fang, X., Shen, T., Pan, K., Zhang, J., et al. (2022). Dose selection of ropivacaine for spinal anesthesia in elderly patients with hip fracture: an up-down sequential allocation study. Clin. Interv. Aging 17, 1217–1226. doi:10.2147/CIA.S371219
Wu, X., Chi, F., Wang, B., Liu, S., Wang, F., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Relationship between preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and postoperative delirium: the PNDABLE and the PNDRFAP cohort studies. Brain Behav. 13 (12), e3281. doi:10.1002/brb3.3281
Xie, S., and Xie, M. (2018). Effect of dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery. Pak J. Pharm. Sci. 31 (5(Special)), 2277–2281.
Xu, W., Li, X., Chen, L., Luo, X., Shen, S., and Wang, J. (2022). Dexmedetomidine pretreatment alleviates ropivacaine-induced neurotoxicity via the miR-10b-5p/BDNF axis. BMC Anesthesiol. 22 (1), 304. doi:10.1186/s12871-022-01810-6
Yoon, S. J., Hyong Kim, T., Joo, S. B., and Eel Oh, S. (2020). Automatic multi-class intertrochanteric femur fracture detection from CT images based on AO/OTA classification using faster R-CNN-BO method. J. Appl. Biomed. 18 (4), 97–105. doi:10.32725/jab.2020.013
Yousef, A. A., Salem, H. A., and Moustafa, M. Z. (2015). Effect of mini-dose epidural dexmedetomidine in elective cesarean section using combined spinal-epidural anesthesia: a randomized double-blinded controlled study. J. Anesth. 29 (5), 708–714. doi:10.1007/s00540-015-2027-7
Zhou, B., Yu, D. D., Xu, X., Wang, J., and Li, J. (2024). Association of preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with the risk of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychogeriatrics 24 (4), 993–1003. doi:10.1111/psyg.13138
Keywords: intertrochanteric femoral fracture, combined spinal epidural anesthesia, dexmedetomidine, ropivacaine, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, delirium, cognitive dysfunction, hemodynamics
Citation: Bai L, Zhao L, Jia F, Liu Y and Li P (2025) Effects of dexmedetomidine-ropivacaine assisted combined spinal-epidural anesthesia on neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and postoperative delirium in elderly patients with intertrochanteric femoral fracture. Front. Pharmacol. 15:1454452. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1454452
Received: 25 June 2024; Accepted: 18 December 2024;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Hong Liu, UC Davis Health, United StatesReviewed by:
Juan Moisés De La Serna, International University of La Rioja, SpainChee Yern Ching, University of Malaya, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Bai, Zhao, Jia, Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lili Bai, QmFpbGlpMDhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ping Li, SXVoci1sekAxNjMuY29t
 Lili Bai
Lili Bai Lina Zhao
Lina Zhao